- Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, IL, United States
Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) has played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of spin-orbit physics in 5d transition metal materials. The progress in RIXS techniques has closely paralleled improvements in energy resolution, which have enabled the study of very low-lying excitations and led to the discovery of numerous new phenomena with significant scientific and technological implications. The multi-bend achromat (MBA) lattice upgrade of third-generation synchrotron sources, such as the Advanced Photon Source (APS), heralds a transformative era by introducing enhancements in brilliance and emittance. These advancements provide an opportunity to push the boundaries of RIXS techniques, meeting the challenges at the research frontiers of material science. This article aims to highlight key instrumental and technical advancements that enable the achievement of meV resolution in RIXS and discuss the impact of such high-resolution RIXS on exploring spin-orbit physics in 5d transition metal materials.
1 Introduction
Quantum materials, where quantum mechanical effects are central to determining their properties, exhibit strong correlations, topological characteristics, and unique electronic, magnetic, and optical behaviors. Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) is a powerful element-specific technique for probing collective excitations of the lattice, charge, spin, and orbital states, providing critical information on the interactions and couplings between different degrees of freedom in these materials (Ament et al., 2011).
RIXS is a second-order process described by the Kramers-Heisenberg formula, where an incident X-ray excites a core electron to a higher energy state, creating a core-hole that decays by emitting an X-ray. The energy difference between the incident and scattered photons corresponds to the energy of excitations within the material. The K-edges of 3d and 4d transition metals (TMs) and the L-edges of 5d TMs are within the regime of hard X-ray RIXS. During this process, quantum numbers, such as spin or orbital angular momentum, can be exchanged between the core and valence electrons, while the total quantum number is conserved. Strong spin-orbit coupling of the L-edge enable RIXS to probe excitations such as spin and orbital flip excitation (Ament et al., 2009). In contrast, K-edge RIXS probes valence quantum-number-conserving excitations, such as two-magnon processes and charge transfer excitations.
Inelastic neutron scattering (INS) is considered the gold standard for probing excitations in materials, offering excellent energy resolution. In comparison, RIXS has inferior energy resolution, and its cross section of RIXS is more complex and less straightforward, making its interpretation more challenging and less transparent. However, RIXS requires only a small sample volume, allowing for the study of thin films, and provides access to a wide energy range, covering the full spectrum of excitations, including lattice, charge, spin, and orbital states. Strong neutron absorbers, such as Ir, reduce the effectiveness of INS by limiting the number of neutrons available for scattering. In contrast, RIXS requires different sets of monochromators and analyzers for different transition metals, resulting in variations in energy resolution.
Among the many technical aspects of RIXS, improving energy resolution is fundamental to advancing our understanding of quantum materials. High energy resolution allows for the detailed study of low-energy excitations, accurate mapping of dispersion relations, deeper insights into electron correlation effects, enhanced sensitivity to weak signals, and the exploration of new quantum phases. The development of hard x-ray RIXS has seen significant advances in energy resolution. The pioneering work by Kao et al. (1996) reported the first hard x-ray RIXS measurement of charge-transfer excitations in NiO. Initially, energy resolution was within a few electron volts (eV), but advancements, particularly the adoption of diced spherical analyzers, refined this to hundreds of millielectron volts (meV). This rapid technological evolution was driven by the establishment of a dedicated RIXS beamline at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory (Abbamonte, 1999; Hill et al., 2007).
Early scientific studies focused on charge excitations in 3d TM oxides, such as high-Tc cuprates and colossal magnetoresistance manganites (Ament et al., 2011). Over a decade, this development achieved more than a tenfold improvement in energy resolution, reaching 120 meV (Hill et al., 2007). This resolution enabled the probing of bimagnon excitations in high-Tc cuprates, illustrating that hard x-ray RIXS offers a window into the spin degree of freedom (Hill et al., 2008).
A subsequent breakthrough came with a novel detection scheme that allowed point-sensitive detection of scattered x-rays (Huotari et al., 2006), achieving energy resolutions in the tens of meV for some of 3d TM K-edges with high detection efficiency (Shvyd’ko et al., 2013). However, the exploration of 5d TM materials marked a significant scientific leap. These materials, characterized by substantial spin-orbit coupling, host a variety of novel quantum states that challenge traditional paradigms of distinct spin and orbital degrees of freedom. RIXS has proven to be an essential tool for addressing these challenges, facilitating the study of spin-orbit physics in 5d transition metal materials with profound implications for both science and technology.
The significant spin-orbit coupling of the 5d L-edge core levels has enabled RIXS to probe single spin flip excitations, such as spin wave excitations. The seminal work by Kim et al. (2012a), showcased the first x-ray measurement capturing the full dispersion of spin wave excitations in Sr2IrO4. Utilizing the Si 844 secondary monochromator and the diced Si spherical analyzer, an energy resolution of 25 meV was achieved, opening avenues for studying extremely low-lying excitations and leading to the discovery of numerous novel phenomena (Kim et al., 2012b; Kim et al., 2014).
As the diced Si spherical analyzer reached maturity in its technological development, further enhancements required exploring new materials for analyzers or developing novel analytical methodologies. A significant breakthrough was achieved for the Ir L3-edge (11.215 keV) using a lower symmetry Quartz crystal (Kim et al., 2018; Said et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2018). Both the diced spherical analyzer and a novel flat crystal analyzer scheme using scattered x-ray collimation (SXC) (Kim et al., 2016) achieved energy resolutions of a few meV. These meV analyzers, combined with meV monochromators, have successfully studied very low meV excitation features in quantum materials, previously inaccessible with a 25 meV resolution (Kim et al., 2020a; Ruiz et al., 2021). Currently, a few meV energy resolution is only available for the Ir L3-edge.
The upgrade of third-generation synchrotron sources to the fourth-generation sources based on multi-bend achromat (MBA) lattice marks the beginning of a transformative era, offering significant enhancements in brilliance and emittance. This upgrade provides a pivotal opportunity to further advance RIXS techniques, particularly in achieving and standardizing a few meV resolutions for all 5d TMs from Ta to Ir, addressing the evolving challenges in 5d TM materials research. Achieving this high resolution depends on the selection of materials, the design of meV monochromators, and the manufacturing of analyzers.
This article explores the energy resolutions provided by lower-symmetry crystals such as Quartz, Silicon Carbide (SiC), and Aluminum Nitride (AlN), and discusses the intrinsic crystal properties relevant to achieving meV resolution for the L2 and L3 edges of 5d TMs from Ta to Ir. It presents the design of meV monochromators compatible with the existing monochromator configuration. The article also discusses the fabrication of diced spherical analyzers, including techniques such as porous vacuum curvature shaping (Said et al., 2022), and examines the scattered x-ray collimation (SXC) RIXS analyzer system (Kim et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2020b). The discussion concludes by showcasing the impact of meV RIXS in advancing our understanding of complex material behaviors in 5d TM materials.
