- 1Zhuhai Da Hengqin Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China
- 2Zhuhai Da Hengqin City Investment Construction Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China
- 3Renmin University of China, Beijing, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Coastal Science and Integrated Management, First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, Qingdao, China
- 5Island Research Center, Ministry of Natural Resources, Pingtan, China
- 6Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Island Conservation and Development (Island Research Center, Ministry of Natural Resources), Pingtan, China
- 7Observation and Research Station of Island and Coastal Ecosystem in the Western Taiwan Strait, Ministry of Natural Resources, Xiamen, China
- 8South China University of Technology, School of Civil Engineering and Transportation, Guangzhou, China
- 9Department of Aquatic Resource Management, Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Sciences, IPB University, Bogor, Indonesia
- 10Center for Coastal and Marine Resource Studies, IPB University, Bogor, Indonesia
- 11Department of Marine Engineering, Myanmar Maritime University, Yangon, Myanmar
Automatically and accurately identifying the deformation zone of coastal slope landslides is crucial for exploring the mechanism of landslides and predicting landslide disasters. To this end, this study proposes an integrated automatic recognition method combining Image Clipping (IC), Image Information Enhancement (IE), Adaptive K-means Clustering Segmentation (AKS), and Optimization (O): IC-IE-AKS-O, which achieves precise extraction of the deformation area in coastal slope landslide images. Firstly, due to the more complex natural environment of field slopes, to extend the monitoring duration, we introduce a hierarchical operation algorithm based on the HSV color model, which effectively mitigates the impact of sunlight, rain, and foggy weather on image recognition accuracy. Secondly, this study proposes a 2D landslide image segmentation technique that combines K-means clustering with global threshold segmentation for landslide images, enabling the segmentation of small image regions with precision. Finally, we combine image information enhancement technology with image segmentation technology. To verify its effectiveness, we identify a landslide image of a coastal slope in Pingtan. The method displays an average relative error of 5.20% and 5.14% in the X and Y directions, respectively. Its advantages are threefold: (1) The combination of image information enhancement and segmentation techniques can more accurately identify landslide areas that appear blurred in the image; (2) expanding the temporal dimension of coastal slope monitoring; (3) providing excellent boundary conditions and segmentation results. The practical application of this method ensures the stable and accurate operation of the coastal slope monitoring system, providing a safeguard for the sustainable development of marine safety.
1 Introduction
Coastal slope landslides usually cause huge casualties and property losses, and seriously restrict the sustainable development of marine ecology (Aksoy and Ercanoglu, 2012; Lan et al., 2022; Bednarczyk, 2018). Accurate identification of landslide deformation areas plays a decisive role in automated coastal slope monitoring (Wang H. et al., 2021; Ju et al., 2023; Ju et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022a). In previous studies, scholars have mostly used image segmentation techniques to identify and determine landslide deformation areas, e.g., Ardizzone used elevation data collected by airborne LiDAR to identify and map landslides caused by rainfall (Ardizzone et al., 2007). Kurtz proposed a hybrid method based on segmentation/classification of regions that can detect and map landslides (Kurtz et al., 2014). Mondini used Very High Resolution (VHR) panchromatic and High Resolution (HR) multispectral satellite maps and proposed a method for semi-automatic identification and mapping of shallow landslides caused by recent rainfall (Mondini et al., 2011). Cheng et al. proposed an automatic landslide detection method based on remotely sensed imagery to achieve landslide mapping (Cheng et al., 2013). Rahardjo et al. used multilayered semantic networks to process satellite imagery and achieve semi-automatic landslide recognition (Rahardjo et al., 2014). Mwaniki utilized image enhancement to improve the accuracy of landslide recognition (Mwaniki et al., 2017). For mainstream automatic recognition with hyperpixel segmentation, Xie proposed a SAR image hyperpixel generation method based on significant difference and spatial distance, which adheres to the target contours and accurately responds to the boundaries of texture details in uneven regions (Xie et al., 2019). Zhu proposed a region merging method, which significantly improves the accuracy of hyperpixel segmentation by constructing a new energy function (Zhu et al., 2016). In order to recognize small-scale landslides, Hashiba extracted landslide regions with high accuracy by checking the appropriate area size using the superpixel SLICO method (Hashiba and Sonobe, 2020). Yang realized the recognition of deformed regions in small-scale landslide areas based on the change of image superpixel roughness during landslide deformation (Yang et al., 2019). Although the research objects of previous scholars are mostly biased towards inland slopes, the wide adaptability of image segmentation methods still provides a feasible basis for the identification of landslide areas on coastal slopes. Scholars have done less research on the identification of landslide areas on coastal slopes.
In addition, the coastal slope environment is relatively complex. Due to factors such as sunlight, rainy, and foggy weather conditions, the collected images are often blurry, which significantly affects the accuracy of image monitoring. If only high-clarity images are collected, the time available for monitoring using these images will also be limited. Therefore, for the identification of landslide areas on coastal slopes, it is necessary to enhance the information of the monitoring images on the basis of image segmentation techniques, so that the information of landslide areas and non-landslide areas in the images is clear, and the feasibility of subsequent monitoring is ensured (Fu et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021). Researchers have also done a lot of research on image enhancement (Iqbal et al., 2020; Fu and Cao, 2020). For example, Tang et al. proposed an AIEBHE method based on adaptive dual HE, which uses the separation point of the histogram as the median intensity and adaptively modifies the limit of each sub-platform histogram (Tang and Mat Isa, 2014). Paul et al. improved the image by using the average of the histogram peaks as a separation threshold and equalizing the blur-based sub-histograms separately (Paul et al., 2021). Ooi et al. proposed the RSIHE method, which is a dynamic quadrant histogram equalization approach under platform constraints, where the cropping limits of the four sub-histograms are determined based on the average image intensity of each self-histogram (Ooi and Mat Isa, 2010). Moreover, the HSV color space is robust to color distortion, so image contrast enhancement can be achieved by converting the image from RGB color space to HSV color space (Liu et al., 2023). In addition, Retinex-based low-light image enhancement is also being widely applied (Meylan and Susstrunk, 2006; Fu et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2022b). However, most of the above studies use existing test sets or landscape maps for testing, while the ones on slope image information enhancement are relatively lacking, making it difficult to solve practical problems.
