- 1Department of Computer Science, Changzhi University, Changzhi, China
- 2College of Geological Engineering and Geomatics, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China
- 3Zhongjin Environmental Technology Co., Ltd., Taiyuan, China
In China, the Loess Plateau’s fragile geological structure leads to complex and variable surface subsidence in old gob areas following coal mining activities. Accurately predicting this residual subsidence remains a significant scientific challenge. In this study, a method for residual subsidence prediction using an Exponential Smoothing Long Short-Term Memory (EsLSTM) model is proposed. The investigation centers on the 18,001# old goaf area of the Yangquan Coal Mine in Shanxi Province. Using Sentinel-1A imagery, continuous SAR data from 98 periods were acquired and processed via Enhanced Distributed Scatter InSAR technology. The EsLSTM model was then developed to capture the subsidence time-series characteristics of all surface scatter points and predict future ground subsidence. The analysis reveals that the EsLSTM model delivered excellent accuracy, achieving an
1 Introduction
Ground subsidence, a geological hazard caused by both anthropogenic activities and natural factors, leads to irreversible damage to the environment and resources (Zhao et al., 2016). As the world’s largest coal producer, China’s economic and social development has been significantly supported by coal resources (Dai and Finkelman, 2018). However, large-scale coal mining has caused severe ecological damage, leading to ground movement and changes that damage mining structures, farmland, roads, railways, pipelines, and more. In severe cases, it can result in collapse craters, ground fissures, landslides, and debris flows, threatening the economic development and social stability of mining areas (Yang et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2020). As a result, monitoring and predicting mine subsidence in old goaf is essential for early disaster warning and safeguarding lives and property (Zhang et al., 2024).
Traditional methods such as GNSS or levelling have advantages of high precision but are labor-intensive, costly, time-consuming, and have low resolution and safety issues (Fuhrmann et al., 2015; Fernandez Galarreta et al., 2015; Lyu et al., 2024). They are not ideal for monitoring old goaf subsidence because of the challenges in maintaining control points and their inability to provide large-area, high-resolution monitoring (Liu et al., 2012).
Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) has emerged as an advanced Earth observation technique that enables precise, high-density, and cost-effective monitoring of ground subsidence across large areas (Yang et al., 2014; He et al., 2021a). Differential InSAR (DInSAR) was first proposed by Klees and Massonnet (1998). This method requires two SAR images and external DEM data. Interferometric processing is applied to the two SAR images, captured before and after deformation in the same target area, to generate an interferogram. The DEM is used to simulate the topographic phase, while the flat ground phase is removed using precise orbit information. High-pass (HP) and low-pass (LP) filtering algorithms are then applied to minimize noise and atmospheric effects. One advantage of this technique is the relative ease of obtaining the necessary data, requiring only two SAR images and corresponding DEM data. However, the initial application of DInSAR for monitoring ground deformation in mining areas faced considerable challenges due to spatial and temporal decorrelation, along with atmospheric disturbances. To overcome these limitations, Time Series InSAR (TSInSAR) techniques were developed, which leverage time series analysis for more accurate monitoring.
TSInSAR techniques are categorized based on the characteristics of scatterers at monitoring points into two types: Permanent Scatterers (PS) and Distributed Scatterers (DS) (Xue et al., 2020). PS points exhibit strong backscatter properties and relatively stable phase information, commonly corresponding to man-made structures like buildings, fences, and rocks, thus being prevalent in urban areas (Parizzi and Brcic, 2011). In contrast, DS points lack dominant scatterers within the resolution cell and are composed of multiple sub-scatterers with similar characteristics (Fornaro et al., 2015). This results in less stable phase information for DS points, making them more susceptible to temporal and spatial decorrelation. However, DS points typically correspond to rooftops, bare land, and fallow fields, effectively complementing the sparse monitoring density of PS points in non-urban areas (Chen et al., 2023).
In 2002, Berardino et al. (2002) introduced the SBAS-InSAR technique to extract deformation information from distributed scatterers. The key principle of this method involves generating interferometric pairs from all SAR images using carefully selected spatial and temporal baseline thresholds to form small baseline sets. This ensures that the baselines within each set are closely aligned. For each small baseline set, surface deformation over time is then calculated using the least squares (LS) method. Singular value decomposition is used to solve for possible ill-conditioned equation parameters between sub-baseline sets (Hu et al., 2023). By combining multiple interferograms, A linear deformation model is built using high-coherence points, allowing for the inversion to determine linear deformation rates and elevation errors. Spatial and temporal filtering then removes residual errors, wiping out atmospheric delays, and unraveling nonlinear deformation patterns hidden beneath the surface.
For mining areas predominantly situated in suburban environments, DSInSAR technology provides more comprehensive surface monitoring information, which has been effectively demonstrated in extensive DSInSAR applications for mining area monitoring (Zhao et al., 2019). While both PS and SBAS methods are individually limited to measuring displacements of PS points and DS pixels, respectively (Ng et al., 2017). Their combined application in processing SAR data can yield more extensive interferometric results, inspired by (Guzzetti et al., 2009), enhanced-DSInSAR(EDS-InSAR) was proposed. This technique combines SBAS and PS methods to obtain surface deformation information. The combination functions analogously to LP and HP filters, respectively, filtering out low spatial resolution components associated with deformation and terrain-related signals, as well as the remaining high spatial frequency components. SBAS plays a dual role in this process: firstly, it generates LP deformation time series and LP residual terrain corresponding to DS points; secondly, SBAS estimates residual atmospheric phase delays that persist after initial correction, using GACOS products and ionospheric propagation models. Next, the PS method is applied to the calibrated interferograms to eliminate the low-pass terrain, deformation, and residual atmospheric effects estimated by the SBAS technique. This process ultimately produces time-displacement data related to the PS points. This approach effectively combines the SBAS and PS methods. As a result, it surpasses the effectiveness of using each method independently. This approach allows simultaneous analysis of strong reflectors and distributed targets, generating low-resolution DS results and high-resolution PS results even in the presence of nonlinear trends. The EDS-InSAR method thus demonstrates significant advantages in obtaining nonlinear surface deformation values, absolute deformation accuracy, and coverage area in mining regions.
Existing ground subsidence prediction methods can be classified into three main categories: mathematical statistical models (Ye et al., 2016), empirical models (Tang et al., 2008), and artificial intelligence models (Fan and Zhang, 2019). Artificial intelligence models are widely used due to their parallel computing capabilities, strong fault tolerance, self learning functions, and high prediction accuracy (Pan et al., 2019). The most classic artificial intelligence model is the Back Propagation (BP) model. However, BP models typically use sparse and discontinuous monitoring data from GPS and levelling, which affects the prediction accuracy of ground subsidence. Furthermore, traditional BP models face challenges in fitting the data due to the large number of weights that require training and their high demand for extensive training datasets. This often results in insufficient samples when applied to InSAR tasks. This can result in low prediction accuracy or model failure in areas with complex deformation patterns.
With the wide application of machine learning, utilizing machine learning methods for time-series prediction based on InSAR data has emerged as a prominent research focus. LSTM (Santra and Lin, 2019) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models (Radman et al., 2021) have been particularly prominent in this field. LSTM networks, designed for sequence data, can capture the temporal characteristics of changes in InSAR data and have achieved significant results in time-series InSAR data prediction. However, LSTM networks focus solely on the temporal features of time-series InSAR data, ignoring spatial information, which can affect the accuracy of time-series InSAR image prediction (Nawaz et al., 2022). CNNs, which actively learn image features, can capture spatial features in time-series images. The introduction of the weight-sharing concept in CNNs reduces the number of trainable parameters, making CNNs widely used in time-series InSAR data prediction (Ma et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2020). However, as a feedforward neural network structure, CNNs default to using the last fully connected layer as the output, which makes it difficult to consider different temporal depth features simultaneously, affecting the prediction accuracy of time-series data (He et al., 2021b). Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of integrating InSAR technology with LSTM networks in predicting ground subsidence. For example, research on the Shigouyi Coalfield in China highlighted the success of combining SBAS-InSAR with LSTM, achieving high prediction accuracy by leveraging the strengths of both technologies (Ma et al., 2023). Moreover, the integration of an Attention LSTM (AT-LSTM) model has shown to significantly enhance prediction accuracy by improving the model’s ability to capture temporal dependencies in subsidence data (Liu and Zhang, 2023). Dynamic models that integrate D-InSAR with LSTM have also been developed to account for time-varying subsidence patterns, further improving prediction capabilities in active mining areas (Hou et al., 2022). Convolutional LSTM (ConvLSTM) (Shi et al., 2015) extends the core ideas of LSTM networks by converting the fully connected states in LSTM into convolutional states. He et al. (2023) discussed the use of ConvLSTM neural networks for spatiotemporal prediction of ground subsidence using InSAR data. However, these studies also reveal certain challenges and limitations. Paper (Ma et al., 2023) uses fewer datasets, which may result in less accuracy of predictions in complex environments. The complexity of models like AT-LSTM in Liu and Zhang (2023) introduces computational demands that may limit their practical application, particularly in real-time monitoring scenarios. Paper (He et al., 2023) does not pay attention to the accuracy of the original data set. When constructing the ConvLSTM prediction model, the incoherent region is interpolated, and the sample error is introduced insubtly, data quality directly affects the performance of the algorithm. Additionally, while these models have proven effective in specific mining areas, their generalizability across different geological settings remains a subject of ongoing research. EsLSTM is proposed by Smyl (2020),it aims to explore and propose a enhanced LSTM prediction algorithm that leverages smoothing models to improve prediction accuracy, has the advantage of reducing noise and variability in data and potential applications in various fields, such as finance forcasting, weather and geology prediction.
