- 1Shanxi Yanchang Petroleum and Mining Co., Ltd., Yulin, Shanxi, China
- 2College of Energy Engineering, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, Shanxi, China
In view of the unknown mechanical response behavior of weak interlayer surrounding rock under complex stress environment, this paper adopts laboratory experimental research method to carry out uniaxial compression and cyclic loading and unloading tests on natural rock mass and water-saturated rock mass, and compares the strength, deformation, failure mode and acoustic emission characteristics of rock mass. The mechanical behavior and warning signal of weak interlayer rock mass under cyclic loading and unloading are studied. The results show that cyclic loading reduces the strength of natural rock mass, and water saturation further weakens the strength of rock mass. The strength attenuation rate of water-saturated rock mass is low, at 60.19%. The average deformation modulus of natural rock mass is 6.571 GPa, and the average deformation modulus of water-saturated rock mass is 3.646 GPa, indicating that water reduces the stiffness of rock mass. The failure modes include splitting shear under uniaxial compression and tensile shear damage under cyclic loading. Acoustic emission analysis found that during the unloading and reloading process, the rock mass has a short “step-like” silent period, and about 70% of the damage occurs in the last silent period before failure. This can be used as a prediction indicator of damage and provide a valuable reference for disaster warning in engineering applications.
1 Introduction
As a type of challenging geology characterized by significant intensity differences, interbedded rock formations frequently lead to safety accidents in coal mining and underground engineering due to their non-uniform deformation properties. The damage mechanisms and precursor characteristics of these rock masses differ from those of homogeneous rock masses (Yong et al., 2006). The unique structural attributes of deep coal rock masses, combined with cyclic loads such as geostress and multiple mining disturbances, inevitably cause damage to the surrounding rock. This damage reduces the rock’s bearing capacity, creates pathways for groundwater flow, and can lead to secondary damage due to the presence of water, exacerbating support issues. Therefore, conducting graded cyclic loading and unloading experiments on both natural and water-saturated interbedded rock samples is crucial. Such studies, which analyze mechanical damage characteristics and acoustic precursors, are vital for preventing and managing stability problems in surrounding rock masses induced by cyclic loading in interbedded rock bodies.
Many scholars have studied the mechanical properties and damage mechanisms of coal rock under complex stress paths. Ouyang et al. (2024) conducted indoor quasi-static uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading and dynamic axial compression tests under impact loads, revealing the damage mechanism of coal bodies under multiple mining disturbances and impact loads. Yang Z. et al. (2024) shows that initial stress suppresses the propagation of intergranular cracks, while the presence of a free face significantly enhances the efficiency of TBM rock fragmentation. Li et al. (2018) indicates that elevated temperatures enhance the ductility of rock salt but reduce its compressive strength. Shang et al. (2018) study investigates the anisotropic direct tensile behavior of laminated and transversely isotropic Midgley Grit sandstone using a particle-based discrete element method. Yang Zheng et al. (2024) coupled thermo-mechanical model reveals that the relative impact on the peak stress of composite interbedded rocks follows the order: interlayer angle, thermal shock temperature, and model size, from greatest to least. Wang et al. (2024a) studied the damage characteristics and macro-micro failure morphology of coal-rock composite structures under cyclic mining stress, and constructed an energy-damage constitutive model of coal-rock composite structures under cyclic loads. Zhang et al. (2022) conducted uniaxial compression tests and acoustic emission tests on sandstone samples in saturated and natural states, and studied the mechanical properties and acoustic emission characteristics of sandstone with different particle sizes in the two states during the failure process. Rong et al. (2022) established a theoretical model of full stress-strain permeability of deep mining coal bodies by segmented characterization. Zhang et al. (2021) analyzed the influence of seepage pressure, confining pressure and deviatoric stress cyclic loading and unloading on the permeability of fractured mudstone, and constructed a mechanical model of fractured mudstone permeability evolution considering complex stress paths. Wang et al. (2024b) studied the influence of different types of sand powder and different binder saturation on the mechanical properties of soft rock samples and their mechanisms. Sun et al. (2017) analyzed the damage evolution of sandstone under multi-stage cyclic loading and proposed a fatigue damage evolution model for rocks. Su (2006), Mingqing and Su (2008) conducted uniaxial and triaxial cyclic unloading tests on marble samples to examine their deformation and strength characteristics. Zhou et al. (2010) investigated the stress-strain curves and peak strength of Xiangjiaba sandstone, presenting a method for calculating damage variables. Additionally, Xu et al. (2023) revealed the “strong-weak” structure and “squeezing-prying” system mechanism of coal and rock masses induced by deep mining in steeply inclined coal seams. Li et al. (2017) established a theoretical model to relate strain under cyclic unloading to the number of cycles, deriving the evolution equation for rock damage variables.
Several researchers (Wu et al., 2015) have also conducted indoor rock mechanical tests on artificial interbedded rock samples. Wu Bo and others examined how changes in the inclination angle of interbedded rock affect damage patterns using physical modeling and numerical simulations. Huang et al., 2020) analyzed the effects of peripheral pressure, inclination angle, and layer-thickness ratio on the damage mechanisms of interbedded rock samples under uniaxial and triaxial loading conditions. Chu et al. (2020) investigated the anisotropy and acoustic emission characteristics of layered sandstone by conducting uniaxial acoustic emission tests on sandstone at different angles, revealing crack extension and acoustic emission patterns.
