- 1China Earthquake Networks Center, Beijing, China
- 2Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China
- 3Institute of Earthquake Forecasting, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China
The first step toward earthquake forecasting is the identification of variables whose spatio-temporal variation can be connected with pre-seismic crustal deformation. Four periods of campaign Global Positioning System (GPS) observations around the Longmenshan fault zone (LFZ) provide important insights in crustal deformation and deep fault slip before the 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake. By using TDEFNODE to invert the coupling fraction and dynamic slip deficit rate of the Longmenshan fault plane before the Wenchuan earthquake, we show that under a background of strong coupling, the compressive slip deficit rate perpendicular to fault increased slightly at first and then decreased; a value of ∼1.5–3.6 mm/a along the central–southern segment from 1999 to 2001 increased to ∼1.9–3.9 mm/a from 2001 to 2004, and then decreased to ∼1.1–2.6 mm/a from 2004 to 2007. The dextral slip deficit rate parallel to fault was ∼6 mm/a from 1999 to 2004, before increasing significantly to ∼9.5 mm/a from 2004 to 2007, when the compressive slip deficit rate decreased. At the same time, large-scale GPS velocity profiles show that compressive shortening deformation in the Eastern Tibet Block, perpendicular to fault, increased slightly from 2001 to 2004, and then decreased from 2004 to 2007. Meanwhile, the dextral shear deformation parallel to fault near the LFZ increased significantly from 2004 to 2007. These findings are in good agreement with those calculated using repeating earthquake sequences, indicating that the deep slip rate of the Longmenshan fault plane may have accelerated several years before the Wenchuan earthquake. Our results demonstrate that GPS data can record pre-seismic preparatory processes, and have the potential for use in medium-term large earthquake forecasting.
Introduction
The 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake occurred on the listric Longmenshan fault zone (LFZ) at the boundary between the Eastern Tibet Block and South China Block. Retrospective studies into anomalies that occurred before the Wenchuan earthquake have improved our understanding of large continental thrust earthquakes. In particular, estimations of stress and strain variation from geophysical observations have revealed pre-seismic preparatory processes. Li et al. (2011) investigated deep slip rate along the ruptured Longmenshan fault plane using repeating earthquake data. The measured in situ deep slip rate varied from 3.5 to 9.6 mm/a for a depth range of 4–18 km, and appeared to increase with depth. Repeating earthquake data from around the world show that the acceleration of the deep slip rate can occur on different time scales before large earthquakes (Kato et al., 2016; Uchida et al., 2016). Using repeating earthquake data, Chen and Li (2018) found that the Hongkou–Wenchuan and Beichuan segments of the LFZ began to show signs of deep slip acceleration to varying degrees in around 2006. Using Global Positioning System (GPS) velocity fields during 1999–2004 and 2004–2007, Jiang et al. (2009) generated profiles across the LFZ, which showed that dextral shear deformation parallel to the LFZ along a span of 500 km to the west side of the LFZ increased during 2004–2007 compared with that during 1999–2004; Zou et al. (2015) also considered that the northeastward movement of the Eastern Tibet Block accelerated relative to the South China block during 2004–2007, which increased the dextral shear deformation of the LFZ. However, these results only relate to surface velocity; as such, there is a need to obtain the acceleration of the deep slip rate via inversion methods using GPS velocity fields.
Pre-seismic preparatory processes are closely related to the coupling fraction and slip deficit rate of the seismogenic fault. The distribution characteristics of the coupling fraction are important basis for assessing the background of seismic risk (Moreno et al., 2010; Loveless and Meade, 2011). Generally, during the seismogenic stage, the coupling fraction of the seismogenic fault will increase before gradually stabilizing (Savage and Prescott, 1978; Meade and Hager, 2005). GPS observations have resulted in an enormous quantity of data that have substantially increased our capacity to investigate earthquake-related processes. Based on GPS velocity fields, the coupling fraction of a fault plane can be obtained by negative dislocation inversion. Spatio-temporal variation of the fault slip deficit rate obtained by inversion can be used to calculate the rate of fault strain energy accumulation (McCaffrey et al., 2013; Li et al., 2021). When the seismogenic fault is strongly coupled, the acceleration of deep slip along the fault plane is an important index to judge the urgency of seismic risk (Kato and Nakagawa, 2014; Uchida et al., 2016; Chen and Li, 2018). By constructing a three-dimensional multi-fault model of the LFZ and its surrounding faults, we used the GPS velocity fields of 1999–2001, 2001–2004, 2004–2007, and 1999–2007 to invert the spatio-temporal evolution distribution of coupling fraction and slip deficit rate of the Longmenshan fault plane before the 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake using the TDEFNODE negative dislocation method (McCaffrey, 2002; McCaffrey, 2009). Variation in the deep slip rates before the earthquake were analyzed; moreover, based on GPS velocity profiles across the LFZ, the evolution of large-scale surface deformation before the earthquake was analyzed according to velocity components perpendicular and parallel to the LFZ. Finally, the dynamic deep–shallow deformation characteristics of the LFZ before the earthquake were comprehensively analyzed based on the deep inversion and surface profile results.
Data and Methodology
GPS Velocities
We performed inversions of four periods of GPS velocity fields: 1999–2001 (160 stations), 2001–2004 (153 stations), 2004–2007 (169 stations), and 1999–2007 (203 stations), with the latter set as the background result, and the first three as dynamic results (Figure 1). The GPS velocity fields were processed using the GAMIT/GLOBK software (Herring et al., 2006), and the computation refers to Wang (2009). The magnitudes of the GPS velocities depend on the reference frame. In this study, in order to observe the relative movement of different blocks more obviously, we have made the GPS velocities be with respect to the South China Block, which causes the GPS velocities to be much smaller than that in the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF). The gray ellipses represent the errors of GPS velocity fields. The eastern and northern median errors of the GPS velocity fields are 1.3 mm/a and 1.1 mm/a in 1999–2001, 2.0 mm/a and 2.0 mm/a in 2001–2004, 1.4 mm/a and 1.4 mm/a in 2004–2007, and 1.1 mm/a and 1.1 mm/a in 1999–2007.
