
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Ecol. Evol., 22 November 2024
Sec. Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2024.1450743
The cotton-melon aphid (Aphis gossypii) is a globally distributed species with highly differentiated populations and various life cycle types. Based on the haplotype classification of the A. gossypii, this study aimed to quantify the effects of latitude, host specialization on transformation of the sexual morph of the A. gossypii. Additionally, symbiotic bacteria potentially involved in the formation of sexual morph were investigated. The results showed that I):The most frequent haplotypes on the 29 host plants were Hap1 (60.42%), Hap17 (13.29%), and Hap4 (7.55%). Haplotypes in cotton fields of 10 geographic populations were predominantly Hap1 and Hap4. II):A. gossypii from the Northwestern inland, the Yellow River basin, and the Yangtze River basin cotton regions all were induced sexual morphs, except for Hap1 from low latitudes. There are also differences in the efficiency of sex aphid induction between haplotypes under the same region/latitude(Jiangsu Yangzhou), which can be corresponded to three life cycle types: holocyclic (Hap1 and Hap4), facultative (Hap17 and Hap1-1), and specialized parthenogenetic (Hap3 and Hap16) life cycle. Interestingly, sexual morphogenesis of A. gossypii with facultative life cycle are more susceptible influenced by the host. Subsequent field surveys in Yangzhou, Jiangsu have also confirmed that the haplotypes capable of sexual morphology transformation under natural rhythm variations are Hap1 and Hap4. It is worth mentioning that these sexual aphids are mainly distributed on some Malvaceae plants, Chinese prickly ash, and pomegranate. However, aphids with specialized parthenogenetic life cycle can complete their entire life history by overwintering on crops or weeds (such as capsella and veronica) in greenhouses or outdoors. III):The relative abundance of Arsenophonus, Pantoea and Enterobacter varied among haplotypes. In particular. the relative abundance of Arsenophonus was generally higher in holocyclic aphids than in anholocyclic aphids in the parthenogenetic morphology. Additionally, Arsenophonus higher in gynoparas and females than in males in the sexual morphology. It can be observed that the aforementioned symbiotic bacteria may play a role in the development of the specialized or reproductive mode of the A. gossypii. The present study contributes to our understanding of the ecological adaptations of the A. gossypii to different climatic conditions and host plants. Moreover, it will furnish a crucial foundation for unravelling the diversification of reproductive modes exhibited by A. gossypii.
Aphis gossypii Glover is a mosaic of sympatric host races (Carletto et al., 2009a) that colonize over 900 plant species (Yan, 1993). The feeding activities of A. gossypii not only cause severe damage but also transmit up to 76 viruses to plants (Zhang et al., 2014), leading to substantial economic losses in global agricultural and forestry production. A. gossypii populations are highly differentiated and have a complex life history, often changing with variations in geography, climate, and host plants (Simon et al., 2002). It is well recognized that A. gossypii has two types of lifecycles, the holocyclic and the unholocyclic forms. The unholocyclic form further includes parthenogenetic, male-producing parthenogenetic and facultative lifecycle (Lambers, 1966). The holocyclic aphid is a typical alternate host aphid species between a woody host (primary host) in winter and a herbaceous host (secondary host) in summer. The holocyclic aphids completes their annual life history usually starting with eggs, going through several phenotypes of fundatrix, fundatrigenia, parthenogenetic females, gynopara, male and sexual female, and then forming new overwintering eggs. In contrast, the unholocyclic aphids reproduce as parthenogenetic aphids throughout the year(Figure 1) (Zhao et al., 1994). The transition between asexual and sexual reproduction has received much attention in current aphid research.
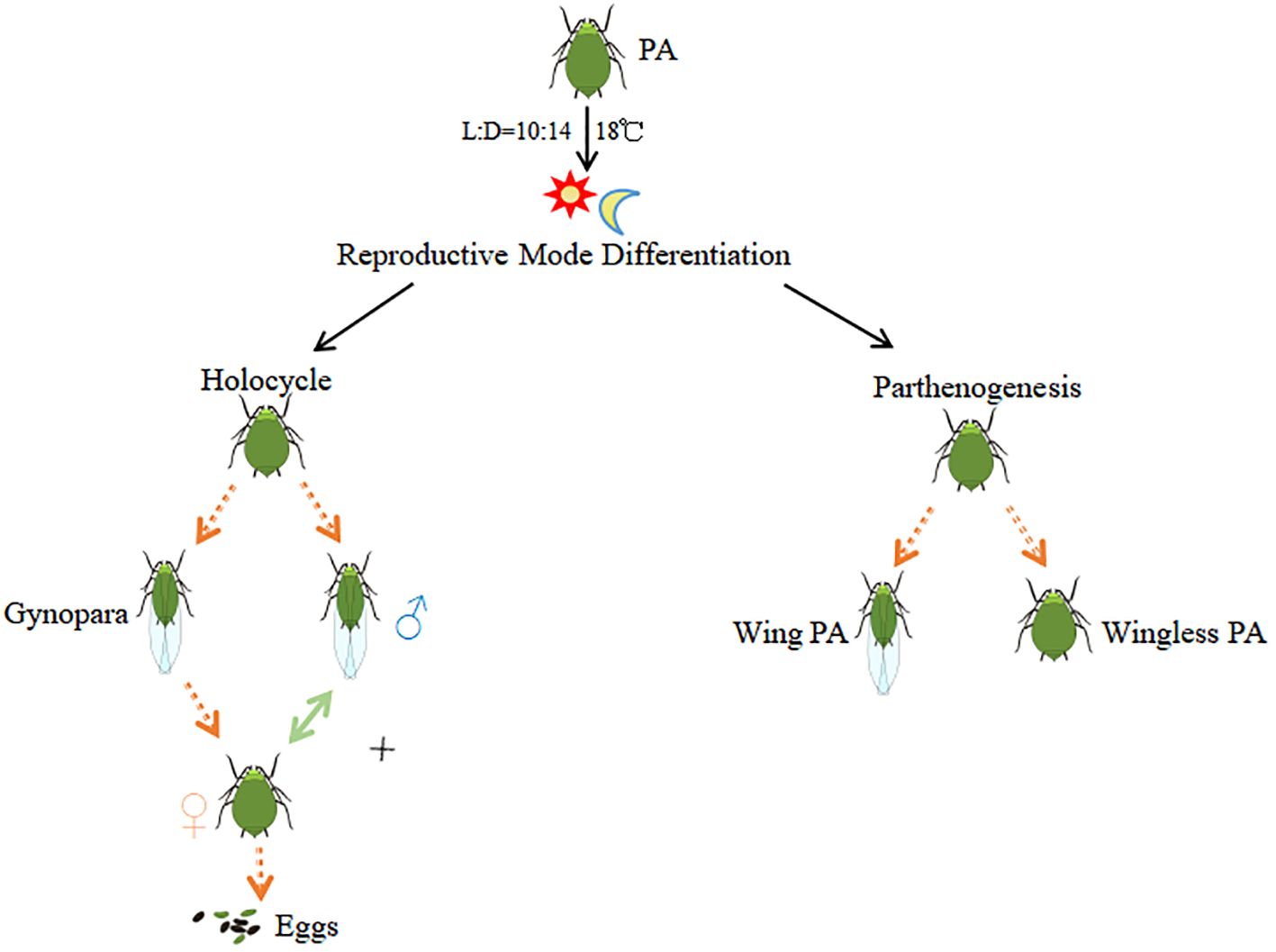
Figure 1. Reproductive mode of Aphis gossypii with different life cycles. PA stands for Parthenogenic Aphids.
It is well known that some parthenogenetic aphids undergo a transformation into sexual aphids during the late fall and early winter months. This change is primarily attributed to a reduction in photoperiod and a decrease in temperature (Gong and Zhang, 2001; Kwon and Kim, 2017; Ji et al., 2023). The photoperiodic signal is conveyed from the brain to the reproductive tract of the aphid, where it modifies the developmental trajectory of future embryos. Instead of undergoing mitotic diploid embryogenesis, the oocyte now proceeds with haploid gametogenesis. The process is completed in 3 successive generations, resulting in the transition from parthenogenesis to sexual reproduction in aphids (Le Trionnaire et al., 2009). Several studies have demonstrated that genes such UGTs (Uridine diphosphate-glycosyltransferases), InR1(insulin receptor 1) and Tret1(trehalose transporter 1) exert significant functions with respect to aphid sexual morphology formation (Ji, 2017; Wang et al., 2024).
The A. gossypii population demonstrate notable host specialization. Host switching bioassays represent the most fundamental biological approach for distinguishing the biotypes of A. gossypii (Guildemond et al., 1994; Liu et al., 2008). Moreover, the rapid advancement of molecular methods, including Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) bands and Microsatellite Loci, are increasingly utilized to distinguish aphid biotypes (Vanlerberghe-Masutti and Chavigny, 1998; Vanlerberghe-Masutti et al., 1999). In recent years, with the wide application of sequencing technology in biotyping, some scholars have found that the mitochondrial cytochrome b (CytB) gene can be used to distinguish between A. gossypii and closely related species (Carletto et al., 2009b; Kim et al., 2011). On the basis of this, a method based on single nucleotide polymorphisms of the complete mitochondrial sequence (CytB and 16S genes) was developed and has since been widely employed for the identification of A. gossypii biotypes in northern China (Wang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2018; Shi, 2022).