2 Lower-symmetry crystals
The reflection bandwidth (ΔEi) and the monochromator bandwidth (ΔEm) primarily determine the energy resolution of the RIXS spectrometer. While these two factors are central to the SXC flat crystal analyzer, additional factors such as the detector pixel contribution (ΔEg) and source size (ΔEs) also play a role in the point-sensitive detection of scattered X-rays by the diced spherical analyzer. The near backscattering reflections achieve the desired throughput with a large angular acceptance and energy resolution (Kushnir and Suvorov, 1990; Gog et al., 2013). Extrinsic contributions, such as crystal strain, imperfect spherical shaping, and degraded collimation, can further impact the resolution.
Hard x-ray optics predominantly utilize silicon (Si) crystals due to the availability of high-quality crystals and extensive research and development in X-ray optics. However, the high structural symmetry of Si limits the number of allowed backscattering Bragg reflections, posing challenges for backscattering analyzers in high-resolution RIXS technique. For a 25 μm pixel detector on a 2 m Rowland circle, the lower limit of the backscattering angle for ΔEg = 10 meV detector pixel contribution ranges from 80.6° to 82.8° for the L2 and L3 edges of 5d TMs from Ta to Ir (Gog et al., 2013). The (844) reflection of Si has a backscattering angle of 85.73° for the Ir L3 edge (11.215 keV), satisfying this requirement. However, no other 5d TM absorption edges have Si reflections that meet this criterion.
Lower-symmetry crystals, such as quartz, 4H/6H-SiC, and 2H-AlN offer broader and denser Bragg reflections, enabling the utilization of optics across a spectrum of both lower and higher X-ray energies. Quartz, specifically α-quartz, has been actively studied for backscattering analyzers (Sutter et al., 2005). High-quality of synthetic quartz crystals has been confirmed by various groups (Sutter et al., 2006; Hönnicke et al., 2013; Huang et al., 2018).
Detailed diffraction properties of quartz for X-ray applications are thoroughly discussed in the work by Huang et al. (2018). Quartz, which belongs to the trigonal crystal system, exhibits threefold rotational symmetry along the c-axis. This, combined with its two enantiomorphic forms (left-handed and right-handed), adds complexity to its diffraction patterns compared to materials with hexagonal symmetry, such as 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN. Reflections from seemingly equivalent lattice planes in quartz can exhibit different properties, including Darwin bandwidth, reflectivity, and angular acceptance, even when they share the same Bragg angle.
Huang et al. (2018) provide a comprehensive list of strong backscattering reflections of quartz with Bragg energies in the medium energy range. Table 1 highlights reflections in quartz that achieve resolutions of around 5 meV or below. In hexagonal systems, the Bragg condition is described by (HKML) with M = - (H + K). There are several complications related to the diffraction properties of certain combinations of H, K, and M, including equivalent reflections resulting from permutations of the in-plane Bragg indices. For simplicity, the backscattering reflections in Table 1 are represented by a single (HKL) reflection for each 5d transition metal absorption edge. Except for the Ta L₃ and Os L₂ edges, the selected reflections have backscattering angles where the contribution of the detector pixel size (25 μm) falls within the 5 meV range.
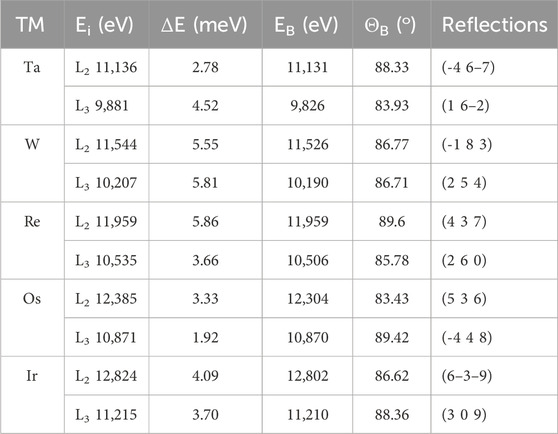
Table 1. Quartz Reflections for meV Energy Resolution at 5d TM Edges. Example reflections in quartz that achieve resolutions of around 5 meV or below are presented. Except for the Ta L₃ and Os L₂ edges, the selected reflections have backscattering angles where the contribution of the detector pixel size (25 μm) falls within the 5 meV range.
4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN currently do not provide the same level of large area lattice perfection as Si and quartz, with a higher density of dislocations and other defects. However, these materials have attracted tremendous attention and efforts from improving growth in recent years due to their exceptional electrical, thermal, and chemical properties, positioning them as key materials for high-power high-temperature electronics and optoelectronics. There is optimism that advancements in crystal growth techniques will lead to higher-quality crystals, potentially extending their use to X-ray applications. Figure 1 shows a white-beam topography of a (001) AlN crystal recorded in earlier days. Dislocations in the basal plane, threading dislocations, and low-angle grain boundaries (LAGB) are visible, along with surface scratches. However, there are also clean areas of a few millimeters in size where intrinsic reflection bandwidths could potentially be obtained. Larger-size AlN crystals with higher crystalline quality (dislocation density <102/cm2) are emerging in the market place (Tsao et al., 2018).
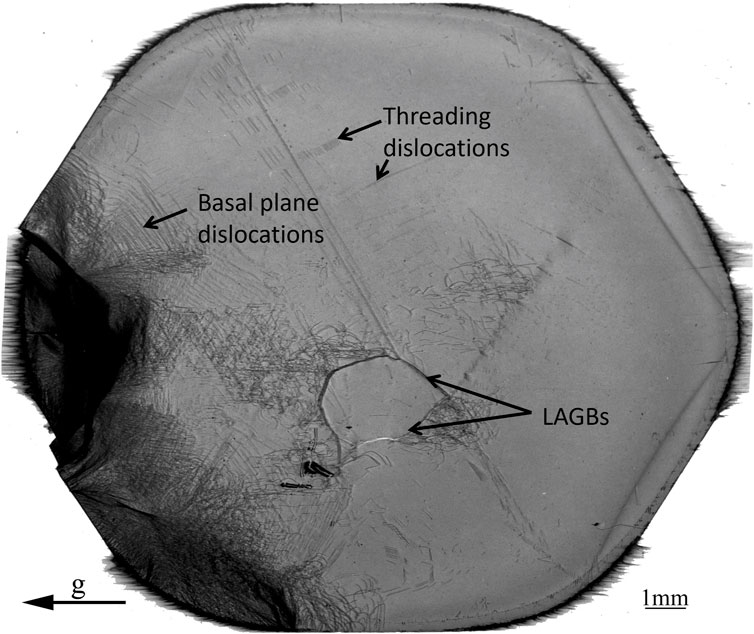
Figure 1. White-beam topography of a (001) 1-inch AlN crystal. Transmission topograph, recorded at the APS beamline 1-BM. g = (11–20) reflection with E = 23 keV.
Table 2 shows reflections in 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN that achieve resolutions of a few meV. Exceptions are seen in the case of AlN, specifically for the Ta L₂, W L₃, and Os L₃ edges. Approximately half of the selected reflections have backscattering angles where the contribution of the detector pixel size (25 μm) is more than 10 meV. In this context, the meV RIXS analyzer can be more effectively realized using the SXC analyzer scheme with 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN.