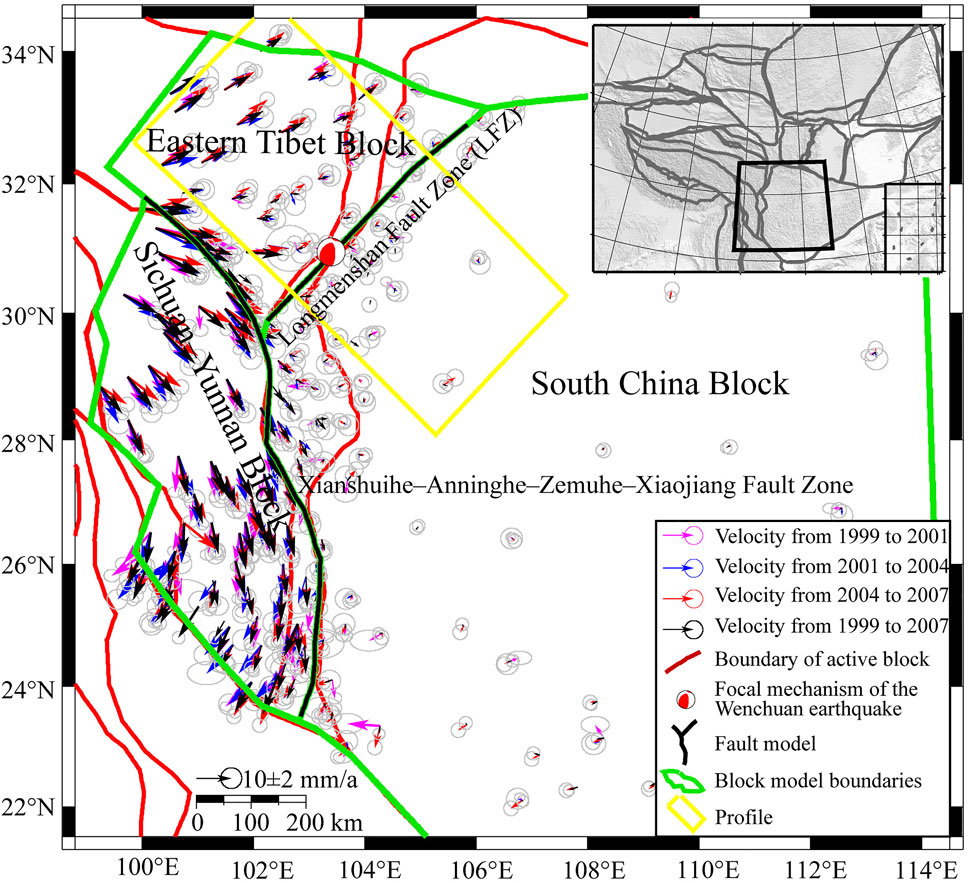
FIGURE 1. Global Positioning System (GPS) velocity fields of the study region with respect to the South China Block during 1999–2001, 2001–2004, 2004–2007, and 1999–2007. The gray ellipses represent the errors of GPS velocity fields, and error ellipses represent 70% confidence. The insert map shows the regional position of study area. The focal mechanism of the Wenchuan earthquake is derived from Global CMT Web Page (https://www.globalcmt.org/CMTsearch.html).
The results of four periods of GPS velocity fields show that, compared with the South China Block, stations in the Eastern Tibet Block exhibited obvious northeastward movement; moreover, the velocity field of 2004–2007 also showed increase northeastward movement. These results indicate deformation across the LFZ was dominated by dextral shear with a certain amount of compressive shortening, and dextral shear increased from 2004 to 2007. At the same time, from northwest to southeast, the velocities of GPS stations in the Eastern Tibet Block gradually decreased, while the velocities of those in the LFZ were gradually close to that of stations in the South China Block. Compared with the South China Block, stations in the Sichuan–Yunnan Block exhibited significant clockwise rotation, indicating left-lateral strike-slip motion dominates the Xianshuihe–Anninghe–Zemuhe–Xiaojiang fault zones, while tensile and compressive motions are relatively weak.
Methodology
Fault locking theory assumes that the movement of GPS stations inside a block includes the block rotation, permanent strain inside the block, and surface elastic deformation at block boundaries due to fault coupling. The principle is as follows:
where X is the position of the GPS station, B is the number of blocks,
Based on the theoretical model of fault locking, TDEFNODE is a Fortran-based program to model elastic lithospheric block movement and deformation using data such as GPS and InSAR velocity fields (https://robmccaffrey.github.io/TDEFNODE/manual/tdefnode_manual.html#cite). Block motions are specified by Euler rotation poles and interseismic backslip is applied along fault planes that separate blocks (McCaffrey, 2002; McCaffrey, 2009), based on the routines of Okada (1985), Okada (1992). The Euler rotation poles, permanent strain inside blocks, and spatial distribution of coupling fraction and slip rate on fault planes are estimated by simulated annealing and grid search. When building the three-dimensional model, faults are specified by longitude-latitude-depth coordinates of nodes along the fault planes. The coupling fraction and fault slip rate at each node are estimated by TDEFNODE; we then divided the fault plane between fault nodes into smaller patches (4 km along strike by 1 km downdip) and used bilinear interpolation to obtain smooth distribution results. The slip deficit rate of fault plane between two blocks is the product of the coupling fraction and the fault slip rate (McCaffrey, 2002; McCaffrey et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2020).
