
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Drug Discov., 15 April 2025
Sec. In silico Methods and Artificial Intelligence for Drug Discovery
Volume 5 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fddsv.2025.1525533
This article is part of the Research TopicEnhancing Drug Discovery Through Structure-Based Design and Computational TechniquesView all 4 articles
Introduction: Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated condition that affects approximately 100 million individuals worldwide. Interleukin 23 (IL-23) serves as a crucial pro-inflammatory cytokine in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases associated with psoriasis. Monoclonal antibody therapies targeting IL-23 inhibit the overactive cytokine signaling that contributes to chronic inflammation across various organ systems. Over the past decade, IL-23 inhibitors have gained significant prominence in the treatment of psoriasis. Natural products have emerged as potential modulators of IL-23 activity, particularly in the context of inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Several well-characterized phytochemicals, including sulforaphane, resveratrol, and curcumin, have demonstrated efficacy in inhibiting the production and function of Th17 cells, which are regulated by IL-23. However, the exploration of natural products specifically related to psoriasis has been limited.
Methods: This study aimed to identify novel candidates derived from natural products for the treatment of psoriasis. To achieve this, 60,000 natural compounds were filtered according to the rule of five (Ro5) and obtained from the ZINC database. These ligands underwent high-throughput virtual screening (HTVS) in molecular docking studies against the IL-23 receptor. The top 50 ligands were subsequently re-evaluated using standard precision (SP), and for enhanced accuracy, the top 19 from the SP protocol were further screened using the extra precision (XP) protocol.
Results and Discussion: The computational screening revealed that the docking energy values for the nineteen ligands binding to the target enzyme ranged from -3.669 to -7.143 kcal/mol. Among these, ligand 1 (L1) exhibited the highest binding energy at -7.143 kcal/mol with IL-23. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation further confirmed the stability of the IL-23-L1 complex, highlighting a robust interaction between L1 and the target enzyme, with Tyr100 being one of the amino acids showing the highest frequency of interaction throughout the simulation. Density functional theory (DFT) analysis using the Becke, three-parameter, Lee-Yang-Parr (B3LYP)/6-31++G(d,p) basis set indicated a promising reactivity profile for the ligands. The analysis of absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) properties suggested that all inhibitor ligands possess favorable pharmacological characteristics, including appropriate molecular weight, lipophilicity, hydrogen bond donors and acceptors, molecular refractivity, topological polar surface area (TPSA), and the number of rotatable bonds, all in accordance with Ro5. Additionally, the physicochemical properties indicate that most ligands are capable of human intestinal absorption (HIA) and possess a wide therapeutic index, suggesting a favorable safety profile.
Psoriasis, an immune-mediated, chronic, non-communicable illness, will impact about 7.5 million individuals in the United States in 2021, accounting for 3.0% of the population (Armstrong et al., 2021). Among the various forms of psoriasis, plaque psoriasis is the most common, accounting for over 80% of all cases. This type is characterized by erythematous, scaly patches, or plaques, primarily located on extensor surfaces, although it can also affect intertriginous areas, nails, soles, and palms. The condition impacts both men and women equally, but it is more prevalent in adults than in children (Paller et al., 2018; Rachakonda et al., 2014). While psoriasis can manifest at any age, there is a bimodal distribution of onset, typically occurring between the ages of 18–39 and 50–69 years (Parisi et al., 2013). The age at which psoriasis begins can be influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. The presence of the HLA-C*06 allele is associated with the early onset of psoriasis (Nair et al., 2006). The pathophysiology of psoriasis is complex and not fully understood; however, it is believed to be linked to the hyperactivation of components of the adaptive immune system (Lin et al., 2002). Various cell types, including natural killer T cells, keratinocytes, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and macrophages, release cytokines that activate myeloid dendritic cells during the initial stages of psoriasis pathogenesis. DNA-LL37 complexes stimulate plasmacytoid dendritic cells to secrete interferon-alpha, which in turn activates myeloid dendritic cells. Upon activation, these myeloid dendritic cells subsequently release ILs, specifically IL-12 and IL-23. Consequently, IL-23 has been identified as a critical therapeutic target for psoriasis. Ustekinumab is the most commonly used anti-IL-12/23-p40 agent, having received approval for the treatment of psoriasis in 2009. It offers the advantages of fewer injections, long-term maintenance, and high rates of remission. Although targeting the IL-23 immune axis is effective for treating various autoimmune diseases, there are risks associated with significant infections and other adverse effects (Aubin et al., 2013; Ru et al., 2021). Briakinumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting IL-12/23-p40 for psoriasis treatment, was associated with severe complications and side effects in a phase III clinical trial. As a result, the drug’s developer withdrew its application for approval from the FDA and the European Medicines Agency in 2011 (Strober et al., 2011; Gordon et al., 2012). Natural products have emerged as potential modulators of IL-23 activity, particularly in the context of inflammatory diseases such as IBD. Several well-characterized phytochemicals, including sulforaphane, resveratrol, and curcumin, have shown efficacy in inhibiting the production and function of Th17 cells, which are regulated by IL-23. However, research on natural products specifically related to psoriasis has been limited. Therefore, this study aimed to identify novel candidates derived from natural products for the treatment of psoriasis. To accomplish this objective, we employed computer-aided structure-based drug design, a specialized field within drug discovery that utilizes computational and theoretical techniques to effectively identify and optimize lead compounds. Virtual screening, which acts as the in silico counterpart to high-throughput screening for extensive compound libraries, plays a vital role in the drug discovery process. This methodology significantly decreases both the time and costs associated with the identification of new drug candidates (Aghahosseinia et al., 2024; Gheidari et al., 2024b; Gheidari et al., 2024c; Gheidari et al., 2024e; Mahmoodi et al., 2024). The existence of comprehensive databases is essential to this approach. Among these, ZINC stands out as one of the largest freely accessible web-based repositories of natural compounds, encompassing over 80,617 molecules (Irwin et al., 2012). This study aimed to identify natural products within the ZINC database through in silico methods, including molecular docking, MD simulation, DFT study, and ADMET predictions, with the goal of discovering compounds that could potentially be more effective than existing drugs and may serve as targets for psoriasis treatment (Figure 1).