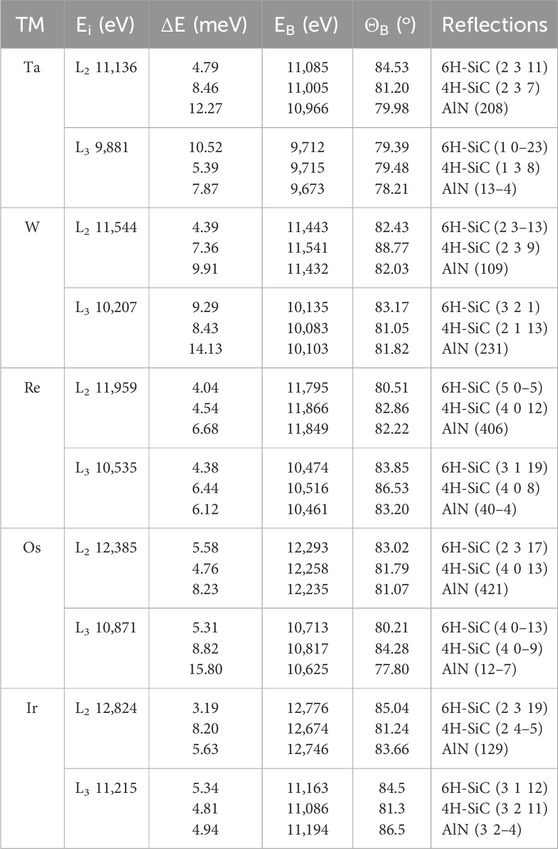
Table 2. 4H-/6H-SiC and AlN reflections for high-energy resolutions at 5d TM edges. Example reflections that achieve resolutions of a few meV are presented. However, there are exceptions in the case of AlN, specifically for the Ta L₂, W L₃, and Os L₃ edges. About half of selected reflections have backscattering angles where the contribution of the detector pixel size (25 μm) is more than 10 meV.
Thermal properties of crystals are crucial for achieving meV energy resolution because intense synchrotron X-rays deliver substantial heat to the crystals, leading to lattice instability and strain, which are directly linked to energy stability and resolution. This issue is particularly significant with the MBA lattice upgrade, such as that implemented at the APS, which generates a small, high-density X-ray beam due to a significantly reduced horizontal emittance.
Table 3 shows thermal conductivity and expansion of quartz, 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN, and Si. Quartz crystal has poor thermal properties. The study by Gog et al. (2018) found that under typical room-temperature operation, the incident power levels that had minimal impact on the Si monochromator caused significant thermal distortions in the first crystal of the two-bounce quartz monochromator, rendering it practically unusable. In contrast, 4H-SiC, 6H-SiC, and 2H-AlN exhibit thermal expansion properties comparable to Si, with only marginal anisotropy. Additionally, in terms of thermal conductivity, 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN outperform Si. In this context, 4H-SiC, 6H-SiC, and 2H-AlN are increasingly recognized as promising candidates for meV X-ray applications, despite their reflections being inferior to those of quartz in terms of energy resolution and backscattering angles.
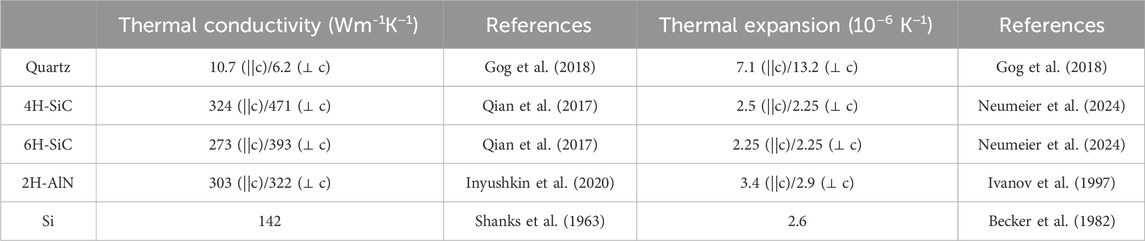
Table 3. Thermal properties of quartz, 4H-SiC, 6H-SiC, 2H-AlN, and Si. Quartz crystal has poor thermal properties. 4H-SiC, 6H-SiC, and 2H-AlN have comparable thermal expansion with Si, but better thermal conductivities than Si.
3 meV monochromators
Si crystal offers an excellent working material for diffractive X-ray optics such as high-resolution monochromators. The intrinsic energy bandwidth associated with a single silicon lattice reflection that is accessible to 10–12 keV X-rays is typically greater than 20 meV. Obtaining smaller bandwidths requires the use of asymmetrically cut crystal surfaces (lattice vector not parallel to crystal surface normal) to disperse the various wavelengths into different directions like a prism. Smaller bandwidths can then be produced by following with either a spatial slit, or an angular slit in the form of another crystal reflection.
One such approach is the doubly nested configuration (+A, -B, -C, +C, +B, -A) shown in Figure 2A (Toellner et al., 2011). Significant wavelength dispersion may be introduced into the beam by choosing low-index reflections with asymmetrically cut surfaces for the first two reflections (for our purposes, A = B=Si(2 2 0), miscut = −11 deg.). The asymmetric surfaces also increase angular acceptance and collimate the transmitted beam, both of which improve overall optic efficiency. The third crystal set (C) is a high-index lattice reflection with a narrow intrinsic energy bandwidth and is cut asymmetrically in a way to reduce its energy-acceptance further. The three subsequent crystals have surface asymmetry angles that are opposite to undo the dispersion introduced by the first three crystals and restore the beam size and direction without a virtual source broadening. This approach can produce few meV energy bandwidths for all the X-ray energies from 9.8 keV to 12.8 keV corresponding to 5d TM L edges for Ta to Ir.
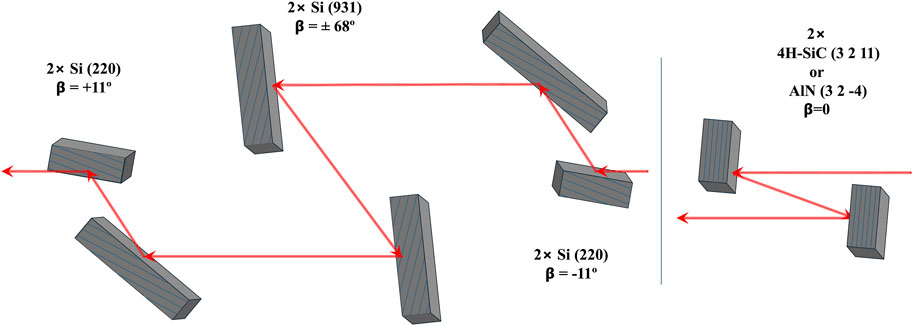
Figure 2. Schematic of the meV monochromator for the Ir L3 edge (11.215 keV). (A) Two bounce monochromator consisting of two symmetric crystals in a parallel configuration. Symmetric-cut 4H-SiC (3 2 11) or AlN (3 2–4) reflections provide about 5 meV bandwith for the 11.215 keV incident X-ray. (B) Six bounce monochromator. The existing monochromator for medium resolutions at the APS consists of two outer pairs of asymmetric-cut Si (220) crystals. A bandwith of 4.5 meV for the 11.215 keV incident X-ray is achieved by adding two-bounce asymmetric-cut Si (931) crystals in between the two outer pairs of asymmetric-cut Si (220) crystals.
