
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Earth Sci. , 26 March 2025
Sec. Geoscience and Society
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2025.1556652
 Wenhai Kou1
Wenhai Kou1 Jiahao Zhai2*
Jiahao Zhai2*As an integral component of China’s intangible cultural heritage (ICH), sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) holds immense significance and importance in cultural inheritance, social cohesion, health promotion, values education, cultural innovation. However, the spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of SICH have not been extensively explored. Therefore, we conducted an in-depth analysis of the spatial patterns and influencing factors of SICH utilizing Geographic Information System (GIS) spatial analysis methods such as geographic concentration index and kernel density estimation. The results reveal that SICH exhibits a spatially clustered distribution, with the highest concentrations in Hebei, Guangdong, and Zhejiang provinces. Notably, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and the Yangtze River Delta region are identified as areas with particularly high densities of SICH. The analysis of natural and human factors indicates that altitude, climate, rivers, GDP, and population density significantly influence the distribution of SICH, while the presence of core cities does not have a notable impact. This research provides valuable insights into the spatial distribution patterns of SICH and offers a foundation for future preservation and promotion strategies.
Cultural heritage is broadly understood as the legacy of physical artifacts (tangible heritage) and intangible attributes (intangible heritage) inherited from past generations. These include monuments, archaeological sites, traditional practices, languages, rituals, and knowledge systems. Globally, cultural heritage is often categorized into two main types: 1) Tangible Cultural Heritage: This includes physical artifacts such as buildings, monuments, landscapes, books, artworks, and archaeological sites. 2) Intangible Cultural Heritage: This encompasses traditions, oral histories, performing arts, social practices, rituals, and knowledge systems. The preservation of cultural heritage is influenced by a range of challenges that vary across regions and nations. These challenges often stem from historical, political, economic, and social factors.
As one of the rich and colorful cultural heritages of the Chinese nation, China’s intangible cultural heritage (ICH) has been inherited and developed over its long history. Its rich connotation and unique forms of expression not only enrich the spiritual life of the Chinese people but also showcase the cultural heritage and creativity of the Chinese nation (Qiu et al., 2024; Lee, 2020). With the changing times and societal development, China’s ICH has garnered significant global attention, with its unique charm and value becoming increasingly prominent.
Recently, ICH has garnered extensive attention, primarily focused on three key areas: 1) The establishment and enhancement of mechanisms for safeguarding and transmission: International organizations, governments, and non-governmental organizations are actively involved in establishing laws, regulations, policies, and measures to safeguard and transmit ICH (Massing, 2018; Xu et al., 2022; Demgenski, 2023; Alshehaby, 2024; Rai, 2024). They also promote the implementation of relevant projects and the cultivation of inherited talents. 2) The role of digital technology in safeguarding ICH: Digital technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality are being widely applied to safeguard and transmit ICH, facilitating its digital recording, display, and dissemination (Chen and Lyu, 2015; Xue et al., 2019; Lvping, 2021; Xie, 2021; Fan, 2024; Fan et al., 2023; Ma and Guo, 2023). 3) The rise of interdisciplinary research: The study of ICH is no longer confined to the field of anthropology but involves interdisciplinary cooperation, including sociology, cultural studies, history, and geography (Luo, 2021; Liu, 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Xiao, 2022; Xie, 2022).
Particularly, the intersection of ICH with geography has become a recent hot topic. The intersection of ICH with geography has become a prominent area of research, with studies utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to analyze the spatial distribution of ICH and its influencing factors. (Wang and Zhan, 2022; Liu and Kang, 2023; Wang et al., 2024). For example, Liu and Kang (2023) examined how geographical factors, such as altitude and climate, affect the distribution of ICH in Xinjiang, China. Similarly, Wang and Zhan (2022) explored the spatial distribution of ICH in the Yellow River Basin, identifying key factors such as river systems and economic development. Research has also focused on the temporal dynamics of ICH distribution. Liu et al. (2022) analyzed the temporal and spatial patterns of ICH along the ancient Qin-Shu roads in Western China, revealing how historical trade routes influenced the distribution of cultural heritage. Additionally, Zhang et al. (2024) investigated the spatial distribution of ICH resources across China, highlighting the role of socioeconomic factors such as GDP and population density. Such efforts aid government cultural departments in gaining a deeper understanding of the distribution patterns of ICH and innovating ideas for its protection.
In particular, sports ICH (SICH) encapsulates the traditions, history, and cultural identity of peoples and regions. Through the transmission of sports activities, individuals gain a deeper understanding of and preserve their cultural traditions. Participation in traditional sports fosters social ties, enhances social identity and solidarity, and promotes physical literacy and overall health. Despite previous studies examining the spatial distribution characteristics of Chinese ICH in various regions and their influencing factors (Nie et al., 2022; Zhang Z. et al., 2022; Pang and Wu, 2023; Wang et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024), there has been a lack of in-depth discussion specifically focusing on SICH. Therefore, this paper selects Chinese SICH as the research object, and based on various spatial analysis methods, elucidates its spatial distribution characteristics and analyze the influence of different natural geography and socio-human factors on its distribution (Ivanovic et al., 2023). The purpose of this study is to delve into the spatial distribution patterns of SICH in China and to analyze the factors that influence these patterns. By employing GIS spatial analysis methods, we aim to uncover the geographical clustering of SICH and to understand how natural and human factors contribute to its distribution. This research is not only significant for academic purposes but also has practical implications for policymakers and cultural preservationists. Understanding the spatial distribution of SICH can inform targeted strategies for its protection and promotion, ensuring that these cultural practices continue to thrive in a rapidly changing world. Furthermore, this study seeks to bridge the gap between sports and geography, two fields that have traditionally been studied in isolation. By integrating geographical methods with the study of sports heritage, we hope to contribute to the emerging field of sports geography, which explores the spatial dimensions of sports and physical activities. This interdisciplinary approach can provide new insights into the ways in which geography shapes cultural practices and vice versa.
