- 1Reproductive Oncology Lab, Division of Natural and Applied Sciences, Duke Kunshan University, Kunshan, Jiangsu, China
- 2Photonics Lab, Division of Natural and Applied Sciences, Duke Kunshan University, Kunshan, Jiangsu, China
- 3Optical Characterization Lab, Division of Natural and Applied Sciences, Duke Kunshan University, Kunshan, Jiangsu, China
- 4Division of Natural and Applied Sciences, Duke Kunshan University, Kunshan, Jiangsu, China
- 5First Affiliated Hospital, Soochow University Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
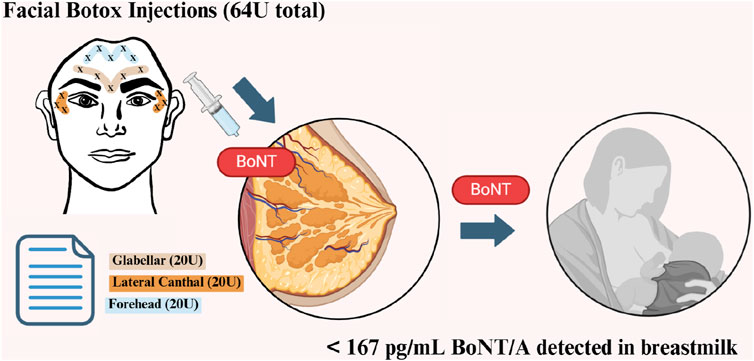
The use of cosmetic Botox (BoNT/A) has become increasingly prevalent among women, even during the post-pregnancy breastfeeding period. However, there is currently a limited understanding of the extent Botox enters breastmilk and its potential effect on the breastfeeding infant. In this study, breastmilk samples were acquired from five women aged between 28 and 45. Three sample sets ranged from 1 h to 1 year after facial Botox treatments (64 U), whereas the remaining two were from women who never received Botox. BoNT/A concentrations in samples were detected using standard Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), unreduced and reduced Western Blotting, confocal micro-Raman Spectroscopy, and Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS). From ELISA, the greatest breastmilk BoNT/A concentration was found from woman 1, 4 days after Botox injection (167 pg/mL). Levels were highest overall in the first week (82.45–167 pg/mL) and around 2 months (132.725 pg/mL) after injection. No clear indication of BoNT/A was detected in Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS), Western Blotting and confocal micro-Raman Spectroscopy, but Western blot and confocal micro-Raman Spectroscopy show promise of development into future means of detection. From our study, the amount of BoNT/A in breastmilk peaks around 4 days (167 pg/mL) and at 2 months (132.725 pg/mL) after facial injection. Even over a year after injection, BoNT/A can be detected. However, all quantities of BoNT/A detected (between 34.4 pg/mL and 167 pg/mL) are likely to be safe for infants.
Highlights
• BoNT/A was detected in the breastmilk of 3 women after facial Botox injections of 64 U.
• Toxin levels peaked in the first week and at around 2 months after injection.
• All detected levels (up to 167 pg/mL) were significantly below the lethal dose for newborns.
1 Introduction
In today’s social media oriented culture, caring about one’s appearance is becoming the new normal. Consequently, there has been a rapid growth of cosmetic procedures, with the most popular, Botox, having developed into a seven billion dollar industry (Hood and Wilson, 2001). These accessible treatments are also seen in pregnant women. During pregnancy, women’s bodies change with expanding bellies, growing breasts, swelling ankles/wrists, and stretch marks developing in the skin as they grow a child. After pregnancy, the immense pressure to “bounce back” evokes body dissatisfaction in some mothers (Gavin et al., 2005; Sweeney and Fingerhut, 2013; Riesco-González et al., 2022). Without strong social support, body insecurities and celebrity posts of a more glamorous motherhood can be significant motivators for some women to seek timely Botox treatments, even during the early lactation period (Williams, 2013). However, it is unknown whether this represents a risk to the newborn.
