
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Ecol. Evol. , 17 March 2025
Sec. Conservation and Restoration Ecology
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2025.1526584
This article is part of the Research Topic Diagnostic Tools and Research Applications to Combat Wildlife Trade Issues View all 4 articles
Introduction: This study was undertaken to explore the applicability of portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF) technology in combating the illegal wildlife trade, specifically focusing on Australia’s Tiliqua species. The research aimed to develop models that could effectively identify species, distinguish between captive-bred and wild individuals, and predict geographic provenance. The hypothesis was that pXRF could achieve high accuracy in species identification and classifications, thereby providing a useful tool for wildlife enforcement efforts.
Methods: The study was conducted using pXRF technology to analyze a range of Tiliqua specimens, including shingleback (T. rugosa) and common blue-tongue (T. scinoides) lizards. Specimens were collected and analyzed in various states—live, dead, and as animal parts. Species specific XGBoost models were developed and tested for accuracy in identifying species and distinguishing between captive and wild individuals. Geographic provenance models were also created, utilizing predictor variables such as soil nutrient groups and hydrological basins to evaluate model performance.
Results: The study found that species-specific models could identify shingleback and common blue-tongue lizards with an accuracy of 70%. Additionally, the models distinguished captive-bred from wild individuals with up to 81% accuracy for blue-tongue lizards and 83% for shinglebacks. Geographic provenance models demonstrated variable performance, achieving up to 83% accuracy but indicating the need for further refinement and more intensive sampling to improve model resolution.
Discussion: The results imply that pXRF technology has significant potential as a tool for wildlife enforcement, providing valuable information for species identification and the classification of individuals as captive or wild. This finding is consistent with prior research highlighting the utility of elemental profiling in wildlife conservation. The study also identifies a critical knowledge gap regarding the impact of captivity duration on elemental profiles, suggesting that future research should focus on refining geographic models and understanding the dynamics of elemental changes over time in captive versus wild specimens. Overall, the integration of pXRF into wildlife enforcement protocols represents a cost-effective and rapid approach to combatting illegal wildlife trade.
The illegal wildlife trade (IWT) poses a significant threat to wildlife globally, contributing to biodiversity loss (Fernandes-Ferreira et al., 2011; Bush et al., 2014), spread of disease (Karesh et al., 2005; Bezerra-Santos et al., 2021), movement of animals beyond their natural ranges (García-Díaz et al., 2016), and extinction (Mandimbihasina et al., 2018). The IWT includes the sale of plants and animals, and their parts for a range of markets including traditional foods and medicines (Lee et al., 2020), textiles (Tapper and Reynolds, 1996), and pets (Siriwat and Nijman, 2018). The IWT is amongst the largest criminal activities in the world, valued at up to USD 20 billion per year in illegal wildlife products (Tow et al., 2021; INTERPOL, 2023).
The selling of animals for pets is one component of the IWT that involves live animals as opposed to animal products, e.g. furs, horns, medicines. The illegal live animal trade includes a range of associated concerns, including significant animal welfare issues (Baker et al., 2013), challenges in rehoming and post-seizure care (Bernstein and Wolf, 2005), accurate species identification (Tlusty et al., 2023) and opportunities for repatriation (Destro et al., 2019).
Knowing where an animal has come from, its geographic provenance, has been identified as one of three key dimensions of the IWT (Roberts and Hinsley, 2020). When a species has a high level of endemism, particularly at the national level, knowledge of geographic provenance allows for the appropriate application of legislation that governs the wild populations (Roberts and Hinsley, 2020). Knowledge of geographic provenance also assists in the repatriation of seized animals (Gaur et al., 2005), directs targeted education and conservation actions (Kahler and Gore, 2012; Farine, 2020), and targeted enforcement (Patel et al., 2015).
The determination of geographic provenance can be achieved using a range of methods including DNA (Ogden and Linacre, 2015; Summerell et al., 2019), species identification for highly endemic species, stable isotopes (Hobson, 1999; Brandis et al., 2018), and x-ray fluorescence (Buddhachat et al., 2016b; Brandis et al., 2023). Previous geographic provenance research used keratin tissue samples, e.g., quills, feathers, scales, and scutes, to demonstrate that elemental data (e.g., Fe. Pb, Ca, Mg, K etc), including stable isotopes (13C and 15N) (Hobson and Wassenaar, 2008) contained in the keratin reflects the geographic location and environment in which the animal grew that tissue (Buddhachat et al., 2016a; Nganvongpanit et al., 2016; Brandis et al., 2021). These findings have significant application to the illegal wildlife trade where animals are frequently taken from the wild and either laundered i.e., presented as captive-bred (Lyons and Natusch, 2011) or traded on the black market (Zimmerman, 2003).
Australia is predominantly an exporter of animals for the IWT (Bezerra-Santos et al., 2021; Toomes et al., 2023). This is driven by the demand for Australian endemic reptiles and birds (Hill et al., 2023; Chekunov et al., 2024) for the exotic pet trade (Alacs and Georges, 2008; Bezerra-Santos et al., 2021; Linacre, 2021), as ~89% of Australian reptiles are found no-where else in the world, making them highly desirable (Chekunov et al., 2024). There is also a large domestic market for wildlife, a study by Toomes et al. (2023) found over 100,000 live animals advertised for sale within a 15-month period (Dec. 2019-March 2020) including both endemic and non-endemic species. In many cases it is challenging to distinguish between legally bred animals and poached wild animals (Brandis et al., 2018). While the captive breeding of many species is legal (under license) (Heinrich et al., 2021), some species are illegally taken from the wild.
This project aimed to develop i) species classification models, ii) captive-wild classification models, and iii) geographic provenance models for the highly traded Tiliqua species, including the shingleback (T. rugosa) and blue-tongue lizards (T. scincoides). These species are highly sought after in the pet trade due to their unique appearances and endemism to Australia. We aimed to provide these models and methods to enforcement agencies allowing them to scientifically judge the provenance of specimens passing through airports and postal systems.
There are eight extant species of the Tiliqua genus. This study focuses on four species common in Australia, T. rugosa, T. scinoides, (including T. scinoides intermedia), T. occipitalis and T. multifasciata. Shingleback (T. rugosa) and blue-tongue lizards (T. scinoides, T. occipitalis, T. multifasicata) are found primarily in Australia (Figure 1) and parts of New Guinea. The shingleback lizard, also known as the two-headed, bob-tailed, and sleepy lizard is endemic to Australia and found across a diverse range of habitat types, including arid and semi-arid regions, woodlands, scrublands, and heathlands. Shingleback lizards are easily recognizable due to their unique appearance. Their bodies are characterized by large, overlapping scales that resemble shingles, providing protection against predators and environmental conditions. Shinglebacks are herbivorous omnivores with a primarily plant-based diet. They consume a variety of vegetation, including fruits, leaves, flowers, and fungi.
