- 1Tianjin Center, China Geological Survey, Tianjin, China
- 2School of Earth Science and Resources, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China
- 3Southern African Mining Research Institute, China Geological Survey, Tianjin, China
- 4Geological Survey Department of Zambia, Lusaka, Zambia
- 5Tianjin Institute of Geological Survey, Tianjin, China
The country's national scale geochemical mapping can provide crucial geochemical support for Zambia's foundational geology, agricultural productivity, environmental conservation, mineral exploitation, and other domains. This study aims to determine the overall abundance and regional distribution of B and Se in Zambian stream sediments, as well as their impact on the environment and on the agricultural output. The median concentrations of B and Se are 12.74 and 0.056 μg/g, respectively. While the concentration of Se was more noticeable, the distribution patterns of B concentration seemed to be more consistent and lacked distinct indicators for agricultural output. It also offers more robust recommendations for future land planning and agricultural growth. In comparison to other tectonic belts, the Domes Region, Lufilian Arc and Choma-Kalomo Block have greater median and average concentrations of Se. Black shales and vast epithermal metallogenic zones are common in the Kawana-Solwezi-Ndola and the Mansa-Mporokoso- Kasama regions, which also have high Se contents. These regions could serve as promising places for the advancement of selenium-enriched agricultural practices.
1 Introduction
Zambia is a landlocked country in central Africa with significant unrealized potential and highly developed agricultural conditions. As a major player in the agricultural partnership known as the “Belt and Road”, Zambia plays an important role. The country has 43.2 million hectares of arable land, which constitutes approximately 58% of the total land area. Zambia covers a substantial land area of 39 million hectares within medium to high-yield food-producting zones. According to studies, there is a significant amount of untapped potential for the development and utilization of arable land, as only 15% of Zambia’s arable land is farmed (Zambia Agri Market Update, 2023). For Zambian agriculture to advance, it is essential to comprehend the quality of arable land and offer scientific guidance on how to improve it. Sediments make up a large portion of the surface or higher layers of the continental crust, and in addition to geochemical research, their chemical elemental characteristics can be used for agricultural and environmental objectives (Papadopoulou Vrynioti et al., 2014; Li et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2014; Castillo et al., 2021; Liu and Lu, 2023; Mao et al., 2023). Many geochemical mapping initiatives have been carried out all around the world in the last 60 years (Xie and Ren, 1993; Cheng et al., 1997; Licht, 2005; Ottesen et al., 2010; Cohen et al., 2012; Smith et al., 2013; Castillo et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2024). Informed decision-making in land management and evaluation has benefited from the use of geochemical survey data to produce maps that show the spatial distribution of chemical elements. Moreover, it aids in the formulating and establishing an agricultural production layout.
Mineral nutrients B and Se are crucial for the growth and development of plants. Boron is a biologically essential trace element nutrient for plants, enhancing the development of reproductive organs by facilitating the movement of carbohydrates and auxin to flowers and fruits (Rogiers et al., 2006; Hu, 2008; Wang et al., 2014). Selenium is a necessary component of both human and animal proteins that include selenium as well as selenium-dependent antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase GSH-Px. It is regarded as the “spark of life” internationally and is involved in balancing the redox reactions in the body (Fordyce et al., 2010; Roman et al., 2014). The transfer of B and Se through metabolic processes makes the amount of B and Se in soil the primary factor influencing its concentration in food, vegetables, feed, and drinking water, which in turn affects human health. Additionally, this transfer method serves as the primary reservoir for the Earth’s ecosystem’s B and Se cycles (EGAS, 1981; EGAS, 1982; Tan et al., 1982; Tan et al., 2002). Meanwhile, studies has demonstrated a strong correlation between elemental concentrations in soil and stream sediments, as well as the effective concentration and total amount of trace nutrients in the soil (Gao et al., 2006; Yang et al., 2019; Bao et al., 2020; Jiang et al., 2021). In order to produce basic information on Se for local agricultural purposes and to perform an initial evaluation of the distribution of B and Se in various regions, identifying areas of enrichment and deficiency, low-density geochemical data from Zambia, at a scale of 1:1,000,000, were used in conjunction with the demarcation of cultivated lands in this paper.
2 Regional setting
2.1 Geological setting
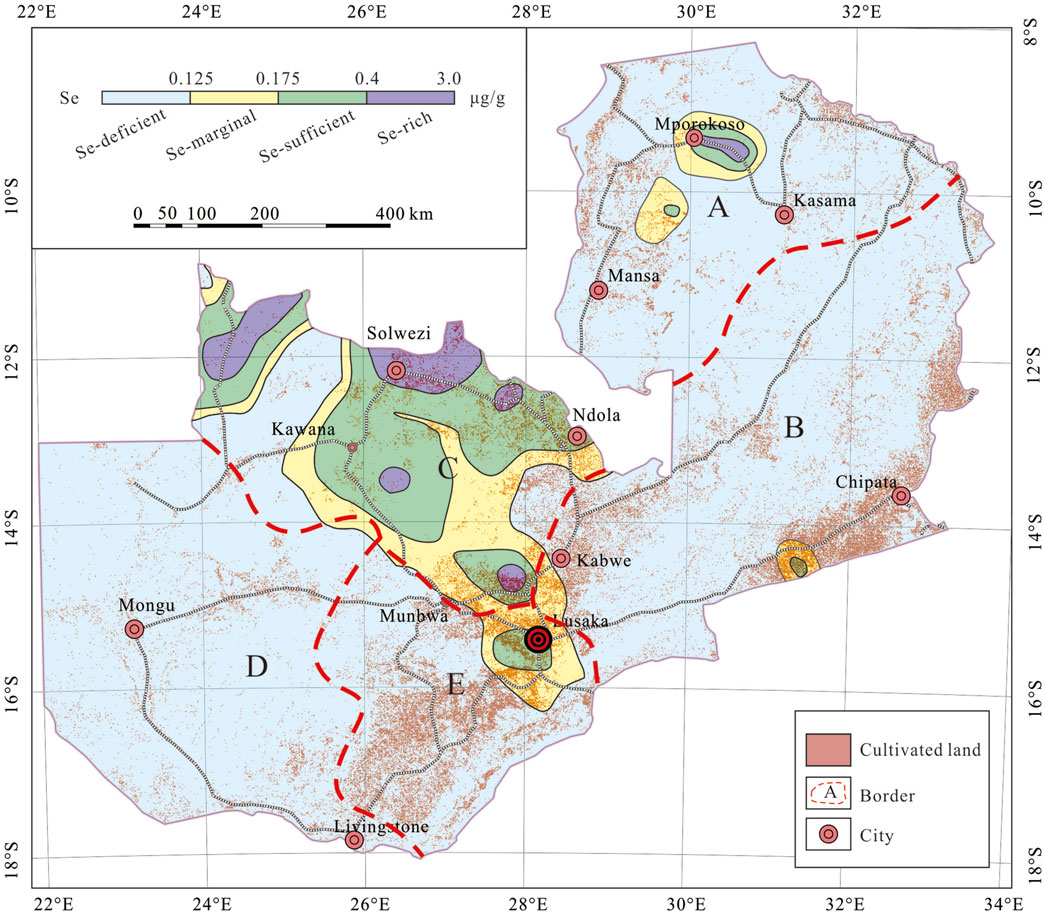
From stable Archaean and early Proterozoic cratons to structurally complicated “mobile belts” and younger cover rocks, Zambia has a broad range of geological terrains (De Waele et al., 2008; Sun et al., 2019a). Zambia’s geological complexity and numerous tectono-thermal events are largely explained by its unique geographic location, sandwiched three major cratons: the massive Kasai Craton to the west, and the Zimbabwe-Kaapvaal (“Kalahari”) and Tanzania cratons to the south and north, respectively (Hanson, 2003; Sanislav et al., 2014). The nation’s geological development has been greatly impacted by the buttressing effects of these stable blocks and intercratonic dislocations (Gabert, 1990; Hanson, 2003; De Waele et al., 2008).
The mainland of Zambia is geologically divided into ten tectonic units (Figure 1): the Kibaran Belt, the Bangweulu Block, the Irumide Belt, the Karoo Graben, the Lufilian Arc Belt, the Domes Region, the Hook Granite Complex, the Zambezi Belt, the Choma-Kalomo Block and the Kalahari Desert (De Waele et al., 2006a).
