- 1Department of Veterinary Sciences, University of Turin, Grugliasco,Turin, Italy
- 2Neuroscience Institute Cavalieri Ottolenghi (NICO), Orbassano, Turin, Italy
- 3Department of Neuroscience “Rita Levi-Montalcini”, University of Turin, Turin, Italy
The forebrain ventricular-subventricular zone (V-SVZ) continuously generates new neurons throughout life. Neural stem cells (type B1 cells) along the lateral ventricle become activated, self-renew, and give rise to proliferating precursors which progress along the neurogenic lineage from intermediate progenitors (type C cells) to neuroblasts (type A cells). Neuroblasts proliferate and migrate into the olfactory bulb and differentiate into different interneuronal types. Multiple factors regulate each step of this process. Newly generated olfactory bulb interneurons are an important relay station in the olfactory circuits, controlling social recognition, reproductive behavior, and parental care. Those behaviors are strongly sexually dimorphic and changes throughout life from puberty through aging and in the reproductive age during estrous cycle and gestation. Despite the key role of sex hormones in regulating those behaviors, their contribution in modulating adult neurogenesis in V-SVZ is underestimated. Here, we compare the literature highlighting the sexual dimorphism and the differences across the physiological phases of the animal for the different cell types and steps through the neurogenic lineage.
Introduction
The subventricular zone-olfactory bulb (V-SVZ-OB) system has fascinated scientists for over than 25 years. In fact, this region harbors, in many mammals, a huge neurogenesis persisting until aging (1). In rodents, this process involves multiple steps, each one of them representing a model for different biological and pathological processes with unique features. In fact, this neurogenic process encompasses a germinal layer located in the ventricular-subventricular zone of the forebrain (V-SVZ), along the ventricle in which neural stem cells undergo self-renewal (2) and differentiation to intermediate progenitors (type C cells), then to immature neurons (type A cells) (3–5). Newly generated, type A, cells undergo tangential migration along the rostral migratory stream (RMS) up to the OB (6, 7). There, they migrate radially to the appropriate cell layer and differentiate into interneurons (8). Neurogenesis is thus a complex process consisting in proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and differentiation occurring in each of those levels with specific features (9, 10). The proper turnover enforced by proliferation, migration as well as apoptosis in the OB, is essential for optimizing olfaction [(11); Figure 1]. Therefore, the study of V-SVZ is capital for many purposes: understanding unregulated cell growth in tumor formations (12, 13), preventing or replacing cell loss in aging (1, 14, 15), decreasing neurodegenerative disease risks (16–18), and improving stroke treatments (18).
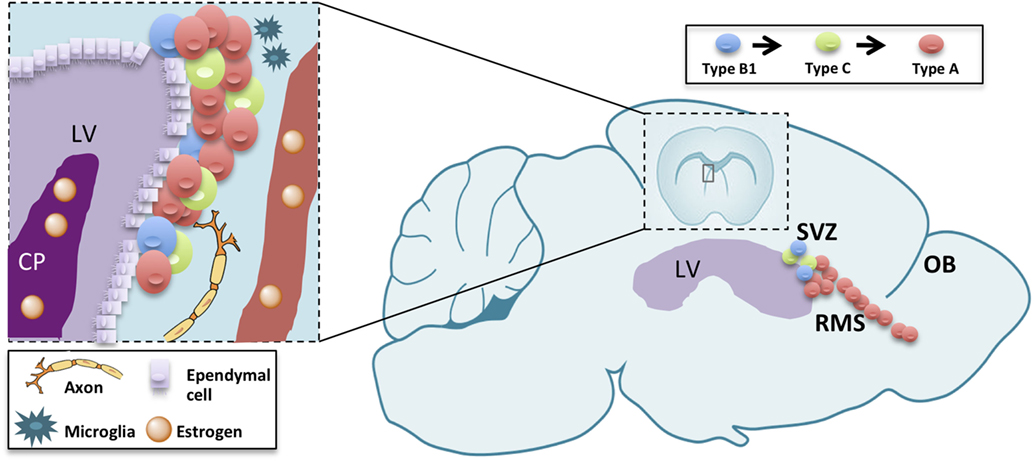
Figure 1. Schematic drawing summarizing adult neurogenesis in the V-SVZ/OB system. Adult neurogenesis is a multiple-step process, occurring in three different subregions: the ventricular-subventricular zone (V-SVZ), the rostral migratory stream (RMS), and the olfactory bulb (OB). Sex hormones reaching the lateral ventricle (LV) through the choroid plexus (CP) or blood vessels (BV) modulate each of those steps either directly on neurogenic lineage or indirectly through other component of the stem-cell niche or the parenchyma.
Despite a huge interest on the endogenous and exogenous factors affecting adult neurogenesis in V-SVZ-OB system (19), few studies have focused on the role of gonadal hormones. This flaw is surprising since steroids have a key role in hippocampal neurogenesis both during development and in adulthood (20–22). Furthermore, V-SVZ-OB system is involved in social and reproductive behaviors, which are strongly regulated by sexual steroids (23, 24) and are targets for xenoestrogens (25–27).Moreover, estrogen receptors (ERs) and enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of steroids such as aromatase, the enzyme converting testosterone (T) into estradiol, are expressed in the V-SVZ (28) and in the OB of adult (29, 30) and developing (31) rats and mice (32). However, while the importance of steroids in the regulation of adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus has been widely studied, its role in the V-SVZ-OB system is more debated. Here, we want to focus on the available data in order to encourage a discussion addressing the open questions in the field.
