- 1School of Civil Engineering, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, China
- 2Guangxi Key Laboratory of Geomechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, China
The creep characteristics of calcareous sand have an important impact on the stability of the structures on the coral islands in the South China Sea. Among the existing creep models for calcareous sand, fewer models consider the particle fragmentation of calcareous sand, which cannot accurately describe the shear creep of calcareous sand around the foundation of island structures. To study the shear creep model of calcareous sand, direct shear creep tests under different vertical and shear stresses and particle sieving tests of calcareous sand before and after the creep tests were carried out on calcareous sand. The results showed that the shear creep curve of calcareous sand exhibits nonlinearity with time, and can be divided into decelerated creep stage and stable creep stage; calcareous sand has different degrees of particle fragmentation during the shear creep test, and the degree of particle fragmentation is greater with the increase of the shear stress level. Based on the test results, combined with the Singh-Mitchell model theory, a model parameter on particle crushing was introduced, and a shear creep model considering particle crushing was established. Through validation, the model curve is closer to the experimental curve and can accurately describe the shear creep of calcareous sand in the South China Sea reefs.
1 Introduction
Calcareous sand, also known as coral sand, is a special marine geotechnical material rich in calcium carbonate, which is widely distributed in the tropical or subtropical sea areas such as the Southern Sea of China (Wang et al., 2011b), Red Sea (Salem et al., 2013), and Maldive Islands (Wen et al., 2021). With the development of Chinese marine economy, the construction of islands and reefs in the South China Sea has reached a certain scale. Due to the characteristics of calcareous sand such as easy breakage, high porosity, irregular shape and low strength, the engineering mechanical properties of calcareous sand are extremely complex (Poulos et al., 1984; Liu and Wang, 1998; Cao et al., 2020). Many studies have reported that time-dependent behavior (creep) on calcareous sand (Lade et al., 2009a; Lade, 2009b; Wang et al., 2018; Sun and Chen, 2019; Wang et al., 2020), which has a certain impact on the stability of island structures and reminds us to pay more emphasis. Till now, many scholars have studied the creep of calcareous sand. Ye et al. (2019) and Cao and Ye, 2019 used a triaxial rheometer to study the creep characteristics of calcareous sand and found that the creep of calcareous sand becomes a decay type steady state creep. Based on the test results, they proposed a four-parameter creep model in which the creep strain is related to time, deviational stress and effective confining pressure. Choo et al. (2020) conducted a comparative study of Tunisia calcareous and Korean standard silica sands through K0 creep tests and found that Tunisia calcareous sand experienced significant particle breakage during creep tests but the particle breakage of silica sand was not obvious. They also found that the particle breakage contributed to the creep deformation of calcareous sand. Xu et al. (2021) investigated the results of a series of large-scale simple shear tests on sandy soils reinforced with randomly distributed fibres and found that the addition of polypropylene and basalt fibres favoured the increase in ultimate shear strength, while glass fibres had little effect. Xu et al. (2024) investigated the micromechanical properties and micrometre-scale pore dissolution characteristics of porous coral reef limestone (CRL), and demonstrated that pore dissolution weakened the macromechanical properties of CRL by estimating the macroscopic E-value using the Mori-Tanaka method and simulation. Shen et al. (2021) proposed a SWCC model considering the effects of fine-grain content and dry density based on the Fredlund-Xing model and measured results. This new model can be used to describe the soil-water characteristics of calcareous silty sands with different fines contents and dry densities. Bai et al. (2023) developed a multiphase ontological model for hydrate-bearing sediments within the framework of particle thermodynamics, taking into account the energy dissipation induced by hydrate dissociation and particle rearrangement at the microscopic level. The model is able to effectively capture the strain hardening and softening of the sediments as well as the swelling properties and loading path effects of the sediments. Bai et al. (2020) established a nonlinear coupled heat-moisture-pollutant transport equation, constructed a new soil-water characteristic curve (SWCC) with hysteresis effect, and verified the hysteresis effect of moisture movement caused by the thermal cycle. Yeernaer and Zhang (2022) carried out the volume creep test of calcareous sand through the triaxial drainage test, and demonstrated a volume creep model of calcareous sand. The results showed that calcareous sand exhibited volume creep characteristics with time under constant confining pressure and the improved Burgers model can describe the volume creep deformation behavior of calcareous sand well. Chen et al. (2022) studied the creep fractal fracture characteristics of calcareous sand and revealed the development of particle breakage and the changes of microscopic pores during creep through one-dimensional compression creep test and microstructure test. Huang L et al., 2022 designed a laboratory uniaxial creep test, measured and established the relationship between creep variable and creep time of calcareous sand-polymer complex under different vertical pressures, and proposed an improved Murayama model of calcareous sand-polyurethane polymer complex. Wang et al. (2018) carried out a triaxial creep test and found that the creep process of calcareous sand can be classified into initial near-linear stage, deceleration stage and steady state stage from the perspective of creep rate. By connecting 2 K bodies and a clay pot, a creep model reflecting the changes of calcareous sand particle rearrangement, frictional sliding and particle breakage was established. By conducting creep tests to study the creep of calcareous sand, a number of creep models have been established by some scholars above. However, most current creep models for calcareous sands do not describe the shear creep of calcareous sands around the foundations of island structures very accurately. In this paper, through direct shear creep tests on China South Sea calcareous sand, the law of shear creep was explored. Based on Singh-Mitchell model (Singh and Mitchell, 1968), an empirical model of calcareous sand shear creep was established and the applicability of this model was verified by another set of test datas.
2 Test samples and methods
2.1 Calcareous sand samples
The calcareous sand samples were obtained from a reef in the South China Sea. According to Chinese current Standard for Geotechnical Test Methods (GB/T50123-2019),before the shear tests, the impurities and soluble salts on the surface of the calcareous sand were washed away by using distilled water and the calcareous sand particles with particularly large particle size were removed by hand. After that, the calcareous sand was dried in the oven for at least 8 h and then the sand particle were sieved to remove >2 mm particles. Through the geotechnical test, the specific gravity (Gs) of the sand sample is 2.74 g/cm3. The maximum dry density (ρmax) and minimum dry density (ρmin) are respectively 1.45 g/cm3 and 1.22 g/cm3.
2.2 Test methods
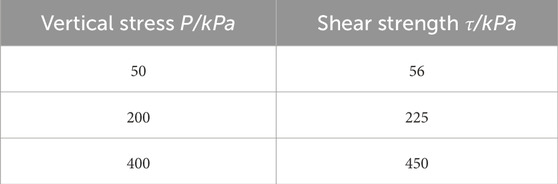
The tests in this paper include straight shear test, straight shear creep test and particle sieving test of calcareous sand before and after the creep test. The strength characteristics of the calcareous sand were determined by straight shear test, the creep characteristics of the calcareous sand were explored by straight shear creep test, and the particle crushing characteristics of the calcareous sand before and after the creep were analysed by particle sieving test. Before the straight shear creep test, ZJ-1 type straight shear instrument was used to carry out the straight shear test, and the test steps were as follows: firstly, 80 g of the calcareous sand samples were put into the shear box, and then the shear box was installed on the instrument. Vertical stress (P) was applied at the top of the shear box, and the sand sample was pre-compressed for 2days. After pre-compression, the specimen was then sheared until the sample reached destruction. Three different vertical stresses were set and the shear rate was set at 0.8 mm/min. At the end of the test, the peak shear strength of the specimens was calculated according to the standard and the results are listed in Table 1.
