
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Earth Sci., 31 January 2025
Sec. Economic Geology
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2025.1442518
This article is part of the Research TopicExploration, Development, and Protection of Earth’s Resources and Environment: Methods, Techniques, Applications, Prospects, Insights, and ProblemsView all 45 articles
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is receiving increasing attention as a technology to mitigate the increasingly serious impacts of climate change. This review explains the CCS process, providing details of important factors influencing its performance, current barriers to its widespread commercialization, and potential pathways for advancement. Integrated data analysis is applied to investigate the multiple factors affecting the storage capacity of CCS sites, including the geological properties of reservoir sites, physicochemical characteristics of CO2, and petrophysical features of rocks. We also review recent developments in CCS technology. Our findings will help guide the precise design of CCS systems and the control of their parameters to improve performance and reliability. Although practical obstacles such as cost and public acceptance remain before CCS can be implemented at a large scale, progress continues to be made in terms of monitoring technologies, evaluation methodologies, and CO2 capture/conversion strategies. In addition, ongoing and future research avenues are also discussed, which include the development of novel monitoring technologies, new possibilities for evaluating long-term storage impacts, and improvements to CO2 capture and conversion methods. The study offers valuable insights into the emerging technology of CCS and may aid future improvement to, for example, its commercial viability, which could aid progress toward international carbon neutrality ambitions.
Climate change has become one of the greatest global challenges. A lot of attention has been focused on attempting to limit emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), one of the main greenhouse gases (Carlin, 2006; Ali et al., 2020). Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a promising technology for controlling atmospheric CO2 levels by its storage in deep geological formations, usually for long periods (Gibbins and Chalmers, 2008) (Figure 1). Although CCS is theoretically useful and has been verified through laboratory studies, it faces a host of obstacles and uncertainties concerning its practical effectiveness, safety, and economic feasibility (Wilberforce et al., 2019; Boot-Handford et al., 2014).
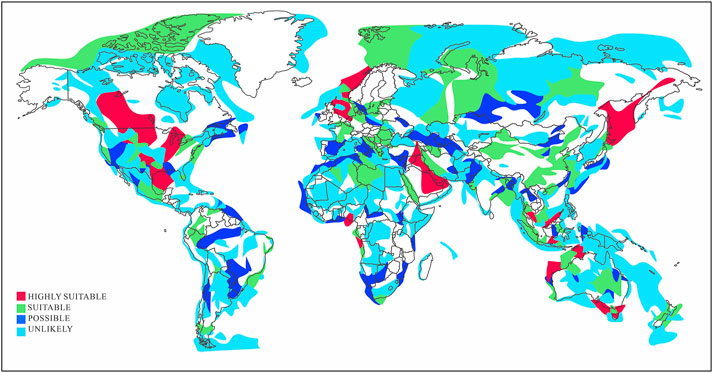
Figure 1. Suitable global storage regions based on the Global COS Institute storage basin assessment database.
Achieving global targets for reductions of net emissions set by international organizations such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and International Energy Agency (IEA) requires a combination of both reductions of absolute emissions and CCS (WG2-7). Implementing CCS directly as CO2 is released from the combustion of fossil fuels is perhaps its most obvious application. This represents a new way of managing emissions from the heavy industry. However, there are many areas requiring research and development before CCS can be used at that scale. These include the design of CCS engineering processes, evaluation of critical parameters for storing CO2, and ensuring the long-term stability and profitability of storage sites (Lepore and Ghose, 2015; Teng and Tondeur, 2007; Ali et al., 2020).
Current research in the field of CCS is centered mainly on improving the efficiency of capture technology, establishing criteria for selecting storage media, and perfecting techniques for the transportation and transformation of CO2. Notably, the study of the long-term behavior of CO2 when stored underground is neglected, including its escape under various geological conditions, hazards from leakage at different stages of the CCS process, and its possible interactions with groundwater. This restricts the scope of feasibility studies and safety assessments, not only for CCS but also for other similar applications (Damen et al., 2006; Zwaan and Smekens, 2009). Ensuring that CCS is both safe and effective in the long term requires full investigation of the parameters, governing the stability and behavior of CO2 storage. These parameters include strata pressure, temperature, and the physical properties and chemical composition of rocks (Lepore and Ghose, 2015; Teng and Tondeur, 2007; Ali et al., 2020).
Gas permeability is regulated by both the physical structure and chemical composition of rocks, which remain stable over geological timescales. It determines the speed at which CO2 spreads throughout a storage area, and hence, it determines the effectiveness of carbon storage in that area. Permeability is, therefore, an important indicator of a site’s long-term safety and storage capacity (Xie et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2020; Bakhshian and Hosseini, 2019). However, there is little in-depth analysis of the way reservoirs of CO2 behave over long periods in different geological environments; particularly lacking are experiments that replicate natural storage processes and monitor conditions for many years to help forecast future behavior (Hui et al., 2019; Psarras et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2016). There is also a lack of the literature explaining the technical and economic risks associated with CCS at scale: the financial liabilities over the long term are unknown, as are the impacts of CCS on the natural environment upon which other industries depend (Zhu et al., 2021; Gomaa et al., 2022).
CCS may potentially restrict CO2 levels in the atmosphere, but it faces many challenges during operation. These include high technical costs disincentivizing the construction of the necessary plants, tepid public acceptance, and a lack of systems to monitor the retention or escape of stored gases (Damen et al., 2006; Pollak and Wilson, 2009; Blackford et al., 2013). Difficulties in gathering and sending information within the geological structure of a storage area can also lead to emerging problems being technically difficult to diagnose and rectify. These issues require resolution before CCS can be industrialized on a large, permanent, and consistent scale (Li and Liu, 2016; Deng et al., 2014; Court et al., 2012). Therefore, the only way to improve the safety and economic efficiency of CCS technology is through rigorous testing of its parameters and long-term stability. The World Energy Council notes that research in this area is receiving increasing attention (Zwaan and Gerlagh, 2009; Anderson, 2016; Dixon and Romanak, 2015).
This review presents a comprehensive analysis of experimental reports concerning the geological storage of CO2 and examines the various parameters influencing its effectiveness. Considering the various factors affecting the efficacy of CCS, this research not only fills gaps in the existing academic literature but also offers strategies to improve what is essentially an undeveloped technology, thus making CCS safer and more commercially viable. These advancements are critical to CCS playing a role in achieving carbon neutrality. Our work considers the essential components of the research, including the empirical field study, comparative analysis of various test configurations, and examination of factors determining the storage efficiency; it then proposes preliminary steps toward assessing possible dangers associated with geological storage. The progress of CCS technology and innovation is discussed, with consideration of strategies to improve both the safety and efficiency across its procedural steps. We consider the design parameters assessed through empirical findings, especially those relevant to the efficiency and stability of CCS. Our survey reveals new research areas, including enhancing of monitoring techniques and finding innovative methodologies for evaluating long-term storage impact. Progress in these areas would undoubtedly influence future CCS research directions.
CCS involves collection of CO2 emissions from human activity and storing them in rocks to lower the atmospheric CO2 concentration and mitigate the global climate crisis. Its main stages are the capture, transport, and secure storage of CO2 with the aim of keeping it permanently out of the atmosphere. CCS technology can be categorized by the storage medium: these include saline aquifers, depleted oil and gas fields, and coal seams (Aminu et al., 2017; Senior et al., 2010; Rasool et al., 2023). Understanding of the efficacy of storage via robust monitoring systems that consider a site’s specific geological, physical, and chemical factors is crucial for determining the potential of CCS (Singleton et al., 2009; Dai et al., 2014; Senior et al., 2010). A complete understanding of these factors and their associated technical details may influence the economic feasibility and safety of CCS (Dixon and Romanak, 2015; Aminu et al., 2017; Singleton et al., 2009) (Figure 2).
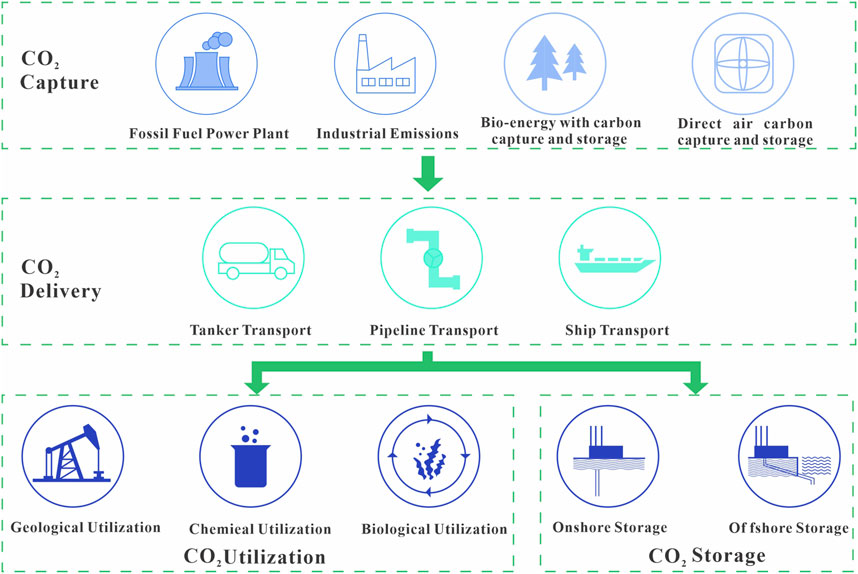
Figure 2. Technical processes of carbon capture, utilization, and carbon storage (CCUS) (modified from Zhang et al., 2020).
The essential principle of CCS is the sequestration of CO2 as either CO2 itself or an alternative form. A combination of physical and chemical methods can be employed to achieve this (Figure 3). The desired final outcome is permanent storage that is achieved in the most reliable manner. This is a highly complex process that draws on many theoretical and practical fields such as compression, conveyance both to and within storage sites, and the physical chemistry of CO2 injection (Iglauer, 2011; Rasool et al., 2023).
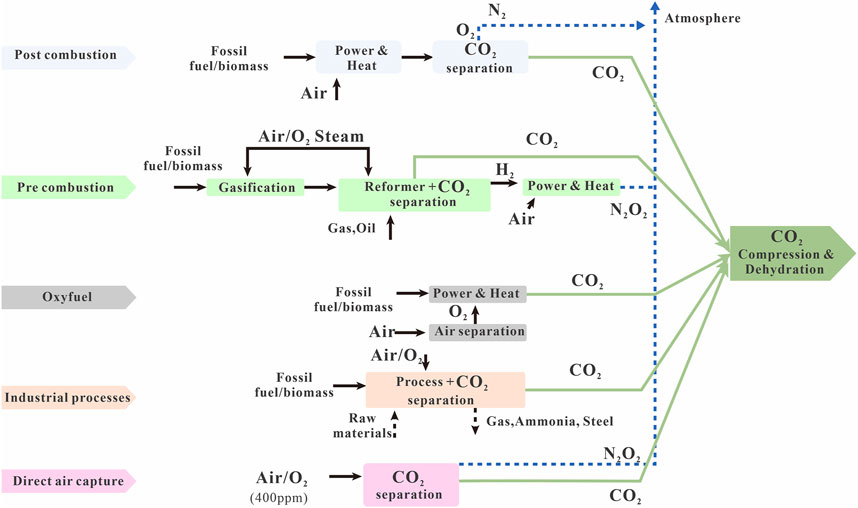
Figure 3. Technologies applicable to carbon capture (modified from Li et al., 2013).
The initial phase features the compression of CO2 from various sources to make it transportable to its ultimate destination. Supercritical CO2 has the density of a liquid and the diffusivity of a gas, which are favorable for its ability to travel to fill large volumes within the pores of volcanic rocks. The van der Waals equation explains how CO2 becomes supercritical before it is compressed beyond its critical pressure, describing the intermolecular interactions and volume control of gas molecules (Equation 1) (Sodeifian et al., 2018; Goos et al., 2011; Zahran et al., 2010):
where P is pressure, Vm is molar volume, T is temperature, R is the universal gas constant, and a and b are van der Waals constants accounting for intermolecular forces and molecular size limitations, respectively.
Injected CO2 is trapped in rocks mainly through physical processes, which may sequester nearly all injected CO2. They rely on natural obstacles such as geological structures to prevent CO2 escape into the atmosphere. A typical example of such a structure is an impermeable cap rock, which is usually a layer of claystone or salt. CO2 is injected through an injection well into porous rock strata, usually sandstone, which has many holes and cracks that provide a large gas-storage space. It can also be sequestrated through forming stable mineral carbonates upon contact with carrier water or rocks (Equations 2, 3) (Kampman et al., 2014). For example,
These reactions underscore the intricacies of the interactions of CO2 within subsurface environments, whereby it reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which can go on to react with magnesium- or calcium-rich silicate minerals. This results in the precipitation of stable carbonate minerals such as calcite (CaCO3) and dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), which can endure over geological timescales, with enduring sequestration of CO2.