Shanxi Province, one of China’s largest coal-producing provinces, has made significant contributions to national economic construction and social development but faces serious threats from ground subsidence disasters. Previous studies on ground subsidence in the Shanxi Coal Mine include research by Xia et al., 2023, whos utilized optical images and the PS method to gather ground subsidence information. Their objective was to detect suspected illegal mining sites by analyzing building subsidence data across a broader area. The study by Shi et al. (2020) analyzes unstable areas in Xiangning County and its surrounding regions using C-band Sentinel-1 datasets collected from March 2017 to 2019. The research identifies several unstable sites exhibiting active slope deformations. They all confirmed the feasibility of InSAR technology in mining area monitoring. However, at present, there is a lack of monitoring and prediction of residual subsidence in old goaf based on the SAR images, especially in the Loess Plateau area of Shanxi Province, which is not conducive to the early warning of subsidence disasters.
This study focuses on the 18,001# workface of the old goaf in the Yangquan Coal Mine, Shanxi Province. High-quality ground subsidence data were first obtained using the Sentinel-1 imagery, processed through EDS-InSAR technology. An EsLSTM model was then developed to effectively capture the temporal dynamics of ground subsidence, revealing the spatiotemporal evolution patterns in the mining areas. The EsLSTM model was subsequently applied to predict future subsidence, offering valuable insights for informed decision-making in the rational development and sustainable use of mineral resources. Additionally, the model provides crucial support for early warning systems, subsidence mitigation strategies, and ecological protection efforts, promoting the long-term sustainability of the mining region.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Site selection
The 18,001# working face of the Yangquan Coal Mine, located in Pingding County, Shanxi Province, is illustrated in Figure 1. The working face lies 342 m below the surface, an area characterized by farmland, walnut trees, cement roads, seasonal rivers, and power supply lines, with surface elevations ranging from 1,053 to 1,301 m. The site has an inclined width of 280 m, a strike length of 2000 m, and covers a mining area of 560,000 square meters. The coal seam presents a gentle monocline, with a dip angle of 2–10° and a thickness of 4.25–4.8 m. Mining operations were carried out between January 2018 and December 2019. Post-mining exploration using radio wave transmission identified geological features such as igneous intrusions, river scours, and collapse columns within the working face.
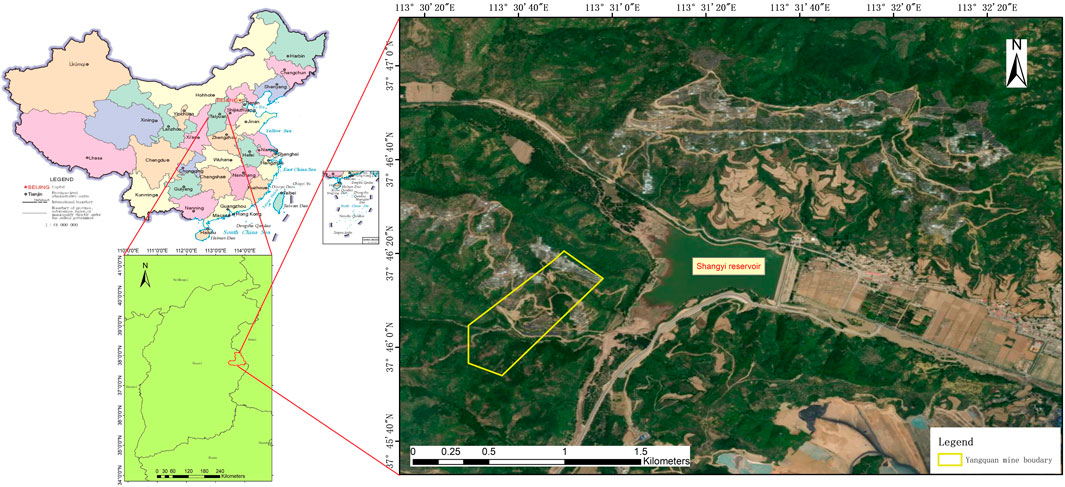
Figure 1. Geographical location of Shangyi resercoir with Yangquan mine. The background is optical remote sensing imagery.
Northeast of the 18,001# working face lies the medium-sized Shangyi Reservoir, primarily used for flood control, with secondary functions of irrigation and water supply. In recent years, the safety of the dam has been compromised by the impact of surrounding goaf areas. Located in the middle-upper part of the Yangquan mining area, the reservoir is influenced by extensive underground mining activities. These mining operations have created widespread goaf regions, leading to surface cracking of varying severity around the reservoir dam at different times. These cracks, caused by underground mining from different periods, have resulted in structural damage to houses and roads in the area. Since August 2019, an increase in damage has been observed in previously affected houses, with new cracks emerging and existing ones widening in the buildings and ground surrounding the reservoir management station. This poses a significant threat to both the safety of the reservoir and nearby property.
The focus of this study is on monitoring deformation around the Shangyi Reservoir, using the 18,001# working face of the Yangquan Coal Mine as a case study to validate the accuracy and reliability of the EsLSTM algorithm.
2.2 Data selection
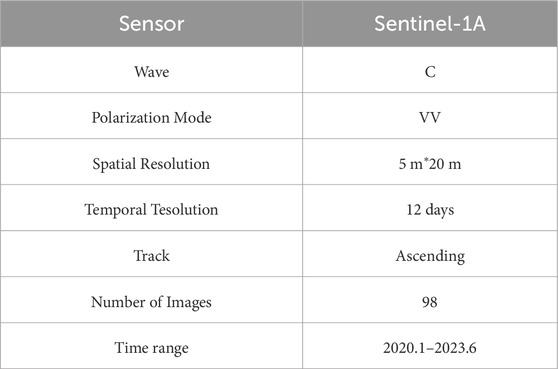
This project utilized C-band data from the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-1 satellites, which have a 12-day revisit cycle and a spatial resolution of 20 m. As part of ESA’s Copernicus program, the Sentinel-1 mission is designed for all-weather, day-and-night radar imaging in a polar orbit, serving both terrestrial and marine applications. Initially, the mission comprised two Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellites, Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B. However, due to the malfunction of Sentinel-1B, only Sentinel-1A is currently operational, extending the observation cycle from the original 6–12 days (see Table 1).
For this project, an account was registered on the Copernicus Open Access Hub, and a Python program was developed for automated data downloading. Sentinel-1 data from January 2020 to June 2023 were downloaded for the study.
The European Space Agency (ESA) provided precise orbit ephemerides (POD) data for all Sentinel-1 SAR data used in the study. The authors also employed a three-arc-second Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Digital Elevation Model (DEM) obtained from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Additionally, the research utilized data from the Generic Atmospheric Correction Online Service for InSAR (GACOS) covering the period from January 2020 to June 2023. GACOS, supported by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) through the Centre for the Observation and Modelling of Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Tectonics (COMET), as well as the LICs and ESA-MOST Dragon-4 programs, employs the Iterative Tropospheric Decomposition (ITD) model (Yu et al., 2018) to separate stratified and turbulent signals from the total tropospheric delay. This process generates high spatial resolution zenith total delay maps, which are used to correct InSAR measurements and for various other applications.
