- 1Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2School of Environment, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
- 3China Logistics Group Science and Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
The burgeoning demand for zirconium, driven by the rapid development of smart devices, low-carbon energy technologies, and other emerging industries, underscores the importance of understanding the dynamics of its global trade network. However, the evolutionary patterns of the international zircon ore trade network and its resilience to disruptions remain unclear. This study constructs the international zircon ore trade network from 2013 to 2022, analyzes its structural evolution at both the network and node levels, and evaluates its robustness in 2022 using five attack strategies: random node removal, random edge removal, edge degradation, targeted removal based on node degree, and targeted removal based on node betweenness centrality. Our findings reveal that: (1) the international zircon ore trade network exhibits a shift in the import market towards Asia, with the export market dominated by Spain, the United States, and Brazil. China plays a crucial role as a bridge connecting various countries, while Japan exerts significant influence within the network; (2) the network is particularly vulnerable to targeted attacks based on node degree and betweenness centrality, highlighting the potential for significant disruption following the removal of key nodes. This study provides valuable insights for ensuring the stable and sustainable supply and consumption of zirconium resources, informing the development of targeted policies for countries and relevant industries.
1 Introduction
Zirconium (Zr), a rare metal characterized by inherent extraction complexities, is widely employed in the fabrication of refractory materials, glass, and ceramics owing to its exceptional properties, encompassing corrosion resistance, high strength, heat resistance, and abrasion resistance. These attributes render it indispensable in critical applications such as nuclear reactors, atomic energy, aerospace, and other vital industrial sectors (Perks and Mudd, 2019). The rapid global advancement of high-end alloy equipment, low-carbon energy technologies, and smart devices has spurred a continuous surge in the demand for zirconium resources, prompting an increasing number of nations to prioritize securing a stable supply of zirconium as a strategic imperativ (Greenblatt et al., 2017; Xiong et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2023a; Fahad et al., 2024). China, as the world’s leading consumer of zirconium resources, has formally designated zirconium as a strategic mineral and implemented a comprehensive suite of policy measures aimed at safeguarding its zirconium resource supply (Yu et al., 2021). Similarly, developed nations such as the United States and Japan have also recognized the criticality of zirconium, incorporating it into their respective lists of critical minerals or rare metal security strategies. These countries are actively pursuing diversification of zirconium resource supply channels and bolstering their strategic reserves of this essential metal (Hayes and McCullough, 2018; Silveira and Resende, 2020; Giese, 2022). Driven by the ongoing emergence of novel technologies and the sustained expansion of the global economy, the strategic significance of zirconium resources is anticipated to escalate further (Zhou et al., 2022). Consequently, international competition for zirconium resources will intensify, and ensuring a secure and stable supply of zirconium will become a crucial determinant of national competitiveness.
Zirconium resources are predominantly derived from alluvial mining operations and exhibit a pronounced geographical concentration. South Africa, Australia, Mozambique, Madagascar, and Senegal collectively account for 90.5% of global reserves (USGS, 2024), resulting in a significant resource deficit for China and other major consuming countries (Zhu et al., 2023b). The significant disparity between global zirconium supply and demand has resulted in a growing reliance on international trade, highlighting the crucial role of the zirconium resource trading network in supporting economic and social development (Chaney, 2014; Geng et al., 2014; Petridis et al., 2020; Gutiérrez-Moya et al., 2021). However, in recent years, the confluence of low-carbon development initiatives and the rapid iteration of advanced technologies has sustained high levels of global zirconium consumption. Consequently, the supply dynamics of zirconium resources and the intricate web of trade dependencies among nations have become increasingly complex, leading to significant shifts in the structural characteristics of the zirconium resource trade network (Gediga et al., 2019). Furthermore, the frequency of recent emergencies, including Australia’s export restrictions, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the Ukrainian crisis, has profoundly highlighted the vulnerability of the zirconium resource trade network to disruptions, underscoring the need for a deeper understanding of its resilience and potential risks (Klimek et al., 2019; Laber et al., 2023). These events have triggered significant fluctuations in zirconium prices, with prices ranging from $1.14/kg in 2021 to $1.62/kg in 2022, and even resulted in resource shortages for some countries. Consequently, ensuring a stable supply of zirconium resources has become a paramount concern for nations worldwide (Henckens et al., 2019). Therefore, elucidating the evolutionary trajectory of the zirconium resource trade network, evaluating its resilience in the face of emergencies, and identifying its vulnerable links hold immense strategic significance. These analyses will enable countries to accurately discern trends in zirconium resource trade patterns, forecast future supply and demand scenarios, formulate more scientifically sound and rational zirconium resource security strategies, and ultimately safeguard the stable global supply of this critical resource.
Extensive research has been conducted on the distribution of zirconium resources, encompassing supply and demand patterns, material metabolism, forms of related industrial development, and prospective applications in representative countries and regions (Zhu et al., 2023a). These studies have yielded valuable insights into the significance of zirconium resources, the current state of their exploitation and utilization, and anticipated future development trajectories. While the international trade network of zirconium ore and its associated risks remain understudied (Li et al., 2021). Indeed, the import and export trade of zirconium ore, as a representative commodity, reflects the specialization of different countries and regions. Moreover, the promising prospects of high-tech applications for zirconium have fostered a global zirconium ore trade network that mirrors the intricate trade and organizational structures among nations, offering insights into emerging geopolitical patterns (Lee and Lee, 2024). Existing studies on mineral resource trade networks have explored various aspects of their structure, evolution, and resilience. A significant body of research has focused on analyzing the topological features of these networks, including network density, average path length, clustering coefficient, and core-periphery structure (Xi et al., 2020; Chang et al., 2023; Shuai et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2023). These studies have revealed important insights into the patterns of connectivity and the distribution of influence within mineral trade networks. Furthermore, researchers have investigated the drivers of network evolution, examining the role of trade policies, technological advancements, and resource endowments in shaping the structure and dynamics of mineral trade (Wang et al., 2023). To assess the resilience of mineral trade networks to disruptions, various analytical methods have been employed. Network centrality analysis has been used to identify key nodes and trade relationships that are critical for maintaining network connectivity (Sun et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2022; Shuai et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023; Xia, 2023; Chen et al., 2024). Scenario simulation and risk assessment approaches have been applied to evaluate the potential impacts of different types of shocks, such as natural disasters, political instability, and economic crises, on mineral trade flows (Chen et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2023). These studies have highlighted the vulnerability of mineral trade networks to specific types of risks and have emphasized the need for proactive risk management strategies. Furthermore, research on mineral resource trade networks has increasingly integrated with studies of supply chain and industrial chain resilience. These studies have examined the interdependencies between mineral trade, supply chain operations, and industrial production, explored strategies for enhancing the resilience of the entire value chain (Hofmann et al., 2018; Diprose et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021; Berthet et al., 2024), and have investigated the role of diversification, inventory management, and collaboration in mitigating supply chain risks and ensuring the stable supply of critical minerals (Althaf and Babbitt, 2021; Liu et al., 2024). These research methodologies and models have been extensively applied in trade network studies across various mineral resources, including copper, iron, aluminum, lithium, cobalt, chromium, and nickel (Nuss et al., 2016; Zhong et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020; Ren et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2024). However, in-depth studies specifically focused on the international trade network of zirconium ore remain urgently needed. The specific characteristics of the structural evolution of the global zirconium ore trade network, at both the network and node levels, have not been adequately explored. Moreover, the impacts and nuanced differences arising from various event shocks on the zirconium trade network have not been effectively quantified. This study aims to address this research gap by constructing a zircon ore trade network, analyzing its structural evolution at both the network and node levels, and evaluating its resilience to various types of disruptions.
