
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Earth Sci., 17 March 2025
Sec. Solid Earth Geophysics
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2025.1517598
This article is part of the Research TopicAdvanced Materials and Technologies for Sustainable Development of Underground ResourcesView all 44 articles
To solve the problem of large deformations and failure of rocks surrounding a dense area at the footwall of a normal fault, we considered the F22 fault in the fourth mining area of Dashucun coal mine in Hebei Province as the research object and conducted onsite investigations of hidden dangers, such as roof caving and wall caving over the roadway. The deformation and failure law of the surrounding rocks was obtained using the FLAC3D numerical simulation method, and the factors influencing such deformation and failure were analyzed. Consequently, the advanced support of the working face and support scheme for the dense roadway area were optimized. After implementing these programs, the results showed that with the exception of the belt rise, where the deformation of the surrounding rock was affected to some extent, the roof subsidence and approach of two gangs in the dense roadway areas could be controlled to within 220 mm and 320 mm, respectively. Hence, we proved that the surrounding rock conditions in the dense roadway area met the needs of the project.
The process of transferring shallow to deep coal resources involves many problems, especially those concerned with geological structures, and fault structures are the most representative of all problems associated with geological structures (Liu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024a; Zhao et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024; Han et al., 2024; Ji et al., 2024; Grapes and Holdgate, 2014; Jahan et al., 2017; Lozos, 2022; Babcock and Bickel, 1984). In addition, given the increasing scale of mine constructions, roadway spacing has become more dense, resulting in dense roadway areas (Li et al., 2024a; Hu et al., 2024; Pengfei et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2024; Potvin, 2009; Young et al., 1989; Kim et al., 2018; Gay et al., 1984; Iannacchione and Tadolini, 2016; Bahrani and Hadjigeorgiou, 2017; Shan et al., 2021; Wojtecki and KnopikZuberek, 2016; Bedford et al., 2022, 2021). However, owing to the superimposed effects of fault influences and mining, the deformation and failure of rocks surrounding dense roadway areas under the fault is serious (Wojtecki et al., 2021; Song et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024b; Xiao et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2025). Therefore, it is necessary to study the deformation and failure law as well as control technology for rocks surrounding dense roadway areas at the footwall of normal faults.
Many scholars have conducted research on the deformation, failure, and control of rocks surrounding dense roadway areas under the influence of faults (Yang et al., 2021; Cao et al., 2024a; Zhang et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2024a). Cai (2016) analyzed the influences of the study parameters on the faults in surrounding rocks using FLAC3D numerical simulations by considering Tongting mine as the engineering background. Wu (2021) considered the Nuodong coal mine subflat cave as their project background and reported that the rocks surrounding roadways in areas affected by fault structures are soft and in a state of plastic failure. Zhang et al. (2024c) analyzed the deformation and failure mechanisms of the surrounding rocks of the rail transportation flat roadway of the Nantun mine as the engineering background using numerical simulations and proposed the concept of divisional support for the actual failure characteristics of the roadway. Jiang and Wang (2014) analyzed the failure characteristics of the roadway perimeter rocks penetrating the F19 fault fragmentation zone of the Liuzhuang coal mine’s east one track alley and proposed a stepwise coupled support scheme based on long-term onsite observations of the mine pressure. Ma et al. (2024b) studied the progressive failure processes and disaster mechanisms caused by interrelated failures of residual coal pillars and rock strata. Li et al. (2024b) considered the roadway II1057 of the Zhuxianzhuang coal mine as the engineering background and proposed the perimeter rock control strategy of grouting along with anchor rods, anchor ropes, M steel belts, steel beams, and metal mesh active support in front of the roadway. At present, many scholars have extensively studied the deformation mechanisms and control of rocks surrounding roadways under the influence of faults by focusing on single roadways (Li et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2025; Jiang et al., 2024; Cao et al., 2024b), but there is insufficient research on dense roadway areas.
In the present work, we draw on the existing results and consider three roadways in the fourth mining district of Dashucun coal mine as the research background to study the deformation and failure law of rocks surrounding a dense roadway area at the footwall of a normal fault along with the necessary control technology.
Dashucun coal mine is located in the northeastern part of Fengfeng Mining District, Wuan City, Hebei Province, which is the fourth mining district of the lower part of the 172404 working face of the coal seam belonging to the Permian Shanxi Formation strata; the coal seam has an average depth of 566 m, a strike length of 999 m, and an average inclination length of 89.4 m, and a stable coal seam with an average coal thickness of 5.3 m. Directly above the coal seam is a layer of siltstone, and the basic top is fine sandstone; the stratigraphic sequence of the coal seam as well as its roof and floor strata are shown in Figure 1.
Dashucun coal mine in the fourth mining district at the footwall of the F22 normal fault is shown in Figure 2, along with three roadways in the mining district belt rise, mining district track rise, and mining district return rise. The three rises are at the same level, and the roadways are 30 m apart from each other to enable production operations in the fourth mining district. The F22 normal fault is only 25 m away from the mining district belt rise.
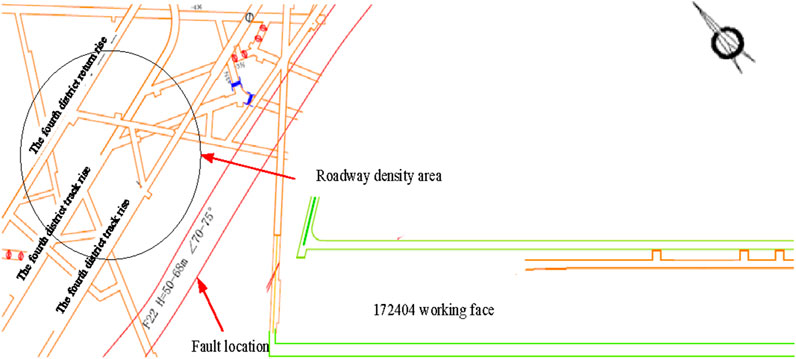
Figure 2. Distribution of the dense roadway area in the fourth mining district of the Dashucun coal mine.
