- 1Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning, China
- 2Department of Urology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning, China
- 3Department of Cardiology, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 4Motor Robotics Institute (MRI), South China Hospital, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Objective: The impact of lipid-lowering medications on chronic kidney disease (CKD) remains a subject of debate. This Mendelian randomization (MR) study aims to elucidate the potential effects of lipid-lowering drug targets on CKD development.
Methods: We extracted 11 genetic variants encoding targets of lipid-lowering drugs from published genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics, encompassing LDLR, HMGCR, PCSK9, NPC1L1, APOB, ABCG5/ABCG8, LPL, APOC3, ANGPTL3, and PPARA. A Mendelian randomization analysis was conducted targeting these drug-related genes. CKD risk was designated as the primary outcome, while estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were assessed as secondary outcomes. Additionally, mediation analysis was performed utilizing 731 immune cell phenotypes to identify potential mediators.
Results: The meta-analysis revealed a significant association between ANGPTL3 inhibitors and a reduced risk of CKD (OR [95% CI] = 0.85 [0.75-0.96]). Conversely, LDLR agonists were significantly linked to an increased risk of CKD (OR [95% CI] = 1.11 [1.02-1.22]). Regarding secondary outcomes, lipid-lowering drugs did not significantly affect eGFR and BUN levels. Mediation analysis indicated that the reduction in CKD risk by ANGPTL3 inhibitors was mediated through modulation of the immune cell phenotype, specifically HLA-DR on CD14+ CD16+ monocytes (Mediated proportion: 4.69%; Mediated effect: -0.00899).
Conclusion: Through drug-targeted MR analysis, we identified a causal relationship between lipid-lowering drug targets and CKD. ANGPTL3 and LDLR may represent promising candidate drug targets for CKD treatment.
1 Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is characterized by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) falling below 60 mL/min per 1.73 m² without clear cause, or the presence of markers of kidney damage, such as proteinuria, for a duration of three months or more (1). Epidemiological data reveal that CKD affects over 10% of the global population, with approximately 9.6% of non-hospitalized adults in the United States afflicted by this condition (2–4). Similar prevalence rates have been observed in Europe, Australia, and Asia (5–7). This widespread incidence of CKD imposes substantial economic burdens, with treatment and care costs surpassing those of many other prevalent diseases (8). CKD is intricately linked with cardiovascular risk factors, including hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and hypertension. Research has established a frequent co-occurrence of CKD and cardiovascular diseases, often referred to as cardiorenal syndrome. Both conditions are underpinned by shared pathogenic mechanisms, such as endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and systemic inflammation of the capillary walls in CKD patients (9, 10). Thus, CKD and cardiovascular diseases are interconnected through common risk factors. Lipids play a crucial role in this association.
Treatments for hyperlipidemia commonly include nicotinic acid, statins, fibrates, and newer lipid-lowering drugs (11–14). Extensive research has been conducted on statins and their relationship with CKD or kidney function, yet these studies remain controversial. Some trials have confirmed renal protective effects and reduced proteinuria (15, 16), while other RCTs show no effect (17). However, the latest meta-analysis of statins and CKD included 33 RCTs, finding no significant differences in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum creatinine levels between the statin and control groups (18). Additionally, lipid-lowering drugs are not limited to statins; non-statin lipid-lowering drugs lack large-scale randomized controlled trials with CKD, and there is still a need for systematic research on whether lipid-lowering drugs directly affect the progression of CKD and levels of eGFR and blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
With the advent of genome-wide association studies (GWAS), Mendelian randomization (MR) has emerged as a potent alternative to randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for elucidating causal relationships. The random allocation of genetic variations (alleles) during meiosis ensures that participants in MR studies are effectively “randomized” based on their alleles. This process mirrors the random assignment in RCTs, where individuals are allocated to either the treatment or control group (19, 20). Such inherent randomization in MR studies significantly reduces the influence of confounding factors, offering a robust approach compared to other research methodologies. Drug-targeted MR analysis has gained traction as a method for inferring the effects of drugs targeting protein-coding genes—such as antagonists, agonists, or inhibitors—on disease risk (21). This approach significantly enhances the evaluation of drug therapy potentials and facilitates the development of novel pharmaceuticals.
We employed drug-targeted MR analysis to investigate the impact of lipid-lowering drugs on CKD and to explore the potential effects of lipid-lowering drug targets on eGFR and BUN.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design
This investigation employs a two-sample Mendelian randomization approach to elucidate the genetic interplay between lipid-lowering drug target genes and CKD. MR relies on three key assumptions: 1) the genetic instrument is strongly associated with the exposure, 2) it is independent of confounders, and 3) it affects the outcome only through the exposure, not via other pathways (22, 23). A schematic overview of the study design is presented in Figure 1.