China’s State Council has published a total of 3,610 national ICH representative project lists on five occasions in 2006, 2008, 2011, 2014, and 2021 (https://www.ihchina.cn, latest access 19 May 2024). These lists include information such as the number, name, category, publication time, type, declared region or unit, protection unit, and province of each ICH project (excluding Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan). However, the list of ICH items published on China’s ICH website does not include geographic coordinates. Fortunately, a spatial distribution dataset of China’s national ICH was obtained, incorporating attributes containing spatial location information, such as the declared regions or units of ICH items, combined with Google imagery and administrative division data. The 3,610 Chinese ICH are categorized into 10 different types of programs including “folk literature”, “traditional music”, “traditional dance”, “traditional drama”, “quyi”, “traditional sports, recreation and acrobatics”, “traditional art“”, “traditional skills”, “traditional medicine”, and “folk custom”. Traditional sports of the Chinese nation originated from production and labor, religious rituals, etc., and have fitness, recreational and competitive values, promote social harmony and economic development, and are national, historical, traditional and inherited. In Chinese traditional sports programs mainly include martial arts, horseback riding, archery, taijiquan, dragon boat racing, dragon and lion dances and so on. In this study, thus, the SICH encompasses not only includes the 166 items of “traditional sports, amusement, and acrobatics” listed under ICH, but also the dragon dance and lion dance. of “traditional dance”. Ultimately, information on the spatial distribution of China’s 232 items of SICH was obtained (Figure 1). Additionally, the influencing factors data, including topography, climate, rivers, GDP, population density and core cities used in this study, were obtained from the Resource and Environmental Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/, latest access 15 June 2024). All data used in this study are shown in Table 1.
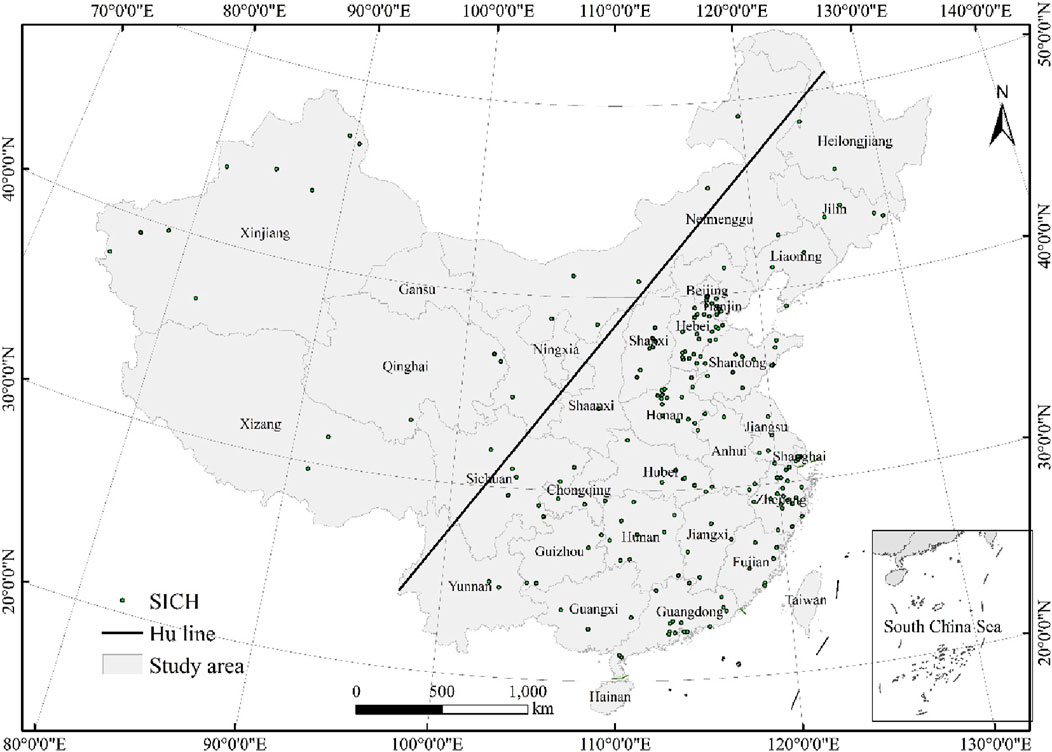
Figure 1. Distribution of sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) in China. Note: The map is based on the standard map No. GS (2019) 1821 downloaded from the website of Standard Map Service of the Ministry of Natural Resources of China, with no modification of the background map. The following map is the same.
With reference to previous studies, we finally chose four indicators to analyze the spatial distribution characteristics of SICH, including the nearest neighbor index, geographic concentration index, imbalance index, and Kernel density estimation (Ma et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). It should be noted that ArcGIS 10.8 software was used to process and analyze the data for this study.
The nearest neighbor index (Nie et al., 2023) can be used to determine whether SICH are characterized by clustered or dispersed distribution in China. It reveals the spatial distribution hierarchy of point elements by comparing the actual nearest neighbor distance and theoretical nearest neighbor distance between point elements in space. The calculation is expressed as shown in Equations 1, 2:
Where: R is the nearest-neighbor index;
Where:
Where: A is the area of the region; n is the number of SICH. When R = 1, the point elements are characterized by random distribution; when R < 1, the point elements are characterized by agglomeration distribution; when R > 1, the point elements are characterized by uniform distribution.
The geographic concentration index (Zhu et al., 2023) assesses the spatial concentration of SICH and indicates the degree of concentration, The calculation is expressed as shown in Equation 3:
Where: G is the geographic concentration index of SICH, xi is the distribution number of SICH in the ith province, T is the total number of SICH in China, and t is the number of provinces in China. G values ranging from 0 to 100. A higher geographic concentration index value signifies a more concentrated distribution of SICH, indicating a more discrete distribution.