2.3 EDS-InSAR
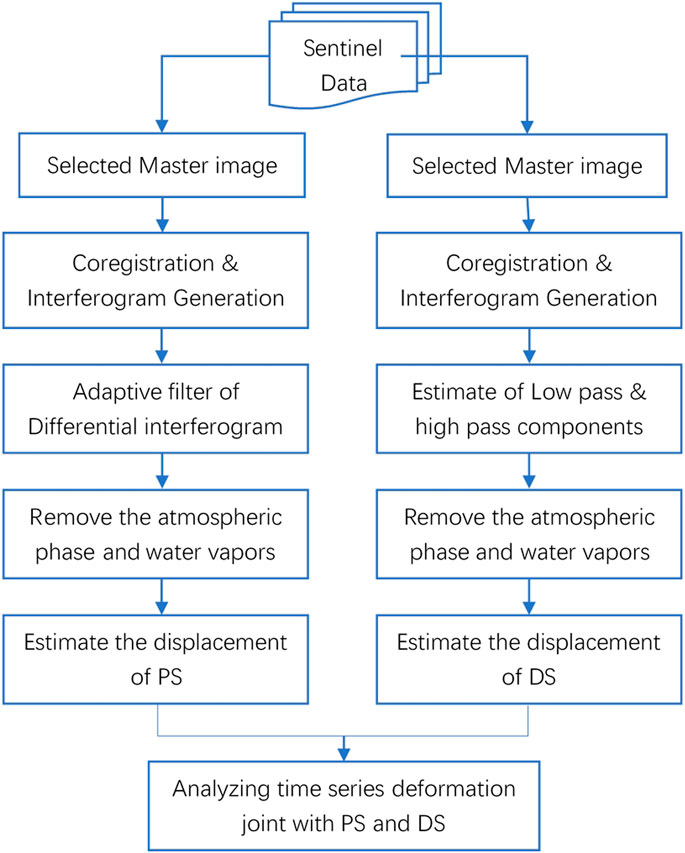
The main steps of the EDS-InSAR technology are divided into three stages. First, identify and process the Permanent Scatterer (PS) pixels. Then, identify and process the Distributed Scatterer (DS) pixels. Finally, combine the PS and DS to obtain comprehensive deformation products of the deformation area, including cumulative deformation, deformation rate, and deformation time-series information. As shown in Figure 2, this is the flowchart of the technology.
The first step involves selecting a master image from the input SLC dataset based on a set baseline threshold, and forming interferometric pairs with the master image and other images. The other images are paired with this master image to form interferometric pairs. All images are co-registered and resampled to the selected master image to ensure the successful generation of interferometric pairs. Each interferometric pair undergoes interferometric processing based on the connection relationship of the pairs. All images need to be registered and resampled to the reference file, which involves oversampling by four factors (at least two) to avoid dense and confusing interference fringes in the case of large baselines. Unlike standard InSAR processing, the PS method does not involve spectral shifting and ordinary Doppler bandwidth filtering because it targets point targets. Differential interferograms are generated for each interferometric pair. The filtered differential interferograms are produced using adaptive filters. The atmospheric phase in the differential interferograms is estimated and removed to generate deformation results, including rates and elevation correction values. The sequences and deformation rates for all PS points are geocoded and projected into the mapping system.
The third step involves analyzing time series deformation jointly with PS and DS. The residual atmospheric phase derived from the SBAS method is utilized to calibrate the PS points. The residual topographic phase obtained using the PS method is used to calibrate the DS points. A comparative analysis is performed between the DS and PS corresponding pixels. Points with significant residuals are eliminated to ensure consistency in the deformation results obtained from both DS and PS targets. Ultimately, deformation information for strong reflectors and distributed targets in the deformation area is obtained.
2.4 Description of the EsLSTM algorithm
This method was first proposed by Smyl in 2019. It integrates the Exponential Smoothing (Es) with the LSTM network. This hybrid approach, which combines statistical modeling with machine learning algorithms, leverages the strengths and mitigates the weaknesses of both. It is capable of effectively learning the global parameters of long sequences and the local parameters of subsequences, achieving cross-learning.
The method starts with deseasonalizing the data using the ES model, followed by predictions made with the LSTM model. Finally, the forecast results are produced. Seasonality is one of the key components of time series, referring to systematic movements that have different average values in certain periods and repeat with similar intensity over time. Seasonal variations can be caused by various factors, such as weather, calendar, or economic conditions. After preprocessing, InSAR mining subsidence sequences can be provided as digital vectors with timestamps.
The sequences themselves exhibit seasonality, but the ground displacement process caused by goaf in mining areas is a stochastic process that does not have seasonal characteristics. To calculate periodical components, it is first necessary to employ a state-space exponential smoothing (ES) model. The initial periodical components for each seriesand the smoothing coefficients are fitted alongside the global neural network weights using stochastic gradient descent (SGD). Once the corresponding series values and parameters are determined, the periodic components can be calculated and applied for deseasonalization. Secondly, for non-seasonal data, the neural network must generate forecasted steps ahead (e.g., 30 points for the annual series of Sentinel-1A), followed by reseasonalization to produce the forecast output. This neural network is not local, enabling it to learn from multiple time-series simultaneously. When a dataset includes a significant number of sequences from unknown sources, it is reasonable to assume that these sequences can be grouped into subsets. In such cases, using separate models for each subset rather than a single model for the entire dataset can potentially improve overall prediction accuracy. However, it is difficult to group these sequences, as those from different sources may exhibit similar characteristics and behaviors. Additionally, using generic metrics for clustering sequences may not effectively improve prediction accuracy. To address this, ensemble learning algorithms train multiple models (including neural networks and persequence parameters) simultaneously and force them to focus on different subsets of sequences, partially solving this issue.
The model uses Holt’s method with multiplicative seasonality, adjusting for trends and seasonal variations in the data. Parameters are optimized using stochastic gradient descent. The LSTM operates on the preprocessed data, generating predictions that are later adjusted to reflect the original seasonal trends. Considering that InSAR timing monitoring values are negative and usually monotonically decreasing, we choose the Holt Gardner (2006) and Holt-Winters Kang et al. (2017) models with multiplicative periodicity. By removing its linear trend, its nonlinear trend can be well learned using neural networks. The updating formula is as follow:
where
As mentioned above, EsLSTM operates on aperiodic, non-normalized. It involves three sets of parameters during the process of predicting the data shown above: Local constants, Global constants, and Local states. Parameters such as initial seasonal components remain unchanged throughout the series. These are learned across multiple series, like the weights in the neural network. These evolve over time, adapting to the changes in the data as the series progresses. Implemented in PyTorch, this approach is particularly suitable for predicting surface deformation in mining areas, where data characteristics require tailored modeling.
2.5 Training process combining EDS-InSAR data with EsLSTM
Based on the principles of EDS-InSAR technology, this paper utilizes continuous time-series radar data with a 12-day interval for small baseline set differential interferometry. All selected SAR images are freely combined to form interferometric pairs according to the criteria of time baseline
Using the coherence coefficient and error estimate values, a filter is set to remove all deformation points with a coherence coefficient less than 0.3 and an error estimate value greater than 10, resulting in
In this study, four exponential smoothing models were combined with the LSTM model to create a model pool consisting of four distinct models. The training set of InSAR monitoring data was used to individually train each model. The performance of each model was evaluated using a validation set, and the model combination was selected adaptively based on the training results.
Given that the trends of each sequence differ and that the model combinations vary significantly, the two best models identified from the training of each sequence were repeatedly trained in steps 2 and 3 until the average error in the validation region began to increase. The model with the smallest error was then chosen as the best model for that sequence.
2.6 Evaluation and performance
In order to quantitatively evaluate the performance of Spatial and Temporal Prediction model of Mining Ground Subsidence Integrating EDS-InSAR with EsLSTM, the following evaluation indexes were selected for accuracy evaluation. These include Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and the Wilmot Consistency Index (WIA).
