
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Ecol. Evol., 18 February 2025
Sec. Conservation and Restoration Ecology
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2025.1539547
This article is part of the Research TopicEcosystem Condition Assessments: Progress towards a Global StandardView all 6 articles
Introduction: Machine learning techniques, renowned for their ability to process complex datasets and uncover key ecological patterns, have become increasingly instrumental in assessing ecosystem services.
Methods: This study quantitatively evaluates individual services—such as water yield, carbon storage, habitat quality, and soil conservation—on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau for the years 2000, 2010, and 2020. A comprehensive ecosystem service index is employed to assess the overall ecological service capacity, revealing spatiotemporal variations in services and exploring the trade-offs and synergies among them. Additionally, machine learning models identify the key drivers influencing ecosystem services, informing the design of future scenarios. The PLUS model is used to project land use changes by 2035 under three scenarios—natural development, planning-oriented, and ecological priority. Based on the land use simulation results for these scenarios, the InVEST model is applied to evaluate various ecosystem services.
Results: During 2000-2020, ecosystem services on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau exhibited significant fluctuations, driven by complex trade-offs and synergies. Land use and vegetation cover were the primary factors affecting overall ecosystem services, with the ecological priority scenario demonstrating the best performance across all services.
Discussion: The research integrates machine learning with the PLUS model, providing more efficient data interpretation and more precise scenario design, offering new insights and methodologies for managing and optimizing ecosystem services on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. These findings contribute to the development of more effective ecological protection and sustainable development strategies, applicable to both the plateau and similar regions.
Ecosystem services (ESs) are the diverse benefits provided by natural ecosystems to human societies (Liu et al., 2023). As global climate change and human activities increasingly affect ecosystems, understanding the spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem services has become essential. It is critical to examine the interactions between different ecosystem services and identify their primary drivers, while also understanding the trends across various scenarios to predict and mitigate future environmental changes. These insights are crucial for developing evidence-based environmental policies and management strategies (Xia et al., 2023).
The study of ecosystem services is a rapidly advancing field within environmental science, with significant contributions from both domestic and international researchers (Hasan et al., 2020; Shen et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2023; Petsch et al., 2023). Assessment methods have evolved from traditional ecological surveys and economic valuations to sophisticated models and comprehensive tools, such as the InVEST (Fang et al., 2022b; Deng et al., 2024), SoIVES (Zhu, 2022), and ARIES models (Aznarez et al., 2024; Pashanejad et al., 2024). Among these, the InVEST model stands out for its ability to provide detailed ecological and economic data analysis, facilitating the quantification and spatial visualization of ecosystem services. This makes it a key tool for assessing the dynamic functions of ecosystem services worldwide (Shi et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2024; Mondal et al., 2024). The relationships between different ecosystem services are complex and characterized by trade-offs and synergies (Deng et al., 2023), which often require balancing to optimize ecological well-being. To explore these trade-offs and synergies, researchers commonly apply overlay analysis (Xu et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022a; Zhao and Pan, 2022; Jiayu et al., 2024), partial correlation analysis (Li et al., 2022b; Shijin and Xiaoqing, 2023; Simeon et al., 2024), or Spearman correlation coefficients (Wang et al., 2020; Zeng et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2023). Ecosystems are inherently adaptive, nonlinear, and multistable, underscoring their complexity. Traditional methods used to study the drivers of ecosystem services, such as multiple regression models (Zhang et al., 2023), principal component analysis (Hu et al., 2022), and geodetectors (Chen et al., 2020; Bi et al., 2023), often struggle to capture the nonlinear patterns and complex interactions in ecological data, which limits their predictive accuracy. As a result, these approaches may fail to effectively capture the dynamic changes in ecosystem service drivers. In contrast, machine learning regression methods excel at identifying nonlinear relationships among variables, handling large and complex datasets, and uncovering intricate interactions and dynamics within ecosystem services. By utilizing machine learning models, it is possible to more accurately track changes in ecosystem services and pinpoint the most significant environmental, social, or economic drivers (Xu et al., 2022b; Almeida et al., 2024; Tian et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2024b). Currently, multi-scenario simulations are a vital tool for assessing how land-use changes affect ecosystem services across varying socio-economic development pathways. Commonly used models include CA-Markov (Beroho et al., 2023), CLUE-S (Gomes et al., 2021; Peng et al., 2021), FLUS (Qiao et al., 2024), and PLUS (Tian et al., 2022; Xie et al., 2022). The PLUS model excels in simulating complex land-use dynamics at a fine spatial scale, providing significant advantages for forecasting both land-use quantities and spatial distributions over extended time series (Liang et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022a). Analyzing trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services, alongside forecasting land-use changes across multiple scenarios, offers deeper insights into how these changes influence service capacity, interactions, and regional benefits. Recently, the PLUS and InVEST models have been employed to predict and assess future land-use alterations and ecosystem service functionality, yielding (Wang et al., 2023; Guo et al., 2024; Pei et al., 2024) robust theoretical results that support regional development models.
While previous research has contributed significantly to theoretical understanding, several limitations persist: (1) Much of the existing work has focused on economically developed eastern regions, arid northern areas, or urbanized zones, typically at the municipal scale. The karst region, one of China’s six major vulnerable ecosystems, is highly susceptible to degradation and faces considerable ecological and economic challenges. However, studies focused on multi-scenario simulations of ecosystem services at a regional scale in the southwestern karst mountains remain limited; (2) Prior studies often concentrated on a narrow set of ecosystem services, neglecting a holistic view of their overall value and interactions, which restricts understanding of their broader impacts; (3) Different machine learning models are suited to different types of data and analytical needs. Proper model selection is crucial for accurate and nuanced assessments of ecosystem services, yet current research often overlooks this aspect, potentially hindering precise evaluations of multidimensional impacts; (4) Previous land-use simulations have typically relied on standardized or generalized scenarios, overlooking the unique influencing factors that shape ecosystem services. This gap may prevent accurate reflection of regional ecological service needs and advantages.
The Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, globally renowned for its distinctive karst landscape, is characterized by unique limestone dissolution features and extensive groundwater systems. It has a complex land-use structure and significant geographical and environmental variability (Hong et al., 2020a). Since 2000, the Chinese government’s Western Development Strategy has aimed to alleviate poverty in the southwestern mountainous regions. While this policy has spurred regional economic development, it has also led to intensified human activities—such as large-scale infrastructure construction and mining—that have severely impacted the natural environment and ecosystems. In response, the government has strengthened ecological protection through initiatives such as the Karst Desertification Restoration Project, leading to some improvements in ecological quality and ecosystem structure in the plateau. Despite these efforts, the rapid pace of economic growth and human disturbance has hindered a comprehensive understanding of the temporal and spatial dynamics of land use and ecosystem services in the region, leaving a substantial gap in research that underscores the need for further investigation.
Building on this context, the present study integrates traditional ecosystem service assessment techniques with advanced machine learning models, accounting for the unique ecological characteristics and conservation needs of the southwestern mountainous region. This approach facilitates a systematic and in-depth exploration of ecosystem services in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. This study employs comprehensive indices to assess ecosystem services, incorporating key factors such as carbon storage, habitat quality, soil conservation, and water yield. This approach accounts for the interactions and potential impacts among these services, establishing a baseline for monitoring their evolution. To improve the accuracy of trend predictions, the study compares various machine learning models, ultimately selecting the gradient boosting model to develop a new framework for analyzing driving mechanisms. This framework quantifies the contributions of different factors to ecosystem services and suggests targeted optimization strategies based on these findings. Finally, the study projects changes in ecosystem services under various future development scenarios, providing robust theoretical guidance for enhancing ecosystem management and decision-making processes, thus advancing regional ecological conservation and promoting sustainable development.
Located in southwestern China (100°–111° E, 22°–30° N), the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau (Figure 1) spans most of Yunnan and Guizhou provinces and extends into parts of Sichuan, Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, and the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Covering approximately 775,400 km², the region boasts an average elevation exceeding 2,000 m. It serves as a crucial center for biodiversity conservation in China, harboring diverse plant and animal species alongside distinctive ecosystems. The plateau plays a vital role in regional ecological stability and global environmental sustainability. However, recent rapid economic growth has exacerbated human-environment conflicts, significantly threatening the region’s ecosystem service capacity.