The imbalance index (Fang et al., 2023) S is utilized to gauge the imbalance of the spatial distribution of SICH within each province, The calculation is expressed as shown in Equation 4:
Where: n denotes the number of provinces in China, and Yi denotes the cumulative percentage of the number of SICHs in each province as a proportion of the total number of SICHs in the country, ranked from largest to smallest. S ranging between 0 and 1. When S = 0, it denotes a uniform distribution of SICH across provinces. Conversely, when S = 1, it signifies that the distribution of SICH is concentrated within one province.
Kernel density estimation (Zhang X. Y. et al., 2022) can transform the spatial distribution of point elements into a visual representation. This method is commonly employed to estimate the spatial distribution of geographic elements, allowing for a more intuitive reflection of spatial agglomeration. Higher values of the kernel density indicate denser distributions of SICH. The calculation is expressed as shown in Equation 5:
Where:
Geo-detector is a statistical method for detecting spatial heterogeneity and revealing driving forces. Geographic detector does not need to consider the problem of multicollinearity of the explanatory variables and is better able to avoid the endogeneity problem of mutual causality between the explanatory variables and the explained variables. In this paper, factor detector is used to explore the influencing factors of spatial differentiation of SICHs. The calculation is expressed as shown in Equation 6:
Where: q denotes the indicator of influence detection of the explanatory variables; Ni and N denote the number of samples in the sub-level region and the number of samples in the whole region, respectively; L denotes the number of sub-regions; σ2 denotes the variance of the explanatory variables in the whole region; and denotes the variance in the sub-regions. Where the value range of q is [0, 1], when q = 0, it means that the factor has no influence on the explanatory variables, and the larger the value of q, the greater the influence of the factor on the explanatory variables.
Overlay analysis is the integration of information from two or more layers into a new layer by means of overlay fusion, which analyzes the correlation between elements by comprehensively comparing the elements in different layers. In this paper, we overlay the geographic location information layers of 232 SICHs with different influencing factors such as topography, climate, and population density, to comparatively analyze the effects of different natural and socioeconomic factors on the distribution of SICHs.
The unbalanced index of SICH in China is calculated as S = 0.32, where 0 < S < 1. Meanwhile, the average nearest neighbor of SICH is determined using GIS, resulting in a distance of 65.62 km, with the corresponding theoretical nearest neighbor distance being 120.05 km. Consequently, the nearest neighbor index is obtained as R = 0.55, indicating a cohesive distribution pattern. On a national scale, the overall distribution of SICH in China is more concentrated in the east and less so in the west. Upon analyzing the spatial distribution of SICH in conjunction with the Hu line, it is evident that the majority of SICH in China is located in the southeastern part of the Hu line. The distribution of SICH varies significantly by region, with the eastern region boasting the highest total of 129 items, accounting for 55.60% of the total. This is followed by the central region with 60 items (25.86%), the western region with 34 items (14.66%), and the northeastern region with only nine items, making up 3.88% (Table 2; Figure 2). At the provincial scale, the five provinces with the highest number of SICH are Hebei, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Shandong, and Beijing, all situated in the eastern region, with 28, 22, 21, 16, and 15 items, respectively. In the central, western, and northeastern regions, the provinces with the highest number of SICH are Henan, Xinjiang, and Jilin, respectively, with 13, 9, and 5 SICH each. Notably, Ningxia and Hainan provinces do not have any presence of SICH.
Taking China’s SICH as the research object, the geographic concentration index model was employed to determine the geographic concentration index of SICH in the region, which is calculated as G = 24.1. With the number of provincial administrative regions in mainland China denoted as n = 31 and the number of SICH as T = 232, if the 232 SICH were evenly distributed across the provincial administrative regions, the average number of traditional villages in each province would be G0 = 7.5. However, upon comparison, G is found to be larger than G0. Therefore, the distribution of SICH in China is observed to be centrally concentrated at the provincial scale. After conducting kernel density estimation of SICH using ArcGIS 10.8, it becomes evident that the highest SICH densities in China are concentrated in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and Zhejiang Province, with higher SICH densities also observed in North China (at the junction of Shanxi, Shandong, Henan, and Hebei provinces) and the Southeast coastal region (Figure 3). Conversely, the lowest SICH density is found in the western side of the Hu line.
The influence coefficient of elevation, q = 0.38, was derived based on the geo-detector, indicating that elevation has a significant effect on the distribution of SICH. Utilizing ArcGIS 10.8 to overlay the analysis of SICH with elevation data, we observe that China’s terrain is roughly distributed across three elevation stages. The first stage lies predominantly above 4,000 m above sea level, the second stage ranges from 1,000 to 2,000 m, and the third stage consists mostly of elevations below 500 m. Notably, the third stage encompasses vital areas such as the North China Plain and the Middle and Lower Yangtze River Plain, where a majority of SICH are situated, as depicted in Figure 4. Fewer SICH are distributed in the second stage, including regions like the Loess Plateau and the Sichuan Basin, while very few are found in regions exceeding 4,000 m above sea level, such as the Tibetan Plateau.