The compound DFT is used to ascertain the density and energy properties of the electron. The Gaussian 09W program (Frisch et al., 2009) is used to do computed analyses of the structure of atoms, molecules, crystals, and surfaces, as well as their interactions. The wavenumbers of the vibrations were determined by calculations utilizing the B3LYP method and a 6-31++G (d,p) basis set. The B3LYP functional is a valuable approach for accurately describing harmonic vibrational frequencies in molecules of small to medium size. The output check files were analyzed using GuassView 6.0. Molecular orbital (MO) analysis is essential in quantum chemistry and has been used to thoroughly characterize chemical behavior. The highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of a molecule are employed to characterize chemical properties such as reactivity, stability, and kinetics. The molecule’s hardness or softness is determined by its hardness (η) value, with softer molecules exhibiting higher reactivity. The electronegativity (X) value indicates the molecule’s ability to attract electrons.
A total of around 60,000 compounds were obtained from the Zinc15 database (https://zinc15.docking.org) utilizing online tools. These compounds were chosen based on their adherence to Lipinski’s Ro5 and their classification as natural products. They were collected for the purpose of conducting virtual screening analyses. The compounds underwent ligand preparation using the LigPrep Wizard (Schrödinger 2017-2 software, LLC, New York). The structures underwent minimization using the optimized potentials for liquid simulations (OPLS) 2005 force field, with the ionization state of each chemical set to neutralize. In addition, tautomer’s and a minimum of 10 conformations per ligand were also produced (LigPrep, 2017).
The crystal structure of IL23A, depicted in Figure 2 and identified by PDB ID: 6wdq (RCSB, 2025), was obtained from the RCSB database at a resolution of 3.40 Å. Its secondary structure comprises several alpha helices and beta sheets, interspersed with multiple loops that contribute to the protein’s three-dimensional conformation. The preparation of the protein included refining hydrogen bonds, incorporating missing hydrogen atoms, optimizing the structure, and removing atomic conflicts and water molecules prior to docking. Ultimately, the protein structure underwent energy minimization and optimization using the OPLS 2005 force field (Protein Preparation Wizard, 2017).
The docking pocket of the IL-12 and IL-23 receptor complexes is primarily formed by the interaction between the shared p40 subunit and the IL-12Rb1 receptor, which is crucial for the binding and signaling of both cytokines. Specifically, the IL-12Rb1 receptor engages the p40 subunit at a highly complementary interface characterized by a significant degree of charge complementarity, where the positively charged loop in p40 interacts with a negatively charged patch in IL-12Rb1, facilitating effective docking and subsequent signal transduction. Prior to docking, the binding site was defined as a grid box using Receptor Grid Generation (Maestro, Schrödinger 2017-2 software, LLC, New York). The grid box was positioned at coordinates X = −16.469875, Y = 31.725000, and Z = −29.749080, with a radius of 20 Å. This grid box is relevant to the inhibition of IL-23R, as shown in Figure 3 (Glassman et al., 2021). The van der Waals radius scaling factor was initially set to 1.0, the partial charge cut-off to 0.25, and the charge scale factor to 1.0, with grid creation (Glassman et al., 2021) performed without any limitations.
The Ligand docking module of Schrödinger used grid-based Ligand Docking with Energetics (GLIDE) (Glide, 2017) in three distinct docking modes: (i) HTVS for docking and scoring; (ii) SP for docking and scoring; and (iii) XP for docking and scoring. The whole library of ligands was screened using HTVS docking and scoring. For each ligand, a mean numerical conformation of Glide, known as G-Score, was determined. A total of 50 ligands, which exhibited the highest G-Score with HTVS, underwent further evaluation utilizing SP docking and scoring. This was done to examine the reliability and correctness of the docking poses. To reduce false-positive results, 19 ligands that were 100% thriving were further screened using XP docking and scoring. As shown in Table 1, these 19 ligands were arranged by their XP G-Score, with the lowest XP G-Score meaning the best result of the docked ligands to the IL23R protein. The detailed 2D and 3D binding interactions of these 19 ligands within the active pocket of IL23R are shown in Supplementary Figure A of the Supplementary Information.
