- 1School of Resources and Environment, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Coal and Coalbed Methane Co-mining, Jincheng, China
- 3Collaborative Innovation Center of Coal Work Safety and Clean High Efficiency Utilization, Jiaozuo, China
Microbially enhanced coalbed methane (MECBM) has important theoretical and practical significance for reforming coal reservoir structure, alleviating greenhouse effects and energy crises and developing new sources of clean energy. In this study, No. 3 coal seams in Qinshui Basin were taken as research objects to analyze the pore structure characteristics after microbial treatment by means of low-temperature nitrogen adsorption (LTNA), mercury porosimetry (MP), and isothermal adsorption/desorption experiments. The results showed that after bioconversion, the specific surface area and pore volume increased from 1.79 m2/g and 0.0018 cm3/g to 4.01 m2/g and 0.0051 cm3/g respectively under liquid nitrogen testing; however, the specific surface area was reduced from 5.398 m2/g to 5.246 m2/g and the pore volume was increased from 0.053 cm3/g to 0.0626 cm3/g under MP. The fractal dimension based on the LTNA data indicated that the fractal dimension of micropores and minipores was increased from 2.73 to 2.60 to 2.89 and 2.81, however the fractal dimension of meso-macropores was decreased from 2.90 to 2.85. The volatile matter and fixed carbon were both reduced from 6.68% to 78.63%–5.09% to 75.63%, and the Langmuir volume and Langmuir pressure were increased from 34.84 cm3/g and 2.73 MPa to 36.34 cm3/g and 3.28 MPa, respectively. This result indicated that microorganism participated in the degradation of coal reservoir and promoted the production of methane gas, the meso-macropores were more obviously modified by microorganism, so that the pore diameter stabilized, the pores became smoother, the specific surface area decreased, and the pore volume increased. These are more beneficial to the adsorption and production of coalbed methane (CBM) after microbial treatment.
Introduction
Coal, as an important energy resource, has been widely used since the industrial revolution. Approximately 71.4% of global fossil fuel reserves are in the form of coal (Faison, 1991; Park and Liang, 2016). However, a series of severe environmental problems have resulted, such as global climate change, extreme weather and land desertification. These problems have seriously affected and restricted the sustainable development of humankind with the development and utilization of coal resources (Fakoussa and Hofrichter, 1999; Formolo et al., 2008; Byamba-Ochir et al., 2017; Su et al., 2021). Exploitation and utilization of coalbed methane (CBM) is of great significance to alleviate these problems. CBM is developed by way of two processes: thermogenic gasification and biogenetic gasification, so it is possible to obtain CBM in artificial conditions through microbial degradation (Fakoussa and Hofrichter, 1999; Park and Liang, 2016). Microbially enhanced coalbed methane (MECBM) has important theoretical and practical significance for reforming coal reservoir structure, alleviating greenhouse effect and energy crises and developing new sources of clean energy (Zhang et al., 2017; Lu et al., 2020; Hou et al., 2021). Meanwhile, the permeability of coal reservoir can be improved by using MECBM. This technique is believed to be related to low metamorphic coal, which is more conducive to microbial degradation (Harris et al., 2008; Robbins et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2020), but the bituminous-coal contents in some countries (such as the United States, Russia, and China) exceed 50% (Mcglade and Ekins, 2015; Lu et al., 2020). Especially in China, commercial CBM gas fields are mainly concentrated in anthracite coal mining areas. Therefore, MECBM research should not only focus on lignite, and but also highly metamorphosed bituminous coal, or even anthracite (Lu et al., 2020), many scholars have investigated this topic (Faiz and Hendry, 2006; Formolo et al., 2008; Boris et al., 2012; Bao et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2020; Ashley et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2021). As a porous medium, the pores of coal are the main accumulation space and migration channels of CBM, and the pore structure not only affects the state of occurrence, adsorption/desorption, diffusion, seepage flow, gas content, but also restricts the ability to exploit CBM (Hudot, 1966; Clarkson et al., 2011; Moore, 2012; Gao et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2018), making it necessary to study the modification of coal pore structures by microorganisms.
