- 1School of Earth Science, East China University of Technology Nanchang, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Ionic Rare Earth Resources and Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources, Jiangxi College of Applied Technology, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
- 3Guangzhou City Market Supervision and Administration Bureau, Ganzhou General Inspection and Testing Institute, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
- 4Department of Natural Resources of Jiangxi province, Jiangxi Mineral Resources Guarantee Service Center, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 5Hefei University of Technology, School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 6Jiangxi Nonferrous Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development Institute, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
The Xiekeng pluton, located in Huichang County, Jiangxi Province, is primarily composed of two-mica monzogranite. The rock features high contents of SiO2 (71.3–77.73 wt%), K2O (4.42–5.62 wt%), K2O/Na2O (1.36–1.87), and with an A/CNK value of 1.11–1.27, a differentiation index (DI) of 90.28–94.47, zircon saturation temperatures of 780°C–806°C, and K/Rb, Nb/Ta, and Zr/Hf ratios of 8.40–11.04, 2.38–9.24, and 25.42–35.37, respectively. It also contains peraluminous minerals such as muscovite, classifying it as a highly fractionated S-type granite. The total rare earth element (ΣREY = ΣREE + Y) contents range from 224.7 to 353.12 ppm, with a relative enrichment in light rare earth elements (ΣLREE/ΣHREY) of 1.55–5.36, and significant fractionation between light and heavy rare earth elements with (La/Yb)N = 3.36–18.48, and pronounced negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu* = 0.08–0.41). Zircon U–Pb dating ages of two-mica monzogranite samples are 241.2 ± 1.8 Ma and 238.3 ± 1.7 Ma, belonging to the Middle Triassic. Zircon εHf(t) values range from −14.93 to −9.12, with depleted mantle model ages (TDM2) of 1.86–2.03 Ga, and whole-rock Nd isotopic model ages (TDM2) are 1.90–1.93 Ga, indicating a source primarily from partial melting of Proterozoic continental crustal clay-rich mudstones. Based on muscovite chemistry, the average formation pressure of the Xiekeng pluton is calculated to be 8.35 kbar (∼30 km paleodepth). This suggests the pluton formed through deep melting and intrusion under a thickened crustal compressional tectonic setting. The Xiekeng pluton is rich in total rare earth elements, with abundant rare earth minerals such as apatite, monazite, xenotime, fluocerite, and bastnäsite, showing geochemical characteristics similar to those of typical Indosinian ion-adsorption REE deposit host rocks, indicating potential for the formation of ion-adsorption REE deposits.
1 Introduction
The South China Block was formed by the collision and amalgamation of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks along the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt during the Neoproterozoic, with reactivation during the Mesozoic (Shu, 2012; Zhao, 2015) (Figure 1A). The Cathaysia Block is composed of Precambrian basement, Paleozoic-Triassic clastic rocks, carbonate cover, and Late Mesozoic continental clastic and volcanic rocks. In contrast, the Yangtze Block, in addition to its Precambrian basement and Paleozoic-Triassic clastic rocks and carbonate cover, and extensive Late Permian Emeishan basalts. The Triassic system, from bottom to top, includes rift volcanic-sedimentary formations, post-arc turbidites, and cratonic inland clastic formations, representing the Indosinian orogeny (Wang and Chen, 2005). Mesozoic granites are widely exposed in SCB, particularly in the southeastern region, with major emplacement ages concentrated in the Indosinian (205–251 Ma) and Yanshanian (67–180 Ma) periods (Zhou et al., 2006), making this region one of the world’s richest areas for W, Sn, U, Nb, Ta, REE, and other polymetallic deposits (Mao et al., 2011; Mao et al., 2013a; Gu et al., 2017; Xiong et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2021). Indosinian granites cover an area of about 21,000 km2, accounting for approximately one-fifth of the granitic area in South China (Sun, 2006; He et al., 2010). These granites are predominantly part of multiphase composite plutons (Guo et al., 2012), with Triassic granites mainly distributed in Hunan, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Guangdong, and surrounding areas, and Permian granites mainly confined to Hainan Island (Figure 1B). The Indosinian granites in South China are predominantly strongly peraluminous S-type granites (A/CNK >1.1), with fewer I-type and A-type granites, consisting of high-potassium granites, monzogranites, and granodiorites (Sun, 2006; Zhou et al., 2006; Sun et al., 2011; Zhao et al., 2013b). Recent reports have included minor amounts of syenite (Wang Q. et al., 2005; Mao et al., 2013b), diorite (Wang Y. J. et al., 2013; Shi et al., 2019), and a few mafic enclaves (Chen et al., 2007; Xu et al., 2014), significantly enriching the understanding of Indosinian magmatism and its tectonic background.
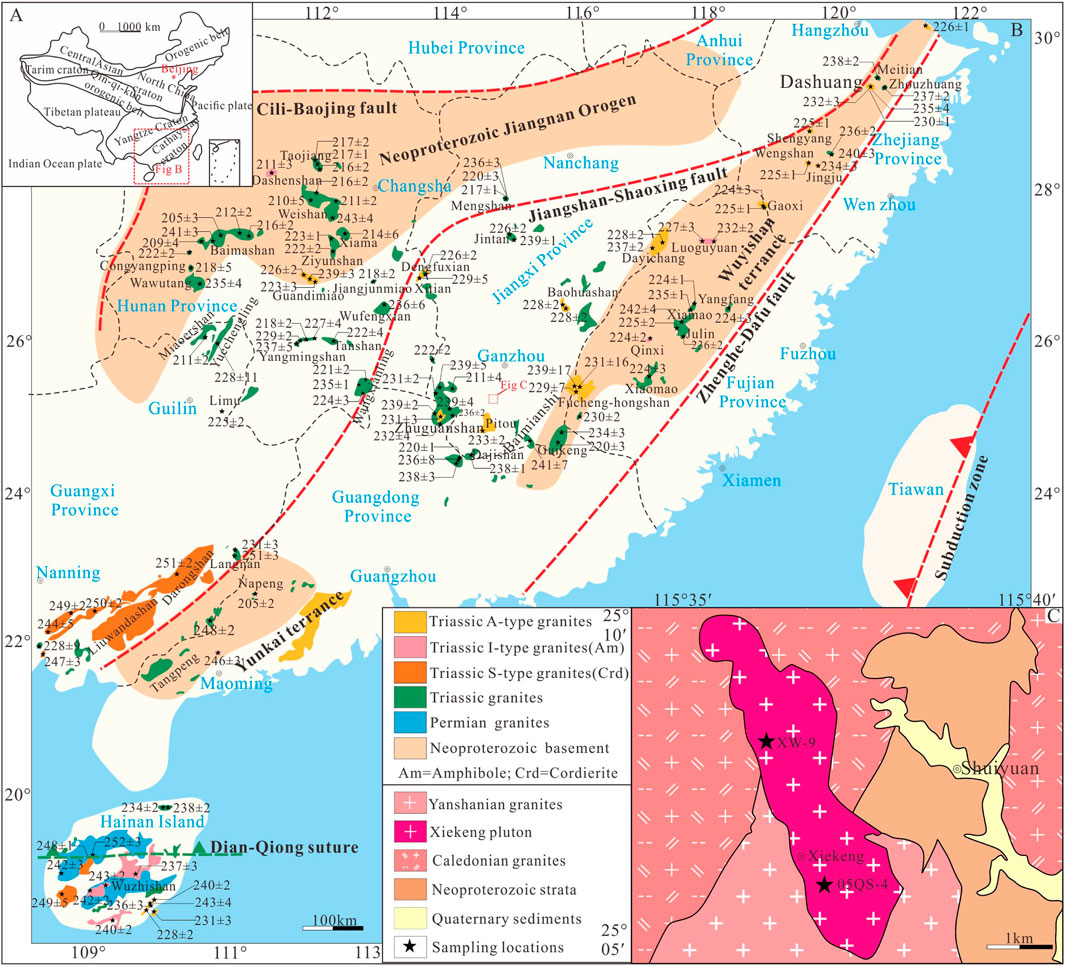
Figure 1. (A) Tectonic location map of South China. (B) Spatial-temporal distribution map of Triassic (Indosinian) granites in South China (Xu et al., 2008). (C) Regional geological map of the Xiekeng pluton, southern Jiangxi.
South China is a significant production area of ion-adsorption REE deposits globally. It is now generally believed that ion-adsorption REE deposits are hosted in granite weathering crusts, therefore, the parental granite may influence the formation of the deposit (Bao and Zhao, 2003; Li and Zhou, 2020). The metallogenic granites are crustal remelting granites, which have relatively high ISr values, low εNd(t) values, and older two-stage model ages. The rare earth metallogenic elements contained in the granites mainly originate from basement rocks (Hua et al., 2003; Xu et al., 2017; Fu et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020). The formation of ion-adsorption REE deposit involves both endogenic and exogenic stages. The endogenic process is essential for the pre-enrichment of rare earth elements. During the endogenic stage, the granites associated with ion-adsorption REE deposit usually have a high rare earth content, and the regoliths show REE patterns that are to a largely extent inherited from the parental rocks (Bao an Zhao, 2008; Fu et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2022). Partial melting and intense separation crystallization are critical factors that influence the concentration and chemical behavior of rare earth elements within magma (Ishihara et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2015; Feng et al., 2022). Geochemical characteristics indicate that the mineralizing granite is an alkaline potassic calc-alkaline granite with a high aluminum content (Fu et al., 2022). In the exogenic stage, the migration-enrichment-differentiation mechanism of rare earth elements is influenced by various factors, including pH, Eh, weathering intensity, as well as the content and properties of clay minerals, along with the permeability coefficient associated with weathering (Wu, 1988; Chi and Liu, 2019; Li et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2022; Fu et al., 2024). The ion-adsorption REE deposits in South China are extensively distributed, with the mineralizing granites primarily located within the weathered crust of Yanshanian granites (e.g., Zudong and Dabu REE deposits, Li et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2024). In contrast, Indosinian mineralizing granites are relatively scarce. Consequently, a detailed examination of the petrological and geochemical characteristics of the Indosinian mineralizing parental rocks is essential for elucidating the influence of magma sources and magmatic processes on rare earth enrichment, as well as their relationship to the Mesozoic tectonic setting.
The Xiekeng pluton, newly discovered during the project team’s field mapping, lacks relevant geochronological data. Here, we conducted LA-ICP-MS zircon U–Pb dating, petrography, mineralogy, whole-rock geochemistry, Lu–Hf, and Sr–Nd isotopic analyses for the newly discovered Xiekeng pluton combining them with published data from Indoinian granites of Gannan, Jiangxi province (e.g., Guo et al., 2011; Wang, 2015; He et al., 2017; Li W. et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022). Then, we discuss the petrogenesis, source characteristics, tectonic setting, and ion-adsorption REE deposits mineralization potential, providing more evidence for evaluating the impact of the Indosinian orogeny on South China and the metallogenic potential of Indosinian granites.
2 Geological background and petrographic characteristics
Southern Jiangxi is located within the Cathaysia Block of the South China Block, bordered by the Jiangshan-Shaoxing Fault Zone to the north and the Zhenghe-Dapu Fault Zone to the southeast. The region features a set of Precambrian crystalline basement rocks overlain by Sinian-Cambrian sedimentary cover. The Devonian, Carboniferous, Cretaceous, and Cambrian systems are in angular unconformity contact. The Indosinian granites in southern Jiangxi province cover a relatively small area, with the main age range of 200–230 Ma. The granites in the area can provide material sources for mineral deposits such as U, REE, and W. (e.g., Dong et al., 2010; Wang, 2015; Li W. et al., 2021). The Xiekeng pluton is distributed in the Shuiyuan Township of Xunwu County, southern Jiangxi. Its tectonic position is in the eastern segment of the Caledonian orogenic belt (Shu et al., 1998), covering an exposed area of approximately 3 km2 and presenting as an irregular NW-oriented laccolith. The exposed strata are from the Upper Neoproterozoic Xunwu Group, with a thickness of about 1,072 m, mainly composed of two-mica-quartz schist, siltstone schist, and metamorphosed quartz sandstone, with medium to thin-bedded siliceous rocks at the base. Geochronology data indicates the Xunwu Group formed during the Neoproterozoic, with detrital zircon U–Pb ages ranging from 570 to 602 Ma (Yang et al., 2022). The Xiekeng pluton intrudes into Neoproterozoic metasedimentary strata (Figures 1C, 2A). The region has experienced intense magmatic activities from the Caledonian to the Yanshanian periods, with evident multiphase activities. The Caledonian Chengkeng pluton adjacent to Xiekeng pluton has zircon U–Pb ages of 440–460 Ma (Yang et al., 2017), the Indochina Fucheng pluton located 8 km southeast of XieKeng pluton has zircon U–Pb ages of 219–227 Ma (Ren et al., 2013). and the Yanshanian Shitouping granites located 10 km north of the Xiekeng pluton have zircon U–Pb ages of around 140 Ma (Cao et al., 2024).
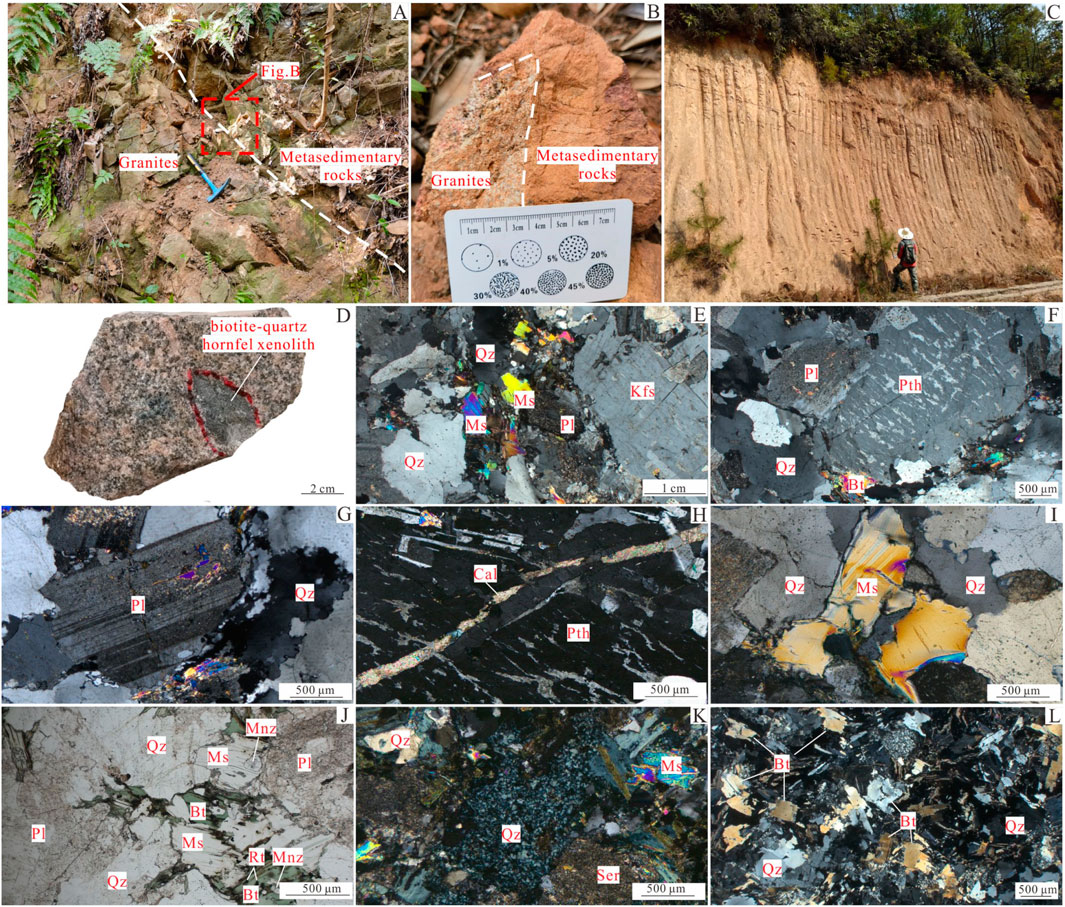

Figure 2. Outcrop photos and microphotographs of the Xiekeng pluton. (A, B) Granites contact relationship with surrounding rocks. (C) Granite weathering crust. (D) Two-mica monzogranite with biotite-quartz schist xenolith. (E–G) Constituent minerals of Two-mica monzogranite (crossed polars). (H) Calcite veins filling striated potassic feldspar. (I) Stress-induced bending deformation of muscovite (crossed polars). (J) Chloritization of biotite (plane polars). (K, L) Biotite-quartz schist xenoliths (crossed polars). Qz-Quartz; Ms-Muscovite; Bt-Biotite; Pl-Plagioclase; Kfs-Potassic feldspar; Pth-Perthite; Mnz-Monazite; Rt-Rutile; Cal-Calcite; Ser-Sericite.
