- 1Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology (NIT), Warangal, India
- 2Centre for Information and Communication Technology (CICT), National Institute of rural Development and Panchayat Raj (NIRDPR), Ministry of Rural Development, Hyderabad, India
- 3Indian Council of Agricultural Research – IIOPR, Pedavegi, India
Hyperspectral data from the Airborne Visible and Infra-Red Imaging Spectrometer – Next-Generation (AVIRIS-NG) offers transformative potential for Earth science research, enabling detailed analysis of land surface processes, resource monitoring, and environmental dynamics. This study presents an automated methodology to optimize the selection of AVIRIS spectral bands, improving the computation of indices critical to Earth science applications. By leveraging multiple hyperspectral bands, the approach enhances the accuracy of indices used to monitor water resources, vegetation health, urban expansion, and built-up areas. The methodology involves calculating indices from all possible AVIRIS band combinations, evaluating their root mean squared error (RMSE) against Sentinel-2 indices, reducing RMSE skewness, and selecting bands with minimal deviation for specific Land Use Land Cover (LULC) categories. The process is automated and employs parallel processing with Python, significantly reducing execution time and enabling scalability for large geospatial datasets. Key indices, including the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), Normalized Difference Red Edge (NDRE), and Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI), Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (GNDVI) were validated using the proposed methodology. Results demonstrate the potential of hyperspectral data to outperform traditional single-band approaches, providing more precise and reliable assessments.
1 Introduction
Hyperspectral data have revolutionized remote sensing by offering detailed spectral information across hundreds of narrow, contiguous bands, enabling fine-grained analysis of surface materials (Hamedianfar et al., 2023). This capability is particularly valuable in Earth sciences, where it supports the study of critical features such as urban growth, water resources, built-up areas and vegetation health. Hyperspectral data provide an unparalleled ability to distinguish subtle variations in surface composition, enhancing the understanding of processes like land-use change, water body dynamics, and ecosystem responses to environmental stresses.
Indices derived from hyperspectral data, such as the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), Normalized Difference Red Edge (NDRE), Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI) and Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (GNDVI), play a crucial role in monitoring Earth surface features. NDWI is widely applied in water resource management, aquaculture mapping, and coastal monitoring (Taloor et al., 2021; Guha et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2021; Laonamsai et al., 2023; Ihsan et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2021; Fu-min et al., 2007). NDRE and GNDVI are essential for assessing vegetation health, monitoring land cover changes, and analyzing vegetation responses to climatic conditions (Frampton et al., 2013; Mangewa et al., 2022; Maccioni et al., 2001; Jorge et al., 2019; Bonfil, 2017; Jiang W. et al., 2021; Lu et al., 2020). NDBI serves as a vital tool for detecting built-up areas, enabling urban planning, infrastructure development, and the analysis of land-use changes (Zheng et al., 2021; Bhatti and Tripathi, 2014; Yasin et al., 2022; Hadeel et al., 2009; Liu and Zhang, 2011; Delogu et al., 2023; Enrique Valdelamar Martínez et al., 2024).
Despite their utility, the high dimensionality of hyperspectral data poses challenges in processing and analysis (Alcaras et al., 2021; Mekuriaw et al., 2017; Omran et al., 2023). Noise removal, dimensionality reduction, and band selection are essential preprocessing steps for extracting meaningful information from these datasets (Rasti et al., 2018; Rasti et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2020). Current research primarily employs single-band combinations to compute indices, which does not fully leverage the rich spectral range offered by hyperspectral sensors (Oppelt, 2002; Zarco-Tejada et al., 1999). Furthermore, existing studies lack comprehensive methodology to select bands of hyperspectral data to compute indices.
The increasing volume and complexity of hyperspectral data necessitate automation in analysis workflows. Parallel processing is a promising solution to mitigate computational bottlenecks, distributing tasks across multiple cores to enhance efficiency and scalability. While parallel processing has been employed in various geospatial analyses, its application in hyperspectral data workflows, particularly for automating band selection, remains under explored. This study addresses these gaps by automating the selection of spectral bands from AVIRIS-NG data for computing key Earth science indices. The approach involves calculating spectral indices from all possible AVIRIS band combinations, comparing them with Sentinel-2-derived indices using root mean squared error (RMSE), and selecting optimal bands based on statistical criteria for specific Land Use Land Cover (LULC) categories. The RMSE serves as a critical metric for quantifying the disparity between datasets and evaluating the accuracy of spectral indices derived from them. RMSE is chosen for its sensitivity to larger deviations, which is crucial in hyperspectral analysis, where even minor discrepancies across bands can impact index reliability. Unlike metrics like Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Mean Bias Deviation (MBD), RMSE’s quadratic weighting emphasizes substantial deviations, helping detect differences in spectral response characteristics. Its interpretability in the same units as the data further facilitate clear assessments of sensor compatibility, supporting accurate, consistent index derivation across sensors. The Skewness correction technique box-cox transformation, is employed to address any asymmetry in the distribution of RMSE values, ensuring robust comparisons between datasets. Subsequently, bands are selected based on their agreement metrics for specific LULC categories.
Automation is achieved through Python-based workflows that leverage parallel processing, significantly reducing computational time and enabling large-scale geo-spatial analysis (Wu et al., 2021). In this study, the efficiency of parallel processing for automating hyperspectral data analysis is evaluated using a high-performance computational machine running the Linux Mint operating system within a virtual box environment. The computational platform boasts 32 cores and 128GB RAM, but to ensure optimal performance and avoid interference with existing processes on the machine, only 25 cores are allocated for computation. By leveraging the multiprocessing capabilities of this setup, the study aims to expedite data processing tasks, such as band selection and spectral index computation, thereby enhancing overall workflow efficiency and reducing computational turnaround times.
By focusing on indices like NDWI, NDRE, NDBI, and GNDVI, this study highlights their relevance in Earth science applications, including water resource management, vegetation health assessment, and urban monitoring. Furthermore, it evaluates the comparability of hyperspectral and multispectral sensors, addressing a critical need for consistent and accurate geo-spatial analyses. This research advances hyperspectral data methodologies by integrating automation and computational efficiency, contributing to a deeper understanding of Earth’s dynamic systems.
2 Study area and data used
The study area is located in Vuyyuru, located in Andhra Pradesh, India, sharing the border of Guntur and Krishna districts (Figure 1). The hyperspectral data from the Airborne Visible and Infra-Red Imaging Spectrometer–Next-Generation (AVIRIS-NG) campaign under Phase 2A, was collected on 26 Feb 2018 Figure 1. The data covers an area between 16°20′N and 80°42′E (site #114). This hyperspectral dataset comprises 430 narrow spectral bands ranging from 380 to 2510 nm at 5 nm intervals and has a spatial resolution of 4 m (Bhattacharya et al., 2024). After undergoing radiometric, atmospheric corrections, and bad band removal processes, the original 430 bands are reduced to 372 bands for analysis.