During the inversion, the value of the uncertainty scaling factor f was applied to the four-stage GPS velocity fields. The inversion estimates the parameters that minimize the reduced chi-squared statistic:
where ri is the residual,
Three-Dimensional Model
The crust of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau migrates eastward and is blocked by the Sichuan Basin (Huang et al., 2021). The high-elevation LFZ is formed at the junction of the two blocks (Figures 1, 2A), resulting in a huge difference in crustal thickness on either side. Referring to the boundaries of active block (Deng et al., 2003), our three-dimensional model included the Longmenshan, Xianshuihe, and Anninghe–Zemuhe–Xiaojiang fault zones, which divide the study area into the Sichuan–Yunnan Block, Eastern Tibet Block, and South China Block (Figure 1). As the area surrounded by the Xianshuihe, Anninghe–Zemuhe–Xiaojiang, Jinshajiang, and Honghe fault zones shares similar movement and deformation characteristics, we regarded it as one block (Gan et al., 2007; Thatcher, 2007). The Eastern Tibet Block is enclosed by the Xianshuihe, Longmenshan, and East Kunlun fault zones (Meade, 2007; Hao et al., 2014).
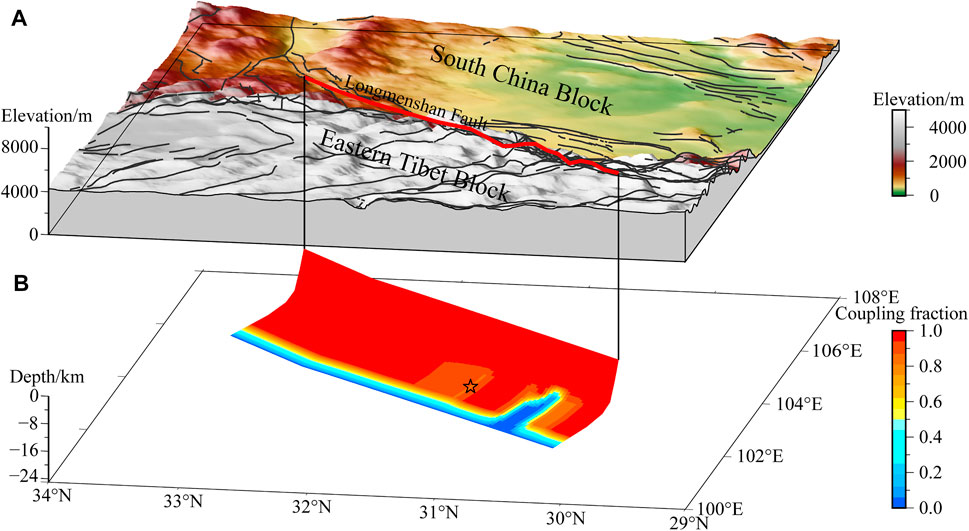
FIGURE 2. (A) Topographic map of the area around the Longmenshan fault zone (LFZ) and (B) spatial distribution of the coupling fraction during 1999–2007. The thin black lines in (A) denote the faults, and the thick red line denotes the surface trace of the LFZ. The black star in (B) denotes the Wenchuan earthquake source location (Liu et al., 2008).
According to results of previous studies (Weimin Wang et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2008; Zhu, 2008; Du et al., 2009; Xu et al., 2009), the Longmenshan fault plane is a listric structure. The total length of the fault plane is 479 km and the total width is 78 km (Figure 2B). We adopted seven depth contours along strike at 0.1, 6, 12, 15, 18, 20, and 22.5 km; the dip angles between the contours were set to 55°, 50°, 20°, 10°, 7°, and 7° from the surface to the bottom of the fault plane (Zhao et al., 2020).
Results
Coupling Fraction
By gradually changing the uncertainty scaling factor f, we identified the f value needed for the optimal solution, of which
The coupling fraction of the optimal model from 1999 to 2007 (Figure 2B) shows that most of the Longmenshan fault plane was strongly coupled along both the strike and dip directions. Only the focal location of the Wenchuan earthquake was partly coupled with coupling fraction of ∼0.88. The only creeping section is a southwestern segment of ∼20 km wide and 12–22.5 km deep (Zhao et al., 2018).
Fault-Normal and Fault-Parallel Slip Deficit Rates
Using the GPS velocity fields of 1999–2001, 2001–2004, and 2004–2007, the coupling fraction of each period was fixed as the background value of 1999–2007 (Figure 2B); then, only the fault-normal and fault-parallel slip deficit rates of the fault plane were inverted to obtain the spatio-temporal evolution process.
Under the strong coupling of the Longmenshan fault plane, the fault-normal compressive deficit rates of the three periods showed an obvious decreasing trend from southwest to northeast, indicating the southwestern segment of the LFZ was subjected to the strongest compression before the Wenchuan earthquake, and compression weakened northeastward. On a temporal scale, the slip deficit rate of the central–southern segment was ∼1.5–3.6 mm/a from 1999 to 2001, before increasing slightly to ∼1.9–3.9 mm/a from 2001 to 2004. Then, from 2004 to 2007, it significantly decreased to ∼1.1–2.6 mm/a (Figure 3). The fault-normal compressive deficit rates in the northeastern segment of the fault plane were small during all three periods, indicating this segment was dominated by strike-slip movement.

FIGURE 3. Spatial distribution of fault-normal slip deficit rates during (A) 1999–2001, (B) 2001–2004, and (C) 2004–2007 along the Longmenshan fault plane. The black star denotes the Wenchuan earthquake source location.
The fault-parallel dextral deficit rates in three periods were uniformly distributed along the whole fault plane, with weak variations along strike and dip directions. Only the creeping area of the southwestern segment had a slip deficit of 0 mm/a. In terms of temporal evolution, the fault-parallel dextral deficit rate was ∼6 mm/a during 1999–2001 and 2001–2004, after which it increased rapidly to ∼9.5 mm/a from 2004 to 2007 (Figure 4).