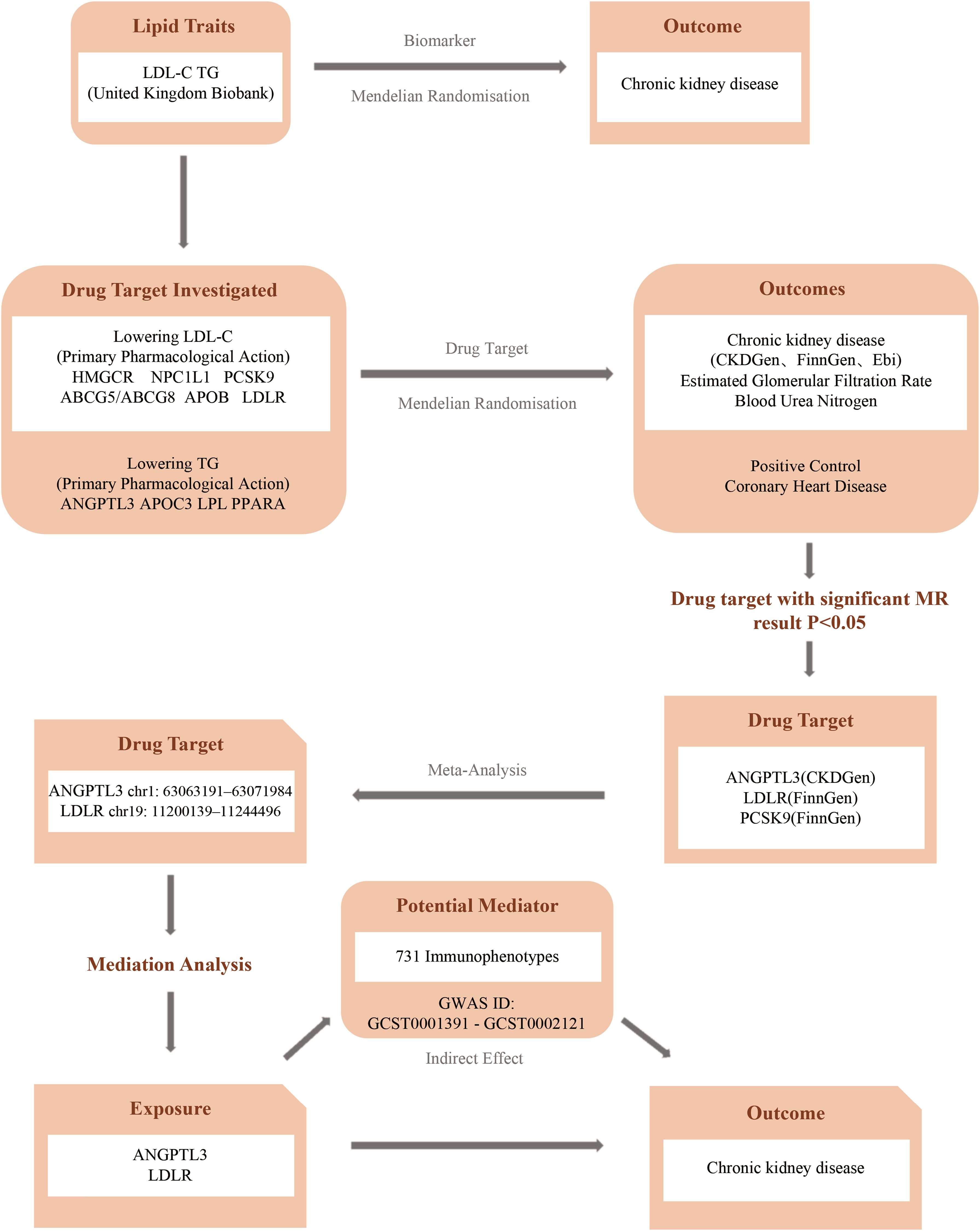
Figure 1. Flowchart of the study. (CKDGen, Chronic Kidney Disease Genetics Consortium; FinnGen, FinnGen Study; EBI, European Bioinformatics Institute).
2.2 Genetic variant selection
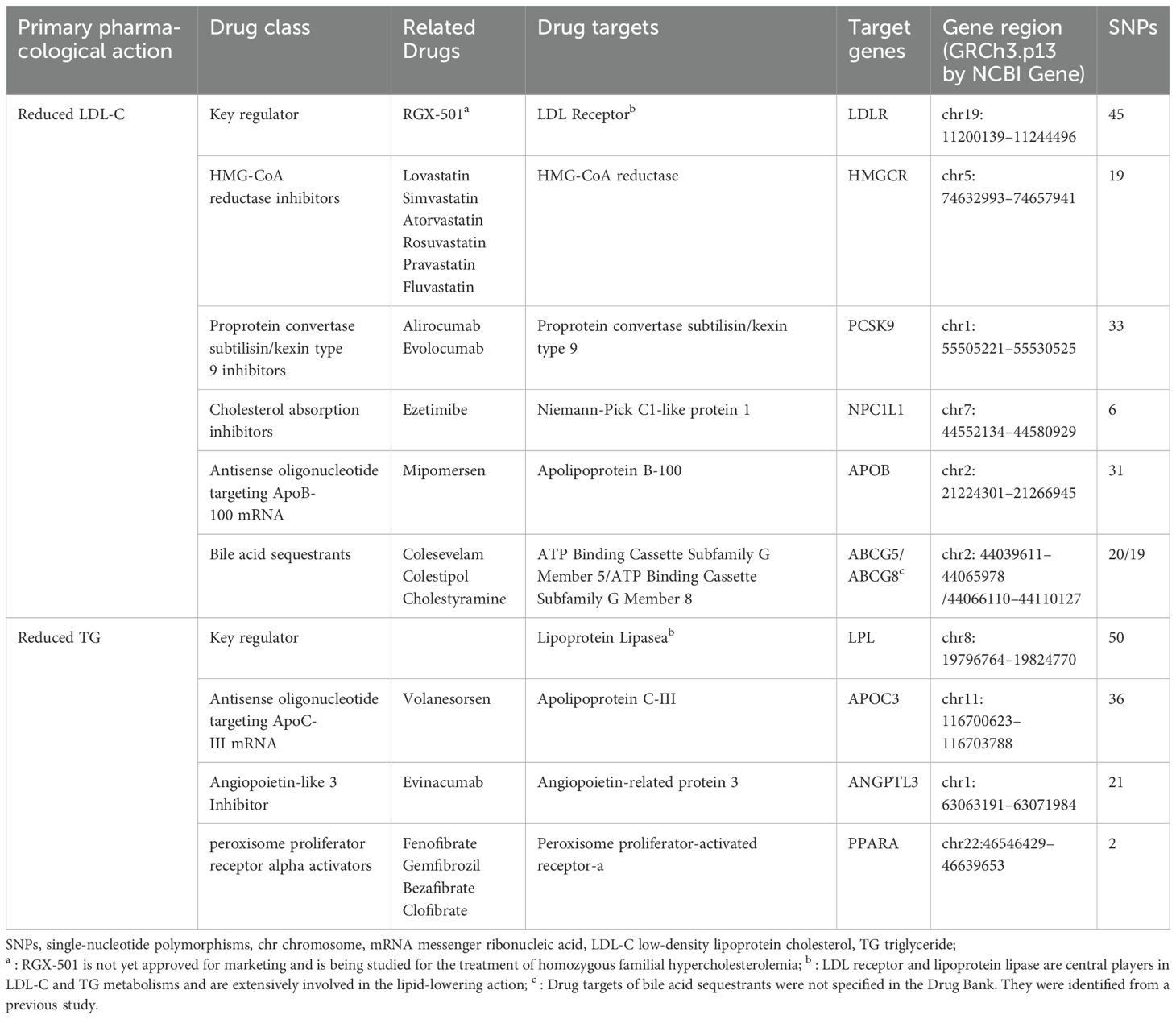
Adhering to the latest dyslipidemia treatment guidelines, we selected a range of widely used lipid-lowering drugs and the most recent therapeutic methods. These included statins, ezetimibe, PCSK9 inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants, mipomersen, fibrates, ANGPTL3 inhibitors, and antisense oligonucleotides targeting apolipoprotein C-III (APOC3) mRNA (24, 25). Utilizing the DrugBank database, we identified the genes encoding the pharmacological targets of these drugs. These target genes were classified into two groups: those that reduce LDL cholesterol (i.e., LDLR, HMGCR, NPC1L1, PCSK9, APOB, ABCG5, and ABCG8) and those that lower triglycerides (i.e., LPL, APOC3, ANGPTL3, and PPARA), as detailed in Table 1.