The rocks of the Xiekeng pluton are reddish in color (Figure 2D), primarily composed of quartz (30%), potassic feldspar (30%), plagioclase (25%), muscovite (8%), and biotite (5%) (Figures 2E–J), showing biotite-quartz schist xenoliths. Quartz appears as anhedral grains ranging from 0.5 to 2.5 mm, and some exhibit undulose extinction (Figure 2E). Perthite is anhedral and tabular, grain ranging from 0.40 to 5.0 mm, and well-developed perthitic texture (Figure 2F) with occasional calcite veins (Figure 2H). Plagioclase is subhedral to anhedral and tabular, with grain sizes ranging from 1 to 3.5 mm, exhibiting polysynthetic twinning and slight sericitization (Figure 2G). Muscovite appears as anhedral flakes, with grain sizes ranging from 0.20 to 1.50 mm, and shows stress-induced bending (Figure 2I). Biotite is anhedral and flaky, with grain sizes ranging from 0.25 to 0.85 mm, generally chloritized, with iron oxide exsolved around chlorite (Figure 2J). Rutile and monazite are often enclosed within biotite (Figure 2J). Hand specimens show clear boundaries between the biotite-quartz schist xenoliths and the host rock (Figure 2D), with quartz in the xenoliths being polycrystalline (Figures 2K, L). Monazite, rutile, xenotime, fluocerite, and bastnäsite are evident within muscovite (Figures 3A–C) in back-scattered electron (BSE). Thorianite is present in xenotime (Figure 3C). Apatite is altered to monazite by hydrothermal processes with well-defined contacts (Figures 3D, E), and thorite develops on the edge of monazite or inside the xenotime (Figures 3F, G). Fluorite fills the interstices between muscovite and potassic feldspar (Figure 3H). Zircon and muscovite are fractured (Figure 3I).
3 Analytical methods
3.1 Major and trace element analyses
Whole-rock major and trace element analyses were conducted at the ALS Laboratory Group (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd. Major elements were determined using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) with a PANalytical PW2424 instrument, with a relative deviation (RD) of less than 5%. Trace elements were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) with an Agilent 7,900 instrument, with a relative deviation (RD) of less than 10%. The standard samples used were GSR3 and GSR5. Detailed procedures are available in Li et al. (2005).
3.2 Zircon U–Pb dating
Two fresh two-mica monzogranite samples (XW-9 and 05QS-4) were selected for in-situ zircon U–Pb dating. The samples were crushed to 100–120 mesh, and zircons were separated using heavy liquid and magnetic separation methods. Zircons with good crystal shapes and clear zonation were handpicked under a binocular microscope, mounted in epoxy resin, and polished to expose their cores. Cathodoluminescence (CL) and back-scattered electron (BSE) imaging were used to select U–Pb spots. This work was completed at Langfang Chenchang Rock Mineral Testing Technology Service Co., Ltd. Zircon U–Pb isotopic dating was performed using a laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) system at the State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resources and Environment, East China University of Technology. The laser ablation system was a GeoLasHD 193 nm excimer laser, and the ICP-MS instrument was an Agilent 7,900. The laser ablation spot size was 32 μm, with a frequency of 5 Hz and an energy density of 6 J/cm2, using He as the carrier gas. Isotopic ratio corrections were made using the 91,500 zircon as an external standard (the recommended age value 1062.4 Ma), the weighted average age of standard zircons 91,500 was 1060.6 ± 5.4 Ma (MSWD = 0.88, n = 12). The TEM (417 Ma) zircon as a monitoring sample. Data processing was performed using the ICPMSDataCal program (Liu et al., 2008, 2010), and concordia diagrams were generated using the Isoplot 3.0 program (Ludwig, 2003). Detailed parameters and procedures can be found in Jackson et al. (2004).
3.3 Zircon Lu–Hf isotopic analysis
Zircon Lu–Hf isotopic analysis was carried out at Nanjing Hongchuang Geological Exploration Technology Service Co., Ltd. The analysis was performed on and near the U–Pb dating spots using a GeoLasHD 193 nm laser ablation system coupled with an Agilent 7900a ICP-MS. The laser spot size was 40 μm, with a frequency of 10 Hz. During the testing process, the average values of 176Hf/177Hf for standard zircon 91,500 and CJ-1 were 0.282310 ± 0.000005 (2σ, n = 14) and 0.282005 ± 0.000014 (2σ, n = 7), respectively, which were in accordance with the recommended 176Hf/177Hf values within the error range (0.282305 ± 0.000003, 2σ; 0.282015 ± 0.000019, 2σ) (Elhlou et al., 2006; Wu et al., 2006; Blichert-Toft, 2008). The parameters used for εHf(t) calculations were as follows: decay constant of 176Lu = 1.865×10⁻11 yr⁻1 (Scherer et al., 2001), chondritic uniform reservoir (CHUR) values of 176Hf/177Hf = 0.282772 and 176Lu/177Hf = 0.0332 (Blichert and Albarède, 1997), and crustal model age (TDM2) calculations using 176Lu/177Hf = 0.015 (Griffin et al., 2002). Isotopic ratio corrections were made using the Plesovice zircon (337.00 ± 0.37 Ma) as an external standard (Sláma et al., 2008), and common lead corrections were made using the ComPbCorr#3.17 program (Andersen, 2002).
3.4 Sr–Nd isotopic analysis
Sr–Nd isotopic analysis was conducted at Nanjing Hongchuang Geological Exploration Technology Service Co., Ltd. The samples were weighed according to their Rb–Sr and Sm–Nd contents, and dissolved in Teflon bombs with mixed 87Rb–84Sr and 149Sm–150Nd spikes using HF, HNO3, and HClO4. Rb, Sr, Sm, and Nd were separated using ion exchange resin columns. Measurements were made using a Thermo Fisher Neptune XT thermal ionization mass spectrometer (TIMS). The analysis process maintained a blank level of Rb, Sr < 100×10⁻12 and Sm, Nd < 50×10⁻12. Detailed analytical procedures can be found in Li et al. (2016). During the sample analysis, the measured 87Sr/86Sr ratio of the international standard NBS987 was 0.710288 ± 0.000028 (2σ, n = 9), and the 143Nd/144Nd ratio of the JNdi-1 standard was 0.512109 ± 0.000012 (2σ, n = 9).
3.5 Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA)
Muscovite electron probe microanalyses were performed at the State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resources and Environment, East China University of Technology. Large, clean, and flat muscovite grains were selected under a microscope for EPMA. The instrument used was a JEOL JXA-8530 with an accelerating voltage of 15 kV, a current of 20 nA, a beam diameter of 5 μm, and a counting time of 20 s. The standards used were olivine (Si), rutile (Ti), almandine (Al), garnet (Fe), wollastonite (Mn), diopside (Mg, Ca), jadeite (Na), orthoclase (K), apatite (P), LiF (F), and scapolite (Cl), with corrections made using the ZAF method. The mica cation numbers and related parameters were calculated based on 22 oxygen atoms, and the Li2O content was calculated as [2.1/(0.356+MgO)]-0.088 (Tischendorf et al., 1999).
4 Analytical results
4.1 Geochemical characteristics
4.1.1 Major elements
The Xiekeng pluton has the same major element geochemical characteristics as the Indosinian granites in southern Jiangxi. The major element results of the Xiekeng pluton are shown in Supplementary Table S1. The SiO2 content ranges from 71.37 to 77.73 wt%, Al2O3 from 12.57 to 14.80 wt%, K2O from 4.42 to 5.62 wt%, and Na2O from 2.84 to 3.41 wt%, with a total alkali (K2O+Na2O) content of 7.67–8.77 wt%, and a K2O/Na2O ratio of 1.36–1.87. The total iron oxide (FeOt) content ranges from 1.03 to 1.79 wt%, and the differentiation index (DI) ranges from 90.28 to 94.47. In the TAS classification diagram (Figure 4A), the samples project into the granite field, in the SiO2 vs. K2O diagram (Figure 4B), the samples plot into the high-K calc-alkaline to shoshonitic series. The aluminum saturation index (A/CNK) values range from 1.11 to 1.27, indicating strong peraluminous characteristics. In the A/CNK vs. A/NK diagram (Figure 4C), the samples project into the strongly-peraluminous field. In the CIPW standard mineral calculation, the content of quartz is 30.81–41.04 wt%, orthoclase content is 26.18–33.53 wt%, albite content is 24.51%–29.0%, anorthite content is 1.27–4.38 wt%, and the content of corundum molecules is 1.31–3.31 wt%. In the Harker diagrams, Al2O3, CaO, FeOt, MgO, TiO2 and MnO contents decrease with increasing SiO2 content (Figure 5).
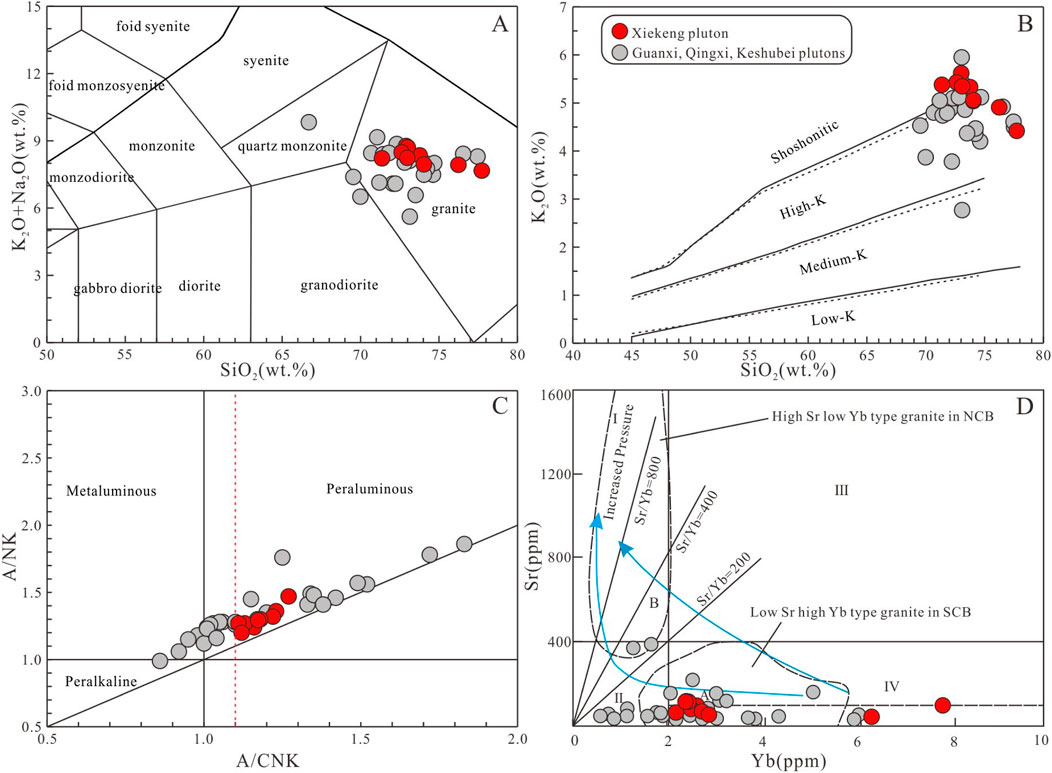
Figure 4. Geochemical classification diagram of Xiekeng pluton. (A) SiO2 vs. K2O+Na2O diagram (fields after Middlemost, 1994). (B) SiO2 vs. K2O diagram (solid line after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; dotted line after Middlemost, 1985) (C) A/CNK vs. A/NK diagram (fields after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989). (D) Yb vs. Sr diagram (fields after Zhang Q. et al., 2006) Data of Guanxi, Qingxi and Keshubei plutons are from Guo et al. (2011); Wang et al. (2015); He et al. (2017) and Li W. et al. (2021).
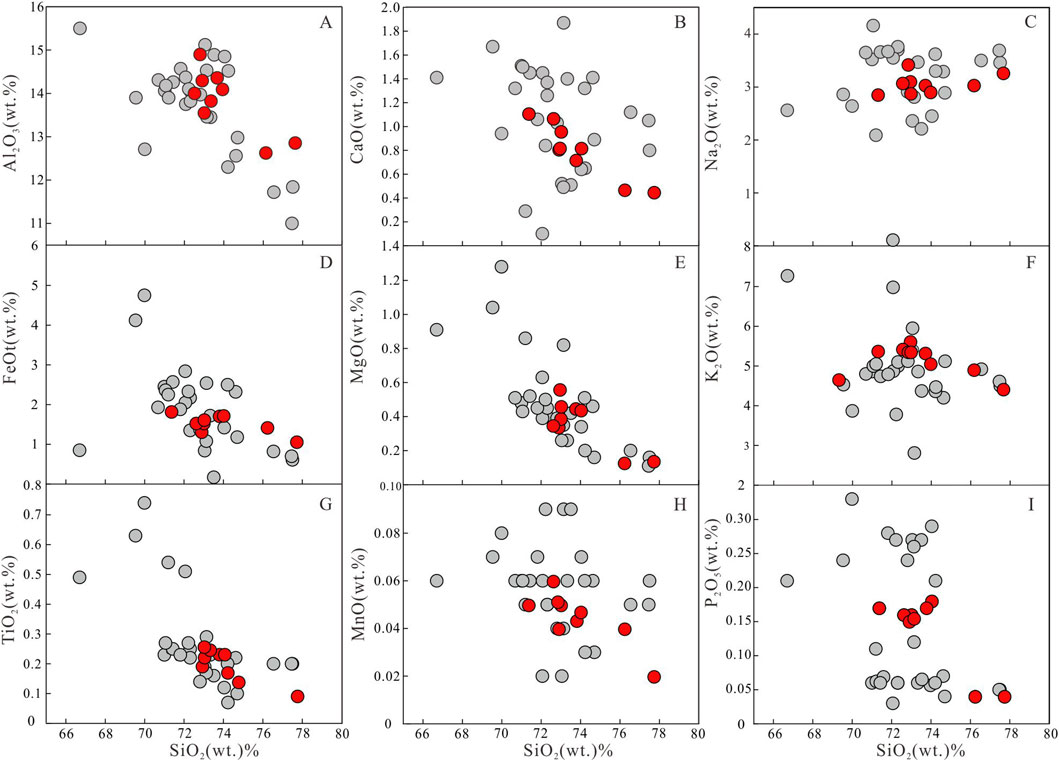
Figure 5. Harker diagrams of Xiekeng pluton. (A) SiO2 vs. Al2O3 diagram. (B) SiO2 vs. CaO diagram. (C) SiO2 vs. Na2O diagram. (D) SiO2 vs. FeOt diagram. (E) SiO2 vs. MgO diagram. (F) SiO2 vs. K2O diagram. (G) SiO2 vs. TiO2 diagram. (H) SiO2 vs. MnO diagram. (I) SiO2 vs. P2O5 diagram.
4.1.2 Trace elements
The Xiekeng pluton has the same trace element geochemical characteristics as the Indosinian granites in southern Jiangxi. The trace element results of the Xiekeng pluton are shown in Supplementary Table S1. The total rare earth element (ΣREY) content ranges from 224.71 to 353.12 ppm (avg. 286.21 ppm), with a typical right-leaning distribution curve indicating significant fractionation between LREE and HREY (Figure 6A). The (La/Yb)N values range from 3.36 to 18.48, indicating relative enrichment of LREE (ΣLREE/ΣHREY) = 1.55 to 5.36, and significant negative Eu anomalies (Eu/Eu* = 0.08–0.41). These characteristics are consistent with those of S-type granites derived from the re-melting of crustal materials in South China (Ling et al., 2006), suggesting significant plagioclase fractionation or a source material poor in plagioclase.
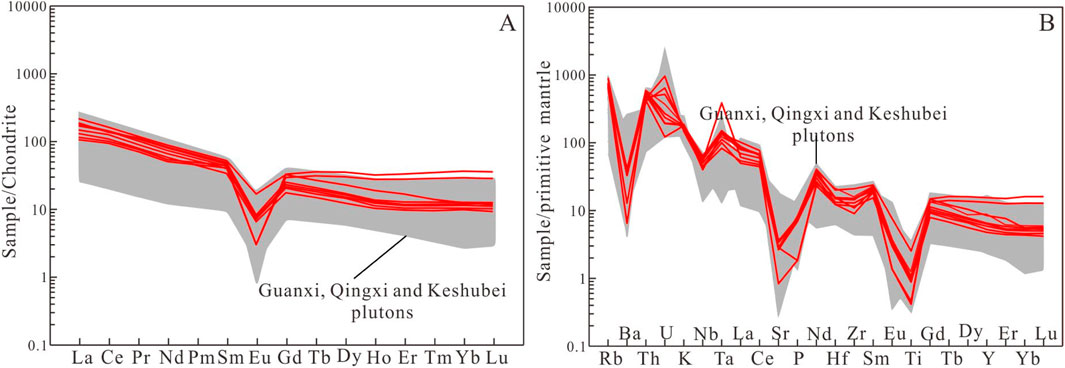
Figure 6. (A) Chondrite-normalized (Sun and McDonough, 1989) REE patterns. (B) primitive mantle-normalized (McDonough and Sun, 1995) trace elements spider diagram. The data sources are the same as Figure 4.
In the trace element spider diagram (Figure 6B), the samples are relatively enriched in Rb, Th, U, Ta, and Gd, and depleted in Ba, Nb, Sr, P, and Ti. The depletion of Sr and Ba suggests plagioclase fractionation, while the depletion of Nb, P, and Ti indicates the presence of residual rutile, apatite, and ilmenite in the source region. The Sr content ranges from 20.1 to 71.2 ppm, and the Yb content ranges from 2.14 to 7.91 ppm. Two samples exhibit relatively high Yb concentrations, which may be attributed to the presence of abundant heavy rare earth minerals within these samples. All samples are plotted in the region characterized by low Sr and high Yb type granite field (Figure 4B).
