
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Earth Sci. , 10 March 2025
Sec. Geoscience and Society
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2025.1447513
This article is part of the Research Topic Gross Ecosystem Product: Valuation of Nature’s Contribution to Human Well-Being View all 6 articles
Forest ecosystems provide many ecosystem services, and payment for these ecosystem services has recently become a policy-relevant issue. This paper puts forward a multi-function quantitative standard (MQECS) for forest ecosystem services based on the Human Development Index and the six distinct forest ecosystem service values. Using the MQECS method, the MQECSi and total ecological compensation amount (TECAi) for forest ecosystem services in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces in 2012 were calculated. The MQECSi of Guangdong and Liaoning were 663.02 and 225.27 RMB·hm−2, and the TECAi of these provinces were 66.82 × 108 and 13.67 × 108 RMB, respectively. The MQECSi of Guangdong is approximately three times that of Liaoning, and the government needs to increase investment per unit forest area by 176.25% and 50.20% of the current compensation amount in Guangdong and Liaoning to achieve the target quantitative compensation standards. Additionally, the MQECS method was also applied to calculate the ecological compensation for forest ecosystem services of different cities in Guangdong and Liaoning. The MQECS method not only considers the local government's ability to pay but also incorporates factors influencing human wellbeing and the valuation of distinct forest ecosystem services. It is suitable for application to current forest management in China.
Forests are multi-functional, renewable resources that provide a great assortment of ecological benefits for humans (Snall et al., 2021), including soil and water conservation, carbon sequestration and oxygen release, nutrient accumulation, air quality improvement, and biodiversity conservation (Costanza et al., 1997; Niu and Wang, 2013; Boskidis et al., 2012). However, forest ecosystems are open systems that provide many of their benefits indirectly. There is often no direct link between the benefactors and the beneficiaries (Yu H. Q. et al., 2023). Ecosystem services, as the foundation of human survival and development, directly determine the state of human wellbeing (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, 2005). As an important component of the ecosystem, humans are in a dynamic equilibrium state of interaction and constraint with various components in the ecosystem (Zhou et al., 2024). Welfare is the ability of humans to freely and selectively engage in ecosystem services such as supply, regulation, culture, and support services. On one hand, continuously changing human conditions can directly or indirectly drive changes in ecosystems, and on the other hand, changes in ecosystems can lead to changes in human wellbeing (Fisher et al., 2014; Leviston et al., 2018). At the same time, many other factors unrelated to the environment can also change human wellbeing, and many natural driving forces are continuously affecting ecosystems (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, 2005). From an economic perspective, the ecosystem services provided by forests constitute positive economic externality (Taye et al., 2021), and these benefits are consumed by non-forestry operations, and even by society as a whole, without any consideration of the costs incurred in the production of ecosystem services or of compensation to those who oversee or are otherwise responsible for the production of these benefits (Naime et al., 2022; Cai et al., 2005).
In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on compensation for ecosystem services in the academic and public sectors (Hou and Wang, 1995; Wu et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2018), which is called payment for ecosystem services (PES) worldwide (Wang et al., 2017). Ecological compensation is an institutional arrangement aimed at protecting and sustainably utilizing ecosystem services, primarily through economic means, and regulating the interests of stakeholders (Ju et al., 2022). The aim of ecological compensation is to optimize resource allocation and adjust the interest relationship between ecological service providers and demanders, realizing the value of ecological capital and services(Gao et al., 2020).‘Forest ecological compensation,' as it is called in China, is a form of value repayment for the ecosystem services that forests provide, objectively reflecting the forests' functional value in a commodity economy (Li et al., 2018). Moreover, forest ecological compensation also serves as a transfer mechanism that internalizes the externality of forest ecosystem services by compensating individuals or companies for the losses or costs resulting from the provision of these functions (Shi et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2024). Based on the cost of afforestation and management of different types of forest resources and the multiple functions of the forest ecosystem, factors such as quantity structure and economic location (Deng et al., 2020) are considered, which are crucial to construct a scientific ecological compensation standard system and establish a comprehensive and diversified forest compensation mechanism for accurately optimizing forest structure, improving forest quality, and enhancing forest ecosystem services (Deng et al., 2011).
However, establishing an optimal compensation mechanism for ecosystem services is a long and involved process (Guan et al., 2024), and some implementation issues await more thorough research, including compensation methods, compensation standards, the scope of forest ecosystem services for which compensation is made, and the management of compensation funds (Zhou et al., 2023; Sierra and Russman, 2006). In some countries, studies of ecological compensation have been carried out, revealing the use of compensation mechanisms and types, including self-organized payments for environmental services, public payments for the management of areas of important ecological function, compensation for the restoration of landscapes affected by mining, and compensation for agro-ecological environmental protection (Liu et al., 2024). Direct investment and subvention from the government was adopted in developed countries, and the strategy of sustainable development of forestry in these countries is unitive between the government and the market (Deng et al., 2011). Some Western countries have also begun to collect ecological taxes and have established a suitable system for ecological taxation, which may be a very important direction for traditional tax innovation (Medynska et al., 2024). Moreover, some Asian countries (Singapore, India, and Korea) and Eastern European countries such as Poland and Hungary have also adopted ecological tax policies. In these countries, governments subsidize forestry services and collect fees from beneficiaries of forest ecosystem services, thereby solving the double relation between material compensation and value compensation of ecological resources (Delgado et al., 2022; Cornelia and Lenuţa, 2012). Three countries, the United States, Brazil, and Costa Rica, have successfully implemented compensation policies for ecosystem services. Their common experience is that the government is the main purchaser of ecosystem services (Lara et al., 2009). The U.S. government chose some active measures to improve the provision of ecosystem services; for example, the government purchased ecosystem services and supplied the compensation funds (Adhikari et al., 2022). In England and France, the income from state-owned forests is not turned back to higher authorities but is used for further forest development, and shortfalls are remedied by government allocations or preferential loans (Wang et al., 2022). German state-owned forests have a budget policy, and funds are appropriated after examination and approval of the budget by the national parliament. The investment of former Soviet Union countries accounted for 10% of state-owned forest management expenditure (Fisher et al., 2008; Hashim et al., 2010).
