
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Earth Sci., 31 March 2025
Sec. Economic Geology
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2025.1524678
This article is part of the Research TopicFormation Mechanism and Heterogeneity Evaluation of Lacustrine Shale ReservoirsView all 5 articles
 Xiaohua Jiang1,2,3
Xiaohua Jiang1,2,3 Rukai Zhu1,2,3*
Rukai Zhu1,2,3* Songtao Wu1,2,3*
Songtao Wu1,2,3* Jingya Zhang1,2,3
Jingya Zhang1,2,3 Zhichao Yu1,2
Zhichao Yu1,2 Modi Guan1,2
Modi Guan1,2 Lihua Ding1,2
Lihua Ding1,2Introduction: Clay minerals are critical components of lacustrine shale systems, where their associated pores govern reservoir properties. The diagenetic transformation of these minerals, particularly illitization, profoundly impacts reservoir quality, yet the mechanisms driving illitization and its influence on pore evolution remain poorly understood. This study investigates the illitization processes and pore characteristics in the Cretaceous Qingshankou Shale (QSK shale) to elucidate their implications for unconventional hydrocarbon storage.
Methods: Core samples from the QSK shale in the Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin, were analyzed using a multi-method approach: field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) for pore morphology, QEMSCAN® for mineralogical mapping, X-ray diffraction (XRD) for clay mineral quantification, and nitrogen adsorption for pore-size distribution analysis.
Results: Key findings include: (i) Clay minerals in the QSK shale are dominated by illite and illite/smectite mixed layers (average >40% content), with intense illitization yielding >60% illite in clay fractions. (ii) Pores within clay minerals (micropores and mesopores <50 nm in illite/illite-smectite; macropores 50–100nm and elongated pores >800nm in chlorite) constitute primary storage spaces, interconnected by microcracks. (iii) Illitization occurs via two pathways: transformation of illite/smectite mixed layers and albite alteration, with the former dominating. Porosity initially increases with illite content (up to ∼30%) but declines progressively beyond this threshold.
Discussion: The threshold effect of illitization on porosity highlights a critical balance between pore generation (via mineral dissolution) and occlusion (from authigenic illite precipitation). These findings provide a mechanistic framework for predicting reservoir quality in lacustrine shale systems, emphasizing the dual role of illitization in enhancing or degrading storage capacity depending on diagenetic maturity.
Lacustrine shale is currently a key focus of exploration in China, with significant breakthroughs achieved in the Ordos Basin, Junggar Basin, and other regions (Fu et al., 2021; Fu et al., 2020; Jianyong et al., 2022; Dongmin et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2018). Unlike the shale in the Ordos Basin and Junggar Basin, the QSK shale in the Gulong Sag of the Songliao Basin does not contain interlayers or has a small total thickness of interlayers, and pure shale is developed (Wenzhi et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2021; Jin et al., 2023). In recent years, important discoveries have also been made in the pure shale with integrated sources and reservoirs. Many wells have obtained industrial oil flow, and multiple development platforms have been established. Lacustrine pure shale has exploration value (Sun et al., 2021; Jin et al., 2023; Wang Y. et al., 2020; Wang G. et al., 2020; Liyun, 2021; Du et al., 2019). The breakthrough in pure shale exploration is highly significant for lacustrine shale exploration. In terms of distribution area, pure shale is generally distributed in the center of the lacustrine basin, covering a wide area. It has a large development thickness and high exploration value. In terms of lithology, pure shale is a true integrated source and reservoir and is also the most typical representative of lacustrine shale with great research significance.
The QSK shale in Gulong has a high clay mineral content, and the clay mineral pores contribute greatly to the reservoir performance. In addition, the illitization is strong due to the influence of diagenesis. The illite content in the Gulong shale is extremely high. Therefore, the effect of illitization on reservoir performance is worth studying. Previous researchers have conducted in-depth and systematic research on shale reservoir characteristics, but there are relatively few studies on pure shale (Wang Y. et al., 2020; Wang G. et al., 2020; Liyun, 2021; Du et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2021; He et al., 2022), especially the research on clay mineral pores and illitization in shale is relatively weak. Due to the high degree of thermal evolution, the Gulong shale has entered the A-B stage of intermediate diagenesis (Feng et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2021). Most of the clay minerals have been converted into illite. How does the illitization occur? What is the impact of illitization on the shale reservoir performance? There are not many studies on the impact of illitization in shale on the reservoir pore structure. Only a few scholars have studied the relationship between illite and pores, and no unified view has been formed (Afagwu et al., 2022; Nadeau et al., 2005; Jiang et al., 2021). Afagwu and Nadeau et al. believed that illite has weaker adsorption capacity than clay minerals such as chlorite, smectite, and kaolinite, and has smaller pores (Afagwu et al., 2022; Nadeau et al., 2005). Shao et al. proposed that illite has a stronger adsorption capacity than other clay minerals. The transformation of smectite to illite in Gulong shale is a low-energy spontaneous reaction. This process releases interlayer water and structural water, resulting in lattice collapse and clay particle volume shrinkage. The clay mineral micro-nano pores are formed. These pores increase the shale reservoir space and increase the adsorption capacity of the reservoir. In addition, the clay mineral illite/smectite mixed layer is rapidly transformed into illite, and the lamellar clay minerals shrink along the lamellation, forming a large number of lamellar fractures (Shao et al., 2021).
Historical experience in conventional oil and gas exploration focusing on sandstone, carbonate rock, etc. did not pay enough attention to clay mineral pores, which has also led to insufficient understanding of clay mineral pores. Although clay mineral pores are small, they play an important role in the shale reservoir, especially pure shale, because of their large total pore volume. Similarly, the impact of clay mineral transformation, such as illitization, on shale reservoir performance is also worthy of in-depth study. For this reason, this paper takes the QSK shale in the Gulong Sag as the research object, focusing on two aspects: (1) the characteristics of clay mineral pore development and its contribution to the pore size of pure shale; (2) how does illitization affect shale reservoir performance? The study of these two issues provides a reference for the optimal selection of pure shale oil sweet spots and also provides support for the enrichment theory of lacustrine shale oil.
The Gulong Sag is located in the northern part of the Songliao Basin, west of the Daqing Changyuan in the central depression area, with an area of about 3,700 km2. The QSK shale and the Nenjiang Formation are lacustrine deposits formed in the late Cretaceous period, during which two large-scale lacustrine progressions occurred and a large area of high-quality mud shale was developed. A set of dark gray and black medium-high maturity shales (Ro ≥ 0.7) were developed in the Qing 1 and 2 Members of the Gulong Sag (Figure 1). In addition, this set of shale has shallow burial depth and a high organic matter content. Industrial oil flows have been obtained from multiple wells, revealing the exploration potential of pure shales. Compared with the Yanchang Formation shale in the Ordos Basin and the Lucaogou Formation shale in the Junggar Basin, this pure shale almostly does not contain interlayers or has thin interlayers. It mainly contains thick mud shale. For the same reason, the clay mineral content is higher.
