- 1Department of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 2Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 3Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 4Jeffrey Cheah School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Monash University Malaysia, Bandar Sunway, Selangor, Malaysia
Phoenixin (PNX) is an emerging neuropeptide that plays a significant role in regulating metabolism and reproduction. This comprehensive review examines findings from human, in vivo, and in vitro studies to elucidate the functions of PNX in metabolic processes. PNX has been identified as a key player in essential metabolic pathways, including energy homeostasis, glucose, lipid and electrolyte metabolism, and mitochondrial dynamics. It modulates food and fluid intake, influences glucose and lipid profiles, and affects mitochondrial biogenesis and function. PNX is abundantly expressed in the hypothalamus, where it plays a crucial role in regulating reproductive hormone secretion and maintaining energy balance. Furthermore, PNX is also expressed in peripheral tissues such as the heart, spleen, and pancreas, indicating its involvement in the regulation of metabolism across central and peripheral systems. PNX is a therapeutic peptide that operates through the G protein-coupled receptor 173 (GPR173) at the molecular level. It activates signaling pathways such as cAMP-protein kinase A (PKA) and Epac-ERK, which are crucial for metabolic regulation. Research suggests that PNX may be effective in managing metabolic disorders like obesity and type 2 diabetes, as well as reproductive health issues like infertility. Since metabolic processes are closely linked to reproduction, further understanding of PNX’s role in these areas is necessary to develop effective management/treatments. This review aims to highlight PNX’s involvement in metabolism and identify gaps in current knowledge regarding its impact on human health. Understanding the mechanisms of PNX’s action is crucial for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of metabolic disorders and reproductive health issues, which are significant public health concerns globally.
1 Introduction
Phoenixin (PNX) is a neuropeptide that has garnered significant interest in the scientific community over the past eight years (1). It has been identified across various species, including humans (2), rodents (3), pigs (4), cows (5), chickens (6), Xenopus (7), and zebrafish (8), highlighting its evolutionary conservation and potential biological significance.
PNX peptide derived from the C-terminal of the small integral membrane protein 20 (SMIM20) and primarily exists in two amidated isoforms: a 14-amino-acid peptide (PNX-14) and a longer, N-terminal-extended 20-amino-acid peptide (3, 9). PNX is widely distributed across various tissues, including the hypothalamus, heart, spleen, thymus, skin, ovaries, testes, adipose tissue, and pancreas (10). Notably, PNX-20 is predominantly expressed in the hypothalamus, while PNX-14 is more abundant in the heart and spinal cord (7, 11). Despite these sequence length variations, they appear to function similarly (9, 12).
PNX was characterized as a reproductive peptide or hormone upon its discovery (12). However, the specific expression levels of PNX in the brain and other tissues with respect to sex differences remain undetermined. In contrast, the well-known reproductive hormones have clearly defined expression patterns. Previous reviews have noted that reproductive hormone expression varies according to sex (13). Reproductive hormones such as gonadotrophin-releasing hormones (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), progesterone, estrogen, and testosterone are present in both sexes (14). However, the expression levels and patterns of these reproductive hormones differ between sexes (15). In terms of localization, GnRH, LH and FSH were not sexually dimorphic (16, 17). However, estrogen and testosterone were localized differently in males and females (18, 19).
Previous studies have shown that the distribution of PNX in the brain is similar in both sexes (12). PNX is expressed in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) and the anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV), both of which contain androgen receptors (AR) in males and females (20). Additionally, estrogen receptors (ER) are present in hypothalamic regions that express PNX, including the paraventricular nucleus (PVN), ARC, and AVPV (20–22). Furthermore, recent reviews have noted that the promoter region of PNX contains binding sites for ER (10). The presence of both AR and ER in PNX-expressing nuclei, along with ER binding sites in the promoter region, suggests that sex may influence the functional role of PNX. Further investigation into the sex-specific expression of PNX is needed to better understand its role and the associated sex-based differences.
PNX exerts its effects primarily through the G protein-coupled receptor 173 (GPR173) (23). The binding of PNX to GPR173 is postulated to activate various intracellular signaling pathways, including the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)/protein kinase A (PKA) (24), cAMP/exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP (Epac) (25), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)/protein kinase B (Akt) (26) and phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Akt Pathway (27, 28) (Figure 1). Regulation of these pathways leads to downstream effects on gene and protein expression, biological processes, and physiological responses. Nonetheless, whether PNX-14 and PNX-20 differ in their bioactivity or bind to distinct receptors or receptor subtypes (24) remains uncertain.
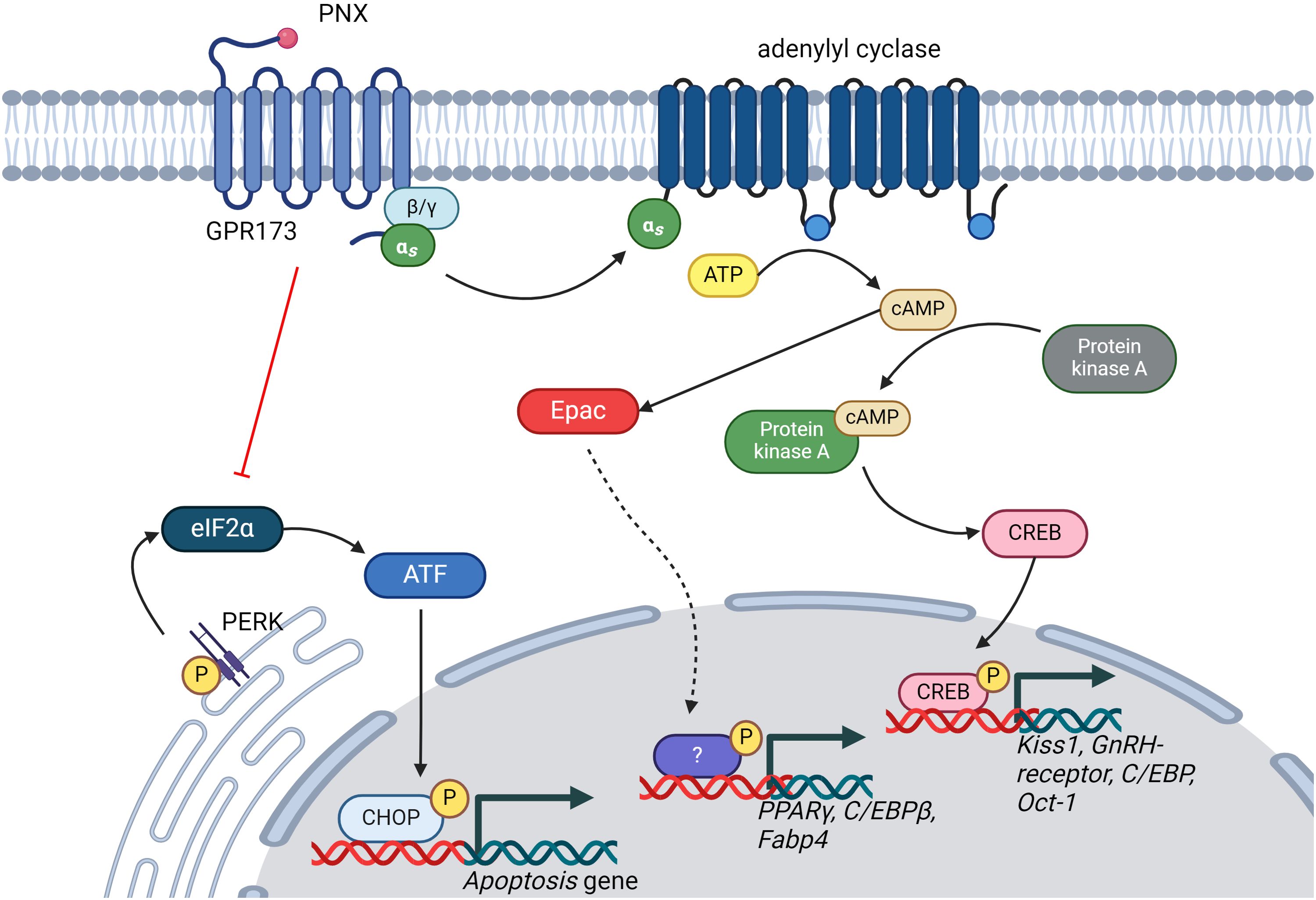
Figure 1. Illustration of the signaling pathways regulated by PNX. PNX has been shown to activate the cAMP/PKA and cAMP/Epac signaling pathways while inhibiting the PERK/eIF2α signaling pathway. This regulation of signaling pathways is crucial for modulating various biological processes, including reproductive systems, glucose and lipid metabolism, and apoptosis. ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB, cAMP-response element binding protein; GnRH, Gonadotropin hormone-releasing hormone; C/EBPs, CAAT-enhancer-binding proteins; Oct-01, Organic cation transporter 1; PPARγ, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma; Fabp-4, Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins 4; ATF, Activating Transcription Factor; CHOP, C/EBP-homologous protein; eIF2α, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α.
Early findings on PNX have demonstrated its crucial roles in reproduction, particularly in regulating reproductive hormone secretion (12, 23). PNX is found to induce the stimulation of LH secretion by potentiating the activity of GnRH. At the gonadal level, PNX affects follicular development and modulates the expression of gonadotropins across various species, including fish and mammals (29). Nonetheless, recent studies have indicated that PNX is involved in a wide range of biological and physiological processes that cover anxiety (2), memory (30), oxidative stress (31), inflammation (108), cell proliferation and differentiation (33). Interestingly, recent studies have highlighted the role of PNX in regulating the biological process of metabolism (31; 34), particularly its influences on the regulation of food and fluid intake, glucose, lipid, and electrolyte metabolism, as well as mitochondrial dynamics and energy homeostasis.
It is well established that reproduction is closely interconnected to metabolic function, as metabolic health significantly influences reproductive processes (35). Various metabolic hormones, such as insulin and leptin, impact the levels of reproductive hormones and, consequently, reproductive function (36). Recent findings on PNX further strengthen the link between these two physiological functions (9). Despite significant progress in understanding the role of PNX, many questions about its involvement in metabolism remain elusive. Discussing the current findings on metabolic regulation by PNX is pivotal, as it holds the potential to unveil groundbreaking insights into its profound influence on energy regulation, metabolic homeostasis, and subsequent health outcomes (9).
Therefore, this scoping review aimed to comprehensively map the current understanding of the role of PNX in metabolism. By identifying knowledge gaps and research trends, this review paves the way for future studies to develop targeted therapeutic strategies that modulate the impact of PNX on metabolism, potentially offering novel treatment options and improving human health. These strategies could address the neuroendocrine dysregulation associated with metabolic diseases, highlighting the broader implications of PNX in maintaining metabolic homeostasis and its potential as a prognostic marker in clinical settings.
2 Materials and methods
This review followed the five stages outlined in the Arksey and O’Malley framework (37).
2.1 Identifying research questions
The following questions guided this scoping review of understanding the role of PNX in metabolism: What are the specific mechanisms underlying the involvement of PNX in energy homeostasis and metabolic regulation? What are the downstream signaling pathways activated by PNX that modulate metabolism regulation? How does PNX affect mitochondrial respiration rates and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production in various metabolic contexts? What is the impact of PNX on glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and pancreatic beta-cell function in health and metabolic disorders? How is PNX dysregulation implicated in the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders such as obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome?
2.2 Identifying relevant studies
A systematic and comprehensive search strategy was employed to identify relevant studies. Four electronic databases (PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar and Web of Science) were used to search for the articles published between 2013 and 2024. The data search was conducted on 30th May 2024 using relevant keywords identified from Medical Subject Headings (MeSH). Keywords used for the data collection were PNX, metabolism, mitochondria, glycolysis and mitochondria respiration.
