
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Digit. Health, 10 April 2025
Sec. Health Communications and Behavior Change
Volume 7 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fdgth.2025.1497680
This article is part of the Research TopicDesigning for Engagement in Digital Health for Chronic and Long-Term CareView all articles
 Muhammad K. Khan1
Muhammad K. Khan1 Ambreen Liaqat1
Ambreen Liaqat1 Ziyad A. Altokhais1
Ziyad A. Altokhais1 Bader A. Alotaibi1
Bader A. Alotaibi1 Maryam Sadiq2*
Maryam Sadiq2* Munazza Rehman3
Munazza Rehman3 Zeeshan Ahsan Allana4
Zeeshan Ahsan Allana4 Hasan N. Tahir1
Hasan N. Tahir1
Introduction: This systematic review and meta-analysis examine the effectiveness of smartphone and Web 2.0 interventions for weight management compared to traditional control interventions. The potential of smartphones and Web 2.0. technologies to transform health care and clinical intervention in the community are tremendous. This potential is incredibly increased by increasing adoption rates for smartphones and internet technologies.
Methodology: Ten randomized control trials published between 2015 and 2024 searched through PubMed and ScienceDirect were included. All studies with open access that assessed a smartphone or app intervention compared to a control group in randomized control trials, with weight-related body measures (i.e., body weight, BMI, waist circumference) and physical activity changes (steps/day) expressed in terms of mean and standard deviation performed in a population of adults were included. Review Manager software, version 5.4 (The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration) was used for statistical analysis.
Results: The results of our study indicate that digital interventions, particularly those utilizing direct communication methods like text messages and social media, significantly promote weight loss and reduce waist circumference (mean difference of −2.12 and −2.81 for weight change and waist circumstances respectively). While reductions in body mass index (BMI) with mean difference of −0.53 were less pronounced, they still favored intervention groups. Subgroup analyses performed to find out the source of heterogeneity revealed that three-arm randomized control trials, studies with larger sample sizes, and interventions lasting around six months showed more consistent and significant effects whereas for sensitivity analysis no significant change in heterogeneity was observed for all parameters. High heterogeneity among studies suggests the need for standardized study designs and intervention protocols in future research.
Conclusions: Despite limitations such as technological issues and engagement variability, these findings underscore the potential of digital health interventions in addressing the global burden of obesity and related non-communicable diseases.
Weight management involves a mix of behaviors, techniques, and bodily processes aimed at helping people reach and maintain a healthy weight (1, 2). The usual approach focuses on achieving a healthy weight through steady, gradual weight loss and then keeping that weight stable. Overweight and obesity are significant global health issues, ranking as the fifth leading cause of death worldwide, with about 3.4 million deaths annually linked to these conditions (3, 4). In 2019, having a higher-than-ideal body mass index (BMI) was estimated to have caused 5 million deaths due to diseases like heart disease, diabetes, cancers, and respiratory and digestive disorders (5). Addressing these issues has become a global health priority. Recent guidelines on preventing and managing non-communicable diseases emphasize the importance of behavioral changes and the need for more user-friendly and effective prevention programs (6).
The rise of smartphones and Web 2.0 technologies holds great promise for transforming healthcare and community-based clinical intervention (7). Numerous studies have explored how smartphones can support health initiatives, such as collecting health data for research and enhancing medical education and clinical practices in the community (8) and as used in support of medical and health care education and clinical practice in the community (9). This potential is incredibly increased by increasing adoption rates for smartphones and internet technologies. The adoption of smartphones and internet technologies continues to grow, with over two-thirds of the world's population using mobile phones. As of April 2024, there were 5.65 billion unique mobile users globally (10). Web 2.0 refers to websites that emphasize user-generated content, ease of use, and interoperability. Social media apps, which are a part of this movement, allow users to create and share content, engaging a large portion of the population (11). Health and fitness apps, in particular, have seen rapid growth. In 2023, these apps generated $3.58 billion in revenue, marking a 9.1% increase from the previous year, with 368 million users (12).
With these trends, research into health interventions using digital technologies is also increasing Studies often look at how these technologies impact general health promotion, including efforts to quit smoking (13) weight management (14) and diet and physical activity or they evaluate the effect on health care delivery programs (15).
This review aims to summarize recent eHealth research on using smartphones and Web 2.0 technologies for weight management, comparing them with other interventions, and provide recommendations for future research and practice.