The resemblance across drugs can be ascribed to molecular properties including hydrophobicity, electronic distribution, hydrogen bonding, molecular weight, bioavailability, reactivity, toxicity, and metabolic stability. The term used to describe this resemblance is “drug likeness,” which pertains to the similarity in molecular attributes and structural properties between recognized drugs and specific compounds (Ertl et al., 2000). Lipinski’s rule is a widely used method for predicting the solubility and permeability of a chemical compound, which in turn determines its eligibility as a potential medicinal agent. Poor absorption or penetration is associated with certain metrics and is more probable when a substance contradicts them. The parameters to be measured are the number of hydrogen bond donors (HBD), the number of hydrogen bond acceptors (HBA), the molecular weight (MW), and the octanol-water partition coefficient (LogP). The acceptable values for these parameters are HBD ≤ 5, HBA ≤ 10, MW ≤ 500, and LogP ≤ 5 (Gheidari et al., 2024a; Gheidari et al., 2024d). The prediction was conducted with a complimentary web-based Swiss ADME service (Daina et al., 2017).
An important aspect of drug design research and development is ensuring the safety of chemical compounds. Therefore, accurately predicting the ADMET characteristics is crucial. In order to determine these abilities, some attributes were used as indicators, namely, Caco-2 cells. Caco-2 cells are a kind of human colon epithelial cancer cell line that serves as a representation of the absorption of drugs and other substances in the human intestine. A substance with a high Caco-2 value exhibits a high level of absorption in the gut. HIA is the mechanism by which drugs taken orally are absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract into the circulation of the human body. The blood-brain barrier’s significance lies in its ability to determine the degree of lipophilicity of compounds, which in turn indicates their likelihood of being successfully absorbed across plasma membranes. P-glycoprotein is a crucial transmembrane protein that actively transports several exogenous chemicals out of cells. The presence of this trait is observed in mammals, fungi, and bacteria, and it is believed to have developed as a protective response to noxious compounds. One of the significant components in the determination of a drug’s safety is plasma protein binding (PPB), in the sense that pharmaceuticals with high PPB have a limited therapeutic index, meaning that compounds with low PPB values are substantially safer. Carcinogenicity refers to the ability of a substance to cause the development of malignant tumors, enhance their occurrence or severity, or accelerate the time it takes for tumors to form after inhalation, ingestion, topical application, or injection. The synthetic accessibility score quantifies the level of simplicity in synthesizing compounds. The predictions were generated with ADMETlab 2.0 (Xiong et al., 2021).
MD simulations can provide a theoretical understanding of how a certain molecule behaves inside the binding pocket (Cuya et al., 2018). This allows for the identification and prediction of more accurate ligand-receptor interactions and the validation of molecular docking findings. MD simulations were conducted by solvating the compound in an explicit orthorhombic water box using the SPC water model. The system was gradually heated to a temperature of 300 K and maintained at constant pressure using the Nose-Hoover thermostatic algorithm and the Martina-Tobias-Klein method. To neutralize the system, sodium chloride salt at a 0.15 M concentration was selected. The system ran for 100 ns on 10,411 frames using Desmond (Desmond, 2017). The Desmond package’s Simulation Interactions Diagram tool was used to analyses the system at frame zero as a reference. The analysis focused on the protein and ligand root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) values in relation to the reference.
For each of the 19 selected ligands L1-L19, optimization in the gas phase using the B3LYP/6-31++G (d,p) basis by means of the Gaussian 09W software package and the Gauss View visualization application was performed, and their values are shown in Table 2. No imaginary frequencies were found, and the geometries of the ligands were changed to have the lowest energy gradient, proving that all structures were in fact local minima.
The FMO orbitals of the 19 selected ligands are shown in Supplementary Figure B of the Supplementary Information. The red and green color distributions represent the positive and negative phases of the MO wave function, respectively. We estimate that several descriptors are essential for evaluating the stability and reactivity of compounds, including the energy gap (∆E gap), hardness (η), softness (S), electronegativity (X), and electrophilicity (ψ). The energy gap represents the difference between the HOMO and the LUMO, with a larger gap indicating greater stability and lower reactivity. In this analysis, L5 exhibits the highest energy gap at 5.482 eV, making it the most stable compound, closely followed by L1 with a gap of 5.331 eV and L14 at 5.225 eV, both suggesting significant stability. Hardness, which measures a compound’s resistance to deformation or change, is defined as half the energy gap. A higher hardness value indicates a more stable and less reactive compound. In this study, L5 leads with a hardness of 2.741, while L1 and L14 also show considerable hardness values of 2.665 and 2.612, respectively. Conversely, L17 has the lowest hardness at 1.487, which correlates with its higher reactivity. Softness, being the inverse of hardness, indicates a compound’s reactivity, with a higher softness value suggesting greater reactivity. In this context, L5 has the lowest softness at 0.182, indicating reduced reactivity, while L9 has the highest softness at 0.298, suggesting it is more reactive. Electronegativity measures a compound’s ability to attract electrons, with a higher value indicating a stronger tendency to attract electrons. In this analysis, L10 has the highest electronegativity at 4.193, followed closely by L8 at 4.132. In contrast, L17 has the lowest electronegativity at 2.205, suggesting it is less effective at attracting electrons. Finally, electrophilicity indicates a compound’s ability to accept electrons in a chemical reaction, with a higher value suggesting a stronger electrophile. L8 stands out with the highest electrophilicity at 4.712, indicating it is a strong electrophile, while L17 has the lowest electrophilicity at 1.635, making it less likely to act as an electrophile. Table 3 shows the energetic properties of ligands L1–L19.