This study aims to achieve a comprehensive understanding of the zircon ore trade network by: (1) mapping the evolution of its structure over the past decade, including key shifts in major trading partners and trade flows; (2) identifying the most influential countries within the network and analyzing their roles in shaping trade patterns; and (3) assessing the network’s vulnerability to disruptions caused by various factors, such as targeted sanctions or natural disasters. The network’s invulnerability will be evaluated using simulations of both random and targeted disruptions to key nodes and edges. Targeted disruptions will focus on major exporters and importers, as well as countries with high betweenness centrality, to understand the potential cascading effects of their removal from the network. This analysis will help identify critical vulnerabilities and potential bottlenecks in the zircon ore trade. The findings of this study will provide valuable insights for policymakers and stakeholders in the zirconium industry. By identifying vulnerable nodes and trade relationships, this research will inform the development of targeted policies to mitigate supply chain risks. ’The remainder of this study is organized as follows: Section 2 delineates the methodological framework, including data sources and processing procedures, the construction of the zirconium ore network model, the selection of structural analysis metrics, and the implementation of the destructive resistance assessment model and its associated measurement metrics. Section 3 presents and discusses the key findings derived from the analysis. Finally, Section 4 summarizes the principal conclusions drawn from this investigation.
2 Methodology
2.1 Data
In order to study zirconium ores and concentrates (HS Code 261510), the core trade commodity in the supply chain of the zirconium industry chain, we obtained all the trade information related to zirconium ores and concentrates from 2013 to 2022 globally from the UN Comtrade Database. We obtained all trade information related to zirconium ores and concentrates from the UN Comtrade Database from 2013 to 2022 on a global scale. Based on obtaining the raw data, we removed internal trade data due to territorial consolidation to avoid double-counting and exaggerated trade volumes. In international trade, trade data of importing and exporting countries may differ due to statistical caliber and reporting time. To ensure the consistency of data, we prioritize the trade data of exporting countries as the final trade flow data. Missing trade volume data were addressed by calculating the average price of zirconium ores and concentrates for the respective year and then dividing the reported trade value by this average price to approximate the missing volume. Outliers in trade values were identified and removed. Specifically, extreme values, likely due to reporting errors, were replaced with the average trade value of the corresponding country in the preceding and succeeding years. Finally, the zirconium flow in zirconium ores was calculated using Equation 1 (Zhu et al., 2023a):
where
2.2 Network construction and structure indicators
2.2.1 Construction of the zirconium ore trade network
A directed weighted network was constructed to represent the zircon ore trade, where nodes represent countries, directed edges represent trade flows from exporting to importing countries, and edge weights represent the volume of zircon ore traded. Complex network analysis is used to construct the international trade network of zirconium ore
2.2.2 Average path length and diameter
Average path length refers to the average of the shortest path lengths between all pairs of nodes in a network, reflecting the overall connectivity tightness of the network and the average efficiency of information or commodity propagation in the network (Chen et al., 2018). Larger values indicate that the average distance between nodes in the network is greater, connectivity is relatively weak, and information or commodities are less efficiently disseminated. Meanwhile, the diameter is an upper limit of the average path length, i.e., the diameter must be greater than or equal to the average path length, which is more concerned with the maximum extension of the network (Parhami and Yeh, 2000). Their formula is described by Equations 2, 3:
where
2.2.3 Density
The density of a trade network represents the ratio of the number of trade connections to the number of all possible trade connections in a trade network (Wise, 2014). It represents the strength of trade relationships between individual nodes (countries or regions) within the network. A higher density indicates that more trade connections exist between the nodes in the network, more frequent trade exchanges, stronger overall network connectivity, and a higher degree of trade integration, but it may also mean that the network is less resistant to risk. The definition is given by Equation 4.
where
2.2.4 Modularity
Within trade networks, modularity is employed to quantify the community structure (Bickel and Chen, 2009), representing the degree to which nodes within the network cluster into distinct groups. This metric can be utilized to understand patterns of trade cooperation among different countries or regions (Karrer and Newman, 2011). It represents the extent to which trade connections in a network are clustered within different groups, compared to randomly connected networks. It usually takes values between −1 and 1. The larger the value, the stronger the community structure of the network and the more pronounced the trade blocs or regionalization. Conversely, a smaller value of modularity indicates a weaker community structure of the network, more decentralized trade connections, and more diversified trading partners for individual countries or regions. The calculation was performed according to Equation 5:
where
2.2.5 Degree
The degree of a node in a trade network represents the number of connections a country or region has in the trade network, i.e., the number of trade relationships that exist between that country or region and other countries or regions (Broido and Clauset, 2019). Entry-degree represents the number of trading partners of a country or region that import zircon ore from other countries or regions. The degree of entry represents the number of trading partners of a country or region that export zirconium ores from other countries or regions. A higher degree indicates that the country or region has more trading partners connected in the trading network and is more active in trade. A larger in-degree indicates that the country or region has more diversified sources of imports and may be less dependent on other countries or regions. In contrast, a larger out-degree indicates that the country or region has a wider export market. Equations 6–8 express the in-degree, out-degree, and degree of node
2.2.6 Betweenness centrality
The betweenness centrality of a node in a trade network represents the importance of a country or region in connecting the trade paths of other countries or regions (Geisberger et al., 2008). In other words, it measures the extent to which a country or region acts as a “bridge” or “middleman” in a trade network. The larger the value, the more important an intermediate position the country or region plays in the trade network, the more trade paths connecting it to other countries or regions, and the more important it is to the trade network. The larger the value, the more important the intermediate position of the country or region in the trade network, the more trade paths connecting other countries or regions, and the greater influence on the overall connectivity of the trade network and information flow. The betweenness centrality of node
2.2.7 Eigenvector centrality
Eigenvector centrality in a trade network represents the influence and importance of a country or region in the network. It considers not only the number of direct trading partners of the country or region, but also the importance of its trading partners. The larger the value, the higher the influence and importance of the country or region in the trade network. This is not only because it has more trading partners but also because it is close to those trading partners that are important in the network, has easier access to trade information and resources, and has more influence on the trade network. It can be expressed as the eigenvector corresponding to the neighbor matrix for the zircon trade network as in Equation 10, which is usually found using an iterative algorithm (Ruhnau, 2000).
where
2.3 Invulnerability evaluation model
Against the background of the deepening development of globalization, the international trade network of zircon ore has become increasingly complex and vulnerable to various emergencies, such as natural disasters, political unrest, economic crises, epidemics, and the failure of any one node or connection may trigger a chain reaction and cause a major impact on the global trade system. To simulate as much as possible the destruction resistance of the zircon ore trade network under various risk events that may occur such as major shocks to large trading countries or hub countries, e.g., economic crises, political turmoil, etc., resulting in their inability to participate in international trade normally, blockades or interruptions of crucial trade corridors or transit countries, e.g., channel blockades, wars, etc., resulting in the obstruction of international trade routes, as well as small-scale localized conflicts, natural disasters, and so on. Five attack strategies were employed to assess the invulnerability of the 2022 zircon ore trade network: node degree attack, node betweenness centrality attack, random node attack, edge weight degradation attack, and random edge attack. The node degree attack simulates scenarios where major trading hubs experience significant disruptions, such as economic crises or political instability, hindering their ability to participate in international trade. The node betweenness centrality attack simulates disruptions to critical transit countries or trade corridors. Nodes with high betweenness centrality represent key intermediaries in the trade network. Attacking these nodes simulates blockades, sanctions, or other disruptions that impede the flow of goods through these crucial channels. The random node attack simulates smaller-scale, localized disruptions, such as natural disasters or unforeseen events affecting individual countries. This attack randomly removes nodes from the network, representing the unpredictable nature of such events. The edge weight degradation attack simulates situations where trade flows are gradually reduced, for example, due to escalating trade tensions, increasing transportation costs, or declining demand. The random edge attack simulates the disruption of specific trade routes due to unforeseen circumstances, such as political disagreements between countries or localized transportation disruptions. Each attack strategy was simulated 20 times, and the arithmetic mean of the results was used to account for the stochastic nature of the attacks and to provide a more robust estimate of the network’s invulnerability.