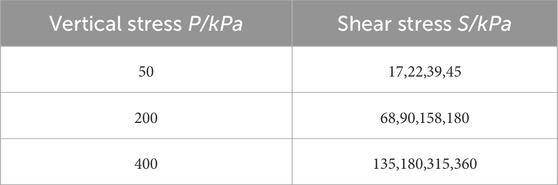
The straight shear creep test was carried out by ZLB-1 triple rheological straight shear apparatus, and the room temperature was kept at 25°C. The maximum allowable load (horizontal and vertical) of the instrument is 600kPa, and the shear strain of the sample can be measured by dial indicators or dial gauge with a maximum range of 10 mm and an accuracy of ±0.1%. Firstly, an 80 g sample of calcareous sand was placed in a shear box, which was then fitted with a shear box and a percentage meter to measure the shear strain of the calcareous sand. Before the horizontal shear stress is applied, the vertical stress is applied until the vertical displacement is less than 0.01 mm/d (Liang et al., 2021) to reduce the influence of compressive creep on the test results. In order to investigate the difference between crushing and non-crushing of calcareous sand, the vertical stress (P) was set to 50,200,400 kPa for the straight shear creep test. Under the above three sets of vertical stresses, shear stress (S) was applied in the manner of loading respectively according to 30%τ, 40%τ, 70%τ and 80%τ. The experimental scheme is shown in Table 2 below. At the beginning of the test, record the readout of the dial indicator or dial gauge at 1, 2, 9, 10, 30, 60, 180, 360 min time nodes. After that, the datas are recorded every 6 h. When many scholars carried out creep tests on calcareous sand, they believed that the creep stability was determined if the deformation rate was less than 0.005 mm/d (Ye et al., 2019; Cao and Ye, 2019; Xue et al., 2020). Considering the difference between the triaxial creep test and the direct shear creep test, and the shear creep of calcareous sand is smaller than the compressive creep, it is reasonable to regard the deformation rate less than 0.002 mm/d as the sign of creep stability in this test. In addition, the test was maintained at 25°C ± 1°C.
3 Test results
3.1 Shear strain-time curve
The data obtained directly from the above tests are horizontal displacements, which need to be converted into shear strains and calculated according to the following Formula 1:
Where ΔL is the horizontal displacement value (mm) recorded by the percentage meter at a certain moment, and d is the inner diameter of the shear box (mm).
The shear strain-time relationship of calcareous sand and the strain rate-time relationship curve of calcareous sand are shown in Figures 1, 2, respectively. Figures 1, 2, it can be seen that the shear creep of calcareous sand is nonlinear, which is divided into decelerating creep stage and stabilizing creep stage, which is similar to the results of creep tests on calcareous sand of South China Sea Reefs in other papers [13,22]. When the shear stress was first applied, the deformation of the calcareous sand specimen increased rapidly, but the deformation rate was decreasing rapidly. With the increase of time, the deformation of calcareous sand gradually slows down, and the creep curve and strain rate curve both tend to be level, and finally reach the creep stability. Under the same vertical stress P, the total strain of the calcareous sand specimen increases with increasing shear stress level D. For example, in Figure 1A, the total strain of the specimen at D = 0.3 is 0.64, and when D is increased to 0.8, the total strain of the specimen is increased to 3.77.
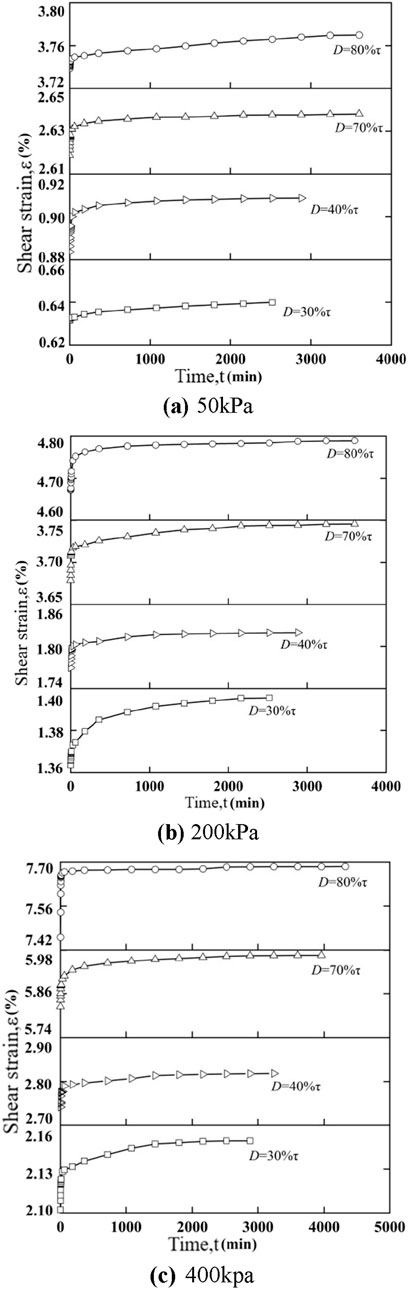
Figure 1. Shear strain-time relationship curve of calcareous sand under different vertical stresses. (A) 50 kPa. (B) 200 kPa. (C) 400 kpa.
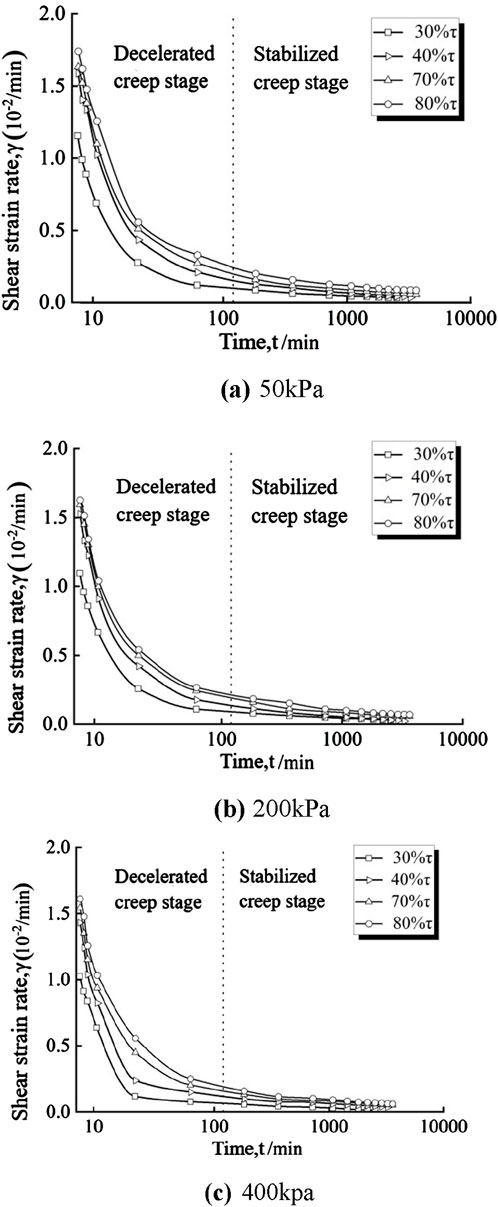
Figure 2. Shear strain rate-time relationship curve of calcareous sand under different vertical stresses. (A) 50 kPa. (B) 200 kPa. (C) 400 kpa.
