- 1State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Resources and Exploration, China University of Petroleum (Beijing), Beijing, China
- 2School of Petroleum Engineering, China University of Petroleum (Beijing), Beijing, China
Considering the differences in reserves and their utilization among gas reservoir area, utilization area and swept area, a reserves zoning producing model was established, and a method for integrating current recovery and limited recovery in gas reservoirs, the reserve analysis method, was proposed. The method was applied to calculate the current recovery and limited recovery of the gas reservoir and assess the potential of the gas reservoir to enhance the recovery, taking the Zizhou gas field in the Ordos Basin of China, the Shan2 tight sandstone gas reservoir, as an example. The results show that the method is able to simultaneously determine the current recovery, limited recovery, planar sweep efficiency, vertical sweep efficiency and gas driving efficiency of a gas reservoir by using four reserve parameters such as the gas reservoir area geological reserves, the producing area geological reserves, the swept area geological reserves, and the remaining geological reserves in the swept area when abandoned. This method is simple and easy to implement, and provides a new way for the evaluation of gas reservoir recovery potential and the study of improving the development method of gas reservoirs.
1 Introduction
Reservoir recovery is an important technical index to measure the effect of comprehensive development of gas reservoirs, and it is also a regular research topic for gas field development researchers (Guo et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2023). Determination of gas recovery is generally divided into two steps, firstly, the recoverable reserves of the gas reservoir when it is abandoned in a specific well network are obtained, and then the ratio between the recoverable reserves of the gas reservoir and its original geological reserves is calculated (Mu et al., 2018; Lu et al., 2024). As the original geological reserves is the natural gas gathering volume in the original geological conditions of the gas reservoir, which is the material basis for the exploitation of the gas reservoir, it can be regarded as a fixed value. Therefore, the key to determine the recovery of the gas reservoir lies in the calculation of recoverable reserves. Recoverable reserves are calculated by different methods, and there are various methods for determining gas reservoir recovery. For example, material balance method, decreasing production method, elastic two-phase method, pressure build-up curve method, logistic method, dynamic reserve analysis method and numerical simulation method (Ren et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2024).
Scholars have shown that gas recovery is closely related to the degree of well network control, and the higher the degree, the greater the gas recovery (Chen et al., 2009; Ren et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2024). In order to characterize the dynamic change of recovery with well network conditions, the author divided the recovery into current recovery and limited recovery. Among them, the current recovery is the recovery of gas reservoir at present well network condition, which can reflect the current development effect of gas reservoir; the limited recovery is the recovery of gas reservoir at perfect well network condition (100% well network control degree), which can reflect the limiting development effect of gas reservoir; the difference between the current recovery and the limited recovery can be used to evaluate the potential of gas reservoir to enhance the recovery. Obviously, according to this categorization, the recoveries that are usually calculated are the current recoveries of the gas reservoir (Chen et al., 2009; Guo et al., 2018; Mu et al., 2018; Ren et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2024; Sun et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2024). However, in the process of gas reservoir development, in order to evaluate the potential of enhancing the recovery of a gas reservoir, in addition to clarifying the current recovery, it is more necessary to implement the limited recovery. Therefore, it is of great significance to consider the current recovery and the limited recovery of a gas reservoir in a unified way, and to establish an integrated calculation method of the current recovery and the limited recovery of a gas reservoir, which is of great significance to effectively assess the potential of gas reservoirs to enhance the recovery, and to guide the adjustment of the development and the excavation of the potentials.
Thus, this paper carries out the research on the integrated calculation method of current recovery and limited recovery of gas reservoirs by taking the example of Shan2 tight sandstone gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field, Ordos Basin, China. Firstly, from the distribution of gas reservoir reserves and its producing law, a reserves zoning producing model is established and an integrated calculation method of current recovery and limited recovery is proposed - the reserve analysis method. Then, the current recovery and limited recovery of the gas reservoir were simultaneously calculated by this method, taking the Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou field as an example. Finally, through the comparison of current recovery and limited recovery, the potential of the gas reservoir to enhance the recovery was evaluated, and a proposal for the adjustment of gas reservoir development was given.