The objectives of this systematic review and meta-analysis are to evaluate the overall effectiveness of smartphone and Web 2.0 interventions in weight management. It seeks to identify the key components of these interventions and analyze the characteristics of the target populations, including demographic and socioeconomic factors. It also targets to determine user adherence and engagement levels, and how these factors influence the success of the interventions. Finally, it aims to highlight gaps in the current literature and propose directions for future research.
The protocol for this study was registered at PROSPERO and the registration no. is CRD42024556096. A systemic literature search of two databases was conducted through May, 2024 to pick out studies related to the efficacy of smartphone and Web 2.0, intervention compared to a control intervention in achieving body measurement and physical activity changes; Medicine (via PubMed; National Library of Medicine, Bethesda, MD; started in 1966) and ScienceDirect (Elsevier; started in 1997). Search strategy used for data search included the words (mobile phone OR smartphone OR Web 2.0, technologies) AND (weight management). In addition, reference lists from relevant original research and reviews were also reviewed.
Studies generated from the databases were screened for inclusion criteria. The study selection process is summarized in Figure 1.
All studies with open access that assessed a smartphone or app intervention compared to a control group in randomized control trials, with weight-related body measures (i.e., body weight, BMI, waist circumference) and physical activity changes (steps/day) expressed in terms of mean and standard deviation performed in population of adults and published between the years of 2015–20124 were included.
The exclusion criteria was as follow
1) no original research i.e., reviews, editorials, or non-research letters
2) case reports
3) data on body measures or physical activity not reported or if reported in other then mean terms
4) no control group
5) participants with any disease except a diagnosis of obesity.
Ethical approval was not required as only published freely accessed data was analyzed.
Data was extracted from articles that met the selection criteria and compiled using a table developed in Microsoft Word. Data such as author, year of publication, sample size, intervention, study outcomes etc. was collected. Study outcomes (change in body weight, BMI, waist circumference and physical activity) were recorded in terms of mean and standard deviation. Two studies (16, 17) provided data in terms of percentage which was then converted into gross values using reverse percentage formulas. Four studies (16, 18–20) were three arm RCTs. In such cases the interventional group involving smartphone or web 2.0, technology exclusively was considered for comparison with the control. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool- robvis, considering random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of output assessment, incomplete outcome data and selective reporting (18). Each was categorized as clearly yes, not sure or clearly no.
For each study, the net effect size was calculated as the change in body weight measures and physical activity outcomes resulting from intervention from baseline till the end of intervention in the intervention group minus the change in the control group identical measures during the same. For studies (16, 17) providing data in percentages following formulas using baseline values were used to calculate gross value in standard measuring units;
Convert the mean percentage change to a decimal:
Calculate the mean difference in standard units:
If there was a need to calculate the standard deviation of the mean percentage difference, it is proportional to the baseline standard deviation:
If the mean and SD for change between baseline and the end of the intervention were not reported (19), it was calculated using the following equation (20).
For mean;
For SD;
Where SDpre corresponds to the SD at baseline, SDpost corresponds to the SD at the end of interventions, and ρ is the correlation coefficient for correlations between measurements taken at baseline and at the end of the intervention assuming it to be perfect i.e., 1.
For body weight, BMI and waist circumference, weighted mean differences were estimated using the random effects models. For physical activity outcomes standardized mean differences were estimated using random effects model. Heterogeneity was quantified with 12 statistics, which describes the proportion of total variation in study estimates as a result of heterogeneity (21). The publication bias was assessed by using Egger's test and funnel plots. Statistical analyses were performed using Review Manager software, version 5.4 (The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration).
The search strategy generated total of 2,629 articles from two different sources. Out of these, 10 articles were included in this meta-analysis (16–20, 24–28). Studies published from 2015 to 2024 were included. All studies included were randomized control trials. The sample size ranges from 30 (19, 22) to 750 (23). The rest of the characteristics of included clinical trials are given in Table 1. Only two studies (19, 22) provided data regarding the change in physical activity in terms of steps/day. For one study the mean change of step/day in intervention group was 7,054.6 whereas in the control group it was 5,002.4. For the second study the intervention group showed a mean change of 736.71 as compared to a control group with mean change of 218.79 in steps/day.
All 10 researches provided data regarding weight change in the experimental and control groups before and after the intervention. The overall mean difference of −2.12 suggests that, on average, the experimental group performs better than the control group. The high I2 value (100%) and significant Chi2 test (P < 0.00001) indicate substantial heterogeneity among the studies. The overall effect is statistically significant (Z = 3.65, P = 0.0003), indicating a significant difference between the experimental and control groups. The funnel plot indicates a low likelihood of publication bias and suggests that the meta-analysis results are robust. The studies are fairly symmetrical around the overall mean difference, with most points close to the vertical line, reinforcing consistency in the effect estimate. Forest plot and funnel plot are given in Figure 2.