3.2 Particle analysis
The initial gradation curve is shown in Figure 3A with a coefficient of inhomogeneity (Cu) of 5.22 and a coefficient of curvature (Cc) of 1.15. By sieving the particles of calcareous sand specimens before and after the direct shear creep test, the evolution of the gradation curves under different vertical stresses was obtained. As can be seen from Figure 3, the mass percentage of larger calcareous sand particles (1–2 mm and 0.5–1 mm) decreased, while the mass percentage of smaller calcareous sand particles (0.25–0.5 mm and 0.075–0.25 mm) increased under constant shear for a long period of time. This suggests that calcareous sand specimens are accompanied by particle fragmentation during shear creep.
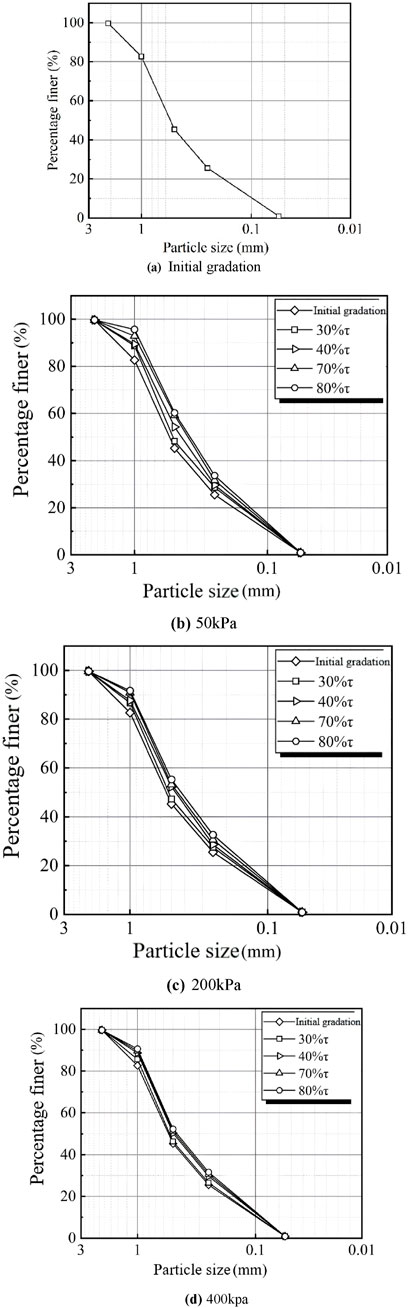
Figure 3. Evolution of particle graduation curves under different vertical stresses. (A) Initial gradation. (B) 50 kPa. (C) 200 kpa. (D) 400 kpa.
4 Creep model
4.1 Singh-Mitchell creep model
Since the creep of calcareous sand has nonlinear characteristics, Singh-Mitchell creep model (Singh and Mitchell, 1968) is commonly used to describe the nonlinear creep behaviour of soils, and the parameters of Singh-Mitchell model are easy to obtain and the model is widely applied, so this creep model is used to describe the shear creep behaviour of calcareous sand, and the model expression is as follows (Equation 2):
Where:
Since the Singh-Mitchell creep model is established based on triaxial tests, the expression of the direct shear creep model for calcareous sand needed to rewritten as:
Where: D is the shear stress level, that is, the ratio of shear stress S to shear strength τ; A, α, m, and t have the same meaning as above.
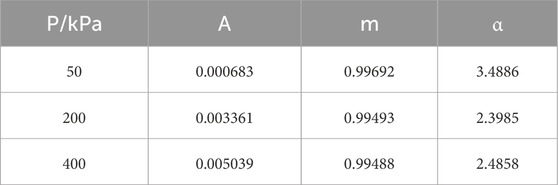
According to the direct shear creep test results in this article, the specific values of Singh-Mitchell model parameters A, α, and m under different vertical stresses were obtained through calculation, as shown in Table 3.
Substitute the specific values in Table 3 into Equation 3 to obtain the following relationship between shear strain and time:
Establish a model fitting curve for the relationship between shear strain and time based on Equations 4–6, and compare it with the direct shear creep test curve in this paper, as shown in Figure 4.
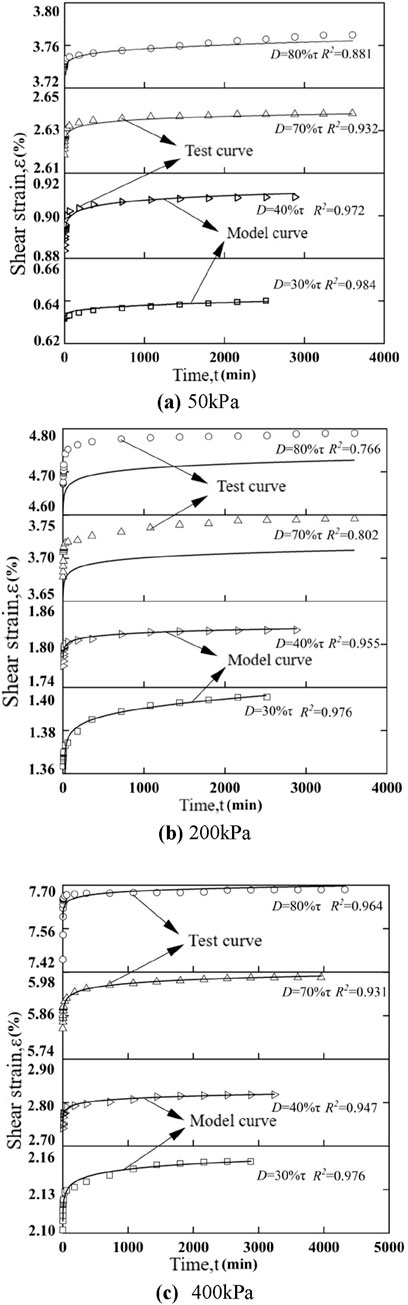
Figure 4. Comparison between Singh-Mitchel model fitting curve and experimental values under different vertical stresses. (A) 50 kPa. (B) 200 kPa. (C) 400 kPa.
From Figure 4, it can be seen that under different vertical stresses, when the shear stress level is low, the error between the model fitting curve and the experimental curve is small. But as the shear stress level increases, the error between the model fitting curve and the experimental curve continues to increase. For example, in Figure 4C, when p = 400 kPa and D = 0.3, the error between the model fitting curve and the experimental curve is very small, and the correlation coefficient R2 between the two curves is 0.976; But when D increases from 0.3 to 0.8, it can be seen that there is a significant error between the model fitting curve and the experimental curve, and the correlation coefficient R2 between the two curves is 0.485. This indicates that at higher shear stress levels, the correlation between the model fitting curve and the experimental curve is not high, and the Singh Mitchell creep model cannot accurately simulate the shear creep deformation of calcareous sand.
4.2 Creep model considering particle breakage
Particle breakage is a significant characteristic which can affect the deformation and the strength of calcareous sand (Hassanlourad et al., 2008; Wu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2018; Huang R et al., 2022). Have reported that calcareous sand is subject to particle breakage under stresses. Li et al. believe that the particle breakage of calcareous sand has an impact on its creep and the particle breakage is positively correlated with the creep deformation. Also, Chen et al. (2019); Chen and Hu (2020) have the similar conclusion in their researches.