The molecular docking technique is extensively employed in drug design and the analysis of biological data, as it offers a computational framework for predicting interactions between small molecules and their biological targets, including proteins and nucleic acids. By simulating the binding affinity and orientation of ligands within the active sites of target macromolecules, molecular docking aids in the identification of potential drug candidates and the optimization of lead compounds. This methodology not only deepens our understanding of molecular interactions but also supports the rational design of therapeutics, thereby expediting the drug discovery process. In this study, 60,000 natural products were docked into the active site of IL23R using HTVS. Fifty ligands that exhibited the highest G-scores from HTVS were subsequently evaluated using SP docking to confirm the reliability and appropriateness of the docking poses. To reduce the likelihood of false-positive results, nineteen ligands demonstrating significant potency were further screened using XP docking. An analysis of the interactions within these protein-ligand complexes was conducted, and the results are summarized in Table 4. The amino acid residues in the active site of IL23R, which include both bonding and non-bonding interactions with ligands L1–L19, are as follows: Ala55, Asn27, Asn29, Asn58, Cys115, Cys59, Gly70, Gly24, Gly116, Glu111, Gln110, His108, Ile25, Ile28, Ile56, Ile71, Leu113, Lys57, Lys72, Lys107, Met99, Ser31, Ser98, Thr102, Thr112, Tyr67, Tyr100, and Asp118.
Due to their favorable interactions inside the active site of IL23R, ligands L1 and L2 are more effective than other ligands. The L1 has a H-bond with the amino acid residue Glu111, which has a length of 2.60 Å. Furthermore, three hydrophobic interactions within IL23R have been observed, with bond lengths of 4.76 Å for Tyr100, 5.05 Å for Ile28, and 5.21 Å for His108. Additionally, ligand L1 demonstrates seven van der Waals interactions involving residues Gln110, Thr102, Ser98, Gly116, Cys115, Leu113, and Thr112. Figure 4 shows detailed 3D and 2D binding interactions of ligand L1 within IL23R’s active pocket.
L2 gained the second-highest score among all ligands due to its robust binding interactions with the active site of the IL23R protein. Ligand L2 forms a total of six hydrogen bonds. These include four H-bonds with the amino acid residues Glu111, Leu113, Gly24, and Asn27, with bond lengths of 2.72, 1.95, 2.31, and 2.45, respectively, and a C-bond with a bond length of 2.83 for Thr112 and a Pi-donor H-bond with a bond length of 3.06 for Asn29. In addition, there are two hydrophobic interactions, with bond lengths of 4.88 Å for Ile28 and 3.90 Å for His108. Also, it forms van der Waals interactions with Tyr67, Thr102, Tyr100, Gln110, His108, Ile25, and Ser31. Figure 5 illustrates the 3D and 2D binding interactions of ligand L2 inside IL23R’s active pocket.
The combined use of MD simulation and docking methods enhanced the confirmation of the obtained results. This enabled us to examine the changes in the structure of the ligand-receptor complex during the duration of the simulation. Simulations provide a thorough examination of the exact motion of each atom over time, allowing us to examine changes and fluctuations in protein patterns. The MD simulation was performed on the best scoring complex of L1 for 100 ns. The dynamic stability of the complexes was assessed by measuring the RMSD of the complex backbone atoms during the whole trajectory to confirm their stability. As illustrated in Figure 6, the plot utilizes the left Y-axis to represent the RMSD of the protein and the right Y-axis to display the ligand RMSD profile that is aligned with the protein backbone.
The frames obtained from the 100 ns trajectory were aligned with the reference frame backbone. The plot shows how much the protein-ligand complex has evolved throughout the simulation in a structural manner. The highest RMSD for the IL23R protein in this simulation is around 7.46 Å at 64.60 ns on frame 6726, whereas the highest ligand RMSD was observed around 21.1 Å at 45.36 ns on frame 4725. The convergence of RMSD values demonstrated that L1 and IL23R maintained their contact throughout the simulation. The root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) is a measure of the average deviation of each atom’s position from its mean position in a given simulation or set of structures. The binding site of the IL23R complexes showed stable RMSF values. There were no significant fluctuations observed in the region where the ligand binds to the protein. The interaction between compound L1 and the binding site residues of IL23R is shown in more detail in Figure 7. The residues that interact with L1 include Gly24, lle25, Thr26, Asn27, lle28, Asn29, The67, Asn69, Gly70, lle71, His96, Ser98, Met99, Tyr100, Thr102, His108, Phe109, Gln110, Glu111, Leu113, Gly116, Lys117, and Asp118, which are shown in green. The RMSF values for the residues in the binding site were found to be around 4 Å.
