- 1Department of Physics, Washera Gerospace and Radar Science Laboratory, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Physics, Wolkite University, Wolkite, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Mathematics, College of Natural and Computational Sciences, Mekdela Amba University, Tulu Awuliya, Ethiopia
Aerosols are microscopic liquid or solid particles that enter the atmosphere through natural and man-made processes. Time series trends and correlations of aerosol optical depth and cloud parameters over Addis Ababa have become the subject of scientific research because of the importance of clouds in controlling climate. In this study, we have examined the temporal variations (time series analysis) in aerosol particles over Addis Ababa and the impact of these variations on various optical properties of clouds using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data from January 2003 to December 2018. The maximum aerosol optical depth (AOD) was found during the summer period, with minimum values in winter. During summer, the air temperature is high, which leads to abundant atmospheric water vapor, facilitating the hygroscopic growth of aerosols. We then analyzed the relationships between AOD and other cloud parameters, namely, water vapor (WV), cloud fraction (CF), cloud top temperature (CTT), and cloud top pressure (CTP), to provide a better understanding of aerosol–cloud interactions. The correlation between AOD and CF and WV was positive for Addis Ababa, while there was a negative correlation with CTT and CTP.
1 Introduction
Our atmosphere is a dynamic system that sustains life on Earth by absorbing shortwave radiation and releasing longwave radiation. It is composed of gases, aerosol particles, and collections of liquid and solid water droplets that form clouds. Atmospheric aerosols are tiny particles, both solid and liquid, that float in the atmosphere (Grythe, 2017; Kafle and Coulter, 2013). Aerosols, which vary spatio-temporally with geographic location, seasons, atmospheric conditions, and local sources, play a crucial role in Earth’s climate and radiation budget. Monitoring the temporal pattern of aerosols, either by ground-based remote sensing or satellite, has significant practical applications, such as traffic control, managing energy budgets, mitigating climate change, and assessing air quality (Alhaj Mohamad, 2015; Balarabe et al., 2015). Aerosol optical depth (AOD), one of the fundamental optical metrics among aerosol properties, can be used to determine the local air pollution level to some extent. The AOD value of a very clear atmosphere is 0.01, whereas that of a very hazy environment is 0.4 (Endale et al., 2024). Additionally, aerosol is extensively used as a subtle but important indication of atmospheric radiation equilibrium and climate change (Wang et al., 2020).
Aerosols have an impact on air quality. The dynamics of aerosols in the atmosphere are intimately linked to local meteorological conditions and the sources of their emissions. Because of their brief lifetime and a variety of dynamic processes, such as transport, deposition, convection, and others, aerosol levels fluctuate across time and space. The amount of scientific evidence showing that atmospheric aerosol particles have a significant influence on Earth’s radiative energy budget and thermodynamics is increasing. Aerosol particles have three main effects on the atmosphere: semi-directly through the absorbed radiation energy by aerosol particles, which can raise the temperature of the surrounding air and cause cloud droplets and ice particles to evaporate; indirectly through affecting the microphysical properties of clouds; and directly through changing the properties of the radiation energy budget through scattering and absorbing solar radiation (Kafle and Coulter, 2013; Myhre et al., 2013). Because clouds play a major role in regulating the climate, scientists are now studying the correlation between aerosols and clouds (Alam et al., 2010; Mahowald and Kiehl, 2003). Variations in aerosols can affect clouds’ optical characteristics both spatially and temporally. Alam et al. (2014) and numerous other studies have investigated aerosol–cloud interactions in the southern and eastern regions of Asia to gain insights into the spatial and temporal variations of aerosols and clouds (Alam et al., 2010; Alam et al., 2014; Kang et al., 2015; Kumar et al., 2009; Tang et al., 2014; Yi et al., 2012).
Ethiopia, with its high population, faces climate change-induced droughts due to reduced forest cover and increased aerosol concentrations. The country’s industrial activities and construction contribute to these issues. As a developing country, it is crucial to address air quality and climate change impacts as the Earth’s atmosphere primarily consists of gases and particles (Etyemezian et al., 2005). Aerosol particles are studied even less than elementary particles and quarks since they cannot be watched through optical microscopes due to their particle size (approximately 100 nm), which is much smaller than the wavelength of visible light. The concentration of aerosol particles varies strongly with time and location.
Ethiopia’s vibrant capital, Addis Ababa, is especially vulnerable to the effects of climate change due to several environmental issues. Despite being a hive of cultural and economic activity, the city is becoming more susceptible to extreme weather conditions such as heat waves, flash floods, and droughts (Cochrane and Costolanski, 2013). These catastrophes are made worse by the city’s unusual location in a valley encircled by mountains, which traps pollution and raises the chance of extreme weather. Dust storms are a common occurrence in Addis Ababa, especially during the dry season, which makes matters more complicated. These storms cause a significant increase in air pollution, resulting in elevated levels of carbon monoxide, sulfates, and nitrates, along with the city’s rapidly developing industrial sector and urbanization. The absence of a strong network for monitoring air pollution from the ground poses a major obstacle in determining the exact amount of these emissions. Fortunately, long-term data on AOD are available because of the deployment of multi-spectral satellite sensors, particularly the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), which provides important insights into the shifting trends in air quality over Addis Ababa.