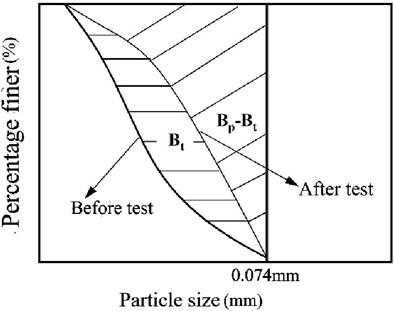
According to the results of the particle sieving test of calcareous sand samples before and after the creep test in Section 3.2, the calcareous sand has different degrees of particle fragmentation during the shear creep test, and the degree of particle fragmentation increases with the increase of the shear stress level. The reason why the error between the calculated curve of the Singh-Mitchell creep model and the test curve is significantly larger at higher shear stress levels is that the effect of particle fragmentation is not considered. In view of this, a creep model that takes into account particle breakage in calcareous sand will be developed in the following. Firstly, the particle fragmentation of calcareous sand at different shear stress levels under different vertical stresses in straight shear creep tests is quantitatively described. In order to describe the particle breakage, Lee and Farhoomand (1967) suggested that the ratio of the change of particle size before and after loading with a content of 15% in the particle grading curve can be used to describe the particle breakage of earth-rock dam filter material. However, the ratio calculated by this method is usually high. Hardin (1985) suggested that the concept of relative crushing rate Br, the ratio of total crushing amount Bt to crushing potential Bp, is used to quantitatively describe the particle breakage. The total crushing amount Bt refers to the area between the crushing grading curve and the initial grading curve in the grading figure, and the crushing potential Bp refers to the area between the initial grading curve and the grading curve with a particle size of 0.074 mm in the particle graduation figure (shown in Figure 5).
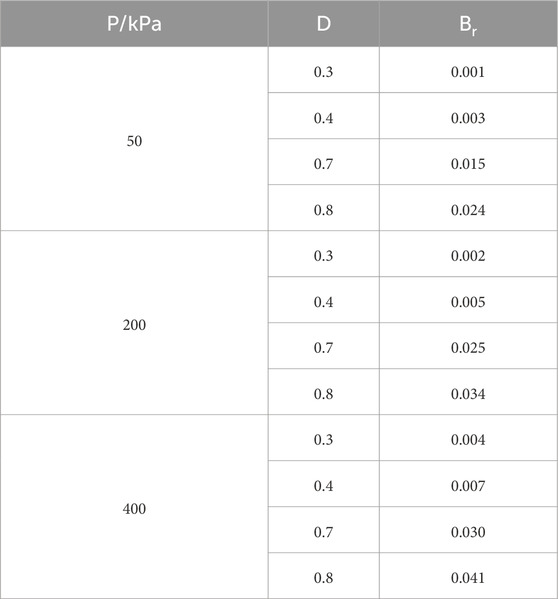
In this paper, we adopted Hardin’s method to obtain the particle breakage index—Br (shown in Table 4).
After the relative fragmentation rate Br is obtained, the relative fragmentation rate Br is introduced into the creep equation to establish a creep model considering particle fragmentation. There are three main factors that cause the creep of calcareous sand: particle rearrangement, particle sliding and particle crushing (Chen, 2020). Since the traditional Singh-Mitchell creep model only considers particle rearrangement and particle sliding, but not particle crushing, this paper introduces a model parameter on particle crushing based on the traditional Singh-Mitchell creep model. Wang et al. (2011a) found that there is an approximately linear relationship between creep caused by particle crushing and particle crushing in the creep process of granular materials:
where:
where A, m and α have the same meaning as in Section 4.1 and Br is a parameter on particle fragmentation. The results of the straight shear creep test were fitted using Equation 8, and the specific values of the parameters A, α, m, and βa of the improved Singh-Mitchell model under different vertical stresses were calculated and are shown in Table 5. Substituting each of the above parameters into Equation 8, the expression of the model was obtained under different vertical stresses:
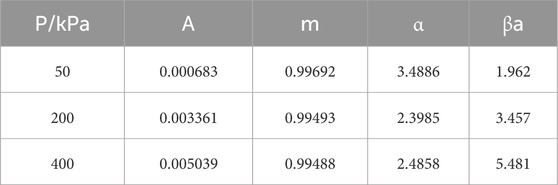
Table 5. The parameters of creep model considering particle breakage under different vertical stresses.
Based on Equations 9–11, the model curves and test curves considering particle crushing under different vertical stresses are plotted in Figure 6.
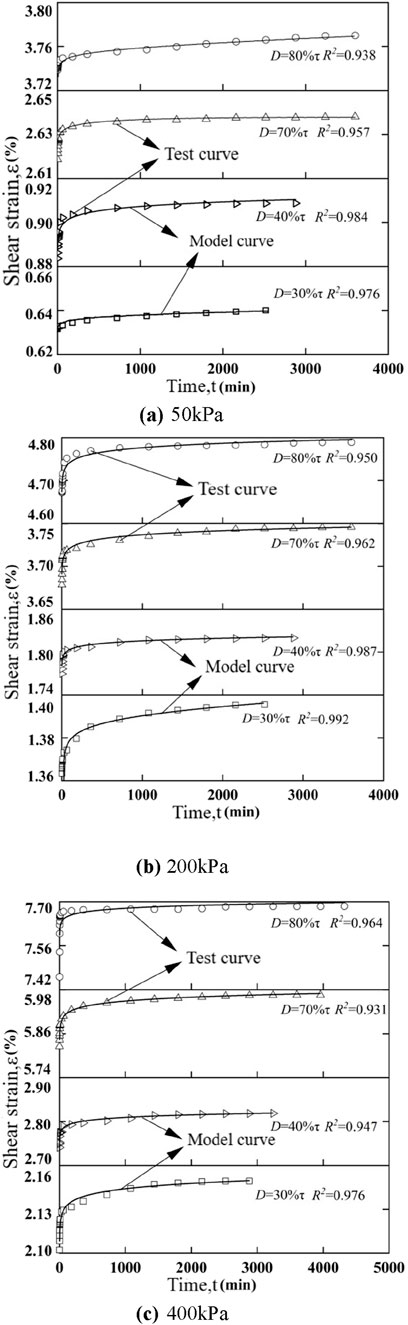
Figure 6. Creep model considering particle breakage fitting curve under different vertical stresses. (A) 50 kPa. (B) 200 kPa. (C) 400 kPa.
By comparing the indoor test curves and the crushing model curves in Figure 6, it can be seen that, regardless of higher or lower shear stress levels, the fitted curves of the calcareous sand shear creep model considering particle crushing are basically consistent with the test values, with correlation coefficients of more than 0.9, which is consistent with the law that the shear creep deformation grows faster at the beginning, and then tends to be stabilised gradually. Compared with the traditional Singh-Mitchell model, this model can more accurately describe the shear creep of calcareous sand around the foundation of island structures. For engineering practice, a combination of empirical modelling and indoor testing can be used to obtain data through multiple sets of tests, use the model to verify the validity of the data, and introduce empirical coefficients for correction if the sample size is large enough.