4.2 Zircon U–Pb dating results
Twenty-five of each sample zircon crystals were selected from two-mica monzogranite samples (XW-9 and 05QS-4) for LA-ICP-MS U–Pb isotopic dating. The CL images and structures of the zircons are shown in Figures 7A, B. The U–Pb isotopic dating results are presented in Supplementary Table S2, and the concordia diagrams and zircon chondrite-normalized REE patterns are shown in Figure 8.
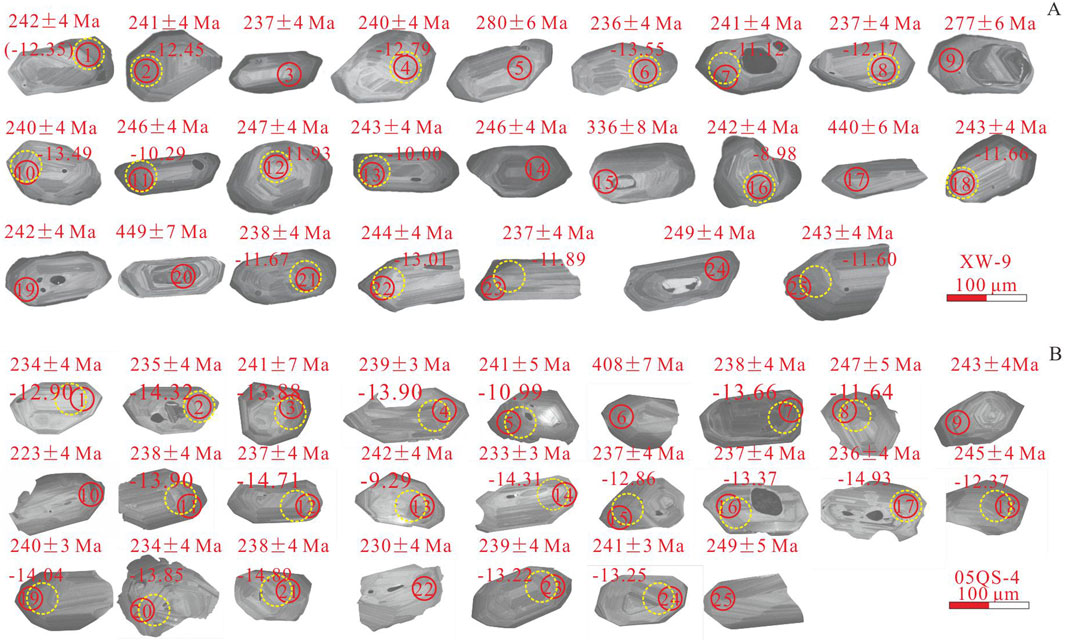
Figure 7. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images for zircons of Xiekeng pluton. The red circles represent the zircon U–Pb dating spots, and the yellow circles represent the zircon-Hf isotope test plots. (A) Sample XW-9. (B) Sample 05QS-4.
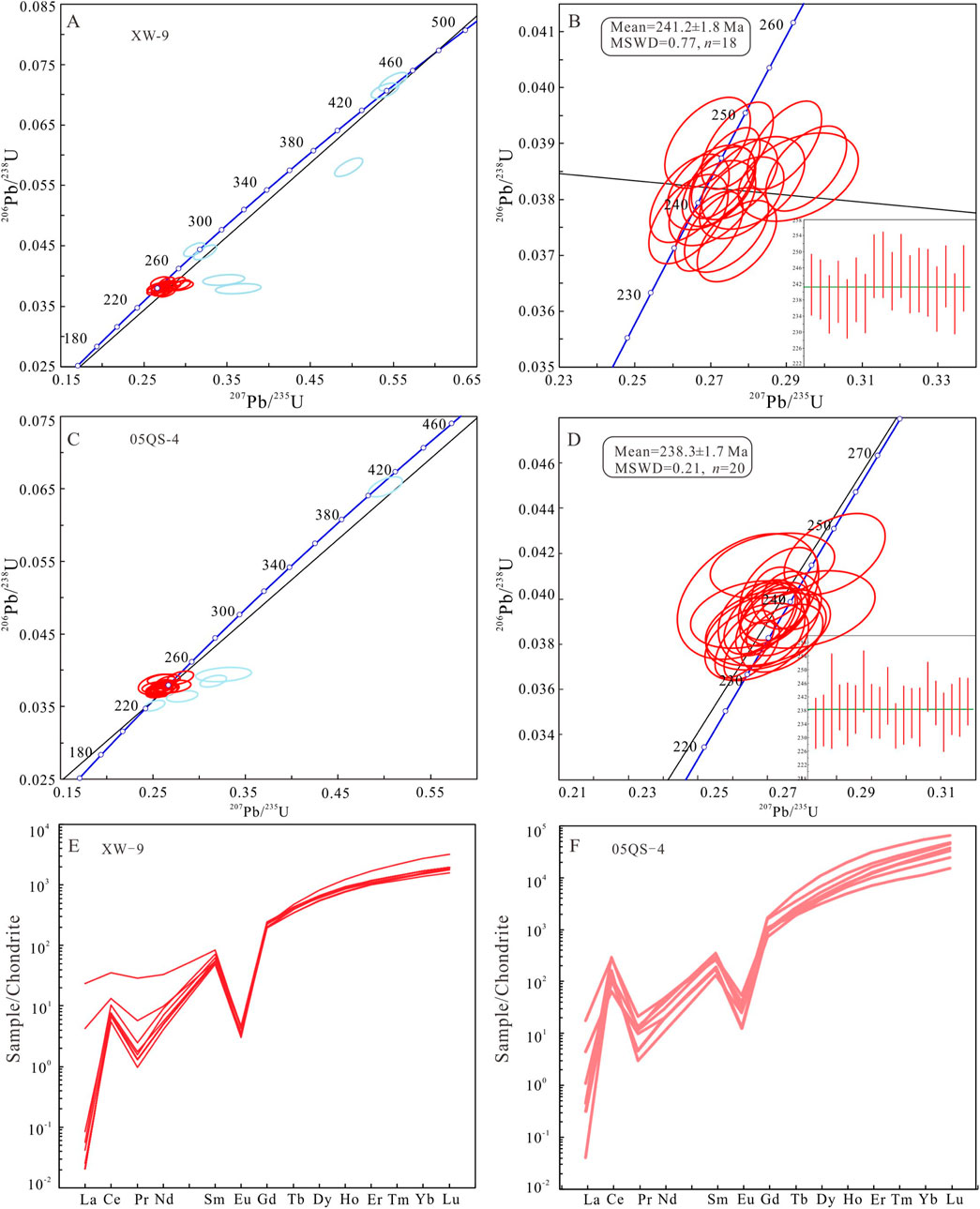
Figure 8. (A–D) Zircon U–Pb Concordia diagrams. (E, F) zircon chondrite-normalized REE patterns (Sun and McDonough, 1989).
Zircon crystals from the sample XW-9 are mostly euhedral, prismatic, with lengths ranging from 70 to 120 µm and length-to-width ratios of 1:1 to 3:1. The Th content ranges from 199 to 475 ppm, U content from 174 to 703 ppm, and Th/U ratios from 0.32 to 2.26, significantly higher than those of metamorphic and hydrothermal zircons (<0.1) (Belousova et al., 2002). The zircons exhibit clear oscillatory zoning and some have core structures, positive Ce anomalies, and heavy REE enrichment (Figure 8E), indicating typical magmatic origin. Data points with concordance less than 90% were excluded (point 10 and 24), while inherited zircon ages of 280 Ma (point 5), 277 Ma (point 9), 336 Ma (point 15), 440 Ma (point 17), and 449 Ma (point 20) were identified as xenocrysts or captured zircons. The remaining 18 points, with concordance greater than 90% (Figure 8A), yielded a weighted mean age of (241.2 ± 1.8) Ma (MSWD = 0.77, n = 18) (Figure 8B), representing the crystallization age of the rock.
Zircon crystals from the sample 05QS-4 are mostly euhedral prismatic, with lengths ranging from 50 to 100 µm and length-to-width ratios of 1:1 to 2:1. The content of zircon ranges from 44 to 482 ppm, U content from 141 to 1,511 ppm, and Th/U ratios from 0.22 to 1.59, showing geochemical characteristics which are similar to sample XW-9 (Figure 8F), indicating magmatic origin. Data points with concordance less than 90% were excluded (point 9 and 25), while inherited zircon ages of 408 Ma (point 6) were identified as xenocrysts or captured zircons, 223 Ma and 230 Ma (point 10 and 22) are relatively younger. The remaining 20 points, with concordance greater than 90% (Figure 8C), yielded a weighted mean age of (238.3 ± 1.7) Ma (MSWD = 0.21, n = 20) (Figure 8D), representing the crystallization age of the rock.
4.3 Zircon Hf isotopic composition
The zircon Hf isotopic data for the Xiekeng pluton are presented in Supplementary Table S3. Given the high closure temperature of the zircon Lu–Hf isotopic system, these data provide important constraints on the genesis and evolution of the zircons (Scherer et al., 2000). Lu–Hf isotope analysis was performed on the basis of zircon U–Pb laser denudation points. The results show 176Hf/177Hf values ranging from 0.00045 to 0.00230 (<0.02), indicating minimal radiogenic Hf accumulation, with initial values representing the present Hf isotopic composition. Zircon crystals from the sample XW-9 have 176Hf/177Hf values ranging from 0.28224 to 0.28236, with εHf(t) values of −13.36 to −9.12 and two-stage model ages (TDM2) of 1.86–2.13 Ga. Zircon crystals from the sample 05QS-4 have 176Hf/177Hf values ranging from 0.28220 to 0.28236, with εHf(t) values of −14.93 to −9.29 and two-stage model ages (TDM2) of 1.86–2.20 Ga. The εHf(t) values of Xiekeng pluton are consistent with the Indosinian granites in south Gannan. In the Age vs. εHf(t) (Figure 9) diagram, the samples plot above the lower crust evolution trend, indicating a crustal origin for the granitoid magmas.
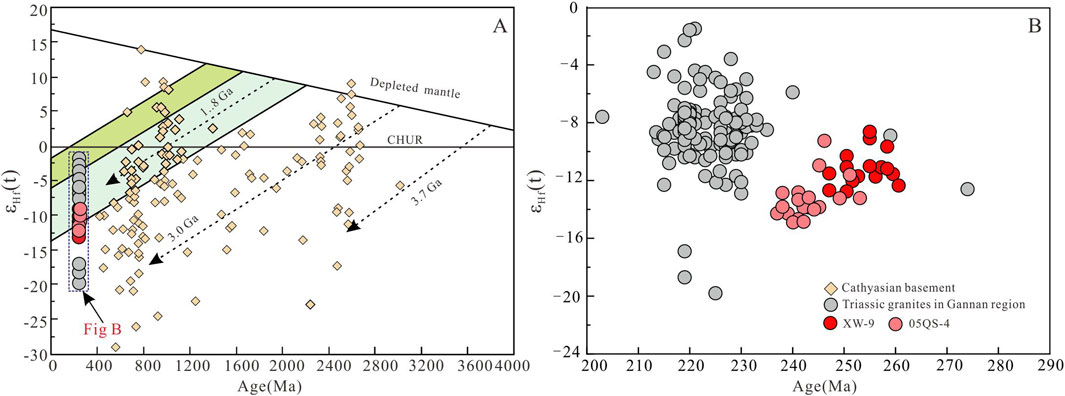
Figure 9. Zircon age vs. εHf(t) diagrams. Cathyasian basement data are from Yu et al. (2010). Triassic granites data in Gannan region, Jiangxi province are from Ren et al. (2013); Gao, (2016); Wang et al. (2015) and Wang H. Z. et al. (2018). (A, B) Age vs. εHf(t) diagram.
4.4 Sr–Nd isotopic characteristics
The Sr–Nd isotopic data for the Xiekeng pluton are shown in Supplementary Table S4. The samples have high (87Sr/86Sr)i values (0.720302–0.726407) and low εNd(t) values (−11.2 to −10.9), with two-stage model ages (TDM2) ranging from 1.90 to 1.93 Ga. In the (87Sr/86Sr)i vs. εNd(t) diagram (Figure 10A), the samples plot in the Mayuan Group area, in the TDM2 vs. εNd(t) diagram (Figure 10B), they plot in the Mesoproterozoic and Paleoproterozoic sedimentary rock areas, and in the age vs. εNd(t) diagram (Figure 10C), they plot in the Mayuan Group area. The εNd(t) values are consistent with those of Indosinian granites in South China (Figure 10D). It can be inferred that the source rock of the Xiekeng pluton is derived from metamorphosed sedimentary rocks.
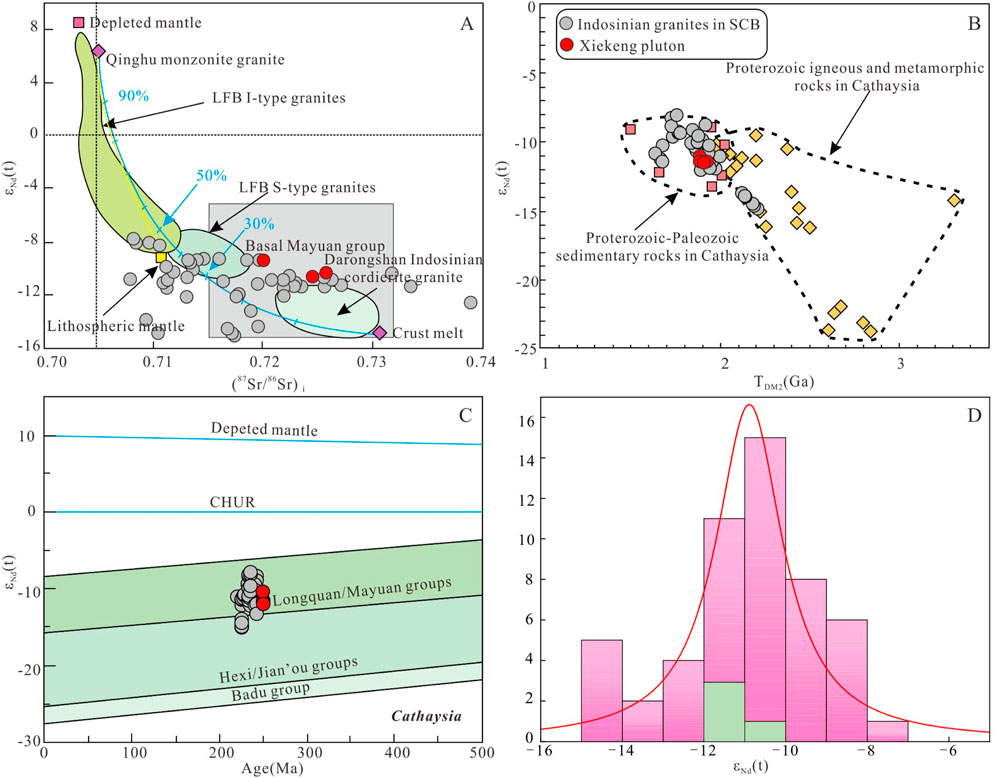
Figure 10. (A) (87Sr/86Sr)i vs. εNd(t) diagram. (B) TDM2 vs. εNd(t) diagram. (C) Age vs. εNd(t) diagram. (D) εNd(t) frequency distribution histogram. Data for Lachlan Fold Belt (LFB) S-type and I-type granites are from Healy et al. (2004), data for depleted mantle end-members are from Xia et al. (2014), data for Qinghu monzonite are from Li et al. (2004), lithospheric mantle and crustal melt end-member data are from Wang Q. et al. (2005) for the Yangfang syenite and Longyuanba biotite granite in western Fujian, data for Indosinian cordierite granite in Darongshan are from Qi et al. (2007), and data for the basement Mayuan Group are from Shen et al. (2000). The data of the Proterozoic igneous and metamorphic rocks and Proterozoic-Paleozoic sedimentary rocks in Cathaysia are from Chen and Jahn, (1998). The data of Indosinian granites, South China are from Zhang M. et al. (2006); Yu et al. (2007); Sun et al. (2011); Mao et al. (2011), Mao et al. (2013a); Xiang et al. (2013); Wang, (2015); Qing et al. (2020); Zhou et al. (2021); Du et al. (2022) and Ma and Guo, (2023).
4.5 Muscovite characteristics
Muscovite electron microprobe analysis results are shown in Supplementary Appendix S5. The muscovite has SiO2 contents of 46.02–49.04 wt%, TiO2 contents of 0.47–0.98 wt%, Al2O3 contents of 28.40–32.46 wt%, FeOt contents of 2.76–6.90 wt%, MgO contents of 0.72–1.86 wt%, Na2O contents of 2.76–6.90 wt%, and K2O contents of 9.39–10.18 wt%. The calculated cation numbers are Si4+ 6.33–6.58, Ti4+ 0.05–0.10, AlⅣ 1.42–1.67, AlⅥ 3.13–3.47, Fe2+ 0.31–0.80, Mg2+ 0.15–0.37, Na+ 0.05–0.17, classifying them as highly siliceous muscovite (Figures 11A,B). The average crystal chemical formula for muscovite in the Xiekeng pluton is K1.69Na0.10Fe0.52Mg0.21Al3.31 [Al1.53Si6.47]O20(OH)4, indicating it is not an ideal pure muscovite KAl2 [AlSi3O10](OH)2, but rather an intermediate product of an isomorphous series with paragonite NaAl2 [AlSi3O10](OH)2 and phengite KAl(Fe, Mg) (Si4O10) (OH)2)7 (Figure 11C).