Summary data for LDL-C and TG levels were derived from two extensive GWAS meta-analyses (26). Instrumental variables representing each lipid-lowering drug target were employed to model the effects of these interventions on lipid levels. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located within ±100 kb of the drug target loci and significantly associated with LDL-C or TG levels (P < 5×10−8) were selected as instrumental variables. To mitigate potential bias, SNPs were filtered based on an effect allele frequency (eaf) > 0.01. To minimize the impact of strong linkage disequilibrium, a linkage disequilibrium(LD) threshold (r2 < 0.3) was set. To avoid potential confounders, we examined each relevant SNP in the LDtrait Tool database to assess confounding factors associated with it (P <5e-8) (27, 28), such as age, hypertension, diabetes, proteinuria, and environmental risk factors like dietary salt intake and pollution (29), excluding SNPs highly correlated with confounding factors.
2.3 Outcome
We utilized coronary heart disease (CHD) and CKD as outcomes for our drug-targeted MR analysis. CHD served as a positive control dataset to validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the lipid-lowering drug targets. The CHD dataset was sourced from GWAS summary statistics, comprising 184,305 participants, including 60,801 cases and 123,504 controls (30). For CKD, the primary outcome, instrumental variables’ summary statistics were obtained from the latest Chronic Kidney Disease Genetics Consortium (CKDGen Consortium) database (31), incorporating relevant GWAS datasets from FinnGen and the ebi database (32). Secondary outcomes included eGFR and BUN, also from the CKDGen Consortium (31). Detailed information can be found in Supplementary Table 1.
To investigate the mediating role of immune cells, we accessed comprehensive GWAS data on immunity. Summary statistics for each immune trait were sourced from the publicly available GWAS Catalog, with accession numbers ranging from GCST9001391 to GCST0002121 (33). We incorporated a total of 731 immunophenotypes, spanning various categories: absolute cell counts (n = 118), median fluorescence intensities (MFI) representing surface antigen levels (n = 389), morphological parameters (MP) (n = 32), and relative cell counts (n = 192).
2.4 Estimation of causal effects
We estimated the causal effects between drug targets and CKD using the inverse variance-weighted method (IVW). Additionally, additional analyses were conducted using the weighted median and weighted model averaging (34–37). In all three analyses, statistically significant IVW results combined with consistent directions provided sufficient evidence of causal effects.