As shown in Figure 3, the rocks surrounding the dense roadway area are supported by anchored cables and anchored rods for the cables. The anchors use left-handed non-longitudinal rebars with length L = 2.4 m and diameter Φ = 20 mm; the row spacings between the anchors are 700 mm × 800 mm. The anchor tray nuts used are standard thick nuts made of M22; the nuts are tightened with a pneumatic wrench and each hole is injected with one ck2345 and two z02345 resin rolls, with the anchor tray being a special steel tray having a diameter of 150 mm and thickness of 10 mm. The nut torques are not less than 140 Nm, tensile strength is 100 kN, anchoring force is 100 kN, and bolting exposure of the nut is 10–50 mm. The anchor spacing at the top is 1,400 mm, and row spacing is 1,400 mm, with the anchor material being a Ф21.6 mm × 5,000 mm stranded wire. For each wire, the pretensioning force is not less than 150 kN, anchoring force is not less than 200 kN, and steel tray has dimensions of 300 mm × 300 mm × 16 mm, with the anchor cable immediately following the headway construction and installation. The entire roadway section is paved with a small-grid metal mesh of dimensions 80 mm × 80 mm that is welded to Φ = 6.5 mm rebar coils of 1.5 m length × 0.9 m width; the meshes are overlapped and networked with two strands of 12-gauge (or four strands of 16-gauge) iron wires at intervals of 160 mm.
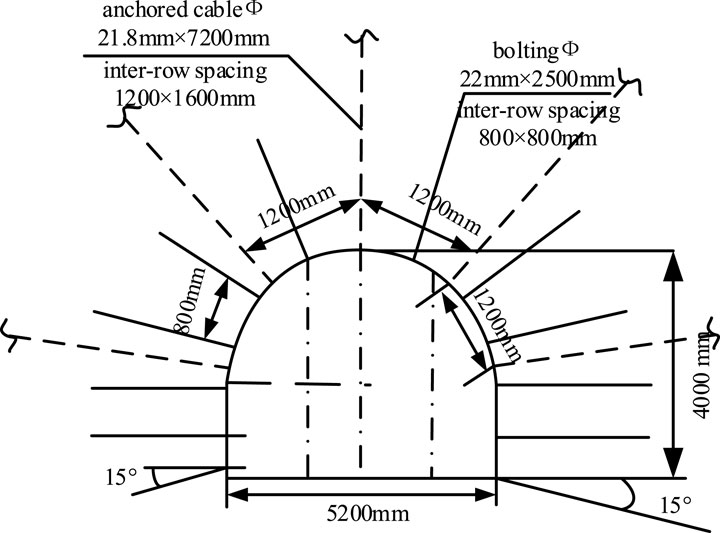
Figure 3. Original support design of the dense roadway area in the fourth mining district of Dashucun coal mine.
Through onsite observations, as shown in Figure 4, the deformation and failure of the dense roadway area was mainly found to be rib spalling, which caused sinking of the anchored cables. Furthermore, localized effects were found in the roofing, where the peripheral rocks of the belt uphill in the dense roadway area of the mining district were damaged seriously. There have been many instances of repair and maintenance in this area, which has not only increased the maintenance cost of the roadway but also resulted in concerns regarding safety hazards. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize the parameters of the surrounding rock supports in the dense roadway area based on actual geological conditions as well as deformation and failure of the surrounding rocks to realize normal production operations in the fourth mining district.
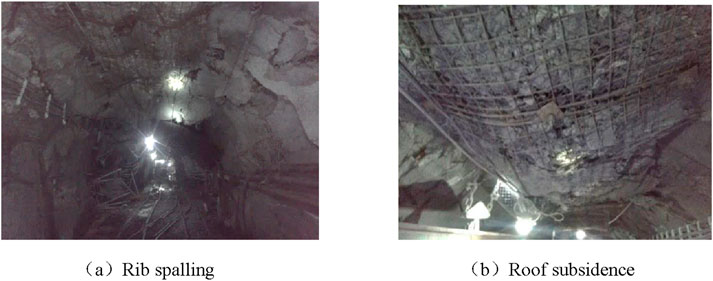
Figure 4. Deformations of the surrounding rocks in the dense roadway area of the fourth mining district of Dashucun coal mine: (A) rib spalling; (B) roof subsidence.
Based on the actual geological conditions of the dense roadway area in Dashucun coal mine, a FLAC3D numerical simulation model was established to study the deformation and failure characteristics of the rocks surrounding the dense roadway area under the influences of different factors.
Two numerical models were established, as shown in Figures 5, 6, with model length × width × height dimensions of 400 m × 250 m × 160 m; the models were divided into 482,400 cells and 508, 958 nodes when there was a fault or into 128,000 cells and 136,161 nodes when there was no fault, with identical boundary constraints and loads applied to both models.
The left and right sides of each model were excluded up to 50 m to reduce the influence of the boundary effect. Here, the X direction of the model constrained the left and right boundary displacements, Y direction constrained the front and rear boundary displacements, and Z direction constrained the lower boundary displacement; the fix command was used to control the boundary velocity of the model, and a pressure of 11.15 MPa was applied to the top of the model. An interface contact surface was adopted for the fault, with a fault dip angle of 70°, drop of 50 m, normal stiffness of 2 GPa, tangential stiffness of 5 GPa, internal friction angle of 45°, and cohesion of 0.5 MPa. The stress and deformation failure of the roof of the dense roadway and two gangs were monitored in the case of both presence and absence of faults. The mechanical properties used in numerical simulation model are shown in Table 1.
The X direction of the model is the advancing aspect of the working face, and the working face advances toward the fault face from far to near. The stress changes in the fault face were monitored for the influences of different factors on the stopping line, and the monitoring points were arranged along the roof and two gangs of the dense roadway area to record changes in the stress and displacement of the area owing to the faults during working face mining. The locations of the measurement points are shown in Figure 7; here, measurement point C is located 20 m below the fault, and measurement points A and B are located 80 m and 40 m above the fault, respectively.