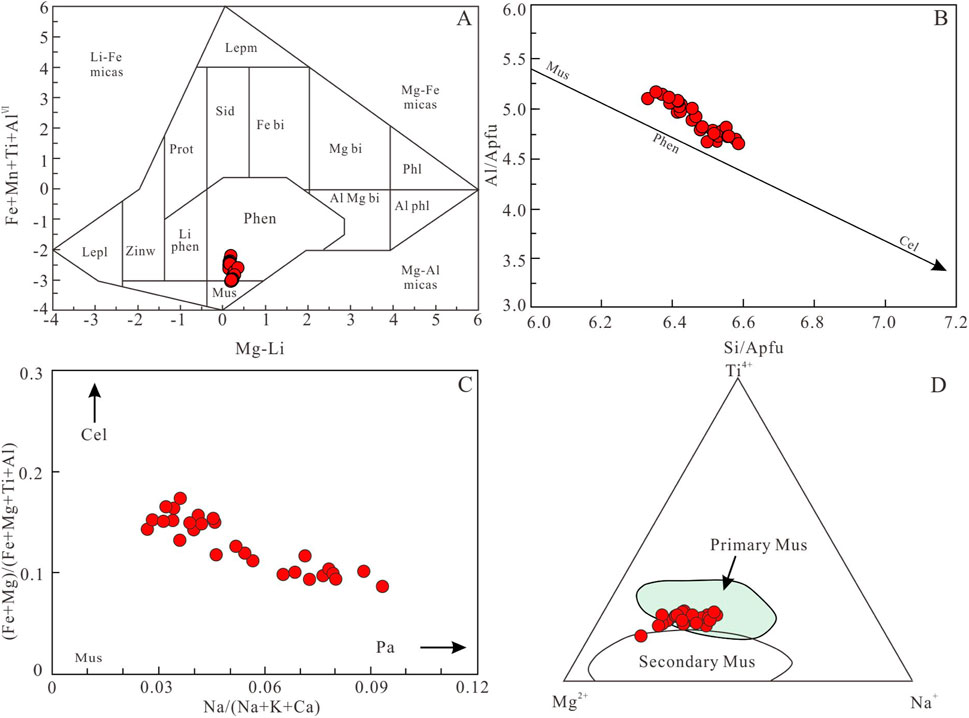
Figure 11. (A) (Mg-Li) vs. (Fe+Mn+Ti+AlⅥ) diagram (Tischendorf et al., 1999). (B) Si vs. Al diagram (Wang et al., 2021). (C) Na/(Na+K+Ca) vs. (Fe+Mg)/(Fe+Mg+Ti+Al) diagram (Clarke, 1981). (D) Ti4+-Mg2+-Na+ ternary diagram (Miller et al., 1981). Lemp-Lepidomelane; Lepl-Lepidolite; Zinw-Zinnwaldite; Prot-Protolithionite; Li phen-Li phengite; Lemp-Lepidomelane; Sid-Siderophyllite; Fe bi-Fe biotite; Li phen-Li phengite; Phen-Phengite; Mus-Muscovite; Mg bi-Mg biotite; Al Mg bi-Al Mg biotite; Phl-Phlogopite, Al phl-Al phlogopite; Cel-Celadonite; Pa-Paragonite.
Under the microscope, the muscovite grains are large with clear edges, showing good crystal habits (Miller et al., 1981; Speer, 1984), indicating primary muscovite characteristics. The muscovite in the peraluminous granite coexisting with biotite, which shows replacement textures, does not significantly differ in composition from primary muscovite (Tao et al., 2014). Generally, primary muscovite has higher TiO2 contents (>0.4%) (Miller et al., 1981), and the TiO2 content of muscovite in the Xiekeng biotite monzogranite ranges from 0.47 to 0.96 wt%, indicating primary muscovite characteristics. In the Mg2+-Na+-Ti4+ diagram (Figure 11D), the samples plot within or near the primary muscovite field.
5 Discussion
5.1 Magmatic age
The specific formation age of the Xiekeng pluton has not been previously reported. In this study, the LA-ICP-MS zircon U–Pb ages of the two-mica monzogranite samples were determined to be 241.2 ± 1.8 Ma and 238.3 ± 1.7 Ma, indicating an Middle Triassic magmatic event, representing typical early Indosinian magmatism in South China, earlier than the Indosinian period granites that have been discovered in the area (Guo et al., 2011; Wang, 2015; He et al., 2017; Li J. et al., 2021). The presence of inherited zircon ages of 277 Ma, 280 Ma, and 336 Ma suggests Hercynian thermal events in the study area, while inherited zircon ages of 456 Ma and 467 Ma reflect the influence of the Caledonian tectonic activities in southern Jiangxi. Indosinian granites in South China can be divided into two stages: the early Indosinian (228–243 Ma, peak around 236 Ma) and the late Indosinian (214–220 Ma, peak around 214–218 Ma). This indicates that South China experienced two significant tectono-magmatic events during the Indosinian orogeny (Wang et al., 2007). Statistical analysis of the ages of Triassic granites in South China shows peak ages at 220 Ma and 236 Ma, consistent with the above stages (Figure 12).
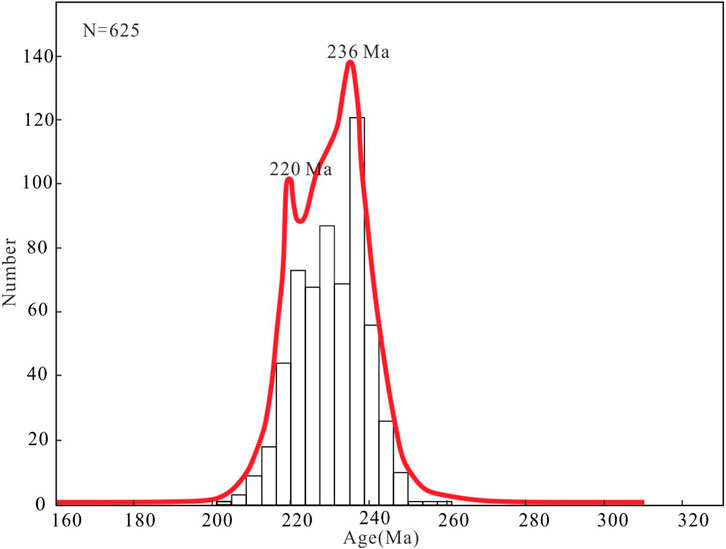
Figure 12. Age frequency distribution diagram of Indosinian granites in SCB. The age data of Indosinian granites in SCB are from Xu et al. (2003); Ding et al. (2006); Dong et al. (2010); He et al. (2010); Guo et al. (2011); Sun et al. (2011); Mao et al. (2013a); Mao et al. (2013b); Ren et al. (2013); Zhao et al. (2013a); Zhao et al. (2013b); Wang, (2015); Gao, (2016); Wang W. B et al. (2018); Qing et al. (2020); Cao et al. (2021) and Li et al. (2021a), Li et al. (2021b), Li et al. (2021c).
5.2 Petrogenesis
Granites are generally classified into I-type, S-type, A-type, and M-type based on their genesis (Chappell and White, 1974; Qiu et al., 2008). Different genetic types of granites usually have distinct magma sources and tectonic settings. M-type granites are derived from the differentiation of basaltic magmas and are rare in nature. I-type granites are characterized by metaluminous to slightly peraluminous compositions, derived from igneous sources, and typically contain hornblende. They have relatively low initial Sr isotope ratios (<0.708), FeOt generally less than 1, and P2O5 negatively correlates with SiO2. A-type granites have low oxygen fugacity, low water content (<2%), low P₂O₅ content (Chappell, 1999; Wang et al., 2000), and are primarily formed in extensional settings, containing alkaline dark minerals (e.g., aegirine, riebeckite), high melting temperatures (900°C), high 10000Ga/Al (>2.6), and high (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) >350 ppm with high FeOt/(FeOt+MgO) ratios. S-type granites are rich in primary garnet, cordierite, muscovite, and have high A/CNK (>1.1) and isotopic signatures indicating derivation from metasedimentary sources.
The Early Indosinian (243–228 Ma) and Late Indochina (243–228 Ma) granites in SCB exhibit a high SiO2 content ranging from 65 to 79 wt% and K2O/Na2O ratios between 1.03 and 3.89, accompanied by A/CNK ratios of 1.0–1.45. These granites are predominantly classified as high-potassium calc-alkaline peraluminous types. In terms of rock classification, I- and S-type granites were primarily distributed during the early Indochina period, whereas I-, S-, and A-type granites were prevalent during the late Indochina period (Xu et al., 2003; Ding et al., 2006; Dong et al., 2010; He et al., 2010; Guo et al., 2011; Sun et al., 2011; Mao et al., 2013a; Ren et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2013a, b; Jiao et al., 2015; Wang, 2015; Gao, 2016; Wang H. Z. et al., 2018; Wang W. B. et al., 2018; Qing et al., 2020; He, 2021; Han, 2023; Sun, 2023). Regional Early Indosinian granites are mainly distributed in Hainan and Guangxi, while Late Indosinian granites are mainly distributed in Jiangxi, Hunan and surrounding areas (Figure 1B). The Xiekeng pluton primarily comprises quartz, plagioclase, potassic feldspar, muscovite, and biotite, with geochemical characteristics of high A/CNK values (1.11–1.27), indicating strongly peraluminous S-type granite (Figure 4C). The Xiekeng pluton has high 10000Ga/Al ratios (2.83–3.23) and enrichment in high field strength elements such as Th, U, Ta, and Gd, which shows similarities with A-type granites (Li X. W. et al., 2010). With increasing research on granites, it has been found that highly differentiated I- and S-type granites can also exhibit characteristics similar to A-type granites, such as 10000Ga/Al > 2.6 and enrichment in high field strength elements (Li and Li, 2007; Wu et al., 2017). As the degree of granitic magma differentiation increases, elements like Li and Rb increase, while Cr, Ni, Sr, and Ba decrease in the residual melt (Lee and Morton, 2015), resulting in lower K/Rb, Zr/Hf, and Nb/Ta ratios (Ballouard et al., 2016). Therefore, K/Rb, Zr/Hf, and Nb/Ta ratios are important indicators of the degree of magmatic differentiation. The K/Rb ratios of the Xiekeng pluton range from 8.40 to 11.04, Nb/Ta ratios from 2.38 to 9.24, and Zr/Hf ratios from 25.42 to 35.37, indicating significant magmatic differentiation and classifying the pluton as highly fractionated granite. In the 10000Ga/Al vs. Zr and (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) vs. (Na₂O+K₂O)/CaO diagrams (Figures 13A,B), the samples plot within the highly fractionated granite field, indicating they are highly fractionated I- or S-type granites. The P2O5 content (0.14–0.18 wt.%) does not show significant variation with SiO2, consistent with the evolution trend of S-type granites (Chappell, 1999). In the Rb vs. Th variation diagram (Figure 13C), the samples exhibit trends consistent with S-type granites. The presence of muscovite, a characteristic mineral of S-type granites, and the A-C-F diagram (Figure 13D) positioning of the samples within the S-type granite field further support this classification. Whole-rock zircon saturation temperatures range from 780°C to 806°C (avg. 791°C), consistent with S-type granite zircon saturation temperatures (Watson, 1979; Zhao et al., 2013b). Thus, the Xiekeng pluton is interpreted as a highly fractionated S-type granite.
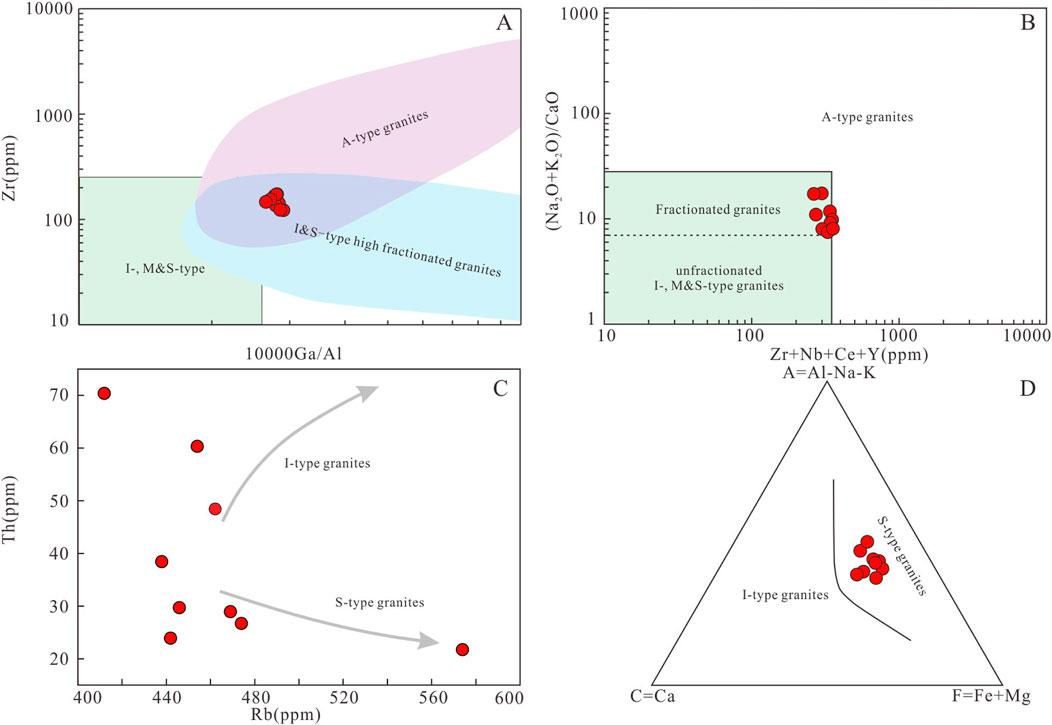
Figure 13. Petrogenetic discriminant diagrams. (A) 10,000 Ga/Al vs. Zr diagram (Whalen et al., 1987; Wu et al., 2017). (B) (Zr+Nb+Ce+Y) vs. (Na2O+K2O)/CaO diagram (Whalen et al., 1987). (C) Rb vs. Th diagram (Chappell, 1999). (D) A-C-F ternary diagram (Nakada and Takahashi, 1979).
5.3 Magmatic pressure
Highly fractionated S-type granites are characterized by the absence of the typical pressure indicator mineral amphibole (Wang et al., 2007), which complicates efforts to constrain the depth of intrusion. Primary muscovite in peraluminous granites can be used as a pressure indicator to calculate magmatic emplacement pressures, and subsequently, the depth of emplacement (Tao et al., 2014). The muscovite barometer, first proposed by Velde (1965) and later modified by Anderson (1996) based on Si content (calculated with 11 oxygen atoms), is used here: P (kbar) = −2.6786Si2+ 43.975Si4+ 0.01253T (°C) – 113.9995. Using a solid-liquid line temperature of 650°C for calculations, the results (Supplementary Table S5) show that the formation pressures of the Xiekeng two-mica monzogranite range from 6.48 to 9.89 kbar (avg. 8.35 kbar). The emplacement depth, calculated using P = ρ·g·H (ρ = 2.7×103 kg/m3, g = 9.8 m/s2), ranges from 24 to 36 km (avg. 30 km). The presence of large, clean, and well-formed primary muscovite grains, similar in size to quartz, potassic feldspar, and plagioclase, indicates crystallization under high-pressure conditions.
5.4 Magma source
Petrographic and geochemical characteristics suggest that the Xiekeng pluton is an S-type granite, derived from the melting of metasedimentary rocks (Chappell et al., 1987). The recent study conducted by Roberts et al. (2024) indicates that the zircons from S-type granites in the Himalayas exhibit the lowest Ce/U and Th/U ratios, which overlap with those observed in metamorphic zircons. This finding further supports that S-type granites are derived from metamorphic rocks. Additionally, the trace element compositions of zircons within the Xiekeng intrusion closely resemble those characteristic of Phanerozoic strongly peraluminous granites (Figure 14A). In the Log (Ce/U) vs. Log (Th/U) diagram, a significant majority of data points fall within the ‘hybrid’ S-type granite region, suggesting that the origin of the Xiekeng pluton is linked to metamorphic rock sources. The CaO/Na₂O ratio can help determine the source rock composition: CaO/Na2O > 0.3 indicates a source rock rich in plagioclase and poor in clay minerals (sandy rocks), while CaO/Na₂O < 0.3 indicates a source rock poor in plagioclase and rich in clay minerals (muddy rocks) (Sylvester, 1998). The CaO/Na2O ratios of the Xiekeng pluton range from 0.14 to 0.36 (Figure 14C), with three samples having CaO/Na₂O > 0.3 (sandy rocks) and six samples having CaO/Na₂O < 0.3 (muddy rocks). The Rb/Sr ratios range from 5.81 to 23.3, and Rb/Ba ratios from 1.58 to 9.71. In the Rb/Sr vs. Rb/Ba diagram, all the samples fall within the shale area (Figure 14D). However, due to the high degree of magmatic differentiation and subsequent late hydrothermal processes, elements such as K, Na, Ca, Rb, Sr, and Ba are particularly susceptible to migration throughout the rock-forming process. Therefore, the Al2O3/TiO2 vs. CaO/Na2O and Rb/Sr vs. Rb/Ba diagrams may not be accurate to distinguish the material composition of source rocks. Most scholars believe that the Indosinian highly differentiated S-type granites in South China originated from metamorphic mudstones (Wang et al., 2007; Mao et al., 2013b; Chen et al., 2007; Gao et al., 2018; Du et al., 2022). In the Eu/Eu* vs. (La/Yb)N diagram (Figure 14E), they fall within the crustal source range, Mg# values range from 13 to 35 (avg = 28 < 40), and the samples fall within the pure crustal range, indicating no mantle source involvement (Figure 14F) (Rapp and Watson, 1995). Zircon Lu–Hf isotopes and whole-rock Sr–Nd isotopes indicate the granites primarily originated from the deep melting or re-melting of ancient crustal materials (Zhu et al., 2009). Thus, we conclude that the source rock of the Xiekeng pluton is likely composed of crustal clay-rich mudstones.