Host specialization is an important factor influencing the reproductive mode of aphids. Takada (1988) investigated the response of 58 asexual clones from 13 regions, 14 families, and 21 species of plants in Japan to a low temperature and short photoperiod. The study recorded that 41.38% of the population exhibited a holocyclic life cycle, 36.21% exhibited a specialized parthenogenetic life cycle, and 15.52% exhibited a male-producing parthenogenetic life cycle, with the remaining 6.9% exhibiting a facultative life cycle. Interestingly, 100% of populations fed on the Malvaceae family (Hibiscus spp.) plants exhibited a holocyclic life cycle, whereas 72.73% of populations fed on the Cucurbitaceae family plants exhibited a parthenogenetic life cycle. Shi (2022) reported that the cotton-specialized aphids could sexually reproduce on cotton and cucumber, while cucumber-specialized aphids could only sexually reproduce on cotton. Additionally, Changes in latitude can lead to diversity in the aphid reproductive modes. According to (Liu et al., 2003), populations of A. gossypii in high-latitude regions (Beijing and Xinjiang, China) were able to induce sexual morphs; however, populations from low-latitude regions (Hainan, China, and Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam) were unable to induce sexual morphs. By comparing previous studies, we found that A. gossypii in the Anyang area of the Yellow River basin (Ji et al., 2021) responded more readily to photoperiod and temperature signals than in the Nanjing area of the Yangtze River basin in China (Gong, 2000).
The occurrence of symbiotic bacteria is pervasive among insects, encompassing primary symbionts, secondary symbionts, and facultative symbionts (Bucher, 1965; Bright and Bulgheresi, 2010). Recent findings indicate that symbiotic bacteria may play a significant role in insect host specialization (Tsuchida et al., 2004) and reproduction (Leonardo and Mondor, 2006; Simon et al., 2011; Li et al., 2021; Gnainsky et al., 2021). The transmission of symbiotic bacteria occurs vertically through eggs or embryos. Previous studies have identified several symbiotic bacteria, including Wolbachia, Spiroplasma, and Arsenophonus, which regulate reproductive processes in insect hosts through cytoplasmic incompatibility, parthenogenesis reproduction, and male killing (Poinsot et al., 2003; Engelstädter and Hurst, 2009; Ferree et al., 2008; Goerzen and Erlandson, 2018), thus resulting in altered sex ratios of the progeny or an increased proportion of female progeny. It is noteworthy that the Arsenophonus has also been observed to play a role in the promotion of host specialization in certain aphid species (Wagner et al., 2015). Several studies have demonstrated that the relative abundance of Arsenophonus is significantly higher in cotton-specialization aphids compared to cucumber-specialization aphids (Cao, 2016; Miao, 2018).
Populations of A. gossypii exhibit greater genotypic diversity and broad host range (Charaabi et al., 2008; Carletto et al., 2009a, b; Razmjou et al., 2010; Komazaki et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2018), but the details of the life cycle divergence of the different biotypes and the reasons for its formation remain unclear. In this study, we aim to investigate the role of host, environmental factors and symbiotic bacteria in driving the formation of different reproductive modes in Aphis gossypii. To achieve this goal:
I. Haplotypes that are diverse and representative in terms of geography and host were selected for sex aphid induction under a low temperature and short photoperiod condition.
II. Tracking and correlation analysis of haplotypes and life cycles in the fields.
III. A comparative study on the diversity and abundance of endosymbiotic bacteria was estimated using 16S rDNA sequencing in various phenotypes of six A. gossypii haplotypes.
From April 2021 to January 2023, A. gossypii samples were collected during different seasons from 29 host plants, mainly in the Yangtze River basin of China. Including cotton(Gossypium hirsutum), cucumber(Cucumis sativus), zucchini(Cucurbita pepo), white gourd(Benincasa hispida), loofah(Luffa cylindrica), pumpkin(Cucurbita maxima), citrus(Citrus reticulata), okra(Hibiscus esulentus), eggplant(Solanum melongena), kidney bean(Phaseolus vulgaris), capsella(Capsella bursa-pastoris), chrysanthemum(Dendranthema morifolium), chilli(Capsicum annuum), Chinese trumpet vine(Campsis grandiflora), boxwoods(Buxus sinica), veronica(Veronica persica), cotton rose hibiscus(Hibiscus mutabilis), hibiscus(Hibiscus syriacus), peppermint(Mentra piperita), dandelion(Taraxacum mongolicum), petunias(Ipomoea nil), pomegranate(Punica granatum), rose(Rosa chinensis), Erigeron annuus, evening primrose(Oenothera biennis), sesame(Sesamum indicum), crofton weed(Ageratina adenophora), pittosporum tobira(Pittosporum tobira), Chinese prickly ash(Zanthoxylum bungeanum). To explore the effect of latitude on the reproductive mode of A. gossypii, samples were collected from cotton fields in four cotton regions: the Yellow River basin, Northwestern inland and the Yangtze River basin, and a low latitude region. Only one individual per plant was collected to avoid sampling the offspring of a single female.
Genomic DNA from single individuals was extracted using a TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit following the protocol described by the manufacturer (Tiangen, Beijing, China), and all extracts were stored at -20°C. The mitochondrial Cytb and 16S gene regions were amplified using CytbF and 16SR primers (Wang et al., 2016) with a size of 917bp, and 577bp of the middle site was selected for comparison with the haplotype published by Zhang et al. (2018).The amplified products were sequenced at Shanghai Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China) and Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China).
I. Different geographic A. gossypii (cotton regions from Langfang, Hebei of the Yellow River basin; Korla, Xinjiang of the Northwestern inland; Yangzhou, Jiangsu; Ezhou, Hubei of the Yangtze River basin; Baoshan, Yunnan of low latitudes region) were collected for the sexual reproduction induction.
II. Different haplotypes of A. gossypii (Hap1, Hap3, Hap4, Hap16, Hap17 and Hap 1-1 were collected from cotton, cucumber, cotton, loofah, zucchini and chrysanthemum plants of Jiangsu province) for the sexual reproduction induction.
III. Hap1, Hap4 and Hap17 (collected from cotton, cotton and zucchini) were maintained on cotton, cucumber, and zucchini leaves for over 10 generations for the sexual reproduction induction, respectively.
All the above colonies in acrylic cages in an insect rearing room (26 ± 1°C, L:D=16:8, RH=65% ± 5%, and a light intensity of 12,000 lx). The population density was controlled to 10 aphids per acrylic cage to avoid the production of winged aphids.
Methods of sexual aphid induction refer to previously described by Ji et al. (2019) with slightly modifications. Before inoculating A. gossypii onto the leaves, the plant leaves were placed in petri dishes containing 1% agar. The fresh agar and leave sections were changed to new ones when needed. New-born first-instar aphids (G1) were introduced to host leaves under a short-day (SD) condition (18 ± 1°C, 65 ± 5% relative humidity, 10 L: 14 D photoperiod) for sexual reproduction induction. The progenies (G2) produced by G1 aphids were transferred to a new plant every two days until G1 died. Numbers of G2 Phenotype were recorded under SD conditions. 10 replicates per treatment. Phenotypic identification of gynoparas and males and parthenogenetic aphids by observation combined with dissection under the stereomicroscope.
The study investigated lifecycle types of A. gossypii from different hosts during the sexually reproducing period (November to December) and the winter (January to February) in Yangzhou, Jiangsu, China. Then, these different lifecycle types of A. gossypii individuals were subjected to mitochondrial sequencing for identification of haplotypes.
For Illumina MiSeq DNA sequence analysis, we collected wingless parthenogenetic adults of Hap1, Hap3, Hap4, Hap16, Hap17, and Hap1-1, as well as gynopara, sexual females, and male adults from Hap1 and Hap4 in Jiangsu Province. Each haplotype was reared under 18 ± 1°C, 65 ± 5% relative humidity, 10 L: 14 D photoperiod, excluding Hap1 and Hap4, which parthenogenetic aphids were obtained under 18 ± 1°C, 65 ± 5% relative humidity, 16 L: 8 D photoperiod. All samples were collected in nuclease-free Eppendorf tubes, immediately immersed in liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80°C for further study.