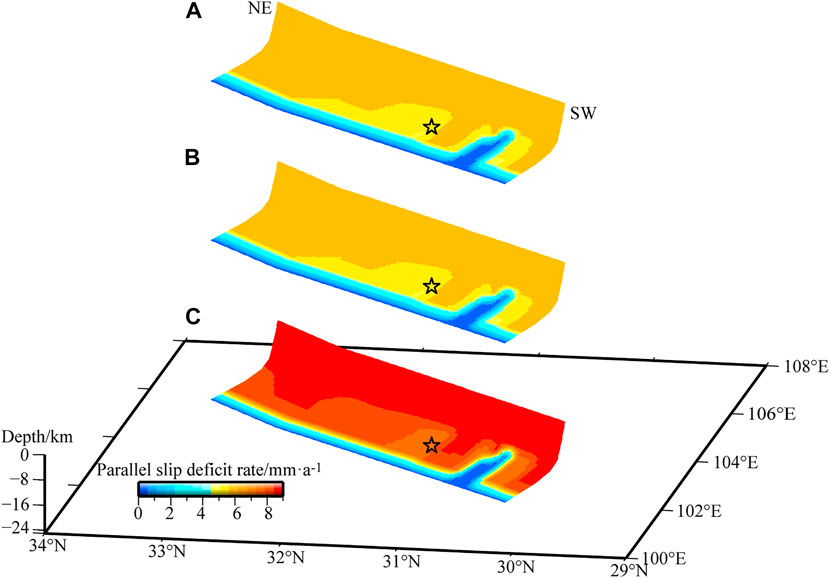
FIGURE 4. Spatial distribution of fault-parallel slip deficit rates during (A) 1999–2001, (B) 2001–2004, and (C) 2004–2007 along the Longmenshan fault plane. The black star denotes the Wenchuan earthquake source location.
The dynamic results of the fault-normal and fault-parallel slip deficit rates during the three periods show that taking the values of 1999–2001 as a baseline, the fault-normal slip deficit rate began to increase slightly from 2001 to 2004, while the fault-parallel slip deficit rate did not change. Subsequently, from 2004 to 2007, the fault-normal slip deficit rate decreased significantly, while the fault-parallel slip deficit rate increased rapidly. This suggests that the accumulation of fault-normal compressive strain energy during 2004–2007 was limited, but that there was rapid accumulation of fault-parallel dextral shear strain energy.
Velocity Profiles
To further analyze the surface continuous deformation characteristics on both sides of the LFZ, a 650 km long velocity profile across the LFZ (Figure 1) was constructed from the three periods of GPS velocity fields; then, dynamic velocity projection results both perpendicular and parallel to the LFZ were obtained (Figure 5).
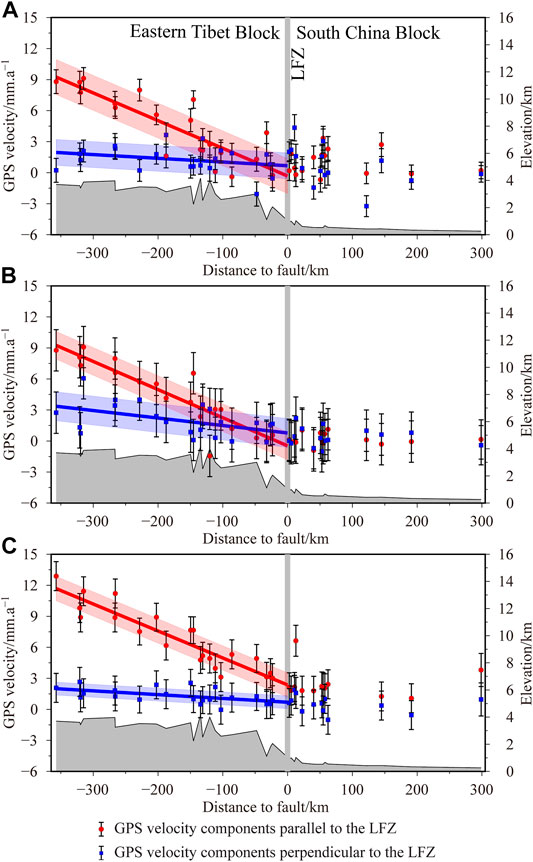
FIGURE 5. Global Positioning System (GPS) velocity profiles across the Longmenshan fault zone (LFZ) during (A) 1999–2001, (B) 2001–2004, and (C) 2004–2007. The topographic profiles are in each figure. The red lines and the blue lines are linear fitting results of the dextral shear rates and compressive shortening rates in the Eastern Tibet Block with one standard deviation, respectively.
The results show that internal deformation of the South China Block and the LFZ were weak before the earthquake. Large scale uniform deformation occurred within the Eastern Tibet Block, and the dextral shear deformation parallel to the LFZ was higher than the compressive shortening deformation perpendicular to the LFZ. A linear model was used to calculate the dextral shear rates and compressive shortening rates over a 357 km span of the Eastern Tibet Block, on the western side of the LFZ. The results for 1999–2001 (Figure 5A) show that the compressive shortening rate was ∼1.28 mm/a, equivalent to strain rate of 0.36 × 10−8/a, and the dextral shear rate was ∼9.57 mm/a, equivalent to strain rate of 2.68 × 10−8/a. The results for 2001–2004 (Figure 5B) show compressive shortening rate of ∼2.58 mm/a, equivalent to strain rate of 0.72 × 10−8/a, and dextral shear rate of ∼9.72 mm/a, equivalent to strain rate of 2.72 × 10−8/a. The results for 2004–2007 (Figure 5C) show compressive shortening rate of ∼1.31 mm/a, equivalent to strain rate of 0.37 × 10−8/a, and dextral shear rate of ∼9.32 mm/a, equivalent to strain rate of 2.61 × 10−8/a.