This study used four primary categories of data: (1) basic data; (2) ecosystem service function assessment data; (3) data on the dominant factors influencing ecosystem services; and (4) data on land use change driving factors. To ensure consistency and accuracy across maps, all datasets were resampled to a spatial resolution of 500 meters and projected in the WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_48N coordinate system. Detailed sources and data processing methods are outlined in Supplementary Table S1.
Focusing on four key ecosystem services—carbon storage (CS), habitat quality (HQ), water yield (WY), and soil conservation (SC)—the study followed these principles: (1) Ecosystem service classification: Based on the millennium ecosystem assessment (MA) framework (Carpenter et al., 2006), these services span regulating, supporting, and provisioning categories, encompassing primary ecosystem functions to facilitate a comprehensive assessment of multifunctionality and service interactions. (2) Regional ecological context: The Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau is characterized by diverse topography and complex ecosystems. The selected services reflect the region’s key ecological features and the primary environmental challenges it faces. Soil conservation and carbon storage are closely tied to forest and land management, while habitat quality and water yield are crucial for biodiversity conservation and water resource management. (3) Data availability and reliability: Each service is supported by mature assessment methods and reliable data, ensuring scientific accuracy and integrity.
The study integrated topography, soil types, and vegetation cover data into the InVEST model, using GIS spatial analysis tools to map and quantify ecosystem services. Parameters for each module were derived from the InVEST Model Manual and established research (Han et al., 2019; Duan et al., 2020; Niu and Shao, 2020; Han et al., 2021; Yuan et al., 2021; Fang et al., 2022a; Li et al., 2022d; Lin et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Pan et al., 2022; Xie and Zhang, 2023; Yang et al., 2024a). To illustrate evolving trends and service interactions, mean values of each service were standardized, eliminating dimensional and magnitude disparities and allowing for consistent comparison across data.
This study utilized the “comprehensive ecosystem services (CES)” framework to assess and quantify ecosystem services on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Using GIS’s raster calculator, the CES index was calculated by aggregating normalized values from four key ecosystem services: carbon storage, habitat quality, water yield, and soil conservation. A higher index score indicates stronger ecosystem service functionality. The selection of these services was guided by the region’s ecological security needs, with each service representing a critical aspect of ecosystem health. Balancing these services is essential for ecosystem stability, which is why an equal-weighting method was employed to ensure each service was regarded with equal importance. The formula used is as follows:
where CES represents comprehensive ecosystem services, and denotes the normalized index of the i-th ecosystem service for pixel a at time t. The indices correspond to the normalized values of each individual ecosystem service.
The study utilized Spearman correlation analysis to quantify the trade-offs and synergistic relationships between ecosystem services. Unlike methods based on raw data values, Spearman correlation analysis does not have strict requirements for the type of data distribution and is a non-parametric statistical testing method aimed at evaluating the strength and direction of the correlation between two variables (Hong et al., 2020b; Karimi et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022b). The correlation coefficient ranges from -1 to +1, where -1 indicates a completely negative correlation, +1 indicates a completely positive correlation, and 0 indicates no correlation (King and Eckersley, 2019).
Spearman correlation analysis is particularly suitable for the evaluation of ecosystem services (Jaligot et al., 2019; Ogbodo et al., 2023). Firstly, it has strong data adaptability, calculating the correlation coefficient by comparing the ranking of data values rather than the original numerical values. Research on ecosystem services often involves data from multiple sources, these data types are diverse and often do not meet the conditions for parametric tests such as normal distribution. The non-parametric nature of Spearman correlation analysis allows it to be directly applied to these data, without the need for complex transformations or processing. For example, in the study of ecosystem services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (Wu et al., 2022), facing multi-source heterogeneous data such as temperature, precipitation, and changes in land use types, Spearman correlation analysis can directly mine the association of ecosystem services in the data without tedious preprocessing, greatly expanding the scope of data analysis. Secondly, Spearman correlation analysis can handle potential skewed distribution in the data, unaffected by outliers, providing a robust tool for revealing interactions between services (Kumar et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024a). Lastly, the results of Spearman correlation analysis are intuitively interpretable, making it easy to understand and explain the research results. In the study of ecosystem services, the positive or negative values of the correlation coefficient can indicate whether the services are synergistic or in a trade-off relationship, and the larger the absolute value of the coefficient, the stronger the synergy or trade-off relationship between these services (Liang et al., 2023). This intuitive presentation greatly reduces the difficulty of interpreting research results, and can quickly judge whether different ecosystem services promote each other, inhibit each other, or have no relation based on the coefficient, providing clear and effective support for the formulation of subsequent ecosystem management decisions.
The analysis used raster cells. First, 10,000 random sampling points were generated across the study area using ArcGIS software, with a minimum distance of 500 meters between points to mitigate spatial autocorrelation. Ecosystem service values for each point were extracted using the “extract values to points” tool, followed by Z-score standardization to achieve dimensionless values. This process created the sample database. Statistical data were then transferred to R programming for Spearman correlation analysis using the “corrplot” package. Correlation coefficients were tested for significance at the 0.01 level.
To assess the key drivers of ecosystem services, this study employed the gradient boosting algorithm. Gradient boosting is an ensemble learning method where weak predictive models are iteratively trained to form a robust composite model (Natekin and Knoll, 2013). In each iteration, the new model corrects the errors of the previous one, minimizing residuals. The predictions from each newly trained model are weighted by a fixed learning rate and added to the overall prediction. This iterative process continues until a set number of iterations is reached or model performance no longer improves. Gradient boosting’s primary strengths are its high predictive accuracy and flexibility, reducing overfitting while accommodating various data types and complex nonlinear relationships. The algorithm can be summarized by the following core formula, which includes initialization, iterative updates, and final model construction.
where represents the initial model’s prediction function; denotes the constant starting value of the prediction, typically the mean or median of the target variable; L is the loss function used to evaluate prediction error; is the actual target value for the i-th data point; N is the total number of the observations in the dataset; represents the pseudo-residual for the i-th observation at iteration t; is the partial derivative of the loss function L with respect to the model prediction ; is the predictive function of the model after the -th iteration. The learning rate controls the influence of each weak learner per iteration. denotes the weak learner trained in the t-th iteration; is the final model predictive function after T iterations; and T represents the total number of iterations.
The selection of appropriate driving factors was crucial for understanding and predicting ecosystem service functions, as it directly influenced the assessment of the factors that affect these services. Drawing on relevant literature (Jia et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022a; Huang and Wang, 2023), the selection criteria for driving factors were as follows: (1) Relevance: Factors should clearly reflect the influence of natural geography, climate, economic, or social factors on ecosystem services; (2) Quantifiability and independence: Overlap among factors should be minimized to facilitate computational analysis; (3) Data accessibility: The precision and credibility of the final results depend on the quality, completeness, and geographic and temporal coverage of the data. Accordingly, nine indicators across four dimensions were selected for analysis of various ecosystem services: climate (precipitation, temperature, potential evaporation), topography (elevation, slope), land characteristics (vegetation fraction, land use), and urbanization (population density, GDP).
This study applied the gradient boosting algorithm to evaluate the significance of driving factors. Feature importance was determined through ranked importance by randomly shuffling the values of individual features and assessing the resulting decrease in model performance. This approach identified the dominant influences on ecosystem services, based on their contribution to model performance. After tuning the model, the dataset was split, allocating 80% for training and 20% for testing. A learning rate of 0.1 and 100 decision trees were used. Model accuracy was evaluated using root mean square error (RMSE) and the coefficient of determination (R²), with the following definitions:
where is the i-th observed value, represents the i-th predicted value, and m is the total number of observations. Lower RMSE values indicate higher predictive accuracy, reflecting smaller deviations between predicted and actual values.
where, represents the mean of all observed values. R² values typically range from 0 to 1, with values closer to 1 indicating a stronger model and better alignment with the observed data.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the gradient boosting model in identifying dominant factors influencing ecosystem services, this study compared it against several advanced machine learning models, including XGBoost, Ridge Regression, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Random Forest (Table 1) (Sannigrahi et al., 2019; Morais et al., 2023; Okumus and Terzi, 2023; Zhou et al., 2024). All models were applied to datasets from 2000, 2010, and 2020, using consistent data splitting ratios and parameter settings. Model performance was assessed by RMSE and R², with models showing lower RMSE and higher R² values considered more precise and reliable (Liu et al., 2024b).