In sum, although numerous researchers have made considerable contributions to the identification of landslide areas on slopes, there is still a paucity of research on the automatic identification of such areas in coastal slopes under complex weather conditions. Therefore, in this paper, a new algorithm is proposed to address the shortcomings of the image information enhancement techniques for actual coastal slopes. The algorithm utilizes the HSV color model and operates hierarchically to achieve the denoising of rain, fog and sunlight in the image. By comparing with other algorithms, it is found that the improved image information enhancement algorithm has a better effect of de-fogging and suppressing excessive waterfall light. Secondly, this paper proposes a two-dimensional segmentation technique for landslide images based on combined K-means clustering with global threshold segmentation, which can segment tiny image regions and provide good boundary conditions and segmentation results to recognize the deformed areas of coastal slopes with high accuracy. The final fusion of image enhancement algorithm and coastal slope landslide area identification method extends the time dimension of monitoring and eliminates the influence of sunlight refraction and rainy and foggy weather on slope monitoring.
2 Automatic identification method
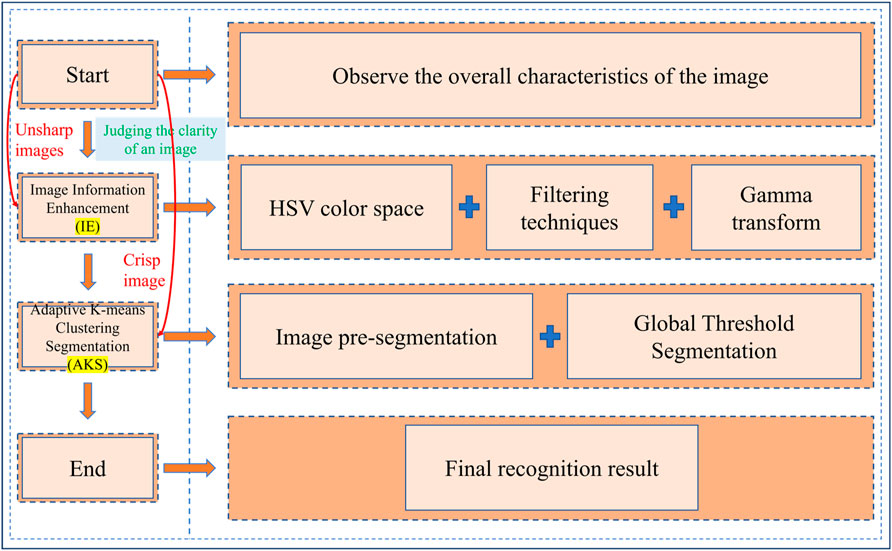
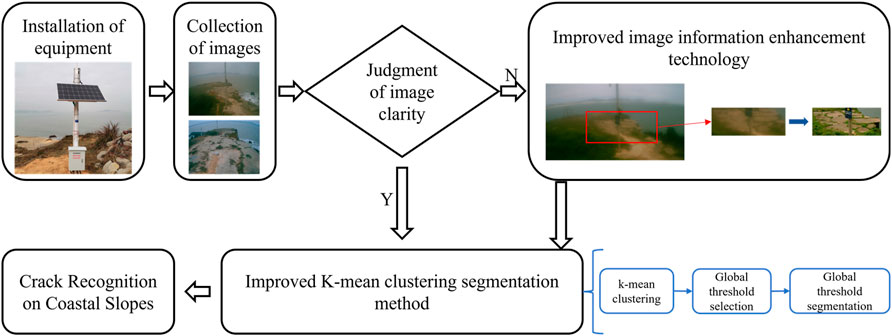
The method of this study is shown in Figure 1. Firstly, the overall characteristics of the collected images are judged. Secondly, the clarity of the images is judged, and the images with lower clarity are segmented using two-dimensional image segmentation algorithm after adopting im-proved information enhancement techniques; for images with higher clarity, they are segmented directly using K-mean clustering algorithm. After segmentation, the image should be denoised to get the final recognition result.
2.1 Image clipping
The saved image data always contains some irrelevant background areas, which causes information confusion and reduces the efficiency and accuracy of image processing. We need to crop the original image and retain the area to be processed.
2.2 Image information enhancement
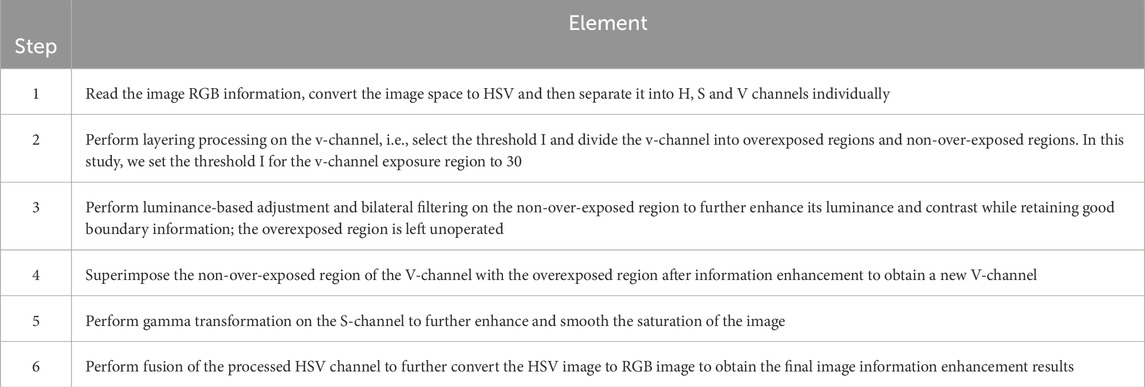
The image samples of field slopes present more complex information, such as rain, fog, and direct sunlight, which can make the RGB information of the image unclear and unable to accurately identify the landslide area. Therefore, it is necessary to use image information enhancement techniques to ensure that the identified image has clear and complete color information. Methods such as the HSV color model, filtering processing, and Gamma transformation are mostly simple and effective and can be used to enhance key image feature information and improve image analysis efficiency. We have selected some common methods and made combinations and improvements to them to find a suitable method for image information enhancement.