In the context of our country, Ethiopia, and its cities, the effects of aerosols on cloud parameters, cloud and aerosol correlation, and temporal variation of aerosols and cloud parameters over an extended period of time have not been extensively reported. A few studies, such as those by Homa et al. (2017), have used data from the Stratospheric Aerosols and Gas Experiment II (SAGE II) satellite to study the stratospheric aerosol climatology over Ethiopia. Getachew (2009) considered the solar irradiance wavelength dependence of AOD using sun photometer data. Eshet and Raju (2022) studied the spatial variation of AOD in selected sectors of Ethiopia. To the authors’ knowledge, there are no studies in the rapidly growing industrial and popular city, Addis Ababa, that consider the long-term temporal trends and correlations of aerosols with cloud parameters. For this reason, our first goal is to examine the temporal monthly, seasonal, and annual temporal changes of MODIS AOD across Ethiopia. The second goal is to investigate the effects of aerosols (AOD) on cloud microphysics by examining the correlations between AOD and different cloud parameters using time series plots and specific correlation coefficient analysis.
2 Materials and methods
Ethiopia’s capital, Addis Ababa (geographic latitude: 9.0351° N and longitude: 38.7663° E), is shown in Figure 1, is a dynamic and rapidly growing city in the center of the East African highlands. It is the biggest city in Ethiopia and one of the biggest in Africa, and it is home to more than 5 million people. A significant hub of the African Union’s economy and culture, Addis Ababa is also the location of the organization’s headquarters. At 2,355 m above sea level, Addis Ababa has a relatively cool and temperate climate. The city has two distinct rainy seasons: a shorter period from March to May and a longer one from June to September. The average annual temperature of Addis Ababa is 16.2°C, with average highs of 21.4°C and average lows of 11.1°C. The aerosol environment of Addis Ababa is dynamic and diverse, impacted by land use, climate, geography, and regional transportation, among other variables. Aerosols can significantly affect precipitation and cloud formation; Addis Ababa is actively conducting research in this area.
We utilized AOD and cloud parameter data from the MODIS Terra and Aqua satellites for the years 2003–2018, available at the link https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/. The utilized AOD data from the Terra satellite and cloud parameters from the Aqua satellite leveraged the distinct overpass times and the strengths of each satellite’s instrument suite. Terra provides morning data, known for its robust AOD retrievals, while Aqua captures afternoon data, offering an improved representation of cloud parameters during this period. By combining these datasets, we enhance temporal coverage and improve the overall accuracy of our analysis, a method aligned with practices observed in previous studies (Alam et al., 2014). For specific analytical needs, cloud top temperature (CTT) data from Aqua and water vapor (WV) data from Terra were utilized in the study. Aqua’s CTT data, relevant for understanding afternoon cloud characteristics, were selected to capture cloud top temperatures during this time. Terra’s WV data, known for its quality and consistency in morning observations, were chosen to assess water vapor in the lower atmosphere. Although these datasets are derived from different times of the day, their combination provides a comprehensive view of atmospheric conditions. The variability introduced by this approach is acknowledged, yet it allows for a broader analysis of atmospheric dynamics and their impacts. Since the AOD at 550 nm is near the solar spectrum, the tip of which is related to significant radiative effects, we focused on it for our investigation over land (Alam et al., 2010). The AOD is calculated at 550 nm from Mie theory using mass concentrations, extinction efficiency, and particle mass density. AOD at 550 nm wavelength is used in this study.
With regard to the Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites, MODIS is a reasonably good instrument that offers helpful data on particles, clouds, moisture, and the ground surface. The Terra and Aqua satellites, which are sun-synchronous and in polar orbit, are home to its sensors. Measurements of the infrared to visible light spectrum are carried out by both satellites. The 36 bands of multispectral data from the MODIS sensor on board the Terra and Aqua earth observation system satellites cover the visible, near-infrared, and far-infrared portions of the spectrum. It covers the entire world and has multi-spatial resolution sensors at 1,000, 500, and 250 m with a temporal resolution of 1–2 days. NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites (launched in December 1999 and May 2002, respectively) are equipped with the MODIS sensor, which has 36 spectral channels that provide data on atmospheric, terrestrial, and oceanic conditions. They are helpful for gathering extensive data on the effects of aerosols on clouds. In-depth analyses of their temporal dynamics; local, regional, and global distributions; and computations involving radiative forcing will, likewise, find great use in them.
Observations are provided by MODIS at moderate temporal (1–2 days) and spatial (250–1 km) resolutions throughout several electromagnetic spectrum regions. Additionally, several aerosol metrics are obtained from MODIS daytime data at a geographical resolution of 10 km. There has been a description of retrievals for cloud parameter investigations by Alam et al. (2010) and Platnick et al. (2003). The techniques/algorithm for calibrating AOD data from the MODIS satellite is also described by Remer et al. (2006).
2.1 Establishment of correlation
In probability theory and statistics, correlation (often measured as a correlation coefficient) indicates the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two random variables. Several different coefficients are used for different situations, with the best known being the Pearson correlation coefficient. This coefficient is obtained by dividing the covariance of the two variables by the product of their standard deviations. A correlation coefficient is a number that quantifies a type of correlation and dependence, representing statistical relationships between two or more values in fundamental statistics. The correlation coefficient is denoted as “
Here, xi, x2, … xn are cloud parameter data.