The selection of underground formations that can safely hold CO2 is crucial. A possible storage site must meet a range of geological criteria. The permanent, leak-proof storage of CO2 depends on a combination of pressure and temperature conditions. The precise requirements greatly complicate and delay the planning and implementation of geological storage projects (Tomić et al., 2018; Llamas and Cienfuegos, 2012; Aminu et al., 2017). Structural trapping occurs when CO2 is physically confined in geological formations such as anticlines, fault traps, or other impermeable barriers that prevent its upward migration. Stratigraphic trapping, on the other hand, involves CO2 being trapped by variations in rock type or by changes in sedimentary layers that form a seal above the injected CO2. Both mechanisms are crucial for ensuring the long-term stability and safety of CO2 storage sites (Figure 4).
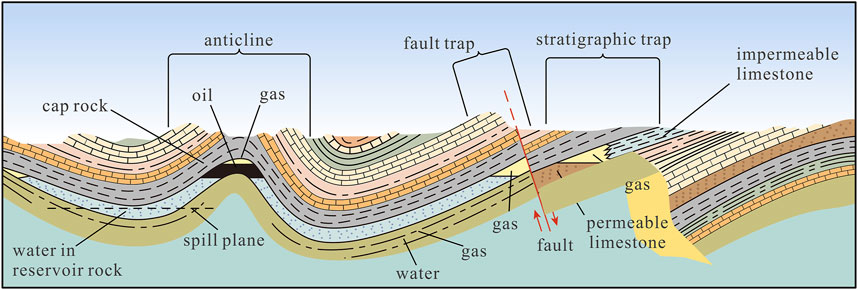
Figure 4. Structural or stratigraphic trapping for CO2 storage (modified from Aminu et al., 2017).
Saline aquifer storage is a core CCS technology. It involves the injection of CO2 into deep brine-saturated geologic strata (Gao et al., 2023; Bacci et al., 2011), achieving continuous, sustainable, and safe storage based on rock formation physicochemical properties and ambient pressure–temperature conditions (Cheng et al., 2015).
A saline aquifer is a subsurface formation containing highly saline aqueous solutions, which is usually located several thousand meters beneath the surface. Such formations occur below a layer of impermeable strata (e.g., shale or mudstone), and they typically contain their own sealing mechanisms (Kampman et al., 2014) of porous and permeable sandstone layers (Jeddizahed and Rostami, 2016). Saline aquifers may absorb and trap huge amounts of CO2 due to their high pressures and limited geological activity. When CO2 is injected into such an aquifer at higher pressure, it becomes supercritical (high density and low viscosity), allowing it to be distributed through, and remain within, the geological matrix (Gao et al., 2016).
CO2 is naturally a gas, but it can exist in other states. Its storage in saline aquifers requires consideration of parameters such as the permeability, porosity, and thickness of the storage medium and the thermodynamic state of CO2 under field conditions (Abdelaal and Zeidouni, 2022; Senger et al., 2015). In addition, Darcy’s law, a basic principle of fluid mechanics describing the flow of fluids through porous media in response to pressure gradients (Equation 4) (Liu et al., 2017), describes CO2 migration during storage as the following:
where Q is the fluid flow rate, k is the permeability of the medium, A is the sectional area available for fluid flow, μ is the viscosity of the fluid, and P2 − P1 is the pressure difference between two different points. One of the most promising examples of industrial-scale CCS development is the Sleipner project in the North Sea near Norway. It involves the injection of CO2 into a saline aquifer in the sub-sea Utsira Formation at depths of 800–1,100 m below sea level. This initiative, begun in 1996, has already sequestered more than a million tons of CO2 per year, and is designed to prevent any leakage into the environment by having an impermeable barrier system (Chadwick et al., 2010; Torus et al., 2023). One of the main challenges facing the storage of CO2 in geological formations is the need to ensure that it becomes spatially distributed throughout the rock while remaining stable within it; monitoring this requires the use of seismic technologies (Torp and Gale, 2004; Park et al., 2017). The success of saline aquifer CO2 storage relies on meticulous assessments and rigorous monitoring protocols (Li et al., 2023; Diao et al., 2015), with each storage project requiring a thorough evaluation of its geological environment to safeguard both operational safety and efficacy (Silva et al., 2015; Jing et al., 2022).
CO2 injection into previously emptied reservoirs essentially reuses existing geological structures and sealing mechanisms that have already supported long-term storage (Solomon et al., 2008). It may combine reduction of atmospheric CO2 levels with enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques to increase the efficiency of oil extraction (Gozalpour et al., 2005; Feder, 2021).
Exploited oil and gas fields are ideal CO2 storage targets because they are inherently able to trap gas and have well-documented geological properties and existing production infrastructure. Such reservoirs have stored gas and oil for tens of millions of years, thus demonstrating their permanence and capacity to hold CO2 indefinitely. In addition, injecting CO2 into oil-bearing strata lowers the viscosity of the oil, which allows it to flow more easily; CO2 can, thus, also increase the productiveness of oil extraction as an EOR technique. The impact of EOR can be described by the change in pre- and post-CO2 injection hydrocarbon production as follows (Equation 5):
where R represents the efficiency of EOR measured as the additional hydrocarbons recovered per unit of injected CO2; Qpre-injection and Qpost-injection denote the production rates of hydrocarbons before and after CO2 injection, respectively; and VCO2 represents the volume of injected CO2. The kinetics of CO2 within oil and gas fields can be modeled using Darcy’s law for fluid flow in porous media (Govindarajan, 2019; Williams et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2017). The Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project at Midale, Saskatchewan, Canada, is a prime example of CO2 storage combined with EOR. The project began in 2000 and is a leading international CO2 storage initiative (Wilson, 2011). It involves transfer of CO2 captured from a North American facility to oil fields located 1.5 km below ground for injection into depleted oil reservoirs (Raistrick et al., 2009). During its operating life, the project has effectively sequestered tens of millions of tons of CO2 while also improving oil production at the oil fields (Mayer et al., 2013).
The combination of CO2 storage and EOR in depleted oil and gas fields is an excellent way for CCS to reduce atmospheric greenhouse gases while improving energy efficiency by enhancing oil field productivity. However, the success of such projects requires rigorous geological investigation of reservoirs and sustained management practices to ensure the safety and efficacy of their structure.
In coal-seam storage, injected CO2 may be stored through its in situ adsorption onto coal (He et al., 2013). This not only fixes CO2 stably over long periods of time but may also promote methane production as an enhanced coal-bed methane (ECBM) extraction technology (Zhang et al., 2011; Pini et al., 2011).
Storage occurs within the micro-porous structure of the coal seams, which provide a large surface for CO2 adsorption, thus allowing considerable amounts of CO2 to be sequestered (Zhang et al., 2011). In addition, CO2 injection may act as an ECBM process by displacing residual methane (CH4) from the coal seam, making it available for recovery (Mukherjee and Misra, 2018). CO2 adsorption in coal seams depends on the coal matrix and pressure and temperature conditions, with greater pressures resulting in larger adsorption (Lin et al., 2017). The adsorption of CO2 in a coal seam is usually interpreted in terms of the Langmuir isotherm model (Equation 6) (He et al., 2013) as follows:
where q is the quantity of CO2 absorbed per unit mass of coal (mol kg–1), qmax denotes the maximum adsorption capacity (mol kg–1), P is pressure (atm), and b is the Langmuir adsorption constant (atm−1) indicating affinity for adsorption. The effectiveness of ECBM extraction and the potential for CO2 storage can be evaluated by assessing changes in the competitive actions between CH4 and CO2 within the coal seam in response to the injected gasses (Reeves, 2003). The Allison Unit in the San Juan Basin, United States, is an example of ECBM technology. It involves injection of CO2 into a coal seam at a depth of ∼900 m to improve methane recovery rates and create localized storage for CO2 (Perera and Ranjith, 2015). The success of this operation demonstrated the simplicity and effectiveness of storing CO2 in coal seams with ancillary methane extraction. Integrated surface and subsurface monitoring found that the CO2 storage maintained its integrity, while methane production increased throughout the project’s implementation.
The application of CO2 storage in coal seams demonstrates CCS as a flexible technology for greenhouse-gas mitigation that may simultaneously enhance energy recovery from reservoirs. Implementation of CCS requires a thorough knowledge of coal seam geology, advanced CO2 injection techniques, and long-term operations to achieve sustainable and safe CO2 storage. Monitoring and verification protocols should be designed to ensure that storage remains functional with transparent operation and environmental preservation. These protocols will be the key to providing an experimental foundation for coal seam CO2 storage.
Assessment of the effectiveness and safety of the CO2 storage process requires specific methodologies. Here, we overview six CCS-related experimental methodologies ranging from micro to macro scales and from laboratory investigations to field applications (Colby et al., 2019; Olanrewaju et al., 2018; Stow et al., 2017). They provide the foundation for all subsequent advancements and implementations of CCS technology.
Microscale simulations explore the phenomena related to CO2 storage in specific situations at the scale of individual pores. Coupling simulations at computational fluid dynamics and molecular dynamics scales can model the transport mechanisms of CO2 and its reaction pathways at a microscale resolution (Smith, 2013; Holland et al., 2015). These reproducible methods provide deep insights into the processes of CO2 storage, thus informing the design of specific, accurate storage specifications and the optimization of technical operations. Macro-scale fluid dynamics simulation is based on general laws and equations of fluid mechanics (Macpherson and Reese, 2008).
Navier–Stokes equations describe the fundamental behavior of fluids, providing information about fluid speed, pressure, and temperature distributions. They form the basis of fluid dynamics simulations, which, in turn, predict the typically complex pathways of CO2 in and around porous media. The equations are as follows (Equation 7) (Macpherson and Reese, 2008):
where u is the fluid velocity vector, t is time, ρ is fluid density, p is fluid pressure, ν is kinematic viscosity, and f represents the external force per unit mass of fluid.
Molecular dynamics simulations probe the mechanisms of CO2 storage, involving many complex molecular movements and interactions. Insights gained enhance the understanding of the movements of CO2 molecules over rock pore walls (Ma and Ranjith, 2019; Trinh et al., 2013; Sun et al., 2016). Such pores could be used as ideal systems to model processes such as adsorption, diffusion, and chemical reactions, with molecular dynamics simulations providing an understanding of the underlying mechanisms (Trinh et al., 2013; Sun E et al., 2017). Such models are computationally expensive, but microscale fluid dynamics simulations are crucial for understanding the complex behavior of CO2 and, thus, for improving the performance of CO2 geological storage. Simulations will continue to be run, both for research and for assessing applications, together with the implementation of new and evolving technologies for CCS.
High-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) experiments are essential for CCS project design. They replicate the extreme conditions found in underground storage sites, allowing investigation of the changes in the physical and chemical properties of CO2 (Rezk and Foroozesh, 2019; Byun and Choi, 2007). Their primary goal is the study of phase behavior, solubility, and reaction kinetics of CO2, as well as its compatibility with different storage substrates (Rezk and Foroozesh, 2019; Yoon and Byun, 2014). These insights are crucial for the development of stable and secure CCS projects.
HPHT experiments are grounded in the theory of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, which describe the way fluids act as pressure and temperature vary. Under HPHT conditions, CO2 might exist as a gas, liquid, supercritical fluid, or in some intermediate state (Byun and Choi, 2007), and thus, it can show greatly varying movement and retention behaviors in storage matrices. For HPHT conditions, the ideal gas law is further developed with the van der Waals equation to include the molecular volume and intermolecular forces of gases (Byun and Choi, 2007).
The solubility of CO2 in water or other fluids changes with variations in pressure and temperature. Therefore, the modified form of Henry’s law is employed here to model solubility and its variation with temperature and pressure (Equation 8) (Teng et al., 1997; Christmas and Bassingthwaighte, 2017):
where C is the solubility of CO2, PCO2 is the partial pressure of CO2, and kH (T, P) is the Henry’s law constant, which is a function of temperature and pressure.
HPHT experiments explore the behavior of CO2 under severe subsurface conditions and thus enhance an understanding of the processes of its underground storage. Results inform the development of strategies to improve the storage, assessment of suitability of potential storage media, and prediction of storage outcomes. The use of HPHT experiments will expand as applications of CCS broaden to include, for example, carbon capture, storage, and utilization (CCUS).
Percolation experiments are crucial for understanding the dynamics of CO2 movement within rocks, along with its distribution and chemical interactions in subsurface geological layers. They reproduce the HPHT conditions of geological storage to allow the quantitative assessment of CO2 interactions (e.g., permeability, adsorption, and reactive behaviors) with multiple rock types (Rodrigues et al., 2012; Mitani et al., 2011). These experiments demonstrate the importance of combining practical work with a sound theoretical framework by providing both empirical data and a theoretical foundation that can advance CCS technology.