Materials and Methods
Coal Samples
The No. 3 coal seams of Early Permian Shanxi formation in Sihe mine, in the southern Qinshui basin of China were taken as research objects to study the pore structure characteristics after microbial treatment. These are typical primary mineable coal beds found in northern China. The study area lies in the southeast of Shanxi Province and forms a part to the western margin of North China Platform. The average thickness of No. 3 coal seam is about 6 m and Ro, Max. is 2.54%. The research area is a focus of CBM research in China, and is the earliest and most successful commercialization area of the CBM industry in China. To maintain the contact between the coal and microorganisms as much as possible, while avoiding the channels becoming blocked by pulverized coal, the particle size of the granular coal specimens was about 20 × 20 mm and a coal sample of 18 kg was loaded into each experimental device. Proximate analysis, low-temperature nitrogen adsorption (LTNA), mercury porosimetry (MP) and isothermal adsorption measurements, and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) were applied to pre-test/post-test samples. Two sets of experimental devices were designed (Figure 1). The test data are summarized in Table 1.
Experimental Procedure
The MECBM treatments were performed using specially designed apparatus (Figure 1). The flora and experimental water were taken from CBM wells in the Sihe mine. The floras were cultured in the laboratory. To ensure the enrichment of methanogens in water samples, fluorescence observation and counting were performed before the experiment under a fluorescence microscope with 420 nm incident light. Preparation of 10 L of substrate was carried out, and the components mainly included glucose, peptone, sodium chloride, beef extract, l-cysteine hydrochloride, resazurin, sodium bicarbonate, and sodium sulfide. The experiment lasted for 47 days (until 72 h no gas production was noted). Two experimental devices produced 10,449 and 11,120 ml of gas respectively, of which the methane content was 4,013 and 4,583 ml.
Test Methods
An Automatic Proximate Analysis Instrument was used to perform proximate analysis (the moisture, ash, and volatile and fixed carbon contents) experiments, as per ISO 17246-2010. A Micromeritics ASAP-2020 automated surface area analyzer (United States) was adopted to perform the low-temperature nitrogen adsorption/desorption experiments, as per the ISO 15901.2-2006 test method over a pore diameter analysis range of 0.35–300 nm. An Automated Isothermal Gas Adsorption/Desorption Experiment System TerraTek ISO-300 (United States) was used to conduct the isothermal adsorption/desorption experiments, as per Chinese National Standard GB/T 19560-2008. All the above tests were completed at the State Key Laboratory of Coal and Coalbed Methane Co-Extraction in China. A Micromeritics Autopore IV 9500 Instrument (United States) was used to perform mercury porosimetry experiments, according to the ISO 15901-1-2005 test method, the particle size of the coal sample used was 4.75–3.35 mm over a pore-diameter analysis range of 7.5 nm–360 μm. The pore characteristics of coal and methanobacteria were observed under FEI Quanta 250 FEG (United States) field emission scanning electron microscopy (these two tests were conducted at Henan Polytechnic University in China).
Results and Discussion
Pore Properties
In this study, the following Xoдot criteria developed in the former USSR were adopted: the pores in a coal specimen were divided into: micropores (<10 nm), minipores (10–100 nm), mesopores (100–1,000 nm), and macropores (>1,000 nm) (Hudot, 1966; Cheng et al., 2021).
From the distribution of specific surface area (Figure 2), the specific surface area of coal samples comprised mostly micropores and minipores. The specific surface area of micropores and minipores of coal samples increased from 93.6% to 97.8% and 96.5% after bioconversion under LTNA test conditions, and the specific surface of micropores and micropores of coal samples decreased from 99.7 % to 99.5% under mercury injection test conditions. From Figures 3, 4A,4B, the specific surface area of micropores of coal samples was found to increase significantly after bioconversion, while that of the minipores increased slightly, and the overall specific surface area increased from 1.79 to 4.01 m2/g on average after LTNA testing; however, the overall specific surface area decreased slightly, from 5.398 to 5.246 m2/g under mercury injection test conditions.