Before DNA extraction, each A. gossypii sample was washed with 70% ethanol and rinsed three times with nuclease-free water. The total DNA was extracted from the samples using the Fast DNA SpinKit for Soil(MP, USA)according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The hypervariable regions V3-V4 of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene were amplified using the primers (F: 5’-CCTAYGGGRBGCASCAG-3’; R: 5’-GGACTACNNGGGTATCTAAT-3’). Thermal cycling consisted of initial denaturation at 98°C for 1 min, followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 98°C for 10 s, annealing at 50°C for 30 s, and elongation at 72°C for 30 s. Finally 72°C for 5 min. The quantity and quality of the DNA were measured using a NanoDrop 2000C spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific). The purified DNA samples were stored at -20°C. Samples with concentrations below 25 ng/µL were excluded from the study. Sequencing libraries were generated usingTruSeq® DNA PCR- Free Sample Preparation Kit(Illumina, USA). At last, the library was sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq platform and 250 bp paired-end reads were generated. The quantification and qualification of PCR products, amplicon generation, PCR product mixing, purification, library preparation, and sequencing were performed on an Illumina MiSeq platform at Beijing Novegene Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
Paired-end reads was assigned to samples based on their unique barcode and truncated by cutting off the barcode and primer sequence. Paired-end reads were merged using FLASH (V1.2.7, http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/FLASH/). Quality filtering on the raw tags were performed under specific filtering conditions to obtain the high-quality clean tags according to the QIIME(V1.9.1, http://qiime.org/scripts/split_libraries_fastq.html) quality controlled process. The tags were compared with the reference database(Silva database (16S), https://www.arb-silva.de/; Unite Database(ITS), https://unite.ut.ee/) using vsearch(https://github.com/torognes/vsearch/) to detect chimera sequences, and then the chimera sequences were removed. Then the Effective Tags finally obtained. The obtained sequences were subjected to bioinformatics analysis, and those with ≥97% similarity were assigned to the same OTUs.
I. Haplotype analysis of A. gossypii: The haplotype sequence alignment was manually done in DNAMan v6.
II. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using Tukey’s test to determine differences in the production of sexual morphs according to different populations under low temperatures and short photoperiods (p < 0.05). All data were statistically analyzed using SPSS 25.0 software, and all graphs were created using GraphPad Prism 9.5 software.
III. Symbiotic bacteria bioinformatics analysis: The sequences of OTUs were annotated using the Mothur method and the SSUrRNA database (Quast et al., 2012) of SILVA138.1 (http://www.arb-silva.de/) (Wang, 2007) to determine their taxonomic classification from phylum to species (Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species). Principal component analysis (PCA) based on Qiime software (Version 1.9.1) was performed to study the α-diversity (Shannon and Simpson diversity indices; Chao1 and ACE estimators). Unifrac distances and UPGMA sample clustering trees were also calculated using Qiime software (Version 1.9.1) to further analyze the community composition of each sample. The Tax4Fun function prediction employs the Nearest Neighbor method, which uses a minimum 16S rRNA sequence similarity for accurate classification.
All sequences were cropped using Contig Express software, and only sequences of length 577 nt were retained. Using DnaSP software, 10 haplotypes were identified among 331 individual A. gossypii sequences. This includes seven reported haplotypes namely Hap1, Hap3, Hap4, Hap7, Hap13, Hap16, Hap17, three unreported haplotypes named Hap1-1, Hap7-1, and Hap17-1. The sequences were aligned clearly, and no insertions or deletions were found. The sequences cover 11 variable sites in the A. gossypii mitochondrial genome sequence fragment.
Results revealed that the dominant haplotype was Hap1, with a total of 200 individuals accounting for 60.42% of the total. The 3 most common host plants of Hap1 are cotton, hibiscus, and pomegranate. Hap17 was the second most frequent haplotype, with 44 individuals, representing 13.29% of the total. The top 3 hosts for Hap17 were chilli, zucchini, and veronica. Additionally, Hap4, Hap3, Hap16, and Hap13 were also detected, with individuals (percentage) of 25 (7.55%), 18 (5.43%), 14 (4.23%), and 16 (4.83%), respectively. The top 3 hosts for Hap 4 were cucumber, cotton, and orka. Interestingly, the percentage of both cotton and cucumber hosts was close in Hap4. The haplotypes of Hap3 showed a high specialization, feeding only on Cucurbitaceae plants or weeds. The top 3 hosts for Hap 3 were cucumber, pumpkin, and zucchini. Hap17-1, Hap1-1, Hap7-1, and Hap7 were relatively less common, with only 6 (1.81%), 5 (1.51%), 2 (0.60%), and 1 (0.30%) individual, respectively (Figure 2).
The haplotypes of A. gossypii from 10 different geographical populations in China were analyzed, resulting in the identification of 3 haplotypes: Hap1, Hap4, and Hap7. Results revealed that the A. gossypii haplotypes were relatively abundant in the cotton fields of Yangzhou, Korla, Wuhan and Ezhou, with more than 2 haplotypes, particularly in Yangzhou, where 3 haplotypes were identified. Only 1 haplotype was found in Langfang, Hefei, Changsha, Nanchang, and Baoshan. Hap1 was the most common in cotton fields in China, followed by the Hap4 (Figure 3).
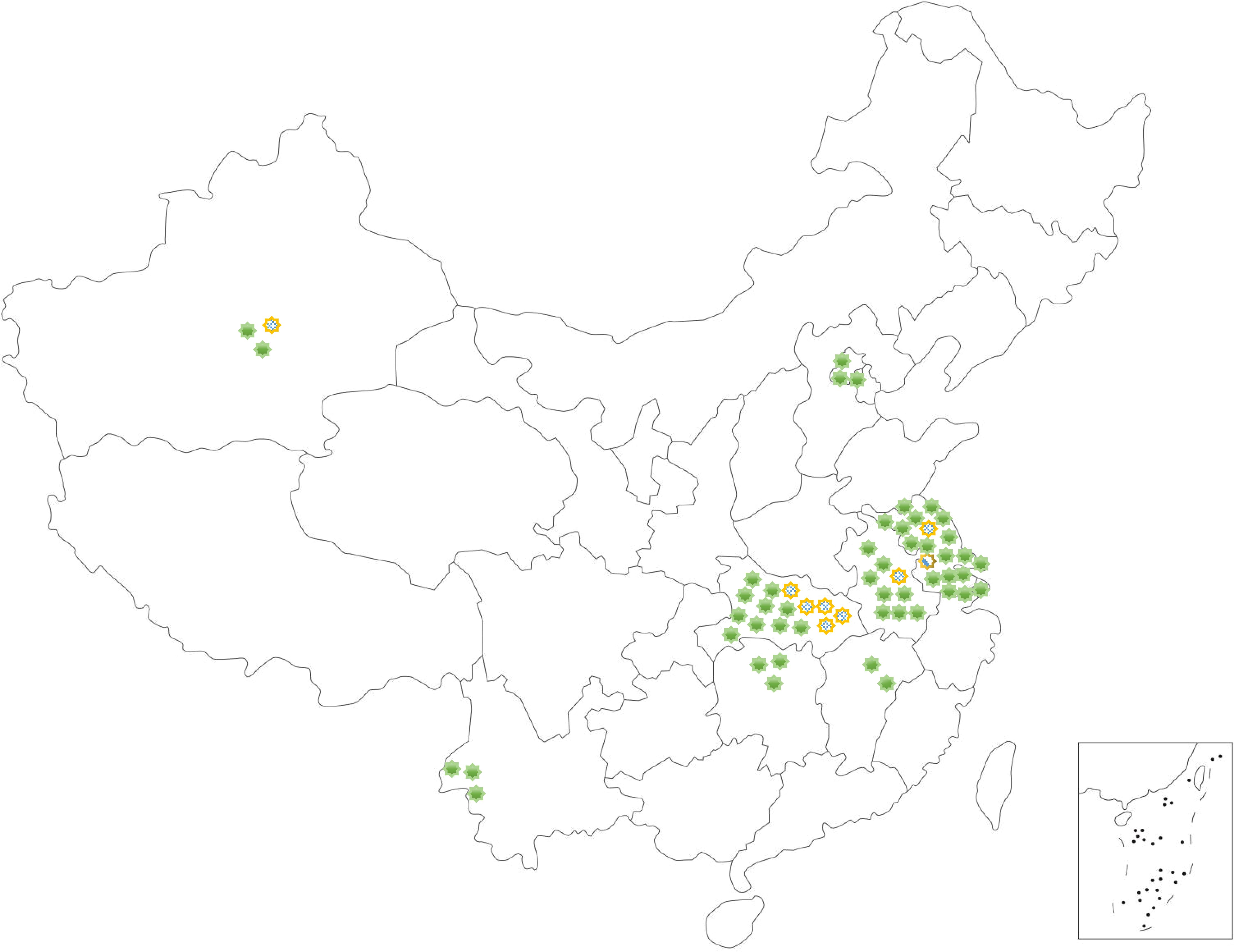
Figure 3. Regional distribution of Aphis gossypii haplotypes in cotton fields. Langfang of Hebei Province (116.3°E, 40.0°N); Korla of Xinjiang Province (85.8°E, 41.8°N); Yangzhou (119.4°E, 32.4°N) of Jiangsu Province; Liuan (116.5°E, 31.6°N) and Hefei of Anhui Province (117.2°E, 31.9°N); Ezhou (114.7°E, 30.4°N) and Wuhan of Hubei Province (114.3°E, 30.5°N), Nanchang of Jiangxi Province (115.8°E, 28.8°N); Changsha of Hunan Province (111.7°E, 29.0°N) and Baoshan of Yunnan Province (99.2°E, 25.1°N) of China in 2021 to 2023 at a total of 10 sites. Green for hap1, flower color for Hap4, slash for Hap7.