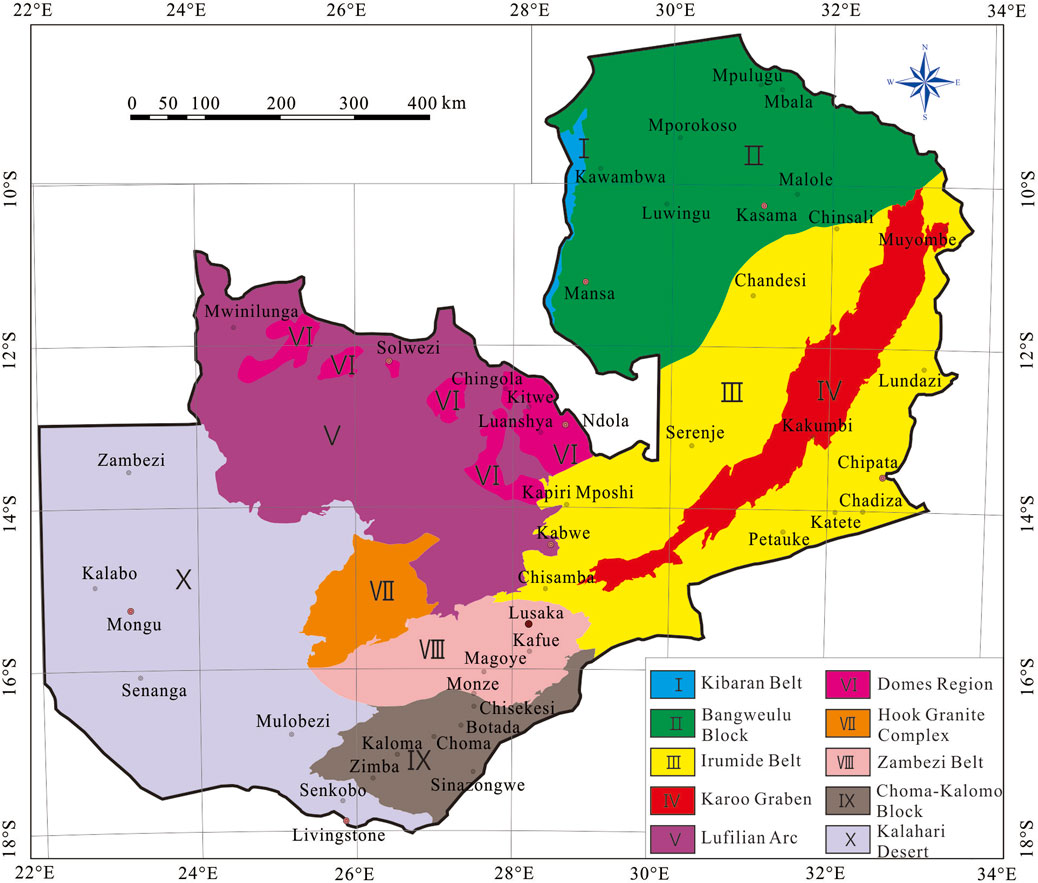
Figure 1. Simplified tectonic map of Zambia (after De Waele et al., 2006a).
The Kibaran belt is a belt of Mesoproterozoic supracrustal units that stretches northeast over about 1,300 km. It is primarily composed of metasedimentary rocks with minor metavolcanic rocks, interspersed with large S-type granitoid massifs and subordinate mafic bodies that are also Mesoproterozoic in age (Kokonyangi et al., 2006; Buchwaldt et al., 2008; Villeneuve et al., 2019). The Bangweulu Block is a crystalline basement composed of schist belts, intruded by metavolcanic rocks and coeval granitoids, and is unconformably overlain by a thick sequence of fluvial, aeolian and lacustrine sediments (Andersen and Unrug, 1984; De Waele et al., 2006a; De Waele et al., 2006b; Sun et al., 2019a; Sun et al., 2021). The Irumide Belt stretches from the center of Zambia to the borders of Tanzania, Malawi, and Zambia in the northeast. It includes deformed basement units and metasedimentary successions, strongly metamorphosed to amphibolite facies, but also well-preserved Palaeoproterozoic volcanic sequences, the whole being intruded by voluminous high-K granitoids during the late-Mesoproterozoic Irumide orogeny (ca. 1.02 Ga) (Rainaud et al., 2003; Rainaud et al., 2005; De Waele et al., 2006b). The Karoo Graben is a region of Quaternary alluvial gravel strata and Mesozoic–Cenozoic sedimentary rocks that is dispersed along the Luano and Luangwa in the middle of the Irumide Belt. The Lufilian Arc Belt, a zone of Neoproterozoic sedimentary strata of the Katanga Supergroup, stretches from the Zambian Copperbelt to the Congolese Copperbelt in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Rainaud, et al., 2005; Ren et al., 2013; Ren et al., 2017; Sun et al., 2019b). Migmatites, gneisses, and deformed granites are found in the Kabompo, Mwombeshi, Solwezi, Luina, Konkola and Lushwishi Domes in the Domes Region of the Lufilian Arc Belt (De Waele et al., 2006b). The Hook Granite Complex in Pan-African formed during the syncollisional stage between the Kalahari and Congo Cratons. It is composed of the bimodal magmatism (mafic to predominantly felsic) and is characterized by both an alkali-calcic and an alkalic suite, with typical A-type (Milani et al., 2015). A thick metasedimentary succession that is unconformably overlaid or in tectonic contact with late Mesoproterozoic basement gneisses and granites in Southern Zambia makes up the Zambezi Belt, an SSW-to SW-vergent fold-and-thrust complex (Katongo et al., 2004; Naydenov et al., 2014). The Choma-Kalomo Block is a Precambrian terrane with a SW-NE trend that is situated in southeast Zambia, consists of a sequence of high-grade metasedimentary gneisses and schists, intruded by Mesoproterozoic granites and granitic gneisses (Glynn et al., 2017). The Kalahari Desert comprises the continental sequence which is subdivided into the sandstones and quartzites of the Barotse Formation and the unconsolidated sands in Western Zambia. According to Kershaw et al. (1972), the sedimentation processes started in the Tertiary and finished in the Quaternary.
2.2 Cropland condition
Zambia has great overall general temperature conditions and a large variety of crops that are suitable for production (Zambia Agri Market Update, 2023). In Zambia, there are primarily two kinds of crops grown: grain crops, which include sunflower, wheat, maize, sweet potatoes, mixed beans, nuts, rice, and soy beans. The most often planted of them are sweet potatoes, maize, soybeans, and mixed beans; the second category consists of economic crops, including avocado, bananas, blueberries, cashew nuts, grapes, groundnuts, mango, macadamia, oranges, and pecans. The most widely distributed planting ranges are for avocado, mango, bananas, and macadamia (Figure 2).
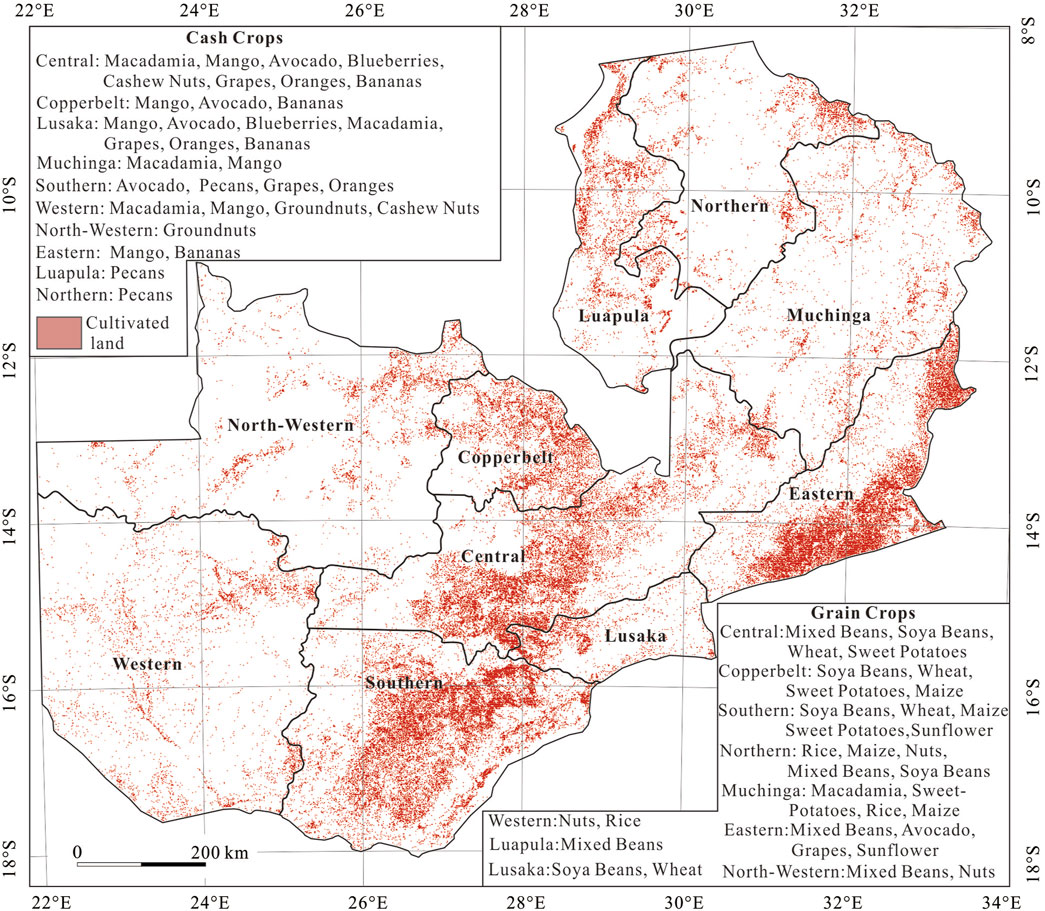
Figure 2. Diversification of crops grown in Zambia (after Zambia Agri Market Update, 2023).