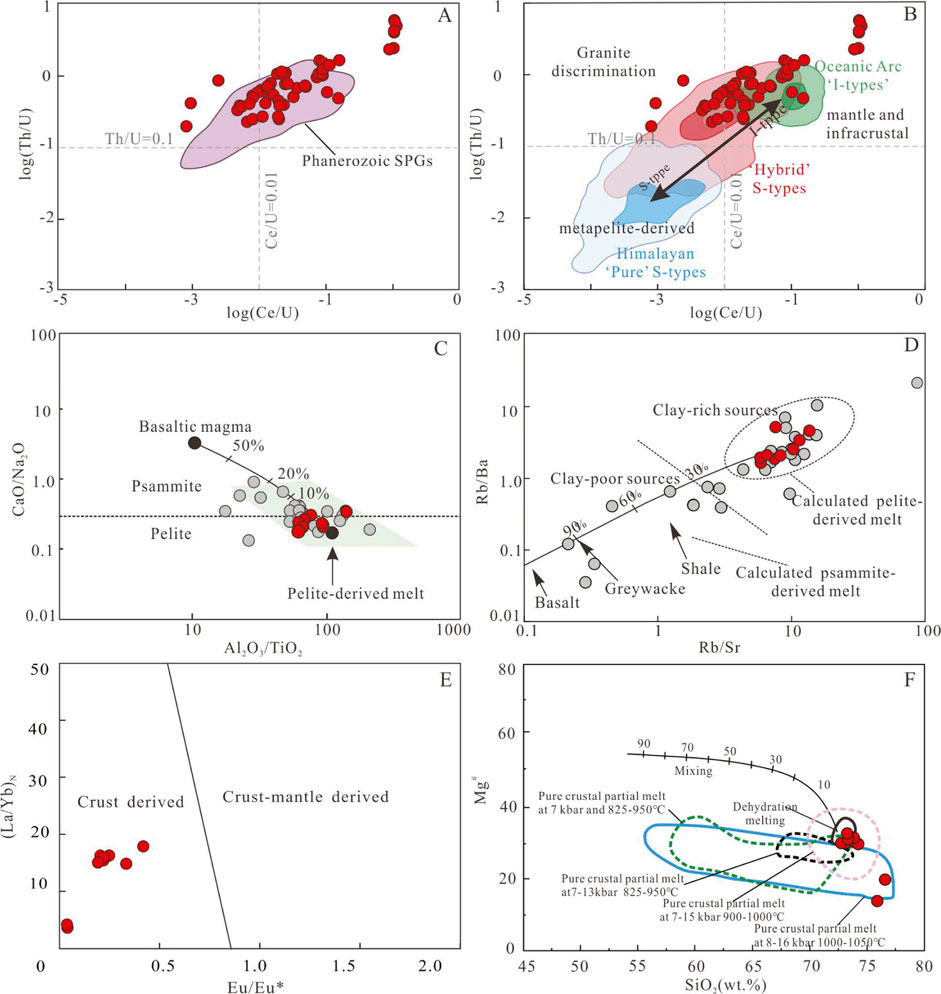
Figure 14. (A, B) Zircons log (Ce/U) vs. log (Th/U) diagrams (Roberts et al., 2024). (C) Al2O3/TiO2 vs. CaO/Na2O diagram (Sylvester, 1998). (D) Rb/Sr vs. Rb/Ba diagram (Sylvester, 1998). (E) Eu/Eu* vs. (La/Yb)N diagram (Chen et al., 2009). (F) SiO2 vs. Mg# diagram (Qing et al., 2020). SPG = Strongly Peraluminous Granites. The fields of pure crustal partial melts determined in experimental studies on dehydration melting of low-K basaltic rocks at 8–16 kbar and 1,000°C–1,050 C (Rapp and Watson, 1995), of moderately hydrous (1.7–2.3 wt% H2O) medium-to high-K basaltic rocks at 7 kbar and 825°C–950 C (Sisson et al., 2005), of pelitic rocks at 7–13 kbar and 825°C–950°C (Patiño Douce and Johnston, 1991), and of biotite gneiss and quartz amphibolite at 7–15 kbar and 900°C–1,000°C (Patiño Douce and Beard, 1995). The data sources are the same as Figure 4.
Trace elements are crucial for determining granite source evolution (Zhao and Zhou, 1997). The Nb/Ta ratios of the Xiekeng pluton range from 2.38 to 9.24 (avg. 7.15), significantly lower than those of chondrites (19.9) and continental crust (13.4) (Taylor and Mc Lennan, 1995), indicating Nb depletion. The Zr/Hf ratios range from 25.42 to 35.37 (avg. 31.79), lower than those of chondrites (34.3) and continental crust (36.7) (Figure 15A) (Chen and Yang, 2015), indicating significant magmatic differentiation. The Rr/Sr ratios range from 5.81 to 23.3 (avg. 9.15), significantly higher than the average global upper crustal values of 0.31 (Gao et al., 1999) for eastern China and 0.32 (Taylor and Mc Lennan, 1995) globally. The Rb/Nb ratios range from 9.22 to 14.66 (avg. 12.19), higher than the global upper crustal Rb/Nb ratio of 4.5 (Taylor and Mc Lennan, 1995). The Nb/U ratios range from 1.55 to 11.09 (avg. 6.44), and Ce/Pb ratios from 1.90 to 4.03 (avg. 2.66), similar to continental crust values (Nb/U = 9, Ce/Pb = 4), suggesting a source rock of mature continental crust. The presence of trapped zircons in the magma also indicates that the Xiekeng pluton originate from the melting of ancient crust. The Zr and Zr/Nb ratios show little variation (Figure 15B), indicating magmatic differentiation influence. The positive correlation between Ba and Sr suggests potassic feldspar crystallization (Figure 15C), while the negative correlation between Sr and Rb/Sr indicates plagioclase fractionation (Figure 15D). The negative correlation between TiO2 and P2O5 suggests the crystallization of apatite and ilmenite (Figure 15E). In the SiO2 vs. FeOt/(FeOt+MgO) diagram (Figure 15F), the samples show iron enrichment characteristics.
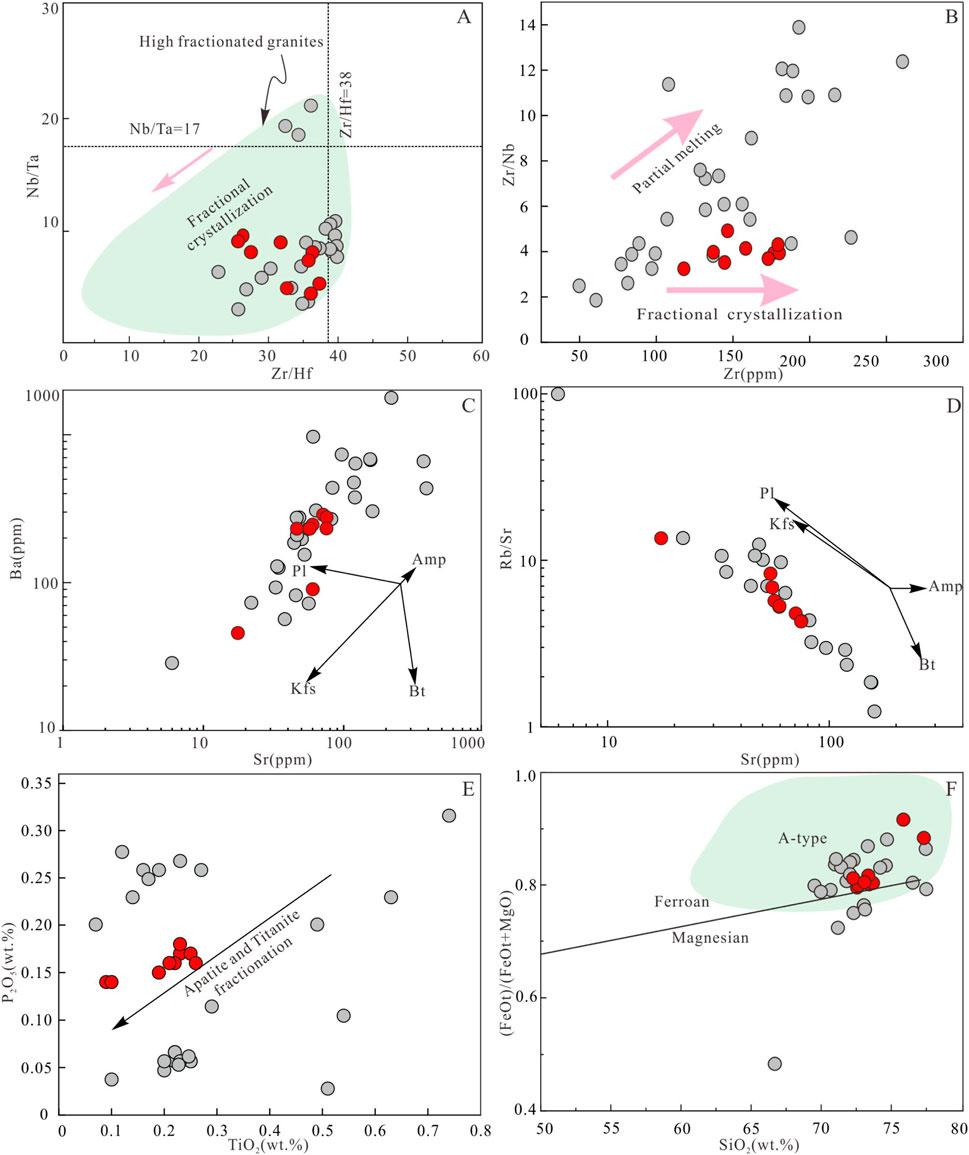
Figure 15. (A) Zr/Hf vs. Nb/Ta diagram (Ballouard et al., 2016). (B) Zr vs. Zr/Nb diagram (Geng et al., 2009). (C) Sr vs. Ba diagram (Rollinson, 1993). (D) Sr vs. Rb/Sr diagram (Rollinson, 1993). (E) TiO2 vs. P2O5 diagram (Yang et al., 2016). (F) SiO2 vs. (FeOt)/(FeOt+MgO) diagram (Whalen et al., 1987). The data sources are the same as Figure 4.
5.5 Tectonic setting
The tectonic evolution of South China during the Indosinian period is highly complex, with significant debate regarding the dynamics of magmatic activities. Various models have been proposed, including: (1) Early Mesozoic intracontinental orogeny (Hsü et al., 1988, 1990), (2) intracontinental crustal stacking and thickening (Wang et al., 2002; Wang Y. J. et al., 2005), (3) subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Block (Charvet et al., 1994; Gilder et al., 1996; Wang Q. et al., 2005; Li and Li, 2007), and (4) lithospheric extension and mafic magma underplating (Guo et al., 1998). While these models partially explain the genesis of granites, they do not fully account for the dynamic background of Indosinian magmatism in South China.
Increasing evidence suggests that the Mesozoic South China Block was subjected to multi-directional compression and crustal thickening (Zhou, 2003; Sun et al., 2005), followed by lithospheric extension and thinning (Guo et al., 1997; Jin et al., 2017). The Triassic tectonic evolution of South China can be divided into two stages: compressional deformation during the Early and Middle Triassic (ages mainly concentrated at 228–243 Ma) and extensional deformation during the Late Triassic (ages mainly concentrated at 206–220 Ma) (Zhang et al., 2012), corresponding to the early and late Indosinian stages, respectively (Wang et al., 2007). The majority of early granites are classified as strongly peraluminous S-type granites, which are thought to have formed in a collisional tectonic setting (Yu et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2013a; Zhao et al., 2013b). In contrast, the late granites may have developed under post-collisional granite tectonic mechanisms (Zhou et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2007; Mao et al., 2011). From 267 to 262 Ma, the Indosinian orogeny began, with the Indochina Block moving northwards and colliding with the South China Block, reaching its zenith during 258–243 Ma, the Paleo-Tethys Ocean closed (Carter et al., 2001), and the South China Block experienced multi-directional compression from surrounding blocks (Mao et al., 2014), leading to crustal thickening to ≤50 km and metamorphism near the suture zone and magmatic activity at around 240 Ma. During 240–225 Ma, the South China Block collided with the North China Block, affecting the entire region and causing widespread folding and thrusting of Devonian to Middle Triassic sedimentary covers, followed by crustal extension (Chen, 1999). Within 10 to 20 Ma following the collision between the Indochina Block and the South China Block, it is likely that the southeastern coastal region of South China entered a phase of stress relaxation. This observation aligns with previous studies indicating that the thickened crust experienced thermal-stress relaxation within a similar timeframe of 10–20 million years (Patinño Douce et al., 1990; Sylvester, 1998), resulting in partial melting of the middle-lower crust and forming early-stage peraluminous granites (Zhou, 2003). Thermal-stress concentration during thickening preferentially released, causing small-scale mafic magma underplating at the base of the thickened crust. This underplated mafic magma, through thermal conduction with surrounding rocks, reached thermal equilibrium within 5–20 Ma, and under the background of further lithospheric thinning, induced large-scale crustal re-melting, forming late-stage granites.
During the Early Mesozoic, the South China Block underwent significant Indosinian tectonic events, colliding and amalgamating with the Sibumasu Block along the Red River south of the Jinsha-Mojiang-Songma line. Subsequently, the South China Block collided with the North China Block, forming the Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt (Figure 17A). Yu et al. (2007) identified two distinct metamorphic-magmatic events (249–225 Ma and 225–207 Ma) slightly lagging behind the two Block collision events, reflecting the large-scale metamorphic orogenic response to the Indosinian tectonic events. Qing et al. (2020) proposed that South China was in a syn-collisional stage from 258 to 231 Ma, transitioning to a post-collisional stage after 231 Ma. The statistics of Indosinian granite (232–253 Ma) in South China Block also support the above views (Figure 16). The Xiekeng pluton formed around 240 Ma, during the syn-collisional stage, and in the (Y+Ta) vs. Rb and R/30-Hf-3Ta geochemical tectonic discrimination diagrams (Figure 16), the samples plot in the syn-collisional field, indicating formation under compressional tectonics. The presence of biotite-quartz schist xenoliths and stress-induced quartz undulose extinction and muscovite bending further support a regional compressional strain regime. We anticipate that intraplating of basaltic magmas would trigger deep (ca.30 km depth) dehydration melting of the early Paleozoic granitoids, forming the early Indosinian Xiekeng S-type granites (Figure 17B).
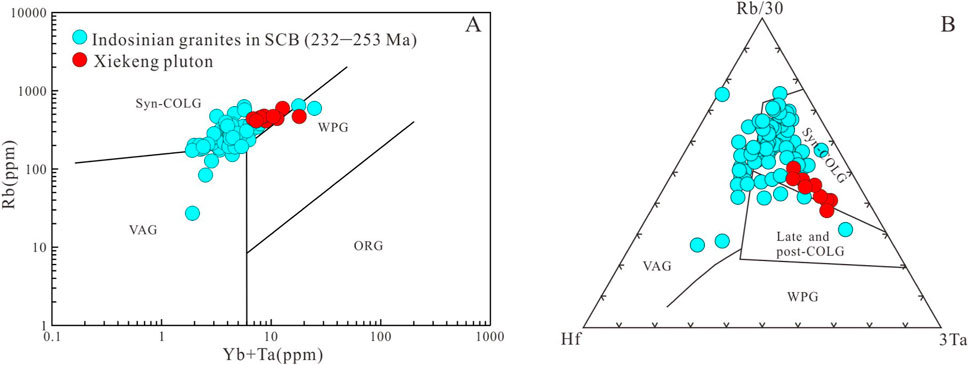
Figure 16. (A) Yb+Ta vs. Rb diagram (Pearce et al., 1984). (B) Rb/30-Hf-3Ta ternary diagram (Hairs et al., 1986). Data of Indosinian granite (232–253 Ma) in SCB are from Zhao et al. (2013a); Zhao et al. (2013b); Gao P. et al. (2014); Jiao et al. (2015); Wang H Z. et al. (2018); Qing et al. (2020); He, (2021); Han, (2023) and Sun, (2023).