The RMSE and MAE are defined as follows:
where
The MAPE and WIA are defined as follows:
In Equations 5, 6, where
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Analysis of EDS-InSAR results
To ensure the reliability of cumulative deformation values derived from EDS-InSAR inversion, stable points were selected based on the average coherence coefficient of the time series deformation values. A comparative analysis of the temporal coherence maps over the study period was conducted. The closer the coherence coefficient is to 1, the more reliable the interferometric measurements. The coherence coefficient is calculated using the following formula:
In Equation 7, where
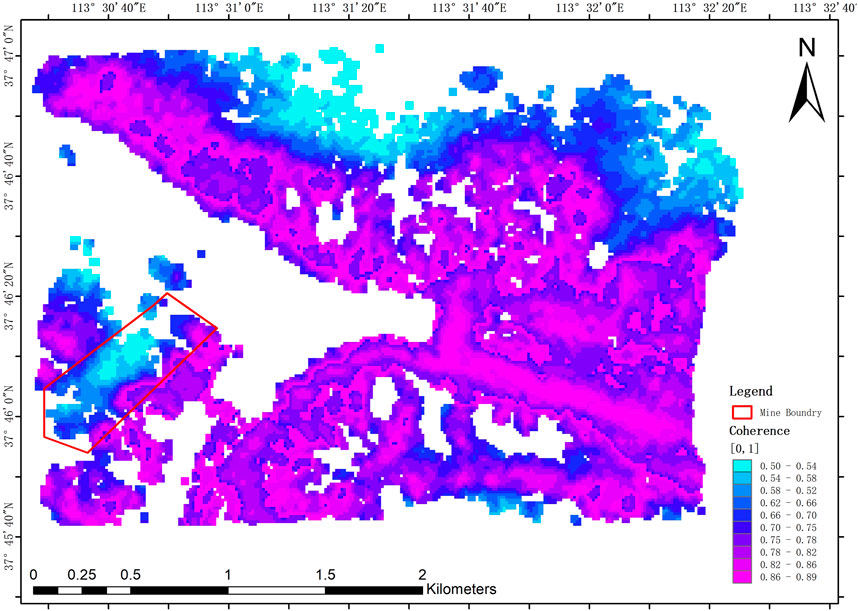
Figure 3 shows the average coherence map generated during data processing. As illustrated, the coherence coefficients within the deformation inversion area throughout the study period remained above 0.3, with an average value of 0.61 and a maximum of 0.89. In theory, a coherence coefficient above 0.3 ensures high-quality interferometric results and accurate phase unwrapping, leading to reliable deformation measurements. Regions with coherence values below 0.3 were excluded from the deformation analysis, represented as blank areas on the map.
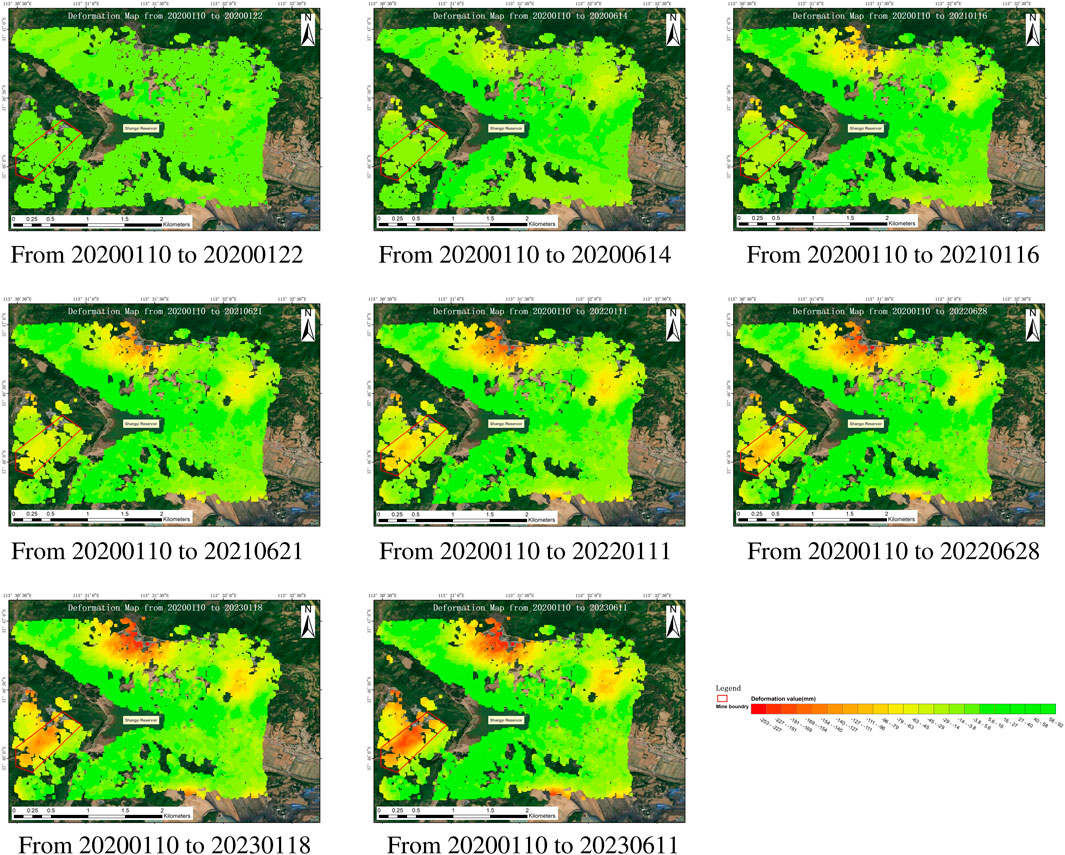
This study employed 98 Sentinel-1A satellite images combined with EDS-InSAR technology to map the temporal cumulative spatial distribution of ground deformation in the Yangquan mining area from January 2020 to June 2023 (Figure 4). The figure clearly illustrates the spatial distribution of ground subsidence, characterized by pronounced non-uniformity and a ring-shaped boundary centered around the Shangyi Reservoir. Field surveys confirmed that this boundary closely aligns with the underground coal mining limits of the Yangquan coal mine, while the area beneath the reservoir is designated as a restricted mining zone.
The study area is a reservoir, with the central region entirely covered by water. This results in specular reflection, leading to radar signal loss and, consequently, a lack of data coverage. Additionally, the northern part of the study area includes underground mining regions, which cause significant surface deformation and introduce errors into the EDS-InSAR monitoring data. Therefore, this study primarily focuses on the 18,001# old goaf region, which experiences slower deformation and provides more reliable deformation monitoring values.
Significant subsidence has been detected in the northern part of the study area, attributed to ongoing coal mining activities. Monitoring data reveals that the maximum cumulative subsidence in this region has reached
Time-series monitoring data from January 2020 to June 2023 indicates no significant subsidence around the Shangyi Reservoir dam, suggesting that underground mining activities at the Yangquan coal mine have not substantially affected the dam’s safety. This conclusion is supported by ground leveling measurements. A comparative analysis of leveling data from the dam and InSAR data collected over the same period validated the reliability of the EDS-InSAR monitoring results, further confirming that mining-induced subsidence near the Shangyi Reservoir has not compromised the safety of the dam or reservoir.
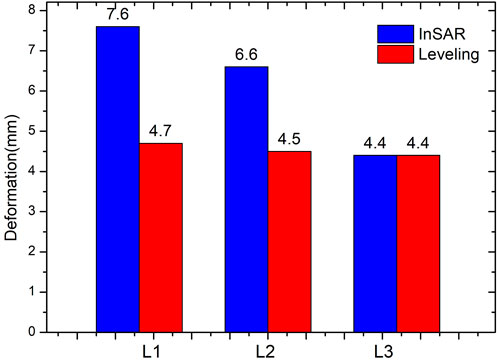
Leveling data from monitoring points on the dam were collected between 2020 and 2023 to verify the accuracy of the InSAR deformation measurements (see Figure 5). The leveling data recorded relative cumulative vertical subsidence values at these points. To ensure consistency, EDS-InSAR vertical subsidence vector monitoring points within a 20-meters buffer zone around the leveling points were extracted for the same period, and their relative subsidence values were calculated. The cumulative InSAR deformation results over the 98 observation periods exhibited an error margin of
The observed difference is primarily attributed to the structure of the reservoir dam. The leveling data represents deformation measurements at a single, precise point, while the InSAR data reflects the average deformation within a 20 m times 20 m area. This difference in spatial resolution leads to the apparent fluctuations in the InSAR data compared to the leveling data. Specifically, the leveling data recorded relative cumulative vertical subsidence values at discrete points. To ensure consistency with the leveling data, we extracted EDS-InSAR vertical subsidence vector monitoring points within a 20-meter buffer zone surrounding the leveling points for the same observation period. The relative subsidence values for these points were calculated accordingly.
Notably, on the southwest side of the Shangyi Reservoir, a slow deformation zone was detected, corresponding to the 18,001# workface. This region exhibited lower spatial decorrelation in the InSAR time series images, with fewer void pixels. Field investigations revealed that mining activities in this area ceased in 2020, classifying it as an old goaf. However, subsidence continued from January 2020 to June 2023, raising concerns due to its proximity to the reservoir. Understanding the future subsidence trends in this region is therefore critical to ensuring the safety of the Shangyi Reservoir.