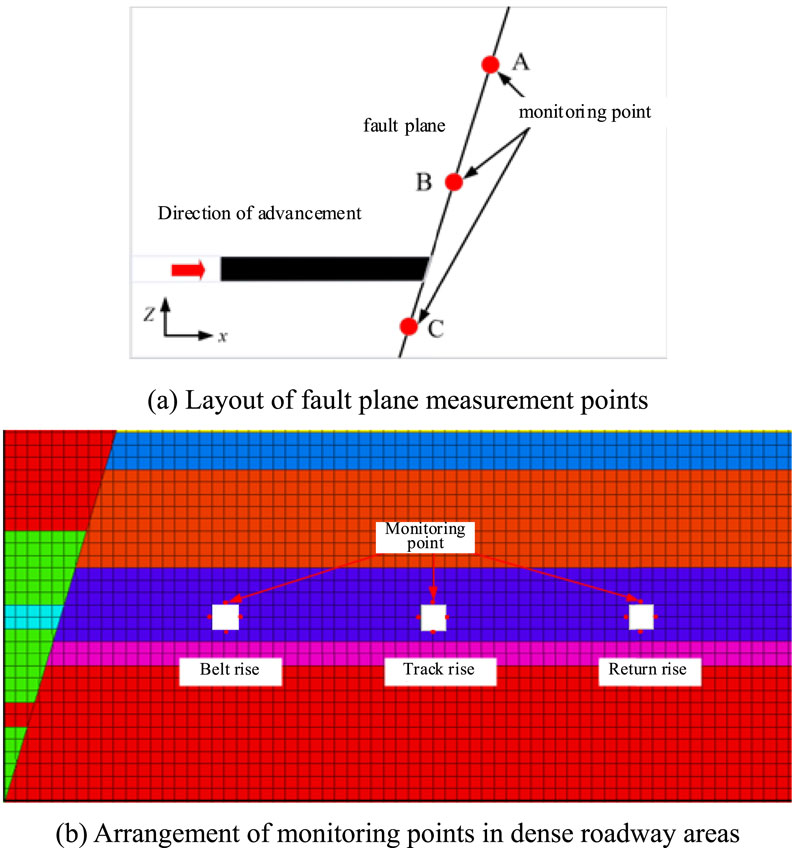
Figure 7. Schematic showing the arrangement of the monitoring points: (A) layout of the fault plane measurement points; (B) arrangement of monitoring points in the dense roadway area.
By ensuring that all other conditions remain unchanged, different roof lithologies were setup separately, as detailed in Table 2. This allowed us to obtain the fault surface slip conditions as well as changes in the displacements of the roof and two gangs in the dense roadway area.
We set the working face mining height to 1 m, 3 m, and 5 m, while ensuring that all other conditions remain unchanged and observed the fault surface slip conditions as well as changes in the displacements of the roof and two gangs in the dense roadway area.
We set the working face mining length to 100 m, 150 m, and 200 m while ensuring that all other conditions remain unchanged and observed the fault surface slip conditions as well as changes in the displacements of the roof and two gangs in the dense roadway area.
We set the advancing speed of the working face to 5 m/d, 10 m/d, and 15 m/d while ensuring that all other conditions remain unchanged and observed the fault surface slip conditions as well as changes in the displacements of the roof and two gangs in the dense roadway area.
After ensuring stress balance of the above two models, three rises were excavated in the same order; then, after calculating the stress balance, the deformation and failure ranges of the rocks surrounding the dense roadway area were counted. The results of these calculations are shown in Figures 8, 9 by considering the uphill belt closest to the fault as the example.
As seen from the figures, when there is no fault, the deformations of the roof and floor of the belt rise are similar, and the deformation of each gang is approximately 8 mm; when a fault exists, the deformation of the left gang is 120 mm, deformation of the right gang is approximately 90 mm, and the roof and floor of the belt rise are closer by approximately 40 mm.
In summary, the deformation and failure ranges of the rocks surrounding the dense roadway area are larger in the presence of the fault, with the maximum increase in deformation being approximately 110% and maximum increase in failure range being approximately 40%; the two gangs show more obvious asymmetric characteristics, and the deformation and failure ranges of the coal gangs on the side close to the fault are larger by 140% and 40% than those on the other side, respectively.
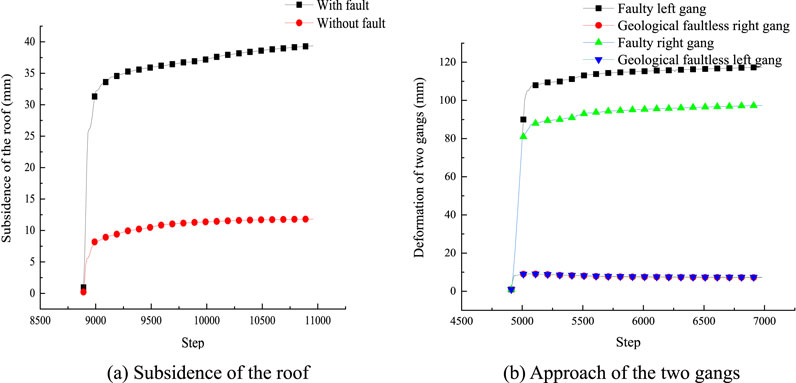
Figure 8. Simulation results of the deformations of the surrounding rocks in the belt rise: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
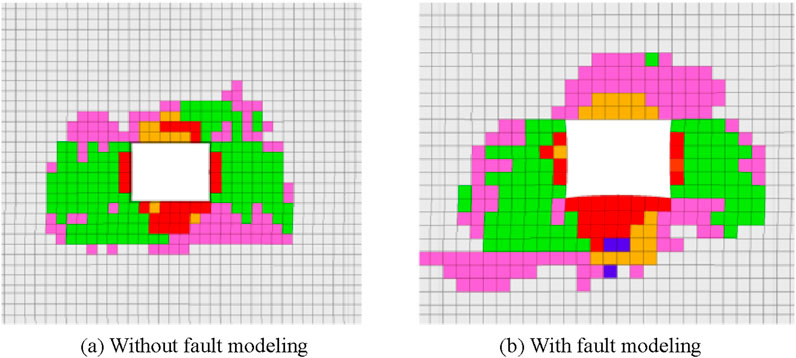
Figure 9. Belt rise surrounding rock failure simulation results: (A) without fault modeling; (B) with fault modeling.