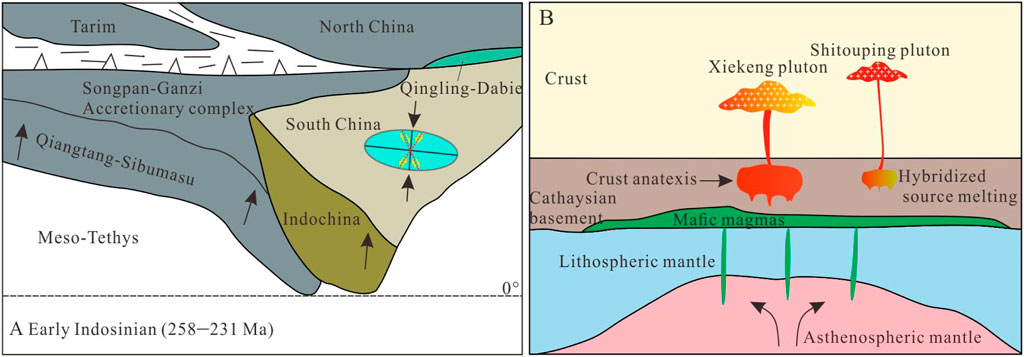
Figure 17. (A) Early Indosinian (ca. 258–231 Ma) tectonic evolution model of the SCB (adapted from Qing et al., 2020). (B) Cartoons showing the generation of Xiekeng pluton.
5.6 Metallogenic potential analysis
It is traditionally believed that the parental rocks for ion-adsorption REE deposits formed mainly during the Yanshanian period (150–190 Ma). However, recent discoveries have identified Indosinian parental rocks for REE deposits, such as the Jiaping deposit in Guangxi (239–254 Ma), the Nan’an-Renhe pluton in Guangxi (260 Ma) (Fu et al., 2022), the Qinfang pluton in Guangxi (250 Ma), the Qingxi pluton in southern Jiangxi (220–225 Ma) (Yu et al., 2012; Wang, 2015; He et al., 2017), the Wuliting granite in southern Jiangxi (237 Ma) (Qiu et al., 2004), and the Lincang granite in Yunan (218–242 Ma) (Lu et al., 2019; Lan et al., 2021). The threshold for ion-adsorption REE deposits is 150 ppm, and higher REE contents in the parental rocks favor mineralization (Zhang et al., 2024). The Xiekeng pluton has total REE contents ranging from 224.71 to 353.12 ppm, significantly exceeding this threshold, with geochemical characteristics similar to those of typical Indosinian ion-adsorption REE parental rocks (Supplementary Appendix S6). Approximately 10 km north of the Xiekeng pluton, the Shitouping ion-adsorption REE deposit has been identified. The primary ore-forming parental rock is characterized as high-silicon and high-potassium calc-alkaline granite. The average thickness of the weathering crust measures 9.52 m, with an average grade of SRE2O3 at 0.088%. The predominant rare earth minerals include bastnäsite-(Ce), synchysite-(Ce), synchysite-(Y), columbite, xenotime, and other rare earth-rich minerals (Cao et al., 2024). During the weathering process, easily weathered rare earth minerals undergo decomposition and release REE3+, while clay minerals adsorb REE3+. The pH value exhibits a gradual increase from the surface soil layer to the semi-weathered layer. In the upper section of the weathering crust, pH levels are acidic; H+ desorb a portion of REE3+, which subsequently migrates to lower regions of the weathering crust along with water flow. As pH increases, clay mineral adsorption of REE3+ intensifies while its migration capacity diminishes-ultimately leading to precipitation and enrichment in deeper layers of the weathering crust (Zhu et al., 2022). Due to their stronger migration ability compared to LREE3+, HREE3+ tends to be preferentially adsorbed by clay minerals when pH approaches neutrality. This phenomenon results in HREE3+ being enriched in deeper strata and contributes to fractionation between light and heavy rare earth elements. Consequently, a “light on top and heavy at the bottom” distribution pattern is observed for rare earth elements within the profile of the weathering crust (Li and Zhou, 2020). A statistical analysis of the parental rocks associated with typical ion-adsorption REE deposits in South China indicates that these deposits are primarily derived from partial melting of metamorphosed conglomeratic sandstone and metamorphosed mudstone (Yang et al., 2024). The Xiekeng pluton is characterized as a high-potassium calc-alkaline to shoshonitic granite, exhibiting significant differentiation along with a high initial strontium ratio (ISr) value ranging from 0.720302 to 0.726407, low εNd(t) values (−11.2 to −10.90), and a two-stage model age (TDM2) estimated at 1.90 to 1.93 Ga. The source rocks is mainly composed of sedimentary rocks. During the formation process, it is conducive to the crystallization and precipitation of rare earth minerals such as apatite, monazite, xenotime, fluocerite, and bastnäsite (Figure 3), and the rich rare earth mineral types are similar to those of the Shitouping deposit. The region in southern Jiangxi is characterized by low hills with minimal elevation differences, conducive to forming complete weathering crusts, adequate rainfall and humid climate (temperatures 18°C–21°C, rainfall 1,500–2000 mm/year), well-developed vegetation preventing erosion of the weathering crust (Figure 2C), and weakly acidic to neutral pH values that favor REE enrichment (Wang D. H. et al., 2013). These factors provide excellent conditions for forming ion-adsorption REE deposits. Therefore, the Xiekeng pluton has significant potential for ion-adsorption type REE mineralization, and further investigation is necessary.
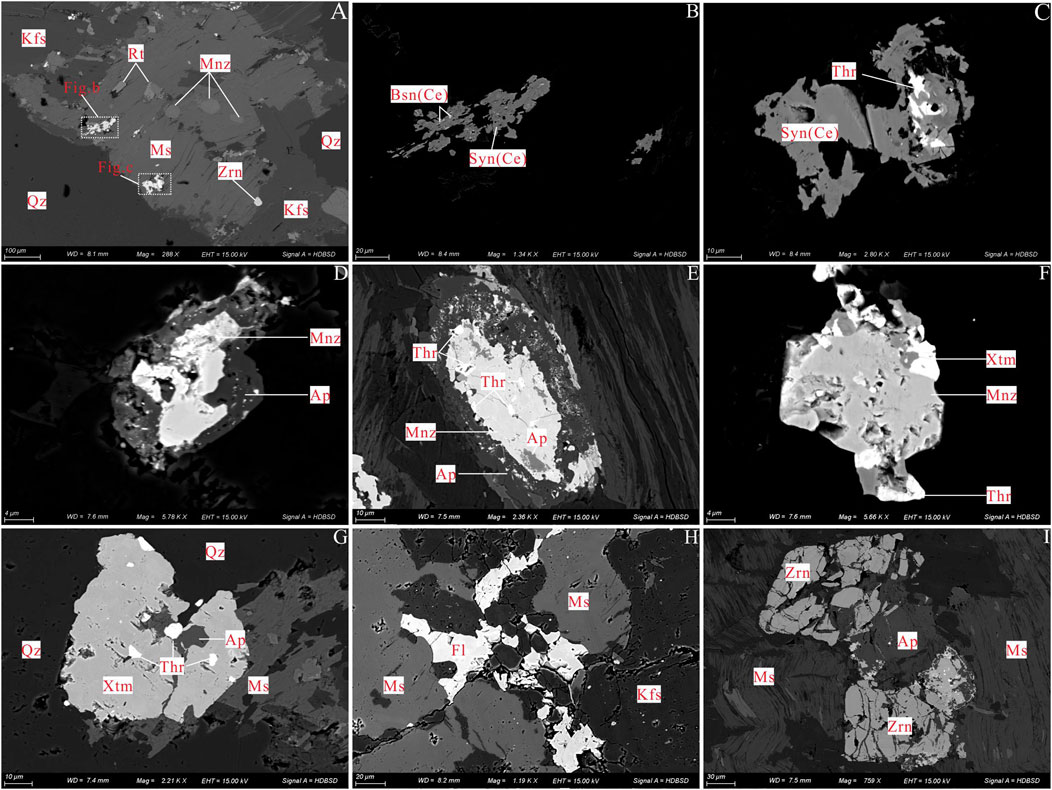
Figure 3. The back-scattered electron (BSE) images of characteristic accessory and REE minerals in Xiekeng pluton. Qz-Quartz; Ms-Muscovite; Kfs-potassic feldspar; Mnz-Monazite; Rt-Rutile; Bsn(Ce)-Bastnäsite-(Ce); Syn (Ce)-Synchysite-(Ce); Thr-Thorite-(Y); Ap-Apatite; Xtm-Xenotime; Fl-Fluorite; Zrn-Zircon. (A–C) Monazite, rutile, xenotime, fuocerite, and bastnäsite are evident within muscovite. (D, E) Apatite is altered to monazite by hydrothermal processes. (F) Monazite is altered to xenotime by fluid. (G) thorite develops inside the xenotime. (H) Fluorite fills the interstices between muscovite and potassic feldspar. (I) Zircon and muscovite are fractured.
6 Conclusion
(1) The Xiekeng pluton is a highly fractionated, strongly peraluminous S-type granite that formed through intracontinental collision-related tectonic setting.
(2) The zircon U–Pb ages of the Xiekeng pluton are 241.2 ± 1.8 Ma and 238.3 ± 1.7 Ma, formed during the Middle Triassic, which coincides with the peak of the Indosinian volcanic activity in South China. The εHf(t) and εNd(t) values suggest that the source is mainly derived from the deep melting or re-melting of ancient crustal materials.
(3) The Xiekeng pluton exhibits geochemical characteristics similar to known ion-adsorption REE mineralizing parental rocks, containing abundant REE minerals that can weather to form ion-adsorption REE deposits.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
DZ: Writing–original draft. TL: Data curation, Writing–original draft. XW: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing–original draft. MC: Software, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. XC: Investigation, Resources, Writing–review and editing. YZ: Project administration, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. LG: Resources, Software, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research is supported by the Geological Exploration Project of Jiangxi province Finance (No. 20220014), Science and Technology Innovation Project of Department of Natural Resources of Jiangxi province (No. ZRKJ20232411; No. ZRKJ20232526) and Key Laboratory of Ionic Rare Earth Resources and Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China (No. 2022IRERE103; 2023IRERE106).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2024.1493594/full#supplementary-material
References
Andersen, T. (2002). Correction of common lead in U–Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem. Geol. 192 (1-2), 59–79. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Anderson, J. L. (1996). Status of thermobarometry in granitic batholiths. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 87, 125–138. doi:10.1130/0-8137-2315-9.125
Ballouard, C., Poujol, M., Boulvais, P., Branquet, Y., Tartese, R., and Vigneresse, J. (2016). Nb-Ta fractionation in peraluminous granites: a marker of the magmatic-hydrothermal transition. Geology 44 (3), 231–234. doi:10.1130/G37475.1
Bao, Z. W., and Zhao, Z. H. (2003). Geochemistry and tectonic setting of the Fogang aluminous A-type granite, Guangdong Province, China–a preliminary study. Geol. Geochem. 31, 52–61. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2003.01.009
Bao, Z. W., and Zhao, Z. H. (2008). Geochemistry of mineralization with exchangeable REY in the weathering crusts of granitic rocks in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 33, 519–535. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.03.005
Belousova, E., Griffin, W., O'Reilly, S. Y., and Fisher, N. (2002). Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 143, 602–622. doi:10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
Blichert-Toft, J. (2008). The Hf isotopic composition of zircon reference material 91500. Chem. Geol. 253, 252–257. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.05.014
Cao, M. X., Wang, X. G., Zhang, D. F., Zhang, Y. W., Gong, L. X., and Zhong, W. (2024). Petrogenesis and REE mineralogical characteristics of shitouping granites in southern Jiangxi province: implication for HREE mineralization in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 168, 106011. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2024.106011
Cao, M. Y., Jiang, S. Y., Su, H. M., and Liu, T. (2021). Indosinian magmatic-hydrothermal metallogenic event in the North Wuyi area, southeastern China: an example from the Chenfang skarn deposit in Jiangxi Province. Ore Geol. Rev. 138, 104386. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104386
Carter, A., Roques, D., Bristow, C., and Kinny, P. (2001). Understanding mesozoic accretion in southeast Asia: significance of Triassic thermotectonism (Indosinian orogeny) in Vietnam. Geology 29 (3), 211–214. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0211:umaisa>2.0.co;2
Chappell, B. W. (1999). Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos 46 (3), 535–551. doi:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
Chappell, B. W., and White, A. J. R. (1974). Two contrasting granite types. Pac. Geol. 8 (2), 172–174.
Chappell, B. W., White, A. J. R., and Wyborne, D. (1987). The importance of residual source material (Restite) in granite petrogenesis. J. Petrol. 28 (6), 1111–1138. doi:10.1093/petrology/28.6.1111
Charvet, J., Lapierre, H., and Yu, Y. W. (1994). Geodynamic significance of the Mesozoic volcanism of southeastern China. J.SE Asian Earth Sci. 9 (4), 387–396. doi:10.1016/0743-9547(94)90050-7
Chen, A. (1999). Mirror-image thrusting in the South China orogenic belt: tectonic evidence from western Fujian, southeastern China. Tectonophysics 305 (4), 497–519. doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00036-0
Chen, J. F., and Jahn, B. M. (1998). Crustal evolution of southeastern China: Nd and Sr isotopic evidence. Tectonophysics 284 (1-2), 101–133. doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00186-8
Chen, J. Y., and Yang, J. H. (2015). Petrogenesis of the Fogang highly fractionated I-type granitoids: constraints from Nb, Ta, Zr and Hf. Acta Petrol. Sin. 31 (3), 846–854. (in Chinese).
Chen, W. F., Chen, P. R., Huang, H. Y., Ding, X., and Sun, T. (2007). Chronological and geochemical studies of granite and enclave in Baimashan pluton, Hunan, South China. Sci. China Ser. D. 50, 1606–1627. doi:10.1007/s11430-007-0073-1
Chen, Y. W., Bi, X. W., Hu, R. Z., and Qin, H. W. (2009). Comparison of geochemical chararcteristic of uranium-and non-uranium-bearing Indosinian granites in guidong composite pluton. Mineral. Petrol. 29 (3), 106–114. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2009.03.016
Chi, R. A., and Liu, X. M. (2019). Prospect and development of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore. J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths 37 (2), 129–140. doi:10.11785/S1000-4343.20190201
Ding, X., Chen, P. R., Chen, W. F., Huang, H. Y., and Zhou, X. M. (2006). Single zircon LA-ICPMS U–Pb dating of Weishan granite (Hunan, South China) and its petrogenetic significance. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 49 (8), 816–827. doi:10.1007/s11430-006-0816-4
Dong, C. Y., Zhao, K. D., Jiang, S. Y., Chen, W. F., Chen, P. R., Ling, H. F., et al. (2010). Zircon geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of granite from the Baimianshi uranium ore district in the southern Jiangxi province. Geol. J. China Univ. 16 (2), 149–160. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2010.02.003
Du, Y., Lu, Y. Y., Zhang, Z. Z., Fu, J. M., Yang, X. Y., Zhao, Z., et al. (2022). Indosinian magmatism and mineralization in the Banjiaoyuan tin deposit, middle Nanling Range, South China: constraints from zircon and cassiterite U–Pb ages, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic compositions. Ore Geol. Rev. 151, 105190. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.105190
Elhlou, S., Belousova, E. A., Griffin, W. L., Pearson, N. J., and O’Reilly, S. Y. (2006). Trace element and isotopic composition of GJ-red zircon standard by laser ablation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 70 (18), A158. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2006.06.1383
Feng, Y. Z., Xiao, B., Chu, G. B., Li, S. S., Wang, J., and Wen, Z. Q. (2022). Late mesozoic magmatism in the Gucheng district: implications for REE metallogenesis in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 148, 105034. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.105034
Fu, W., Li, X. T., Feng, Y. Y., Feng, M., Peng, Z., Yu, H. X., et al. (2019). Chemical weathering of S-type granite and formation of Rare Earth Element (REE)-rich regolith in South China: critical control of lithology. Chem. Geol. 520, 33–51. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.05.006
Fu, W., Zhao, Q., Luo, P., Li, P. Q., Lu, J. P., Zhou, H., et al. (2022). Mineralization diversity of ion-adsorption type REE deposit in southern China and its critical influence by parent rocks. Acta Geol. Sin. 96 (11), 3901–3925. doi:10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2022233
Fu, X. N., Yi, Z. B., Fu, W., Liu, J. C., Han, Z. X., Fang, G. C., et al. (2024). Mineralogy and weathering of REE minerals in the Liuchen granite, Guangxi, southern China: implications for HREE enrichment in the granite regolith. Ore Geol. Rev. 169, 106099. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2024.106099
Gao, P. (2016). A geochemical study of Mesozoic granites from the Nanling range in South China (Dissertation). Hefei: University of Science and Technoiogy of China. (in Chinese).