3 Methods
3.1 Sampling
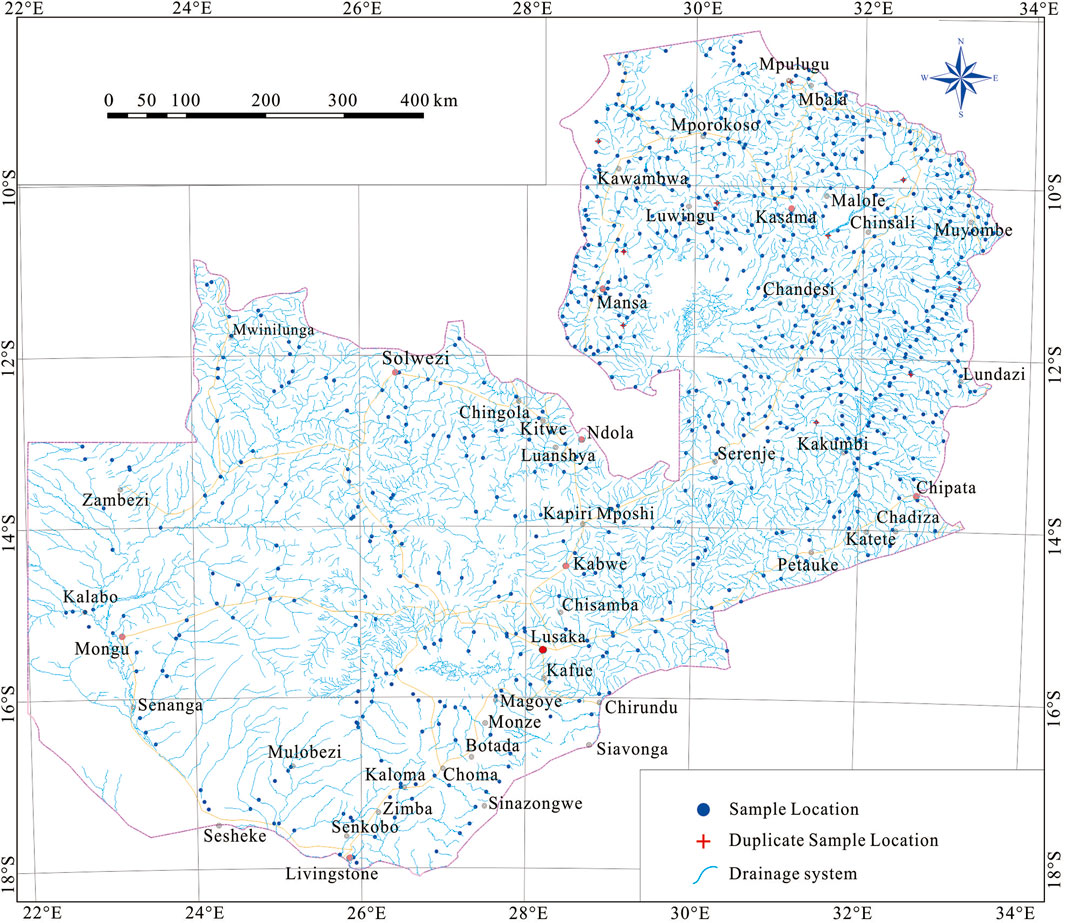
Determining the quantities and geographic distributions of B and Se elements across Zambia is an objective of the national low-density geochemical mapping (Figure 3). Samples were collected every about 500–3,500 km2 (mostly 500–1,500 km2) of catchment area in large rivers, corresponding to a sampling density of about one sample per 1,000 km2. Sampling was conducted in the dry season, with each sample collected from three locations typically at an interval of 50 m along a river and weighing approximately 4 kg. The samples were air-dried and sieved at the campsites, with fractions below 20 meshes being retained (Wang et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2018; 2019). A total of 735 field samples were collected at 735 sampling sites (Figure 3), covering about 95% of Zambia.
3.2 Laboratory analysis and quality control
In the laboratory, samples were ground to 200 mesh (0.074 mm) with an agate mill for further analysis. The B was determined by the emission spectroscopy. After being treated with a dilute (1:1) aqua regia, the Se concentrations were determined using an AFS-8330 atomic fluorescence spectrometer. The above tests and analyses were completed at the Rock and Mineral Analysis Center of Henan Province, China. The analytical quality was strictly controlled by analyzing national certified reference materials (GSS3a, GSS43, and GSS44; Center for National Standard Reference Material of China), laboratory code samples, and duplicate samples throughout the tests and analyses.
The recovery rates of B and Se were within 100%. The duplicate samples, comprising about 2% of the collected samples, were analyzed, with relative standard deviations of less than 5%. The method detection limits (MDLs) of B, and Se were 0.1 and 0.01 μg/g, respectively, with reportable rates ranging from 95% to 100%. This underscores that high-quality experimental data could be obtained for further research. More details regarding the analytical methods and quality control system are stated by Zhang et al. (2012) and Caritat et al. (2018).
3.3 Data processing and spatial analysis
ArcGIS 10.8 developed by Esri was utilized to process the analytical data. For additional spatial analysis, a spatial database comprising point features was created. The concentrations of B, and Se were chosen for further analysis. Following statistical calculation, the results of critical statistical parameters—means, minima, maxima, and percentiles—were exported to Microsoft Excel 2010 for further analysis.
Geoexpl 2016 (International version), developed by the Development Research Center of China Geological Survey, was employed to plot geochemical maps through data gridding. Using an exponentially weighted Euclidean distance model (CGS, 2016), the interpolation of raw analytical data was conducted to create a regular output grid measuring 25 km × 25 km, with a search radius of 100 km. A total of 18 color zones were determined using percentiles 0–2.5%, 2.5%–5%, 5%–10%, 10%–15%, 15%–20%, 20%–25%, 25%–30%, 30%–40%, 40%–50%, 50%–60%, 60%–70%, 70%–75%, 75%–80%, 80%–85%, 85%–90%, 90%–95%, 95%–97.5%, and 97.5%–100%. The geochemical anomaly map was plotted using the classification of outer, middle, and inner anomaly zones based on the cumulative frequencies of 85%, 95%, and 97.5%. To enhance the readability and comprehensibility of the map showing the B and Se distributions, different shades of color, namely, 2.5 (dark blue), 25 (blue), 50 (green), 75 (yellow), 85 (red), and 97.5 (dark red), were assigned to percentiles. Additionally, IBM SPSS Statistics 20 and Excel were used for statistical calculation Figures 7A, B.
4 Results
4.1 Concentrations of B and Se in Zambia
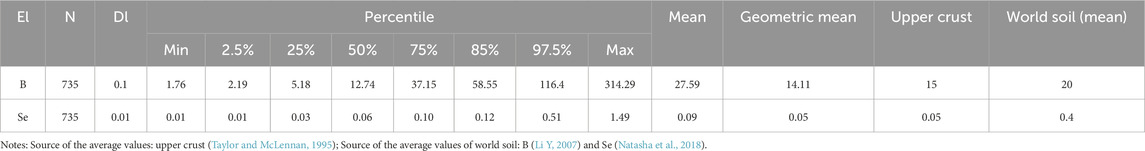
The statistical summary, histograms and boxplots displaying the statistical distribution of B and Se in stream sediments of Zambia are shown in Table 1 and Figure 4, respectively. The histograms show roughly log-normal distributions (Figure 4), indicating that industrial pollution and human activity have little effect on the concentrations of B and Se, which are mostly due to natural processes.
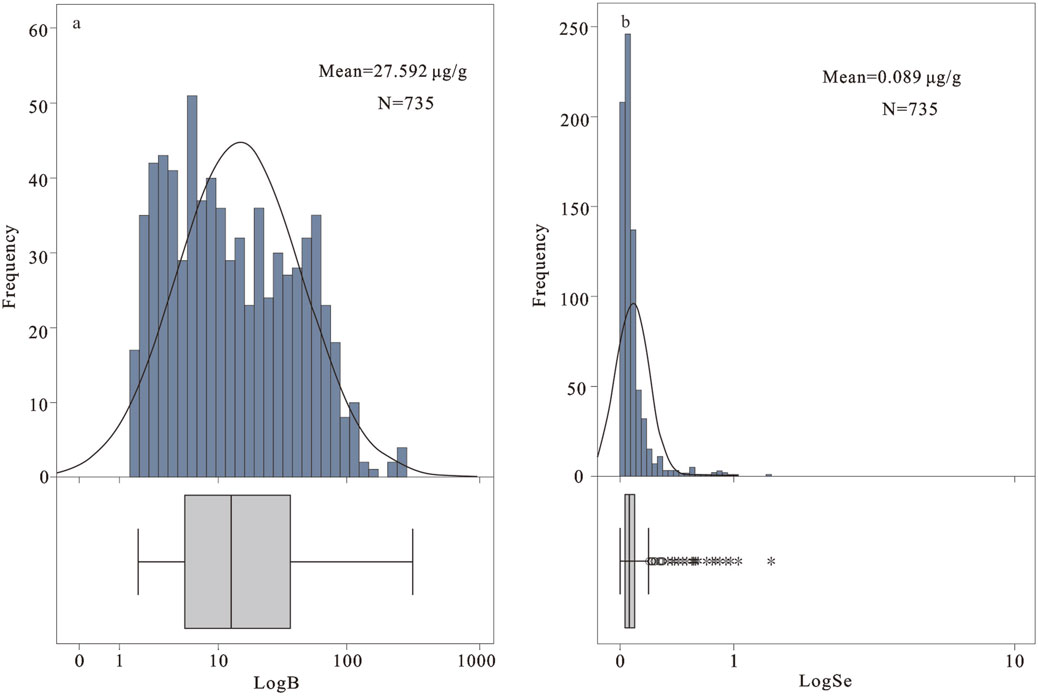
Figure 4. (A) Histograms and boxplots displaying the distribution of B concentration in stream sediment samples; (B) Histograms and boxplots displaying the distribution of Se concentration in stream sediment samples.
The concentration of B in stream sediments ranges from 1.76 μg/g to 314.29 μg/g, with a geometric mean of 14.11 μg/g. The average value is 27.59 μg/g, which is higher than that of the upper crust (15 μg/g, Taylor and McLennan, 1995) and the average values of world soil (20 μg/g, Kamona and Friedrich, 2007), suggesting that B is relatively enriched in stream sediments of Zambia. The histogram shows that the analytical data of B are roughly characterized by a log-normal distribution and the concentration is mostly concentrated between P25 and P85 (5.18 μg/g −58.55 μg/g), with a considerable number of consecutive upper mild outliers (Figure 4A). The concentration of Se in stream sediments ranges from 0.01 to 1.49 μg/g, with a geometric mean of 0.05 μg/g. The average value is 0.09 μg/g, which is higher than that of the upper crust (0.05 μg/g, Taylor and McLennan, 1995), suggesting that Se is relatively enriched in stream sediments of Zambia. The histogram indicates that the Se concentration was concentrated between P25 and P75 (0.03 μg/g −0.10 μg/g), and the boxplot shows that there are a considerable number of consecutive upper mild outliers and a few upper extreme outliers (Figure 4B).