5 Numerical modeling of particle flow in calcareous sand
5.1 Numerical modeling of PFC2D particle flow
The shear creep behavior of calcareous sand specimens under different levels of vertical and shear stresses was numerically simulated using PFC2D particle flow software to reveal the shear creep of calcareous sand and the particle crushing mechanism in the shear creep process from a fine viewpoint, and further verify the applicability of the shear creep model considering the particle crushing of calcareous sand.
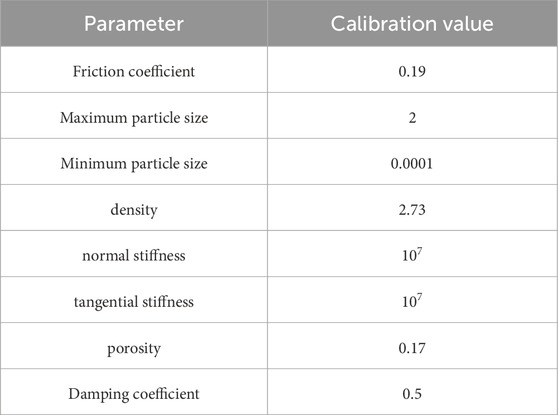
In the PFC2D numerical model, there are many model parameters that are usually difficult to obtain from indoor experiments but need to be calibrated before running the PFC2D particle flow program. Determining reasonable fine-scale parameters is a critical step in numerical simulation (Li et al., 2023). Typically, most researchers use the trial-and-error method to calibrate the model parameters, i.e., by continuously adjusting the model parameters and performing trial-and-error calculations until the closest experimental results are found, and then selecting this set of model parameters for formal simulations (Fu et al., 2023).
In the numerical simulation of the PFC2D particle flow model, the parameters such as density, porosity, and maximum and minimum particle sizes are directly used from the indoor experiments. The remaining fine-scale parameters such as particle surface friction coefficient, normal stiffness, tangential stiffness, and damping coefficient are selected by the ‘trial-and-error’ method, and the initial values of these parameters are based on Gao et al. (2023), Lu, 2022, and then through the analysis and trial-and-error of the change trend of the simulation results for many times, the fine-tuning parameters were continuously fine-tuned in order to achieve the simulation curves and the indoor creep test curves with the same change trend, but the simulation values and experimental values are allowed to have a difference. Eventually, the shear strain curves of the simulation results showed a rapid increase followed by a smooth development, corresponding to the decelerated creep stage and the stable creep stage in the experiment, respectively. Finally, the main fine view parameters of calcareous sand were obtained as shown in Table 6 below.
5.2 Simulation results and analysis
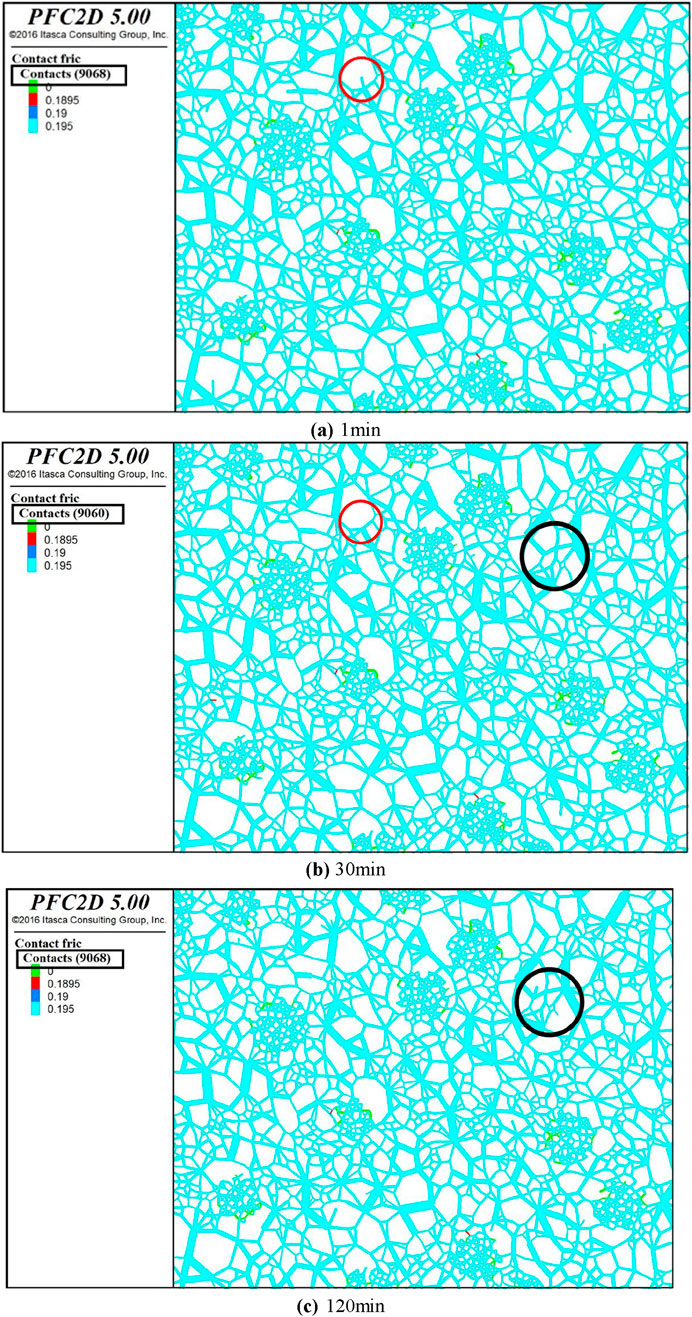
By running the PFC2D particle flow program with p = 400 kPa and D = 0.8 for the test group of calcareous sand, we get the variation of the contact force chain of its particle flow numerical model at different computation times as shown in Figure 7 below.
The factors that cause creep in calcareous sands are particle rearrangement, particle sliding and particle fragmentation, while the forms of particle fragmentation can be classified into three types, i.e., overall fragmentation, localised fragmentation and apparent abrasive damage (Chen, 2020). Multiple transfer paths are formed between particles through contact, and the transfer of force between particles is known as force chain. In Figure 7, the sky blue lines indicate the contact force chains of calcareous sand particles, the thicker lines indicate the strong force chains, the thinner lines indicate the weak force chains, and the numbers inside the brackets of Contacts represent the total number of particles in contact. The contact force chains in this numerical model are not uniformly distributed and change over time, and the total number of contacts also changes over time, as shown by the rounded and boxed boxes in the figure.
The disappearance of the force chain indicates that the particles originally in contact with each other did not produce interaction force at a certain moment, it can be inferred that at this time there is a sudden fracture of the particles, that is, in the macroscopic creep of particles in the long-term constant shear stress under the action of the local crushing or the overall crushing. The effect of the disappearance of the force chain on macroscopic creep is inferred according to the creep factor. First is the particle rearrangement, shear start, the particles are affected by the force and change the contact position, at this time the shear strain is very fast, the force chain is roughly formed; then the particle sliding, the particles mainly occur in the local crushing and abrasive damage, the particle surface and the edge of the load production occurs in the abrasive and crushing, the formation of a number of fine particles as well as a large number of powder particles, the local crushing will result in the disappearance of the contact force chain; and finally, the particles as a whole crushing, the overall crushing. Finally, there is overall particle crushing, in which the particles are loaded and crushed as a whole, forming several small particles with relatively small sizes, and the contact force chain disappears as well.