Sexual Dimorphism in V-SVZ-OB System
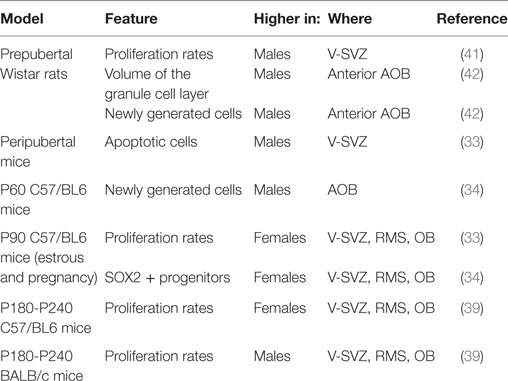
Sexual dimorphism in the V-SVZ-OB system is an open question. Only few studies compared the two sexes and most of them are limited to a few ages. Indeed, the extent of neurogenesis in this region changes along life and it is likely to be affected by changes in the endocrine system.
Neurogenesis is more prominent in adult female mice compared with males. In 3-month-old C57/BL6J mice, females displayed higher proliferating rates in V-SVZ, RMS, and OB, and lower apoptotic cells in V-SVZ in both estrus and pregnancy (33) than males. Similarly, the number of neuronal progenitors (SOX2+) in the V-SVZ of females was higher than males in young adults but not in pups (34).
On the other hand, in other studies, the density of apoptotic cells in accessory (AOB) and main (MOB) OB was similar in the two sexes (35). Some differences affect transiently specific features of the V-SVZ-OB system. For instance, peripubertal males displayed higher rates of apoptosis (33), as well as of proliferation in the V-SVZ compared with females (35), but, in 2-month-old animals, the proliferation rate in the V-SVZ is similar in the two sexes and 1 month later there was a similar supply of newly generated cells in both the MOB and the AOB (35).
Multiple factors may explain the discrepancy among the data. From a technical point of view, the methods used to assess cell proliferation may highlight a different subset of the cycling population. In fact, while the total number of cycling cells identified with PCNA was measured by Diaz (33), the study of Nunez-Parra (35) highlighted only the cells in the S-phase, labeled by BrdU 2 h after the injection of the marker. Thus, it may reflect differences in the cell-cycle length between the two ages, or differences in the composition of the V-SVZ, e.g., a decrease in the number of type C cells, which have a longer S-phase length compared with type A cells (4, 5) or even differential sensitivities of BrdU antibodies (36), although the use of two different anti-BrdU antibodies by Nunez-Parra et al. is likely to have decreased this issue. Moreover, since different subregions in the V-SVZ give rise to different interneurons in the OB (37), it is possible that sexual dimorphism is limited to some of them. In addition to that, the extent of neurogenesis is dissimilar in different mouse strains (38) and it might be differently regulated. In fact, other reports indicate that the higher number of proliferating cells in the V-SVZ of females is limited to mature animals, i.e., 6–8 months old (39). Interestingly, this dimorphism is abolished (SJL/J) or reverted (BALB/C) in different strains (39). Accordingly, in two months old C57BL6 mice, the density of newly generated cells is higher in the AOB of males than females, while no sexual dimorphism has been reported for MOB (34). Similarly, no sexual dimorphism was observed in the number of newly generated cells in the AOB of young-adult CD1 mice, although the age of those mice was not specified (40).
In Wistar rats, males exhibited a higher number of proliferating cells than females and this sexual dimorphism was already established before puberty (41). The higher proliferation at the level of the ventricle does not lead to a sex difference in the density of newly generated cells in the MOB, but only in the volume of the granular layer in the anterior part of the AOB, larger in males than in females [(42); Table 1].
Beside the cells belonging to the neurogenic linage, neural stem-cell niche encompass other structures, namely blood vessels (43, 44), microglia (45, 46), and choroid plexus (47). Both blood vessels (48), microglia (49, 50), and choroid plexus (51) are deeply affected by sex steroids. These structures, thus, may mediate the effect of sex steroids on adult neurogenesis (Figure 1).
Moreover, V-SVZ neurogenesis may also be modulated in a trans-synaptic way by other neuronal circuits which may be sensible to sexual steroids, e.g., serotonin or dopamine system (52, 53), and cholinergic neurons (54).
In general, estrogens are neuroprotective and stimulate differentiation and proliferation while progestins and androgens stimulate differentiation and cell survival (21). However, the V-SVZ-OB system has its unique features. In conclusion, a number of factors can affect adult neurogenesis in the V-SVZ-OB system, and it is likely that some of them are sexually dimorphic and change throughout lifetime. In this picture, the endocrine system may play a key role.
Hormonal Regulation of V-SVZ Neurogenesis in Adult Females
Circulating hormone levels dramatically change during the life of female rodents, during both estrous cycle and pregnancy. These changes may affect neurogenesis. In particular, E2 levels control the estrous cycle, pregnancy, and sexual behavior (32, 55).
Since OB has a key role in mother’s offspring recognition, it is not surprising that the rate of neurogenesis in V-SVZ transiently increase during pregnancy (56). Indeed, two peaks of cell proliferations were observed at gestation day 7 and at postpartum day 7, while at delivery the neurogenic rate is similar to matched aged virgin females (56). The first peak is evident also in females mated with sterile males, so it depends on maternal hormonal levels rather than on the embryo. However, this effect is mediated by prolactin rather than E2 or progesterone (56, 57). However, E2 may have an indirect role, since it stimulates prolactin release (58).