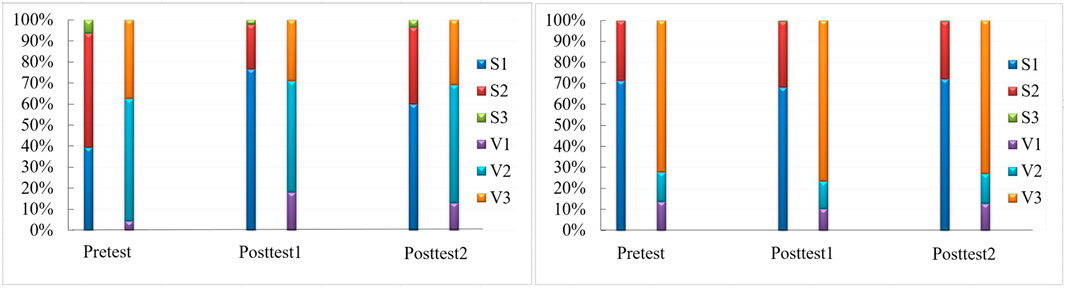
FIGURE 2. Percentage of specific surface area and pore volume in each pore size interval (left panel: LTNA; right panel: MP). S1∼S3 and V1∼V3 are specific surface area ratios and the pore volume ratios of micropores, minipores, and meso-macropores, respectively.
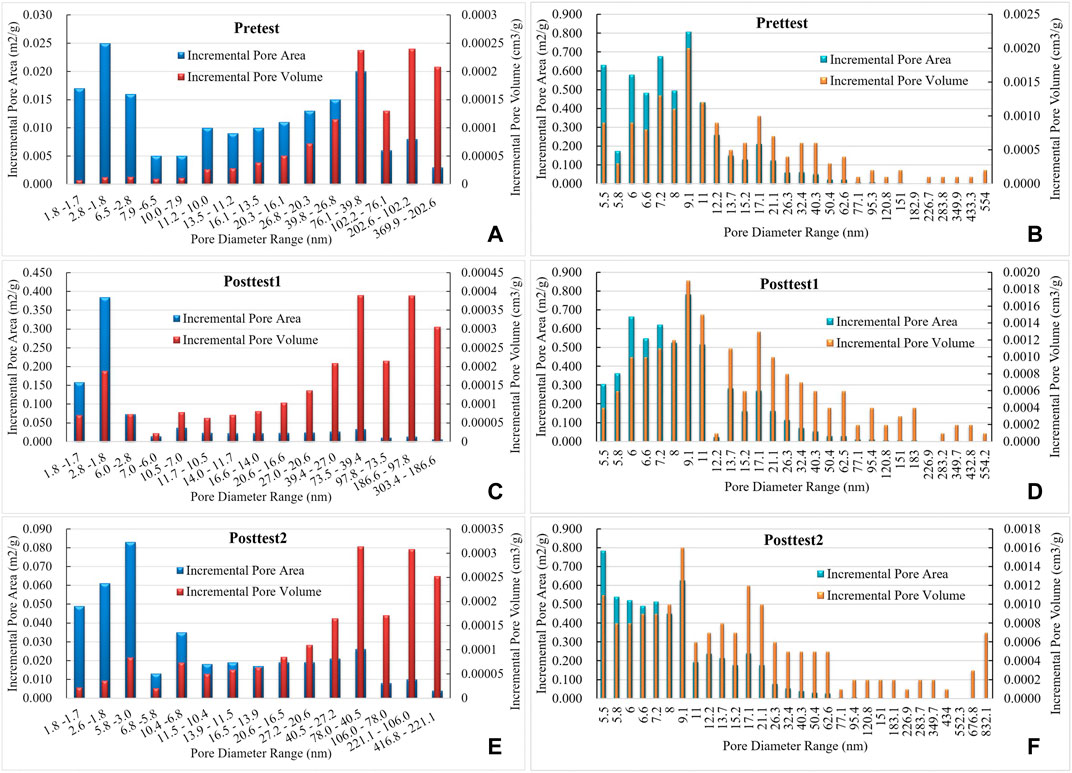
FIGURE 3. Specific surface area and pore volume distribution characteristics based on pore distribution change according to LTNA measurements for (A) (C) (E) and MP measurements for (B) (D) (F); the left ordinate is the incremental pore area (m2/g) and the right ordinate denotes the incremental pore volume cm3/g).