In studies of water-bearing states, Wang et al. (2017) analyzed the deformation characteristics of dry and water-saturated sandstones under cyclic loading, focusing on the evolution and distribution of energy. Shan et al. (2018), Shan and Lai (2018) developed a coupled flow-solid model for fractured coal rock considering regional stress to study fracture field evolution and coupled flow-solid characteristics. Guo et al. (2014) examined the water stability and mechanical properties of dissolved tuffs in natural and saturated conditions, highlighting the impact of hydraulic action. Dong et al. (2014) explored the mechanical and acoustic properties of deep amphibolite under dry and saturated conditions, proposing a criterion for assessing rock damage proximity. Wang et al. (2016) tested natural and saturated coal samples, identifying differences in acoustic emission pulse signals, energy, and frequency with stress, and summarizing precursor information for instability. Lai et al. (2020) analyzed time-frequency characteristics and damage laws of coal samples using acoustic emission waveform spectral analysis under uniaxial loading. Zhang et al. (2020) investigated damage evolution and precursors using acoustic emission from coal samples under multi-stage strain and stress loading. Li et al. (2019) examined changes in the Felicity ratio and loading/unloading response ratios of various rocks under incremental cyclic loading. Quchao et al. (2009) explored strength characteristics and the Felicity effect in sillimanite under uniaxial cyclic loading. Finally, Sun et al. (2019) studied crack expansion and evolution under cyclic loading using triaxial testing and acoustic emission signals.
Many previous studies have examined the effects of different loading methods, the presence of interlayer structures, and varying water content states on rock mechanical properties and acoustic precursors in isolation. However, in real engineering scenarios, these factors often interact, leading to significant deterioration in rock strength. Comprehensive research considering the combined impact of cyclic loading and various water content states on interbedded rock samples is limited. Therefore, this paper conducts uniaxial cyclic loading tests to analyze the mechanical and acoustic characteristics of interbedded rock samples under two different water-bearing conditions. It is the first to systematically consider the combined effects of cyclic loading-unloading and water saturation on the mechanical behavior of interbedded rock masses, offering critical insights into their mechanical responses and failure mechanisms.
2 Experimental design and methodology
2.1 Specimen characteristics and dimensions
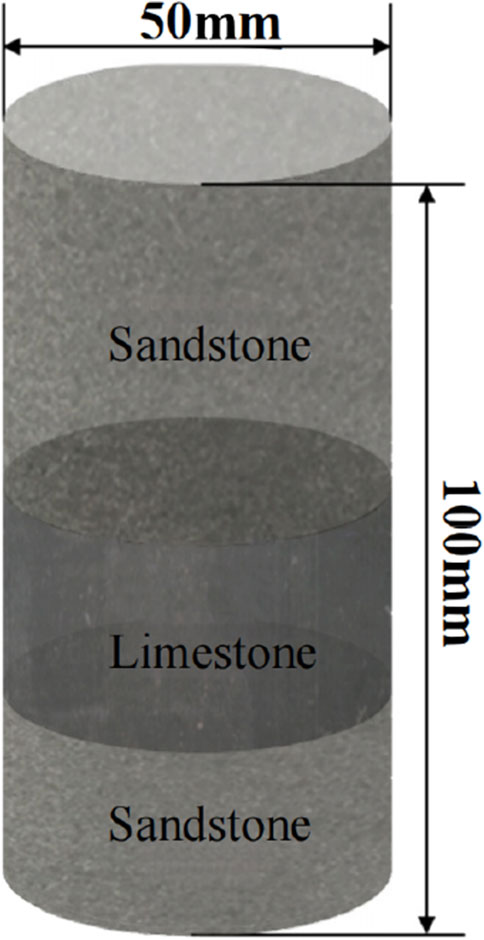
For this test, a natural interlayer rock sample composed of sandstone-graystone-sandstone was selected. According to the national standard for determining the physical and mechanical properties of coal and rock, the sample was processed into a standard cylindrical specimen with dimensions of φ50mm × 100 mm. The processing precision ensured that the non-parallelism of the two end surfaces was within 0.05mm, the deviation in the diameter of the upper and lower ends was no more than 0.3mm, and the axial deflection angle was within 0.25°. The surface of the specimen was smooth and free from defects. The structure of the interlayer within the test piece is illustrated in Figure 1.
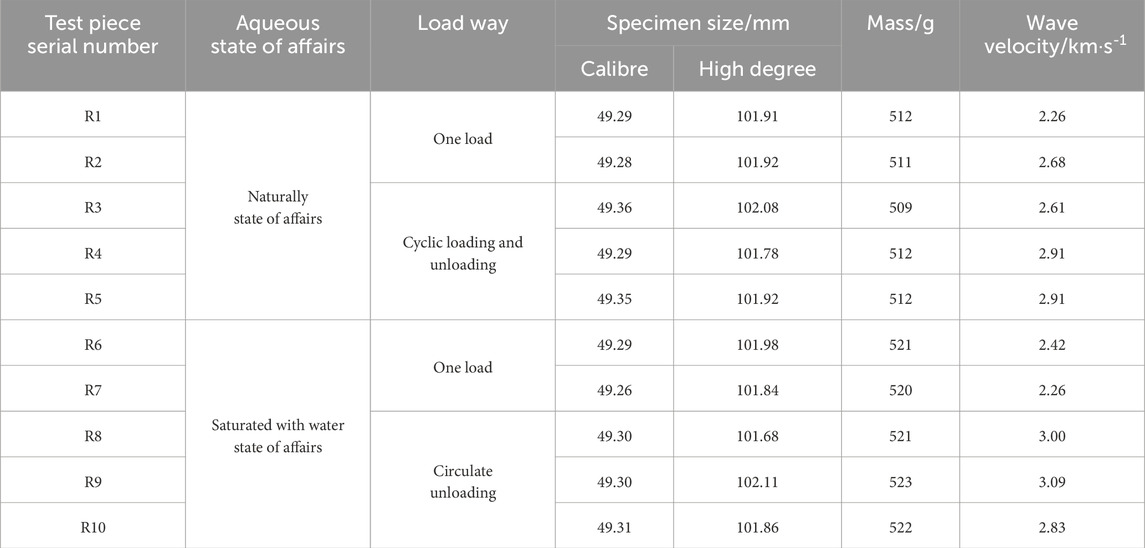
Ten standard specimens, labeled R1 to R10, were prepared. Their physical parameters, including diameter, height, and wave speed, were measured prior to testing. The specific grouping, numbering, and measurement results are shown in Table 1. The ten specimens are divided into two groups: one group consists of five specimens in a natural state, placed in a desiccator with water at the bottom, ensuring that the bottom of the specimens is 20 mm above the water surface to maintain a certain level of humidity; the other group consists of five specimens in a water-saturated state, which are immersed in a water container. Water is added three times at intervals of 2 hours until the water level is 20 mm above the specimens. After 48 h of immersion, the specimens are taken out, the surface water is dried, and they are packaged in plastic bags, awaiting testing.