Although injected Botox is regarded as safe, BoNT/A has a history of being a deadly toxin when ingested orally (Ting and Freiman, 2004). Given that an oral dose as small as 1
In clinical treatments for pregnant women, Botox doses have varied from 1.25 to 300 U (Brandt et al., 2009; Morgan et al., 2006). Cosmetic Botox doses are lower, with a standard of 20 U for dermatology (Satriyasa, 2019). One U, i. e., mouse unit, refers to the lethal dose that kills 50% of mice (Ting and Freiman, 2004). For humans, a lethal dose of Botox by injection is around 3000 U (Ting and Freiman, 2004). Therefore, Botox treatments have almost unanimously been found to be safe and free from long lasting side effects in clinical trials (Brandt et al., 2009). Due to a high molecular weight and neurospecificity to its intramuscular targets, BoNT/A, the active ingredient of Botox, is not likely to spread far systemically or enter breastmilk (Hilderbrand et al., 1961). However, many other drugs have been detected in breastmilk previously (Sachs and Drugs, 2013; Julsgaard et al., 2023).
A recent study on Botox was conducted in four patients receiving facial injections. In two of the patients (receiving 54 U and 92 U, respectively), no BoNT/A was detected in breastmilk (Hudson et al., 2024). In the other two women, between 85.24 and 746.82 pg/mL were detected 0–5 days post-injection (Hudson et al., 2024). In the LactMed database, other case reports related to Botulinum toxin and breastmilk are sparse and are related to maternal botulism from food, not Botox injections (Sachs and Drugs, 2013). These cases are few in number, sample size, and time points measured.
Breastmilk, produced in the alveoli of breasts, derives its nutrients from the circulatory system, thus being prone to contamination by contents of the mother’s bloodstream (Sachs and Drugs, 2013). Despite potential harms, the benefits of breastmilk are wide-spanning and well-studied. Breastfeeding benefits both the mother and newborn by reducing obesity, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers (Binns et al., 2016; Neves et al., 2021). For the newborn, breastmilk from the first 2 days after birth provides high amounts of antibodies and immune cells. Afterwards, it continues to provide important proteins, sugars, vitamins, minerals, hormones, and growth factors (Bhora et al., 1995; Ahmed et al., 2004). For the mother, breastfeeding can reduce stress, fatigue, and depression (Figueiredo et al., 2014). Therefore, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends mothers to initiate breastfeeding within the first hours of life and exclusively breastfeed for at least 6 months (Tucker and O’Malley, 2022; World Health Organization WHO, 2023). However, mothers with certain diseases or maternal medications proven to pose risks to babies are an exception and are advised not to breastfeed (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC, 2023).
With the currently limited number of studies published, the Food Drug Administration (FDA) warns against women using Botox during pregnancy and breastfeeding (Medication Guide BOTOX Cosmetic for Injection, 2011). Our study aims to inform this recommendation by quantifying BoNT/A levels in breastmilk post-injection via standard, i. e., ELISA, and non-standard i.e., Western Blotting, confocal micro-Raman spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry techniques.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and participants
The study participants were three lactating women between the ages of 35 and 45 who underwent their most recent Botox treatment more than a year ago. Additionally, two breastfeeding women aged 28 to 32 who have never received Botox treatment served as controls (Table 1). Women received BoNT/A injections (BOTOX® Cosmetic onabotulinumtoxinA, United States) treatment for glabellar lines, lateral canthal lines, and forehead lines in accordance with the FDA Botox medication guide (BOTOX, 1989). They received 20 U, 24 U, and 20 U at the 3 sites respectively, totaling 64 U per woman. All women were instructed to express around 100 mL of breastmilk per breast for 30 min using a manual pump. Notably, it cannot be excluded that not all milk in the breast was collected by this method. Around 200 mL of each sample was collected in separate labeled sterile bags (MEDELA,ZG) before their latest treatment and 1, 6, 24, 36, 48, and 72 h after treatment. All women received no further Botox treatments for the entire duration of the study. Samples were immediately frozen in participants’ home freezers at

Table 1. Summary of participant data and samples collected from 3 women who have received facial Botox injections and 2 women who have never received Botox.All women had weights between 48–65 kg and heights between 160–175 cm.