Table 4 presents C-crystal choices with expected performances for the various 5d TM L edges assuming the A and B crystals are fixed as above. This approach allows one to cover the various TM edges by only changing the C-crystal. Energy tuning/scanning over tens of electron-Volts is achieved by crystal rotation with negligible change in performance. Thermal loading caused by an intense X-ray beam especially on the C-crystals may require separate angle and temperature control on individual crystals to achieve performance.
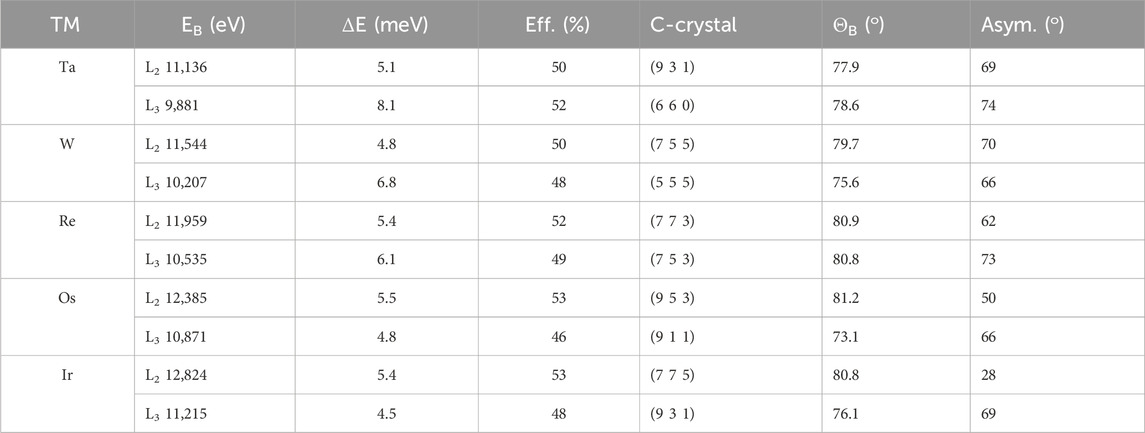
Table 4. Six-bounce HRMs assuming 2×(2 2 0)-2×(h k l)-2×(2 2 0) with a 11-degree asymmetry angle on the outer (2 2 0) reflections.
The simplest solution for achieving a meV-resolution monochromator is a two symmetric crystal monochromator scheme in a parallel configuration, as shown in Figure 2B. In this setup, the first crystal disperses the incident X-rays, and the second crystal cancels out this dispersion, resulting in a low energy bandwidth. However, as previously discussed, no suitable Si reflections are available, and quartz is impractical due to its poor thermal conductivity and expansion. These limitations make it impossible to use Si and quartz for achieving a meV bandwidth for 5d transition metal edges in the two symmetric crystal monochromator scheme.
In contrast, 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN are promising candidates due to their comparable thermal expansion coefficients and superior thermal conductivities compared to those of Si. Contrary to the case in the analyzer, the two symmetric crystal monochromator scheme only requires a small clean area of a matching in size with the incident X-ray beam which is further reduced in the recent MBA lattice synchrotron upgrade. Unlike the analyzer, the two symmetric crystal monochromator scheme only requires a small clean area matching the size of the incident X-ray beam, which has been further reduced in the recent MBA lattice synchrotron upgrade. As shown in Table 2, 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN provide approximately 5 meV bandwidths for most 5d TM edges. Figure 3B illustrates examples of symmetric-cut 4H-SiC (3 2 11) or AlN (3 2–4) reflections, which offer about a 5 meV bandwidth for the 11.215 keV incident X-ray.
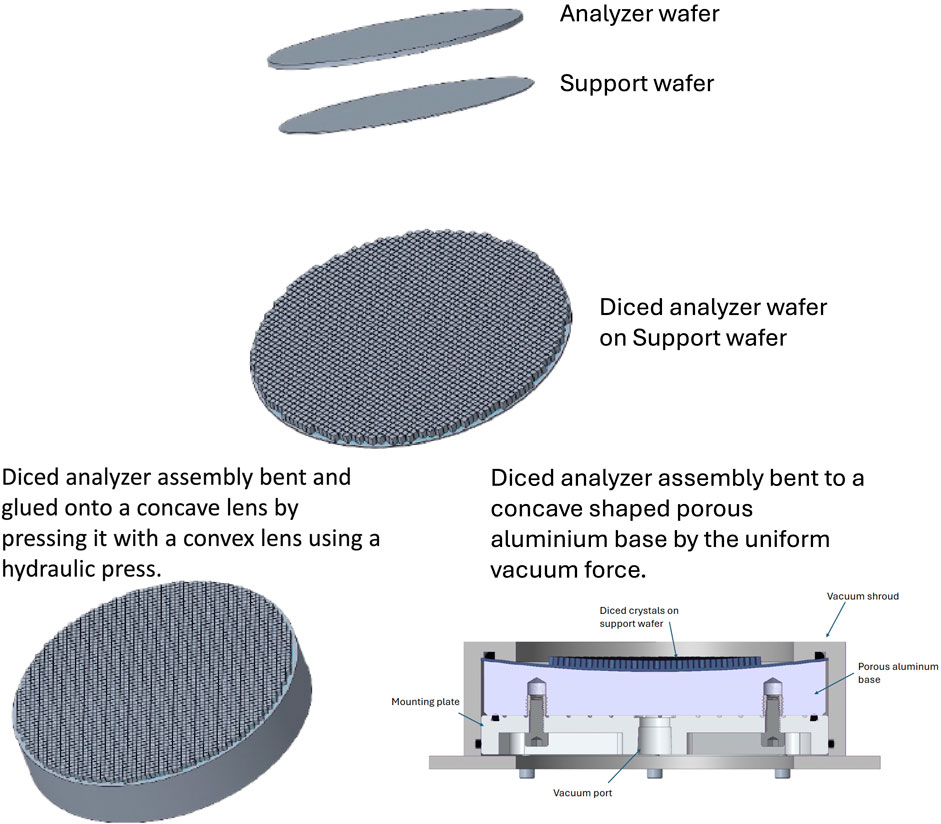
Figure 3. The schematic of the main steps to fabricate a diced spherical RIXS analyzer. (A, B) a diced analyzer assembly is prepared through processes of dicing, bonding and etching. (C) The conventional method for creating a diced spherical analyzer involves pressing the diced analyzer assembly against a convex lens using a hydraulic press. (D) A new method for spherical shaping of the diced analyzer assembly utilizes a uniform vacuum force applied to the assembly through a concave-shaped porous aluminum base.
4 meV analyzers
A practical RIXS instrument requires a large solid-angle acceptance to collect sufficient scattered photons from the sample. Spherical diced analyzers are the most efficient method for this purpose and are thus commonly used in standard RIXS spectrometers with point-sensitive detection of scattered X-rays (Huotari et al., 2006). While silicon diced analyzers have reached a mature technological stage, fabricating analyzers using other crystals such as quartz, 4H/6H-SiC, and 2H-AlN presents numerous technical challenges.