2 Methods
2.1 Reserves zoning producing model
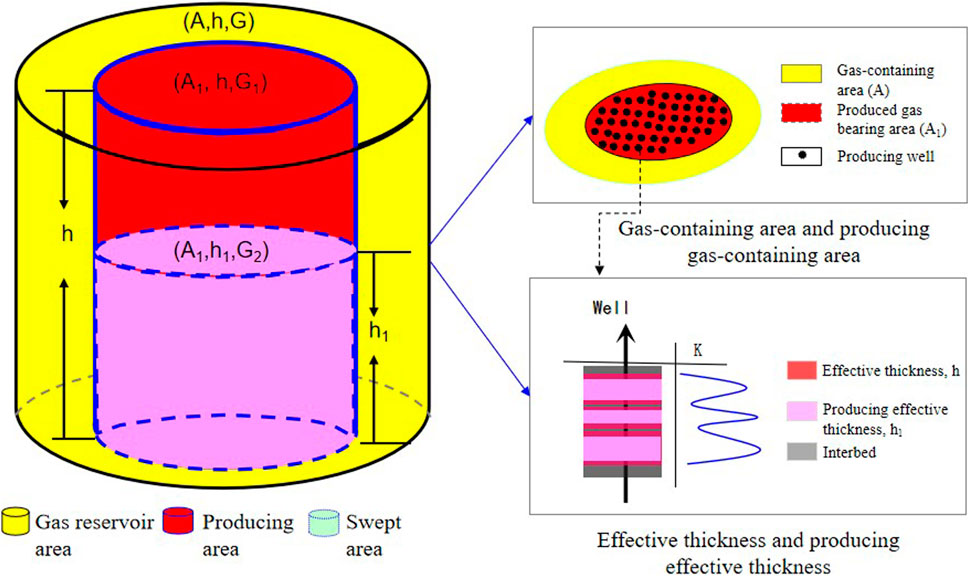
The distribution and utilization of gas reservoir reserves are regular and characterized by space zoning. Based on this, the reserves zoning producing model is established, which is divided into three spatial areas, including gas reservoir area, producing area and swept area (Figure 1).
As shown in Figure 1, each of the three regions is characterized by different characteristics:
1) Different connotation. The gas reservoir area represents the overall distribution space of the gas reservoir, and the reserves in this area are the original geological reserves of the gas reservoir; the producing area represents the part of the gas reservoir area controlled by the well network, and the reserves in the producing area are the geological reserves in the part of the gas reservoir area controlled by the well network; and the swept area represents the part of the producing area that is involved in the seepage, and the reserves in the swept area are the geological reserves in the part of the producing area that is involved in the seepage.
2) Different geometric scales. The gas reservoir area corresponds to the reservoir gas-containing area (
3) Different reserve sizes. Gas reservoir area geologic reserves (
4) Different stability of reserves. The gas reservoir area geological reserve is the natural gathering amount of gas under the original geological conditions of the gas reservoir, which is the material basis for the development of the gas reservoir, and does not change with the development process, so it can be regarded as a constant value. The producing area geological reserve is related to the degree of well network control and it changes with the development process, so it is a variable value. In general, the more perfect the well network is, and the closer the producing gas-containing area is to the gas-containing area, the larger the geological reserve of producing area is. When the perfect well network (well network control degree 100%) is reached, the producing gas-containing area is equal to the gas-containing area, and the producing area reserve is equal to the gas reservoir area reserve. The swept area geologic reserve is related to both the degree of well network control and the vertical heterogeneity, and changes with the development process as a variable. The gas reservoir area geological reserve is the natural gathering amount of gas under the original geological conditions of the gas reservoir, which is the material basis for the development of the gas reservoir, and does not change with the development process, so it can be regarded as a constant value. The producing area geological reserve is related to the degree of well network control and it changes with the development process, so it is a variable value. In general, the more perfect the well network is, and the closer the producing gas-containing area is to the gas-containing area, the larger the geological reserve of producing area is. When the perfect well network (well network control degree 100%) is reached, the producing gas-containing area is equal to the gas-containing area, and the producing area reserve is equal to the gas reservoir area reserve. The swept area geologic reserve is related to both the degree of well network control and the vertical heterogeneity, and changes with the development process as a variable. The weaker the vertical heterogeneity is, the closer the producing effective thickness is to the effective thickness, and the closer the swept area reserve is to the producing area reserve.