2.2 Test equipment and systems
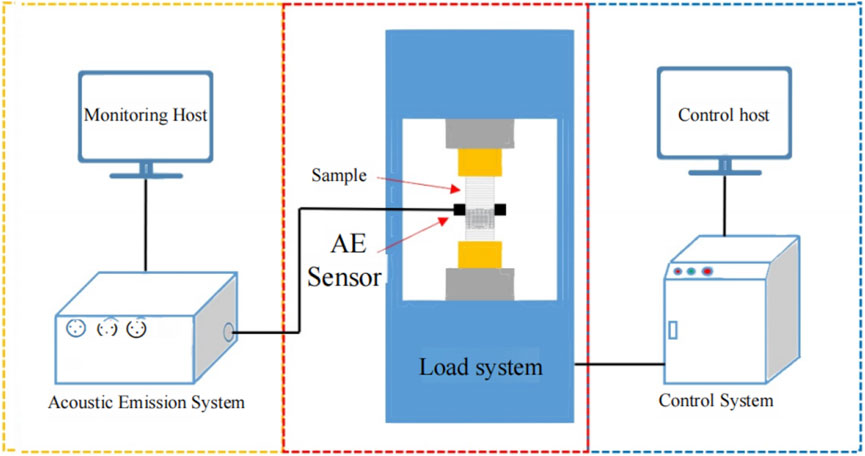
The testing was conducted at the Key Laboratory of Western Mining and Disaster Prevention, Xi’an University of Science and Technology. For this purpose, the Shenzhen Wanmei HCT-605A electro-hydraulic servo pressure tester was employed. This equipment is capable of simultaneously recording load and displacement values, with a maximum testing force of 600 kN and an accuracy class of 0.5, in accordance with the precision standards outlined in the Engineering Rock Test Methods. Acoustic emission was monitored using the SAEU2S multi-channel system from Beijing Shenghua Xingye Technology Co., Ltd., which tracks real-time data on count, amplitude, and energy during compression testing. The system was configured with a sampling frequency of 1 MHz, a detection threshold of 40 dB to minimize noise interference, and a front gain set to 40 dB. The test setup is depicted in Figure 2.
Prior to commencing the test, to ensure non-destructive data acquisition, a layer of petroleum jelly was applied between the sensor and the specimen to serve as a coupling agent. Two acoustic emission (AE) sensors were secured in the middle of the specimen using rubber bands. Both the loading system and the acoustic emission system were synchronized in terms of timing. The press was then activated to apply load to the specimen, while acoustic emission signals were continuously recorded throughout the loading process until specimen failure occurred. Following the specimen’s destruction, loading was halted, and the collected data were saved.
2.3 Experimental program and design
Based on the project rock body’s endowment environment and the influence of mining disturbance, this test is divided into two loading modes: (1) uniaxial compressive loading at one time; (2) uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading. According to the results of uniaxial compressive test, the peak increment of the two loading is about 20% of the uniaxial compressive strength, to ensure that each specimen is destroyed after 4–5 times of cycling, so it is determined that the natural specimen starting load is 30kN, and the cyclic gradient is 30kN; and the starting load of the water-saturated specimen is 9kN, and the cyclic gradient is 9 kN.
3 Mechanical characterization of interbedded rock samples
This study utilizes the Wanmei electro-hydraulic servo press to measure the uniaxial compression and cyclic loading-unloading mechanical parameters of interlayer specimens in both natural and water-saturated conditions. The experimental results are used to analyze the stress-strain curves, peak strength, and the average modulus of loading and unloading for the interlayer rock samples.
3.1 Characterization of stress-strain curves
The uniaxial compression and cyclic loading-unloading stress-strain curves for typical specimens in both natural and saturated states are presented in Figure 3 (1) As illustrated in Figure 3A, the natural state specimen exhibits distinct brittle failure under uniaxial compression, with a sudden destruction upon reaching peak strength, resulting in a complete loss of load-bearing capacity. In contrast, the water-saturated specimen shows noticeable behavior during the yield stage after the peak, maintaining some load-bearing capacity post-peak. Figures 3B, C reveal that while the stress-strain curves of both specimens display similar behavior before the peak in cyclic loading, there are significant differences in the post-peak rupture stages. The natural state specimen experiences abrupt failure upon reaching peak stress, demonstrating typical brittle characteristics. Conversely, the saturated state specimen shows a gradual decrease in bearing capacity after reaching peak strength, with the macro-fracture developing quickly along the longitudinal direction and primarily occurring near the interlayer contact surface. This suggests that the interlayer structure substantially influences the rock specimen’s strength. (2) Cai et al. (2001), Cai and Brown (2017) that the full stress-strain curve can be divided into two segments from the peak strength: the left segment represents the strain energy stored in the specimen, while the right segment indicates the energy dissipated during failure. For natural specimens, the energy stored before the peak is abruptly released as kinetic energy at the peak point, leading to noticeable ejection of broken rock fragments and rock powder, accompanied by dynamic sounds. In contrast, the water-saturated specimens develop microfissures during the yield stage, with energy being gradually released after the peak. These specimens remain intact post-failure, indicating that water alters the degree of rock damage and affects the energy collection, dissipation, and release processes. The transformation in rock behavior due to water highlights its potential to weaken the rock body, which is relevant for engineering applications like water softening methods to mitigate impact ground pressure and other hazards (Lai et al., 2020a; Lai et al., 2020b; Cui et al., 2019). (3) As shown in the partially enlarged sections of Figures 3B, C, both specimens exhibit a sudden drop in strain during each unloading stage while stress remains nearly constant, typically occurring at the same stress levels, which is indicative of elastic aftereffects.
