
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Earth Sci., 03 May 2024
Sec. Geohazards and Georisks
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2024.1363559
Outburst floods can affect the survival adaptability of fish. Although the survival adaptability of many fish species under low steady-flow conditions has been studied, research on the survival adaptability of fish species under large outburst flood conditions is lacking. This paper takes the 2018 Baige landslide dam as an example. A breach model was developed to calculate the outburst discharge of the landslide dam. The outburst flood hydrograph is simulated with the breach model, which shows that the difference between the peak discharge of the dam break simulation results and the measured data is 0.13×104 m3/s. In addition, the simulated hydrographs are the same as the measured hydrographs. Furthermore, a two-dimensional fish habitat model was used to analyse the adaptability of Schizothorax to survival during the breaching process. For the survival adaptability of Schizothorax, we observed that as the flow rate increased the weighted usable area (WUA) decreased, which indicated a decrease in the adaptability of Schizothorax survival. In contrast, as the flow rate decreased and the WUA increased, the survival adaptability of Schizothorax improved. In addition, the WUA of Schizothorax changed with the substrate of the riverbed; the smaller the channel suitability index (CSI) the greater the WUA. This study revealed the impact of outburst floods triggered by landslide dam failure on the survival adaptability of Schizothorax, and a method for assessing the impact of outburst floods on fish habitat adaptability is provided.
An outburst flood triggered by landslide dam failure is a highly destructive and dangerous disaster. The southeastern part of the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau has obvious terrain undulations, which makes it one of the most prone areas to landslide dam failure and flood disasters in China (Shi et al., 2017). Landslide dams are mainly composed of rock blocks and debris that accumulate in valleys and often block rivers. Statistics indicate that 44%–51% of landslide dams fail within 1 week, 59%–71% fail within 1 month, and 83% fail within 6 months after blockage. Furthermore, floods caused by barrier lake outbursts can propagate tens or even hundreds of miles downstream (Huggel et al., 2002).
Every year, approximately 2.5 billion people around the world are threatened by floods and approximately 70% of these flood events are related to outburst floods (Herget et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2019; Alfieri et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2023). In the last century, floods, such as the catastrophic floods caused by heavy rains in Hubei Province, China, in 1931 and 1945 (Zong and Chen, 2000; Wang and Plate, 2002) and Bangladesh in 1974 (Hamidifar and Nones, 2023a; Hamidifar and Nones, 2023b), and floods in central China in 1975 (Liu et al., 2019) and in Venezuela in 1999 (Altez and Revet, 2005), have had extremely serious impacts on humans. This is especially true in China as the impacts of climate change and human activities intensify and the frequency and severity of outburst floods are also increasing (Gao et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023). For example, outburst floods were triggered by the Sedongpu landslide dam failure in the Brahmaputra River, China, in 2018 (An et al., 2021), and outburst floods were triggered by the Baige landslide dam in the Jinsha River, China, in 2018 (Yang et al., 2022). This trend has caused serious damage to river ecosystems, which serve as important habitats for fish species. The adaptability of fish to flood events has become one of the key factors that determines their survival and reproduction (Pires et al., 2008; Wesner, 2011; Ding, 2005).
The adaptive impacts of flood events on fish are manifold. First, the increase in water level caused by floods not only changes the living environment of fish but also directly affects their physiological functions (Bolland et al., 2015; Hung et al., 2022). Changes in water level can cause hypoxia in fish because the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the water fluctuates as the water level rises and falls. In addition, floods carry large amounts of sediment and pollutants, which may cause harm to the respiratory and digestive systems of fish (Perna and Pearson, 2008). Changes in water pH and temperature caused by flooding may also have an impact on fish growth and reproduction. For example, fluctuations in pH may affect fish bone development and reproductive behaviour, while changes in temperature may affect fish metabolic rates and reproductive cycles (Warren et al., 2010; Solovyev et al., 2018).
Floods not only impact water quality but also lead to damage and loss of fish habitat such as aquatic plants, stones, and trees. However, floods are crucial for the survival and reproduction of fish (Jiménez Segura et al., 2010) and flooding events may also affect fish behaviour. For example, flooding may cause fish to escape or gather in specific areas and thereby affect their normal foraging and breeding behaviours (Boavida et al., 2011; Hogberg and Pegg, 2016).
Water depth, flow velocity, and the composition of streambed material have been identified as major factors affecting fish habitat (Palmer et al., 2007). To date, many scholars have used different methods to study the habitats of fish in different areas. For example, Grüss et al. (2021) utilized the nearshore fish atlas of Alaska and ShoreZone databases to identify Gadus macrocephalus in the boreal region of southeastern Alaska as well as Walleye pollock in Prince William Sound. Boudreault et al. (2021) used probability density functions to study Atlantic salmon in the Sainte Marguerite River (Quebec, Canada). Baynes et al. (2023) used generalized linear multiple regression models to study fish species in the Conasauga River in Georgia, United States. Furthermore, the WUA parameter is also usually used to evaluate the habitat of fish. For example, with respect to the WUA parameter, Wang et al. (2023) studied the survival adaptability of fish in mountain areas, and Hung et al. (2022) studied the survival adaptability of fish in the Zengwen River.
This study calculated the outburst flood discharge of the Baige landslide dam and analysed the adaptive habits of fish in the area using WUA parameters and fish habitat models. By studying the changes in fish habitat during the flood process, we explored the impact of floods on fish survival adaptability during the outburst process and changes in fish survival adaptability. Specifically, we selected Schizothorax in the river as the fish species of interest. This paper provides a method and reference for research on fish habitats during outburst floods.
The Jinsha River is located in the southeastern part of the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau. The river has a total length of 3,484 km, the basin area reaches 5×106 km2, and it is one of the tributaries of the Yangtze River Basin (Wang et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2017; Shi et al., 2017). The Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau region has obvious terrain relief characteristics. The steep slopes cut by major rivers in mountainous areas aggravate the terrain conditions of landslide dam events. The Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau suture zone, which is a strongly tectonic fracture zone, plays a crucial role in the development of landslide dam events (Liang et al., 2018; Liao et al., 2018).
On 10 October 2018, a large-scale landslide occurred on the Jinsha River in the border area between Sichuan Province and Tibet. The landslide blocked the Jinsha River and formed a barrier lake that affected the Sichuan, Yunnan, and Tibet Provinces (Li et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2021).