Comparison of the three periods shows that compressive shortening strain did not change significantly near the LFZ and was essentially distributed horizontally. Meanwhile, GPS stations inside the Eastern Tibet Block recorded significantly increase of crustal shortening strain from 2001 to 2004, followed by weakening from 2004 to 2007. This is broadly consistent with the result that the fault-normal compressive deficit rate increased at first and then decreased. Although the dextral shear strain inside the Eastern Tibet Block did not increase during 2004–2007, the dextral shear rate near the LFZ was significantly enhanced. Within a range of ∼100 km to the west of the LFZ, northeastward shear during the first two periods was essentially 0, while it increased obviously during 2004–2007 (Jiang et al., 2009). This may indicate that the dextral movement of the whole Eastern Tibet Block increased from 2004 to 2007, and under the background of fault strong coupling, the dextral shear deformation of part of the South China Block near the LFZ also increased (Figure 5C). This is consistent with the result of the rapidly increase of fault-parallel dextral deficit rate from 2004 to 2007.
Discussion
Acceleration Process of Deep Slip Along the Longmenshan Fault Plane
Interseismic surface horizontal slip rates of the LFZ inferred from GPS (Shen et al., 2005; Gan et al., 2007; YanZhao Wang et al., 2008) and geological data (Ma et al., 2005; Zhou et al., 2006) before the 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake are very slow (<2–3 mm/a; Zhang et al., 2010). However, the low slip rate observed at the surface may not reflect the state of accumulated strain at depth, where the devastating Wenchuan earthquake nucleated (Chen and Li, 2018). The deep rate (6–9.5 mm/a) derived in this study from the inversion of GPS velocities is two to three times higher than the above GPS and geological rates, but similar to the slip rate estimated over a depth range of 4–18 km using repeating earthquakes (3.5–9.6 mm/a; Li et al., 2011). At the same time, Zhao et al. (2008) calculated the accumulated Benioff strain using the earthquake catalogue, while Chen et al. (2015) conducted a two-dimensional viscoelastic finite-element simulation; both showed that the deep slip rate along the Longmenshan fault plane is higher than the shallow near-surface slip rate.
Chen and Li (2018) analyzed 10 repeating earthquake sequences detected in the central and northern segments of the LFZ (Figure 6), and found that the S06 and S07 sequences at 14–16 km depth near Hongkou–Wenchuan (Figure 6C) and the S10–12 sequences at 4.3–9.5 km depth near Beichuan (Figure 6E) exhibited different degrees of medium-term slip acceleration in around 2006. This is consistent with our results, in which the dextral slip deficit rate increased rapidly to ∼9.5 mm/a from 2004 to 2007. Both indicate that the deep slip rate of the Longmenshan fault plane may have accelerated before the Wenchuan earthquake. This may reflect a deformation response to a high stress state caused by increased tectonic loading of the Eastern Tibet Block before the Wenchuan earthquake; that is, lateral shear deformation increased in the northeastern direction after the accumulation of thrust elastic strain reached its limit in the seismogenic region. At the same time, the slip variation may not be a dominant factor until the long-term elastic strain accumulation on the fault reaches a sufficient level to be released in one large earthquake.
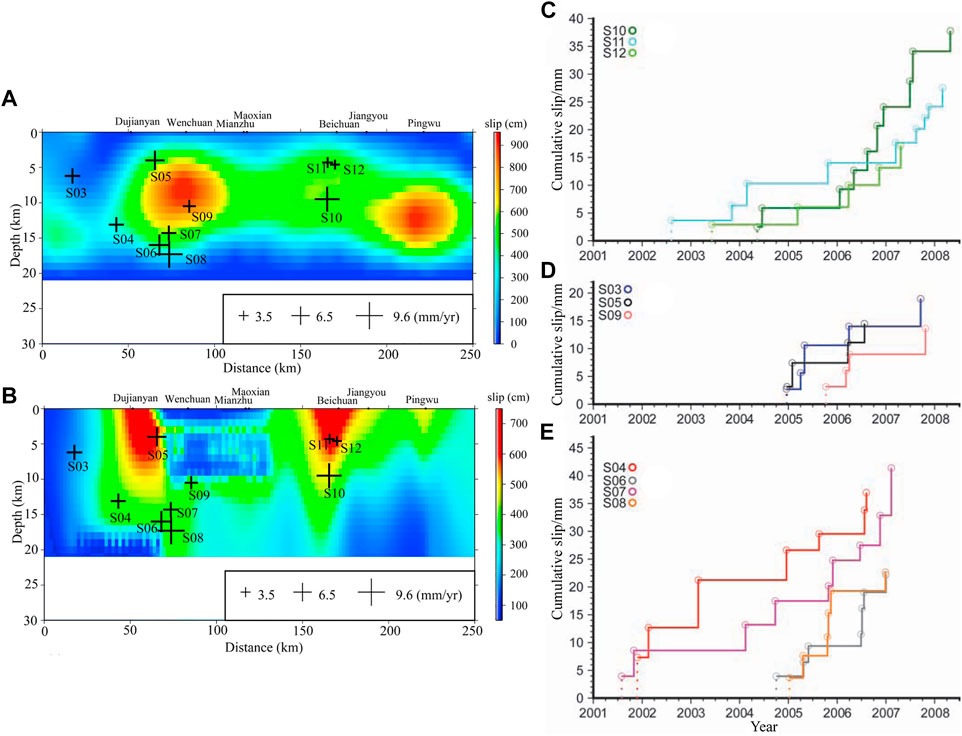
FIGURE 6. Estimated slip rates shown together with (A) coseismic slip inverted from teleseismic waveform data and (B) coseismic slip inverted from geodetic data. (C–E) Cumulative slip calculated from the 10 repeating earthquake sequences in the Longmenshan fault zone (LFZ). The sizes of the crosses in (A) and (B) are proportional to the slip rate (Li et al., 2011; Chen and Li, 2018).