This study developed land use scenarios for 2035 tailored specifically to the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Nine driving factors were selected based on their data availability, relevance, variability, and quantifiability. These factors, which include aspect, annual average precipitation, elevation, slope, annual average temperature, GDP, population density, distance to national highways, and nighttime lights, combine both natural and socio-economic elements. The LEAS module of the PLUS model was used to examine the influence of these factors, informing the creation of land expansion strategies. Subsequently, the CARS module simulated the spatial distribution of land use across the study area. This simulation integrated strategies and predictive outcomes from LEAS while considering neighboring effects and plot characteristics through cellular automata rules.
Land use changes on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau result from complex interactions between natural environmental factors and human activities. These interactions are shaped by geographical conditions, socio-economic development, and policy regulations. In light of the plateau’s prevailing conditions, national land and space planning, and insights from the Gradient Boosting model’s ecosystem service driver assessment, three land use scenarios for 2035 were developed: natural development, planning-oriented, and ecological priority.
The natural development scenario assumes that land use changes from 2000 to 2020 will continue without considering policy or regulatory constraints. In this scenario, the land use pattern evolves linearly based on historical trends, serving as a theoretical baseline for the other scenarios. The planning-oriented scenario integrates national land use policies, environmental regulations, and regional development strategies. It prioritizes policy tools and planning measures to guide land use changes, ensuring alignment with territorial spatial planning goals. The ecological priority scenario focuses on enhancing ecosystem services by prioritizing land use and vegetation cover. Stringent ecological protection policies are implemented to preserve and enhance ecosystem functions. Under this scenario, land use changes undergo thorough ecological impact assessments, with strict limitations on the expansion of construction land and encroachment into ecological zones. Measures to increase vegetation cover and expand water source protection areas are introduced to improve ecosystem resilience, while ecological restoration projects, such as converting cropland to forests and restoring grasslands and wetlands, are promoted.
To align with these development scenarios, key parameters of the PLUS model—including the transfer matrix, neighborhood weight, land use demand, and areas with restricted conversion—were defined.
1. Transfer Matrix: The transfer matrix represents the dynamics of land use conversion between various types. If a specific land type is eligible for conversion to another, the corresponding matrix value is set to 1; otherwise, it is set to 0. As shown in Supplementary Table S2, the transfer matrix from 2000 to 2020, alongside the Markov transfer probabilities for the study area, was used to establish matrices for six land types under different scenarios, reflecting local socio-economic trends and environmental policies.
2. Land Use Demand: In the natural development scenario, projections for land use requirements in 2035 were generated using the linear regression module of the PLUS model, based on data from 2010 and 2020. For the planning-oriented scenario, the area control ranges for land use types—such as forestland, cropland, and building land—were examined for the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau based on policy documents like the “Guizhou Provincial Territorial Spatial Planning (2021-2035)” and “Yunnan Provincial Territorial Spatial Planning (2021-2035).” These documents informed the simulation of planned land use areas for 2035. The model assumed a 20% reduction in the transfer of cropland to forestland and grassland, and a 40% reduction in its conversion to building land. Conversely, the transfer of forestland and grassland to cropland was increased by 20%, while the transfer to building land was reduced by 40%. Similarly, the transfer of water bodies to cropland increased by 30%, while their conversion to building land decreased by 50%. Transfers from building land to cropland were boosted by 30%, and unutilized land conversion to building land was also increased by 30%. In the ecological priority scenario, ecological protection was emphasized, particularly for forestland, grassland, and water bodies. The model further increased the transfer of cropland to forestland and grassland by 20%, while reducing its conversion to building land by 50%. Transfers from forestland and grassland to cropland and building land were reduced by 40%, while conversion of water bodies to building land dropped by 60%. The transfer of building land to cropland was increased by 30%, and unutilized land conversion to forestland and grassland was raised by 20%, with a 10% decrease in its conversion to building land. The anticipated land use demands for 2035 were calculated using the Markov model, based on these rules for each scenario (Supplementary Table S3).
3. Neighborhood Weights: Neighborhood weights represent the relative influence of various driving factors on land use decisions during simulations of land use change. A higher weight indicates a stronger influence on land use outcomes, while a lower weight denotes a lesser effect. These weights range from 0 to 1. In this study, neighborhood weights for different land use types across the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau were determined by analyzing the expansion of land use from 2000 to 2020. The calculations were refined iteratively using the PLUS software, drawing on existing studies (Li et al., 2022c; Duan et al., 2023) (Supplementary Table S4).
4. Restricted Conversion Areas. Restricted conversion areas are identified through a binary raster map, where each cell represents a geographic location. A value of 1 indicates that the land use type in that location can change, while a value of 0 signifies it remains fixed. In the natural development scenario, land use changes followed historical trends and natural dynamics, with no conversion restrictions. In the planning-oriented scenario, ecological function protection areas were established as constraints to limit their conversion to other land types. In the ecological priority scenario, nature reserves, ecological function protection areas, and primary river zones were designated as protected areas, preventing their conversion to other land uses.
5. Accuracy Verification. Land use data from 2000 and 2010 were used to project the 2020 land use scenario for the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, which was then compared with actual land use statistics from 2020. The model’s accuracy was assessed using the Kappa and figure of merit (FoM) coefficients. The kappa coefficient of 0.860523 indicates substantial agreement (values above 0.8 are considered high), while the FoM coefficient of 0.215106 slightly exceeds the standard range of 0.1-0.2 (Wang et al., 2022b). These results confirm that the PLUS model effectively captured land use dynamics in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, meeting the study’s accuracy requirements and proving its utility for forecasting land use changes through 2035.
The InVEST model was used to evaluate ecosystem service performance across different scenarios, reassessing each service based on the outcomes of land use simulations. Trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services were analyzed under various management and policy scenarios.
Figure 2 illustrates the spatial distribution of ecosystem services across the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Water yield services were more abundant in the eastern regions, particularly in areas with flat terrain and ample rainfall, such as Pu’er, Tongren, Zhangjiajie, and Huaihua. In contrast, central Yunnan, including areas around Kunming, and much of Guizhou, experienced lower water yields due to terrain variability and reduced precipitation. Habitat quality patterns remained generally stable, although low-quality areas expanded gradually from 2000 to 2020, especially in the densely populated and economically active central and southern regions, including Kunming, Guiyang, Qujing, Zhaotong, Baise, and Bijie. Urban expansion increasingly threatened cropland, forestland, and grassland habitats, accelerating the fragmentation of high-quality habitats near urban centers. Carbon storage distribution aligned closely with land use types. High carbon storage values were concentrated in forested and grassland areas, particularly in Enshi Prefecture and Zhangjiajie, where extensive vegetation cover enhanced carbon sequestration. Conversely, areas with significant cropland or urban development, such as Dali Prefecture, Kunming, Guiyang, Yuxi, Qujing, and Baise, displayed lower carbon storage due to urbanization’s impact on vegetation and land cover. Soil conservation services followed a similar trend, with higher values in areas with robust vegetation cover and lower values in regions with sparse vegetation. For instance, cities such as Guiyang, Qujing, Liupanshui, and Bijie saw urban expansion that reduced soil conservation. Conversely, areas with abundant vegetation, such as Lincang, Panzhihua, and Liangshan Prefecture, exhibited stronger soil conservation. Overall, the spatial distribution of ecosystem services revealed strong heterogeneity, influenced by both natural conditions and human activities. Areas with high ecosystem service capacity were concentrated in regions such as Zigui County, Xingshan County, and Shimen County, where natural vegetation was well-preserved, biodiversity was rich, and human intervention was minimal. In contrast, southeastern regions such as Kunming, Dali Prefecture, and Yuxi displayed weaker ecosystem service capacity, impacted by lower vegetation cover, land degradation, and intense human activities such as agriculture, mining, and urban development.