2.3 Study selection
Two independent authors screened citation titles and abstracts and then reviewed potentially relevant articles in full, with a third author responsible for resolving any arising conflicts. The screening process was carried out using Covidence. The systematic scoping review employed a stringent selection process to ensure the reliability and comprehensiveness of the included studies. Initially, articles were screened against predefined inclusion criteria, tailored to the review’s objectives. Duplicate articles were rigorously identified and removed to eliminate redundancy and maintain data accuracy. Subsequently, non-English language articles were excluded to ensure consistency and facilitate understanding. Furthermore, abstracts from conferences and symposiums were omitted to prioritize full-text articles, enhancing the depth of the review. Theses and dissertations were also excluded to focus exclusively on peer-reviewed research, emphasizing the inclusion of high-quality, published studies. Review articles and book chapters were similarly excluded to prioritize original research findings, thereby enabling a comprehensive analysis of the current knowledge landscape. By adhering to these strict exclusion criteria, the review aimed to provide a systematic and rigorous synthesis of relevant research findings, minimizing potential bias and ensuring the reliability of the conclusions drawn.
2.4 Data charting process
Following the application of rigorous inclusion and exclusion criteria, the selected articles underwent meticulous data extraction. A structured form was employed to gather essential details from each study, encompassing the types of experiments conducted, the specific areas of investigation, and the key findings pertaining to PNX biological function. A qualitative synthesis of the extracted data was then conducted to analyze PNX’s role in metabolism. This synthesis involved systematically evaluating and comparing the findings from the included studies, thereby offering a comprehensive assessment of the available evidence regarding PNX’s impact on metabolic processes.
2.5 Summarizing results
The results based on PNX’s effects on mitochondrial function, glycolytic metabolism, and mitochondrial respiration were organized under the following categories: types of PNX, action of PNX, findings, and outcomes. We reported the review following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines –an extension for a scoping review.
3 Results
The systematic review identified 23 full-text articles for comprehensive quantitative analysis from 1124 manuscripts (Figure 2). Based on the reviewed articles, studies on the effect of PNX on metabolism were conducted using diverse experimental designs and involved various sex-specific models or organisms. A comprehensive summary of studies on the role of PNX in metabolic regulation and its therapeutic potential is presented in Table 1 and outlined in the following subsections.
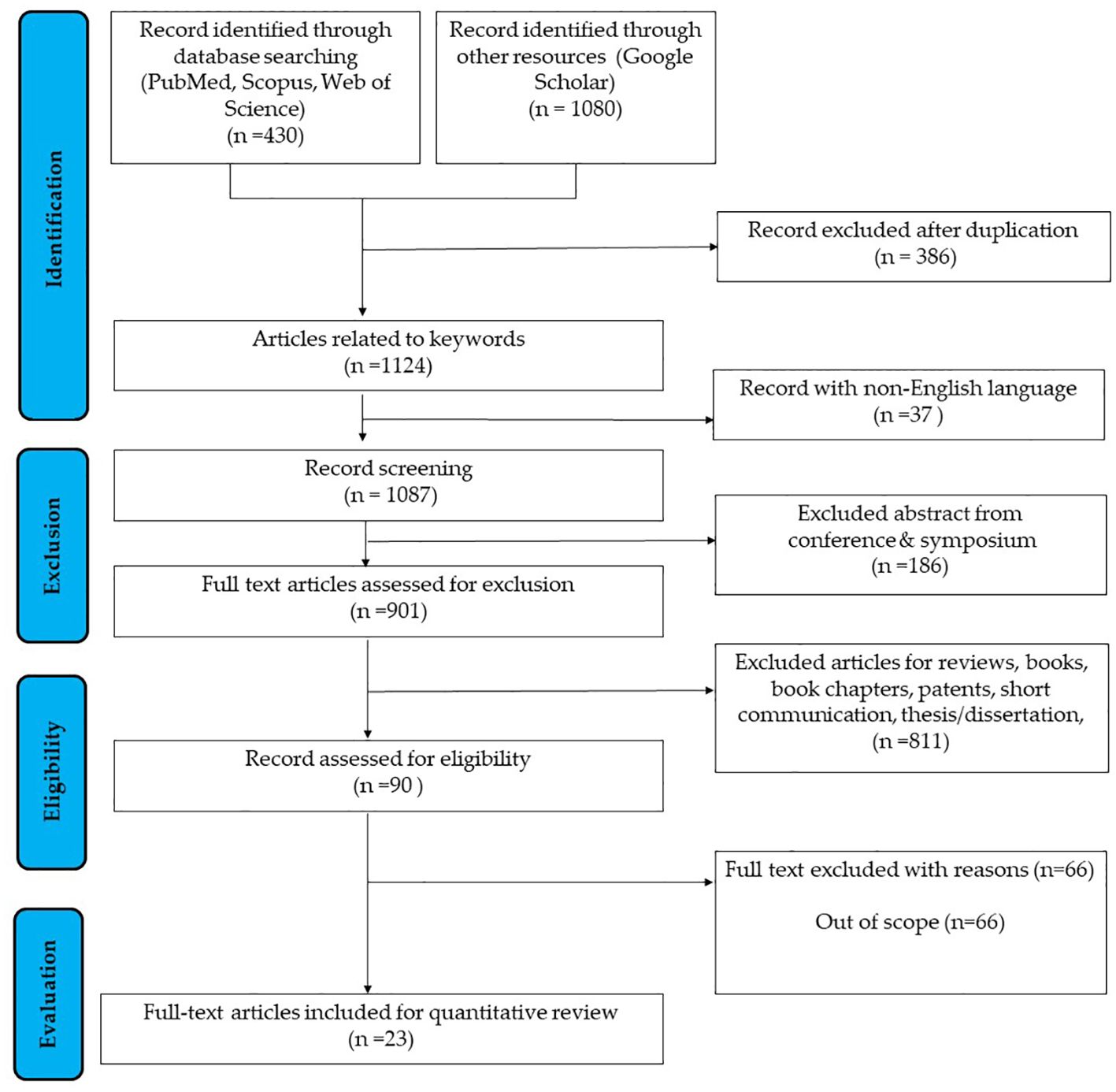
Figure 2. Flowchart outlining the search strategy employed in researching the correlation between PNX and metabolism (37).
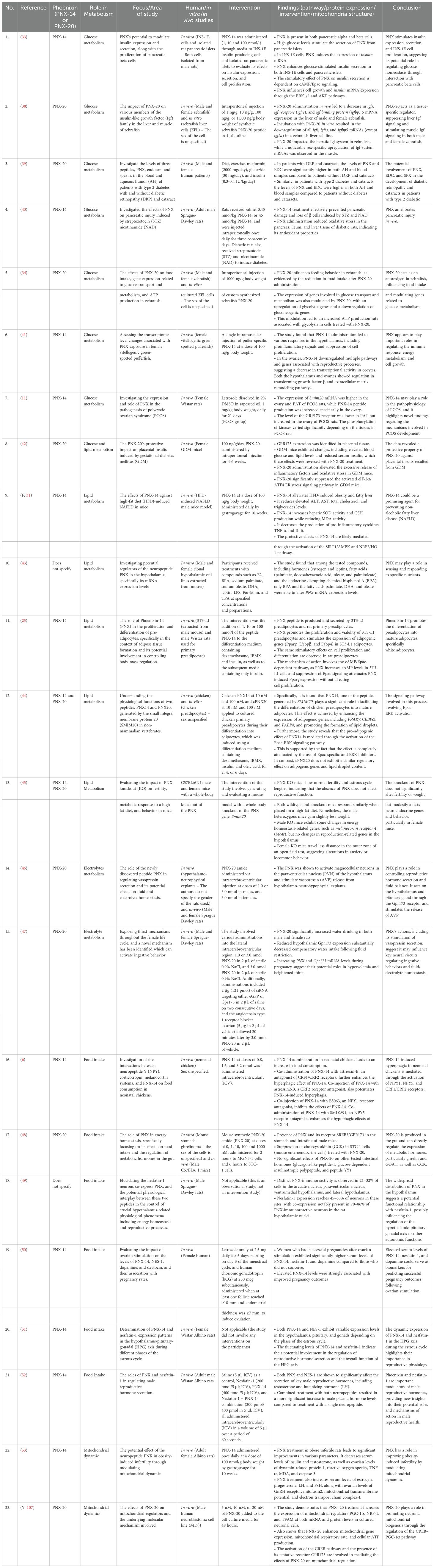
Table 1. Summary of studies related to insights of PNX into metabolic regulation and therapeutic potential.
3.1 Experimental designs
These 23 articles were categorized based on their experimental designs into three groups: in vivo, in vitro, and studies combining both in vivo and in vitro approaches. Of these studies, 19 were conducted using in vivo models, nine were conducted in vitro, and six were designed to investigate both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, the review included 12 studies focusing on PNX-14, nine studies examining PNX-20, one study focusing on both PN-14 and PNX-20 and two studies that did not specify any isoform of PNX.
3.2 PNX and sexual differences
The full-text articles identified were categorized according to the sex of the organisms or the cell sources, including humans, rats, mice, zebrafish and pufferfish. This classification is illustrated in Figure 3 and elicited in Table 1. Among the 23 studies, 15 investigated male subjects, while 14 focused on female subjects. Additionally, seven studies included both sexes to examine the role of PNX. This distribution indicates a generally balanced interest in exploring the role of PNX across sexes, with a slight preference for male subjects. However, six studies utilized in vivo or in vitro models without specifying the sex.
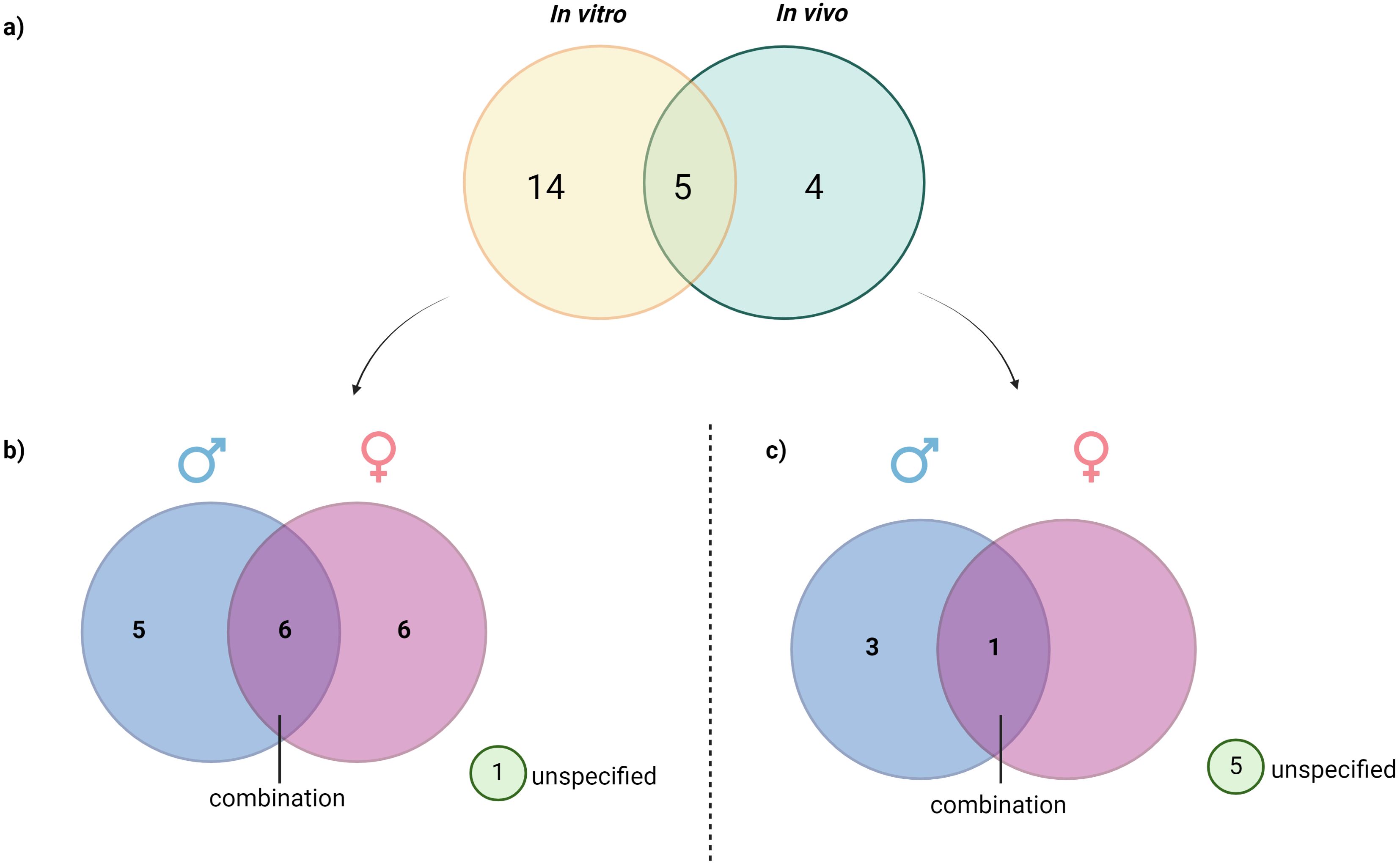
Figure 3. Distribution of reviewed studies by experimental type and subject sex: (A) Classification of reviewed studies based on the type of study, (B) Distribution of reviewed in vivo studies based on sex, (C) Distribution of in vitro study based on sex. This figure illustrates the breakdown of analyzed in vitro and in vivo studies, further categorized by the sex of subjects used (male, female, or unspecified). The visualization allows for a quick assessment of sex representation across different experimental approaches, highlighting trends in the inclusion of male, female, or sex-unspecified subjects and revealing any gaps in sex-specific research within the reviewed studies.