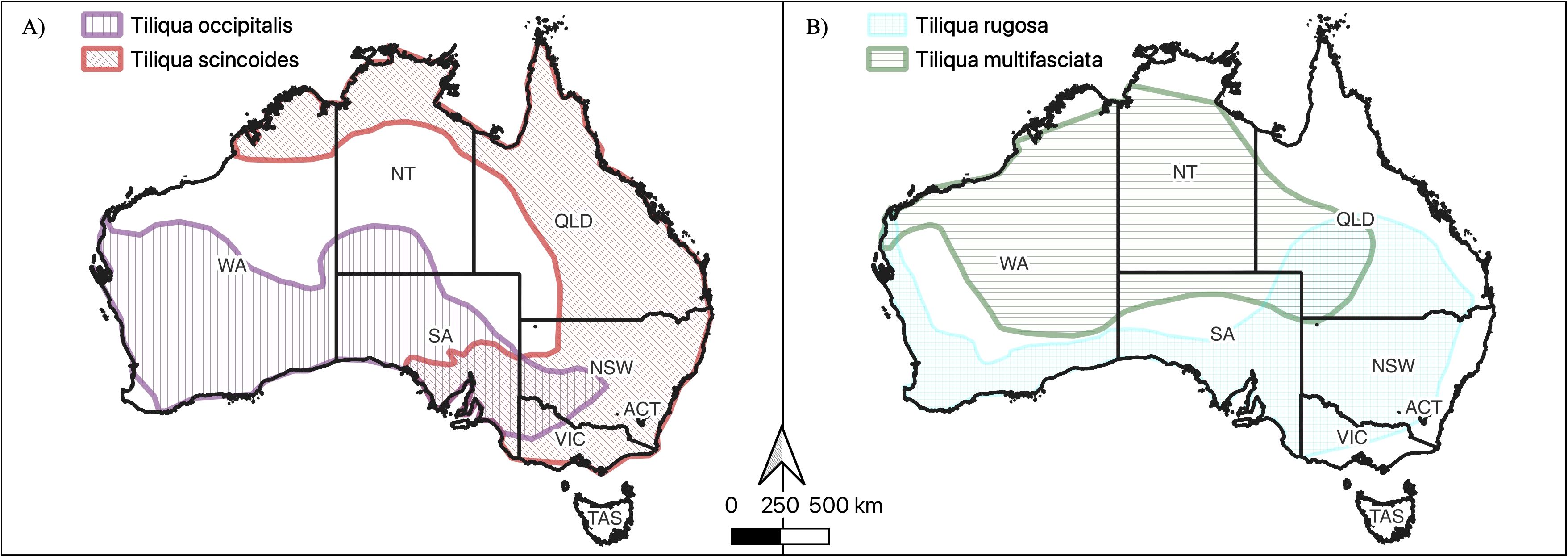
Figure 1. Distribution maps of (A) western blue-tongue (T. occipitalis) and common/Eastern blue-tongue (T. scincoides including the overlapping ranges of T. scincoides scincoides and T. scincoides intermedia), and (B) shingleback (T. rugosa) and Centralian blue-tongue (T. multifasciata). Data source: Atlas of Living Australia.
Shinglebacks form monogamous pairs that can be long lasting (Bull et al., 1998). This aspect of their ecology can make captive breeding challenging as pair bonds need to form prior to reproducing, which may not necessarily occur (Heinrich et al., 2021). Shingleback lizards exhibit relatively low reproductive rates compared to other lizard species. They typically produce only one or two offspring per year (Bull et al., 1998). While not currently listed as endangered, the shingleback lizard faces threats due to habitat loss, road mortality, and the illegal pet trade. They are amongst the most illegally traded reptile species out of Australia. A study by Heinrich et al. (2021) identified 236 illegally traded shingleback lizards seized by authorities from Western Australia between 2011-2019.
Blue-tongue lizards are a large skink (up to 60cm) with a distinctive blue-tongue. There are five Australian species and two sub-species, T. scincoides scincoides, eastern blue-tongued skink, and T. scincoides intermedia, northern blue-tongued skink. Blue-tongue lizard distributions overlap with that of shinglebacks and they are frequently encountered in the same habitats (Figure 1). They are also a target for the illegal pet trade due to their unusual blue-tongues (Mancera et al., 2014). Toomes et al. (2023) reported 1076 T. scinoides listed for sale over a 14-week period in 2019-2020. Unlike the shingleback they have large litters and do not exhibit pair bond behaviors (Shea 1992), making them easier to breed in captivity.
To acquire data that was representative of both captive and wild shinglebacks we sourced animals from a range of geographic locations and organizations. Captive animals were sourced from zoos, wildlife hospitals and private collections, while wild animals were located in the wild at identified shingleback habitat (expert knowledge, (Atlas of Living Australia, ). Animal location was recorded for each individual. Animals with unknown location included animals presented for veterinary care at wildlife hospitals and road-kill specimens contributed by other organizations where origin was not recorded.
Species identification was based on lizard morphology. Shingleback and blue-tongue lizards are very visually distinct and could be confidently identified. Blue-tongue species identification was undertaken by trained reptile experts based on morphology.
Animal condition, hereafter referred to as sample state, was classified into three categories. ‘Natural’, this included alive and recently deceased animals (e.g. roadkill), ‘thawed’, specimens that had been frozen and thawed prior to scanning, and ‘dried’, roadkill specimens that had naturally dried.
An Olympus Vanta M-Series portable x-ray fluorescence (pXRF) device (4-watt X-ray tube with tungsten (W) anode, 8-50keV, silicon drift detector), with three beam energies (10, 40, and 50keV) was used to scan all specimens. The Vanta pXRF provides elemental concentrations as a percentage for 42 elements calculated via Olympus’ on-board algorithm. The Vanta has an on-board CalCheck tool to verify and maintain accuracy, this was used periodically during sampling to ensure the device remained calibrated. Extensive methods testing was undertaken to determine the optimal scanning methods (Brandis et al., 2024).