Geological flow experiments, on the other hand, explore physical phenomena determining fluid migration through rock matrices. They are designed to represent industrial CO2 storage under real field conditions, thus allowing the investigation of the flow of CO2 though pore spaces in rocks under various pressure and temperature conditions. The experiments can thus verify the impacts of physical and chemical transformations that occur during CCS. A key principle is Darcy’s law, in which parameters such as porosity (ϕ) are important determinants of rock storage capacity (Krishnamurthy et al., 2017). The model reveals not only the permeability of CO2 in a given rock type but also the changes to, for example, the pore structure that occur through chemical reactions of CO2 with the rock.
Data from core flow experiments relate to the establishment of a storage regime for CO2. The data can only be accurately determined through a combination of measurement and computation. The resulting extensive information brings together crucial parameters such as optimal injection pressure, temperature of CO2 storage, risks of CO2 leakage, and specific construction parameters that are needed to ensure both the safety and efficiency of a planned storage site. These experiments are, therefore, key for the technological development of CCS, providing vital information for the development and improvement of storage methods.
Seismic monitoring and imaging must be integrated into any CCS project to provide essential subsurface information on flow configuration dynamics and predict long-term stability of the underground repository. High-resolution 3D images of CO2 storage sites can be created using seismic wave detection and analysis to evaluate storage performance and safety (Sun H et al., 2017; Pinard et al., 2016).
The physical principles of seismic waves, combined with seismic surveillance and imaging technology, are crucial for the understanding of how these waves propagate through subsurface structures. Technologies for the detection and analysis of seismic wave velocities and reflections provide valuable information on geological features and fluid distributions underground. Analysis of the data provides information about underground geology, such as lithology, fracture networks, and fluid migration pathways (Gu et al., 2004; Minato, 2012). Seismic-wave velocity is directly related to rock characteristics by the following Equation 9:
where Vp is the velocity of P waves (compressional waves), K is the mass modulus of the rock, G is its shear modulus, and ρ is its density. Different areas are identified by estimating the speed of P-waves across the reservoir, and variations in the modulus and density of the rocks can be inferred to locate the presence and type of CO2 in the area.
Seismic reflection allows the imaging of surfaces of structures, with impedance contrast between rock layers determining the amplitude of the reflected waves (Equation 10) (Schreiter et al., 2015; Moon et al., 1993):
The reflection coefficient (R) depends on the impedance (Z, which is the product of density (ρ) and acoustic velocity (V)) of two contacting media (i.e., Z1 and Z2). Measurement of reflections at different depths can provide detailed 3D images of layers in a repository, showing exactly where CO2 migrates to and accumulates. In the field of CCS, there is a strong demand for seismic reflection modeling along with methods to check and verify images compiled by various techniques. These include investigations of material properties, measurements of seismic wave velocities, and imaging of subsurface structures using reflected-wave data (Behzadi et al., 2011). The impedance relationship is the key for the analytical interpretation of rock properties from seismic wave velocity data, e.g., the injection of CO2 and/or enhanced pore pressure in the shallow subsurface might relate to potential-induced seismicity (Song et al., 2014).
Seismic reflection imaging can visualize CO2 distributions and migration pathways deep underground. It has been used to assess the efficiency, long-term stability, and safety of CO2 storage in CCS projects (Rørheim et al., 2021). The integration of CO2 monitoring technology with imaging techniques will greatly improve the assessment and analysis of CCS, thus allowing strict monitoring and control of underground CO2 emissions. This technological framework is useful for ensuring the secure and effective geological storage of CO2 (Shin et al., 2022).
Electrical resistivity imaging is a geophysical method used to remotely image shallow subsurface structural features and subsurface fluid distributions based on the assessment of spatial variations in electrical impedance in the soil or subsurface through measurements taken at the surface above boreholes. Spectroscopic imaging is also crucial for CCS projects as it can be applied in monitoring flow path signatures and, thus, following the distribution and migration of CO2 during its injection and long-term storage (Breen et al., 2012; Carrigan et al., 2013).
Resistivity imaging is based on the differing electrical conductivities of various subsurface materials whose resistivity depends on parameters such as rock type, declivity, water content, salinity, and CO2 content (Bosch et al., 2016; Doetsch et al., 2013). As gaseous or supercritical CO2 dissolves in groundwater, it changes the conductivity of the water, thereby altering the overall resistivity distribution. Subsurface CO2 can, thus, be indirectly observed by monitoring subsurface resistivity changes. This is a powerful tool for mapping the migration and distribution of CO2 underground (Bosch et al., 2016).
Archie’s law is an empirical formula describing the resistivity of a saturated porous medium, and is applicable to the dynamic observation and imaging of resistivity (Equation 11) (Schön, 2015):
where R represents resistivity (subscripts t and w denote rock and water, respectively), ϕ represents porosity, and Sw represents water saturation. Constants a, m, and n are associated with the rock type. This equation links rock resistivity to its porosity and water saturation level and the resistivity of pore water. Concerning CCS, injection of CO2 alters the properties of pore water (including Rt), a change that can be effectively monitored using resistivity imaging technology.
Resistivity imaging involves the placing of a set of electrodes at specific locations either on the surface or in boreholes with the goal of characterizing the resistivity distribution of materials by injection of the current and measurement of the potential difference (Equation 12):
where V is the potential difference between the electrodes, ρ is the resistivity of the subsurface media, I is the applied current, and r is the distance from the measurement point to the current source. Combining Archie’s law with resistivity imaging allows changing resistivity to reflect to the progression of CO2 down and across the underground space. In CCS projects, comparison of the resistivity distribution before and after CO2 injection facilitates quantitative evaluation of the migration pathway, rate, and geophysical endmember distribution of CO2 underground (Raab et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2016). The technique can be applied in monitoring the effectiveness and safety of the storage environment (Christensen et al., 2006; Christensen and Kanikicharla, 2013; Börner et al., 2013), thus making it an important component of assessments of CO2 storage projects.
Overall, electrical resistivity imaging, with its ability to directly image the subsurface CO2 distribution, is a key tool in the field of CCS, characterizing the behavior of CO2 in deep geological storage and supporting the design and monitoring of storage projects. Further technological developments are expected to establish electrical resistivity tomography as a key to the success of CCS (Börner et al., 2013; Nakatsuka et al., 2010).
Isotopic tracing is an essential geochemical method widely used in geological research and environmental monitoring, including the field of CCS. The determination of shifts in particular isotopic ratios can provide detailed information about geophysical processes, sources of fluid flow, and chemical signatures. Isotopic tracing can thus assess the origin, travel paths, and in situ changes of CO2 deposited in CCS projects (Flude et al., 2016; Mayer et al., 2015).
Isotopic tracing is based on the theoretical principles of isotopic fractionation and isotopic labeling. Isotopic fractionation is the irregular variation in the production and release of different isotopes during natural processes. Isotopic labeling refers to the addition of substances with well-defined isotopic ratios to a system to tag particular processes or reactions (Gilfillan et al., 2008). Isotopic fractionation is described as follows for 13C and 12C (Equation 13):
where δ13C represents the per mil (‰) deviation in the sample carbon isotopic composition (13C/12C ratio) relative to that of the standard substance. Isotopic fractionation is generally applied in isotope geochemistry, based on the sample isotopic ratio relative to that of an international standard. Changes in the isotopic composition of CO2 during storage indicate CO2 migration and reaction pathways during storage. Isotopic tracing uses the theories of isotopic fractionation and isotopic labeling to allow the use of a tracer that can provide unique information about CCS projects. For example, comparison of isotopic compositions of in- and ex-situ CO2 can be applied in determining the CO2 origin, investigating its migration pathways within the subsurface, and detecting potential leaks (Barth et al., 2015; Johnson and Mayer, 2011). Isotopic ratio variations pertaining to CO2, groundwater, or rocks can enhance the understanding of pathways by which reactions occur in different storage environments (Myrttinen et al., 2015; Mayer et al., 2015). Stable and radiogenic isotope-specific analyses, thus, assist in the formulation of behavioral models of CO2 in CCS projects and in the assessment of storage performance and environmental compatibility (Flude et al., 2017; Shin et al., 2020). For example, an experiment may involve injection of isotopically labeled CO2 into the subsurface of a CCS site, with subsequent sampling and isotopic analysis over time, characterizing its migration and transformation within the storage area and providing vital information regarding the operation of the storage facility, localization of carbon storage, and the long-term safety of the project (Flude et al., 2017).
Overall, isotopic tracing provides information helpful in assessing the geological storage of CO2, enhancing understanding and aiding optimization of CCS technology. Developments in analysis technology and increasing knowledge of isotopic systems will increase the importance of this technique in Earth science and environmental engineering.
The ensemble of methodologies for assessing CCS processes thus covers a range of perspectives, from micro to macro, and includes fluid dynamics simulation, HPHT experiments, core flow experiments, seismic monitoring and imaging, electrical resistivity imaging, isotopic tracing, and other methods. With respect to the mechanisms of CO2 storage underground, micro-scale experiments elucidate the behavior of CO2 in porous rock, and HPHT experiments simulate the deep underground storage environment to provide important insights into the physical and chemical behavior of CO2. Core flow experiments measure the permeability and reactivity of CO2 in rock media. Seismic monitoring and imaging provide 3D illustrations of CO2 migration pathways, and electrical resistivity imaging indirectly monitors the migration and distribution of CO2 through changes in resistivity. Isotopic tracing elucidates the source and migration of CO2 to provide a unique view of storage processes. The combined application of these techniques provides a detailed understanding of the geological storage behavior of CO2, benefitting the future deployment of CCS for secure and sustainable carbon management.
The performance of a CCS process depends largely upon several important, but broadly defined, factors that govern the safety, security, and economic sustainability of any CO2 underground storage operation. Efficient storage strategies and project feasibility evaluations must consider these top-level drivers, provided they can be well-defined. This section reviews three factors that are fundamental for the success of geological CO2 storage: the properties of rocks, behavior of CO2, and geological reservoir conditions.
Rock permeability describes the overall ability of fluids to move within its pores. As it determines fluid flow in rocks, permeability is crucial for CCS as it describes the extent to which injected CO2 can be distributed throughout subsurface formations (Wang et al., 2017). Permeability is controlled by the pore structure of the rock (Yu et al., 2019), which is influenced by the size, shape, and connectivity of the pores along with the existence of fractures. Rocks such as sandstones, with highly interconnected pores or fracture gorges, show high permeability and, thus, allow CO2 to flow in large volumes (Yang and Chen, 2022).
Pore shape and connectivity greatly influence the shape and distribution of fluid flow pathways, and thus, they profoundly affect the delivery of fluid into the rock (Lamur et al., 2017). Fractures markedly enhance permeability by providing paths for a high-velocity fluid flow. Permeability not only affects CO2 injection but also influences the final storage capacity and safety of a reservoir. The quick distribution of CO2 through high-permeability rock layers helps minimize pressure build-up during injection and, thus, the risk of surface leakage (Cai, et al., 2019). However, beyond a certain point, high permeability may facilitate uncontrolled fracture development, undermining the security of a reservoir and leading to unexpected CO2 migration, which would require careful monitoring and management.
The Sleipner project in the North Sea exemplifies permeability’s pivotal role in CCS, where injection into highly permeable sandstone layers allows effective CO2 distribution. By precisely controlling the injection pressure and monitoring CO2 distribution, the Sleipner project has achieved long-term stable CO2 storage, affirming the viability and safety of high-permeability rock layers as CCS reservoirs (Bernabé et al., 2011).
Overall, much importance should be given to permeability when planning and designing CCS projects, selecting reservoir sites, and developing injection strategies as it greatly influences the safety and sustainability of a project. Therefore, permeability must be thoroughly characterized when engineering a reservoir to ensure that CO2 is stored in the safest and most economical manner while also ensuring high storage efficiency.
Porosity is defined as the two-phase void space within a rock relative to its total volume (Tian and Wang, 2018). For CCS, it indicates a geological body’s CO2 storage capacity as it represents the availability of rock internal space to store and transfer fluids, thus dictating the safety and efficiency of CO2 storage. Porosity is determined by the action of sediments during their deposition (i.e., the sedimentary conditions) and post-depositional geological changes (e.g., compaction and dissolution) (Lamy-Chappuis et al., 2014; Cui et al., 2018). Studies classifying porosity have identified certain categories as being particularly effective for CO₂ storage, highlighting the importance of not only the overall porosity but also the spatial distribution of porosity within the reservoir. Proper classification and understanding of porosity characteristics are essential for optimizing the storage capacity and ensuring the long-term stability and efficiency of CCS projects. Additionally, the dissolution of CO2 may create new pores or expand the pore volume by enlarging the original pores (Luquot et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2021).