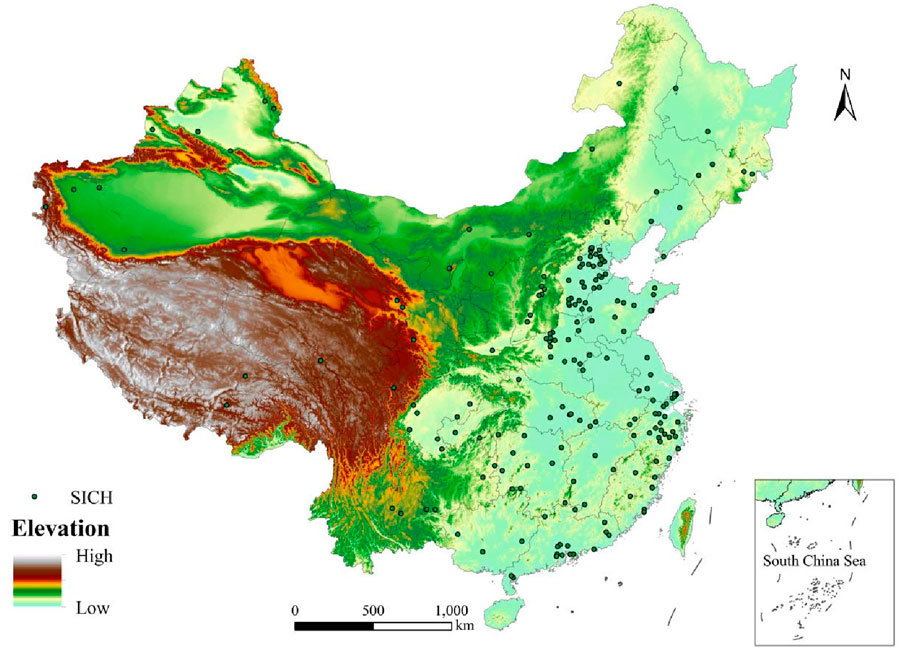
Figure 4. The relationship between the distribution of sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) and elevation in China.
Analysis of China’s SICH distribution across seven major climate zones reveals that SICH predominantly occurs in the warm temperate semi-humid zone, north subtropical humid zone, and marginal tropical humid zone, collectively accounting for over 85.78% of the total distribution (Figure 5). Specifically, 93 SICHs are located in the warm temperate semi-humid zone (40.09%), followed by the northern subtropical humid zone (34.91%), and the marginal tropical humid zone (10.78%). Meanwhile, the mid-temperate arid zone, mid-temperate semi-humid zone, mid-temperate semi-arid zone, and plateau temperate semi-arid zone each have 10, 8, 8, and 7 SICHs, respectively.
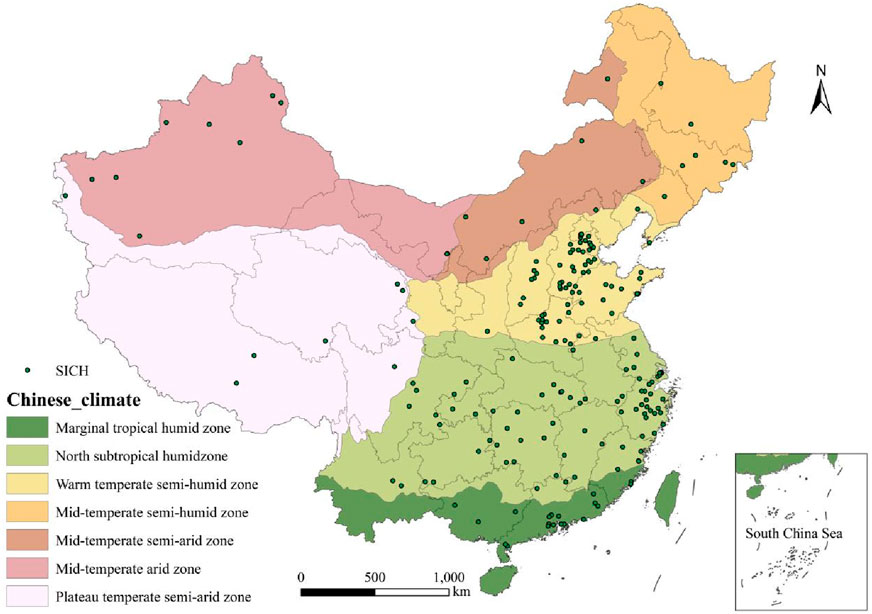
Figure 5. The relationship between the distribution of sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) and climate in China.
Overlaying the analysis of major river systems in mainland China reveals a close relationship between the spatial distribution of SICH and river systems. The overall distribution pattern aligns with the direction of major rivers (Figure 6). The number of SICHs located within 5 km, 10 km, 15 km and 20 km along the river is 54,70,91 and 109 respectively, so it can be seen that the river has a relatively obvious influence on the distribution of SICHs. Several provinces, such as Shanxi, Guangdong, Hubei, and Sichuan, exhibit more pronounced distribution patterns along rivers, suggesting a strong correlation between SICH formation and river distribution, likely attributed to early human settlements often forming near large rivers.
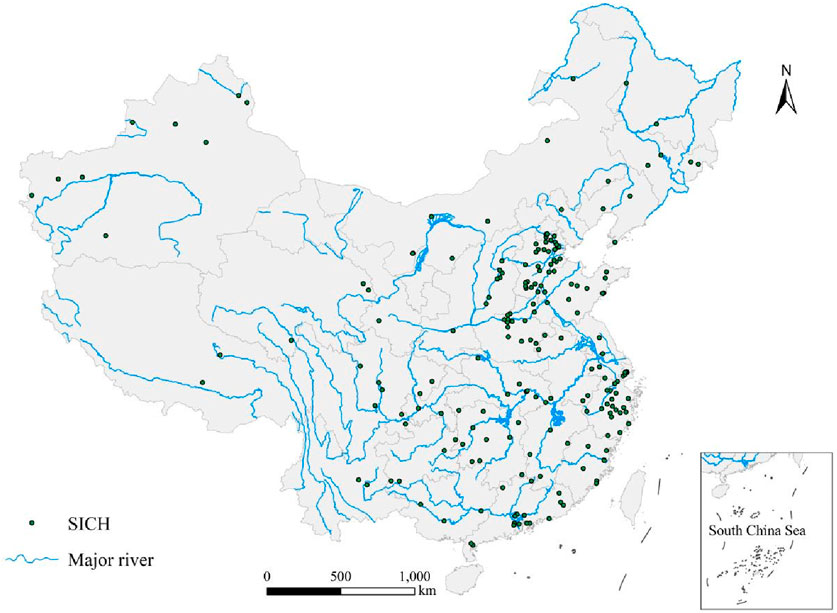
Figure 6. The relationship between the distribution of sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) and river in China.