Lizards were scanned at the base of the tail where it meets the body, just below the back leg hip joints of the lizard (Figure 2a). This scanning location was easy to consistently locate across all individuals and provided a thick cross section of tissue for x-ray attenuation. To ensure all x-rays were attenuated and there was no scanning of surfaces underneath the lizard we placed the lizard on a custom-made scanning stage with a silica cylinder block place under the tail (Figure 2b) (Brandis et al., 2024).
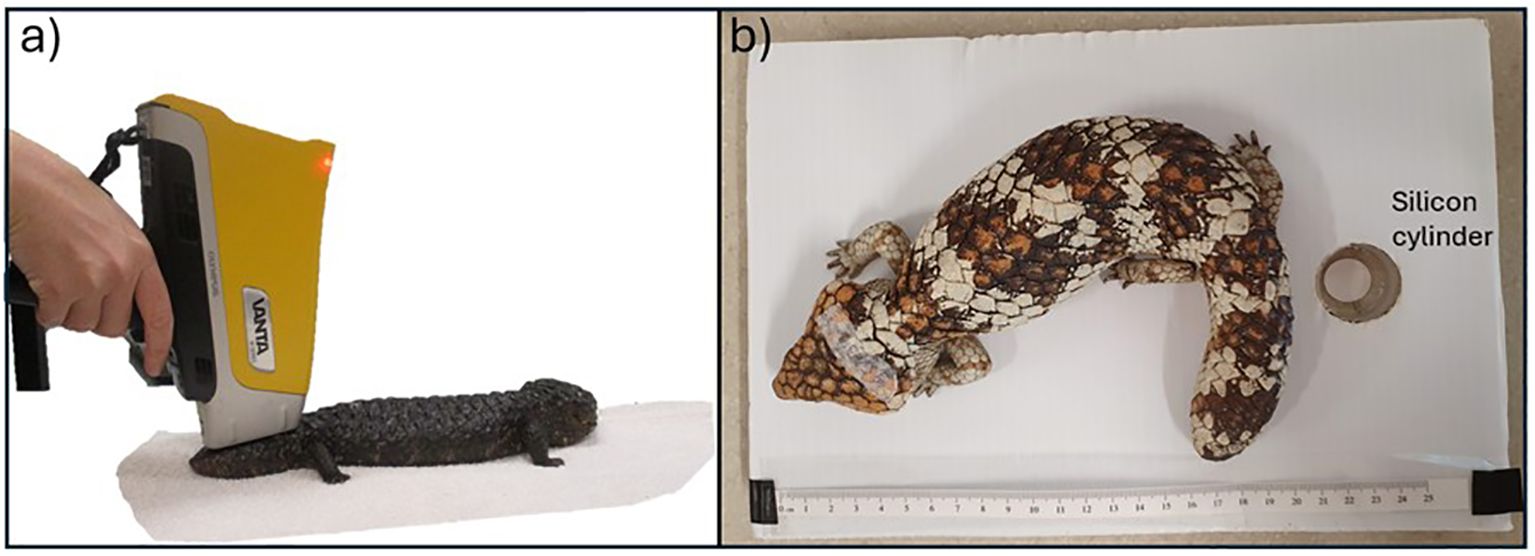

Figure 2. (a) Scanning a shingleback using an Olympus Vanta pXRF, and (a) shingleback lizard on custom made scanning platform with silicon cylinder shown over which the tail is placed prior to scanning.
Scans were conducted for a total duration of 60 seconds, which equates to 20 seconds per energy level beam. This is the minimum scan time for each beam and has been chosen to limit radiation exposure while maximizing data collection. This exposure time falls below accepted radiation exposure limits for small animals and produces less energy than a standard full body x-ray. Importantly, as radiation exposure is cumulative, each live lizard was scanned only once. A short scan time is also necessary as the lizard must be detained and remain still for that time period.
Data from the Vanta were exported as JSON files and processed in R (R Core Team, 2023) using the jsonlite (Ooms et al., 2023) package with relevant beam spectra data processed using the xrftools (Dunnington, 2023) package. Spectra processing included associating known characteristic fluorescence energies for elements to the correct spectra energy range, and baseline measurement and reduction applying a gaussian smoothing filter before shaping into dataframes using the tidyverse (Wickham, 2023) package.
To ensure that elements analyzed were present in the samples we checked for diagnostic peaks in the beam spectra data. We excluded any elements that did not match their Kα1 and Kβ2 peaks (Thomson et al., 2009). This approach allowed us to remove all non-biologically relevant elements. Elements below the limits of detection were not included in analyses.
The beam spectra data were arranged in dataframes, which we used to build predictive models using the XGBoost package (Chen et al., 2021). The tree-based XGBoost classifier has the ability to capture non-linear relationships and to handle collinearity between predictors (Chen and Guestrin, 2016). To minimize risks in overstating model performance as a result of imbalanced classes in the training data (Roberts et al., 2021), where a model can simply learn to always predict the most dominant class, we downsampled to the least represented class of interest. Any factors within that class were randomly represented. For example, when predicting species we downsampled to the minimum number per species, with the individuals kept or dropped to meet the minimum number being randomly selected in the bigger groups. This first model was built to discriminate between common blue-tongue lizards and shingleback lizards. Only these two species were kept in the model as they had the largest sample sizes (Table 1), downsampled to 78 samples each.
To further avoid overstating model performance through a lucky training testing split, 100 train-test splits (80%-20%) were run per modelling task, training a separate model each time and pooling test set model performance metrics. We also partitioned the training data to ensure we had equal numbers of representative samples from each predictive class. This further ensures our final results avoid bias and more accurately reflect a real-world result (Roberts et al., 2021).
Model training for each iteration was halted after model performance on the held-out watchlist dataset stopped improving after 50 rounds in order to reduce model overfitting. Model performance was evaluated using multi-class log-loss functions and the multi-class softmax model objective. All models had a learning rate of 0.3, and max tree depth of 6. Model probabilities for captive or wild were then converted to a prediction by taking the highest assigned probability as the final predicted class. To determine model accuracy, we compared the actual classification against the predicted class for the test set data, and report on the average model accuracy and standard deviation across the 50 model runs. Variable importance was calculated for each train-test iteration and summarized to gauge the most important variables in general. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were produced for each model to evaluate model performance, exploring true positive rates (sensitivity) against the false positive rate (specificity), alongside the Area Under the Curve (AUC) performance metric, where 1 is a perfect model, and 0.5 is no better than random (Robin et al., 2011). We produced these metrics for both binary and multiclass models, using a one-vs-all approach (Robin et al., 2011). To further explore misclassifications in multiclass models, we also generated confusion matrices to examine the patterns of misclassification across different groups.