2.5 Meta-analysis
The odds ratio (OR) served as the primary combined statistic (38). Studies exhibiting significant heterogeneity, defined as I² > 50%, were analyzed using a random effects model. Conversely, studies with I² < 50% were considered homogeneous and analyzed using a fixed effects model. Data calculations were performed using the ‘meta’ package in R Studio, and the plots were generated using GraphPad Prism 9.
2.6 Quality controls
Heterogeneity was evaluated using both the MR Egger and Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW) methods. Cochran’s Q test assessed the heterogeneity of genetic instruments, with a p-value > 0.05 indicating no significant heterogeneity. The MR Egger regression was employed to evaluate horizontal pleiotropy, where a p-value > 0.05 suggested no evidence of pleiotropy (39, 40). To ensure result robustness, a leave-one-out analysis was conducted, sequentially removing each SNP to assess the stability of the IVW results.
2.7 Mediation MR analysis
Given the intricate relationship between the immune system and CKD progression, it is plausible that immune cells mediate the effects of lipid-lowering drugs on CKD. We employed a “two-sample” MR approach to evaluate the potential mediating effects of 731 immune cell phenotypes on CKD progression. This method, compared to multivariable MR approaches, reduces bias due to high linkage disequilibrium (LD) between genetic variants. All statistical analyses were conducted using RStudio software.
3 Results
3.1 Positive control analysis
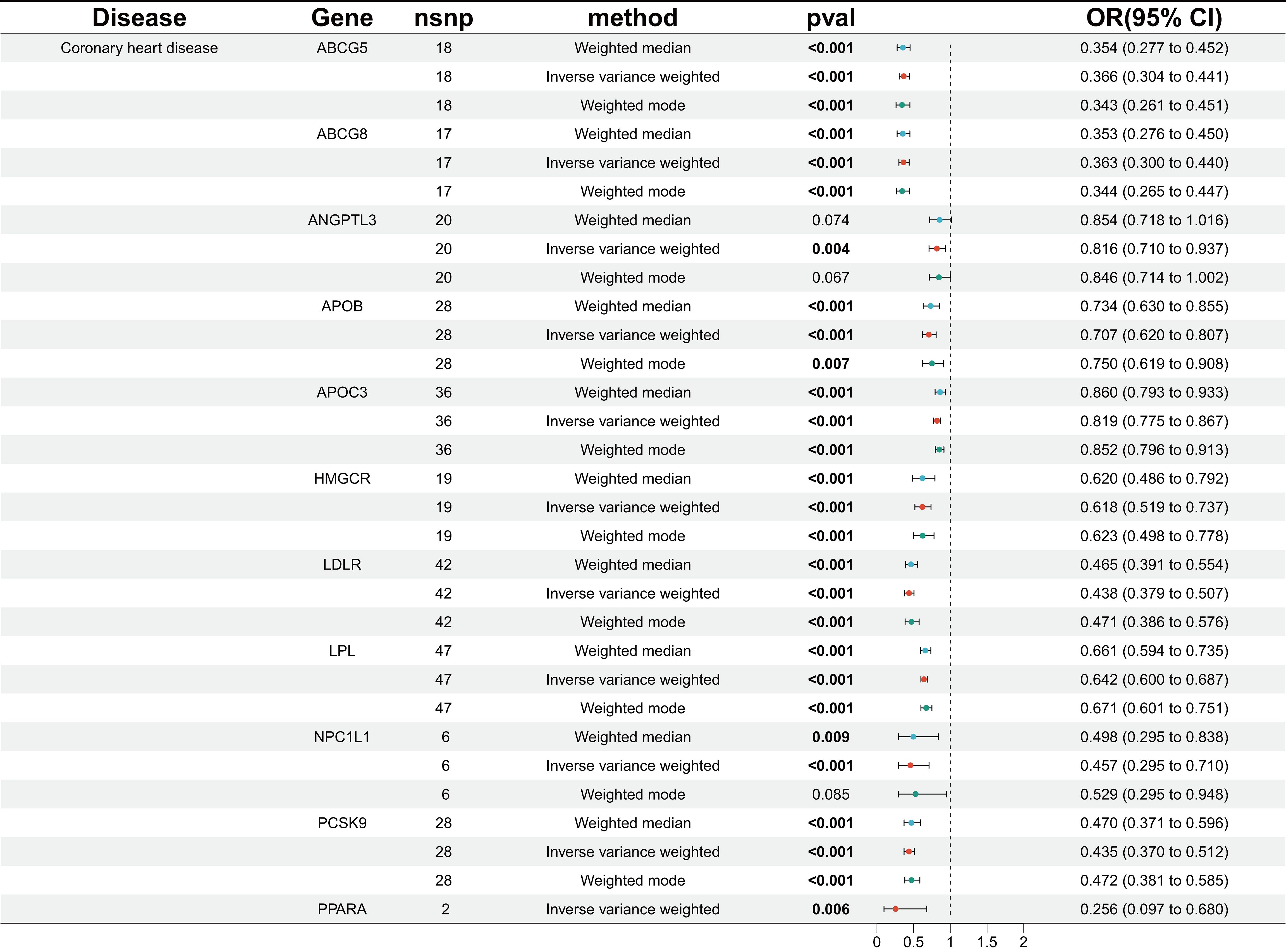
We identified genetic variants linked to various lipid-lowering drug targets, including LDLR agonists, HMGCR inhibitors, NPC1L1 inhibitors, PCSK9 inhibitors, APOB inhibitors, and ABCG5 agonists targeting LDL-C, as well as APOC3 inhibitors, LPL agonists, ANGPTL3 inhibitors, and PPARA agonists targeting TG. In the MR analysis evaluating CHD as the outcome, 11 drug-related target points significantly reduced the risk of CHD, as anticipated (Figure 2).
3.2 The causal relationship between drug targets and primary outcomes
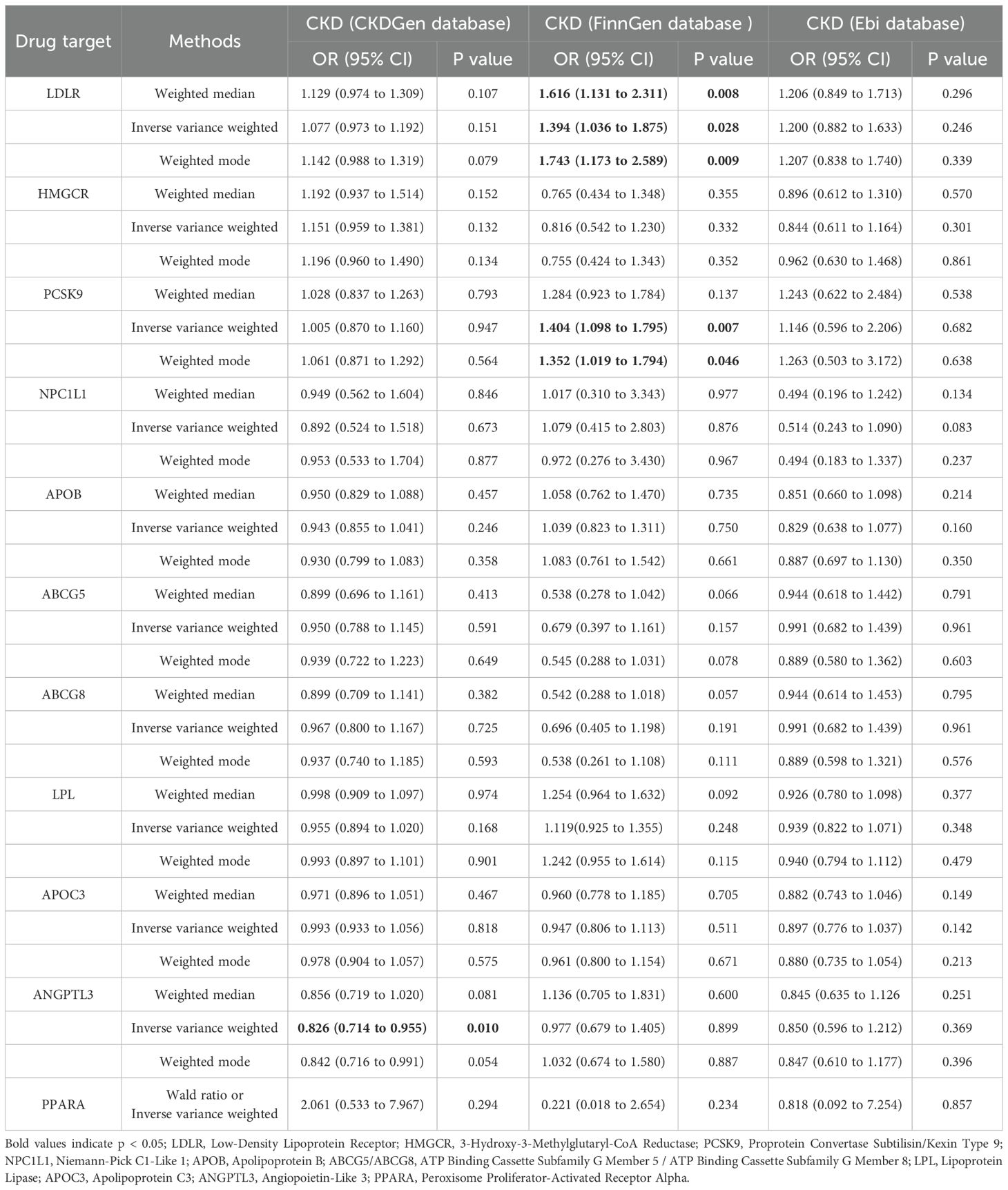
According to the IVW results, ANGPTL3 inhibitors were significantly associated with a reduced risk of CKD in the CKDGen database (OR [95% CI] = 0.826 [0.714, 0.955], p = 0.010). Conversely, in the FinnGen database, LDLR agonists (OR [95% CI] = 1.394 [1.036, 1.875], p = 0.028) and PCSK9 inhibitors (OR [95% CI] = 1.404 [1.098, 1.795], p = 0.007) were significantly associated with an increased risk of CKD. The results of the MR analysis are summarized in Table 2.