2.4 Indicators of invulnerability
In order to reflect the overall connectivity and functionality of the network after an attack or failure, we measure the network’s destructiveness in terms of its overall connectivity efficiency and maximum connectivity size.
2.4.1 Global efficiency
Global efficiency refers to the average reciprocal length of the shortest trade paths between all pairs of countries in the network, which represents the convenience or efficiency of trade between all countries in the entire network. Higher global efficiency means lower costs and higher trade efficiency between countries in the network (Shang et al., 2021; Engsig et al., 2024). A trade network with high global efficiency can resume trade exchanges more quickly and maintain trade stability after a shock. The global efficiency is calculated as in Equation 11:
2.4.2 Largest connected component size
In trade networks, Largest Connected Component (LCC) size refers to the proportion of nodes
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structural evolution of global zirconium ore trade network
Figure 1A illustrates the fundamental trade scale of the international zircon ore trade from 2013 to 2022, encompassing the number of participating countries, the number of bilateral trade relationships, and the overall trade volume. The number of countries engaged in zircon ore trade increased from 110 to 115, while the number of bilateral trade relationships rose from 530 to 570. Both metrics exhibit a consistent pattern of short-term fluctuations with comparable frequencies, superimposed upon a long-term trend of steady growth. This observation underscores the continuous expansion of the international zircon ore trade and the intensification of trade linkages. The overall trade volume demonstrated a generally upward trajectory from 2013 to 2019, reaching a peak of 587,200 tons in 2017, representing the highest recorded value within the decade. This surge in trade volume may be attributed to the recovery of the global economy and the burgeoning demand for zircon ore in emerging economies. However, the subsequent 3 years witnessed a sustained decline, with trade volume plummeting to levels approaching those observed in 2015. This downturn can be plausibly linked to factors such as the escalation of global trade frictions and the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. Notably, a rebound in trade volume materialized thereafter, with year-on-year increases, highlighting the resilience and recovery capacity of the international zircon ore trade.
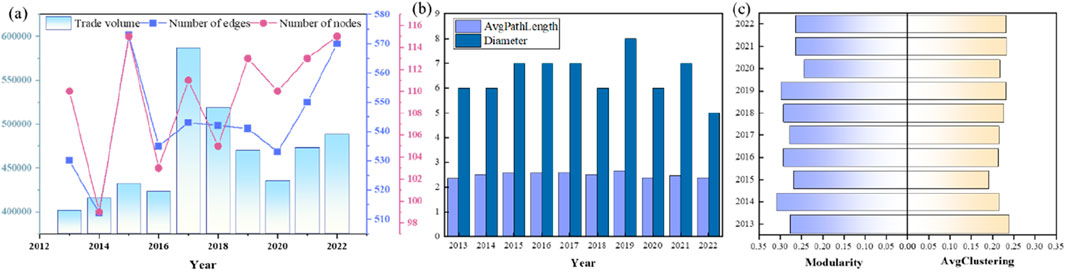
Figure 1. Changes in network structure indicators. (A) Shows the variation of nodes, edges, and trade volume. (B) Shows the evolution of diameter and average path length. The evolution of density and modularity is shown in (C).
Within the same temporal boundaries, the overall connectivity of the zircon ore trade network exhibits a comparable pattern of fluctuations, as depicted in Figure 1B. The average path length has remained relatively stable, oscillating between 2 and 3. This observation suggests that, on average, zircon ore trade between any two countries has typically necessitated the involvement of only 2 to 3 intermediary countries over the past decade. This finding further implies that the trajectory of global economic development during this period has not exerted a substantial influence on the ease of international zircon ore trade. This phenomenon may be indicative of a strong path dependence within the zircon ore trade or a limited impact of broader structural changes in the global trade network on this specific commodity. In contrast, the diameter of the network has displayed more pronounced fluctuations, ranging from 5 to 8 and reaching a peak of 8 in 2019. This heightened volatility in the length of the longest trade path within the network suggests a degree of instability and vulnerability to external shocks. Specifically, it implies that alterations in the trade policies of key countries or the occurrence of significant geopolitical events could potentially elongate trade paths, thereby increasing transaction costs and potentially disrupting the flow of zircon ore.
Regarding the degree of local aggregation and community structure, as illustrated in Figure 1C, the average clustering coefficient exhibited an initial increase from 0.276 in 2013 to 0.307 in 2014. This upward trend suggests a growing propensity for countries to engage in trade with the trading partners of their existing partners during this period, leading to the formation of more tightly knit trade circles. Localized connectivity intensified, with individual countries and their trading partners exhibiting a greater likelihood of establishing connections, indicating a gradual strengthening of regional trade integration tendencies. However, the subsequent years witnessed a decline in the average clustering coefficient, reaching a nadir of 0.243 in 2020. This decline may be attributed to the rise of global trade protectionism and the escalation of trade frictions. A rebound subsequently occurred, with the average clustering coefficient recovering to approximately the 2015 level (0.262) by 2022, reflecting the adaptability and resilience of the trade network in response to external shocks. The network’s modularity has consistently fluctuated within a range of 0.191–0.239, generally remaining at a relatively low level. This suggests that the community structure within the zircon ore trade network is not particularly pronounced, indicating a greater degree of decentralization in trade linkages among countries. The relatively weak community structure reflects the high level of globalization characterizing the international zircon ore trade, where trade relationships transcend geographical boundaries and regional blocs, fostering a more interconnected and interdependent global market.
Figure 2 visually depicts the international zircon ore trade network in 2013, 2018, and 2022 (Figures 2A–C, respectively), utilizing a Gephi plot for network visualization. Countries belonging to the same community are represented by the same color, while the direction of arrows indicates the direction of zircon ore trade flow. Line thickness corresponds to the magnitude of trade flow, and countries are identified using their respective ISO 2006 three-digit code. To provide a comprehensive illustration, we analyze the trade patterns and pivotal roles of each country, encompassing all participating nations in the zircon ore trade network. A visual examination of the network evolution from left to right reveals that despite a relatively modest increase in the number of bilateral trade relationships, the number of distinct communities has risen from three in 2013 to five in 2018. Notably, these communities encompass member countries from all continents, suggesting that international zircon ore trade is not constrained by geographical proximity. This observation indicates a growing trend towards decentralization within the overall structure of the zircon ore trade network. Regional trade integration appears to be gaining momentum, as evidenced by the diversification of trade partnerships among countries. Countries are increasingly inclined to establish trade linkages with a wider array of partners, rather than confining themselves to traditional trading relationships. This shift reflects the influence of factors such as the ongoing restructuring of global value chains and the ascendance of emerging economies on the evolving architecture of the zircon ore trade network.