Box length represents the interquartile range (25th to 75th percentiles) and contains the median (thick black line). “○”:stands for values between 1.5 and 3 times box length (interquartile range) from the lower or upper edge of the box; “*“: stands for values more than 3 times box length from the lower or upper edge of the box (Kürzl, 1988; Tukey, 1977).
4.2 General distributions of B and Se throughout Zambia
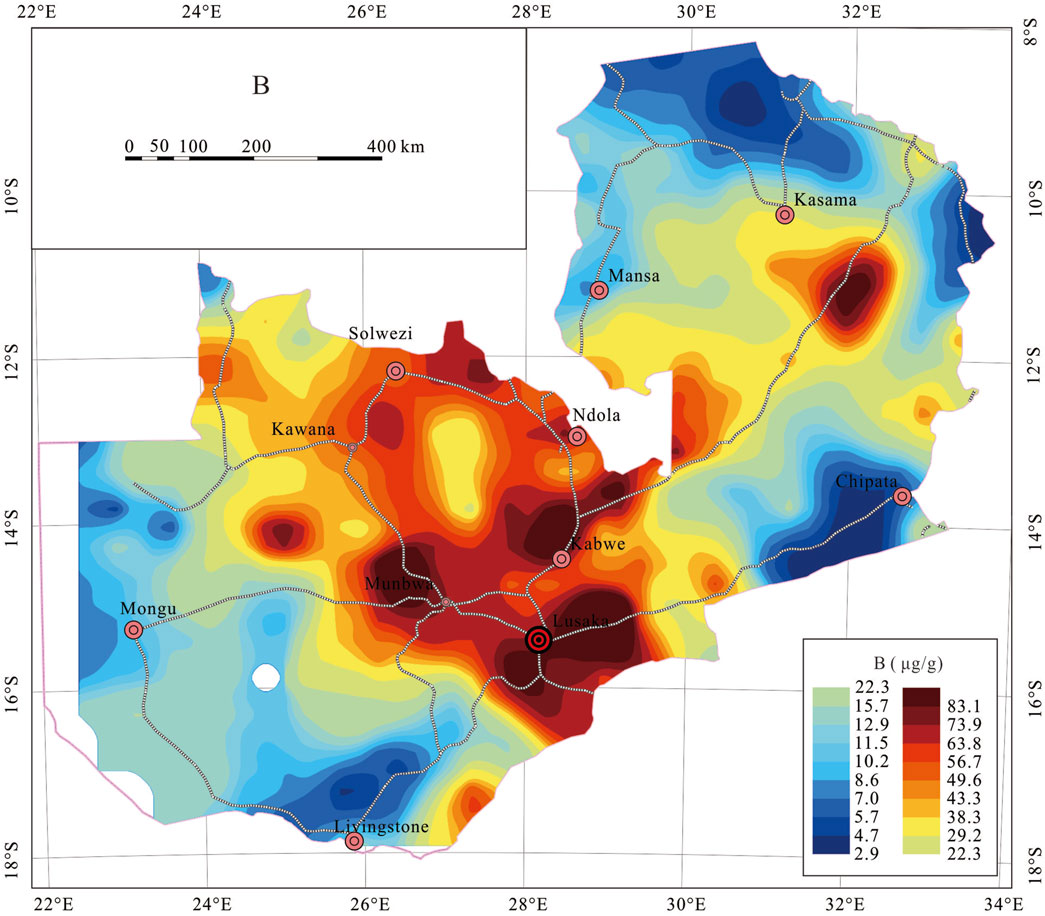
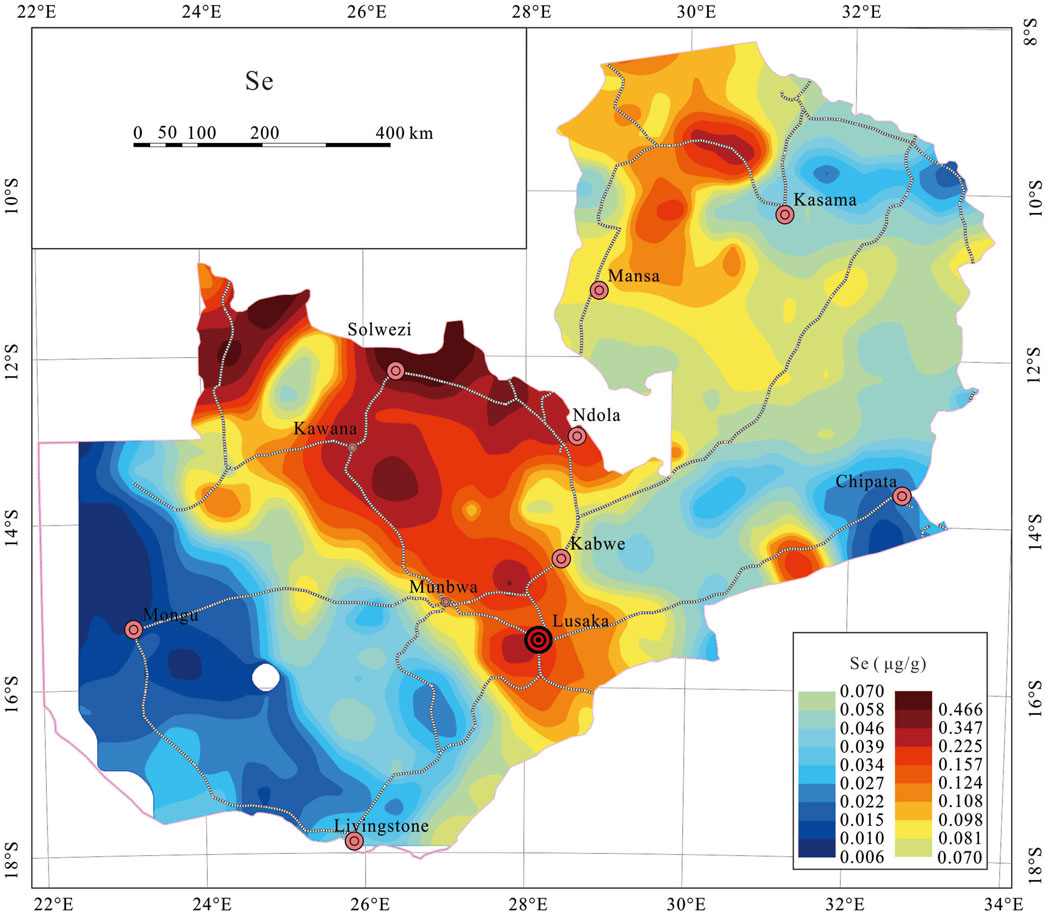
The amount of B and Se found in stream sediments is closely connected to the amount of each element in the parent material (Zhu and Zheng, 2001; Zhu et al., 2008; Fordyce, 2013; Tian et al., 2016). The enrichment of B is usually related to volcanic activity and the distribution of metamorphic sedimentary rocks (Ma et al., 2016; Li et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2022), while Se elements are mainly affected by carbonaceous shale, carbonate rocks, and low-temperature hydrothermal mineralization activities (Rudnick and Gao, 2003; Cui et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2021). The geochemical contour maps (Figures 5, 6) illustrate the spatial distributions of B and Se across Zambia. Low concentrations of both B and Se are mostly found in blocks, whereas high concentraitons are typically found scattered throughout the mobile belts. The stratigraphic sequence of geological units primarily influences their dispersion, the specifics are as follows:
4.2.1 General distribution of B
High B concentrations (>P75) are mainly distributed in the following three regions (Figure 5): (1) Areas surrounding Lusaka and Munbwa; (2) the northern Kabwe; (3) the eastern Solwezi area. The distribution patterns are usually banded or faceted (Figure 5), which are commonly related to volcanic and metamorphic sedimentary rocks of the Irumide Belt and the Lufilian Arc. The southeast of Kasama also has high B concentrations, which are associated with metamorphic sedimentary rocks from the Irumide Belt.
Low B concentrations (<P25) are mainly distributed in the Mongu area in Western Province and the Kasama area in the northeast (Figure 5), which are mostly related to sedimentary strata of the Bangweulu block and the Kalahari desert.
4.2.2 General distribution of Se
High Se concentrations (>P75) are mainly distributed in the following four regions (Figure 6): (1) Kawana-Solwezi-Ndola; (2) the northeastern Kasama; (3) Lusaka; (4) Northwest of Zambia. The distribution patterns are typically banded or faceted (Figure 6), and they are frequently associated with gray-black shale and low-temperature hydrothermal mineralization activities of the Lufilian Arc, the Demes Region and the Zambezi Belt.
Sedimentary layers of the Bangweulu block and the Kalahari desert are primarily responsible for the low Se contents (<P25) seen in the Mongu area in Western Province and the Kasama area in the northeast (Figure 6). Furthermore, although though the Chipata area is located in an active orogenic zone, its Se content is rather low, further research is necessary to determine the causes behind this.
4.3 Distributions of both B and Se in relation to Zambia’s tectonic framework
Because the enrichment of B and Se is generally linked to volcanic activity, metamorphic sedimentary rocks, carbonaceous shale, carbonate rocks, and low-temperature hydrothermal mineralization processes, the concentration of both B and Se varies significantly amongst different structural units (Rudnick and Gao, 2003; Ma et al., 2016; Cui et al., 2017; Li et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2022). The statistical results of B and Se concentrations in Zambia’s different tectonic terranes are shown in Table 2, while Figure 7 displays the statistical distributions as boxplots.