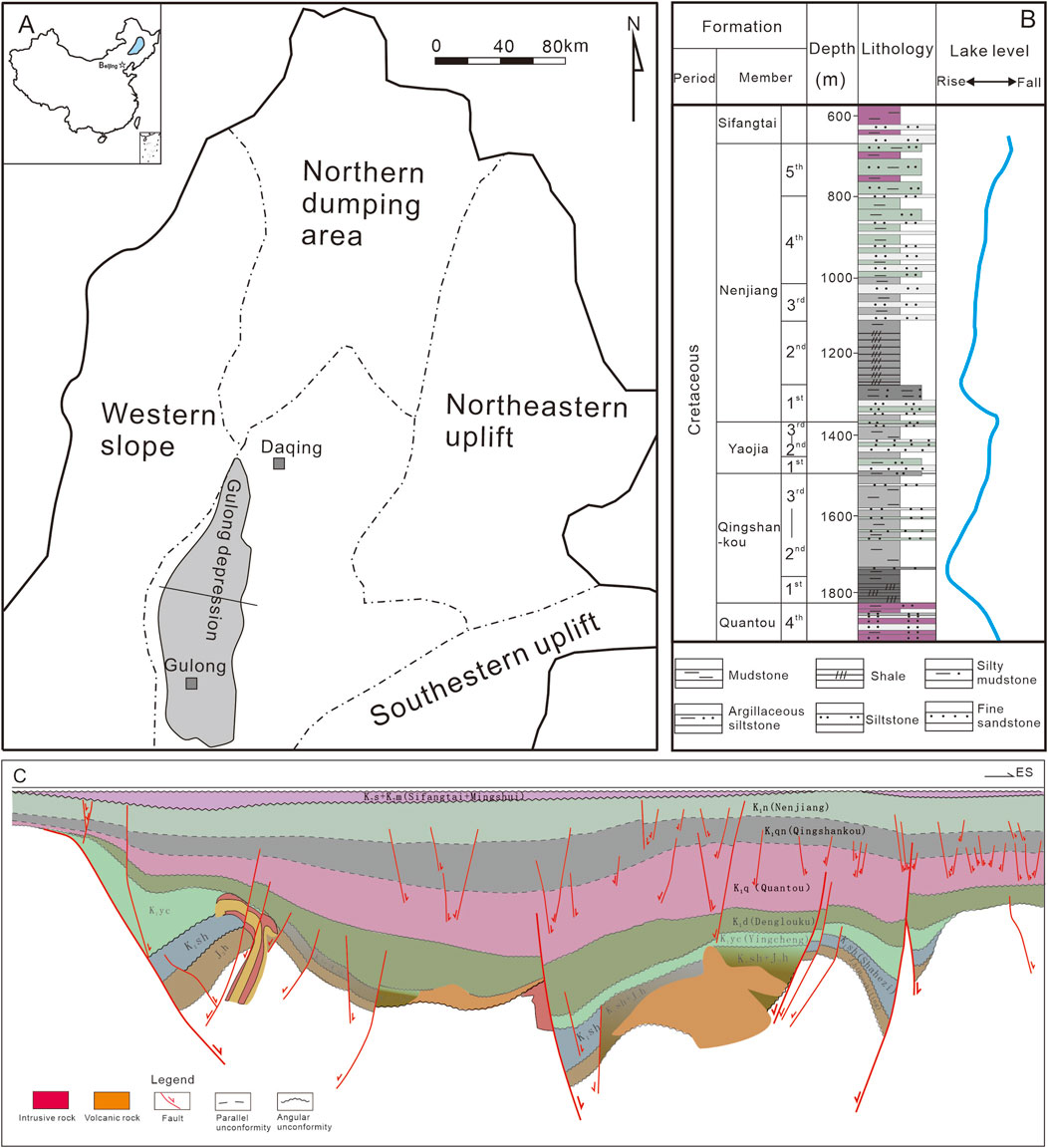
Figure 1. Location map and the stratigraphic column of the study area. (A) Location map. (B) stratigraphic column. (C) Geological cross-section.
The research focuses on the black shale of the Gulong QSK shale in the Songliao Basin. The experimental samples were selected drill core samples from typical shale oil wells SL1,SL2 with high clay mineral content in Qingshankou Formation. The samples are divided into two categories include block samples and powdered samples. The block samples are used for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis and high-pressure mercury injection experiments, while powder samples are used for X-ray diffraction (XRD) and low-temperature nitrogen adsorption analyses. These methods provide data on the whole-rock composition and pore structure of the samples.
This study was mainly completed in the laboratory of the National Energy Tight Oil and Gas Research and Development Center. According to the research purpose, this experiment is divided into three parts. The specific methods and processes are as follows: (1) Analysis of rock mineral components. The experimental instrument used is the Rigaku X-ray diffractometer to analyze the 200-mesh powder sample. The instrument model used for XRD non-clay soil mineral analysis is Smart Lab. The experiment was completed at a working voltage of 45 kV and a working current of 150mA; The experiment was completed at a working voltage of 48 kV and a working current of 100 mA. It is used to obtain rock mineral components and clay mineral composition analysis; (2) Clay mineral characteristic analysis. A high-resolution scanning electron microscope was used to obtain electron microscope photos of clay minerals. The instrument model used was the high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscope Apreo, FEI Company, United States. The working voltage was 2.00 kV and the working distance was 4.0 mm.Samples for SEM analyses were polished by argon ion. (3) EDS (energy dispersive spectrometry) analysis was used to analyze elements and minerals. (4) Pore structure analysis. Low-temperature nitrogen adsorption instrument and a high-pressure mercury injection experiment were used. The low-temperature nitrogen adsorption experiment was completed at Peking University. The instrument used was an ASAP2020-specific surface area analyzer. The experiment used shale powder samples with a particle size of 200 mesh. The specific surface area used Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) specific surface area. According to the desorption curve determined by the Barret-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) theory, the pore volume was calculated, and the equivalent pore distribution was quantitatively analyzed. The high-pressure mercury injection experiment was completed at China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). The instrument used was a Mack Auto Pore V 9620 high-pressure mercury injection instrument. Before the experiment, the shale was cut into cubes with a side length of 1 cm, and the six faces of the cubic shale sample were polished with a grinder. The sample was then placed in a 60°C oven for more than 48 h until the mass no longer changed. Finally, the sample was placed in a room-temperature drying oven for testing.
The QSK shale in the Gulong Sag of the Songliao Basin is a set of high-clay, organic-rich shale (Figure 2), with an average TOC content of 2%, a feldspar content of about 5%–37% with an average of 10%, and a quartz content of about 20%–65% with an average of 30%. The clay mineral content is generally high with an average of more than 40% and a maximum of up to 65%. Similar to the lacustrine shales in other basins (Wu et al., 2022; GanLin et al., 2021), affected by sedimentation, astronomical cycles, etc. (Zhu et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhang T. et al., 2023; Jin et al., 2020; Fu et al., 2022; Qingtao et al., 2024; Zhang R. et al., 2023), the QSK shale developed laminae, mainly clay laminae, felsic laminae, and ostracod laminae. Due to the high degree of thermal evolution, the vitrinite reflectance (Ro) of the QSK shale in the Gulong Sag has reached more than 1.3%, and the shale has entered the late stage of intermediate diagenesis. Among the clay minerals, illite is the primary one, accounting for an average of 66% of the clay minerals and a maximum of 82%. The second is the illite/smectite mixed layer, with an average content of about 2.1%. At the same time, a small amount of chlorite is developed, with an average content of about 1.3% (Figure 3).
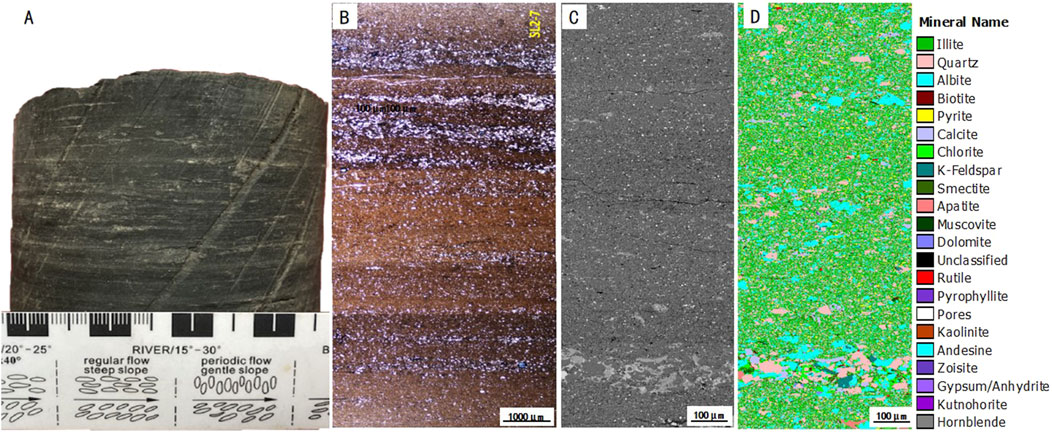
Figure 2. Core and microscopic photos of QSK shale. (A) core photo, showing felsic and clay mineral lamina. (B) Micrograph of thin Section. (C) SEM-BSE image. (D) Qemscan image.