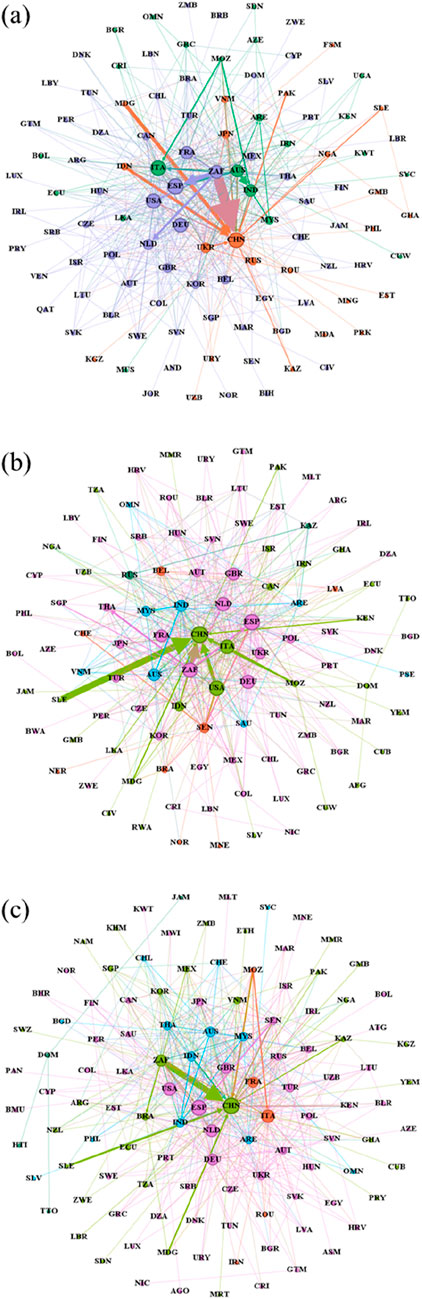
Figure 2. Evolution of the international trade network for zircon ore. (A) Shows the international trade network of zircon ore in 2013. (B) Shows the international trade network of zircon ore in 2018. (C) The international trade network of zircon ore in 2022.
Furthermore, the pluralistic community structure of the zircon ore trade network can, to some extent, mitigate systemic risk by distributing dependencies and reducing the impact of localized disruptions. China has consistently maintained a pivotal role within the zircon ore trade network throughout the 2013–2022 period, serving as the most significant importer of zircon ore and South Africa’s largest customer in terms of trade volume. It is noteworthy that, in contrast to 2013 and 2018, South Africa and China were members of the same community in 2022. This alignment suggests that cooperative frameworks such as the BRICS partnership and the Belt and Road Initiative have significantly bolstered trade and collaboration between the two nations. Interestingly, while the bilateral trade volume between China and the United States had already reached a substantial scale in 2013, their trade interactions primarily focused on labor-intensive and resource-based products. Their participation in distinct regional trade agreements resulted in their placement in different communities within the network. However, by 2018, bilateral trade linkages between China and the United States had intensified considerably, accompanied by a deeper integration of their respective roles within the global value chain, leading to their inclusion within the same community. The 2022 analysis reveals that these two countries once again belong to separate communities. This realignment carries significant implications not only for China and the United States but also for the broader landscape of global trade and the global economy.
Within the global zirconium ore import market spanning the period from 2013 to 2022, China, India, and Italy have consistently exhibited robust import demand, consistently ranking among the top five importers, as depicted in Figure 3A. This sustained prominence underscores their status as major consumers of zircon ore, highlighting their continued reliance on this resource for diverse applications in industries such as ceramics, refractories, and nuclear energy. The remaining major participants in the import market demonstrate a discernible geographical shift over time. Initially dominated by European countries such as France, Poland, and the Netherlands, the composition of leading importers has gradually transitioned towards North American countries like Mexico and Canada, and subsequently towards Asian countries including Japan and Thailand. This geographical realignment can be attributed to several factors, including the rapid economic expansion of the Asian region, the ongoing transfer of industries, and the promotion of regional trade integration initiatives. These developments have collectively fueled a surge in demand for zircon ore within Asian economies. On the export side, Spain, the United States, and Brazil have emerged as the three dominant suppliers of zircon ore (Figure 3B), owing to their abundant reserves and established technical expertise in mining and processing. Concurrently, European countries such as Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands have maintained a consistent presence in the export trade, potentially fulfilling intermediary roles by importing zircon ore from source countries and subsequently re-exporting it to other destinations. Notably, Australia and China have steadily enhanced their positions within the export market. This trend can be linked to Australia’s intensified efforts in zircon ore extraction and the burgeoning development of China’s zircon ore processing industry, suggesting a shift in the global landscape of zircon ore production and trade.
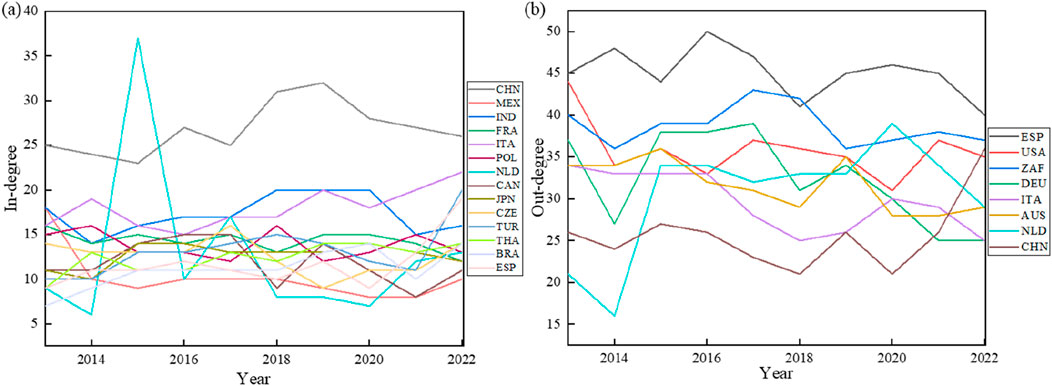
Figure 3. Changes in the in and out-degree of major nodes. (A) The change in the top 5 countries regarding inwardness from 2013–2022. (B) The change in the top 5 countries regarding outgoing degrees in 2013–2022.
Within the international zircon ore trade network spanning the period from 2013 to 2022, the betweenness centrality of individual countries remained generally below 0.27, as depicted in Figure 4A. Notably, no single country consistently occupied a position within the top five over the long term. This observation indicates a relatively dispersed distribution of information and resource flow paths within the network, suggesting the absence of a persistently dominant intermediary. Countries exhibit a relatively equitable distribution of positional power within the network, with no single nation wielding the capacity to exert absolute control over the flow of information or resources between other countries. The absence of an absolute central node functioning as a “hub” or “bridge” points towards a relatively balanced network structure. This balanced configuration can potentially mitigate trade risks and enhance the overall stability of the zircon ore trade network. Despite the prevailing balance, China stands out as a notable participant. Its betweenness centrality has remained comparatively high throughout most of the analyzed period, signifying its considerable influence within the network. This aligns with China’s prominent position in both the import and export markets, as discussed previously, confirming its crucial role as a vital nexus connecting other countries within the zircon ore trade network. The analysis of eigenvector centrality, however, reveals a contrasting picture (Figure 4B), highlighting disparities in influence among trading nations. Japan’s eigenvector centrality value consistently surpasses that of other countries, starting at 0.504 in 2013 and steadily increasing to remain above 0.9 throughout the remainder of the period. This underscores Japan’s formidable influence within the zircon ore trade network, stemming from its status as a major global consumer of zircon ore and its close trade relationships with numerous other key players, including China and South Korea. As a major consumer, shifts in Japan’s demand for zircon ore exert a significant impact on the market, rendering its position within the trade network paramount. China occupies the second position in terms of influence based on eigenvector centrality. However, its value has experienced a decline from 0.59 in 2013 to 0.153 in 2022, suggesting a diminishing influence within the zircon ore trade network over the past decade.