In the adult female mouse, E2 has an inhibitory effect on V-SVZ-OB neurogenesis in both V-SVZ and OB. First, it decreases cell proliferation in the V-SVZ in different models. The number of proliferating cells in the V-SVZ is lower during estrus, than proestrus (39). Moreover, in ovariectomized females, acute E2 supplementation for one day, with a dose comparable to the estrus, decreases cell proliferation in the V-SVZ (59). On the other hand, this effect was not detected by long-term treatment [3 weeks (60)] or with a lower dose of E2 (61), comparable with diestrus (62). Differences in the effect of ovariectomy may be due to an interplay of many component of the neural stem-cell niche. In fact, ovariectomized mice express both ERα and ERβ, but E2 supplementation selectively upregulates ERβ (51). T metabolite 5α-dihydrotestosterone (5αDHT) decreases the expression of AR in the choroid plexus of ovariectomized mice (51).
Male pheromones stimulate the production of ovarian hormones (63) as well as the neurogenesis in adult females (35, 64, 65). However, E2 does not increase neurogenesis (66), nor cell proliferation in V-SVZ or neuroblasts density in OB, but it decreases cell survival in AOB, but not in MOB (24).
In the OB, E2 has different effects depending on the region. In the MOB, in adulthood rather than during development, E2 is able to impair the survival of newly generated cells (59) and MOB functionality (60). Interestingly, as demonstrated in aromatase-KO mice, developmental E2 has the opposite effect in the AOB: the absence of E2 during development decreases the survival of adult generated cells in the AOB. This phenotype can be reverted by adult E2 treatment. On the contrary, the lack of estrogens during development neither alters cell proliferation in the V-SVZ, nor its response to E2 (60).
In contrast to mice, the proliferation rate in the rat V-SVZ does not change during pregnancy, while it increases at delivery (67). As for mice, E2 role in female rat is highly debated. Proliferation in the V-SVZ is not affected neither by ovariectomy nor by acute T or E2 supplementation (41). No studies are available on the long-term effects of ovariectomy despite it deeply alter choroid plexus transcriptome which may indirectly affect the neural stem-cell niche (68). However, E2 decreases the survival of newly generated cells in the AOB, but not in the MOB [(29, 30); Figure 2; Table 2].
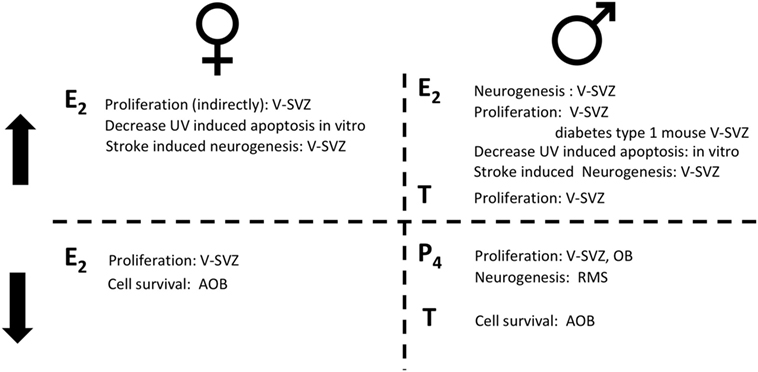
Figure 2. The role of sex hormones in adult neurogenesis for females (left) and for males (right). On the top, steroid hormones induce an increase (↑) in the reported actions; on the bottom steroid hormones induce a decrease (↓) in the reported actions. Estradiol (E2); progesterone (P4); testosterone (T).
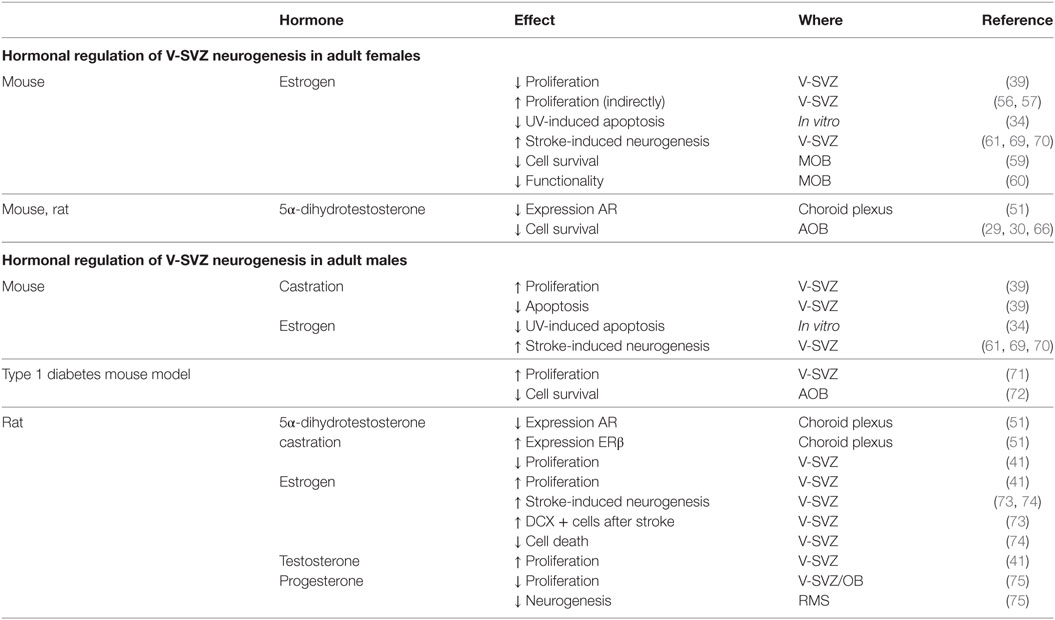
Table 2. Summary of the hormonal regulations in the subventricular zone-olfactory bulb (V-SVZ-OB) system of adult male and female rodents.