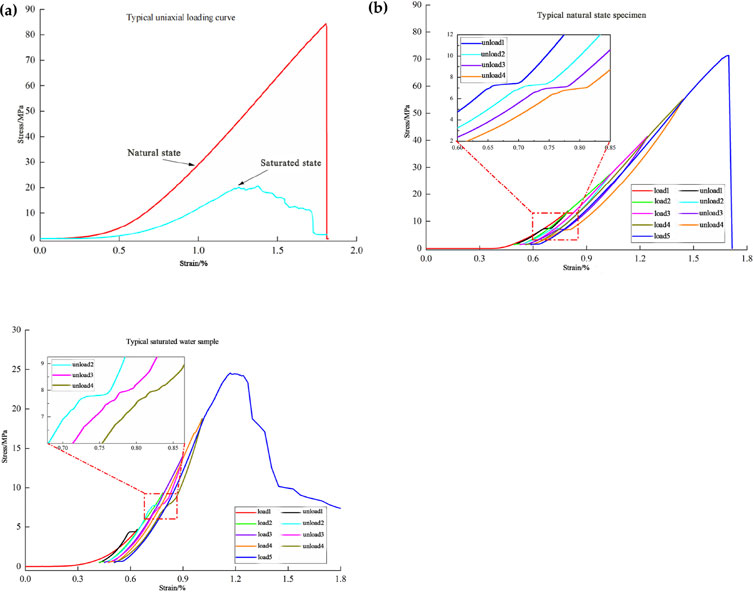
Figure 3. Stress-strain curves of typical natural and water-saturated specimens. (A) Single-axis primary loading. (B) Cyclic loading of natural specimens. (C) Cyclic loading of saturated specimens.
3.2 Characterization of intensity changes
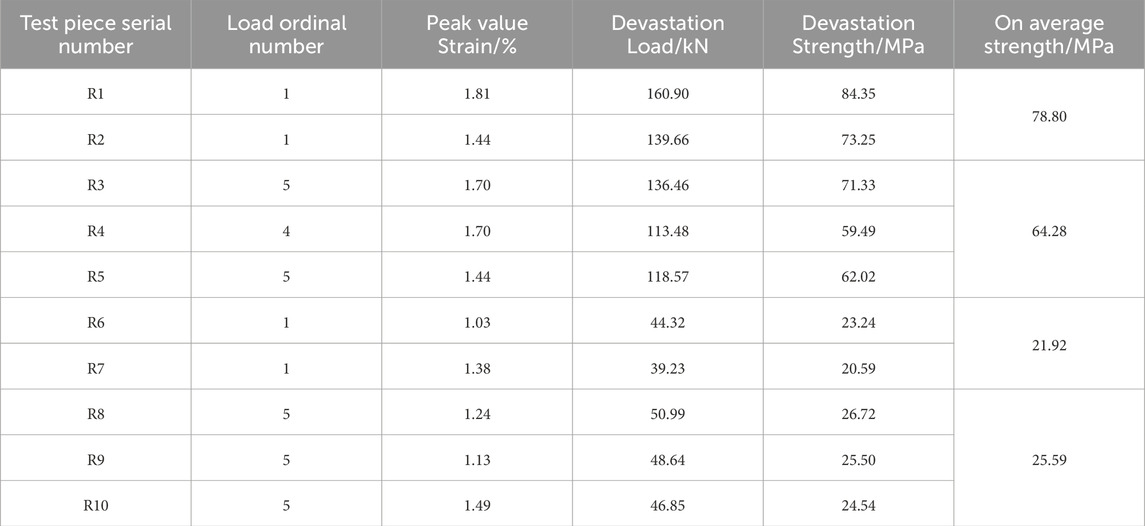
Based on the test results, the average peak strength of the natural specimen under uniaxial compression was found to be 78.80 MPa, while the average peak strength of the water-saturated specimen was 21.92 MPa. The uniaxial compressive strength served as the reference value for the cyclic unloading tests conducted on specimens with different water content states. The mechanical parameters obtained from both loading methods are summarized in Table 2.
A comparison of the specimen strengths under two loading methods-uniaxial loading and uniaxial cyclic loading-unloading-reveals that the average strength of specimens subjected to cyclic loading-unloading is 14.52 MPa lower than that under uniaxial loading, representing an 18.43% reduction. For water-saturated specimens, the strength under cyclic loading is 38.69 MPa lower than that of the natural specimens, indicating a 60.19% decrease. This highlights the significant impact of cyclic loading-unloading and the combined effect of water on the strength degradation of interlayer specimens.
The observed strength reduction is closely related to the composition of the interlayer specimen. The interlayer tuff, primarily composed of calcium carbonate, is prone to dissolution when exposed to carbon dioxide-containing water. During the water saturation process, CO₂-containing water molecules infiltrate the tuff’s pore spaces, causing the dissolution of some calcium carbonate. This dissolution is macroscopically reflected as a decrease in the sample’s strength.