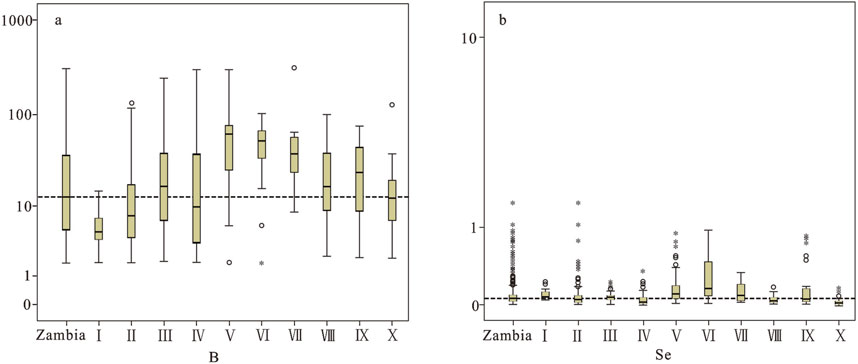
Figure 7. (A) Boxplots displaying statistical variation of B concentrations (μg/g) in different tectonic terranes of Zambia; (B) Boxplots displaying statistical variation of Se concentrations (μg/g) in different tectonic terranes of Zambia (for summary statistics refer to Table 1).
The dotted lines represent the median concentrations of each element across different tectonic terranes. The box length represents the interquartile range (25th to 75th percentile) and contains the median (thick black line). “○“stands for 1.5 to 3 times box length (interquartile) from the upper or lower edge of the box; “*” stands for more than 3 times box length from the lower or upper edge of the box (Kürzl, 1988; Tukey, 1977). Note: Zambia-All samples; I-Kibaran Belt; II-Bangweulu Block; III-Irumide Belt; IV-Karoo Graben; V-Lufilian Arc Belt; VI-Domes Region; VII-Hook Granite Complex; VIII-Zambezi Belt; IX-Choma-Kalomo Block and X-Kalahari Desert.
In Zambia, element B is comparatively rich, particularly in the Lufilian Arc, Domes Region, and Hook Granite Complex areas. The lower limit of B concentration in the Domes Region is significantly higher than the national median value. Se is relatively abundant in Zambia, especially in the Lufilian Arc, Domes Region, and Choma Kalomo Block areas, where it is mainly influenced by an extensive low-temperature metallogenic domain and widely distributed black shales. Black shales and low-temperature mineralization activities are prevalent in the Lufilian Arc and Domes Region, where the greatest mean values of B and Se are found (Kamona and Friedrich, 2007; Kampunzu et al., 2009; Van Wilderode et al., 2013; Sun et al., 2019a; Sun et al., 2019b). The Kalahari Desert, where quartz-rich Aeolian sandy deposits formed, has the lowest mean values of B and Se (Figure 7; Table 2).
5 Discussion
5.1 Relationship between stream sediment and soil
There is a significant correlation between the geochemical content of different elements in soil and water sediment (Zhou et al., 1998; Zhang et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2017), as the surface bedrock forms a common parent material for soil and water sediment after weathering and erosion (Darnley et al., 1995; Lancianese and Dinelli, 2015). Yan et al. (1995) found that the concentrations of 70 elements in various types of sediments in China were essentially consistent with soil background values; Zhang et al. (2005) compared high-precision sediment data from water systems with the corresponding background values of soil elements from the National Environmental Protection Bureau and found that the background values of soil elements in Zhejiang obtained by the two geochemical methods had high consistency; Through comparison study, Yang (2014) discovered that majority of elements in the stream sediment of the Pearl River basin and the nearby soil are essentially the same or related in comparable ways; The average values of 39 elements were also found by Shi et al. (2016) to be similar to the soil background values (Figure 8); Hou (2019) conducted a systematic sampling comparison of sediment in the Qinggeda Lake system and its surrounding soil in Xinjiang, China, and discovered that the majority of the element content between the two was similar. As a result, the elements that are beneficial to humans and necessary for plant growth that are found in stream sediments can also be used to ascertain the distribution of these components in soil, which can be used to assess the quality of the local farmland and give residents advice on how to best develop and manage farmland (Zhu et al., 1994; Zhang et al., 2005).
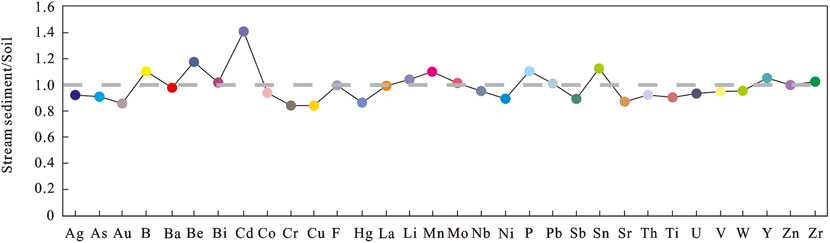
Figure 8. Plot of the average values of 39 elements in stream sediments against the background values of soil in China, showing that the ratios are almost close to 1. Noten: The values in stream sediments and soil are after Shi et al., 2016.
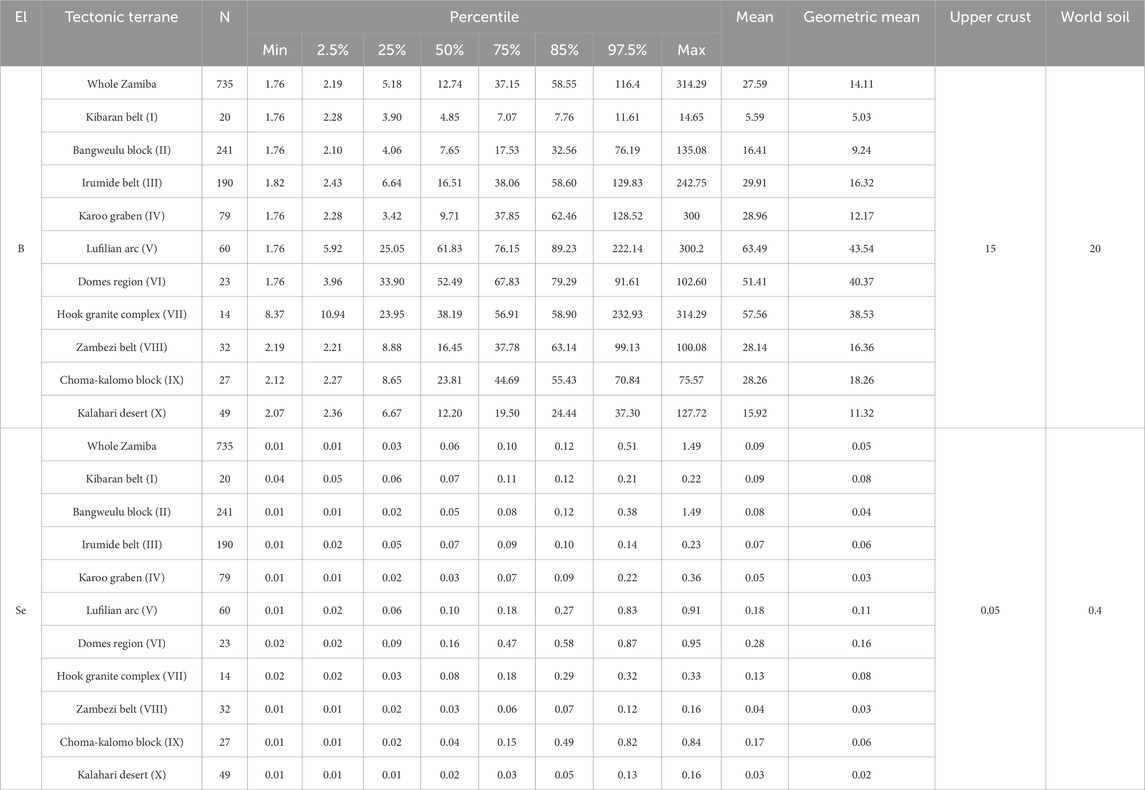
5.2 Status of existing cultivated land in Zambia
In Zambia, the element B is comparatively abundant, and its minimum value is likewise greater than the lower limit of boron fertilizer application (>1). Compared to the overall distribution of B, the composition of the Se is more regular and provides more information for future agricultural growth and land planning. This suggests that the research of future land resource exploitation in connection to Zambia’s Se distribution pattern is the primary subject of this paper.
Five levels were used to determine the threshold levels for a Se-classification method (Tan, 1989; DZ/T 0295-2016, 2024; Dinh et al., 2018): Se-deficient (<0.125 μg/g); Se-marginal (0.125 μg/g −0.175 μg/g); Se-sufficient (0.175 μg/g −0.40 μg/g), Se-rich (0.40 μg/g −3.0 μg/g), and Se-excessive (>3.0 μg/g). The Se content of 626 samples (85.16%) was less than 0.125 μg/g and these soils were classified as Se-deficient; the Se content of 41 samples (5.58%) was between 0.125 and 0.175 μg/g and these soils were classified as Se-marginal; the Se content of 44 samples (5.99%) was between 0.175 and 0.400 μg/g and these soils were classified as Se-sufficient; the Se content of 24 samples (3.27%) was between 0.400 and 3.000 μg/g and these soils were classified as Se-rich. In general, Se content in the sediment of water system in Zambia is low.
The existing cultivated land in Zambia can be categorized into five regions based on the distributions of cultivated land in sub-Saharan Africa, as reported by GlobeLand30 (2020), as well as the distributions of geological units and river basins (Sun et al., 2025). The details are as follows: (A) the Mansa-Mporokoso-Kasama area in the northeastern Zambia; (B) the Kabwe-Chipata area in the southeastern Zambia; (C) the Kawana-Solwezi-Ndola area in the northern Zambia; (D) the Mongu area in the western Zambia; (E) the Livingstone-Munbwa-Lusaka area in the southern Zambia (Figure 9).