As seen from Figure 10, as the hardness of the rock properties of the roof increases, the displacement at each measuring point changes such that the deformations at the measurement points A, B, and C decrease. When the rock properties belong to the soft rock stratum, the relative deformation between points A and B is 24 mm; when the rock properties belong to the hard rock stratum, the relative deformation between points A and B is 12 mm, which means that the deformation between the two points is reduced by 100% with respect to that of the soft rock stratum.
As seen from Figure 11, as the lithologies of the roof and floor change, the movements of the top and bottom of the dense roadway area as well as the two gangs decrease. When the roof is a hard rock stratum, the movements of the two gangs at the three roadways are 401 mm, 398 mm, and 370 mm, while the corresponding roof and floor movements are 200 mm, 120 mm, and 80 mm; compared to a soft rock stratum, the movements of the two gangs decrease by 5%, 5.1%, and 8%, while the corresponding roof and floor deformations decrease by 13%, 25%, and 33.3%. Thus, when the lithology is hard rock stratum, it is evident that the deformations and faults in the dense roadway area are relatively lower and that this stratum effectively reduces the approach amount of the dense roadway area.
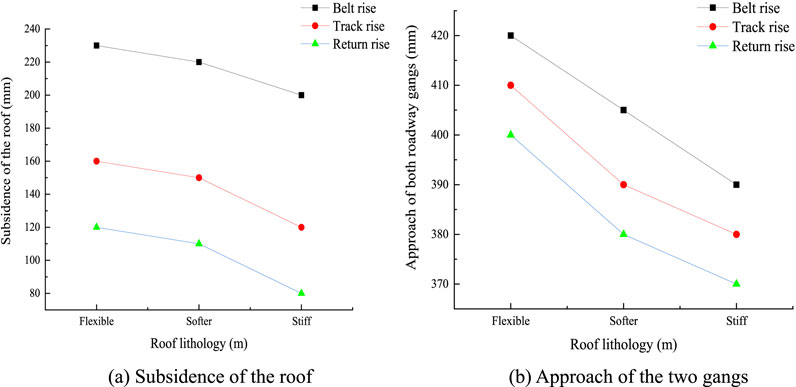
Figure 11. Displacement changes in the dense roadway area for different roof lithologies: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
As seen from Figure 12, when the mining height is increased from 1 m to 3 m and 5 m, the relative deformation at each measurement point shows a small change.
As seen from Figure 13, when the mining height increases from 1 m to 5 m, the maximum displacement of the roof and floor is 218 mm, and the displacement of the two gangs is 334 mm; further, the minimum displacement of the roof and floor is 120 mm, and the displacement of the gangs is 205 mm owing to the fact that the mining district’s backwind rise is farther away from the working face and faults, resulting in a smaller influence of the mining movement.
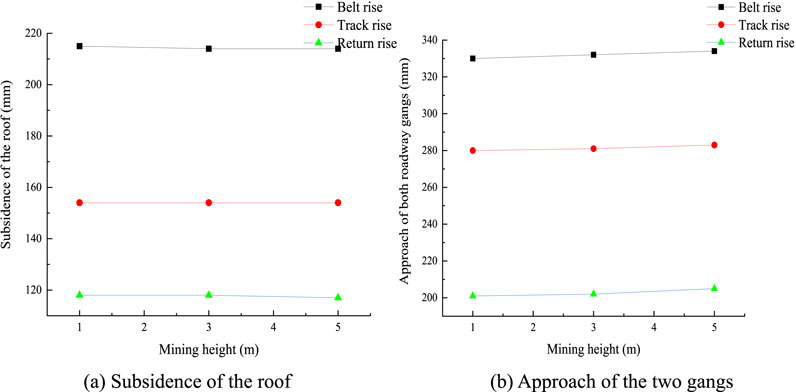
Figure 13. Displacement changes in the dense roadway area for different mining heights: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
As seen from Figure 14, from the relative deformations of the fault, when the working face advances from 150 m to 200 m, the relative deformation between points A and B is 28 mm and that between points B and C is 11 mm.
As seen from Figure 15, when the mining length of the working face increases from 100 m to 200 m, the maximum movement of the roof and floor in the belt uphill of the mining district increases by 19.3%, and the corresponding movement of the two gangs increases by 14.3%; the roof and floor movement in the rail uphill increases by 37.5%, and the corresponding movement of two gangs increases by 12%; the roof and floor movement in the return air uphill increases by 40%, and the corresponding movement of the two gangs increases by 20%.
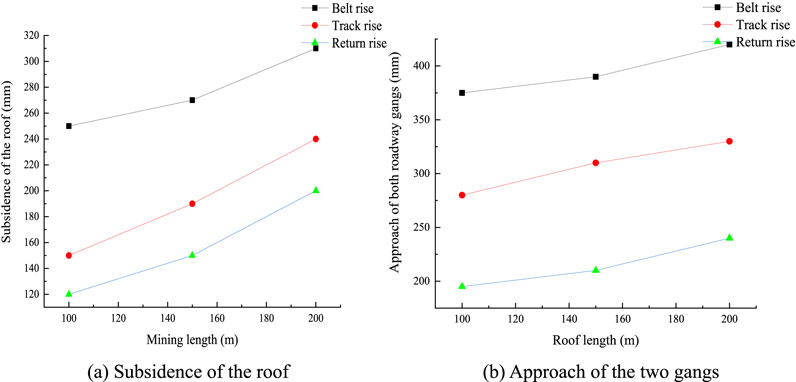
Figure 15. Displacement changes in the dense roadway area for different mining lengths: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
As seen from Figure 16, as the advancing speed increases, the fault closer to the working face is affected more, and the deformations at points B and C are obviously larger than that at point A.
As seen from Figure 17, changing the advancing speed has only a small influence on the dense roadway area. When the rate of advancement is 15 m/d, the maximum roof and floor rise of the belt in the mining district is 210 mm, and the corresponding maximum rise of the two gangs is 380 mm.