The 2021 survey yielded a total of 7 haplotypes in the spring, 4 in the summer, and 4 in the fall. The data revealed that, among the three periods, Hap1 haplotypes were the most prevalent, while Hap1, Hap3, Hap4, and Hap17 haplotypes were identified across all 3 seasons in 2021. The findings from the 2022 survey indicated that the seasons with the highest diversity of haplotypes were still spring and fall. The number of haplotypes observed in the spring, summer, and fall were 5, 3, and 6, respectively. In comparison to the 2021 survey results, the number of Hap17 exhibited a notable increase, while Hap1 demonstrated consistent dominance during the spring and fall seasons (Figure 4).
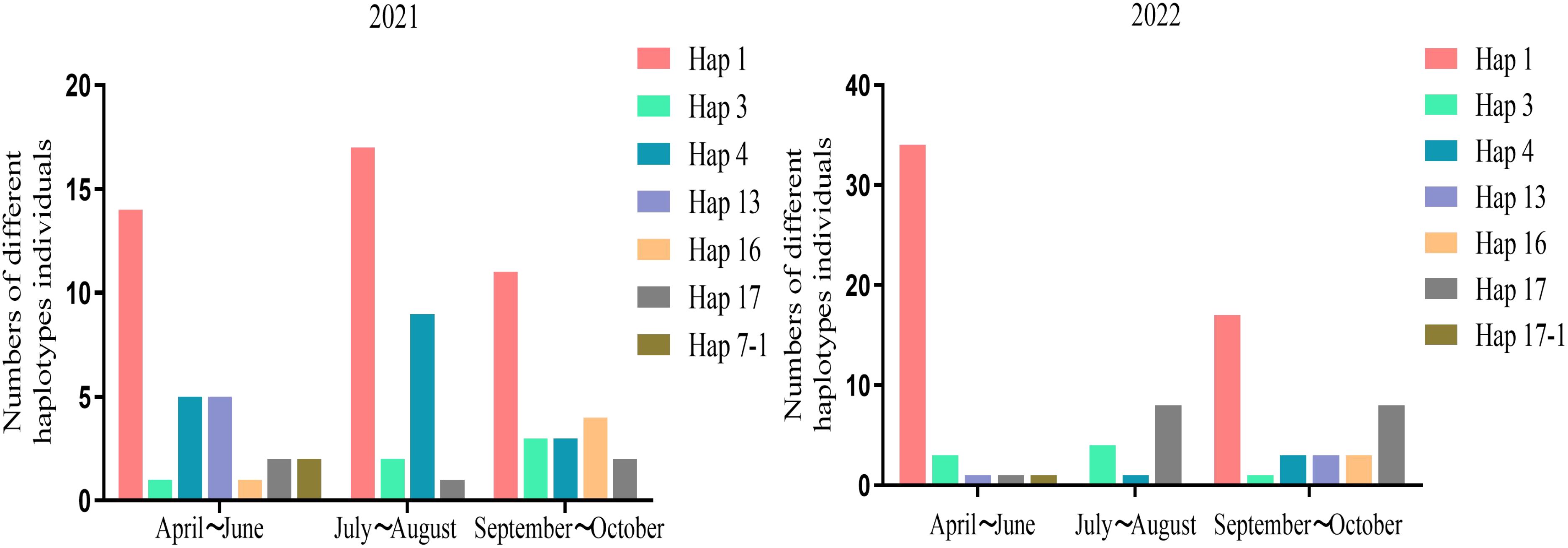
Figure 4. The haplotype distribution of Aphis gossypii populations in different seasons in 2021 and 2022 respectively.
Low temperatures and short photoperiods as key factors to stimulate sexual reproduction in A. gossypii. This stimulation resulted in the production of 3 phenotypes: parthenogenetic aphids, gynopara, and males. A significant effect among different geographic populations was observed. Our results demonstrated that sexual morphs could be induced in all geographic populations except for the Baoshan population (Figure 5C). The highest transition rate of A. gossypii to gynopara morphs was observed in Hap1 and Hap4 of Ezhou, with 73.81% and 72.37% respectively. This was followed by the Langfang Hap1(57.63%), the Korla Hap4 (56.43%), and the Yangzhou Hap1(56.25%) (Table 1). Besides, the Langfang Hap1 had the highest proportion of males, accounting for 25.42%, followed by the Ezhou Hap4 and Hap1, with proportions of 24.23% and 23.89% respectively. The Korla Hap4 and the Yangzhou Hap1 had a low proportion of males, accounting for 14.78% and 13.26% respectively (Table 1). Moreover, only 2.30% and 3.40% of Hap1 and Hap4 of Ezhou maintained parthenogenetic reproduction, while the proportion of parthenogenetic aphids in the Langfang Hap1, Korla Hap4, and Yangzhou Hap1 were 16.95%, 28.80% and 30.48%, respectively (Table 1).
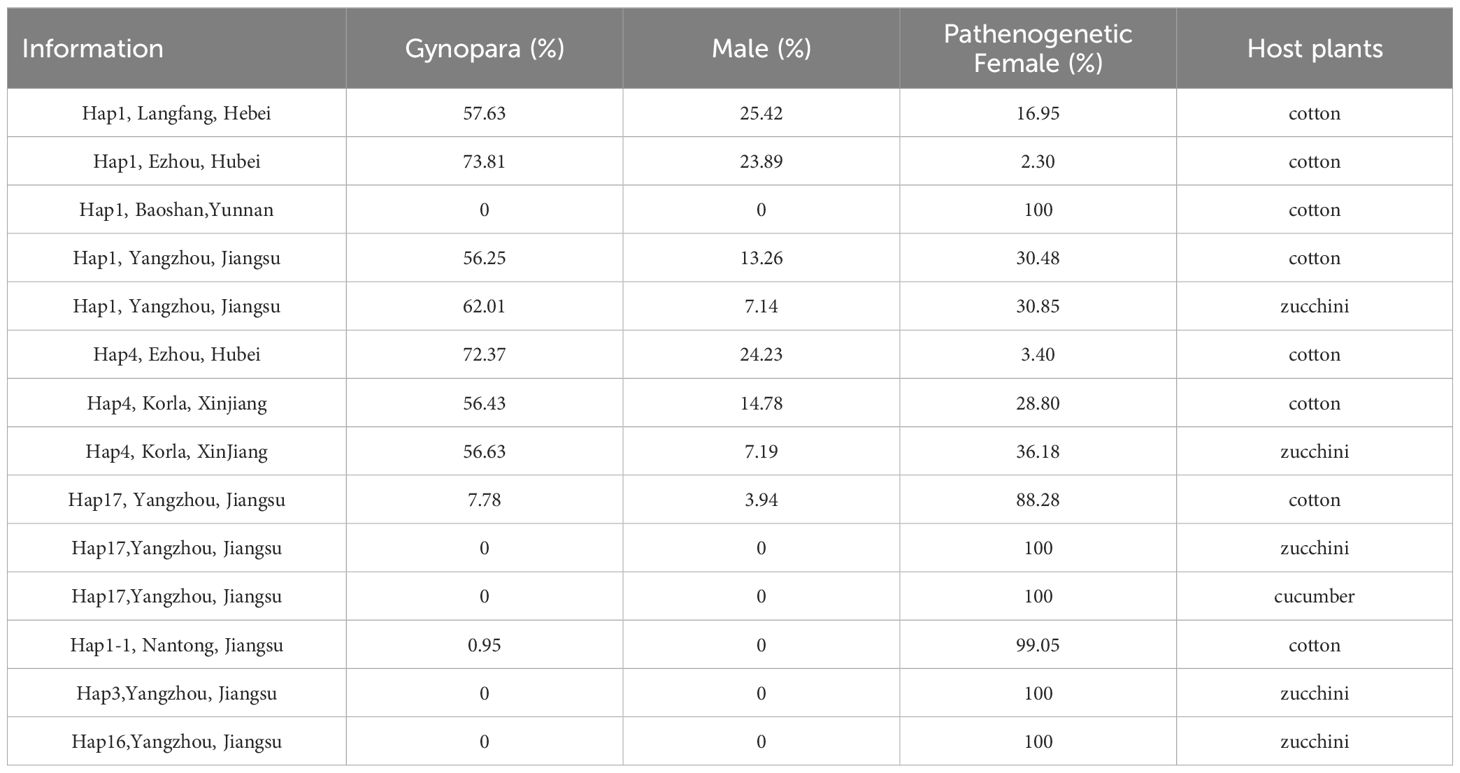
Table 1. Statistics on the proportion of morph produced by G1 generations in different Aphis gossypii populations.
Also, there were a significant difference in the timing of sexual induction among the aphids from various geographical region. Except for the Yangzhou Hap1 population (Figure 5D), where the gynopara morphs appeared later (day 4 of G1 generation offspring), the other populations developed into gynopara morphs at the beginning of G1 offspring (Figures 5A, B, E, F). Besides, the earliest emergence of males was observed in the Hap1 in Langfang (day 8 of G1 generation offspring), followed by the Hap1 in Ezhou (days 10 of G1 generation offspring), the Hap4 in Ezhou and the Hap4 in Korla (day 12 of the G1 generation offspring). The latest emergence of males (days 14 of G1 generation offspring) was observed in the Hap1 population in Yangzhou (Figures 5A, B, D–F).