Due to the landslide, a barrier lake with a volume of approximately 2.5×107 m3 was formed. On November 13, an explosive flood occurred with a peak flow of 3.1×104 m3/s (Ouyang et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2019; Fan et al., 2020; Li et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2022). This catastrophic flood event not only destroyed many bridges (Figure 1D) but also had a catastrophic impact on the lives of more than 20,000 people and a serious impact on fish habitats (An et al., 2021).
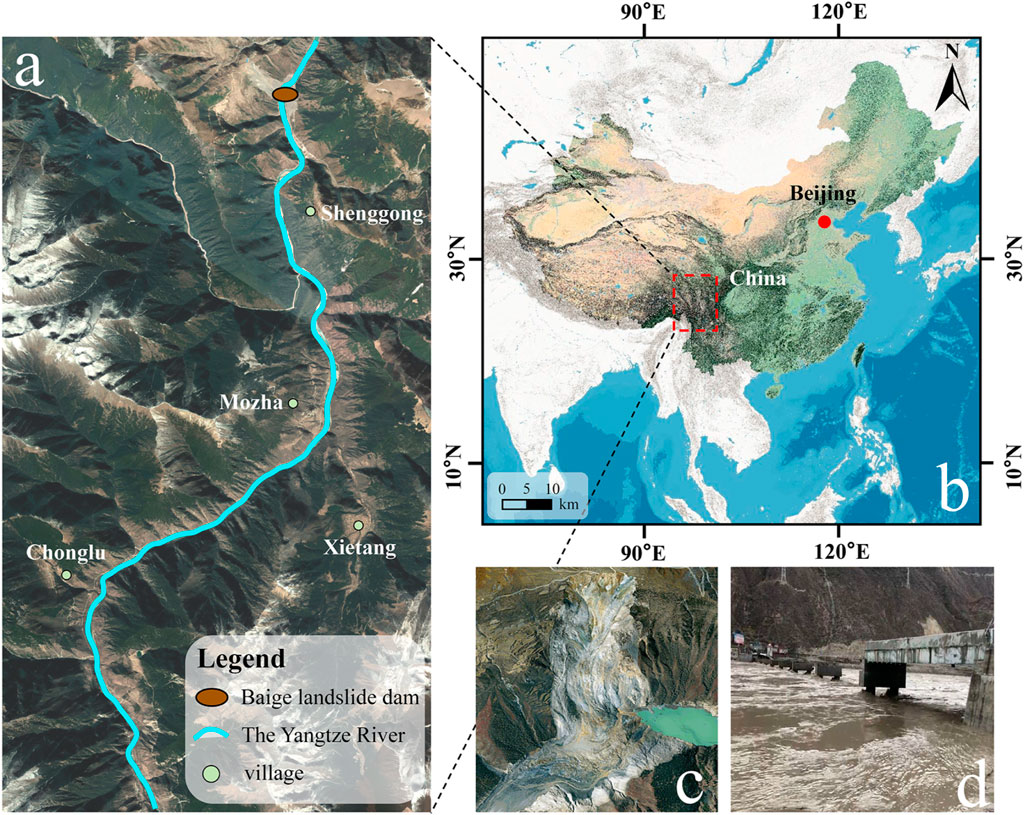
Figure 1. Study area and location of the Baige landslide dam. (A). Study area map (www.google.cn). The study area covers a 14 km range from the Baige landslide dam downstream. (B). Study area coordinate map (from the ArcGIS base map). (C). The overall view of the Baige landslide dam and the diagram of blocking the river (www.dili360.com). (D). A picture of the Jinsha River Bridge damaged by outburst floods (99°00′41″E, 29°46′01″N; news.cctv.com).
This paper examines the 14 km river range downstream of the Baige landslide dam as the study area (Figure 1A). The data used in this paper were obtained from Landsat eight remote sensing images.
The physics-based simplified dam failure model is currently the most widely used simulation model in disaster risk assessment. This study simulates the dam failure process through a dam failure model that considers the erosion process.
Due to the impounding characteristics of the barrier lake, when the dam starts to breach, the water level and volume of the barrier lake undergo changes influenced by inflows from the upstream basin and outflows from the breach. By combining the area curve of the barrier lake, the water level of the barrier lake can be determined. According to the principle of water balance, the variation in the volume of the barrier lake is calculated using Eq. 1:
where t is the time (s); V is the volume of water in the reservoir (m3); As is the surface area of the reservoir (m2); Zs is the elevation of the water level (m); Qin is the inflow (m3/s); Qk is the breach flow (m3/s); and Qspill is the spillway flow (m3/s). By combining the area curve of the barrier lake, the water level of the barrier lake can be determined, as shown in Eq. 2:
where Hs is the water level of the lake (m); p1, p2, and p3 are the parameters; and H0 is the reference height (m).
In this paper, the burst discharge is calculated using Eq. 3 (Coleman et al., 2002):
In the equation, Q is the flow rate (m3/s); A is the flow cross-sectional area (m2); h is the head at the flow calculation point; and Cd is the flow coefficient.
For the erosion calculation, the Meyer-Peter and Muller sediment transport equation was adopted (Meyer-Peter and Müller, 1948) Eqs 4, 5. The equation is as follows:
in:
In Eq. 5,the θ follows Eq. 6 as
In the equation, ϕ is the dimensionless sediment transport rate; θ is the dimensionless shear stress; θcr is the dimensionless critical shear stress; C is the correction coefficient; τ is the shear stress (N/m2); Qs is the sediment transport rate per unit width (m2/s); D50 is the median particle size (m); ρ is the density of water (kg/m3); ρs is the density of sediment (kg/m3); and g is the gravitational acceleration (m/s2). Among them, C=8 (Li, 2011), and in general, the dimensionless critical shear stress is θcr =0.047.
During the overtop bursting process, vertical and lateral erosion occurs at the breach. These two erosion processes can be calculated using Eq. 7. According to the conservation of soil mass, the vertical erosion of a breach can be expressed as (Xue et al., 2021):
where Δz is the change in elevation of the breach bottom (m); p is the porosity (%); L is the length of the breach channel (m); and Δt is the time change (s).
In addition, the Manning coefficient was calculated with Eq. 8 (Larsen and Lamb, 2016).
where rd and rbr are the hydraulic roughness conversion parameters and σbr is the standard deviation of the bedrock elevation (m).
The Manning coefficient we calculated is n=0.0557 m1/3S with the above equation. Table 1 shows the data used in this paper. Figure 2 shows the storage capacity curve of the barrier lake (Liu et al., 2021). All variables are shown in TABLE A1.