5) Different impacts on recovery. Gas recovery is the ratio of the recoverable reserves of a gas reservoir when abandoned to its original geologic reserves under specific well network conditions. Therefore, the gas recovery mainly depends on the relative sizes of the swept area and the gas reservoir area under specific well network conditions. Generally, the closer the producing area (
2.2 Current recovery and limited recovery integration calculation methods
2.2.1 Reserve forms of recovery
For a given gas reservoir, the recovery is the ratio of the final volume of natural gas recovered (or recoverable reserves) to the original geologic reserves of the gas reservoir, i.e.,:
Considering the reserves zoning producing model (Figure 1), Equation 1 can be expressed as:
Since the recoverable reserves (
Therefore, the gas reservoir recovery can be fully expressed in reserve form by Equations 2 and 3:
Equation 4 provides a method for calculating the gas reservoir recovery, showing that to calculate the gas reservoir recovery, it is only necessary to determine four macroscopic reserve parameters such as the gas reservoir area geologic reserve (
In the formula:
2.2.2 Reserve calculation methods
For constant-volume reservoirs, the gas reservoir geologic reserves (
Equations 5–8 Explanation:
1) All four geologic reserves can be expressed by the volumetric method formula.
2) Although all four geological reserves can be expressed by the volumetric method, the methods used to verify the four geological reserves are not the same in the process of gas reservoir development. Among them, gas reservoir area geological reserves and producing area geological reserves are generally accounted for by static method, and the volumetric method is mainly used; because it is difficult to accurately calibrate the producing area effective thickness
In the formula:
2.2.3 The coefficient form of recovery
Substituting Equations 5–8 into Equation 4 gives the coefficient form of the gas reservoir recovery:
Where,A is the planar sweep efficiency, B is the vertical sweep efficiency, and C is the gas driving efficiency, and the expressions are respectively:
In the formula:
Equations 9–12 illustrate:
1) The gas recovery is essentially the multiplication of the planar sweep efficiency, the vertical sweep efficiency and the gas driving efficiency.
2) The planar sweep efficiency, the vertical sweep efficiency and the gas driving efficiency can be determined by four macro reservoir parameters. That is, the reservoir form of recovery and the coefficient form can be converted to each other. Equations 10–12, which establish the conversion relationship between four reserve parameters (
3) Producing area geological reserves are related to the degree of well network control, so the planar sweep efficiency is also related to the well network perfection; Swept area geological reserves are related to vertical heterogeneity, so the vertical sweep efficiency is also related to vertical heterogeneity; Remaining geological reserves in the swept area at the time of abandoned are related to the abandoned pressure, so the gas driving efficiency is also related to the abandoned pressure.
4) In the production process, the well network is adjustable and controllable, and with the improvement of well network control, the planar sweep efficiency increases gradually; while the vertical heterogeneity belongs to the geological factors, which is difficult to be adjusted, so the vertical sweep efficiency in the development process is relatively stable; the gas driving efficiency is only related to the reservoir abandoned pressure, which is limited by the reservoir process technology and the development level, which is difficult to be adjusted, so the gas driving efficiency is generally also relatively stable. Therefore, improving the planar sweep efficiency is an important way to improve the recovery of the gas reservoir when the specific gas reservoir process technology and development level are certain (Dai et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2024).
2.2.4 Current recovery and limited recovery calculations
As gas field exploitation progresses and the well network is improved, the recovery of the gas reservoir will also change.In order to characterize the current and final state of the dynamic change of the recovery, it is divided into current recovery and limited recovery. Among them, the current recovery is the recovery under the current well network conditions of the gas reservoir, which is an important index to measure the effectiveness of the current gas reservoir exploitation, and is also a regular research topic for gas field development workers.
Since gas reservoirs have current recovery in both reserve and coefficient form, there are, in principle, 2 methods of calculating current recovery. Among them, it is calculated by utilizing the coefficient form, as in Equation 9; and it is calculated by utilizing the reserve form, as in Equation 4.