2.3 Image segmentation technology
Image segmentation is a key technology in computer vision, involving dividing an image into multiple regions or objects. Segmentation methods based on thresholding, edges, regions, and clustering are mostly simple and effective and can be used to obtain key image feature information and improve image analysis efficiency. We have chosen the above four image segmentation methods to identify a small number of different coastal slope landslide images to find a suitable segmentation method for the landslide area. After the selection of the image segmentation method is completed, it is usually necessary to improve different methods, such as the fusion of threshold and clustering segmentation methods, to achieve automatic identification of images.
2.4 Optimization
The initial recognition image usually contains a considerable amount of noise and features that are not connected to other areas, so we should remove the noise. In addition, if there is a considerable amount of noise near the target boundary and at the connected target boundary in the initial recognition result image, we need to perform morphological operations on the image to eliminate the impact of noise.
3 Method application
3.1 Research data
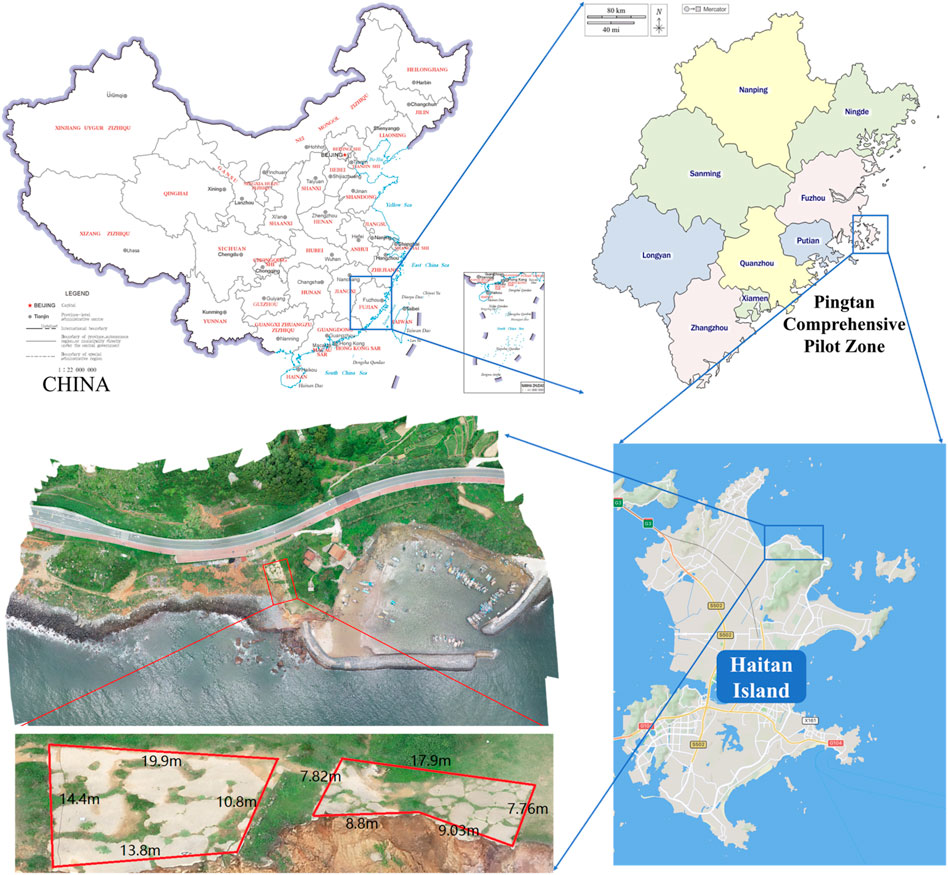
The area studied in this paper is located within the Pingtan Comprehensive Pilot Zone (Deng et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2023; Su et al., 2021; Deng et al., 2022), Fujian Province (Figure 2).
Pingtan Island is located between 25°15′and 25°45′north latitude and 119°32′and 120°10′east longitude. The area is mainly composed of marine plains. There are 126 islands and 702 rocky reefs in Pingtan Comprehensive Pilot Zone, with a winding coastline. The annual precipitation is 1,196.2 mm and the average annual temperature is 19.5°C. Pingtan Island is located on the northwest side of the Taiwan Strait, bordering the Pacific Ocean, and is one of the most frequent areas in China for typhoon coastal slopes. With steep mountain ranges and the development of sea-eroded terraces in the area, the coastal side slopes are subjected to seawater intrusion all year round. This has led to various types of natural disasters, resulting in serious impacts on the production and life of the people in the region. An image monitoring system has been set up in the study area, and the monitoring is a long-term unattended automated dynamic monitoring, capturing photographs at regular intervals.
As shown in Figure 3, we first set up an automatic monitoring system at the experimental site, using a pre-programmed RGB high-definition camera to capture images every 10 mins from 9:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m. under various weather conditions, including sunny, cloudy, and rainy days. The camera was installed at a fixed height of approximately 15 m and positioned at a 45-degree angle. The proposed method was then applied to process the actual images of the Pingtan coastal slope.
3.2 Image data preprocessing
In the image monitoring platform, we found that when the time is between 9:00 and 19:00, sunlight is more abundant, which can meet the requirements of two-dimensional monitoring. Even if the area under study is affected by rainy and foggy weather, it is still possible to meet the monitoring requirements through the existing light conditions and the improved image information enhancement technique proposed above.