The River2D software was used for the numerical simulation of the habitat in this paper (Boskidis et al., 2018; Baek et al., 2021). River2D is a two-dimensional model of habitat simulation designed specifically for natural streams and rivers. It is a finite element method model that is now used in various studies and works around the world (Lu et al., 2021; Oliveira et al., 2016; Blackburn and She, 2021). The software uses the shallow water equation to analyse the flow hydrodynamic characteristics in the river channel. Among them, the continuity equation and momentum equation constitute governing equations. These equations include the water continuity equation and the kinetic energy conservation equation in the x and y directions (Oliveira et al., 2016; Baek et al., 2021).
River2D requires detailed terrain data for the study area in the form of x, y, and z, where x and y represent geographical coordinates and z represents terrain elevation. Using DEM data, a large number of x, y, and z point coordinates were obtained and represent the river terrain and its characteristics (Boskidis et al., 2018).
These points are introduced into the River2D-BDE to create the digital terrain of the river and provide a background for simulating the model. Then, the digital model elevation generated in the above process is introduced into River2D-MESH to generate the research area grid.
The inflow boundary adopts unsteady flow, i.e., the outburst hydrograph, and the outflow boundary adopts the open boundary.
The WUA parameter was used to evaluate the fish habitat. The WUA can be obtained by the Eq. 9:
In the equation, CSF(Vi,Di,Ci) is the combined suitability value where i is the number of divided units; Vi is the flow velocity CSF of subarea I; Di is the water depth CSF of subarea I; Ci is the bottom material or coverage CSF of subarea i; and Ai is the bottom area of subarea i (m2). Considering the compensation effects among the factors that constitute the habitat, the Eq. 10 for the suitability value of the habitat combination is:
Schizothorax, a common fish that lives near the Baige landslide dam, was selected as the research object. In previous studies, several scholars determined the hydraulic suitability curve (HSC) of Schizothorax through field surveys, as shown in Figure 3 (Hung, H. et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2019).
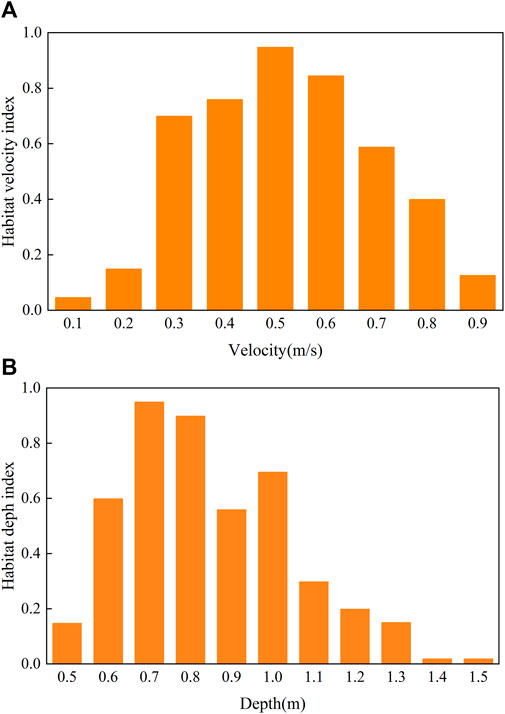
Figure 3. Schizothorax adaptability curve. (A) Curves showing the ability of Schizothorax to adapt to flow velocity. (B) An adaptability curve of Schizothorax to current depth.
Fish habitats can also be affected by differences in the substrate. When outburst floods occur, these floods will carry a large amount of sediment and transport the sediment to downstream areas, which causes changes in the river substrate and affects fish habitats. This paper focuses specifically on the adaptability of Schizothorax to survive under different substrate conditions. The applied substrate data are listed in the following table 2:
The research methods and steps are shown in Figure 4, and the process is divided into five total steps. The first stage is the data preparation stage; the prepared data are input into the dam breach model, the dam break model is established, and the outburst flow curve is calculated. The hydrograph curve is combined with the topographic and Manning coefficient data in River2D to establish a Schizothorax habitat model, and finally, the results are exported for analysis.
The simulation results of the Baige landslide dam outburst flood is shown in Figure 5. The characteristics of the flow curve indicate that it first rises rapidly to peak flow and then drops to a stable stage. This is consistent with the characteristics of the measured data. In addition, the peak discharge of the simulation results is 2.96×104 m3/s, and the measured discharge is 3.09×104 m3/s (Carling, 2013). There is only a 4.39% difference between the two, which shows that the simulation results are consistent with the measured data. Additionally, the time interval between the measured data and simulated data is 2 h.
The simulation results show that the breach model developed in this paper is suitable for calculating the outburst discharge of landslide dams.
To facilitate the research, we divided the outburst flow into three parts (Figure 5). The flow before peak flow is Qq, the flow at peak flow is Qt, and the flow after peak flow is Qh.
In the simulation, we selected the flow velocity and flow depth adaptability of Schizothorax in the entire study area when Qq=10000 m3/s, Qt=30000 m3/s and Qh=900 m3/s (Figure 6). As shown in Figures 6A–C, when Qt=30000 m3/s, Schizothorax has the smallest flow velocity adaptability area, which is mainly distributed in a large part of the area and is 0–4.5 km away from the Baige landslide dam. At Qh=900 m3/s, Schizothorax has the largest flow velocity adaptability area and covers the entire river channel. At Qq=10000 m3/s, the distribution characteristics of the flow velocity adaptability are similar to those at Qh=900 m3/s, but the overall area is much smaller than that at Qh=900 m3/s.