In China, studies of compensation for ecosystem services were carried out more recently. The “Regulations on Ecological Protection Compensation” promulgated by the State Council in April 2024 marked significant progress in the legalization of ecological protection compensation in China, and China became the world's first country to comprehensively legislate on ecological protection compensation. China's policy of compensation for forest ecosystem services was formally put forward in 1989, and it includes fees imposed upon activities leading to the destruction or degradation of forest ecosystems, fees collected from the beneficiaries of ecosystem services, and compensation for individual or regional ecological conservation activities (Shang et al., 2018). The funding system for Chinese forest ecological compensation was first listed in the Forest Law of the People's Republic of China in 1998. The traditional approach to the provision of environmental services has been through ecological compensation payments made directly from the government to the supplier of forest ecosystem services (such as the very large “Grain for Green” program). In 2001, the Ministry of Finance and the National Bureau of Forestry designated 658 counties in 11 provinces and 24 state-level natural reserves as experimental units that would receive subsidies for ecosystem services, marking the first implementation of a compensation policy for ecosystem services in the country. In 2004, the Central Government Financial Compensation Fund for forest ecological compensation was formally established in China (Niu et al., 2012). The forestry subsidy policy implemented in China promotes land greening, improves forest quality, enhances forest ecosystem services, and ensures the basic livelihood of the people (Lu et al., 2020). Han and Chen (2021) found that forestry subsidy policies can directly increase transfer payment income, effectively improve the forestry production capacity of forest workers, and increase their household income.
Selomane et al. (2015) evaluated the contribution of nature-based sectors (agriculture, forestry, and fisheries) to income and employment rates and found that from 1991 to 2010, nature-based sectors helped 18% of the world's population escape poverty and provided 37% of employment opportunities. Yang et al. (2013) constructed indicators reflecting the degree of dependence of human wellbeing on ecosystem services, including income from food, meat, and non-timber forest products that represent the contribution of provisioning services, electricity subsidies obtained due to protecting watersheds that represent the contribution of regulating services, and ecological tourism income that represents the contribution of cultural services. At present, studies on compensation for forest ecosystem services are mostly policy compensation studies, and individual reports are mainly concerned with the size of ecological compensation payments. However, the ecological compensation payment size may be too large and far beyond local governments' ability to afford, resulting in non-achievement of the desired ecological benefits (Chen et al., 2020). The regional development level and actual carrying capacity should be considered comprehensively in reasonable ecological compensation. There are many studies using the compensation coefficient method, which is based on integrating Engel's coefficient with the Peel growth curve model (Liang, 2008). The Peel growth curve model is used to express the enhancement of human ecological awareness and payment ability. Engel's coefficient is a measure of residential food expenditure as a proportion of the total consumer spending and does not take into account the relationship between forest ecosystem services and human wellbeing. So, the above ecological compensation methods are only based on the national economic level and cannot reflect the actual value of forest ecosystem services. It caused the phenomenon of coexistence of inadequate compensation and overcompensation; the benefit of the compensation funds was low, and it seriously reduced the project implementation effects. The essence of ecological compensation is that the forest ecological benefit value should be balanced between the beneficiary, who should pay for forest ecosystem services, and the supplier, who should gain from providing forest ecosystem services (Farley and Costanza, 2010). The ecological compensation standard should be the embodiment of combining information about both the beneficiary and the supplier of forest ecosystem services.
The present study integrates domestic and international theories and methods of compensation for ecosystem services and puts forward the multi-functional quantitative ecological compensation standard (MQECS) for forest ecosystem services based on the Human Development Index (HDI) and the values of six distinct forest ecosystem services (11 quantitative indicators). It takes into account the contribution of the supplier of forest ecosystem services and the contribution of the beneficiary (the national and local governments' ability to afford). Moreover, by the MQECS method, the ecological compensation standards for forest ecosystem services in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces and in different city levels within the single provinces in 2012 were calculated. It showed that the MQECS method and analysis was reasonable and feasible and supported the quantitative operationalization of the administration of forest ecosystem services compensation policy in China.
Guangdong province is located in southern China (Figure 1), with 21 provincial-level cities. Guangdong belongs to the East Asian monsoon region, with central subtropical, southern subtropical, and tropical climates from north to south. Precipitation is abundant, with an average annual precipitation of 1,777 mm, showing a trend of high in the south and low in the north, and is mainly concentrated from April to September, accounting for more than 80% of the annual precipitation. The average annual temperature is 22.3°C. The forest resource area in Guangdong province was 892.71 × 104 hm2, and the volume was 3.98 × 108 m3.
Liaoning province is located in the northeast part of China (Figure 1), belonging to the warm temperate continental monsoon climate zone. It has the same period of rain and heat, sufficient sunlight, and an average annual temperature of 5°C–11°C. The annual precipitation is between 400 and 1,150 mm, decreasing from east to west. The rainy season lasts from July to August, accounting for approximately 70% of the annual precipitation. The forest resource area in Liaoning province was 449.51 × 104 hm2, and the volume was 2.62 × 108 m3.