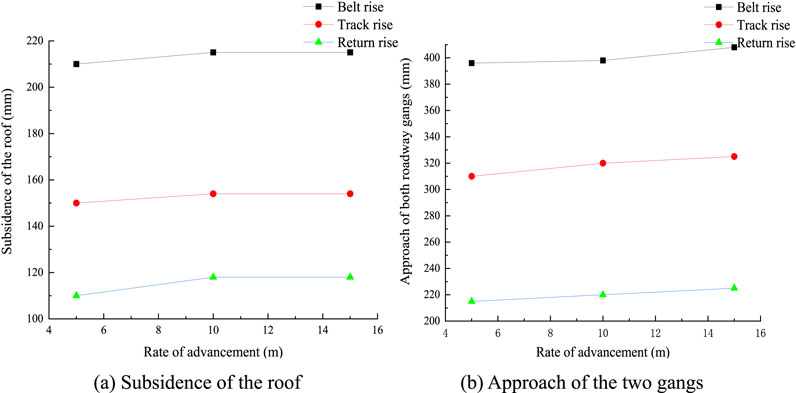
Figure 17. Approach of the dense roadway area for different advancing speeds: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
By studying the effects of the roof lithology, mining height, mining length, and advancement rate of the working face on the deformation and failure of rocks surrounding a dense roadway area in a fault disc, the following observations were obtained. When the rock lithology is stiff, the possibility of fault slip is smaller, and the subsidences of the roof and softer rock stratum of the gang in the dense roadway area are reduced. As the mining length of the working face increases, there is a greater possibility of fault slip, and the movements of the roof, floor, and gangs in the dense roadway area are more obvious. Mining height and advancement rate of the working face have few effects on the fault slip and rocks surrounding the dense roadway area, but a higher rate of advancement results in increased deformations of the roof and gangs.
The monopole supports in the roadway below the 172404 working face were eliminated, and all of these were replaced with grouting and ordinary anchored cables for advanced support. The row spacing of the anchored cables was 1.0 m, and each row had three anchored cables (two grouted and one ordinary) of Ф22 mm × 7.5 m stranded wires; further, the anchoring force was not less than 200 kN, and the pretensioning force was not less than 150 kN. The ordinary anchored cable was located at the centerline of the roadway, and the two grouting anchored cables are arranged symmetrically about the centerline at distances of 1.2 m each; the spacing of the anchored cables from the front and back of the existing support structure in each row is 0.5 m, as shown in Figure 18.
The roadway support was mainly based on anchored cable supports, and the uphill of the mining district and joint lane were supported by anchored cable spraying. In the event of broken roof, soft rock, coal seam section, faults, and tectonics, it is necessary to reduce the row spacing of the anchored cables and anchor beams, adopt 36U shed supports, and also adopt internal anchoring and external frame composite supports with increased support strengths in special cases.
We chose ordinary 335 rebar bolting with Ф22 mm × 2.5 m for the left section of the rise roadway support, MG500 rebar bolting with Ф22 mm × 2.5 m to locally strengthen the left support section, and square bolting pallets of 300 mm × 300 mm × 16 mm. The bolting equivalent steel pallets were produced and pressed into curved shapes. The pallets for the roof of the roadway were arranged along the middle, and the bolts were spaced in rows of 800 mm × 800 mm with the bolting force being not less than 100 kN. The test resistance to pull out the bolts was not less than 90% of the designed value. For the gang part, the distances between the rows of bolts was not more than 800 mm × 800 mm, design bolting force was not less than 60 kN, and test resistance to pull out the bolts was not less than 90% of the designed value.
The anchored net was fabricated by welding Φ7 mm round steel wires into a structure of length × width 2 m × 1 m having a mesh of 100 mm × 100 mm; the anchored net overlap was not less than 100 mm, and double strands of 12-gauge iron wires were used for the connections or hooking.
The anchored cables were made of Ф21.8 mm prestressed steel strands of length L = 7.2 m; each anchor cable supports two pallets of sizes 300 mm × 300 mm × 16 mm and 150 mm × 150 mm × 14 mm along with a single KM22-1860 model lock. A total of five anchored cables were arranged along the roof of the roadway, and the spacing between the rows was not more than 1.2 m × 1.6 m. The designed anchoring force of each anchored cable was not less than 140 kN, and the prestress was not less than 90% of the designed value. The support scheme used in this study is shown in Figure 19.
To research the control effects of peripheral rock supports in dense roadway areas, the monitoring procedures used herein mainly included observations of the surface displacements of the rocks surrounding the roadways, and the main equipment used for monitoring was the laser range finder.
The monitored area mainly comprises the areas of the belt rise, track rise, and return rise in the mining district. Each monitoring point or station was equally spaced at a certain interval so as to reduce errors and improve the accuracy of monitoring. Among these points, since the mining district belt rise is close to the fault location, the points were equally spaced 50 m apart to better monitor the changes in the dense roadway area. For the mining district track rise, the measurement points were arranged back to the wind rise every 60 m. The monitoring area and locations of the measurement stations are shown in Figure 20.
To obtain the deformations of the rocks surrounding the dense roadway area under the influence of the working face mining, it was necessary to ensure the rationality of the surrounding rock control technology. A laser range finder was used to monitor the deformations of the dense roadway area, which was mainly obtained in terms of the movements of the roof and floor as well as two gangs; the monitoring was conducted once every three days or so to evaluate the effects of the support procedures on the roof. The specific monitoring data are shown in Figures 21–23.