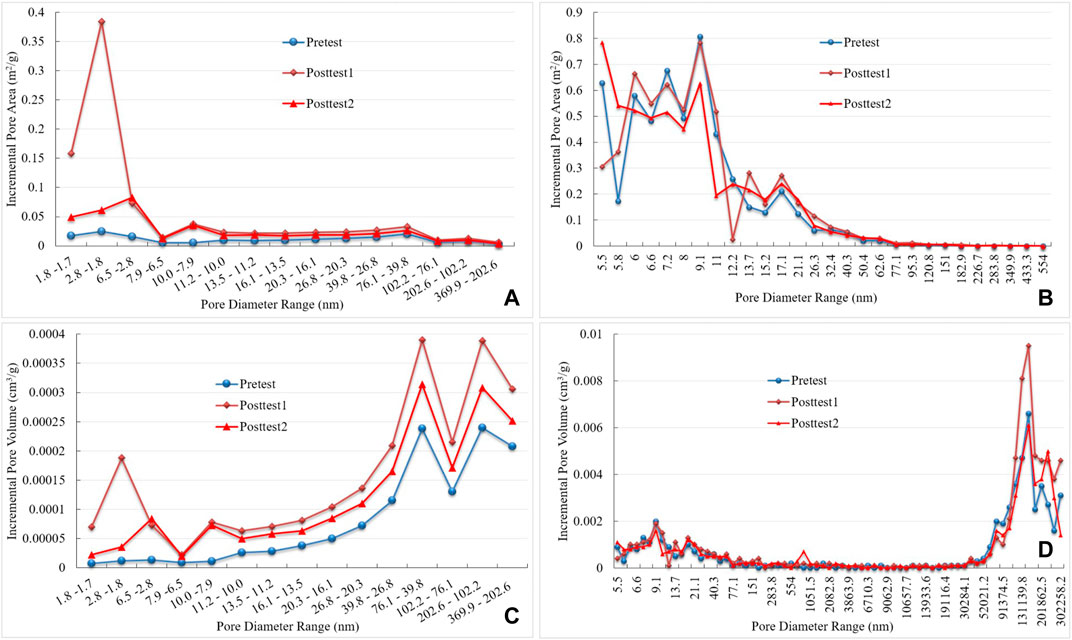
FIGURE 4. The changes in specific surface area and pore volume based on pore size change [(A,C): LTNA; (B,D): MP].
Different from the specific surface area, the contribution of pore volume arose mainly from minipores, mesopores, and macropores (Figure 3), the contribution of meso-macropores increased from 72.4 % to 76.7% and 73.1% after bioconversion under MP test conditions (Figure 2). The contribution of micropores to the pore volume increased from 4.34 % to 18.0% and 12.98% under the LTNA test, although the contribution of micropores to the increase in pore volume after the experiment was large, the proportion of micropores to the increase in the pore volume remained small. As can be seen from Figures 4C,D, the pore volume of coal samples increased from 0.0018 cm3/g (LTNA) and 0.0530 cm3/g (MP) before testing to 0.0051 cm3/g (LTNA) and 0.0626 cm3/g (MP) after testing in LTNA and MP conditions, respectively (Table 1).
The differences in the data of specific surface area and pore volume between the LTNA and MP tests methods are mainly based on two reasons: one is that MP focuses on macropores and mesopores, while LTNA is more advantageous for micropores and minipores; the other is that according to the experimental results, microbial modification of mesopores is greater, which reduces the specific surface area of mesopores and increases the pore volume.