3.3 Effects of PNX-14 on metabolism
This review identified PNX-14 as playing a significant role in various metabolic processes. PNX-14 has been reported to influence both glucose and lipid metabolism, highlighting its importance in energy regulation. Additionally, since metabolic processes are closely linked with food intake, PNX-14 has been found to regulate feeding behavior, further emphasizing its involvement in maintaining metabolic balance.
3.3.1 PNX-14 and glucose metabolism
PNX-14 studies have demonstrated prominent findings on the regulation of glucose metabolism. PNX-14 modulates the expression and secretion of insulin through an in vitro study (33). Two cells were used in this study: neuroscreen-1 (INS-1E) cells and isolated rat pancreatic islets; both cells were isolated from male rats. In this study, the treatment of PNX-14 on INS-1E insulin-producing cells induces the expression of insulin mRNA. Furthermore, treatment of 100 nmol/l of PNX-14 with 16.7 nmol/l of glucose on INS-1E cells and rat pancreatic islets increased insulin secretion. Apart from inducing the expression and secretion of insulin, PNX-14 was shown to increase the proliferation of INS-1E insulin-producing cells. From this study, two major signaling pathways modulated these effects in response to PNX-14 treatment (33). The PNX-14 were shown to modulate the ERK1/2 and protein kinase B (Akt) pathways that influence insulin mRNA expression and cell proliferation. The role of PNX-14 in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion is mediated through the cAMP/Epac signaling pathway.
The effect of PNX-14 on glucose metabolism, particularly on pancreatic tissue, was further elucidated in vivo setting (40). This study investigated the effects of PNX on pancreatic injury induced by streptozotocin (STZ) and nicotinamide (NAD). The PNX-14 treatment was administered intraperitoneally once daily for three consecutive days. The PNX-14 treatment significantly prevented damage and loss of β cells induced by STZ and NAD. This effect of PNX-14 in preventing cell damage and loss was postulated mediated through antioxidant properties (40). Interestingly, the PNX-14 treatment was shown to reduce the level of oxidative stress in the pancreas, ileum, and liver tissue of diabetic rats. Additionally, high-dose PNX-14 (45 nmol/kg PNX-14) treatment reduced fasting blood glucose levels in these diabetic rats without influencing plasma insulin concentrations or insulin mRNA expression.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a well-known metabolic disorder resulting from hyperandrogenism, ovulatory dysfunction and insulin insensitivity. The expression of PNX-14 in this metabolic disease has been studied using an animal model. This research measured the expression of PNX-14 and GPR173 in the serum, ovary and periovarian adipose tissue (PAT) in female PCOS rats compared to female control rats. The findings of this research show that the smim-20 mRNA levels in the ovary and PAT significantly increased in PCOS rats compared to control rats. Furthermore, the serum PNX-14 levels were significantly increased in PCOS rats (11). In addition, the alteration of PNX-14 and GPR173 expression was associated with the changes in the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (11), postulating the possible role of PNX-14 in the pathophysiology of PCOS.
The effect of PNX-14 in vivo was also further elucidated using fish or non-mammal animal models. This study used female vitellogenic green-spotted pufferfish. The puffer-specific PNX-14 was administered through a single intramuscular injection at a dose of 100 ng/g body weight. The transcriptomic analysis was performed in the hypothalamus and ovary. The findings demonstrated that the PNX-14 treatment changes the gene sets related to immune responses, including cytokine signaling and natural killer cell activation in both the hypothalamus and ovary. Interestingly, the findings show that PNX-14 modulates the diabetes-related and glucose metabolism gene expression in the hypothalamus alone. The study suggested that PNX-14 plays an important role in regulating the immune response and energy metabolism.
3.3.2 PNX-14 and lipid metabolism
Apart from glucose metabolism, PNX-14 shows a prominent role in modulating lipid metabolism in several studies. Firstly, the role of PNX-20 was determined using high-fat diet (HFD)-induced non-fatty acid liver disease (NAFLD) male mice (31). The PNX-20 was administered daily by gastrogavage for 10 weeks at a dose of 100 ng/g body weight. The findings of this study show that PNX-14 reduces elevated levels of ALT, AST, total cholesterol, and triglycerides in HFD-induced obesity and fatty liver mice. In addition, PNX-14 increases hepatic SOD activity and GSH production while reducing MDA activity. The protective effects of PNX-14 are likely mediated through the activation of the sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)/AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and Nuclear respiratory factor 2 (NRF2)/heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) pathway. From this study, PNX-14 has been postulated to have protective effects against high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mice (31).
Another study of PNX-14 shows its role in pre-adipocyte proliferation and differentiation (25). This study used an in vitro approach that utilized the use of 3T3-L1 cells (extracted from male mice) and primary preadipocytes (extracted from male Wistar rats). The PNX-14 treatment using 1, 10 or 100 nmol/l of the peptide PNX-14 to the differentiation medium containing dexamethasone, IBMX and insulin, as well as to the subsequent media containing only insulin. There are several key findings from this study. Firstly, the PNX peptide is produced and secreted by 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and rat primary preadipocytes. Secondly, the PNX-14 treatment promotes the proliferation and viability of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and stimulates the expression of adipogenic genes (Pparγ, C/ebpβ, and Fabp4) in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Furthermore, the same stimulatory effects on cell proliferation and differentiation are observed in rat preadipocytes with PNX-14 treatment. This study shows the differentiation of preadipocytes into mature adipocytes, particularly white adipocytes, was through the cAMP/Epac-dependent pathway (25). Therefore, PNX-14 is postulated to promote the differentiation of preadipocytes into mature adipocytes, specifically white adipocytes.
The role of PNX-14 in lipid metabolism is further studied in non-mammalian vertebrate settings. This study utilized an in vitro study in which they used chicken preadipocytes (44). The chicken PNX-14 was used to treat the preadipocytes at 10 nM and 100 nM. The finding shows that the cPNX-14 enhanced the expression of adipogenic genes, including PPARγ, CEBPα, and FABP4, and promoted the formation of lipid droplets. Furthermore, the study reveals that the pro-adipogenic effect of PNX14 is mediated through the activation of the Epac-ERK signaling pathway. The similarity of findings with the mammalian animal model highlights PNX evolutionary conservation and potential as a therapeutic target across species (44).
Despite using the intervention by treating in vivo and in vitro with PNX-14, the knockout method has also been utilized to understand the role of PNX-14. A recent study utilized C57BL/6NJ male and female mice with a whole-body knockout of the PNX to evaluate the impact of PNX knockout (KO) on fertility, metabolic response to a high-fat diet, and behavior in mice (45). The findings of this study show that PNX KO mice show normal fertility and estrous cycle lengths. Furthermore, the male PNX KO mice exhibit some changes in energy homeostasis-related genes, such as melanocortin receptor 4 (Mc4r), but no changes in reproduction-related genes in the hypothalamus (45). In addition, both wildtype and knockout mice respond similarly when placed on a high-fat diet. Nonetheless, the male heterozygous mice gain slightly less weight. Meanwhile, female PNX KO mice travel less distance in the outer zone of an open field test, suggesting alterations in anxiety or locomotor behavior. Therefore, this study postulated that the knockout of PNX does not significantly alter fertility or weight but modestly affects neuroendocrine genes and behavior, particularly in female mice.
3.3.3 PNX-14 and food intake regulation
The role of PNX-14 in food intake has garnered significant attention from the researcher. Several studies have been conducted to evaluate the potential role of PNX-14 in food intake regulation. A recent study was conducted to determine the impact of ovarian stimulation on the levels of PNX-14, NES-1, dopamine, and oxytocin and their association with pregnancy rates among pregnant women (50). This prospective case-control study found that elevated levels of the neuropeptides PNX-14, nesfatin-1 (NES-1), and dopamine, along with decreased oxytocin (OT) levels, were associated with positive pregnancy rates in infertile women after ovarian stimulation (50). From this study, PNX-14, nesfatin-1, and dopamine are postulated to serve as potential biomarkers for predicting successful pregnancy outcomes following ovarian stimulation.
The findings from the prospective case-control study mentioned before are consistent with the findings using an in vivo setting. In this study, female Wistar Albino rats were used to determine the PNX-14 and nesfatin-1 expression patterns in the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis during different phases of the estrous cycle (51). The findings of this study show that both PNX-14 and nesfatin-1 exhibit variable expression levels in the hypothalamus, pituitary, and gonads, depending on the phase of the estrous cycle. Therefore, it is postulated that the fluctuating levels of PNX-14 and nesfatin-1 indicate their potential involvement in regulating reproductive hormone secretion and the overall function of the HPG axis. In addition, the co-expression of PNX-14 and NES-1 shows an association between a reproductive system and energy homeostasis through food intake regulation (51).
Further study on the PNX-14 effect on food regulation was conducted using adult male Wistar Albino rats (52). This study determined the role of PNX-14 and NES-1 in regulating male reproductive hormone secretion. This study used saline as a control, NES-1 (200 pmol), PNX-14 (400 pmol), and NES-1 + PNX-14 combination (200 pmol/400 pmol) as treatment group. All compounds were administered intracerebroventricularly (ICV) in a volume of 5 μl for 60 seconds. The findings of this study show that both PNX-14 and NES-1 are shown to significantly affect the secretion of key male reproductive hormones, including testosterone and LH. Interestingly, combined treatment with both neuropeptides resulted in a more significant increase in male plasma hormone levels than treatment with a single neuropeptide. Therefore, the findings from this study postulated that PNX-14 and NES-1 are modulators of male reproductive hormones, providing new insights into their potential in male reproductive health and food intake.
The role of PNX-14 was also elucidated using an intervention setting in an in vivo setting. A study of chickens has shown that intracerebroventricular (ICV) injections of PNX-14 increased food consumption in neonatal chickens (6). Co-administration of PNX-14 with Astressin-B, an antagonist of CRF1/CRF2 receptors, further enhances the hyperphagic effect of PNX-14. In addition, the co-injection of PNX-14 with astressin2-B, a CRF2 receptor antagonist, also potentiates PNX-14-induced hyperphagia. Meanwhile, co-injection of PNX-14 with B5063, an NPY1 receptor antagonist, inhibits the effects of PNX-14. Lastly, co-administration of PNX-14 with SML0891, an NPY5 receptor antagonist, enhances the hypophagia effects of PNX-14. From these findings, it is postulated that PNX-14-induced hyperphagia in neonatal chickens. Furthermore, this study suggested that the hyperphagia activation is mediated by activating NPY1, NPY5, and CRF1/CRF2 receptors.