3.3 Characterization of deformation modulus
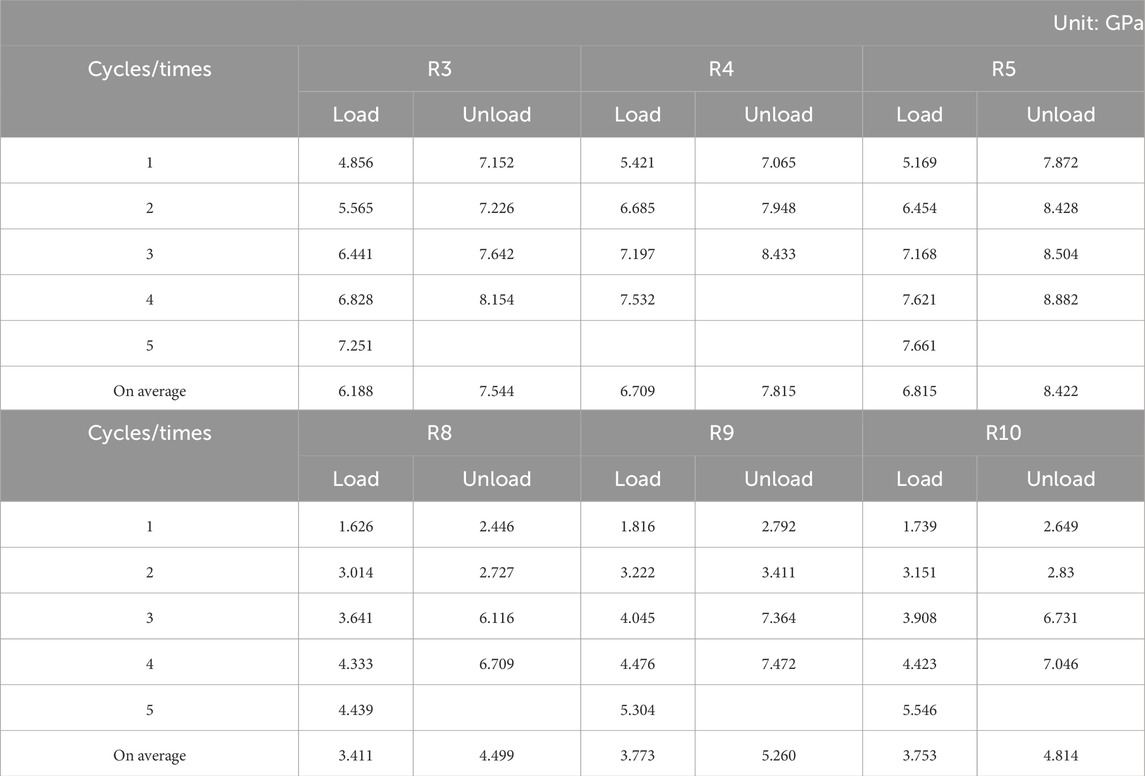
The modulus of elasticity is a crucial parameter that reflects the stiffness of rock materials. As depicted in Figure 4, the modulus of elasticity of the specimen varies dynamically throughout the loading and unloading process. To determine the deformation modulus for both loading and unloading phases, the slopes of the nearly linear segments in each cycle were calculated. The results of these calculations are presented in Table 3.
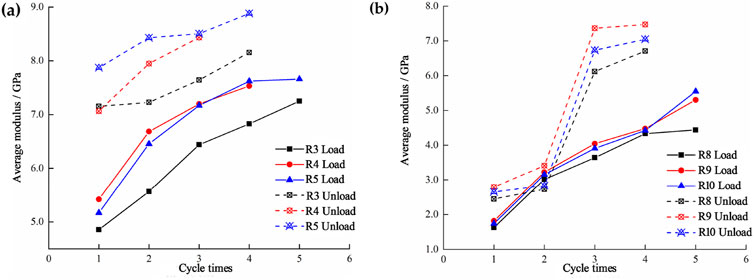
Figure 4. Cyclic loading and unloading average modulus - number of cycles curve. (A) Natural pecimens. (B) Water-saturated specimens.
According to Table 3, the average deformation modulus during loading for natural specimens is 6.571 GPa, while the average modulus during unloading is 7.927 GPa. For saturated specimens, the average loading deformation modulus is 3.646 GPa, and the unloading modulus is 4.858 GPa. The natural specimens exhibit higher loading and unloading moduli compared to the saturated specimens, indicating that water saturation reduces the stiffness of the specimens.
Figure 4 illustrates that while the deformation modulus for both natural and saturated specimens shows different detailed patterns, the overall trend is an increase with the number of cycles. Notably, during the second loading phase, there is a significant rise in the deformation modulus, reflecting a rapid increase in specimen stiffness. Subsequent cyclic loading still leads to an increase in modulus, but at a slower rate.
This is primarily due to the initial compaction of primary fissures and closure of microfissures during cyclic loading. Upon unloading, a small portion of the compacted fissures may begin to recover, but the majority remain closed, resulting in increased overall stiffness. Consequently, the elastic modulus shows a more pronounced increase during the second loading phase. In the following loading and unloading cycles, the deformation of the specimens becomes more coordinated with increasing cyclic stress levels, approaching elastic behavior, and the deformation modulus gradually increases and stabilizes.
3.4 Damage characterization
Different loading methods must result in different damage patterns, and Figure 5 shows typical damage photos of specimens in two water content states under different loading methods.
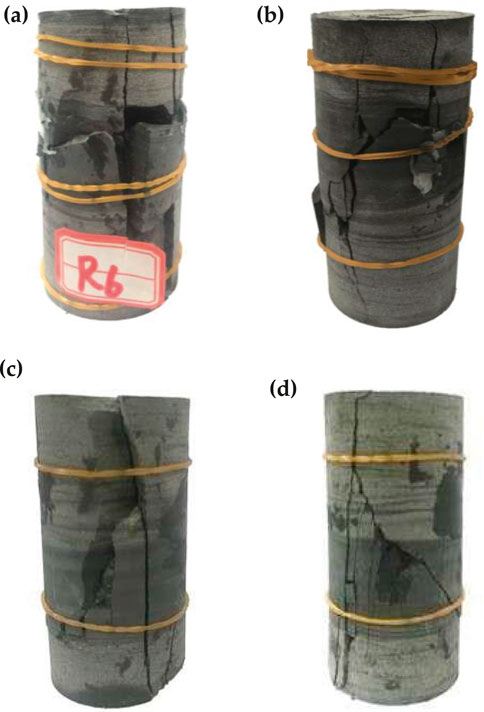

Figure 5. Damage pattern of typical interlayer specimen. (A) Natural primary loading. (B) Water-saturated primary loading. (C) Natural cyclic loading. (D) Saturated water cycle loading.