The different effects of E2 in mice and rats may be related with the lack of ERα and ERβ in the mouse V-SVZ (76) and with the presence of ERα receptor in the rat (28), although other pathways may be involved (21). For example, no information is available at the moment, concerning the expression of membrane ER (GPER) in rodent V-SVZ.
Hormonal Regulation of V-SVZ Neurogenesis in Adult Males
The effect of sexual steroids is complex also in males. In fact, castration increased the number of proliferating cells and decreased the number of apoptotic ones in the V-SVZ of C57BL6 and SJL/J adult males, i.e., 6–8 months old (39).
Neurogenesis is influenced by pheromones related to aggressive (35) and paternal behavior (77, 78). In fact, the response to pheromones is sex specific and affected by hormonal levels. Indeed, female pheromones stimulate neurogenesis in adult males (64), although the survival of newly generated cells in the AOB in males does not change after opposite sex pheromones exposure, as in females (65). Interestingly, male pheromones as well as female ones, enhance proliferation in the V-SVZ of males (35), although it did not change the ratio of SOX2 cells among the BrdU labeled ones (64). However, low T levels feminize neurogenic response, increasing newly generated cell survival in the AOB, following male pheromone exposure, without affecting cell proliferation in RMS and V-SVZ, leading to attraction to male cues (72).
E2 have a neuroprotective effect on V-SVZ precursors. In fact, it is able to restore proliferation in a type 1 diabetes mouse model (71). Only a few choroid plexus genes are altered by castration in rats (68): ERβ expression increased when compared with sham operated rats (51), while ARs expression decreased after 5αDHT treatment (51).
Unlike in females, T or E2 are required for maintaining physiological neurogenic rate in the V-SVZ of peripubertal rats (41). In fact, the number of proliferating cells and the number of type C progenitors is restored by hormonal treatment in castrated rats, but this effect is restricted to the lateral wall of the V-SVZ (41).
Progesterone and its metabolites, decrease cell proliferation in the V-SVZ-OB of adult rats [2 months old (75)]. The number of newly generated cells in the final part of the RMS is decreased by progesterone metabolites. It is not clear, however, whether this effect is due to a reduction in cell proliferation, of cell survival or, less likely, in the migration rate (Figure 2; Table 2).
Hormonal Regulation of V-SVZ Neurogenesis in Pathological Conditions
Beside an effect in physiological conditions, sex steroids may have a neuroprotective role after different insults. In fact, while no effect of sex steroid treatment was observed on cell death in vitro, E2 prevented apoptosis after UV insults in both male- and female-derived V-SVZ cells, whereas no T effect was reported [(34); Table 2].
Stroke induced an increase in the number of newly generated cells, which was significantly higher in females. As for UV-induced apoptosis, E2 enhances neurogenesis after ischemic stroke, in vivo, in mice of both sexes (61, 69, 79) and rats (73). This increase is present 96 h but not 24 h after stroke (61). The presence of ERα and ERβ, as well as AR is required for the stroke-induced neurogenesis in female mice, since it is abolished in transgenic mice lacking those receptors (69). Interestingly, those receptors are not directly expressed in the V-SVZ (61) suggesting that they may act indirectly through other cells.
Gonadal hormones are supposed to have a key role also in many diseases which display a different incidence and severity in the two sexes (80). V-SVZ neurogenesis may have a prominent role in some of them as: Parkinson disease (17, 81), Multiple sclerosis (82, 83), Alzheimer disease (84), autism (85), schizophrenia (86), and in psychiatric and cognitive disorders (87). However, only limited data are available on the effect of neuroactive steroids on the V-SVZ neurogenesis in those diseases. Moreover, many studies report controversial data on changes in the V-SVZ neurogenesis that may be related on the experimental model as in Parkinson disease (17).
Concluding Remarks
Despite the huge amount of studies on adult neurogenesis in the V-SVZ-OB system, still few data focus on its regulation by steroids. The role of steroids on V-SVZ-OB neurogenesis is highly complex. Generally, neurogenesis is more affected by T in males, while E2 has a higher influence on females. However, the same hormone may determine a different effect depending on sex, age, strain, brain region, and neurogenic process. It is also possible that the different extent of V-SVZ-OB neurogenesis may reflects behavioral differences described among many strains of mice (88) as observed in other brain regions (89, 90). Those differences may be genetic (91, 92) or depend on a lack of maternal care during development (93). Profound differences exist between males and females. Some of them are actively determined by steroids levels in adults, while others are established during development. Moreover, sexual hormone’s levels changes along life. Important species-specific differences exist between different rodent models. Despite some similarities, adult neurogenesis is regulated by different factors in the V-SVZ-OB system compared with the SGZ of the hippocampus. Furthermore, different cell populations, or different steps of the neurogenic lineage may be sensible to a specific hormone.
The extent of adult neurogenesis in the V-SVZ-OB changes along with each of the above mentioned parameters. However, it is not clear which features are directly or indirectly involved. It is, thus, important to consider all those parameters altogether.
Author Contributions
All the authors equally contributed to the search for the sources and to the writing of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Fondazione Cavalieri Ottolenghi for hosting our laboratories in its premises.