3.4 Effects of PNX-20 on metabolism
Similarly, PNX-20 is implicated in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, as well as food intake. However, this review reveals that PNX-20 has additional roles beyond those shared with PNX-14. Specifically, PNX-20 has been reported to influence electrolyte metabolism and mitochondrial dynamics—functions not attributed to PNX-14. This suggests that while both PNXs share some common metabolic roles, PNX-20 may have broader effects on metabolic processes.
3.4.1 PNX-20 and glucose metabolism
Besides PNX-14, studies on PNX-20 reveal its role in glucose metabolism. Firstly, the animal study has shown that the PNX-20 treatment ameliorated the symptoms of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) (42). This study used female GDM mice, and the PNX-20 treatment was administered through intraperitoneal injection for 4-6 weeks. From this study, the PNX receptor, GPR173, was identified in placental tissue. Furthermore, PNX-20 treatment has been shown to reverse elevated blood glucose and lipid levels and reduce serum insulin exhibited in GDM mice. In addition, PNX-20 treatment alleviated the excessive release of inflammatory factors and oxidative stress in GDM mice. In terms of signaling pathways, PNX-20 significantly suppressed the activated eIF-2α/ATF4 ER stress signaling pathway in GDM mice. Therefore, this study postulated that PNX-20 has protective properties against placental insults resulting from GDM.
Interestingly, the role of PNX-20 in glucose metabolism was further studied in the non-vertebrate study (38). This study used in vivo (male and female zebrafish) and in vitro (cultured ZFL cells - The sex of the cell is unspecified). The custom synthesized zebrafish PNX-20 was administered intraperitoneal injection at 1000 ng/g body weight. The finding of this study shows that PNX-20 significantly downregulated the mRNA expression of insulin growth factor (IGFs), IGF receptors (IGFRs), and IGF binding protein 5 (igfbp5) in the liver of both male and female zebrafish (38). A contradicting finding was observed in the muscle where PNX-20 treatment significantly upregulated the mRNA expression of IGFs and IGF receptors (38). Furthermore, PNX-20 treatment in zebrafish significantly increased the mRNA expression of glycolytic genes and decreased the gluconeogenic genes (34). In addition, a higher ATP production rate from glycolysis was observed with PNX-20 treatment. Thus, this study postulated that PNX-20 acts as an anorexigenic molecule in zebrafish, influencing food intake and modulating genes related to glucose metabolism.
3.4.2 PNX-20 and lipid metabolism
Similar to PNX-14, PNX-20 is prominent in modulating lipid metabolism in several studies. Firstly, the in vivo study used female GDM mice to determine the effect of PNX-20 in lipid metabolism. The PNX-20 treatment was administered through intraperitoneal injection for 4-6 weeks at 100 ng/g/day. The finding from this study found that PNX-20 improved the lipid profile, including the total serum cholesterol (TCH), serum triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Therefore, this study postulated that PNX-20 plays a significant role in regulating lipid metabolism, particularly in terms of cholesterol and lipoprotein levels.
A contrary finding on the effect PNX-20 in lipid metabolism was observed in chickens (44). This study utilized an in vitro study in which they used chicken preadipocytes. In this study, both PNX-14 and PNX-20 were used as treatment. In addition, the effect of these two PNX isomers were compared. The findings from this study show that the treatment of PNX-20 did not affect the expression of adipogenic genes and lipid droplet content (44). This study postulated that the PNX-20 is not involved in the regulation of lipid metabolism in chickens.
Besides the intervention study, a recent study has demonstrated that male KO (PNX-14 & 20) mice exhibited changes in energy homeostasis-related genes, such as melanocortin receptor 4 (Mc4r), but did not show alterations in reproduction-related genes in the hypothalamus (45). From this study, it is postulated that the knockout of PNX, which includes PNX-20, resulted in changes in the regulation of lipid metabolism, particularly in the regulation of obesity.
3.4.3 PNX-20 and electrolyte metabolism
From the reviewed articles, the effect of PNX on electrolyte metabolism is only studied using the PNX-20 isoform. Firstly, a recent study used male and female Sprague-Dawley rats to elucidate thirst mechanisms throughout the female life cycle, and a novel mechanism has been identified which can activate ingestive behavior (47). The PNX-20 was administrations into the lateral intracerebroventricular region at the dosage of 1.0 or 3.0 nmol PNX-20 This study demonstrated that PNX-20 increases water intake in both male and female rats, suggesting its involvement in hypervolemia and heightened thirst during pregnancy (47). Therefore, it is postulated that PNX-20 may influence key neural circuits regulating ingestive behaviors and fluid/electrolyte homeostasis.
Another study used in vitro (hypothalamic-neurophysical explants –sex unspecified) and in vivo (male and female Sprague Dawley rats) to elucidate the role of PNX-20 in regulating vasopressin secretion and its potential effects on fluid and electrolyte homeostasis (46). The PNX-20 was administered via intracerebroventricular injection at doses of 1.0 or 3.0 nmol in males and 3.0 nmol in females. The findings of this study show that PNX-20 stimulates vasopressin release from hypothalamic-neurohypophysial explants, indicating its role in controlling fluid and electrolyte homeostasis (46). Therefore, this study postulated that PNX-20 plays a role in controlling reproductive hormone secretion and fluid balance.
3.4.4 PNX-20 and food intake
Besides fluid intake regulation, PNX-20 regulates the expression of metabolic hormones that are involved in regulating food intake. Only one study elucidates the role of PNX in energy homeostasis, specifically focusing on its effects on food intake and the regulation of metabolic hormones in the gut (48). This study used in vitro (MGN3-1 cells and STC-1 cells, mouse stomach ghrelinoma – the sex of the cells is unspecified) and in vivo (male C57BL/6 J mice). The in vivo is meant to determine the expression level of PNX-20 in the stomach and intestine. The mouse synthetic PNX-20 amide (PNX-20) was used to treat both cells at doses of 0, 1, 10, 100 and 1000 nM for 2 hours to MGN3-1 cells and 6 hours to STC-1 cells. The findings of this study show that PNX-20 and its receptor SREB3/GPR173 is expressed in the stomach and intestine of male mice. Furthermore, the PNX-20 upregulate the mRNA expression of ghrelin and ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) and suppresses the mRNA expression of cholecystokinin (CCK) in STC-1 cells (48). This study postulated that PNX-20 directly regulates the expression of metabolic hormones, particularly ghrelin, GOAT and CCK.
3.4.5 PNX-20 and mitochondrial dynamics
Apart from PNX-14, PNX-20 is also involved in regulating the mitochondrial dynamic. A recent study elucidates the effects of PNX-20 on mitochondrial regulators and the underlying molecular mechanism involved (107). This study used in vitro [male human neuroblastoma cell line (M17)] and PNX-20 at dosages of 5 nM, 10 nM, or 20 nM as a treatment for this cell. The findings of this study show that PNX- 20 treatment increases the expression of mitochondrial regulators PGC-1α, NRF-1, and TFAM at both mRNA and protein levels in cultured neuronal cells. Furthermore, PNX-20 enhances mitochondrial gene expression, mitochondrial respiratory rate, and cellular ATP production. In addition, the activation of the CREB pathway, along with the PNX receptor, GPR173, plays a role in mediating the effects of PNX-20 on mitochondrial regulation. From these findings, this study postulated that PNX-20 plays a role in promoting neuronal mitochondrial biogenesis by regulating the CREB–PGC-1α pathway.
3.5 Effects of PNX (unspecified) on metabolism
Three studies did not specify whether PNX-14 or PNX-20 was being measured. In these articles, the authors generally refer to the compound as PNX. Nevertheless, these studies highlighted the findings on the impact of PNX on glucose and lipid metabolism and food intake.
3.5.1 PNX and glucose metabolism
A recent study investigates the levels of three peptides, PNX, endocan, and spexin, in the blood and aqueous humor (AH) of patients with type 2 diabetes with and without diabetic retinopathy (DRP) and cataract (39). This study recruited male and female patients, and the PNX level was measured. The investigation of PNX in the blood and aqueous humor of patients with type 2 diabetes with and without diabetic retinopathy and cataracts has found interesting findings. The levels of PNX were significantly higher in the aqueous humor and blood of patients with diabetic retinopathy and cataracts and patients with diabetes mellitus and cataracts compared to patients with only cataracts (39). This study postulated that PNX is involved in the development of diabetic retinopathy and cataracts in patients with type 2 diabetes.
3.5.2 PNX and lipid metabolism
Apart from glucose metabolism, a non-intervention study investigates the potential regulators of the PNX mRNA expression in the hypothalamus (43). This in vitro study used male and female clonal hypothalamic cell lines extracted from mice. This has shown that the expression of PNX was upregulated by the fatty acids palmitate, DHA, and oleate, suggesting a role for PNX in lipid metabolism and nutritional sensing (43). Thus, this study postulated that PNX may play a role in sensing and responding to specific nutrients.
3.5.3 PNX and food intake
A previous study elucidates the potential physiological interplay between PNX and NES-1 peptides in controlling crucial hypothalamus-related physiological phenomena, including energy homeostasis and reproductive processes (49). This is an observational study that used male Sprague–Dawley rats. The findings have shown that NES-1 and PNX have a similar distribution pattern in the rat hypothalamus (49). These findings suggest that PNX has a potential functional relationship with NES-1, possibly influencing the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis regulation or other autonomic functions.
4 Discussion
This systematic scoping review of 23 studies highlights the multifaceted roles of PNX peptides in metabolic regulation, drawing on a wide range of human, in vivo (vertebrate and non-vertebrate) and in vitro studies. The findings indicate that phoenixin significantly influences complex metabolic regulation, including energy homeostasis, food and fluid intake, glucose and lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial dynamics. Moreover, the review highlights the interplay between metabolic functions and reproductive health of PNX, particularly in conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). These findings suggest that phoenixin is a pivotal regulatory peptide with substantial implications for both metabolic and reproductive health, warranting further research into its underlying mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
4.1 The Expression of PNX
It is well documented that PNX-20 is mainly expressed in the central nervous system (CNS), particularly in the hypothalamus, and PNX-14 is expressed in the peripheral system. In the hypothalamus, PNX is highly expressed in key regions such as the paraventricular nucleus (PVN), supraoptic nucleus (SON), arcuate nucleus (ARC), and anteroventral periventricular nucleus (AVPV) (Figure 4) (10). Out of these regions, ARC and PVN are primarily responsible for the regulation of metabolism (54, 55). Within the ARC, PNX has been observed to co-express with various neuropeptides such as NES-1 (51), neuropeptide Y (NPY) (56), and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) (57). These peptides collectively play essential roles in the complex signals network regulating hunger, energy expenditure, and overall metabolic processes. In the PVN, several key hormones and neuropeptides that are responsible for metabolism are expressed in these nuclei, including corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and oxytocin (OT) (58). The expression of PNX in both nuclei indicates the presence of interaction with each other to regulate metabolic processes through both synergistic and antagonistic effects. This phenomenon has been observed with the reproductive neuropeptide kisspeptin, which seems to directly interact with both NPY/AgRP and POMC/CART neurons in a bidirectional manner (59).