Porosity is thus critical to CCS. Although simply increasing porosity might suggest that the reservoir capacity would increase (Gershenzon et al., 2015), given that elevated porosity facilitates successful CO2 storage, both the magnitude of porosity and its spatial distribution affect the speed and pathways of CO2 migration and consequently the thermal stability and effectiveness of storage. Therefore, accurate porosity determination is crucial for site selection and the operation of CCS projects (Li et al., 2019). A detailed study of site porosity and permeability was undertaken for the Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project to investigate the capability of the formation to store CO2 captured from a nearby synthetic ammonia plant (Riding, 2005; Jensen et al., 2011). Findings indicated that the target reservoir was of high porosity and good permeability, and thus, it was suitable for CO2 injection with long-term storage safety and physical and chemical stability.
This implies that porosity is at least as important, if not more so, than total storage capacity in retaining CO2 in the subsurface. The precise assessment of porosity is necessary to ensure the safety of the injection scheme and storage process, to assess effective burial capacity, and thus allow oilfields to become permanently secure and enduringly stable CO2 reservoirs.
Mechanical strength characterizes the resistance of rock to deformation and failure, and it is an important physical parameter affecting the integrity of a potential CCS reservoir (e.g., Tarokh et al., 2020), predicting rock response to the injection of CO2 under high-pressure, and is closely related to the long-term integrity and safety of the reservoir. The mechanical strength of a rock depends on its mineral composition, structure, stress state, and prior geological processes (Zou et al., 2018). Sandstones augmented with quartz tend to be more robust than rocks rich in clay minerals (Jun et al., 2017).
Mechanical robustness is critical to CCS in many ways. The first consideration is the need for sufficient mechanical strength to avoid irreversible deformation or failure of a reservoir due to the overburden of high-pressure injected CO2 and thus ensure stability against glacial loss or leakage (Asamoto et al., 2013). Surface subsidence or trigger events are also prevented if the reservoir and cap rocks are mechanically strong enough to protect the storage process and maintain environmental integrity and public safety (Verdon et al., 2011). The Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project demonstrates the crucial utility of mechanical strength for CCS. Prior to the start of the project, long-term geological surveys and rock mechanical tests were undertaken to confirm that the reservoir mechanical strength was compatible with the secure storage of abundant amounts of CO2 (Rinaldi et al., 2013). Laboratory tests were performed to assess the compressive and shear strength, proving that the reservoir was stable and secure under different pressure and temperature conditions (Dempsey et al., 2014). Impedance monitoring during CO2 injection and throughout the project searched for anomalies that might have affected mechanical integrity (Li et al., 2014). These wide-ranging testing and monitoring efforts for 12 years indicated no technical problems with mechanical integrity.
Overall, a CCS project cannot function without sufficient mechanical strength. Rock strength is crucial for reservoir storage efficiency, security, and the general ability to have a positive environmental effect.
The physical and chemical properties of CO2 influence its movement and long-term stability in the subsurface, ultimately controlling the evolution of the phase state of injected CO2 after injection and during sequestration (Fatah et al., 2020). These behaviors are relevant to the design and deployment of CCS projects.
The physical behavior of CO2 includes transitions among its gas, liquid, solid, and supercritical states, its mobility, and its diffusivity, all of which directly depend on temperature and pressure conditions. Therefore, these properties are of fundamental importance to CCS (Chapoy et al., 2013).
For example, an important consideration is the complex temperature- and pressure-dependent transition of the ice phase of CO2. Although CO2 is gaseous under most surface conditions, increasing temperature and pressure can cause it to be in a liquid or supercritical state (Zhang et al., 2017). Supercritical CO2 occurs at conditions above its critical temperature (31.1°C) and pressure (73.8 bar). It exhibits low viscosity and high density, which are specific physical properties ideal for permeating rock pores, and good solubility (DePaolo and Bourg, 2017). The Sleipner CCS project is a good example of the use of CO2 properties: the gas is supercritically compressed before injection into sandstone 800–1,100 m deep (Bickle et al., 2007); the temperature and pressure conditions are such that CO2 is supercritical and able to flow easily through rock pores to widely fill the reservoir space, thus increasing the storage capacity (Mwenketishi et al., 2023).
Understanding of the phenomena associated with the physical properties of CO2 is essential for ensuring storage security. The low viscosity and high diffusivity of supercritical CO2 mean that it tends to spread quickly throughout a reservoir, so careful monitoring and management are needed to avoid surface leaks or infiltration into groundwater.
The physical properties of CO2 strongly affect the design and operation of CCS projects. Full consideration of them undoubtedly improves storage effectiveness and ensures the safety, dependability, and long life of the storage operations. These properties can be managed through the fine regulation of a few injection-related variables in response to data acquired during monitoring and sensing. The Sleipner project provides an example of engineering results achievable by considering the physical properties of CO2.
CO2 undergoes a series of complex chemical reactions when interacting with various phases such as water and rock minerals. Such reactions are critical to CCS, influencing the stability, efficiency, and environmental cost of CO2 storage over the long term (DePaolo and Bourg, 2017).
An important chemical reaction of CO2 is its hydration to carbonic acid (H2CO3) when CO2 dissolves in water (Wang et al., 2013), along with dissociation to HCO3− and H+ (Equation 14). Reactions such as this not only have a detrimental impact on the groundwater in the host rock but may also lead to further reactions involving minerals, such as the dissolution or deposition of carbonate (Equation 15) (Rodrigues et al., 2012).
Reactions of dissolved CO2 that are relevant to carbon sequestration include its reaction with calcium- or magnesium-bearing minerals to form carbonate minerals (Assi et al., 2019), which trap CO2 (or any other injected gas) by immobilizing it, effectively permanently, as a solid mineral (Gadikota et al., 2020).
The complex chemical behavior of CO2 and the sequences of reactions it can undergo in the natural environment, primarily with water and rock minerals, are critical considerations in the context of CCS as they influence the stability, efficiency, and long-term environmental implications of CO2 storage (DePaolo and Bourg, 2017).
The key reactions of CO2 are those with water to form carbonate and carbonic acid. The dissolution of CO2 in water forms carbonic acid, which acidifies the water by further reacting to form carbonate and hydrogen (H+) ions (Wang et al., 2013). Other reactions involving rock minerals include mineral dissolution (less prevalent) and carbonate precipitation (more prevalent), and they are common in the groundwater environment of CCS sites (Rodrigues et al., 2012).
The efficiency, safety, and environmental implications of CCS are closely related to the geological characteristics of the reservoir. The geological structure, depth, cap-rock integrity, and geological stability collectively influence the technical feasibility and effectiveness of underground CO2 storage (Barth et al., 2015; Hangx et al., 2011). An ideal reservoir should have a highly permeable and porous geological structure that facilitates the entry and distribution of CO2 for storage; it should be at an appropriate depth to prevent stored CO2 from being in a supercritical state to enhance CO2 storage by reducing the required storage volume; it should have an impermeable and unfractured cap rock to prevent CO2 leakage (Yan et al., 2014) and a stable geologic setting to minimize geological risks associated with geological phenomena. Consideration of these geological aspects is an essential part of the planning and implementation for any CCS effort to guarantee that the storage of CO2 will be long-lasting and environmentally safe (Iglauer, 2011).
Properties (e.g., composition, structure, position, and interactions) of the geological structure covering rock layers used for underground CO2 storage are crucial to CCS projects. The complexity and distribution of geological features influence the feasibility of CO2 storage, the migration of CO2, and its eventual confinement and entrapment (Verdon et al., 2013).
The characteristics of geological structures in sedimentary environments emerge over geological epochs, starting with the formation and progressing to later balances of the crust and weathering processes (Gaus et al., 2005). The combination of these factors results in rock layers having a range of physical and chemical properties such as permeability, porosity, and mechanical strength. For example, sedimentary formations are typically highly porous and permeable, making them favorable for CO2 storage, while the higher densities of igneous and metamorphic rocks reduce their capacity for CO2 storage.
The geological structure must be considered when evaluating a site for CO2 storage. A homogeneous, continuous, and permeable layer may enable CO2 to spread over a large area of heterogeneous reservoirs, assisting its distribution. On the other hand, reservoirs with complex geological features such as faults or discontinuities might encounter increased uncertainties and risks of leakage during storage (Li and Liu, 2016). As a result, the planning and operation of any project must be assisted by sound geological knowledge.
The Sleipner CCS project demonstrates the importance of the geological structure. It is located within a sedimentary North Sea basin, with passive and laterally pervasive sandstone bodies comprising the storage component. The sandstone matrix is permeable, porous, and capped by thick shale layers, which together make a geological setting conducive to CO2 storage (Audigane et al., 2007). Detailed geological surveys and exploration of the area concluded that its geological structure could satisfactorily meet the demands of safe and effective CO2 containment.
Ultimately, the success or failure of a CCS project depends on the site geology. The geological structure of any potential site for CO2 injection must be well-known to verify that the reservoir will be able to safely and effectively store CO2 in the long term. The Sleipner project represents an example of successful storage based on proper geological preparation.
Depth is a key factor for CCS as it affects the physical state of CO2, the safety risks, and economics of storage. As the depth increases, temperature and pressure increase, thus allowing CO2 to be in a supercritical state, which is important for its safe and efficient storage (Ishida et al., 2012).
Regarding mitigation pathways, the supercritical phase is also favorable for the efficient movement of CO2 through the medium (Valle et al., 2019). Supercritical CO2 has the low viscosity of a gas and the density of a liquid, which together promote its diffusion through and storage in underground rock formations (Yamamoto et al., 2012). The optimum depth for a reservoir is thus one at which CO2 can be stored effectively.
Depth also affects the capacity and cost of storage and the technology required to prepare and maintain the site. On a small scale, increasing depth increases reservoir safety, but it incurs higher costs of drilling and preparatory research (Parisio and Vilarrasa, 2020).
The Sleipner project stores up to a megaton of CO2 per year in sedimentary rock layers at depths of 800–1,100 m. At these depths, CO2 remains supercritical, minimizing the storage footprint and preserving long-term stability (Gimeno et al., 2017). The Sleipner project thus highlights the applicability and effectiveness of deep CO2 storage after careful planning, considering the depth, expenditure, and security (Wang and Wang, 2018).
Overall, depth is a key consideration in planning CCS projects, governing the stored CO2 physical state, reservoir storage capacity, and project economic and technical requirements. Knowledge of depth and its critical effects on CCS influences the planning, implementation, and operation of a storage site, thus enabling socio-economically and environmentally sound projects. Knowledge gained from the Sleipner project will be essential for future CCS projects, providing insights into the role that depth plays in the permanent storage of CO2.
The importance of cap-rock integrity for CCS lies in the ability of rock layers above the reservoir to prevent migration of CO2 to the surface or its co-migration along cap-rock pathways into overlying groundwater systems. Cap-rock integrity is a primary validator of the safety and environmental protection of storage operations (Kaldi et al., 2013).
Cap rock comprises rocks derived from the same geological period as those of the reservoir. Its integrity depends on factors such as rock type, but more essentially, it depends on its permeability, thickness, and the occurrence of micro-fractures and faults. Ideally, cap rocks should have low permeability, with examples including impermeable shales or salt layers that significantly hinder fluid migration (Kolawole et al., 2021). The continuity and homogeneity of the cap rock are of prime importance, with any type of fracture, fault, or discontinuity potentially acting as a leakage pathway for CO2 (Frash et al., 2017).
Cap-rock integrity is thus important for the long-term stability and environmental safety of CO2 sequestration, which are the most common areas of concern in CCS projects. An effective cap-rock seal is needed to prolong underground CO2 storage, prevent leakage, and reduce the harmful impact on the groundwater quality of CO2 emissions (Newell and Martinez, 2020). The balance between the pressure required for effective storage and the pressure that the cap rock can withstand may be so restrictive that characterizing and assessing the cap rock are of crucial significance for the preparation and planning of any CCS project to ensure safety margins. For example, the Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project stores CO2 in deep sedimentary rocks located under a thick succession of shale layers. Shale is a promising cap-rock candidate due to its very low permeability and good continuity. Detailed geological surveys and cap-rock evaluations have determined the ongoing geological integrity of this site with a good storage capacity for CO2 (Zhang et al., 2021). Processes for assessing storage formations and cap rocks were initially developed for (and later employed at) this project, ensuring its success.
Overall, preservation of cap-rock integrity is essential for the operational success of CCS. Most large-scale CCS operations are currently located in deep saline aquifer formations, and the cap rock ensures their safety and stability after the initial filling, so it is necessary to carefully assess and select cap rocks that are sufficiently strong to ensure the safety and reliability of storage projects and reduce the environmental impact.