The appearance of the force chain indicates an expansion of the strain, the position of the crushed particles is adjusted under the continuous action of the shear force, the internal pore space is refilled, the particles are again in contact with each other, and the force is generated again.
Figures 8, 9 below show the single particle fragmentation of calcareous sand at different moments. In order to better study the particle crushing in the model, two representative rigid clumps are selected as the analysis object. The rigid clumps are composed of several dark green particles (the surrounding red, green and sky blue particles are ordinary particles, which can be ignored), and the magnitude of the contact force between the particles inside the clumps is indicated by different colors, with the red color being the largest, followed by the orange, yellow, and green colors, and the blue color being the smallest. Red is the largest, followed by orange, yellow and green, and blue is the smallest. The author named the two rigid clusters as particles A and B, respectively, located in different positions of the shear box.
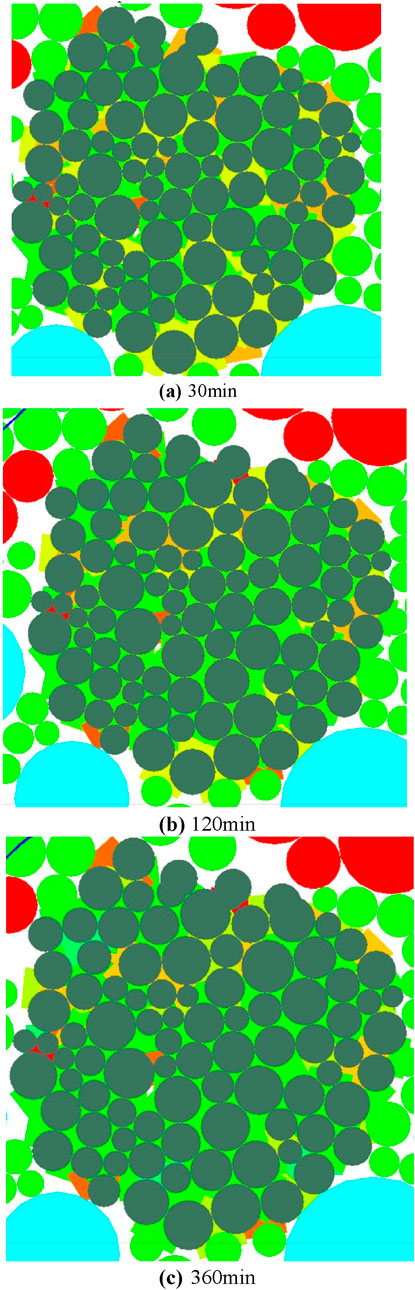
Figure 8. Particle fragmentation of particle A at different moments. (A) 30 min (B) 120 min (C) 360 min.
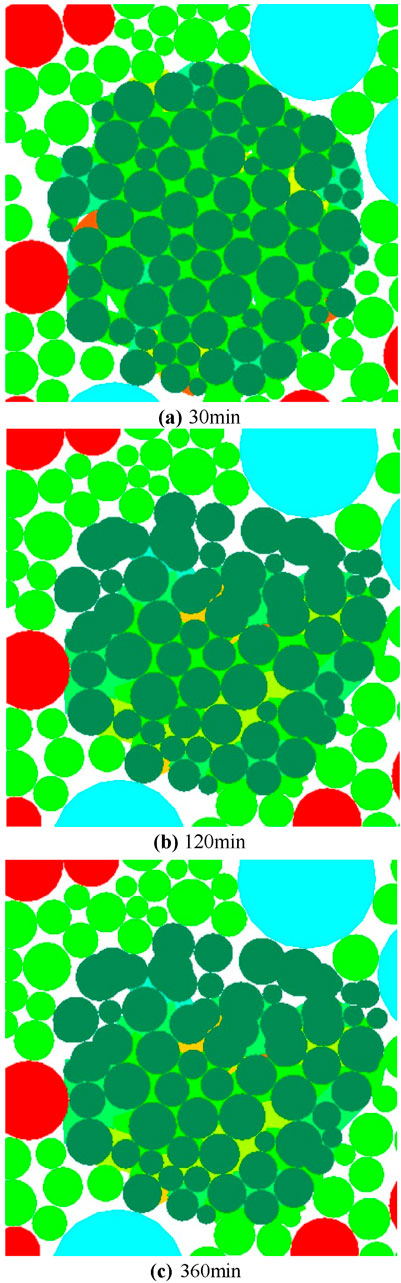
Figure 9. Particle fragmentation of particle B at different momentsmoments. (A) 30 min (B) 120 min (C) 360 min.
Stress corrosion is a phenomenon in which damage occurs to a material under specific stress conditions, and in the calcareous sand shear tests in this paper, stress corrosion manifested itself in the form of abrasion and crack damage of the particles. Stress corrosion of calcareous sand is caused by the interaction between the contact stresses on the surface of calcareous sand and its internal structure. The creation of cracks is usually hidden, mainly concentrated in stress concentrations and structural weaknesses, while the cracks formed weaken the strength of calcareous sand particles. Over time, under the action of shear, these stress corrosion-induced cracks will expand along the locations of low tectonic strength, eventually leading to the complete destruction of the calcareous sand particles.
Combined with Figure 7 it is found that the calcareous sand specimens have different degrees of particle fragmentation at different moments; and the fine-scale mechanism of calcareous sand shear creep can be obtained: at the initial stage, the calcareous sand specimens are relatively loose, and the particles are relatively less tightly adhered to each other. Therefore, the particles of calcareous sand specimen in the early stage of the shear stress applied to the particles of the first relative sliding, and there is no obvious particle crushing phenomenon, in the numerical model for the calcareous sand specimen affected by the external force, clump internal particle contact force increases, macroscopically manifested as a rapid increase in the shear strain of the calcareous sand; with the development of time, this time, the calcareous sand specimen occurs in a part of the particles of the crushing, the shear creep of the calcareous sand specimen. This is due to the constant shear stress calcium sand particles are stress ‘corrosion’, part of the calcium sand particles of the number of microcracks with the growth of time began to increase, and toward the development of larger cracks, calcium sand microstructure inside the qualitative change, in the numerical model is specifically expressed as a rigid cluster clump inside the particles of the relative displacement, the contact force between the particles occurred displacement, and the contact force between particles is also gradually reduced. This led to the deterioration of the mechanical parameters of the calcareous sand particles, i.e., the calcareous sand particles underwent stress corrosion, and could no longer withstand the shear stress specified in the original test, and eventually fractured along the cracks, and the particles were crushed; later on, the larger particles in the calcareous sand specimen were gradually crushed into smaller particles, and the smaller particles were adjusted through the position, and gradually the pore spaces inside the calcareous sand specimen were filled up, and the creep deformation of calcareous sand continued to grow. The creep deformation of the calcareous sand continues to grow; finally, the particle crushing of the calcareous sand reaches the threshold value and no longer grows, and the creep deformation of the calcareous sand also reaches stability in the end.
Particles A and B have different internal contact forces at the same moment due to their different positions. At the calculation time of 30 min, i.e., at the beginning of the direct shear creep test, particle A, which is closer to the shear surface, is subjected to a higher stress first (represented by the contact force in red in Figure 9), and also undergoes stress corrosion before particle B, which ultimately manifests itself in the crushing of particle B. The two representative particles, however, are not subjected to the same stress. However, both representative particles will experience the following particle crushing process: stress - stress corrosion - crushing.