Human and social factors may also play an important role in influencing the distribution of SICH, so we chose GDP, population density, and core cities to analyze the correlation between the distribution of SICH and the level of economic development, population distribution, and the distance to the provincial capital city. By overlaying the GDP and population density data, it can be observed that the higher the GDP and population density, the greater the number of SICH and the more concentrated their distribution (Figures 7, 8). This trend is especially evident in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta regions. The coefficient of influence of both GDP and population density based on the geo-detector was derived to be q = 0.21, indicating that the role of GDP and population density in influencing the distribution of SICH is almost always the same.
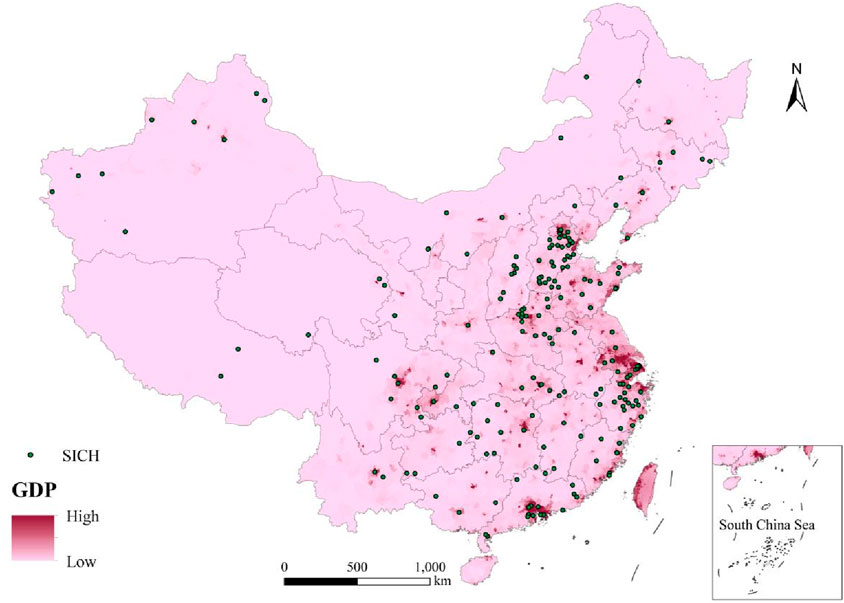
Figure 7. The relationship between the distribution of sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) and GDP in China.
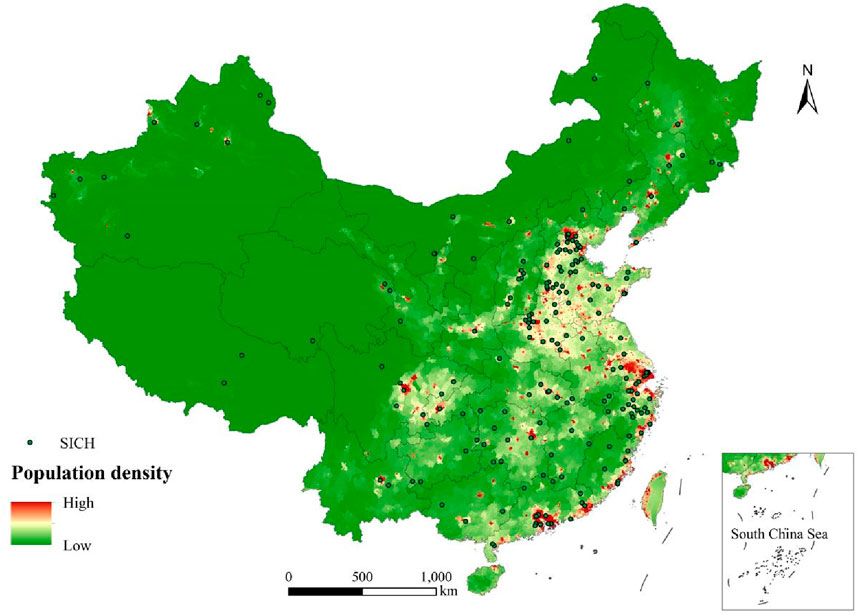
Figure 8. The relationship between the distribution of sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) and population density in China.
The level of economic development affects the construction of sports facilities, the organization of events, and the development of the sports industry. Economically developed regions can often invest more resources to support the inheritance and development of sports culture, such as building gymnasiums, training coaches, and organizing sports events. Additionally, economic status also influences people’s ability and willingness to participate in sports activities. Residents of economically developed regions may be more likely to engage in sports activities, thereby contributing to the transmission and development of sports intangible cultural heritage.
Population size and structure directly affect the transmission and development of sports culture. Densely populated areas tend to have richer sporting activities and cultural traditions because more people participate in and support these activities, allowing for better transmission of SICH. Overall, it can be concluded that the level of population density and GDP have a significant impact on the distribution of SICH.
Meanwhile, we created 20 km and 50 km buffer zones around the provincial capital cities to explore whether the distribution of SICH is correlated with the distance from the core city. From Figure 9, it can be observed that the relationship between the two is not significant overall. The number of SICHs located within 20 km and 50 km of the core city is 30 and 70 respectively. However, provincial capital cities generally have a distribution of SICH, and in more remote areas such as the Northeast, Northwest, and Southwest regions, SICH tends to be distributed near provincial capital cities.