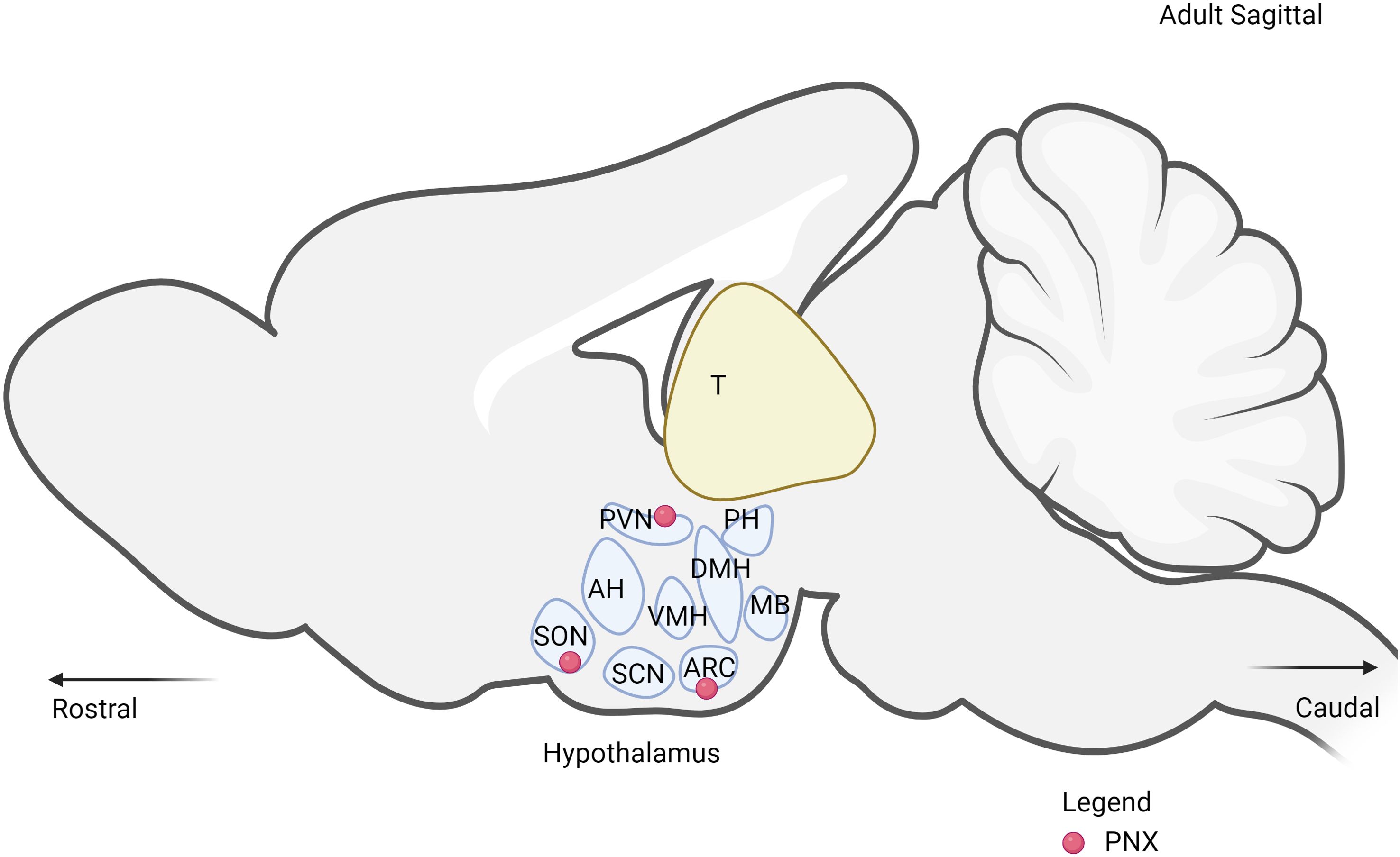
Figure 4. The expression of PNX in the hypothalamus. PVN, paraventricular nucleus; SON, supraoptic nucleus; ARC, arcuate nucleus; DMH, dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; SCN, suprachiasmatic nucleus; MB, mammillary bodies; PH, posterior hypothalamus.
Beyond the CNS, PNX is expressed in various peripheral organs involved in metabolic regulation, including the heart, pancreas, and adipose tissue. The expression of PNX in the heart is implicated in cardiovascular regulation by modulating heart contractility and relaxation in normal and obese rats (60). Proper cardiac function is essential for maintaining optimal blood flow and nutrient delivery to tissues, influencing overall metabolic efficiency (61). In the pancreas, the expression of PNX influences insulin secretion (33). Furthermore, PNX has been found to alleviate pancreatic injury induced by streptozotocin (STZ) and nicotinamide (NAD) in diabetic rats (40). Lastly, the presence of PNX in adipose tissue promotes the differentiation of preadipocytes into mature adipocytes through pathways such as cAMP/Epac and Epac-ERK, enhancing adipogenesis and playing a critical role in lipid storage and utilization (25). The dual expression of PNX in both the hypothalamus and peripheral organs highlights its integrative role in coordinating metabolic functions.
Apart from the expression of PNX, the reviewed studies demonstrate a significant interest in the sex-specific effects of PNX on metabolic regulation. Among the 23 studies examined, the distribution suggests a relatively balanced interest in understanding the role of PNX across sexes, though there is a slight emphasis on male subjects. Both phoenixin and nesfatin-1 significantly increased the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), LH, and testosterone in rat plasma without inducing any changes in plasma GnRH, thus indicating that both these neuropeptides play a synergistic role in regulating male sex hormones (52). Furthermore, a previous study has shown that PNX modulates the expression of estrogen and progesterone in obesity-induced female rats (53). These findings emphasized the integration between reproduction and metabolism regulation modulation through PNX in both sexes.
Interestingly, one study has indicated that PNX treatment exerts different mechanisms of action in different sexes (34). This study demonstrates that PNX treatment upregulates the expression of ghrelin O-acyl-transferase (GOAT), peptide YY (PYY) and cholecystokinin (CCK), which only can be observed in female fish (34). All these proteins play a significant role in regulating appetite, digestion, and overall metabolic processes (32, 62, 63). For instance, a previous study demonstrated that estrogen increases CCK mRNA levels (64). Additionally, PNX has been shown to elevate estrogen levels (53) and this suggests its mechanism of action may depend on the sex of the organism. Therefore, future studies must specify the sex of the organism model being used to elucidate the differential effects of PNX based on sex, which has often been neglected.
Most of the studies reviewed here that highlight PNX expression have been conducted predominantly in animal models. There is a notable paucity of research investigating PNX expression in human subjects or human-derived samples. This gap underscores the need for further exploration into the mechanisms underlying the actions of PNX to fully comprehend its physiological roles and potential therapeutic benefits. To translate findings from animal models into clinical practice, additional research is crucial to elucidate how PNX operates at the molecular level and how its modulation could impact human metabolic disorders. Such investigations are essential for identifying the therapeutic potential of PNX and developing targeted treatments for conditions where metabolic dysregulation plays a key role.
4.2 PNX and glucose metabolism
The involvement of PNX-14 in regulating insulin expression and secretion from pancreatic β cells suggests a critical regulatory function in managing glucose homeostasis and treating conditions like type 2 diabetes (33). The expression of PNX in pancreatic cells is induced by elevated glucose levels. A recent review has identified that the Pnx or SMIM20 gene contains several transcription factor binding sites. Notable putative sites within the promoter of this gene include those for activating transcription factor (ATF) from the CREB family, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimer, glucocorticoid receptor (GR), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), estrogen receptor (ER), CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP), and octamer-binding transcription factor 1 (OCT1) (10). It is postulated that these transcription factors are influenced by high glucose levels, which enhance or suppress their activity, leading to the regulation of genes involved in metabolism, energy balance, stress response, and inflammation, as well as the expression of the Pnx or SMIM20 gene. This complex regulatory network ensures proper cellular adaptation to elevated glucose levels, maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
The presence of PNX receptors and regulatory elements in the liver affects the expression of genes involved in glucose transport and metabolism, insulin-like growth factor expression, and ATP production (34). This influence alters glucose processing, ATP production, and gene expression related to glucose transport, potentially affecting liver function and glucose metabolism. These findings are supported by previous research showing that the activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway leads to the phosphorylation of CREB, which subsequently increases the expression of GLUT responsible for glucose uptake (65). Therefore, it is postulated that PNX may improve insulin resistance in diabetic patients by modulating gene expression in the pancreas and enhancing glucose uptake in the liver. Further studies in mammalian settings would strengthen this postulation as the current findings are demonstrated in a non-mammalian model.
Specifically, PNX-14’s regulation of insulin expression and secretion from pancreatic beta cells suggests a role in managing glucose homeostasis and treating conditions like type 2 diabetes (33). Its ability to alleviate NAFLD and exhibit cardioprotective effects during ischemia/reperfusion injury highlights its therapeutic potential in addressing liver and cardiac disorders associated with metabolic dysfunction (31, 60). Additionally, PNX-14’s promise in improving obesity-induced infertility by modulating mitochondrial dynamics underscores its potential role in reproductive health issues linked to metabolic disorders (53).
4.3 PNX and lipid metabolism
Lipid metabolism involves the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells, including the breakdown or storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids. It consists of a balance between the catabolism and anabolism of lipids. Dysregulation of lipid metabolism can lead to metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases (66). The recent findings have indicated the emerging role of PNX in modulating lipid metabolism.
As mentioned before, the promoter of Pnx or SMIM20 gene consists of putative binding sites for several transcription factors known to regulate lipid metabolism (10). Transcription factors such as NF-κB, PPAR-RXR and C/EBP have been identified as key regulators of lipid metabolic pathways (67–70). Therefore, it is suggested that the expression of PNX is directly influenced by these transcription factors, thereby linking the regulatory role of PNX to lipid metabolism. Recent findings have supported this hypothesis, showing that fatty acids such as palmitic acid, docosahexaenoic acid and oleatecan modulate the expression of PNX (43).
Previous study has demonstrated that PNX promotes the differentiation of preadipocytes into mature adipocytes through the cAMP/Epac-dependent pathway (25). The activation of Epac influences various downstream signaling molecules and pathways, leading to adipogenesis (71, 72). By enhancing the differentiation of adipocytes, PNX helps increase the number of fat cells capable of storing lipids, thereby playing a role in lipid homeostasis. This function is particularly relevant in the context of obesity, where proper adipocyte differentiation and function can mitigate the adverse effects of excess lipid accumulation (73). Additionally, PNX has been shown to have protective effects against high-fat diet-induced NAFLD in mice (31). NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, often due to dysregulated lipid metabolism, inflammation, and oxidative stress. (74). Previous studies demonstrated that PNX ameliorate the inflammation and oxidative stress (75, 76). Thus, it is suggested that PNX has protective effects prevent the pathological fat accumulation and could lead to novel therapeutic approaches for treating lipid metabolism disorders.
In non-mammalian vertebrates, PNX facilitates adipocyte differentiation via the Epac-ERK signaling pathway (44). The ERK pathway is well-known for its role in cell growth and differentiation as well as lipid metabolism (77). Furthermore, previous study has shown that the ERK is found to modulate the adipogenesis process (78). Further study is required to elucidate mechanism on how PNX regulates ERK pathways in details. The conservation of this mechanism across species highlights the evolutionary importance of PNX in lipid metabolism and suggests its potential as a therapeutic target not only in humans but also in other animals. Furthermore, PNX has the ability to mitigate endothelial cell dysfunction and regulate hyperphagia. The ability of PNX to regulate lipid metabolism through these conserved pathways underscores its versatility and significance as potential therapeutic applications in maintaining metabolic health conditions such as obesity.
4.4 PNX and electrolyte metabolism
Electrolytes are essential for maintaining cellular function, fluid balance, and overall homeostasis, and any imbalance can lead to significant health issues (79, 80). Notably, PNX is expressed in the hypothalamic region such as PVN and SON that secretes vasopressin and oxytocin (9, 81).Furthermore, previous finding of PNX has shown to stimulates vasopressin secretion (46). Therefore, PNX is suggested to have potential therapeutic applications in managing conditions related to fluid and electrolyte imbalance, such as dehydration and hyponatremia. (46, 47).