To find out the correlation between AOD at 550 nm and other cloud parameters such as CF, CTP, CTT, and WV, the common location and the common period of data are first identified. The monthly average data for the 16-year period from January 2003 to December 2018 are considered to identify the relationship.
2.2 Linear regression
Linear regression is a statistical approach that attempts to model the relationship between two variables by fitting a linear equation to observed data. Here, one variable is considered a dependent variable, and one or more explanatory variables are considered the independent variable. The case of one explanatory variable is known as simple linear regression. After performing the analyses, the regression statistics can be used to predict the dependent variable based on the known independent variable. The regression equation is expressed as Equation 2 as follows.
Here, X is the explanatory (independent) variable, and Y is the dependent variable (response or outcome). The variable ‘b’ is the slope of the line and has been obtained from the linear regression equation, which is the mean temporal aerosol optical depth and cloud parameters over 16 years as a function of altitude and months of the year, and a is the intercept.
3 Results and discussion
This section contains the analyzed data and their interpretation and discussions in detail, which are related to the study in this work. The present study analyzes the effect of aerosols on cloud parameters over Addis Ababa using MODIS satellite datasets for the 16-year period from January 2003 to December 2018. The statistical analyses of aerosol optical depth and cloud parameters have been studied.
3.1 Time series analysis
Long-term time series analysis can provide trends, i.e., monthly (seasonally) and annual information. In this study, a time series is a collection of observations taken at specified times but at equal intervals. The cyclical trend of the time series was used in studying the temporal variations of cloud fraction (CF), cloud top pressure (CTP), cloud top temperature (CTT), water vapor (WV), and AOD at 550 nm over Addis Ababa for a 16-year period (January 2003–December 2018).
3.2 Seasonal variations of AOD
The seasonal variations of monthly mean AOD values at a wavelength of 550 nm over Addis Ababa have been plotted from January 2003 to December 2018, as shown in Figure 2A. High mean AOD values (0.33) were observed during the summer season. A similar increase in AOD during the summer season has previously been reported by different authors (Alam et al., 2014; Balakrishnaiah et al., 2012). The winter season shows much lower aerosol loading (0.13). Aerosol loading in the Addis Ababa region is low after the summer rainfall washes out most of the aerosol concentration. Generally, in summer, air temperatures are high, leading to the air holding abundant atmospheric water vapor that facilitates the hygroscopic growth of aerosols (Li et al., 2019; Luoma et al., 2019; Mahowald and Kiehl, 2003). Similar results were also reported by authors regarding an increase in aerosol concentration that changes from season to season (Pan et al., 2010). The rapid increase in AOD in the summer season may cause adverse effects on agricultural crops and human health. Increased aerosol loading may also likely affect rainfall.
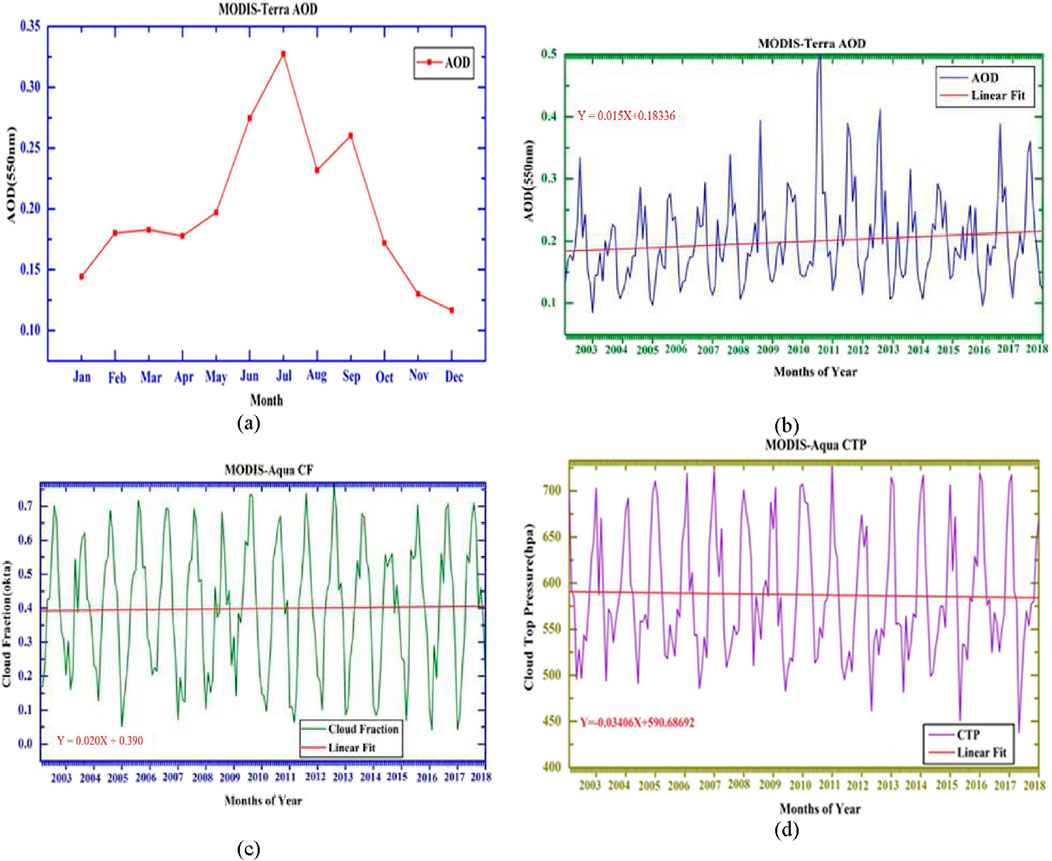
Figure 2. Time series analysis of (A) seasonal AOD, (B) annual AOD, (C) CF, and (D) CTP for the 16-year period (January 2003–December 2018) over Addis Ababa.