Out of 10, 7 studies provided data regarding waist circumference. The forest plot indicates that the experimental treatment consistently outperforms the control across the included studies, with a combined mean difference of −2.81 95% CI ranging from −4.06 to −1.57. The Z-test for the overall effect is 4.43 (P < 0.00001), showing a statistically significant overall effect favoring the experimental treatment. The results are statistically significant, despite high heterogeneity, suggesting that the experimental treatment is generally more effective, but the effect size varies between studies. The funnel plot indicates a low likelihood of publication bias. Forest and funnel plots are given in Figure 3.
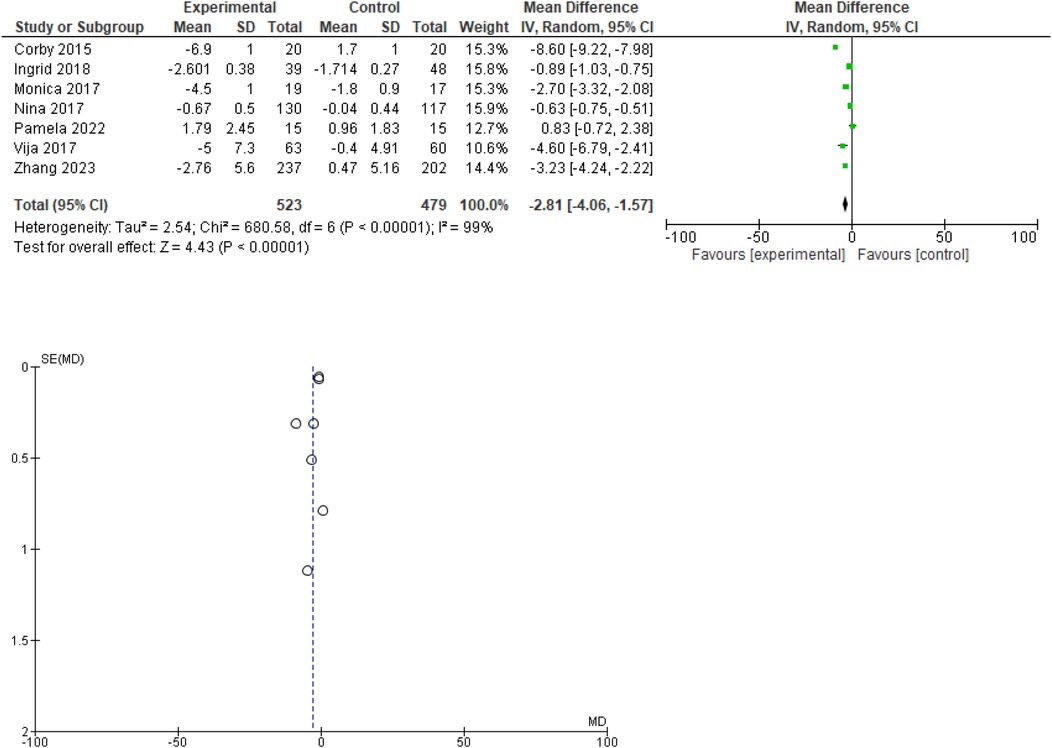
Figure 3. Forest plot for change in waist circumference(cm). Funnel plot for change in waist circumference.
Out of 10, 5 studies provided data regarding BMI. In the forest plot the overall mean difference suggests a small reduction in body weight in the experimental group compared to the control group, but the confidence interval includes zero, indicating that this result is not statistically significant at the 95% confidence level.
High heterogeneity (I2 = 98%) suggests substantial variability among the study results, which should be explored further to understand the sources of this heterogeneity. The funnel plot indicates a low likelihood of publication bias. Forest and funnel plots are given in Figure 4.
To find out the source of high heterogeneity, we performed sensitivity analysis by excluding one study at a time. Sensitivity analysis done for change in body weight produced a variety of values for pooled WMDs ranging from −160 to −2. 55 with the exclusion of (24) producing maximum deviation from original pooled WMDs whereas no significant change in heterogeneity was observed in any case. For change in waist circumference, the range for pooled MDs was −1.56 to −3.35 with heterogeneity not varying significantly. For change in BMI, the range was −0.31 to −0.96 with no significant change in heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis shows that excluding individual studies does not significantly change the overall heterogeneity. This reinforces that the observed variability is systematic and not due to outliers.
