- 1Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 3Rehabilitation Department, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
Aims: Previous studies on the association between vitamin E and blood pressure (BP) levels are controversial. Our study aimed to evaluate the association between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and systolic and diastolic BP in an adult population with diabetes and without diabetes.
Methods: Our study data were obtained from a biomarker project of the Midlife in the United States (MIDUS) study. A total of 1068 subjects were included, and the associations between alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol levels and systolic and diastolic BP were further analyzed by smooth curve and multivariate linear regression analyses.
Results: Our smooth curve analysis showed an almost linear correlation between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and systolic and diastolic BP. Furthermore, we found that blood gamma-tocopherol levels were positively and independently associated with systolic BP (B=0.427, 95% CI 0.067-0.787, P=0.020) and diastolic BP (B=0.289, 95% CI 0.072-0.507, P=0.009) when the data were adjusted for age, gender, body mass index (BMI), ever smoked cigarettes regularly, number of years of consuming alcohol and regular exercise or activity for 20 minutes or more at least 3 times/week. Consistently, blood alpha-tocopherol levels were also positively associated with systolic BP (B=0.150, 95% CI 0.064-0.235, P=0.001) and diastolic BP (B=0.056, 95% CI 0.004-0.107, P=0.035) after these variables were adjusted. However, these significant relationships exist only in subjects without diabetes, but not in subjects with diabetes.
Conclusions: We observed for the first time that blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels were positively associated with systolic and diastolic BP in subjects without diabetes.
Introduction
Hypertension has been considered a global, common, important public health problem (1, 2). Existing evidence reported that approximately 9.4 million people died of hypertension and its complications, such as coronary heart disease, heart failure and stroke, on a worldwide scale (3), and the hypertensive population might exceed 500 million in the next decade (4). Although many etiologies or risk factors, including aging, obesity, a high-salt diet, less exercise, high social pressure and others for hypertension, have been identified, we are unable to do anything about these risk factors or the intervention is not sufficiently effective (5). Therefore, early prevention of hypertension has important clinical significance for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Nitric oxide (NO) mainly originated from renal tubular cells and vascular endothelium plays an important role in keeping blood pressure (BP) within a normal range (6). Previous studies have suggested that reduced NO expression contributes to the development of hypertension (7). For example, one study reported increased expression of reactive oxygen species (ROS), elevated oxidative stress and a low inflammatory response in hypertensive subjects, which can reduce NO bioavailability (8). NO bioavailability can be regulated and controlled by excessive ROS production in hypertensive patients (9). Importantly, the cellular production of antioxidants can also promote NO expression due to the beneficial properties of antioxidants in scavenging free radicals. Antioxidants play vital roles in reducing ROS production and increasing NO bioavailability (10).
As an antioxidant, vitamin E is a type of fat soluble vitamin that includes four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. All vitamin E forms also have relatively consistent antioxidant properties (11). Existing studies have demonstrated that vitamin E can exert protective effects on endothelial function in the vasculature by scavenging ROS and exerting anti-inflammatory properties, which can further promote NO expression and bioavailability (11, 12). One study also showed that compared with placebo, vitamin E supplementation for approximately 7 months could lower BP in mild hypertensive subjects (13). Moreover, some clinical trials have suggested the beneficial impacts of vitamin E supplementation on BP in different populations (14, 15).
However, few studies have investigated the association between blood vitamin E levels and BP in the adult population with diabetes. We conducted a cross-sectional analysis to investigate the association between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and BP in the adult population with diabetes and without diabetes.
Methods
Our study data were obtained from the Midlife in the United States (MIDUS) study, involving more than seven thousand nonhospitalized adults aged from 25 to 75 years. The MIDUS study started in 1995 (16), and a 9-year follow-up (MIDUS 2) was conducted between 2004 and 2006 with 4,963 subjects (17). A subgroup of these subjects participated in a biomarker study (N = 1255) (18). Each subject was invited to undergo a comprehensive examination at clinical research centers. The comprehensive physical examination, biological sample collection and medical history records were conducted by trained medical staff. Full details of the MIDUS study biomarker protocol are available elsewhere (17–19). In the biomarker study, fasting blood samples were obtained from patients before breakfast, and then these samples were sent to the MIDUS Biocore laboratory for further analysis. In the present study, blood levels of gamma-tocopherol, alpha-tocopherol, hemoglobin A1c %, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were analyzed. A history of diabetes was registered as “diagnosed with diabetes” or “without diabetes” in this dataset. In summary, after excluding subjects with missing data (N=187) in the biomarker study, the remaining 1068 subjects were included and further analyzed in our cross-sectional analysis. Accordance to the Declaration of Helsinki, all protocols in present study were granted full ethical approval as part of the MIDUS 2 Biomarker Project and informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Confounding variables
The following variables were included as confounding variables at the biomarker clinic visit: age, sex (male and female), body mass index (BMI), smoking (ever smoked cigarettes regularly), drinking (number of years of alcohol consumption) and physical activity (regular exercise for 20 minutes or more at least 3 times/week or not). BMI is defined as weight (kg) divided by the square of height (m2).