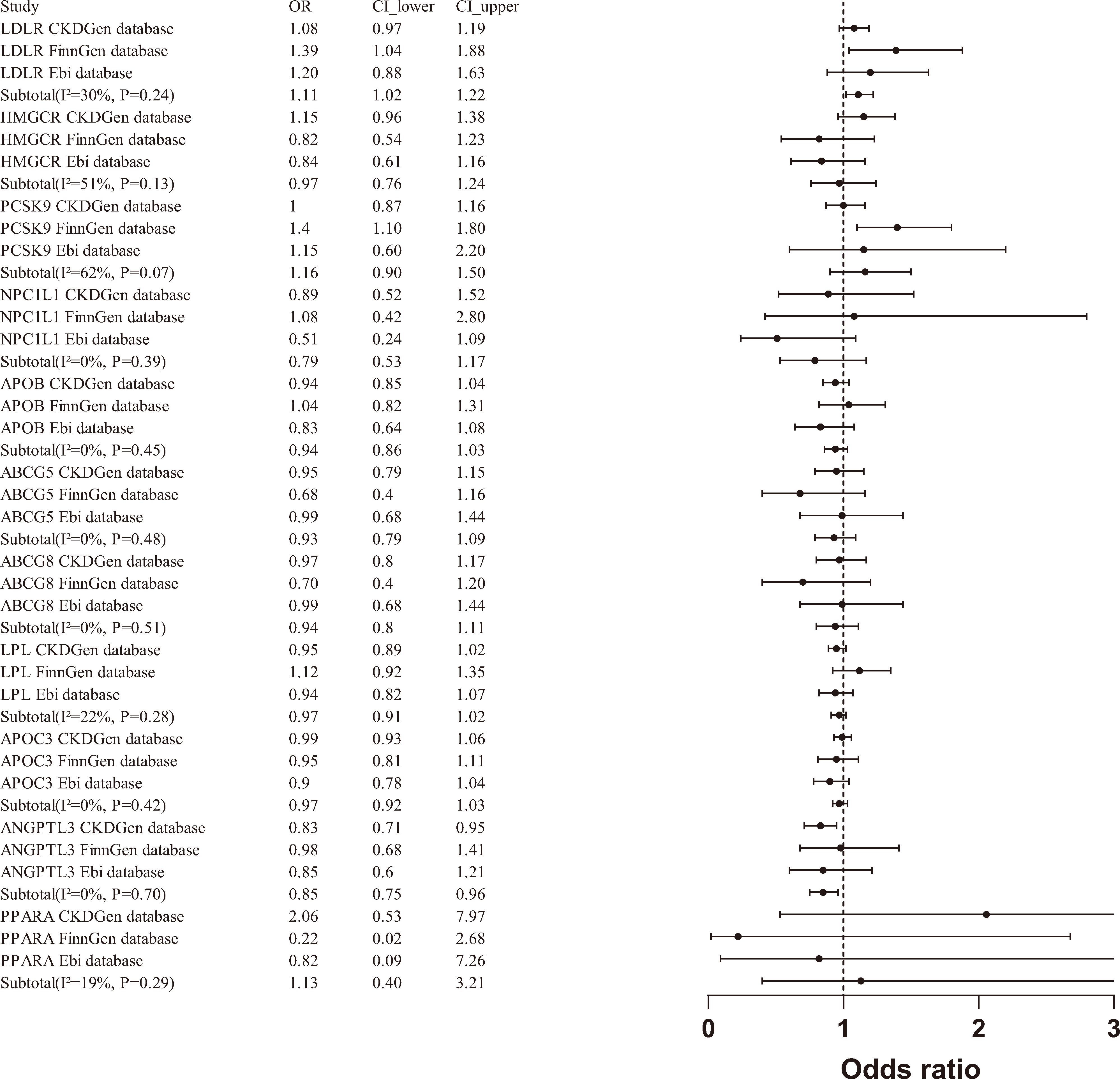
A meta-analysis of the MR results from the three databases revealed a significant association between LDLR agonists and an increased risk of CKD (OR [95% CI] = 1.11 [1.02 - 1.22]), as well as a significant association between ANGPTL3 inhibitors and a reduced risk of CKD (OR [95% CI] = 0.85 [0.75-0.96]). However, when aggregating data from the three databases, PCSK9 inhibitors (OR [95% CI] = 1.16 [0.90-1.50]) and other drug targets were not significantly associated with the risk of CKD(Figure 3).
3.3 The causal relationship between drug targets and secondary outcomes
In the MR analysis with eGFR and BUN as outcomes, although multiple drug targets showed associations with these outcomes, their impact was negligible (Supplementary Figures 9, 10).
3.4 Sensitivity analysis
Cochrane’s Q and MR Egger regression equations were employed to evaluate heterogeneity and horizontal pleiotropy levels. Significant horizontal pleiotropy was found when examining the causal relationship between LPL agonists and CKD (FinnGen) and eGFR (CKDGen) (CKD: p = 0.0311; eGFR: p = 0.0140) (Supplementary Tables 13, 14). To ensure more reliable results, we applied stricter criteria to select instrumental variables, adjusting the linkage disequilibrium parameter from r2 < 0.3 to r2 < 0.2. Subsequent MR analysis did not reveal significant horizontal pleiotropy, and these updated results were included in the meta-analysis (Supplementary Table 15). Sensitivity analysis results for certain drug targets and outcomes exhibited heterogeneity (p < 0.05) (Supplementary Tables 13, 14), while leave-one-out analysis indicated no significant differences in the results after the removal of any SNP (Supplementary Figures 1-5).
3.5 Mediation analysis
To investigate these intermediary pathways, we employed the coefficient product method in our mediation analysis, focusing on LDLR agonists and ANGPTL3 inhibitors. The findings suggest that ANGPTL3 inhibitors mitigate the risk of CKD by modulating the immune cell phenotype of HLA-DR on CD14+ CD16+ monocytes (Mediated proportion: 4.69%; Mediated effect: -0.00899) (Supplementary Figure 11, Supplementary Table 16), although the mediating effect remains relatively modest.