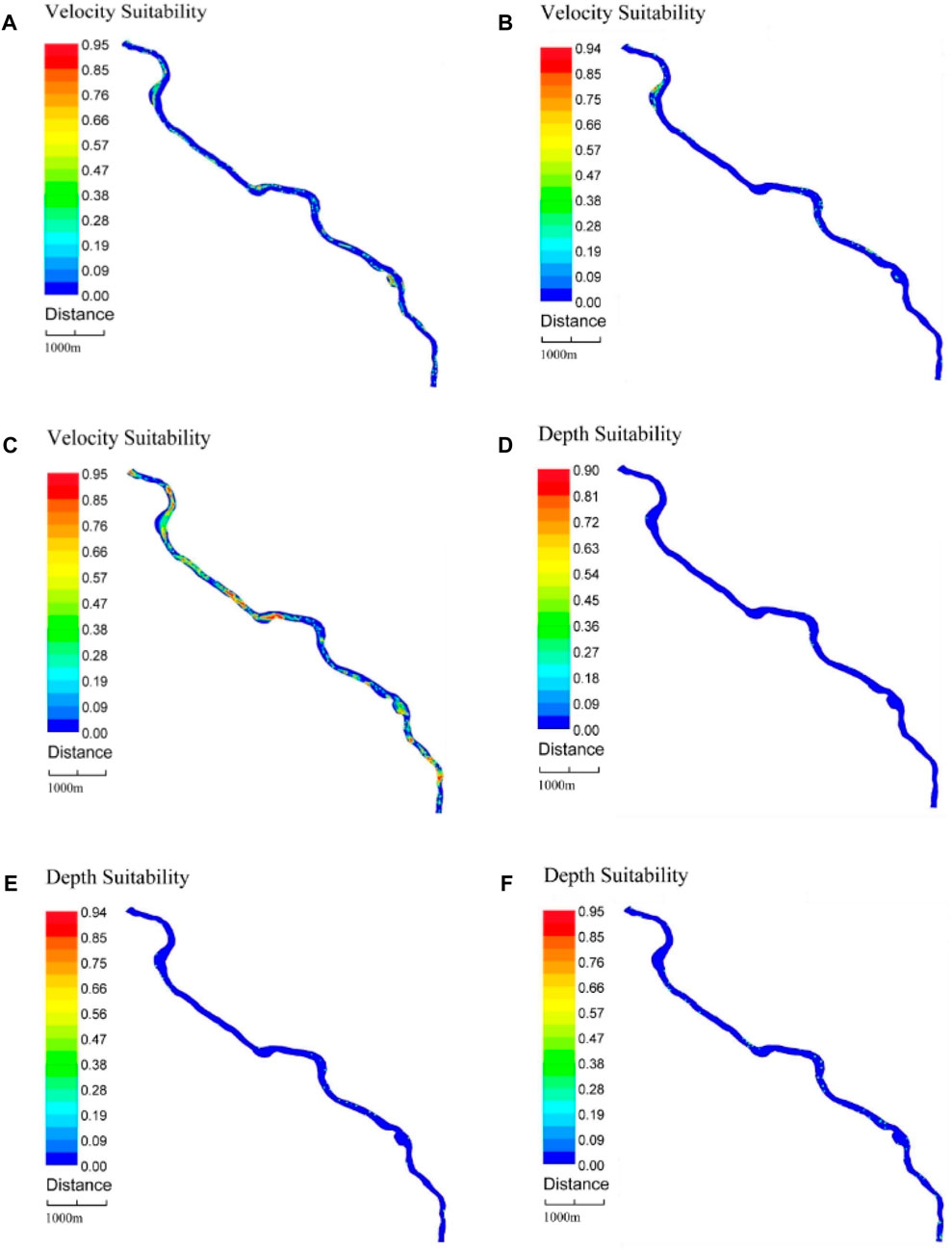
Figure 6. Flow velocity and depth adaptability of Schizothorax in the river channel. (A) Flow velocity adaptability when Qq=10000 m3/s. (B) Flow velocity adaptability when Qt=30000 m3/s. (C) Flow velocity adaptability when Qh=900 m3/s. (D) Flow depth adaptability when Qq=10000 m3/s. (E) Flow depth adaptability when Qt=30000 m3/s. (F) Flow depth adaptability when Qh=900 m3/s.
The flow depth adaptability is shown in Figures 6D–F. When Qq=10000 m3/s, the flow depth adaptability near the Baige landslide dam is 4.5 km, which is within the range of 8.6 km–12.5 km and accounts for a large proportion of the entire study area. At Qt=30000 m3/s, the flow depth adaptability is the lowest across the entire study area. When Qh=900 m3/s, the flow depth has the greatest adaptability and a wide distribution range.
In summary, when an outburst flood occurs, the greater the flow is, the smaller the adaptability zone of the Schizothorax flow velocity and flow depth, whereas the smaller the flow is the larger the adaptability zone. Overall, the adaptive zone of Schizothorax tended to decrease within the study area as the outburst flood flow increased.
Figure 7 shows that as the substrate adaptability increased, the WUA of Schizothorax under different flow rates also increased. The relationships between the WUA and substrate indices under each flow rate are similar.
Specifically, when Qt=30000 m3/s and Qh=25000 m3/s, the difference in WUA values between the two is small, and the WUA value when Qh=25000 m3/s is greater than the WUA value when Qt=30000 m3/s. Similarly, when Qq=20000 m3/s and Qh=15000 m3/s, the WUA values are almost equal, and the WUA value of Qh=15000 m3/s is greater than the WUA value of Qq=20000 m3/s. When Qq=10000 m3/s and Qh=5,000 m3/s, the difference in WUA values is small, and the WUA value when Qh=5,000 m3/s is greater than the WUA value when Qq=20000 m3/s. Among all traffic flows, when Qh=900 m3/s, the WUA value is the largest. In addition, as the flow rate and substrate adaptability increase, the WUA growth rate under each flow rate also differs. When the substrate adaptability increases from 0.565,065 to 0.827,863, the growth rate is the largest when Qh=900 m3/s, and the growth rate is the smallest when Qt=30000 m3/s. This shows that under low-flow conditions (Qh=900 m3/s), the changes in the WUA of Schizothorax to substrate adaptability are more drastic.
Figure 8 shows that regardless of the substrate adaptability of Schizothorax, the entire histogram shows similar characteristics under different flow rates, which shows a trend of changes in the outburst flow curve from large to small and then to large. Specifically, as the flow rate changes, the WUA first increases, then decreases, and then increases on the outburst flow curve. In addition, regardless of the substrate adaptability, when Qt=30000 m3/s, the WUA reaches its minimum value, and when Qh=900 m3/s, the WUA reaches its maximum value. This shows that in the survival adaptability analysis of Schizothorax, discharge had the most significant impact on the WUA.