We set 2012 as the evaluation base year. The data from the statistical yearbook of Guangdong and Liaoning provinces were collected in the calculation of ecological compensation, including the total residential consumer food expenditure, healthcare expenditure, cultural and educational entertainment products expenditure, and gross domestic product (GDP).
When calculating ecosystem services, three data sources including the forest resource data, eco-station and experiment data, and public data were coupled and integrated (Figure 2). The forest resource inventory data contain the forest areas and volume from the second category survey of forest resources in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces. The data collected by the eco-stations and experiments in the study area and adjacent areas, all based on the national standards “Methodology for field long-term observation of forest ecosystem” (SFA, 2016), and the data on different dominant trees, species origins, stand ages, and site conditions were collected. Meanwhile, the public data released via government statistics and prices include social expenses such as water purification costs and sewage charges. When forest ecosystem service quality is transformed into value quantity, it conforms to the principles of “equivalent substitution” and “weight equivalent balance.”
The HDI is a measure of the overall situation of human development in a region. Its computation incorporates measures of a region's average achievements in three main dimensions: health and longevity, knowledge acquisition, and standard of living (Klugman et al., 2011). HDI can be calculated using the equation:
where HDI is the Human Development Index, IL is the life expectancy index, IE is the education index, and IG is the gross national finance income (GNI) index. LACT, LMAX, and LMIN represent the actual value, maximum value, and minimum value of life expectancy, respectively. EACT, EMAX, and EMIN represent the actual value, maximum value, and minimum value of education, respectively. GACT, GMAX, and GMIN represent the actual value, maximum value, and minimum value of the GNI per capital, respectively.
In addition, the dimension indicators related to the HDI happen to be basically consistent with human wellbeing factors such as health, basic material conditions for maintaining high-quality life, safety, and good social relationships. These factors are closely related to forest ecosystem services, and in economic statistics, these factors correspond precisely to a part of household consumption. Overall, the HDI is a parameter that is relatively easy to calculate, has a simple calculation method, can be calculated using readily available data, and is applicable to different social groups. HDI can also serve as an important indicator of social progress and development.
The ecological compensation standard should be the embodiment of combining the information on both the beneficiary and the supplier (Yu et al., 2005). Integrating domestic and international theories and methods of compensation for ecosystem services, the multi-functional quantitative ecological compensation standard (MQECS) for forest ecosystem services is put forward based on the contribution of those services to dimensions of human wellbeing considered in the computation of the HDI. MQECS is a method that considers not only the multiple functions of the forest ecosystem but also the relationship between ecosystem services and human wellbeing, and the contribution of the beneficiary (the national and local governments' ability to afford) is also considered. So, the MQECS is applicable to the current situation of forest ecosystem services in China's provinces (or cities). The specific method and process are introduced as follows:
where MQECSi is the multi-functional quantitative ecological compensation standard for forest ecosystem services in province (or city) i, RMB hm-2; SUNHDIi represents the contribution of the supplier of forest ecosystem services in a province (or city) i, %; BEFCIi represents the contribution of the beneficiary of forest ecosystem services in a province (or city) i, %; Vi represents the total value of forest ecosystem services in a province (or city) i, RMB; and Ai represents the forest area of a province (or city) i, hm2.
SUNHDIi is the basic consumption index of human development of a province (or city) i. It can be calculated by the following equation:
where C1, C2, and C3 represent total residential consumer food expenditure, healthcare expenditure, and cultural and educational entertainment products expenditure, respectively, RMB. GDPi represents the gross domestic product of province (or city) i, RMB. These data can be obtained from the statistical yearbook.
BEFCIi is the finance compensation ability index of province (or city) i. It can be calculated by the following equation:
where Gi represents the gross finance income of province (or city) i, in RMB; GNI represents gross national finance income, in RMB. These data can be obtained from the statistical yearbook.
Vi includes the values of six distinct services, that is, water conservation, soil conservation, carbon sequestration and oxygen release, nutrient accumulation, atmosphere environmental purification, and biodiversity conservation (Niu and Wang, 2013). Moreover, the provision of these ecological services was evaluated using 11 quantitative indicators (Table 1), according to the “Specifications for assessment of forest ecosystem services” (SFA, 2020), and Vi can be calculated by the following equation:
where VR is the value for the quantity of water regulated per year; VW is the value of water quality purification per year; VS is the value of fixed soil per year; VF is the value of fertility maintained per year; Vc is the value of carbon sequestration per year; Vo is the value of oxygen released per year; VT is the value of N, P, and K accumulated in NPP per year; VA is the value of anions produced per year; VP is the value of pollutants absorbed per year; VD is the value of dust absorbed per year; and VB is the total conservation value of species diversity per year. The data source is mentioned in Figure 2 and calculated with equations in Table 1.