4 Discussion
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a prevalent condition that can lead to cardiovascular disease, renal failure, and other complications, imposing a significant societal burden due to its high prevalence and economic impact (5, 8). As a result, the epidemiology and pathogenesis of CKD are increasingly attracting global scholarly attention. Extensive experimental and clinical data indicate that hyperlipidemia is a critical shared risk factor for both CKD and cardiovascular diseases. Current research shows that abnormalities in lipid levels, akin to those in cardiovascular disease pathogenesis, are strongly associated with CKD through mechanisms such as endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and the direct toxic effects of lipids on renal cells (9, 10, 41).
This investigation employed Mendelian randomization to elucidate the causal linkages between genetic targets of lipid-lowering therapeutics and the susceptibility to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Our findings reveal a notable correlation between the activation of the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene and an elevated risk of CKD, presenting an odds ratio (OR) of 1.11 (95% CI: 1.02 to 1.22). Conversely, inhibiting the ANGPTL3 gene correlates with a reduced CKD risk, indicated by an OR of 0.85 (95% CI: 0.75 to 0.96). These findings underscore the diverse impacts of lipid regulatory pathways on renal health, highlighting the complexity of lipid metabolism in CKD progression.
Emerging research supports a significant link between ANGPTL3 inhibition and reduced CKD risk, with several studies underscoring the protective role of ANGPTL3 inhibition in renal diseases (42–45). ANGPTL3 is a pivotal regulator of lipid metabolism, modulating the activity of key enzymes like lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and endothelial lipase, which influence plasma levels of triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Recent studies have demonstrated that ANGPTL3 inhibitors not only improve lipid profiles but also offer renal benefits by mitigating lipid-induced glomerular injury and preserving endothelial function (46). Moreover, ANGPTL3’s role in lipid metabolism extends to regulating the production and clearance of VLDL, a vital carrier of triglycerides in the blood. By enhancing VLDL metabolism, ANGPTL3 inhibitors may improve the clearance of lipid particles, thereby reducing the risk of lipid accumulation and consequent renal damage (47).
Research has established that LDLR is a crucial receptor for removing LDL-C from plasma via endocytosis, and it is one of the genes associated with autosomal dominant familial hypercholesterolemia (48, 49). The activation of LDLR primarily facilitates the clearance of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol from the bloodstream, which is advantageous for reducing cardiovascular risk. However, our data indicate that LDLR activation may also exacerbate kidney disease. This adverse effect is likely due to the pathological accumulation of cholesterol in renal cells, leading to lipid toxicity—accumulated lipids disrupt cell function and induce cellular stress and damage (50–52). Further studies have shown that lipid accumulation in renal cells can promote cellular dysfunction and damage through mechanisms such as oxidative stress and inflammation, common pathways exacerbating kidney disease. For instance, excessive lipid accumulation in renal cells is linked with increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which intensifies oxidative stress and accelerates the progression of diabetic nephropathy. This stress not only impacts cell vitality but also triggers inflammatory responses, further deteriorating renal function (52). Additionally, statin drugs often elevate circulating levels of lipoprotein (a) despite reducing LDL cholesterol levels, potentially heightening residual cardiovascular risks and advancing CKD progression (53). Understanding LDLR’s dual role in cardiovascular and renal health is crucial for developing targeted therapies that mitigate the adverse effects of cholesterol accumulation in the kidneys while leveraging its cardiovascular benefits.
In the FinnGen database, PCSK9 inhibitors (OR [95%] = 1.404 [1.098, 1.795], p=0.007) were significantly associated with an increased risk of CKD occurrence. However, after meta-analyzing data from three databases (CKDGen, FinnGen, Ebi), PCSK9 inhibitors and other drug targets were found to have no significant correlation with the risk of CKD occurrence (OR[95%]=0.1.16 [0.90-1.50]), reflecting the advantages of meta-analysis and the credibility of our results. The association between PCSK9 levels and the occurrence and progression of CKD remains contentious, and there is still no direct data on PCSK9 inhibitor administration in CKD patients. Observational studies on PCSK9 levels in CKD patients have shown conflicting results. Rogavec et al. and Elewa et al. found that PCSK9 levels were higher in subjects receiving statin therapy within the same CKD group (p < 0.05) (54, 55). However, Elewa et al. also observed a positive correlation between PCSK9 levels and total cholesterol, although it was not statistically significant (p = 0.078) (55). Abujrad et al. and Konarzweski et al. found no significant correlation between lipid parameters in CKD patients undergoing hemodialysis and PCSK9 levels (56, 57). Current studies on PCSK9 levels in CKD patients are observational, lacking direct data on the impact of PCSK9 inhibitors on CKD outcomes. Our study fills this gap and validates the conclusions of current reviews, finding no significant correlation between PCSK9 levels and estimated GFR and CKD. Further research is still needed to confirm and elucidate the clinical significance of these observational findings (58).
In MR analysis with eGFR and BUN as outcomes, it was surprising to find that the impact of lipid-lowering drug targets on eGFR was negligible, suggesting that lipid-lowering drugs do not directly affect CKD progression by influencing eGFR levels. The latest meta-analysis of statins and CKD included 33 RCT studies, which similarly found no significant difference in eGFR and serum creatinine levels between the statin group and the control group (18). CKD patients undergoing statin therapy may improve kidney function by reducing urinary albumin and protein excretion or increasing creatinine clearance. The mechanistic insights provided by our mediation analysis further highlight the role of immune regulation in the context of CKD. CD14+ CD16+ monocytes are typically in an activated functional state in CKD patients, contributing to renal inflammation and immune-mediated damage (59). HLA DR, as an important antigen-presenting molecule, reflects the activation level of immune cells (60). In CKD, elevated expression of HLA DR is commonly associated with an overactive immune response and tissue damage. We observed that the protective effect of ANGPTL3 inhibitors may partially mediate through alterations in immune cell phenotypes, particularly the expression of HLA DR on CD14+ CD16+ monocytes. The mediated proportion of this effect was 4.69%, with a mediated effect size of -0.00899, underscoring a potential new pathway by which ANGPTL3 inhibition may confer kidney protection. However, the mediation effect was modest, and the results did not demonstrate significant correlation, warranting cautious interpretation of these findings.