The temporal changes in ecosystem services are summarized in Table 2. Water yield decreased from 0.3088 in 2000 to 0.2693 in 2010, then rebounded to 0.3010 by 2020. While it did not return to its 2000 value, a positive trend emerged. Habitat quality slightly declined from 0.7764 in 2000 to 0.7735 in 2010, and further decreased to 0.7596 by 2020, largely driven by increased human activity, land use changes, and natural habitat degradation. Carbon storage showed a modest decrease, from 0.8793 in 2000 to 0.8789 in 2010, and further to 0.8716 by 2020, reflecting vegetation degradation and forest loss. Conversely, soil conservation increased from 0.0405 in 2000 to 0.0442 in 2010, and further to 0.0557 by 2020, likely due to more effective soil and water conservation measures and vegetation restoration efforts. The normalized mean of comprehensive ecosystem services declined from 2.0052 in 2000 to 1.9661 in 2010, but rebounded to 1.9881 by 2020.
Overall, ecosystem services on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau displayed fluctuations over the past two decades. Water yield and comprehensive ecosystem services initially declined but later increased, while habitat quality and carbon storage steadily declined. In contrast, soil conservation capacity consistently improved. These trends suggest progress in water protection and land management, though challenges persist in habitat protection and carbon storage. Enhanced monitoring and assessment of ecosystem services are critical to promptly identifying regional changes and providing a scientific basis for effective conservation and management strategies.
Figure 3 presents a Spearman correlation analysis revealing six statistically significant relationships (P < 0.05) among four ecosystem services. Figures 3A–C show the correlation analysis for the years 2000, 2010, and 2020, respectively. The analysis indicates a persistent negative correlation between water yield and habitat quality (WY-HQ), water yield and carbon storage (WY-CS), and habitat quality and soil conservation (HQ-SC). In contrast, positive correlations were observed between habitat quality and carbon storage (HQ-CS) and between carbon storage and soil conservation (CS-SC). The strongest correlation was between habitat quality and carbon storage (HQ-CS), with correlation coefficients exceeding 0.9 throughout the study period, while the weakest, and most declining, was the correlation between water yield and soil conservation (WY-SC). Figure 3D illustrates the evolving correlations from 2000 to 2020, with blue arrows indicating synergistic optimization and red arrows showing trade-off deterioration. Notably, the correlations between water yield and habitat quality (WY-HQ) and between water yield and carbon storage (WY-CS) exhibited a trend toward synergy, while other service pairs showed trade-off dynamics. Over the long term, a strong synergistic relationship was sustained between habitat quality and carbon storage, while the relationships between water yield, habitat quality, and carbon storage, although optimizing, continued to exhibit some trade-offs. The relationship between soil conservation and other services revealed more complex dynamics, exhibiting both synergies and trade-offs.
An analysis of various machine learning models, as presented in Table 3, reveals their performance in addressing multiple ecosystem service drivers. Overall, gradient boosting consistently outperformed other models across various time points and ecosystem service indicators, demonstrating the lowest RMSE and highest R². This indicates superior predictive accuracy and model fit, particularly for the carbon storage (CS) indicator, where gradient boosting consistently achieved exceptionally high predictive accuracy across all years. In comparison, other models such as XGBoost performed well on certain indicators, achieving an R² of 0.9408 for the water yield (WY) in 2000. However, their overall performance did not match that of gradient boosting, likely due to constraints in parameter tuning and model complexity. As a linear model, ridge regression generally exhibited weaker performance, particularly in terms of R², which tended to be lower than that of other models. Support vector machines (SVM) displayed higher RMSE and lower R² values, with notable overfitting on the CS indicator, as evidenced by negative R² values. Random Forest showed strong performance in some cases, such as achieving an R² of 0.9999 for the CS indicator in 2000, but its overall performance still lagged behind gradient boosting.
In summary, gradient boosting’s exceptional performance underscores its reliability and effectiveness in assessing ecosystem service drivers. This success can be attributed to its iterative error-correction process and high adaptability to complex data relationships. While other models had strengths, gradient boosting was the clear leader in this specific application, making it the primary machine learning tool for this research.
The gradient boosting model was used to derive relative importance scores for nine explanatory variables influencing five ecosystem service response variables in 2000, 2010, and 2020. As shown in Table 4, precipitation emerged as the primary determinant of water resource generation, directly influencing annual water yield. Land use consistently proved the dominant factor affecting habitat quality and carbon storage, with scores exceeding 1.8 and approaching 2.0 for these services, highlighting its crucial role in optimizing ecosystem services. Vegetation cover was identified as a key factor for soil conservation, effectively preventing soil erosion and emerging as the main driver of this service. Notably, scores for vegetation cover exceeded 1.5 in both 2000 and 2010, underscoring the importance of protecting and enhancing vegetation to mitigate soil erosion. Overall, land use diversity and management significantly impacted multiple ecosystem services, with high vegetation cover generally linked to better service outcomes. Consequently, land use and vegetation cover were identified as the critical factors influencing comprehensive ecosystem services. Although precipitation had some influence on ecosystem services, its effect was secondary to that of land use and vegetation cover. This importance assessment improves understanding of ecosystem service trends and provides a foundation for defining ecological priority scenarios in the PLUS model.
Projections for land use in 2035 were developed across three scenarios: natural development, planning-oriented, and ecological priority. As shown in Table 5, the natural development scenario predicted growth in cropland and built-up land, accompanied by a decrease in forestland area, suggesting that natural development would lead to some forestland conversion. In the planning-oriented scenario, both cropland and forestland areas showed slight increases, indicating that sustainable policies are supporting agricultural development and forest conservation. Additionally, the expansion of built-up land was limited to 10,711 km², less than in the natural development scenario, highlighting efforts to control urban sprawl. The ecological priority scenario, focused on ecological protection, saw increases in forestland and grassland areas to 454,417 km² and 126,817.75 km², respectively, emphasizing the conservation and expansion of these ecologically sensitive areas. In contrast, cropland and built-up land areas were reduced to 176,805.5 km² and 9,277.25 km², respectively, reflecting a policy prioritizing the protection of natural resources, ecosystem services, and biodiversity.
Figure 4 illustrates the spatial distribution of land use across different scenarios. In the natural development scenario, land use followed historical trends. Cropland was scattered, with a concentration in central areas. Forestland covered a large expanse, while urban areas expanded significantly around major cities, reflecting accelerated urbanization. In the planning-oriented scenario, although cropland increased in area, its distribution became more concentrated and organized, particularly in regions suitable for agriculture. Forestland expanded slightly in ecologically sensitive and border areas, reflecting enhanced conservation efforts. The growth of urban areas was more controlled, consistent with urban planning and land use policies. In the ecological priority scenario, forestland had the greatest coverage, particularly in the western and northern regions. Cropland decreased, concentrating in areas with poor ecological conditions or minimal environmental impact. Urban expansion was strictly controlled, confined to existing urban zones, reducing encroachment on natural areas. Water bodies and grasslands were well protected, especially in ecological function zones and biodiversity hotspots.
Based on the simulated land use types for 2035 under different scenarios in the PLUS model, and considering data consistency and availability, the 2020 climate data was used to calculate the water yield, habitat quality, carbon storage, and soil conservation of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau for 2035. The cumulative ecosystem service value (Table 6) was then calculated and compared with the historical period. In the natural development scenario, ecosystem services were weak. Water yield was slightly lower than in 2020, with no significant improvement. Habitat quality declined slightly, suggesting that without substantial policy intervention, habitats could degrade due to human activities and natural development trends. Carbon storage also declined marginally, while soil conservation improved slightly. Overall, the ecosystem services score was slightly lower than in 2020. In the planning-oriented scenario, ecosystem services showed slight improvements compared to the natural development scenario. Habitat quality and soil conservation were enhanced, indicating that strategic land use and conservation measures could improve habitat conditions and reduce soil erosion. Carbon storage remained close to 2020 levels, reflecting the effectiveness of forestland protection efforts. The overall ecosystem services score improved, demonstrating the benefits of integrated land management. In the ecological priority scenario, all ecosystem service indicators showed the greatest improvement. Water yield, habitat quality, carbon storage, and soil conservation all exceeded 2020 levels, highlighting the advantages of prioritizing ecological protection. Comprehensive ecological restoration efforts significantly enhanced ecosystem service quality.