Using the methods outlined above, we next explored the ability to discriminate between captive and wild lizards.
We built three models to explore the impact different variables had on model performance to predict captive-wild status. Model 1 included all lizard species, Model 2 included an additional predictor variable for species, while Model 3 included variables for sample state and species, where sample state was a categorical variable differentiating between natural samples (i.e. live or freshly dead), thawed samples (dead, frozen and then thawed) and dried samples (roadkill that had been dead a long time).
We also ran two models on shinglebacks only, the first using all samples regardless of sample state, and the second excluding dried samples as we know water content can affect the pXRF reading (Brandis et al., 2024). Finally, we ran a captive-wild prediction model for common blue tongues alone.
Geographic provenance predictive models were built using shingleback and common blue-tongue data (Table 1) (excluding animals with unknown location). To test the spatial resolution at which the geographic provenance models could reliably predict location we tested the models using different geographic units. These were; Australian states (with the Australian Capital Territory and New South Wales combined to increase sample sizes; Figure 1; Appendix 1) to represent jurisdictional and enforcement boundaries; hydrological basin boundaries (Geoscience Australia, 1997) including one model using four river basins and another including three river basins (due to sample sizes; Appendix 1) to constrain the elemental variation in the environment and so should act as an environmental derived grouping; and K-means clustering as a way to find natural groupings in the data. K-means is an algorithm that partitions a dataset based on the similarity of points by iteratively assigning points to the nearest centroids and updating those centroids until convergence. This was performed in QGIS with both five and ten distinct groups (reduced to eight due to sample size) (Appendix 1).
We also explored whether we could predict provenance according to the soil nutrients type, management type, and soil type (Appendix 1) (Australian Government Department of Agriculture, and Fisheries and Forestry, 2022) in three separate models, as we hypothesized that soil nutrients may influence diet and diet characteristics thereby influencing elemental abundances (Underwood, 1977).
In July and August 2023, we scanned 33 lizards that had been intercepted in the postal system by Australian enforcement agencies. To demonstrate and test the applicability of this research we applied our captive-wild models to inform enforcement agents. The predicted captive-wild status was made for each lizard based on the mean of results following 100 model runs. Lizards were classified as captive or wild when the probability mean exceeded the mean ± SD of the alternative classification (Appendix 2).
We sampled a total of 317 lizards from a range of geographic locations (Table 1) and wildlife organizations across Australia. Eighty percent of species sampled were shinglebacks, while 20% were blue-tongues. Thirty percent of shingleback lizards were captive while 70%, were wild, and 57% eastern blue-tongues were captive and 43% were wild.
We excluded 22 elements from our analyses due to their due to absences in their Kα1 and/or Kβ2 peaks. Elements kept were Al, As, Ba, Br, Ca, Cd, Cl, Cu, Fe, Hg, I, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Ni, P, Rb, S, Se, Sn, Sr, Ti, Zn, and Zr.
The state of our samples varied, with the majority being in their natural state n=214, with smaller samples of dried n=58 and thawed n=45 specimens (Table 2).
Species (shingleback and common blue-tongue) predictive models had a mean accuracy of 70.53% (n=156). Key discriminatory elements between species were Cu, P, and As (Appendix 3.1). Model AUC was 0.756, suggesting the model performed moderately well (Appendix 4.1).
All captive-wild models had mean accuracies >80% (Table 3). Including species and sample state as predictors in the models increased accuracy from ~80% to ~83% in the all species models, indicating it was important to include these variables (Table 3).
Separating the species resulted in high accuracy models, predicting between captive and wild blue-tongues at 81.80% accuracy and shinglebacks at 83.49% (including species and samples state as factors) (Table 3). The removal of dried shingleback sample data from the model reduced mean accuracy to ~80% (Table 3).
Key discriminatory elements were relatively consistent between models that included shinglebacks, with Cl and Rb important in all seven models containing shinglebacks. Key discriminatory elements in the blue-tongue models included Rb, P, Mo, S and Z (Table 4; Appendix 3.2). When exploring the confusion matrices for the captive-wild models we consistently saw the highest misclassifications where wild lizards were being classified as captive (Appendix 5.1).
The lowest AUC was for the shingleback only model with no dried samples at 0.864, and the highest was the shingleback model that included all samples at 0.894, meaning all captive- wild models were high performing (Appendix 4.2).
Geographic provenance models were highly dependent on sample size (Table 4). The best model explored the placement of 174 samples across soil nutrient groups, (including species as a factor) with a mean accuracy of ~85%, however the other soil factors we explored did not produce high accuracies, noting these groups had low sample size (n=10) (Table 4). The next best performing model included 3 basins with a mean accuracy of ~77% (n=28). Adding a fourth basin lowered the sample size to 10 per basin resulting in a reduction in mean accuracy to ~52%. The most common misclassifications occurred between the South-West Coast and the South Australian Gulf, despite their physical distance (Appendix 1, Appendix 5.2).
Assigning geographic provenance per state was fairly accurate at 74%, but this is with the ACT included inside NSW. Separating the ACT would result in a very small sample size per state. The most common misclassifications occurred between NSW and SA (Appendix 5), which is unsurprising considering some collected samples were right on the border of these two states (Appendix 1).
Using k-means to find natural groupings in the data achieved an accuracy of ~65% when grouping to 5 groups each of 42 individuals. The most common misclassifications occurred between groups 0 and 2, the eastern NSW cluster and the South Australian cluster (Appendix 1, Appendix 5.2). Increasing to 8 groups greatly decreased the accuracy (and sample size) (Table 4).
Species was repeatedly an important predictor to contain in the models, suggesting there are geographic provenance differences amongst species (Appendix 3.1).
AUC values varied from 0.559 for the soil management groups to 0.886 for the three basin model (Appendix 4.3).
Both shingleback (n=23) and blue-tongue lizards were seized (n=10) as part of confiscations bought into wildlife hospitals by authorities between August and December 2023. Of the 23 shinglebacks, 8 were classified as captive, 6 wild and 9 were undetermined (i.e. the probability mean did not exceed the mean ± SD of the alternative classification of the 100 models runs). Five blue-tongues were classified as captive, 1 wild, and 4 were undetermined (Appendix 2). We could therefore predict the provenance of ~61% of the shinglebacks and 60% of the blue-tongues with confidence.