Figure 3 outlines the main steps involved in fabricating high-resolution analyzers. The process begins with bonding an analyzer crystal wafer to a support wafer, followed by forming free-standing crystallites, typically on the order of mm2, through dicing. The entire assembly is then pressed and glued onto a concave lens with the desired radius. A final etching step is performed to relieve any mechanical strain induced by dicing.
Dicing and wet etching of silicon are well-established and straightforward processes, largely due to advancements in the semiconductor industry. However, these processes are far more challenging for harder and more complex materials like quartz, 4H/6H-SiC, and 2H-AlN. The difficulty increases depending on the wafer orientation, requiring specialized blades and optimized procedures. Etching harder materials such as 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN necessitates high-temperature etching in very aggressive acids, complicating the bonding process and making it nearly impossible to fabricate the analyzers.
High-quality single quartz crystal boules are commercially available, and research and development for high-resolution X-ray applications have focused on quartz (Sutter et al., 2005; Sutter et al., 2006; Hönnicke et al., 2013; Huang et al., 2018). One specific issue encountered during dicing quartz is the potential for cracking. Etching quartz is a prolonged process, taking about 8–10 h to remove 30 microns. The free-standing crystallites are bonded to the support wafer using high-resistance HF epoxy. However, the longer the etching process, the higher the chance that the epoxy fails, as the acid seeps under the glue, causing many of the pixels to fall off.
Despite these challenges, a diced spherical analyzer using the (309) quartz reflection was successfully manufactured, offering the best energy resolution for RIXS at the Ir L₃ edge (Said et al., 2018). Additionally, a new apparatus has been developed that allows the support wafer to be bent to the proper radius without using a convex lens to form the spherical shape. This new bending mechanism uses a porous vacuum base, where the vacuum force holds a thin crystal assembly, including a diced crystal wafer of the desired material, on a support substrate (Said et al., 2022). This technique eliminates the need for permanent bonding, allowing for correction of figure errors, avoiding long-term degradation of the permanent bond, and making both the substrate and crystal reusable, substantially reducing process and material costs.
These advancements instill optimism in the field, demonstrating that continued research and development can overcome the technical challenges of fabricating high-resolution X-ray optics. The R&D effort includes developing direct bonding between the analyzer crystal and the support wafer to eliminate the need for adhesive, which cannot withstand aggressive etching processes.
To avoid fabrication challenges, a flat crystal RIXS analyzer system using scattered X-ray collimation was built and tested (Kim et al., 2018). Sufficient solid-angle acceptance is achieved by a collimating mirror, and the narrow angular acceptance of meV reflections is matched by further collimation with an asymmetric crystal.
The (309) quartz reflection for the Ir L₃-edge (11.215 keV) is the first example demonstrating the feasibility of a meV-resolution RIXS analyzer for 5d transition metal edges. Figure 4A shows the SXC energy resolutions of the quartz (309) reflection alongside the 25 meV resolution of a diced Si (844) analyzer. The four-bounce Si (844) monochromator provides a resolution of ΔEm ≈ 8.9 meV, while the two-bounce quartz (309) monochromator achieves ΔEm ≈ 3.7 meV. A significantly reduced X-ray flux, which induces negligible thermal distortion in quartz, was used for the two-bounce quartz monochromator. The estimated energy resolutions of the (309) reflection from two different monochromator measurements are 4.3 meV and 4.1 meV, respectively.
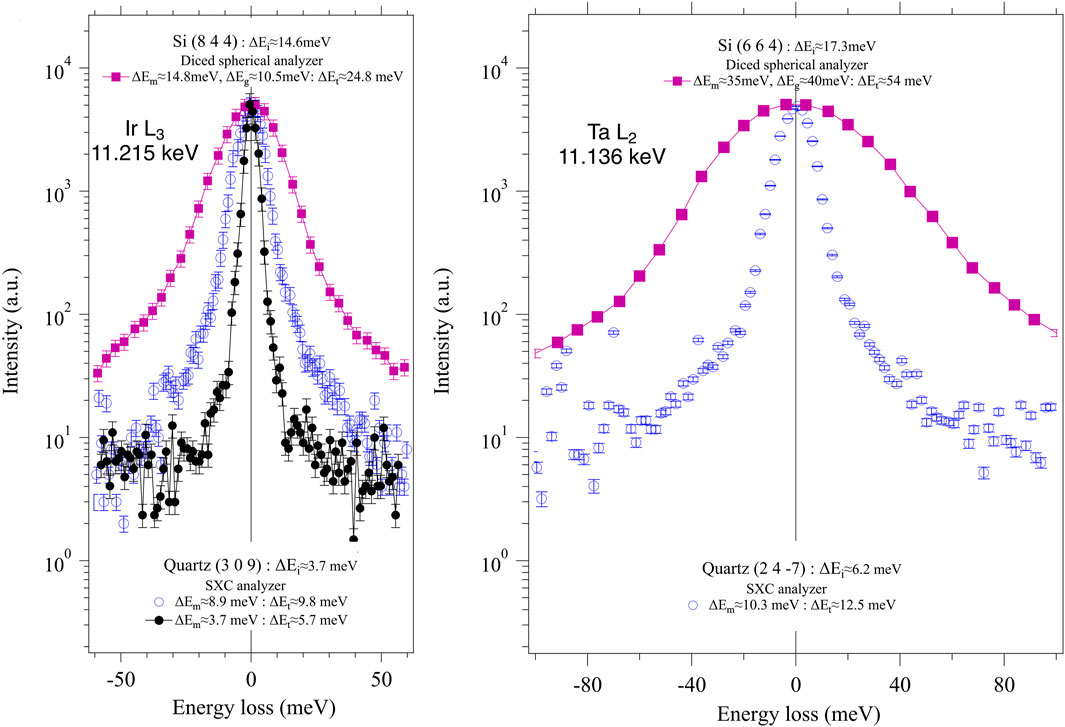
Figure 4. RIXS spectral resolutions. (A) Ir L3 11.215 keV: The total energy resolution (ΔEt) estimates of Quartz (3 0 9) are compared with that of Si (8 4 4). The intrinsic resolution of the crystal reflection (ΔEi), monochromator resolution (ΔEm), and detector pixel contribution (ΔEg) are indicated. A diced spherical analyzer is used for Si (8 4 4), while an SXC analyzer is used for Quartz (3 0 9). The two-bounce Si (8 4 4) reflection provides ΔEm≈14.8 meV, the four-bounce Si (8 4 4) reflection provides ΔEm≈8.9 meV, and the two-bounce Quartz (3 0 9) reflection provides ΔEm≈3.7 meV. (B) Ta L2 11.136 keV: ΔEt estimate of Quartz (2 4–7) are compared with that of Si (6 4 4). A diced spherical analyzer is used for Si (6 4 4), while an SXC analyzer is used for Quartz (2 4–7). The four-bounce asymmetric Si (4 4 0) monochromator provides ΔEm≈35 meV and the four-bounce Si (6 6 4) provides ΔEm≈10.3 meV. In both cases, the low symmetry Quartz crystals provide the solution for achieving meV energy resolution for Ir L3 and Ta L2.