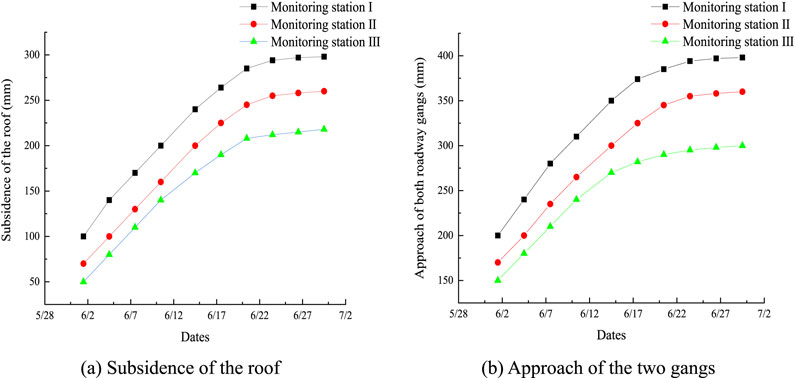
Figure 21. Monitoring results of the belt rise surrounding rocks in the mining district: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
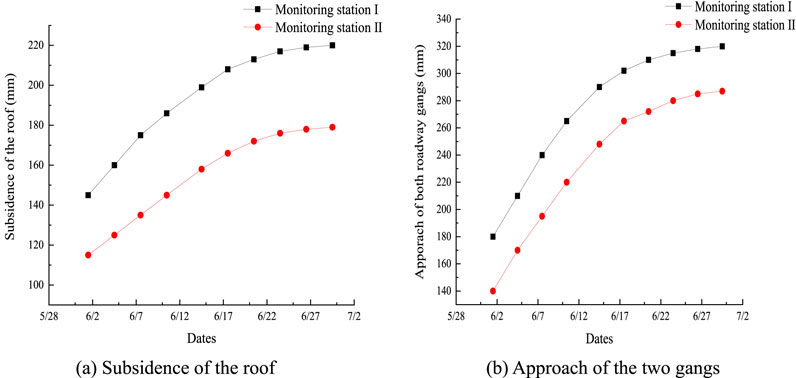
Figure 22. Monitoring results of the track rise surrounding rocks in the mining district: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
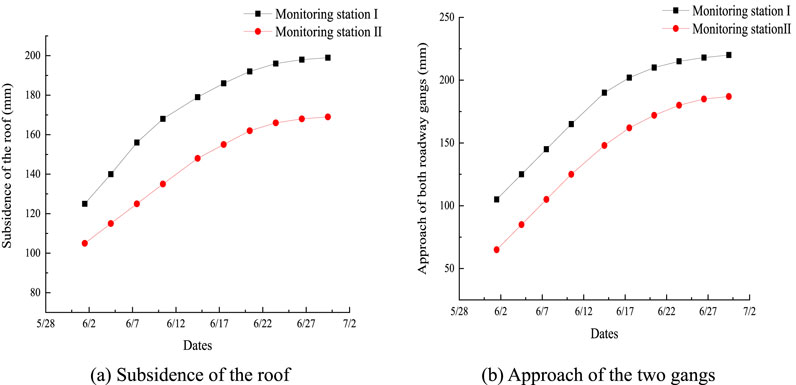
Figure 23. Monitoring results of the return rise surrounding rocks in the mining district: (A) subsidence of the roof; (B) approach of the two gangs.
By monitoring of the roof subsidence and the approach of the two roadway gangs in the belt rise of the mining district, we found that the roof and two gangs of all three stations were unstable in the early stages of mining but gradually stabilized at the late stage. The roof subsidence of station Ⅰ was stable at 289 mm, and the approach of the two gangs was stable at approximately 400 mm. The roof subsidence of station Ⅱ was stable at 255 mm, and the approach of the two gangs was stable at 360 mm. The roof subsidence of station Ⅲ was stable at 210 mm, and the approach of the two gangs was stable at 289 mm. Compared with the movements of station Ⅰ, the roof and two gangs of stations Ⅱ and Ⅲ decreased by 13.3% and 37.6% and by 11.1% and 38.4%, respectively.
The roof subsidence at station Ⅰ was 220 mm, and the two gangs moved closer to 320 mm, which are respectively 31.3% and 25% lower than those uphill of the mining district. The roof subsidence at station Ⅱ was 188 mm, and the two gangs moved closer to 288 mm, which are respectively 35.6% and 25% lower than those of monitoring station Ⅱ in the rise of the mining district. By monitoring the surrounding rocks in the track rise of the mining district, it was found that the closer the roadway was to the working face and fault, the more it was affected by the mining.
From the monitoring results of the surrounding rocks in the return rise of the mining district, it was seen that the roof subsidence of station Ⅰ was 188 mm, and the approach of the two gangs is approximately 220 mm, which are, respectively, 53.7% and 81.8% lower than those of the belt rise in the mining district. The roof subsidence of station Ⅱ was 170 mm, and the approach of the two gangs was 190 mm, which are respectively 70% and 110% lower than those of the belt rise. Since the return rise of the mining district is far from the fault, it is less affected by the mining and the fault.
From the deformation results of the rocks surrounding the dense roadway area, it is seen that the belt rise in the mining district is affected to a greater extent while the track rise and return rise are less affected.
The monitoring results for the dense roadway area are shown in Table 3. It was found that only the deformations of the belt rise in the mining district were slightly larger while those of the track rise and return rise were smaller. Therefore, we have shown that there are no serious deformations in the dense roadway area in the later stages after adopting the corresponding control measures for the surrounding rocks and that these measures are effective.
(1) In this study, we focused exclusively on an illustrative example concerning the occurrence of faults in the context of coal mine disaster prevention and control. However, it is important to note that faults, as ubiquitous geological features, can play crucial roles in various geoscientific domains, including tunnels, bridges, and beyond. Consequently, investigation of such faults holds profound significance in the field of earth sciences.
(2) In this work, we identified the deformation and failure characteristics of the rocks surrounding coalmine roadways influenced by faults. Additionally, we propose a control scheme that is specifically tailored to address issues arising from the influences of such faults. The implementation of the proposed scheme demonstrated favorable outcomes, offering valuable insights and serving as a reference for coal mines with comparable geological conditions.
(1) From the numerical simulations, we concluded that the deformations and failures of rocks surrounding dense roadway areas are larger when affected by faults, with the maximum increase in deformation being approximately 110% and that of the failure range being approximately 40%. Both roadway gangs in such areas have obvious asymmetric characteristics. The deformation and failure of the coal gangs on the side close to the fault are larger by 140% and 40%, respectively, compared to those on the other side.
(2) By studying the effects of roof lithology, mining height, mining length, and advancement rate of the working face on the deformation and failure of the surrounding rocks in the dense roadway area under a fault, it was found that the roof lithology and mining height had significant effects while the working face mining length and rate of advancement had smaller effects.