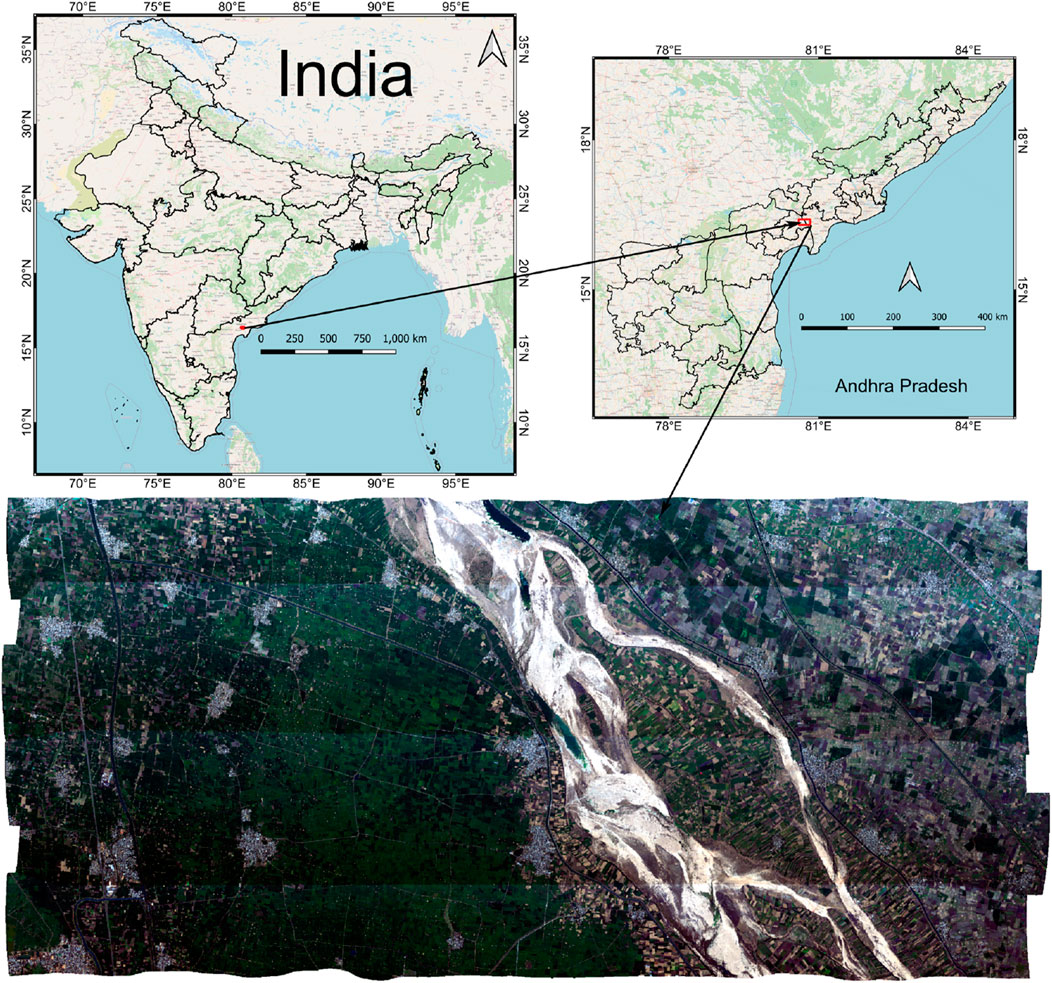
Figure 1. Study area map of Vuyyuru, Andhra Pradesh, India. True Color Composite (TCC) of AVIRIS (hyperspectral) image.
In addition to the AVIRIS-NG data, the study also incorporates data from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission. Sentinel-2 comprises two polar-orbiting, multispectral satellites, Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B, which are phased at 180° and share the same sun-synchronous orbit. These satellites offer a wide swath of 290 km and revisit the same area every 5 days. The Sentinel-2 data used in the study was acquired on 25 Feb 2018. This dataset includes 13 bands, encompassing visible, near-infrared (NIR) bands with a spatial resolution of 10 m, and Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) bands with a spatial resolution of 20 m. The Sentinel-2 data was corrected, and the reflectance values were used directly for the study.
3 Methodology
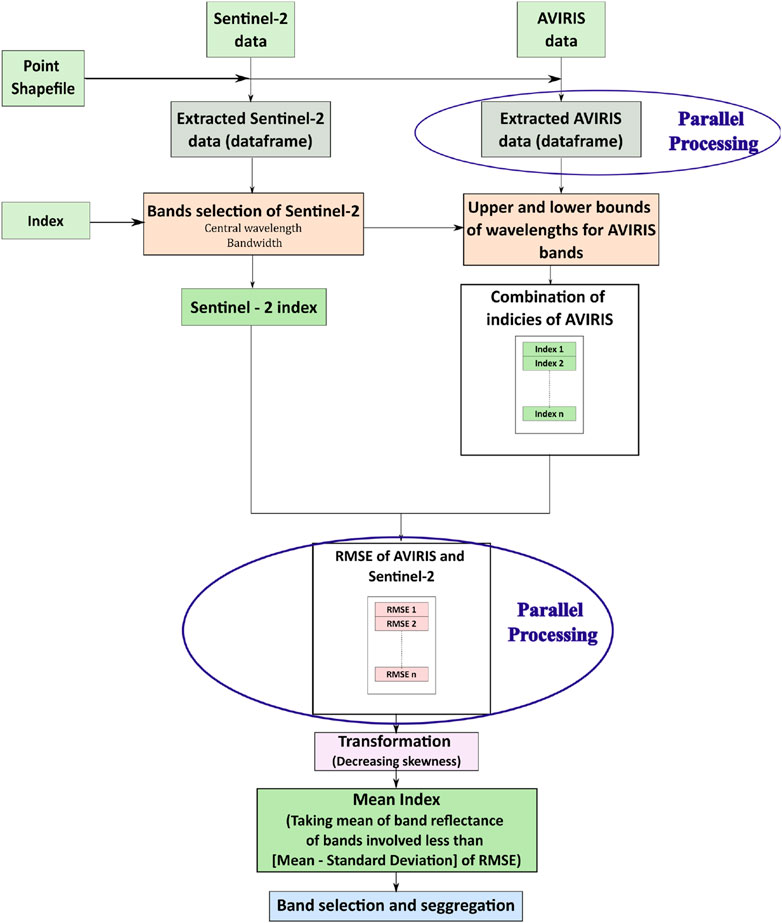
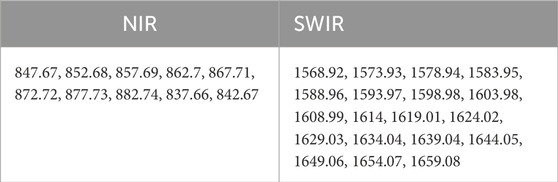
This study employs an automated Python-based framework to streamline hyperspectral band selection and index comparison between AVIRIS and Sentinel-2 imagery, focusing on the efficient processing of spectral indices. The methodology starts with user-defined input parameters, including paths to AVIRIS and Sentinel-2 imagery, a shapefile containing LULC classes (such as Barren Land, River Sand, Urban, Vegetation, and Water), an output directory, and a target spectral index. Based on the selected index, Sentinel-2 bands are identified by calculating their central wavelengths and bandwidths to establish upper and lower bounds (Table 1). These bounds are then applied to the AVIRIS dataset to retrieve corresponding bands within the defined wavelength range, ensuring spectral alignment across sensors. For each LULC class, all possible band combinations within the range are calculated to compute the spectral indices, allowing for detailed inter-sensor analysis. The accuracy of these spectral indices is quantified using the RMSE, which provides a measure of the difference between Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS indices across each LULC class. To further normalize and refine RMSE values, a Box-Cox transformation is applied, which corrects for any skewness and enables more robust statistical comparisons. The final band selection process applies an RMSE threshold (Mean–Standard Deviation) to identify the bands with minimal spectral error for each LULC class. Additionally, the mean bands of index are chosen based on their frequency of occurrence across all LULC classes, prioritizing bands that consistently appear in the low-error subset. This automated pipeline integrates essential spatial and statistical operations, significantly enhancing the reproducibility and efficiency of hyperspectral band selection and inter-sensor spectral comparison, thus supporting robust and large-scale hyperspectral data analysis across diverse land cover types. The whole methodology is illustrated in Figure 2.