Surface Fractal Dimension
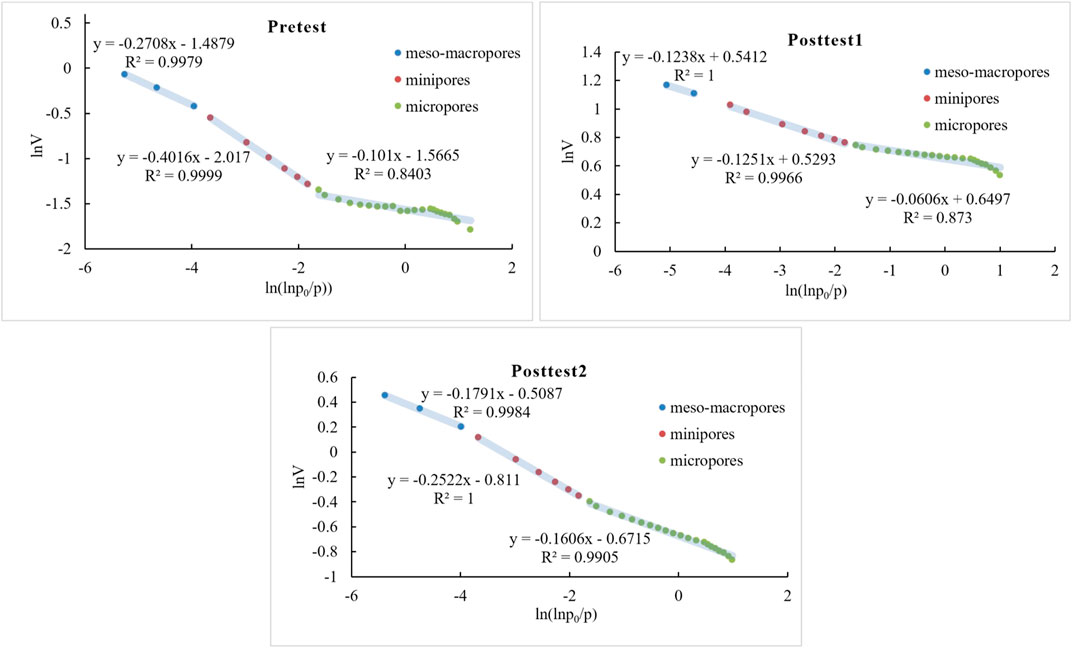
The pore structure of coal has strong heterogeneity and anisotropy, with fractal characteristics (Zhang et al., 2017), therefore, the fractal dimension is often used to quantify and characterize the pore structure in coal reservoirs (Wang et al., 2021). In this study, the Frenkel-Halsey-Hill (FHH) fractal model was used to estimate the fractal dimension from the LTNA data. The FHH equation can be expressed as (Lowell et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2014):
where
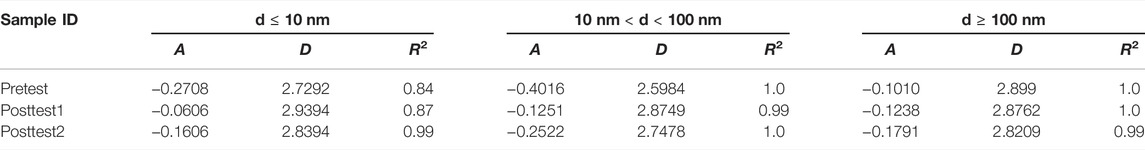
According to Eq. 1, there must be a linear relationship between ln V and ln (ln (P0/P)) when the pores have fractal characteristics. As can be seen from Figure 5, the bilogarithmic coordinates show a significant linear relationship, indicating that the pores of coal samples can be characterized by fractal theory. It is noteworthy that there are two different formulae available for calculating D with A based on the different situations: Eq. 2,3 (Pfeifer and Avnir, 1984; Avnir and Jaroniec, 1989; Ismail and Pfeifer, 1994; Yao et al., 2008; Dou et al., 2021). Eq. 2 is applicable to the membrane/gas interface controlled by van der Waals force, and Eq. 3 is applicable to the interface controlled by liquid–gas tension. In this study, many of these D values are less than 2 as calculated using Eq. 2, which is unrealistic, so D is calculated using Eq. 3 (Table 2).
To study the effect of microbial action on pore structure of coal, the data are divided into three regions to calculate the fractal dimension, d ≤ 10 nm, 10 nm < d < 100 nm, d ≥ 100 nm. The fractal results showed that when d ≤ 10 nm, the fractal dimension of coal after microbial treatment was increased from 2.73 to 2.89, when 10 nm < d < 100 nm, the fractal dimension D was increased from 2.60 to 2.81, however, when d ≥ 100 nm, the fractal dimension D was reduced from 2.90 to 2.85, The results indicated that the surface irregularities of mesopores and macropores decreased, the pores became smoother and the pore volume decreased after the bioconversion (Figure 6). This finding was consistent with the aforementioned research (the pore structure evolution model is shown in Figure 7).