2.2 Sample preparation and dialysis
Breastmilk sample aliquots were centrifuged at 1,500
Dialysis of breastmilk was performed overnight at
2.3 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Breastmilk BoNT/A concentrations were measured in duplicates by a commercial ELISA kit for Human Botulinum Toxin Type A (BTX-ELISA, China). ELISA was performed on samples spanning from 6 h to 5 months following the manufacturer’s instructions and as outlined (Table 2).
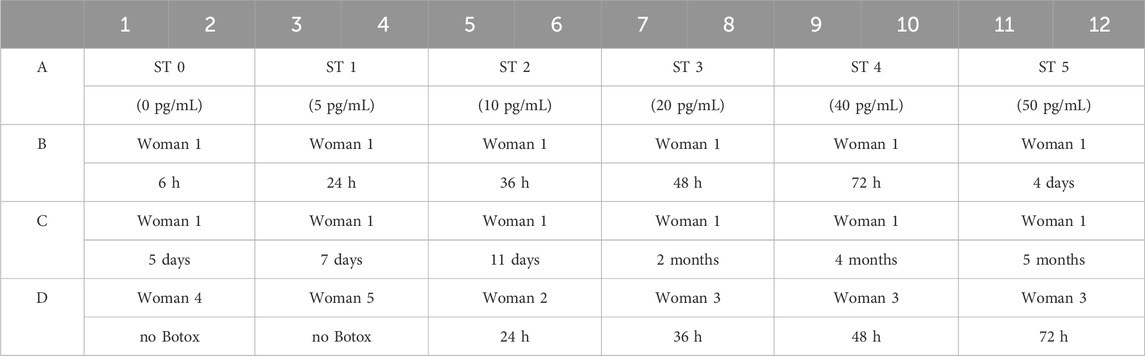
Table 2. Breastmilk samples loaded in ELISA plate wells. Each sample was loaded in duplicate. The first row consists of the standards provided by the manufacturer to produce the standard curve.
2.3.1 ELISA plate analysis
The ELISA plate was read by a Varioskan LUX microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., United States). Values of each pair of duplicates were averaged. BoNT/A concentration versus absorbance of the standard curve was plotted following the manufacturer’s manual. The absorbance of standard 1 (0 pg/mL) was subtracted from all other absorbance values. From these adjusted average absorbances, concentrations of the breastmilk samples were determined. See the Supplementary Appendix for full ELISA methods.
2.4 Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and Western Blot
The next method applied was Western Blotting. Western Blotting included non-reducing and reducing methods in which BoNT/A bands would be expected at different kDAs. The inactive BoNT/A protein has a molecular weight of 150 kDa, consisting of a light chain (50 kDa) and heavy chain (100 kDa) connected by a disulfide bond (Rossetto et al., 2006).
The detection used a primary antibody specific to the 1,280 -
See the Supplementary Appendix for full Western Blotting methods.
2.4.1 Non-reducing PAGE
Samples from 24, 36, and 48 h were subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using non-reducing conditions. In this procedure, the toxin shows only the protein band formed by units of molecular weight at 150 kDa.
2.4.2 Reducing PAGE
Samples across a longer span of time were subjected to reducing electrophoresis. In reducing PAGE, the toxin is resolved into its heavy (molecular weight = 100 kDa) and light (molecular weight = 50 kDa) subunits due to breakage of disulfide bonds (Grenda et al., 2021).
2.5 Confocal micro-Raman Spectroscopy
Next we were interested in investigating the BoNT/A concentration in breastmilk with a non-standard technique, i.e., confocal micro-Raman Spectroscopy.