CCS is a key technology for mitigation of climate change, although its implementation faces various challenges, which are solvable, but only through full-system solutions. The effective implementation of CCS projects is broadly associated with overcoming the technical obstacles related mainly to the permanence of the site and ensuring the integrity of a reservoir against any CO2 leakage (Allinson et al., 2017). Scientific inquiry and technological innovation have proven to be immensely effective in addressing such challenges. The need for continuous surveillance is indicated by the Sleipner project (Norway), where highly sophisticated technologies are employed to successfully track CO2 flows, thereby confirming the stability and safety of storage (Ringrose, 2016). Different CCS technologies vary greatly in cost per ton of sequestered CO2 and in CO2 management potential (Figure 5). Natural sinks, such as afforestation and reforestation, represent the lowest-cost options, while industrial CCUS systems have varying costs depending on the carbon concentration in the stream. Direct air capture and storage is the most expensive method, but it offers almost infinite scalability. This comparison underscores the need for continued innovation in reducing costs and enhancing the scalability of CCS technologies.
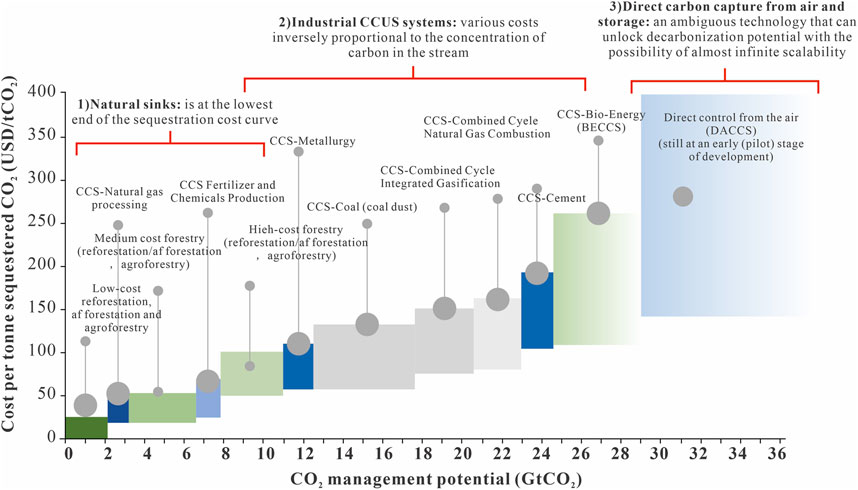
Figure 5. Carbon sequestration cost (USD/tCO2) with respect to emission reduction potential (GtCO2) of various technologies (modified from Li et al., 2013).
The high economic costs of implementing CCS prevent its wide commercial deployment. Addressing this requires governments to introduce subsidies and carbon-pricing instruments to mitigate financial uncertainties and foster innovation in technology and its application. These financial mechanisms would not only help reduce costs but also expand the adoption of CCS. For example, in the United States, CCS initiatives are supported by tax credits, which help alleviate economic risks. An additional consideration is the assessment of the spectrum of risks facing CO2–EOR projects. The main risks are outlined in Figure 6, which categorizes them as political, sociological, technological, environmental, and economic risks, with some mitigation strategies. Political risks include sanctions and regulatory restrictions, which can be addressed through alternative strategies and compliance. Sociological risks encompass skill shortages and pandemics, which can be managed via institutional measures. Technological risks such as accidents and inefficiencies are best countered with emergency systems and monitoring technologies. Environmental risks include gas leaks and groundwater contamination, and they can be mitigated through infrastructure improvements. Economic risks such as price volatility and high costs can be managed through flexible investment policies. The risk matrix (Figure 6) displays the probability and impact of each risk using color coding from green (low risk) to red (critical risk). For example, oil-price volatility is marked as being ‘almost certain’ with ‘severe’ impact, indicating high priority, while the ‘minor’ impact of groundwater contamination is ‘unlikely’ to occur, reflecting a lower priority. This framework can aid the prioritization and management of critical risks to assist successful CO2–EOR implementation. (Shogenova et al., 2013).
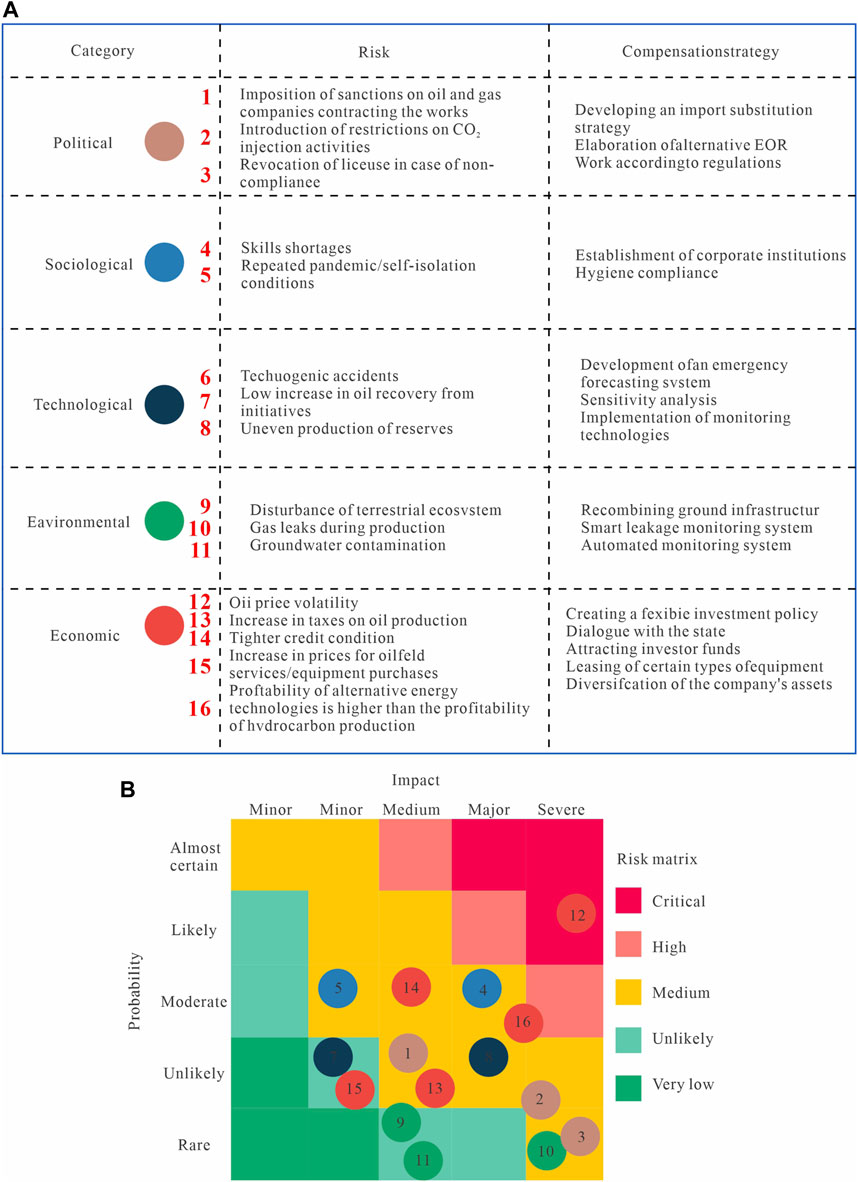
Figure 6. Risk assessment of factors affecting CO2–EOR projects: (A) factors itemized with mitigation strategies; (B) matrix displaying the risk factors in terms of probability and impact with traffic-light color coding (modified from Vega and Kovscek, 2010).
Finally, there is public mistrust of CCS technology, highlighting the critical need for education and public outreach to enhance societal acceptance. The Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project successfully increased the understanding and support through community outreach efforts (Boyd et al., 2013). Overcoming the many barriers that CCS technology faces requires comprehensive strategies, including ongoing research and development, effective policies, fostering of public trust, and encouragement of international cooperation. The evolution of CCUS technology across four key phases is illustrated in Figure 7. The embryonic phase (1920s–1970s) marked the early use of CO₂–EOR for oil production. The formation phase (1980s–1990s) witnessed the establishment of key climate organizations such as the IPCC along with early demonstration projects. During the shock growth phase (1990s–2016), international climate efforts stalled, and progress was slower than expected. Finally, in the fast growing phase (2016s–2022s), CCUS adoption accelerated, spurred on by the 2015 Paris Agreement, global warming targets, and increased focus on negative emissions, with more than 65 commercial projects started by 2020. Environmental consciousness is increasing globally, and international consensus is gradually forming regarding actions against climate change. As global attention shifts and support for CCS technology increases, practical engineering applications and technological progress will see further innovations that will increase the role of CCS in mitigating climate change and achieving carbon neutrality.
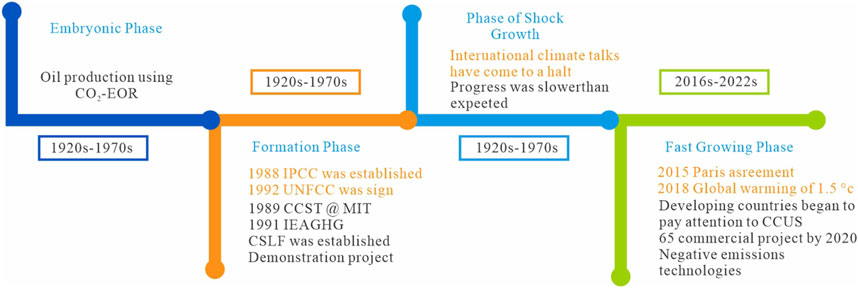
Figure 7. Timeline of advancements in worldwide uptake of carbon capture, utilization, and carbon storage (CCUS) technology.
KD: writing–original draft. YX: writing–review and editing. GY: writing–original draft. TL: data curation and writing–review and editing. HZ: writing–review and editing. HS: methodology, supervision, writing–review and editing. HY: writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Authors KD, YX, GY, TL, HZ, and HS were employed by CNPC Engineering Technology R&D Company Limited.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abdelaal, M. M., and Zeidouni, M. (2022). Injection data analysis using material balance time for CO2 storage capacity estimation in deep closed saline aquifers. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 208, 109385. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109385
Ali, K. A., Ahmad, M., and Yusup, Y. (2020). Issues, impacts, and mitigations of carbon dioxide emissions in the building sector. Sustainabilityi 12 (18), 7427. doi:10.3390/su12187427
Allinson, K., Burt, D., Campbell, L., Constable, L., Crombie, M., Lee, A., et al. (2017). Best practice for transitioning from carbon dioxide (CO2) enhanced oil recovery EOR to CO2 storage. Energy Procedia 114, 6950–6956. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1837
Aminu, M. D., Nabavi, S., Rochelle, C., and Manović, V. (2017). A review of developments in carbon dioxide storage. Appl. Energy 208, 1389–1419. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.015
Anderson, S. T. (2016). Risk, liability, and economic issues with long-term CO2 storage—a review. Nat. Resour. Res. 26, 89–112. doi:10.1007/s11053-016-9303-6
Asamoto, S., Guen, Y. L., Poupard, O., and Capra, B. (2013). Well integrity assessment for CO2 injection: a numerical case study on thermo-mechanical behavior in downhole CO2 environments. Eng. Comput. 30 (6), 842–853. doi:10.1108/EC-05-2012-0117
Assi, A., Federici, S., Bilo, F., Zacco, A., Depero, L., and Bontempi, E. (2019). Increased sustainability of carbon dioxide mineral sequestration by a technology involving fly ash stabilization. Materials 12 (17), 2714. doi:10.3390/ma12172714
Audigane, P., Gaus, I., Czernichowski-Lauriol, I., Pruess, K., and Xu, T. (2007). Two-dimensional reactive transport modeling of CO2 injection in a saline aquifer at the Sleipner site, North Sea. Am. J. Sci. 307 (10), 974–1008. doi:10.2475/07.2007.02
Bacci, G., Korre, A., and Durucan, S. (2011). Experimental investigation into salt precipitation during CO2 injection in saline aquifers. Energy Procedia 4, 4450–4456. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.399
Bakhshian, S., and Hosseini, S. (2019). Prediction of CO2 adsorption-induced deformation in shale nanopores. Fuel 241, 767–776. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2018.12.095
Barth, J., Mader, M., Myrttinen, A., Becker, V., Geldern, R., and Mayer, B. (2015). Advances in stable isotope monitoring of CO2 under elevated pressures, temperatures and salinities: selected results from the project CO2ISO-LABEL. Geol. Storage CO2–Long Term Secur. Aspects Geotechnol. Sci. Rep. 22, 59–71. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-13930-2_3
Barth, J., Nowak, M., Zimmer, M., Norden, B., and Geldern, R. (2015). Monitoring of cap-rock integrity during CCS from field data at the Ketzin pilot site (Germany): evidence from gas composition and stable carbon isotopes. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 43, 133–140. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.10.017
Behzadi, H., Alvarado, V., and Mallick, S. (2011). CO2 saturation, distribution and seismic response in two-dimensional permeability model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45 (21), 9435–9441. doi:10.1021/es201969a
Bernabé, Y., Zamora, M., Li, M., Maineult, A., and Tang, Y. (2011). Pore connectivity, permeability, and electrical formation factor: a new model and comparison to experimental data. J. Geophys. Res. 116. doi:10.1029/2011JB008543
Bickle, M., Chadwick, A., Huppert, H. E., Hallworth, M. A., and Lyle, S. (2007). Modelling carbon dioxide accumulation at Sleipner: implications for underground carbon storage. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 255 (1-2), 164–176. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.013
Blackford, J., Hattam, C., Widdicombe, S., Burnside, N., Naylor, M., Kirk, K., et al. (2013). CO2 leakage from geological storage facilities: environmental, societal and economic impacts, monitoring and research strategies. Geol. Storage carbon dioxide (CO2), 149–178. doi:10.1533/9780857097279.2.149
Boot-Handford, M. E., Abanades, J. C., Anthony, E. J., Blunt, M. J., Brandani, S., Mac Dowell, N., et al. (2014). Carbon capture and storage update. Energy Environ. Sci. 7 (1), 130–189. doi:10.1039/c3ee42350f.Blunt
Börner, J., Herdegen, V., Repke, J., and Spitzer, K. (2013). The impact of CO2 on the electrical properties of water bearing porous media – laboratory experiments with respect to carbon capture and storage. Geophys. Prospect. 61, 446–460. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.2012.01129.x
Bosch, D., Ledo, J., Queralt, P., Bellmunt, F., Luquot, L., and Gouze, P. (2016). Core-scale electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) monitoring of CO2-brine mixture in Fontainebleau sandstone. J. Appl. Geophys. 130, 23–36. doi:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2016.03.039
Boyd, A., Liu, Y., Stephens, J., Wilson, E., Pollak, M., Peterson, T., et al. (2013). Controversy in technology innovation: contrasting media and expert risk perceptions of the alleged leakage at the Weyburn carbon dioxide storage demonstration project. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 14, 259–269. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.01.011
Breen, S., Carrigan, C., LaBrecque, D., and Detwiler, R. (2012). Bench-scale experiments to evaluate electrical resistivity tomography as a monitoring tool for geologic CO2 sequestration. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 9, 484–494. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.04.009
Byun, H.-S., and Choi, M.-Y. (2007). High pressure phase behaviour of the binary mixture for the 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 2-hydroxypropyl acrylate, and 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate in supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 39 (6), 855–861. doi:10.1016/j.jct.2006.11.010
Cai, J., Zhang, Z., Wei, W., Guo, D., Li, S., and Zhao, P. (2019). The critical factors for permeability-formation factor relation in reservoir rocks: pore-throat ratio, tortuosity and connectivity. Energy 188, 116051. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2019.116051
Carlin, A. P. (2006). Global climate control: is there a better strategy than reducing greenhouse gas emissions? Univ. Pa. Law Rev. 155, 1401. doi:10.22004/ag.econ.280850
Carrigan, C., Yang, X., LaBrecque, D., Larsen, D., Freeman, D., Ramirez, A., et al. (2013). Electrical resistance tomographic monitoring of CO2 movement in deep geologic reservoirs. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 18, 401–408. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.04.016
Chadwick, R., Williams, G., and White, J. (2010). High-resolution imaging and characterization of a CO2 layer at the Sleipner CO2 storage operation, North Sea using time-lapse seismics. First Break 34, 77–85. doi:10.3997/1365-2397.34.2.83911
Chapoy, A., Nazeri, M., Kapateh, M., Burgass, R., Coquelet, C., and Tohidi, B. (2013). Effect of impurities on thermophysical properties and phase behaviour of a CO2-rich system in CCS. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 19, 92–100. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.08.019
Cheng, G., Ruina, X., and Pei-xue, J. (2015). Numerical simulation of the dispersion of supercritical CO2 storage in saline aquifers. J. Tsinghua Univ. 55 (10), 1105–1109.