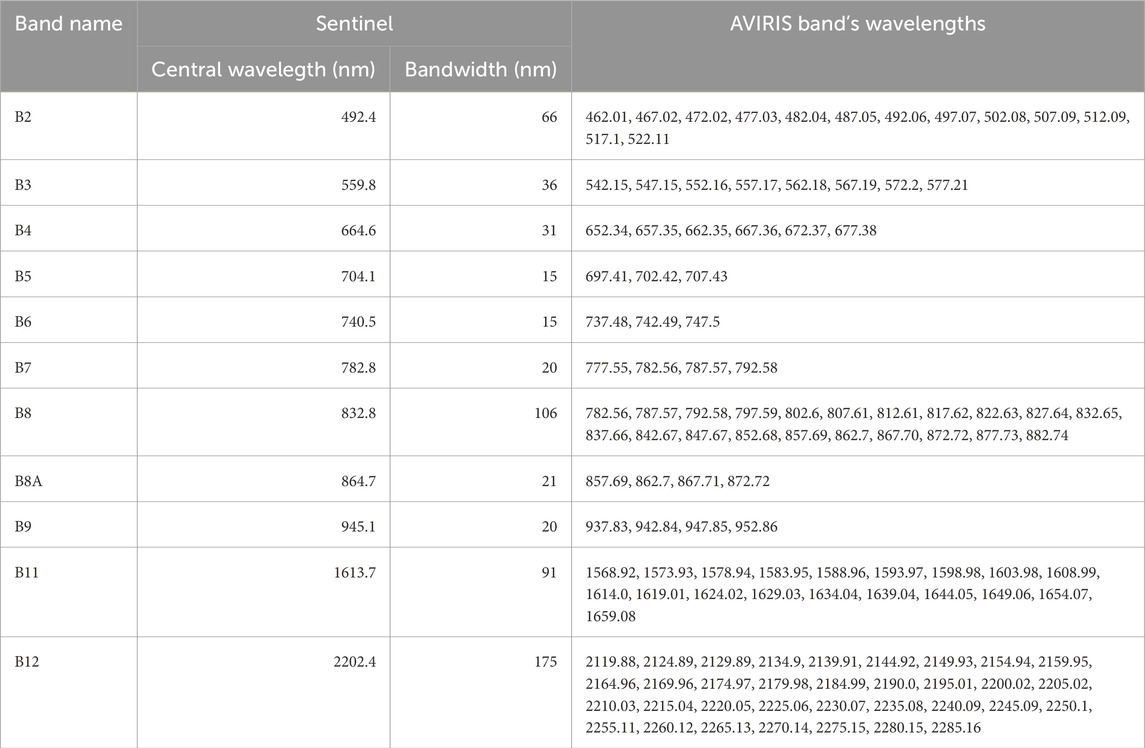
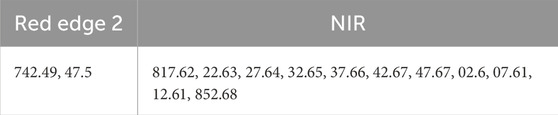
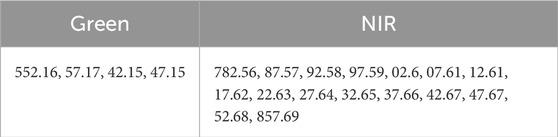
Table 1. AVIRIS wavelengths for corresponding Sentinel-2 bands: (source: Sentinel-2 resolutions, 2024).
3.1 Procedure for band selection
The band selection process involves extracting data from both AVIRIS and Sentinel-2, calculating the normalized difference, computing the RMSE between the normalized differences of AVIRIS and Sentinel-2, transforming the RMSE, and finally selecting the bands.
3.1.1 Extraction of AVIRIS and Sentinel-2 data
The process of extracting raster values to a point shapefile involves working with a sampling shapefile containing points with unique IDs, where the “class” field represents LULC classifications. The extraction process for AVIRIS and Sentinel-2 reflectance values to the sampling shapefile differs due to the structure of the raster data. AVIRIS data is a raster file comprising 372 bands with a 5 nm bandwidth. The AVIRIS data is accessed using the rasterio library, and the values are extracted using the point_query tool from the rasterstats library. During the extraction process, each band number is attached to the dataframe. Since the wavelength information is not directly attached to the raster data, a dataframe containing band numbers and corresponding wavelengths is prepared to attach the wavelengths to the extracted values.
The explanation of the extracted data within the output file comprises fields such as id, class, point_id, value, band_no, and wavelength. The id field represents a unique serial number for each data entry, while the class field contains the LULC classification obtained from the point shapefile. Additionally, the point_id field provides a unique ID assigned to each point in the shapefile. The value field stores the reflectance value extracted from the raster data, and the band_no field indicates the band number assigned by iterating through the raster data. Lastly, the wavelength field attaches the corresponding wavelength to each band number.
Regarding Sentinel-2 data, its structure differs from AVIRIS. Sentinel-2 bands are stored as separate files when downloaded from the European Space Agency website. Bands are selected based on the index, such as Green and NIR bands for computing NDWI. These selected bands are accessed individually using rasterio, then extracted to the point shapefile and appended to the pandas dataframe for further processing.
3.1.2 Calculation of normalized difference
Sentinel-2 data comprise several spectral bands, typically ranging from visible light to shortwave infrared. When calculating normalized differences with Sentinel-2 data, usually two bands are selected. These bands are chosen based on their spectral characteristics and the index of interest being analyzed. For example, the NDWI uses the Green and near-infrared (NIR) bands to quantify water in a particular area. In the developed Python script, the Sentinel-2 dataframe consists of the central wavelength and bandwidth of each Sentinel-2 band. Unlike Sentinel-2, AVIRIS doesn't have predefined bands with specific names like Green or NIR. Instead, AVIRIS bands are typically numbered, and their wavelengths may not directly correspond to those of Sentinel-2 bands. In the developed Python script, AVIRIS dataframe consists of information about AVIRIS band numbers and their corresponding wavelengths. Since AVIRIS bands may not align perfectly with Sentinel-2 bands, we need to find the closest matching AVIRIS bands for each Sentinel-2 band. This matching is done based on the central wavelength and bandwidth of Sentinel-2 bands compared to the wavelengths of AVIRIS bands. The Python script defines a function to find the AVIRIS bands that are in the wavelength range of a given Sentinel-2 band. Once the closest matching AVIRIS band is found for each Sentinel-2 band, the normalized difference is calculated. This involves obtaining reflectance values from both Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS for the selected bands and applying the desired formula. The Python script includes a function to calculate the normalized difference using reflectance values from the matched bands. The script iterates over each Sentinel-2 band, finds the corresponding AVIRIS bands, and calculates the normalized difference.
To calculate normalized differences, need to select two bands at a time from this dataframe. The Python script retrieves the first and second band dataframes separately from the function, likely to facilitate pairing each band with every other band for calculating the normalized differences. After separating the bands into first and second dataframes, the unique () method from pandas is employed. The unique () method is used to extract unique combinations of wavelengths from the first and second band dataframes. This ensures that each unique combination of wavelengths is considered for calculating the normalized differences. Once unique combinations of wavelengths are retrieved, normalized differences are computed for all the combinations of AVIRIS data. The result of each calculation is saved to a dataframe, likely likely with columns representing the wavelength combinations and their corresponding normalized differences. This dataframe serves as a structured format to store and analyze the computed normalized differences for further interpretation and visualization. The computed normalized differences for each combination of wavelengths are saved to a dataframe. Organizing the results in a dataframe facilitates efficient comparison and interpretation of the normalized differences among various combinations of Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS bands.
3.1.3 Computing the RMSE for the normalized difference between AVIRIS and Sentinel-2
The RMSE is computed between the normalized differences obtained from Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS data. For each combination of normalized differences, the RMSE is calculated using the mean_squared_error function from the scikit-learn (sklearn) library. This involves comparing the normalized differences obtained from both Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS data for all possible combinations. The computed RMSE values for each combination of normalized differences are stored in the pandas dataframe.
3.1.4 Transformation of RMSE
After computing the RMSE values, the skewness of these values is reduced. Skewness refers to the asymmetry of the distribution of data. In this case, applying the box-cox transformation, available in the scipy library, reduces the skewness of the RMSE values. The box-cox transformation is a statistical method used to stabilize variance and make data more normally distributed. By transforming the RMSE values, it becomes easier to interpret and analyze the distribution of errors between Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS data.