Given this, the study selected this region as the test area and utilized it as the training dataset for the EsLSTM model developed in the research. The model is designed to predict deformation trends in the area, providing early warning data to help protect the integrity of the Shangyi Reservoir.
3.2 EsLSTM prediction results
In this study, we successfully obtained 98 periods of time-series ground subsidence data for the surface above the 18,001# workface of old goaf in the Yangquan coal mine, covering the period from January 2020 to June 2023. A total of 700 Enhanced Distributed Scatterer (EDS) points were extracted, providing detailed time-series deformation values. Using these deformation data, we generated a new time-series deformation dataset through a sliding window approach. This dataset was then used to develop an EsLSTM prediction model to forecast future deformation trends.
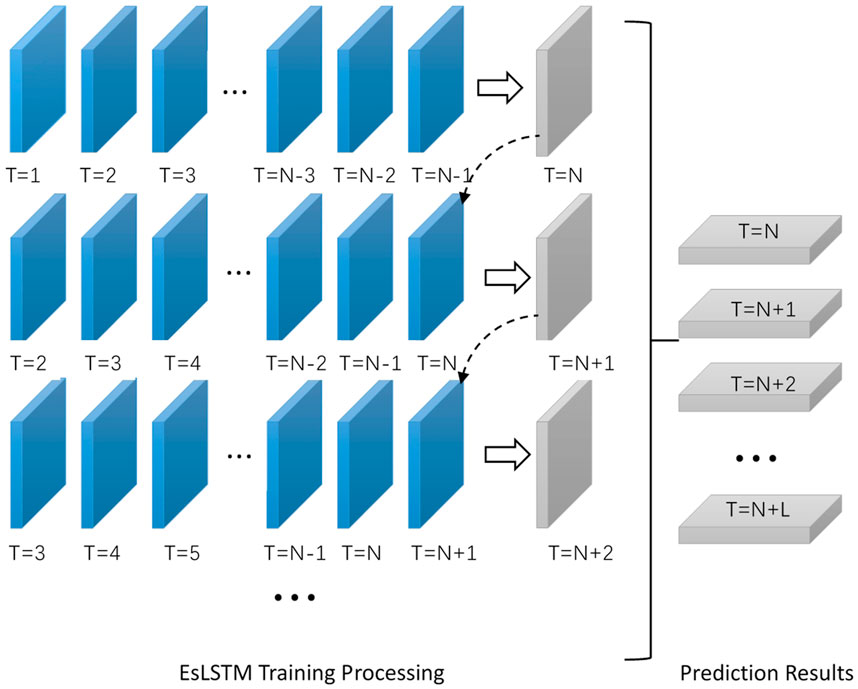
For the 700 EDS deformation time-series data points, we conducted 700 independent model training processes. The specific training procedure is illustrated in Figure 6. Here, The blue cuboids on the left side of the diagram represent the time series data at different temporal instances
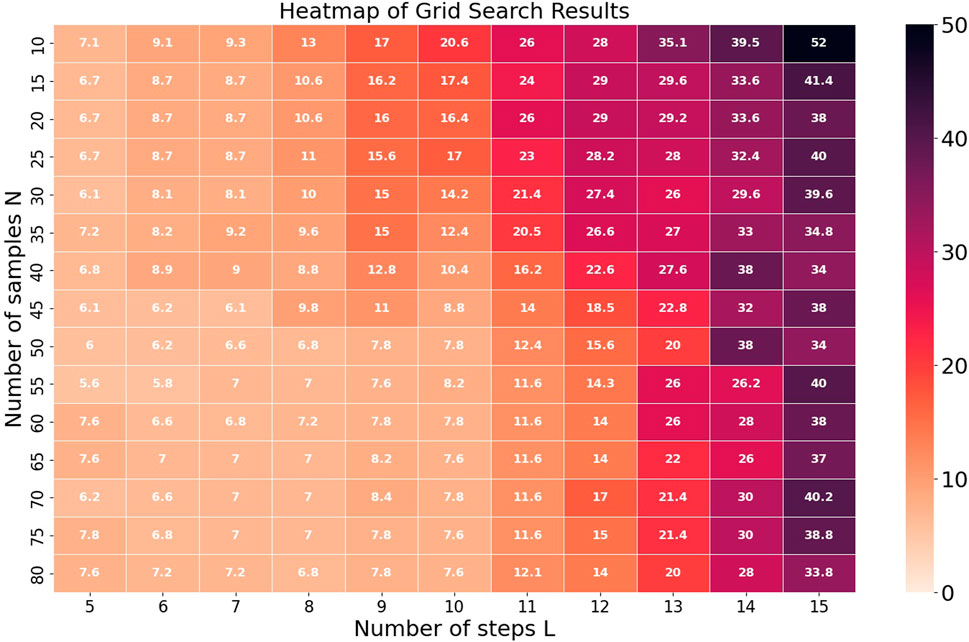
To determine the optimal sample length and prediction time step, we designated the final 15 periods of time-series data in the dataset as the validation set. By evaluating the model’s performance under various parameter configurations on this validation set, we aimed to optimize the model’s prediction accuracy and generalization capability.
In this study, to balance model computational efficiency, prediction accuracy, and hardware resource constraints, we systematically selected the training sample length
Analysis of the heatmap indicates that shorter prediction time steps
Based on this analysis and the trends observed in the heatmap, setting
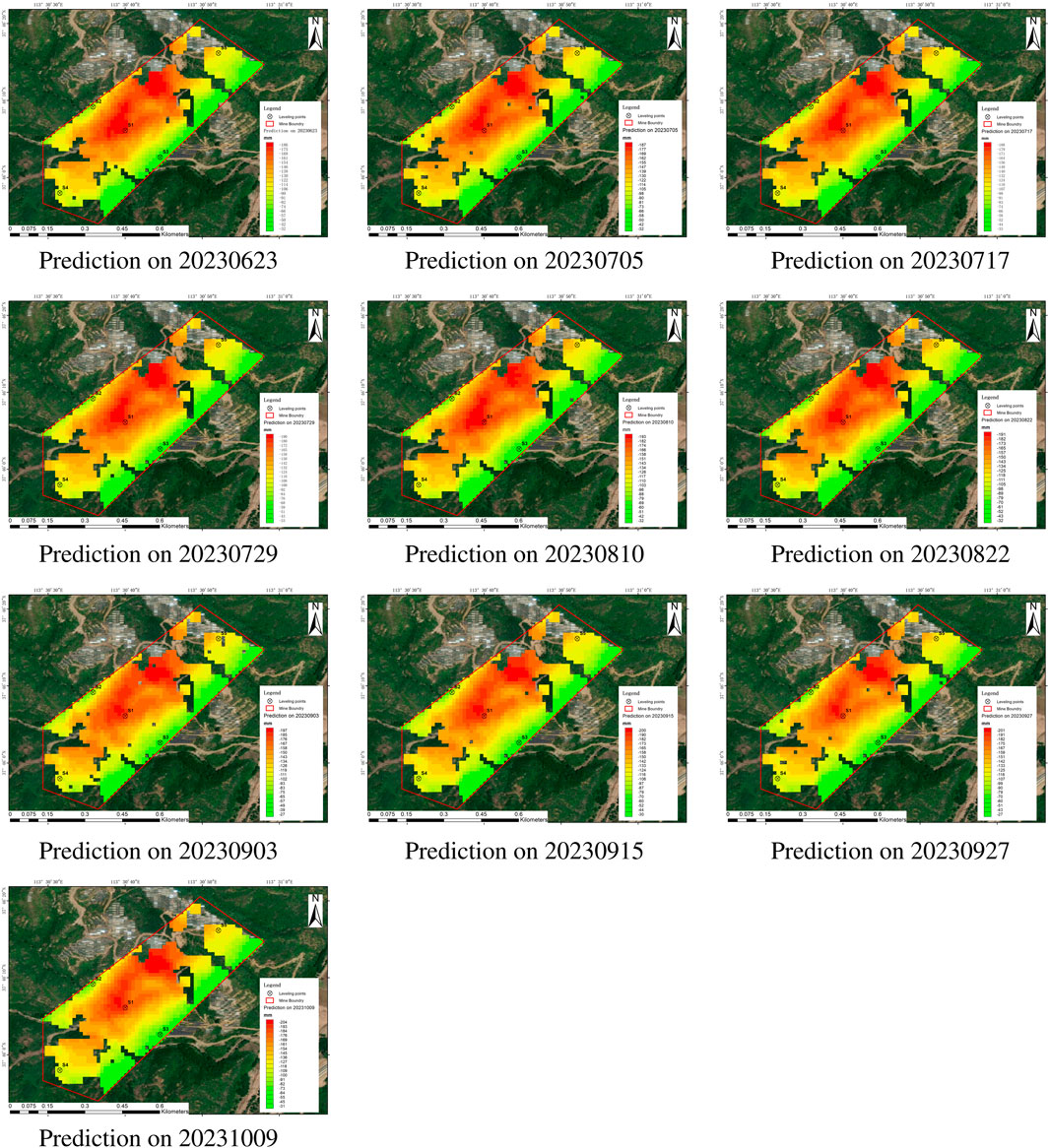
Leveraging the 98 cycles of EDS-InSAR monitoring data and optimized hyperparameters, this study utilizes the InSAR deformation image from 11 June 2023, as the final input for time-series analysis. The EsLSTM prediction model developed was employed to forecast the surface deformation of the 18,001# old goaf at Yangquan Coal Mine for the next 120 days using a recursive prediction method. As illustrated in Figure 8, the model performed recursive predictions over 10 time steps, extending the forecast to 9 October 2023. The figure demonstrates that, despite the cessation of mining activities at the 18,001# old goaf, the cumulative surface subsidence continued to increase over the more than 4-month period following the monitoring. The spatial pattern of the subsidence area remained stable, forming a characteristic subsidence funnel. By 9 October 2023, the maximum cumulative subsidence reached
4 Discussion
To assess the reliability of the EsLSTM model’s predictions, we used the time-series InSAR deformation data from 11 June 2023, as a test sample within the validation dataset. This data was compared in detail with the model’s predictions, as shown in Figure 9. Panel A of Figure 9 displays the InSAR-measured deformation data for 11 June 2023, while Panel B presents the EsLSTM model’s predicted deformation data for the same date.