As shown in Figure 4, the information in the original monitoring image includes ocean, grass, sky and slope information, while the area we want to recognize only includes the slope information in the image. The irrelevant background increases the difficulty of recognition and makes the recognition information more complicated. Therefore, the interference of irrelevant information needs to be removed. After comparative analysis (time, accuracy, ease of operation and characteristic information of the slope monitoring image), we found that the physical coordinates of the area where the cracks are generated in the slope do not change much, so we can use the way of setting up the mask to remove the interference of irrelevant background, so as to make the recognition information more specific.
3.3 Multi-indicator image clarity discrimination methods
3.3.1 Brenner gradient function
The Brenner gradient function is a simple gradient evaluation function that evaluates image sharpness by calculating the square of the difference between the gray levels of two adjacent pixels. This method is simple and easy to use, but it has some limitations.
where,
The Brenner gradient function computes the squared differences in intensity between a pixel and its neighbors in both horizontal and vertical directions. By squaring the differences and summing them up, the function amplifies large intensity changes and suppresses small ones. This amplification of intensity changes enhances the detection of edges.
3.3.2 Tenengrad gradient function
The Tenengrad gradient function is a method used to evaluate image sharpness, which uses the Sobel operator to extract the gradient values in the horizontal and vertical directions respectively. This method is able to assess image sharpness more accurately, but the amount of computation is also relatively large.
where
Here,
The Tenengrad gradient function relies on the gradient information of the image. For sharp images, the gradient values in edge regions are typically large, resulting in a higher Tenengrad gradient value. Conversely, blurry images have smaller gradient values in edge regions, leading to a lower Tenengrad gradient value. Thus, computing the Tenengrad gradient function allows for the assessment of image sharpness, with larger values indicating sharper images.
We use two evaluation metrics to assess the clarity of the read images. Based on the existing images with high clarity, we judge the thresholds
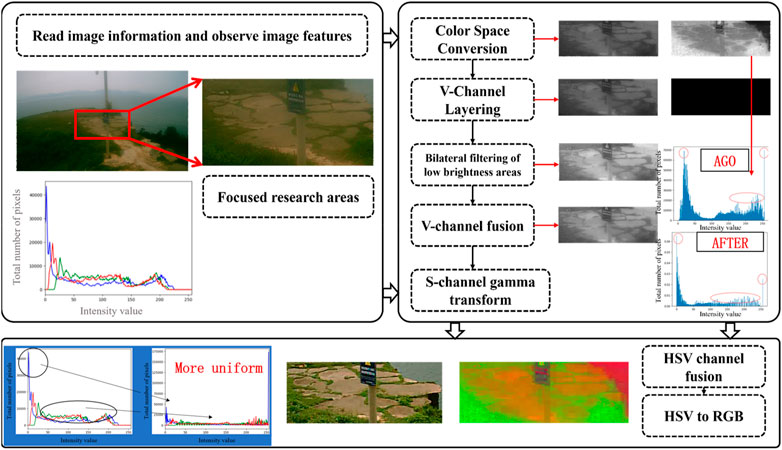
3.4 Image information enhancement based on HSV color space
In this section, we have used HSV color model and bilateral filtering with gamma transform to process the images in different haze cases. This is because:
(1) The colors in the RGB color space are mixed by the three base colors of red, green and blue. Although it can express rich color information, it is not intuitive enough for the expression of image brightness information. The HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value) color model is a way of representing colors based on how humans perceive them. It decomposes colors into three components:
1) Hue: Represents the type of color, indicating its position on the color wheel. Hue is typically represented as an angle ranging from 0° to 360°, starting from red, passing through yellow, green, cyan, blue, magenta, and looping back to red. Hue determines the basic category of the color.
2) Saturation: Describes the purity or intensity of a color. Saturation measures the amount of gray in a color. Higher saturation values result in more vivid colors, closer to pure colors, while lower saturation values produce desaturated or pastel colors. A saturation of 0 results in a grayscale color, containing only brightness information.
3) Value: Represents the brightness or lightness of a color. Value measures the brightness of the color. Higher values result in brighter colors, while lower values lead to darker colors. A value of 0 corresponds to black, and maximum value corresponds to white.
The HSV color model provides a more intuitive way to describe colors, making color adjustments easier and more consistent with human perception. By manipulating these three components—hue, saturation, and value—one can generate a wide range of colors and achieve easier color selection, editing, and matching.
(2) Filtering techniques are constantly evolving with the aim of separating information at different scales in an image more accurately. Bilateral filtering is a nonlinear spatial filtering method that takes into account the Euclidean distance and the difference between the values of the output pixel and other pixels in the neighborhood when determining the filter coefficients (Nabahat et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2022; Niu and Wang, 2022; Rajyalakshmi et al., 2022; Lv et al., 2022). This means that it considers the difference between the spatial domain and the value domain at the same time. On the other hand, methods that only consider the spatial domain (e.g., Wiener filtering and Gaussian filtering) are not very effective in protecting the edge information; methods that only consider the value domain blur the whole image and do not effectively protect the detail information. The bilateral filter integrates the spatial domain and the value domain to influence the filtering, and can keep the edge clear in noise reduction and smoothing, which is an excellent edge preserving filter.
(3) Gamma transform (Qi et al., 2022; Tang et al., 2022; Wang W. et al., 2021) is mainly used to correct images with too much or too little gray and enhance their contrast. It achieves the correction effect by enhancing the details in low or high gray areas. For images that are overexposed resulting in high overall brightness and low contrast, image information enhancement is particularly effective using Gamma transform.
The flow of the image information enhancement technique developed in this paper is shown in Figure 5, and the specific steps are detailed in Table 1.
After the image quality enhancement, the clarity of the image is further improved, and the influence of rainy and foggy weather on image monitoring is eliminated.