Raman spectra for samples of woman 1 at 48 h, 72 h, and 1+ year, samples from woman 2 at 6 h and 1 year, and negative control samples from women 4 and 5 were collected at room temperature using a confocal micro-Raman Spectrometer (LabRAM HR Evolution, HORIBA Scientific, JP). See the Supplementary Appendix for the full methods.
2.6 Liquid chromatography - mass spectrometry (LC-MS)
Liquid Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) was used to analyze unprocessed breastmilk samples of 1 mL taken at 6 and 48 h post-Botox administration. Mass spectrometry was outsourced to the company PTM Bio Hangzhou China. See the Supplementary Appendix for the full methods.
3 Results
Using a commercially available ELISA kit, concentrations of BoNT/A ranging from 0 to 167 pg/mL were detected in all breastmilk samples of women that received Botox treatment, while no BoNT/A was detected in the control group (Figure 1). The highest concentration observed was in the sample from woman 1, 4 days after the injection (167 pg/mL). This is in line with the Hudson et al. observations that found peaks at 3 and 5 days, respectively, in two women (Hudson et al., 2024). We observed that after the first week, circulating BoNT/A concentrations decrease to a low concentration of 24.4 pg/mL at 11 days, before another peak of 132.725 pg/mL at 2 months (Figure 1).
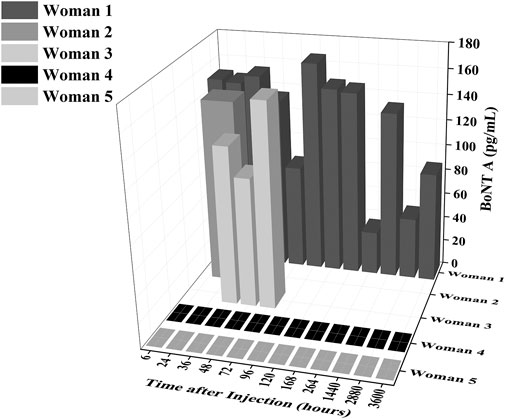
Figure 1. Concentrations of BoNT/A in ELISA samples as a function of time and as a function of breastmilk samples. The level of BoNT/A in breastmilk generally decreases over time after the first week (6–168 h) but has a distinct peak again at 2 months (1,440 h).
3.1 Western blot results
In the negative control lysate, samples from woman 4 and woman 5, who have never had received treatment of BoNT/A showed the absence of 150 kDa marker for BoNT/A. The Western blots of samples from women post-Botox revealed the presence of fluctuating 150 kDa and 100 kDa (See Supplementary Appendix).
3.2 Raman spectroscopy results
In Raman Spectroscopy, several characteristic peaks of breastmilk and BoNT/A were detected (See Supplementary Appendix). Peaks at 918
3.3 Mass spectrometry results
In the 6 h sample, 22,666 peptides were detected, consisting of 22,097 unique peptides and 3,191 identified proteins. In the 48 h sample, 22,333 peptides were detected, with 21,688 unique peptides and 3,140 identified proteins (See Supplementary Appendix). BoNT/A was not clearly detected among these peptides.
4 Discussion
Botox has been extensively used in clinical treatments for conditions such as excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), muscle stiffness (spasticity), enlarged facial muscles (facial muscular hypertrophy), muscle spasms, migraines and cosmetic treatments (Young and Young, 2021). As more women delay pregnancies and seek to continue breastfeeding beyond the WHO-recommended 2 years, and with others experiencing migraines or desiring post-pregnancy improvements, there is insufficient information available regarding the safety of using BoNT/A during breastfeeding for infants. Due to the currently limited information on the detection of BoNT/A in breastmilk, we tested the above methods to provide a better sense of the risk versus benefit assessment.