Through the programmed simulation, the numerical model of calcareous sand particles flow for p = 400kPa, D = 0.8 test group and other test groups are compared with the experimental results and empirical model as shown in Figure 10. Similar conclusions can be drawn from the analyses that the main cause of particle breakage is stress ‘corrosion’ of calcareous sand particles.
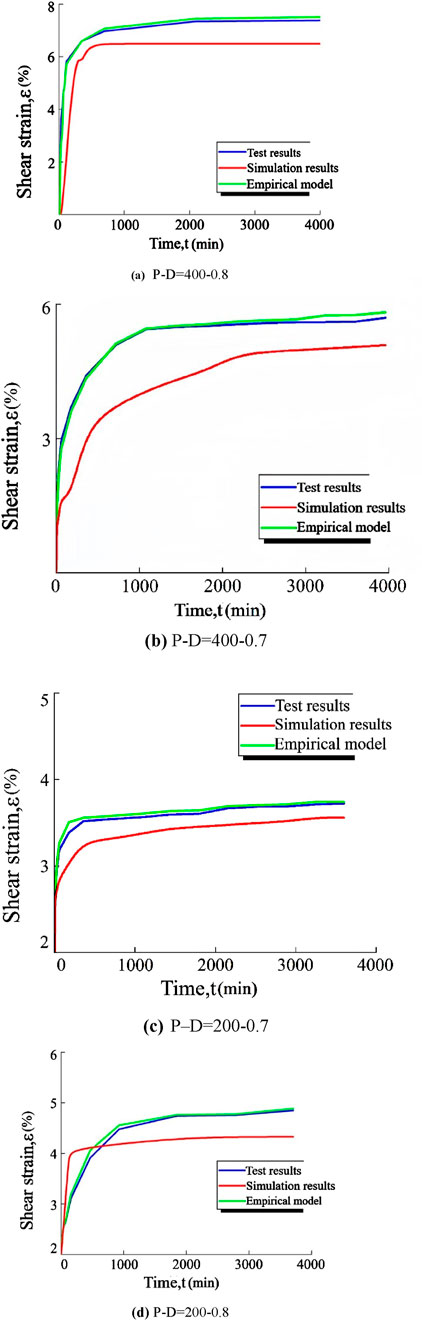
Figure 10. Numerical modeling of particle flow in calcareous sands of other tests compared with experimental results and experimental model. (A) P-D = 400–0.8. (B) P-D = 400–0.7. (C) P–D = 200–0.7. (D) P-D = 200–0.8.
5.3 Error analysis
As can be seen from Figure 10, although the numerical simulation curves and the experimental curves and the empirical model curves have a good similarity, there is a slight error in the comparison results. The gap between the numerical model and the indoor experimental results is mainly due to the fact that the numerical model has not taken into account the shape difference of calcareous sand, which cannot completely simulate the calcareous sand occlusion with each other and lead to small stress. Moreover, the contact of calcareous sand particles in the real situation is more complicated, and the state of each particle is not the same, so it is not possible to achieve complete consistency with the reality in the calibration of fine view parameters. The current simulation can achieve good similarity between the numerical model curves of particle flow in most of the test groups and the indoor test curves, which have the same trend of change, and can simulate the shear creep of calcareous sand close to the real situation, which assists in the verification of the crushing model in section 4.2.
6 Conclusion
Through the direct shear creep test of calcareous sand, the creep curve of calcareous sand under constant load was obtained, and the creep model was studied based on the test results. The conclusions are as follows:
(1) The shear creep of calcareous sand is nonlinear and can be divided into two stages: decelerating creep stage and stable creep stage. With the increase of shear stress level, creep deformation increases.
(2) Particle breakage is one of the factors affecting the shear creep of calcareous sand, which can amplify the creep deformation. When the load is low, the particle breakage is not obvious. However, when the load rises, more particle breakage occurs during creep.
(3) The traditional Singh-Mitchell creep model was used to simulate the shear creep law of calcareous sand, and it was found that the Singh-Mitchell model curves had a small error with the experimental curves at lower shear stress levels, but did not agree with the experimental curves at higher shear stress levels
(4) Capable of considering the shear creep induced by the fragmentation of calcareous sand particles was developed by introducing a parameter βa on particle fragmentation. After comparison with the experimental results, the model can accurately describe the shear creep of calcareous sand around the foundation of the South China Sea reef structures.
(5) By comparing with the results of the direct shear creep tests and the empirical model, the numerical model of calcareous sand particle flow established based on the PFC2D particle flow procedure has good similarity with the test curves and the empirical model curves. The shear strain shows a trend of rapid increase followed by stable development, which can reasonably describe the shear creep deformation of calcareous sand under real conditions and verify the validity of the crushing model.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
BT: project administration, funding acquisition, supervision, conceptualization and writing–review and editing. XH: Writing–original draft, writing–review and editing, data curation and formal analysis. WZ: Writing–original draft, investigation, methodology, and formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42367020), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2024GXNSFAA010450), and the project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Geotechnical Mechanics and Engineering (2016-A-01).
Acknowledgments
We thank all authors for their contributions, the reviewers for valuable comments, and the Frontiers Editorial Office for improving the lay out of this Research Topic.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bai, B., Xu, T., Nie, Q., and Li, P. (2020). Temperature-driven migration of heavy metal Pb2+ along with moisture movement in unsaturated soils. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 153, 119573. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119573
Bai, B., Zhou, R., Yang, G., Zou, W., and Yuan, W. (2023). The constitutive behavior and dissociation effect of hydrate-bearing sediment within a granular thermodynamic framework. Ocean. Eng. 268, 113408. doi:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113408
Cao, M., and Ye, J. H. (2019). Creep-stress-time four parameters mathematical model of calcareous sand in South China Sea. Rock Soil Mech. 40 (5), 1771–1777. doi:10.16285/j.rsm.2018.1267
Cao, P., Jiang, M. J., and Ding, Z. J. (2020). Effects of particle size on mechanical behaviors of calcareous sand under triaxial conditions. Jpn. Geotech. Soc. Spec. Publ. 8 (5), 182–187. doi:10.3208/jgssp.v08.c54
Chen, B., Chao, D. J., Wu, W. J., and Hu, J. M. (2019). Study on creep mechanism of coral sand based on particle breakage evolution law. J. Vibroengineering 21 (4), 1201–1214. doi:10.21595/jve.2019.20625
Chen, B., Deng, J., Hu, J. M., Zhang, J. L., and Zhang, T. (2022). Macro and micro experimental study on fractal fragmentation characteristics of calcareous sand during one-dimensional creep. Rock Soil Mech. 43 (7), 1–11. doi:10.16285/j.rsm.2021.1723
Chen, B., and Hu, J. M. (2020). Fractal behavior of coral sand during creep. Front. Earth Sci. 8, 134. doi:10.3389/feart.2020.00134
Chen, J. M. (2020). “Creep behavior and equation including particle breakage for calcareous,”. Xiangtan University. Master Thesis. doi:10.27426/d.cnki.gxtdu.2020.000654
Choo, H., Kwon, M., Touiti, L., and Jung, Y. (2020). Creep of calcareous sand in Tunisia: effect of particle breakage at low stress level. Int. J. Geo-Engineering 11 (1), 16–20. doi:10.1186/s40703-020-00123-2
Fu, X., Hou, D., and Li, Q. (2023). Characterization and calibration of flow macro fine-scale parameters of soft soil creep particles. Geotech. Found. 37 (03), 501–505.