This project has further demonstrated the applicability of pXRF data to applications that can assist in combating the illegal wildlife trade (Buddhachat et al., 2016b, 2017; Brandis et al., 2018, 2023). We successfully developed a range of species-specific models to assist in combating the illegal trade of Australia’s Tiliqua species.
Species models were able to identify species (shingleback (T. rugosa) and common blue-tongues (T. scinoides)) with reasonable (70%) accuracy. These findings are supported by those of Buddhachat et al. (2016b) who also demonstrated high (94%) species accuracy models for Asian and African elephants. Species models are of particular importance when complete specimens are not available and species identification cannot be done visually. This is relevant to those species which are often traded as animal parts e.g. pangolin scales, or derived products e.g. powders, meat (Xu et al., 2016). With further validation this method may provide an alternative to genetic testing (Mwale et al., 2017).
The downsampling method used in the species models to minimize risks in overstating model performance as a result of imbalanced classes in the training data (Roberts et al., 2021), includes the potential for some data to be discarded. This method may result in data loss from the majority class, in this case shinglebacks. The results presented here are promising, but may be improved with the use of alternative approaches including k-fold cross validation where all observations are used in each iteration of the model (Guo et al., 2019).In addition strategic data collection should seek to reduce data imbalances, thereby reducing the potential for information loss when downsampling. Noting however, the challenges associated with sampling wild, free ranging animals.
We also developed models that were able to accurately distinguish captive bred from wild Tiliqua species. All models performed well (Table 3) with the highest performing models being those that were species specific, blue-tongue models mean accuracy of 82.41% and shingleback models 83.49%. These findings are supported by previous studies developing captive-wild model for short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) (Brandis et al., 2018), Palawan forest turtle (Siebenrockiella leytensis) and Palawan cockatoo (Cacatua haematuropygia) (Brandis et al., 2023). Interpretation of the confusion matrices (Appendix 5.1), show that the highest misclassifications where wild lizards were being classified as captive. The implication of this includes potential underrepresenting of poaching.
Key discriminatory elements, particularly in the shingleback models included chlorine (Cl). Chlorine is an abundant element in the Earth’s crust and commonly associated with salts (Haynes et al., 2014). Wild shingleback habitat and sampling areas corresponded with areas of elevated soil salinity (Ivushkin et al., 2018) providing a possible explanation for the importance of Cl to distinguish between wild and captive animals. However, understanding the drivers of specific elemental abundances in animals, which are derived from its diet are complex and likely influenced by many biotic and abiotic processes (McLeod et al., 2025).
Sample state (dried, thawed, natural) has been shown to impact on the measurements of specific elements within lizards (specifically Ca, Cu, LE, P, Rb, Sr and Zn) (Brandis et al., 2024), however model testing found that inclusion of data from all sample types resulted in marginally increased model performance (Table 3). Inclusion of data from different sample states allows for a an increased sample size and flexible model that can be applied to a range of traded animal products, live, dead, and animal parts e.g. skins (Nijman et al., 2012).
Geographic provenance model results were variable reflecting the predictor variables tested (Table 4). Soil nutrient groups and hydrological basins were included in the highest performing models 85.11% and 77.32% respectively. Models that performed best were those with few classification groups, e.g. the 3-basin model performed better than the 4-basin model, similarly the 2-soil group model performed better than the 15-group model (Table 4). The reason for this is the lack of replicates within each of the groupings used. Development of higher accuracy, finer spatial scale models would require more intensive sampling within each of the identified spatial groups. The ability to do this, and the spatial resolution at which these models could work will be dependent upon the species’ movement ecology i.e. does it move across the landscape, e.g. birds, and the density at which it is distributed. Uncommon and sparsely distributed species would necessitate large scale geographic provenance models due to the ability to collect sufficient data.
Despite the limited geographic scope of this study, it provides additional evidence that these data types i.e. elemental profiles of animal tissues, can be successfully used to identify geographic provenance. This is supported by previous studies have used these data to assign geographic provenance and movement patterns for waterbirds (Brandis et al., 2021), and crocodiles (Markich et al., 2002), geographic provenance for traded Philippine species (Brandis et al., 2023), and seafood provenance (Gopi et al., 2019; Malo et al., 2023). This range of research demonstrates the potential of these methods to be applied more broadly while also acknowledging the data requirements discussed above.
Species targeted by the illegal wildlife trade are often threatened species with inherently reduced populations (Zimmerman, 2003; Willcox et al., 2019) making it challenging to collect data from a sufficient number of individuals to build robust models. For species that have feathers, scales or shells that are removed from the animal, either via natural process e.g. moult, or for trade e.g. pangolin scales, it is possible to use these sample types to obtain the necessary data without having the live animal. Noting that species identification and source would initially need to be confirmed in order to build predictive models. Alternative data sources that may represent the elemental profile of the animal, including environmental surrogates are a new area of research that aims to address this issue.
The application of our methods and models to the seized lizards demonstrated the ability of this method to be part of the evidence gathering procedure and provide additional information to the prosecution process. While it may not necessarily meet the standard of proof by legal definitions, it does for scientific purposes, as shown by results presented here (Loevinger, 1992). It provides additional information for enforcement agencies on which to base decisions and take action. Noting that it is unlikely we can ever confirm the origins of the seized animals to validate our captive-wild classifications (their histories can never be known). We can however use additional information such as the overall health and appearance of the animal (presence of ticks, body condition, deformities caused by malnutrition, and color morphologies not found in the wild) to further support our classifications (Lyons and Natusch, 2015).
While it is impossible to independently validate the source of the seized animals in this test case, factors that impact on the accuracy of the captive-wild determination will include any associated with diet and the incorporation of elements into tissue. These include i) how closely the captive diet resembles that of a wild diet, ii) how diet varies with habitat of wild animals, and iii) underlying environmental differences that are carried through the food web e.g. soil elemental profiles (Hooda, 2010; Tack, 2010). Captive-wild models built on data that incorporates these types of variability for each state (captive or wild) will provide more robust models with greater confidence in classification, however classification accuracy maybe reduced. Independent validation, where possible, should be sought to support the results of these models to increase applicability to law enforcement.