To some extent, almost all medications transfer from blood to breastmilk (Sachs and Drugs, 2013). The transfer of drugs into breastmilk is influenced by protein binding, lipid solubility, and ionization (Wanat, 2020). With regards to the pharmacokinetics of Botox in the mother, Botox inhibits acetylcholine secretion in neurons of the peripheral nervous system, entering the nerve terminal almost immediately after injection (Bakheit et al., 1997; Carruthers et al., 2005; Schantz and Johnson, 1997). The binding and internalization of Botox have a half-time of 10 min at body temperature, i. e.,
With the quantitative BoNT/A breastmilk concentrations determined by ELISA, our concentrations were lower than the 2024 Hudson et al. study, by about 2 to 10-fold (Hudson et al., 2024). The recent study from Hudson et al. found that 8 of the 16 samples had varying levels of botulinum toxin ranging from 85.24 to 746.82 pg/mL, while 8 samples had no toxin detected (Hudson et al., 2024). The variation in outcomes might be influenced by the ELISA kits which detect different epitopes. Enzyme linked immunoassays (ELISA) vary in sensitivity and specificity mainly due to different types of both detection and capture antibodies (Rød et al., 2017). For instance, commercial ELISA kits tested different values of total corticosterone in the same serum samples (Rød et al., 2017). Metabolic variances in the breakdown of Botox could also have played a role. The body’s uptake, circulation, and excretion of BoNT/A is complicated, and metabolism can differ based on genetics or lifestyle choices. In particular, BoNT/A uptake to nerve endings increases with activity and temperature, reducing initial Botox concentrations but increasing later concentrations circulation (Hallett, 2015).
However, the duration of our study continued longer, with samples up to 5 months after Botox injection. The effects of Botox injection decrease after 2 months when it is fully metabolized, and it is generally at 3–4 months when effects completely wear off and a new injection is needed (Brandt et al., 2009). Which corresponds to the second peak 2 months after injection. Because this study design anticipated the peaks to be in the first days, the samples collected later in the study were more sparse (at 2 months, 4 months, 5 months). Therefore, further work could be done with more samples around 2–4 months collected and tested to more accurately determine this second peak.
One additional unanticipated result was exactly how long traces of BoNT/A can remain in the body. Due to prior treatment of the lactating women over 1 year before this study, the original negative “pre Botox” controls we used in Western blots were from women 1, 2, and 3. Because these women had all received Botox procedures for a time longer than 1 year ago, this led to inconclusive results and being unable to find differentiating molecular weight bands on the gel. However, upon acquiring breastmilk samples from women 4 and 5, who had never had Botox before in their lifetime, bands at 150 kDa were not observed. This indicates that even after over a year since a facial injection, detectable amounts of BoNT/A may still be present in circulation.
Our study and previous ones have had a limited sample size and cover only facial Botox injection procedures. Future studies can be done to further elucidate how Botox metabolism changes with different ages, race, physical characteristics, injections, and lifestyles. Maternal concentrations of BoNT/A were not measured, but future work could measure serum levels in mothers. Our study was also limited in that adverse effects on the breastfed infants were not measured. Beyond lethal dosage, the No Observed Effect Level (NOEL) is also of interest. Because oral BoNT/A intake is highly dangerous with no medicinal use, there are no reports of an oral NOEL. However, 2 studies of mothers with Botulism breastfeeding have reported no adverse effects in the infants (Middaugh, 1978; Geiger, 1938). Future work to determine urine, stool, or blood concentrations of BoNT/A in infants and monitor adverse effects of Botulism would be further directions. However, given that the highest value was 167 pg/mL, this is less than 1 in 20,000ths of the lethal dose 3.5
Based on an average intake of 670 mL of breastmilk/day, a breastfed infant would ingest 0.112
Based on our knowledge, this study is the first to examine breastmilk from lactating women for presence of BoNT/A using Western blot, confocal micro-Raman Spectroscopy, and Mass Spectrometry. While concentrations were too low for Mass Spectrometry to detect, Western Blotting and confocal micro-Raman Spectroscopy showed promise of future development for detecting Botox (See Supplementary Appendix). In terms of methods, ELISA was the most effective for our purposes, as it had a clear standard curve and straightforward interpretation. The BTX-ELISA kit also had high specificity, with detection and quantification limits in pg/mL based on the standard solutions provided. Together with the results from Hudson et al., this study supports the conclusion that facial BoNT/A injections does not require the interruption of breastfeeding (Hudson et al., 2024).