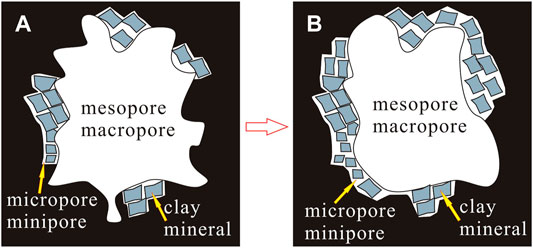
FIGURE 7. A conceptual pore structure evolution model with microbial treatment. (A) Pore structure before microbial treatment. (B) Pore structure after microbial treatment.
Proximate Analysis and Adsorption Characteristics
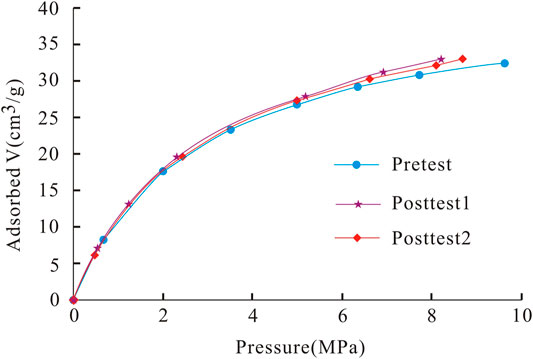
From the perspective of industrial analysis (Table 1), compared with pre-test values, the moisture content, ash yield, and clay content of coal samples increased from 2.99%, 13.13 % and 4.13%–5.53%, 15.65 % and 7.37%, respectively, while the volatile matter and fixed carbon contents reduced from 6.68%, 78.63 %–5.09% and 75.63%, respectively. This showed that microorganisms participated in the degradation of coal reservoir and promoted the generation of methane gas.
The curves of the methane adsorption on samples can be drawn according to the Langmuir model Eq. 4:
where V is the adsorption volume, VL denotes the Langmuir volume,
Conclusion
In this study, No. 3 coal seams in Qinshui Basin were taken as the research objects to observe the pore structure characteristics after microbial treatment, and the following conclusions can be drawn.
The contribution of micropores and minipores to the specific surface area of coal samples reached more than 93%, and the contribution was further increased after microbial treatment. After bioconversion, the specific surface area increased from 1.79 to 4.01 m2/g under LTNA test conditions, while the specific surface area decreased from 5.398 to 5.246 m2/g under MP test conditions. The fractal dimension of micropores and minipores increased from 2.73 and 2.60 to 2.89 and 2.81, respectively, but the fractal dimension of meso-macropores decreased from 2.90 to 2.85.
The pore volume of coal samples arose mainly from minipores, mesopores, and macropores, and the contribution of minipores, mesopores, and macropores to the increase in the pore volume was more than 70%. The pore volume of coal samples increased from 0.0018 cm3/g to 0.0530 cm3/g to 0.0051 cm3/g to 0.0626 cm3/g after testing under LTNA and MP test conditions, respectively.
The volatile matter and fixed carbon were both reduced from 6.68 % to 78.63% to 5.09 % to 75.63%, and the Langmuir volume and Langmuir pressure increased from 34.84 cm3/g and 2.73 MPa to 36.34 cm3/g and 3.28 MPa, respectively.
The results demonstrated that microorganism participated in the degradation of coal reservoir and promoted the production of methane gas. The meso-macropores were more obviously modified by the microorganisms, so that the pore diameter stabilized, the pores became smoother, the specific surface area decreased, and the pore volume increased. After microbial treatment, the coal body was more conducive to the adsorption of methane gas. The increase of Langmuir pressure was more conducive to the subsequent production of CBM.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author Contributions
DG searched the literature; DG and BG analyzed the data and wrote the paper; KT and HR treated samples and performed the experiments; HG processed some data and drew some maps.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41402094), the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum, Beijing (No. PRP/open-2008) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (No. NSFRF220411).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the staff of the State Key Laboratory of Coal and Coalbed Methane Co-mining, especially Professor Baoyu Wang and Bin Hu, they put forward the research direction and provide a good experimental environment. Special thanks are given to the reviewers for their valuable advice and comments on the manuscript.