Statistical analysis
All of the data were analyzed by using SPSS 26.0 and EmpowerStats. P ≤ 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant results. For the purpose of the study, all included study samples were divided into two groups (diagnosed with diabetes and without diabetes) according to the history of diabetes. These continuous variables were analyzed using the Mann–Whitney U test, and categorical variables were analyzed by the chi-square test. Then, a smooth curve was performed to evaluate the associations between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and systolic and diastolic BP. Furthermore, multivariate linear regression models were used to evaluate the associations of blood alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol levels and BP by adjusting for confounding factors. Confounding factors, including age and sex, were included in Model 1. Adjustment of confounding factors, including age, sex and BMI, was performed in Model 2. In Model 3, adjustments for age, sex, BMI, ever smoked cigarettes regularly and number of years consuming alcohol were performed. In Model 4, adjustments for age, sex, BMI, ever smoked cigarettes regularly, number of years consuming alcohol were and regular exercise for 20 minutes or more at least 3 times/week were performed. Finally, to investigate whether diabetes has an impact on the relationships between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and systolic and diastolic BP, stratified analysis was performed by adding “ever diagnosed with diabetes” as the stratification variable.
Results
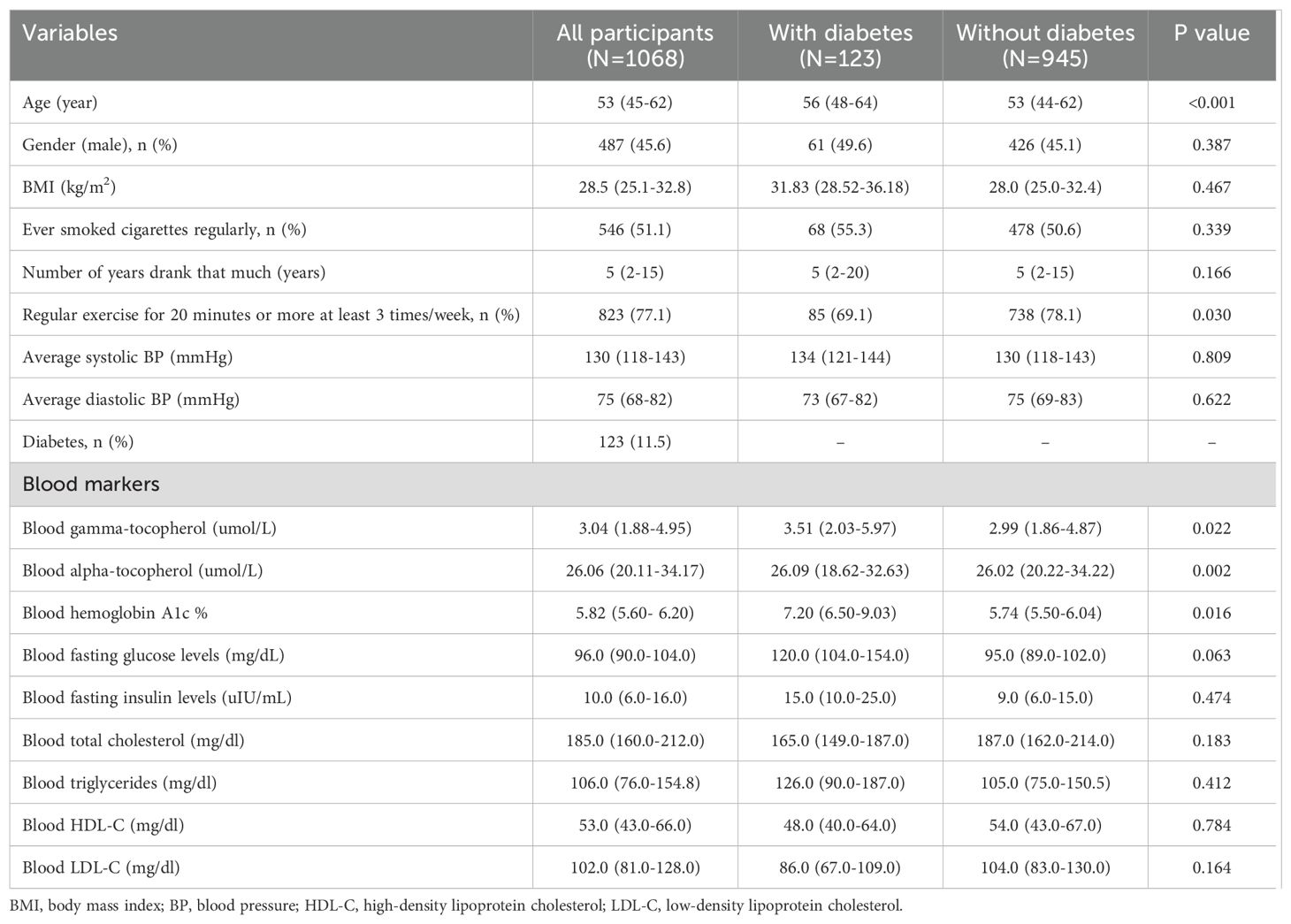
The demographic characteristics and lifestyles of all included participants are described in Table 1. The median age of participants was 53 years, and 487 participants were male (45.6%). The median values of blood gamma-tocopherol and alpha-tocopherol levels were 3.04 µmol/L and 26.06 µmol/L, respectively. The median systolic BP and diastolic BP values were 130 mmHg and 75 mmHg, respectively. These participants were divided into two groups (diagnosed with diabetes and without diabetes). Participants diagnosed with diabetes tended to have a higher age and lower rate of physical activities and had higher levels of blood gamma-tocopherol and alpha-tocopherol than participants never diagnosed with diabetes (all P <0.05). However, differences in systolic and diastolic BP were not noted between the group diagnosed with diabetes and the group without diabetes.