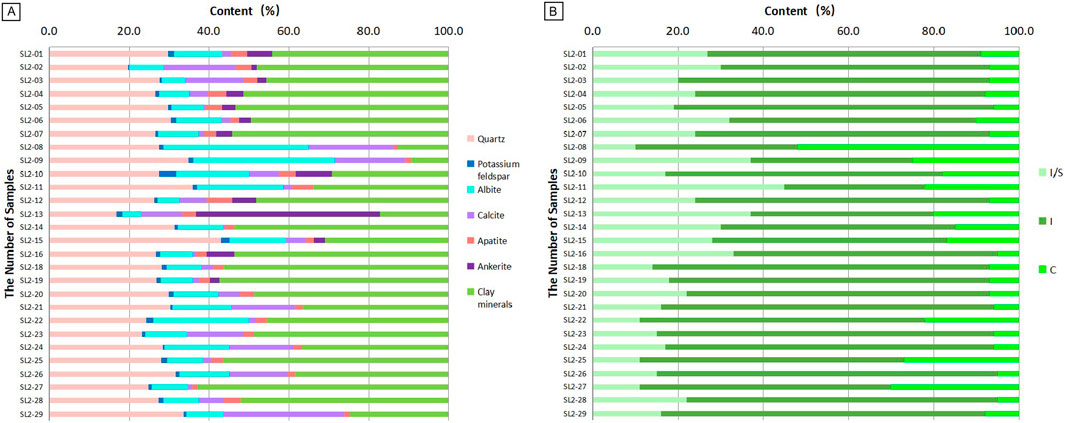
Figure 3. Mineral and clay mineralogical composition of the QSK shale (I-illite, I/S-illite/smectite mixed layers, C-chlorite). (A) Mineral composition bar chart. (B) Clay mineral composition bar chart.
Affected by the high degree of evolution, the main clay minerals in the QSK shale are illite and illite/smectite mixed layers, containing a small amount of chlorite. Due to the small particle size of clay minerals, usually at the micro-nano level, to observe the characteristics of clay minerals, high-resolution scanning electron microscopy must be used for analysis. From the scanning electron microscope photos, it can be seen that illite is gray - dark gray, hair-like, flanking, and fine crystals. The illite/smectite mixed layer is gray-dark gray, leaf-like, and wool-like. Chlorite is relatively light in color, grayish white, plate-like, long strips, and coarse crystals. At the same time, clay minerals develop intragranular/intergranular pores due to their special crystal structure and distribution (Figure 4). Clay mineral pores are the main pore type of Gulong shale, contributing greatly to the shale reservoir. They are mainly inter-crystalline pores and inter-granular pores of illite and illite/smectite mixed layers. Due to the high organic matter content in the Gulong Shale, most of the clay mineral pores are filled with organic matter, and some of the filled organic matter forms new organic pores under hydrocarbon generation (Figures 4B, D).
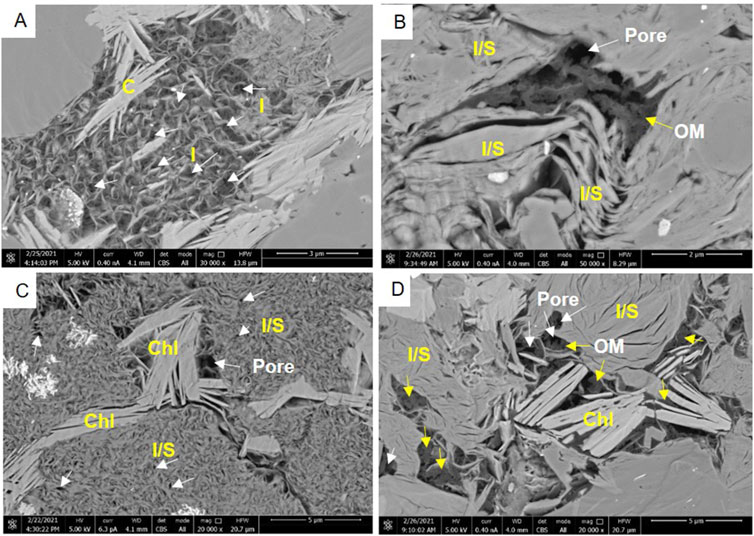
Figure 4. Electron microscope backscatter images of clay minerals and pores (A) Hair-like illite is developed, and a large number of honeycomb-like nanopores are formed between illite particles, with a pore size of 20–50 nm. (B) Illite/smectite mixed layers are developed, the pores are filled with organic matter, and organic pores are developed. (C) The illite/smectite mixed layer is inlaid with chlorite. The illite/smectite mixed layer has a small particle size and a pore size of less than 100 nm. The framework pores formed by chlorite minerals are large and mostly narrow and long with microcracks. Illite/smectite mixed layers, chlorite, and organic matter are developed in combination. (D) The intergranular pores of the illite/smectite mixed layers and chlorite are filled with organic matter. (White arrows represent pores, yellow arrows represent organic matter; I-illite, I/S-illite/smectite mixed layers, C-chlorite, OM-organic matter).
To better study the pore structure of clay minerals, clay mineral laminae were selected for research, ensuring data representativeness and statistical significance. These laminae consist primarily of clay minerals, where clay mineral pores are well-developed. The clay mineral laminae were stripped out by wire-cutting technology to conduct nitrogen adsorption experiments. The study found that the clay mineral pores are mainly mesopores and micropores less than 50 nm. The pores are mostly developed in the two intervals of 50 nm and 3 nm. Regarding pore quantity, it can be seen that there are many small pores around 3 nm (Figure 5). By comparing the pores of felsic laminae and ostracod laminae, it is not difficult to find that clay mineral pores have a larger specific pore volume and specific surface area.
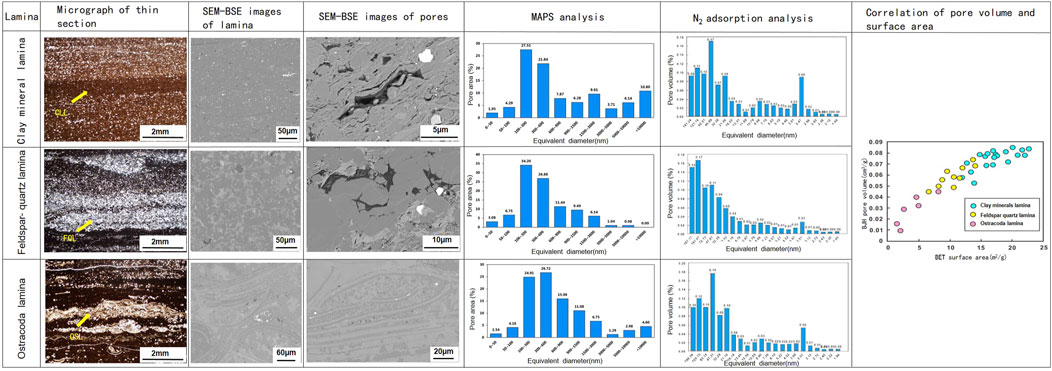
Figure 5. Microscopic photos and pore distribution histograms of different types of laminae. (CLL-clay mineral lamina, FQL-feldspar-quartz lamina, OLL-ostracoda lamina).
Scanning electron microscope Maps image analysis found that clay mineral lamina have better porosity than felsic laminae and ostracod laminae. In Map analysis, it should be noted that, approximatively take the plane porosity as the porosity, meanwhile, the pores with length-width ratio greater than 10 were defined as fractures. Through the study of different laminae samples, it was found that the total porosity of clay mineral lamina is 1.2%, of which pores account for 98.6% and fractures account for 1.4%. The total porosity of felsic laminae is 0.65%, of which pores account for 99.7% and fractures account for 0.3%; the total porosity of ostracod laminae is 0.4%, of which pores account for 97% and fractures account for 3% (Figure 5). Therefore, it can be seen that the total pore volume of clay laminae is larger, and micro-fractures are developed. It also proves that clay mineral micro-fractures are more developed.