3.5 Adaptive K-means clustering segmentation
In this subsection, we propose an automatic identification method of two-dimensional slope instability region combining K-means clustering and global threshold segmentation algorithm. The core idea of the K-means clustering image segmentation method is to group the pixels of the image using the K-means clustering algorithm, so that pixels with similar features are grouped together, while pixels with different features are grouped into different groups. During initialization, the algorithm randomly selects K pixels as cluster centers. Then, the algorithm traverses each pixel in the image, calculates their distances to each cluster center, and assigns each pixel to the group where the closest cluster center is located. After grouping the pixels, the algorithm recalculates the center of each cluster, which is the average of the features of all pixels in that cluster. Then, the algorithm repeats the steps of pixel assignment and cluster center update until the cluster centers no longer change or the preset number of iterations is reached. Through this method, the image is segmented into K regions, with pixels in each region having similar features. This segmentation helps extract target objects from the image or simplify the image content, facilitating subsequent image processing and analysis.
After determining the recognition location, we use K-mean clustering to pre-segment the image, and test it by setting different K values to select the optimal solution. When K=2, due to the mask setting, the slope area and the mask area are distinguished into two classes, and the landslide information cannot be reflected in the slope area; when K=8, K=16, K=64, due to the high number of set clusters, the slope area is over-divided, which results in the variability of the threshold setting in later data processing, and the continuity of the process cannot be guaranteed; when K=4, the mask area, the landslide area, non-landslide area and other information are accurately distinguished into four categories, which makes later data processing easier. Therefore, in this paper, K=4 is the optimal setting value.
Global threshold segmentation (Liu et al., 2022) is the use of a threshold value to segment the entire image into two regions: the target object and the background object. The threshold is usually a constant value that can be determined from global information. In this subsection, we observe the grayscale histograms of the pre-segmented image at different moments. Since the K value is chosen as 4, the grayscale values in the grayscale histogram of the pre-segmented image contain only four pieces of information, in which the grayscale value of the landslide region is higher than the other three types of information. So, in this subsection, the global threshold value is chosen as 100, which can separate the landslide region from the other regions (Figure 6).
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Image information enhancement results and discussion
4.1.1 Image information enhancement results
We apply the improved image enhancement technique to the fuzzy monitoring images in different time periods and get the results as in Figure 7.
4.1.2 Objective evaluation
Subjective evaluation is easily affected by external factors. In order to objectively verify the merits of the algorithm, two image quality evaluation metrics are introduced in this section for judgment (Zhao et al., 2017).
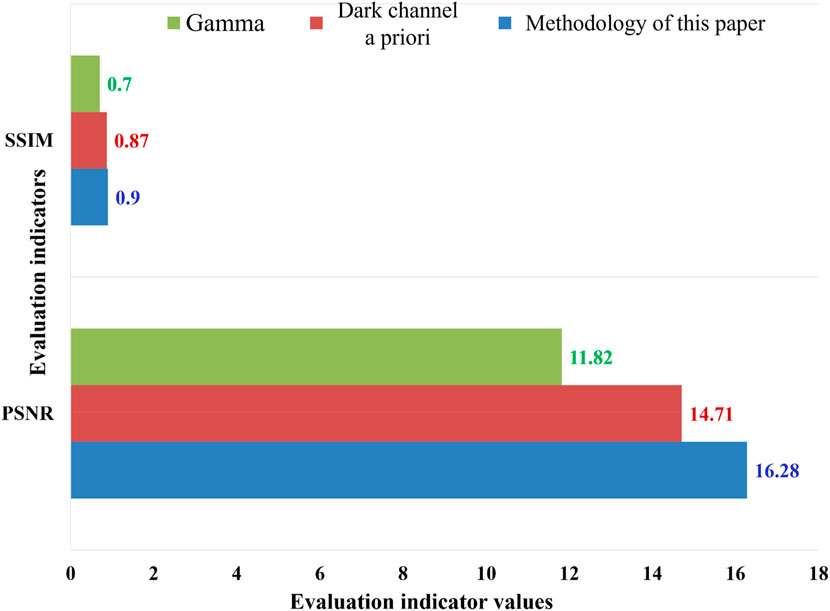
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) is a commonly used metric to measure the degree of image variations; the larger the PSNR value, the lesser the image variations, the lesser the distortion, and the better the image quality. Structural similarity (SSIM) is used to evaluate the quality by comparing the differences between images before and after processing. It calculates the product of image contrast, structural information and brightness as a comprehensive evaluation criterion; the higher the SSIM value, the better the processing effect.
As can be seen from Figure 8, the peak signal-to-noise ratio of this paper’s algorithm is 16.28, and the structural similarity is 0.90, which is significantly better than other algorithms. The objective evaluation index proves the superiority of this paper’s image information enhancement technology and its adaptability to the actual situation of coastal slopes.