Limited recovery refers to the recovery under the condition of perfect well network of the gas reservoir, which is an important index to measure the development effect of the gas reservoir at the time of perfect well network, and is of great significance in determining the medium and long term development potential of the gas reservoir. If it is assumed that the planar sweep efficiency under perfect well network condition is 100%, then the limited recovery is essentially the multiplication of gas driving efficiency and vertical sweep efficiency, that is, the coefficient corresponding to the limited recovery is in the form of:
Substituting Equations 11, 12 into Equation 13, the form of reserves corresponding to the limited recovery can be obtained as:
In the formula:
Since gas reservoir limited recovery has both reserve and coefficient forms, there are, in principle, 2 methods of calculating the limited recovery. Among them, it is calculated by using the coefficient form, as in Equation 13, and by using the reserve form, as in Equation 14.
It is well known that in the process of gas reservoir development, four reserve parameters (
3 Applications
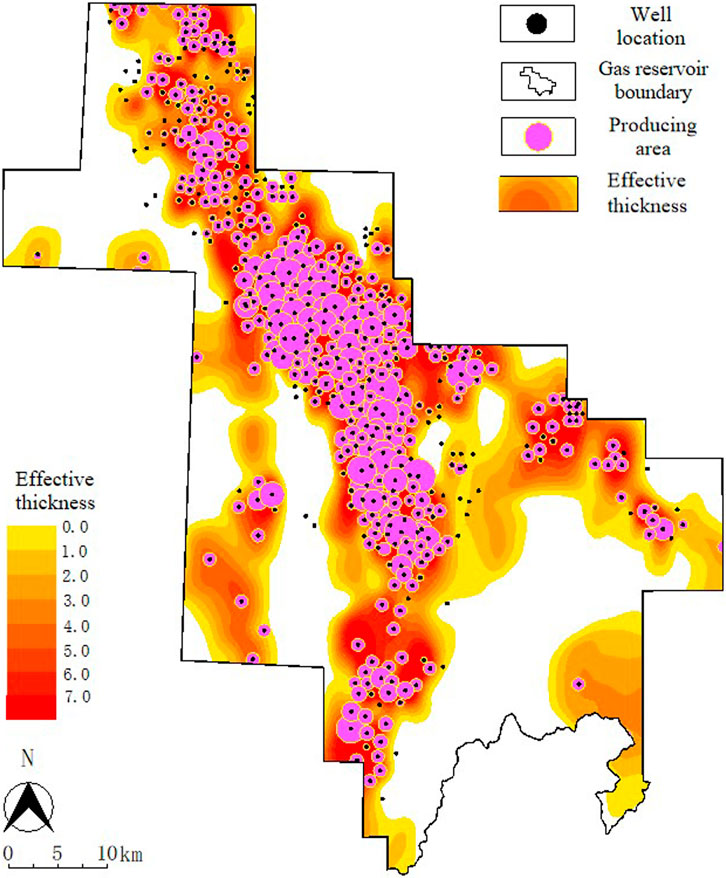
The Zizhou gas field Shan2 gas reservoir is located in Yulin City, Shaanxi Province, China, within the territory of Mili, Zizhou, Suide and Qingjian counties, the regional tectonics is in the eastern part of the Yi-Shaan slope in the Ordos Basin, and the main producing layer is the Shan2 section of the Shanxi Formation of the Upper Paleozoic Permian Lower Series. The Zizhou gas field Shan2 gas reservoir is located in Yulin City, Shaanxi Province, China, within the territory of Mili, Zizhou, Suide and Qingjian counties, the regional tectonics is in the eastern part of the Yi-Shaan slope in the Ordos Basin, and the main producing layer is the Shan2 section of the Shanxi Formation of the Upper Paleozoic Permian Lower Series. The gas reservoir is a typical tight sandstone gas reservoir, with outside-source forming and near-source storage characteristics (Zhao et al., 2013); the reservoir is offshore lake braided river delta plain deposition (An et al., 2014), and currently the reservoir has evolved to the mesogenetic B stage (Gao et al., 2013); the reservoir has low porosity and low permeability, with an average porosity of 4.94%, and an average permeability of 0.78 × 10−3 μm2 (Wang et al., 2022). The gas reservoir was put into development in 2007, and is currently in the middle to late stage of development, and the core area in the part of the main sand zone has been basically produced (Figure 2).