We also performed subgroup analysis by dividing studies on the basis of study design, sample size, study duration and type of intervention to find out the source of heterogeneity. Details are given in Table 2.
Interventions generally show a significant reduction in body weight and waist circumference, especially in studies with larger sample sizes and those conducted for about 6 months.
For BMI, significant reductions are observed mainly in studies with moderate sample sizes and 6-month duration.
These findings suggest that digital interventions, especially those using more direct communication methods like text messages and emails, can effectively reduce body weight, waist circumference, and BMI over certain periods and sample sizes.
The study design (whether the study is an RCT or a three-arm RCT) and the duration of the study (especially around 6 months) seem to be the primary factors contributing to the variation in the meta-analysis results. These factors likely influence the effectiveness and consistency of the interventions being analyzed.
Different study designs might involve variations in control conditions or additional intervention groups. This can lead to differences in observed effect sizes because the comparison conditions are not uniform across studies. The effectiveness of the intervention might be context-dependent. Differences in how interventions are implemented can cause variation in results.
The length of the study can influence how long participants adhere to the intervention, as well as how sustainable the intervention's effects are. Shorter studies might show initial benefits that don't persist, while longer studies might reveal whether these benefits are maintained or diminish over time.
Future research should consider these sources of heterogeneity, potentially focusing on more standardized study designs and appropriate durations to reduce variability and increase the reliability of findings.
The risk of bias assessment for each Cochrane item and each included study in shown in Figure 5. The table indicates that while many studies have strong methodologies in several areas, allocation concealment is a recurring issue. This could affect the overall reliability and validity of the findings in the meta-analysis. Addressing these biases in future research would improve the quality and robustness of evidence. Details are given in Figure 5.
The present systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of smartphone and Web 2.0 interventions for weight management compared to traditional control interventions. The findings indicate that digital interventions, especially those employing direct communication methods like text messages, emails, or social media, have significant potential in promoting weight loss and reducing waist circumference. These results are consistent with previous studies that have underscored the utility of digital health technologies in weight management and other health behavior changes. One of the previous meta-analyses suggested that mobile phone app interventions compared with various control interventions significantly reduced body weight by 1.04 kg, reduced BMI by 0.43 kg/m2, and non-significantly increased physical activity by an SMD of 0.40 (25). While these reductions in body weight and BMI are modest, it is unrealistic to expect that a single intervention, like mobile apps, would result in significant weight loss compared to other control methods (26).
Significant research in mobile interventions has particularly concentrated on text-messaging, or SMS-based, interventions. A prior meta-analysis (27) revealed that mobile phone interventions led to notable reductions in body weight and BMI compared to control groups, showing decreases of −1.44 kg and −0.24 units, respectively. Another systematic review provided strong evidence from RCTs that mobile technology interventions promote short-term weight loss (28). Additionally, a systematic review encompassing seven studies highlighted the positive effects of text messaging or mobile apps in reducing physical inactivity and overweight/obesity (29). However, another review indicated that many weight-loss apps yield inconsistent results (30).
This meta-analysis revealed a statistically significant reduction in body weight in the intervention groups compared to the control groups, with a pooled weighted mean difference (WMD) of −2.12 kg. This finding aligns with existing literature suggesting that digital interventions can effectively support weight loss efforts through mechanisms such as self-monitoring, feedback, and social support. The reduction in waist circumference was also notable, with a pooled WMD of −2.81 cm, reinforcing the beneficial impact of these interventions on abdominal obesity, which is a crucial marker for metabolic health.
While the reduction in BMI was less pronounced and not always statistically significant, the trend was still favorable toward the intervention groups. This could be due to the heterogeneity of the studies included, as well as variations in the duration and intensity of the interventions. Only two studies provided data on physical activity changes, indicating a significant increase in steps per day among intervention participants, which is consistent with findings from other research emphasizing the role of physical activity in weight management.
High heterogeneity was observed in the meta-analyses of body weight, waist circumference, and BMI, which was not substantially reduced by sensitivity analysis. This suggests that the variability in study designs, intervention types, sample sizes, and durations significantly influenced the outcomes. Subgroup analyses indicated that three-arm RCTs, studies with larger sample sizes, and interventions lasting around six months showed more consistent and significant effects. This finding highlights the importance of considering study design and duration in future research to enhance the reliability and applicability of results. The risk of bias assessment indicated that while many studies had strong methodologies in several areas, allocation concealment was a recurring issue, which could affect the overall reliability of the findings. Ensuring robust allocation concealment in future studies would help improve the quality and robustness of evidence.