3.1.5 Selection of bands
The process begins by associating specific bands with different LULC categories. This association is based on the mean minus the standard deviation of the transformed RMSE values. The mean minus the standard deviation is a measure of central tendency that also accounts for variability in the data. Lower values of mean minus standard deviation indicate better agreement between the Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS data for a particular band and LULC category. Therefore, bands with lower mean minus standard deviation values are chosen as they represent better agreement or similarity between the two datasets for a specific LULC category.
After selecting bands for each LULC category based on mean minus standard deviation values, the selection of bands is determined. This determination is made by identifying the bands with the highest frequency among the selected LULC bands. In other words, among the bands selected for each LULC category, the ones that are most frequently chosen across all categories are considered the final selection of bands. This approach ensures that the chosen bands are not only representative of individual LULC categories but are also consistent across different categories. By selecting bands with the highest frequency, the final set of bands is likely to capture the common spectral characteristics relevant to multiple LULC categories, enhancing the overall accuracy and reliability of the analysis.
In the research conducted by Peddinti et al., (2021), Set-1 encompasses all the bands relevant to various LULC categories. This comprehensive inclusion ensures that it captures the unique spectral characteristics across all the land covers, making it versatile. On the other hand, Set-4 is curated to include only the most frequently occurring bands across different LULC types. By setting a frequency threshold of greater than 3, the study optimized the wavelength selection to be representative of the majority of LULC categories. This approach strikes a balance, with Set-1 providing breadth in coverage and Set-4 focusing on high-frequency, common bands, collectively offering an effective and efficient solution.
4 Results
The band selection process for indices such as NDWI, NDRE, GNDVI, and NDBI is meticulously executed according to the established methodology. This involves identifying optimal band combinations to ensure the most accurate computation of each index. Figure 3 provides a visual representation of the datasets used in both the testing and validation phases of the study. Specifically, the test dataset is employed to determine the most suitable AVIRIS bands for each index, utilizing a range of spectral and statistical analyses. Once the optimal bands are selected, the validation dataset is used to compare and verify the results, ensuring the selected bands provide consistent and accurate index calculations. This dual-phase approach helps to confirm the reliability and applicability of the chosen bands across different datasets and conditions.
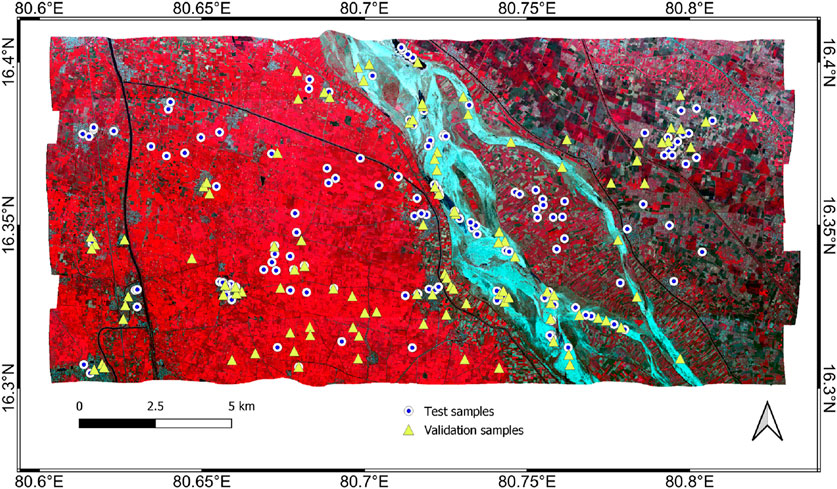
Figure 3. Test and validation samples utilized in the study, along with a False Color Composite (FCC) of the AVIRIS-NG image.
4.1 Band selection for NDWI
The Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) is calculated as the normalized difference between the green bands and near-infrared (NIR), as represented by Equation 1 (Jiang J. et.al., 2021).
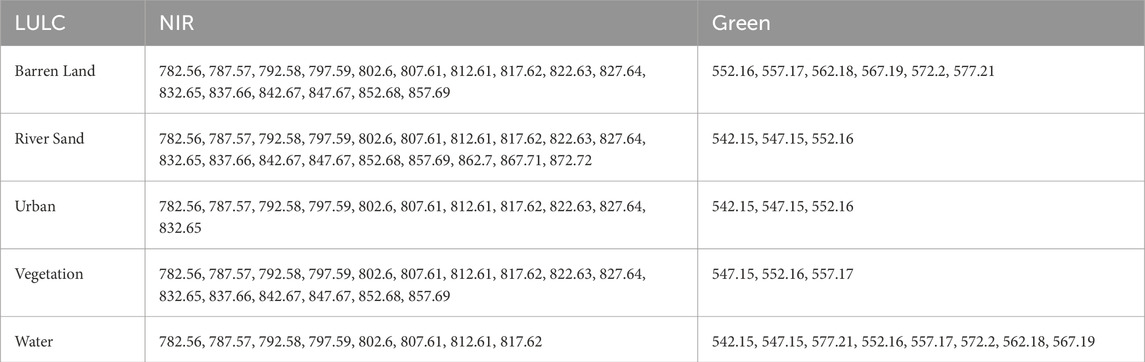
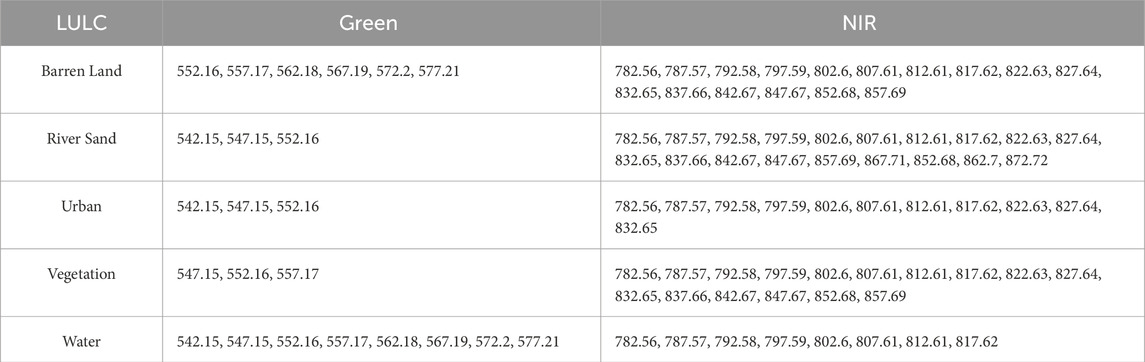
Table 2 shows the selected AVIRIS bands corresponding to different LULC categories for NDWI analysis. Table 3 shows the chosen AVIRIS bands for NDWI computation.
4.2 Band selection for NDRE
The Normalized Difference Red-Edge index (NDRE) is calculated as the normalized difference between the near-infrared (NIR) and Red Edge (RE) bands, as represented by Equation 2 (Liu et al., 2023).
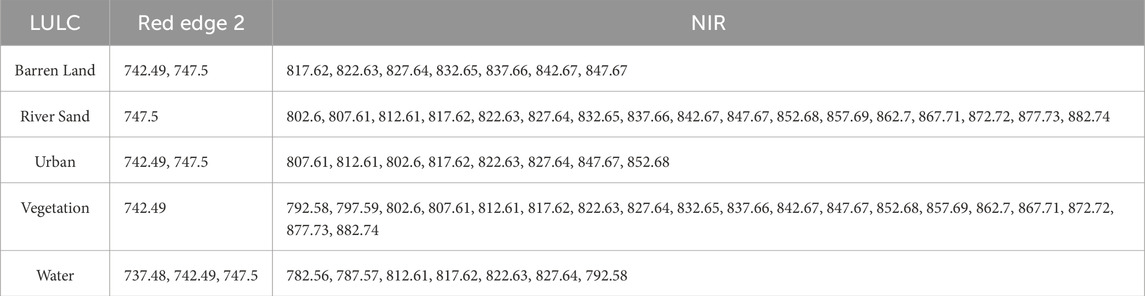
Table 4 shows the selected AVIRIS bands corresponding to different LULC categories for NDRE analysis. Table 5 shows the chosen AVIRIS bands for NDRE computation.