Regional Pre-Seismic Deformation Does Not Correspond to Coseismic Displacement
The elastic strain released by a large earthquake is accumulated for a long time before the earthquake. Therefore, the inter-seismic deformation field and coseismic deformation field should exhibit reverse and complementary magnitudes (Jiang et al., 2009; Wu et al., 2015). Based on our analysis, before the Wenchuan earthquake, the thrust component of the central and southwestern segments of the LFZ was large, while that of the northeastern segment, which is mainly strike-slip, was small. This is consistent with the basic characteristics of field measurement of the Wenchuan earthquake, which was dominated by a thrust rupture at the focal location with the strike-slip component becoming larger northeastward (He et al., 2011), until it became a fully strike-slip rupture (Xu et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2011). However, before the Wenchuan earthquake, the relative movement and deformation of the regional crust did not correspond to the coseismic displacement field in terms of magnitude. The coseismic displacement field showed that compressive strain release consistent with elastic rebound also occurred in the Sichuan Basin, to the east of the LFZ (Jiang et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2011; Wu et al., 2015), while no compressive strain accumulation was observed in the three periods before the earthquake (Figure 5). The coseismic displacement field mainly shows compressive strain release on both sides of the rupture zone (Jiang et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2011; Wu et al., 2015), while large scale deformation of the Eastern Tibet Block was mainly dextral shear deformation before the earthquake (Figure 5).
This mismatch may be due to the long process of strain accumulation before large earthquakes. Immediately prior to the Wenchuan earthquake, the seismogenic area near the LFZ was at a stalemate, with significant deformation restricted after elastic compressive deformation of the crust reached its limit. In other words, the crustal deformation of strain accumulation corresponding to the strain release displayed in the coseismic displacement had occurred earlier, but was not observed completely because the GPS observation time was too short. This indicates that multi-year observations before earthquakes cannot fully represent inter-seismic processes. At the same time, it highlights the need for encompassing longer timescales when investigating seismogenic deformation fields before large earthquakes (Jiang et al., 2009).
Conclusion
In this study, we used four periods of GPS velocity fields to analyze the spatio-temporal dynamics of deep slip rate and surface deformation in the LFZ before the 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake. Before the earthquake, the Longmenshan fault plane was strongly coupled. The fault-normal slip deficit rate increased from 2001 to 2004, and then decreased from 2004 to 2007; meanwhile, the fault-parallel slip deficit rate increased substantially during 2004–2007, indicating that the deep slip rate of the fault plane may have accelerated. GPS velocity profiles confirm this phenomenon, which may indicate that thrust elastic strain in the seismogenic region of the Wenchuan earthquake struggled to accumulate after reaching the limit and was more conducive to dextral shear deformation under the enhancement background of large-scale NE-trending crustal movement. The results of this study have important implications for medium-term forecasting of large continental thrust earthquakes, which may require observations over long timescales.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author Contributions
JiZ designed the research and wrote the manuscript. ZY created some figures. JR, ZJ, and QY performed data interpretation and edited the manuscript. ZZ, CY, and JZ edited the manuscript. AN analyzed the results and edited the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant numbers 2018YFC1503606, 2018YFE0109700, and 2017YFC1500502) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 11672258).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to three reviewers for constructive comments and suggestions. We thank Min Wang for providing GPS velocity field datasets. English language editing was performed by Tornillo Scientific.
References
Chen, Q. F., and Li, L. (2018). Deep Deformation of the Longmenshan Fault Zone Related to the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake. Chin. Sci. Bull. 63, 1917–1933. (in Chinese with an English abstract). doi:10.1360/n972018-00362
Chen, Q. F., Hua, C., Li, L., and Cheng, J. (2015). Viscoelastic Simulation of Deep Tectonic Deformation of the Longmenshan Fault Zone and its Implication for strong Earthquakes. Chin. J. Geophys. 58, 4129–4137. (in Chinese with an English abstract). doi:10.6038/cjg20151120
Deng, Q. D., Zhang, P. Z., Ran, Y. K., Yang, X. P., Min, W., and Chu, Q. Z. (2003). Basic Characteristics of Active Tectonics of China. Sci. China Ser. D-earth Sci. 46 (4), 356–372. doi:10.1360/03ys9030
Du, F., Wen, X. Z., Zhang, P. Z., and Wang, Q. L. (2009). Interseismic Deformation across the Longmenshan Fault Zone before the 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan Earthquake. Chin. J. Geophys. 52 (11), 2729–2738. (in Chinese with an English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.11.007
Gan, W. J., Zhang, P. Z., Shen, Z. K., Niu, Z., Wang, M., Wan, Y., et al. (2007). Present-day Crustal Motion with the Tibetan Plateau Inferred from GPS Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 112, B08426. doi:10.1029/2005jb004120
Hao, M., Wang, Q., Shen, Z., Cui, D., Ji, L., Li, Y., et al. (2014). Present Day Crustal Vertical Movement Inferred from Precise Leveling Data in Eastern Margin of Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 632, 281–292. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.06.016
He, H., Wei, Z., Chen, C., and Shi, F. (2011). On-site Determination of Slip Vectors along the Longmenshan Fault during the Mw 7.9 Wenchuan, China, Earthquake of May 12, 2008. J. Asian Earth Sci. 41, 274–282. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.02.015
Herring, T. A., King, R. W., and McClusky, S. C. (2006). GPS Analysis at MIT, Release 10.3. Cambridge: Massachussetts Institute of Technology.