4.2 Image segmentation results and discussion
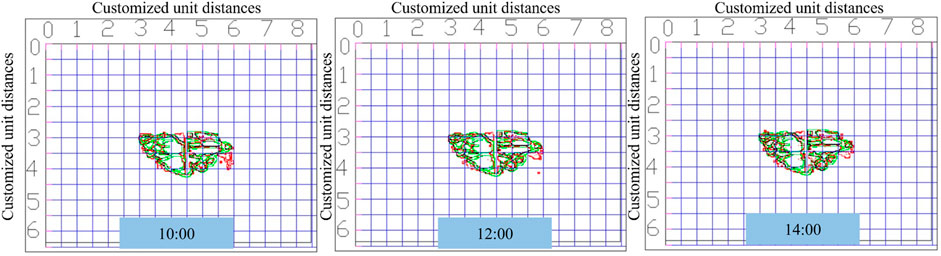
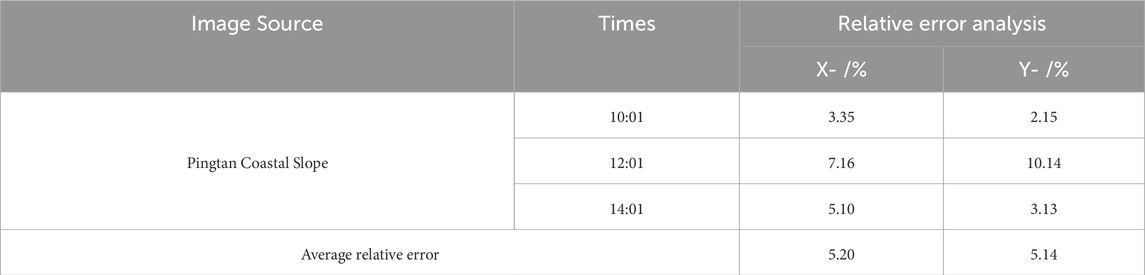
In this subsection, as shown in Figure 9, we manually draw three actual damage maps of landslide areas at different time periods and compare them with the contours recognized by this paper’s method (IC-IE-AKS-O) to get the damage contour area comparison effect map. We import the contour comparison map into CAD, and use CAD to draw the point coordinates of different contours. The damaged area contour follows the principle of “x coordinate is the same y is different” or “x coordinate is different y is the same” to randomly select the coordinate points on the contour map, extract the corresponding coordinate points on the contour and carry out the relative error calculation. The error calculation formula is contained in Equations (6) and (7) (Yuan et al., 2023). The results of the error calculation are shown in Table 2.
Here,
As shown in Table 2, the relative error in the X and Y directions using the IC-IE-AKS-O method is 5.20% and 5.14%, respectively. These values fall within the acceptable range for automatic landslide detection and represent a significant improvement over conventional image segmentation techniques commonly employed in coastal slope monitoring. Traditional methods, such as K-means clustering and basic thresholding, often struggle to cope with the complex environmental challenges of coastal regions, especially in adverse weather conditions. By integrating advanced image enhancement techniques and employing a multi-stage segmentation process, our method consistently delivers higher accuracy, even when the original images are affected by fog or sunlight refraction. Additionally, our method excels in segmenting small regions with high precision, distinguishing it from other approaches that tend to over-segment or under-segment images based on the chosen number of clusters.
Future research will aim to further refine the algorithm to reduce segmentation errors, particularly in cases where the slope surface is composed of heterogeneous materials or when rapid changes in weather conditions occur during monitoring. Furthermore, we plan to explore additional optimizations to enhance computational efficiency, enabling real-time application in dynamic monitoring systems.
4.3 The role of image information enhancement
In the actual slope image segmentation, due to the influence of variable weather conditions at the site, under the fixed time selection, i.e., 9:00–19:00, the performance of the slope monitoring image information is not obvious in some time periods, and the landslide deformation areas cannot be accurately recognized even with the K-mean clustering algorithm. Using image information enhancement technology, the slope monitoring image information within these time periods can be significantly enhanced, and by combining it with the improved K-mean clustering segmentation party, the time range of landslide monitoring is expanded, the basic data of landslide monitoring is enriched, and the recognition accuracy of landslide areas is improved, which makes the program run steadily under the time series.
4.4 Analysis of the factors influencing errors
From the error analysis results of the method in this paper, it can be seen that there are still minor errors in the identification method. One of the factors contributing to the errors in this approach is the variability in environmental conditions, including changes in sunlight, fog, and rain, which may affect the image clarity and segmentation accuracy. Additionally, the removal of irrelevant background information might not always be perfect, leading to small inconsistencies in the segmented regions. In terms of image resolution, slight differences between monitoring intervals can also introduce segmentation errors, particularly in areas with fine details.
To mitigate these errors, several steps have been taken. First, the multi-indicator image clarity discrimination methods (e.g., Brenner gradient function, Tenengrad gradient function) ensure that only images meeting a specific clarity threshold are processed. Additionally, the use of the HSV color space for image enhancement, combined with bilateral filtering and gamma correction, helps to reduce the impact of varying lighting conditions on the segmentation results. Furthermore, the combination of K-means clustering with global threshold segmentation provides robust boundaries, reducing segmentation errors in landslide regions with complex contours. These measures have helped keep the relative error within a relatively low range (∼5%).
5 Conclusion
In this paper, we proposed a complete set of landslide deformation area identification methods (IC-IE-AKS-O) for a coastal slope. First, a new algorithm was proposed according to the deficiencies of the current image enhancement technology. Through experimental comparison, it was found that the improved algorithm has better visual de-fogging effect and has practical application value. Secondly, a landslide image segmentation technique based on combined K-means clustering with global thresh-old segmentation was proposed. It is hereby summarized that: the fusion of image information enhancement technology and image segmentation technology expands the time range of field slope monitoring, which makes the recognition under the influence of rain, fog and sunshine have higher accuracy and robustness compared with the simple image segmentation method; the preprocessing of the image can effectively provide convenience for the pre-segmentation of the image in the later stage, while the original image cannot be well recognized due to the redundancy of information; the image segmentation method based on the K-mean clustering can be more effective for the smallest landslides. The image segmentation method based on K-mean clustering can segment tiny image regions and can provide good boundary conditions and segmentation results. The relative error calculation results show that the method proposed in this paper has low relative errors in the X and Y directions, which are 5.20% and 5.14%, respectively, and can recognize the deformation regions of micro-fractured coastal slopes with high accuracy.