A current critical knowledge gap in this area of research is the length of time taken for a ‘wild’ animal to become ‘captive’ with regards to its elemental profile. For example, if lizards have been taken from the wild and kept in captivity for a period of weeks or months, do they then resemble captive raised lizards? The variables influencing the length of time will depend upon; 1) how well the captive diet resembles a wild diet, and 2) the tissue sampled for any particular species and 3) the turnover rate of keratin for a particular species. Keratin tissues are chemically inert once grown and provide a time capsule of diet (Wassenaar, 2008), while muscle is in constant flux determined by diet. Species with keratin tissues such as feathers, nails, horns, long hair will retain the ‘wild’ profile for longer than other animals. With regards to the seized lizards sampled as part of our study 30 had been kept at wildlife care facilities for between 7 to 28 days post seizure prior to pXRF scanning. Casual analysis of the data shows that all shingleback lizards kept for 28 days classified as captive. While the chance of being classified as wild increased with fewer days between seizure and scanning. However, this does not account for the period of time in which the poacher may have kept the animal prior to trading it.
Addressing the period of time it takes for a ‘wild’ animal to become ‘captive’ with regards to its elemental profile is complex. It is likely to be species specific and will vary between tissue types and growth rate. It may also vary with animal age and active growth periods. However, the most challenging part is the need to repeatedly sample the same individual animal over time to measure change. The impact of repeated x-ray exposure on reptiles of this size is unclear and raises ethical considerations. Other considerations when using the pXRF for studies of biological samples include addressing sample property assumptions including sample state and type, thickness, location of scan on the animal, and duration of scanning (Brandis et al., 2024). These were accounted for in our sampling methods as detailed in the Methods section.
Validation of the results presented in this study will be fundamental for the transfer of methods from research to forensic science (Ogden and Linacre, 2015). Two components of this method that would benefit from independent result validation are species identification and geographic provenance. Both of which are critically important when prosecuting illegal actions requiring a high burden of proof. Further development of species identification models and confidence in the results would benefit from the use of independent species validation, e.g. DNA (Cronin et al., 1991). This is of particular importance for samples that consist of animal parts or derivatives where no visual classification is possible. Similarly, the geographic provenance models could be independently validated using DNA (Ogden and Linacre, 2015) and/or stable isotopes (Vander Zanden et al., 2018).
In conclusion, our study has demonstrated the potential of pXRF technology as a tool to combat the illegal wildlife trade by providing species identification, distinguishing between wild and captive individuals and predicting geographic provenance with high accuracy. The geographic provenance models, while showing variability in performance, offer a promising direction for identifying the origins of illegally traded wildlife, although further refinement and intensive sampling will be necessary for higher resolution applications. The ability of pXRF to contribute to the evidence-gathering process in wildlife crime cases reinforces its value, although there remain unknowns around the influence of time spent in captivity on elemental profiles. Overall, this method is a cost and time effective addition to the fight against the illegal wildlife trade.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The animal study was approved by Animal care and ethics approvals under which this work was done include UNSW 21/46B, Taronga Conservation Society 3d/12/20, Perth Zoo 2022-9, Zoos Victoria ZV22021. NSW Scientific license SL102562, ACT License LT202128, SA Scientific Research License Q27084-2, WA Fauna License FO25000354-2. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
KB: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. DR: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Taronga Conservation Society funded the research.
Taronga Conservation Society Australia, Creature Features, WA Wildlife, Murdoch University, Macquarie University, Sydney Zoo, Mulligans Flat ACT Parks and Conservation Service, Perth Zoo, Zoos Victoria, Kanyana Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre, Flinders University South Australia, Featherdale Wildlife Park.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fevo.2025.1526584/full#supplementary-material
Alacs E., Georges A. (2008). Wildlife across our borders: a review of the illegal trade in Australia. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 40, 147–160. doi: 10.1080/00450610802491382
Atlas of living Australia. Available online at: http://www.ala.org.au (Accessed 21 June 2024).
Australian Government Department of Agriculture, and Fisheries and Forestry (2022). “Australian national map layers” (Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry). Available at: https://www.agriculture.gov.au/abares/aclump/multi-criteria-analysis/Australian-national-map-layers (Accessed September 15, 2024).
Baker S. E., Cain R., van Kesteren F., Zommers Z. A., D’Cruze N., Macdonald D. W. (2013). Rough trade. BioScience 63, 928–938. doi: 10.1525/bio.2013.63.12.6
Bernstein M., Wolf B. M. (2005). Time to feed the evidence: what to do with seized animals. Environ. Law Rep. News Anal. 35, 10679–10689.
Bezerra-Santos M. A., Mendoza-Roldan J. A., Thompson R. C. A., Dantas-Torres F., Otranto D. (2021). Illegal wildlife trade: A gateway to zoonotic infectious diseases. Trends Parasitol. 37, 181–184. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2020.12.005
Brandis K. J., Francis R. J., Zawada K. J. A., Hasselerharm C. D., Ramp D. (2024). Advancing the application of pXRF for animal samples. PloS One 19, e0297830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297830
Brandis K. J., Mazumder D., Gadd P., Ji B., Kingsford R. T., Ramp D. (2021). Using feathers to map continental-scale movements of waterbirds and wetland importance. Conserv. Lett., e12798. doi: 10.1111/conl.12798
Brandis K. J., Meagher P., Schoppe S., Zawada K., Widmann I., Widmann P., et al. (2023). Determining the provenance of traded wildlife in the Philippines. Anim. (Basel) 13, 2165. doi: 10.3390/ani13132165
Brandis K. J., Meagher P. J., Tong L., Shaw M., Mazumder D., Gadd P., et al. (2018). Novel detection of provenance in the illegal wildlife trade using elemental data. Sci. Rep. 8, 15380. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33786-0
Buddhachat K., Brown J. L., Thitaram C., Klinhom S., Nganvongpanit K. (2017). Distinguishing real from fake ivory products by elemental analyses: A Bayesian hybrid classification method. Forensic Sci. Int. 272, 142–149. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.01.016
Buddhachat K., Klinhom S., Siengdee P., Brown J. L., Nomsiri R., Kaewmong P., et al. (2016a). Elemental analysis of bone, teeth, horn and antler in different animal species using non-invasive handheld X-ray fluorescence. PloS One 11, e0155458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155458
Buddhachat K., Thitaram C., Brown J. L., Klinhom S., Bansiddhi P., Penchart K., et al. (2016b). Use of handheld X-ray fluorescence as a non-invasive method to distinguish between Asian and African elephant tusks. Sci. Rep. 6, 24845. doi: 10.1038/srep24845
Bull C. M., Baghurst B. C. (1998). Home range overlap of mothers and their offspring in the sleepy lizard, Tiliqua rugosa. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 42, 357–362.