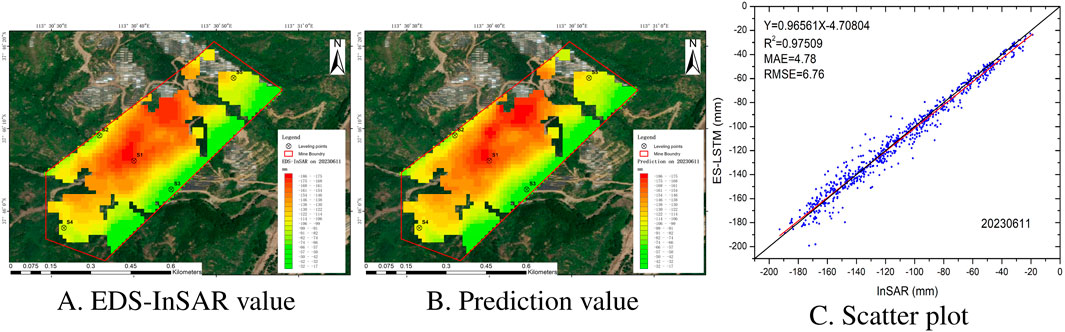
Figure 9. Scatter plot of correlation between InSAR real value and predicted value. (A) EDS-InSAR value. (B) Prediction value. (C) Scatter plot.
Panel C is a scatter plot illustrating the correlation between InSAR observations and EsLSTM predictions on 11 June 2023. The red line represents the correlation fit, while the black line serves as a reference for perfect prediction, denotes the ideal case where
To assess the performance of the EsLSTM model, we utilized several statistical metrics. The correlation coefficient
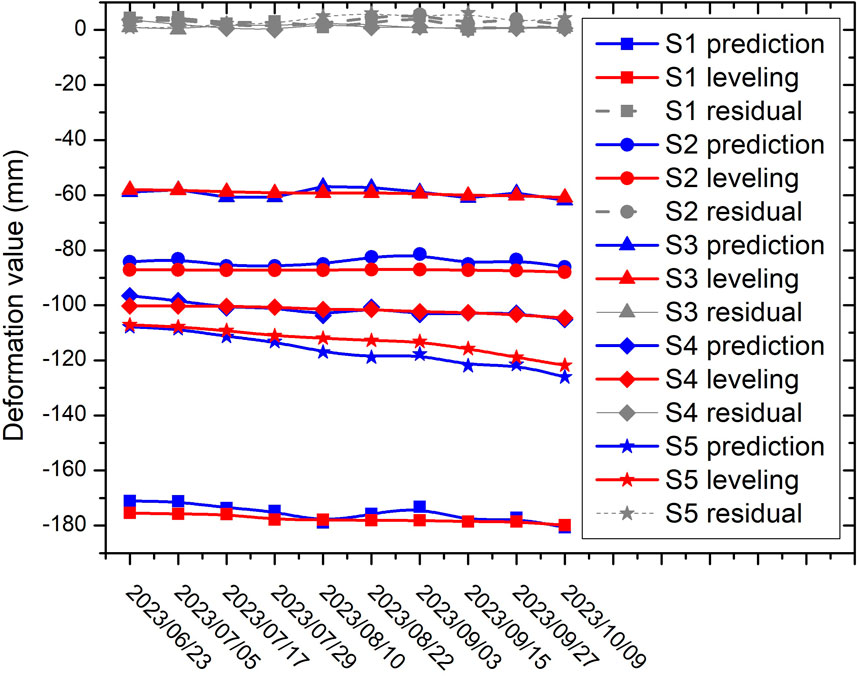
To further validate the model’s accuracy, we collected elevation benchmark data from five monitoring points on the surface above the 18,001# old goaf of the Yangquan coal mine for the year 2020. Additionally, deformation observation data for these points from 2023 were gathered. Using this data, we computed the surface deformation for these monitoring points post-June 2023 and employed it as a test set to evaluate the EsLSTM model’s predictions, as depicted in Figure 8.
Figure 10 presents a comparison of the measured leveling data and the EsLSTM model’s predictions for the five monitoring points. The results reveal a strong fit between observed values and model predictions, with residuals predominantly fluctuating near zero. This indicates that the EsLSTM spatiotemporal prediction model is not only theoretically robust but also demonstrates high predictive accuracy in practical applications, affirming its efficacy as a reliable tool for forecasting ground subsidence in mining areas.
The prediction results illustrated in Figure 8 indicate a stabilization of the accumulated subsidence at the coal mine workface. Furthermore, the deformation curves for the five leveling points shown in Figure 10 tend to flatten, suggesting that surface deformation in this region is stabilizing and the risk of geological disasters is low.
The predicted curves at the S1, S2, and S5 locations, as shown in the figure, exhibit certain discrepancies compared to the leveling monitoring curves. Analysis of historical subsidence curves reveals that during the rainy season each year, the loess layer on the surface in this region absorbs water and swells, resulting in a brief uplift period observed by radar. The EsLSTM model successfully learned this characteristic from the sample data, leading to a slight uplift in the predicted results for the S1 and S2 areas. However, the bedrock layer monitored by leveling data does not exhibit this phenomenon, causing the predicted values to exceed the leveling measurements. In the S3 and S4 areas, this phenomenon is less evident due to the terrain; these areas are located on slopes where rainwater can drain away smoothly. At S5, which is situated near the mining boundary, underground collapses occurred after mining ceased. These collapses partially filled the underground voids, leading to stabilized surface subsidence. While the EsLSTM model captured the subsidence characteristics, it failed to account for the geological features, resulting in predicted values that are lower than the leveling measurements.
The EsLSTM algorithm employed in this study predicts deformation by learning historical subsidence patterns. However, this approach inherently limits the interpretability of the predictions. When historical deformation patterns involve events such as fractures or collapses in unique geological structures, abrupt changes in subsidence values can emerge. For example, the observed pattern on 3 September 2023, where the predicted curves initially show a slow decline followed by an accelerated decrease, likely reflects the algorithm’s adaptation to the historical subsidence patterns. This prediction does not necessarily imply that the actual deformation trend in these areas will conform to such behavior.