3.3 Annual variations in aerosol optical depth
Figure 2B shows the annual variations in AOD over Addis Ababa for the 16-year period from January 2003 to December 2018. The analysis identifies the highest AOD value, or peak, within each year of the study. The maximum peak was observed in July 2011 (0.52), while the minimum was recorded in December 2003 (0.09). The mean annual cycle of AOD was calculated to understand its monthly changes.
A linear regression analysis applied to the time series data (represented by the red line in the figure) reveals a positive slope, indicating an increasing trend in AOD during the study period. The regression equation, Y = 0.015X+0.18336, suggests that the AOD has been increasing annually by a factor of 0.015. The slope of the regression line, which has a p-value of 0.02, confirms that this upward trend is statistically significant. This upward trend in AOD indicates an increased tendency of the atmosphere to absorb light over the years. The highest AOD values were recorded during the summer months (June, July, and August), while the lowest values were observed in the winter months (December, January, and February). These results align with previous studies (Kulmala et al., 1999), which attributed the higher AOD in summer to increased humidity, leading to the growth of aerosol particles and stronger vertical convection during this season.
3.4 Temporal patterns of the cloud fraction
As indicated in Figure 2C, there is an increasing trend in the cloud fraction over the 16-year period from January 2003 to December 2018 in Addis Ababa. Each peak represents the maximum CF value observed within each year of the study. The highest peak was observed around July 2013 (0.77), while the lowest peak occurred in December 2016 (0.04).
Clouds significantly impact the climate, and changes in the climate system, in turn, affect cloud formation. This interrelationship creates a complex system of climate feedback. Clouds modulate the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface and influence the water balance. They reflect some incoming solar radiation away from the Earth and absorb some of the outgoing radiation reflected from the surface. An increase in cloud cover generally correlates with a decrease in solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface, partly due to the direct effect of aerosols. Aerosols cool the surface by reducing the amount of solar radiation, which decreases evaporation, moisture movement, and, consequently, cloud cover. The red trend line in the figure shows an increase in cloud fraction over time, described by the equation Y = 0.020X+0.390. This indicates that the cloud fraction has been increasing by a factor of 0.020 from 1 year to the next. The slope of this regression line has a p-value of 0.03, indicating that the increasing trend in cloud fraction is statistically significant. This provides strong evidence that the observed increase in cloud fraction over the period is unlikely due to random chance. A possible change in the amount of aerosols and cloud characteristics could have contributed to this trend. The CF exhibits its highest values in the summer months (June, July, and August) and its lowest values in the winter months (December, January, and February).
3.5 Temporal patterns of the cloud top pressure
Figure 2D shows the CTP over Addis Ababa for the 16-year period from January 2003 to December 2018. The analysis identifies the peak CTP value within each year of the study. The maximum peak was observed in December 2011 (725.70 hPa), while the minimum was recorded in April 2017 (437.96 hPa).
The red line in Figure 2D represents a linear regression analysis with the equation Y = – 0.03406X + 590.68692, indicating a decreasing trend in CTP over the study period. The slope of this regression line has a p-value of 0.005, confirming that the decreasing trend is statistically significant. This suggests that the average cloud top pressure has been decreasing annually, implying an increase in cloud top height. The CTP values are highest in winter (December, January, and February) and lowest in spring (March, April, and May). Since atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude, lower CTP values correspond to higher cloud tops, which are capable of producing significant rainfall.
3.6 Temporal patterns of the cloud top temperature
Figure 3A shows the CTT over Addis Ababa for the 16-year period from January 2003 to December 2018. The maximum CTT peak was observed in December 2015 (284.79K), while the minimum was recorded in April 2017 (259.05K).
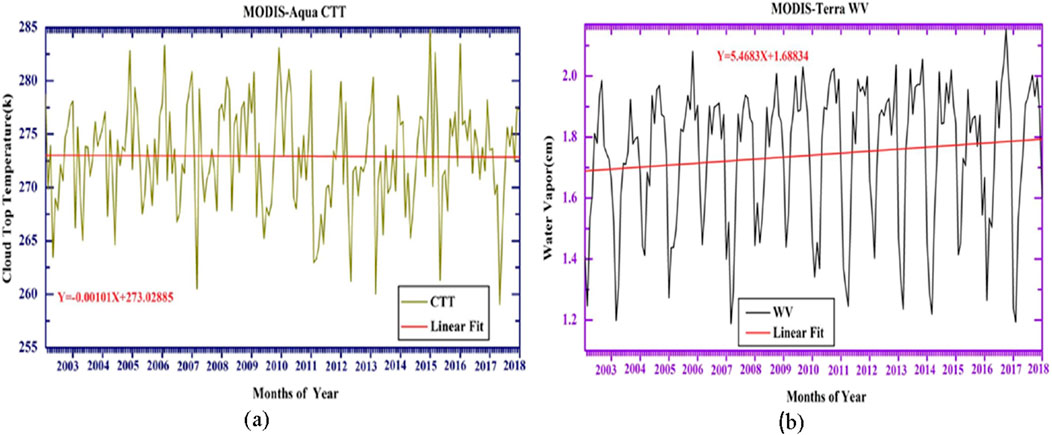
Figure 3. Time series analysis of (A) CTT and (B) WV for the 16-year period (January 2003–December 2018) over Addis Ababa.