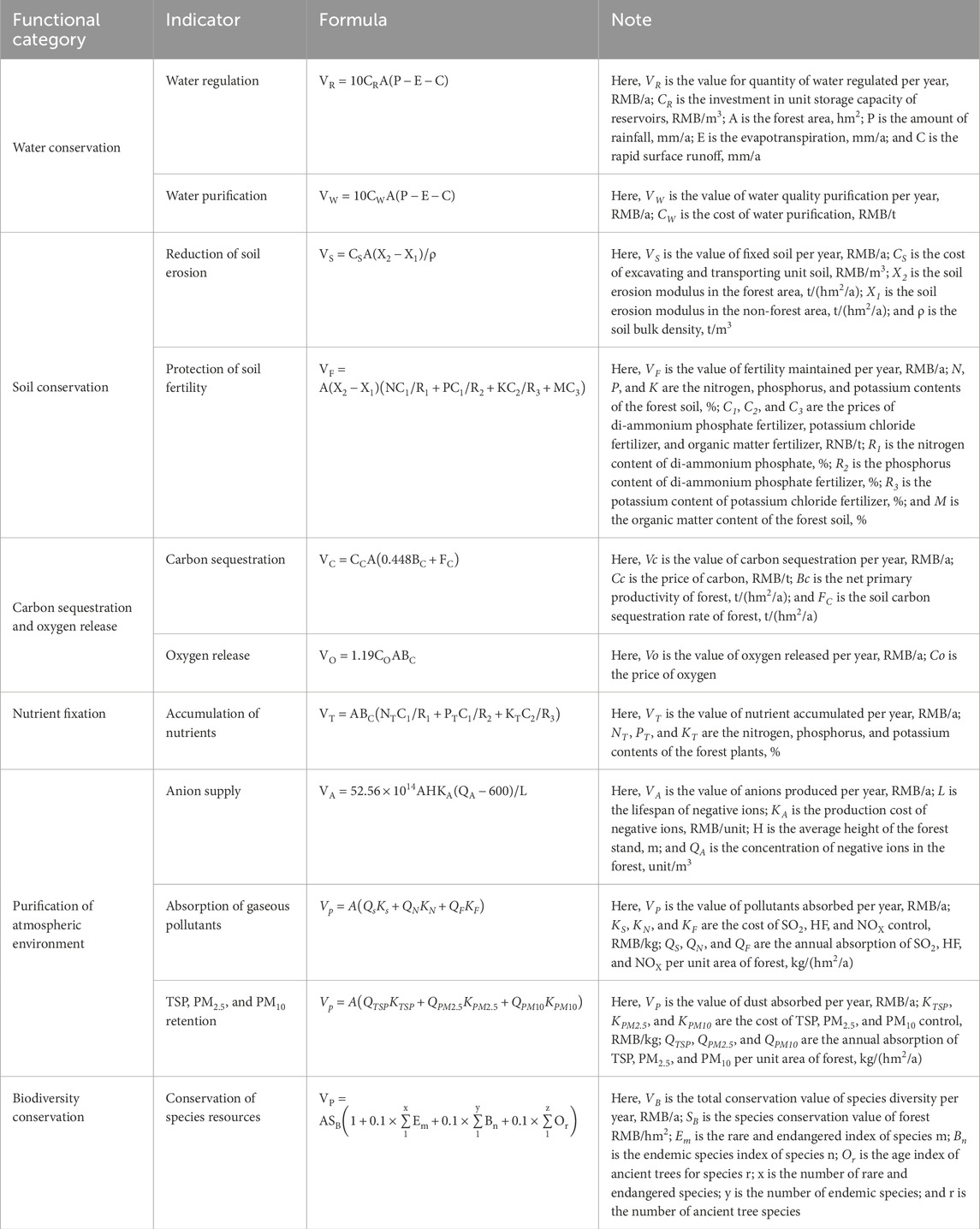
Table 1. Evaluation of the indicator system and formula of the assessment of forest ecosystem function.
In this study, we choose the forest ecological benefit compensation allocation coefficient to determine the total amount and the amount of compensation received by each city. The calculation formula for the distribution coefficient of forest ecological benefit compensation is as follows:
where Dij, in %, represents the distribution coefficient of forest ecological benefits in province i, city j; Vij, in RMB/a, is the forest ecological benefits of province i, city j; and Vi, in RMB/a, is the forest ecological benefits of province i.
From this, the total amount of MQECSij in forest ecological benefits compensation that each region (city) should receive can be calculated as follows:
where
In our study, the MQECS for forest ecosystem services were put forward based on the dimensions of the HDI. It is thus linked not only to human wellbeing but also to the financial income condition of each province (or city). In order to achieve the calculated MQECSi (the target compensation standard), a provincial (city's) government would have to take the measures necessary to promote the realization according to the calculated MQECSi. The increase in investment necessary to close the gap between the calculated MQECSi and the current compensation amount of the provincial government is given as follows:
where Yi', in %, represents the percentage of increased investment amount accounted for the current compensation amount; and SCi' is the current compensation amount of the provincial government i in RMB hm-2.
The value of forest ecosystem services in Guangdong province was 7031.28 × 108RMB/a, and the value per unit area was 7.88 × 104RMB/hm2. Among them, water conservation accounted for 44.54% of the total ecosystem services, which was the highest function, followed by biodiversity conservation, and the smallest function was nutrient fixation (Table 2).
The value of forest ecosystem services in Liaoning province was 2953.20 × 108RMB/a, and the value per unit area was 6.57 × 104RMB/hm2. The sorting of various functions was consistent with that of Guangdong province. Water conservation, as the leading function, accounted for 39.37% of the total ecosystem services (Table 2).
Using the statistical yearbook data of Guangdong and Liaoning provinces, the basic consumption index of human development of a province (the SUNHDIi), the finance compensation ability index of a province (the BEFCIi), the MQECSi, and the total ecological compensation amount (TECAi) for forest ecosystem services in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces in 2012 were calculated.
The SUNHDIi and BEFCIi of Guangdong province were higher than those of Liaoning province in 2012 (Table 3), and the MQECSi of Guangdong province was approximately three times that of Liaoning province. The TECAi of forest ecosystem services of Guangdong and Liaoning provinces accounted for 1.83% and 1.01% of the provincial gross finance income (Gi), respectively. The TECAi of Guangdong province was approximately five times that of Liaoning province.