(3) This work proposes an optimal scheme for surrounding rock control based on onsite monitoring. After the implementation of the proposed measures, the results showed that except for the belt rise, where the deformations of the surrounding rocks were affected to some extent, the roof subsidence and the approach of the two gangs in the dense roadway area were controlled to within 220 mm and 320 mm, respectively. This proves that the surrounding rock conditions in the dense roadway area meet the needs of the project.
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
QM: writing–original draft and writing–review and editing. SB: funding acquisition, methodology, supervision, and writing–review and editing. RZ: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, and writing–original draft. XL: writing–review and editing. CX: conceptualization and writing–review and editing. XL: funding acquisition, supervision, and writing–review and editing.
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 52174122, 52374218, and 52304093), Excellent Youth Fund of Shandong Natural Science Foundation (no. ZR2022YQ49), Young Expert of Taishan Scholar in Shandong Province (no. tsqn202211150), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (no. 2023M741968), and Research Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Coal Resources and Safe Mining at China University of Mining and Technology (no. SKLCRSM23KF012).
Author CX was employed by China Energy Construction Group Epply Co.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Babcock, C. O., and Bickel, D. L. (1984). “Constraint the missing variable in the coal burst problem,” in Proceedings of the 25th US symposium on rock mechanics (Evanston, Illinois: Northwestern University), 639–647.
Bahrani, N., and Hadjigeorgiou, J. (2017). Explicit reinforcement models for fully-grouted rebar rock bolts. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. 9 (2), 267–280. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.07.006
Bedford, J. D., Faulkner, D. R., Allen, M. J., and Hirose, T. (2021). The stabilizing effect of high pore-fluid pressure along subduction megathrust faults: evidence from friction experiments on accretionary sediments from the Nankai Trough. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 574, 117161. 0012-821X. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2021.117161
Bedford, J. D., Faulkner, D. R., and Lapusta, N. (2022). Fault rock heterogeneity can produce fault weakness and reduce fault stability. Nat. Commun. 13, 326. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-27998-2
Cai, S. H. (2016). Research and application of contact surface method and weakening method in FLAC3D fault simulation.
Cao, M. H., Yang, S. Q., Du, S. G., Li, Y., and Wang, S. S. (2024a). Study on fault-slip process and seismic mechanism under dynamic loading of hard roof fracture disturbance. Eng. Fail. Anal. 163, 108598. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2024.108598
Cao, X., Jiang, T., Shimada, H., Sasaoka, T., and Hamanaka, A. (2024b). Influence of CO2 nano-bubble water concentration and curing time on the macroscopic and microscopic mechanical properties of cemented backfill materials. J. Of Build. Eng. 98, 111099. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.111099
Chen, C., Wei, J., Zhang, T., Zhang, H., and Liu, Y. (2025). Effect of abrasive volume fraction on energy utilization in suspension abrasive water jets based on VOF-DEM method. Powder Technol. 449, 120427. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2024.120427
Gay, N. C., Spencer, D., Wyk, J. J. V., and Heever, PKVD (1984). “The control of geological and mining parameters on seismicity in the Klerksdorp gold mining district,” in Proceedings of rockbursts and seismicity in mines (Johannesburg: South African institute of mining and metallurgy), 107–120.
Grapes, R. H., and Holdgate, G. R. (2014). Earthquake clustering and possible fault interactions across Cook Strait, New Zealand, during the 1848 and 1855 earthquakes. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 57 (3), 312–330. doi:10.1080/00288306.2014.907579
Han, Z., Qiu, M., Teng, C., Shi, L., Gai, G., and Zhao, J. (2024). Theoretical and numerical investigations of the floor failure characteristics affected by coal mining near complex fault structures. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 24517. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-74832-4
Hu, Q. J., Feng, X. J., Ding, Z., Aihemaiti, A., Sa, L., and Cao, X. (2024). Failure mechanism features and precursor characteristics of coal roadway groups in fault zone under confined conditions. Eng. Fail. Anal. 161, 108274. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2024.108274
Iannacchione, T., and Tadolini, S. C. (2016). Occurrence, predication, and control of coal burst events in the U.S. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 26 (1), 39–46. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.11.008
Jahan, I., Castagna, J., Murphy, M., and Kayali, M. A. (2017). Fault detection using principal component analysis of seismic attributes in the Bakken Formation, Williston Basin, North Dakota, USA. Interpretation-a J. Subsurf. Charact. 5 (3), T361–T372. doi:10.1190/int-2016-0209.1
Ji, S., Lai, X., Cui, F., Liu, Y., Pan, R., and Karlovšek, J. (2024). The failure of edge-cracked hard roof in underground mining: an analytical study. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 183, 105934. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2024.105934
Jiang, K. Q., and Wang, L. H. (2014). Research on control technology of surrounding rock of soft rock roadway in deep well through fault and fracture zone. Coal Eng. 46 (03), 42–44.