The transition rate of A. gossypii to sexual morphs varies greatly among different haplotypes. The results indicated that Hap1, 4, 17, and 1-1 (Figures 5B, D, E, H, J) could be transformed into sexual forms under low temperatures and short photoperiod. However, the transition rate of the sexual morph of Hap1 and Hap4 was significantly higher than Hap17, and Hap1-1. Specifically, the gynopara and male morphs of Hap17 appeared later, on the sixth day and 16 of the G1 generation offspring. Only 1.50% of individuals converted to gynopara morphs and 0.83% converted to males. Besides, Hap1-1 sexual morphs appeared extremely late, on the tenth day of G1 generation offspring. The transition rate of gynopara morph of Hap1-1 was only 0.95% and no male transitions were observed (Table 1). Moreover, the offspring of Hap3 and Hap16 did not develop into sexual morphs (Figures 5L, M, Table 1). The detailed comparison of the holocyclic (Hap 1) and parthenogenetic (Hap 3) reproductive phenotypes of A. gossypii can be seen in (Figure 6).
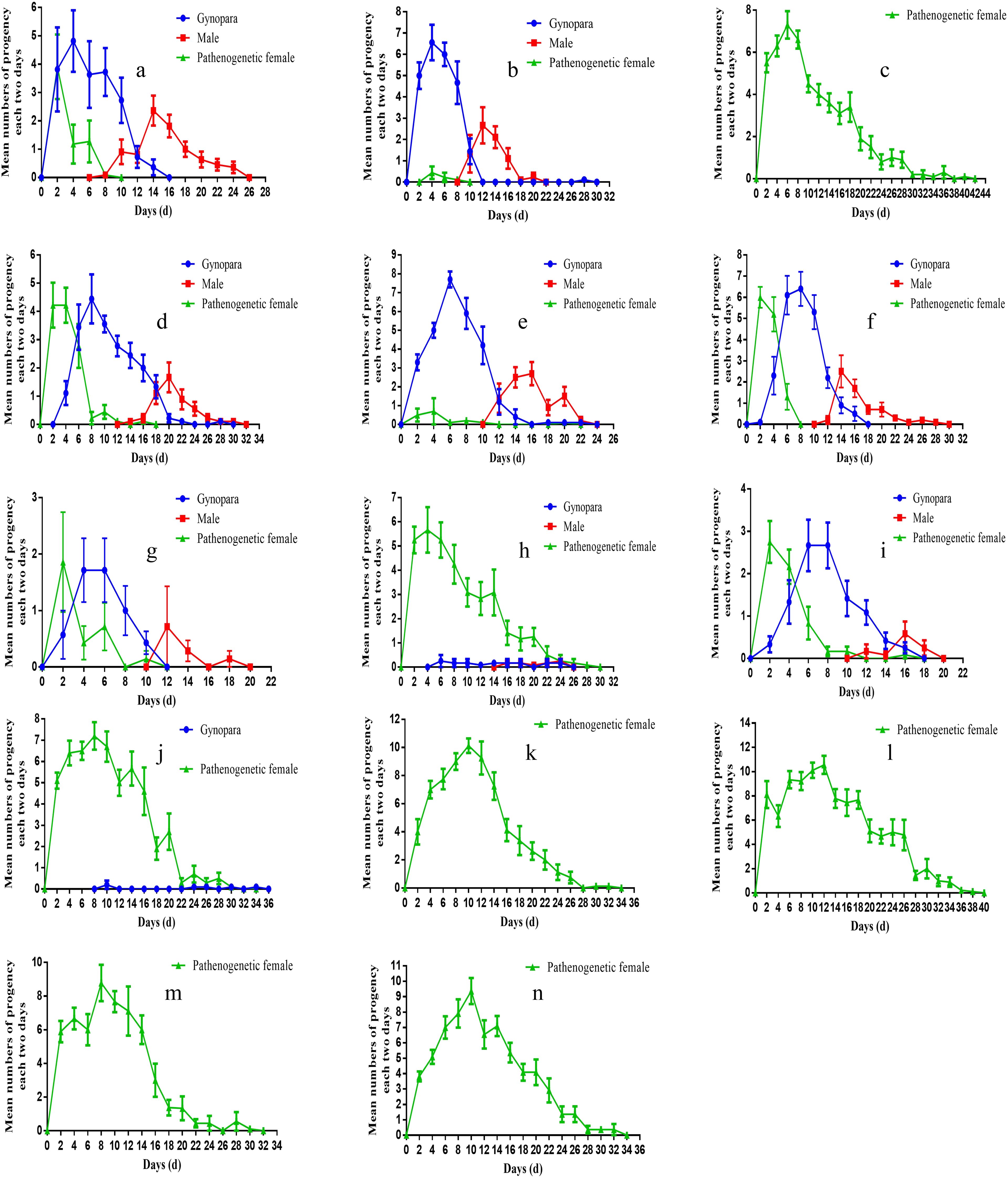
Figure 5. Dynamics of the different types of morphs produced (parthenogenetic females, gynoparea or males) when the lineages are placed under photoperiod conditions that normally induce the production of sexual morphs of Aphis gossypii. (A) Langfang, Hebei Hap1 (cotton), (B) Ezhou,Hubei Hap1 (cotton), (C) Baoshan,Yunnan Hap1 (cotton), (D) Yangzhou, Jiangsu Hap1 (cotton), (E) Ezhou, Hubei Hap4 (cotton), (F) Korla, Xinjiang Hap4 (cotton), (G) Yangzhou, JiangsuHap1 (zucchini), (H) Yangzhou, Jiangsu Hap17 (cotton), (I) Korla, XinJiang Hap4 (zucchini), (J) Nantong, Jiangsu Hap1-1 (cotton), (K) Yangzhou, Jiangsu Hap17 (zucchini), (L) Yangzhou, Jiangsu Hap3 (zucchini), (M) Yangzhou, Jiangsu Hap16 (zucchini), (N) Yangzhou, Jiangsu Hap17 (cucumber).
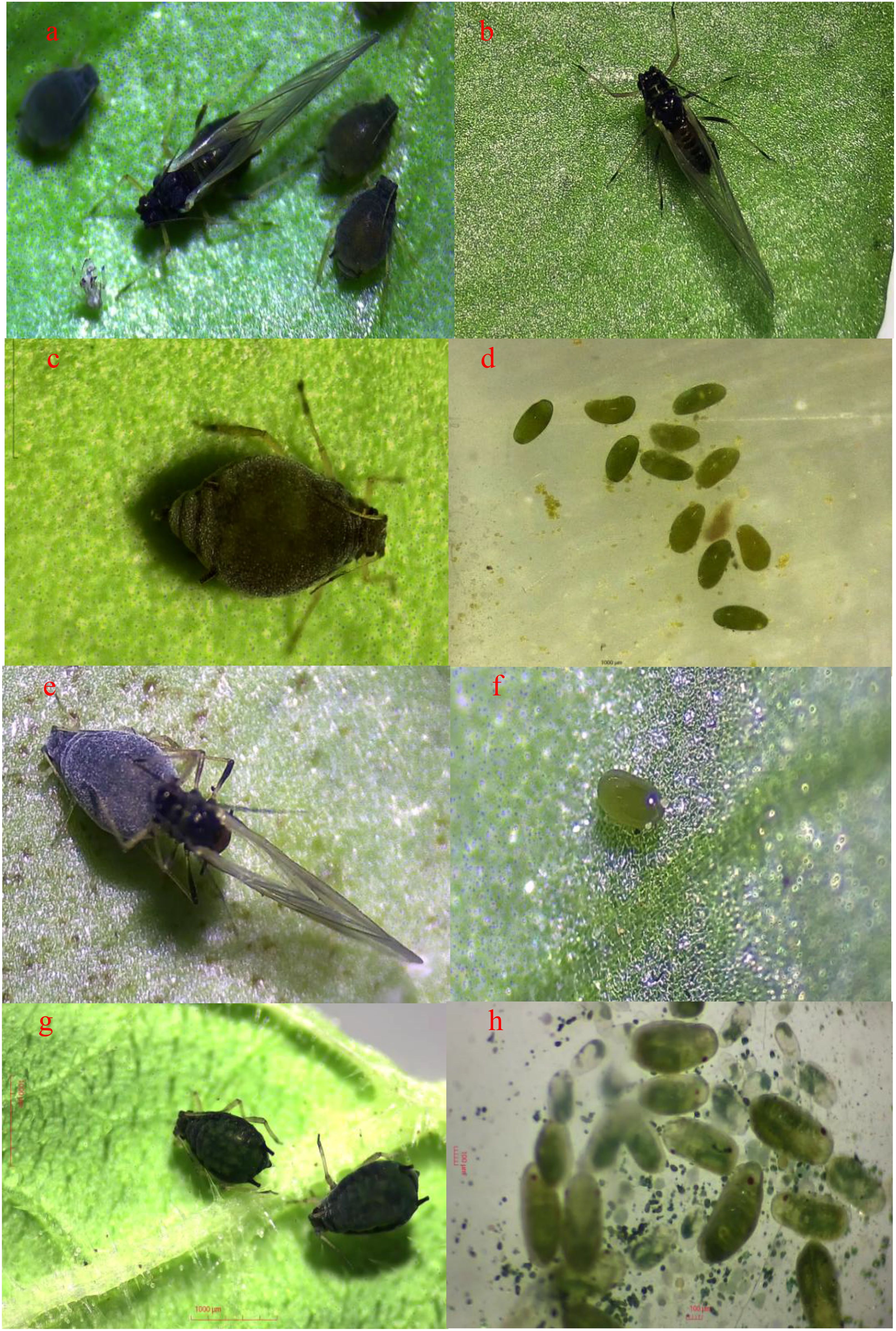

Figure 6. Phenotypes of Hap1 and Hap3 under low temperature and short photoperiod. Hap1: (A): Gynopara (wing); (B) Male; (C) Sex female; (D) Eggs (anatomical figure) of sex female; (E) Mating of female and male (wing); (F) Fertilized eggs laid by female and male after mating. Hap3: (G) parthenogenetic aphid; (H) embryos by parthenogenetic aphid (anatomical figure).