Huang, Z. C., Ji, C., Wu, H. T., Shi, Y. T., Geng, J. Q., Xu, M. J., et al. (2021). Review on the Crustal Structures and Deformations in the southeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Rev. Geophy. Planet. Phys. 52 (3), 291–307. (in Chinese with an English abstract). doi:10.19975/j.dqyxx.2021-005
Jiang, Z. S., Fang, Y., Wu, Y. Q., Wang, M., Du, F., and Ping, J. J. (2009). The Dynamic Process of Regional Crustal Movement and Deformation before Wenchuan MS8.0 Earthquake. Chin. J. Geophys. 52 (2), 505–518. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Kato, A., Fukuda, J. i., Kumazawa, T., and Nakagawa, S. (2016). Accelerated Nucleation of the 2014 Iquique, Chile Mw 8.2 Earthquake. Sci. Rep. 6, 24792. doi:10.1038/srep24792
Kato, A., and Nakagawa, S. (2014). Multiple Slow-Slip Events during a Foreshock Sequence of the 2014 Iquique, Chile Mw 8.1 Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 5420–5427. doi:10.1002/2014gl061138
Li, L., Chen, Q. f., Niu, F., and Su, J. (2011). Deep Slip Rates along the Longmen Shan Fault Zone Estimated from Repeating Microearthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. 116, B09310. doi:10.1029/2011jb008406
Li, Y. C., Nocquet, J. M., Shan, X. J., and Song, X. G. (2021). Geodetic Observations of Shallow Creep on the Laohushan-Haiyuan Fault, Northeastern Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 126, e2020JB021576. doi:10.1029/2020jb021576
Liu, Q. Y., Chen, J. H., Li, S. C., Li, Y., Guo, B., Wang, J., et al. (2008). The MS8.0 Wenchuan Earthquake: Preliminary Results from the Western Sichuan mobile Seismic Array Observations. Seismol. Geol. 30 (3), 584–596. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Loveless, J. P., and Meade, B. J. (2011). Spatial Correlation of Interseismic Coupling and Coseismic Rupture Extent of the 2011 MW= 9.0 Tohoku-Oki Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L17306 (17). doi:10.1029/2011gl048561
Ma, B. Q., Su, G., and Hou, Z. (2005). Late Quaternary Slip Rate in the central Part of the Longmenshan Fault Zone from Terrace Deformation along the Minjiang River. Seismol. Geol. 27, 234–242. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
McCaffrey, R. (2002). “Crustal Block Rotations and Plate Coupling,”. Plate Boundary Zones. Editors S. Stein, and J. T. Freymueller (Washington D.C.: AGU Geodynamics Series), 30, 101–122.
McCaffrey, R., King, R. W., Payne, S. J., and Lancaster, M. (2013). Active Tectonics of Northwestern U.S. Inferred from GPS-Derived Surface Velocities. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 118 (2), 709–723. doi:10.1029/2012jb009473
McCaffrey, R., Qamar, A. I., King, R. W., Wells, R., Khazaradze, G., Williams, C. A., et al. (2007). Fault Locking, Block Rotation and Crustal Deformation in the Pacific Northwest. Geophys. J. Int. 169, 1315–1340. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246x.2007.03371.x
McCaffrey, R. (2009). Time-dependent Inversion of Three-Component Continuous GPS for Steady and Transient Sources in Northern Cascadia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36 (7), 1–5. doi:10.1029/2008gl036784
Meade, B. J., and Hager, B. H. (2005). Block Models of Crustal Motion in Southern California Constrained by GPS Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 110 (B3), 1–19. doi:10.1029/2004jb003209
Meade, B. J. (2007). Present-day Kinematics at the India-Asia Collision Zone. Geol 35 (1), 81–84. doi:10.1130/g22924a.1
Moreno, M., Rosenau, M., and Oncken, O. (2010). 2010 Maule Earthquake Slip Correlates with Pre-seismic Locking of Andean Subduction Zone. Nature 467 (7312), 198–202. doi:10.1038/nature09349
Okada, Y. (1992). Internal Deformation Due to Shear and Tensile Faults in a Half-Space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 82 (2), 1018–1040. doi:10.1785/bssa0820021018
Okada, Y. (1985). Surface Deformation Due to Shear and Tensile Faults in a Half-Space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 75 (4), 1135–1154. doi:10.1785/bssa0750041135
Savage, J. C., Gan, W., and Svarc, J. L. (2001). Strain Accumulation and Rotation in the Eastern California Shear Zone. J. Geophys. Res. 106 (B10), 21995–22007. doi:10.1029/2000jb000127
Savage, J. C., and Prescott, W. H. (1978). Asthenosphere Readjustment and the Earthquake Cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 83 (B7), 3369–3376. doi:10.1029/jb083ib07p03369
Shen, Z. K., Lü, J. N., Wang, M., and Bürgmann, R. (2005). Contemporary Crustal Deformation Around the Southeast Borderland of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 110, B11409. doi:10.1029/2004jb003421
Thatcher, W. (2007). Microplate Model for the Present-Day Deformation of Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 112 (B1). doi:10.1029/2005jb004244
Thomas, M. Y., Avouac, J. P., Champenois, J., Lee, J. C., and Kuo, L. C. (2014). Spatiotemporal Evolution of Seismic and Aseismic Slip on the Longitudinal Valley Fault, Taiwan. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 119 (6), 5114–5139. doi:10.1002/2013jb010603
Uchida, N., Iinuma, T., Nadeau, R. M., Bürgmann, R., and Hino, R. (2016). Periodic Slow Slip Triggers Megathrust Zone Earthquakes in Northeastern Japan. Science 351, 488–492. doi:10.1126/science.aad3108