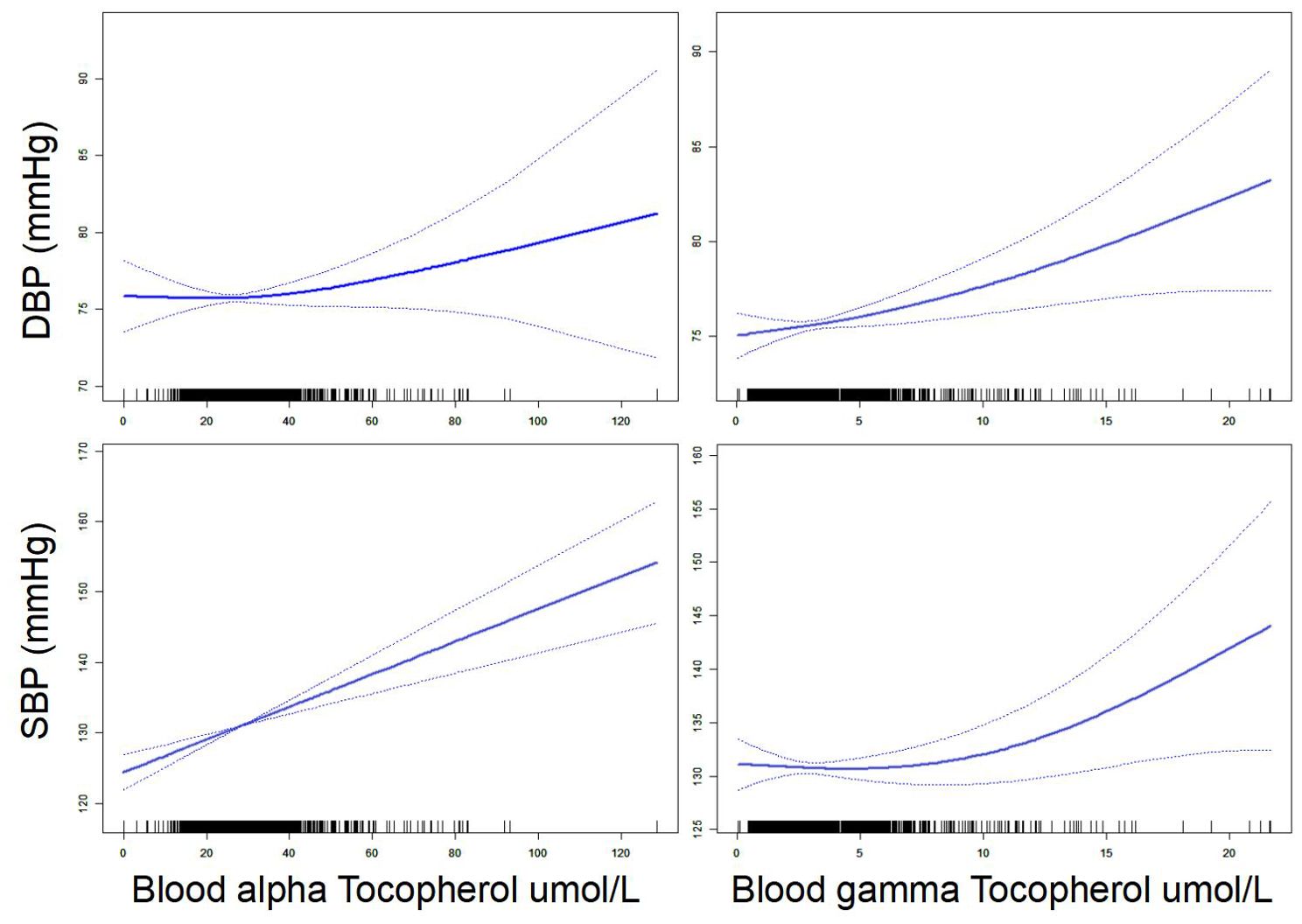
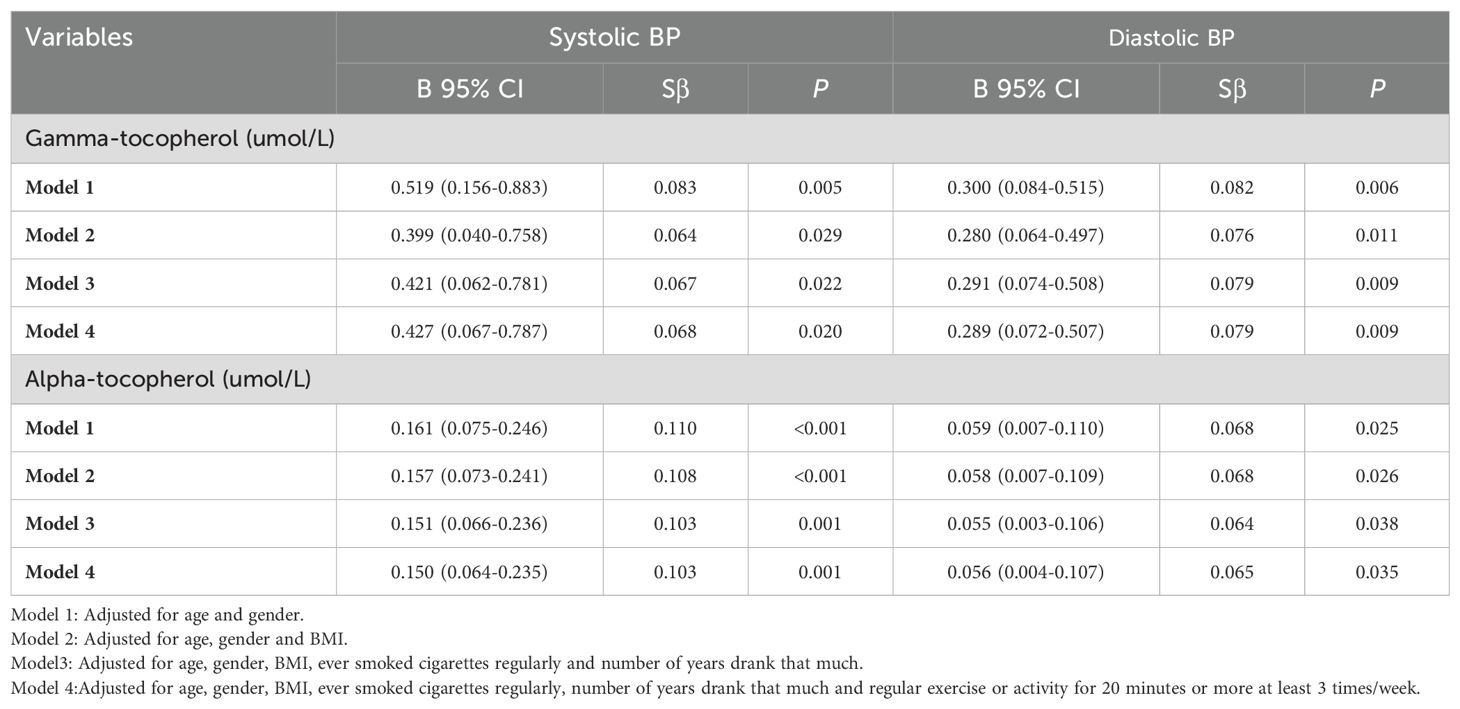
First, our smooth curve analysis showed an almost linear correlation between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and systolic and diastolic BP (Figure 1). For further clarity of the association between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and BP, multivariate linear regression analysis was used. Our results suggested that blood gamma-tocopherol levels were positively related to systolic BP (B=0.519, 95% CI 0.156-0.883, P=0.005) and diastolic BP (B=0.300, 95% CI 0.084-0.515, P=0.006) when age and gender were adjusted in Model 1 (Table 2). Similarly, blood alpha-tocopherol levels were positively related to systolic BP (B=0.161, 95% CI 0.075-0.246, P<0.001) and diastolic BP (B=0.059, 95% CI 0.007-0.110, P=0.025) after adjusting for age and gender in Model 1. Furthermore, these positive associations between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and systolic and diastolic BP changed slightly after adjusting for BMI, ever smoked cigarettes regularly and number of years of alcohol consumption in Models 2 and 3. Finally, we found that blood gamma-tocopherol levels were still positively associated with systolic BP (B=0.427, 95% CI 0.067-0.787, P=0.020) and diastolic