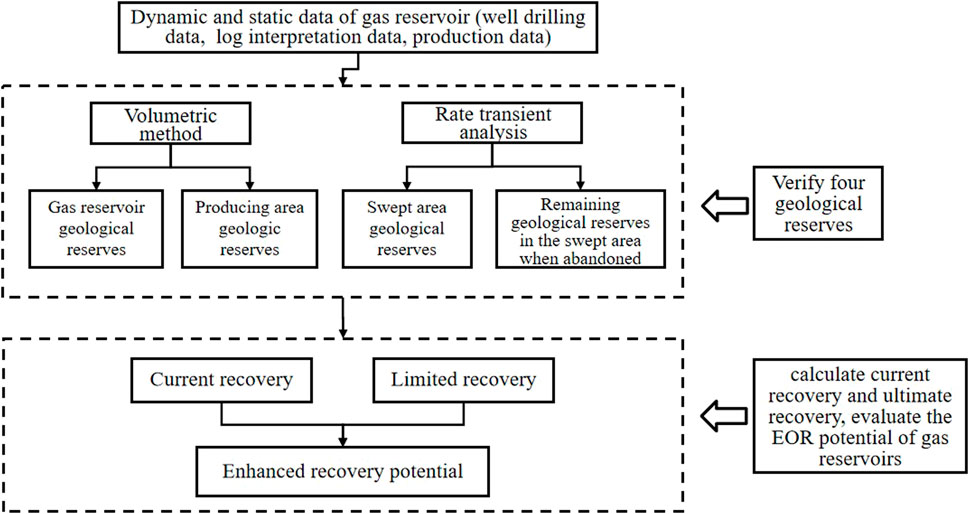
Taking the Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field as an example, reserve analysis method is applied to carry out the integrated calculation of current recovery and limited recovery in the gas reservoir and evaluate the potential of the gas reservoir to improve the recovery. The specific calculation process is shown in Figure 3:
3.1 Verification of 4 geological reserves
1) Verification of gas reservoir area geological reserves (
The Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field is in the middle to late stage of development, and the dynamic and static data accumulated in the gas reservoir over the years are very rich, which provide a reliable data base for the reserve calculation by the volumetric method. Using the drilling, logging interpretation, high-pressure physical properties and production dynamic data of 492 wells, we circled the gas-containing area and gas-containing area of the gas reservoir (Figure 2), determined the gas reserves parameters, and verified the gas-containing area geologic reserves and the producing area geologic reserves by using the volumetric method. Calculation results (Table 1) show that the gas reservoir area has a geological reserve of 1083.4 × 108 m3 and the producing area has a geological reserve of 679.3 × 108 m3.
2) The rate transient analysis method (RTA) was used to determine the swept area geologic reserves (

Table 1. Table of calculation results of geological reserves of Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field.
At present, the wellhead external delivery pressure (or booster suction pressure) optimized for booster extraction in Zizhou gas field is 2.0 MPa, and according to the method of calculating the pressure drop of the gas-phase vertical pipe flow, the bottomhole flow pressure is back-calculated downward from the wellhead external delivery pressure, and then the abandonment formation pressure is calculated by using the production capacity equation (Hao and Yan, 1999). According to the above method, the abandoned formation pressure of the gas reservoir is 3.5 MPa. Based on the determination of the abandoned pressure, considering the characteristics of low permeability, strong heterogeneity, and large differences in the drainage area of gas wells in tight sandstone reservoirs, in order to ensure the accuracy of the calculations, the rate transient analysis method (RTA) is used to verify the dynamic geological reserves and the remaining geological reserves when abandoned for each well. Finally, the swept area geological reserves and the remaining geological reserves when abandoned were determined based on the cumulative results of a single well (Fan et al., 2024). Calculation results (Table 1) show that the swept area geological reserve of the gas reservoir is 383.1 × 108 m3, and the remaining geological reserve in the swept area when abandoned is 49.4 × 108 m3.
3.2 Calculation of current recovery and limited recovery and assessment of the potential for enhanced recovery in gas reservoirs
Based on the four reserve parameters, the current recovery was calculated by Equation 4, the limited recovery was calculated by Equation 14, and the difference between the two was used to evaluate the potential of the reservoir to enhance the recovery. The calculation results show that (Table 2), the current recovery of Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field is 30.8%, and the limited recovery is 47.9%. Overall, the current recovery of the reservoir is very low and the limited recovery is not good, and both of them are less than 50%.