Funding
We acknowledge the support from Fondazione Cavalieri Ottolenghi, the University of Torino (Ricerca locale to SG, GP, and GCP), and Fondazione CRT—RF 2015.2564 (to SG). This study was supported by Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca—MIUR projects “Dipartimenti di Eccellenza 2018–2022” to the Dept. of Neurosciences “Rita Levi Montalcini” and to the Dept. of Veterinary Sciences.
References
1. Apple DM, Solano-Fonseca R, Kokovay E. Neurogenesis in the aging brain. Biochem Pharmacol (2017) 141:77–85. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2017.06.116
2. Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A. Proliferating subventricular zone cells in the adult mammalian forebrain can differentiate into neurons and Glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1993) 90(5):2074–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.5.2074
3. Doetsch F, García-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A. Cellular composition and three-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zone in the adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci (1997) 17(13):5046–61.
4. Ponti G, Obernier K, Guinto C, Jose L, Bonfanti L, Alvarez-Buylla A. Cell cycle and lineage progression of neural progenitors in the ventricular-subventricular zones of adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2013) 110(11):E1045–54. doi:10.1073/pnas.1219563110
5. Ponti G, Obernier K, Alvarez-Buylla A. Lineage progression from stem cells to new neurons in the adult brain ventricular-subventricular zone. Cell Cycle (2013) 12(11):1649–50. doi:10.4161/cc.24984
6. Luskin MB. Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron (1993) 11(1):173–89. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(93)90281-U
7. Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A. Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science (1994) 264(5162):1145–8. doi:10.1126/science.8178174
8. Gheusi G, Lepousez G, Lledo P-M. Adult-born neurons in the olfactorybulb: integration and functional consequences. Curr Top Behav Neurosci (2013) 15:49–72. doi:10.1007/7854_2012_228
9. Barral S, Beltramo R, Salio C, Aimar P, Lossi L, Merighi A. Phosphorylation of histone H2AX in the mouse brain from development to senescence. Int J Mol Sci (2014) 15(1):1554–73. doi:10.3390/ijms15011554
10. Capilla-Gonzalez V, Lavell E, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Guerrero-Cazares H. Regulation of subventricular zone-derived cells migration in the adult brain. Adv Exp Med Biol (2015) 853:1–21. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16537-0_1
11. Mouret A, Lepousez G, Gras J, Gabellec MM, Lledo PM. Turnover of new-born olfactory bulb neurons optimizes olfaction. J Neurosci (2009) 29(39):12302–14. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3383-09.2009
12. Jackson EL, Alvarez-Buylla A. Characterization of adult neural stem cells and their relation to brain tumors. Cells Tissues Organs (2008) 188(1–2):212–24. doi:10.1159/000114541
13. Kusne Y, Sanai N. The SVZ and its relationship to stem cell based neuro-oncogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol (2015) 853:23–32. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16537-0_2
14. Luo J, Daniels SB, Lennington JB, Notti RQ, Conover JC. The aging neurogenic subventricular zone. Aging Cell (2006) 5(2):139–52. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00197.x
15. Capilla-Gonzalez V, Herranz-Perez V, Garcia-Verdugo JM. The aged brain: genesis and fate of residual progenitor cells in the subventricular zone. Front Cell Neurosci (2015) 9:365. doi:10.3389/fncel.2015.00365
16. Lamm O, Ganz J, Melamed E, Offen D. Harnessing neurogenesis for the possible treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Comp Neurol (2014) 522(12):2817–30. doi:10.1002/cne.23607
17. van den Berge SA, van Strien ME, Hol EM. Resident adult neural stem cells in Parkinson’s disease—the brain’s own repair system? Eur J Pharmacol (2013) 719(1–3):117–27. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.058
18. Zhang Z, Chopp M. Neural stem cells and ischemic brain. J Stroke (2016) 18(3):267–72. doi:10.5853/jos.2016.00206
19. Lim DA, Alvarez-Buylla A. Adult neural stem cells stake their ground. Trends Neurosci (2014) 37(10):563–71. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2014.08.006
20. Mahmoud R, Wainwright SR, Galea LA. Sex hormones and adult hippocampal neurogenesis: regulation, implications, and potential mechanisms. Front Neuroendocrinol (2016) 41:129–52. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.03.002
21. Heberden C. Sex steroids and neurogenesis. Biochem Pharmacol (2017) 141:56–62. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2017.05.019
22. Galea LAM, Duarte-Guterman P. Hormones and the regulation of adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus and beyond: where are we now? Introduction to the special issue on hormonal regulation of adult neurogenesis: implications for disease. Front Neuroendocrinol (2016) 41:1–2. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.06.001
23. Peretto P, Paredes RG. Frontiers in neurosciencesocial cues, adult neuro-genesis, and reproductive behavior. In: Mucignat-Caretta C, editor. Neurobiology of Chemical Communication. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis(c) (2014).