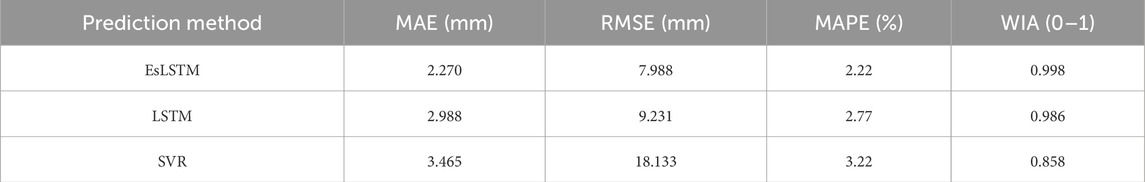
To thoroughly evaluate the performance of the EsLSTM model, we carried out a comparative analysis against established methods. Specifically, SVR and LSTM were selected as benchmark models. These comparison models were trained on the same dataset, and their predictions were evaluated. Detailed descriptions of the SVR and LSTM models can be found in our Papers Sui et al. (2020) and Ma et al. (2023), where their implementation and evaluation methods are outlined comprehensively. Due to space constraints, we did not reiterate those details in this paper. To facilitate a rigorous evaluation, we employed four metrics: MAE, RMSE, MAPE, and WIA. The detailed results of these metrics are presented in Table 2.
The data presented in Table 2 illustrates that the EsLSTM model surpasses the other models across all four evaluation metrics. Notably, the EsLSTM model achieved the lowest error values for MAE, RMSE, MAPE, underscoring its superior prediction accuracy. This comparative analysis highlights that, within the context of this study, the EsLSTM model offers greater precision and reliability in predictions compared to both SVR and LSTM.
Compared to the EsLSTM and LSTM models, the SVR model exhibited lower accuracy, primarily due to its high sensitivity to parameter selection. This sensitivity led to a decrease in prediction precision in certain areas with smaller deformation, such as the edges of mining regions. The LSTM model demonstrated lower accuracy than the EsLSTM model, which can be attributed to the absence of adaptive normalization. As a result, the LSTM model struggled to accurately capture the features of time-series data, particularly when dealing with training data exhibiting significant fluctuations (e.g., at the center of mining-induced deformations, geologically vulnerable zones, or collapse areas), leading to lower prediction accuracy. The SVR model’s accuracy was lower than that of the LSTM and EsLSTM models due to its heavy reliance on hyperparameters and kernel functions for the prediction of large-scale and high-dimensional data. During the prediction process involving a vast amount of mining area data, the SVR model was unable to achieve real-time updates of hyperparameters and kernel functions, rendering it incapable of adapting to time-sequential settlement data with varying characteristics. This led to significant prediction accuracy discrepancies (for instance, at the central and peripheral locations of mining deformations, where the deformation data characteristics are markedly different, the SVR was unable to autonomously update the hyperparameter search range and kernel functions). For readers interested in a more comprehensive comparison and analysis, we refer to the relevant sections in Sui et al. (2020) and Ma et al. (2023).
5 Conclusion
This study employed 98 Sentinel-1A satellite images spanning 2020 to 2023, in conjunction with EDS-InSAR technology, to construct a comprehensive cumulative deformation map of the Yangquan mining area. The analysis identified several subsidence zones, notably centered around the Shanyi Reservoir, with the maximum cumulative subsidence reaching
Focusing on the 18,001# old goaf, the closest old mining void to the Shanyi Reservoir, this study developed an EsLSTM prediction model utilizing time-series InSAR deformation data. The comparison of the model’s predictions with actual InSAR deformation data from 11 June 2023, revealed a high level of accuracy, with a correlation coefficient
Additionally, the EsLSTM model was employed to perform a 120-day prediction of surface deformation for the 18,001# old goaf using a recursive prediction approach. The results suggest that, as of October 2023, subsidence at the workface continues to escalate, with a projected maximum cumulative subsidence of 204 mm. The subsidence center is shifting southwest, indicating that voids are predominantly situated on the southwestern side of the tunnel. As the residual subsidence area increasingly distances itself from the Shanyi Reservoir, its potential impact on reservoir safety diminishes. Consequently, continued real-time monitoring and prediction of subsidence at the 18,001# old goaf are recommended to ensure the safety of the Shanyi Reservoir.
While the structure and training process of the model have been designed to be adaptive, enabling predictions of residual deformation in old mine subsidence areas in other regions, its generalization ability still requires further evaluation. Specifically, it is necessary to re-assess the number of training samples and prediction steps to optimize the model for different geological environments. Future research will focus on testing the model under various geological conditions to evaluate its universality and applicability. These efforts aim to enhance the model’s performance in regional subsidence monitoring and provide more comprehensive insights into its practical use in different contexts.
The prediction model developed in this study relies solely on time-series InSAR data, without considering environmental factors such as rainfall, topography, and geological conditions. While this approach has shown promising results, it may not fully capture the variability introduced by these environmental factors, which are known to influence surface deformation patterns. To address this limitation, future research should focus on transitioning from single-factor predictions based exclusively on InSAR deformation values to multi-factor predictive methods. For instance, real-time rainfall data and topography data could be incorporated into the model as additional input variables. Moreover, integrating the mining probability integral method with geological parameters as inputs into the EsLSTM framework could enhance the model’s ability to account for complex geological conditions. By doing so, the EsLSTM model’s generalization capabilities can be significantly improved.
Ultimately, future efforts will aim to develop a comprehensive multi-parameter modeling framework that includes environmental variables to further enhance the accuracy and reliability of subsidence predictions. This approach is expected to improve the model’s adaptability and robustness across diverse geological environments, ensuring broader applicability in subsidence monitoring and risk assessment.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
FM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing–original draft. QZ: Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing–original draft. LS: Conceptualization, Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (Grant Number: 202103021223381, 202303021222271), the Fundamental Research Program of Changzhi City (Grant Number: JC202401). Supported by a grant from Changzhi University Key Laboratory of Intelligent Human-Machine Cooperative Control.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yangquan Coal Mine Co., Ltd. for providing the leveling-points data and the staff at 18001# Coal Mine for allowing us to conduct our studies at the experimental site.
Conflict of interest
Author QZ was employed by Zhongjin Environmental Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Berardino, P., Fornaro, G., Lanari, R., and Sansosti, E. (2002). A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential sar interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geoscience and Remote Sens. 40, 2375–2383. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2002.803792
Chen, Y., Li, J., Li, H., Gao, Y., Li, S., Chen, S., et al. (2023). Revealing land surface deformation over the yineng backfilling mining area, China, by integrating distributed scatterer sar interferometry and a mining subsidence model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 16, 3611–3634. doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3250419
Chen, Y., Tong, Y., and Tan, K. (2020). Coal mining deformation monitoring using sbas-insar and offset tracking: a case study of yu county, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 13, 6077–6087. doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3028083
Dai, S., and Finkelman, R. B. (2018). Coal as a promising source of critical elements: progress and future prospects. Int. J. Coal Geol. 186, 155–164. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2017.06.005
Fan, Z., and Zhang, Y. (2019). Summary of the application of intelligent algorithms in the prediction of ground subsidence. Surv. Spatial Geogr. Inf. 42, 183–188. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2019.05.054
Fernandez Galarreta, J., Kerle, N., and Gerke, M. (2015). Uav-based urban structural damage assessment using object-based image analysis and semantic reasoning. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 15, 1087–1101. doi:10.5194/nhess-15-1087-2015
Fornaro, G., Verde, S., Reale, D., and Pauciullo, A. (2015). Caesar: an approach based on covariance matrix decomposition to improve multibaseline–multitemporal interferometric sar processing. IEEE Trans. Geoscience Remote Sens. 53, 2050–2065. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2014.2352853