(A) The Mansa-Mporokoso-Kasama area: This area is located in the northeastern Zambia, which is home to several rivers, primarily the Chambeshi, Kalungwish, Luapula, and Lufubu rivers, all of which have abundant water resources. The Bangweulu Block, which comprises metamorphic volcanic rocks, schists, conglomerate, intrusive granite rocks, and tuff, make up the geological backdrop. Although the region as a whole has relatively low levels of Se, classified as Se-deficient, the Mpokoroso area contains a significant proportion of Se-rich covering. A comparatively low rate of arable land utilization is a result of the small population distribution in northeastern Zambia (Figure 9). Nonetheless, the region has abundance of water resources, and low levels of industrial contamination, particularly in Se-rich areas where agricultural cultivation benefits local community, ideal for rice cultivation that has a high capacity to enrich selenium.
(B) The Kabwe-Chipata area: This area is located in the southeastern part of Zambia, with concentrated arable lands developed primarily along the Luangwa River, without the development of carbonaceous shale and carbonate rocks with a high Se content (Li et al., 2017; Qin et al., 2017). The region’s geological setting is primarily composed of clastic sedimentary rocks and metamorphic complexes found in the Karoo Graben and Irumide Belt. As a result, this region has a low voerall abundance of selenium and no regions that are rich in it. The bulk of the region is Se-deficient, with the exception of a few Se-sufficient regions in Chipata’s western section. The region is unfavorable for Se agricultural production.
(C) The Kawana-Solwezi-Ndola area: This area is located in the Central and Copperbelt Provinces of the northern part of Zambia. It is part of the Kafue River basin and is Zambia’s primary agriculture planting area. It is the area in Zambia with the highest concentration of selenium, featuring the greatest total selenium content. The dominant geological setting are the Lufilian Arc Belt and Domes Region, featuring extensive clastic sedimentary rocks, granitic intrusive rocks, and carbonaceous shale. Layers of carbonaceous shale and substantial low-temperature hydrothermal activity involving elements like zinc, lead, and copper may be the main causes of the region’s elevated Se content. This region is a prospective agricultural center in Zambia because of its large population, excellent transportation, particularly well suited for planting legumes and roots that have a high capacity to enrich selenium.
(D) The Mongu area: This area is located in the western part of Zambia, belonging to the Zambezi River basin. The general geological settting in the region consists of quartz sandstone and loose sand from the Kalahari Desert, and the area has an abundance of water resources. It is not suitable for the development of Se-rich agriculture since it is a Se-deficient area with the lowest total Se level.
(E) The Livingstone-Munbwa-Lusaka area, it is a part of the Kafue River basin in southern Zambia. In addition, it is the region with the largest population density and widest distribution of arable land. The Hook Granite Complex, Choma Kalomo Block, and Zambezi Belt contain metamorphic sedimentary rocks and granite intrusive rocks that make up the majority of the geological background. The total Se concentration in the region is rather low, and there are no Se-rich areas. Only a limited area around Lusaka has Se-sufficient conditions, primarily as a result of low-temperature hydrothermal activities that produced silver, zinc, and lead. The region is not suitable for the development of Se-rich agriculture because of the generally low selenium content in the soil, even though its agricultural development is relatively high than other area and the majority of the crops grown there are legumes and other plants with strong selenium enrichment ability.
6 Conclusion
This paper investigates the regional distribution and total abundance of B and Se in Zambian stream sediments, as well as their connection to the growth of Se-rich agriculture on the Sino-Zambian Cooperation project. Measured B and Se concentrations ranged from 1.76 μg/g −314.29 μg/g (with a median of 12.74 μg/g) and 0.01 μg/g −1.49 μg/g (with a median of 0.056 μg/g), respectively. The median of boron is likewise greater than the lower limit of boron fertilizer application (>1.0 μg/g). The concentrations of Se in Zambia varied significantly by regional. The areas of Kabwe-Chipata, Mongu, and Livingstone-Munbwa-Lusaka have low concentrations of Se because they lack carbonaceous shale and carbonate rocks. Black shales and large-scale epithermal metallogenic regions were dominant in the Kawana-Solwezi-Ndola and Mansa-Mporokoso-Kasama areas, respectively, where high contents of Se were discovered, especially appropriate for the planting of roots and legumes with a high selenium-enriching capability. Regional variances are greatly influenced by a combination of geological surroundings and human activity. Our efforts can significantly contribute to formulating a national strategy aimed at preventing endemic selenium-related diseases and promoting selenium-enriched agriculture.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JR: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. JW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Software, Writing–review and editing. LZ: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. FH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. XW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. KX: Data curation, Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. CM: Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. AD: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. SC: Project administration, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.This research was jointly financially supported by the Sino–Zambian Cooperation in Geological and Geochemical Mapping at a scale of 1:1000000 in Kasama, Northern Province of Zambia (2012–2015), the China–Aid Airborne Geophysical Survey and Geochemical and Geological Mapping Technical Cooperation Project (2015–2019), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42003041), and the Geological survey of International Cooperation in Southern Africa project (DD20230125).
Acknowledgments
Many thanks are given to all participants for their hard work in field sampling, laboratory analysis, and data processing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Andersen, L. S., and Unrug, R. (1984). Geodynamic evolution of the Bangweulu block, northern Zambia. Precambrian Res. 25, 187–212. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(84)90032-9
Bao, D. Z., You, G. Z., and Yuan, S. B. (2020). Correlation analysis of soil available state, corresponding total amount, PH and organic matter in cultivated land of Xingren City, Guizhou Province. Guizhou Geol. 37 (3), 404–408. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Buchwaldt, R., Toulkeridis, T., Todt, W., and Ucakuwun, E. K. (2008). Crustal age domains in the Kibaran belt of SW-Uganda: combined zircon geochronology and Sm-Nd isotopic investigation. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 51, 4–20. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2007.11.001
Caritat, P. D., Reimann, C., Smith, D. B., and Wang, X. Q. (2018). Chemical elements in the environment: multi-element geochemical datasets from continental-to national-scale surveys on four continents. Appl. Geochem. 89, 150–159. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.11.010
Castillo, P., Serra, I., Townley, B., Aburto, F., Lopez, S., Tapia, J., et al. (2021). Biogeochemistry of plant essential mineral nutrients across rock, soil, water and fruits in vineyards of Central Chile. Catena 196, 104905. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2020.104905
Cheng, H. X., Shen, X. C., Yan, G. S., Gu, T. X., Lai, Z. M., and Xie, X. J. (1997). “Wide-spaced floodplain sediment sampling covering the whole of China: pilot survey for international geochemical mapping,” in Proceedings of the 30th international geological congress. Geochemistry. Editor X. J. Xie, 19, 89–109.
Cohen, D. R., Rutherford, N. F., Morisseau, E., Christoforou, E., and Zissimos, A. M. (2012). Anthropogenic versus lithological influences on soil geochemical patterns in Cyprus. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 12 (4), 349–360. doi:10.1144/geochem2011-111
Cui, Z. W., Huang, J., Peng, Q., Yu, D. S., Wang, S. S., and Liang, D. L. (2017). Risk assessment for human health in a seleniferous area, Shuang'an, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24, 17701–17710. doi:10.1007/s11356-017-9368-8
Darnley, A. G., Björklund, A., Bølviken, B., Gustavsson, N., Koval, P. V., Plant, J. A., et al. (1995) “A global geochemical database for environmental and resource management,”. Pairs, France: Final report of IGCP Project 259, 1–122. UNESCO.
De Waele, B., Johnson, S. P., and Pisarevsky, S. A. (2008). Palaeoproterozoic to Neoproterozoic growth and evolution of the eastern Congo Craton: its role in the Rodinia puzzle. Precambrian Res. 160 (1-2), 127–141. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.020
De Waele, B., Kampunzu, A. B., Mapani, B. S. E., and Tembo, F. (2006b). The mesoproterozoic irumide belt of Zambia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 46, 36–70. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2006.01.018
De Waele, B., Liégeois, J. P., Nemchin, A. A., and Tembo, F. (2006a). Isotopic and geochemical evidence of proterozoic episodic crustal reworking within the irumide belt of south-central Africa,the southern metacratonic boundary of an Archaean Bangweulu Craton. Precambrian Res. 148, 225–256. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.05.006
Dinh, Q. T., Cui, Z., Huang, J., Tran, T. A. T., Wang, D., Yang, W., et al. (2018). Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: a review. Environ. Int. 112, 294–309. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035
DZ/T 0295-2016 (2024). Specification of land quality geochemical assessment. Geol. Mineral Industry Stand. People's Repub. China 24.
EGAS (1981). Relationship between the distribution of keshan disease and selenium concentration in food grain in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 36, 369–376.
EGAS (1982). Geographical distribution of selenium content in human hair in keshan disease and non-disease zones in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 37, 136–143.
Fordyce, F. M. (2013). “Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment,” in Essentials of medical geology. Editors O. Selinus, B. Alloway, J. A. Centeno, R. B. Finkelman, R. Fuge, U. Lindhet al. (New York: Springer), 375–416.