Using the MQECS method, our study also explored the ecological compensation for forest ecosystem services of city levels within a single province. Therefore, the MQECSi and the TECAi for forest ecosystem services of different cities in Guangdong province (Table 4) and Liaoning province (Table 5) in 2012 were calculated. The MQECSi for forest ecosystem services of different cities in Guangdong province ranged from 456.86 to 985.37 RMB·hm−2, with the highest standard for Zhaoqing and the lowest standard for Dongguan. The MQECSi for forest ecosystem services of different cities in Liaoning province ranged from 165.94 to 275.80 RMB·hm−2, with the highest standard calculated for Benxi and the lowest standard for Chaoyang. The change trend of TECAi is consistent with that of the MQECSi.
According to the relevant regulations of the two provinces, the compensation standard in 2012 was 240RMB/hm2 and 150RMB/hm2, respectively. The government needs to increase investment per unit area by 176.25% and 50.20% (Yi') of the compensation amount in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces, respectively, to achieve the target quantitative compensation levels. These results indicate that improvements in the standard of living heighten the value of the contribution of forest ecosystems to the environmental quality (Gao et al., 2023). If the government can dedicate approximately 1% of the annual finance income to forest ecosystem service compensation in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces, the human wellbeing index can be improved accordingly. Moreover, the provincial governments can afford the TECAi for forest ecosystem services calculated by the MQECS method. So, the calculated ecological compensation results in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces not only consider the local government's ability to pay but also incorporate factors influencing human wellbeing and the valuation of distinct forest ecosystem services, and the MQECS method was reasonable and feasible. Since 2018, Liaoning province has implemented tending fund subsidies for ecological forests for the Grain for Green project, and the subsidy standard is 300 RMB/hm2. In 2024, Guangdong province provided a basic compensation of 585 yuan/hm2 for non-commercial forests at or above the provincial level in general areas. At the same time, additional incentive compensation (60 RMB/hm2 higher than the basic compensation standard) will be arranged for areas with high forest quality so that areas with good forest quality can receive higher compensation standards and prioritize the improvement of standards for this part of the region in future years. The policy compensation method does not differentiate between the contribution of the supplier and the contribution of the beneficiary (Kuai et al., 2024; Huang et al., 2023). The MQECS method improves upon the deficiencies of some other compensation methods.
The MQECSi was positively correlated with the total value of the forest ecosystem services (Vi) and negatively correlated with the forest area of the city (Ai). Obviously, this distribution of compensation was not consistent with the economic development standards of different cities in Guangdong province. According to the statistical yearbook data of Guangdong province in 2012, the gross finance income of Zhongshan, Zhuhai, Foshan, Dongguan, Shantou, and Shenzhen accounted for 44.86% of the total gross finance income of Guangdong province, but the gross finance income of these cities with higher TECAi, such as Zhaoqing, Heyuan, Shaoguan, Qingyuan, Meizhou, and Huizhou, accounted for only 8.20% of the total gross finance income of Guangdong province. From these data, it can be seen that the cities with higher gross finance income are burdened with lower TECAi for forest ecosystem services in Guangdong province.
According to the statistical yearbook data of Liaoning province in 2012, the gross finance income of Shenyang and Dalian accounted for 56.68% of the total gross finance income of Liaoning province, but the cities with more TECAi, such as Dandong, Fushun, Benxi, and Chaoyang, accounted for only 14.12% of the total gross finance income of Liaoning province. These results were similar to those obtained for Guangdong province, and the TECAi for forest ecosystem services was related not only to the gross finance income of these cities but also to the total forest area and the total value of the forest ecosystem services. The results indicate that there is a certain degree of cost–benefit imbalance among cities in Liaoning and Guangdong provinces. Therefore, establishing a horizontal ecological protection compensation mechanism is crucial to alleviate this imbalance to a certain extent (Kroeger et al., 2019). One of the basic tasks of horizontal ecological compensation of forests is to determine reasonable and feasible compensation standards (Yu Y. Y. et al., 2023). In order to achieve a long-term stable and balanced state of horizontal ecological compensation and conservation in forests, it is necessary to calculate compensation standards that meet external forest conservation and internal environmental governance and take compensation actions (Norden et al., 2019). The MQECS method is suitable for calculating the horizontal ecological compensation for forests.
Forest ecological compensation is a policy tool to solve the contradiction between ecological environment governance and socio-economic development (Deng et al., 2020). The ecological compensation standard for forests should be higher than the relevant opportunity costs incurred during the planting process of forest land, thereby effectively improving the enthusiasm of the compensated subjects to protect the natural ecological environment (Engel et al., 2008). Establishing a reasonable forest ecological compensation mechanism is a practical need. This study explores a path that mainly focuses on vertical ecological compensation fiscal transfer payments and horizontal value exchanges, supplemented by market incentive mechanisms to enhance the enthusiasm of the public to participate in ecological compensation (Niu et al., 2024). China has a vast territory and needs to be studied from specific perspectives based on the actual situation in different regions. The current forest ecological compensation standards are mainly calculated from three perspectives: input cost, ecosystem service value, and compensation willingness. From the current situation, there is a problem of “one size fits all,” and the compensation standards are too low, which is not conducive to building a scientific ecological compensation mechanism. Such a method cannot fully mobilize the enthusiasm of forest managers. Other ecosystem services compensation mechanisms do not consider local governments' ability to pay or local levels of economic and social development and suggest compensation payments that are unaffordable (Ouyang et al., 2016). These mechanisms fail to achieve an appropriate compensation for forest ecosystem services. In contrast, the MQECS method takes the fiscal condition of the provinces and factors of human wellbeing into account; therefore, it is applicable to the present situation of forest ecosystem services compensation in China's provinces and cities.