Cheng, Y., Zeng, M., Lu, Z., Du, X., Yin, H., and Yang, L. (2020). Effects of supercritical CO2 treatment temperatures on mineral composition, pore structure and functional groups of shale: implications for CO2 sequestration. Sustainability 12, 3927. doi:10.3390/su12093927
Christensen, N. B., Sherlock, D., and Dodds, K. (2006). Monitoring CO2 injection with cross-hole electrical resistivity tomography. Explor. Geophys. 37, 44–49. doi:10.1071/EG06044
Christensen, J. H., and Kanikicharla, K. K. (2013). “Climate phenomena and their relevance for future regional climate change,” Climate change 2013 the physical science basis: Working group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change (Cambridge University Press), 1217–1308.
Christmas, K., and Bassingthwaighte, J. (2017). Equations for O2 and CO2 solubilities in saline and plasma: combining temperature and density dependences. J. Appl. physiology 122 (5), 1313–1320. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01124.2016
Colby, S., Thomas, D. G., Nuñez, J. R., Baxter, D. J., Glaesemann, K. R., Brown, J. M., et al. (2019). ISiCLE: a quantum chemistry pipeline for establishing in silico collision cross section libraries. Anal. Chem. 91 (7), 4346–4356. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04567
Court, B., Elliot, T., Dammel, J. A., Buscheck, T., Rohmer, J., and Celia, M. (2012). Promising synergies to address water, sequestration, legal, and public acceptance issues associated with large-scale implementation of CO2 sequestration. Mitig. Adapt. Strategies Glob. Change 17, 569–599. doi:10.1007/s11027-011-9314-x
Cui, G., Wang, Y., Rui, Z., Chen, B., Ren, S., and Zhang, L. (2018). Assessing the combined influence of fluid-rock interactions on reservoir properties and injectivity during CO2 storage in saline aquifers. Energy 155, 281–296. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2018.05.024
Dai, K., Li, X., Song, X., Chen, G., Pan, Y., and Huang, Z. (2014). Monitoring of CO2 geological storage based on the passive surface waves. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 24, 707–711. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.07.007
Damen, K., Faaij, A., and Turkenburg, W. (2006). Health, safety and environmental risks of underground CO2 storage – overview of mechanisms and current knowledge. Clim. Change 74, 289–318. doi:10.1007/s10584-005-0425-9
Dempsey, D., Kelkar, S., Pawar, R., Keating, E., and Coblentz, D. (2014). Modeling caprock bending stresses and their potential for induced seismicity during CO2 injection. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 30, 223–236. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2014.01.005
Deng, H., Bielicki, J., Fitts, J., Peters, C., and Oppenheimer, M. (2014). Policy implications of monetized leakage risk from geologic CO2 storage reservoirs. Energy Procedia 63, 6852–6863. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.719
DePaolo, D., and Bourg, I. (2017). Chemistry, geology, and carbon mitigation. Accounts Chem. Res. 50 (9), 2055. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00349
Diao, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Li, X., and Cao, H. (2015). Short-term safety risk assessment of CO2 geological storage projects in deep saline aquifers using the Shenhua CCS Demonstration Project as a case study. Environ. Earth Sci. 73, 7571–7586. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3928-8
Dixon, T., and Romanak, K. (2015). Improving monitoring protocols for CO2 geological storage with technical advances in CO2 attribution monitoring. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 41, 29–40. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.05.029
Doetsch, J., Kowalsky, M., Doughty, C., Finsterle, S., Ajo-Franklin, J., Carrigan, C., et al. (2013). Constraining CO2 simulations by coupled modeling and inversion of electrical resistance and gas composition data. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 18, 510–522. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.04.011
Fatah, A., Bennour, Z., Ben Mahmud, H., Gholami, R., and Hossain, M. (2020). A review on the influence of CO2/shale interaction on shale properties: implications of CCS in shales. Energies 13 (12), 3200. doi:10.3390/en13123200
Feder, J. (2021). Modeling evaluates CO2 EOR, storage potential in depleted reservoirs. J. Petroleum Technol. 73 (06), 63–64. doi:10.2118/0621-0063-JPT
Flude, S., Györe, D., Stuart, F., Żurakowska, M., Boyce, A., Haszeldine, R., et al. (2017). The inherent tracer fingerprint of captured CO2. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 65, 40–54. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2017.08.010
Flude, S., Johnson, G., Gilfillan, S., and Haszeldine, R. S. (2016). Inherent tracers for carbon capture and storage in sedimentary formations: composition and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50 (15), 7939–7955. doi:10.1021/acs.est.6b01548
Frash, L., Carey, J., Ickes, T., and Viswanathan, H. (2017). Caprock integrity susceptibility to permeable fracture creation. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 64, 60–72. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2017.06.010
Gadikota, G., Matter, J., Kelemen, P., Brady, P., and Park, A. (2020). Elucidating the differences in the carbon mineralization behaviors of calcium and magnesium bearing alumino-silicates and magnesium silicates for CO2 storage. Fuel 277, 117900. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117900
Gao, J., Li, X., Cheng, G., Luo, H., and Zhu, H. (2023). Structural evolution and characterization of organic-rich shale from macroscopic to microscopic resolution: the significance of tectonic activity. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 10 (2), 84–90. doi:10.46690/ager.2023.11.03
Gao, P., Zhou, Q., and Wang, Y. (2016). Modelling and Simulation of CO2 dispersion from high pressure pipelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 305, 173–181.
Gaus, I., Azaroual, M., and Czernichowski-Lauriol, I. (2005). Reactive transport modelling of the impact of CO2 injection on the clayey cap rock at Sleipner (North Sea). Chem. Geol. 217 (3-4), 319–337. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.12.016
Gershenzon, N. I., Ritzi, R. W., Dominic, D. F., Mehnert, E., and Okwen, R. T. (2015). Modeling the effects of small-scale heterogeneity on CO2 migration in deep saline aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 83, 123–133. doi:10.2113/2022/8267559
Gibbins, J., and Chalmers, H. (2008). Carbon capture and storage. Energy Policy 36, 4317–4322. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2008.09.058
Gilfillan, S. M. V., Lollar, B. S., Holland, G., Blagburn, D., Stevens, S., Schoell, M., et al. (2008). Solving the carbon balance puzzle in CCS: evidence from natural analogues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105 (51), 20455–20460.