BP (B=0.289, 95% CI 0.072-0.507, P=0.009) when further adjusting for regular exercise or activity for 20 minutes or more at least 3 times/week in Model 4. Consistently, blood alpha-tocopherol levels were also positively associated with systolic BP (B=0.150, 95% CI 0.064-0.235, P=0.001) and diastolic BP (B=0.056, 95% CI 0.004-0.107, P=0.035).
To assess whether diabetes has an impact on this relationship between blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels and systolic and diastolic BP, stratified analysis by adding “diagnosed with diabetes” as the hierarchical variable was performed. As shown in Table 3, blood gamma-tocopherol levels were significantly associated with systolic BP (B=0.446, 95% CI 0.044-0.849, P=0.030) and diastolic BP (B=0.317, 95% CI 0.075-0.560, P=0.010) in subjects without diabetes after adjusting for age, gender, BMI, ever smoked cigarettes regularly, number of years consuming alcohol and regular exercise or activity for 20 minutes or more at least 3 times/week in Model 4. Similarly, blood alpha-tocopherol levels were still significantly associated with systolic BP (B=0.149, 95% CI 0.057-0.241, P=0.002) and diastolic BP (B=0.062, 95% CI 0.007-0.118, P=0.028) in subjects without diabetes after adjusting for the same confounding factors in Model 4.