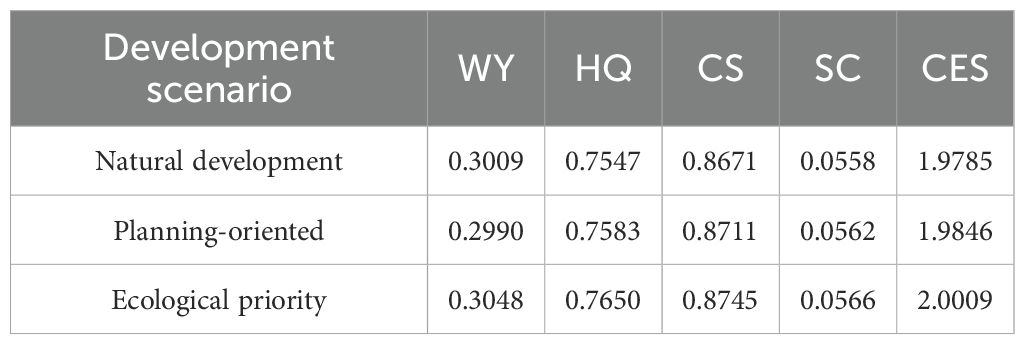
Table 6. Normalized mean values of ecosystem services under different development scenarios in 2035.
Spatial patterns of ecosystem service functions in 2035 exhibited distribution characteristics similar to those from 2000 to 2020 (Figure 5). In all scenarios, water yield remained low in the central and southern regions, with high-value areas concentrated in the northeast, including Changde, Yichang, Zhangjiajie, Luzhou, and Yibin. Habitat quality improved in the ecological priority scenario, especially in well-managed areas such as Zunyi, Tongren, and Zigui. Carbon storage variation across scenarios was minimal, with low-value regions in central areas such as Anshun, Bijie, and Guiyang. Soil conservation showed slight improvements in all scenarios, with low-value areas in central and western regions, including Guiyang, Bijie, Qujing, Kunming, and Chuxiong. In the natural development scenario, ecosystem service distribution followed past trends. The planning-oriented scenario saw improvements in ecosystem service capacity, particularly in Baise, Qiandongnan, and Guiyang, reflecting the benefits of planning measures. The ecological priority scenario demonstrated optimal ecosystem service performance, serving as an ideal model for how enhanced ecological protection and sustainable management can improve services, particularly in regions such as Dali, Chuxiong, Yuxi, and Kunming, where initial ecological value was low.
The 2035 predictions revealed that different development scenarios affected the trade-offs and synergies between ecosystem services in distinct ways (Figure 6). In the natural development scenario, the trade-off between HQ-WY and HQ-CS slightly intensified compared to 2020, while synergies between HQ-CS and CS-SC weakened. This shift likely resulted from the absence of interventions in the natural development scenario. In the planning-oriented scenario, although negative correlations persisted between HQ-WY and CS-WY, the competitive dynamics were somewhat reduced. Positive correlations among CS-HQ, SC-HQ, and SC-CS were stronger than in the natural development scenario, suggesting that proper planning and management can mitigate service conflicts and enhance synergies. The ecological priority scenario demonstrated the most favorable outcome for fostering synergies between ecosystem services, with higher levels of synergy observed in HQ-CS, HQ-SC, and CS-SC. Moreover, trade-offs between WY-HQ, WY-CS, and WY-SC were somewhat alleviated. This scenario emerged as the most effective in balancing ecosystem services.
The PLUS-InVEST model was used to assess and predict future developments and ecosystem services in the study area, consistent with the methodologies of Huang et al (Huang et al., 2023a, 2023; Kulaixi et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2024). Temporal and spatial analyses of ecosystem services show that carbon storage is predominantly concentrated in land types with high vegetation cover, such as forests. As forestland areas fluctuate, carbon storage in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau correspondingly increases or decreases, supporting the findings of Wang Rongyao et al (Wang et al., 2022a). Land use strongly influences temporal and spatial variations in habitat quality on the Plateau. The rapid expansion of urban areas increases habitat fragmentation, reducing connectivity, a trend partially corroborated by Xie Bo et al (Xie and Zhang, 2023). Vegetation stabilizes soil through its root systems, thus reducing erosion. Consequently, vegetation coverage is a critical factor in soil conservation. In the economic hub of the Plateau, where vegetation cover is sparse and human impact is significant, soil conservation capacity is limited, aligning with the findings of Chen Ran et al (Ran et al., 2020). Water production is constrained by various factors. In the eastern region, with its gentle terrain and extensive grasslands, the area functions as the primary watershed of the Plateau. Li Jinghao et al. (Jinghao et al., 2024) demonstrated that water production services are higher in the east and lower in the west, a pattern consistent with this study’s results. Overall, ecosystem service functions in the area initially declined before rebounding, echoing the findings of Zhang Hao et al. (Zhang et al., 2020) regarding ecosystem health in southwestern China.
The trade-off and synergy analysis revealed that, both historically and in future projections, a trade-off exists between water yield and habitat quality, carbon storage, and soil conservation in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. This trade-off is due to disturbances in the natural ecological environment caused by water regulation and the expansion of water bodies. However, strong synergistic relationships were observed between habitat quality, carbon storage, and soil conservation. In particular, habitat quality and carbon storage are highly synergistic, with regions of high habitat quality typically exhibiting greater biodiversity. Diverse plant communities enhance carbon fixation and storage, highlighting the interdependence of biodiversity, ecosystem services, and vegetation health. These findings are consistent with the research by Zhang Mei et al (Zhang et al., 2015). The identification of key drivers influencing ecosystem services shows that land use practices and vegetation cover directly impact the types and quality of services ecosystems provide. Extensive forests and grasslands deliver rich biodiversity, effective carbon storage, and water conservation services. In contrast, unchecked urban expansion and agricultural development lead to habitat fragmentation, diminishing the ecosystem’s natural regulatory capacity, supporting the conclusions of Schirpke et al (Schirpke et al., 2023).
Traditional land use simulations typically rely on empirical methods or broad macro-level policy frameworks. While these approaches offer foundational planning insights, they often lack robust data support, resulting in substantial uncertainty in decision-making. As a result, management strategies may be overly generalized, lacking specificity. This study addresses this gap by incorporating the Gradient Boosting model, which enables the identification and quantification of key drivers influencing ecosystem services. This data-driven model, which utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze large-scale data, identifies the most significant factors impacting various ecosystem services. By providing a precise foundation for scenario design, it enhances the accuracy of future land management simulations. The research found that, in the ecological priority scenario, ecosystem service performance exceeded that of both the natural development and planning-oriented scenarios. This suggests that scenario designs incorporating the advantages of key driving factors offer substantial implementation value. By adjusting the distribution of dominant factors and optimizing land use structures, ecosystem services were not only enhanced but also promoted greater inter-service synergy, reducing trade-offs between services. Compared to traditional empirical approaches, this data-driven optimization is more precise and efficient.
The integration of machine learning techniques with ecological models in this study provides a scientific framework for future ecosystem service management, with potential applications in other regions. In complex ecosystems, identifying the dominant factors influencing ecological service systems enables the application of tailored management strategies, improving the precision of scenario designs. Future land management efforts should prioritize not just the optimization of individual services but also the management of multifunctional land uses. This includes strategically managing agricultural and urban areas to protect and restore ecological functions, thereby enhancing a broad range of ecosystem services. Relying on quantitative models and dynamic monitoring will help ensure that land use optimization delivers both immediate benefits and long-term ecosystem stability. This approach will improve policy formulation and implementation, addressing complex ecological challenges while promoting sustainable environmental development.
This study combined the InVEST, Gradient Boosting, and PLUS models. While the model’s accuracy has been validated and meets the research requirements, several issues warrant further attention:
First, the InVEST model’s parameter settings were primarily based on literature from the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. While these parameters provide a scientific foundation for the assessment, the region’s ecosystem services are influenced by various factors, and the dynamics of ecosystem processes and human activities may result in discrepancies between model parameters and actual conditions. Future work should focus on refining these parameters, potentially through detailed field surveys and data collection, to ensure the InVEST model accurately reflects the region’s ecological realities, thus enhancing the reliability of the assessments.
Second, the study analyzed the impact of individual driving factors on ecosystem services in isolation, overlooking the complex interactions among these factors. These interactions—whether synergistic, suppressive, or feedback-driven—can significantly influence ecosystem outcomes. Future research should adopt a multifactorial approach to better understand the interrelationships among driving factors, offering a more comprehensive understanding of ecosystem service dynamics.