In the future, we plan to extend the application of the IC-IE-AKS-O method to a broader range of geographic areas, encompassing both coastal and inland slopes with diverse geological conditions. To improve the method’s adaptability, we will fine-tune it for regions with varying soil compositions, vegetation coverage, and climatic conditions. For instance, inland slopes may experience distinct weather patterns, such as frost or drought, which could impact the effectiveness of the image enhancement and segmentation algorithms. We anticipate that, with adjustments to the HSV color space parameters and clustering techniques, the proposed model will achieve similar performance in other environments.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
PL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Writing–original draft. WL: Methodology, Writing–original draft. DL: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. CC: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. TF: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. RG: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. AD: Writing–review and editing. MH: Writing–review and editing. ZL: Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported jointly by the National Key Research and Development Plan (2022YFC3800801), Fundamental Research Fund “Construction of the Key Laboratory of Coastal Science and Inte grated Management” (Nos: 2022L08, 2021L08); Science and Technology Service Network Initiative (2022T3051); Ministry of Natural Resources Operational Special Project (Nos: GW0422002, GW0122004, TZ0122001); the Innovation Group Project of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai) (No: SML2023SP222); Research Project on Representative Islands Platform for Resources, Ecology, and Sustainable Development (No: 102121221620000009001), and the China Oceanic Development Foundation Project (No: Z.220109).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the handling editor and reviewers whose valuable and constructive comments greatly improved this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors PL and WL were employed by Zhuhai Da Hengqin Co., Ltd. Author PL was employed by Zhuhai Da Hengqin City Investment Construction Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aksoy, B., and Ercanoglu, M. (2012). Landslide identification and classification by object-based image analysis and fuzzy logic: an example from the azdavay region (kastamonu, Turkey). Comput. and Geosciences 38, 87–98. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2011.05.010
Ardizzone, F., Cardinali, M., Galli, M., Guzzetti, F., and Reichenbach, P. (2007). Identification and mapping of recent rainfall-induced landslides using elevation data collected by airborne lidar. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 7, 637–650. doi:10.5194/nhess-7-637-2007
Bednarczyk, Z. (2018). Identification of flysch landslide triggers using conventional and ‘nearly real-time’ monitoring methods - an example from the carpathian mountains, Poland. Eng. Geol. 244, 41–56. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.012
Cheng, G., Guo, L., Zhao, T., Han, J., Li, H., and Fang, J. (2013). Automatic landslide detection from remote-sensing imagery using a scene classification method based on BoVW and pLSA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 34, 45–59. doi:10.1080/01431161.2012.705443
Deng, Y., Čuka, A., Fu, Y., and Wu, J. (2023). Multiple paths towards eco islands and blue development: conference report. Mar. Policy 149, 105526. doi:10.1016/j.marpol.2023.105526
Deng, Y., Randallb, J., and Ye, F. (2022). Island ecological restoration and management practices based on nature: conference report. Mar. Policy 143, 105188. doi:10.1016/j.marpol.2022.105188
Fu, Q., Jung, C., and Xu, K. (2018). Retinex-based perceptual contrast enhancement in images using luminance adaptation. IEEE Access 6, 61277–61286. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2870638
Fu, X., and Cao, X. (2020). Underwater image enhancement with global-local networks and compressed-histogram equalization. Signal Process. Image Commun. 86, 115892. doi:10.1016/j.image.2020.115892
Fu, X., Wang, W., Huang, Y., Ding, X., and Paisley, J. (2021). Deep multiscale detail networks for multiband spectral image sharpening. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32, 2090–2104. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2996498
Gao, J., An, T., Zhang, H., Zhang, K., Shen, J., He, G., et al. (2023). The evaluation method of the marine spatial suitability for islands from the perspective of sustainable development: a case study of the pingtan islands. Sustainability 15, 8996. doi:10.3390/su15118996
Hashiba, H., and Sonobe, M. (2020). Extraction of scattered small-scale landslides distribution by object-based classification using optical high-resolution satellite images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 1213–1218. doi:10.5194/isprs-archives-XLIII-B3-2020-1213-2020
Iqbal, M., Ali, S. S., Riaz, M. M., Ghafoor, A., and Ahmad, A. (2020). Color and white balancing in low-light image enhancement. Optik 209, 164260. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164260
Ju, L.-Y., Xiao, T., He, J., Wang, H.-J., and Zhang, L.-M. (2022). Predicting landslide runout paths using terrain matching-targeted machine learning. Eng. Geol. 311, 106902. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106902
Ju, L.-Y., Zhang, L.-M., and Xiao, T. (2023). Power laws for accurate determination of landslide volume based on high-resolution LiDAR data. Eng. Geol. 312, 106935. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106935
Kurtz, C., Stumpf, A., Malet, J.-P., Gançarski, P., Puissant, A., and Passat, N. (2014). Hierarchical extraction of landslides from multiresolution remotely sensed optical images. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 87, 122–136. doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.11.003
Lan, H., Tian, N., Li, L., Wu, Y., Macciotta, R., and Clague, J. J. (2022). Kinematic-based landslide risk management for the sichuan-tibet grid interconnection Project (STGIP) in China. Eng. Geol. 308, 106823. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106823
Liu, C., Shu, X., Pan, L., Shi, J., and Han, B. (2023). Multiscale underwater image enhancement in RGB and HSV color spaces. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 72, 1–14. doi:10.1109/TIM.2023.3298395
Liu, Q., Li, N., Jia, H., Qi, Q., and Abualigah, L. (2022). Modified remora optimization algorithm for global optimization and multilevel thresholding image segmentation. Mathematics 10, 1014. doi:10.3390/math10071014