Gao, P., Zhao, Z. F., and Zheng, Y. F. (2014a). Petrogenesis of Triassic granites from the Nanling range in South China: implications for geochemical diversity in granites. Lithos 210-211, 40–56. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.09.027
Gao, P., Zheng, Y. F., Chen, Y. X., Zhao, Z. F., and Xia, X. P. (2018). Relict zircon U–Pb age and O isotope evidence for reworking of Neoproterozoic crustal rocks in the origin of Triassic S-type granites in South China. Lithos 300-301, 261–277. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2017.11.036
Gao, S., Luo, T. C., Zhang, B. R., Zhang, H. F., Han, Y. W., Zhao, Z. D., et al. (1999). Structure and composition of the continental crust in East China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 43 (2), 129–140. doi:10.1007/BF02878511
Gao, W. L., Wang, Z. X., Song, W. J., Wang, D. X., and Li, C. L. (2014b). Zircon U–Pb geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications of Triassic A-type granites from southeastern Zhejiang, South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 96, 255–268. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.024
Geng, H. Y., Sun, M., Yuan, C., Xiao, W. J., Xian, W. S., Zhao, G. C., et al. (2009). Geochemical, Sr–Nd and zircon U–Pb–Hf isotopic studies of Late Carboniferous magmatism in the West Junggar, Xinjiang: implications for ridge subduction? Chem. Geol. 266, 364–389. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.07.001
Gilder, S. A., Gill, J., Coe, R. S., Zhao, X. X., Liu, Z. W., Wang, G. X., et al. (1996). Isotopic and paleomagnetic constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of South China. J. Geophys. Res. 107 (B7), 16137–16154. doi:10.1029/96JB00662
Griffin, W. L., Wang, X., Jackson, S. E., Pearson, N. J., O'Reilly, S. Y., Xu, X. S., et al. (2002). Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: in-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos 61 (3-4), 237–269. doi:10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8
Gu, H., Yang, X., Deng, J., Duan, L., and Liu, L. (2017). Geochemical and zircon U–Pb geochronological study of the Yangshan A-type granite: insights into the geological evolution in south Anhui, eastern Jiangnan Orogen. Lithos 284-285, 156–170. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2017.04.007
Guo, C. L., Chen, Y. C., Lin, Z. Y., Lou, F. S., and Zeng, Z. L. (2011). SHRIMP zircon U–Pb dating geochemistry and zircon Hf isotopic characteristics of granitoids in Keshuling granites Jiangxi Province and their genetic analysis. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 30 (4), 567–580. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.04.002
Guo, C. L., Zheng, J. H., Lou, F. S., and Zeng, Z. L. (2012). Petrography, genetic types and geological dynamical settings of the Indosinian granitoids in South China. Geotecton. Metallog. 36 (3), 457–472. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.020
Guo, F., Fan, W. M., and Lin, K. (1998). Nature of the Precambrian crust and underplating of early Mesozoic basaltic magmas in south Hunan province. Geotecton. Metallog. (Suppl.) 2, 19–22. (in Chinese). doi:10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.1998.s1.004
Guo, F., Fan, W. M., Lin, K., and Lin, Y. X. (1997). A study on the chronology and genesis of gabbro inclusions in Daoxian county, Hunan Province. Chin. Sci. Bull. 42 (15), 1661–1664. (in Chinese).
Han, Z. C. (2023). Metallogenic tectonic background of Indosinian ion adsorption type REE deposits: a case study from the granite in Southeast Guangxi (Dissertation). Guilin, China: Guilin Univ. Technol. (in Chinese).
Harris, N. B. W., Pearce, J. A., and Tindle, A. G. (1986) Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism, Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ., 19, 67–81. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.019.01.04
He, C., Xu, C., Zhao, Z., Kynicky, J., Song, W. L., and Wang, L. Z. (2017). Petrogenesis and mineralization of REE-rich granites in Qingxi and Guanxi, Nanling region, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 81, 309–325. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.021
He, C. K. (2021). Genetic relation and tectonic significance of Indosinian granites and mixed rocks in Hetai gold deposit, Guangdong province (Dissertation). Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. (in Chinese).
He, Z. Y., Xu, X. S., and Niu, Y. L. (2010). Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic granite-syenite-gabbro association from inland South China. Lithos 119 (3-4), 621–641. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.016
Healy, B., Collins, W. J., and Richards, S. W. (2004). A hybrid origin for Lachlan S-type granites: the Murrumbidgee Batholith example. Lithos 78 (1-2), 197–216. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.047
Hsü, K. J., Li, J. L., Chen, H. H., Wang, Q. C., Sun, S., and Şengör, A. M. C. (1990). Tectonics of South China: Key to understanding west Pacific geology. Tectonophysics 183 (1-4), 9–39. doi:10.1016/0040-1951(90)90186-C
Hsü, K. J., Sun, S., Li, J. L., Chen, H. H., Pen, H. P., and Şengör, A. M. C. (1988). Mesozoic overthrust tectonics in south China. Geology 16 (5), 418–421. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0418:MOTISC>2.3.CO;2
Hua, R. M., Chen, P. R., Zhang, W. L., Liu, X. D., Lu, J. J., Lin, J. F., et al. (2003). Metallogenic systems related to mesozoic and cenozoic granitoids in South China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 46 (8), 816–829. doi:10.1007/BF02879525
Huang, J., He, H. P., Tan, W., Liang, X. L., Ma, L. Y., Wang, Y. Y., et al. (2021). Groundwater controls REE mineralisation in the regolith of South China. Chem. Geol. 577, 120295. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120295
Ishihara, S., Hua, R., Hoshino, M., and Murakami, H. (2008). REE abundance and REE minerals in granitic rocks in the Nanling range, Jiangxi Province, southern China, and generation of the REE-rich weathered crust deposits. Resour. Geol. 58 (4), 355–372. doi:10.1111/j.1751-3928.2008.00070.x
Jackson, S. E., Pearson, N. J., Griffin, W. L., and Belousova, E. A. (2004). The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol. 211 (1-2), 47–69. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.017
Jiao, S. J., Li, X. H., Huang, H. Q., and Deng, X. G. (2015). Metasedimentary melting in the formation of charnockite: petrological and zircon U–Pb–Hf–O isotope evidence from the Darongshan S-type granitic complex in southern China. Lithos 239, 217–233. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.10.004
Jin, X. B., Wang, L., Xiang, H., Liu, Z. P., Duan, G. L., and Li, Z. Y. (2017). Petrogenesis of diabase from Jiangshiqiao in Taojiang city, Hunan province: Constrains from geochemistry, geochronology and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopes. Geol. Bull. China. 36 (5), 750–760. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.05.007
Lan, X. J., Zhang, B. T., Lu, W. J., Zhao, X. D., Li, X. L., Wang, M. B., et al. (2021). Ore controlling factors and ore-search prospect of rare-earth deposits of the ion adsorp-tion type in the Menghai area, Yunnan Province. Geol. Explor 57 (4), 0935–0946. (in Chinese). doi:10.12134/j.dzykt.2021.04.017
Lee, C. T. A., and Morton, D. M. (2015). High silica granites: terminal porosity and crystal settling in shallow magma chambers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 409, 23–31. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2014.10.040
Li, C. F., Wang, X. C., Guo, J. H., Chu, Z. Y., and Feng, L. J. (2016). Rapid separation scheme of Sr, Nd, Pb and Hf from a single rock digest using a tandem chromatography column prior to isotope ratio measurements by mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 31, 1150–1159. doi:10.1039/C5JA00477B
Li, J., Huang, H. Y., Liu, Z. J., Zhang, T. L., Fang, S. Y., and Zou, M. L. (2021a). LA-ICP-MS U–Pb ages and trace element compositions of zircon from Indosinian granites in middle Zhuguangshan. Geotecton. Metallog. 45 (6), 1216–1262. (in Chinese). doi:10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2021.06.007
Li, J. L. (1993). Lithosphere structure and geological evolution in southeast China. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press. (in Chinese).
Li, M. Y. H., and Zhou, M. F. (2020). The role of clay minerals in formation of the regolith-hosted heavy rare earth element deposits. Am. Mineral. 105 (1), 92–108. doi:10.2138/am-2020-7061
Li, M. Y. H., Zhou, M. F., and Williams-Jones, A. E. (2019). The genesis of regolith-hosted heavy rare earth element deposits: insights from the World-Class Zudong deposit in Jiangxi province, South China. Econ. Geol. 114 (3), 541–568. doi:10.5382/econgeo.4642
Li, W., Liu, C. H., Tan, Y., Chen, W., Lu, J., and Chen, Z. W. (2021b). Zircon U–Pb age, petro-geochemical and mineralization characteristics of Keshuling granites in southern Jiangxi Province. Geol. Rev. 67 (5), 1309–1320. (in Chinese). doi:10.16509/j.georeview.2021.06.071
Li, X., Wang, L. Z., Tu, B., Tian, Y., Xie, G. G., Zhang, J. Y., et al. (2021c). Zircon geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Taibao pluton in northwest Guangdong province. Earth Sci. 46 (4), 1199–1216. doi:10.3799/dqkx.2020.193
Li, X. H., Chung, S. L., Zhou, H. W., Lo, C. H., Liu, Y., and Chen, C. H. (2004). “Jurassic intraplate magmatism in southern Hunan-eastern Guangxi: 40Ar/39Ar dating, geochemistry, Sr–Nd isotopes and implications for tectonic evolution of SE China,”. Aspects of the tectonic evolution of China, Editor J. Malpas, C. J. Fletcher, and J. C. Aitchison (London, United Kingdom: Geol Soc London Spec Publ), 226, 193–216. doi:10.1144/gsl.sp.2004.226.01.11
Li, X. H., Li, W. X., Wang, X. C., Li, Q. L., Liu, Y., and Tang, G. Q. (2009). Role of mantle-derived magma in genesis of early Yanshanian granites in the Nanling Range, South China: in situ zircon Hf–O isotopic constraints. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 39 (7), 1262–1278. doi:10.1007/s11430-009-0117-9
Li, X. H., Qi, C. S., Liu, Y., Liang, X. R., Tu, X. L., Xie, L. W., et al. (2005). Petrogenesis of the Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanic rocks along the western margin of the Yangtze Block: new constraints from Hf isotopes and Fe/Mn ratios. Chin. Sci. Bull. 50, 2481–2486. doi:10.1360/982005-287
Li, X. W., Mo, X. X., Zhao, Z. D., and Zhu, D. C. (2010a). A discussion on how to discriminate A-type granite. Geol. Bull. China. 29 (2-3), 278–285. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.02.012
Li, Y. J., Wei, J. H., Wu, G., Tan, J., Shi, W. J., Zhao, S. Q., et al. (2013). Early Triassic diorite-porphyrite dikes from the Shilu area, Hainan Island: zircon U–Pb age and tectonic implication. Earth Sci. 38, 241–252. (in Chinese). doi:10.3799/dqkx.2013.025
Li, Z., Qiu, J. S., and Zhou, J. C. (2010b). Geochronology, geochemistry, and Nd–Hf isotopes of early Palaeozoic-early Mesozoic I-type granites from the Hufang composite pluton, Fujian, South China: crust–mantle interactions and tectonic implications. Int. Geol. Rev. 54 (1), 15–32. doi:10.1080/00206814.2010.496542
Li, Z. X., and Li, X. H. (2007). Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: a flat-slab subduction model. Geology 35 (2), 179–182. doi:10.1130/G23193A.1
Ling, H. F., Shen, W. Z., Sun, T., Jiang, S. Y., Jiang, Y. H., Ni, P., et al. (2006). Genesis and source characteristics of 22 Yanshanian granites in Guangdong province: study of element and Nd-Sr isotopes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 22 (11), 2687–2703. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.11.00
Liu, Y. S., Gao, S., Hu, Z. C., Wang, D. B., and Zong, K. (2010). Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-north China orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. J. Petrol. 51 (1-2), 537–571. doi:10.1093/petrology/egp082
Liu, Y. S., Hu, Z. C., Gao, S., Günther, D., Xu, J., Gao, C. G., et al. (2008). In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 257 (1-2), 34–43. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Lu, L., Wang, D. H., Wang, C. H., Zhao, Z., Feng, W. J., Xu, X. C., et al. (2019). Mineralization regularity of ion-adsorption type REE deposits on Lincang granite in Yunnan Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 93 (6), 1466–1478. doi:10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2019181
Ludwig, K. R. (2003). User's manual for Isoplot 3.00-A geochronological Toolkit for microsoft excel.
Ma, Z. W., and Guo, F. (2023). Indosinian tectonic transition in Yunkai Massif: petrological and geochemical constraints from two-mica granite in Yangchun area, South China. Geotecton. Metallog. 47 (5), 1183–1207. (in Chinese). doi:10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2023.05.014
Maniar, P. D., and Piccoli, P. M. (1989). Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 101 (5), 635–643. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Mao, J. R., Cheng, Y. B., Chen, M. H., and Pirajno, F. (2013a). Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Min. Deposita 48 (3), 267–294. doi:10.1007/s00126-012-0446-z
Mao, J. R., Li, Z. L., and Ye, H. M. (2014). Mesozoic tectono-magmatic activities in South China: retrospect and prospect. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 57, 2853–2877. doi:10.1007/s11430-014-5006-1
Mao, J. R., Takahashi, Y., Kee, W. S., Li, Z. L., Ye, H. M., Zhao, X. L., et al. (2011). Characteristics and geodynamic evolution of Indosinian magmatism in South China: a case study of the Guikeng pluton. Lithos 127 (3-4), 535–551. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.09.011
Mao, J. R., Ye, H. M., Liu, K., Li, Z. L., Takahashi, Y., Zhao, X. L., et al. (2013b). The indosinian collision–extension event between the South China block and the palaeo-pacific plate: evidence from indosinian alkaline granitic rocks in dashuang, eastern Zhejiang, South China. Lithos 172-173, 81–97. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.04.004
McDonough, W. F., and Sun, S. S. (1995). The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 120 (3-4), 223–253. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
Middlemost, E. A. K. (1985). Magmas and magmatic rocks. London: Longman, 1–266. doi:10.1017/S0016756800026716
Middlemost, E. A. K. (1994). Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth Sci. Rev. 37 (3-4), 215–224. doi:10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Nakada, S., and Takahashi, M. (1979). Regional variation in chemistry of the Miocene intermediate to felsic magmas in the Outer Zone and the Setouchi province of southwest Japan. J. Geol. Soc. Jpn. 85, 571–582. doi:10.5575/geosoc.85.571
Patinño Dounce, A. E., Humphreys, E. D., and Johnston, A. D. (1990). Anatexis and metamorphism in Tectonically thickened continental crust exemplified by the Sevier hinterland, western North America. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 97 (3-4), 290–315. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(90)90048-3
Patiño Douce, A. E., and Beard, J. S. (1995). Dehydration-melting of biotite gneiss and quartz amphibolite from 3 to 15 kbar. J. Petrol. 36, 707–738. doi:10.1093/petrology/36.3.707
Patiño Douce, A. E., and Johnston, A. D. (1991). Phase equilibria and melt productivity in the pelitic system: implications for the origin of peraluminous granitoids and aluminous granulites. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 107, 202–218. doi:10.1007/BF00310707
Pearce, J. A., Harris, N. B. W., and Tindle, A. G. (1984). Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J. Petrol. 25 (4), 956–983. doi:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Peccerillo, R., and Taylor, S. R. (1976). Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 58, 63–81. doi:10.1007/BF00384745
Qi, C. S., Deng, X. G., Li, X. W., Li, X. H., Yang, Y. H., and Xie, L. W. (2007). Origin of the Darongshan-Shiwandashan S-type granitoid belt from southeastern Guangxi: geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic constraints. Acta Petrol. Sin. 23 (2), 403–412. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.019
Qing, L., Jiang, Y. H., and Du, F. G. (2020). Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of early Indosinian A-type granites in the Xinxing pluton, southern South China. Mineral. Petrol. 114, 217–242. doi:10.1007/s00710-020-00701-3
Qiu, J. S., Mcinnes, B. I. A., Xu, X. S., and Allen, C. M. (2004). Zircon ELA-ICP-MS dating for Wuliting pluton at Dajishan, southern Jiangxi and new Recognition about its relation to tungsten mineralization. Geol. Rev. 50 (2), 125–133. (in Chinese). doi:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.02.003
Qiu, J. S., Xiao, E., Hu, J., Xu, X. S., Jiang, S. Y., and Li, Z. (2008). Petrogenesis of highly fractionated I-type granites in the coastal area of northeastern Fujian province: constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 24 (11), 2468–2484. (in Chinese).