24. Brus M, Trouillet AC, Hellier V, Bakker J. Estradiol-induced neurogenesis in the female accessory olfactory bulb is required for the learning of the male odor. J Neurochem (2016) 138(3):457–68. doi:10.1111/jnc.13677
25. Rodriguez-Gomez A, Filice F, Gotti S, Panzica G. Perinatal exposure to genistein affects the normal development of anxiety and aggressive behaviors and nitric oxide system in CD1 male mice. Physiol Behav (2014) 133:107–14. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.05.020
26. Hicks KD, Sullivan AW, Cao J, Sluzas E, Rebuli M, Patisaul HB. Interaction of bisphenol A (BPA) and soy phytoestrogens on sexually dimorphic sociosexual behaviors in male and female rats. Horm Behav (2016) 84:121–6. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.06.010
27. Ho SM, Cheong A, Adgent MA, Veevers J, Suen AA, Tam NN, et al. Environmental factors, epigenetics, and developmental origin of reproductive disorders. Reprod Toxicol (2017) 68:85–104. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.07.011
28. Isgor C, Watson SJ. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta mRNA expressions by proliferating and differentiating cells in the adult rat dentate gyrus and subventricular zone. Neuroscience (2005) 134(3):847–56. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.05.008
29. Hoyk Z, Varga C, Parducz A. Estrogen-induced region specific decrease in the density of 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine-labeled cells in the olfactory bulb of adult female rats. Neuroscience (2006) 141(4):1919–24. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.05.053
30. Hoyk Z, Csákvári E, Gyenes A, Siklós L, Harada N, Párducz A. Aromatase and estrogen receptor beta expression in the rat olfactory bulb: neuroestrogen action in the first relay station of the olfactory pathway? Acta Neurobiol Exp (2014) 74(1):1–14.
31. Horvath TL, Wikler KC. Aromatase in developing sensory systems of the rat brain. J Neuroendocrinol (1999) 11(2):77–84. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2826.1999.00285.x
32. Bakker J, Baum MJ. Role for estradiol in female-typical brain and behavioral sexual differentiation. Front Neuroendocrinol (2008) 29(1):1–16. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2007.06.001
33. Diaz D, Valero J, Airado C, Baltanas FC, Weruaga E, Alonso JR. Sexual dimorphic stages affect both proliferation and serotonergic innervation in the adult rostral migratory stream. Exp Neurol (2009) 216(2):357–64. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.12.013
34. Kim JY, Casaccia-Bonnefil P. Interplay of hormones and p53 in modulating gender dimorphism of subventricular zone cell number. J Neurosci Res (2009) 87(15):3297–305. doi:10.1002/jnr.21940
35. Nunez-Parra A, Pugh V, Araneda RC. Regulation of adult neurogenesis by behavior and age in the accessory olfactory bulb. Mol Cell Neurosci (2011) 47(4):274–85. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2011.05.003
36. Leuner B, Glasper ER, Gould E. Thymidine analog methods for studies of adult neurogenesis are not equally sensitive. J Comp Neurol (2009) 517(2):123–33. doi:10.1002/cne.22107
37. Merkle FT, Mirzadeh Z, Alvarez-Buylla A. Mosaic organization of neural stem cells in the adult brain. Science (2007) 317(5836):381–4. doi:10.1126/science.1144914
38. Li Q, Michaud M, Stewart W, Schwartz M, Madri JA. Modeling the neurovascular niche: murine strain differences mimic the range of responses to chronic hypoxia in the premature newborn. J Neurosci Res (2008) 86(6):1227–42. doi:10.1002/jnr.21597
39. Tatar C, Bessert D, Tse H, Skoff RP. Determinants of central nervous system adult neurogenesis are sex, hormones, mouse strain, age, and brain region. Glia (2013) 61(2):192–209. doi:10.1002/glia.22426
40. Oboti L, Savalli G, Giachino C, De Marchis S, Panzica GC, Fasolo A, et al. Integration and sensory experience-dependent survival of newly-generated neurons in the accessory olfactory bulb of female mice. Eur J Neurosci (2009) 29(4):679–92. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06614.x
41. Farinetti A, Tomasi S, Foglio B, Ferraris A, Ponti G, Gotti S, et al. Testos-terone and estradiol differentially affect cell proliferation in the subventricular zone of young adult gonadectomized male and female rats. Neuroscience (2015) 286:162–70. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.050
42. Peretto P, Giachino C, Panzica GC, Fasolo A. Sexually dimorphic neurogenesis is topographically matched with the anterior accessory olfactory bulb of the adult rat. Cell Tissue Res (2001) 306(3):385–9. doi:10.1007/s00441-001-0471-1
43. Colin-Castelan D, Ramirez-Santos J, Gutierrez-Ospina G. Differential vascular permeability along the forebrain ventricular neurogenic niche in the adult murine brain. J Neurosci Res (2016) 94(2):161–9. doi:10.1002/jnr.23682
44. Tavazoie M, Van der Veken L, Silva-Vargas V, Louissaint M, Colonna L, Zaidi B, et al. A specialized vascular niche for adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell (2008) 3(3):279–88. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2008.07.025
45. Lenz KM, McCarthy MM. A starring role for microglia in brain sex differences. Neuroscientist (2015) 21(3):306–21. doi:10.1177/1073858414536468
47. Silva-Vargas V, Maldonado-Soto AR, Mizrak D, Codega P, Doetsch F. Age-dependent niche signals from the choroid plexus regulate adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell (2016) 19(5):643–52. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2016.06.013
48. Akishita M, Yu J. Hormonal effects on blood vessels. Hypertens Res (2012) 35(4):363–9. doi:10.1038/hr.2012.4