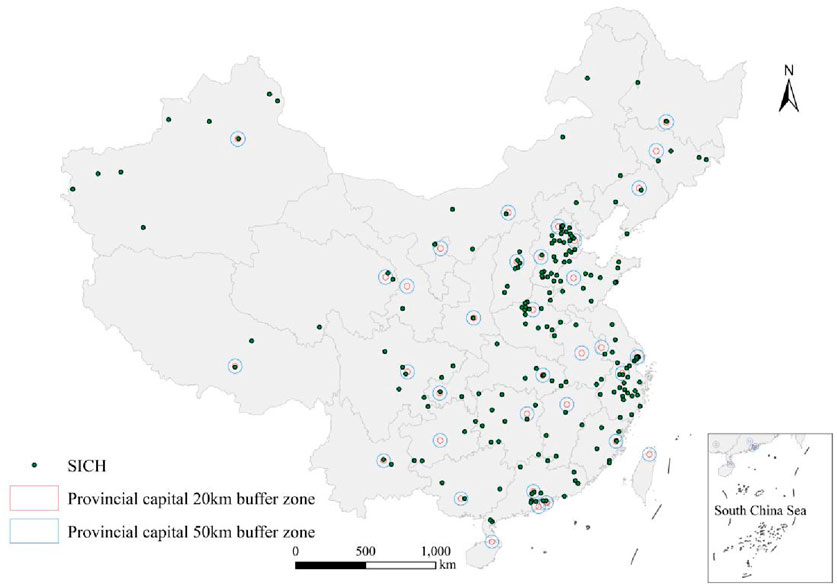
Figure 9. The relationship between the distribution of sports intangible cultural heritage (SICH) and provincial capital city in China.
The analysis of the spatial distribution of Sports Intangible Cultural Heritage (SICH) in China, as revealed through GIS spatial analysis, offers profound insights into the underlying patterns and factors that shape the preservation and proliferation of this cultural asset. This study confirms the spatial clustering of SICH across various regions, particularly in Hebei, Guangdong, and Zhejiang, which aligns with their rich historical and cultural backgrounds, along with strong regional identities. The evident clustering in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and the Yangtze River Delta reflects the strong cultural and economic influence these areas exert. These regions are historically significant and have benefitted from early and sustained economic development, fostering environments conducive to the preservation and promotion of SICH. This concentration suggests that cultural heritage, including sports, is not uniformly distributed but rather thrives in areas with a robust combination of historical depth and economic prosperity.
The significant impact of natural geographic factors such as altitude, climate, and proximity to rivers on the distribution of SICH indicates that environmental conditions play a crucial role in shaping cultural practices. For instance, traditional sports and games often evolve in response to the local environment, leading to the development of unique SICH in regions with favorable natural conditions. This finding supports the notion that the physical environment has historically influenced the creation and maintenance of cultural practices, which in turn contributes to the regional diversity of SICH. This aligns with previous studies that have highlighted the role of geography in shaping cultural heritage, such as the work by Liu and Kang (2023), who found that geographical factors like altitude and climate significantly influence the distribution of ICH in Xinjiang, China. The influence of socioeconomic factors, particularly GDP and population density, underscores the relationship between economic vitality and cultural heritage preservation. Regions with higher economic output and denser populations are likely to have more resources and institutional support for cultural activities, including the safeguarding of SICH. This correlation highlights the importance of economic development in fostering cultural continuity and innovation. Similar findings have been reported by Zhang et al. (2024), who observed that economically developed regions in China tend to have a higher concentration of ICH resources due to greater investment in cultural preservation and promotion. However, the finding that core cities do not significantly affect SICH distribution suggests that while urban areas are important cultural hubs, the preservation of SICH is not solely dependent on metropolitan influence. Instead, it thrives in a broader range of environments, including rural and less urbanized areas, where traditional practices are more likely to be maintained. This finding contrasts with some previous studies, such as those by Wang and Zhan (2022), who argued that urban centers play a pivotal role in the preservation of ICH due to their access to resources and infrastructure. This discrepancy may be due to the unique nature of sports-related cultural heritage, which often has deep roots in local communities and may be less dependent on urban centers for its survival.
Moreover, the relationship between cultural heritage and geo-heritage is an important aspect that warrants further exploration. Geo-heritage, which refers to the natural features of the landscape that have significant scientific, educational, cultural, or aesthetic value, is intrinsically linked to cultural heritage. The natural environment not only provides the physical setting for cultural practices but also shapes the cultural identity and traditions of a region. For example, the rivers, mountains, and climate of a region can influence the types of sports and recreational activities that develop there, thereby contributing to the region’s unique cultural heritage. In China, the preservation of natural values is closely tied to the conservation of cultural heritage, as many traditional practices and rituals are deeply rooted in the natural landscape.
The findings of this study have several implications for the preservation and promotion of SICH. The spatial clustering and the influence of both natural and human factors suggest that targeted efforts in specific regions could enhance the effectiveness of preservation initiatives. Policymakers should consider these spatial patterns when designing strategies for the protection and promotion of SICH. Additionally, the limited impact of core cities on SICH distribution highlights the need for policies that support cultural heritage in diverse settings, not just in urban centers. This study contributes to a deeper understanding of the diversity of Chinese sports culture by illustrating how SICH is influenced by a complex interplay of geographic and socioeconomic factors. Recognizing these influences can help in formulating strategies to protect and innovate within the realm of SICH, ensuring that these cultural practices continue to thrive in a modernizing society. The promotion of SICH, informed by an understanding of its spatial distribution, can lead to greater cultural cohesion and economic benefits, particularly through cultural tourism and related industries. Given the spatial clustering of SICH in regions like Hebei, Guangdong, and Zhejiang, region-specific policies should be developed. In high-density areas, integrating SICH into cultural tourism and urban planning can promote sustainable development. In regions with fewer SICH items, efforts should focus on documenting and revitalizing endangered traditions through community involvement and funding. Community-based programs and educational initiatives are essential for engaging local populations in preserving SICH. Digital technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and digital archives, can enhance accessibility and global awareness of SICH. Economic incentives, including government funding and public-private partnerships, are crucial for supporting conservation projects. Additionally, integrating traditional sports into modern recreational activities and promoting sports tourism can ensure the relevance of SICH in contemporary society. Finally, international collaboration and UNESCO recognition can elevate the global profile of China’s SICH, fostering cultural exchange and mutual understanding. These strategies will help preserve SICH while promoting cultural and economic benefits.