Rapp, R. P., and Watson, E. B. (1995). Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust-mantle Recycling. J. Petrol. 36 (4), 891–931. doi:10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Ren, H. T., Wu, J. Q., and Ye, X. F. (2013). Zircon U–Pb age and geochemical characteristics of peraluminous fine⁃grained granite in western part of the Fucheng pluton, Jiangxi Province. Geol. J. China Univ. 19 (2), 327–345. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.02.015
Roberts, N. M. W., Yakymchuk, C., Spencer, C. J., Keller, C. B., and Tapster, S. R. (2024). Revisiting the discrimination and distribution of S-type granites from zircon trace element composition. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 663 (1), 118638. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2024.118638
Rollinson, H. R. (1993). Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation. London: Longman Scientific Technical. doi:10.4324/9781315845548
Scherer, E., Munker, C., and Mezger, K. (2001). Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock. Science 293, 683–687. doi:10.1126/science.1061372
Scherer, E. E., Cameron, K. L., and Blichert-Toft, J. (2000). Lu–Hf garnet geochronology: closure temperature relative to the Sm-Nd system and the effects of trace mineral inclusions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 64 (19), 3413–3432. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00440-3
Shen, W. Z., Ling, H. F., Li, W. X., and Wang, D. Z. (2000). Crust evolution in Southeast China: evidence from Nd model ages of granitoids. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 43 (1), 36–49. doi:10.1007/BF02877829
Shi, Y., San, H. Y., Guo, Z. C., Liu, X. J., Wang, X. Y., Wu, X. K., et al. (2019). LA-ICP-MS zircon U–Pb dating and Hf isotope compositions of the sillite from Ludong in Fuchuan, Northeastern Guangxi. J. Guilin Inst. Technol. 39 (2), 291–300. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2019.02.005
Shu, L. S. (2012). An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block. Geol. Bull. China. 31 (7), 1035–1053. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003
Shu, L. S., Sun, Y., Wang, D. Z., Faure, M., Charvet, J., and Monie, P. (1998). Mesozoic doming extensional tectonics of Wugongshan, South China. Sci. China Ser. D. 41, 601–608. doi:10.1007/BF02878742
Sisson, T. W., Ratajeski, K., Hankins, W. B., and Glazner, A. F. (2005). Voluminous granitic magmas from common basaltic sources. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 148, 635–661. doi:10.1007/s00410-004-0632-9
Sláma, J., Koler, J., Condon, D. J., Crowley, J. L., Gerdes, A., Hanchar, J. M., et al. (2008). Plešovice zircon-A new natural reference material for U–Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 249 (1-2), 1–35. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005
Sun, J. (2023). Petrogenesis and geological significance of early and late Triassic igneous rocks in Guangxi and Guangdong (Dissertation). Guilin, China: Guilin Univ. Technol. (in Chinese).
Sun, S. S., and McDonough, W. F. (1989). Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 42 (1), 313–345. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Sun, T. (2006). A new map showing the distribution of granites in South China and its explanatory notes. Geol. Bull. China 25 (3), 332–335. (in Chinese).
Sun, T., Zhou, X. M., Chen, P. R., Li, H. M., Zhou, H. Y., Wang, Z. C., et al. (2005). Strongly peraluminous granites of Mesozoic in Eastern Nanling Range, southern China: petrogenesis and implications for tectonics. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 48, 165–174. doi:10.1360/03yd0042
Sun, Y., Ma, C. Q., Liu, Y. Y., and She, Z. B. (2011). Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of late Triassic aluminous A-type granites in southeast China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 42 (6), 1117–1131. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.007
Sylvester, P. J. (1998). Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos 45 (1-4), 29–44. doi:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3
Tao, J. H., Li, W. X., Cai, Y. F., and Cen, T. (2014). Mineralogical feature and geological significance of muscovites from the Longyuanba Indosinian and Yanshannian two-mica granites in the eastern Nanling Range. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 57 (6), 1150–1157. doi:10.1007/s11430-013-4716-0
Taylor, S. R., and Mc Lennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 33 (2), 241–265. doi:10.1029/95RG00262
Tischendorf, G., Forster, H. J., and Gottesmann, B. (1999). The correlation between lithium and magnesium in trioctahedral micas; improved equations for Li2O estimation from MgO data. Mineral. Mag. 63 (1), 57–74. doi:10.1180/002646199548312
Velde, B. (1965). Phengite micas; Synthesis, stability, and natural occurrence. Am. J. Sci. 263 (10), 886–913. doi:10.2475/ajs.263.10.886
Wang, B. H., Hu, R. G., Si, J. T., Zhao, Y. L., Liu, X. J., Li, S. S., et al. (2021). Chemical variation and significance of white mica in granite porphyry from Gaofeng tin-polymetallic deposit in Dachang ore field. Guangxi. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 41 (3), 471–483. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2021.03.001
Wang, D. H., Zhao, Z., Yu, Y., Zhao, T., Li, J. K., Dai, J. J., et al. (2013a). Progress, problems and research orientation of Ion-adsorption type rare earth resources. J. Rock Min. Anal. 32 (5), 796–802. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.05.020
Wang, H. Z., Zhao, Y. L., Chen, P. R., Ling, H. F., and Wu, J. Q. (2018a). Petrogenesis of the Zhulanbu composite pluton and its implications for tectonic setting. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 37 (2), 175–196. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2018.02.001
Wang, L., Xu, C., Zhao, Z., Song, W., and Kynicky, J. (2015). Petrological and geochemical characteristics of Zhaibei granites in Nanling region, Southeast China: implications for REE mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 64, 569–582. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.004
Wang, L. L. (2015). Geochemistry and petrogenesis of early paleozoic-Mesozoic granites in Ganzhou, Jiangxi province, South China block (Ph.D. Thesis). Beijing, China: China Univ. Geosci. (in Chinese).
Wang, Q., Li, J. W., Jian, P., Zhao, Z. H., Xiong, X. L., Bao, Z. W., et al. (2005a). Alkaline syenites in eastern Cathaysia (South China): link to Permian-Triassic transtension. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 230 (3-4), 339–354. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.11.023
Wang, Q., Zhao, Z. H., and Xiong, X. L. (2000). The ascertainment of Late-Yanshanian A-type granite in Tongbai-Dabie orogenic belt. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 19 (4), 297–306. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2000.04.002
Wang, W. B., Li, J. H., Xin, Y. J., Sun, H. S., and Yu, Y. Q. (2018b). Zircon LA-ICP-MS U–Pb dating and geochemical analysis of the Darongshan-Shiwandashan granitoids in southwestern South China and their geological implications. Acta Geosci. Sin. 39 (2), 179–188. (in Chinese). doi:10.3975/cagsb.2017.111802
Wang, X. F., and Chen, X. H. (2005). Stratigraphic division and correlation of different geological ages in China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese).
Wang, Y. J., Fan, W. M., Guo, F., Li, H. M., and Liang, X. Q. (2002). U–Pb dating of early Mesozoic granodioritic intrusions in southeastern Hunan Province, South China and its petrogenetic implications. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 45, 280–288. doi:10.1360/02yd9030
Wang, Y. J., Fan, W. M., Liang, X. Q., Peng, T. P., and Shi, Y. R. (2005b). SHRIMP zircon U–Pb age of Indosinian granites in Hunan province and its genetic implications. Chin. Sci. Bull. 50, 1395–1403. doi:10.1360/982004-603
Wang, Y. J., Fan, W. M., Sun, M., Liang, X. Q., Zhang, Y. H., and Peng, T. P. (2007). Geochronological, geochemical and geothermal constraints on petrogenesis of the Indosinian peraluminous granites in the South China Block: a case study in the Hunan Province. Lithos 96 (3-4), 475–502. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.11.010
Wang, Y. J., Fan, W. M., Zhang, G. W., and Zhang, Y. H. (2013b). Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China block: Key observations and controversies. Gondwana Res. 23 (4), 1273–1305. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.019
Watson, E. B. (1979). Apatite saturation in basic to intermediate magmas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 6 (12), 937–940. doi:10.1029/GL006i012p00937
Watson, E. B., and Harrison, T. M. (1983). Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 64, 295–304. doi:10.1016/0012-821x(83)90211-x
Whalen, J. B., Currie, K. L., and Chappell, B. W. (1987). A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol 95 (4), 407–419. doi:10.1007/BF00402202
Wu, C. Y. (1988). The study of ion-adsorbed type of rare earth deposits in weathering crust from south Jiangxi and north Guangdong provinces. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci. Ph.D. thesis).
Wu, F. Y., Li, X. H., Zheng, Y. F., and Gao, S. (2007). Lu–Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrol. Sin. 23 (2), 185–220. (in Chinese). doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2007.02.001
Wu, F. Y., Liu, X. C., Ji, W. Q., Wang, J. M., and Yang, L. (2017). Highly fractionated granites: recognition and research. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 60, 1201–1219. doi:10.1007/s11430-016-5139-1
Wu, F. Y., Yang, Y. H., Xie, L. W., and Xu, P. (2006). Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U–Pb geochronology. Chem. Geol. 234 (1-2), 105–126. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003
Xia, Y., Xu, X. S., Zou, H. B., and Liu, L. (2014). Early Paleozoic crust–mantle interaction and lithosphere delamination in South China Block: evidence from geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes of granites. Lithos 184-187, 416–435. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.11.014
Xiang, T. F., Sun, T., Chen, P. R., and Wang, K. X. (2013). Discovery of an Indosinian granite: Luoguyan pluton in Northwestern Fujian province, South China, and its petrogenesis and tectonic significance. Geol. J. China Univ. 19 (2), 274–292. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.02.011
Xiong, Y. Q., Jiang, S. Y., Wen, C. H., and Yu, H. Y. (2020). Granite-pegmatite connection and mineralization age of the giant Renli Ta-Nb deposit in South China: constraints from U–Th–Pb geochronology of coltan, monazite, and zircon. Lithos 358-359, 105422. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105422
Xu, C., Kynický, J., Smith, M. P., Kopriva, A., Brtnický, M., Urubek, T., et al. (2017). Origin of heavy rare earth mineralization in South China. Nat. Commun. 8, 14598. doi:10.1038/ncomms14598
Xu, H. J., Ma, C. Q., Zhao, J. H., and Zhang, J. F. (2014). Magma mixing generated Triassic I-type granites in South China. J. Geol. 122 (3), 329–351. doi:10.1086/675667
Xu, X. B., Li, Q. M., Gui, L., Su, Y. P., and Zhang, X. F. (2018). Early mesozoic tectonic transition of the eastern South China block: constraints from late Triassic Dashuang complex in eastern Zhejiang province. Int. Geol. Rev. 61 (8), 997–1015. doi:10.1080/00206814.2018.1490931
Xu, X. S., Deng, P., O’Reilly, S. Y., Griffin, W. L., Zhou, X. M., and Tan, Z. Z. (2003). Single zircon LAC-ICP-MS U–Pb dating of Guidong complex (SE China) and its petrogenetic significance. Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 1328–1334. doi:10.1007/BF03184074
Xu, Y., Lv, Q. T., Shi, D. N., Zhang, Y. Q., Yan, J. Y., and Xu, Z. W. (2022). Upper mantle velocity structure beneath the eastern South China Block and implications for late Mesozoic magmatism. J. Asian Earth Sci. 224, 105013. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.105013
Yang, J. H., Peng, J. T., Zheng, Y. F., Hu, R. Z., Bi, X. W., Zhao, J. H., et al. (2016). Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic Shuikoushan peraluminous I-type granodioritic intrusion in Hunan Province, South China: middle-lower crustal reworking in an extensional tectonic setting. J. Asian Earth Sci. 123, 224–242. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.04.008
Yang, S. W., Lou, F. S., Zhang, F. R., Ding, P. X., Cao, Y. B., Xu, Z., et al. (2017). Anatexis-ceremonies magmatism activity of the Qishan granitic pluton in southern Jiangxi: chronological study of zircon U–Pb precise dating. Acta Geol. Sin. 91 (4), 864–875. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.04.012
Yang, S. W., Lou, F. S., Zhang, F. R., Zhou, C. H., Xia, M., Ling, L. H., et al. (2022). Detrital zircon U–Pb geochronology of the Xunwu formation in Cathaysia block and its geological significance. J. East China Univ. Technol. 45 (3), 207–222. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2022.03.002
Yang, Y. Y., Li, N. B., Jiang, Y. H., and Zhao, X. (2024). Geochemical differences of parent rocks for ion-adsorption LREE and HREE deposits: a case study of the Guanxi and Dabu granite plutons. Geotecton. Metallog. 48 (2), 232–247. (in Chinese). doi:10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2024.02.004
Yu, D. S., Xu, D. R., Wang, Z. L., Xu, K., Huang, Q. Y., Zou, S. H., et al. (2021). Trace element geochemistry and O-S-Pb-He-Ar isotopic systematics of the Lishan Pb-Zn-Cu hydrothermal deposit, NE Hunan, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 133, 104091. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104091
Yu, J. H., O’Reilly, S. Y., Wang, L. J., Griffin, W. L., Zhou, M. F., Zhang, M., et al. (2010). Components and episodic growth of Precambrian crust in the Cathaysia Block, South China: evidence from U–Pb ages and Hf isotopes of zircons in Neoproterozoic sediments. Precambrian Res. 181 (1-4), 97–114. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.05.016
Yu, J. H., Wang, L. J., Wang, X. L., Qiu, J. S., and Zhao, L. (2007). Geochemistry and geochronology of the Fucheng complex in the southeastern Jiangxi province, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 23 (6), 1441–1456. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.020
Yu, Y., Chen, Z. Y., Chen, Z. H., Hou, K. J., Zhao, Z., Xu, J. X., et al. (2012). Zircon U–Pb dating and mineralization prospective of the Triassic Qingxi pluton in southern Jiangxi province. Geotecton. Metallog. 36 (3), 413–421. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.014
Yuan, S. D., Williams-Jones, A. E., Mao, J. W., Zhao, P. L., Yan, C., and Zhang, D. L. (2018). The origin of the Zhangjialong tungsten deposit, South China; Implications for W-Sn mineralization in large granite batholiths. Econ. Geol. 113 (5), 1193–1208. doi:10.5382/econgeo.2018.4587
Zhang, D. F., Wang, X. G., He, T., Cao, M. X., Lv, T. T., Gong, L. X., et al. (2024). Petrogenesis and geological significance of the Caledonian heavy rare earth ore parent rock in southern Jiangxi Province. Geoscience 38 (4), 959–979. (in Chinese). doi:10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.095
Zhang, M., Chen, P. R., Huang, G. L., and Ling, H. F. (2006a). The research on the geochemical characteristics of Longyuanba composite pluton in Nanling region. Uranium Geol. 22, 336–344. (in Chinese). doi:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.07.005
Zhang, Q., Wang, X., Li, C. D., Jin, W. J., and Jia, X. Q. (2006b). A granite classification based on pressures. Geol. Bull. Geol. Surv. China. 25 (11), 1274–1278. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.11.004
Zhang, Y. Q., Dong, S. W., Li, J. H., Cui, J. J., Shi, W., Su, J. B., et al. (2012). The new progress in the study of mesozoic tectonics of South China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 33 (3), 257–279. (in Chinese). doi:10.3975/cagsb.2012.03.01
Zhao, G. (2015). Jiangnan orogen in South China: developing from divergent double subduction. Gondwana Res. 27 (3), 1173–1180. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.004
Zhao, K. D., Jiang, S. Y., Chen, W. F., Chen, P. R., and Ling, H. F. (2013a). Zircon U–Pb chronology and elemental and Sr–Nd–Hf isotope geochemistry of two Triassic A-type granites in South China: implication for petrogenesis and Indosinian transtensional tectonism. Lithos 160-161, 292–306. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.11.001
Zhao, K. D., Li, J. R., Ling, H. F., Chen, P. R., Chen, W. F., and Sun, T. (2013b). Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of two stage Indosinian granites from the Xiajiang uranium ore deposit, Jiangxi Province: implication for Indosinian tectonics and genesis of uranium-bearing granites in South China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 29 (12), 4349–4361. (in Chinese).
Zhao, Z. H., and Zhou, L. D. (1997). REE geochemistry of some alkali-rich intrusive rocks in China. Sci. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 40 (2), 145–158. doi:10.1007/BF02878373
Zhou, D., Hu, J., Yang, W. Q., Chen, Q., Wang, X. D., Wang, L., et al. (2021). Formation age and petrogenesis of the Xinxing pluton in western Guangdong: constraint on the closure of the East Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Geol. China. 48 (6), 1896–1923. (in Chinese). doi:10.12029/gc20210618
Zhou, X. M. (2003). My thinking about granite geneses of South China. Geol. J. China Univ. 9 (4), 556–565. (in Chinese). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.04.009
Zhou, X. M., Sun, T., Shen, W. Z., Shen, W. Z., Shu, L. S., and Niu, Y. L. (2006). Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: a response to tectonic evolution. Episodes 29 (1), 26–33. doi:10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i1/004
Zhu, D. C., Mo, X. X., Wang, L. Q., Zhao, Z. D., Niu, Y. L., Zhou, C. Y., et al. (2009). Petrogenesis of highly fractionated I-type granites in the Zayu area of eastern Gangdese, Tibet: constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 52 (9), 1223–1239. doi:10.1007/s11430-009-0132-x
Keywords: two-mica monzogranite, Pb-Hf-Sr-Nd isotopes, S-type granites, metallogenic potential, Indosinian orogeny, Xiekeng pluton
Citation: Zhang D, Lv T, Wang X, Cao M, Chen X, Zhang Y and Gong L (2025) Petrogenesis of REE-rich two-mica granite from the Indosinian Xiekeng pluton in South China Block with implications for REE metallogenesis. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1493594. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1493594
Received: 09 September 2024; Accepted: 04 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Zhongliang Wang, China University of Geosciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Minh Pham, Ho Chi Minh City University of Science, VietnamThyego Silva, Water and Climate Agency of Pernambuco, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Lv, Wang, Cao, Chen, Zhang and Gong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiangaung Wang, MzUyMjUyNjU1QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Defu Zhang
Defu Zhang Tingting Lv3
Tingting Lv3