4.3 Band selection for GNDVI
The Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDWI) is calculated as the normalized difference between the near-infrared (NIR) and green bands, as represented by Equation 3 (Bautista et al., 2022).
Table 6 shows the selected AVIRIS bands corresponding to different LULC categories for GNDVI analysis. Table 7 shows the chosen AVIRIS bands for GNDVI computation.
4.4 Band selection for NDBI
The Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI) is calculated as the normalized difference between the Short Wave Infrared (SWIR) and near-infrared (NIR), as represented by Equation 4 (Zhao and Pan, 2023).
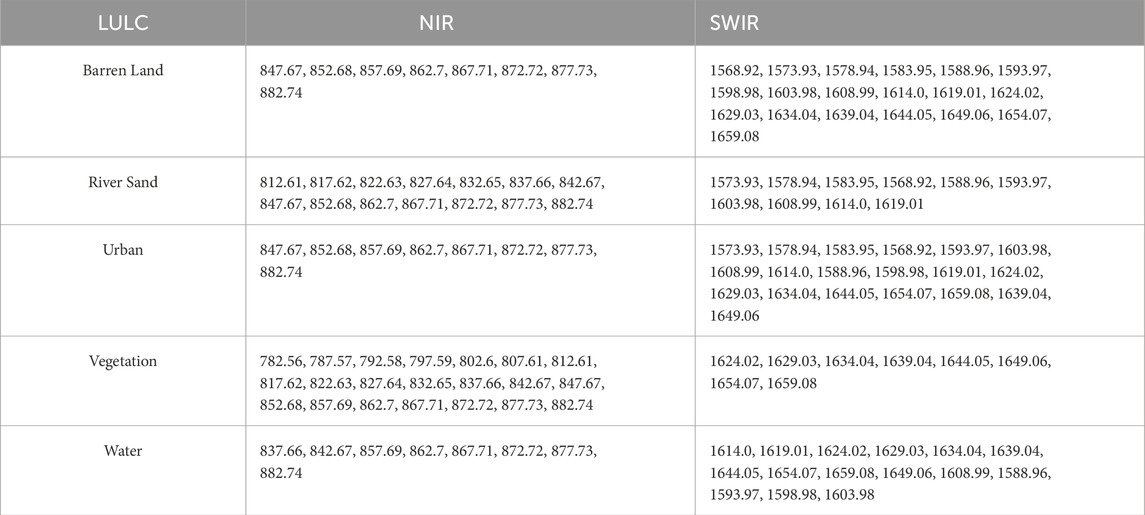
Table 8 shows the selected AVIRIS bands corresponding to different LULC categories for NDBI analysis. Table 9 shows the chosen AVIRIS bands for NDBI computation.
4.5 Parallel processing for the implementation of automation of selected bands
Parallel processing is employed to efficiently handle the large number of iterations necessary for the task, delivering a significant advantage over conventional sequential methods like for loops and while loops. By distributing the workload across multiple processors or threads, it minimizes computation time, accelerates task completion, and boosts overall efficiency. This reduction in processing time not only enhances productivity but also allows for the handling of more complex or larger-scale problems that would be impractical with sequential approaches.
5 Discussion
For most land cover classes for NDWI, the RMSE values in the adopted methodology are generally lower compared to the mean of all bands and single central bands. The adopted methodology consistently exhibits lower RMSE values across different land cover classes, indicating higher agreement and stability in NDWI values (Figure 4). Notably, the “Water” class demonstrates a substantial reduction in RMSE values in the adopted Methodology, suggesting consistency and accuracy in water index values derived using the proposed methodology. Barren Land, while exhibiting slightly higher RMSE values, still demonstrates relatively good agreement and stability when compared to single central bands.
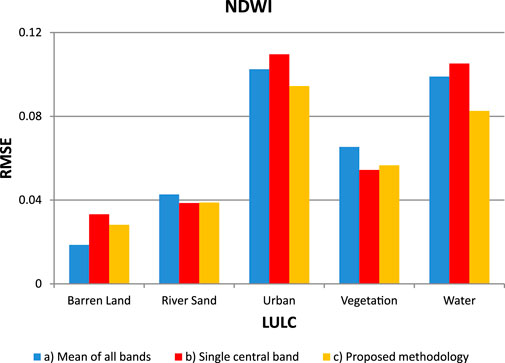
Figure 4. The comparison between the RMSE of Sentinel image and AVIRIS for NDWI is conducted through: a) calculating the mean of all AVIRIS bands falling within the range of Sentinel 2 bandwidth, b) single central bands of AVIRIS data, and c) bands of AVIRIS data selected based on the proposed methodology.
Therefore, the selected methodology exhibits robustness in deriving NDWI values across various land cover types. The methodology consistently outperforms the mean of all AVIRIS bands and single central bands approaches, demonstrating its effectiveness in providing accurate and consistent water index values. While challenges may exist in accurately characterizing barren land, the adopted methodology presents a favorable outcome, indicating its reliability in water index assessment across diverse land cover types.
Figure 5 illustrates the root mean squared error (RMSE) values of Sentinel-2 and AVIRIS NDRE corresponding to the mean of all bands, single central bands, and the proposed methodology across various LULC categories. The adopted methodology consistently demonstrates lower RMSE values compared to the mean of all bands and single central bands across all land cover classes. This consistency suggests that the chosen methodology effectively enhances the agreement and stability of NDRE values across diverse land cover types. Vegetation exhibits the lowest RMSE value when the mean of all bands is considered. However, it's noteworthy that this RMSE value is lower than that derived from the single central bands. Urban areas consistently show higher RMSE values, even though the adopted methodology has lower RMSE values. Water bodies demonstrate moderate RMSE values, indicating variability in NDRE values. The bands selected using adopted methodology consistently outperform the mean of all bands and single central bands approaches, indicating its effectiveness in providing accurate and consistent NDRE values.
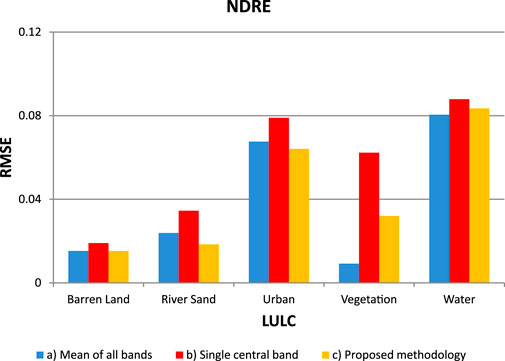
Figure 5. The comparison between the RMSE of Sentinel image and AVIRIS for NDRE is conducted through: a) calculating the mean of all AVIRIS bands falling within the range of Sentinel 2 bandwidth, b) single central bands of AVIRIS data, and c) bands of AVIRIS data selected based on the proposed methodology.
Across all land cover classes, the proposed methodology consistently yields lower RMSE values compared to those obtained by considering the mean of all bands for GNDVI (Figure 6). The methodology also generally demonstrates RMSE values lower than those derived from a single central band, indicating its effectiveness in calculating GNDVI value using the proposed methodology. In the “Barren Land” and “Vegetation” classes, the proposed methodology’s RMSE values fall between those of the mean of all bands and single central bands.
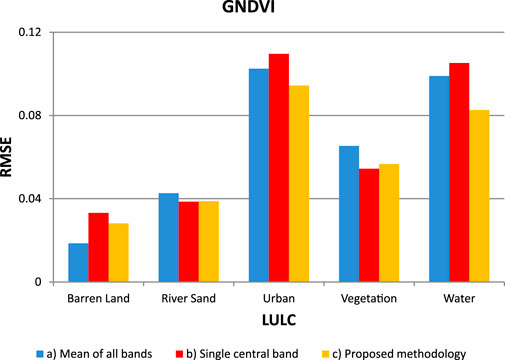
Figure 6. The comparison between the RMSE of Sentinel image and AVIRIS for GNDVI is conducted through: a) calculating the mean of all AVIRIS bands falling within the range of Sentinel 2 bandwidth, b) single central bands of AVIRIS data, and c) bands of AVIRIS data selected based on the proposed methodology.