Fuhrmann, T., Caro Cuenca, M., Knöpfler, A., van Leijen, F., Mayer, M., Westerhaus, M., et al. (2015). Estimation of small surface displacements in the Upper Rhine Graben area from a combined analysis of PS-InSAR, levelling and GNSS data. Geophys. J. Int. 203, 614–631. doi:10.1093/gji/ggv328
Gardner, E. S. (2006). Exponential smoothing: the state of the art—part ii. Int. J. Forecast. 22, 637–666. doi:10.1016/j.ijforecast.2006.03.005
Guzzetti, F., Manunta, M., Ardizzone, F., Pepe, A., Cardinali, M., Zeni, G., et al. (2009). Analysis of ground deformation detected using the sbas-dinsar technique in umbria, central Italy. Pure Appl. Geophys. 166, 1425–1459. doi:10.1007/s00024-009-0491-4
He, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, W., Yan, H., Zhang, L., and Liu, T. (2021a). Ts-insar analysis for monitoring ground deformation in lanzhou new district, the loess plateau of China, from 2017 to 2019. Adv. SPACE Res. 67, 1267–1283. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2020.11.004
He, Y., Yao, S., Chen Yi, H., and Zhang, L. (2023). Spatio-temporal prediction of time-series insar land subsidence based on convlstm neural network. Geomatics Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 48, 1–21. doi:10.13203/j.whugis20220657
He, Y., Zhao, Z., Yang, W., Yan, H., Wang, W., Yao, S., et al. (2021b). A unified network of information considering superimposed landslide factors sequence and pixel spatial neighbourhood for landslide susceptibility mapping. Int. J. Appl. EARTH OBSERVATION GEOINFORMATION 104, 102508. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2021.102508
Hou, Z., Yang, K., Li, Y., Gao, W., Wang, S., Ding, X., et al. (2022). Dynamic prediction model of mining subsidence combined with d-insar technical parameter inversion. Environ. Earth Sci. 81, 307. doi:10.1007/s12665-022-10423-8
Hu, J., Wu, W., Motagh, M., Wang, F., Pan, J., Pan, S., et al. (2023). Fim-based dsinsar method for mapping and monitoring of reservoir bank landslides: an application along the lancang river in China. Landslides 20, 2479–2495. doi:10.1007/s10346-023-02097-5
Kang, Y., Hyndman, R. J., and Smith-Miles, K. (2017). Visualising forecasting algorithm performance using time series instance spaces. Int. J. Forecast. 33, 345–358. doi:10.1016/j.ijforecast.2016.09.004
Klees, R., and Massonnet, D. (1998). Deformation measurements using sar interferometry: potential and limitations. Geol. Mijnb. 77, 161–176. doi:10.1023/a:1003594502801
Liu, C., Zhou, F., Gao, J., and Wang, J. (2012). Some problems of gps rtk technique application to mining subsidence monitoring. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 22, 223–228. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2012.03.001
Liu, Y., and Zhang, J. (2023). Integrating sbas-insar and at-lstm for time-series analysis and prediction method of ground subsidence in mining areas. Remote Sens. 15, 3409. doi:10.3390/rs15133409
Lyu, B., Liu, B., Xie, B., Xiao, H., Liu, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2024). Study on insar deformation information extraction and stress state assessment in a railway tunnel in a plateau area. Front. Earth Sci. 12. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1367978
Ma, F., Sui, L., and Lian, W. (2023). Prediction of mine subsidence based on insar technology and the lstm algorithm: a case study of the shigouyi coalfield, ningxia (China). REMOTE Sens. 15, 2755. doi:10.3390/rs15112755
Ma, P., Zhang, F., and Lin, H. (2020). Prediction of insar time-series deformation using deep convolutional neural networks. REMOTE Sens. Lett. 11, 137–145. doi:10.1080/2150704X.2019.1692390
Nawaz, S. A., Li, J., Bhatti, U. A., Shoukat, M. U., and Ahmad, R. M. (2022). Ai-based object detection latest trends in remote sensing, multimedia and agriculture applications. Front. PLANT Sci. 13, 1041514. doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.1041514
Ng, A. H.-M., Ge, L., Du, Z., Wang, S., and Ma, C. (2017). Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring subsidence induced by longwall mining activity using radarsat-2, sentinel-1 and alos-2 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observation Geoinformation 61, 92–103. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2017.05.009
Pan, H., Zhao, Y., Zhang, W., Bai, Y., and Han, Y. (2019). Prediction of surface subsidence with improved bp neural network based on adaboost. Coal Sci. Technol. 47, 161–167. doi:10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2019.02.027
Parizzi, A., and Brcic, R. (2011). Adaptive insar stack multilooking exploiting amplitude statistics: a comparison between different techniques and practical results. IEEE Geoscience Remote Sens. Lett. 8, 441–445. doi:10.1109/LGRS.2010.2083631
Radman, A., Akhoondzadeh, M., and Hosseiny, B. (2021). Integrating insar and deep-learning for modeling and predicting subsidence over the adjacent area of lake urmia, Iran. GISCIENCE and REMOTE Sens. 58, 1413–1433. doi:10.1080/15481603.2021.1991689
Santra, A. S., and Lin, J.-L. (2019). Integrating long short-term memory and genetic algorithm for short-term load forecasting. ENERGIES 12, 2040. doi:10.3390/en12112040
Shi, X., Chen, Z., Wang, H., Yeung, D.-Y., Wong, W.-k., and Woo, W.-c. (2015). “Convolutional lstm network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting,” in Advances in neural information processing systems 28 (NIPS 2015). Editors C. Cortes, N. Lawrence, D. Lee, M. Sugiyama, and R. Garnett (Montreal: CANADA).
Shi, X., Zhang, L., Zhong, Y., Zhang, L., and Liao, M. (2020). Detection and characterization of active slope deformations with sentinel-1 insar analyses in the southwest area of shanxi, China. REMOTE Sens. 12, 392. doi:10.3390/rs12030392
Smyl, S. (2020). A hybrid method of exponential smoothing and recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting. Int. J. Forecast. 36, 75–85. doi:10.1016/j.ijforecast.2019.03.017
Sui, L., Ma, F., and Chen, N. (2020). Mining subsidence prediction by combining support vector machine regression and interferometric synthetic aperture radar data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 9, 390. doi:10.3390/ijgi9060390
Sun, J., Wauthier, C., Stephens, K., Gervais, M., Cervone, G., La Femina, P., et al. (2020). Automatic detection of volcanic surface deformation using deep learning. J. Geophys. RESEARCH-SOLID EARTH 125. doi:10.1029/2020JB019840
Tang, Y.-Q., Cui, Z.-D., Wang, J.-X., Yan, L.-P., and Yan, X.-X. (2008). Application of grey theory-based model to prediction of land subsidence due to engineering environment in shanghai. Environ. Geol. 55, 583–593. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1009-y
Xia, Y., Xia, F., Hui, Z., Li, H., Wan, R., and Ai, J. (2023). Combined ps-insar technology and high-resolution optical remote sensing for identifying illegal underground mining in the suburb of yangquan city, shanxi province, China. REMOTE Sens. 15, 3565. doi:10.3390/rs15143565
Xue, F., Lv, X., Dou, F., and Yun, Y. (2020). A review of time-series interferometric sar techniques: a tutorial for surface deformation analysis. IEEE Geoscience Remote Sens. Mag. 8, 22–42. doi:10.1109/MGRS.2019.2956165
Yang, C., Zhang, q., Zhao, C., and Ji, l. (2014). Small baseline bubset insar technology used in datong basin ground subsidence, fissure and fault zone monitoring. Geomatics Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 39, 945–950. doi:10.13203/j.whugis20130656
Yang, Z., Li, Z., Zhu, J., Yi, H., Hu, J., and Feng, G. (2017). Deriving dynamic subsidence of coal mining areas using insar and logistic model. Remote Sens. 9, 125. doi:10.3390/rs9020125
Ye, S., Luo, Y., Wu, J., Yan, X., Wang, H., Jiao, X., et al. (2016). Three-dimensional numerical modeling of land subsidence in shanghai,China. Hydrogeology J. 24, 695–709. doi:10.1007/s10040-016-1382-2
Yu, C., Li, Z., Penna, N. T., and Crippa, P. (2018). Generic atmospheric correction model for interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 123, 9202–9222. doi:10.1029/2017jb015305
Zhang, G., Xu, Z., Chen, Z., Wang, S., Liu, Y., and Gong, X. (2024). Analyzing surface deformation throughout China’s territory using multi-temporal insar processing of sentinel-1 radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 305, 114105. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2024.114105
Zhao, C., Li, Z., Tian, B., Zhang, P., and Chen, Q. (2019). A ground surface deformation monitoring insar method using improved distributed scatterers phase estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 12, 4543–4553. doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2946729
Keywords: EDS-InSAR, mines, deformation, prediction, eslstm algorithm
Citation: Ma F, Zhang Q and Sui L (2025) Prediction of old goaf residual subsidence integrating EDS-InSAR with EsLSTM in the Loess Plateau, China. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1511785. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1511785
Received: 15 October 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 17 January 2025.
Edited by:
Rui Yong, Ningbo University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yunfeng Ge, China University of Geosciences Wuhan, ChinaWen-pei Wang, China Geological Survey, China
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Zhang and Sui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fei Ma, bWFmZWlAY3pjLmVkdS5jbg==
 Fei Ma
Fei Ma Qingbin Zhang3
Qingbin Zhang3