The analysis shows that the average CTT has been decreasing, as indicated by the regression equation Y = −0.00101X+273.02885, having slope and p-value of 0.065. This suggests a slight decrease in CTT over time. However, the associated p-value of 0.065 indicates that this trend is not statistically significant. The higher p-value suggests that the observed trend may be influenced by external factors, such as changes in atmospheric conditions, land use, or other environmental variables, rather than a true underlying trend.
The CTT has the highest value in winter (December, January, and February) and the lowest value in spring (March, April, and May). It is the atmospheric temperature at the level of the cloud top. Accurate information on cloud top temperature is needed in order to properly retrieve many atmospheric and surface properties. It also plays an important role in the net earth radiation budget studies. The changes in CTTs and variability could give further insight into aerosol indirect effects. The brightness temperature is used as a representative of CTT. In general, colder CTT corresponds to higher rainfall rates for convective clouds. Low temperature indicates high cloud tops with greater thickness and a larger probability of rain. CTT peaks for heavy rain along with −5°C to 0°C (Barrett and Martin, 1981).
3.7 Temporal patterns of the water vapor
Figure 3B shows the WV values for the 16-year period from January 2003 to December 2018 over Addis Ababa. The maximum WV peak was observed in September 2017 (2.15), while the minimum was recorded in February 2008 (1.19).
The gradient line in Figure 3B, represented by the equation Y = 5.4683X + 1.68834, indicates an increasing trend in WV over the study period. The p-value associated with the slope is 0.0095, confirming that this trend is statistically significant. WV content in the atmosphere is highly variable due to factors such as temperature changes, atmospheric circulation, and other micro-physical processes. The atmospheric capacity for holding water vapor doubles with every ten-degree Celsius increase in temperature (Kaufman et al., 2005).
4 Correlation between AOD and cloud parameters
Aerosols introduce a complicating factor due to their hygroscopic nature. In this analysis, AOD is used as a proxy for aerosol concentration to explore its relationship with various cloud parameters. We conducted correlation studies on a monthly basis across different years from January 2003 to December 2018. This section presents the correlation between MODIS-derived AOD and cloud parameters, including CF, CTP, CTT, and WV for the Addis Ababa region. The following subsections provide time series plots to illustrate temporal variations in AOD and cloud parameters and detailed discussions of the relationships between AOD and each cloud parameter, supported by statistical correlation analysis. Several studies have successfully used time series plots to illustrate temporal variations in AOD, cloud parameters, and their correlation. For example, Alam et al. (2010) utilized time series plots to effectively display the temporal patterns and trends in AOD, cloud parameters, and their correlation. These plots allowed the researchers to observe seasonal and annual changes, providing insights into long-term trends and temporal dynamics. Similarly, Alam et al. (2014) employed time series plots to present the temporal variations of AOD and cloud parameters. The authors demonstrated how these plots could reveal significant temporal trends and correlations, supporting their analysis of atmospheric conditions over time.
In this study, we chose to use time series plots in Figure 4 to align with these established practices in the literature. Time series plots allow for the visualization of trends, annual cycles, and anomalies, which are crucial for understanding the temporal behavior of AOD, cloud parameters, and their correlation.
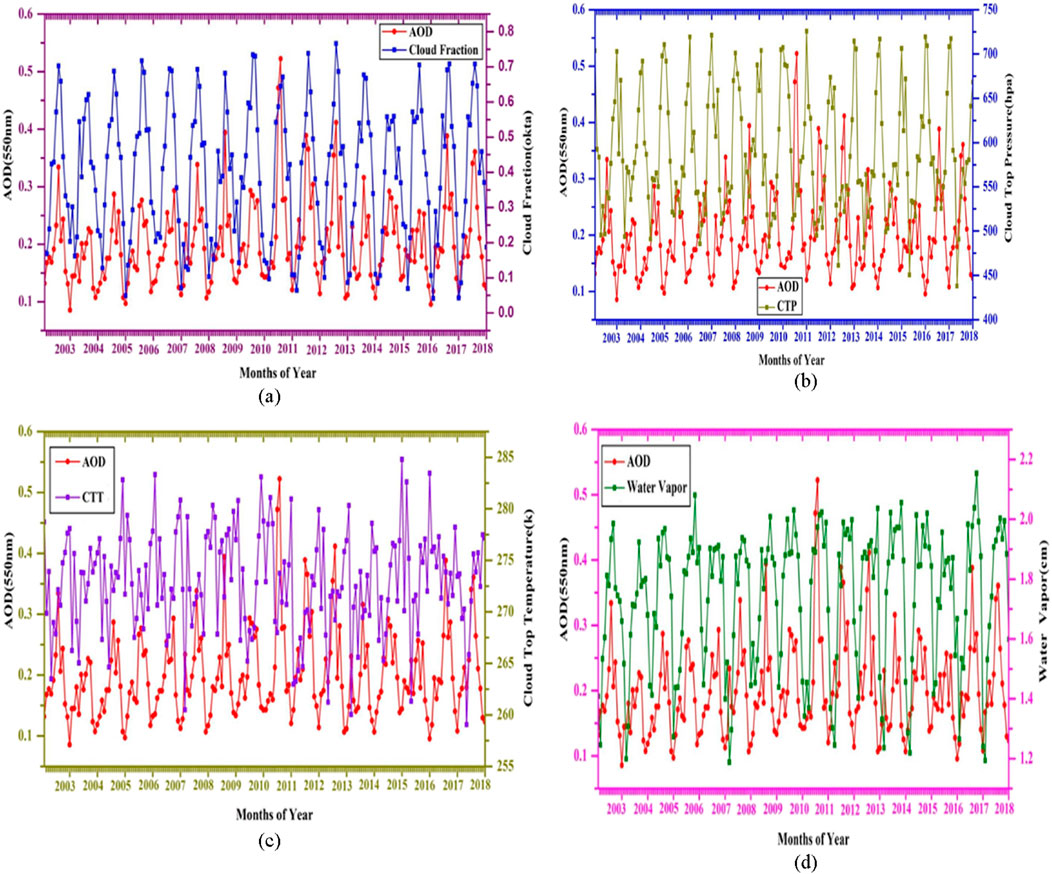
Figure 4. Correlation of aerosol optical depth and (A) cloud fraction, (B) cloud top pressure, (C) cloud top temperature, and (D) water vapor for the 16-year period (January 2003– December 2018) over Addis Ababa.