Another example is shown in Figure 4B, illustrating the SXC energy resolutions of the quartz (24–7) reflection for the Ta L₂-edge, alongside the 54 meV resolution of a diced Si (664) analyzer. The four-bounce Si (664) monochromator provides a resolution of ΔEm ≈ 10.3 meV, and the estimated energy resolution of the (24–7) reflection is 7.1 meV, close to the theoretical value of 6.2 meV.
When designing high-resolution X-ray optics, it is crucial to consider not only the crystal quality but also the thermal properties of the crystal. Lower thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity are essential for achieving high-energy resolution in high-heat-load optics like monochromators. However, such thermal properties are less critical for analyzers, as they have a larger surface area and the heat load is minimal. In this context, the poor thermal properties of quartz do not pose a significant problem in the development of meV-resolution quartz analyzers.
4.1 meV study of 5d transition metal
5d transition metal materials are distinguished by the large spatial extent of their 5d orbitals, strong spin-orbit coupling, and significant electron correlation effects. These characteristics lead to complex electronic, magnetic, and structural properties, and result in a range of fascinating phenomena, including unconventional magnetism, topological phases, and exotic superconductivity (Witczak-Krempa et al., 2014). These intriguing behaviors make 5d transition metal materials a rich field of study in condensed matter physics.
5d TM materials are particularly well-suited for hard x-ray RIXS for several reasons. First, the L-edges of 5d TMs fall within the hard x-ray regime. Second, these materials have a high x-ray cross-section due to their large atomic number (Z) and the greater number of core electrons. Third, the spin and orbit degree of freedoms of 5d valence electrons exchange those quantum numbers with the strong spin-orbit coupled L core electrons, opening effective channels for spin and orbit collective excitations such as magnon and orbiton. These spin and orbital collective excitations possess low energy scales, propelling the development of meV resolution. Figure 4A shows the measured RIXS spectral resolutions using Si (844) and Quartz (309) with matching resolution monochromators, demonstrating that the Quartz (309) provides meV energy resolutions.
Identifying 5d TM materials particularly suitable for RIXS also contributes to a broader understanding of material properties and fundamental physics. The cyclical process of discovery and innovation continues to drive progress in both spectroscopy techniques and the scientific knowledge they uncover. Here, we explore several immediate cases for the meV RIXS study, paving the way for further exploration and inviting even more intriguing examples.
Sr2IrO4 is a prototypical material that has spurred broad interest in spin-orbit physics (Kim et al., 2008; Kim et al., 2009). It is also the first 5d transition metal oxide where RIXS has showcased the full dispersion of magnon and orbiton excitations (Kim et al., 2012a; Kim et al., 2014). Although Heisenberg exchange interactions dominate, the magnon at the magnetic zone center is not a gapless Goldstone mode but instead exhibits a few meV magnon gap (Jackeli and Khaliullin, 2009; Porras et al., 2019). Raman scattering measurements have shown that this zone-center magnon is highly sensitive to uniaxial strains (Kim et al., 2022). An outstanding question remains the dispersion relation near the magnetic zone center, which defines the magnon velocity and has important implications for both fundamental understanding and applications. Despite extensive studies, Sr2IrO4 continues to reveal surprising quantum phenomena, such as a spin nematic phase (Kim et al., 2024). The phase mode associated with the quadrupolar order occurs at a similar energy as the magnon of the antiferromagnetic order. In both cases, the combination of meV energy resolution and high momentum resolution offers the best opportunity to resolve outstanding questions, specifically distinguishing the phase mode from the magnon and understanding the magnon velocity associated with the magnon gap change.
The observation of elusive quantum spin liquid is a central aim in the field of spectroscopy. Honeycomb iridates have received much attention as candidates for the Kitaev quantum-spin-liquid ground state (Jackeli and Khaliullin, 2009). A key experimental challenge is to observe the putative fractionalized excitations in these honeycomb iridates. RIXS is predicted to be an effective spectroscopic probe of the fractionalized excitations in Kitaev honeycomb materials (Halász et al., 2016). The Kitaev energy scale ranges from 15 to 24 meV (2020a). The energy scale of the fractionalized excitations in Kitaev honeycomb materials is calculated to be distributed within one order of magnitude of the Kitaev energy scale, that is, from 150 to 240 meV. Because these fractionalized excitations are only probed in spin-conserving scattering, analyses focus on scatterings with parallel polarization of incident and scattered x-rays, making elastic scatterings significant. Although the energy scale of the fractionalized excitation is high, the meV energy resolution is essential.
Topological states of matter are a profound manifestation of quantum mechanics, showcasing unique properties that arise from the quantum behavior of particles. Although still rare, recent years have seen an increasing number of experimentally discovered topological materials. Furthermore, recent computations have shown that many more materials are topological in both 2D and 3D (Vergniory et al., 2022). Recent theoretical works have demonstrated that RIXS provides direct measurements of topologically non-trivial bands through distinct momentum and energy-resolved scattering intensities (Kourtis, 2016; Lee et al., 2023; Schüler et al., 2023). For hard X-ray RIXS, 3D topological materials are particularly relevant. For example, Weyl semimetals feature topologically non-trivial bulk properties. A notable example is TaAs, a space inversion-breaking material, which is the first experimentally discovered Weyl semimetal. TaAs possesses 12 pairs of Weyl nodes in the bulk (Lv et al., 2015). Four pairs (W1) in the kz = 0 plane are about 2 meV above the Fermi level, while eight pairs (W2) in the finite kz plane are about 21 meV below the Fermi level. The meV energy resolution is essential to access these low energy scales. Figure 4B shows RIXS spectral resolution for the Ta L2 at 11.139 keV. Due to the use of a rather poor monochromator with a 10.3 meV resolution, the total energy resolution is 12.5 meV. However, this measurement demonstrates that Quartz (2 4–7) can achieve meV energy resolution when a matching meV monochromator is used.
5 Conclusion
Improving energy resolution is a critical milestone in the advancement of spectroscopy techniques. Over the past 3 decades, significant technical and scientific progress has been made in RIXS (Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering) research at third-generation synchrotron sources like APS (Advanced Photon Source). Today, standard RIXS experiments routinely achieve energy resolutions in the tens of meV range. The upgrade of third-generation synchrotron sources to a multi-bend achromat (MBA) lattice promises substantial improvements in brilliance and emittance, offering a pivotal opportunity to establish few-meV energy resolution in RIXS as a routine capability in the coming decades.
This article focuses on applications involving the L2 and L3 edges of 5d transition metals from Ta to Ir. Lower symmetry crystals, such as quartz, 4H/6H-SiC, and 2H-AlN, provide immediate solutions for backscattering analyzers capable of achieving meV energy resolution. Among these, quartz crystals have already demonstrated diffraction quality sufficient for meV energy resolution. However, the crystal quality of 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN still needs improvement due to their high defect densities, which currently limit their ability to reach the required meV resolution. Despite this, intense research and development efforts are underway to enhance the quality of these crystals, driven by their attractive properties, such as large band gaps and high thermal conductivity (Neumeier et al., 2024).