Wang, M. (2009). Analysis of GPS Data with High Precision and Study on Present-Day Crustal Deformation in China. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Wang, Q., Qiao, X. J., Lan, Q. G., Jeffrey, F., Yang, S. M., Xu, C. J., et al. (2011). Rupture of Deep Faults in the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake and Uplift of the Longmen Shan. Nat. Geosci. 4, 634–640. doi:10.1038/ngeo1210
Weimin Wang, W. M., Zhao, L. F., Li, J., and Yao, Z. X. (2008). Rupture Process of the MS8.0 Wenchuan Earthquake of Sichuan, China. Chin. J. Geophys. 51 (5), 1403–1410. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Wu, Y., Jiang, Z., Zhao, J., Liu, X., Wei, W., Liu, Q., et al. (2015). Crustal Deformation before the 2008 Wenchuan Ms8.0 Earthquake Studied Using GPS Data. J. Geodynamics 85, 11–23. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2014.12.002
Xu, X., Wen, X., Yu, G., Chen, G., Klinger, Y., Hubbard, J., et al. (2009). Coseismic Reverse- and Oblique-Slip Surface Faulting Generated by the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. Geology 37 (6), 515–518. doi:10.1130/g25462a.1
YanZhao Wang, Y., Wang, E., Shen, Z., Wang, M., Gan, W., Qiao, X., et al. (2008). GPS-constrained Inversion of Present-Day Slip Rates along Major Faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan Region, China. Sci. China Ser. D-earth Sci. 51, 1267–1283. doi:10.1007/s11430-008-0106-4
Zhang, P. Z., Wen, X. Z., Shen, Z. K., and Chen, J. H. (2010). Oblique, High-Angle, Listric-Reverse Faulting and Associated Development of Strain: The Wenchuan Earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 38, 353–382. doi:10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152602
Zhang, P. Z., Xu, X. W., Wen, X. Z., and Ran, Y. K. (2008). Slip Rates and Recurrence Intervals of the Longmen Shan Active Fault Zone, and Tectonic Implications for the Mechanism of the May 12 Wenchuan Earthquake, 2008, Sichuan, China. Chin. J. Geophys. 51 (4), 1066–1073. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Zhao, J., Ren, J. W., Liu, J., Jiang, Z. S., Liu, X. X., Liang, H. B., et al. (2020). Coupling Fraction and Relocking Process of the Longmenshan Fault Zone Following the 2008 Mw7.9 Wenchuan Earthquake. J. Geodynamics 137, 101730. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2020.101730
Zhao, J., Ren, J. W., Jiang, Z. S., Liu, X. X., Niu, A. F., Yan, W., et al. (2018). Fault Locking and Deformation Characteristics in Southwestern Segment of Longmenshan Fault. J. Seismol. Res. 41 (2), 216–225. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Zhao, J., Wu, Y. Q., Jiang, Z. S., Niu, A. F., Liu, J., Wang, L. F., et al. (2013). Fault Locking and Dynamic Deformation of the Longmenshan Fault Zone before the 2013 Lushan MS7.0 Earthquake. Acta Seismol, Sin. 35 (5), 681–691. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2013.05.007
Zhao, J., Zhan, W., Ren, J. W., Jiang, Z. S., Gu, T., Liu, J., et al. (2021). GPS Time Series Inversion of the Healing Process of the Middle Segment of the Longmenshan Fault after the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica 50 (1), 37–51. (in Chinese with an English abstract). doi:10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200047
Zhao, Y. Z., Wu, Z. L., Jiang, C. S., and Zhu, C. Z. (2008). Present Deep Deformation along the Longmenshan Fault by Seismic Data and Implications for the Tectonic Context of the Wenchuan Earthquake. Acta Geol. Sin. 82, 1778–1787. (in Chinese).
Zhou, R. J., Li, Y., Densmore, A. L., and Ellis, M. A. (2006). Active Tectonics of the Eastern Margin of the Tibet Plateau. J. Mineral. Petrol. 26 (2), 40–51. doi:10.19719/j.cnki.1001-6872.2006.02.007
Zhu, J. S. (2008). The Wenchuan Earthquake Occurrence Background in Deep Structure and Dynamics of Lithosphere. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 35 (4), 348–356. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Zou, Z. Y., Jiang, Z. S., Wu, Y. Q., Wei, W. X., Fang, Y., and Liu, X. X. (2015). Dynamic Characteristics of Crustal Movement in north-south Seismic belt from GPS Velocity Field before and after the Wenchuan Earthquake. Chin. J. Geophys. 58 (5), 1597–1609. (in Chinese with an English abstract). doi:10.6038/cjg20150512
Keywords: wenchuan earthquake, longmenshan fault zone, fault coupling fraction, GPS velocity profiles, acceleration process of deep slip rate, pre-seismic preparatory processes, earthquake forecasting
Citation: Zhao J, Yuan Z, Ren J, Jiang Z, Yao Q, Zhou Z, Yue C, Zhong J and Niu A (2022) Acceleration of Deep Slip Along the Longmenshan Fault Plane Before the 2008 M8.0 Wenchuan Earthquake. Front. Earth Sci. 10:830317. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.830317
Received: 07 December 2021; Accepted: 21 February 2022;
Published: 24 March 2022.
Edited by:
Giovanni Martinelli, National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, ItalyReviewed by:
Mattia Crespi, Geodesy and Geomatics Division—DICEA Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyAlexis Rigo, UMR8538 Laboratoire de géologie de l’Ecole Normale Supérieure (LG-ENS), France
Vladimir Kostoglodov, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Yuan, Ren, Jiang, Yao, Zhou, Yue, Zhong and Niu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anfu Niu, TmFmY3NiMjAwNEBzZWlzLmFjLmNu
 Jing Zhao
Jing Zhao Zhengyi Yuan1
Zhengyi Yuan1 Anfu Niu
Anfu Niu