Liu, W., Hou, X., Duan, J., and Qiu, G. (2020). End-to-End single image fog removal using enhanced cycle consistent adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process 29, 7819–7833. doi:10.1109/TIP.2020.3007844
Liu, Z., Yin, H., Mi, Y., Pu, M., and Wang, S. (2021). Shadow removal by a lightness-guided network with training on unpaired data. IEEE Trans. Image Process 30, 1853–1865. doi:10.1109/TIP.2020.3048677
Lv, H., Shan, P., Shi, H., and Zhao, L. (2022). An adaptive bilateral filtering method based on improved convolution kernel used for infrared image enhancement. SIViP 16, 2231–2237. doi:10.1007/s11760-022-02188-1
Meylan, L., and Susstrunk, S. (2006). High dynamic range image rendering with a retinex-based adaptive filter. IEEE Trans. Image Process 15, 2820–2830. doi:10.1109/TIP.2006.877312
Mondini, A. C., Guzzetti, F., Reichenbach, P., Rossi, M., Cardinali, M., and Ardizzone, F. (2011). Semi-automatic recognition and mapping of rainfall induced shallow landslides using optical satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 115, 1743–1757. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2011.03.006
Mwaniki, M. W., Kuria, D. N., Boitt, M. K., and Ngigi, T. G. (2017). Image enhancements of landsat 8 (OLI) and SAR data for preliminary landslide identification and mapping applied to the central region of Kenya. Geomorphology 282, 162–175. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.01.015
Nabahat, M., Modarres Khiyabani, F., and Jafari Navmipour, N. (2022). Optimization of bilateral filter parameters using a whale optimization algorithm. Res. Math. 9, 2140863. doi:10.1080/27684830.2022.2140863
Niu, D., and Wang, J. (2022). Elevator car vibration signal denoising method based on CEEMD and bilateral filtering. Sensors 22, 6602. doi:10.3390/s22176602
Ooi, C., and Mat Isa, N. (2010). Adaptive contrast enhancement methods with brightness preserving. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron 56, 2543–2551. doi:10.1109/TCE.2010.5681139
Paul, A., Sutradhar, T., Bhattacharya, P., and Maity, S. P. (2021). Infrared images enhancement using fuzzy dissimilarity histogram equalization. Optik 247, 167887. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167887
Qi, M., Cui, S., Chang, X., Xu, Y., Meng, H., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Multi-region nonuniform brightness correction algorithm based on L-channel gamma transform. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2022/2675950
Rahardjo, H., Nio, A. S., Harnas, F. R., and Leong, E. C. (2014). Comprehensive instrumentation for real time monitoring of flux boundary conditions in slope. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 9, 23–43. doi:10.1016/j.proeps.2014.06.015
Rajyalakshmi, C., Rao, K. R. M., and Rao, R. R. (2022). Compressed high resolution satellite image processing to detect water bodies with combined bilateral filtering and threshold techniques. TS 39, 669–675. doi:10.18280/ts.390230
Su, M. M., Wall, G., Wu, B., Xu, H., Fu, X., and Deng, Y. (2021). Tourism place making through the bioluminescent “blue tears” of pingtan islands, China. Mar. Policy 133, 104744. doi:10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104744
Tang, J. R., and Mat Isa, N. A. (2014). Adaptive image enhancement based on Bi-histogram equalization with a clipping limit. Comput. and Electr. Eng. 40, 86–103. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2014.05.017
Tang, X., Wang, X., Hou, J., Wu, H., and He, P. (2022). Research on improved gamma transform face image preprocessing fusion algorithm under complex lighting conditions. RACSC 15, e220322186189. doi:10.2174/2666255813999200922142705
Wang, H., Zhang, L., Yin, K., Luo, H., and Li, J. (2021a). Landslide identification using machine learning. Geosci. Front. 12, 351–364. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2020.02.012
Wang, W., Yuan, X., Chen, Z., Wu, X., and Gao, Z. (2021b). Weak-light image enhancement method based on adaptive local gamma transform and color compensation. J. Sensors 2021, 1–18. doi:10.1155/2021/5563698
Wang, Y., Chen, J., Han, Y., and Miao, D. (2022b). Combining attention mechanism and Retinex model to enhance low-light images. Comput. and Graph. 104, 95–105. doi:10.1016/j.cag.2022.04.002
Wang, Y., Dong, J., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Deng, S., Zhang, G., et al. (2022a). Refined InSAR tropospheric delay correction for wide-area landslide identification and monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 275, 113013. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2022.113013
Wu, L., Fang, L., Yue, J., Zhang, B., Ghamisi, P., and He, M. (2022). Deep bilateral filtering network for point-supervised semantic segmentation in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Image Process 31, 7419–7434. doi:10.1109/TIP.2022.3222904
Xie, T., Huang, J., Shi, Q., Wang, Q., and Yuan, N. (2019). PSDSD-A superpixel generating method based on pixel saliency difference and spatial distance for SAR images. Sensors 19, 304. doi:10.3390/s19020304
Yang, Y., Song, S., Yue, F., He, W., Shao, W., Zhao, K., et al. (2019). Superpixel-based automatic image recognition for landslide deformation areas. Eng. Geol. 259, 105166. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105166
Yuan, C., Li, Q., Nie, W., and Ye, C. (2023). A depth information-based method to enhance rainfall-induced landslide deformation area identification. Measurement 219, 113288. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2023.113288
Zhao, L., Dai, W., Soman, S., Hackney, D. B., Wong, E. T., Robson, P. M., et al. (2017). Using anatomic magnetic resonance image information to enhance visualization and interpretation of functional images: a comparison of methods applied to clinical arterial spin labeling images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36, 487–496. doi:10.1109/TMI.2016.2615567
Keywords: landslide, image information enhancement, k-means, hsv, average relative error
Citation: Li P, Li W, Liu D, Chen C, Fan T, Gu R, Damar A, Htet MH and Lin Z (2024) IC-IE-AKS-O: an automatic recognition method for coastal slope landslide areas. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1485086. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1485086
Received: 23 August 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 07 October 2024.
Edited by:
Wen Nie, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Chao Cao, Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, ChinaLong Jiang, Hohai University, China
Copyright © 2024 Li, Li, Liu, Chen, Fan, Gu, Damar, Htet and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dahai Liu, ZGFoYWlAcnVjLmVkdS5jbg==, bGl1ZGFoYWlAZmlvLm9yZy5jbg==; Chun Chen, NTY4Njc2MzIyQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Peng Li1,2
Peng Li1,2 Dahai Liu
Dahai Liu Chun Chen
Chun Chen Tianhui Fan
Tianhui Fan Renguo Gu
Renguo Gu