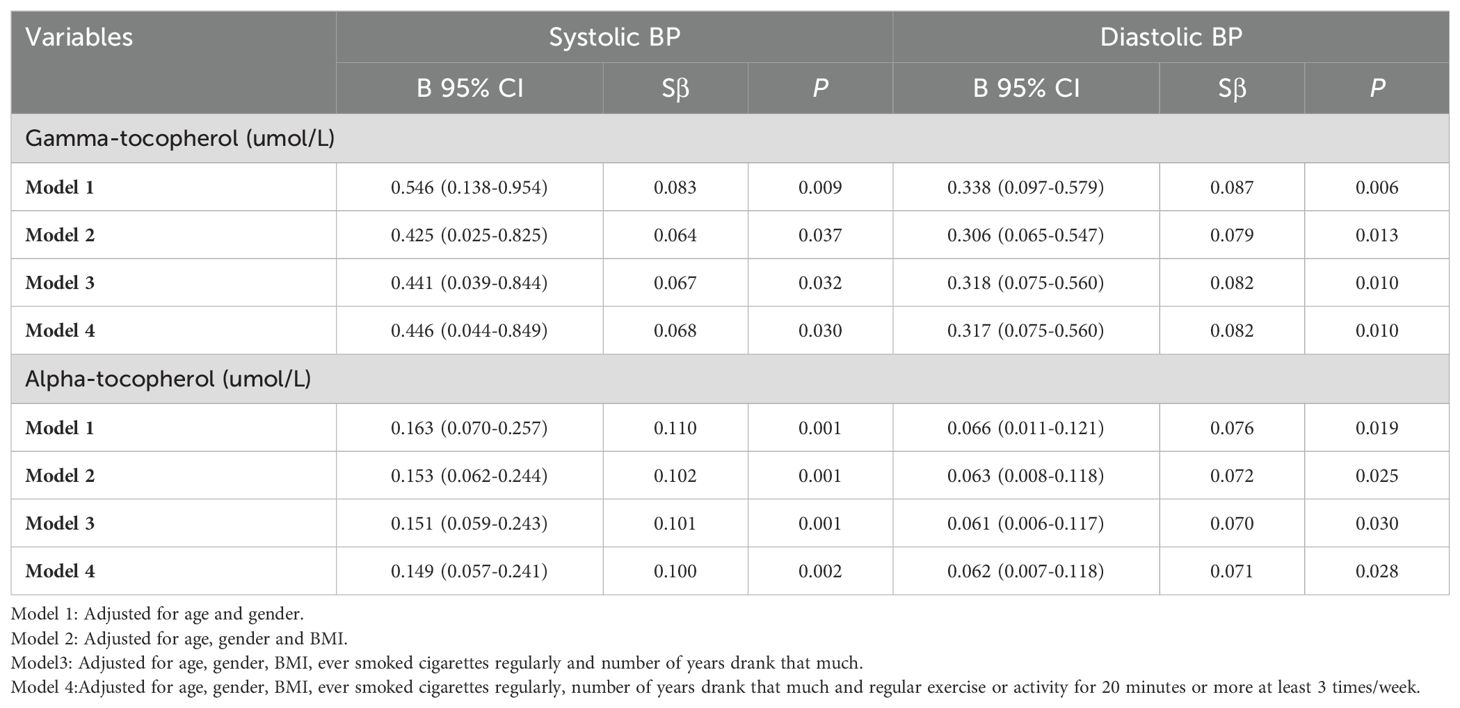
Table 3. Relationship between blood gamma-tocopherol and alpha-tocopherol levels and BP in patients without diabetes (N=945).
However, inconsistently, blood gamma-tocopherol levels were not related to systolic BP (B=0.315, 95% CI -0.564-1.195, P=0.479) or diastolic BP (B=0.230, 95% CI -0.285-0.745, P=0.378) in subjects with diabetes after adjustments were made in Model 4 (Table 4). Additionally, blood alpha-tocopherol levels were not related to systolic BP (B=0.092, 95% CI -0.140-0.325, P=0.433) or diastolic BP (B=-0.012, 95% CI -0.149-0.124, P=0.858) in subjects with diabetes after adjusting for the same confounding factors in Model 4.