Not much attention has been given to the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient of the analyzer crystal, as well as the temperature stability of RIXS analyzers. In the context of tens of meV energy resolution, meV fluctuations could be ignored. However, as we move toward establishing stable meV RIXS measurements, controlling these thermal properties becomes essential. Additionally, challenges arise in the processes of dicing and etching these crystals, with the anisotropic properties of lower symmetry crystals making uniform dicing and etching more difficult.
We introduced the meV monochromator design using six-bounce asymmetric-cut Si reflections. This design utilizes the existing four-bounce monochromator of the sector 27ID RIXS beamline at APS. The absence of virtual source broadening in the six-bounce meV monochromator is optimal for high X-ray focusing. Energy tuning/scanning over tens of eV is achieved by crystal rotation with negligible change in performance.
We also explore the potential use of 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN for the meV monochromator. Quartz, however, is unsuitable for this application due to its low thermal conductivity, which leads to significant thermal distortions. Conversely, 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN offer very high thermal conductivities, several times greater than that of silicon, making them more suitable for high-precision applications. In the upgraded APS, the X-ray beam is expected to be nearly isotropic in both vertical and horizontal directions, necessitating a small defect-free region for achieving meV energy resolution. Two-bounce monochromators made from 4H/6H-SiC and 2H-AlN crystals, which are straightforward to operate in terms of temperature and angle control, can provide meV monochromatized incident X-rays.
Just as machine learning and artificial intelligence improve understanding through exposure to more examples, human cognition deepens its grasp of new concepts and phenomena with increased experimental data. In scientific and technical research, understanding emergent phenomena enhances with more examples, refining intuition, theories, and models. Establishing meV energy resolution as a standard in RIXS will enable the accumulation of detailed meV excitation spectra in quantum materials that exhibit emergent phenomena, significantly advancing our exploration and discovery of spin-orbit physics in 5d transition metal materials.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
JK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XH: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. TT: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The use of the Advanced Photon Source at the Argonne National Laboratory was supported by the US Department of Energy (Contract DE-AC02-06CH11357).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbamonte, P. (1999). Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering from insulating cuprates. PhD thesis. Urbana, IL: University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign.
Ament, L. J., Ghiringhelli, G., Sala, M. M., Braicovich, L., and van den Brink, J. (2009). Theoretical demonstration of how the dispersion of magnetic excitations in cuprate compounds can be determined using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 (11), 117003. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.117003
Ament, L. J. P., van Veenendaal, M., Devereaux, T. P., Hill, J. P., and van den Brink, J. (2011). Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering studies of elementary excitations. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 705–767. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.83.705
Becker, P., Scyfried, P., and Siegert, H. (1982). The lattice parameter of highly pure silicon single crystals. Z. für Phys. B Condens. Matter 48, 17–21. doi:10.1007/BF02026423
Gog, T., Casa, D. M., Knopp, J., Kim, J., Upton, M. H., Krakora, R., et al. (2018). Performance of quartz-and sapphire-based double-crystal high-resolution (-10 meV) RIXS monochromators under varying power loads. J. synchrotron Radiat. 25 (4), 1030–1035. doi:10.1107/S1600577518005945
Gog, T., Casa, D. M., Said, A. H., Upton, M. H., Kim, J., Kuzmenko, I., et al. (2013). Spherical analyzers and monochromators for resonant inelastic hard X-ray scattering: a compilation of crystals and reflections. J. synchrotron Radiat. 20 (1), 74–79. doi:10.1107/S0909049512043154
Halász, G. B., Perkins, N. B., and Van Den Brink, J. (2016). Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering response of the Kitaev honeycomb model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 (12), 127203. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.127203
Hill, J. P., Blumberg, G., Kim, Y.-J., Ellis, D. S., Wakimoto, S., Birgeneau, R. J., et al. (2008). Observation of a 500 meV collective mode in La2−xSrxCuO4 and Nd2CuO4 using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 097001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.097001
Hill, J. P., Coburn, D. S., Kim, Y.-J., Gog, T., Casa, D. M., Kodituwakku, C. N., et al. (2007). A 2 m inelastic X-ray scattering spectrometer at CMC-XOR, Advanced Photon Source. J. Synchrotron Rad. 14, 361–365. doi:10.1107/S0909049507018006
Hönnicke, M. G., Huang, X., Cusatis, C., Koditwuakku, C. N., and Cai, Y. Q. (2013). High-quality quartz single crystals for high-energy-resolution inelastic X-ray scattering analyzers. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 46 (4), 939–944. doi:10.1107/S0021889813004731
Huang, X. R., Gog, T., Kim, J., Kasman, E., Said, A. H., Casa, D. M., et al. (2018). Correct interpretation of diffraction properties of quartz crystals for X-ray optics applications. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 51 (1), 140–147. doi:10.1107/S1600576717018155
Huotari, S., Albergamo, F., Vankó, Gy., Verbeni, R., and Monaco, G. (2006). Resonant inelastic hard x-ray scattering with diced analyzer crystals and position-sensitive detectors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 053102. doi:10.1063/1.2198805
Inyushkin, A. V., Taldenkov, A. N., Chernodubov, D. A., Mokhov, E. N., Nagalyuk, S. S., Ralchenko, V. G., et al. (2020). On the thermal conductivity of single crystal AlN. J. Appl. Phys. 127, 205109. doi:10.1063/5.0008919
Ivanov, S. N., Popov, P. A., Egorov, G. V., Sidorov, A. A., Kornev, B. I., Zhukova, L. M., et al. (1997). Thermophysical properties of aluminum nitride ceramic. Phys. Solid State 39, 81–83. doi:10.1134/1.1129837
Jackeli, G., and Khaliullin, G. (2009). Mott insulators in the strong spin-orbit coupling limit: from heisenberg to a quantum compass and Kitaev models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 (1), 017205. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.017205
Kao, C.-C., Caliebe, W. A., Hastings, L., and Gillet, J.-M. (1996). X-ray resonant Raman scattering in NiO: resonant enhancement of the charge-transfer excitations. Phys. Rev. B 54, 16361–16364. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.54.16361
Kim, B. J., Jin, H., Moon, S. J., Kim, J. Y., Park, B. G., Leem, C. S., et al. (2008). Novel J eff= 1/2 Mott state induced by relativistic spin-orbit coupling in Sr2IrO4. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 (7), 076402. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.076402