One of the primary limitations of this study is the reliance on national-level ICH data, which may not fully capture the richness and diversity of SICH at the provincial or local levels. While the national ICH lists provide a broad overview, they may exclude certain locally significant SICH items that have not been formally recognized at the national level. This omission could lead to an underestimation of the true distribution and diversity of SICH across China. Future research should incorporate provincial and local ICH data to provide a more granular understanding of SICH distribution and its cultural significance. The study employs qualitative analysis to interpret the spatial patterns and influencing factors of SICH. While this approach provides valuable insights, it is subject to potential biases and errors, particularly in the interpretation of socio-cultural and historical contexts. For instance, the classification of SICH items and the identification of influencing factors may be influenced by the researchers’ subjective judgments. To mitigate these risks, future studies could adopt mixed-methods approaches, combining qualitative analysis with quantitative validation techniques, such as surveys or expert interviews, to ensure more robust and reliable conclusions. To date, there are a total of 3,610 items of ICH in China, while the SICH targeted in this study includes only 232 items. The small sample size may lead to some biases in the research results. Additionally, we did not conduct an in-depth evaluation of the temporal development of SICH, focusing instead solely on the analysis of the existing spatial patterns. Future research could build on these findings by exploring the temporal dynamics of SICH distribution—how these patterns have evolved over time and how they might change in response to ongoing economic and environmental changes. Additionally, comparative studies with other forms of intangible cultural heritage or with SICH in other countries could provide broader insights into the universal and unique aspects of cultural heritage distribution.
The limitations identified in this study highlight several avenues for future research. First, there is a need for more detailed data collection at the provincial and local levels to capture the full diversity of SICH across China. Second, incorporating temporal analysis would provide insights into how SICH distribution has evolved over time and how it might continue to change in response to ongoing economic and environmental shifts. Finally, adopting mixed-methods approaches and expanding the sample size could enhance the robustness and generalizability of the findings. By acknowledging these limitations, the study can provide a more balanced and nuanced understanding of the spatial distribution of SICH in China, while also guiding future research efforts to address these gaps.
In this study, we conducted an in-depth exploration of the spatial distribution characteristics of SICH in China and its influencing factors based on GIS spatial analysis methods, employing nearest-neighbor indices, geographic concentration indices, imbalance indices, and kernel density estimation. The main conclusions are as follows: 1) The spatial distribution of SICH in China is unbalanced, generally exhibiting a pattern of more prevalence in the east and less in the west, particularly concentrating in the eastern region, on the east side of the Hu line. Hebei, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Shandong, and Beijing are identified as having the highest number of SICH, all situated in the eastern region. 2) The areas with the highest density of SICH distribution include the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and Zhejiang Province. Moreover, SICH is also more prevalent in North China (i.e., Shanxi, Shandong, Henan, and Hebei) and Southeast coastal areas, whereas SICH in other regions exhibited a scattered distribution. 3) By analyzing six influencing factors such as altitude, climate, river, GDP, population density, and core city, it was found that SICH is predominantly distributed in areas with lower altitude and suitable climate, closely related to the distribution of rivers. Additionally, regions with the highest GDP and population density also exhibit the highest distribution of SICH. However, the distribution of SICH appears unaffected by the presence of core cities (i.e., the provincial capital city).
By employing GIS spatial analysis methods, the study provides a comprehensive understanding of the spatial distribution of SICH across China. This is crucial for policymakers, urban planners, and cultural heritage conservationists who need to make informed decisions based on the geographical concentration and dispersion of such heritage sites. By identifying key factors such as altitude, climate, river distribution, GDP, and population density that influence the distribution of SICH, the research provides a foundation for further studies aimed at understanding the underlying causes of these spatial patterns. This can help in predicting future trends and in the formulation of targeted conservation strategies. The findings can inform national and regional policies related to cultural heritage preservation, economic development, and urban planning. For instance, knowing that SICH is concentrated in areas with high GDP and population density can help in allocating resources more effectively for conservation efforts. Overall, this research provides valuable new insights into the spatial distribution of SICH in China and the factors influencing it, offering a solid foundation for future studies and policy-making in the field of cultural heritage conservation.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
WK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. JZ: Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Planning Project for Philosophy and Social Sciences in Shanxi Province (2023YJ026), the Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China (2024-063), the Philosophy and Social Science Project of Shanxi Universities in 2022 (2022w014), the Industry-University Cooperative Education Project of the Ministry of Education in 2024 (230900591223344) and the National Educational Planning Project - Ministry of Education Youth Project: Spatial Narratives and Educational Inheritance of Folk Sports in the Yellow River Basin (ELA210436).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alshehaby, F. (2024). Assessing the legal protection of intangible cultural heritage in Saudi arabia: a critical analysis in the context of the 2003 UNESCO convention. Laws 13, 13. doi:10.3390/laws13020013
Chen, J., and Lyu, D. (2015). “The digitalization of Chinese paper-cut: intangible cultural heritage protection and culture communication,” in 5th international conference on education, management, information and medicine (EMIM). Shenyang: PEOPLES R CHINA, 391–395.
Demgenski, P. (2023). “Onstage: exhibiting intangible cultural heritage in China,” in China perspectives, 7–17.