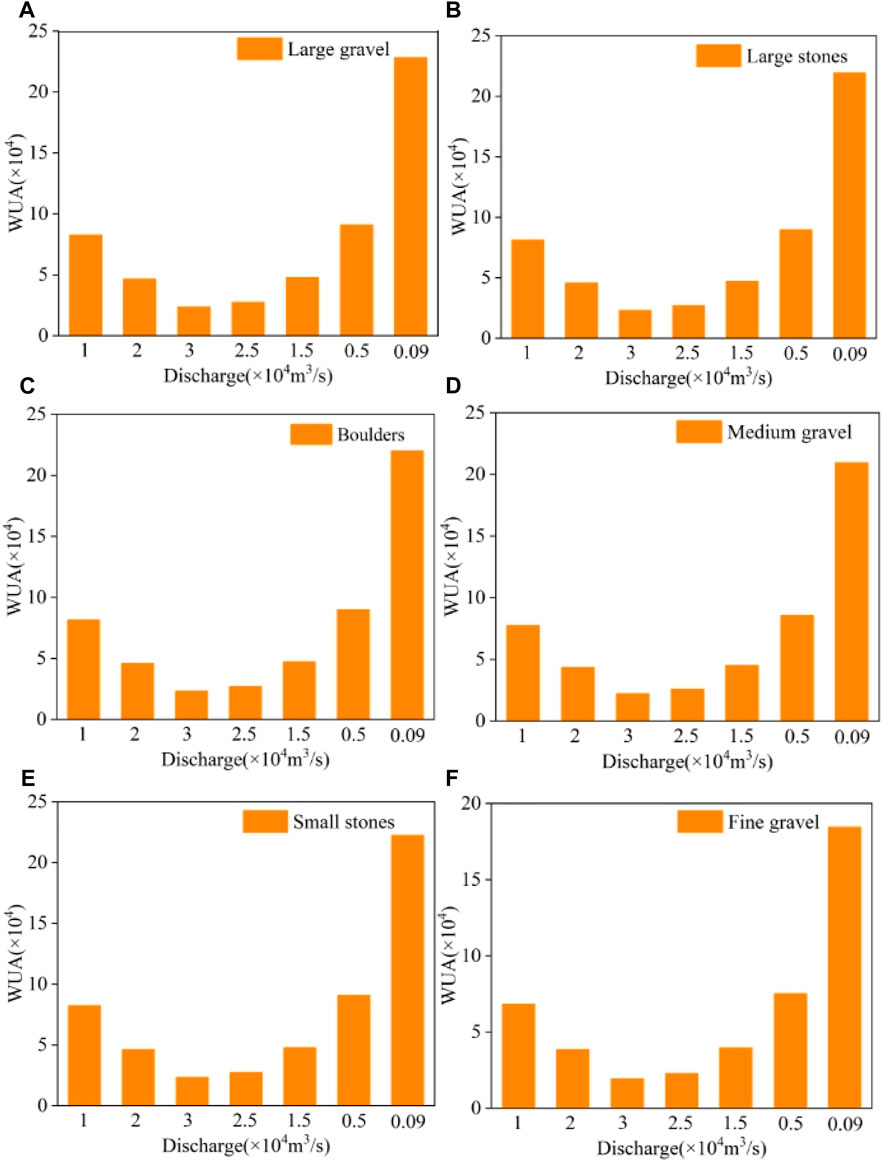
Figure 8. WUA graphs under different flow rates. (A) WUA under large gravel. (B) WUA under large stones. (C) WUA under boulders. (D) WUA under medium gravel. (E) WUA under small stones. (F) WUA under fine gravel.
Many studies have shown that adaptability varies among different fish species in different regions. For example, Hung et al., (2022) used the River2D model to conduct WUA simulations of three different fish species in the Tseng Wen River under ten different constant flows (Figure 9A). Figure 9A shows that when the discharge occurred in the range of 3.38–3,550 m3/s, the WUA of these three fishes tended to increase, while in the range of 3,350–9,490 m3/s, the WUA of Cyprinidae and Gobiidae tended to decrease and the WUA of Balitoridae tended to increase. This shows that the survival adaptability of various fish species changes under different flow conditions, which is attributed to their different flow velocity and flow depth adaptability curves under the same substrate adaptability. Boskidis et al., (2018) also used the River2D model to simulate the habitats of four different fish species in the 134 km channel of the Nestos River basin under five different constant flows. The WUA results are shown in Figure 9B. Similar to the research results of Hsuan-Ju Hung et al. (2022), the WUA of different fish species showed a changing trend under different flow rates, among which the WUA of Alburnoides strymonicus decreased when the flow rate increased.
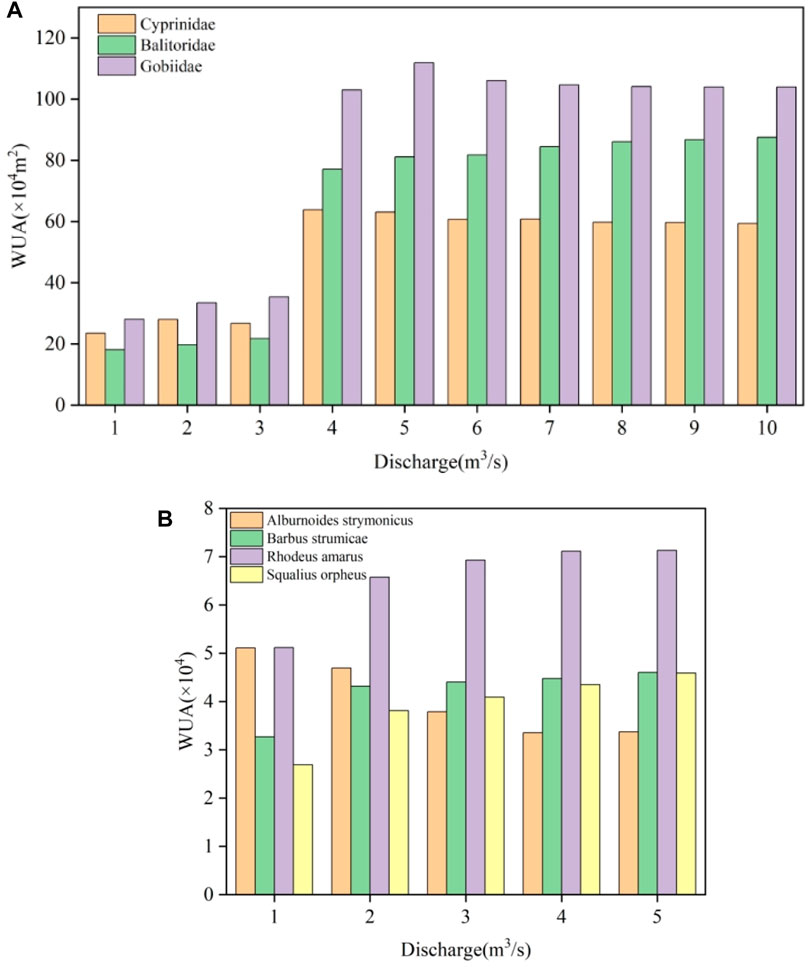
Figure 9. Fish WUA Results. (A) Results from a study by Hung et al. (2022) (B) Results from a study by Boskidis et al. (2018).