4.1 Correlation between AOD and cloud fraction
Figure 4A illustrates the temporal correlation between AOD and CF for Addis Ababa. On the left side of the Y-axis, AOD values are displayed, while the right side shows CF values. The figure indicates that CF generally increases with increasing AOD, with both parameters exhibiting similar trends over time. Specifically, CF increased with AOD from May to June and then decreased to its lowest value in December over the entire study period. The correlation coefficient between AOD and CF was 0.678, with a corresponding p-value of 0.005, indicating that this correlation is statistically significant. This relationship may be partly explained by relative humidity (RH), as Myhre et al. (2007) found that higher RH near clouds can increase AOD due to greater water uptake by aerosols. Kaufman et al. (2005) also observed that cloud cover increases with increasing aerosol concentrations, potentially due to changes in large-scale atmospheric circulation. Regions of low atmospheric pressure, such as those influenced by the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ), tend to accumulate aerosols and moisture, creating favorable conditions for cloud formation (Chou et al., 2002; Kaufman et al., 2005). Given that the Ethiopian sector lies within the ITCZ, this convergence of moisture and aerosols likely contributes to the observed correlation between AOD and CF.
4.2 Correlation between AOD and CTP
The correlation between AOD and CTP for the Addis Ababa region over the period from 2003 to 2018 is shown in Figure 4B. A negative correlation between CTP and AOD has been noticed over the entire period. Correlation coefficients for AOD and CTP were −0.582 (p = 0.018). This statistically significant result suggests a meaningful inverse relationship between AOD and CTP during the study period. Several studies (Kaufman et al., 2005; Myhre et al., 2007) have reported that CTP decreased as AOD increased due to the suppression of precipitation by increasing cloud lifetime and, thus, affecting the cloud albedo and changing the cloud top pressure. Myhre et al. (2007) reported that cloud top pressure also decreases with AOD because the cloud’s effective radius increases with a decreasing cloud top pressure of convective clouds. This is supported by the cloud fraction increase with AOD and cloud top pressure decrease with cloud fraction (Balakrishnaiah et al., 2012).
4.3 Correlation between AOD and CTT
To understand the relationship between atmospheric and surface properties, CTT is an important factor, as it also plays a significant role in studies of the Earth’s radiation budget. The temporal correlation between AOD and CTT for the Addis Ababa region from 2003 to 2018, as shown in Figure 4C, indicates that CTT increased as AOD decreased throughout the study period. This relationship is characterized by a negative correlation, with a correlation coefficient of −0.314 (p = 0.24). Despite this negative correlation, the cloud top temperature was found to be relatively insensitive to changes in aerosol number. This suggests that while aerosols affect cloud properties such as particle size near the cloud top, optical thickness, and cloud fraction, they do not significantly alter the cloud top temperature or induce substantial longwave radiative forcing. Moreover, increasing anthropogenic aerosol loading can influence cloud top temperature and humidity profiles through the induced secondary circulation, thus affecting the cloud top temperature, as suggested by Sekiguchi et al. (2003).
4.4 Correlation between AOD and WV
Aerosols can influence the Earth’s atmosphere through interactions with water vapor (Myhre et al., 2007). Figure 4D shows the time series plot for AOD and WV in the Addis Ababa region from 2003 to 2018. The correlation coefficient between AOD and WV is 0.427 (p = 0.10), indicating a positive relationship between the two variables over the study period. This result aligns with findings from other studies (Alam et al., 2010; Alam et al., 2014; Ranjan et al., 2007).
Increased water vapor during summer corresponds with higher AOD, suggesting that aerosols may experience hygroscopic growth. This observation is consistent with Ranjan et al. (2007). During winter, lower aerosol concentrations lead to reduced WV. The water-absorbing ability of aerosols varies by type; for instance, dust particles can become hygroscopic if coated with soluble inorganic aerosols (Myhre et al., 2007). The hygroscopic nature of aerosols is influenced by factors such as humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and temperature (Aloysius et al., 2009). Aerosol water uptake affects particle size, chemical composition, and optical properties, impacting cloud formation through condensation processes.