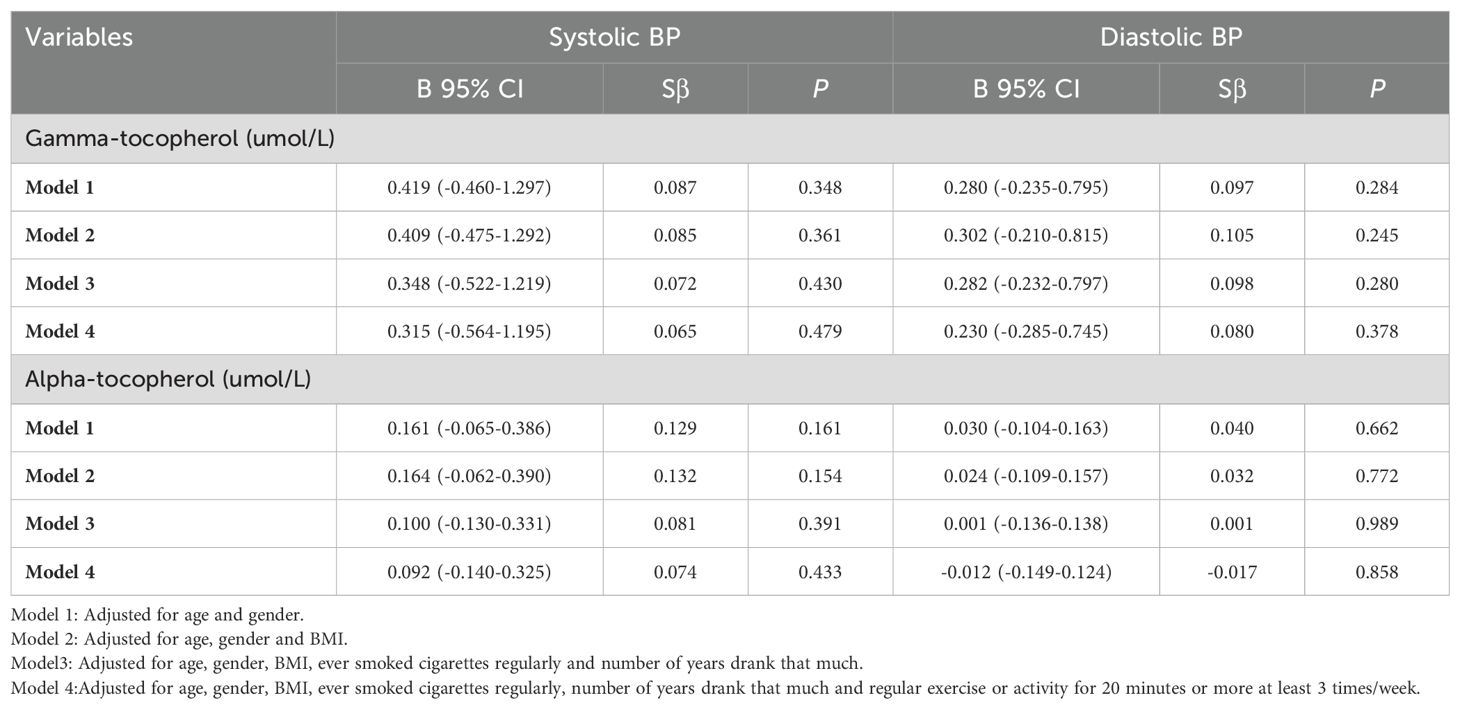
Table 4. Relationship between blood gamma-tocopherol and alpha-tocopherol levels and BP in patients with diabetes (N=123).
Discussion
Our study first identified blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels as independently associated with BP in subjects without diabetes but not in subjects with diabetes. The association was consistent in our regression models adjusted for a great range of confounding factors, including demographic characteristics and lifestyle. One of the important explanations for the effect of vitamin E in BP is the NO system (19). NO originating from the vascular endothelium plays a vital role in regulating BP, and endothelial dysfunction caused by various pathological factors subsequently increases BP (20). A systemic excessive accumulation of ROS caused by oxidative stress can eliminate NO and lower NO bioavailability (6). Vitamin E, as a lipid-soluble vitamin, has many important effects on cell protection and the immune system (12). Vitamin E can attenuate oxidative stress and neutralize ROS and thus can improve NO production and bioavailability (12).
In fact, the effect of vitamin E on BP has been investigated in some studies, and these conclusions were inconsistent. For example, previous studies have reported that vitamin E supplementation of 200 IU/day could lead to a greater than 20% reduction in systolic BP over 7 months in hypertensive patients (13). However, a clinical trial demonstrated that vitamin E supplementation of 400 IU daily for 8 weeks did not lower BP levels in a middle-aged and elderly population (21). In view of this finding, a recent meta-analysis of the association between vitamin E supplementation and BP was performed (22). The meta-analysis included 839 participants from 18 clinical trials and reported that supplementation with vitamin E can significantly decrease systolic BP but not diastolic BP (22). Inconsistent with our results, increased blood alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol levels were associated with elevated systolic and diastolic BP in subjects without diabetes but not in subjects with diabetes. These inconsistent results may account for the inclusion of sample populations with different ages, lifestyles, dietary habits, concomitant diseases, various blood measurements and data analysis methods. Consistent with our results, another clinical trial reported no change in diastolic BP after alpha-tocopherol supplementation of 1200 IU/day for 8 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (23). Additionally, some clinical studies also showed that vitamin E supplementation had no impact on systolic BP in hypertensive subjects (24). However, these studies did not measure blood vitamin E levels, and only oral intake of vitamin E was evaluated, which may be one of the important reasons for the inconsistent results.
Importantly, recent research also implied that vitamin E may have a negative impact on health. For example, an analysis from a cross-sectional study in Germany suggested that increased serum levels of vitamin E were related to a higher content of visceral fat and an increased risk of metabolic syndrome (25), which is similar to our results. However, another study found an inverse association between vitamin E consumption and metabolic syndrome and subsequently showed mild improvement in insulin resistance after three months (26). But, oral intake of vitamin E was assessed in this study instead of its blood levels. Additionally, retinol binding protein (RBP) plays a vital role in maintaining serum levels of vitamin A. Elevated serum RBP levels are associated with higher BP, serum triglyceride levels, BMI and insulin resistance (27, 28). A basic experiment showed similar results that the number of RBP4 variants was related to a higher risk of hypertriglyceridemia (29). Previous studies surrounding oral intake and serum levels of vitamins have also discovered conflicting results in a Korean population. In a study including 404 old adults in Korea, Kim et al. observed an inverse association between oral and serum vitamin (retinol and α-tocopherol) levels and the risk of metabolic syndrome in elderly women (30). Similarly, increased intake of vitamin E was related to a reduced prevalence of metabolic syndrome (31). However, Cho et al. reported that high serum α-tocopherol levels contributed to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome (32), which is consistent with our results.