Through the analysis of the pores of samples with different clay mineral contents, it was found that the specific pore volume and specific surface area are proportional to the clay mineral content (Figure 5). It has been previously mentioned that the pore size and morphology of different types of clay minerals are different. To further explore the pore contribution of different types of clay minerals, the correlation between pore parameters and clay mineral content was studied. The study showed that, for illite, the nitrogen adsorption BJH pore volume is proportional to the illite content, while the mercury injection (MIP) porosity is not strongly correlated with the illite content. For chlorite, the mercury injection porosity is proportional to the chlorite content, but not strongly correlated with the nitrogen adsorption BJH pore volume. At the same time, the nitrogen adsorption BJH pore volume and mercury injection porosity are not strongly correlated with the illite/smectite mixed layer content (Figure 6). It is known that the effective pore size characterization ranges of nitrogen adsorption and mercury injection are different. The effective pore characterization range of nitrogen adsorption is 2 nm–100 nm, while the effective pore characterization range of mercury injection is 100 nm-900 μm. Therefore, we can analyze that the pores developed in illite are mainly within the characterization range of nitrogen adsorption, that is, 2 nm–100 nm pores. However, the pores of chlorite are relatively large, with pore sizes ranging from tens of nanometers to micrometers.
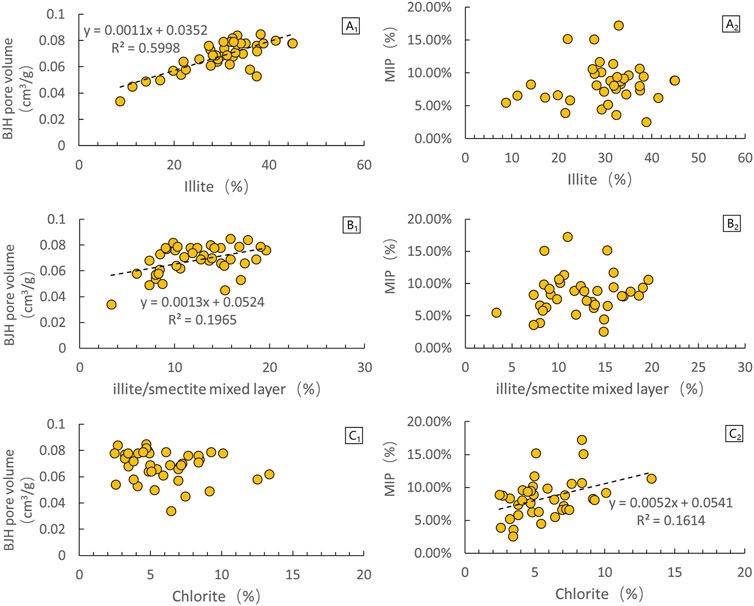
Figure 6. Correlation diagrams between specific BJH pore volume, mercury injection porosity, and different clay minerals (MIP-mercury injection porosity). (A1, A2) Correlation diagram between porosity and illite content. (B1, B2) Correlation between porosity and illite/smectite mixed layer content. (C1, C2) Correlation between porosity and chlorite content.
Based on the study of pore size, FIB-SEM was used to carry out three-dimensional characterization of the pores of different clay minerals. The analysis results show that the pores of illite and illite/smectite mixed layers are mainly composed of pores with a pore size of less than 50 nm (Figure 7), which is consistent with the research of S Kaufhold et al. that about 80% of the pores of clay minerals in shale are 30 nm in size (Kaufhold et al., 2016). The width of micro-fractures is typically greater than 800 nm. The pores of chlorite are relatively large, with macropores of 50–100 nm and narrow pores greater than 800 nm. In general, the pore space connectivity of clay minerals is poor and relies on micro-fractures for communication.
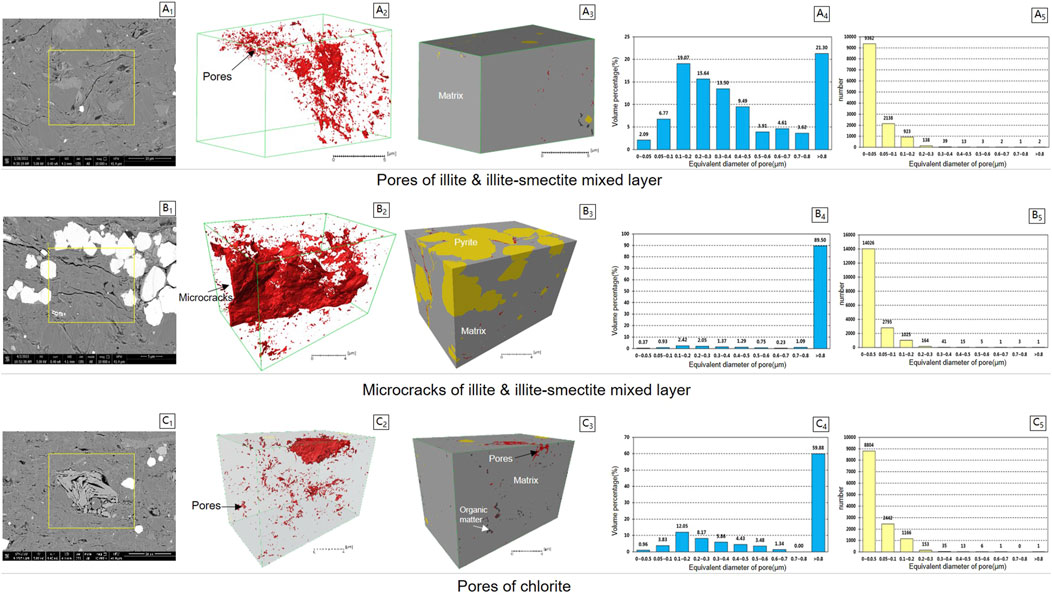
Figure 7. FIB-SEM 3D analysis results of pores in different types of clay minerals. (A1, B1, C1) SEM image of clay mineral pores. (A2, B2, C2) 3D photo of pores,the red areas represents pores, and the continuous red patchy area represents cracks. (A3, B3, C3) 3D micro-scale map of the rock sample showing different components: gray indicates the matrix, yellow represents pyrite, black denotes organic matter, and red highlights pores. (A4, B4, C4) Distribution of pore volume percentage as a function of pore size (A5, B5, C5) Distribution of pore number as a function of pore size.
As the research findings above indicate, shale porosity is positively correlated with the content of illite and chlorite in clay minerals, and since illite dominates the clay mineral composition, it is crucial to investigate the process of illitization.
Based on the basic theory of diagenetic mineral transformation, combined with energy distribution spectrum (EDS) analysis, two illitization processes were discovered: the transformation of illite/smectite mixed layer to illite and the transformation of feldspar to illite.
Illite is not a single mineral but a group of clay minerals with a mica structure, which was called hydromica in the past. Illite is rich in potassium, high in aluminum, and low in iron. The molecular formula of illite is K<1(Al,R2+)2 [(Si,Al)Si3O10][OH]2·nH2O, of which R represents divalent metal cations, mainly Mg2+, Fe2+, etc. The formula of smectite is Na, Ca)0.33(Al, Mg)2 [Si4O10](OH)2·nH2O, which contains a small amount of Na, Ca, Mg. Compared with illite, smectite lacks potassium and has a low aluminum content. Experimental studies have also shown that when the temperature is 100°C–130°C and the ratio of K+ to H+ is close to that of normal seawater, smectite loses interlayer water and transforms into illite. However, smectite cannot be simply transformed into illite through ion exchange, because smectite is a typical 3:1 clay mineral with hydrated cations and water molecules as interlayers. With the increase of burial depth, temperature, and pressure, part of the interlayer water of smectite will be released, causing some interlayer collapse and leading to the rearrangement of the lattice and the adsorption of alkaline cations. It forms a smectite/illite mixed layer mineral, namely, an illite/smectite mixed layer. Then, it further transforms into illite. It is generally believed that the depth range of smectite to illite/smectite mixed layer transformation should be between 1,200 and 3,500 m (Xia et al., 2018; Hower et al., 1976; Zhao and Zhang, 1990; Ren, 1992).
Under acidic conditions, potassium feldspar dissolves, providing potassium ions to stimulate the transformation of the illite/smectite mixed layer into illite, and generating chlorite at the same time (molecular formula: (Mg.Fe.Al)6 [(Si.Al)4O6](OH)8) and micro-crystalline quartz (Equation 1). The particle size of these micro-crystalline quartz particles is generally less than 3 microns, and they are semi-automorphic or anthropomorphic. The particles often exist in the form of many micro-crystalline quartz aggregates. Since interlayer water is removed during the transformation of the illite/smectite mixed layer into illite, new pores are formed during the transformation. Meanwhile, since the unit structural height is reduced from 1.5 nm to 1 nm the smectite structure collapses when smectite is transformed into illite. Therefore, micro-fractures–fractures (Xingyuan and Dongbo, 2016) are generated. Through EDS element analysis, evidence was found that the transformation of illite/smectite mixed layers to illite in the Gulong QSK shale (Figure 8). According to EDS element analysis (Figure 8B), the distribution of different minerals was clarified (Figure 8A). In the blue circle area of Figure 8C, hair-like illite can be seen, which is transformed from the illite/smectite mixed layers. In addition, many micro-pores can be seen in the illite (Figure 8D).