References
Ashley, K., Davis, K. J., Martini, A., Vinson, D. S., Gerlach, R., Fields, M. W., et al. (2021). Deuterium as a Quantitative Tracer of Enhanced Microbial Methane Production. Fuel 289 (1), 119959. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119959
Avnir, D., and Jaroniec, M. (1989). An Isotherm Equation for Adsorption on Fractal Surfaces of Heterogeneous Porous Materials. Langmuir 5 (6), 1431–1433. doi:10.1021/la00090a032
Bao, Y., Tang, J., and Ju, Y. (2020). CBM Accumulation Mechanism and Micro- and Nano-Pore Structure Evolution Characteristics of Coal during Biogasification. GEOLOGICAL REVIEW s1, 149–150. (in Chinese with English Abstract). doi:10.16509/j.georeview.2020.s1.057
Byamba-Ochir, N., Shim, W. G., Balathanigaimani, M. S., and Moon, H. (2017). High Density Mongolian Anthracite Based Porous Carbon Monoliths for Methane Storage by Adsorption. Appl. Energ. 190, 257–265. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.12.124
Chen, R., Qin, Y., Zhang, P., and Wang, Y. (2018). Changes in Pore Structure of Coal Caused by CS2 Treatment and its Methane Adsorption Response. Geofluids 2018, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2018/7578967
Cheng, Y., Zhang, X., Lu, Z., Pan, Z. j., Zeng, M., Du, X., et al. (2021). The Effect of Subcritical and Supercritical CO2 on the Pore Structure of Bituminous Coals. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 94 (10), 104132. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2021.104132
Clarkson, C. R., Rahmanian, M., Kantzas, A., and Morad, K. (2011). Relative Permeability of CBM Reservoirs: Controls on Curve Shape. Int. J. Coal Geology. 88 (4), 204–217. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2011.10.003
Dou, W., Liu, L., Jia, L., Xu, Z., Wang, M., and Du, C. (2021). Pore Structure, Fractal Characteristics and Permeability Prediction of Tight Sandstones: a Case Study from Yanchang Formation, Ordos basin, china. Mar. Pet. Geology. 123, 104737. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104737
Faison, B. D. (1991). Biological Coal Conversions. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 11, 347–366. doi:10.3109/07388559109040624
Faiz, M., and Hendry, P. (2006). Significance of Microbial Activity in Australian Coal Bed Methane Reservoirs -- a Review. Bull. Can. Pet. Geology. 54 (3), 261–272. doi:10.2113/gscpgbull.54.3.261
Fakoussa, R. M., and Hofrichter, M. (1999). Biotechnology and Microbiology of Coal Degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 52, 25–40. doi:10.1007/s002530051483
Formolo, M., Martini, A., and Petsch, S. (2008). Biodegradation of Sedimentary Organic Matter Associated with Coalbed Methane in the Powder River and San Juan Basins, U.S.A. Int. J. Coal Geology. 76 (1), 86–97. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2008.03.005
Gao, D., Li, M., Wang, B., Hu, B., and Liu, J. (2017). Characteristics of Pore Structure and Fractal Dimension of Isometamorphic Anthracite. Energies 10 (11), 1881. doi:10.3390/en10111881
Guo, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Li, Z., Liang, W., et al. (2021). Feasibility Study of Enhanced Biogenic Coalbed Methane Production by Super-critical Co2 Extraction. Energy 214, 118935. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2020.118935
Harris, S. H., Smith, R. L., and Barker, C. E. (2008). Microbial and Chemical Factors Influencing Methane Production in Laboratory Incubations of Low-Rank Subsurface Coals. Int. J. Coal Geology. 76 (1-2), 46–51. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2008.05.019
Hou, H., Liang, G., Shao, L., Tang, Y., and Mu, G. (2021). Coalbed Methane Enrichment Model of Low-Rank Coals in Multi-Coals Superimposed Regions: a Case Study in the Middle Section of Southern Junggar basin. Front. Earth Sci. 15 (2), 256–271. doi:10.1007/s11707-021-0917-6
Ismail, I. M. K., and Pfeifer, P. (1994). Fractal Analysis and Surface Roughness of Nonporous Carbon Fibers and Carbon Blacks. Langmuir 10 (5), 1532–1538. doi:10.1021/la00017a035