The pursuit of material happiness by humans is neither equally important nor is it synchronous with the human wellbeing provided by ecosystem services (Zhou et al., 2024). There is a time gap between the two. Only when the happiness of human material life is satisfied will we begin to pursue the happiness brought by the ecological environment. However, at present, this time difference cannot be expressed as a specific parameter in the calculation formula of the multi-functional quantitative compensation coefficient for provincial forest ecological benefits. This needs to be addressed as much as possible in the next step of work.
Ecosystems are unevenly distributed in space and have different flow rates, resulting in mismatched ecological services and their beneficiaries at the spatial and temporal levels (Yu et al., 2021), which requires ecological compensation. The value of forest ecosystem services is essentially a measure of the costs and benefits of traditional market spillovers. Through corresponding compensation, externalities are introduced into the decision-making process of economic actors, thereby achieving ecologically friendly behavior among different social entities (Yu H. Q. et al., 2023). There is a certain consistency between the theory of ecosystem service flow and the theory of ecological compensation (Du et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024), which provides new technical support for the formulation of ecological compensation policies. Current forest ecological compensation is still mainly based on vertical transfer payments, which causes a series of problems such as low compensation standards, limited coverage, single funding channels, and high financial pressure (Deng et al., 2011). Using the MQECS method to rely on the ecological benefits of forests for reasonable compensation also realizes the transformation of ecological compensation from policy-based compensation to quantitative compensation based on the ecological function of forest ecosystem. Further exploration of inter-regional forest horizontal ecological compensation mechanisms is conducive to alleviating central financial pressure, promoting regional development equity, and establishing a relatively complete and reasonable ecological compensation mechanism to better promote the improvement of forest ecosystem quality and the enhancement of ecological product supply capacity.
This study puts forward the multi-functional quantitative ecological compensation standard (MQECS) for forest ecosystem services based on the HDI. The ecosystem services of six distinct forest ecosystem services (11 quantitative indicators) in Guangdong and Liaoning provinces were 7031.28 × 108RMB/a and 2953.20 × 108RMB/a, respectively. The MQECS for forest ecosystem services of Guangdong and Liaoning provinces in 2012 were 663.02 RMB·hm-2 and 225.27 RMB·hm−2, and the MQECS of Guangdong province was approximately three times that of Liaoning province. The MQECS of a single city in Guangdong province ranged from 456.86 to 985.37 RMB·hm-2, while in Liaoning it ranged from 165.94 to 275.80 RMB·hm−2. The economic development level of different provinces (or cities) has an important influence on the MQECS and TECA for ecosystem services.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
XN: conceptualization, methodology, project administration, and writing–review and editing. TX: conceptualization, methodology, and writing–original draft. BW: conceptualization, methodology, and writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Forest and grassland ecosystem assessment and value accounting (91210-2024).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adhikari, R. K., Grala, R. K., Petrolia, D. R., Grado, S. C., Grebner, D. L., and Shrestha, A. (2022). Landowner willingness to accept monetary compensation for managing forests for ecosystem services in the southern United States. For. Sci. 68 (2), 128–144. doi:10.1093/forsci/fxab063
Boskidis, I., Gikas, G. D., Sylaios, G. K., and Tsihrintzis, V. A. (2012). Hydrologic and water quality modeling of lower nestos river basin. Water Resour. Manag. 26, 3023–3051. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0064-7
Cai, B. C., Wen, L. Q., and Lu, G. F. (2005). The theoretical discussion on ecological compensation mechanism. Ecol. Econ. 1, 47–50. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2005.01.011
Chen, Y., Dou, S. Q., and Xu, D. Y. (2020). The effectiveness of eco-compensation in environmental protection -A hybrid of the government and market. J. Environ. Manage. 280, 111840. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111840
Cornelia, P. G., and Lenuţa, T. C. (2012). Trends in the evolution of environmental taxes. Procedia Econo. Finance 3, 716–721. doi:10.1016/s2212-5671(12)00219-5
Costanza, R., d'Arge, R., de Groot, R., Farber, S., Grasso, M., Hannon, B., et al. (1997). The value of the world's ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 387 (6630), 253–560. doi:10.1016/s0921-8009(98)00020-2
Delgado, F. J., Freire-González, J., and Presno, M. J. (2022). Environmental taxation in the European Union: are there common trends? Econ. Anal. Policy 73, 670–682. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2021.12.019
Deng, C., Zhang, S. G., Lu, Y. C., and Li, Q. F. (2020). Determining the ecological compensation standard based on forest multifunction evaluation and financial net present value analysis: a case study in southwestern Guangxi, China. J. Sustain. For. 39 (7), 730–749. doi:10.1080/10549811.2020.1723644
Deng, H., Zheng, P., Liu, T., and Liu, X. (2011). Forest ecosystem services and eco-compensation mechanisms in China. Environ. Manage. 48, 1079–1085. doi:10.1007/s00267-011-9742-0
Du, H. Q., Zhao, L., Zhang, P. T., Li, J. X., and Yu, S. (2023). Ecological compensation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on ecosystem services flow. J. Environ. Manag. 331, 117230. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117230