Bush E. R., Baker S. E., Macdonald D. W. (2014). Global trade in exotic pets 2006-2012. Conserv. Biol. 28, 663–676. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12240
Chekunov S., Stringham O., Toomes A., Prowse T., Cassey P. (2024). Scale of unregulated international trade in Australian reptiles and amphibians. Conserv. Biol. 38, e14355. doi: 10.1111/cobi.14355
Chen T., Guestrin C. (2016). “Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system,” in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery), 785–794. doi: 10.1145/2939672.2939785
Chen T., He T., Benesty M., Khotilovich V., Tang Y., Xxxh. C. (2021). Xgboost: extreme gradient boosting. 1–4, R package version 1.3.2.1 1. Available online at: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/xgboost/vignettes/xgboost.pdf.
Cronin M. A., Palmisciano D. A., Vyse E. R., Cameron D. G. (1991). Mitochondrial DNA in wildlife forensic science: species identification of tissues. Wildlife Soc. Bull. 19, 94–105.
Destro G. F. G., de Fernandes V., de Andrade A. F. A., De Marco P., Terribile L. C. (2019). Back home? Uncertainties for returning seized animals to the source-areas under climate change. Glob Chang Biol. 25, 3242–3253. doi: 10.1111/gcb.14760
Dunnington D. (2023). xrftools: XRF tools for R. Available online at: https://github.com/paleolimbot/xrftools (Accessed February 01, 2024).
Farine D. R. (2020). Mapping illegal wildlife trade networks provides new opportunities for conservation actions. Anim. Conserv. 23, 145–146. doi: 10.1111/acv.12577
Fernandes-Ferreira H., Mendonça S. V., Albano C., Ferreira F. S., Alves R. R. N. (2011). Hunting, use and conservation of birds in Northeast Brazil. Biodiversity Conserv. 21, 221–244. doi: 10.1007/s10531-011-0179-9
García-Díaz P., Ross J. V., Woolnough A. P., Cassey P. (2016). The illegal wildlife trade is a likely source of alien species. Conserv. Lett. 10, 690–698. doi: 10.1111/conl.12301
Gaur A., Reddy A., Annapoorni S., Satyarebala B., Shivaji S. (2005). The origin of Indian Star tortoises (Geochelone elegans) based on nuclear and mitochondrial DNA analysis: A story of rescue and repatriation. Conserv. Genet. 7, 231–240. doi: 10.1007/s10592-005-9002-z
Geoscience Australia (1997). Australia’s river basins 1997 (Australian Government). Available at: https://ecat.ga.gov.au/geonetwork/srv/eng/catalog.search/metadata/42343 (Accessed September 15, 2024).
Gopi K., Mazumder D., Sammut J., Saintilan N. (2019). Determining the provenance and authenticity of seafood: A review of current methodologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 91, 294–304. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.07.010
Guo L., Liu J., Lu R. (2019). Subsampling bias and the best-discrepancy systematic cross validation. Sci. China Mathematics 64, 197–210. doi: 10.1007/s11425-018-9561-0
Haynes W. M. (2014). (Ed.). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 95th ed. CRC Press. doi: 10.1201/b17118
Heinrich S., Toomes A., Shepherd C. R., Stringham O. C., Swan M., Cassey P. (2021). Strengthening protection of endemic wildlife threatened by the international pet trade: The case of the Australian shingleback lizard. Anim. Conserv. 25 (1), 91–100. doi: 10.1111/acv.12721
Hill K. G. W., Stringham O. C., Moncayo S., Toomes A., Tyler J. J., Cassey P., et al. (2023). Who’s a pretty bird? Predicting the traded abundance of bird species in Australian online pet trade. Biol. Invasions 26, 975–988. doi: 10.1007/s10530-023-03221-1
Hobson K. A. (1999). Tracing origins and migration of wildlife using stable isotopes: a review. Oecologia 120, 314–326. doi: 10.1007/s004420050865
Hobson K. A., Wassenaar L. I. (2008). Tracking animal migration with stable isotopes (USA: Elsevier Academic Press).
Hooda P. S. (2010). “Assessing bioavailability of soil trace elements,” in Trace elements in soils. ed. Hooda P. S.. (Blackwell Publishing), 227–265. doi: 10.1002/9781444319477
INTERPOL (2023). Illegal wildlife trade has become one of the ‘world’s largest criminal activities’. Available online at: https://www.interpol.int/News-and-Events/News/2023/Illegal-wildlife-trade-has-become-one-of-the-world-s-largest-criminal-activities (Accessed May 08, 2024).
Ivushkin K., Bartholomeus H., Bregt A. K., Pulatov A., Bui E. N., Wilford J. (2018). Soil salinity assessment through satellite thermography for different irrigated and rainfed crops. Internatl. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinformation 68, 230–237.
Kahler J. S., Gore M. L. (2012). Beyond the cooking pot and pocket book: Factors influencing noncompliance with wildlife poaching rules. Int. J. Comp. Appl. Criminal Justice 36, 103–120. doi: 10.1080/01924036.2012.669913
Karesh W. B., Cook R. A., Bennett E. L., Newcomb J. (2005). Wildlife trade and global disease emergence. Emerging Infect. Dis. 11, 1000–1002. doi: 10.3201/eid1107.050194
Lee T. M., Sigouin A., Pinedo-Vasquez M., Nasi R. (2020). The harvest of tropical wildlife for bushmeat and traditional medicine. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 45, 145–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-102016-060827
Linacre A. (2021). Wildlife crime in Australia. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 5, 487–494. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20200288
Lyons J. A., Natusch D. J. D. (2011). Wildlife laundering through breeding farms: Illegal harvest, population declines and a means of regulating the trade of green pythons (Morelia viridis) from Indonesia. Biol. Conserv. 144, 3073–3081. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2011.10.002
Lyons J., Natusch D. (2015). “Methodologies for differentiating between wild and captive-bred CITES-listed snakes,” in CITES twenty-eighth meeting of the animals committee (Tel Aviv: CITES).