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Kyle Fruh, Duke Kunshan University; Bing Luo, Duke Kunshan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
HG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZX: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. RK: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. PT: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. CZ: Resources, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. FK: Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. DK: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. FS: Resources, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Duke Kunshan University Start-Up funds, Duke Kunshan University Undergraduate Studies Signature Work Research Grant, Synear and Wang-Cai Biochemistry grants, and Kunshan Municipal Government research funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fdsfr.2024.1480515/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmed, L., Islam, S. N., Khan, M., Huque, S., and Ahsan, M. (2004). Antioxidant micronutrient profile (vitamin E, C, A, Copper, Zinc, Iiron) of colostrum: association with maternal characteristics. J. Trop. Pediatr. Environ. Child Health 50, 357–358. doi:10.1093/tropej/50.6.357
Al-Saleem, F. H., Ancharski, D. M., Ravichandran, E., Joshi, S. G., Singh, A. K., Gong, Y., et al. (2008). The role of systemic handling in the pathophysiologic actions of Botulinum toxin. Exp. Ther. 326 (3), 856–863. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.136242
Anderson, P. O., and Valdés, V. (2015). Variation of milk intake over time: clinical and pharmacokinetic implications. Mary Ann. Liebert, Inc. Publ. 10 (3), 142–144. doi:10.1089/bfm.2014.0170
Arnon, S. S., Schechter, R., Inglesby, T. V., Henderson, D. A., Barlett, J. G., Ascher, M. S., et al. (2001). Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: medical and public health management. JAMA 285 (8), 1059–1070. doi:10.1001/jama.285.8.1059
Bakheit, A. M. O., Ward, C. D., and McLellan, D. L. (1997). Generalised botulism-like syndrome after intramuscular injections of Botulinum toxin Type A: a report of two cases. J. neurology, Neurosurg. psychiatry 62 (2), 198. doi:10.1136/jnnp.62.2.198
Bhora, F., Dunkin, B., Aly, H., Bass, B., Sidawy, A., Harmon, J., et al. (1995). Effect of growth factors on cell proliferation and epithelialization in human skin. J. Surg. Res. 59 (2), 236–244. doi:10.1006/jsre.1995.1160
Binns, C., Lee, M., and Low, W. Y. (2016). The long-term public health benefits of breastfeeding. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 28 (1), 7–14. doi:10.1177/1010539515624964
Black, J. D., and Dolly, J. O. (1986). Interaction of 125I-labeled Botulinum neurotoxins with nerve terminals. II. autoradiographic evidence for its uptake into motor nerves by acceptor-mediated endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 103 (2), 535–544. doi:10.1083/jcb.103.2.535
BOTOX (1989). BOTOX (onabotulinumtoxinA) for injection, for intramuscular, intradetrusor, or intradermal use. accessed on April 14, 2024.
Brandt, F., Swanson, N., Baumann, L., and Huber, B. (2009). Randomized, placebo-controlled study of a new botulinum toxin type a for treatment of glabellar lines: efficacy and safety. Dermatol. Surg. 35 (12), 1893–1901. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2009.01235.x
Brooks, V. B. (1954). The action of Botulinum toxin on motor-nerve filaments. J. Physiology 123 (3), 501–515. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005067
Carruthers, A., Carruthers, J., and Said, S. (2005). Dose-ranging study of Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of glabellar rhytids in females. Dermatol. Surg. 31 (4), 414–422. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31107
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2023). When breastfeeding or feeding expressed milk is not recommended. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/contraindications-to-breastfeeding.html.