The distribution and variation of ecosystem services vary across different spatial scales. This study, primarily focused on random sampling points for analysis, may not fully capture the comprehensive changes in ecosystem services. Future research should incorporate high-resolution remote sensing data and advanced raster analysis techniques, integrated with regional ecological characteristics. By adapting research scales dynamically according to specific objectives, it will be possible to explore internal disparities in ecosystem services, providing more precise evidence for policy development.
In conclusion, future studies should continue to innovate in areas such as localizing model parameter optimization, incorporating multifactor interaction effects, and enhancing the precision and adaptability of spatial scales. These advancements will support a more comprehensive assessment and sustainable management of ecosystem services, not only in the study area but also in other regions.
This study focused on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, analyzing the spatiotemporal evolution of habitat quality, water yield, soil conservation, carbon storage, and overall ecosystem services between 2000 and 2010. Projections for 2035 were made under three scenarios: natural development, planning-oriented, and ecological priority. The analysis evaluated the changes in ecosystem services across these scenarios, highlighting trade-offs and synergies. The findings underscore the impact of different management strategies on ecosystem services, with the key conclusions summarized below:
Ecosystem services in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau fluctuated over the past two decades. Water yield and overall ecosystem services initially declined but later increased, while habitat quality and carbon storage showed a steady decline. In contrast, soil conservation improved continuously. These trends suggest progress in water conservation and land management, but challenges persist in habitat protection and carbon storage. Future ecological planning should prioritize expanding nature reserves, forest restoration, and converting farmland to forest in areas with low carbon storage to stabilize key ecosystems and enhance carbon storage.
The analysis identified land use and vegetation cover as critical factors influencing ecosystem services. Optimizing land use and enhancing vegetation cover are essential for boosting the region’s ecological service capacity, providing a solid foundation for future land management. Additionally, precipitation influences certain ecosystem services, necessitating dynamic land management strategies that respond to natural changes like precipitation variations, ensuring flexibility in policy adaptation.
Simulation results across different scenarios highlight the importance of policy direction and ecological protection measures in improving ecosystem services. In the natural development scenario, ecosystem services remained weak due to the lack of effective policy intervention, with declines observed in some areas. The planning-oriented scenario saw improvements through land use adjustments and policy interventions, particularly in habitat quality and soil conservation. The ecological priority scenario demonstrated the most significant improvement in ecosystem services, particularly in carbon storage and habitat quality, reinforcing the effectiveness of strengthened ecological protection policies and restoration efforts. Future land use and ecological management should emphasize scientific planning, area-specific ecological strategies, and precise protection measures.
In the natural development scenario, conflicts and trade-offs among ecosystem services were prominent, particularly between water conservation and both carbon storage and habitat quality. The planning-oriented scenario, guided by policy, alleviated some of these conflicts and enhanced synergies. The ecological priority scenario, however, yielded the best results in fostering synergistic interactions. This scenario achieved strong coordination among services, especially in the interactions between water conservation, habitat quality, and carbon storage, all of which significantly improved. Therefore, strengthening ecological priority policies, fostering synergistic effects among services, and introducing collaborative management mechanisms are crucial in ensuring coordinated development. Additionally, dynamic monitoring and regulation of ecosystem service relationships are essential for long-term success.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Y-LP: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. H-NP: Validation, Writing – review & editing. W-YC: Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.72204191); and the Graduate Innovative Fund of Wuhan Institute of Technology (No. CX2023350).
We thank Charlesworth Author Services (https://www.cwauthors.com.cn/) for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fevo.2025.1539547/full#supplementary-material
Almeida B., David J., Campos F. S., Cabral P. (2024). Satellite-based Machine Learning modelling of Ecosystem Services indicators: A review and meta-analysis. Appl. Geogr. 165, 103249. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2024.103249
Aznarez C., Kumar S., Marquez-Torres A., Pascual U., Baró F. (2024). Ecosystem service mismatches evidence inequalities in urban heat vulnerability. Sci. Total Environ. 922, 171215. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171215
Beroho M., Briak H., Cherif E. K., Boulahfa I., Ouallali A., Mrabet R., et al. (2023). Future scenarios of land use/land cover (LULC) based on a CA-markov simulation model: case of a Mediterranean watershed in Morocco. Remote Sens. 15, 1162. doi: 10.3390/rs15041162
Bi Y., Zheng L., Wang Y., Li J., Yang H., Zhang B. (2023). Coupling relationship between urbanization and water-related ecosystem services in China’s Yangtze River economic Belt and its socio-ecological driving forces: A county-level perspective. Ecol. Indic. 146, 109871. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109871
Carpenter S. R., DeFries R., Dietz T., Mooney H. A., Polasky S., Reid W. V., et al. (2006). Millennium ecosystem assessment: research needs. Science 314, 257–258. doi: 10.1126/science.1131946
Chen T., Feng Z., Zhao H., Wu K. (2020). Identification of ecosystem service bundles and driving factors in Beijing and its surrounding areas. Sci. Total Environ. 711, 134687. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134687
Deng G., Jiang H., Zhu S., Wen Y., He C., Wang X., et al. (2024). Projecting the response of ecological risk to land use/land cover change in ecologically fragile regions. Sci. Total Environ. 914, 169908. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.169908
Deng X., Xiong K., Yu Y., Zhang S., Kong L., Zhang Y. (2023). A review of ecosystem service trade-offs/synergies: enlightenment for the optimization of forest ecosystem functions in karst desertification control. Forests 14, 88. doi: 10.3390/f14010088
Duan X. Y., Chen Y., Wang L. Q., Zheng G. D., Liang T. (2023). The impact of land use and land cover changes on the landscape pattern and ecosystem service value in Sanjiangyuan region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Manage. 325, 116539. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116539
Duan X., Rong L., Bai Z., Gu Z., Ding J., Tao Y., et al. (2020). Effects of soil conservation measures on soil erosion in the Yunnan Plateau, southwest China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 75, 131–142. doi: 10.2489/jswc.75.2.131
Fang Z., Ding T., Chen J., Xue S., Zhou Q., Wang Y., et al. (2022b). Impacts of land use/land cover changes on ecosystem services in ecologically fragile regions. Sci. Total Environ. 831, 154967. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154967
Fang F. Y., Fang Q., Yu W. Y., Fan C. H., Zi R. Y., Zhao L. S. (2022a). RUSLE model evaluation of the soil and water conservation ratio of the Guizhou Province in China between 2000 and 2019. Sustainability 14, 8219. doi: 10.3390/su14138219
Gomes E., Inácio M., Bogdzevič K., Kalinauskas M., Karnauskaitė D., Pereira P. (2021). Future land-use changes and its impacts on terrestrial ecosystem services: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 781, 146716. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146716
Guo W., Teng Y., Li J., Yan Y., Zhao C., Li Y., et al. (2024). A new assessment framework to forecast land use and carbon storage under different SSP-RCP scenarios in China. Sci. Total Environ. 912, 169088. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169088
Han H. Q., Yang G. B., Zhang Y. J. (2021). Changes in freshwater ecosystem services from 1960 to 2017 under climate change in Guizhou, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 19, 171–189. doi: 10.15666/aeer/1901_171189
Han H. Q., Yin C. Y., Zhang C. Q., Gao H. J., Bai Y. M. (2019). Response of trade-offs and synergies between ecosystem services and land use change in the Karst area. Trop. Ecol. 60, 230–237. doi: 10.1007/s42965-019-00026-z
Hasan S. S., Zhen L., Miah M. G., Ahamed T., Samie A. (2020). Impact of land use change on ecosystem services: A review. Environ. Dev. 34, 100527. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2020.100527
Hong Y., Ding Q., Zhou T., Kong L., Wang M., Zhang J., et al. (2020b). Ecosystem service bundle index construction, spatiotemporal dynamic display, and driving force analysis. Ecosystem Health Sustainability 6, 1843972. doi: 10.1080/20964129.2020.1843972