Gao, X., Gao, Y., Sun, K. T., and Shi, T. G. (2023). Particle fragmentation and energy evolution in calcareous sands during shearing. 62(6), 11–21. doi:10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2023d023
Hardin, B. (1985). Crushing of soil particles. J. Geotechnical Eng. 111 (10), 1177–1192. doi:10.1061/(asce)0733-9410(1985)111:10(1177)
Hassanlourad, M., Salehzadeh, H., and Shahnazari, H. (2008). Dilation and particle breakage effects on the shear strength of calcareous sands based on energy aspects. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 6 (8), 108–119.
Huang L, L., Liu, X., and Lan, H. X. (2022). Investigation on characteristic shape of calcareous sand and associated effect on undrained shear strength. J. Eng. Geol. 32 (02), 378–386. doi:10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2022-0049
Huang R, R., Guo, C. C., Cao, D. F., and Liu, Z. X. (2022). An improved Murayama rheology model to describe the creep behavior of the mixture composed by calcareous sand and polyurethane polymer grouting. J. Eng. Geol. 32 (01), 295–302. doi:10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0737
Lade, P. V. (2009b). “Creep, stress relaxation, and rate effects in sand,” in Proceedings of the 17th international conference on soil Mechanics and geotechnical engineering. Alexandria: IOS Press.
Lade, P. V., Liggio, C. D., and Nam, J. (2009a). Strain rate, creep, and stress drop-creep experiments on crushed coral sand. J. Geotechnical Environ. Geoengin. 135 (7), 941–953. doi:10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000067
Lee, K. L., and Farhoomand, I. (1967). Compressibility and crushing of granular soil in anisotropic triaxial compression. Can. Geotechnical J. 4 (1), 68–86. doi:10.1139/t67-012
Li, Z., Liu, G., and Yan, C. (2023). Research on particle flow model construction and fine-scale parameter calibration method for rocks containing primary hidden microfractures. J. Eng. Geol. 31 (6), 1842–1853. doi:10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0594
Liang, R. K., Zhang, Q. J., Zhang, C., Li, D., Su, D., and Li, Q. (2021). Creep characteristics and model parameters of Qianhai soft soil. Rock Soil Mech. 43 (Suup2), 133–136.
Liu, C. Q., and Wang, and R. (1998). Preliminary research on physical and mechanical properties of calcareous sand. Rock Soil Mech. 19 (1), 32–37. doi:10.16285/j.rsm.1998.01.006
Lu, Z. C. (2022). “Research on crushing mechanism of calcareous sand considering real particle shape,”. Jiangsu University of Science and Technology. [dissertation/master's thesis]. [Zhenjiang]. doi:10.27171/d.cnki.ghdcc.2022.000870
Poulos, H. G., Chua, E. W., and Hull, T. S. (1984). Settlement of model footings on calcareous sand. Geotech. Eng. 15, 21–35.
Salem, M., Elmamlouk, H., and Agaiby, S. (2013). Static and cyclic behavior of North Coast calcareous sand in Egypt. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 55 (12), 83–91. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2013.09.001
Shen, J. H., Hu, M. J., Wang, X., Zhang, C. Y., and Xu, D. S. (2021). SWCC of calcareous silty sand under different fines contents and dry densities. Front. Environ. Sci. 9, 682907. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2021.682907
Singh, A., and Mitchell, J. K. (1968). General stress-strain-time function for soils. J. Clay Mech. Found. Div. 94 (SM1), 21–46. doi:10.1061/jsfeaq.0001084
Sun, Y., and Chen, C. (2019). Fractional order creep model for coral sand. Mech. Time-Dependent Mater. 23 (4), 465–476. doi:10.1007/s11043-018-9400-5
Wang, J., Fan, P., Wang, M., Dong, L., Ma, L., and Gao, L. (2020). Experimental study of one-dimensional compression creep in crushed dry coral sand. Can. Geotechnical J. 57 (12), 1854–1869. doi:10.1139/cgj-2019-0406
Wang, Y. S., Ma, L. J., Wang, M. Y., Lv, Y. R., Lu, D., and Fan, P. X. (2018). A creep constitutive model incorporating deformation mechanisms for crushable calcareous sand. Arabian J. Geosciences 11 (20), 623–628. doi:10.1007/s12517-018-3982-8
Wang, C., Zhan, C., and He, P. (2011a). Creep and particle breakage bahavior of rockfill in triaxial compression testing. J. Civ. Archit. Environ. Eng. 33, 57–62.
Wang, X. Z., Jiao, Y. Y., Wang, R., Hu, M. J., Meng, Q. S., and Tan, F. Y. (2011b). Engineering characteristics of the calcareous sand in Nansha Islands. South China Sea. Eng. Geol. 120 (1), 40–47. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.03.011
Wen, B., Yuan, N. Z., Kong, L. W., and Chen, C. (2021). Application practice and settlement estimation of composite ground for high-rise buildings on coral sand site of hydraulic fill. China Civ. Eng. J. 54 (12), 85–93. doi:10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.12.006
Wu, X. H., Cai, Y. Q., Xu, S. F., Zhuang, Y. C., Wang, Q. X., and Wang, Z. (2020). Effects of size and shape on the crushing strength of coral sand particles under diametral compression test. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 80 (2), 1829–1839. doi:10.1007/s10064-020-01972-y
Xu, D., Zhang, S., and Qin, Y. (2024). Study of the micromechanical properties and dissolution characteristics of porous coral reef limestone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 129 (11), e2024JB029131. doi:10.1029/2024JB029131
Xu, D. S., Yan, J. M., and Liu, Q. (2021). Behavior of discrete fiber-reinforced sandy soil in large-scale simple shear tests. Geosynth. Int. 28 (6), 598–608. doi:10.1680/jgein.21.00007
Xue, P., Zhou, X. Q., Cai, Y. Y., Ma, L. J., Liao, R. G., and Yu, J. (2020). Triaxial creep characteristics and empirical model for saturated coral sand. Rock Soil Mech. 42 (Suup2), 255–260.
Ye, J. H., Cao, M., and Li, G. (2019). Preliminary study on the creep characteristics of calcareous sand from reclaimed coral reef islands in South China Sea. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 38 (6), 1242–1251. doi:10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0695
Yeernaer, H., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Preliminary experimental study on the volumetric creep of calcareous coral sand. Soil Eng. Found. 36 (1), 89–92.
Keywords: calcareous sand, shear creep, direct shear creep tests, Singh-Mitchell model, particle breakage, particle flow
Citation: Tang B, Huang X and Zhong W (2025) Study on shear creep model of calcareous sand in China South Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1525037. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1525037
Received: 11 November 2024; Accepted: 19 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaolei Liu, Ocean University of China, ChinaReviewed by:
Dongsheng Xu, Wuhan University of Technology, ChinaBing Bai, Beijing Jiaotong University, China
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Huang and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Tang, dGFuZ2JpbkBnbHV0LmVkdS5jbg==
 Bin Tang
Bin Tang Xingyun Huang
Xingyun Huang Weitao Zhong
Weitao Zhong