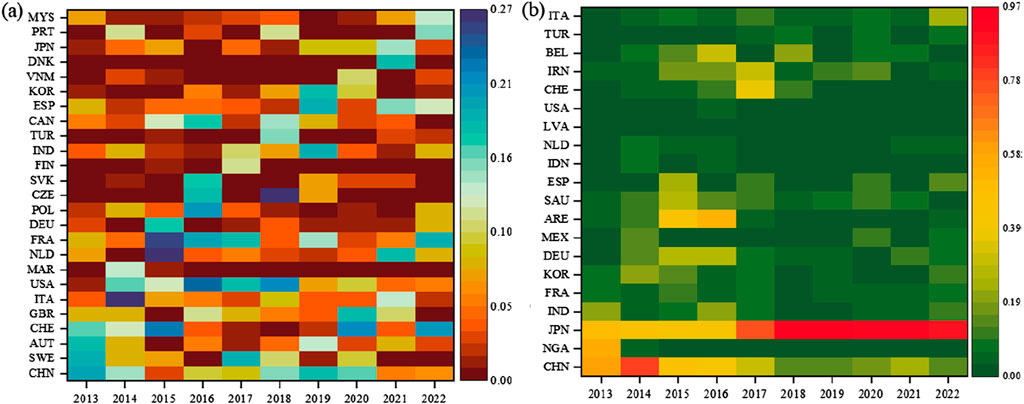
Figure 4. Changes in Node Betweenness Centrality and Eigenvector Centrality. (A) Changes in the top 5 countries ranked by betweenness centrality from 2013 to 2022. (B) Changes in the top 5 countries ranked by eigenvector centrality from 2013 to 2022.
3.2 Invulnerability simulation of the global zirconium ore trade network
To assess the resilience of the zircon ore trade network against potential disruptions, predict vulnerabilities, and evaluate its capacity to withstand malicious attacks, we conducted a comprehensive simulation analysis on the 2022 network using five distinct attack strategies. This analysis aimed to explore the ramifications of various attack strategies on the network’s structural integrity and overall functionality. The initial global efficiency of the 2022 network was 0.19, while the initial size of the largest connected component (LCC) was 0.38. Figure 5A visually depicts the changes in global efficiency of the 2022 zircon ore trade network under each of the five attack strategies as the proportion of removed nodes or edges increases. The random node attack strategy reveals a stepwise decline in global efficiency as critical nodes are progressively removed from the network. This pattern highlights the presence of key nodes whose removal disproportionately impacts network connectivity, underscoring their importance in maintaining the network’s overall functionality.
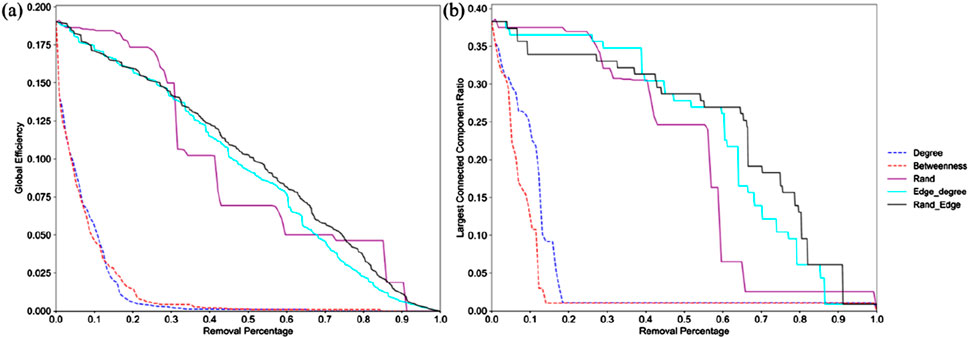
Figure 5. Changes in Global Efficiency and LCC Size under Different Attack Strategies. (A) Represents global efficiency. (B) Represents the LCC Size.
Conversely, random edge attacks and edge weight descending attacks demonstrate a near-linear decline in global efficiency, suggesting a less pronounced disruption to the network structure. This difference arises because removing edges or reducing edge weights does not directly eliminate nodes, thereby preserving a greater degree of connectivity within the network. Notably, when the removal proportion is below 0.3, random edge attacks and edge weight descending attacks prove to be more disruptive than random node attacks. This phenomenon may be attributed to the presence of redundant edges within the network, where the removal of a limited number of edges or the reduction of edge weights exerts a relatively minor impact on the overall network structure.
Node degree attacks and node betweenness centrality attacks exhibit a similar trend in reducing global efficiency, as both strategies prioritize the removal of key nodes, resulting in comparable levels of network damage. However, while the difference is subtle, node degree attacks tend to reduce global efficiency to zero more rapidly.
Figure 5B presents the corresponding results for the size of the largest connected component (LCC). When the node removal proportion is below 0.3, random node removal and edge weight descending removal strategies demonstrate even less disruptive effects than random edge removal. However, random node removal subsequently leads to a more accelerated decline in LCC size, with the network’s LCC size diminishing to only 0.026 when the node removal proportion reaches 0.68. In contrast, the two edge attack strategies can more swiftly reduce the network’s LCC size to a lower level (0.008). This disparity arises because the removal of edges directly severs connections between nodes, leading to a rapid deterioration of network connectivity.
Unlike the observations for global efficiency, node betweenness attacks exhibit a faster reduction in LCC size compared to node degree attacks. When the proportion of attacked nodes reaches 0.13, the network’s LCC size stabilizes at 0.1, whereas node degree attacks necessitate a removal proportion of 0.19 to achieve the same effect. This discrepancy indicates that the removal of nodes characterized by higher betweenness centrality exerts a more substantial impact on network connectivity. Beyond this point, the network’s LCC size remains constant until all nodes are removed, signifying not a robust network but rather the absence of any remaining pathways for inter-nodal communication.
3.3 Discussion
This study has elucidated the evolutionary trajectories of the international zircon ore trade network, identified pivotal nodes within the network architecture, and evaluated its overall stability and resilience in the face of potential disruptions. These findings provide a robust scientific foundation for governments and enterprises to formulate evidence-based policies and strategies that enhance the security and sustainability of zircon ore supply chains. Several key takeaways from this investigation merit particular attention:
The COVID-19 pandemic have exerted profound and multifaceted impacts on the international zircon ore trade. The global COVID-19 pandemic inflicted severe damage on the economies of numerous countries, triggering widespread production stagnation across various industries worldwide. The mining and processing of zircon ore experienced significant disruptions, while demand plummeted precipitously, culminating in a marked downturn in the global zircon ore market (Younis et al., 2023). In addition to rapid economic expansion, industrial transfer, and regional trade integration in Asia, factors such as the emergence of trade barriers, the restructuring of global value chains, heightened market uncertainty, intensified geopolitical competition, specific policies (e.g., environmental regulations, industrial subsidies), changes in demand for specific zircon products (e.g., for nuclear energy), and shifts in transportation costs and trade routes could also contribute to the observed shifts (Wen et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2024). In light of these experiences, countries should proactively address the potential threats posed by similar events to the security of their domestic zircon ore supply. Strategies to ensure a stable and resilient supply of zircon ore include the establishment of strategic reserves of zircon resources and the strengthening of international cooperation mechanisms to mitigate supply chain vulnerabilities and enhance collective resilience in the face of future shocks.