Beyond its central actions, PNX is also expressed in peripheral tissues such as the kidneys, which are vital for electrolyte regulation (12). Interestingly, the GPR173 also has found expressed in the kidney tissue (82). The kidneys organ is responsible to filter blood, reabsorb essential electrolytes, and excrete waste products, thus maintaining electrolyte balance (83). The presence of PNX and its receptor may influence renal function by modulating the activity of various ion channels and transporters involved in electrolyte reabsorption and excretion. This regulation is crucial for maintaining the balance of sodium, potassium, calcium, and other vital electrolytes. Conditions such as obesity, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are often associated with disruptions in electrolyte metabolism (84–86). Understanding the mechanisms by which PNX regulates electrolyte balance is particularly relevant for therapeutic studies in the context of metabolic disorders.
4.5 PNX and food intake regulation
Food intake is essential for metabolism as it provides the calories and nutrients needed for energy production, growth, and maintenance of bodily functions (87). Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats from food are metabolized to produce energy, regulate blood glucose levels, and synthesize important biomolecules. Imbalances in food intake can disrupt these metabolic processes, leading to disorders such as obesity and diabetes (88–90).
PNX plays a multifaceted role in the regulation of food intake, primarily through its actions within the hypothalamus (91). Previous study has demonstrated that PNX increases food intake during the day while suppressing it at night (92). This finding suggests that PNX plays a role in regulating diurnal patterns of appetite, potentially influencing eating behavior based on the time of day. Recent reviews suggest that personalizing mealtimes may reduce circadian misalignment, enhance overall health, and help prevent metabolic disorder (93). By promoting daytime food intake and curbing nocturnal consumption, PNX may help align eating patterns with the natural circadian rhythms of the body, which could be beneficial for maintaining energy balance and metabolic health. Furthermore, the regulation of food intake by PNX is mediated through interactions with NPY1/NPY5 and CRF1/CRF2 receptors (6). Interestingly, CRF1 and CRF2 receptors are associated with the stress response and energy balance (94, 95). This dual mechanism suggests that PNX influences food intake by engaging both orexigenic neuropeptide pathways and stress-related signaling systems.
In infertile women with PCOS undergoing ovarian stimulation, higher baseline levels of nesfatin-1 (NES-1) and oxytocin (OT) were associated with pregnancy, while post-stimulation elevated phoenixin (PNX-14) levels predicted pregnancy. Pregnant women also showed increased post-stimulation levels of PNX-14, NES-1, and dopamine (DA) but decreased OT levels compared to non-pregnant counterparts. Additionally, a negative association between NES-1 and PNX was observed in pregnant participants, indicating potential roles for these neuroendocrine factors in reproductive success and their connection to metabolism warrants further investigation (50). Similarly, another study highlights their potential importance in regulating autonomic functions critical for maintaining metabolic homeostasis. With both NES-1 and PNX showing similar brain distributions, their co-expression in key hypothalamic nuclei suggests a potential role in metabolic regulation. Given the hypothalamus’s central role in integrating metabolic signals and regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, the wide distribution of PNX in conjunction with NES-1 suggests a possible involvement in metabolic pathways influencing reproductive health. Understanding the interplay between these neuropeptides and metabolic processes could provide insights into their roles in both metabolic regulation and reproductive function, warranting further investigation in contemporary neuroscience (49).
4.6 PNX and mitochondrial dynamics
Mitochondrial dynamics is comprising processes such as mitochondrial biogenesis, fission, fusion, and mitophagy (96). These processes are essential for maintaining cellular health and function. PNX has been shown to influence mitochondrial biogenesis through its interaction with key signaling pathways, including the cAMP/PKA and Epac-ERK pathways (107). By modulating these pathways, PNX can enhance the production of mitochondria, which is particularly important in tissues with high energy demands, such as muscle and brown adipose tissue (97). Furthermore, the promotion of neuronal mitochondrial biogenesis by PNX indicates potential neuroprotective effects and utility in managing neurodegenerative diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction (107).
Another study has explored the impact of phoenixin on obesity-induced infertility in female rats (53). The study revealed that PNX treatment significantly ameliorated several markers of metabolic and reproductive dysfunction. Specifically, PNX increased the expression of mitofusin 2 (Mfn2), electron transport chain (ETC) complex-I and mitochondrial transmembrane potential. These changes were accompanied by improvements in ovarian histopathology, decreased serum levels of insulin and testosterone, as well as ovarian levels of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1), reactive oxygen species (ROS), TNF-α, MDA, and caspase-3. Therefore, it is suggested that PNX can counteract the adverse effects of obesity on fertility by modulating mitochondrial dynamics and reducing oxidative stress. Collectively, these insights pave the way for further exploration of phoenixin as a therapeutic agent in metabolic, fertility, and neurodegenerative disorders.
4.7 Integration with reproductive functions
Metabolism and reproduction are integrated through a complex, multifaceted process (98). This integration ensures that reproductive success is closely aligned with the metabolic state of an organism. PNX has emerged as a significant mediator in this interplay, influencing both metabolic and reproductive functions (9). Metabolic hormones like insulin and leptin are known to influence reproductive hormone levels (99, 100). PNX modulates the activity of these metabolic hormones, thereby indirectly affecting reproductive hormones such as GnRH and LH (12). This hormonal interplay ensures that reproductive activities are aligned with the metabolic state of the organism (101).
Reproductive processes are energy-intensive and demand a well-regulated energy balance (102). PNX contributes to this balance by interacting with hormones that regulate appetite and energy expenditure, ensuring adequate energy availability for reproductive activities (33, 38, 45). Furthermore, PNX plays a significant role in mitochondrial dynamics, encompassing biogenesis, fission, fusion, and mitophagy (53, 107). These processes are vital for maintaining mitochondrial health and energy production, which are crucial for both metabolic and reproductive health (103, 104). Efficient mitochondrial function supports the energy needs of cellular processes and the synthesis of hormones and signaling molecules essential for reproduction.
Understanding the integrative role of PNX in metabolism and reproduction opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions. One pertinent example is PCOS, a disorder characterized by metabolic and reproductive dysfunctions, including insulin resistance, obesity, and irregular menstrual cycles (105). Studies have shown that PNX influences insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake, which are crucial factors in managing insulin resistance in PCOS (33). By modulating these metabolic pathways, PNX has the potential to alleviate some of the metabolic burdens associated with PCOS. Additionally, the role of PNX in lipid metabolism, including the regulation of lipogenesis and lipolysis (25, 31), could help manage obesity and its related complications in PCOS patients. Given the intriguing potential role of PNX in regulating reproduction and metabolism, a recent study demonstrated that knocking out the PNX gene did not affect fertility (45). This observation may be attributed to compensatory mechanisms that ensure the survival and continuity of the organism (106). Thus, warrant further study to elucidate the role of PNX in fertility.
Given the dual role of PNX in regulating both metabolic and reproductive functions, it presents a unique therapeutic target for managing PCOS. Further research is essential to fully elucidate the mechanisms through which PNX exerts its effects on metabolic and reproductive pathways in PCOS. Clinical studies exploring PNX levels in PCOS patients and the impact of PNX-based therapies on metabolic and reproductive outcomes are particularly warranted.
5 Future direction
Most of the studies reviewed have been conducted in animal models, including rats and zebrafish, and in vitro cell cultures. While these models provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of PNX action, the relevance of these findings to human physiology remains an open question. Future research should focus on validating these findings in human tissues and clinical studies to ascertain the translational potential of PNX as a therapeutic target. Meanwhile, the precise mechanisms through which PNX exerts its effects are not fully understood. Both PNX-14 and PNX-20 are known to interact with the G protein-coupled receptor 173 (GPR173), but the downstream signaling pathways and receptor interactions need further elucidation. Understanding the specific pathways activated by PNX, such as the cAMP/PKA pathway and CREB phosphorylation, is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic interventions. Additional mechanistic studies are needed to delineate how PNX modulates these pathways in different tissues and under various physiological and pathological conditions.
The actions of PNX appear to be context-dependent, with some studies reporting contradictory findings. For instance, while PNX-14 has been shown to enhance insulin secretion and protect against NAFLD, other studies might not observe these effects under different experimental conditions. This variability suggests that PNX’s effects might be influenced by factors such as dosage, the specific isoform used (PNX-14 vs. PNX-20), and the physiological state of the organism. Future studies should aim to standardize experimental conditions and dosages to better compare results across different studies. In addition, PNX’s role in the neuroendocrine regulation of metabolism is particularly intriguing. The peptide’s ability to influence reproductive hormones, such as LH and FSH, and its involvement in food intake and stress responses point to a broader role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis. PNX’s interaction with the GnRH system and its impact on neuroendocrine functions suggest that it could serve as a bridge linking metabolic and reproductive health.
Further research should explore these neuroendocrine interactions in more detail to understand how PNX contributes to overall metabolic regulation and its potential implications for disorders such as PCOS and T2DM. The potential prognostic significance of PNX in metabolic disorders needs to be investigated further. Elevated levels of PNX-20 in individuals with type 2 diabetes and its association with diabetic complications suggest that PNX could serve as a biomarker for disease progression. Studies should aim to establish clear correlations between PNX levels and clinical outcomes in metabolic disorders. This could involve longitudinal studies tracking PNX levels in patients over time to determine their predictive value for disease onset and progression. The diverse effects of PNX-14 and PNX-20 on insulin secretion, liver function, cardiovascular health, and adipogenesis highlight their potential as therapeutic targets. Developing PNX-based therapies could involve designing peptide analogs or small molecules that modulate PNX signaling. Such therapies could be aimed at enhancing insulin secretion in diabetes, protecting against liver and cardiac injuries, or improving reproductive health in conditions like obesity-induced infertility. Clinical trials will be necessary to evaluate the efficacy and safety of these potential treatments.
Despite these advancements, several limitations remain. Most studies focus on animal models, raising questions about translatability to human physiology. Variability in experimental designs and methodologies complicates data synthesis and interpretation. Additionally, while many studies highlight PNX’s beneficial effects, some contradictory findings suggest context-dependent actions that require further elucidation. Understanding PNX signaling mechanisms and receptor interactions remains incomplete, necessitating additional research to delineate its mode of action in metabolism.
6 Conclusion
In conclusion, PNX peptides, particularly PNX-14 and PNX-20, exhibit a wide range of effects on metabolic processes, hormonal regulation, and cellular function. While the current body of research provides a strong foundation, many questions remain regarding the mechanisms of PNX action, its relevance to human health, and its potential as a therapeutic target. Addressing these questions through rigorous mechanistic studies, translational research, and clinical trials will be crucial for harnessing the therapeutic potential of PNX in metabolic disorders and related conditions. The prognostic significance of PNX in the wider neuroendocrine scenario also warrants further investigation, offering potential insights into the role of PNX in metabolic homeostasis and disease.
Author contributions
AM: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BM: Writing – review & editing. MY: Writing – review & editing. NS: Writing – review & editing. SM: Writing – review & editing. NM: Writing – review & editing. FJ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. NA: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The author acknowledges the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS), grant number FRGS/1/2023/SKK10/UKM/03/2 funded by the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), Malaysia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ATF, Activating Transcription Factor; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; C/EBPs, CAAT-enhancer-binding proteins; CHOP, C/EBP-homologous protein; CREB, cyclic AMP response element-binding protein; eIF2α, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; GOAT, ghrelin O-acyltransferase; GPR173, G protein-coupled receptor 173; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; LH, luteinizing hormone; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NS-1, neuroscreen-1; Oct-1, Organic cation transporter 1; PPARγ, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma; PCOS, polycystic ovarian syndrome; PKA, protein kinase A; PNX, phoenixin; SMIM20, small integral membrane protein 20; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
References
1. Liang H, Zhao Q, Lv S, Ji X. Regulation and physiological functions of phoenixin. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9:956500. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.956500
2. Hofmann T, Weibert E, Ahnis A, Elbelt U, Rose M, Klapp BF, et al. Phoenixin is negatively associated with anxiety in obese men. Peptides. (2017) 88:32–6. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2016.12.011
3. Lyu R-M, Huang X-F, Zhang Y, Dun SL, Luo JJ, Chang J-K, et al. Phoenixin: a novel peptide in rodent sensory ganglia. Neuroscience. (2013) 250:622–31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.07.057
4. Hermanowicz B, Bogus-Nowakowska K, Palasz A, Wiaderkiewicz R, Robak A. Phoenixin is present in hypothalamic neuroendocrine nuclei of the domestic pig-immunohistochemical study. Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis. (2015) 75).