In summary, there are many factors that affect the survival adaptability of fish and the most important is discharge. The same substrate often depends on the flow velocity and flow depth adaptability of the fish itself. Limitations.
This study explored the adaptability of Schizothorax to outburst floods in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. However, the adaptations of other fish species within this study area have not yet been investigated, which provides ample scope for future research to gain an in-depth understanding of the survival strategies and adaptive mechanisms of different fish species during flooding events. Notably, the topographic changes caused by outburst floods were not considered in this study. However, this study assumed that the topography of the river channel remained unchanged during the flood process. In fact, floods may cause changes in riverbed and bank morphology. In addition, this study only calculated the adaptability of Schizothorax within 14 km downstream of the Baige landslide dam. We do not yet know the adaptability of fish in further downstream areas.
Although this study is somewhat limited, it reveals the survival adaptability of Schizothorax in the event of outburst floods and under different substrate conditions. This study provides a reference for research on the survival adaptability of fish under unsteady flow and large flow conditions. However, the lack of real substrate data for the riverbed in the study area limits our conclusions about the actual impact of substrate on Schizothorax.
This article provides a detailed simulation of the Baige landslide dam failure in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River and the habitat of Schizothorax. First, the outburst discharge of the dam break model was analysed and compared with the measured flow rate. By comparing measured data and simulation results, we determined that the simulated discharge was consistent with measured data. This is sufficient to demonstrate that the breach model developed in this paper is effective for discharge calculations during dam failure. At the same time, River2D was used to simulate the adaptability of Schizothorax.
To assess the adaptability of Schizothorax, we evaluated two different adaptability parameters under seven different flow rates and six different substrates. The results show that as the outburst discharge increased, the WUA of Schizothorax decreased. The conclusion is the same as that for increasing substrate adaptability. Overall, the method developed in this paper provides a method for studying the impacts of outburst floods on fish habitats.
In future work, expanding the research objects to include more fish types in the study area may be considered. At the same time, the impact of changes in river topography could be considered and more detailed and in-depth research could be conducted to explore the potential impact of these factors on fish adaptability.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
XX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Supervision, Visualization. TW: Software, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. QJ: Software, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XA: Software, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (Grant No. 2019QZKK0906), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42177149), the CRSRI Open Research Program (Program SNCKWV2019733/KY), Gansu Province’s 2021 Key Talent Project (Grant No. 2021RCXM066), Gansu Academy of Sciences Applied Research and Development Project (Grant No. 2021JK-07), Key Laboratory of Sediment Science and Northern River Training program (Grant No. IWHR-SEDI-2022-02).
We thank all of the funds for their support and River2D software (www.river2d.ca).
Author XJ was employed by China Power Construction Group Kunming Survey Design & research Institute Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alfieri, L., Dottori, F., Salamon, P., Wu, H., and Feyen, L. (2020). Global modeling of seasonal mortality rates from river floods. Earth's Future 8 (9), e2020EF001541. doi:10.1029/2020EF001541
Altez, R., and Revet, S. (2005). Contar los muertos para contar la muerte: discusión en torno al número de fallecidos en la tragedia de 1999 en el estado Vargas–Venezuela [J]. Revista Geográfica Venezolana 46, 21–43.
An, H., Ouyang, C., and Zhou, S. (2021). Dynamic process analysis of the Baige landslide by the combination of DEM and long-period seismic waves. Landslides 18, 1625–1639. doi:10.1007/s10346-020-01595-0
Baek, K. O., Lee, J. M., Ku, T. G., and Kim, Y. D. (2021). Evaluation of by-pass fishway operation for attraction efficiency based on GPS drifter field experiments. Water 13 (16), 2302. doi:10.3390/w13162302
Baynes, A. Y., Freeman, M. C., McKay, S. K., and Wenger, S. J. (2023). Habitat associations of riverine fishes among rocky shoals. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 32 (2), 336–347. doi:10.1111/eff.12690
Bejarano, M. D., Jansson, R., and Nilsson, C. (2018). The effects of hydropeaking on riverine plants: a review. Biol. Rev. 93 (1), 658–673. doi:10.1111/brv.12362
Blackburn, J., and She, Y. (2021). One-dimensional channel network modelling and simulation of flow conditions during the 2008 ice breakup in the Mackenzie Delta, Canada. Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 189, 103339. doi:10.1016/j.coldregions.2021.103339
Boavida, I., Pinheiro, A., Santos, J., and Ferreira, M. T. (2011). Does boulder placement improve habitat for stream fish. Paper presenterat vid EUROMECH Colloquium. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249657640.