Engel, S., Pagiola, S., and Wunder, S. (2008). Designing payments for environmental services in theory and practice: an overview of the issues. Ecol. Econ. 65 (4), 663–674. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.03.011
Farley, J., and Costanza, R. (2010). Payments for ecosystem services: from local to global. Ecol. Econ. 69, 2060–2068. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2010.06.010
Fisher, B., Turner, K., Zylstra, M., Brouwer, R., Groot, R. D., Farber, S., et al. (2008). Ecosystem services and economic theory: integration for policy-relevant research. Ecol. Appl. 18, 2050–2067. doi:10.1890/07-1537.1
Fisher, J. A., Patenaude, G., Giri, K., Leweis, K., Meir, P., Pinho, P., et al. (2014). Understanding the relationships between ecosystem services and poverty alleviation: a conceptual framework. Ecol. Sev. 7, 34–45. doi:10.1016/j.ecoser.2013.08.002
Gao, S., Bull, J. W., Baker, J., Ermgassen, S. O. E., and Milner-Gulland, E. J. (2023). Analyzing the outcomes of China's ecological compensation scheme for development-related biodiversity loss. Conserv. Sci. Prac. 5, e13010. doi:10.1111/csp2.13010
Gao, X. L., Huang, B. B., Hou, Y., Xu, W. H., Zheng, H., Ma, D. C., et al. (2020). Using ecosystem service flows to inform ecological compensation: theory and application. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17 (9), 3340. doi:10.3390/ijerph17093340
Guan, D. J., Chen, S., Zhang, Y. X., Liu, Z. F., Peng, G. D., and Zhou, L. L. (2024). Influencing factors and the establishment of a basin ecological compensation mechanism from the perspective of water conservation: a case study of the upper Yangtze River in China. J. Clean. Prod. 456, 142332. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142332
Han, F., and Chen, Y. R. (2021). How forest subsidies impact household income: the case from China. Forests 12 (08), 1076–1090. doi:10.3390/f12081076
Hashim, M., Marghany, M. M., Okuda, T., and Numata, S. (2010). Risk assessment mapping of landscape development based on ecological service and goods in Malaysia lowland tropical rainforest. J. Environ. Sci. Engin. 4, 58–69.
Hou, Y. Z., and Wang, Q. (1995). The research on accounting of Chinese forest resources. World For. Res. 9, 51–56.
Huang, Y. L., Lou, G. Y., and Yao, J. B. (2023). Research on the profit contribution of forest ecological benefits based on policy and market-tools compensation projects in nanping. Sustainability 15 (6), 5465. doi:10.3390/su15065465
Ju, F., Zhou, J. J., and Jiang, K. (2022). Evolution of stakeholders' behavioral strategies in the ecological compensation mechanism for poverty alleviation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 176, 105915. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105915
Klugman, J., Rodriguez, F., and Choi, H. J. (2011). The HDI 2010: new controversies, old critiques. Hum. Dev. Res. Pap. 1. UNDP - HDRO 9, 249–288. doi:10.1007/s10888-011-9178-z
Kroeger, T., Klemz, C., Boucher, T., Fisher, J. R. B., Acosta, E., Cavassani, A. T., et al. (2019). Returns on investment in watershed conservation: application of a best practices analytical framework to the Rio Camboriú Water Producer program, Santa Catarina, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 657, 1368–1381. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.116
Kuai, C. J., Huang, Y. A., and Wang, F. E. (2024). A framework for eco-compensation in the Yangtze River Delta region of China based on multiple policy objectives. J. Clean. Prod. 436, 140370. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140370
Lara, A., Little, C., Urrutia, R., McPhee, J., Álvarez-Garretón, C., Oyarzún, C., et al. (2009). Assessment of ecosystem services as an opportunity for the conservation and management of native forests in Chile. For. Ecol. Manag. 258, 415–424. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2009.01.004
Leviston, Z., Walker, I., Green, M., and Price, J. (2018). Linkages between ecosystem services and human wellbeing: a Nexus Webs approach. Ecol. Indic. 93, 658–668. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.052
Li, T., Zhang, Q. G., and Zhang, Y. (2018). Modelling a compensation standard for a regional forest ecosystem: a case study in yanqing district, Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Hel. 15 (4), 565. doi:10.3390/ijerph15040565
Liang, D. (2008). Global review of payments for forest ecosystem services in theory and practice: international experiences and trends. For. Econ. 12, 7–15. doi:10.13843/j.cnki.lyjj.2008.12.003
Liu, J. M., Su, X. J., Liu, Y. M., and Shui, W. (2024). A review of research on progress in the theory and practice of eco-product value realization. Land 13 (3), 316. doi:10.3390/land13030316
Lu, S., Sun, H. S., Zhou, Y., Qin, F., and Guan, X. L. (2020). Examining the impact of forestry policy on poorand non-poor farmers'income and production input in collective forest areas in China. J. Clean. Prod. 276 (12), 123784. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123784
Medynska, T., Loboda, N., Nohinova, N., Oliynyk, N., and Borutska, Y. (2024). Optimization of ecological taxation: role in the formation of environmental protection budgets. Int. J. Environ. Imp. 15 (13), 10604. doi:10.18280/ijei.070102
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005). Ecosystems and human well-being: biodiversity SynthesisM. World Resour. Washingt.DC.
Naime, J., Angelsen, A., Garzon, A., Carrilho, C. D., Selviana, V., Demarchi, G., et al. (2022). Enforcement and inequality in collective PES to reduce tropical deforestation: effectiveness, efficiency and equity implications. Glob. Environ. Change 74, 102520. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2022.102520
Niu, J. J., Mao, C. M., and Xiang, J. (2024). Based on ecological footprint and ecosystem service value, research on ecological compensation in Anhui Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111341. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111341
Niu, X., and Wang, B. (2013). Assessment of forest ecosystem services in China: a methodology. J. Food, Agri. and Environ. 11, 2249–2254.