Lowell, S., Shields, J. E., Thomas, M. A., and Thommes, M. (2004). Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer Netherlands. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-2303-3
Lu, Y., Chai, C., Zhou, Z., Ge, Z., and Yang, M. (2020). Influence of Bioconversion on Pore Structure of Bituminous Coal. Asia‐pac J. Chem. Eng. 15 (1), 1–15. doi:10.1002/apj.2399
Mcglade, C., and Ekins, P. (2015). The Geographical Distribution of Fossil Fuels Unused when Limiting Global Warming to 2 °C. Nature 517 (7533), 187–190. doi:10.1038/nature14016
Moore, T. A. (2012). Coalbed Methane: A Review. Int. J. Coal Geology. 101, 36–81. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2012.05.011
Park, S. Y., and Liang, Y. (2016). Biogenic Methane Production from Coal: A Review on Recent Research and Development on Microbially Enhanced Coalbed Methane (MECBM). Fuel 166, 258–267. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2015.10.121
Pfeifer, P., and Avnir, D. (1984). Erratum: Chemistry in Noninteger Dimensions between Two and Three. I. Fractal Theory of Heterogeneous Surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 80 (7), 4573. doi:10.1063/1.447307
Robbins, S. J., Evans, P. N., Esterle, J. S., Golding, S. D., and Tyson, G. W. (2016). The Effect of Coal Rank on Biogenic Methane Potential and Microbial Composition. Int. J. Coal Geology. 154-155, 205–212. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2016.01.001
Su, E., Liang, Y., and Zou, Q. (2021). Structures and Fractal Characteristics of Pores in Long-Flame Coal after Cyclical Supercritical CO2 Treatment. Fuel 286 (1), 119305. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119305
Wang, J., Jiang, F., Zhang, C., Song, Z., and Mo, W. (2021). Study on the Pore Structure and Fractal Dimension of Tight Sandstone in Coal Measures. Energy Fuels 35 (5), 3887–3898. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c03991
Wawrik, B., Mendivelso, M., Parisi, V. A., Suflita, J. M., Davidova, I. A., Marks, C. R., et al. (2012). Field and Laboratory Studies on the Bioconversion of Coal to Methane in the san juan basin. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 81 (1), 26–42. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01272.x
Yao, Y., Liu, D., Tang, D., Tang, S., and Huang, W. (2008). Fractal Characterization of Adsorption-Pores of Coals from North China: An Investigation on CH4 Adsorption Capacity of Coals. Int. J. Coal Geology. 73 (1), 27–42. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2007.07.003
Zhang, R., Liu, S., Bahadur, J., Elsworth, D., Wang, Y., Hu, G., et al. (2017). Changes in Pore Structure of Coal Caused by Coal-To-Gas Bioconversion. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 3840. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-04110-z
Zhang, S., Tang, S., Tang, D., Huang, W., and Pan, Z. (2014). Determining Fractal Dimensions of Coal Pores by FHH Model: Problems and Effects. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 21, 929–939. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2014.10.018
Keywords: microbially enhanced coalbed methane (MECBM), pore structure, fractal theory, coalbed methane, qinshui basin
Citation: Gao D, Guo H, Guo B, Tan K and Ren H (2022) Impact of Microbially Enhanced Coalbed Methane on the Pore Structure of Coal. Front. Earth Sci. 10:869917. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.869917
Received: 05 February 2022; Accepted: 14 March 2022;
Published: 30 March 2022.
Edited by:
Yiwen Ju, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Haihai Hou, Liaoning Technical University, ChinaRun Chen, China University of Mining and Technology, China
Copyright © 2022 Gao, Guo, Guo, Tan and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Di Gao, Z2FvZGkxMTE5QDE2My5jb20=; Bianqing Guo, Z3VvYmlhbnFpbmdAaHB1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Di Gao
Di Gao Huiling Guo1
Huiling Guo1