Fordyce, F. M., Brereton, N., Hughes, J., Luo, W., and Lewis, J. (2010). An initial study to assess the use of geological parent materials to predict the se concentration in overlying soils and in five staple foodstuffs produced on them in Scotland. Sci. Total Environ. 408 (22), 5295–5305. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.08.007
Gabert, G. (1990). Lithostratigraphic and tectonic setting of gold mineralization in the Archean cratons of Tanzania and Uganda, East Africa. Precambrian Res. 46 (1-2), 59–69. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(90)90066-y
Gao, H. Y., Shi, R. G., and Zhao, Y. J. (2006). Statistical relationship between bioavailable Zn and total Zn concentration in soil under non-continous spatio-temporal condition. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 26 (8), 1400–1403. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2006.08.027
GlobeLand30 (2020). Un-spider. Available at: https://www.un-spider.org/links-and-resources/data-sources/land-cover-map-globeland-30-ngcc.
Glynn, S. M., Master, S., Wiedenbeck, M., Davis, D. W., Kramers, J. D., Belyanin, G. A., et al. (2017). The proterozoic choma-kalomo block, SE Zambia: exotic terrane or a reworked segment of the Zimbabwe craton? Precambrian Res. 298, 421–438. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.06.020
Hanson, R. E. (2003). Proterozoic geochronology and tectonic evolution of southern Africa. Geol. Soc. 206 (1), 427–463. doi:10.1144/gsl.sp.2003.206.01.20
Hou, F. L. (2019). Study on the heavy metal pollution and environment capacity in water, surface sediments and riparian soils of Qinggeda Lake. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 1–126. Ph. D thesis.
Hu, L. (2008). Effect of boron fertilizer application on yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco planted in yellow soil. South China Agric. 2 (9), 1–3. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-890X.2008.05.001
Jiang, B., Wang, S. T., Sun, Z. B., Zhang, H. R., Liu, Y., and Liu, Q. (2021). Available contents of soil nutrient elements and their influencing factors in Qingzhou City, Shandong Province. Soils 53 (6), 1221–1227. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2021.06.016
Kamona, F., and Friedrich, G. H. (2007). Geology, mineralogy and stable isotope geochemistry of the Kabwe carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, Central Zambia. Ore Geol. Rev. 30 (3), 217–243. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.02.003
Kampunzu, A. B., Cailteux, J. L. H., Kamona, A. F., Intiomale, M. M., and Melcher, F. (2009). Sediment-hosted Zn-Pb-Cu deposits in the central african Copperbelt. Ore Geol. Rev. 35 (3-4), 263–297. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.02.003
Katongo, C., Koller, F., Kloetzli, U., Koeberl, C., Tembo, F., and De Waele, B. (2004). Petrography, geochemistry, and geochronology of granitoid rocks in the Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic Lufilian-Zambezi belt, Zambia: implications for tectonic setting and regional correlation. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 40 (5), 219–244. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2004.12.007
Kershaw, M., Drysdall, A. R., and Johnson, R. L. (1972). Records of the geological survey, 12. Lusaka: Geological Survey Department of Zambia, 117.
Kokonyangi, J., Kampunzu, A. B., Armstrong, R., Yoshida, M., Okudaira, T., Arima, M., et al. (2006). The mesoproterozoic kibaride belt (Katanga, SE D.R. Congo). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 46, 1–35. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2006.01.017
Kürzl, H. (1988). Exploratory data analysis: recent advances for the interpretation of geochemical data. J. Geochem. Explor. 30 (1-3), 309–322. doi:10.1016/0375-6742(88)90066-0
Lancianese, V., and Dinelli, E. (2015). Different spatial methods in regional geochemical mapping at high density sampling: an application on stream sediment of Romagna Apennines, Northern Italy. J. Geochem. Explor. 154, 143–155. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.12.014
Li, L. X., Zi, J. W., Li, H. M., Rasmussen, B., Wilde, S. A., Sheppard, S., et al. (2019). High-grade magnetite mineralization at 1.86 Ga in Neoarchean banded iron formations, Gongchangling, China: in-situ U-Pb Geochronology of metamorphic-hydrothermal zircon and monazite. Econ. Geol. 114 (6), 1159–1175. doi:10.5382/econgeo.4678
Li, M., Xi, X. H., Xiao, G. Y., Cheng, H. X., Yang, Z. F., Zhou, G. H., et al. (2014). National multi-purpose regional geochemical survey in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 139, 21–30. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.06.002
Li, Y. (2007). The research of characteristic of environmental geochemistry of boron in kuandian county, liaoning Province. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 1–60. Ph. D thesis.
Li, Z., Liang, D. L., Peng, Q., Cui, Z. W., Huang, J., and Lin, Z. Q. (2017). Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability: a review. Geoderma 295, 69–79. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.02.019
Licht, O. A. B. (2005). Human health risk areas in the State of Paraná, Brazil: results fromlow density geochemical mapping. Terrae 2, 9–19.
Liu, H. L., Nie, L. S., Wang, X. Q., Zhang, Y. B., Wang, W., and Liu, D. S. (2019). Regional geochemical of beryllium in the Altay area across the Border between China and Mongolia. Geol. Explor. 55 (1), 95–102. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.12134/j.dzykt.2019.01.009
Liu, H. L., Wang, X. Q., Nie, L. S., Wang, W., Chi, Q. H., and Liu, D. S. (2018). Regional geochemistry of niobium and tantalum across the boundary of China and Mongolia in the altay metallogenic belt. Geoscience 32 (5), 1063–1073. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, H. L., Wang, X. Q., Zhang, B. M., Han, Z. X., Wang, W., Chi, Q. H., et al. (2021). Concentration and distribution of selenium in soils of mainland China, and implications for human health. J. Geochem. Explor. 220, 106654. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106654
Liu, Y., and Lu, N. (2023). Hot topics and frontier evolution on soil heavy metals risk assessment in China. North China Geol. 46 (04), 61–69. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.19948/j.12-1471/P.2023.04.08
Ma, Y. B., Bagas, L., Xing, S. W., Zhang, S. T., Wang, R. J., Li, N., et al. (2016). Genesis of the stratiform Zhenzigou Pb-Zn deposit in the North China Craton: Rb-Sr and C-O-S-Pb isotope constraints. Ore Geol. Rev. 79, 88–104. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.05.009
Mao, K. Z., Li, H. M., Ming, Q., Liu, H., Zhao, H., Lu, B. S., et al. (2023). Health risk assessment in the groundwater of a certain mine in Hunan. North China Geol. 46 (03), 57–66. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.19948/j.12-1471/P.2023.03.08
Milani, L., Lehmann, J., Naydenov, K. V., Saalmann, K., Kinnaird, J. A., Daly, J. S., et al. (2015). A-type magmatism in a syn-collisional setting: the case of the Pan-African Hook Batholith in Central Zambia. Lithos 216-217, 48–72. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.11.029
Natasha, S. M., Niazi, N. K., Khalid, S., Murtaza, B., Bibi, I., Rashid, M. I., et al. (2018). A critical review of selenium biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system with an inference to human health. Environ. Pollut. 234, 915–934. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.019
Naydenov, K. V., Lehmann, J., Saalmann, K., Milani, L., Kinnaird, J. A., Charlesworth, G., et al. (2014). New constraints on the pan-african orogeny in Central Zambia: a structural and geochronological study of the Hook batholith and the mwembeshi zone. Tectonophysics 637, 80–105. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.09.010
Ottesen, R. T., Bogen, J., Finne, T. E., Andersson, M., Dallmann, W. K., Eggen, O. A., et al. (2010). Geochemical atlas of Norway, Part 2: geochemical atlas of spittsbergen-chemical composition of overbank sediments. Geol. Surv. Nor. Trondheim Norges Geol. undersokelse, 1–160.
Papadopoulou-Vrynioti, K., Alexakis, D., Bathrellos, G. D., Skilodimou, H. D., Vryniotis, D., and Vassiliades, E. (2014). Environmental research and evaluation of agricultural soil of the Arta plain, western Hellas. J. Geochem. Explor. 136, 84–92. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.10.007
Qin, H. B., Zhu, J. M., Lin, Z. Q., Xu, W. P., Tan, D. C., Zheng, L. R., et al. (2017). Selenium speciation in seleniferous agricultural soils under different cropping systems using sequential extraction and x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ. Pollut. 225, 361–369. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2017.02.062
Rainaud, C., Master, S., Armstrong, R. A., and Robb, L. J. (2003). A cryptic mesoarchaean terrane in the basement to the central african Copperbelt. J. Geol. Soc. 160 (1), 11–14. doi:10.1144/0016-764902-087
Rainaud, C., Master, S., Armstrong, R. A., and Robb, L. J. (2005). Geochronology and nature of the palaeoproterozoic basement in the central african Copperbelt (Zambia and the democratic republic of Congo), with regional implications. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 42, 1–31. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.08.006
Ren, J. P., Wang, J., Liu, X. Y., He, S. F., He, F. Q., and Xu, K. K. (2013). Research progresses on the Cu-Co deposits of lufilian area in the mid-southern Africa. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 32 (5), 142–152. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren, J. P., Wang, J., Zuo, L. B., Liu, X. Y., Dai, C. C., Xu, K. K., et al. (2017). Zircon U-Pb and biotite 40Ar/39Ar geochronology from the Anzan emerald deposit in Zambia. Ore Geol. Rev. 91, 612–619. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.034
Rogiers, S. Y., Greer, D. H., Hatfield, J. M., Orchard, B. A., and Keller, M. (2006). Mineral sinks within ripening grape berries (Vitis vinifera L). Vitis 45 (3), 115–123. doi:10.5073/VITIS.2006.45.115-123
Roman, M., Jitaru, P., and Barbante, C. (2014). Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health. Metallomics 6 (1), 25–54. doi:10.1039/c3mt00185g
Rudnick, R. L., and Gao, S. (2003). “The composition of the continental crust,” in The Crust, vol. 3. Treatise on geochemistry. Editors H. D. Holland, and K. Condie (Amsterdam: Elsevier Pergamon), 1–64.