Figure 5 shows that under uniaxial loading conditions, the damage mode of both specimens is primarily through-split shear damage. This is characterized by vertical tensile cracks that penetrate the laminar surface and a significant development of transverse cracks within the tuff. In contrast, under cyclic loading, both specimens exhibit mixed tensile-shear damage. This includes vertical tensile cracks as well as monoclinic, tilted shear cracks that extend through the tuff layer.
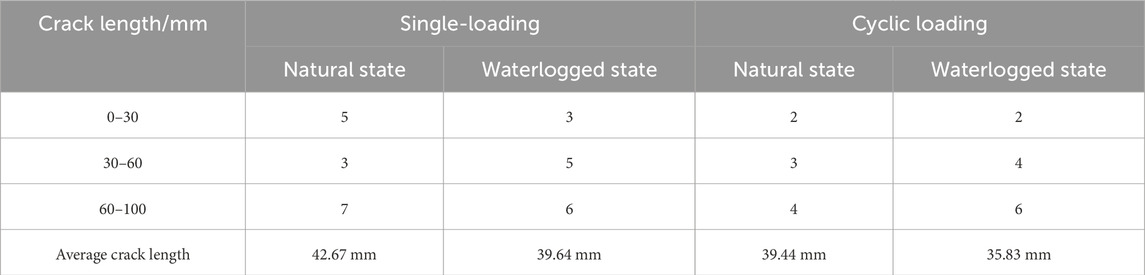
To quantitatively assess the extent of damage, the number of cracks of various lengths was observed and counted. The results of these crack statistics for typical specimens are summarized in Table 4.
The comparison of crack statistics for four typical specimens indicates that the average crack length in natural state specimens is generally greater than that in water-saturated specimens. Additionally, specimens subjected to single loading exhibit a longer average crack length compared to those undergoing cyclic loading and unloading.
In engineering practice, this suggests that different precautions should be taken based on the specific conditions of the engineering rock body. For instance, tailored in-situ modifications can be proposed according to the observed damage modes. Methods such as water injection or pre-loading through blasting can be employed to soften the rock in advance. This approach is crucial for preventing and managing safety risks associated with rock damage in engineering applications.
4 Acoustic characterization of interbedded rock samples
During loading and unloading, rocks generate acoustic emission signals that provide insights into the damage and destruction characteristics of specimens throughout the cyclic loading and unloading process. By analyzing parameters such as rise count, energy, and amplitude, we can uncover the damage behavior of the specimens.
To analyze the time-dependent variation in acoustic emission and stress, both parameters were normalized. This normalization allows for simultaneous analysis of the two factors, facilitating a more comprehensive understanding of their interrelationship.
4.1 Damage analysis of rock samples using acoustic emission parameters
Rudajev et al. (2000), following extensive research on acoustic emission technology, have found that rising count and energy are effective indicators of internal rock damage. Consequently, this paper primarily utilizes rising counts and cumulative energy to quantitatively describe the damage characteristics of the interlayer specimens. Additionally, the internal microelement strength damage variable of the rock is defined as Equations 1, 2 (Yun et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2009).
Where Nt and Et represent the cumulative rise counts and cumulative energy of the specimen at loading time t, respectively. N0 and E0 are the cumulative acoustic emission rise counts and cumulative energy of the specimen at the point of complete failure. DN denotes the damage variable based on acoustic emission rise counts for the specimen up to time t, while DE epresents the damage variable based on acoustic emission energy for the specimen at the same loading time t. The stress, rise count, damage versus time curves of water-saturated and natural specimens under cyclic loading are shown in Figure 6. From the comparison of the two figures, it can be seen that the number of acoustic emission events of the water-saturated specimen is significantly less than that of the natural specimen, which is due to the absorption of the acoustic emission signal by moisture, and most of them are low-amplitude events (40–45 dB), statistically speaking, the low-amplitude events of the natural specimen accounted for 89.48% of the total events, and the ratio of the water-saturated specimen is 81.42%, but before the damage of the specimen, both specimens have more high-amplitude events.
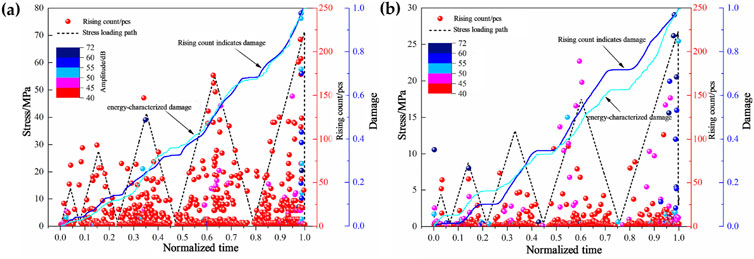
Figure 6. Time evolution curve of stress, rise count and damage variable. (A) Natural specimens. (B) Water-saturated specimens.
4.2 Characterization of damage precursors of interbedded rock samples under cyclic loading
Figure 6 illustrates that the damage of specimens, as characterized by acoustic emission rise counts and energy, is generally synchronized, though details vary. The damage curve for natural specimens shows an almost linear increase, with a brief “step” calm period during the low-stress “unloading-reloading” phase, where damage remains relatively stable. However, under high stress conditions, the unloading phase still induces irreversible damage, indicating that high stress is a significant factor in rock damage.
In contrast, the damage curve for water-saturated specimens is more erratic but follows a similar overall trend. Water-saturated specimens experience a longer “step” calm period compared to natural specimens. After this calm period, damage continues to accumulate until the specimen fails.