Hong L., Huang Y., Peng S. (2020a). Monitoring the trends of water-erosion desertification on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China from 1989 to 2016 using time-series Landsat images. PloS One 15, e0227498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227498
Hu X., Hou Y., Li D., Hua T., Marchi M., Paola Forero Urrego J., et al. (2023). Changes in multiple ecosystem services and their influencing factors in Nordic countries. Ecol. Indic. 146, 109847. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109847
Hu C., Wang Z., Li J., Liu H., Sun D. (2022). Quantifying the temporal and spatial patterns of ecosystem services and exploring the spatial differentiation of driving factors: a case study of Sichuan Basin, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.927818
Huang X., Liu J., Peng S. Y., Huang B. M. (2023a). The impact of multi-scenario land use change on the water conservation in central Yunnan urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 147, 109922. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109922
Huang X., Wang L. (2023). Spatial heterogeneity and factors influencing ecosystem services in the yimeng mountainous area. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 32, 2637–2655. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/161329
Huang Y., Xie F. T., Song Z. J., Zhu S. B. (2023b). Evolution and multi-scenario prediction of land use and carbon storage in Jiangxi Province. Forests 14, 1933. doi: 10.3390/f14101933
Jaligot R., Chenal J., Bosch M. (2019). Assessing spatial temporal patterns of ecosystem services in Switzerland. Landscape Ecol. 34, 1379–1394. doi: 10.1007/s10980-019-00850-7
Jia G. L., Dong Y. L., Zhang S. Y., He X. Y., Zheng H. F., Guo Y. J., et al. (2022). Spatiotemporal changes of ecosystem service trade-offs under the influence of forest conservation project in Northeast China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.978145
Jiang L., Wang Z., Zuo Q., Du H. (2023). Simulating the impact of land use change on ecosystem services in agricultural production areas with multiple scenarios considering ecosystem service richness. J. Cleaner Production 397, 136485. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136485
Jiayu C., Jiefu X., Kang G., Yiwu W. (2024). Balancing urban expansion with ecological integrity: An ESP framework for rapidly urbanizing small and medium-sized cities, with insights from Suizhou, China. Ecol. Inf. 80, 102508. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2024.102508
Jinghao L., Shujun L., Zhijie W. (2024). Multi-scenario simulation of spatiotemporal changes of land use pattern and ecosystem services in yunnan-guizhou plateau based on FLUS and inVEST models. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 31, 287–298. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2024.03.004
Karimi J. D., Corstanje R., Harris J. A. (2021). Bundling ecosystem services at a high resolution in the UK: trade-offs and synergies in urban landscapes. Landscape Ecol. 36, 1817–1835. doi: 10.1007/s10980-021-01252-4
King A. P., Eckersley R. J. (2019). “Chapter 2 - descriptive statistics II: bivariate and multivariate statistics,” in Statistics for Biomedical Engineers and Scientists. Eds. King A. P., Eckersley R. J. (Academic Press), 23–56.
Kulaixi Z., Chen Y. N., Li Y. P., Wang C. (2023). Dynamic evolution and scenario simulation of ecosystem services under the impact of land-use change in an arid inland river Basin in Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 15, 2476. doi: 10.3390/rs15092476
Kumar S., Meena R., Tiwari A. K., Singh R., Patel S. K., Singh G. S. (2023). Perceptions of impacts and management of invasive alien plants: a case study from Mirzapur, India. Front. Forests Global Change 6. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2023.1194076
Li Y., Li J. L., Chu J. L. (2022c). Research on land-use evolution and ecosystem services value response in mountainous counties based on the SD-PLUS model. Ecol. Evol. 12, e9431. doi: 10.1002/ece3.9431
Li Q., Li W., Wang S., Wang J. (2022b). Assessing heterogeneity of trade-offs/synergies and values among ecosystem services in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 140, 109026. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109026
Li Y., Qi S., Li J. J. (2022d). Assessment of the impacts of soil and water conservation measures on basin hydrology within a small karst basin Guizhou Province China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 31, 1289–1307.
Li J. H., Xie B. G., Gao C., Zhou K. C., Liu C. C., Zhao W., et al. (2022a). Impacts of natural and human factors on water-related ecosystem services in the Dongting Lake Basin. J. Cleaner Production 370, 133400. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133400
Liang G., Fang F., Lin Y., Zhang Z. (2024). Spatiotemporal characteristics of typical ecosystem services and their spatial responses to driving factors in ecologically fragile areas in upper yellow river, China. Chin. Geographical Sci. 34, 674–688. doi: 10.1007/s11769-024-1445-6
Liang X., Guan Q., Clarke K. C., Liu S., Wang B., Yao Y. (2021). Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Computers Environ. Urban Syst. 85, 101569. doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2020.101569
Liang M., Han T., Ma J., Li R., Yang Y., Qiu X., et al. (2023). Response of temperate forest ecosystem services to rainfall: A case study in the forest nature reserves of northern China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2023.1132396
Lin T., Wu D. F., Yang M. Z., Ma P. F., Liu Y. Y., Liu F., et al. (2022). Evolution and simulation of terrestrial ecosystem carbon storage and sustainability assessment in karst areas: A case study of Guizhou Province. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19, 16219. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192316219
Liu Y., Fu B., Wang S., Rhodes J. R., Li Y., Zhao W., et al. (2023). Global assessment of nature’s contributions to people. Sci. Bull. (Beijing) 68, 424–435. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2023.01.027
Liu L. F., Li J., Wang J. L., Liu F., Cole J., Sha J. M., et al. (2022). The establishment of an eco-environmental evaluation model for southwest China and eastern South Africa based on the DPSIR framework. Ecol. Indic. 145, 109687. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109687
Liu L., Liu Y., Kong L., Zhong Z., Fang X. (2024a). How do changes in ecosystem services multifunctionality influence human wellbeing? Evidence from the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration in China. Land Degradation Dev. 35, 5224–5236. doi: 10.1002/ldr.5292
Liu Q., Qiao J., Li M., Huang M. (2024b). Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their drivers at different spatial scales in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 908, 168486. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168486
Mondal I., Naskar P. K., Alsulamy S., Jose F., Hossain S. K. A., Mohammad L., et al. (2024). Habitat quality and degradation change analysis for the Sundarbans mangrove forest using invest habitat quality model and machine learning. Environment Dev. Sustainability, 1–26. doi: 10.1007/s10668-024-05257-2
Morais T. G., Jongen M., Tufik C., Rodrigues N. R., Gama I., Fangueiro D., et al. (2023). Characterization of portuguese sown rainfed grasslands using remote sensing and machine learning. Precis. Agric. 24, 161–186. doi: 10.1007/s11119-022-09937-9
Natekin A., Knoll A. (2013). Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front. Neurorobot 7. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2013.00021
Niu L. N., Shao Q. Q. (2020). Soil conservation service spatiotemporal variability and its driving mechanism on the Guizhou Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 12, 2187. doi: 10.3390/rs12142187
Ogbodo U. S., Liu S., Feng S., Gao H., Pan Z. (2023). Trade-offs and synergies among 17 ecosystem services in Africa: A long-term multi-national analysis. Remote Sens. 15, 3588. doi: 10.3390/rs15143588
Okumus D. E., Terzi F. (2023). Ice floes in urban furnace: Cooling services of cemeteries in regulating the thermal environment of Istanbul’s urban landscape. Urban Climate 49, 101549. doi: 10.1016/j.uclim.2023.101549
Pan J. Y., Wang J. L., Gao F., Liu G. J. (2022). Quantitative estimation and influencing factors of ecosystem soil conservation in Shangri-La, China. Geocarto Int. 37, 14828–14842. doi: 10.1080/10106049.2022.2091160
Pashanejad E., Kharrazi A., Araujo-Gutierrez Z. M. F., Robinson B. E., Fath B. D., Parrott L. (2024). A functional connectivity approach for exploring interactions of multiple ecosystem services in the context of agricultural landscapes in the Canadian prairies. Ecosystem Serv. 68, 101639. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2024.101639
Pei X., Zhao X., Liu J., Liu W., Zhang H., Jiao J. (2024). Habitat degradation changes and disturbance factors in the Tibetan plateau in the 21st century. Environ. Res. 260, 119616. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119616
Peng K., Jiang W., Ling Z., Hou P., Deng Y. (2021). Evaluating the potential impacts of land use changes on ecosystem service value under multiple scenarios in support of SDG reporting: A case study of the Wuhan urban agglomeration. J. Cleaner Production 307, 127321. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127321