Kim, B. J., Ohsumi, H., Komesu, T., Sakai, S., Morita, T., Takagi, H., et al. (2009). Phase-sensitive observation of a spin-orbital Mott state in Sr2IrO4. Science 323 (5919), 1329–1332. doi:10.1126/science.1167106
Kim, H., Kim, J. K., Kwon, J., Kim, J., Kim, H. W. J., Ha, S., et al. (2024). Quantum spin nematic phase in a square-lattice iridate. Nature 625 (7994), 264–269. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06829-4
Kim, H. H., Ueda, K., Nakata, S., Wochner, P., Mackenzie, A., Hicks, C., et al. (2022). Giant stress response of terahertz magnons in a spin-orbit Mott insulator. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 6674. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34375-6
Kim, J., Casa, D., Said, A., Krakora, R., Kim, B. J., Kasman, E., et al. (2018). Quartz-based flat-crystal resonant inelastic x-ray scattering spectrometer with sub-10 meV energy resolution. Sci. Rep. 8, 1958. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-20396-z
Kim, J., Casa, D., Upton, M. H., Gog, T., Kim, Y.-J., Mitchell, J. F., et al. (2012a). Magnetic excitation spectra of Sr2IrO4 probed by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering: establishing links to cuprate superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 177003. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.177003
Kim, J., Chaloupka, J., Singh, Y., Kim, J. W., Kim, B., Casa, D., et al. (2020a). Dynamic spin correlations in the honeycomb lattice Na2IrO3 measured by resonant inelastic x-ray scattering. Phys. Rev. X 10 (2), 021034. doi:10.1103/PhysRevX.10.021034
Kim, J., Daghofer, M., Said, A. H., Gog, T., Van Den Brink, J., Khaliullin, G., et al. (2014). Excitonic quasiparticles in a spin-orbit Mott insulator. Nat. Commun. 5, 4453. doi:10.1038/ncomms5453
Kim, J., Said, A. H., Casa, D., Upton, M. H., Gog, T., Daghofer, M., et al. (2012b). Large spin-wave energy gap in the bilayer iridate Sr3Ir2O7: evidence for enhanced dipolar interactions near the mott metal-insulator transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 (15), 157402. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.157402
Kim, J., Shi, X., Casa, D., Qian, J., Huang, X., and Gog, T. (2016). Collimating Montel mirror as part of a multi-crystal analyzer system for resonant inelastic X-ray scattering. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 23 (4), 880–886. doi:10.1107/S1600577516007426
Kim, J. K., Casa, D., Huang, X., Gog, T., Kim, B. J., and Kim, J. (2020b). Montel mirror based collimating analyzer system for high-pressure resonant inelastic X-ray scattering experiments. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 27 (4), 963–969. doi:10.1107/S1600577520005792
Kourtis, S. (2016). Bulk spectroscopic measurement of the topological charge of weyl nodes with resonant x rays. Phys. Rev. B 94 (12), 125132. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.94.125132
Kushnir, V. I., and Suvorov, E. V. (1990). X-Ray backscattering on perfect crystals (2θ≈ π). Phys. status solidi (a) 122 (1), 391–404. doi:10.1002/pssa.2211220138
Lee, S., Jin, K. H., Kang, B., Kim, B. J., and Cho, G. Y. (2023). Metrology of band topology via resonant inelastic x-ray scattering. Phys. Rev. B 107 (4), 045129. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.107.045129
Lv, B. Q., Xu, N., Weng, H. M., Ma, J. Z., Richard, P., Huang, X. C., et al. (2015). Observation of weyl nodes in TaAs. Nat. Phys. 11 (9), 724–727. doi:10.1038/nphys3426
Neumeier, J. J., Shvyd’ko, Y. V., and Haskel, D. (2024). Thermal expansion of 4H and 6H SiC from 5 K to 340 K. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 187, 111860. doi:10.1016/j.jpcs.2023.111860
Porras, J., Bertinshaw, J., Liu, H., Khaliullin, G., Sung, N. H., Kim, J. W., et al. (2019). Pseudospin-lattice coupling in the spin-orbit Mott insulator Sr2IrO4. Phys. Rev. B 99 (8), 085125. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.99.085125
Qian, X., Jiang, P., and Yang, R. (2017). Anisotropic thermal conductivity of 4H and 6H silicon carbide measured using time-domain thermoreflectance. Mater. Today Phys. 3, 70–75. doi:10.1016/j.mtphys.2017.12.005
Ruiz, A., Breznay, N. P., Li, M., Rousochatzakis, I., Allen, A., Zinda, I., et al. (2021). Magnon-spinon dichotomy in the Kitaev hyperhoneycomb β− Li2IrO3. Phys. Rev. B 103 (18), 184404. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.103.184404
Said, A. H., Gog, T., Wieczorek, M., Huang, X., Casa, D., Kasman, , et al. (2018). High-energy-resolution diced spherical quartz analyzers for resonant inelastic X-ray scattering. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 25 (2), 373–377. doi:10.1107/S1600577517018185
Said, A. H., Kim, J. H., Aran, E. K., and Gog, T. (2022). Novel fabrication technique for high-resolution spherical crystal analyzers using a microporous aluminium base. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 29 (3), 749–754. doi:10.1107/S1600577522001886
Schüler, M., Schmitt, T., and Werner, P. (2023). Probing magnetic orbitals and Berry curvature with circular dichroism in resonant inelastic X-ray scattering. npj Quantum Mater. 8 (1), 6. doi:10.1038/s41535-023-00538-x
Shanks, H. R., Maycock, P. D., Sidles, P. H., and Danielson, G. C. (1963). Thermal conductivity of silicon from 300 to 1400°K. Phys. Rev. 130 (5), 1743–1748. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.130.1743
Shvyd’ko, Yu. V., Hill, J. P., Burns, C. A., Coburn, D. S., Brajuskovic, B., Casa, D., et al. (2013). MERIX-Next generation medium energy resolution inelastic X-ray scattering instrument at the APS. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 188, 140–149. doi:10.1016/j.elspec.2012.09.003
Sutter, J. P., Baron, A. Q., Ishikawa, T., and Yamazaki, H. (2005). Examination of Bragg backscattering from crystalline quartz. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 66 (12), 2306–2309. doi:10.1016/j.jpcs.2005.09.044
Sutter, J. P., Baron, A. Q., Miwa, D., Nishino, Y., Tamasaku, K., and Ishikawa, T. (2006). Nearly perfect large-area quartz: 4 meV resolution for 10 keV photons over 10 cm2. J. synchrotron Radiat. 13 (3), 278–280. doi:10.1107/S0909049506003888
Toellner, T. S., Alatas, A., and Said, A. H. (2011). Six-reflection meV-monochromator for synchrotron radiation. J. Synchrotron Rad. 18, 605–611. doi:10.1107/S0909049511017535
Tsao, J. Y., Chowdhury, S., Hollis, M. A., Jena, D., Johnson, N. M., Jones, K. A., et al. (2018). Ultrawide-bandgap semiconductors: research opportunities and challenges. Adv. Electron. Mater. 4 (1), 1600501. doi:10.1002/aelm.201600501
Vergniory, M. G., Wieder, B. J., Elcoro, L., Parkin, S. S., Felser, C., Bernevig, B. A., et al. (2022). All topological bands of all nonmagnetic stoichiometric materials. Science 376 (6595), eabg9094. doi:10.1126/science.abg9094
Keywords: resonant inelastic X-ray scattering, 5d transition metal, MeV energy resolution, lower symmetry crystal, magnetic excitations
Citation: Kim J, Huang X, Toellner T and Said A (2024) Advances in hard X-ray RIXS toward meV resolution in the study of 5d transition metal materials. Front. Electron. Mater. 4:1487856. doi: 10.3389/femat.2024.1487856
Received: 28 August 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 03 October 2024.
Edited by:
Umesh Kumar, The State University of New Jersey, United StatesReviewed by:
Alex Frano, University of California, San Diego, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Kim, Huang, Toellner and Said. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jungho Kim, amhraW1AYW5sLmdvdg==
 Jungho Kim
Jungho Kim Xiangrong Huang
Xiangrong Huang