Based on the observations, the “step” calm period and the occurrence of high-amplitude events preceding specimen failure can serve as precursor indicators of damage in both natural and water-saturated interbedded rock samples, both in laboratory settings and field engineering applications. A damage level of approximately 70% is identified as a precursor warning threshold for rupture instability.
Figure 6 shows that the damage of the specimens during the last “step” calm period before failure is around 70%. Following this calm period, the occurrence of high-amplitude events increases with load, leading to eventual specimen failure. Therefore, a damage level of 70% is proposed as a precursor warning value for rupture and destabilization, providing a reference for early warning in both laboratory experiments and field engineering rock disaster prediction.
5 Conclusion
This study provides valuable precursor indicators for predicting the impending instability of interbedded rock masses, offering a new theoretical basis for preventing and managing rock mass stability issues caused by cyclic loading in engineering practice.
(1) Different loading methods and water content states significantly affect the strength of interlayer specimens. Under cyclic loading, the strength of natural state specimens decreased by 18.43% compared to uniaxial loading. In contrast, for specimens subjected to uniaxial loading, those with saturated conditions showed a 72.18% reduction in strength compared to natural specimens. Similarly, under cyclic loading, the strength of saturated specimens decreased by 60.19% compared to natural specimens.
(2) The average modulus of interlayer specimens increases with the number of loading cycles. As cyclic stress levels rise, the deformation of both soft and hard interlayers becomes more coordinated, leading to a slower growth rate of the average modulus during loading and unloading, which eventually stabilizes. The damage modes of specimens vary with different loading conditions. Generally, the average crack length in natural specimens is greater than in water-saturated specimens after damage. Similarly, specimens subjected to uniaxial compressive loads exhibit a longer average crack length compared to those subjected to cyclic loading.
(3) Monitoring of acoustic emission signals reveals that the number of acoustic emission events in water-saturated specimens is significantly lower than in natural specimens. The damage curves, based on acoustic emission signals, indicate that both specimen types experience a short “step” calming period during “unloading-reloading.” However, the “step” calming period is notably longer for water-saturated specimens compared to natural specimens. For both specimen types, the damage associated with the final “step” calm period is approximately 70%. This value is thus used as a precursor warning for rupture and destabilization of interlayer specimens, providing valuable insights for predicting potential disasters in both laboratory settings and field engineering applications.
The limitations of this study lie in the experimental conditions, the influence of long-term hydraulic effects, a single perspective on failure mechanisms, and insufficient model applicability, pointing to the need for further exploration of rock degradation and stability prediction across multiple scales and conditions in future research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
DW: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Author DW was employed by Shanxi Yanchang Petroleum and Mining Co., Ltd.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Cai, M., Jin'an, W., and Shuanghong, W. (2001). Energy analysis and comprehensive prediction of rockburst in deep mining rock body of Linglong Gold Mine. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 20 (1), 38–42.
Cai, M. F., and Brown, E. T. (2017). Challenges in the mining and utilization of deep mineral resources. Engineering 3 (4), 432–433. doi:10.1016/j.eng.2017.04.027
Chu, C., Wu, S., Zhang, S., Guo, P., and Zhang, M. (2020). Mechanical behavior anisotropy and fracture characteristics of laminated sandstone. J. Central South Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 51 (8), 2232–2246.
Cui, F., Yang, Y. B., Lai, X. P., Jia, C., and Shan, P. (2019). Experimental study on the effect of advancing speed and stoping time on the energy release of overburden in an upward mining coal working face with a hard roof. Sustainability 12 (1), 37. doi:10.3390/su12010037
Dong, X., Yang, T., Wang, P., Zhang, P., and Zhao, Y. (2014). Experimental study on acoustic emission characteristics during cyclic loading and unloading of dry and saturated rocks. J. Coal 39 (7), 1243–1247.
Guo, J., Liu, X., and Qiao, C. (2014). Experimental study on mechanical properties and energy mechanism of karst tuff under natural and water-saturated condition. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 33 (2), 296–308.
Huang, F., Zhou, Y., Li, T., and Hu, X. (2020). Indoor experimental study on mechanical properties and damage patterns of soft and hard interbedded rock. J. Coal. 45 (S1), 230–238.
Lai, X., Dai, J., and Chao, L. (2020a). Characterization of overburden linkage disaster in sharp inclined coal seam mining. J. Coal 45 (1), 122–130.
Lai, X., Zhang, S., Cui, F., Wang, Z., Xu, H., and Fang, X. (2020b). Energy release law of water-bearing coal rock damage evolution process and key pregnant acoustic emission signal pickup. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 39 (3), 433–444.
Lai, X. P., Ren, J., Cui, F., Shan, P., Dai, J., Xu, H., et al. (2020). Study on vertical cross loading fracture of coal mass through hole based on AE-TF characteristics. Appl. Acoust. 166, 107353. doi:10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107353
Li, S., Liu, C., Speng, S., and Lu, Y. (2017). Research on fatigue deformation characteristics and damage modeling of sandstone under uniaxial graded cyclic loading conditions. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 46 (1), 8–17.
Li, S., Zhou, M., Gao, Z., Chen, D., Zhang, J., and Hu, J. (2019). Experimental study on acoustic emission characteristics of rocks before peak strength under incremental cyclic loading and unloading. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 38 (4), 724–735.
Li, W., Zhu, C., Yang, C., Duan, K., and Hu, W. (2018). Experimental and DEM investigations of temperature effect on pure and interbedded rock salt. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 56, 29–41. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2018.05.020
Liu, B., Huang, J., Wang, Z., and Li, L. (2009). Damage evolution and acoustic emission characterization of uniaxially compressed coal rock. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 28 (S1), 3234–3238.
Mingqing, Y., and Su, C. (2008). Experimental study on strengthening effect of cyclic loading on marble specimens. J. Solid Mech. 29 (1), 66–72.
Ouyang, Z., Liu, Y., Li, C., Shi, Q., Li, W., Yi, H., et al. (2024). An experimental study of the evolutionary patterns of mechanical properties of coalsunder multiple mining disturbances. Coal Geol. and Explor. 52 (10), 72–84.