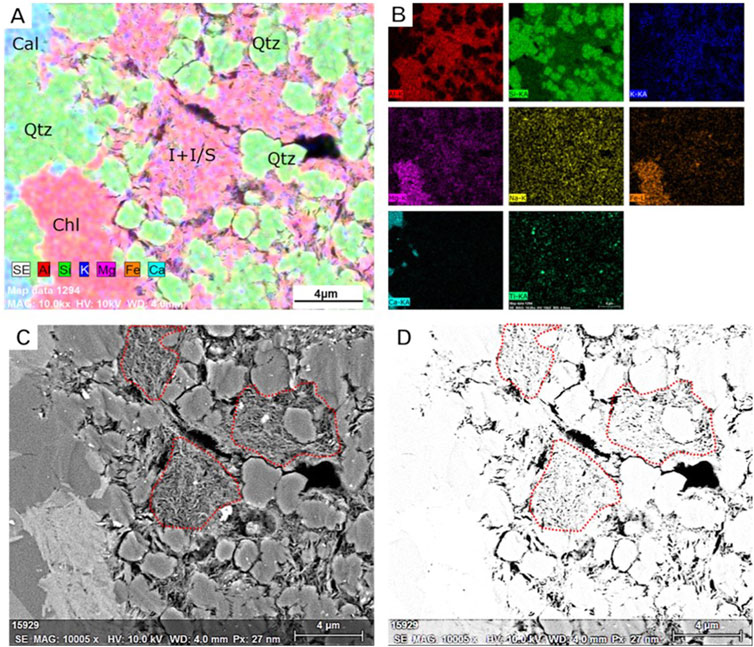
Figure 8. Evidence of illite/smectite mixed layer to illite transformation under EDS. (A) EDS element fusion diagram. (B) EDS single element distribution diagram. (C) SEM electron microscope photo. (D) SEM processed photo, the black areas represent pores.
Potassium feldspar and albite are the main types of feldspar in Gulong Shale, with albite being the main type. Both types of feldspar have the possibility of transforming into illite.
The molecular formula of potassium feldspar is KAlSi3O8. Since shale is different from sandstone in clastic rock and is a closed system, there is generally no additional source of K+. Potassium feldspar can be converted into illite in two ways. One way is that Potassium feldspar first transforms into kaolinite and then further converts into illite. The other way is that it converts directly into illite. The former does not require the consumption of H+ (Cai et al., 2023; Sijing et al., 2009), while the latter does. According to the mineral composition of Gulong shale, there is almost no kaolinite and the potassium feldspar content is also very small. It is mainly the coexistence of illite and quartz. It is speculated that if potassium feldspar is converted into illite, it should be a clay mineral conversion that occurs where the content of potassium feldspar and kaolinite is almost the same.
The molecular formula of albite is: NaAlSi3O8, The content of albite in Gulong shale is high, with an average of more than 10%. Under acidic conditions, potassium feldspar dissolves, providing potassium ions and stimulating the transformation of albite to illite. However, a large number of illite/smectite mixed layers will be generated during the process, and then the illite/smectite mixed layers will be transformed into illite. In this process, silica will also precipitate to form authigenic quartz and form micro-nanopores. Through EDS elemental analysis, evidence of the transformation of albite to illite was found (Figure 9). It can be seen that the reddish part in the albite area in Figure 9A is the transformation of albite to illite.The yellow areas in the image represent residual albite. Clearly, it is challenging to identify albite based solely on SEM analysis, as its granular structure is highly degraded, and the original grain boundaries have become indistinct. Fortunately, we have discovered more definitive evidence of albite illitization (Figure 10). In Figure 10, illitization is observed within an albite grain. The illitized zones exhibit significant depletion of sodium (Na) (indicated by black arrows in Figures 10–a2) and numerous secondary quartz grains have been identified in adjacent regions. (represented by scattered green dots in Figures 10–a2). Due to the limited extent of illitization in these areas, the amount of quartz generated is relatively small. In contrast, regions with more extensive illitization (Figures 10–b1) show a greater quantity of quartz formation (represented by green areas in Figures 10–b2), Interestingly, illitization of albite appears to preferentially initiate along grain margins.
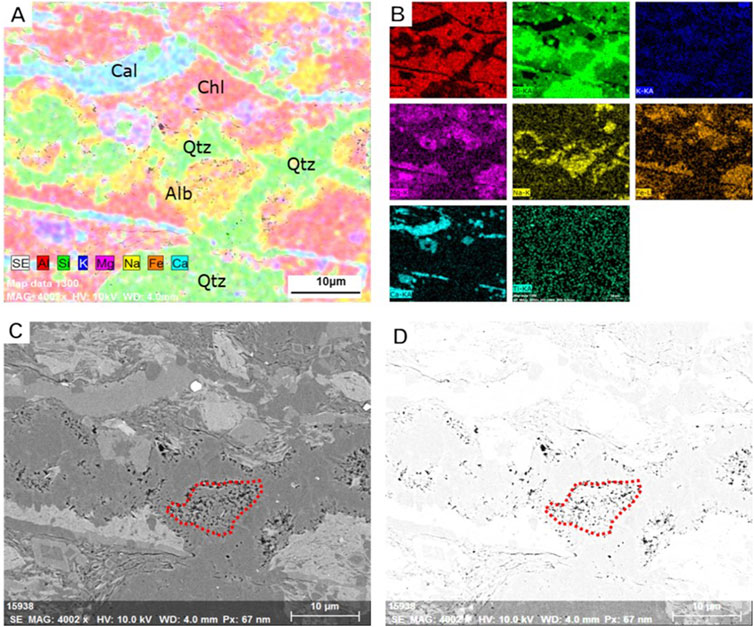
Figure 9. Evidence of Albite-to-Illite Transformation under EDS. (A) EDS element fusion diagram. (B) EDS single element distribution diagram. (C) SEM electron microscope photo. (D) SEM processed photo, the black areas represent pores.
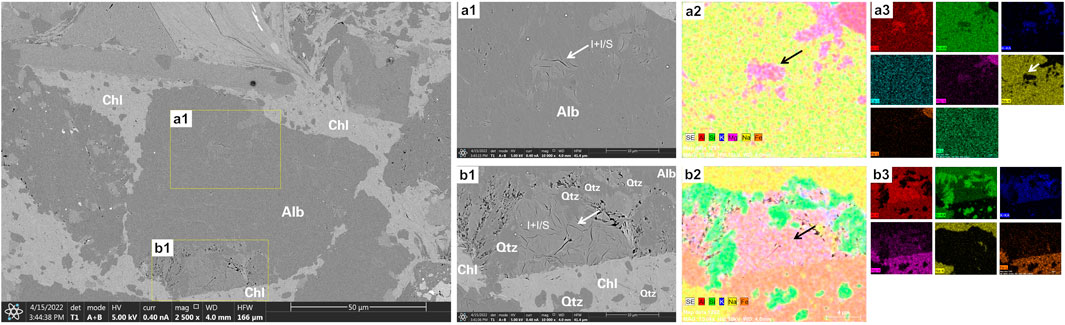
Figure 10. Differential illitization patterns observed within albite grain SEM electron microscope photo. (a1, b1) Magnified SEM micrograph of image (a2, b2) Element fusion diagram of EDS. (a3, b3) single element distribution diagram of EDS.the black arrow represent the illitization area.
To better understand the illite formation process, the correlation changes in mineral content were further studied. It was found that the illite content increased to varying degrees with the decrease of the illite/smectite mixed layer and albite content, and had no obvious relationship with potassium feldspar, which proved that the possibility of direct illitization of potassium feldspar was small. It also confirmed the transformation of illite/smectite mixed layer and albite to illite (Figure 11).