Ligand-protein interactions, including hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic, ionic, and water bridges, can be monitored throughout the simulation. As depicted in Figure 8, Gly24, Ser98, and Tyr100 had the most interactions with the ligand during the simulation duration. Moreover, over at least 40% of the simulation period, Ser98 and Tyr100 demonstrated a variety of interactions, encompassing hydrophobic water-bridged and hydrogen-bond interactions with the ligand. Consequently, this residue experienced numerous interactions throughout the entire simulation time.
As shown in Figure 9, various properties of L1 are examined over a 100-ns MD simulation. Fluctuations in RMSD indicate structural changes in the ligand over time. Low RMSD values suggest structural stability, while significant fluctuations may indicate instability and conformational changes. The radius of gyration (Rg) graph measures the “extent” of the ligand, reflecting its spatial distribution. Variations in this metric can provide insights into the ligand’s compactness or expansion; higher rGyr values suggest a more extended structure, whereas lower values indicate a more compact conformation. The intramolecular hydrogen bond (intra-HB) graph displays the number of internal hydrogen bonds within the ligand. Fluctuations in this graph can signify changes in structural stability and internal interactions, with an increase in the number of hydrogen bonds typically contributing to greater structural stability. The molecular surface area (MolSA) graph calculates the MolSA of the ligand using a 1.4 Å probe radius. This measurement helps assess the ligand’s surface area available for interactions with other molecules, and variations in this graph may indicate changes in the ligand’s accessibility to its environment. The accessible surface area (SASA) graph represents the surface area of the ligand that is accessible to solvent molecules, providing insights into the ligand’s exposure in a solvent environment. Fluctuations in this graph may reflect changes in the ligand’s interactions with the solvent. Finally, the polar surface area (PSA), graph indicates the surface area contributed solely by oxygen and nitrogen atoms within the ligand, helping to assess the ligand’s polarity. Variations in this graph may suggest changes in the ligand’s polar characteristics and their implications for biological interactions.
The Physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, and medicinal chemistry features mentioned for our top 19 natural product candidates are shown in Table 5. None of the candidates violate Lipinski’s rule because their results are in the favorable range. The pharmacokinetic parameters revealed that except for ligand L2, the rest are highly absorbed after oral administration through the GI tract. This may be attributed to its higher MW (491.54 g/mol), elevated TPSA of 143.630 Å2, LogP of 2.100, and the presence of five HBD and HBA, all of which hinder its ability to permeate biological membranes and interact effectively within the GI tract. The structural alarms and pan-assay interference (PAINS) have been utilized in medicinal chemistry to forecast the presence of unstable, reactive, and toxic fragments in a compound’s structure (Brenk et al., 2008; Baell and Holloway, 2010). Except for ligand L17, which has a het_pyridiniums_A alarm, other ligands in PAINS descriptors have zero alarms. The synthetic accessibility score (SA score) is a metric used to evaluate the ease of synthesizing drug-like molecules. It was observed that all the ligands possess a favorable SA score, indicating that they can be readily synthesized. The use of CaCo-2 cells, which are generated from human colon epithelial cells, is a widely accepted approach for studying the intestinal absorption of medicines in people. The CaCo-2 cell permeability findings for all ligands L1–L19 were observed to be within a satisfactory range, indicating that these ligands exhibit favorable intestinal membrane permeability. The study revealed that ligands L2, L4, L8, L10, L11, L12, L16, L17, and L19 have inhibitory effects on Plasma glycoprotein (PGP). Conversely, ligands L5, L9, L14, L15, and L18 do not demonstrate inhibitory activity against PGP. Additionally, ligands L2, L12, and L14 have been identified as P-glycoprotein (PGP) substrates, but the other ligands do not exhibit PGP substrate activity. The computed values for HIA indicate that all substances possess a high likelihood of being effectively absorbed through the intestinal membrane. The assessment of PPB has significance in the evaluation of medication safety. Drugs exhibiting a high PPB value (>90%) are associated with a narrow therapeutic index, whereas those with a low PPB value are considered to be comparatively safer. In the current