49. Habib P, Beyer C. Regulation of brain microglia by female gonadal steroids. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol (2015) 146:3–14. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.02.018
50. Rebuli ME, Gibson P, Rhodes CL, Cushing BS, Patisaul HB. Sex differences in microglial colonization and vulnerabilities to endocrine disruption in the social brain. Gen Comp Endocrinol (2016) 238:39–46. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2016.04.018
51. Santos CR, Duarte AC, Quintela T, Tomas J, Albuquerque T, Marques F, et al. The choroid plexus as a sex hormone target: functional implications. Front Neuroendocrinol (2017) 44:103–21. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.12.002
52. Young SZ, Taylor MM, Bordey A. Neurotransmitters couple brain activity to subventricular zone neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci (2011) 33(6):1123–32. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07611.x
53. Tong CK, Chen J, Cebrian-Silla A, Mirzadeh Z, Obernier K, Guinto CD, et al. Axonal control of the adult neural stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell (2014) 14(4):500–11. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2014.01.014
54. Paez-Gonzalez P, Asrican B, Rodriguez E, Kuo CT. Identification of distinct ChAT(+) neurons and activity-dependent control of postnatal SVZ neurogenesis. Nat Neurosci (2014) 17(7):934–42. doi:10.1038/nn.3734
55. Taziaux M, Keller M, Bakker J, Balthazart J. Sexual behavior activity tracks rapid changes in brain estrogen concentrations. J Neurosci (2007) 27(24):6563–72. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1797-07.2007
56. Shingo T, Gregg C, Enwere E, Fujikawa H, Hassam R, Geary C, et al. Pregnancy-stimulated neurogenesis in the adult female forebrain mediated by prolactin. Science (2003) 299(5603):117–20. doi:10.1126/science.1076647
57. Larsen CM, Grattan DR. Prolactin, neurogenesis, and maternal behaviors. Brain Behav Immun (2012) 26(2):201–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2011.07.233
58. Amenomori Y, Chen CL, Meites J. Serum prolactin levels in rats during different reproductive states. Endocrinology (1970) 86(3):506–10. doi:10.1210/endo-86-3-506
59. Brock O, Keller M, Veyrac A, Douhard Q, Bakker J. Short term treatment with estradiol decreases the rate of newly generated cells in the subventricular zone and main olfactory bulb of adult female mice. Neuroscience (2010) 166(2):368–76. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.050
60. Veyrac A, Bakker J. Postnatal and adult exposure to estradiol differentially influences adult neurogenesis in the main and accessory olfactory bulb of female mice. FASEB J (2011) 25(3):1048–57. doi:10.1096/fj.10-172635
61. Suzuki S, Gerhold LM, Bottner M, Rau SW, Dela Cruz C, Yang E, et al. Estradiol enhances neurogenesis following ischemic stroke through estrogen receptors alpha and beta. J Comp Neurol (2007) 500(6):1064–75. doi:10.1002/cne.21240
62. Nelson JF, Felicio LS, Osterburg HH, Finch CE. Differential contributions of ovarian and extraovarian factors to age-related reductions in plasma estradiol and progesterone during the estrous cycle of C57BL/6J mice. Endo-crinology (1992) 130(2):805–10. doi:10.1210/endo.130.2.1733727
63. Bronson FH, Maruniak JA. Differential effects of male stimuli on follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, and prolactin secretion in prepubertal female mice. Endocrinology (1976) 98(5):1101–8. doi:10.1210/endo-98-5-1101
64. Koyama S, Soini HA, Foley J, Novotny MV, Lai C. Stimulation of cell proliferation in the subventricular zone by synthetic murine pheromones. Front Behav Neurosci (2013) 7:101. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00101
65. Oboti L, Schellino R, Giachino C, Chamero P, Pyrski M, Leinders-Zufall T, et al. Newborn interneurons in the accessory olfactory bulb promote mate recognition in female mice. Front Neurosci (2011) 5:113. doi:10.3389/fnins.2011.00113
66. Oboti L, Trova S, Schellino R, Marraudino M, Harris NR, Abiona OM, et al. Activity dependent modulation of granule cell survival in the accessory olfactory bulb at puberty. Front Neuroanat (2017) 11:44. doi:10.3389/fnana.2017.00044
67. Furuta M, Bridges RS. Gestation-induced cell proliferation in the rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res (2005) 156(1):61–6. doi:10.1016/j.devbrainres.2005.01.008
68. Quintela T, Marcelino H, Deery MJ, Feret R, Howard J, Lilley KS, et al. Sex-related differences in rat choroid plexus and cerebrospinal fluid: a cDNA microarray and proteomic analysis. J Neuroendocrinol (2016) 28(1). doi:10.1111/jne.12340
69. Li J, Siegel M, Yuan M, Zeng Z, Finnucan L, Persky R, et al. Estrogen enhances neurogenesis and behavioral recovery after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab (2011) 31(2):413–25. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2010.181
70. Cheng Y, Su Q, Shao B, Cheng J, Wang H, Wang L, et al. 17Beta-estradiol attenuates poststroke depression and increases neurogenesis in female ovariectomized rats. Biomed Res Int (2013) 2013:392434. doi:10.1155/2013/392434
71. Saravia F, Revsin Y, Lux-Lantos V, Beauquis J, Homo-Delarche F, De Nicola AF. Oestradiol restores cell proliferation in dentate gyrus and subventricular zone of streptozotocin-diabetic mice. J Neuroendocrinol (2004) 16(8):704–10. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2004.01223.x
72. Schellino R, Trova S, Cimino I, Farinetti A, Jongbloets BC, Pasterkamp RJ, et al. Opposite-sex attraction in male mice requires testosterone-dependent regulation of adult olfactory bulb neurogenesis. Sci Rep (2016) 6:36063. doi:10.1038/srep36063