5. Kras K, Ropka-Molik K, Muszyński S, Arciszewski MB. Expression of Genes Encoding Selected Orexigenic and Anorexigenic Peptides and Their Receptors in the Organs of the Gastrointestinal Tract of Calves and Adult Domestic Cattle (Bos taurus taurus). Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 25:533. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010533
6. Rajaei S, Zendehdel M, Rahnema M, Hassanpour S, Asle-Rousta M. Mediatory role of the central NPY, melanocortine and corticotrophin systems on phoenixin-14 induced hyperphagia in neonatal chicken. Gen Comp Endocrinol. (2022) 315:113930. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2021.113930
7. Lyu R-M, Cowan A, Zhang Y, Chen Y-H, Dun SL, Chang J-K, et al. Phoenixin: a novel brain-gut-skin peptide with multiple bioactivity. Acta Pharmacologica Sin. (2018) 39:770–3. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.195
8. Rajeswari JJ, Unniappan S. Phoenixin-20 stimulates mRNAs encoding hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal hormones, is pro-vitellogenic, and promotes oocyte maturation in zebrafish. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:6264. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63226-x
9. Billert M, Rak A, Nowak KW, Skrzypski M. Phoenixin: more than reproductive peptide. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:8378. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218378
10. McIlwraith EK, Zhang N, Belsham DD. The regulation of phoenixin: A fascinating multidimensional peptide. J Endocrine Soc. (2022) 6:bvab192. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvab192
11. Kalamon N, Błaszczyk K, Szlaga A, Billert M, Skrzypski M, Pawlicki P, et al. Levels of the neuropeptide phoenixin-14 and its receptor GRP173 in the hypothalamus, ovary and periovarian adipose tissue in rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 528:628–35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.101
12. Yosten GL, Lyu RM, Hsueh AJ, Avsian-Kretchmer O, Chang JK, Tullock CW, et al. A novel reproductive peptide, phoenixin. J Neuroendocrinol. (2013) 25:206–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02381.x
13. Norris DO, Lopez KH. Hormones and reproduction of vertebrates (Vol. 1). Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States: Academic Press (2010).
14. McEwen BS, Milner TA. Understanding the broad influence of sex hormones and sex differences in the brain. J Neurosci Res. (2017) 95:24–39. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23809
15. Szadvári I, Ostatníková D, Durdiaková JB. Sex differences matter: males and females are equal but not the same. Physiol Behav. (2023) 259:114038. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2022.114038
16. Kauffman AS. Gonadal and nongonadal regulation of sex differences in hypothalamic Kiss1 neurones. J Neuroendocrinol. (2010) 22:682–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02030.x
17. Roper LK, Briguglio JS, Evans CS, Jackson MB, Chapman ER. Sex-specific regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion by synaptotagmin 9. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:8645. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9645
18. Handelsman DJ, Hirschberg AL, Bermon S. Circulating testosterone as the hormonal basis of sex differences in athletic performance. Endocrine Rev. (2018) 39:803–29. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00020
19. Hess RA, Cooke PS. Estrogen in the male: a historical perspective. Biol Reprod. (2018) 99:27–44. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy043
20. Brock O, De Mees C, Bakker J. Hypothalamic expression of oestrogen receptor α and androgen receptor is sex-, age-and region-dependent in mice. J Neuroendocrinol. (2015) 27:264–76. doi: 10.1111/jne.12258
21. Liu X, Shi H. Regulation of estrogen receptor α expression in the hypothalamus by sex steroids: implication in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Int J Endocrinol. (2015) 2015:949085. doi: 10.1155/2015/949085
22. Oyola MG, Thompson MK, Handa AZ, Handa RJ. Distribution and chemical composition of estrogen receptor β neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the female and male mouse hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. (2017) 525:3666–82. doi: 10.1002/cne.24295
23. Stein LM, Tullock CW, Mathews SK, Garcia-Galiano D, Elias CF, Samson WK, et al. Hypothalamic action of phoenixin to control reproductive hormone secretion in females: importance of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor Gpr173. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. (2016) 311:R489–96. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00191.2016
24. Treen AK, Luo V, Belsham DD. Phoenixin activates immortalized GnRH and kisspeptin neurons through the novel receptor GPR173. Mol Endocrinol. (2016) 30:872–88. doi: 10.1210/me.2016-1039
25. Billert M, Wojciechowicz T, Jasaszwili M, Szczepankiewicz D, Waśko J, Strowski MZ, et al. Phoenixin-14 stimulates differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via cAMP/Epac-dependent mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Biol Lipids. (2018) 1863:1449–57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.09.006
26. Xu S, Hu Z, Chen Y, Min X, Bai C, Jiang T, et al. Activation of GPR173 alleviates neuropathic pain and chronic inflammation. J Biomed Nanotechnology. (2022) 18:2566–72. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2022.3447
27. Mcilwraith EK, Belsham DD. Phoenixin: uncovering its receptor, signaling and functions. Acta Pharmacologica Sin. (2018) 39:774–8. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.13
28. Yu Z, Wu H, Wang Y. Phoenixin-14 promotes the recovery of neurological dysfunction after spinal cord injury by regulating microglial polarization via PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2022) 41:09603271221111345. doi: 10.1177/09603271221111345
29. Wang M, Chen H-P, Zhai Y, Jiang N, Liu JY, Tian CX, et al. Phoenixin: Expression at different ovarian development stages and effects on genes ralated to reproduction in spotted scat, Scatophagus argus. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B: Biochem Mol Biol. (2019) 228:17–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2018.10.005
30. Jiang J, He Z, Peng Y, Jin W, Wang Z, Mu L, et al. Phoenixin-14 enhances memory and mitigates memory impairment induced by Aβ1-42 and scopolamine in mice. Brain Res. (2015) 1629:298–308. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.10.030
31. Yang F, Huang P, Shi L, Liu F, Tang A, Xu S. Phoenixin 14 inhibits high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in experimental mice. Drug Design Dev Ther. (2020) 14:3865–74. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S258857
32. Zeng Q, Ou L, Wang W, Guo D-Y. Gastrin, cholecystokinin, signaling, and biological activities in cellular processes. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:112. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00112
33. Billert M, Kołodziejski PA, Strowski MZ, Nowak KW, Skrzypski M. Phoenixin-14 stimulates proliferation and insulin secretion in insulin producing INS-1E cells. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res. (2019) 1866:118533. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118533
34. Rajeswari JJ, Blanco AM, Unniappan S. Phoenixin-20 suppresses food intake, modulates glucoregulatory enzymes, and enhances glycolysis in zebrafish. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. (2020) 318:R917–28. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00019.2020
35. Choudhury AA, Rajeswari VD. Gestational diabetes mellitus-A metabolic and reproductive disorder. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2021) 143:112183. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112183
36. Oghbaei H, Fattahi A, Hamidian G, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Ziaee M, Mahmoudi J. A closer look at the role of insulin for the regulation of male reproductive function. Gen Comp Endocrinol. (2021) 300:113643. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2020.113643
37. Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Method. (2005) 8:19–32. doi: 10.1080/1364557032000119616
38. Rajeswari JJ, Vélez EJ, Unniappan S. Liver and muscle-specific effects of phoenixin-20 on the insulin-like growth factor system mRNAs in zebrafish. Growth Hormone IGF Res. (2022) 63:101456. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2022.101456
39. Celik F, Aydin S. Blood and aqueous humor phoenixin, endocan and spexin in patients with diabetes mellitus and cataract with and without diabetic retinopathy. Peptides. (2022) 150:170728. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170728
40. Ozdemir-Kumral ZN, Sen E, Yapici HB, Atakul N, Domruk OF, Aldag Y, et al. Phoenixin 14 ameloriates pancreatic injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by alleviating oxidative burden. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2022) 74:1651–9. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgac055
41. Breton TS, Murray CA, Huff SR, Phaneuf AM, Tripp BM, Patuel SJ, et al. Phoenixin-14 alters transcriptome and steroid profiles in female green-spotted puffer (Dichotomyctere nigroviridis). Sci Rep. (2022) 12:9454. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13695-z
42. Chi X, Li Z, Zhang L, Xie X, Huang M. Phoenixin-20 ameliorates gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) symptoms and placental insults in an experimental mouse model. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 101:108171. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108171
43. McIlwraith EK, Loganathan N, Belsham DD. Phoenixin expression is regulated by the fatty acids palmitate, docosahexaenoic acid and oleate, and the endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Front Neurosci. (2018) 12:838. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00838
44. Liu T, Yang M, Wu Y, Bu G, Han X, Du X, et al. PNX14 but not PNX20 as a novel regulator of preadipocyte differentiation via activating Epac-ERK signaling pathway in Gallus gallus. Gen Comp Endocrinol. (2023) 335:114232. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2023.114232
45. McIlwraith EK, Loganathan N, Mak KW, He W, Belsham DD. Phoenixin knockout mice show no impairment in fertility or differences in metabolic response to a high-fat diet, but exhibit behavioral differences in an open field test. J Neuroendocrinol. (2024), e13398. doi: 10.1111/jne.13398
46. Gasparini S, Stein LM, Loewen SP, Haddock CJ, Soo J, Ferguson AV, et al. Novel regulator of vasopressin secretion: phoenixin. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. (2018) 314:R623–8. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00426.2017
47. Haddock CJ, Almeida-Pereira G, Stein LM, Yosten GL, Samson WK. A novel regulator of thirst behavior: phoenixin. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. (2020) 318:R1027–35. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00023.2020
48. Mukherjee K, Unniappan S. Mouse gastric mucosal endocrine cells are sources and sites of action of Phoenixin-20. Peptides. (2021) 141:170551. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170551
49. Pałasz A, Rojczyk E, Bogus K, Worthington JJ, Wiaderkiewicz R. The novel neuropeptide phoenixin is highly co-expressed with nesfatin-1 in the rat hypothalamus, an immunohistochemical study. Neurosci Lett. (2015) 592:17–21. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.02.060
50. Piróg M, Jach R, Ząbczyk M, Natorska J. Increased serum levels of phoenixin-14, nesfatin-1 and dopamine are associated with positive pregnancy rate after ovarian stimulation. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:6991. doi: 10.3390/jcm12226991
51. Ak TP, Yaman M, Bayrakdar A, Bulmus O. Expression of phoenixin-14 and nesfatin-1 in the hypothalamo–pituitary–gonadal axis in the phases of the estrous cycle. Neuropeptides. (2023) 97:102299. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2022.102299
52. Guvenc G, Altinbas B, Kasikci E, Ozyurt E, Bas A, Udum D, et al. Contingent role of phoenixin and nesfatin-1 on secretions of the male reproductive hormones. Andrologia. (2019) 51:e13410. doi: 10.1111/and.13410
53. Basha EH, Eltokhy AK, Eltantawy AF, Heabah NA, Elshwaikh SL, El-Harty YM. Linking mitochondrial dynamics and fertility: Promoting fertility by phoenixin through modulation of ovarian expression of GnRH receptor and mitochondrial dynamics proteins DRP-1 and mfn-2. Pflügers Archiv-European J Physiol. (2022) 474:1107–19. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02739-y
54. Jais A, Brüning JC. Arcuate nucleus-dependent regulation of metabolism—pathways to obesity and diabetes mellitus. Endocrine Rev. (2022) 43:314–28. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab025
55. Yousefvand S, Hamidi F. Role of paraventricular nucleus in regulation of feeding behavior and the design of intranuclear neuronal pathway communications. Int J Pept Res Ther. (2020) 26:1231–42. doi: 10.1007/s10989-019-09928-x