Fan, Q. (2024). Research on intangible cultural heritage resource description and knowledge fusion based on linked data. The Electronic Library, 42, 521–535. doi:10.1108/EL-01-2023-0018
Fan, Q., Sun, C., and Zhang, M. (2023). Research on the knowledge organization of intangible cultural heritage spatiotemporal data from a digital humanities perspective. Knowl. Organ. 50, 526–541. doi:10.5771/0943-7444-2023-8-526
Fang, Y., Lu, H., Huang, Z., and Zhu, Z. (2023). Spatiotemporal distribution of Chinese traditional villages and its influencing factors. Econ. Geogr. 43, 187–196. doi:10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2023.09.020
Ivanovic, M., Lukic, T., Milentijevic, N., Bojovic, V., and Valjarevic, A. (2023). Assessment of geosites as a basis for geotourism development: a case study of the Toplica District, Serbia. Open Geosci. 15. doi:10.1515/geo-2022-0589
Lee, J. (2020). Promoting majority culture and excluding external ethnic influences: China’s strategy for the UNESCO ?intangible? cultural heritage list. Soc. Identities 26, 61–76. doi:10.1080/13504630.2019.1677223
Liu, C., and Kang, L. (2023). How do geographical factors affect the distribution of intangible cultural heritage: a case study of Xinjiang, China. Sustainability 15, 8943. doi:10.3390/su15118943
Liu, Y. (2022). “Application of digital technology in intangible cultural heritage protection,” in Mobile information systems 2022.
Liu, Y., Chen, M., and Tian, Y. (2022). Temporal and spatial patterns and influencing factors of intangible cultural heritage: ancient Qin-Shu roads, Western China. Herit. Sci. 10, 201. doi:10.1186/s40494-022-00840-0
Luo, Y. (2021). Safeguarding intangible heritage through edutainment in China's creative urban environments. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 27, 170–185. doi:10.1080/13527258.2020.1780463
Lvping, S. (2021). Blockchain technology for management of intangible cultural heritage. Scientific programming 2021.
Ma, X. D., Zhang, Y. K., Li, Y., Li, Y. J., and Lin, F. Y. (2023). Spatial-temporal distribution and evolution of the socialist built heritage in China, 1949-1978. Herit. Sci. 11, 214. doi:10.1186/s40494-023-01060-w
Ma, Z., and Guo, Y. (2023). Leveraging intangible cultural heritage resources for advancing China's knowledge-based economy. J. Knowl. Econ. 15, 12946–12978. doi:10.1007/s13132-023-01643-9
Massing, K. (2018). Safeguarding intangible cultural heritage in an ethnic theme park setting - the case of Binglanggu in Hainan Province, China. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 24, 66–82. doi:10.1080/13527258.2017.1362571
Nie, X., Ma, M., Ji, J., and Zheng, L. (2023). The spatial distribution of traditional intangible cultural heritage medicine of China and its influencing factors. Herit. Sci. 11, 90. doi:10.1186/s40494-023-00929-0
Nie, X., Xie, Y., Xie, X., and Zheng, L. (2022). The characteristics and influencing factors of the spatial distribution of intangible cultural heritage in the Yellow River Basin of China. Herit. Sci. 10, 121. doi:10.1186/s40494-022-00754-x
Pang, L., and Wu, L. (2023). Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of intangible cultural heritage in beijing-tianjin-hebei. Herit. Sci. 11, 19. doi:10.1186/s40494-023-00862-2
Qiu, L., Rahman, A. R. A., and Dolah, M. S. b. (2024). Innovative design of agricultural tourism souvenirs to promote the inheritance and promotion of intangible cultural heritage. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 61, 359–368. doi:10.21162/PAKJAS/24.121
Rai, A. (2024). The 2003 intangible cultural heritage convention in armed conflict: an integrated reading of obligations towards culture in conflict. Leiden J. Int. Law 37, 167–190. doi:10.1017/s0922156523000572
Wang, J., Chen, M., Zhang, H., and Ye, F. (2023). Intangible cultural heritage in the Yangtze River Basin: its spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors. Sustainability 15, 7960. doi:10.3390/su15107960
Wang, X., and Zhan, S. (2022). “Exploring the spatial distribution of ICH by geographic information system (GIS),” in Mobile information systems 2022.
Wang, X., Zhang, T., Duan, L., Liritzis, I., and Li, J. (2024). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of intangible cultural heritage in the Yellow River Basin. J. Cult. Herit. 66, 254–264. doi:10.1016/j.culher.2023.11.024
Xiao, L. (2022). Intangible cultural heritage reproduction and revitalization: value feedback, practice, and exploration based on the IPA model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 1–13. doi:10.1155/2022/8411999
Xie, J. (2022). Innovative design of artificial intelligence in intangible cultural heritage. Scientific programming 2022.
Xie, R. (2021). “Intangible cultural heritage high-definition digital mobile display technology based on VR virtual visualization,” in Mobile information systems 2021.
Xu, Y., Tao, Y., and Smith, B. (2022). China's emerging legislative and policy framework for safeguarding intangible cultural heritage. Int. J. Cult. Policy 28, 566–580. doi:10.1080/10286632.2021.1993838
Xue, K., Li, Y., and Meng, X. (2019). An evaluation model to assess the communication effects of intangible cultural heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 40, 124–132. doi:10.1016/j.culher.2019.05.021
Zhang, X. Y., Xiang, H., and Liu, R. (2022a). Spatial pattern and influencing factors of intangible cultural heritage of music in Xiangxi, central China. Herit. Sci. 10, 39. doi:10.1186/s40494-022-00672-y
Zhang, Z., Cui, Z., Fan, T., Ruan, S., and Wu, J. (2024). Spatial distribution of intangible cultural heritage resources in China and its influencing factors. Sci. Rep. 14, 4960. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-55454-2
Zhang, Z., Li, Q., and Hu, S. (2022b). Intangible cultural heritage in the Yellow River Basin: its spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and differentiation causes. Sustainability 14, 11073. doi:10.3390/su141711073
Keywords: sports, intangible cultural heritage, spatial distribution, GIS, China
Citation: Kou W and Zhai J (2025) Spatial distribution patterns and influencing factors of sports intangible cultural heritage in China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1556652. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1556652
Received: 07 January 2025; Accepted: 04 March 2025;
Published: 26 March 2025.
Edited by:
Marcelo Cohen, Federal University of Pará, BrazilReviewed by:
Aleksandar Valjarević, University of Belgrade, SerbiaCopyright © 2025 Kou and Zhai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiahao Zhai, emhhaWpoQGp4bnUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.