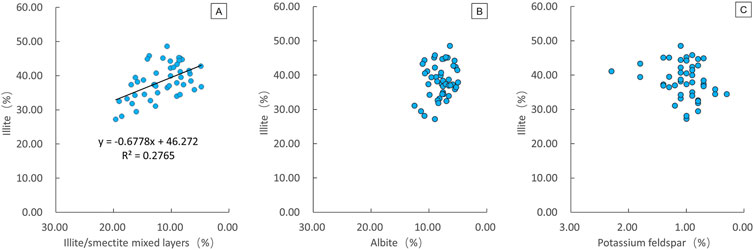
Figure 11. Scatter plot of correlation between illite content and different mineral contents. (A) Correlation between illite content and illite/smectite mixed layer content. (B) Correlation between illite content and albite content. (C) Correlation between illite content and potassium feldspar content.
In addition, through the study of the mineral composition of the clastic rocks in the Gulong Sag, it was found that the content of potassium feldspar was low, and the feldspar was mainly plagioclase (Table 1). It was inferred that the content of potassium feldspar in the sedimentary parent source was originally low, but was mainly plagioclase. Therefore, it was believed that the illitization of feldspar was mainly the transformation of plagioclase to illite. The Qemscan analysis showed that plagioclase was mainly albite, that is, albite was transformed into illite.
Although potassium feldspar can undergo albitization under certain conditions, previous studies have suggested that the degree of albitization should be less than 7%–10% (Cai et al., 2023). In addition, as mentioned earlier, the potassium feldspar content in the QSK shale sedimentary parent rock in the Gulong Sag is not high, so the possibility of potassium feldspar albitization is even smaller. Albite is mainly the primary albite in the sedimentary parent rock.
By reviewing a large number of domestic and international literature, it was found that previous understandings of the impact of illitization on porosity vary. Most scholars believe that illitization reduces reservoir porosity (Tang et al., 1994; Higgs et al., 2007; Andras et al., 2016; Lahann, 2004; Finlayson et al., 2017; Cheng, 2006). Only a few scholars believe that illitization can improve reservoir properties (Schicker et al., 2021; Lin-Gang et al., 2012; Liu, 2009; Dong, 2017; Huo et al., 2019). However, this study reveals that the illitization process leads to an initial increase followed by a decrease in the porosity of shale reservoirs.
As mentioned above, the pores of illite and illite/smectite mixed layers are mainly composed of pores with a pore size of less than 50 nm, and pores with a pore size of 50 nm and 3 nm are developed. To further investigate the impact of illitization on the pore structure of shale reservoirs, three samples were selected for analysis. The information of these three samples is shown in Table 2. The clay mineral content of samples SL2-40, SL2-03, and SL2-42 increases sequentially, and the illite content also increases accordingly (Table 2). Nitrogen adsorption results indicate that the pore size distribution exhibits two peaks at 40–50 nm and 3 nm (Figure 12). From sample SL2-40 to SL2-03, the clay mineral content increases from 34.5% to 45.6%, and the absolute illite content increases from 22.3% to 33.29%. Correspondingly, nitrogen adsorption analysis shows that the total pore volume increases from 0.058 cm3/g to 0.080 cm3/g, indicating an overall increase in porosity. The increased porosity is primarily attributed to pores with sizes of 40–50 nm, with the proportion of 40–50 nm pore volume increasing from 19% to 27%. From sample SL2-03 to SL2-42, the clay mineral content increases from 45.6% to 61.5%, and the absolute illite content increases from 33.29% to 44.90%. However, nitrogen adsorption analysis reveals that the total pore volume decreases from 0.080 cm3/g to 0.077 cm3/g, indicating a reduction in total porosity. The decrease is mainly observed in pores with sizes of 40–50 nm, with the proportion of 40–50 nm pore volume decreasing from 27% to 24%, although the volume of 3 nm pores increases from 4% to 9%. From this, it can be observed that as the clay mineral content and the absolute illite content increase, the porosity of the shale reservoir exhibits a trend of initially increasing and then decreasing.
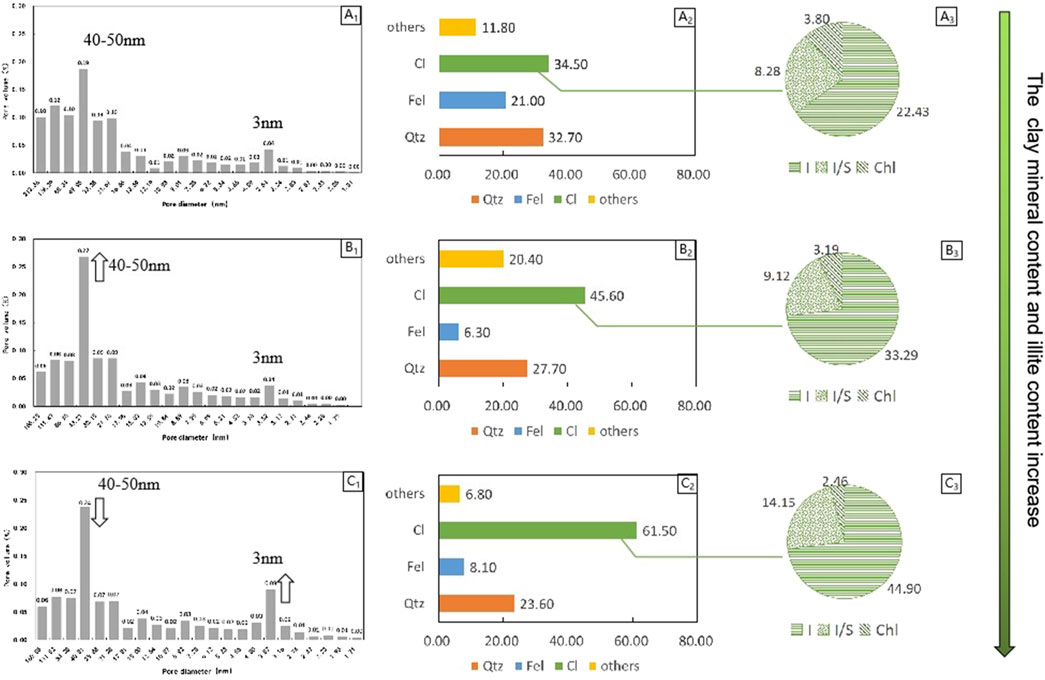
Figure 12. Pore size distribution of samples with different illite contents. (A1, B1, C1) Pore size distribution histograms from nitrogen adsorption analysis, (A2, B2, C2) Mineral composition diagrams, (A3, B3, C3) Clay mineral composition diagrams.cI-clay minerals, Fel-feldspar,Qtz-quartz, I-illite, I/S-illite/smectite mixed layers, Chl-chlorite.
To further understand the trend, statistics were conducted on shales with different clay mineral contents. It was found that with the increase of illite content, the pores increased to a certain extent and then there would be an inflection point to decrease. The porosity began to decrease after the absolute illite content reached about 30% (Figure 13).
Since there are numerous factors influencing shale reservoir properties—such as diagenetic environment, fluids, and others, in addition to mineral composition—and given that clay minerals constitute only a portion of its composition, the 30% threshold may not be an exact inflection point. For instance, it could also be 38%, as indicated by the blue line in Figure 13. However, based on current research findings, this value is highly significant and serves as a valuable reference. Further clarification of this issue may be achieved by conducting additional experiments with more samples in the future.
The reasons for the initial increase and subsequent decrease in shale porosity due to illitization are explored as follows. In the early stages of diagenesis, the degree of illitization is low, and the illite content is minimal. During this stage, the rock is characterized by relatively high amounts of rigid minerals such as feldspar, quartz, and carbonate, which provide strong support to the rock framework. Concurrently, the illitization process is observed to generate some micropores, thereby contributing to an increase in total porosity. As diagenesis progresses and illitization intensifies, a reduction in the total porosity of the reservoir is noted, primarily attributed to two factors. First, the continuous increase in illite content is accompanied by a corresponding decrease in non-clay minerals such as quartz and feldspar, which weakens the rock’s resistance to compaction and reduces pore space. Second, as illustrated in Figure 12, the increase in illite content is correlated with a decrease in chlorite content. As previously discussed, chlorite is associated with the development of relatively larger pores compared to illite. Therefore, the reduction in chlorite content leads to a decrease in larger pores, resulting in an overall decline in porosity.