Jiang, T., Zhu, C., Qiao, Y., Sasaoka, T., Shimada, H., Hamanaka, A., et al. (2024). Deterioration evolution mechanism and damage constitutive model improvement of sandstone–coal composite samples under the effect of repeated immersion. Phys. Of Fluids 36 (5). doi:10.1063/5.0208619
Kim, B. H., Larson, M. K., and Lawson, H. E. (2018). Applying robust design to study the effects of stratigraphic characteristics on brittle failure and bump potential in a coal mine. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 28, 137–144. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2017.10.003
Li, H. B., Pan, W. P., Hua, X. Z., and Luan, B. (2024a). Instability characteristics of surrounding rock and surrounding rock control technology of deep coal roadway crossing the fault: a case study of Zhuxianzhuang coal mine. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 15 (1), 23. doi:10.1080/19475705.2024.2366376
Li, H. B., Pan, W. P., Hua, X. Z., and Luan, B. (2024b). Instability characteristics of surrounding rock and surrounding rock control technology of deep coal roadway crossing the fault: a case study of Zhuxianzhuang coal mine. Geomatics Nat. Hazards and Risk 15 (1), 1–23. doi:10.1080/19475705.2024.2366376
Li, X., Liu, X., Tan, Y., Chen, A., Wang, H., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Rheological mechanical properties and its constitutive relation of soft rock considering influence of clay mineral composition and content. Int. J. Coal Sci. and Technol. 10, 48. doi:10.1007/s40789-023-00615-3
Liu, G. J., Peng, Y. X., Wu, L., Cheng, Y., Dong, D., Jia, L., et al. (2024). Stability prediction of surrounding rock in tunnel crossing fault zone based on cusp catastrophe theory. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 28 (9), 4146–4157. doi:10.1007/s12205-024-2478-1
Lozos, J. C. (2022). Dynamic rupture modeling of coseismic interactions on orthogonal strike-slip faults. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49 (5). doi:10.1029/2021gl097585
Ma, Q., Liu, X., Tan, Y., Wang, R., Xie, W., Wang, E., et al. (2024a). Experimental study of loading system stiffness effects on mechanical characteristics and kinetic energy calculation of coal specimens. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 57 (11), 9941–9957. doi:10.1007/s00603-024-04054-7
Ma, Q., Liu, X. L., Qian, R. P., Tan, Y., and Li, B. Q. (2024b). Progressive failure processes and mechanisms of disasters caused by interrelated failure of residual coal pillars and rock strata. Sci. Total Environ. 954, 176181. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176181
Pengfei, L., Lu, J., Wang, E., and Chen, X. (2021). The mechanical criterion of activation and instability of Normal Fault induced by the movement of Key stratum and its disaster-causing mechanism of rockburst in the hanging wall mining. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021 (1), 6618957. doi:10.1155/2021/6618957
Potvin, Y. (2009). Strategies and tactics to control seismic risks in mines. J. S Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 109 (3), 177–186.
Shan, R., Li, Z., Wang, C., Wei, Y., Bai, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021). Research on the mechanism of asymmetric deformation and stability control of near-fault roadway under the influence of mining. Eng. Fail. Anal. 127, 105492. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105492
Song, D., Shi, W., Liu, M., He, X., Lu, R., and Zhang, J. (2024). Wave propagations in crossing-fault tunnels and their effects on the dynamic response characteristics of tunnel surrounding rock. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 83 (6), 253. doi:10.1007/s10064-024-03751-5
Wang, C., Liu, J., Chen, L., Liu, J., Wang, L., and Liao, Y. (2024). Creep constitutive model considering nonlinear creep degradation of fractured rock. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 34, 105–116. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2023.11.008
Wojtecki, Ł., and KnopikZuberek, M. W. M. (2016). The influence of a local fault zone on high energy tremor occurrence during longwall mining of a coal seam. Acta geophys. 64, 1164–1175. doi:10.1515/acgeo-2016-0040
Wojtecki, Ł., Kurzeja, J., and Knopik, M. (2021). The influence of mining factors on seismic activity during longwall mining of a coal seam. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 31, 429–437. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.01.010
Wu, X. K. (2021). Research on control technology of loose and soft surrounding rock roadway in tectonic stress area.
Xiao, Z., Gu, S., Zhang, Y., and Wang, H. (2023). An effective control method of rock burst induced by shear instability of fault structure under complicated geological conditions. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 82 (4), 105. doi:10.1007/s10064-023-03119-1
Yang, R., Ma, T., Kang, Y., Du, H., Xie, S., and Ma, D. (2025). A fractal model for gas-water relative permeability in inorganic shale considering water occurrence state. Fuel 381 (Part D), 133664. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2024.133664
Yang, Y., Fang, Z., Ji, G., Zhao, B., and Wei, S. (2021). Study on mechanical properties and control technology of surrounding rock in the fracture zone of a roadway. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021. doi:10.1155/2021/6628593
Yang, Z., Tao, M., Fei, W., Yin, T., Gu, X., and Narsilio, G. A. (2024). A coupled thermo-mechanical model for investigating cracking and failure of composite interbedded rock. Eng. Geol. 339, 107645. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2024.107645
Young, R. P., Talebi, S., Hutchins, D. A., and Urbancic, T. I. (1989). Analysis of mining-induced microseismic events at Strathcona Mine. Sudbury, Canada: Birkhäuser Basel.
Zhang, J., Dong, Y., Chen, Y., Jiang, Y., Sun, H., Fan, Y., et al. (2018). Comparative analysis of roadway reinforcement effects based on fluid-solid coupling in the fractured zone of water-rich fault. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018. doi:10.1155/2018/6238910
Zhang, S., Liu, X., and Wang, E. (2024c). Quantitative evaluation of the onset and evolution for the non-Darcy behavior of the partially filled rough fracture. Water Resour. Res. 60, e2023WR036494. doi:10.1029/2023wr036494
Zhang, S., Liu, X., Wang, E., Qian, R., Wang, M., and Ma, Q. (2024b). A novel model of hydraulic aperture for rough single fracture: insights from fluid inertial and fracture geometry effects. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 129, e2024JB029018. doi:10.1029/2024jb029018
Zhang, W., Hu, L., Yao, Z. B., Xiong, Y. R., Zhao, J., Ma, T., et al. (2024a). In-situ and experimental investigations of the failure characteristics of surrounding rock through granites with biotite interlayers in a tunnel. Eng. Geol. 343, 107816. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2024.107816
Zhang, Z., Chen, F., Li, N., Swoboda, G., and Liu, N. (2017). Influence of fault on the surrounding rock stability of a tunnel: location and thickness. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 61, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.tust.2016.09.003
Zhao, J., Chen, J., Huilin, X., Zhao, Z., and Xinguo, Z. (2022). Dynamic mechanical response and movement evolution characteristics of fault systems in the coal mining process. Pure Appl. Geophys., 1–14.
Keywords: mine disaster, deformation and control technology, surrounding rock, dense roadway area, normal fault
Citation: Ma Q, Bai S, Zhang R, Li X, Xie C and Liu X (2025) Research on the deformation and failure law and control technology of surrounding rock in the dense roadway area in footwall of normal fault. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1517598. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1517598
Received: 26 October 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 17 March 2025.
Edited by:
Hao Shi, Anhui University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Tianqi Jiang, Kyushu University, JapanCopyright © 2025 Ma, Bai, Zhang, Li, Xie and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shangyu Bai, U2hhbmd5dTAyMDRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.