5 Conclusion
The present investigation has revealed the temporal trends and temporal correlation between AOD and different cloud parameters derived from MODIS data on board the Aqua and Terra satellites for the period from January 2003 to December 2018 over Addis Ababa. The time series analysis of AOD clearly shows an increasing trend from January 2003 to December 2018 over Addis Ababa. This increment in aerosol loading might be due to major influential sources such as rapid urbanization, resulting in an increase in automobile transportation, industrial emissions, a large number of construction activities, and the increase in the amount of aerosols produced from biomass burning. The dense population, geography affected by terrain and local sources, climate, and economy are also closely related to aerosol climatology. The AOD exhibits seasonal variation, with lower values in the winter months (January/February) and higher values during the summer season (June/July). The reason for high values of AOD in summer is higher air temperatures, which tend to hold abundant atmospheric water vapor, facilitating the hygroscopic growth of aerosols. The correlation between AOD and CF was found to be high and positive for Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, due to convergence zones (ITCZ) that accumulate aerosols and water vapor, thus generating conditions favorable for cloud formation. In contrast, a negative correlation was observed between AOD and CTP and CTT. AOD increased as CTT decreased throughout the period of study. The correlation between AOD and WV is positive (correlation coefficient = 0.427). We observed that WV is also higher during the summer, matching the increase in AOD and indicating the possibility of hygroscopic growth of aerosols. Changes in water uptake of aerosols can, therefore, lead to changes in both direct and indirect radiative forces on the climate.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/.
Author contributions
GY: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing–review and editing, and writing–original draft. DF: software, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing, formal analysis, and methodology. TM: conceptualization, data curation, validation, visualization, writing–review and editing, and writing–original draft. YW: data curation, investigation, visualization, writing–review and editing, and writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge NASA’s Earth Science Enterprise for providing MODIS data products for this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alam, K., Iqbal, M. J., Blaschke, T., Qureshi, S., and Khan, G. (2010). Monitoring spatio-temporal variations in aerosols and aerosol–cloud interactions over Pakistan using MODIS data. Adv. Space Res. 46 (9), 1162–1176. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2010.06.025
Alam, K., Khan, R., Blaschke, T., and Mukhtiar, A. (2014). Variability of aerosol optical depth and their impact on cloud properties in Pakistan. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 107, 104–112. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2013.11.012
Alhaj Mohamad, F. (2015). Retrieval of aerosol optical depth from MODIS data at 500 m resolution compared with ground measurement in the state of Indiana.
Aloysius, M., Mohan, M., Suresh Babu, S., Parameswaran, K., and Krishna Moorthy, K. (2009). Validation of MODIS derived aerosol optical depth and an investigation on aerosol transport over the South East Arabian Sea during ARMEX-II. Ann. Geophys. 27, 2285–2296. doi:10.5194/angeo-27-2285-2009
Balakrishnaiah, G., Reddy, B. S. K., Gopal, K. R., Reddy, R., Reddy, L., Swamulu, C., et al. (2012). Spatio-temporal variations in aerosol optical and cloud parameters over Southern India retrieved from MODIS satellite data. Atmos. Environ. 47, 435–445. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.10.032
Balarabe, M., Abdullah, K., and Nawawi, M. (2015). Seasonal variations of aerosol optical properties and identification of different aerosol types based on AERONET data over sub-Sahara West-Africa. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 6 (1), 13–28. doi:10.4236/acs.2016.61002
Chou, M.-D., Chan, P.-K., and Wang, M. (2002). Aerosol radiative forcing derived from SeaWiFS-retrieved aerosol optical properties. J. Atmos. Sci. 59 (3), 748–757. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(2002)059<0748:arfdfs>2.0.co;2
Cochrane, L., and Costolanski, P. (2013). Climate change vulnerability and adaptability in an urban context: a case study of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Int. J. Sociol. Anthropol. 5 (6), 192–204. doi:10.5897/ijsa2013.0459
Endale, T. A., Raba, G. A., Beketie, K. T., and Feyisa, G. L. (2024). Exploring the trend of aerosol optical depth and its implication on urban air quality using multi-spectral satellite data during the period from 2009 to 2020 over dire dawa, Ethiopia. Nat. Environ. and Pollut. Technol. 23 (1), 1–15. doi:10.46488/nept.2024.v23i01.001
Eshet, A., and Raju, J. P. (2022). Daily and seasonal variation of aerosol optical depth and angstrom exponent over Ethiopia using MODIS data. Pollution 8 (1), 315–329.
Etyemezian, V., Tesfaye, M., Yimer, A., Chow, J., Mesfin, D., Nega, T., et al. (2005). Results from a pilot-scale air quality study in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Atmos. Environ. 39 (40), 7849–7860. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.08.033
Getachew, A. (2009). The study of aerosol microphysical and optical parameters, total columnar ozone and water vapor content derived from sunphotometer. Addis Ababa University.
Grythe, H. (2017). Quantification of sources and removal mechanisms of atmospheric aerosol particles. Stockholm: Department of Environmental Science and Analytical Chemistry.
Homa, M. G., Tsidu, G. M., and Nega, D. T. (2017). Stratospheric aerosol climatology over Ethiopia and retrieval of its size distribution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 1–14.