Due to the limited scope of this research, several issues remain that warrant further investigation. Firstly, the impact of secondary quartz generated during the illitization process on porosity remains unclear. It is yet to be determined whether secondary quartz tends to block pores or supports the rock framework, thereby mitigating porosity reduction caused by compaction. Secondly, it is suggested that the effects of illitization on reservoirs vary depending on the lithology. Specifically, differences are expected between sandstone and shale reservoirs, as the former represents an open system while the latter is a relatively closed system. These two systems exhibit distinct fluid environments, which directly influence the elements and PH conditions required for the illitization process. To date, only a limited number of studies have addressed this aspect (Guanghui et al., 2015; Ehrenberg, 1990). Further work and more in-depth research are required to fully elucidate these issues.
(1) The QSK shale has a high clay mineral content, with an average of more than 40%, among which, illite accounts for more than 60%. Illite has a great influence on the reservoir porosity of shale.
(2) In paticular, clay mineral pores are the main pore type in the QSK shale and contribute greatly to the overall porosity of shale reservoir. The pore morphology and pore size of different clay minerals are different. The pores of illite and illite/smectite mixed layers are mainly with a size less than 50 nm, while those in chlorite are relatively large, with macropores in the range of 50–100 nm and elongated pores larger than 800 nm. Micro-fractures are developed in clay minerals, and the width of micro-fractures is generally greater than 800 nm. Micro-fractures effectively connect the pores of clay minerals and improve reservoir property.
(3) Two types of illitization processes were revealed in the QSK shale: illitization of illite/smectite mixed layers and albite illitization. The illitization of illite/smectite mixed layers is the dominant process. The illitization process increases the pores in clay minerals and the total porosity, thus improving the reservoir performance to a certain extent. However, the porosity decreases with illite content when it is larger 30%.
(4) The results from this study bring at least two challenges to traditional understanding.(i) clay mineral pores dominate the pore system. For many different types of reservoirs, pores developed in brittle minerals such as quartz and feldspar were the main pore types while the clay minerals was generally considered detrimental to reservoir property; (ii)Illitization processes improve the pore system. Illitization was believed to reduce the porosity in sandstone. However, this study confirmed a positive effect of illitization with illite content up to 30%, subsequently increase in illite would lead to porosity reduction. Certainly, more works are merit for a deep understanding of this process.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
XJ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation. RZ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources. SW: Resources, Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology. JZ: Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources. ZY: Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization. MG: Writing–review and editing, Formal Analysis, Software. LD: Writing–review and editing, Software, Visualization.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
We thank China National Petroleum Corporation’s permission to publish this paper. This work is sponsored by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42090025), We thank members of our research community from Daqing Oilfield and RIPED for the data and ideas they contributed. We thank the reviewers for the insightful feedback and comments, which have improved the manuscript substantially.
Authors XJ, RZ, SW, JZ, ZY, MG, and LD were employed by China National Petroleum Corporation.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Afagwu, C., Mahmoud, M., Alafnan, S., Alqubalee, A., ElHusseiny, A., and Patil, S. (2022). Pore volume characteristics of clay-rich shale: critical insight into the role of clay types, aluminum and silicon concentration. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 47 (9), 12013–12029. doi:10.1007/s13369-022-06720-w
Andras, P., Aplin, A. C., Goulty, N. R., Sargent, C., Derkowski, A., and Pluijm, B. A. V. D. (2016). Clay mineral transformations and associated compaction of siliciclastic mudstones[C]//Eage shale workshop.
Cai, L. X., Yang, T., Tian, J., Yi, J., and Ren, Q. (2023). Advances in studies of development and growth mechanisms of clay minerals in tight sandstone reservoirs. Acta Sedimentol. sin. 41 (06), 1859–1889. doi:10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2023.010
Cheng, X. (2006). Laws of clay mineral transfommation and reservoir porosity evolution: a case study of Fu lll member of taixing oil field in subei basin. Petroleum Geol. and Oil field Dev. Daqing (01), 43-45+105–106. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3754.2006.01.011
Dong, J. (2017). The influence of clay mineral transformation on shale pores. Shandong Chem. Ind. (46), 125–127.
Du, J., Hu, S., Pang, Z., Lin, S., Hou, L., and Zhu, R. (2019). The types, potentials and prospects of continental shale oil in China. China Pet. Explor. 24 (05), 560–568. doi:10.3969/i.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.003
Ehrenberg, S. N.(1990). Potassium-leached zones at the contacts of the garn formation, mid-Norwegian continental shelf: evidence for the role of shale in sandstone diagenesis: ABSTRACT. Aapg Bull. 74(5), 647–648. doi:10.1306/44B4B03B-170A-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Feng, Z., Liu, B., Shao, H., Wang, C., Hong, S., Wang, J., et al. (2020). The diagenesis evolution and accumulating performance of the mud shale in Qingshankou Formation in Gulong area, Songliao Basin. Petroleum Geol. and Oilfield Dev. Daqing 39 (03), 72–85. doi:10.19597/J.ISSN.1000-3754.202004057
Finlayson, A., Melvin, A., Guise, A., and Churchill, J. (2017). Controls on the reservoir quality of late cretaceous springar formation deep-water fan systems in the vring basin.
Fu, J., Liu, X., Shixiang, L., Qiheng, G., Xinping, Z., Weiwei, Y., et al. (2021). Discovery and resource potential of shale oil of chang 7 member, triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. China Pet. Explor. 26 (05), 1–11. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.05.001
Fu, J., Shixiang, Li, Niu, X., Deng, X., and Zhou, X. (2020). Geological characteristics and exploration of shale oil in chang 7 member of triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 47 (05), 870–883.
Fu, X., Qi'an, M., Qiang, Z., Wang, Z., Jin, M., and Bai, Y. (2022). Cyclicity of organic matter abundance and lithofacies paleogeography of Gulong shale in Songliao Basin. Petroleum Geol. and Oilfield Dev. Daqing 41 (03), 38–52. doi:10.19597/J.ISSN.1000-3754.202111071
Guanghui, Y., Yingchang, , Gluyas, J., Li, X., Xi, K., Wang, Y., et al. (2015). Feldspar dissolution, authigenic clays, and quartz cements in open and closed sandstone geochemical systems during diagenesis: typical examples from two sags in Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Aapg Bull. 99, 2121–2154. doi:10.1306/07101514004
He, W., Cui, B., Wang, F., Wang, Y., Meng, Q., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Study on reservoir spaces and oil states of the CretaceousQingshankou formation in Gulong sag, Songliao Basin. Geological Rev. 68 (02), 693–741. doi:10.16509/j.georeview.2021.12.001
Higgs, K. E., Zwingmann, H., Reyes, A. G., and Funnell, R. H. (2007). Diagenesis, porosity evolution, and Petroleum emplacement in tight gas reservoirs, taranaki basin, New Zealand. J. Sediment. Res. 77 (12), 1003–1025. doi:10.2110/jsr.2007.095
Hower, J., Eslinger, E. V., Hower, M. E., and Perry, E. A. (1976). Mechanism of burial metamorphism of argillaceous sediment: 1. Mineralogical and chemical evidence. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 87 (87), 725–737. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1976)872.0.CO;2
Hua, G., Wu, S., Oiu, Z., Jing, Z., Xu, J., and Guan, M. (2021). Lamination texture and its effect on reservoir properties: a Case Study of longmaxi shale, sichuan basin. Acta Sedimentol. sin. 39 (2), 281–296. doi:10.14027/j.issn.1000
Huang, S., Huang, K., Feng, W., Tong, H., and Zhang, X.(2009). Mass exchanges among feldspar, kaolinite and illite and their influences on secondary porosity formation in clastic diagenesis - A case study on the Upper Paleozoic, Ordos Basin and Xuiiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression. Geochimica 38(05), 498–506. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.05.009
Huo, Q., Zeng, H., Fu, L., Zhang, X., and Fan, Q. (2019). Accumulating characteristics and pore evolution for member qing mud shale in north Songliao Basin. Petroleum Geol. and Oilfield Dev. Daqing 38 (01), 1–8. doi:10.19597/j.issn.1000-3754.201808040
Jiang, X., Wu, S., Hou, L., Zhang, J., Guan, M., Zhai, F., et al. (2021). Porosity evolution in lacustrine organic-matter-rich shales with high claly minerals content. Front. Earth Sci. (Lausanne). 9. doi:10.3389/feart.2021.766093
Jianyong, X., Xinjiang, C., Wenbo, Li, Jingsheng, Z., Xiaohu, W., Yanjie, C., et al. (2022). Exploration and practice of benefit development of shale oil in Jimsar Sag.Junggar Basin. China Pet. Explor. 27 (01), 99–110. doi:10.3969/i.issn.1672-7703.2022.01.009
Jin, C., Dong, W., Bai, Y., Lv, J., Fu, X., Li, J., et al. (2020). Lithofacies characteristies and genesis analysis of Gulong shale in Songliao Basin. Petroleum Geol. and Oilfield Dev. Daqing 39 (03), 35–44. doi:10.19597/J.ISSN.1000-3754.202005016
Jin, Z., Zhang, Q., Zhua, R., Dong, L., Fu, J., Liu, G., et al. (2023). Classification of lacustrine shale oil reservoirs in China and its significance. Oil and Gas Geol. 44 (04), 801–819. doi:10.11743/ogg20230401
Kaufhold, S., Grathoff, G., Halisch, M., Plotze, M., Ostertag-Henning, C., et al. (2016). Comparison of methods for the determination of the pore system of a potential German gas shale. 163, 190. doi:10.1346/cms-wls-21.13
Lahann, R. W. (2004). AAPG annual meeting, april 18-21, 2004 - Dallas, Texas: a broader view of framework Weakening. Search & discovery, 2004.