Gimeno, B., Artal, M., Velasco, I., Blanco, S. T., and Fernández, J. (2017). Influence of SO2 on CO2 storage for CCS technology: evaluation of CO2/SO2 co-capture. Appl. Energy 206, 172–180. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.048
Gomaa, I., Guerrero, J., Heidari, Z., and Espinoza, D. (2022). Experimental measurements and molecular simulation of carbon dioxide adsorption on carbon surface. SPE Reservoir Evaluation and Engineering, 1–14. doi:10.2118/210264-PA
Goos, E., Riedel, U., Zhao, L., and Blum, L. (2011). Phase diagrams of CO2 and CO2 - N2 gas mixtures and their application in compression processes. Energy Procedia 4, 3778–3785. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.312
Govindarajan, S. (2019). An overview on extension and limitations of macroscopic Darcy’s law for a single and multi-phase fluid flow through a porous medium. Int. J. Min. Sci. (IJMS) Volume. 5, 1–21. doi:10.20431/2454-9460.0504001
Gozalpour, F., Ren, S., and Tohidi, B. (2005). CO2 EOR and storage in oil reservoir. Oil and Gas Sci. Technol. 60 (3), 537–546. doi:10.2516/ogst:2005036
Gu, K., Wang, G., and Li, J. (2004). Migration based SAR imaging for ground penetrating radar systems. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar Navigation 151 (5), 317–325. doi:10.1049/ip-rsn:20040973
Hangx, S., Spiers, C., and Peach, C. (2011). The mechanical behavior of anhydrite and the effect of deformation on permeability development - implications for caprock integrity during geological storage of CO2. Energy Procedia 4, 5358–5363. doi:10.1111/j.1468-8123.2010.00299.x
He, Q., Mohaghegh, S., and Gholami, V. (2013). A field study on simulation of CO2 injection and ECBM production and prediction of CO2 storage capacity in unmineable coal seam. J. Petroleum Eng. 2013, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2013/803706
Holland, D. M., Lockerby, D., Borg, M., Nicholls, W., and Reese, J. (2015). Molecular dynamics pre-simulations for nanoscale computational fluid dynamics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 18, 461–474. doi:10.1007/s10404-014-1443-6
Hui, D., Pan, Y., Luo, P., Zhang, Y., Sun, L., and Lin, C. (2019). Effect of supercritical CO2 exposure on the high-pressure CO2 adsorption performance of shales. Fuel 247, 57–66. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2019.03.013
Iglauer, S. (2011). Dissolution trapping of carbon dioxide in reservoir formation brine – a carbon storage mechanism, 233–262. doi:10.5772/20206
Ishida, T., Aoyagi, K., Niwa, T., Chen, Y., Murata, S., Chen, Q., et al. (2012). Acoustic emission monitoring of hydraulic fracturing laboratory experiment with supercritical and liquid CO2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 39 (16). doi:10.1029/2012GL052788
Jeddizahed, J., and Rostami, B. (2016). Experimental investigation of injectivity alteration due to salt precipitation during CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 96, 23–33. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.06.014
Jensen, G., Nickel, E., Whittaker, S., and Rostron, B. (2011). Site assessment update at Weyburn-Midale CO2 sequestration project, Saskatchewan, Canada: new results at an active CO2 sequestration site. Energy Procedia 4, 4777–4784. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.442
Jing, T., Fu, J., Zhou, J., Ma, X., Diao, Y., Liu, T., et al. (2022). An automatic modeling approach for the potential evaluation of CO2 geological storage in the deep saline aquifer. Front. Energy Res. 10, 957014. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2022.957014
Johnson, G., and Mayer, B. (2011). Oxygen isotope exchange between H2O and CO2 at elevated CO2 pressures: implications for monitoring of geological CO2 storage. Appl. Geochem. 26, 1184–1191. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.04.007
Jun, Y.-S., Zhang, L., Min, Y., and Li, Q. (2017). Nanoscale chemical processes affecting storage capacities and seals during geologic CO2 sequestration. Accounts Chem. Res. 50 (7), 1521–1529. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00654
Kaldi, J., Daniel, R., Tenthorey, E., Michael, K., Schacht, U., Nicol, A., et al. (2013). Containment of CO2 in CCS: role of caprocks and faults. Energy Procedia 37, 5403–5410. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.458
Kampman, N., Bickle, M., Wigley, M., and Dubacq, B. (2014). Fluid flow and CO2-fluid-mineral interactions during CO2-storage in sedimentary basins. Chem. Geol. 369, 22–50. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.11.012
Kim, J., Nam, M., and Matsuoka, T. (2016). Monitoring CO2 drainage and imbibition in a heterogeneous sandstone using both seismic velocity and electrical resistivity measurements. Explor. Geophys. 47, 24–31. doi:10.1071/EG15002
Kolawole, O., Ispas, I., Kumar, M., Weber, J., Zhao, B., and Zanoni, G. (2021). How can biogeomechanical alterations in shales impact caprock integrity and CO2 storage? Fuel 291, 120149. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120149
Krishnamurthy, P. G., Senthilnathan, S., Yoon, H., Thomassen, D., Meckel, T., and DiCarlo, D. (2017). Comparison of Darcy's law and invasion percolation simulations with buoyancy-driven CO2-brine multiphase flow in a heterogeneous sandstone core. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 155, 54–62. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2016.10.022
Lamur, A., Kendrick, J., Eggertsson, G. H., Wall, R., Ashworth, J., and Lavallée, Y. (2017). The permeability of fractured rocks in pressurised volcanic and geothermal systems. Sci. Rep. 7, 6173. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-05460-4
Lamy-Chappuis, B., Angus, D., Fisher, Q., Grattoni, C., and Yardley, B. (2014). Rapid porosity and permeability changes of calcareous sandstone due to CO2-enriched brine injection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 399–406. doi:10.1002/2013GL058534
Lepore, S., and Ghose, R. (2015). Carbon capture and storage reservoir properties from poroelastic inversion: a numerical evaluation. J. Appl. Geophys. 122, 181–191. doi:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2015.09.015
Li, D., Zhang, L., Ren, B., and Ren, S. (2014). Experimental study of CO2-sensitive chemicals for enhanced sealing of leakage pathways in CO2 geological storage process. Energy Procedia 63, 4646–4657. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.498
Li, L., Zhao, N., Wei, W., and Sun, Y. (2013). Review of research progress on CO2 capture, storage, and utilization in Chinese Academy of Sciences. Fuel 108, 112–130. doi:10.1016/J.FUEL.2011.08.022
Li, Q., and Liu, G. (2016) “Risk assessment of the geological storage of CO2: a review,” in Geologic carbon sequestration: understanding reservoir behavior, 249–284. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-27019-7_13
Li, H., Jiang, H. D., Yang, B., and Liao, H. (2019). An analysis of research hotspots and modeling techniques on carbon capture and storage. Sci. Total Environ. 687, 687–701. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.013
Li, R., Wang, P., Wang, Z., Cheng, H., and Zhang, K. (2023). Strategy to enhance geological CO2 storage capacity in saline aquifer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 50 (3), e2022GL101431. doi:10.1029/2022gl101431
Lin, J., Ren, T., Wang, G., Booth, P., and Nemcik, J. (2017). Experimental study of the adsorption-induced coal matrix swelling and its impact on ECBM. J. Earth Sci. 28, 917–925. doi:10.1007/s12583-017-0778-9
Liu, N., Pan, L., and Cheng, J. (2017). Numerical modeling of CO2 and brine leakage through open fracture in a fault zone: open channel flow or Darcy flow. Geofluids 2017, 1–21. doi:10.1155/2017/9035032
Llamas, B., and Cienfuegos, P. (2012). Multicriteria decision methodology to select suitable areas for storing CO2. Energy and Environ. 23 (2-3), 249–264. doi:10.1260/0958-305X.23.2-3.249
Luquot, L., Roetting, T., and Carrera, J. (2014). Characterization of flow parameters and evidence of pore clogging during limestone dissolution experiments. Water Resour. Res. 50, 6305–6321. doi:10.1002/2013WR015193
Ma, Z., and Ranjith, P. (2019). Review of application of molecular dynamics simulations in geological sequestration of carbon dioxide. Fuel 255, 115644. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115644
Macpherson, G., and Reese, J. (2008). Molecular dynamics for fluid mechanics in arbitrary geometries. Int. Conf. Nanochannels, Microchannels, Minichannels 48345, 969–976. doi:10.1115/ICNMM2008-62277
Mayer, B., Humez, P., Becker, V., Dalkhaa, C., Rock, L., Myrttinen, A., et al. (2015). Assessing the usefulness of the isotopic composition of CO2 for leakage monitoring at CO2 storage sites: a review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 37, 46–60. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.02.021
Mayer, B., Shevalier, M., Nightingale, M., Kwon, J.-S., Johnson, G., Raistrick, M., et al. (2013). Tracing the movement and the fate of injected CO2 at the IEA GHG Weyburn-Midale CO2 Monitoring and Storage project (Saskatchewan, Canada) using carbon isotope ratios. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 16, S177–S184. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.01.035
Minato, S. (2012). Applications and development of seismic interferometry by crosscorrelation and multidimensional deconvolution.
Mitani, Y., Arsyad, A., Ikemi, H., Kuze, K., and Oura, S. (2011). A new flow pump permeability test applied on supercritical CO2 injection to low permeable rocks. Int. J. JCRM 7 (1), 25–31. doi:10.11187/ijjcrm.7.25
Moon, W., Kim, J., Lodha, G., Serzu, M., and Soonawala, N. (1993). Application of high resolution seismic reflection techniques for fracture mapping in crystalline rocks. Eng. Geol. 34 (3-4), 261–280. doi:10.1016/0013-7952(93)90093-R
Mukherjee, M., and Misra, S. (2018). A review of experimental research on Enhanced Coal Bed Methane (ECBM) recovery via CO2 sequestration. Earth-Science Rev. 179, 392–410. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.02.018
Mwenketishi, G., Benkreira, H., and Rahmanian, N. (2023). A comprehensive review on carbon dioxide sequestration methods. Energies 16 (24), 7971. doi:10.3390/en16247971
Myrttinen, A., Jeandel, E., Ukelis, O., Becker, V., Geldern, R., Blum, P., et al. (2015). Carbon and oxygen isotope indications for CO2 behaviour after injection: first results from the Ketzin site (Germany). Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 4, 1000–1006. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.02.005
Nakatsuka, Y., Xue, Z., García, H. A., and Matsuoka, T. (2010). Experimental study on CO2 monitoring and quantification of stored CO2 in saline formations using resistivity measurements. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 4, 209–216. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.01.001
Newell, P., and Martinez, M. (2020). Numerical assessment of fault impact on caprock seals during CO2 sequestration. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 94, 102890. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.102890
Olanrewaju, A., Beaugrand, M., Yafia, M., and Juncker, D. (2018). Capillary microfluidics in microchannels: from microfluidic networks to capillaric circuits. Lab a Chip 18 (16), 2323–2347. doi:10.1039/c8lc00458g
Parisio, F., and Vilarrasa, V. (2020). Sinking CO2 in supercritical reservoirs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 47, e2020GL090456. doi:10.1029/2020GL090456
Park, J., Sauvin, G., and Vöge, M. (2017). 2.5D inversion and joint interpretation of CSEM data at sleipner CO2 storage. Energy Procedia 114, 3989–3996. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1531
Perera, M. S. A., and Ranjith, P. G. (2015). Enhanced coal bed methane recovery: using injection of nitrogen and carbon dioxide mixture. Handb. clean energy Syst., 1–19. doi:10.1002/9781118991978.hces218
Pinard, H., Garambois, S., Métivier, L., Dietrich, M., Sénéchal, G., and Rousset, D. (2016) Full-waveform inversion of GPR data acquired between boreholes in Rustrel carbonates. EDP Sci. 12. doi:10.1051/e3sconf/20161201002
Pini, R., Marx, D., Burlini, L., Storti, G., and Mazzotti, M. (2011). Coal characterization for ECBM recovery: gas sorption under dry and humid conditions, and its effect on displacement dynamics. Energy Procedia 4, 2157–2161. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.101
Pollak, M. F., and Wilson, E. (2009). Risk governance for geological storage of CO2 under the clean development mechanism. Clim. Policy 9, 71–87. doi:10.3763/cpol.2008.0528
Psarras, P., Holmes, R., Vishal, V., and Wilcox, J. (2017). Methane and CO2 adsorption capacities of kerogen in the eagle ford shale from molecular simulation. Accounts Chem. Res. 508, 1818–1828. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00003
Raab, T., Weinzierl, W., Wiese, B., Rippe, D., and Schmidt-Hattenberger, C. (2020). Development of an electrical resistivity tomography monitoring concept for the svelvik CO2 field lab, Norway. Adv. Geosciences 54, 41–53. doi:10.5194/adgeo-54-41-2020
Raistrick, M., Hutcheon, I., Shevalier, M., Nightingale, M., Johnson, G., Taylor, S. W., et al. (2009). Carbon dioxide-water-silicate mineral reactions enhance CO2 storage; evidence from produced fluid measurements and geochemical modeling at the IEA Weyburn-Midale Project. Energy Procedia 1 (1), 3149–3155. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2009.02.097
Rasool, M. H., Ahmad, M., and Ayoub, M. (2023). Selecting geological formations for CO2 storage: a comparative rating system. Sustainability 15 (8), 6599. doi:10.3390/su15086599
Reeves, S. (2003). “Coal-seq project update: field studies of ECBM recovery/CO2 sequestration in coalseams,” in In greenhouse gas control technologies-6th international conference (Pergamon), 557–562. doi:10.1016/B978-008044276-1/50089-1
Rezk, M., and Foroozesh, J. (2019). Phase behavior and fluid interactions of a CO2-Light oil system at high pressures and temperatures. Heliyon 5, e02057. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02057
Riding, J. (2005) “The IEA Weyburn CO2 monitoring and storage project: integrated results from Europe,” in Greenhouse gas control technologies, 7. Elsevier Science Ltd, 2075–2078. doi:10.1016/B978-008044704-9/50275-5
Rinaldi, A. P., Rutqvist, J., and Cappa, F. (2013). Geomechanical effects on CO2 leakage through fault zones during large-scale underground injection. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 19, 117–131. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.11.001
Ringrose, P. (2016). CO2 Capture and Storage-Developing industrial-scale CCS projects in Norway. In 78th EAGE conference and exhibition., 1, 1–5. European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers. doi:10.3997/2214-4609.201601661
Rodrigues, L. G., Nunes, J. P., and Guérillot, D. (2012). “Evolution of seismic responses due to CO2 injection in carbonates including chemical reactions and rock-physics model,” in In ECMOR XIII-13th European Conference on the Mathematics of oil recovery. cp-307 (European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers). doi:10.3997/2214-4609.20143247
Rørheim, S., Bhuiyan, M., Bauer, A., and Cerasi, P. (2021). On the effect of CO2 on seismic and ultrasonic properties: a novel shale experiment. Energies 14 (16), 5007. doi:10.3390/en14165007
Schön, J. H. (2015). Physical properties of rocks: fundamentals and principles of petrophysics. Elsevier.