The host also affects the occurrence of sexual morphs of A. gossypii. Hap1, 17, and 4 were chosen for inducing sexual morphs on three host plants cotton, cucumber, and zucchini, respectively. The results revealed that only Hap17 was capable of establishing populations on all three hosts, while Hap1 and Hap4 could only establish populations on cotton and zucchini. The sexual morph ratio of Hap1 and Hap4 phenotypes was skewed when induced on zucchini compared to the original host cotton. The ratio of sexual morphs among Hap1 was gynoparae biased skewed on zucchini, shifting from 56.25% and 13.26% (cotton) to 62.01% and 7.14% (zucchini) (Table 1). Meanwhile, Hap1 produced both gynopara and male morphs 2 days earlier on zucchini compared to cotton (Figure 5G-zucchini, D-cotton). After host transition, the proportion of parthenogenetic, gynopara, and male morphs of Hap4 changed from 28.80%, 56.43%, and 14.78% on the original host cotton plant to 36.18%, 56.63%, and 7.20% on zucchini, respectively (Table 1). There was no change in the timing of gynopara and males produced by Hap4 on zucchini and cotton (Figure 5F-zucchini and I-cotton). Notably, the reproductive mode of Hap17 is greatly influenced by host change (Figures 5H, K, N). The sexual morphs of Hap17 can be induced in the cotton host but not in the zucchini and cucumber hosts (Table 1).
The result revealed that sexual morphs of A. gossypii were only observed on plants of the mallow family (cotton, hibiscus, cotton rose hibiscus and okra), Chinese prickly ash, and pomegranate. Sexual morphs were not detected on citrus, capsella, chrysanthemum, chilli, veronica, erigeron annuus, loofah, cucumber, and zucchini. These haplotypes of sexual individuals were Hap1 and Hap4 (Table 2).
Winter survey results revealed that A. gossypii in the Yangtze River basin overwinter through parthenogenesis on crops or weeds such as veronica, capsella, dandelion, and crofton weed in greenhouses or outdoors. Capsella is an extremely suitable overwintering host for A. gossypii. Almost all haplotypes could be found on capsella, followed by veronica (Figure 7).
The V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified from different haplotypes, and reproductive types of A. gossypii samples analyses were sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq PE 300 platform. In total, 60451.36 effective tags were obtained, with an average base number of 25639041.56 bp. The average length of the effective tags was 423.14 bp (Supplementary Table S1). Among different haplotypes of parthenogenesis populations, the Hap3.P, Hap4.P, and Hap17.P aphids were found to have significantly higher bacterial abundance estimates than the Hap1.P aphids in ACE and Chao1 index analyses (Supplementary Figure S1). Among different reproductive types, parthenogenesis populations Hap1.P were found to have significantly lower bacterial abundance estimates than the sexual populations Hap1.M, Hap4.F, Hap4.M, and Hap4.G (Supplementary Figure S1). The PCA-based studies of the 25 samples revealed all clusters together, except for two Hap4.F, two Hap4.G, one Hap4.M, one Hap4.P, one Hap1.M, one Hap17.P, and one Hap3.P sample (Supplementary Figure S2).
The analysis of the microbial community composition showed that the dominant symbiotic bacterial phylum among the samples is Proteobacteria. The dominant symbiotic bacterial genus differed between samples. In the parthenogenesis aphids Hap3, Hap16, and Hap17, Buchnera was the most abundant genus. While both the gynopara and female morphs of Hap1 and Hap4 were dominated by Arsenophonus, it is worth noting that the relative abundance of Arsenophonus is generally higher in sexual aphids (except Hap4.M) compared to parthenogenetic aphids. Additionally, the relative abundance of Arsenophonus is higher in gynopara and female aphids compared to their respective male aphids. The relative abundance of Arsenophonus in sexual aphids Hap4.F, Hap4.M, Hap4.G, Hap1.F, Hap1.M, and Hap1.G was 22.37, 4.54, 42.89, 63.77, 22.42, and 69.70%, respectively. The relative abundance of parthenogenetic aphids Hap1.P, Hap4.P, Hap3.P, Hap17.P, Hap1-1.P(Ntj.P), and Hap16.P was 10.35, 19.79, 2.06, 2.06, 3.68, and 0.54%, respectively (Figure 8).
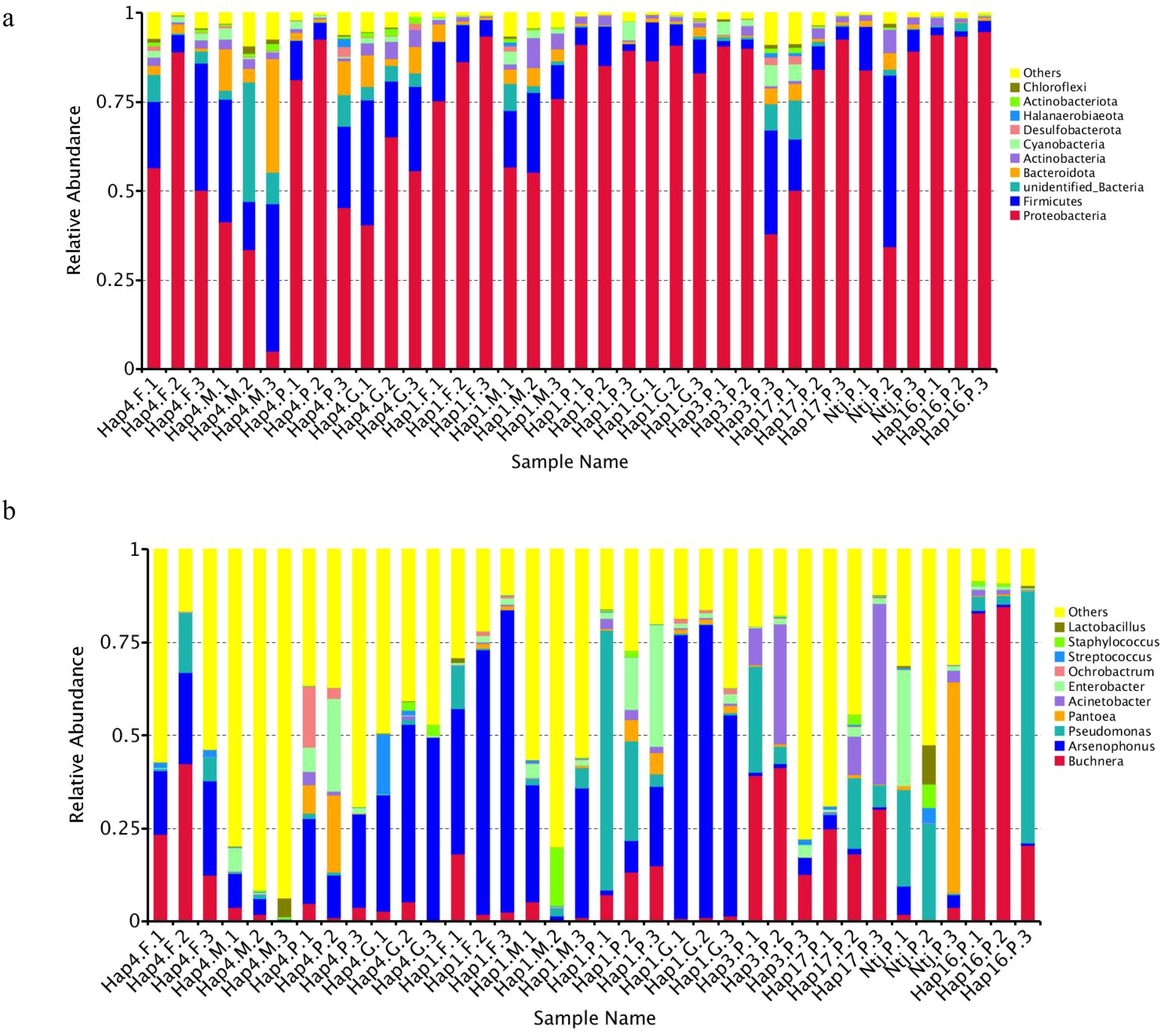
Figure 8. Relative abundance of species at the phylum and genus (A, B) level among different treatments.