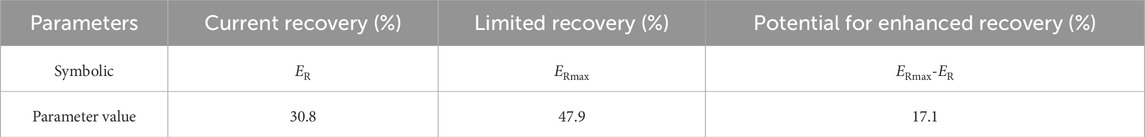
Table 2. Table of calculation results of current recovery and limited recovery of Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field.
The geological reserve of Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field is 1083.4 × 108 m3, and the current recovery is 30.8%, indicating that the recoverable reserve of the gas reservoir under the current well network condition is 333.7 × 108 m3; the limiting recovery of the gas reservoir is 47.9%, indicating that the recoverable reserve of the gas reservoir under the condition of perfecting the well network is 518.9 × 108 m3; there is a difference of 17.1% between the current recovery and the limiting recovery. The difference between current recovery and limited recovery is 185.3 × 108 m3, indicating that this gas reservoir has a great potential to enhance the recovery.
3.3 Method reliability test
In order to test the reliability of the reserve analysis method on the calculation results of the current recovery and limited recovery of the gas reservoir, numerical simulation method was used to predict the recoverable reserves when abandoned of the gas reservoir under the current well network conditions. The result shows that the final recoverable reserve of the gas reservoir when abandoned is 329.2 × 108 m3, and based on this prediction result, combined with the gas reservoir area geologic reserve (1083.4 × 108 m3) and producing area geologic reserve (679.3 × 108 m3), the current recovery of the gas reservoir is determined to be 30.4%, and the limited recovery is determined to be 47.2% respectively by using the Equations 4, 14. This result is in good agreement with the current recovery (30.8%) and limited recovery (47.9%) calculated by the reserve analysis method, indicating that the calculation results of the reserve analysis method are reliable (Figure 4).
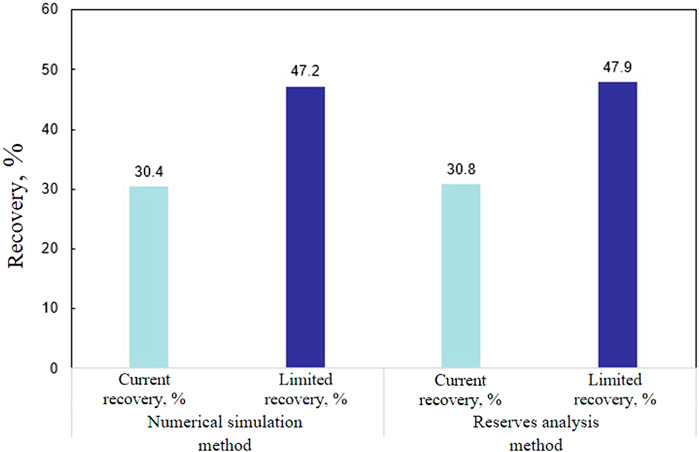
Figure 4. Comparison of recovery calculation results between numerical simulation method and reserves analysis method for Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field.
4 Discussion
Reserve and coefficient forms of recovery can be converted to each other. Equations 10–12, establish the conversion relationship between 4 reservoir parameters (
Calculation results show that (Table 3), the planar sweep efficiency of Shan2 reservoir in Zizhou gas field is 64.4%, which is not high; the vertical sweep efficiency is 54.9%, which is low; and the gas driving efficiency is 87.1%, which indicates that the gas driving efficiency of pressure boosting production is high. According to this analysis, it is believed that the low planar sweep efficiency and low vertical sweep efficiency of Shan2 gas reservoir are the main reasons for the low current recovery (30.8%) of the gas reservoir. As it is difficult to fundamentally change both the vertical sweep efficiency and the gas driving efficiency under the condition that the existing process technology and development level remain unchanged. Therefore, maximizing the planar sweep efficiency is still an effective way to substantially increase the recovery of this gas reservoir.