Niu, X., Wang, B., Liu, S., Liu, C., Wei, W., and Kauppi, P. E. (2012). Economical assessment of forest ecosystem services in China: characteristics and implications. Ecol. Compl. 11, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.ecocom.2012.01.001
Nordén, A., Coria, J., Jónsson, A. M., Lagergren, F., and Lehsten, V. (2019). Divergence in stakeholders' preferences: evidence from a choice experiment on forest landscapes preferences in Sweden. Ecol. Ecno. 132, 179–195. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.09.032
Ouyang, Z. Y., Zheng, H., Xiao, Y., Polasky, S., Liu, J. G., Xu, W. H., et al. (2016). Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 352 (6292), 1455–1459. doi:10.1126/science.aaf2295
Selomane, O., Reyers, B., Biggs, R., Tallis, H., and Palasky, S. (2015). Towards integrated social–ecological sustainability indicators: exploring the contribution and gaps in existing global data. Ecol. Econ. 118, 140–146. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.07.024
Shang, W., Gong, Y., Wang, Z., and Stewardson, M. J. (2018). Eco-compensation in China: theory, practices and suggestions for the future. J. Environ. Manage. 210, 162–170. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.077
Shi, X. L., Zhang, J. Y., Lu, J., Zhao, T. R., Yang, H. O., Aria, A., et al. (2024). Global trends and innovations in forest ecological compensation: an interdisciplinary analysis. Forests 15 (4), 631. doi:10.3390/f15040631
Sierra, R., and Russman, E. (2006). On the efficiency of environmental service payments: a forest conservation assessment in the Osa Peninsula, Costa Rica. Ecol. Econ. 59, 131–141. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.10.010
Snall, T., Trivino, M., Mair, L., Bengtsson, J., and Moen, J. (2021). High rates of short-term dynamics of forest ecosystem services. Nat. Com. 4, 951–957. doi:10.1038/s41893-021-00764-w
State Forestry Administration (2016). Methodology for long-term observation of forest ecosystem GB/T 33027-2016. Beijing, China: Standards Press of China. (In Chinese).
State Forestry Administration (2020). Specifications for assessment of forest ecosystem services GB/T 38582-2020. Beijing, China: Standards Press of China. (In Chinese).
Taye, A. F., Folkersen, M. V., Fleming, C. M., Buckwell, A., Mackey, B., Diwakar, K. C., et al. (2021). The economic values of global forest ecosystem services: a meta-analysis. Ecol. Econ. 154, 110687. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107145
Wang, L., Lv, T. H., Zhang, X. M., Hu, H., and Cai, X. (2022). Global research trends and gaps in ecological compensation studies from 1990 to 2020: a scientometric review. J. Nat. Conserv. 65, 126097. doi:10.1016/j.jnc.2021.126097
Wang, P., Poe, G. L., and Wolf, S. A. (2017). Payments for ecosystem services and wealth distribution. Ecol. Econ. 132, 63–68. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.10.009
Wang, X. M., Liu, P., Wei, C. T., Xu, N. Z., Zhao, P., and Wen, D. (2024). Research on ecological compensation based on ecosystem service flow: a case study in Guangdong province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 480, 144090. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144090
Wu, C. S., Lu, R. R., Zhang, P., and Dai, E. F. (2024). Multilevel ecological compensation policy design based on ecosystem service flow: a case study of carbon sequestration services in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 921, 171093. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171093
Yang, H. B., Yang, W., Zhang, J. D., Connor, T., and Liu, J. G. (2018). Revealing pathways from payments for ecosystem services to socioeconomic outcomes. Sci. Adv. 4, eaao6652. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aao6652
Yang, W., Dietz, T., Liu, W., Luo, J. Y., and Liu, J. G. (2013). Going beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: an index system of human dependence on ecosystem services. Plos One 8 (5), e64581. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064581
Yang, Y., Zhu, Y., and Zhao, Y. W. (2024). Improving farmers' livelihoods through the eco-compensation of forest carbon sinks. Renew. Sust. Enger. Rev. 198, 114401. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2024.114401
Yu, X. X., Lu, S. W., Jin, F., Chen, L. H., Rao, L. Y., and Lu, G. Q. (2005). The assessment of the forest ecosystem services evaluation in China. Acta Eco. Sin. 25 (8), 2096–2102. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.08.038
Yu, H., Xie, W., Sun, L., and Wang, Y. (2021). Identifying the regional disparities of ecosystem services from a supply-demand perspective. Resour. Conser. Recyc. 169, 105557. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105557
Yu, H. Q., Yang, J. M., and Wan, Z. X. (2023). Horizontal compensation standards for forest ecological benefits inTingjiang (hanjiang) river basin based on the perspective of water retention service. Sci. Silvae Sin. 59 (2), 1–9. doi:10.11707/j.1001-7488.LYKX20220696
Yu, Y. Y., Li, J., Han, L. Q., and Zhang, S. J. (2023). Research on ecological compensation based on the supply and demand of ecosystem services in the Qinling-Daba Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 154, 110687. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110687
Zhou, Y. C., Huang, Q. X., He, C. Y., Chen, P. Y., Yin, D., Zhou, Y. H., et al. (2024). A bibliographic review of the relationship between ecosystem services and human well-being. Environ. Dev. Sustain. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-04791-3
Keywords: forest ecosystem services, multi-function quantitative ecological compensation, human development index, sustainability, human wellbeing
Citation: Niu X, Xu T and Wang B (2025) Payments for forest ecosystem services in China: a multi-function quantitative ecological compensation standard based on the Human Development Index. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1447513. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1447513
Received: 11 June 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Fang Yu, Chinese Academy for Environmental Planning, ChinaReviewed by:
Peng Gao, Shandong Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Niu, Xu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bing Wang, d2FuZ2JpbmdAY2FmLmFjLmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.