The relative abundance of Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter in parthenogenetic aphids was higher than that in sexual aphids. Specifically, the mean relative abundance of Pseudomonas was 15.99% in parthenogenetic populations and 2.76% in sexual aphid populations. Additionally, the mean relative abundance of Acinetobacter was 6.63% in parthenogenetic populations and 0.25% in sexual aphid populations.
Also, the abundance of Pantoea and Enterobacter varied among haplotypes in parthenogenetic populations. The relative abundance of Pantoea was higher in Hap1.P, Hap4.P, and Ntj.P populations (4.84, 9.52, and 19.32%) compared to Hap3.P, Hap17.P, and Hap16.P populations (0.36, 0.42, and 0.23%). Similarly, the relative abundance of Enterobacter was higher in Hap1.P, Hap4.P, and Hap1-1.P populations (16.18, 10.90, and 10.83%) compared to Hap3.P, Hap17.P, and Hap16.P populations (1.78, 1.60, and 0.75%) (Figure 8).
The type of host colonized by aphids exerts a profound influence on their reproductive strategy, which may be related to the long-term adaptation of the A. gossypii to its respective specialized host plants. Furthermore, differences in the growth characterization, nutrients, and compounds of the host plants result in the differentiation of A. gossypii populations and even symbiotic bacteria within them. This may be a significant factor contributing to the observed differences in reproductive patterns. In this study, the lifecycle types of six haplotypes in Yangzhou region were categorized into three types based on whether aphids are capable of sexual reproduction and whether they are influenced by the host.
The type I is the holocyclic lifecycle, which refers to populations that have a high proportion of sexual aphid transformations under a low temperature and short photoperiod. This type is not affected by host changes (Hap1 and Hap4). Hap1 corresponds to the cotton-type aphid (Zhang et al., 2018), which is the most abundant haplotype and colonizes the largest number of host species in nature. The 3 most common host plants of Hap1 are cotton, hibiscus, and pomegranate, a typical hetero-host-holocyclic life history type (the second host cotton, the first hosts hibiscus and pomegranate) (Dixon, 1998; Geng and Liu, 2010). Meanwhile, the results of the field survey confirmed that the vast majority of sexual morphs in the field environment of Yangzhou were Hap1. The Hap4 has a transitional host reference, which includes both hetero-host-holocyclic (cotton-hibiscus or pomegranate), and many unholocyclic lifecycle hosts (cucurbit hosts) (Figure 2). Indeed, sexual morphs of Hap4 populations were found in all field surveys, but apparently the number of individuals was not as large as in Hap1.
The type II is the facultative lifecycle, including Hap17 and Hap1-1, which develops a small number of sexual forms only feeding on certain plant (cotton) hosts under induced conditions. The Hap17, with the second highest host abundance, did not show a host pattern consistent with a hetero-host holocyclic life cycle (Figure 2). The top 3 hosts for Hap17 were chilli, zucchini, and veronica. Moreover, no sexual morphs of Hap17 were detected in the field. In the laboratory-induced experiments, there were only a few sexual morphs were found on cotton, and none on the two Cucurbitaceae hosts. Thus, Hap17 serves as a representative of facultative life-history whose reproductive mode varies from host to host. In this investigation, Hap1-1, whose host range could not be determined due to its scarcity, had similar sex aphid-inducing characteristics to Hap17.
The type III is the specialized parthenogenetic lifecycle, which is unable to produce sexual stages under the induction condition (including Hap3 and Hap16 types). The haplotypes of A. gossypii in group IV corresponded precisely to the melon-specialized populations, as reported by Zhang et al. (2018). The haplotypes in this group showed a high specialization, feeding mainly on Cucurbitaceae and weeds (Zhang et al., 2018).We tried to feed them on cotton hosts to induce sexual aphids, but unfortunately these two haplotypes did not colonize cotton. Moreover, in both laboratory induction experiments and field surveys, Hap3 and Hap16 were found to reproduce solely through parthenogenesis. According to Thomas et al. (2012), the melon aphid may originate from wild plants. Importantly, winter field surveys identified Capsella and Veronica as important transfer hosts of the melon-aphid, serving as vital food sources for the continued survival of specialized parthenogenetic aphid populations in the Yangtze River Basin during the winter. The discovery of important winter hosts provides ample evidence to explain how this species of cotton aphid in spends its cold winters.
However, the lifecycle types of these haplotypes are not static, and even the same haplotype originating in different regions can present different life cycles. Geography is another critical factor that influences the reproductive transformation in aphid (Blackman, 1974; Wiktelius, 1982). Prolonged favorable environmental conditions can lead to the loss of the sexual reproductive stage in aphids (Liu et al., 2003). Hap1 only from the low latitude region (Baoshan, Yunnan) did not exhibit reproductive transformation. This is due to the fact that the climate of the Yunnan region of China is warmer during all four seasons in comparison to the other three regions. In conditions conducive to survival, parthenogenetic reproductive strategy can result in a rapid increase in aphid populations. In contrast, the presence of sexual reproductive strategy, has a significant inhibitory effect on population growth while simultaneously ensuring the perpetuation of offspring. Therefore, in regions with more extreme climatic conditions, cotton aphids tend to reproduce sexually in order to ensure the continuation of their offspring, rather than to continue expanding their populations.
This study also found that the abundance of Arsenophonus were significantly higher in holocyclic lifecycle aphids than in parthenogenetic aphids. Notably, the relative abundance of Arsenophonus was higher in gynopara and female aphids compared to male aphids. Studies have shown that Arsenophonus can cause Nasonia vitripennis male embryo mortality, resulting in a skew towards female sexual development in hosts (Ferree et al., 2008; Goerzen and Erlandson, 2018). In summary, we suggest that Arsenophonus may play an important role in the reproductive transition of A. gossypii, especially in the formation of gynopara and female aphids. However, the effects associated with Arsenophonus on aphids remain poorly understood and merit further study. Additionally, the relative abundance of Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter are commonly higher in parthenogenetic aphids than in sexual aphids. It has been demonstrated that the intestinal symbiotic bacterium Acetobacter pomorum plays an important role in oocyte production in the ovaries of Drosophila melanogaster (Elgart et al., 2016). Furthermore, Pseudomonas putida has been observed to stimulate oviposition in the olive fruit fly, Bactrocera oleae. The number of eggs laid by B. oleae that had been fed diets containing P. putida was significantly higher than that of females that had been fed only sucrose (Sacchetti et al., 2014). Unfortunately, there is limited research on the involvement of these bacteria in aphid reproductive function. Future research will focus on the isolation and in cell-free culture of the symbiotic bacterium Arsenophonus, the dynamics of the symbiotic bacteria during the formation of different reproductive phenotypes of the A. gossypii, as well as the use of antibiotics to remove and replenish Arsenophonus to validate its function in the reproductive transition of the aphids. The present study provides a new idea to aphid control through the utilization of symbiotic bacteria that regulate reproduction.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
ZL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. XF: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MA: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HS: Writing – review & editing. TJ: Writing – review & editing. SZ: Writing – review & editing. YY: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0201907).
We are very grateful to Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences and the Korla Base of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Heshke Township for providing aphid samples.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fevo.2024.1450743/full#supplementary-material.
Bright M., Bulgheresi S. (2010). A complex journey: transmission of microbial symbionts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8, 218–230. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2262
Bucher P. (1965). Endosymbiosis of Animals with plant microorganisms (New York: Interscience Publishers), 1725–1727.
Cao W. J. (2016). Effects of a facultative endosymmbiont Arsenophonous nasoniae on biological traits of Aphis gossypii. [master's thesis]. Nanjing Agricultural University.
Carletto J., Blin A., Vanlerberghe-Masutti F. (2009b). DNA-based discrimination between the sibling species Aphis gossypii Glover and Aphis frangulae Kaltenbach. Systematic Entomology. 34, 307–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3113.2008.00458.x
Carletto J., Lombaert E., Chavigny P., Brevault T., Lapchin L., Vanlerberghe-Masutti F. (2009a). Ecological specialization of the aphid Aphis gossypii Glover on cultivated host plants. Mol. Ecol. 18, 2198–2212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04190.x
Charaabi K., Carletto J., Chavigny P., Marrakchi M., Makni M., Vanlerberghe-Masutti F. (2008). Genotypic diversity of the cotton-melon aphid Aphis gossypii (Glover) in Tunisia is structured by host plants. Bull. Entomological Res. 98, 333–341. doi: 10.1017/S0007485307005585
Dixon A. F. G. (1998). Aphid ecology: an optimization approach. 2nd ed (London: Chapman & Hall), 128–130.