73. Zheng J, Zhang P, Li X, Lei S, Li W, He X, et al. Post-stroke estradiol treatment enhances neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of rats after permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience (2013) 231(Suppl C):82–90. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.042
74. Brown CM, Suzuki S, Jelks KA, Wise PM. Estradiol is a potent protective, restorative, and trophic factor after brain injury. Semin Reprod Med (2009) 27(3):240–9. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1216277
75. Giachino C, Galbiati M, Fasolo A, Peretto P, Melcangi RC. Effects of progesterone derivatives, dihydroprogesterone and tetrahydroprogesterone, on the subependymal layer of the adult rat. J Neurobiol (2004) 58(4):493–502. doi:10.1002/neu.10290
76. Merchenthaler I, Lane MV, Numan S, Dellovade TL. Distribution of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in the mouse central nervous system: in vivo autoradiographic and immunocytochemical analyses. J Comp Neurol (2004) 473(2):270–91. doi:10.1002/cne.20128
77. Mak GK, Weiss S. Paternal recognition of adult offspring mediated by newly generated CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci (2010) 13(6):753–8. doi:10.1038/nn.2550
78. Feierstein CE. Linking adult olfactory neurogenesis to social behavior. Front Neurosci (2012) 6:173. doi:10.3389/fnins.2012.00173
79. Cheng M-F. Hypothalamic neurogenesis in the adult brain. Front Neuroendocrinol (2013) 34(3):167–78. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2013.05.001
80. Panzica G, Melcangi RC. Structural and molecular brain sexual differences: a tool to understand sex differences in health and disease. Neurosci Bio-behav Rev (2016) 67:2–8. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.04.017
81. He XJ, Nakayama H. Transiently impaired neurogenesis in MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology (2015) 50:46–55. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2015.07.007
82. Mecha M, Feliu A, Carrillo-Salinas FJ, Mestre L, Guaza C. Mobilization of progenitors in the subventricular zone to undergo oligodendrogenesis in the Theiler’s virus model of multiple sclerosis: implications for remyelination at lesions sites. Exp Neurol (2013) 250:348–52. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.10.011
83. Akkermann R, Beyer F, Kury P. Heterogeneous populations of neural stem cells contribute to myelin repair. Neural Regen Res (2017) 12(4):509–17. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.204999
84. Zhang P, Xie MQ, Ding YQ, Liao M, Qi SS, Chen SX, et al. Allopregnanolone enhances the neurogenesis of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in APPswe/PSEN1 mice. Neuroscience (2015) 290:214–26. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.01.019
85. Kotagiri P, Chance SA, Szele FG, Esiri MM. Subventricular zone cytoarchitecture changes in autism. Dev Neurobiol (2014) 74(1):25–41. doi:10.1002/dneu.22127
86. Liu YH, Lai WS, Tsay HJ, Wang TW, Yu JY. Effects of maternal immune activation on adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone-olfactory bulb pathway and olfactory discrimination. Schizophr Res (2013) 151(1–3):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.09.007
87. Apple DM, Fonseca RS, Kokovay E. The role of adult neurogenesis in psychiatric and cognitive disorders. Brain Res (2017) 1655:270–6. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2016.01.023
88. Kohl J, Autry AE, Dulac C. The neurobiology of parenting: a neural circuit perspective. Bioessays (2017) 39(1):1–11. doi:10.1002/bies.201600159
89. Mathieson WB, Wilkinson M, Brown RE, Bond TL, Taylor SW, Neumann PE. FOS and FOSB expression in the medial preoptic nucleus pars compacta of maternally active C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Brain Res (2002) 952(2):170–5. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03078-0
90. Mathieson WB, Taylor SW, Marshall M, Neumann PE. Strain and sex differences in the morphology of the medial preoptic nucleus of mice. J Comp Neurol (2000) 428(2):254–65. doi:10.1002/1096-9861(20001211)428:2<254::AID-CNE5>3.0.CO;2-A
91. Holmes A, Wrenn CC, Harris AP, Thayer KE, Crawley JN. Behavioral profiles of inbred strains on novel olfactory, spatial and emotional tests for reference memory in mice. Genes Brain Behav (2002) 1(1):55–69. doi:10.1046/j.1601-1848.2001.00005.x
92. Levy F, Keller M. Olfactory mediation of maternal behavior in selected mammalian species. Behav Brain Res (2009) 200(2):336–45. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.12.017
Keywords: ventricular-subventricular zone, sexual dimorphism, estrogens, testosterone, neural stem cells, puberty, estrous cycle, pregnancy
Citation: Ponti G, Farinetti A, Marraudino M, Panzica GC and Gotti S (2018) Sex Steroids and Adult Neurogenesis in the Ventricular-Subventricular Zone. Front. Endocrinol. 9:156. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00156
Received: 19 November 2017; Accepted: 22 March 2018;
Published: 09 April 2018
Edited by:
Takayoshi Ubuka, Monash University Malaysia, MalaysiaReviewed by:
John W. Cave, Weill Cornell Medicine, United StatesEmmanuel Moyse, François Rabelais University, France
Copyright: © 2018 Ponti, Farinetti, Marraudino, Panzica and Gotti. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Giovanna Ponti, Z2lvdmFubmEucG9udGlAdW5pdG8uaXQ=
 Giovanna Ponti
Giovanna Ponti Alice Farinetti
Alice Farinetti Marilena Marraudino
Marilena Marraudino GianCarlo Panzica
GianCarlo Panzica Stefano Gotti
Stefano Gotti