Some potential mechanisms regarding the negative impacts of antioxidants on CVD health have been proposed. Also, several plausible explanations for vitamin E exist. First, the relationship between serum alpha-tocopherol levels and adipose tissue may affect this association. The content of visceral adipose tissue was positively related to the alpha-tocopherol/cholesterol ratio, which was associated with a higher odds ratio for metabolic syndrome (25). Second, the metabolite levels of tocopherol in blood and urine samples were significantly reduced in patients with metabolic syndrome compared with the healthy population, suggesting that tocopherol catabolism is significantly retarded in these subjects with metabolic syndrome (33). These results seem to partly explain the positive association between vitamin E and BP in subjects without diabetes.
Our study has several notable strengths. On the one hand, we are the first to report that blood vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol) levels were positively associated with BP in subjects without diabetes but not in subjects with diabetes after adjusting for a great range of confounding factors, including demographic characteristics and lifestyle. On the other hand, our study included a large sample of data from MIDUS, and the analysis was performed by professional researchers. Furthermore, we directly evaluated serum alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol levels, which reflect the real relationship between vitamin E within the human bod and BP, rather than the oral intake of vitamin E. This information expands data presented in the few relevant studies. Certainly, this study also has several limitations. First, although various confounding factors were adjusted in the study given that these factors may influence blood vitamin E levels, some confounding factors, such as medications and other relevant clinical data that should also be evaluated as confounding variables, cannot be fully eliminated. Second, serum levels of vitamin E were measured only at a single period of time, which might cause survivorship biases in the cross-sectional design. Third, our study lacked data on the postmenopausal status and it may affect the results obtained. Fourth, using many various covariates in our regression analysis may cause overfitting of the model, leading to bias in the results. Fifth, given that this study is a post hoc analysis, biases cannot be excluded. Finally, we did not further investigate the mechanisms underlying the association of blood vitamin E with BP.
In conclusion, we revealed that blood vitamin E levels were positively associated with BP in subjects without diabetes rather than those with diabetes. These results are inconsistent with the traditional understanding that antioxidants can improve BP.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
All protocols in present study were granted full ethical approval as part of the MIDUS 2 Biomarker Project and informed consent was obtained from each participant. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
RW: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. YS: Data curation, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YH: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The study is supported by supported by Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20242BAB25434), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20224BAB216019) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (82060059).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. (2005) 365:217–23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17741-1
2. Campbell NR, Lackland DT, Niebylski ML. The hypertension pandemic: an evolutionary perspective. Physiol (Bethesda). (2017) 32:112–25. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00026.2016
3. Campbell NR, Lackland DT, Niebylski ML, World Hypertension League Committee, International Society of Hypertension Executive Committee. High blood pressure: why prevention and control are urgent and important: a 2014 fact sheet from the World Hypertension League and the International Society of Hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). (2014) 16(8):551–3. doi: 10.1111/jch.12372
4. Fuentes R, Ilmaniemi N, Laurikainen E, Tuomilehto J, Nissinen A. Hypertension in developing economies: a review of population-based studies carried out from 1980 to 1998. J Hypertens. (2000) 18:521–9. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018050-00003
5. Fuchs FD, Whelton PK. High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension. (2020) 75:285–92. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14240
6. Brunner H, Cockcroft JR, Deanfield J, Donald A, Ferrannini E, Halcox J, et al. Endothelial function and dysfunction. Part II: Association with cardiovascular risk factors and diseases. A statement by the Working Group on Endothelins and Endothelial Factors of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. (2005) 23:233–46. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200502000-00001
7. Rajapakse NW, Giam B, Kuruppu S, Head GA, Kaye DM. Impaired l-arginine-nitric oxide pathway contributes to the pathogenesis of resistant hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond). (2019) 133:2061–7. doi: 10.1042/CS20190851
8. Huang PL, Huang Z, Mashimo H, Bloch KD, Moskowitz MA, Bevan JA, et al. Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nature. (1995) 377:239–42. doi: 10.1038/377239a0
9. Maarman GJ. Natural antioxidants as potential therapy, and a promising role for melatonin against pulmonary hypertension. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2017) 967:161–78. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-63245-2_10
10. Incalza MA, D'Oria R, Natalicchio A, Perrini S, Laviola L, Giorgino F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul Pharmacol. (2018) 100:1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.05.005