The bands selected using the proposed methodology consistently outperform both the mean of all bands and single central bands in providing accurate and consistent GNDVI assessments across different land cover classes. In the “Urban” class, the methodology yielded an RMSE value of 0.0944, compared to 0.1025 and 0.1096 for the mean of all bands and single central bands, respectively. This underscores our proposed methodology’s effectiveness in reducing noise and enhancing the reliability of GNDVI values, essential for vegetation assessment and monitoring applications.
While there are slight variations in RMSE values across land cover classes, the proposed methodology consistently yields RMSE values that are marginally lower than those obtained from considering the mean of all bands and single central bands fro NDBI. In the case of “Water,” the proposed methodology’s RMSE value is notably lower compared to the other two approaches. Overall, while there are differences in RMSE values across different land cover classes, there is no significant difference between the proposed methodology and the other approaches (Figure 7).
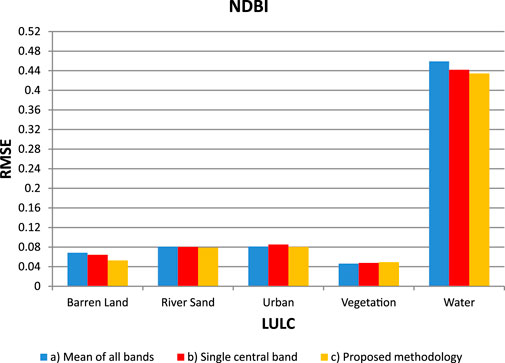
Figure 7. The comparison between the RMSE of Sentinel image and AVIRIS for NDBI is conducted through: a) calculating the mean of all AVIRIS bands falling within the range of Sentinel 2 bandwidth, b) single central bands of AVIRIS data, and c) bands of AVIRIS data selected based on the proposed methodology.
Comparing the RMSE values for the Normalized Difference Built-Up Index (NDBI) across different land cover classes, it's evident that our adopted methodology doesn't exhibit any detrimental effects. While there are slight variations in RMSE values across different approaches, including considering the mean of all bands and single central bands, bands selected using our methodology consistently maintain comparable or slightly lower RMSE values. This indicates that our adopted methodology effectively reduces noise and enhances the reliability of NDBI assessments without introducing any negative impacts on the accuracy of the results. Thus, it can be concluded that there is no adverse effect associated with the utilization of our methodology for NDBI computation across various land cover types.
The band selection approach enhances the results across diverse LULC types by prioritizing spectral bands that consistently exhibit high relevance and reliability. By focusing on bands that capture key biophysical and biochemical properties across various LULC classes, such as vegetation, urban areas, water bodies, and barren land, this method minimizes variability in spectral indices and ensures robust results. This is particularly beneficial for indices, which rely on precise discrimination of spectral features to accurately represent vegetation health, water presence, or urban areas. Additionally, the approach yields lower RMSE values compared to methods using all band reflectances or single central bands, demonstrating superior alignment with LULC spectral characteristics. By avoiding overfitting to specific datasets, the method enhances the transferability of results across regions and datasets, ensuring broader applicability. This current approach effectively mitigates these challenges through robust metrics like RMSE, ensuring reliable, transferable, and scalable hyperspectral analysis.
5.1 Parallel processing
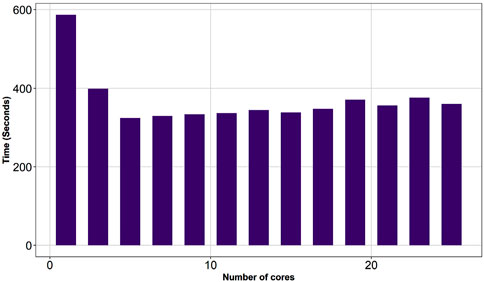
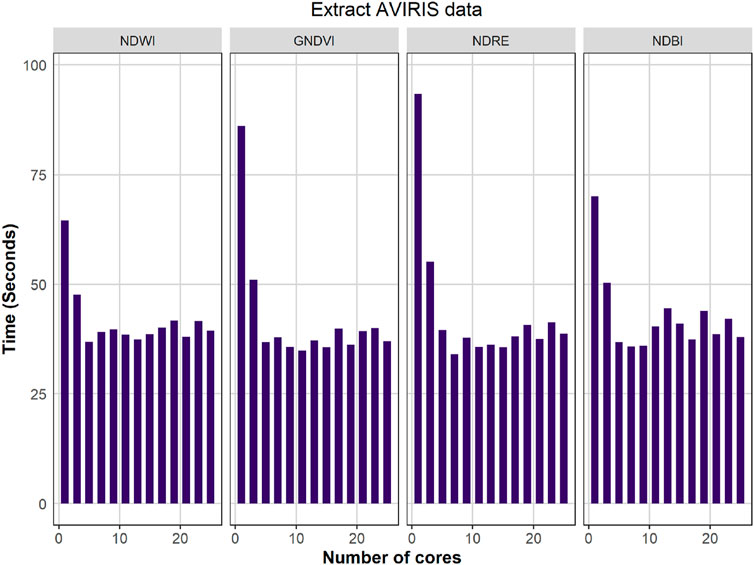
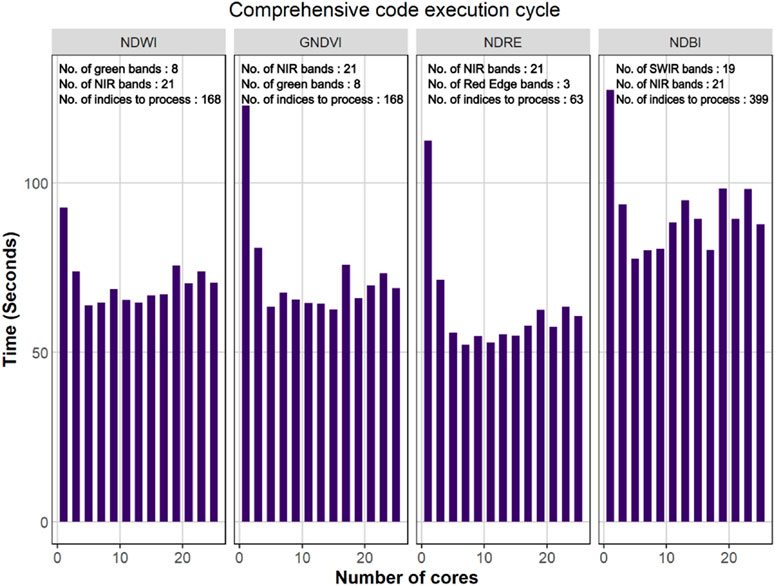
Parallel processing is employed to manage the extensive iteration required in the processing task, offering a significant improvement over traditional sequential approaches, such as simple for loops or while loops. By leveraging parallel processing, the computation time can be substantially reduced, leading to enhanced efficiency and productivity. Initially, AVIRIS data is extracted to the point shapefile, resulting in a significant reduction in execution time by up to 62% (see Figure 8). To optimize efficiency, the code is structured to avoid redundant extraction of AVIRIS data if the extracted file already exists in the output folder. Subsequently, all possible combinations of indices are computed. For example, the computation of NDWI involves pairing NIR and red bands from the AVIRIS-NG dataset, which encompasses 8 green bands and 21 NIR bands within the sentinel wavelength range (see Table 1). These combinations are computed and stored as CSV files. Furthermore, the RMSE is calculated for AVIRIS indices compared to Sentinel indices. The effectiveness of parallel processing for all indices is demonstrated in Figure 9, showcasing a notable decrease in execution time by 48% for NDWI, 62% for GNDVI, 59% for NDRE, and 51% for NDBI. The comprehensive code execution cycle, encompassing band selection for different indices, is illustrated in Figure 10, depicting maximum reductions in execution time by 31% for NDWI, 49% for GNDVI, 53% for NDRE, and 39% for NDBI. In the present study, 25 cores are employed to run the process, with optimization occurring for 30%–50% of these cores. Beyond this range, the time taken for execution increases as the basic functionalities of the computational platform is affected. The RMSE calculation for NDBI takes longer due to the higher number of indices, highlighting the need for optimized parallel processing configurations for efficient computational workflows. Parallel processing is crucial for AVIRIS band selection due to the high-dimensional nature of hyperspectral data, computational intensity of data extraction, spectral index calculations, and the need to evaluate multiple band combinations. By leveraging parallel processing, researchers can significantly reduce execution time and improve productivity. This approach facilitates the efficient selection of optimal AVIRIS bands for various indices and enables the handling of large datasets. Ultimately, parallel processing unlocks the potential of hyperspectral data for advanced applications, including environmental monitoring, agricultural management, and target detection, by providing timely and accurate insights.