56. Zhang L, Hernandez-Sanchez D, Herzog H. Regulation of feeding-related behaviors by arcuate neuropeptide Y neurons. Endocrinology. (2019) 160:1411–20. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00056
57. Mizuno TM, Makimura H, Mobbs CV. The physiological function of the agouti-related peptide gene: the control of weight and metabolic rate. Ann Med. (2003) 35:425–33. doi: 10.1080/07853890310012076
58. Qin C, Li J, Tang K. The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus: development, function, and human diseases. Endocrinology. (2018) 159:3458–72. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-00453
59. Harter CJ, Kavanagh GS, Smith JT. The role of kisspeptin neurons in reproduction and metabolism. J Endocrinol. (2018) 238:R173–83. doi: 10.1530/JOE-18-0108
60. Rocca C, Scavello F, Granieri MC, Pasqua T, Amodio N, Imbrogno S, et al. Phoenixin-14: detection and novel physiological implications in cardiac modulation and cardioprotection. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2018) 75:743–56. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2661-3
61. Jacob M, Chappell D, Becker BF. Regulation of blood flow and volume exchange across the microcirculation. Crit Care. (2016) 20:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1485-0
62. Reid AM, Wilson PW, Caughey SD, Dixon LM, D’Eath RB, Sandilands V, et al. Pancreatic PYY but not PPY expression is responsive to short-term nutritional state and the pancreas constitutes the major site of PYY mRNA expression in chickens. Gen Comp Endocrinol. (2017) 252:226–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.07.002
63. Zhao T-J, Liang G, Li RL, Xie X, Sleeman MW, Murphy AJ, et al. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) is essential for growth hormone-mediated survival of calorie-restricted mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2010) 107:7467–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002271107
64. Vigil P, Meléndez J, Petkovic G, Del Río JP. The importance of estradiol for body weight regulation in women. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:951186. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.951186
65. Kim MO, Lee YJ, Park JH, Ryu JM, Yun SP, Han HJ. PKA and cAMP stimulate proliferation of mouse embryonic stem cells by elevating GLUT1 expression mediated by the NF-κB and CREB/CBP signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-General Subj. (2012) 1820:1636–46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.05.008
66. Natesan V, Kim S-J. Lipid metabolism, disorders and therapeutic drugs–review. Biomolecules Ther. (2021) 29:596. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2021.122
67. Bitto A, Tatom N, Krivak T, Grotz P, Kaeberlein M. Evidence that C/EBP-β LAP increases fat metabolism and protects against diet-induced obesity in response to mTOR inhibition. Front Aging. (2021) 2:738512. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2021.738512
68. Gervois P, Torra IP, Fruchart J-C, Staels B. Regulation of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism by PPAR activators. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2000) 38(1):3–11. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2000.002
69. Guo Q, Jin Y, Chen X, Ye X, Shen X, Lin M, et al. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2024) 9:53. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01757-9
70. Payne VA, Au W-S, Lowe CE, Rahman SM, Friedman JE, O’Rahilly S, et al. C/EBP transcription factors regulate SREBP1c gene expression during adipogenesis. Biochem J. (2010) 425:215–24. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091112
71. Petersen RK, Madsen L, Pedersen LM, Hallenborg P, Hagland H, Viste K, et al. (cAMP)-mediated stimulation of adipocyte differentiation requires the synergistic action of Epac-and cAMP-dependent protein kinase-dependent processes. Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 28:3804–16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00709-07
72. Reverte-Salisa L, Siddig S, Hildebrand S, Yao X, Zurkovic J, Jaeckstein MY, et al. EPAC1 enhances brown fat growth and beige adipogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. (2024) 26:113–23. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01311-9
73. Jakab J, Miškić B, Mikšić Š, Juranić B, Ćosić V, Schwarz D, et al. Adipogenesis as a potential anti-obesity target: A review of pharmacological treatment and natural products. Diabetes Metab syndrome Obes. (2021) 14:67–83. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S281186
74. Deprince A, Haas JT, Staels B. Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease. Mol Metab. (2020) 42:101092. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101092
75. Yao B, Lv J, Du L, Zhang H, Xu Z. Phoenixin-14 protects cardiac damages in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes mice model through SIRT3. Arch Physiol Biochem. (2024) 130:110–8. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2021.1981946
76. Yilmaz N, Hudaykulıyeva J, Gul S. Phoenixin-14 may ameliorate testicular damage caused by torsion-detorsion by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in prepubertal rats. Tissue Cell. (2024) 88:102405. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2024.102405
77. Jiao P, Feng B, Li Y, He Q, Xu H. Hepatic ERK activity plays a role in energy metabolism. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2013) 375:157–66. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.05.021
78. Wu S-C, Lo Y-M, Lee J-H, Chen C-Y, Chen T-W, Liu H-W, et al. Stomatin modulates adipogenesis through the ERK pathway and regulates fatty acid uptake and lipid droplet growth. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4174. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31825-z
79. Merrill AE, Chambliss AB. Water and electrolyte balance. In: Contemporary practice in clinical chemistry. Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States: Elsevier (2020). p. 651–63.
80. Shrimanker I, Bhattarai S. Electrolytes. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541123/ (Accessed July 24, 2023).
81. Christ-Crain M, Ball S. 2015The neurohypophysis: endocrinology of vasopressin and oxytocin. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc. (2000).
82. Jiang M, Liu J, Jiang D, Pan Q, Shi H, Huang Y, et al. Characterization and expression analysis of gpr173a and gpr173b revealed their involvement in reproductive regulation in spotted scat (Scatophagus argus). Aquaculture Rep. (2022) 25:101239. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101239
83. Ellison D, Farrar FC. Kidney influence on fluid and electrolyte balance. Nurs Clinics. (2018) 53:469–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2018.05.004
84. Iqbal S, Klammer N, Ekmekcioglu C. The effect of electrolytes on blood pressure: a brief summary of meta-analyses. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1362. doi: 10.3390/nu11061362
85. Khan RN, Saba F, Kausar SF, Siddiqui MH. Pattern of electrolyte imbalance in Type 2 diabetes patients: Experience from a tertiary care hospital. Pakistan J Med Sci. (2019) 35:797. doi: 10.12669/pjms.35.3.844
86. Stookey J, Barclay D, Arieff A, Popkin B. The altered fluid distribution in obesity may reflect plasma hypertonicity. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2007) 61:190–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602521
87. Woods SC, Ramsay DS. Food intake, metabolism and homeostasis. Physiol Behav. (2011) 104:4–7. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.026
88. Guyenet SJ, Schwartz MW. Regulation of food intake, energy balance, and body fat mass: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:745–55. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2525
89. Morton GJ, Meek TH, Schwartz MW. Neurobiology of food intake in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2014) 15:367–78. doi: 10.1038/nrn3745
90. O’hearn M, Lara-Castor L, Cudhea F, Miller V, Reedy J, Shi P, et al. Incident type 2 diabetes attributable to suboptimal diet in 184 countries. Nat Med. (2023) 29:982–95. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02278-8
91. Schalla MA, Stengel A. The role of phoenixin in behavior and food intake. Peptides. (2019) 114:38–43. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2019.04.002
92. Schalla M, Prinz P, Friedrich T, Scharner S, Kobelt P, Goebel-Stengel M, et al. Phoenixin-14 injected intracerebroventricularly but not intraperitoneally stimulates food intake in rats. Peptides. (2017) 96:53–60. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.08.004
93. Boege HL, Bhatti MZ, St-Onge M-P. Circadian rhythms and meal timing: impact on energy balance and body weight. Curr Opin Biotechnol. (2021) 70:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2020.08.009
94. Domin H, Śmiałowska M. The diverse role of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and its CRF1 and CRF2 receptors under pathophysiological conditions: Insights into stress/anxiety, depression, and brain injury processes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2024) 105748. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105748
95. Richard D, Lin Q, Timofeeva E. The corticotropin-releasing factor family of peptides and CRF receptors: their roles in the regulation of energy balance. Eur J Pharmacol. (2002) 440:189–97. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(02)01428-0
96. Tilokani L, Nagashima S, Paupe V, Prudent J. Mitochondrial dynamics: overview of molecular mechanisms. Essays Biochem. (2018) 62:341–60. doi: 10.1042/EBC20170104
97. Carpentier AC, Blondin DP, Virtanen KA, Richard D, Haman F, Turcotte É.E. Brown adipose tissue energy metabolism in humans. Front Endocrinol. (2018) 9:447. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00447
98. Yang F, Zhao S, Wang P, Xiang W. Hypothalamic neuroendocrine integration of reproduction and metabolism in mammals. J Endocrinol. (2023) 258. doi: 10.1530/JOE-23-0079
99. Al-Hussaniy HA, Alburghaif AH, Naji MA. Leptin hormone and its effectiveness in reproduction, metabolism, immunity, diabetes, hopes and ambitions. J Med Life. (2021) 14:600. doi: 10.25122/jml-2021-0153
100. Sliwowska JH, Fergani C, Gawałek M, Skowronska B, Fichna P, Lehman MN. Insulin: its role in the central control of reproduction. Physiol Behav. (2014) 133:197–206. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.05.021
101. Garcia-Garcia R. Integrative control of energy balance and reproduction in females. Int Scholarly Res Notices. (2012) 2012:121389. doi: 10.5402/2012/121389
102. Schneider JE. Energy balance and reproduction. Physiol Behav. (2004) 81:289–317. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.02.007
103. Bentov Y, Yavorska T, Esfandiari N, Jurisicova A, Casper RF. The contribution of mitochondrial function to reproductive aging. J assisted Reprod Genet. (2011) 28:773–83. doi: 10.1007/s10815-011-9588-7
104. Das M, Sauceda C, Webster NJ. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity and reproduction. Endocrinology. (2021) 162:bqaa158. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa158
105. Li Y, Chen C, Ma Y, Xiao J, Luo G, Li Y, et al. Multi-system reproductive metabolic disorder: significance for the pathogenesis and therapy of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Life Sci. (2019) 228:167–75. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.046
106. Hylin MJ, Kerr AL, Holden R. Understanding the mechanisms of recovery and/or compensation following injury. Neural plasticity. (2017) 2017:7125057. doi: 10.1155/2017/7125057
107. Yang Y, Lv Y, Liu J, Zhang S, Li Y, Shi Y. Phoenixin 20 promotes neuronal mitochondrial biogenesis via CREB–PGC-1α pathway. J Mol Histol. (2020) 51:173–81. doi: 10.1007/s10735-020-09867-8
Keywords: phoenixin (PNX), metabolism, mitochondria, glycolysis, mitochondrial respiration
Citation: Muzammil AN, Barathan M, Yazid MD, Sulaiman N, Makpol S, Mohamed Ibrahim N, Jaafar F and Abdullah NAH (2024) A systematic scoping review of the multifaceted role of phoenixin in metabolism: insights from in vitro and in vivo studies. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1406531. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1406531
Received: 25 March 2024; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 27 September 2024.
Edited by:
Olfa Masmoudi-Kouki, University Tunis El Manar, TunisiaReviewed by:
Marek Skrzypski, Poznan University of Life Sciences, PolandCarolina Dalmasso, University of Kentucky, United States
Copyright © 2024 Muzammil, Barathan, Yazid, Sulaiman, Makpol, Mohamed Ibrahim, Jaafar and Abdullah. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nur Atiqah Haizum Abdullah, YXRpcWFoLmhhaXp1bUB1a20uZWR1Lm15; Faizul Jaafar, RmFpenVsLkphYWZhckBtb25hc2guZWR1
 Adiba Najwa Muzammil1
Adiba Najwa Muzammil1 Muttiah Barathan
Muttiah Barathan Muhammad Dain Yazid
Muhammad Dain Yazid Nadiah Sulaiman
Nadiah Sulaiman Suzana Makpol
Suzana Makpol Norlinah Mohamed Ibrahim
Norlinah Mohamed Ibrahim Faizul Jaafar
Faizul Jaafar Nur Atiqah Haizum Abdullah
Nur Atiqah Haizum Abdullah