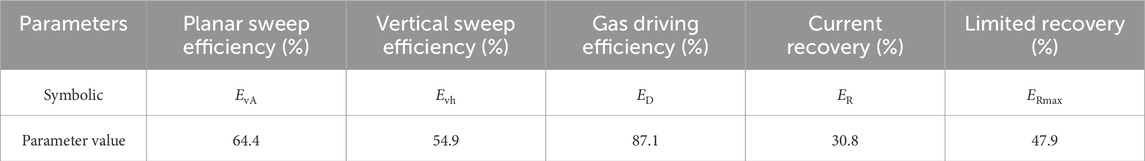
Table 3. Table of calculation results of planar sweep efficiency, vertical sweep efficiency and gas driving efficiency of Shan2 gas reservoir in Zizhou gas field.
Of course, further increasing the vertical sweep efficiency or gas driving efficiency is also very important to enhance the recovery of the gas reservoir. However, the premise is that the existing technology and development level of the gas reservoir also need to be significantly improved. Therefore, how to increase the vertical sweep efficiency and gas driving efficiency is still an important issue in gas reservoir development research. Especially for tight sandstone gas reservoirs, how to improve the vertical sweep efficiency is particularly important.
5 Conclusion
In this paper, the differences in reserves and their production and utilization among gas reservoir area, swept area and producing area are considered comprehensively, a reserves zoning producing model is established, and a method for integrating current recovery and limited recovery in gas reservoirs, the reserve analysis method, is proposed. The method can utilize four macroscopic storage parameters, including the gas reservoir area geological reserves, producing area geological reserves, swept area geological reserves, and the remaining geological reserves in the swept area when abandoned, to find the current recovery and the limited recovery of the gas reservoir, and evaluate the potential of gas reservoirs to improve the recovery. At the same time, the method can also determine the reservoir planar sweep efficiency, vertical sweep efficiency and gas driving efficiency, which can help to clarify the main controlling factors affecting the recovery of the gas reservoir and improve the development method of the gas reservoir. The method is simple and easy to implement, with wide applicability, and provides an effective technical way for the assessment of gas reservoir recovery potential, which is of great significance for improving the development method and enhancing the recovery of the gas reservoir.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Methodology, Project administration, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Visualization. JW: Writing–review and editing, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization. YS: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. SP: Investigation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by National Science and Technology Major Special Project - Oil and Gas Major Special Project (2016ZX05047-005); National Science and Technology Major Special Project (2017ZX05035004).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
An, W., Yang, W., Shi, X., Yang, Y., and Feng, Y. (2014). Reunderstanding of sedimentary facies of Shan23 of the Middle Permian in Zizhou gas field. J. Xi'an Shiyou Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 29 (03), 20–26. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2014.03.004
Chen, H., Li, Z., Jin, Z., Sun, Y., Chen, J., and Zhao, G. (2024). Microscopic characteristics of ultra-low permeability reservoirs in the Shigang Oilfield of the Subei Basin and strategies for enhancing oil recovery. Petroleum Geol. Exp. 46 (03), 638–646. doi:10.11781/sysydz202403638
Chen, S., Zhang, N., Liu, J., and Chen, S. (2009). Discussion on EOR technologies in late development period of Carboniferous gas reservoirs in East Sichuan basin. Nat. Gas. Ind. 29 (05), 92–94+143. doi:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.05.021
Dai, J., Ren, Q., and Mu, Z. (2018). Effect of well pattern control level on gas reservoir recovery:A case study of well A in jingbian gas field. Sci. Technol. Eng. 18 (30), 70–74. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.30.011
Deng, J., Liu, C., Zhang, Z., Jiang, J., and Zhou, W. (2024). A new calculation method of water sweep efficiency in water drive reservoir. Petrochem. Ind. Technol. 31 (06), 155–157. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2024.06.053
Fan, Z., Lei, X., Li, H., Li, B., Dai, J., Chen, D., et al. (2024). Evaluation of production effect and analysis of production potential of tight sandstone gas reservoir in the late stage of stable production: a case study of Shan 2 gas reservoir, Zizhou gas field. Sci. Technol. Eng. 24 (21), 8917–8924. doi:10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2305880
Gao, H., Li, T., Xie, Y., and Xu, Z. (2013). Diagenesis and favorable diagenetic facies belts of subfacies tight sandstone reservoirs in delta front: a case study of Shan23 member sandstone in Zizhou Gas field, Ordos Basin. Geoscience 27 (02), 373–381. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.016
Guo, J., Guo, Z., Cui, Y., Meng, D., Wang, G., Ji, G., et al. (2018). Recovery factor calculation method of giant tight sandstone gas field. Acta Pet. Sin. 39 (12), 1389–1396. doi:10.7623/syxb201812007
Hao, Y., and Yan, J. (1999). A new method to determine the abandonment formation pressure of gas well. Oil gas recovery Technol. 1999 (04), 77–82.