Bolland, J. D., Nunn, A. D., Lucas, M. C., and Cowx, I. (2015). The habitat use of young-of-the-year fishes during and after floods of varying timing and magnitude in a constrained lowland river. Ecol. Eng. 75, 434–440. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.12.009
Boskidis, I., Kokkos, N., Sapounidis, A., Triantafillidis, S., Kamidis, N., Koutrakis, E., et al. (2018). Ecohydraulic modelling of Nestos River Delta under low flow regimes. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiology 18 (4), 391–400. doi:10.1016/j.ecohyd.2018.06.004
Boudreault, J., St-Hilaire, A., Chebana, F., and Bergeron, N. E. (2021). Modelling fish physico-thermal habitat selection using functional regression. J. Ecohydraulics 6 (2), 105–120. doi:10.1080/24705357.2020.1840313
Carling, P. A. (2013). Freshwater megaflood sedimentation: what can we learn about generic processes? Earth-Science Rev. 125, 87–113. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.06.002
Coleman, S. E., Andrews, D. P., and Grant Webby, M. (2002). Overtopping breaching of noncohesive homogeneous embankments. J. Hydraulic Eng. 128 (9), 829–838. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2002)128:9(829)
Ding, W. (2005). Aquatic animal conservation: challenges and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 12 (6), 323–324. doi:10.1065/espr2005.11.005
Dykes, A. P., and Bromhead, E. N. (2018). New, simplified and improved interpretation of the Vaiont landslide mechanics. Landslides 15 (10), 2001–2015. doi:10.1007/s10346-018-0998-9
Fan, X., Yang, F., Siva, S. S., Xu, Q., Feng, Z., Mavrouli, O., et al. (2020). Prediction of a multi-hazard chain by an integrated numerical simulation approach: the Baige landslide, Jinsha River, China. Landslides 17, 147–164. doi:10.1007/s10346-019-01313-5
Fang, K., Zhang, J., Tang, H., Hu, X., Yuan, H., Wang, X., et al. (2023). A quick and low-cost smartphone photogrammetry method for obtaining 3D particle size and shape. Eng. Geol. 322, 107170. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107170
Gao, Y., Zhao, S., Deng, J., Yu, Z., and Rahman, M. (2021). Flood assessment and early warning of the reoccurrence of river blockage at the Baige landslide. J. Geogr. Sci. 31 (11), 1694–1712. doi:10.1007/s11442-021-1918-9
Grüss, A., Pirtle, J. L., Thorson, J. T., Lindeberg, M. R., Neff, A. D., Lewis, S. G., et al. (2021). Modeling nearshore fish habitats using Alaska as a regional case study. Fish. Res. 238, 105905. doi:10.1016/j.fishres.2021.105905
Hamidifar, H., Akbari, F., and Rowiński, P. M. (2022). Assessment of environmental water requirement allocation in anthropogenic rivers with a hydropower dam using hydrologically based methods—case study. Water 14 (6), 893. doi:10.3390/w14060893
Hamidifar, H., and Nones, M. (2023a). Hydro-morphodynamic responses of rivers to the construction of hydropower dams: a case study–the Kor River, Iran. Hydrological Sci. J. 68 (11), 1567–1577. doi:10.1080/02626667.2023.2230197
Hamidifar, H., and Nones, M. (2023b). Spatiotemporal variations of riverine flood fatalities: 70 years global to regional perspective. River 2 (2), 222–238. doi:10.1002/rvr2.45
Herget, J., Schütte, F., and Klosterhalfen, A. (2015). Empirical modelling of outburst flood hydrographs. Z. fur Geomorphol. Suppl. 59 (3), 177–198. doi:10.1127/zfg_suppl/2015/S-59224
Hogberg, N. P., and Pegg, M. A. (2016). Assessment of fish floodplain use during an extreme flood event in a large, regulated river. Hydrobiologia 765, 27–41. doi:10.1007/s10750-015-2394-y
Hu, Y., Yu, Z., and Zhou, J. (2020). Numerical simulation of landslide-generated waves during the 11 october 2018 baige landslide at the Jinsha River. Landslides 17 (10), 2317–2328. doi:10.1007/s10346-020-01382-x
Huggel, C., Kääb, A., Haeberli, W., Teysseire, P., and Paul, F. (2002). Remote sensing based assessment of hazards from glacier lake outbursts: a case study in the Swiss Alps. Can. Geotechnical J. 39 (2), 316–330. doi:10.1139/t01-099
Hung, H. J., Lo, W. C., Chen, C. N., et al. (2022). Fish’habitat area and habitat transition in a river under ordinary and flood flow [J]. Ecol. Eng. 179, 106606. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2022.106606
Jjiménez-Segura, L. F., Palacio, J., and Leite, R. (2010). River flooding and reproduction of migratory fish species in the Magdalena River basin, Colombia. Ecol. Freshw. fish 19 (2), 178–186. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0633.2009.00402.x
Kafle, L., Xu, W. J., Zeng, S. Y., and Nagel, T. (2022). A numerical investigation of slope stability influenced by the combined effects of reservoir water level fluctuations and precipitation: a case study of the Bianjiazhai landslide in China. Eng. Geol. 297, 106508. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106508
Lamsal, D., Sawagaki, T., Watanabe, T., and Byers, A. C. (2016). Assessment of glacial lake development and prospects of outburst susceptibility: chamlang South Glacier, eastern Nepal Himalaya. Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk 7 (1), 403–423. doi:10.1080/19475705.2014.931306
Larsen, I. J., and Lamb, M. P. (2016). Progressive incision of the channeled scablands by outburst floods. Nature 538 (7624), 229–232. doi:10.1038/nature19817
Li, J., Cao, Z., Cui, Y., Fan, X., Yang, W., Huang, W., et al. (2021). Hydro-sediment-morphodynamic processes of the baige landslide-induced barrier Lake, Jinsha River, China. J. Hydrology 596, 126134. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126134
Li, W. (2011). Study on sediment transport behavior of solid Boundary,2011, 2011: 1-107.in China. doi:10.6842/NCTU.2011.00644
Liang, L., Dai, F., Jiang, H., and Zhong, N. (2018). A preliminary study on the soft–sediment deformation structures in the late Quaternary lacustrine sediments at Tashkorgan, northeastern Pamir, China. Acta Geol. Sinica-English Ed. 92 (4), 1574–1591. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.13644
Liao, H., Yang, X., Xu, F., Xu, H., and Zhou, J. w. (2018). A fuzzy comprehensive method for the risk assessment of a landslide-dammed lake. Environ. earth Sci. 77, 750–814. doi:10.1007/s12665-018-7946-9
Liu, D., Cui, Y., Jin, W., Wang, H., and Tang, H. (2023). Channel aggradation triggered by dam failure amplifies the damage of outburst flood. Landslides 20 (7), 1343–1362. doi:10.1007/s10346-023-02026-6
Liu, D., Cui, Y., Wang, H., Jin, W., Wu, C., Bazai, N. A., et al. (2021). Assessment of local outburst flood risk from successive landslides: case study of Baige landslide-dammed lake, upper Jinsha river, eastern Tibet. J. Hydrology 599, 126294. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126294
Liu, W., Carling, P. A., Hu, K., Wang, H., Zhou, Z., Zhou, L., et al. (2019). Outburst floods in China: a review. Earth-Science Rev. 197, 102895. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102895
Lu, S., Cai, W., Shao, W., Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., Faisal, M., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Ecological water requirement in upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River based on flow components and Hydraulic index. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (20), 10956. doi:10.3390/ijerph182010956
Makrakis, S., Bertão, A. P. S., Silva, J. F. M., Makrakis, M. C., Sanz-Ronda, F. J., and Celestino, L. F. (2019). Hydropower development and fishways: a need for connectivity in rivers of the Upper Paraná Basin. Sustainability 11 (13), 3749. doi:10.3390/su11133749
Meyer-Peter, E., and Müller, R. (1948). Formulas for bed-load transport, In IAHSR 2nd Meeting. http://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:4fda9b61-be28-4703-ab06-43cdc2a21bd7.