Quchao, X. U., Xating, F., and Chen, B. (2009). Uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading test and acoustic emission characterization of silica. Geotechnics 30 (10), 2929–2934.
Rong, T., Liu, K., Zhou, H., Guan, C., Chen, Y., and Ren, W. (2022). Study on the evolution law of deep coal permeability under mining stress. Chin. J. Geotechnical Eng. 44 (06), 1106–1114.
Rudajev, V., Vilhelm, J., and Lokajík, T. (2000). Laboratory studies of acoustic emission prior to uniaxial compressive rock failure. Int. J. Rock Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 37 (4), 699–704.
Shan, P., Cui, F., Cao, J., Lai, X., Sun, H., and Yang, Y. (2018). Experiment on flow-solidity coupling characteristics of fractured coal rock considering regional ground stress characteristics. J. Coal 43 (1), 105–117.
Shan, P. F., and Lai, X. P. (2018). Numerical simulation of the fluid-solid coupling process during the failure of a fractured coal-rock mass based on the regional geostress. Transp. Porous Media 124 (3), 1061–1079. doi:10.1007/s11242-018-1110-6
Shang, J., Duan, K., Gui, Y., Handley, K., and Zhao, Z. (2018). Numerical investigation of the direct tensile behaviour of laminated and transversely isotropic rocks containing incipient bedding planes with different strengths. Comput. Geotechnics 104, 373–388. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.11.007
Su, C. (2006). Yang Shengqi. Experiment on deformation and strength characteristics of rock samples under cyclic loading and unloading. J. Hohai Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 34 (6), 667–671.
Sun, A., Hu, M., Hua, J., Gao, Y., Chen, J., Si, D., et al. (2019). Characteristics of acoustic emission signals and spatio-temporal evolution law during uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading of sandstone. J. Hohai Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 47 (5), 462–467.
Sun, B., Zhu, Z. D., Shi, C., and Luo, Z. (2017). Dynamic mechanical behavior and fatigue damage evolution of sandstone under cyclic loading. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 94, 82–89. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.03.003
Wang, X., Jiang, L., Li, Y., Zhang, L., Sainoki, A., Mitri S, H., et al. (2024a). Experimental study on the mechanical behavior and failure characteristics of rock analogs with filled internal fractures: a new method by sand powder 3D printing. Constr. Build. Mater. 427, 136261. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.136261
Wang, H., Yang, T., Liu, H., Zhao, Y., and Deng, W. (2017). Mechanical properties and energy evolution of dry and saturated sandstone under cyclic loading. Geotechnics 38 (6), 1600–1608.
Wang, K., Zuo, X., Du, F., Sun, J., Ju, Y., and Feng, C. (2024b). Macro-mesoscopic perspective damage characteristics and en-ergy-damage constitutive model of coal-rock composite structures subjected to cyclic loading. J. ofChina Coal Soc. 49 (2), 767–784.
Wang, X., Liu, X., Shen, R., and Deng, X. (2016). Experimental study on load damage acoustic emission characteristics of natural and water-saturated coal samples. Coal Mine Saf. 47 (1), 28–32.
Wu, B., Wu, L., Luo, J., and Jia, S. (2015). Research on uniaxial compression breakage law of soft and hard interbedded rock model. Hydropower Energy Sci. 33 (4), 123–126.
Xu, H., Lai, X., Shan, P., Yang, Y., Zhang, S., Yan, B., et al. (2023). Energy dissimilation characteristics and shock mechanism of coal-rock mass induced in steeply-inclined mining: comparison based on physical simulation and numerical calculation. Acta Geotech. 18, 843–864. doi:10.1007/s11440-022-01617-2
Yang, Z., Tao, M., Fei, W., Yin, T., Gu, X., and Narsilio, G. A. (2024b). A coupled thermo-mechanical model for investigating cracking and failure of composite interbedded rock. Eng. Geol. 339, 107645. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2024.107645
Yang, Z., Tao, M., Yin, T., Memon, M. B., and Ranjith, P. G. (2024a). Grain-based modeling for heterogeneous rock fragmentation under stressed conditions and TBM cutter spacing optimization. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 57, 10467–10489. doi:10.1007/s00603-024-04099-8
Yong, M. T., Ming, C. K., and Juang, C. H. (2006). An experimental investigation of the failure mechanism of simulated transversely isotropic rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 43 (8), 1163–1181. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.03.011
Yun, Y., Zhang, H., Liang, B., and Zhang, Y. (2021). Acoustic emission test on tensile damage characteristics of sandstone under freeze-thaw cycles. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 38 (04).
Zhang, G., Deng, Z., Jiang, J., Li, S., Mo, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2020). Research on acoustic emission characteristics of coal with strong impact propensity under different loading methods. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 37 (5), 977–982.
Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Song, S., Zhao, Y., and Li, H. (2022). Mechanical properties and acoustic emission characteristics of sandstone under naturaland saturated conditions. Coal Geol. and Explor. 50 (2), 98–105.
Zhang, Yu, Ting-ting, Y. U., Tong, Z., Shu-yan, L. I. U., and Jia-wen, Z. (2021). Experimental study of the permeability evolution of fractured mudstone under complex stress paths. Chin. J. Eng. 43 (7), 903–914.
Keywords: cyclic loading-unloading, strength degradation, acoustice mission, water saturation, rock mechanics
Citation: Wei D (2025) Mechanical and acoustic characteristics of interbedded rock samples under cyclic loading-unloading conditions. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1499993. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1499993
Received: 22 September 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 05 June 2025.
Edited by:
Weiyao Guo, Shandong University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Dexing Li, China University of Mining and Technology, ChinaZheng Yang, Monash University, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dong Wei, enN5ZDk1MDUyNEB5ZWFoLm5ldA==
 Dong Wei
Dong Wei