Petsch D. K., de Mello Cionek V., Thomaz S. M., dos Santos N. C. L. (2023). Ecosystem services provided by river-floodplain ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 850, 2563–2584. doi: 10.1007/s10750-022-04916-7
Qiao X., Li Z., Lin J., Wang H., Zheng S., Yang S. (2024). Assessing current and future soil erosion under changing land use based on InVEST and FLUS models in the Yihe River Basin, North China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 12, 298–312. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2023.07.001
Ran C., Wang S. J., Bai X. Y., Tan Q., Zhao C. W., Luo X. L., et al. (2020). Trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services in Southwestern China. Environ. Eng. Sci. 37, 669–678. doi: 10.1089/ees.2019.0499
Sannigrahi S., Chakraborti S., Joshi P. K., Keesstra S., Sen S., Paul S. K., et al. (2019). Ecosystem service value assessment of a natural reserve region for strengthening protection and conservation. J. Environ. Manage. 244, 208–227. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.095
Schirpke U., Tasser E., Borsky S., Braun M., Eitzinger J., Gaube V., et al. (2023). Past and future impacts of land-use changes on ecosystem services in Austria. J. Environ. Manage. 345, 118728. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118728
Shen J., Li S., Liu L., Liang Z., Wang Y., Wang H., et al. (2021). Uncovering the relationships between ecosystem services and social-ecological drivers at different spatial scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Cleaner Production 290, 125193. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125193
Shi Z., Xiang F., Guo Y. (2023). Ecological risk of geohazards and its combination patterns: A case study of an ecologically fragile region, NW China. Ecol. Inf. 77, 102153. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2023.102153
Shijin W., Xiaoqing P. (2023). Permafrost degradation services for Arctic greening. CATENA 229, 107209. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2023.107209
Simeon M., Wana D., Woldu Z. (2024). Spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem services in response to climate variability in Maze National Park and its environs, southwestern Ethiopia. PloS One 19, e0307931. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307931
Tian L., Tao Y., Fu W., Li T., Ren F., Li M. (2022). Dynamic simulation of land use/cover change and assessment of forest ecosystem carbon storage under climate change scenarios in Guangdong Province, China. Remote Sens. 14, 2330. doi: 10.3390/rs14102330
Tian Y., Zhang Q., Tao J., Zhang Y., Lin J., Bai X. (2024). Use of interpretable machine learning for understanding ecosystem service trade-offs and their driving mechanisms in karst peak-cluster depression basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 166, 112474. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112474
Wang S., Fei T., Li W., Zhang A., Guo H., Du Y. (2022b). Incorporation of intra-city human mobility into urban growth simulation: A case study in Beijing. J. Geographical Sci. 32, 892–912. doi: 10.1007/s11442-022-1977-6
Wang Z., Lechner A. M., Yang Y., Baumgartl T., Wu J. (2020). Mapping the cumulative impacts of long-term mining disturbance and progressive rehabilitation on ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 717, 137214. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137214
Wang R., Zhao J., Chen G., Lin Y., Yang A., Cheng J. (2023). Coupling PLUS–InVEST model for ecosystem service research in Yunnan Province, China. Sustainability 15, 271. doi: 10.3390/su15010271
Wang R., Zhao J., Lin Y., Chen G., Cao Q., Feng Y. (2022a). Land change simulation and forest carbon storage of central Yunnan urban agglomeration, China based on SSP-RCP scenarios. Forests 13, 2030. doi: 10.3390/f13122030
Wu L., Sun C., Fan F. (2022). Multi-criteria framework for identifying the trade-offs and synergies relationship of ecosystem services based on ecosystem services bundles. Ecol. Indic. 144, 109453. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109453
Wu Q., Wang L., Wang T. Y., Ruan Z. Y., Du P. (2024). Spatial-temporal evolution analysis of multi-scenario land use and carbon storage based on PLUS-InVEST model: A case study in Dalian, China. Ecol. Indic. 166, 112448. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112448
Xia H., Yuan S., Prishchepov A. V. (2023). Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resources Conserv. Recycling 189, 106767. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106767
Xie L., Wang H., Liu S. (2022). The ecosystem service values simulation and driving force analysis based on land use/land cover: A case study in inland rivers in arid areas of the Aksu River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 138, 108828. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108828
Xie B., Zhang M. M. (2023). Spatio-temporal evolution and driving forces of habitat quality in Guizhou Province. Sci. Rep. 13, 6908. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33903-8
Xu L., Liu X., Tong D., Liu Z., Yin L., Zheng W. (2022a). Forecasting urban land use change based on cellular automata and the PLUS model. Land 11, 652. doi: 10.3390/land11050652
Xu J., Wang S., Xiao Y., Xie G., Wang Y., Zhang C., et al. (2021). Mapping the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service relationships and bundles in Ningxia, China. J. Cleaner Production 294, 126216. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126216
Xu X., Yu J., Wang F. (2022b). Analysis of ecosystem service drivers based on interpretive machine learning: a case study of Zhejiang Province, China. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 29, 64060–64076. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20311-0
Yang B., Xue D. Q., Miao P. P. (2024a). Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of ecosystem supply and demand bundles: A case study in the sichuan-yunnan ecological buffer area, China. Sustainability 16, 4977. doi: 10.3390/su16124977
Yang Y., Yuan X., An J., Su Q., Chen B. (2024b). Drivers of ecosystem services and their trade-offs and synergies in different land use policy zones of Shaanxi Province, China. J. Cleaner Production 452, 142077. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142077
Yuan L., Yue K. Q., Gu Z. K., Chen H., Chi Y. K. (2021). Analysis of rainfall factors and soil erosion in different soil and water conservation measures in the karst plateau-mountain. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 30, 5343–5349. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/135824
Zeng J., Xu J., Li W., Dai X., Zhou J., Shan Y., et al. (2022). Evaluating trade-off and synergies of ecosystem services values of a representative resources-based urban ecosystem: A coupled modeling framework applied to Panzhihua City, China. Remote Sens. 14, 5282. doi: 10.3390/rs14205282
Zhang J., Guo W., Cheng C., Tang Z., Qi L. (2022a). Trade-offs and driving factors of multiple ecosystem services and bundles under spatiotemporal changes in the Danjiangkou Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 144, 109550. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109550
Zhang M., Huang X., Chuai X., Yang H., Lai L., Tan J. (2015). Impact of land use type conversion on carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems of China: A spatial-temporal perspective. Sci. Rep. 5, 10233. doi: 10.1038/srep10233
Zhang H., Sun J., Deng W., Peng L. (2020). Ecosystem health: assessment framework, spatial evolution, and regional optimization in Southwest China. Chin. Geographical Sci. 30, 142–156. doi: 10.1007/s11769-020-1101-8
Zhang Z., Wan H., Peng S., Huang L. (2023). Differentiated factors drive the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services in Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 11, 108573. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2023.1168313
Zhang T., Zhang S., Cao Q., Wang H., Li Y. (2022b). The spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem services bundles and the social-economic-ecological drivers in the Yellow River Delta region. Ecol. Indic. 135. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108573
Zhao T., Pan J. (2022). Ecosystem service trade-offs and spatial non-stationary responses to influencing factors in the Loess hilly-gully region: Lanzhou City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 846, 157422. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157422
Zhou B., Chen G. P., Yu H. R., Zhao J. S., Yin Y. (2024). Revealing the nonlinear impact of human activities and climate change on ecosystem services in the karst region of Southeastern Yunnan using the XGBoost-SHAP model. Forests 15, 1420. doi: 10.3390/f15081420
Keywords: ecosystem services, scenario analysis, ecological protection, machine learning, Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, land use
Citation: Li Y, Peng Y-L, Peng H-N and Cheng W-Y (2025) Assessment and multi-scenario prediction of ecosystem services in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau based on machine learning and the PLUS model. Front. Ecol. Evol. 13:1539547. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2025.1539547
Received: 04 December 2024; Accepted: 28 January 2025;
Published: 18 February 2025.
Edited by:
Athanasios Kallimanis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceReviewed by:
Aliya Baidourela, Xinjiang Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Peng, Peng and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yu-Ling Peng, eXVsaW5ncGVuZ3dpdEAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.