5.2 Future scope
Future research in hyperspectral data band selection could expand by incorporating additional non-normalized indices tailored to specific materials and environmental conditions, enhancing applications across fields like mineral exploration. Advanced machine learning models, especially deep learning, could improve classification and prediction accuracy, while advances in GPU and cloud computing may soon enable real-time hyperspectral processing, beneficial for applications such as climate change and disaster response. Band selection using various sensors and standardized frameworks would increase data consistency, and field validation across diverse environments could strengthen the indices’ applicability in areas like urban heat mapping and marine studies.
6 Conclusion
Python code was developed using open-source libraries to select bands from hyperspectral imagery using different indices such as NDWI, GNDVI, NDRE, and NDBI. Peddinti et al. (2021) included bands within the range of Sentinel-2 bandwidth in their study.
The results demonstrate lower RMSE values across various land cover classes for NDWI values, with a notable reduction in the Water class. While the Barren Land class may exhibit slightly higher RMSE values, it still maintains relatively good agreement and stability compared to single central bands. Similarly, the adopted methodology consistently shows lower RMSE values compared to the mean of all bands and single central bands across all land cover classes for NDRE values. While vegetation displays the lowest RMSE value with the mean of all bands, it's important to note that this value is still lower than that derived from single central bands. Conversely, urban areas consistently exhibit higher RMSE values despite lower RMSE values. For GNDVI, the proposed methodology consistently yields lower RMSE values across various land cover classes compared to considering the mean of all bands. It also generally demonstrates lower RMSE values compared to those derived from single central bands, indicating its effectiveness in calculating GNDVI values. Similarly, for NDBI, the proposed methodology consistently yields slightly lower RMSE values across various land cover classes compared to considering the mean of all bands and single central bands. Notably, in the Water class, the proposed methodology’s RMSE value is notably lower than the other approaches. Overall, while differences in RMSE values exist across different land cover classes, there is no significant difference between the proposed methodology and the other approaches. In addition to the proposed methodology, single central bands were considered to assess performance.
The proposed methodology demonstrates superior accuracy and reliability in deriving spectral indices (NDWI, NDRE, GNDVI, NDBI) across diverse land cover types by yielding consistently lower RMSE values compared to the mean of all bands and single central bands. It excels in earth science applications including water resource management, vegetation health assessment, and urban monitoring, with notable improvements in noise reduction and index stability. Parallel processing enhances efficiency, reducing computation time by up to 62%, making the approach scalable for large datasets. The methodology’s robustness, transferability, and broad applicability make it a valuable tool for advanced hyperspectral data analysis and environmental monitoring. Also the proposed methodology outperformed both the mean of all AVIRIS bands and single central bands, providing superior results. Parallel processing significantly reduced execution time, especially for AVIRIS data extraction and index computation. Optimized coding prevented redundant data extraction, further enhancing efficiency. Utilizing 25 cores, optimal performance was achieved with 30%–50% of the cores, while higher usage impacted execution time. Longer computation times for NDBI were due to the greater number of indices involved. Overall, the approach ensured accurate results with improved computational efficiency.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
VP: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. VM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. SM: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. SK: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the Editor-in-Chief, Handling Editor, and reviewers for their critical comments, which have helped enhance the technical aspects of the manuscript. We also extend our thanks to the Space Applications Center (SAC) – ISRO, Ahmedabad, for providing AVIRIS-NG data and the necessary support under the AO project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alcaras, E., Parente, C., and Vallario, A. (2021). Automation of pan-sharpening methods for pléiades images using GIS basic functions. Remote Sens. 13 (8), 1550. doi:10.3390/rs13081550
Bautista, A. S., Fita, D., Franch, B., Castiñeira-Ibáñez, S., Arizo, P., Sánchez-Torres, M. J., et al. (2022). Crop monitoring strategy based on remote sensing data (Sentinel-2 and planet), study case in a rice field after applying glycinebetaine. Agronomy 12 (3), 708. doi:10.3390/agronomy12030708
Bhattacharya, B. K., Saxena, M., Green, R. O., Rao, S., Srinivasulu, G., Sharma, S., et al. (2024). Ahmedabad: ISRO. Available at: https://vedas.sac.gov.in/aviris_web/pdf/Overview_AVIRIS_NG_Phase_1_campaign.pdf (Accessed March 13, 2024).
Bhatti, S. S., and Tripathi, N. K. (2014). Built-up area extraction using Landsat 8 OLI imagery. GIScience Remote Sens. 51 (4), 445–467. doi:10.1080/15481603.2014.939539
Bonfi, D. J. (2017). Wheat phenomics in the field by RapidScan: NDVI vs. NDRE. Israel. J. Plant. Sci. 64 (3-4), 41–54. doi:10.1080/07929978.2016.1249135
Delogu, G., Caputi, E., Perretta, M., Ripa, M. N., and Boccia, L. (2023). Using PRISMA hyperspectral data for land cover classification with artificial intelligence support. Sustain. Switz. 15 (18), 13786. doi:10.3390/su151813786
Enrique Valdelamar Martínez, D., Saba, M., and Torres Gil, L. K. (2024). Assessment of asbestos-cement roof distribution and prioritized intervention approaches through hyperspectral imaging. Heliyon 10 (3), e25612. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25612
Frampton, W. J., Dash, J., Watmough, G., and Milton, E. J. (2013). Evaluating the capabilities of Sentinel-2 for quantitative estimation of biophysical variables in vegetation. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 82, 83–92. doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.04.007
Guha, S., Govil, H., and Besoya, M. (2020). An investigation on seasonal variability between LST and NDWI in an urban environment using Landsat satellite data. Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk 11 (1), 1319–1345. doi:10.1080/19475705.2020.1789762
Hadeel, A. S., Jabbar, M. T., and Chen, X. (2009). Application of remote sensing and GIS to the study of land use/cover change and urbanization expansion in Basrah province, Southern Iraq. Geo-Spatial Inf. Sci. 12 (2), 135–141. doi:10.1007/s11806-009-0244-7
Hamedianfar, A., Laakso, K., Middleton, M., Törmänen, T., Köykkä, J., and Torppa, J. (2023). Leveraging high-resolution long-wave infrared hyperspectral laboratory imaging data for mineral identification using machine learning methods. Remote Sens. 15 (19), 4806. doi:10.3390/rs15194806
Ihsan, K. T. N., Harto, A. B., Sakti, A. D., and Wikantika, K. (2023). Monitoring coastal areas using ndwi from landsat image data from 1985 based on cloud computation google earth engine and apps. Int. Archives Photogrammetry, Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. - ISPRS Archives 48 (M-3–2023), 109–114. doi:10.5194/isprs-archives-XLVIII-M-3-2023-109-2023