Malo N., Mazumder D., Crawford J., Gadd P., Gopi K., Saintilan N., et al. (2023). Evaluating the application of portable handheld X-ray fluorescence (XRF) scanner for determining seafood provenance: A case study on penaeus monodon. Foods 12, 2874. doi: 10.3390/foods12152874
Mancera K., Murray P., Gao Y., Lisle A., Phillips C. (2014). The effects of simulated transport on the behaviour of eastern blue tongued lizards (Tiliqua scincoides). Animal Welfare 23 (3), 239–249. doi: 10.7120/09627286.23.3.239
Mandimbihasina A. R., Woolaver L. G., Concannon L. E., Milner-Gulland E. J., Lewis R. E., Terry A. M. R., et al. (2018). The illegal pet trade is driving Madagascar’s ploughshare tortoise to extinction. Oryx 54, 188–196. doi: 10.1017/s0030605317001880
Markich S. J., Jeffree R. A., Harch B. D. (2002). Catchment-specific element signatures in estuarine crocodiles žCrocodylus porosus/from the Alligator Rivers Region, northern Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 287, 83–95. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00995-0
McLeod A. M., Leroux S., Little C. L., Massol F., Vander Wal E., Wiersma Y. F., et al. (2025). Quantifying elemental diversity to study landscape ecosystem function. Trends Ecol. Evol. 40, 57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2024.09.007
Mwale M., Dalton D. L., Jansen R., De Bruyn M., Pietersen D., Mokgokong P. S., et al. (2017). Forensic application of DNA barcoding for identification of illegally traded African pangolin scales. Genome 60, 272–284. doi: 10.1139/gen-2016-0144
Nganvongpanit K., Buddhachat K., Klinhom S., Kaewmong P., Thitaram C., Mahakkanukrauh P. (2016). Determining comparative elemental profile using handheld X-ray fluorescence in humans, elephants, dogs, and dolphins: Preliminary study for species identification. Forensic Sci. Int. 263, 101–106. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.03.056
Nijman V., Shepherd C. R., Mumpuni, Sanders K. L. (2012). Over-exploitation and illegal trade of reptiles in Indonesia. Herpetological J. 22.
Ogden R., Linacre A. (2015). Wildlife forensic science: A review of genetic geographic origin assignment. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 18, 152–159. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.02.008
Ooms J., Lang D. T., Hilaiel L. (2023). jsonlite: A simple and robust JSON parser and generator for R. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1403.2805 (Accessed February 01, 2024).
Patel N. G., Rorres C., Joly D. O., Brownstein J. S., Boston R., Levy M. Z., et al. (2015). Quantitative methods of identifying the key nodes in the illegal wildlife trade network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 7948–7953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500862112
R Core Team (2023). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing (Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing). Available at: http://www.R-project.org (Accessed February 01, 2024).
Roberts M., Driggs D., Thorpe M., Gilbey J., Yeung M., Ursprung S., et al. (2021). Common pitfalls and recommendations for using machine learning to detect and prognosticate for COVID-19 using chest radiographs and CT scans. Nat. Mach. Intell. 3, 199–217. doi: 10.1038/s42256-021-00307-0
Roberts D. L., Hinsley A. (2020). The seven forms of challenges in the wildlife trade. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 13, 1–5. doi: 10.1177/1940082920947023
Robin X., Turck N., Hainard A., Tiberti N., Lisacek F., Sanchez J.-C., et al. (2011). pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinf. 12, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-77
Siriwat P., Nijman V. (2018). Illegal pet trade on social media as an emerging impediment to the conservation of Asian otters species. J. Asia-Pacific Biodiversity 11, 469–475. doi: 10.1016/j.japb.2018.09.004
Summerell A. E., Frankham G. J., Gunn P., Johnson R. N. (2019). DNA based method for determining source country of the short beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) in the illegal wildlife trade. Forensic Sci. Int. 295, 46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.11.019
Tack F. M. G. (2010). “Trace elements: general soil chemistry, principles and processes,” in Trace elements in soils. ed. Hooda P. S.. (Blackwell Publishing), 9–37. doi: 10.1002/9781444319477
Tapper S., Reynolds J. (1996). “The wild fur trade: historical and ecological perspectives,” in The exploitation of mammal populations. Eds. Taylor V. J., Dunstone N. (Springer, Dordrecht).
Thomson A., Attwoord D., Gullikson E., Howells M., Kim K.-J., Kirz J., et al. (2009). X-ray data booklet (California: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory).
Tlusty M. F., Cawthorn D.-M., Goodman O. L. B., Rhyne A. L., Roberts D. L. (2023). Real-time automated species level detection of trade document systems to reduce illegal wildlife trade and improve data quality. Biol. Conserv. 281. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2023.110022
Toomes A., Moncayo S., Stringham O. C., Lassaline C., Wood L., Millington M., et al. (2023). A snapshot of online wildlife trade: Australian e-commerce trade of native and non-native pets. Biol. Conserv. 282. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2023.110040
Tow J. H., Symes W. S., Carrasco L. R. (2021). Economic value of illegal wildlife trade entering the USA. PloS One 16, e0258523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258523
Underwood E. J. (1977). Trace elements in human and animal nutrition (New York, USA: Academic Press).
Vander Zanden H. B., Nelson D. M., Wunder M. B., Conkling T. J., Katzner T. (2018). Application of isoscapes to determine geographic origin of terrestrial wildlife for conservation and management. Biol. Conserv. 228, 268–280. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2018.10.019
Wassenaar L. I. (2008). “An introduction to light stable isotopes for use in terrestrial animal migration studies,” in Tracking animal migration with stable isotopes, 1 ed. Eds. Hobson K. A., Wassenaar L. I. (Academic Press, London).
Wickham H. (2023). tidyverse: easily install and load the ‘tidyverse. Available online at: https://tidyverse.tidyverse.org (Accessed February 01, 2024).
Willcox D., Nash H. C., Trageser S., Kim H. J., Hywood L., Connelly E., et al. (2019). Evaluating methods for detecting and monitoring pangolin (Pholidata: Manidae) populations. Global Ecol. Conserv. 17, e00539. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00539
Xu L., Guan J., Lau W., Xiao Y. (2016). “An overview of Pangolin trade in China,” in TRAFFIC briefing paper (Cambridge: TRAFFIC).
Keywords: Australia, shingleback, blue-tongue, pXRF, captive, wild, poaching
Citation: Brandis KJ, Zawada K, Meagher P, Ramp D and Francis R (2025) Development of tiliqua species provenance models for use in combating the illegal wildlife trade. Front. Ecol. Evol. 13:1526584. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2025.1526584
Received: 12 November 2024; Accepted: 27 February 2025;
Published: 17 March 2025.
Edited by:
Astrid Andersson, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Brandis, Zawada, Meagher, Ramp and Francis. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kate J. Brandis, S2F0ZS5CcmFuZGlzQHVuc3cuZWR1LmF1
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.