11. Galli F, Azzi A, Birringer M, Cook-Mills JM, Eggersdorfer M, Frank J, et al. Vitamin E: Emerging aspects and new directions. Free Radic Biol Med. (2017) 102:16–36. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.017
12. Sen CK, Rink C, Khanna S. Palm oil-derived natural vitamin E alpha-tocotrienol in brain health and disease. J Am Coll Nutr. (2010) 29:314S–23S. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2010.10719846
13. Boshtam M, Rafiei M, Sadeghi K, Sarraf-Zadegan N. Vitamin E can reduce blood pressure in mild hypertensives. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. (2002) 72:309–14. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831.72.5.309
14. Chiu HF, Venkatakrishnan K, Golovinskaia O, Wang CK. Impact of micronutrients on hypertension: evidence from clinical trials with a special focus on meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2021) 13:588. doi: 10.3390/nu13020588
15. Wang Q, Xu X, Zeng Z, Zheng X, Ye K, Huo X. Antioxidant alterations link polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to blood pressure in children. Sci Total Environ. (2020) 732:138944. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138944
16. Brim OG, Baltes PB, Bumpass LL, Cleary PD, Featherman DL, Hazzard WR, et al. Midlife in the United States (MIDUS 1), 1995–1996 (ICPSR 2760; Version V18) [Data set]. ICPSR (2019). doi: 10.3886/ICPSR02760.v18
17. Ryff C, Almeida DM, Ayanian J, Carr DS, Cleary PD, Coe C, et al. Midlife in the United States (MIDUS 2), 2004–2006 (ICPSR 4652; Version V7) [Data set]. ICPSR (2017). doi: 10.3886/ICPSR04652.v7
18. Ryff CD, Seeman T, Weinstein M. Midlife in the United States (MIDUS 2): Biomarker Project, 2004–2009 (ICPSR 29282; Version V9) [Data set]. ICPSR (2019). doi: 10.3886/ICPSR29282.v9
19. Guan SP, Seet RCS, Kennedy BK. Does eNOS derived nitric oxide protect the young from severe COVID-19 complications? Ageing Res Rev. (2020) 64:101201. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101201
20. Dikalova AE, Pandey A, Xiao L, Arslanbaeva L, Sidorova T, Lopez MG, et al. Mitochondrial deacetylase sirt3 reduces vascular dysfunction and hypertension while sirt3 depletion in essential hypertension is linked to vascular inflammation and oxidative stress. Circ Res. (2020) 126:439–52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315767
21. Mottram P, Shige H, Nestel P. Vitamin E improves arterial compliance in middle-aged men and women. Atherosclerosis. (1999) 145:399–404. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9150(99)00073-8
22. Emami MR, Safabakhsh M, Alizadeh S, Asbaghi O, Khosroshahi MZ. Effect of vitamin E supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens. (2019) 33:499–507. doi: 10.1038/s41371-019-0192-0
23. Gazis A, White DJ, Page SR, Cockcroft JR. Effect of oral vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) supplementation on vascular endothelial function in Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Med. (1999) 16:304–11. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00049.x
24. Palumbo G, Avanzini F, Alli C, Roncaglioni MC, Ronchi E, Cristofari M, et al. Effects of vitamin E on clinic and ambulatory blood pressure in treated hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens. (2000) 13:564–7. doi: 10.1016/S0895-7061(00)00244-2
25. Waniek S, di Giuseppe R, Plachta-Danielzik S, Ratjen I, Jacobs G, Koch M, et al. Association of vitamin E levels with metabolic syndrome, and MRI-derived body fat volumes and liver fat content. Nutrients. (2017) 9:1143. doi: 10.3390/nu9101143
26. Manning PJ, Sutherland WH, Walker RJ, Williams SM, De Jong SA, Ryalls AR, et al. Effect of high-dose vitamin E on insulin resistance and associated parameters in overweight subjects. Diabetes Care. (2004) 27:2166–71. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.9.2166
27. Graham TE, Yang Q, Blüher M, Hammarstedt A, Ciaraldi TP, Henry RR, et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. (2006) 354:2552–63. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa054862
28. Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. (2005) 436:356–62. doi: 10.1038/nature03711
29. Wu Y, Li H, Loos RJ, Qi Q, Hu FB, Liu Y, et al. RBP4 variants are significantly associated with plasma RBP4 levels and hypertriglyceridemia risk in Chinese Hans. J Lipid Res. (2009) 50:1479–86. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P900014-JLR200
30. Kim MH, Lee HS, Park HJ, Kim WY. Risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome in Korean elderly. Ann Nutr Metab. (2007) 51:533–40. doi: 10.1159/000112977
31. Ahn S, Jun S, Shin J, Ham D, Choi E, Joung H. Association between intake of antioxidant vitamins and metabolic syndrome prevalence among korean adults (P24-001-19). Curr Dev Nutr. (2019) 3:nzz044.P024–001–19. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzz044.P24-001-19
32. Cho SW, Kang JY, Park YK, Paek YM, Choi TI. A 12-week worksite health promotion program reduces cardiovascular risk factors in male workers with the apolipoprotein E2 and apolipoprotein E3 genotypes, but not in apolipoprotein E4 genotype. Nutr Res. (2009) 29(8):542–50. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2009.08.002
Keywords: alpha-tocopherol, gamma-tocopherol, blood pressure, diabetes, linear regression
Citation: Wan R, Su Y, Zhu M and Huang Y (2024) The association between blood vitamin E and blood pressure in an adult population with and without diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1431293. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1431293
Received: 11 May 2024; Accepted: 16 October 2024;
Published: 06 November 2024.
Edited by:
José Luis Lázaro Martínez, Complutense University of Madrid, SpainReviewed by:
Medicharla Venkata Jagannadham, University of Hyderabad, IndiaMostafa Waly, Sultan Qaboos University, Oman
Iman Razeghian-Jahromi, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2024 Wan, Su, Zhu and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Huang, aHluYW5jaGFuZzg4ODhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Rong Wan
Rong Wan Yuhao Su2
Yuhao Su2 Ying Huang
Ying Huang