Li, X., Wang, J., Tan, X., Hu, L., and Liang, M. (2018). The dewatering transformation and thermal DynamicMechanism of clay mineral in shale diagenesis. J. Petrochem. Univ. 31 (01), 61–70. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-396X.2018.01.011
Liu, Bo, Sun, J., Zhang, Y., He, J., Fu, X., Yang, L., et al. (2021). Reservoir space and enrichment model of shale oil in the first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Changling Sag, southern Songliao Basin, NE China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 48 (03): 521–535. doi:10.11698/PED.2021.03.08
Liu, L. (2009). “Mass exchanges among feldspar, kaolinite and illite and their influen ces on secondary porosity formation in clastic diagenesis—a case study on t he Upper Paleozoic,” in Ordos Basin and xujiahe formation, western sichuan depression. Geochimica.
Liyun, L. (2021). National demonstration zone for annual production of million tons of shale oil settles in daqing Oilfield. Sci. Technol. Dly. doi:10.28502/n.cnki.nkjrb.2021.004844
Nadeau, P. H., Bjrkum, P. A., and Walderhaug, O. (2005). Petroleum system analysis: impact of shale diagenesis on reservoir fluid pressure, hydrocarbon migration, and biodegradation risks. Petroleum Geol. North-West Eur. Glob. 1 (1), 1267–1274. doi:10.1144/0061267
Qingtao, M., Hu, F., Liu, Z., Sun, P., and Liu, R. (2024). Lithofacies types and genesis of fine-grained sediments in Terrestrial Depression lake basin: taking upper cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin as an example. J. Jilin Univ. Sci. Ed. 54 (01), 20–37. doi:10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20230314
Schicker, A., Gier, S., Schieber, J., and Krois, P. (2021). Diagenesis of the malmian mikulov formation source rock, Vienna basin: focus on matrix and pores. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 129 (1), 105082. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105082
Shao, H., Gao, B., Pan, H., Chen, G., and Li, L. (2021). Diagenesis-pore evolution for Gulong shale in Songliao Basin. Petroleum Geol. and Oilfield Dev. Daqing 40 (05), 56–67. doi:10.19597/J.ISSN.1000
Sun, L., He, L., He, W., Li, G., Zhanng, S., Zhu, R., et al. (2021). An analysis of major scientific problems and research paths of Gulong shale oil in Daqing Oilfield, NE China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 48 (03), 453–463. doi:10.11698/PED.2021.03.02
Tang, Z., Parnell, J., and Ruffell, A. H. (1994). Deposition and diagenesis of the lacustrine-fluvial cangfanggou group (uppermost permian to lower triassic), southern Junggar Basin, NW China: a contribution from sequence stratigraphy. J. Paleolimnol. 11 (1), 67–90. doi:10.1007/bf00683271
Wang, G., Wang, F., Meng, Q., and Gu, S. (2020b). Strategic significance and research direction for Gulong shale oil. Petroleum Geol. and Oilfield Dev. Daqing 39 (03), 8–19.
Wang, X., Yang, Z., Guo, X., Chen, X., Li, W., and Zhan, L. (2019). Practices and prospects of shale oil exploration in jimsar sag of Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 40 (04), 402–413. doi:10.7657/j.issn.1000-9752.2019.04.002
Wang, Y., Liang, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, B., Zhao, Y., Liu, X., et al. (2020a). Resource potential and exploration direction of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin. Petroleum Geol. and Oilfield Dev. Daqing 39 (03), 20–34. doi:10.19597/J.ISSN.1000-3754.202005032
Wu, L.- G, Li, X.- S, Guo, X. B., Luo, Q. S., Liu, X. J., Chen, X., et al. (2012). Diagenetic evolution and formation mechanism of dissolved pore of shale oil reservoirs of Lucaogou formation in Malang sag. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2012.03.007
Wu, S., Zhu, R., and Zhong, L. (2022). Laminar structure of typical continental shales and reservoir quality evaluationin central-western basins in China. China Pet. Explor. 27 (05), 62–72. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2022.05.006
Yang, Z., Lianhua, H., Lin, S., Xia, L., Lijun, Z., Songtao, W., et al. (2018). Geologic characteristics and exploration potential of tight oil and shale oil in Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar sag. China Pet. Explor. 23 (04), 76–85. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.04.009
Zhang, R., Jin, Z., Zhu, R., Li, M., Hui, X., Wei, R., et al. (2023b). Investigation of deposition rate of terrestrial organic-rich shales in China and itsimplications for shale oil exploration. Oil and Gas Geol. 44 (04), 829–845. doi:10.11743/ogg20230403
Zhang, T., Zhu, R., Cai, Y., Wang, H., Lu, D., Zhou, H., et al. (2023a). Distribution of organic matter in the Qingshankou Formation shale, Gulong sag,Songliao Basin observed within an isochronous sequence stratigraphic framework. Oil and Gas Geol. 44 (04), 869–886. doi:10.11743/ogg20230406
Zhi, D., Song, Y., He, W., Jia, X., Zou, Y., and Huang, L. (2019). Geological characteristics, resource potential and exploration direction of shale oil in Middle-lower permian, Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 40 (04), 389–401.
Zhao, X., and Zhang, Y. (1990). Clay minerals and clay mineral analysis. Beijing: China Ocean Press.
Zhao, X., and He, D. (2016). Clay mineral and application in oil and gas exploration and development. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press.
Zhao, W., Zhu, R., Zhang, J., and Yang, J. (2023). Classification, exploration and development status and development trend of continental shale oil in China. China Pet. Explor. 28 (04), 1–13. doi:10.3969/i.issn.1672-7703.2023.04.001
Zhu, R., Mengying, Li, Yang, J., Zhang, S., Cai, Y., Cao, Y., et al. (2022). Advances and trends of fine-grained sedimentology. Oil and Gas Geol. 43 (02), 251–264. doi:10.11743/ogg20220201
Keywords: clay minerals, illitization, gulong shale, pore characteristics, reservoir performance
Citation: Jiang X, Zhu R, Wu S, Zhang J, Yu Z, Guan M and Ding L (2025) Pore characteristics of clay minerals in the Qingshankou shale,Songliao Basin, China: unravelling the effects of illitization. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1524678. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1524678
Received: 08 November 2024; Accepted: 07 March 2025;
Published: 31 March 2025.
Edited by:
Wenbin Tang, Chengdu University of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Jiang, Zhu, Wu, Zhang, Yu, Guan and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rukai Zhu, enJrQHBldHJvY2hpbmEuY29tLmNu; Songtao Wu, d3VzdEBwZXRyb2NoaW5hLmNvbS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.