Sanislav, I. V., Wormald, R. J., Dirks, P. H. G. M., Blenkinsop, T. G., Salamba, L., and Joseph, D. (2014). Zircon U-Pb ages and Lu-Hf isotope systematics from late-tectonic granites, geita greenstone belt implications for crustal growth of the Tanzania craton. Precambrian Res. 242, 187–204. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.12.026
Shi, C. Y., Liang, M., and Feng, B. (2016). Average background values of 39 chemical elements in stream sediments of China. Earth Sci. 41 (2), 234–251. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3799/dqkx.2016.018
Smith, D. B., Smith, S. M., and Horton, J. D. (2013). History and evaluation of national-scale geochemical data sets for the United States. Geosci. Front. 4, 167–183. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2012.07.002
Sun, H. W., Ren, J. P., Wang, J., Gu, A. L., Wu, X. Y., He, F. Q., et al. (2021). Age and geochemistry of the granitoids from the Lunte area, Northeastern Zambia: implications for magmatism of the Columbia supercontinent. China Geol. 4 (4), 658–672. doi:10.31035/cg2021048
Sun, H. W., Ren, J. P., Wang, J., Yu, J. Z., Zuo, L. B., Wu, X. Y., et al. (2025). Spatial distributions, potential sources, and ecological risks of heavy metals in stream sediments in Zambia. J. Geochem. Explor. 270, 107659. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2024.107659
Sun, H. W., Ren, J. P., Wang, J., Zuo, L. B., Gu, A. L., Wu, X. Y., et al. (2024). Enrichment characteristics and metallogenic significance of rare elements in Zambia: based on 1:1,000,000 geochemical mapping. Geol. J. 59 (3), 934–950. doi:10.1002/gj.4900
Sun, H. W., Wang, J., Ren, J. P., Tang, W. L., Liu, X. Y., Zuo, L. B., et al. (2019b). Metallogenic evolution and prospecting potential of Katanga-Zambia polymetallic metallogenic belt in central Africa. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 38 (1), 121–131. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun, H. W., Wang, J., Ren, J. P., Zuo, L. B., and Gu, A. L. (2019a). Sedimentary stratigraphic characteristics of the mporokoso basin in the north-eastern Zambia. Geol. Rev. 65 (1), 232–245. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.16509/j.georeview.2019.01.016
Tan, J. A. (1989). The atlas of endemic diseases and their environment. Beijing, PR China: Science Press.
Tan, J. A., Zhang, D. X., Hou, S. F., Zhu, W. Y., and Li, R. B. (1982). The relation of Keshan disease to the natural environment and the background of selenium nutrition. Acta Nutr. Sin. 4 (3), 175–182. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tan, J. A., Zhu, W. Y., Wang, W. Y., Li, R. B., Hou, S. F., Wang, D. C., et al. (2002). Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 284, 227–235. doi:10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00889-0
Taylor, S. R., and McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 33, 241–265. doi:10.1029/95rg00262
Tian, H., Ma, Z. Z., Chen, X. L., Zhang, H. Y., Bao, Z. Y., Wei, C. H., et al. (2016). Geochemical characteristics of selenium and its correlation to other elements and minerals in selenium-enriched rocks in Ziyang county, Shaanxi province, China. J. Earth Sci. China 27, 763–776. doi:10.1007/s12583-016-0700-x
Van Wilderode, J., Heijlen, W., De Muynck, D., Schneider, J., Vanhaecke, F., and Muchez, P. (2013). The Kipushi Cu-Zn deposit (DR Congo) and its host rocks: a petrographical,stable isotope (O, C) and radiogenic isotope (Sr, Nd) study. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 79, 143–156. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2012.11.011
Villeneuve, M., Gärtner, A., Kalikone, C., Wazi, N., Hofmann, M., and Linnemann, U. (2019). U-Pb ages and provenance of detrital zircon from metasedimentary rocks of the Nya-Ngezie and Bugarama groups (D. R. Congo): a key for the evolution of the Mesoproterozoic Kibaran-Burundian Orogen in Central Africa. Precambrian Res. 328, 81–98. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2019.04.003
Wang, Q. Y., Fan, X. W., Zhang, S. R., and Xie, T. Q. (2014). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of Mn and B in southern longquan mountain of renshou county. Resour. Dev. and Mark. 30 (3), 259–262. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2014.03.001
Wang, X. K., Zhang, Y. X., Huang, B., Xie, E. Z., Fan, Y. N., Hu, W. Y., et al. (2021). Accumulation and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in a city typical of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 58 (1), 82–91. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.11766/trxb201909160391b
Wang, X. Q., Chi, Q. H., Liu, H. Y., Nie, L. S., and Zhang, B. M. (2007). Wide-spaced sampling for delineation of geochemical provinces in desert terrains, northwestern China. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 7 (2), 153–161. doi:10.1144/1467-7873/07-124
Wang, X. Q., Han, Z. X., Wang, W., Zhang, B. M., Wu, H., Nie, L. S., et al. (2019). Continental-scale geochemical survey of lead (Pb) in mainland China's pedosphere: concentration, spatial distribution and influences. Appl. Geochem. 100, 55–63. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.11.003
Wang, X. Q., Liu, X. M., Han, Z. X., Zhou, J., Xu, S. F., Zhang, Q., et al. (2015). Concentration and distribution of mercury in drainage catchment sediment and alluvial soil of China. J. Geochem. Explor. 154, 32–48. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.01.008
Wang, X. W., Meng, Q. Y., Yan, J. T., Hu, K., and Wang, H. (2017). Application of geochemical data in the assessment of soil environment quality in a region of Shanxi. Gold 38 (2), 70–73. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.11792/hj20170217
Xie, X. J., and Ren, T. X. (1993). National geochemical mapping and environmental geochemistry — progress in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 49, 15–34. doi:10.1016/0375-6742(93)90037-m
Xu, K. K., Sun, H. W., Xie, W., He, F. Q., Liu, X. Y., Sun, K., et al. (2023). Characteristics of B, Zn and Se in stream sediments of Tanzania and their agricultural applications: based on 1:1000000 geochemical survey. China Geol. 6 (1), 1–14. doi:10.31035/cg2022049
Yan, M. C., Chi, Q. H., Gu, T. X., and Wang, C. S. (1995). Average element content of various sediments in China. Geophys. and Geochem. Explor. 19 (6), 468–472. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, M. L., Ma, Y. H., Huang, W. X., Chen, L. M., Cui, J. Y., Wu, L. C., et al. (2019). Study on the correlation between available state, total amount and ph of soil Cd and Pb. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 46 (4), 74–80. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2019.04.011
Yang, S. L. (2014). Geochemical characteristics of metal elements in sediments and soils in the upper reaches of the Pearl River. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1–147. Ph. D thesis.
Yang, Z. F., Yu, T., Hou, Q. Y., Xia, X. Q., Feng, H. Y., Huang, C. L., et al. (2014). Geochemical evaluation of land quality in China and its applications. J. Geochem. Explor. 139, 122–135. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.07.014
Zambia Agri Market Update (2023). Knightfrank. Available at: https://content.knightfrank.com/research/2630/documents/en/zambia-agri-market-update-2022-2023-10027.pdf.
Zhang, C. L., Huang, L. Y., Feng, Z. M., and Yuan, H. (2005). The application of stream sediments analytical data to the evalution of soil environment quality of Zhejiang province. Geophys. and Geochem. Explor. 29 (4), 329–333. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2005.04.013
Zhang, L., Qin, Y. W., Zheng, B. H., Jia, J., and Lei, K. (2011). Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments from typical areas in the Bohai Sea. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 31 (8), 1676–1684. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Q., Bai, J. F., and Wang, Y. (2012). Analytical scheme and quality monitoring system for China Geochemical Baselines. Earth Sci. Front. 19 (3), 33–42. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z
Zhao, Y., Zhang, P., Bi, Z. W., Kou, L. L., Yang, H. Z., and Chen, J. (2022). Key role of sedimentary formation played in the mineralization process of the paleoproterozoic Yangmugan boron deposit in Liaodong peninsula, NE China. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 44 (2), 207–219. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.19814/j.jese.2021.12056
Zhou, G. H., Zhu, L. X., and Ma, S. M. (1998). Application of regional geochemical data to increasing of crop yield. Geol. Prospect. 34 (1), 45–49. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu, J. M., Wang, N., Li, S. H., Li, L., Su, H. C., and Liu, C. X. (2008). Distribution and transport of selenium in Yutangba, China: impact of human activities. Sci. Total Environ. 392, 252–261. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.12.019
Zhu, J. M., and Zheng, B. S. (2001). Distribution of selenium in a mini-landscape of yutangba, enshi, hubei province, China. Appl. Geochem. 16, 1333–1344. doi:10.1016/s0883-2927(01)00047-6
Keywords: catchment sediment, geochemical mapping, soil of cultivated land, agricultural applications, Zambia
Citation: Sun H, Ren J, Wang J, Zuo L, He F, Wu X, Xu K, Mukofu C, Dokowe AP and Cao S (2025) Concentration and distribution of B and Se in stream sediments of Zambia and their agricultural implications. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1454929. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1454929
Received: 04 July 2024; Accepted: 17 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Aboubakar Sako, University of Ouagadougou, Burkina FasoReviewed by:
Aboubakar Sako, University of Ouagadougou, Burkina FasoEduardo Duarte Marques, Geological Survey of Brazil, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Ren, Wang, Zuo, He, Wu, Xu, Mukofu, Dokowe and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongwei Sun, ODA3NTQ0OTQ2QHFxLmNvbQ==; Junping Ren, cmpwMjMzM0AxMjYuY29t
 Hongwei Sun
Hongwei Sun Junping Ren1,3*
Junping Ren1,3*