Our study is subject to certain inevitable limitations. Firstly, MR analysis primarily evaluates causal relationships between exposures and outcomes. While it is adept at discerning the direction of these associations, it falls short in quantifying their magnitude and cannot substitute for clinical trials in practical settings. Secondly, drug-targeted MR analysis may not accurately capture the effects of short-term administration or different routes of administration. Lastly, due to limited GWAS data resources, our MR analysis was conducted exclusively on a European population, which may limit the generalizability of our findings to other ethnicities.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, our drug-targeted MR analysis demonstrated that ANGPTL3 inhibitors significantly reduce the risk of CKD, while LDLR activators are significantly associated with an increased risk of CKD. Furthermore, the study found that lipid-lowering drugs do not significantly impact eGFR and BUN levels. These findings suggest that ANGPTL3 and LDLR are promising candidate drug targets for CKD treatment. However, further validation through basic and clinical research is necessary.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GO: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LP: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JP: Methodology, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JS: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Shenzhen Medical research special fund project; project approval number: A2302048.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024.1434145/full#supplementary-material
References
1. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney diseases: Off J Natl Kidney Foundation. (2002) 39:S1–266.
2. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet (London England). (2024). doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2
3. Coresh J, Byrd-Holt D, Astor BC, Briggs JP, Eggers PW, Lacher DA, et al. Chronic kidney disease awareness, prevalence, and trends among U.S. adults, 1999 to 2000. J Am Soc Nephrology: JASN. (2005) 16:180–8. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004070539
4. Stevens LA, Coresh J, Greene T, Levey AS. Assessing kidney function–measured and estimated glomerular filtration rate. New Engl J Med. (2006) 354:2473–83. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra054415
5. de Zeeuw D, Hillege HL, de Jong PE. The kidney, a cardiovascular risk marker, and a new target for therapy. Kidney Int Supplement. (2005) 98:S25–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.09805.x
6. Hallan SI, Coresh J, Astor BC, Asberg A, Powe NR, Romundstad S, et al. International comparison of the relationship of chronic kidney disease prevalence and ESRD risk. J Am Soc Nephrology: JASN. (2006) 17:2275–84. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005121273
7. Chen J, Wildman RP, Gu D, Kusek JW, Spruill M, Reynolds K, et al. Prevalence of decreased kidney function in Chinese adults aged 35 to 74 years. Kidney Int. (2005) 68:2837–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00757.x
8. Collins AJ, Foley RN, Chavers B, Gilbertson D, Herzog C, Johansen K, et al. United States Renal Data System 2011 Annual Data Report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease & end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am J Kidney diseases: Off J Natl Kidney Foundation. (2012) 59:A7, e1–420. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.11.015
9. Gai Z, Wang T, Visentin M, Kullak-Ublick GA, Fu X, Wang Z. Lipid accumulation and chronic kidney disease. Nutrients. (2019) 11. doi: 10.3390/nu11040722
10. Sharma K, Ramachandrarao S, Qiu G, Usui HK, Zhu Y, Dunn SR, et al. Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:1645–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI32691
11. Wierzbicki AS, Kim EJ, Esan O, Ramachandran R. Hypertriglyceridaemia: an update. J Clin pathology. (2022) 75:798–806. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2021-207719
12. Aguilar-Salinas CA, Gómez-Díaz RA, Corral P. New therapies for primary hyperlipidemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 107:1216–24. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab876
13. Parhofer KG, Laufs U. The diagnosis and treatment of hypertriglyceridemia. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int. (2019) 116:825–32. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0825
14. Bosco G, Di Giacomo Barbagallo F, Spampinato S, Lanzafame L, Di Pino A, Piro S, et al. Management of statin intolerant patients in the era of novel lipid lowering therapies: A critical approach in clinical practice. J Clin Med. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062444
15. Douglas K, O’Malley PG, Jackson JL. Meta-analysis: the effect of statins on albuminuria. Ann Internal Med. (2006) 145:117–24. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-2-200607180-00009
16. Idzerda NMA, Pena MJ, Parving HH, de Zeeuw D, Heerspink HJL. Proteinuria and cholesterol reduction are independently associated with less renal function decline in statin-treated patients; a post hoc analysis of the PLANET trials. Nephrology dialysis transplantation: Off Publ Eur Dialysis Transplant Assoc - Eur Renal Assoc. (2019) 34:1699–706. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy159
17. Baigent C, Landray MJ, Reith C, Emberson J, Wheeler DC, Tomson C, et al. The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with simvastatin plus ezetimibe in patients with chronic kidney disease (Study of Heart and Renal Protection): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London England). (2011) 377:2181–92. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60739-3
18. Zhao L, Li S, Gao Y. Efficacy of statins on renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Renal failure. (2021) 43:718–28. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1915799
19. Sekula P, Del Greco MF, Pattaro C, Köttgen A. Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data. J Am Soc Nephrology: JASN. (2016) 27:3253–65. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016010098
20. Birney E. Mendelian randomization. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. (2022) 12. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041302
21. Evans DS. Target discovery for drug development using mendelian randomization. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton NJ). (2022) 2547:1–20. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2573-6_1
22. Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Sterne JA, Timpson N, Davey Smith G. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med. (2008) 27:1133–63. doi: 10.1002/sim.v27:8
23. Li R, Peng L, Deng D, Li G, Wu S. Potential causal association between aspirin use and erectile dysfunction in European population: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1329847. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1329847
24. Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:111–88. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455
25. Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: A report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. (2019) 139:e1082–e143. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000625
26. Richardson TG, Sanderson E, Palmer TM, Ala-Korpela M, Ference BA, Davey Smith G, et al. Evaluating the relationship between circulating lipoprotein lipids and apolipoproteins with risk of coronary heart disease: A multivariable Mendelian randomisation analysis. PloS Med. (2020) 17:e1003062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003062
27. Machiela MJ, Chanock SJ. LDassoc: an online tool for interactively exploring genome-wide association study results and prioritizing variants for functional investigation. Bioinf (Oxford England). (2018) 34:887–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx561
28. Lin SH, Brown DW, Machiela MJ. LDtrait: an online tool for identifying published phenotype associations in linkage disequilibrium. Cancer Res. (2020) 80:3443–6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0985