investigation, it was shown that ligands L1, L2, L3, L4, L6, L8, L10, L13, L14, L16, L17, and L19 exhibited low PPB values. This finding suggests that these particular ligands have a wide therapeutic index, indicating a favorable safety profile. Conversely, the other ligands did not demonstrate similar safety characteristics. The volume of distribution (VD) at steady state, denoting the apparent VD subsequent to the medication achieving uniform dispersion across all tissues after a sufficient amount of time. A VD value greater than 0.5 signifies that the medication exhibits efficient distribution within the plasma, whereas a VD value lower than −0.5 suggests the drug’s limited capability to traverse the cell membrane (Kufareva and Abagyan, 2012). The anticipated VD value for all ligands L1–L19 suggests that the medicine exhibits satisfactory dispersion throughout the plasma. Compounds that have CBrain/CBlood values greater than 1 are categorized as possessing central nervous system (CNS) activity, whereas compounds with CBrain/CBlood values below 1 are characterized as lacking CNS activity. Compounds that exhibit action in the central nervous system (CNS) are capable of traversing the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) and inducing adverse effects on the central nervous system (Ajay et al., 1999). According to the data presented in Table 6, all of the ligands L1–L19 have CBrain/CBlood values below 1, indicating that they are not capable of crossing the BBB. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes play a crucial role in the metabolism of various compounds, including drugs, environmental chemicals, and endogenous substances. These enzymes are responsible for the oxidative metabolism of a wide range of substrates, influencing drug efficacy and toxicity. Understanding the substrate specificity and activity of different CYP enzymes is essential for predicting drug interactions, optimizing therapeutic regimens, and minimizing adverse effects. For CYP1A2, ligands such as L7, L8, L17, and L19 exhibit strong substrate activity, indicating that they are likely to be efficiently metabolized by this enzyme. In contrast, L1 and L2 show minimal interaction, suggesting a lower likelihood of influencing the metabolism of other drugs processed by CYP1A2. In the case of CYP3A4, L16 and L19 are notable substrates, indicating efficient metabolism, while L2 demonstrates weak substrate activity, suggesting limited metabolism by CYP3A4. For CYP2C9, L14 shows strong substrate activity, whereas L17 exhibits minimal interaction. Regarding CYP2C19, L17 demonstrates strong substrate activity, indicating efficient metabolism, while L2 shows weak interactions, suggesting limited metabolism by CYP2C19. Lastly, for CYP2D6, L3 is a strong substrate, indicating efficient metabolism. Half-life (T1/2) is defined as the time required for the concentration of a drug in the bloodstream to decrease by half. This parameter is crucial for determining the duration of action of a drug and its elimination kinetics. Ligands such as L14, L15 exhibit short half-lives. These ligands are eliminated relatively quickly from the body, which may necessitate more frequent dosing to maintain therapeutic levels. L2 and L16 have the longest half-lives among the ligands studied. Such ligands may remain in the system longer, potentially leading to prolonged therapeutic effects. However, they may also accumulate in the body if dosed too frequently, increasing the risk of side effects. Clearance rate (CL) refers to the volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed per unit time. It is a crucial parameter that helps determine the dosing regimen of a drug. Ligands such as L1, L3, L5, L9, L13, L15, and L17 have moderate clearance rates. This suggests that they can be eliminated at a reasonable pace, allowing for effective therapeutic management without frequent dosing. Ligands with lower clearance rates, such as L2 and L14, indicate that these substances remain in the body longer, which may necessitate careful monitoring to avoid toxicity, particularly in patients with compromised liver or kidney function. Toxicology research plays a crucial role in the field of drug design as it facilitates the identification and assessment of the deleterious effects of newly developed substances on living creatures. The assessment of toxicity indices for ligands L1–L19 indicated that, with the exception of ligands L11, L12, L16, L17, L18, and L19, the remaining ligands were judged to possess non-carcinogenic properties. Furthermore, the AMES toxicity evaluation indicated that the ligands L3, L11, L12, L16, L17, and L19 show no discernible toxicity.
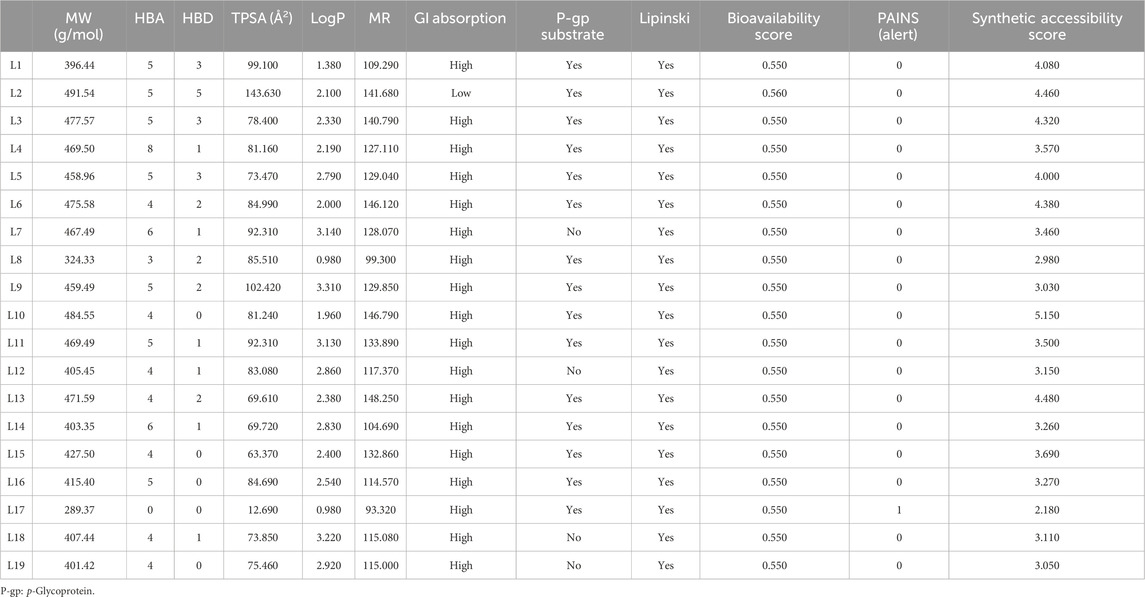
Table 5. Physicochemical, pharmacokinetics, and medicinal chemistry properties of the ligands L1-L19.