Our invulnerability simulation reveals that targeted attacks, specifically those based on node degree and betweenness centrality, pose substantial risks to the zircon ore trade network. A targeted attack based on node degree might involve the disruption of major trading hubs like key exporting countries (e.g., South Africa, Australia) or major importing countries (e.g., China, India), causing significant trade volume reduction and trade route blockades. Likewise, a targeted attack on countries with high betweenness centrality, which often act as crucial intermediaries in the trade network, could disrupt the overall flow of goods and information, fragmenting the network and leading to increased transaction costs, and reduced global efficiency. These disruptions would not only affect trade flows directly but also cascade to downstream industries, such as ceramics and aerospace, due to the increased difficulties in obtaining zircon ore and the resulting price volatility. The network invulnerability analysis demonstrates that betweenness attacks are the most detrimental overall to the zircon ore trade network’s integrity. This finding implies that the removal of nodes characterized by high betweenness centrality inflicts the most substantial damage on network connectivity and global efficiency. However, the preceding analysis of node betweenness centrality indicates that no single country consistently occupies a dominant intermediary position within the international zircon ore trade network. This apparent paradox—a network characterized by equitable standing among its nodes yet exhibiting heightened susceptibility to betweenness attacks—warrants further examination. In actuality, the equitable status of countries within the network does not necessarily translate into enhanced stability for individual participants in the international zircon ore trade. On the contrary, this seemingly balanced structure can render the network vulnerable to widespread disruption upon the removal of even a single node with relatively high betweenness centrality. This vulnerability arises because, within a relatively balanced network architecture, each node can potentially fulfill a crucial intermediary role in specific trade pathways. Even if a country’s overall trade volume is modest or its direct trade connections with other countries are limited, it may still serve as a critical link between vital trading partners. The removal of such a node would effectively sever these pathways, leading to a substantial decline in network connectivity and potentially triggering cascading failures throughout the system. This finding presents a concerning prospect for all participants in the international zircon ore trade. It signifies that a localized trade disruption in any single country, regardless of its perceived importance, could potentially have far-reaching consequences, propagating through the network and impacting a wide range of trading partners. Therefore, countries cannot afford to adopt a myopic focus solely on their major trading partners. They must also diligently assess the potential impact of disruptions originating in countries with whom they may not have direct trade relations, as the indirect effects of such disruptions can be substantial and cannot be disregarded. Although degree centrality attacks exhibit a greater impact on global efficiency than betweenness centrality attacks, they have a lesser effect on the size of the LCC. This suggests that while high-degree nodes are crucial for overall network connectivity, nodes with high betweenness centrality play a more significant role in maintaining the integrity of the largest connected subgraph. This could be because these nodes act as bridges between different clusters within the network. Removing them effectively fragments the network, leading to a more rapid decline in LCC size.
To mitigate these vulnerabilities, Zirconium industry participants must take proactive measures to enhance the resilience of the supply chain. These steps include: (1) conducting regular supply chain risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities; (2) investing in research and development to explore alternative materials that reduce dependence on zirconium; (3) diversifying procurement practices to lower reliance on individual suppliers; and (4) establishing collaborative mechanisms across the industry to share resources and mitigate risks. By diversifying supply sources, optimizing trade routes, strengthening information sharing, developing alternative materials to zircon, and promoting sustainable zircon mining and processing, we can make the global zirconium ore trade network more resilient to disruptions. This will require a coordinated effort from governments, industries, and international organizations, with a focus on long-term strategic planning and a commitment to global cooperation.
The analysis of the evolving structural characteristics and resilience of the international zircon ore trade network underscores the interconnectedness and interdependence inherent in the globalized economy, highlighting that no participant in international trade can remain insulated from the actions and circumstances of others. To foster the healthy and sustainable development of the international zircon ore trade and ensure the stability and security of both domestic and global markets, it is imperative that countries actively engage in the global trading system, foster deeper international collaboration, and cultivate a more open, inclusive, and resilient trade network architecture by expanding and diversifying trade partnerships, exploring and developing alternative trade routes, establishing and improving risk early warning mechanisms, and actively participating in the formulation and refinement of international trade rules and norms. Only through the concerted efforts of all participating nations, guided by a commitment to establishing mutually beneficial trade partnerships and fostering a spirit of shared responsibility, can we effectively address global challenges such as trade frictions, pandemic-induced shocks, and other unforeseen disruptions, thereby collectively safeguarding the stability and security of the international zircon ore trade network and ensuring its continued contribution to global economic prosperity and sustainable development. Strategies for enhancing resilience include diversifying supply sources, optimizing trade routes, strengthening information sharing, developing alternative materials to zircon, and promoting sustainable zircon mining and processing. For example, businesses should explore new trade routes and partnerships with emerging zircon producers in regions like Africa and South America. Establishing an information sharing platform could enhance risk awareness and early warning capabilities. Investing in research and development of zircon substitutes could also mitigate reliance on this resource.
4 Conclusion
Zircon, a critical strategic resource with extensive applications in sectors such as nuclear energy, aerospace, chemicals, and ceramics, exhibits a highly concentrated distribution of global reserves, primarily located in a few countries like Australia and South Africa. Consequently, numerous nations rely heavily on frequent international trade of zircon ore to acquire sufficient resources to support the development of their respective industries, rendering a stable zircon ore supply crucial for their economic prosperity and national security. To gain a comprehensive understanding of the evolutionary dynamics within the international zircon ore trade, identify key actors within the trade network, and provide empirical evidence and decision-making support for the sustainable development of individual countries and relevant industries, this study constructs a zircon ore international trade network spanning from 2013 to 2022 and employs complex network analysis methods to conduct a rigorous and systematic investigation of the network’s structural characteristics, the evolution of national roles, and its resilience to potential disruptions, with the primary findings summarized as follows.
The international zircon ore trade network exhibits characteristics of scale expansion, stable yet vulnerable connectivity, fluctuating local clustering, and an indistinct community structure. The number of participating countries and bilateral trade relationships has demonstrated consistent growth, while the overall trade volume has followed a trajectory of initial increase, a sharp decline, and a gradual recovery. The average path length has remained relatively stable, oscillating between 2 and 3, indicating the absence of significant shifts in trade facilitation over the analyzed period. The average clustering coefficient experienced an initial increase from 2013 to 2014, suggesting a strengthening of regional trade integration trends, followed by a subsequent decline and a rebound after 2020, highlighting the network’s adaptability to external shocks. The network modularity has consistently remained at a low level, signifying an unclear community structure characterized by relatively dispersed trade connections and implying a high degree of globalization within the international zircon ore trade.
China has consistently maintained a pivotal role within the zircon ore trade network, serving as a major importer and a primary trading partner of South Africa, with bilateral trade cooperation between the two countries experiencing significant strengthening in recent years. India and Italy remain prominent consumers of zircon ore, exhibiting continued growth in demand. Spain, the United States, and Brazil have emerged as major suppliers, while Australia and China have steadily enhanced their export positions within the global market. Geographically, Asian countries have witnessed a surge in demand for zircon ore, leading to a gradual shift in the import market from Europe and the United States towards Asia. Regarding national roles within the network, betweenness centrality values are generally low, with no single country consistently occupying a dominant intermediary position. This observation suggests a relatively balanced network structure, characterized by a more equitable distribution of influence among participating nations. Japan exhibits the highest eigenvector centrality, underscoring its considerable influence within the zircon ore trade network, stemming from its position as a major consumer and its close trade ties with other key players in the market.