Kafle, D., and Coulter, R. (2013). Micropulse lidar-derived aerosol optical depth climatology at ARM sites worldwide. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118 (13), 7293–7308. doi:10.1002/jgrd.50536
Kang, N., Kumar, K. R., Yin, Y., Diao, Y., and Yu, X. (2015). Correlation analysis between AOD and cloud parameters to study their relationship over China using MODIS data (2003-2013): impact on cloud formation and climate change. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 15 (3), 958–973. doi:10.4209/aaqr.2014.08.0168
Kaufman, Y. J., Koren, I., Remer, L. A., Rosenfeld, D., and Rudich, Y. (2005). The effect of smoke, dust, and pollution aerosol on shallow cloud development over the Atlantic Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102 (32), 11207–11212. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505191102
Kulmala, M., Hienola, J., Pirjola, L., Vesala, T., Shimmo, M., Altimir, N., et al. (1999). A model for NOx–O3–terpene chemistry in chamber measurements of plant gas exchange. Atmos. Environ. 33 (14), 2145–2156. doi:10.1016/s1352-2310(99)00069-2
Kumar, K. R., Narasimhulu, K., Reddy, R., Gopal, K. R., Reddy, L. S. S., Balakrishnaiah, G., et al. (2009). Temporal and spectral characteristics of aerosol optical depths in a semi-arid region of southern India. Sci. total Environ. 407 (8), 2673–2688. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.028
Li, Z., Wang, Y., Guo, J., Zhao, C., Cribb, M. C., Dong, X., et al. (2019). East Asian study of tropospheric aerosols and their impact on regional clouds, precipitation, and climate (EAST-AIRCPC). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 124 (23), 13026–13054. doi:10.1029/2019jd030758
Luoma, K., Virkkula, A., Aalto, P., Petäjä, T., and Kulmala, M. (2019). Over a 10-year record of aerosol optical properties at SMEAR II. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 19 (17), 11363–11382. doi:10.5194/acp-19-11363-2019
Mahowald, N. M., and Kiehl, L. M. (2003). Mineral aerosol and cloud interactions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30 (9). doi:10.1029/2002gl016762
Myhre, G., Myhre, C., Samset, B., and Storelvmo, T. (2013). Aerosols and their relation to global climate and climate sensitivity. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 4 (5), 7.
Myhre, G., Stordal, F., Johnsrud, M., Kaufman, Y., Rosenfeld, D., Storelvmo, T., et al. (2007). Aerosol-cloud interaction inferred from MODIS satellite data and global aerosol models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 7 (12), 3081–3101. doi:10.5194/acp-7-3081-2007
Pan, L., Che, H., Geng, F., Xia, X., Wang, Y., Zhu, C., et al. (2010). Aerosol optical properties based on ground measurements over the Chinese Yangtze Delta Region. Atmos. Environ. 44 (21-22), 2587–2596. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.04.013
Platnick, S., King, M. D., Ackerman, S. A., Menzel, W. P., Baum, B. A., Riédi, J. C., et al. (2003). The MODIS cloud products: algorithms and examples from Terra. IEEE Trans. geoscience Remote Sens. 41 (2), 459–473. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2002.808301
Ranjan, R. R., Joshi, H., and Iyer, K. (2007). Spectral variation of total column aerosol optical depth over Rajkot: a tropical semi-arid Indian station. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 7 (1), 33–45. doi:10.4209/aaqr.2006.08.0012
Remer, L. A., Tanré, D., Kaufman, Y. J., Levy, R., and Mattoo, S. (2006). Algorithm for remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol from MODIS: collection 005. Natl. Aeronautics Space Adm. 1490.
Sekiguchi, M., Nakajima, T., Suzuki, K., Kawamoto, K., Higurashi, A., Rosenfeld, D., et al. (2003). A study of the direct and indirect effects of aerosols using global satellite data sets of aerosol and cloud parameters. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 108 (D22). doi:10.1029/2002jd003359
Tang, J., Wang, P., Mickley, L. J., Xia, X., Liao, H., Yue, X., et al. (2014). Positive relationship between liquid cloud droplet effective radius and aerosol optical depth over Eastern China from satellite data. Atmos. Environ. 84, 244–253. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.08.024
Wang, S., Cohen, J. B., Lin, C., and Deng, W. (2020). Constraining the relationships between aerosol height, aerosol optical depth and total column trace gas measurements using remote sensing and models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 20 (23), 15401–15426. doi:10.5194/acp-20-15401-2020
Keywords: moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer, aerosol optical depth, cloud fraction, cloud top pressure, cloud top temperature and water vapor
Citation: Yirga G, Fekrie D, Menberu T and Workineh Y (2024) Time series trends and correlations of aerosol optical depth and cloud parameters over Addis Ababa. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1452075. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1452075
Received: 20 June 2024; Accepted: 14 October 2024;
Published: 29 October 2024.
Edited by:
Pavla Dagsson-Waldhauserova, Agricultural University of Iceland, IcelandReviewed by:
Jianfeng Li, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (DOE), United StatesChunsong Lu, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Yirga, Fekrie, Menberu and Workineh. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Getnet Yirga, Z2V0bmV0eWlyZ2E0MUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Getnet Yirga
Getnet Yirga Demelash Fekrie1
Demelash Fekrie1 Yenesew Workineh
Yenesew Workineh