Jiang, J., Wang, C., Wang, H., Fu, Z., Cao, Q., Tian, Y., et al. (2021b). Evaluation of three portable optical sensors for non-destructive diagnosis of nitrogen status in winter wheat. Sensors 21 (16), 5579. doi:10.3390/s21165579
Jiang, W., Ni, Y., Pang, Z., Li, X., Ju, H., He, G., et al. (2021a). An effective water body extraction method with new water index for sentinel-2 imagery. WaterSwitzerl. 13 (12), 1647. doi:10.3390/w13121647
Jorge, J., Vallbé, M., and Soler, J. A. (2019). Detection of irrigation inhomogeneities in an olive grove using the NDRE vegetation index obtained from UAV images. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 52 (1), 169–177. doi:10.1080/22797254.2019.1572459
Laonamsai, J., Julphunthong, P., Saprathet, T., Kimmany, B., Ganchanasuragit, T., Chomcheawchan, P., et al. (2023). Utilizing NDWI, MNDWI, SAVI, WRI, and AWEI for estimating erosion and deposition in ping river in Thailand. Hydrology 10 (3), 70. doi:10.3390/hydrology10030070
Liu, K., Kayad, A., Sozzi, M., Sartori, L., and Marinello, F. (2023). Headland and field Edge performance assessment using yield maps and sentinel-2 images. Sustain. Switz. 15 (5), 4516. doi:10.3390/su15054516
Liu, L., and Zhang, Y. (2011). Urban heat island analysis using the landsat TM data and ASTER Data: a case study in Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 3 (7), 1535–1552. doi:10.3390/rs3071535
Lu, B., Dao, P. D., Liu, J., He, Y., and Shang, J. (2020). Recent advances of hyperspectral imaging technology and applications in agriculture. Remote Sens. 12 (16), 2659. doi:10.3390/RS12162659
Maccioni, A., Agati, G., and Mazzinghi, P. (2001). New vegetation indices for remote measurement of chlorophylls based on leaf directional reflectance spectra. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 61 (1–2), 52–61. doi:10.1016/S1011-1344(01)00145-2
Mangewa, L. J., Ndakidemi, P. A., Alward, R. D., Kija, H. K., Bukombe, J. K., Nasolwa, E. R., et al. (2022). Comparative assessment of UAV and sentinel-2 NDVI and GNDVI for preliminary diagnosis of habitat conditions in burunge wildlife management area, Tanzania. Earth Switz. 3 (3), 769–787. doi:10.3390/earth3030044
Mekuriaw, A., Heinimann, A., Zeleke, G., Hurni, H., and Hurni, K. (2017). An automated method for mapping physical soil and water conservation structures on cultivated land using GIS and remote sensing techniques. J. Geogr. Sci. 27 (1), 79–94. doi:10.1007/s11442-017-1365-9
Omran, A., Schröder, D., Sommer, C., Hochschild, V., and Märker, M. (2023). A GIS-based simulation and visualization tool for the assessment of gully erosion processes. J. Spatial Sci. 68 (4), 685–702. doi:10.1080/14498596.2022.2133020
Oppelt, N. (2002). Monitoring of plant chlorophyll and nitrogen status using the airborne imaging spectrometer AVIS. development. [WWW Document]. Available at: https://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/354/1/Oppelt_Natascha.pdf (Accessed April 3, 2024)
Pan, B., Cai, S., Zhao, M., Cheng, H., Yu, H., Du, S., et al. (2023). Predicting the surface soil texture of cultivated land via hyperspectral remote sensing and machine learning: a case study in jianghuai hilly area. Appl. Sci. Switz. 13 (16), 9321. doi:10.3390/app13169321
Peddinti, V. S. S., Mandla, V. R., Mesapam, S., and Kancharla, S. (2021). Selection of optimal bands of AVIRIS – NG by evaluating NDVI with Sentinel-2. Earth Sci. Inf. 14, 1285–1302. Blackburn 1998. doi:10.1007/s12145-021-00662-x
Rasti, B., Ghamisi, P., and Benediktsson, J. A. (2020). Hyperspectral mixed Gaussian and sparse noise reduction. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 17 (3), 474–478. doi:10.1109/lgrs.2019.2924344
Rasti, B., Scheunders, P., Ghamisi, P., Licciardi, G., and Chanussot, J. (2018). Noise reduction in hyperspectral imagery: overview and application. Remote Sens. 10 (3), 482–528. doi:10.3390/rs10030482
Sentinel-2 resolutions (2024). Spatial and spectral resolutions of Sentinel-2 data. Available at: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/missions/sentinel-2/instrument-payload/resolution-and-swath (Accessed March 28, 2024).
Taloor, A. K., Singh Manhas, D., and Chandra Kothyari, G. (2021). Retrieval of land surface temperature, normalized difference moisture index, normalized difference water index of the Ravi basin using Landsat data. Appl. Comput. Geosciences 9, 100051. doi:10.1016/j.acags.2020.100051
Wang, F.- M., Huang, J.- F., Tang, Y.- L., and Wang, X.- Z. (2007). New vegetation index and its application in estimating leaf area index of rice. Rice Sci. 14(3), 195–203. doi:10.1016/S1672-6308(07)60027-4
Wu, Z., Sun, J., Zhang, Y., Wei, Z., and Chanussot, J. (2021). Recent developments in parallel and distributed computing for remotely sensed big data processing. Proc. IEEE 109 (8), 1282–1305. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2021.3087029
Xu, Y., Hu, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Yin, Y., and Wu, G. (2021). Mapping aquaculture areas with multi-source spectral and texture features: a case study in the pearl river basin (guangdong), China. Remote Sens. 13 (21), 4320. doi:10.3390/rs13214320
Yasin, M. Y., Abdullah, J., Noor, N. M., Yusoff, M. M., and Noor, N. M. (2022). Landsat observation of urban growth and land use change using NDVI and NDBI analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1067 (1), 012037. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1067/1/012037
Zarco-Tejada, P. J., Miller, J. R., Mohammed, G. H., Nolan, T. L., and Sampson, P.(1999). Canopy optical indices from infinite reflectance and canopy reflectance models for forest condition monitoring: application to hyperspectral CASI data 3, 1878–1881. doi:10.1109/IGARSS.1999.772125
Zhao, C., and Pan, Y. (2023). A novel spectral index for mapping blue colour-coated steel roofs (BCCSRs) in urban areas using Sentinel-2 data. Int. J. Digital Earth 16 (1), 2862–2884. doi:10.1080/17538947.2023.2241427
Zheng, Y., Tang, L., and Wang, H. (2021). An improved approach for monitoring urban built-up areas by combining NPP-VIIRS nighttime light, NDVI, NDWI, and NDBI. J. Clean. Prod. 328, 129488. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129488
Zheng, Y. B., Huang, T. Z., Le Zhao, X., Jiang, T. X., Ma, T. H., and Ji, T. Y. (2020). Mixed noise removal in hyperspectral image via low-fibered-rank regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 58 (1), 734–749. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2019.2940534
Keywords: AVIRIS, automation, band selection, hyperspectral data, indices, parallel processing
Citation: Peddinti VSS, Mandla VR, Mesapam S and Kancharla S (2025) Automating band selection for hyperspectral indices: bridging AVIRIS-NG and Sentinel-2 satellite data for earth science applications. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1487160. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1487160
Received: 27 August 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 27 January 2025.
Edited by:
M. Arasumani, University of Greifswald, GermanyReviewed by:
Suresh Devaraj, Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, IndiaKumaresan M., National Institute of Technical Teachers Training and Research (NITTTR), India
Copyright © 2025 Peddinti, Mandla, Mesapam and Kancharla. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Venkata Ravibabu Mandla, cmF2aS5tYW5kbGFAZ21haWwuY29t
 Veerendra Satya Sylesh Peddinti
Veerendra Satya Sylesh Peddinti Venkata Ravibabu Mandla
Venkata Ravibabu Mandla Shashi Mesapam
Shashi Mesapam Suresh Kancharla
Suresh Kancharla