29. Mallamaci F, Tripepi G. Risk factors of chronic kidney disease progression: between old and new concepts. J Clin Med. (2024) 13. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030678
30. Nikpay M, Goel A, Won HH, Hall LM, Willenborg C, Kanoni S, et al. A comprehensive 1,000 Genomes-based genome-wide association meta-analysis of coronary artery disease. Nat Genet. (2015) 47:1121–30. doi: 10.1038/ng.3396
31. Wuttke M, Li Y, Li M, Sieber KB, Feitosa MF, Gorski M, et al. A catalog of genetic loci associated with kidney function from analyses of a million individuals. Nat Genet. (2019) 51:957–72. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0407-x
32. Pattaro C, Teumer A, Gorski M, Chu AY, Li M, Mijatovic V, et al. Genetic associations at 53 loci highlight cell types and biological pathways relevant for kidney function. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10023. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10023
33. Orrù V, Steri M, Sidore C, Marongiu M, Serra V, Olla S, et al. Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy. Nat Genet. (2020) 52:1036–45. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0684-4
34. Burgess S, Scott RA, Timpson NJ, Davey Smith G, Thompson SG. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur J Epidemiol. (2015) 30:543–52. doi: 10.1007/s10654-015-0011-z
35. Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, Burgess S. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. (2016) 40:304–14. doi: 10.1002/gepi.2016.40.issue-4
36. Hartwig FP, Davey Smith G, Bowden J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int J Epidemiol. (2017) 46:1985–98. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyx102
37. Li R, Huang G, Li Y, Huang M, Huang Y, Li Y, et al. Assessing the role of statin therapy in bladder cancer: evidence from a Mendelian Randomization study. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1427318. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1427318
38. Lortie CJ, Filazzola A. A contrast of meta and metafor packages for meta-analyses in R. Ecol evolution. (2020) 10:10916–21. doi: 10.1002/ece3.v10.20
39. Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. (2018) 50:693–8. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7
40. Zhang Y, Ou G, Li R, Peng L, Shi J. Causal relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Postgraduate Med J. (2024). doi: 10.1093/postmj/qgae163
41. Agrawal S, Zaritsky JJ, Fornoni A, Smoyer WE. Dyslipidaemia in nephrotic syndrome: mechanisms and treatment. Nat Rev Nephrology. (2018) 14:57–70. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.155
42. Ji B, Liu J, Ma Y, Yin Y, Xu H, Shen Q, et al. Minnelide combined with Angptl3 knockout completely protects mice with adriamycin nephropathy via suppression of TGF-β1-Smad2 and p53 pathways. Int immunopharmacology. (2023) 115:109656. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109656
43. Ji B, Liu J, Yin Y, Xu H, Shen Q, Yu J. Minnelide combined with anti-ANGPTL3-FLD monoclonal antibody completely protects mice with adriamycin nephropathy by promoting autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis. Cell Death disease. (2023) 14:601. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06124-0
44. Li G, Lu D, Wang J, Yue S, Tan M, Liu M, et al. ANGPTL3 is involved in kidney injury in high-fat diet-fed mice by suppressing ACTN4 expression. Lipids Health disease. (2022) 21:90. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01700-3
45. Ma Y, Chen Y, Xu H, Du N. The influence of angiopoietin-like protein 3 on macrophages polarization and its effect on the podocyte EMT in diabetic nephropathy. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1228399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1228399
46. Su X, Peng DQ. New insights into ANGPLT3 in controlling lipoprotein metabolism and risk of cardiovascular diseases. Lipids Health disease. (2018) 17:12. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0659-y
47. Chen J, Fang Z, Luo Q, Wang X, Warda M, Das A, et al. Unlocking the mysteries of VLDL: exploring its production, intracellular trafficking, and metabolism as therapeutic targets. Lipids Health disease. (2024) 23:14. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01993-y
48. Go GW, Mani A. Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family orchestrates cholesterol homeostasis. Yale J Biol Med. (2012) 85:19–28.
49. Santos PC, Pereira AC. Type of LDLR mutation and the pharmacogenetics of familial hypercholesterolemia treatment. Pharmacogenomics. (2015) 16:1743–50. doi: 10.2217/pgs.15.113
50. Chae SY, Kim Y, Park CW. Oxidative stress induced by lipotoxicity and renal hypoxia in diabetic kidney disease and possible therapeutic interventions: targeting the lipid metabolism and hypoxia. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122083
51. Mitrofanova A, Merscher S, Fornoni A. Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrology. (2023) 19:629–45. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00741-w
52. Njeim R, Alkhansa S, Fornoni A. Unraveling the crosstalk between lipids and NADPH oxidases in diabetic kidney disease. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051360
53. Tsimikas S. A test in context: lipoprotein(a): diagnosis, prognosis, controversies, and emerging therapies. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 69:692–711. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.11.042
54. Rogacev KS, Heine GH, Silbernagel G, Kleber ME, Seiler S, Emrich I, et al. PCSK9 plasma concentrations are independent of GFR and do not predict cardiovascular events in patients with decreased GFR. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0146920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146920
55. Elewa U, Fernández-Fernández B, Mahillo-Fernández I, Martin-Cleary C, Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, et al. PCSK9 in diabetic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Invest. (2016) 46:779–86. doi: 10.1111/eci.2016.46.issue-9
56. Konarzewski M, Szolkiewicz M, Sucajtys-Szulc E, Blaszak J, Lizakowski S, Swierczynski J, et al. Elevated circulating PCSK-9 concentration in renal failure patients is corrected by renal replacement therapy. Am J nephrology. (2014) 40:157–63. doi: 10.1159/000365935
57. Abujrad H, Mayne J, Ruzicka M, Cousins M, Raymond A, Cheesman J, et al. Chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis is associated with decreased serum PCSK9 levels. Atherosclerosis. (2014) 233:123–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.12.030
58. Pavlakou P, Liberopoulos E, Dounousi E, Elisaf M. PCSK9 in chronic kidney disease. Int Urol nephrology. (2017) 49:1015–24. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1505-2
59. Lee JW, Cho E, Kim MG, Jo SK, Cho WY, Kim HK. Proinflammatory CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes are associated with vascular stiffness in predialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Res Clin practice. (2013) 32:147–52. doi: 10.1016/j.krcp.2013.08.001
Keywords: chronic kidney disease, lipid-lowering drug, lipids, Mendelian randomization analysis, estimated glomerular filtration rate
Citation: Zhang Y, Ou G, Peng L, Pan J, Zhang S and Shi J (2025) Genetic association analysis of lipid-lowering drug target genes in chronic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1434145. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1434145
Received: 13 June 2024; Accepted: 23 December 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Caixia Sun, Nanyang Technological University, SingaporeReviewed by:
Mingming Wang, Jiangsu University, ChinaZhai Weijie, First Affiliated Hospital of Jilin University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Ou, Peng, Pan, Zhang and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianguo Shi, c2pnX2Nvb2xAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Shaohua Zhang, MjJ6c2hAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yi Zhang
Yi Zhang Guangyang Ou
Guangyang Ou Lei Peng
Lei Peng Jian Pan
Jian Pan Shaohua Zhang
Shaohua Zhang Jianguo Shi
Jianguo Shi