Different attack strategies demonstrate varying degrees of impact on the network’s global efficiency and the size of the largest connected component (LCC). Random edge attacks exert the least disruptive effect, followed by edge weight descending attacks. Random node attacks induce a stepwise decline in network performance, underscoring the critical role that key nodes play in maintaining overall network connectivity. Both node degree attacks and node betweenness centrality attacks lead to a rapid decline in global efficiency, highlighting the significant disruption caused by the removal of these central nodes. However, node degree attacks exhibit a faster rate of network degradation compared to node betweenness centrality attacks. Notably, node betweenness centrality attacks prove to be more detrimental to LCC size than node degree attacks, indicating that the removal of nodes characterized by higher betweenness centrality exerts a more substantial impact on overall network connectivity. These findings emphasize the importance for countries to proactively acknowledge potential risks and vulnerabilities within the zircon ore trade network, strengthen international cooperation mechanisms to enhance collective resilience, and mitigate over-reliance on individual key nodes to promote a more robust and stable trade environment.
This research, grounded in data meticulously collected from the UN Comtrade database, provides a comprehensive analysis of the international zircon ore trade network’s structure, national roles, and resilience, yielding valuable insights with significant implications for ensuring the sustainable global supply of zircon resources. While our analysis employed five distinct node and edge removal methods to simulate the impact of sudden, disruptive events on the network, this approach may not fully encompass the complexities of all potential risks and vulnerabilities. The network analysis model simplifies the complexity of the real-world trade system, assuming static trade relationships and not fully accounting for dynamic factors such as policy changes, technological advancements, or shifts in market demand. This simplification may not fully capture the nuances of the dynamic interactions between countries. External factors, such as geopolitical conflicts, environmental regulations, and trade policy changes could also significantly impact the trade dynamics but were not included in our model. This might affect the predictive power of our model, particularly on a longer time scale. Future research should build upon these findings by incorporating more sophisticated attack simulation techniques, considering dynamic attack scenarios and their impacts on the entire supply chain; developing cascading failure models to better understand how disruptions propagate through the network and the potential magnitude of their impact; utilizing dynamic network analysis methodologies to explore the time-varying characteristics of the trade network; incorporating external factors like geopolitical risk and environmental policy into the analysis; conducting micro-level studies to investigate the trade behavior and risk management strategies of individual companies. These future research directions will lead to a more comprehensive and practical understanding of the zircon ore trade network and enhance the development of robust policies and strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
FL: Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. WL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. MX: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. QL: Methodology, Visualization, Writing–review and editing, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition. JW: Writing–review and editing, Resources, Supervision, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Distinguished Young Scholars Project 72304045, General Program Project 72074199, Major Program Project 71991483), Geological exploration project funded by Sichuan government “General Survey of Dayuanzi Phosphorate in Mabian Yi Autonomous County, Leshan City, Sichuan Province (DZ202401).”
Conflict of interest
Author JW was employed by China Logistics Group Science and Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Althaf, S., and Babbitt, C. W. (2021). Disruption risks to material supply chains in the electronics sector. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 167, 105248. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105248
Berthet, E., Lavalley, J., Anquetil-Deck, C., Ballesteros, F., Stadler, K., Soytas, U., et al. (2024). Assessing the social and environmental impacts of critical mineral supply chains for the energy transition in Europe. Glob. Environ. Change 86, 102841. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2024.102841
Bickel, P. J., and Chen, A. (2009). A nonparametric view of network models and Newman–Girvan and other modularities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106 (50), 21068–21073. doi:10.1073/pnas.0907096106
Broido, A. D., and Clauset, A. (2019). Scale-free networks are rare. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 1017. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08746-5
Cats, O., and Krishnakumari, P. (2020). Metropolitan rail network robustness. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 549, 124317. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2020.124317
Chaney, T. (2014). The network structure of international trade. Am. Econ. Rev. 104 (11), 3600–3634. doi:10.1257/aer.104.11.3600
Chang, L., Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., and Mohsin, M. (2023). Role of mineral resources trade in renewable energy development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 181, 113321. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2023.113321
Chen, G., Kong, R., and Wang, Y. (2020). Research on the evolution of lithium trade communities based on the complex network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 540, 123002. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2019.123002
Chen, W., Jiang, Y., and Liu, Z. (2024). Unveiling structural differentiation in the global nickel trade network: a product chain perspective. J. Geogr. Sci. 34 (4), 763–778. doi:10.1007/s11442-024-2226-y
Chen, Z., An, H., An, F., Guan, Q., and Hao, X. (2018). Structural risk evaluation of global gas trade by a network-based dynamics simulation model. Energy 159, 457–471. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.166
Diprose, R., Kurniawan, N., Macdonald, K., and Winanti, P. (2020). Regulating sustainable minerals in electronics supply chains: local power struggles and the ‘hidden costs’ of global tin supply chain governance. Rev. Int. Political Econ. 29 (3), 792–817. doi:10.1080/09692290.2020.1814844
Engsig, M., Tejedor, A., Moreno, Y., Foufoula-Georgiou, E., and Kasmi, C. (2024). DomiRank Centrality reveals structural fragility of complex networks via node dominance. Nat. Commun. 15 (1), 56. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-44257-0
Fahad, M., Waqar, A., and Kim, B. (2024). Effective-performance of inorganic and organic (barium zirconium titanate/polyvinylidene fluoride) piezoelectric composite for energy harvesting and self-powered smart IoT-based electronics. J. Alloys Compd. 985, 174033. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2024.174033
Gediga, J., Morfino, A., Finkbeiner, M., Schulz, M., and Harlow, K. (2019). Life cycle assessment of zircon sand. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 24, 1976–1984. doi:10.1007/s11367-019-01619-5
Geisberger, R., Sanders, P., and Schultes, D. (2008). “Better approximation of betweenness centrality,” in Proceedings of the meeting on algorithm engineering and expermiments. San Francisco, California: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 90–100.
Geng, J.-B., Ji, Q., and Fan, Y. (2014). A dynamic analysis on global natural gas trade network. Appl. Energy 132, 23–33. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.06.064
Giese, E. C. (2022). Strategic minerals: global challenges post-COVID-19. Extr. Industries Soc. 12, 101113. doi:10.1016/j.exis.2022.101113
Greenblatt, J. B., Brown, N. R., Slaybaugh, R., Wilks, T., Stewart, E., and McCoy, S. T. (2017). The future of low-carbon electricity. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 42 (1), 289–316. doi:10.1146/annurev-environ-102016-061138
Gutiérrez-Moya, E., Adenso-Díaz, B., and Lozano, S. (2021). Analysis and vulnerability of the international wheat trade network. Food Secur. 13, 113–128. doi:10.1007/s12571-020-01117-9
Hayes, S. M., and McCullough, E. A. (2018). Critical minerals: a review of elemental trends in comprehensive criticality studies. Resour. Policy 59, 192–199. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2018.06.015
Henckens, M., Biermann, F., and Driessen, P. (2019). Mineral resources governance: a call for the establishment of an international competence center on mineral resources management. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 141, 255–263. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.033
Hofmann, H., Schleper, M. C., and Blome, C. (2018). Conflict minerals and supply chain due diligence: an exploratory study of multi-tier supply chains. J. Bus. Ethics 147 (1), 115–141. doi:10.1007/s10551-015-2963-z
Hu, X., Wang, C., Lim, M. K., Bai, X., and Yao, C. (2021). Evaluating waste and scrap trade risks in Belt and Road Initiative countries. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 173, 105728. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105728
Karrer, B., and Newman, M. E. J. (2011). Stochastic blockmodels and community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E 83 (1), 016107. doi:10.1103/physreve.83.016107
Klimek, P., Varga, J., Jovanovic, A. S., and Székely, Z. (2019). Quantitative resilience assessment in emergency response reveals how organizations trade efficiency for redundancy. Saf. Sci. 113, 404–414. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2018.12.017
Laber, M., Klimek, P., Bruckner, M., Yang, L., and Thurner, S. (2023). Shock propagation from the Russia-Ukraine conflict on international multilayer food production network determines global food availability. Nat. Food 4 (6), 508–517. doi:10.1038/s43016-023-00771-4
Lee, C.-C., and Lee, C.-C. (2024). Not all are alike: assessing the effect of geopolitical risk on regional renewable energy development in China. Renew. Energy 222, 119763. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2023.119763
Li, Y., Gao, X., An, S., Zheng, H., and Wu, T. (2021). Network approach to the dynamic transformation characteristics of the joint impacts of gold and oil on copper. Resour. Policy 70, 101967. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101967
Liu, W., Li, X., Wang, J., Zhong, J., Wang, M., and Yang, J. (2024). Knowledge mapping of research on securing the supply chain for critical minerals: a scientometrics and text mining approach. J. Clean. Prod. 434, 140312. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140312
Ma, W., Li, C., Kou, J., Wang, X., Yang, H., Xue, B., et al. (2024). The Sino-US trade friction would exacerbate global inequalities in achieving SDGs. J. Clean. Prod. 446, 141218. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141218
Nuss, P., Chen, W.-Q., Ohno, H., and Graedel, T. (2016). Structural investigation of aluminum in the US economy using network analysis. Environ. Sci. & Technol. 50 (7), 4091–4101. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b05094
Parhami, B., and Yeh, C.-H. (2000). “Why network diameter is still important,” in Proc. International Conf. Communications in Computing, 271–274.