Dressler, D., and Benecke, R. (2007). Pharmacology of therapeutic botulinum toxin preparations. Disabil. Rehabilitation 29, 1761–1768. doi:10.1080/09638280701568296
Figueiredo, B., Canário, C., Tendais, I., Pinto, T. M., Kenny, D. A., and Field, T. (2014). Breastfeeding is negatively affected by prenatal depression and reduces postpartum depression. Psychol. Med. 44 (5), 927–936. doi:10.1017/S0033291713001530
Gavin, N. I., Gaynes, B. N., Lohr, K. N., Meltzer-Brody, S., Gartlehner, G., and Swinson, T. (2005). Perinatal depression: a systematic review of prevalence and incidence. Obstetrics and Gynecol. 106 (5), 1071–1083. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000183597.31630.db
Geiger, J. C. (1938). Concerning botulism outbreak in tucumcari, New Mexico. Cal. West Med. 48 (1), 58.
Grenda, T., Grenda, A., Krawczyk, P., and Kwiatek, K. (2021). Botulinum toxin in cancer therapy—current perspectives and limitations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 106, 485–495. doi:10.1007/s00253-021-11741-w
Hallett, M. (2015). Explanation of timing of botulinum neurotoxin effects, onset and duration, and clinical ways of influencing them. Toxicon 107, 64–67. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.07.013
Hilderbrand, G., Lamanna, C., and Heckly, R. (1961). Distribution and particle size of type A Botulinum toxin in body fluids of intravenously injected rabbits. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 107 (2), 284–289. doi:10.3181/00379727-107-26604
Hood, W. W., and Wilson, C. S. (2001). The literature of bibliometrics, scientometrics, and informetrics. Scientometrics 52, 291–314. doi:10.1023/a:1017919924342
Hudson, C., Wilson, P., Lieberman, D., Mittelman, H., and Parikh, S. (2024). Analysis of breast milk samples in lactating women after undergoing Botulinum toxin injections for facial rejuvenation: a pilot study, Facial Plastic Surgery and Aesthetic Medicine.
Julsgaard, M., Mahadevan, U., Vestergaard, T., Mols, R., Ferrante, M., and Augustijns, P. (2023). Tofacitinib concentrations in plasma and breastmilk of a lactating woman with ulcerative colitis. Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology 8 (8), 695–697. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00158-9
Malizio, C., Goodnough, M., and Johnson, E. (2000). Purification of Clostridium Botulinum type A neurotoxin. Methods Mol. Biol., 27–39. doi:10.1385/1-59259-052-7:27
Medication Guide BOTOX Cosmetic for Injection (2011). Medication guide BOTOX cosmetic for injection.
Middaugh, J. (1978). Botulism and breast milk. N. Engl. J. Med. 298 (6), 343. doi:10.1056/nejm197802092980620
Morgan, J., Iyer, S., Moser, E., Singer, C., and Sethi, K. (2006). Botulinum toxin A during pregnancy: a survey of treating physicians. J. Neurology, Neurosurg. and Psychiatry 77 (1), 117–119. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2005.063792
Neves, P. A. R., Vaz, F. S. J. S., Baker, P., Gatica-Domínguez, G., Piwoz, E., Rollins, N., et al. (2021). Rates and time trends in the consumption of breastmilk, formula, and animal milk by children younger than 2 years from 2000 to 2019: analysis of 113 countries. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 5 (9), 619–630. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00163-2
Riesco-González, F. J., Antúnez-Calvente, I., Vázquez-Lara, J. M., Rodríguez-Díaz, L., Palomo-Gómez, R., Gómez-Salgado, J., et al. (2022). Body image dissatisfaction as a risk factor for postpartum depression. Medicina 58 (6), 752. doi:10.3390/medicina58060752