Lu, R., Cheng, S., Lei, X., Ruan, H., and Wu, C. (2024). A new method for fast calculation recovery factor of offshore gas reservoir. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology Science and Technology Edition, 1–10.
Mu, Z., Dai, J., Zhao, Z., Lu, L., Dai, H., and Zhang, Z. (2018). Study on predicting the recovery efficiency of low permeability gas reservoirs. Petroleum Geol. Eng. 32 (06), 70–72+120. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2018.06.018
Ren, Q., Dai, J., and Mu, Z. (2018). Study on influencing factors of gas reservoir recovery factor and its enlightenment: a case study of well area A in Jingbian Gas Field. Nat. Gas. Geosci. 29 (09), 1376–1382. doi:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.06.015
Sun, H., Yang, Y., Fang, J., Fan, Z., Wu, G., Yuan, F., et al. (2024). Technological synergy for enhancing hydrocarbon recovery and its applications. Oil and Gas Geol. 45 (03), 600–608. doi:10.11743/ogg20240302
Wang, X., Ye, S., Zhou, K., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Study on the correlation between tight sandstone reservoir characteristics and gas and water distribution in Shan23 of Zizhou area. J. Northwest Univ. Nat. Sci. Edtion 52 (05), 868–877. doi:10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbzr.2022-05-014
Wang, Z., Liu, Z., Du, Y., Tan, Z., Hu, J., Yang, S., et al. (2016). Asplitting method of oil and gas production in multiple completion wells of multiayerd reservoir. Nat. Gas. Geosci. 27 (10), 1878–1882. doi:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.10.1878
Wu, Z., Jiang, Q., Zhou, Y., He, Y., Sun, Y., Tian, W., et al. (2023). Key technologies and orientation of EGR for the Sulige tight sandstone gas field in the Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas. Ind. 43 (06), 66–75. doi:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2023.06.006
Yang, Z., Zhao, Z., and Qian, L. (2024). Grey correlation analysis of factors affecting the recovery rate of tight sandstone gas reservoirs. J. Beijing Inst. Petrochem. Technol. 32 (02), 25–30. doi:10.19770/j.cnki.issn.1008-2565.2024.02.005
Zhang, M. (2010). Evaluation techniques of dynamic reserves:Case history of low-permeability and heterogeneous reservoirs in Changqing gas fields. Nat. Gas. Ind. 30 (4), 50–53. doi:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.04.011
Zhang, Q., Chen, J., Zeng, L., Wei, H., Yang, J., and Lei, L. (2023). Study on enhanced oil recovery technology for low permeability complex oil and gas reservoirs. Energy Chem. Industry 44 (06), 59–62. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7906.2023.06.037
Keywords: tight sandstone gas reservoirs, current recovery, limited recovery, recovery enhancement potential, calculation methods
Citation: Dai J, Wu J, Shi Y, Lei X and Pi S (2024) Research on the integrated calculation method of current recovery and limited recovery in tight sandstone gas reservoirs. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1485125. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1485125
Received: 23 August 2024; Accepted: 22 October 2024;
Published: 20 December 2024.
Edited by:
Kun Shi, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaCopyright © 2024 Dai, Wu, Shi, Lei and Pi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinyou Dai, MTA1NTg0ODc3N0BxcS5jb20=
 Jinyou Dai1,2*
Jinyou Dai1,2* Junzhe Wu
Junzhe Wu