Schreiter, L., Hloušek, F., Hellwig, O., and Buske, S. (2015). Characterization of seismic reflections from faults in a crystalline environment, Schneeberg, Germany. Geophys. Prospect. 63 (4), 1015–1032. doi:10.1111/1365-2478.12255
Senger, K., Tveranger, J., Braathen, A., Olaussen, S., Ogata, K., and Larsen, L. (2015). CO2 storage resource estimates in unconventional reservoirs: insights from a pilot-sized storage site in Svalbard, Arctic Norway. Environ. Earth Sci. 73, 3987–4009. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3684-9
Senior, W. J., Kantorowicz, J., and Wright, I. (2010). Geological storage of carbon dioxide: an emerging opportunity. Geol. Mag. 7, 1165–1169. doi:10.1144/0071165
Shin, W. J., Ryu, J., Choi, H. B., Yun, S., and Lee, K. S. (2020). Monitoring the movement of artificially injected CO2 at a shallow experimental site in Korea using carbon isotopes. J. Environ. Manag. 258, 110030. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.110030
Shin, Y., Ji, H. G., Park, S. E., and Oh, J. W. (2022). 4D seismic monitoring with diffraction-angle-filtering for carbon capture and storage (CCS). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 11 (1), 57. doi:10.3390/jmse11010057
Shogenova, A., Piessens, K., Ivask, J., Shogenov, K., Martínez, R., Flornes, K., et al. (2013). CCS directive transposition into national laws in europe: progress and problems by the end of 2011. Energy Procedia 37, 7723–7731. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.718
Silva, G. D., Ranjith, P., and Perera, M. (2015). Geochemical aspects of CO2 sequestration in deep saline aquifers: a review. Fuel 155, 128–143. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2015.03.045
Singleton, G., Herzog, H., and Ansolabehere, S. (2009). Public risk perspectives on the geologic storage of carbon dioxide. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 3, 100–107. Read more. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.07.006
Smith, E. R. (2013). On the coupling of molecular dynamics to continuum computational fluid dynamics. Sch. Mech. Eng. doi:10.25560/15610
Sodeifian, G., Sajadian, S. A., Razmimanesh, F., and Saadati Ardestani, N. (2018). A comprehensive comparison among four different approaches for predicting the solubility of pharmaceutical solid compounds in supercritical carbon dioxide. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 35 (10), 2097–2116. doi:10.1007/s11814-018-0125-6
Solomon, S., Carpenter, M., and Flach, T. (2008). Intermediate storage of carbon dioxide in geological formations: a technical perspective. Int. J. Greenh. gas control 2 (4), 502–510. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2008.04.004
Song, X., Dai, K. S., Chen, G., Pan, Y., and Zhong, Z. (2014). Sensitivity study of surface waves for CO2 storage monitoring. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 20, 180–188. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.11.008
Stow, S., Causon, T. J., Zheng, X., Kurulugama, R. T., Mairinger, T., May, J. C., et al. (2017). An interlaboratory evaluation of drift tube ion mobility-mass spectrometry collision cross section measurements. Anal. Chem. 89 (17), 9048–9055. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01729
Sun, H., Sun, W., Zhao, H., Sun, Y., Zhang, D., Qi, X., et al. (2016). Adsorption properties of CH4 and CO2 in quartz nanopores studied by molecular simulation. RSC Adv. 6 (39), 32770–32778. doi:10.1039/C6RA05083B
Sun E, E., Westman, E., Fahrman, B., and, X., and Ma, X. (2017). Monitoring of rock stress redistribution in geological CO2 sequestration. Resour. Environ. and Eng. 2, 108–113. doi:10.15273/GREE.2017.02.020
Sun H, H., Zhao, H., Qi, N., Qi, X., Zhang, K., Sun, W., et al. (2017). Mechanistic insight into the displacement of CH4 by CO2 in calcite slit nanopores: the effect of competitive adsorption. RSC Adv. 6 (106), 104456–104462. doi:10.1039/C6RA23456A
Tarokh, A., Makhnenko, R., Kim, K., Zhu, X., Popovics, J., Šegvić, B., et al. (2020). Influence of CO2 injection on the poromechanical response of Berea sandstone. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 95, 102959. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2020.102959
Teng, F., and Tondeur, D. (2007). Efficiency of Carbon storage with leakage: physical and economical approaches. Energy 32 (4), 540–548. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2006.07.027
Teng, H., Yamasaki, A., Chun, M., and Lee, H. (1997). Solubility of liquid CO2 in water at temperatures from 278 K to 293 K and pressures from 6.44 MPa to 29.49 MPa and densities of the corresponding aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 29 (12), 1301–1310. doi:10.1006/jcht.1997.0249
Tian, Z. W., and Wang, J. Y. (2018). Lattice Boltzmann simulation of dissolution-induced changes in permeability and porosity in 3D CO2 reactive transport. J. Hydrology 557, 276–290. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.12.037
Tomić, L., Karović-Maričić, V., Danilovic, D., and Crnogorac, M. (2018). Criteria for CO2 storage in geological formations. Podzemni radovi. (32), 61–74. doi:10.5937/PodRad1832061T
Torp, T., and Gale, J. (2004). Demonstrating storage of CO2 in geological reservoirs: the Sleipner and SACS projects. Energy 29, 1361–1369. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2004.03.104
Torus, B., Arista, K., Wulan, E., Lubis, M., Herawati, I., and Pranowo, W. (2023). 4D seismic inversion and rock physic modeling to monitor CO2 injection at carbon capture and storage project in the Utsira Formation, sleipner field, North Sea, Norway. J. Earth Energy Eng. 12 (2s), 40–52. doi:10.25299/jeee.2023.14088
Trinh, T. T., Vlugt, T., Hägg, M. B., Bedeaux, D., and Kjelstrup, S. (2013). Selectivity and self-diffusion of CO2 and H2 in a mixture on a graphite surface. Front. Chem. 1, 38. doi:10.3389/fchem.2013.00038
Valle, L., Grima Olmedo, C., Rodriguez Pons, R., and Llopis Albert, C. (2019). Experimental device to evaluate mineral trapping in sandstones as a means of supercritical CO2 (scCO2) storage. DYNA 94 (6), 614–619. doi:10.6036/9202
Vega, B., and Kovscek, A. (2010). “Carbon dioxide sequestration through enhanced oil recovery: a review of storage mechanisms and technological applications,” in Carbon capture and storage (CCS) techniques. Editor A. D. McDonald (Woodhead Publishing), 104–126. doi:10.1533/9781845699581.1.104
Verdon, J., Kendall, J. M., Stork, A., Chadwick, R. A., White, D. J., and Bissell, R. C. (2013). Comparison of geomechanical deformation induced by megatonne-scale CO2 storage at Sleipner, Weyburn, and in Salah. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110 (29), E2762–E2771. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302156110
Verdon, J. P., Kendall, J. M., White, D. J., and Angus, D. A. (2011). Linking microseismic event observations with geomechanical models to minimise the risks of storing CO2 in geological formations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 305 (3-4), 143–152. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.02.048
Wang, F., Mi, Z., Sun, Z., Li, X., Lan, T., Yuan, Y., et al. (2017). Experimental study on the effects of stress variations on the permeability of feldspar-quartz sandstone. Geofluids 2017, 1–15. doi:10.1155/2017/8354524
Wang, H., Alvarado, V., Bagdonas, D. A., McLaughlin, J. F., Kaszuba, J. P., Grana, D., et al. (2021). Effect of CO2-brine-rock reactions on pore architecture and permeability in dolostone: implications for CO2 storage and EOR. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 107, 103283. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2021.103283
Wang, J. G., and Wang, H. (2018). Sealing efficiency analysis for shallow-layer caprocks in CO2 geological storage. Environ. Earth Sci. 77 (21), 738. doi:10.1007/s12665-018-7924-2
Wang, T., Wang, H., Zhang, F., and Xu, T. (2013). Simulation of CO2-water-rock interactions on geologic CO2 sequestration under geological conditions of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 76 (1-2), 307–314. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.08.014
Wang, X., Zhai, Z., Jin, X., Wu, S., Li, J., Sun, L., et al. (2016). Molecular simulation of CO2/CH4 competitive adsorption in organic matter pores in shale under certain geological conditions. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 43, 841–848. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30100-8
Wilberforce, T., Baroutaji, A., Soudan, B., Al-Alami, A. H., and Olabi, A. G. (2019). Outlook of carbon capture technology and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 657, 56–72. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.424
Williams, G., Chadwick, R., and Vosper, H. (2018). Some thoughts on Darcy-type flow simulation for modelling underground CO2 storage, based on the Sleipner CO2 storage operation. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 68, 164–175. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2017.11.010
Wilson, M. (2011). “The ieaghg weyburn-midale CO2 monitoring and storage project: a project overview and a rebuttal to recent accusations of a leak from the reservoir,” in 73rd EAGE Conference and Exhibition-Workshops. 2011, cp-239 (European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers). doi:10.3997/2214-4609.20144725
Xie, W., Wang, M., Vandeginste, V., Chen, S., Yu, Z., Wang, J., et al. (2022). Adsorption behavior and mechanism of CO2 in the Longmaxi shale gas reservoir. RSC Adv. 12, 25947–25954. doi:10.1039/d2ra03632k
Yamamoto, H., Nanai, S., Zhang, K., Audigane, P., Chiaberge, C., Ogata, R., et al. (2012). “Numerical simulation of long-term fate of CO2 stored in deep reservoir rocks on massively parallel vector supercomputer,”, 10. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 80–92. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-38718-0_11
Yan, W., Ning, W., Yongsheng, W., Maoshan, C., and Xiaochun, L. (2014). Preliminary cap rock integrity analysis for CO2 geological storage in saline aquifers based on geochemical tests in Shenhua CCS demonstration project, China. Energy Procedia 63, 2994–2999. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.322
Yang, Y., and Chen, H. (2022). Dynamic changes of pore structure during CO2 mineral sequestration in shale. In SPE improved oil recovery conference? D021S019R002. Spe. doi:10.2118/209375-MS
Yoon, S. D., and Byun, H. S. (2014). Experimental measurement and correlation of phase behavior for the CO2+heptafluorobutyl acrylate and CO2+heptafluorobutyl methacrylate systems at high pressure. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31, 522–527. doi:10.1007/s11814-013-0256-8
Yu, H., Zhang, Y., Ma, Y., Lebedev, M., Ahmed, S., Li, X., et al. (2019). CO2-Saturated brine injection into unconsolidated sandstone: implications for carbon geosequestration. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 124 (11), 10823–10838. doi:10.1029/2018JB017100
Zahran, F., Pando, C., Cabañas, A., and Renuncio, J. R. (2010). Measurements and modeling of high-pressure excess molar enthalpies and isothermal vapor–liquid equilibria of the carbon dioxide + N,N-dimethylformamide system. J. Supercrit. Fluids 55 (3), 566–572. doi:10.1016/j.supflu.2010.09.020
Zhang, D., Cui, Y., Liu, B., Li, S., Song, W.-l., and Lin, W. (2011). Supercritical pure methane and CO2 adsorption on various rank coals of China: experiments and modeling. Energy and Fuels 25 (4), 1891–1899. doi:10.1021/ef101149d
Zhang, F., Ye, B., and Xua, L. (2017). “Measurement of supercritical CO2 permeability in porous rock at reservoir conditions,” in In advances in laboratory testing and modelling of soils and shales (ATMSS) (Springer International Publishing), 69–77. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-52773-4_7
Zhang, K., Sang, S., Zhou, X., Changjiang, L., Ma, M., and Niu, Q. (2021). Influence of supercritical CO2-H2O-caprock interactions on the sealing capability of deep coal seam caprocks related to CO2 geological storage: a case study of the silty mudstone caprock of coal seam no. 3 in the Qinshui Basin, China. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 106, 103282. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2021.103282
Zhang, Z., Pan, S., Li, H., Cai, J., Olabi, A., Anthony, E., et al. (2020). Recent advances in carbon dioxide utilization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 125, 109799. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2020.109799
Zhu, H., Huang, C., Ju, Y., Bu, H., Li, X., Manping, Y., et al. (2021). Multi-scale multi-dimensional characterization of clay-hosted pore networks of shale using FIBSEM, TEM, and X-ray micro-tomography: implications for methane storage and migration. Appl. Clay Sci. 213, 106239. doi:10.1016/J.CLAY.2021.106239
Zou, Y., Sihai, L., Ma, X., Zhang, S., Ning, L., and Ming, C. (2018). Effects of CO2–brine–rock interaction on porosity/permeability and mechanical properties during supercritical-CO2 fracturing in shale reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 49, 157–168. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2017.11.004
Zwaan, B., and Gerlagh, R. (2009). Economics of geological CO2 storage and leakage. Clim. Change 93, 285–309. doi:10.1007/s10584-009-9558-6
Keywords: carbon capture and storage, storage efficiency, geological conditions, technology innovation, carbon neutrality
Citation: Dai K, Xia Y, Yuan G, Liu T, Zhang H, Song H and Yuan H (2025) Experimental procedures, influencing parameters, and future prospects of geological sequestration of carbon dioxide. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1442518. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1442518
Received: 02 June 2024; Accepted: 06 January 2025;
Published: 31 January 2025.
Edited by:
Hongjian Zhu, Yanshan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Chen Zhang, Chengdu University of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Dai, Xia, Yuan, Liu, Zhang, Song and Yuan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kun Dai, RGFpa3VuNjY1NUAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.