Rios-Leyvraz, M., and Yao, Q. (2023). The volume of breast milk intake in infants and young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mary Ann. Liebert, Inc. Publ. 18 (3), 188–197. doi:10.1089/bfm.2022.0281
Rød, A. M. K., Harkestad, N., Jellestad, F. K., and Murison, R. (2017). Comparison of commercial elisa assays for quantification of corticosterone in serum. Nat. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 1–5. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06006-4
Rossetto, O., Morbiato, L., Caccin, P., Rigioni, M., and Montecucco, C. (2006). Presynaptic enzymatic neurotoxins. J. Neurochem. 97, 1534–1545. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03965.x
Sachs, H. C., and Drugs, C. O. (2013). The transfer of drugs and therapeutics into human breast milk: an update on selected topics. Pediatrics 132 (3), e796–e809. doi:10.1542/peds.2013-1985
Satriyasa, B. K. (2019). Botulinum toxin (botox) a for reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles: a literature review of clinical use and pharmacological aspect. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol 12, 223–228. doi:10.2147/CCID.S202919
Schantz, E. J., and Johnson, E. A. (1997). Botulinum toxin: the story of its development for the treatment of human disease. Perspect. Biol. Med. 40 (3), 317–327. doi:10.1353/pbm.1997.0032
Sweeney, A. C., and Fingerhut, R. (2013). Examining relationships between body dissatisfaction, maladaptive perfectionism, and postpartum depression symptoms. J. Obstetric, Gynecol. and Neonatal Nurs. 42 (5), 551–561. doi:10.1111/1552-6909.12236
Ting, P. T., and Freiman, A. (2004). The story of Clostridium botulinum: from food poisoning to Botox. Clin. Med. J. - Lond. 4 (3), 258–261. doi:10.7861/clinmedicine.4-3-258
Tucker, Z., and O’Malley, C. (2022). Mental health benefits of breastfeeding: a literature review. Cureus 14 (9), e29199. doi:10.7759/cureus.29199
Wanat, K. (2020). Biological barriers, and the influence of protein binding on the passage of drugs across them. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47 (4), 3221–3231. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05361-2
Williams, B. M. (2013). This is not what motherhood looks like”: mothers’ interpretations of cultural representations on the celebrity pregnant and post-partum body Louisville, KY: University of Louisville. Ph.D. thesis
World Health Organization (WHO) (2023). Infant and young child feeding. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infant-and-young-child-feeding.
Young, M., and Young, K. (2021). Scientific review of the aesthetic uses of Botulinum toxin type A. Archives craniofacial Surg. 22, 1–10. doi:10.7181/acfs.2021.00003
Keywords: breastfeeding, botulinum neurotoxin type A, ELISA, Western blot, confocal micro-Raman spectroscopy, mass spectrometry (LC-MS)
Citation: Gu H, Xu Z, Koviazina R, Tan P, Zheng C, Kappes F, Kotsifaki DG, Shen F and Tsigkou A (2025) Detection of nontoxic BoNT/A levels in post-facial Botox injection breastmilk. Front. Drug Saf. Regul. 4:1480515. doi: 10.3389/fdsfr.2024.1480515
Received: 14 August 2024; Accepted: 11 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Michael Ceulemans, KU Leuven, BelgiumCopyright © 2025 Gu, Xu, Koviazina, Tan, Zheng, Kappes, Kotsifaki, Shen and Tsigkou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anastasia Tsigkou, YW5hc3Rhc2lhLnRzaWdrb3VAZHVrZWt1bnNoYW4uZWR1LmNu; Domna G. Kotsifaki, ZG9tbmEua290c2lmYWtpQGR1a2VrdW5zaGFuLmVkdS5jbg==
 Helene Gu
Helene Gu Zhenyu Xu
Zhenyu Xu Renata Koviazina
Renata Koviazina Pengcheng Tan
Pengcheng Tan Changcheng Zheng
Changcheng Zheng Ferdinand Kappes
Ferdinand Kappes Domna G. Kotsifaki
Domna G. Kotsifaki Fangrong Shen
Fangrong Shen Anastasia Tsigkou
Anastasia Tsigkou