Elgart M., Stern S., Salton O., Gnainsky Y., Heifetz Y., Soen Y. (2016). Impact of gut microbiota on the fly’s germ line. Nat. Commun. 7, 11280. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11280
Engelstädter J., Hurst G. D. D. (2009). The ecology and evolution of microbes that manipulate host reproduction. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Systematics 40, 127–149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.110308.120206
Ferree P. M., Avery A., Azpurua J., Wilkes T., Werren J. H. (2008). A bacterium targets maternally inherited centrosomes to kill males in Nasonia. Curr. Biol. 18, 1409–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.07.093
Geng T. L., Liu X. D. (2010). The capacity to produce sexual generation and reproductive modes of the autoecious aphid Aphis gossypii Glover on an overwintering host, Hibiscus Syriacus. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 33, 45–48. doi: 10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2010.05.008
Gnainsky Y., Zfanya N., Elgart M., Omri E., Brandis A., Mehlman T., et al. (2021). Systemic regulation of host energy and oogenesis by microbiome-derived mitochondrial coenzymes. Cell Rep. 34, 108583. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108583
Goerzen D. W., Erlandson M. A. (2018). Infection of the chalcid parasitoid Pteromalus venustus Walker (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) with the male-killing symbiont Arsenophonus nasoniae (Gamma-Proteobacteria: Enterobacteriaceae). J. Invertebr Pathol. 154, 24–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2018.03.013
Gong P. (2000). Molecular genetics studies of cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Homotera: Aphididae) on population differentiation and artificial induction of sexuales (PHD, China: Nanjing Agricultural University). doi: 10.7666/d.Y410031
Gong P., Zhang X. (2001). The inducement of temperature and photoperiod to produce sexuales of Aphis gossypii glover. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 28, 318–324. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2001.04.007
Guildemond J. A., Tigges W. T., Vrijer P. W. F. D. (1994). Host races of aphis gossypii (Homoptera: aphididae) on cucumber and chrysanthemum. Environ. Entomology 23, 1235–1240. doi: 10.1093/ee/23.5.1235
Ji J. C. (2017). Research on reproductive plasticity of cotton aphid and related platform establishing (University of Chinese Academy of Sciences).
Ji J. C., Zhang S., Cui J. J., Luo J. Y., Zhang X. X., Zhu X. Z. (2019). A new method for the induced indoors induction of gynoparas, female and male aphids of the cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii), CN201910352763.5.
Ji J., Shi Q., Zhang K., Chen L., Zhu X., Li D., et al. (2023). Sexually dimorphic morphology, feeding behavior and gene expression profiles in cotton aphid Aphis gossypii. Pest Manage. Sci. 79, 5152–5161. doi: 10.1002/ps.7718
Ji J., Zhang S., Ningbo H. F., Luo J. Y., Gao X. K., Niu L., et al. (2021). Insights into wing dimorphism in the worldwide agricultural pest Aphis gossypii, the host-alternating aphid. J. Cotton Res. 4, 5. doi: 10.1186/s42397-021-00080-w
Kim H., Lee S., Jang Y. (2011). Macroevolutionary patterns in the Aphidini Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae): diversification, host association, and biogeographic origins. Public Library Sci. 6, e24749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024749
Komazaki S., Toda S., Shigehara T., Kanazaki S., Izawa H., Nakada K., et al. (2011). The genetic structure of Aphis gossypii populations in Japanese fruit orchards. Entomologia Experimentalis Applicata 140, 171–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1570-7458.2011.01145.x
Kwon S., Kim D. (2017). Effects of temperature and photoperiod on the production of sexual morphs of Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Jeju, Korea. J. Asia-Pacific Entomology 20, 53–56. doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2016.11.006
Lambers H. R. D. (1966). Polymorphism in aphididae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 11, 47–78. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.11.010166.000403
Leonardo T., Mondor E. (2006). Symbiont modifies host life-history traits that affect gene flow. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 273, 1079–1084. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2005.3408
Le Trionnaire G., Francis F., Jaubert-Possamai S., Bonhomme J., De Pauw E., Gauthier J. P., et al. (2009). Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of seasonal photoperiodism in the pea aphid. BMC Genomics 10, 456. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-456
Li H. W., Zhao C. W., Yang Y., Zhou Z. X., Qi J. W., Li C. R. (2021). The influence of gut microbiota on the fecundity of Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Insect Sci. 21, 1–9. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieab061
Liu J., Wu K. M., Zhao K. J., Guo Y. Y. (2003). The ecological adaptability of Aphis gossypii collected from different climate zones to temperature and photoperiod. Acta Ecologica Sin. 23, 863–869. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.05.004
Liu X. D., Zhai B. P., Zhang X. X. (2008). Specialized host-plant performance of the cotton aphid is altered by experience. Ecol. Res. 23, 919–925. doi: 10.1007/s11284-007-0458-9
Miao N. H. (2018). Effects of the endosymbiont Arsenophonus Nasoniae on host use of Aphis Gossypii Glover (China: Nanjing Agricultural University).
Poinsot D., Charlat S., Merçot H. (2003). On the mechanism of Wolbachia induced cytoplasmic incompatibility: Confronting the models with the facts. BioEssays: News Rev. Molecular Cell. Dev. Biol. 25, 259–265. doi: 10.1002/bies.10234
Quast C., Pruesse E., Yilmaz P., Gerken J., Glckner F. O. (2012). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 4, D590–D596. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1219
Razmjou J., Vorburger C., Moharramipour S., Mirhoseini S. Z., Fathipour Y. (2010). Host-associated differentiation and evidence for sexual reproduction in Iranian populations of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomologia Experimentalis Applicata 134, 191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1570-7458.2009.00951.x
Sacchetti P., Ghiardi B., Granchietti A., Stefanini F. M., Belcari A. (2014). Development of probiotic diets for the olive fly: Evaluation of their effects on fly longevity and fecundity. Ann. Appl. Biol. 164, 138–150. doi: 10.1111/aab.12088
Shi Q. Y. (2022). Effects of host plant conversion on reproductive patterns of two different host biotype cotton aphid. Chin. Acad. Agric. Sci. Thesis. doi: 10.27630/d.cnki.gznky.2022.000676
Simon J., Boutin S., Tsuchida T., Koga R., Gallic J. F. L., Frantz A., et al. (2011). Facultative symbiont infections affect aphid reproduction. PloS One 6, e21831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021831
Simon J. C., Rispe C., Sunnucks P. (2002). Ecology and evolution of sex in aphids. Trends Ecol. Evol. 17, 34–39. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(01)02331-X
Takada H. (1988). Interclonal variation in the photoperiodic response for sexual morph production of Japanese Aphis gossypii Glover (Hom., Aphididae). J. Appl. Entomology 106, 188–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0418.1988.tb00582.x
Thomas S., Boissot N., Vanlerberghe-Masutti F. (2012). What do spring migrants reveal about sex and host selection in the melon aphid? BMC Evolutionary Biol. 12, 47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-12-47
Tsuchida T., Koga R., Fukatsu T. (2004). Host plant specialization governed by facultative symbiont. Science 303, 1989–1989. doi: 10.1126/science.1094611
Vanlerberghe-Masutti F., Chavigny. P. (1998). Host-based genetic differentiation in the aphid Aphis gossypii Glover, evidenced from RAPD fingerprints. Mol. Ecol. 7, 905–914. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.1998.00421.x
Vanlerberghe-Masutti F., Chavigny P., Fuller S. (1999). Characterization of microsatellite loci in the aphid species Aphis gossypii Glover. Mol. Ecol. 8, 693–695. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.1999.00876.x
Wagner S. M., Martinez A. J., Ruan Y. M., Kim K. L., Lenhart P. A., Dehnel A. C., et al. (2015). Facultative endosymbionts mediate dietary breadth in a polyphagous herbivore. Funct. Ecol. 29, 1402–1410. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12459
Wang Q. (2007). Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 5261–5267. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Wang S. J., Huang W. J., Li M. T., Wang N., Liu X., Chen M. H., et al. (2024). RpUGT344J7 is involved in the reproduction switch of Rhopalosiphum padi with holocyclic life cycle. Insect Sci. 31, 1073–1089. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.13325
Wang L., Zhang S., Luo J. Y., Wang C. Y., Lv L. M., Zhu X. Z., et al. (2016). Identification of Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) biotypes from different host plants in North China. PloS One 11, e0146345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146345
Yan C. B. (1993). The occurrence and integrated control of cotton aphids. Xinjiang Farmland Reclamation Sci. Technol. 2, 26–28.
Zhang S., Luo J. Y., Wang L., Wang C. Y., Lv L. M., Zhang L. J., et al. (2018). The biotypes and host shifts of cotton-melon aphids Aphis gossypii in northern China. J. Integr. Agric. 17, 2066–2073. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61817-3
Zhang S., Lv L. M., Wang C. Y., Luo J. Y., Li C. H., Cui J. J. (2014). Study on cotton aphid-borne viruses via high-throughput sequencing technology. Cotton Sci. 26, 539–545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7807.2014.06.009
Keywords: Aphis gossypii, life cycle, host specialization, reproductive plasticity, endosymbiotic bacteria
Citation: Liu Z, Fang X, Askar M, Su H, Jing T, Zhang S and Yang Y (2024) The haplotypes distribution, reproductive mode differentiation and related symbiotic bacteria analysis in Aphis gossypii from diverse hosts in Yangtze river basin in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 12:1450743. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2024.1450743
Received: 18 June 2024; Accepted: 23 October 2024;
Published: 22 November 2024.
Edited by:
Ghada Abd-Elmonsef Mahmoud, Assiut University, EgyptReviewed by:
Jiufeng Wei, Shanxi Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Liu, Fang, Askar, Su, Jing, Zhang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yizhong Yang, eXp5YW5nQHl6dS5lZHUuY24=; Shuai Zhang, c2h1YWl6aGFuZ0B5enUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.