This research investigates the targeting of the IL-23 protein, recognized as a significant pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases related to psoriasis. Utilizing virtual screening and molecular docking techniques, a total of nineteen lead natural products were identified. The docking analysis demonstrated that these ligands possess high binding affinities for the IL-23 protein, with L1 exhibiting the highest binding affinity, as indicated by a docking score of −7.143. L1 establishes a hydrogen bond with Glu111, participates in seven van der Waals interactions, and forms three hydrophobic interactions with the IL-23 protein. The RMSD analysis confirmed that L1 consistently maintained stable interactions with critical residues of IL-23, suggesting that the L1-IL-23 complex remained thermodynamically stable throughout the 100 ns simulation trajectory. DFT analysis employing the B3LYP/6-31++G (d,p) basis set revealed a favorable reactivity profile for the ligands. Additionally, the analysis of ADMET properties indicated that the newly identified inhibitors possess favorable pharmacological characteristics and comply with Lipinski’s rule. The physiological assessment revealed that, with the exception of L1, the other ligands demonstrate high gastrointestinal absorption. To validate the anti-IL-23 potential of these identified ligands and to address the limitations inherent in silico analyses, further laboratory and clinical investigations are necessary. Such studies will enhance the understanding of the safety and efficacy of the identified ligands in the treatment of psoriasis. This study provides significant insights into the binding mechanisms of the IL-23 enzyme in psoriasis, indicating that future research on the efficacy of these lead compounds in animal models of psoriasis may facilitate clinical trials and the development of innovative therapeutic strategies for this challenging condition.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
DG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ME: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fddsv.2025.1525533/full#supplementary-material
Aghahosseinia, F., Bayat, M., Sadeghiana, Z., Gheidari, D., and Safari, F. (2024). Synthesis, molecular docking study, MD simulation, ADMET, and drug likeness of new thiazolo[3,2-a]pyridine-6,8-dicarbonitrile derivatives as potential anti-diabetic agents. PLoS ONE 19, e0306973. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0306973
Ajay, G. W., Bemis, M. A., and Murcko, M. A. (1999). Designing libraries with CNS activity. J. Med. Chem. 42, 4942–4951. doi:10.1021/jm990017w
Armstrong, A. W., Mehta, M. D., Schupp, C. W., Gondo, G. C., Bell, S. J., and Griffiths, C. E. (2021). Efficacy and safety of briakinumab in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis: results from a phase III, randomized controlled trial. JAMA Dermatol 157, 940–946. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2007
Aubin, F., Carbonnel, F., and Wendling, D. (2013). The complexity of adverse side-effects to biological agents. J. Crohns Colitis 7 (4), 257–262. doi:10.1016/j.crohns.2012.06.024
Baell, J. B., and Holloway, G. A. (2010). New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 53, 2719–2740. doi:10.1021/jm901137j
Brenk, R., Schipani, A., James, D., Krasowski, A., Gilbert, I. H., Frearson, J., et al. (2008). Lessons learnt from assembling screening libraries for drug discovery for neglected diseases. Chem. Med. Chem. 3, 435–444. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200700139
Cuya, T., Gonçalves, A. d. S., da Silva, J. A. V., Ramalho, T. C., Kuca, K., and França, T. C. C. (2018). The role of the oximes HI-6 and HS-6 inside human acetylcholinesterase inhibited with nerve agents: a computational study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 36, 3444–3452. doi:10.1080/07391102.2017.1389307
Daina, A., Michielin, O., and Zoete, V. (2017). SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 7, 42717. doi:10.1038/srep42717
Ertl, P., Rohde, B., and Selzer, P. (2000). Virtual screening of compound libraries: a comparison of different approaches. J. Med. Chem. 43, 3714–3717. doi:10.1021/jm000942e
Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., Scuseria, G. E., Robb, M. A., Cheeseman, J. R., et al. (2009). Gaussian 09, revision A.02. Wallingford, CT, USA: Gaussian, Inc.