Perks, C., and Mudd, G. (2019). Titanium, zirconium resources and production: a state of the art literature review. Ore Geol. Rev. 107, 629–646. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.02.025
Petridis, N. E., Petridis, K., and Stiakakis, E. (2020). Global e-waste trade network analysis. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 158, 104742. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104742
Ren, S., Li, H., Wang, Y., Guo, C., Feng, S., and Wang, X. (2021). Comparative study of the China and US import trade structure based on the global chromium ore trade network. Resour. Policy 73, 102198. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102198
Ruhnau, B. (2000). Eigenvector-centrality — a node-centrality? Soc. Netw. 22 (4), 357–365. doi:10.1016/s0378-8733(00)00031-9
Shang, Q., Zhang, B., Li, H., and Deng, Y. (2021). Identifying influential nodes: a new method based on network efficiency of edge weight updating. Chaos An Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 31 (3), 033120. doi:10.1063/5.0033197
Shuai, J., Zhao, Y., Xiong, X., Shuai, C., and Wang, J. (2023). The co-opetition relationships of critical mineral resources for the solar PV industry between China and the world major powers. J. Clean. Prod. 426, 139171. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139171
Silveira, J. W., and Resende, M. (2020). Competition in the international niobium market: a residual demand approach. Resour. Policy 65, 101564. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101564
Sun, X., Liu, Y., Guo, S., Wang, Y., and Zhang, B. (2021). Interregional supply chains of Chinese mineral resource requirements. J. Clean. Prod. 279, 123514. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123514
Sun, X., Shi, Q., and Hao, X. (2022). Supply crisis propagation in the global cobalt trade network. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 179, 106035. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.106035
Tian, H., Wang, L., Du, Y., Sun, Y., Wu, F., Ye, H., et al. (2022). One-step natural pyrite-assisted mechanochemical detoxification of Cr(VI) in soda ash Chromite Ore Processing Residue: effectiveness, mechanisms, and life cycle analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 380, 134958. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134958
USGS (2024). Zirconium and hafnium statistics and information. Available at: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/national-minerals-information-center/zirconium-and-hafnium-statistics-and-information.
Wang, C., Zhao, L., Lim, M. K., Chen, W.-Q., and Sutherland, J. W. (2020). Structure of the global plastic waste trade network and the impact of China’s import Ban. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 153, 104591. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104591
Wang, Y., Chen, L., Wang, X., Tang, N., and Kang, X. (2023). Trade network characteristics, competitive patterns, and potential risk shock propagation in global aluminum ore trade. Front. Energy Res. 10, 1048186. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2022.1048186
Wen, T., Li, P., Chen, L., and An, Y. (2023). Market reactions to trade friction between China and the United States: evidence from the soybean futures market. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. 8 (3), 325–341. doi:10.1016/j.jmse.2022.12.002
Wise, S. (2014). Can a team have too much cohesion? The dark side to network density. Eur. Manag. J. 32 (5), 703–711. doi:10.1016/j.emj.2013.12.005
Xi, X., Zhou, J., Gao, X., Wang, Z., and Si, J. (2020). Impact of the global mineral trade structure on national economies based on complex network and panel quantile regression analyses. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 154, 104637. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104637
Xia, L.-J. (2023). Study on the characteristics and evolution of international tin ore trade based on a complex network perspective. Int. J. Wirel. Inf. Netw., 1–10. doi:10.1007/s10776-021-00525-8
Xiong, X., Zeng, X., Zhang, Z., Pell, R., Matsubae, K., and Hu, Z. (2023). China’s recycling potential of large-scale public transport vehicles and its implications. Commun. Eng. 2 (1), 56. doi:10.1038/s44172-023-00106-y
Xu, H.-C., Wang, Z.-Y., Jawadi, F., and Zhou, W.-X. (2023). Reconstruction of international energy trade networks with given marginal data: a comparative analysis. Chaos, Solit. & Fractals 167, 113031. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2022.113031
Younis, H., Alsharairi, M., Younes, H., and Sundarakani, B. (2023). The impact of COVID-19 on supply chains: systematic review and future research directions. Operational Res. 23 (3), 48. doi:10.1007/s12351-023-00790-w
Yu, S., Duan, H., and Cheng, J. (2021). An evaluation of the supply risk for China's strategic metallic mineral resources. Resour. Policy 70, 101891. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101891
Zhao, L., Yang, Y., Bai, X., Chen, L., Lu, A.-L., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Structure, robustness and supply risk in the global wind turbine trade network. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 177, 113214. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2023.113214
Zhong, W., Dai, T., Wang, G., Li, Q., Li, D., Liang, L., et al. (2018). Structure of international iron flow: based on substance flow analysis and complex network. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 136, 345–354. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.05.006
Zhou, X., Zhang, H., Zheng, S., and Xing, W. (2022). The global recycling trade for twelve critical metals: based on trade pattern and trade quality analysis. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 33, 831–845. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2022.08.011
Zhu, X., Ding, Q., and Chen, J. (2022). How does critical mineral trade pattern affect renewable energy development? The mediating role of renewable energy technological progress. Energy Econ. 112, 106164. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106164
Zhu, X., Geng, Y., Gao, Z., Tian, X., Xiao, S., and Houssini, K. (2023a). Investigating zirconium flows and stocks in China: a dynamic material flow analysis. Resour. Policy 80, 103139. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.103139
Keywords: zirconium, trade network, invulnerability, supply chain security, complex network
Citation: Luo F, Liu W, Xu M, Liu Q and Wang J (2025) Evolution characteristics and invulnerability simulation analysis of global zirconium ore trade network. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1496579. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1496579
Received: 14 September 2024; Accepted: 23 December 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Guochang Wang, Saint Francis University, United StatesReviewed by:
Jiaquan Li, Beijing Institute of Technology, ChinaGe Yin, University College London, United Kingdom
Guochang Xu, National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), Japan
Copyright © 2025 Luo, Liu, Xu, Liu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junbo Wang, d2FuZ2p1bmJvMjAxOUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Fanjie Luo1
Fanjie Luo1 Wei Liu
Wei Liu Junbo Wang
Junbo Wang