Muñoz-Mas, R., Lopez-Nicolas, A., Martinez-Capel, F., and Pulido-Velazquez, M. (2016). Shifts in the suitable habitat available for brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) under short-term climate change scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 544, 686–700. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.147
Oliveira, I. D. C. E., Silva, D. D. D., Guedes, H. A. S., Dergam, J. A., and Ribeiro, C. B. D. M. (2016). One-and two-dimensional ecohydraulic modeling of formoso river (MG). Eng. Agrícola 36, 1050–1062. doi:10.1590/1809-4430-eng.agric.v36n6p1050-1062/2016
Ouyang, C., An, H., Zhou, S., Wang, Z., Su, P., Wang, D., et al. (2019). Insights from the failure and dynamic characteristics of two sequential landslides at Baige village along the Jinsha River, China. Landslides 16, 1397–1414. doi:10.1007/s10346-019-01177-9
Palmer, M., Allan, J. D., Meyer, J., and Bernhardt, E. S. (2007). River restoration in the twenty-first century: data and experiential knowledge to inform future efforts. Restor. Ecol. 15 (3), 472–481. doi:10.1111/j.1526-100X.2007.00243.x
Peng, M., and Zhang, L. M. (2012). Breaching parameters of landslide dams. Landslides 9, 13–31. doi:10.1007/s10346-011-0271-y
Perna, C., and Pearson, R. G. (2008). Temporal dynamics of fish assemblages in small seasonal streams in the Queensland tropics[J]. Aust. J. Zool. 56 (1), 65–73.
Pires, A. M., Magalhães, M. F., Moreira Da Costa, L., Alves, M. J., and Coelho, M. M. (2008). Effects of an extreme flash flood on the native fish assemblages across a Mediterranean catchment. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 15 (1), 49–58. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2400.2007.00570.x
Shi, Z. M., Xiong, X., Peng, M., Zhang, L. M., Xiong, Y. F., Chen, H. X., et al. (2017). Risk assessment and mitigation for the Hongshiyan landslide dam triggered by the 2014 Ludian earthquake in Yunnan, China. Landslides 14, 269–285. doi:10.1007/s10346-016-0699-1
Shijin, W., Dahe, Q., and Cunde, X. (2015). Moraine-dammed lake distribution and outburst flood risk in the Chinese Himalaya. J. Glaciol. 61 (225), 115–126. doi:10.3189/2015JoG14J097
Solovyev, M. M., Izvekova, G. I., Kashinskaya, E. N., and Gisbert, E. (2018). Dependence of pH values in the digestive tract of freshwater fishes on some abiotic and biotic factors. Hydrobiologia 807, 67–85. doi:10.1007/s10750-017-3383-0
Tian, S., Chen, N., Wu, H., Yang, C., Zhong, Z., and Rahman, M. (2020). New insights into the occurrence of the baige landslide along the Jinsha River in Tibet. Landslides 17 (5), 1207–1216. doi:10.1007/s10346-020-01351-4
Wang, Z. Y., and Plate, E. J. (2002). Recent flood disasters in China. Proc. Institution Civ. Engineers-Water Marit. Eng. 154 (3), 177–188. doi:10.1680/wame.2002.154.3.177
Wang, Y., Xia, J., Cai, W., Liu, Z., Li, J., Yin, J., et al. (2023). Response of fish habitat quality to weir distribution change in mountainous river based on the two-dimensional habitat suitability model[J]. Sustainability 15 (11), 8698. doi:10.3390/su15118698
Wang, S. J., Qin, D. H., and Xiao, C. D. (2015). Moraine-dammed Lake distribution and outburst flood risk in the Chinese Himalaya. J. Glaciol. 61, 115–126. doi:10.3189/2015JoG14J097
Warren, D. R., Mineau, M. M., Ward, E. J., and Kraft, C. E. (2010). Relating fish biomass to habitat and chemistry in headwater streams of the northeastern United States. Environ. Biol. Fishes 88, 51–62. doi:10.1007/s10641-010-9617-x
Wesner, J. S. (2011). Shoaling species drive fish assemblage response to sequential large floods in a small midwestern USA stream. Environ. Biol. fishes 91, 231–242. doi:10.1007/s10641-011-9775-5
Xu, F., Yang, X., and Zhou, J. (2017). Dam-break flood risk assessment and mitigation measures for the Hongshiyan landslide-dammed lake triggered by the 2014 Ludian earthquake. Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk 8 (2), 803–821. doi:10.1080/19475705.2016.1269839
Xue, R., Zhang, X., Cai, Y., Wang, M., Deng, Q., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Numerical simulation of landslide dam overtopping failure considering headward erosion. J. Hydrology 601, 126608. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126608
Yang, Z., Liu, W., Garcia-Castellanos, D., Ruan, H., Luo, J., Zhou, Y., et al. (2022). Geomorphic response of outburst floods: insight from numerical simulations and observations––The 2018 Baige outburst flood in the upper Yangtze River. Sci. Total Environ. 851, 158378. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158378
Zhang, L., Xiao, T., He, J., and Chen, C. (2019). Erosion-based analysis of breaching of Baige landslide dams on the Jinsha River, China, in 2018. Landslides 16, 1965–1979. doi:10.1007/s10346-019-01247-y
Zhou, Z., Deng, Y., and Li, Y. (2019). The ecological water demand of Schizothorax in Tibet based on habitat area and connectivity. Int. J. Environ. Res. public health 16 (17), 3045. doi:10.3390/ijerph16173045
Zong, Y., and Chen, X. (2000). The 1998 flood on the Yangtze, China. Nat. Hazards 22, 165–184. doi:10.1023/A:1008119805106
Keywords: outburst floods, dam breach Model, River2D Model, WUA, fish habitat
Citation: Xie X, Jiang X, Wen T, Jiang Q and An X (2024) The impact of floods triggered by natural dam breakage on the adaptability of downstream river fish—the 2018 baige outburst flood in the upper reaches of the Yangtze river in China. Front. Earth Sci. 12:1363559. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1363559
Received: 31 December 2023; Accepted: 01 April 2024;
Published: 03 May 2024.
Edited by:
Chong Xu, Ministry of Emergency Management, ChinaReviewed by:
Michael Nones, Polish Academy of Sciences, PolandCopyright © 2024 Xie, Jiang, Wen, Jiang and An. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiangang Jiang, anhnamltQDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.