Gheidari, D., Mehrdad, M., and Karimelahi, Z. (2024a). Virtual screening, molecular docking, MD simulation studies, DFT calculations, ADMET, and drug likeness of Diaza-adamantane as potential MAPKERK inhibitors. Sci. Rep. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-3084-0
Gheidari, D., Mehrdad, M., and Bayat, M. (2024b). Synthesis, docking, MD simulation, ADMET, drug likeness, and DFT studies of novel furo[2,3-b]indol-3a-ol as promising Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 14, 3084. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-53514-1
Gheidari, D., Mehrdad, M., and Bayat, M. (2024c). Novel indenopyrrol-4-one derivatives as potent BRDT inhibitors: synthesis, molecular docking, drug-likeness, ADMET, and DFT studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 42, 7860–7873. doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2242502
Gheidari, D., Mehrdad, M., and Hoseini, F. (2024d). Virtual screening, molecular docking, MD simulation studies, DFT calculations, ADMET, and drug likeness of Diaza-adamantane as potential MAPKERK inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1360226. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1360226
Gheidari, D., Mehrdad, M., and Bayat, M. (2024e). Synthesis, molecular docking analysis, molecular dynamic simulation, ADMET, DFT, and drug likeness studies: novel Indeno[1,2-b]pyrrol-4(1H)-one as SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. PLoS ONE 19 (3), e0299301. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0299301
Glassman, C. R., Mathiharan, Y. K., Jude, K. M., Su, L., Panova, O., Lupardus, P. J., et al. (2021). Structural basis for IL-12 and IL-23 receptor sharing reveals a gateway for shaping actions on T versus NK cells. Cell. 184 (4), 983–999.e24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.018
Gordon, K. B., Langley, R. G., Gottlieb, A. B., Papp, K. A., Krueger, G. G., Strober, B. E., et al. (2012). A phase III, randomized, controlled trial of the fully human IL-12/23 MAb briakinumab in moderate-to-severe psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 132 (2), 304–314. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.304
Irwin, J. J., Sterling, T., Mysinger, M. M., Bolstad, E. S., and Coleman, R. G. (2012). ZINC: a free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 52 (7), 1757–1768. doi:10.1021/ci3001277
Kufareva, I., and Abagyan, R. (2012). Methods of protein structure comparison. Methods Mol. Biol. 857, 231–257. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-588-6_10
Lin, L., Ambikairajah, E., and Holmes, W. H. (2002). Speech enhancement for nonstationary noise environment. Asia-Pacific Conf. Circuits Syst. 1, 177–180. doi:10.1109/apccas.2002.1114931
Mahmoodi, N., Bayat, M., Gheidari, D., and Sadeghian, Z. (2024). In silico evaluation of cis-dihydroxy-indeno[1,2-d]imidazolones as inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3: synthesis, molecular docking, physicochemical data, ADMET, MD simulation, and DFT calculations. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 28 (4), 101894. doi:10.1016/j.jscs.2024.101894
Nair, R. P., Stuart, P. E., Nistor, I., Hiremagalore, R., Chia, N. V. C., Jenisch, S., et al. (2006). Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78 (5), 827–851. doi:10.1086/503821
Paller, A. S., Singh, R., Cloutier, M., Gauthier-Loiselle, M., Emond, B., Guérin, A., et al. (2018). Prevalence of psoriasis in children and adolescents in the United States: a claims-based analysis. J. Drugs Dermatol 17 (2), 187–194.
Parisi, R., Symmons, D. P., Griffiths, C. E., and Ashcroft, D. M.Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy IMPACT project team (2013). Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Investig. Dermatol. 133 (2), 377–385. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.339
Protein Preparation Wizard (2017). Schrödinger suite 2017-1: protein preparation wizard. New York: Schrödinger, LLC.
Rachakonda, T. D., Schupp, C. W., and Armstrong, A. W. (2014). Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol 70 (3), 512–516. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.013
RCSB (2025). RCSB protein Data Bank. Available at: www.rcsb.org/pdb.
Ru, Y., Ding, X., Luo, Y., Li, H., Sun, X., Zhou, M., et al. (2021). Adverse events associated with Anti-IL-23 agents: clinical evidence and possible mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 12, 670398. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.670398
Strober, B. E., Crowley, J. J., Yamauchi, P. S., Olds, M., and Williams, D. A. (2011). Efficacy and safety results from a phase III, randomized controlled trial comparing the safety and efficacy of briakinumab with etanercept and placebo in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 165 (3), 661–668. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10419.x
Keywords: natural compounds, Interleukin-23, virtual screening, ADMET, drug-likeness, dynamic simulation
Citation: Gheidari D, Mehrdad M and Etedali M (2025) Identification of natural compounds as potential inhibitors of Interleukin-23: virtual screening, ADMET, drug-likeness, and dynamic simulation. Front. Drug Discov. 5:1525533. doi: 10.3389/fddsv.2025.1525533
Received: 04 December 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 15 April 2025.
Edited by:
Arif Nur Muhammad Ansori, Universitas Airlangga, IndonesiaReviewed by:
Amit Kumar Banerjee, Indian Institute of Chemical Technology (CSIR), IndiaCopyright © 2025 Gheidari, Mehrdad and Etedali. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Davood Gheidari, ZGF2b29kZ2hlaWRhcmlAZ21haWwuY29t; Morteza Mehrdad, bV9tZWhyZGFkNEB5YWhvby5jb20=
†ORCID: Davood Gheidari, orcid.org/0000-0003-2106-1753; Morteza Mehrdad, orcid.org/0000-0003-4597-9518
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.