Mobile text messaging, phone calls and support through social media play a crucial role in weight management by providing continuous support, motivation, and information to individuals. These interventions leverage the ubiquity and convenience of mobile phones to deliver personalized reminders, tips, and encouragement, which can enhance adherence to dietary and physical activity recommendations. Text messages can also facilitate behavior change by promoting self-monitoring and goal setting, both of which are key components of successful weight management. Additionally, the interactive nature of SMS allows for timely feedback and social support, which are important for maintaining motivation and overcoming obstacles.
Mobile apps that are well-designed hold the promise of transforming health interventions by utilizing technology to reach populations in unprecedented ways, leveraging the unique features of smartphone software. This rapid market growth raises the issue of regulation, especially with the increasing number of advertising claims regarding their efficacy. Researchers are calling for more studies to provide robust scientific evidence on the actual effectiveness of these apps. The constant accessibility of mobile phones ensures that users can manage and reinforce healthy behaviors at any time through a range of communications and applications. These fitness and weight-loss apps allow users to monitor their diet, weight and physical activity, make healthier grocery and restaurant choices, prepare nutritious meals (29) and participate in health interventions (35). Furthermore, users do not need additional devices like pedometers to keep track of their physical activity.
Mobile apps, text messages, social media support, and phone calls for weight management have several limitations. Technological issues, such as app compatibility and functionality, can hinder user experience. Privacy concerns arise due to the sensitive nature of health data. Engagement levels vary, with some users losing interest over time. Personalized feedback is often limited, reducing the effectiveness of interventions. Information overload from constant notifications can be overwhelming. Additionally, accessibility issues affect those who are less tech-savvy or economically disadvantaged. Lastly, the overall effectiveness of these interventions varies, often needing to be combined with other strategies for optimal results.
The results of this meta-analysis underscore the potential of digital health interventions in weight management. However, future research should aim to standardize study designs and intervention protocols to reduce heterogeneity and improve comparability. Moreover, longer follow-up periods are necessary to assess the sustainability of the observed benefits. Addressing methodological issues such as allocation concealment and ensuring rigorous randomization processes will also enhance the quality of future research.
This study's limitations include high heterogeneity among the included trials, which indicates variability in study designs and intervention protocols that could affect the consistency of the results. Additionally, the reliance on self-reported data for physical activity and body measurements may introduce reporting biases. The exclusion of non-English studies and the limited number of trials available for certain outcomes may also affect the generalizability of the findings. Lastly, potential technological issues and variability in user engagement with digital interventions were not thoroughly explored.
In conclusion, this systematic review and meta-analysis provide robust evidence supporting the use of smartphone and Web 2.0 technologies in weight management interventions. These findings have important implications for public health strategies aimed at addressing the global burden of obesity and related non-communicable diseases.
MK: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZA: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. BA: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. MR: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZA: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HT: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
We would like to acknowledge the support of Shaqra University, Saudi Arabia throughout the study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. CDC- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About Healthy Weight and Growth | Healthy Weight and Growth | CDC. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/healthy-weight-growth/about/index.html (Accessed May 20, 2024).
2. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease. Understanding Adult Overweight & Obesity - NIDDK. Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/adult-overweight-obesity (Accessed May 20, 2024).
3. Kedir S, Hassen K, Melaku Y, Jemal M. Determinants of overweight and/or obesity among school adolescents in Butajira town, southern Ethiopia. A case-control study. PLoS One. (2022) 17(6):e0270628.35763506
4. Kostova D, Richter P, Van Vliet G, Mahar M, Moolenaar RL. The role of noncommunicable diseases in the pursuit of global health security. Health Secur. (2022) 19(3):288–301. doi: 10.1089/hs.2020.0121
5. Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Abdollahi M, et al. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet. (2020) 396(10258):1223–49. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30752-2
6. Matheson GO, Shultz R, Klügl M, Engebretsen L, Bendiksen F, Steffen K, et al. Prevention and management of non-communicable disease: the IOC consensus statement, Lausanne 2013. Br J Sports Med. (2013) 47(16):1003–11. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-093034
7. Boulos MN, Wheeler S, Tavares C, Jones R. How smartphones are changing the face of mobile and participatory healthcare: an overview, with example from eCAALYX. Biomed Eng Online. (2011) 10:1–4.21244718
8. Blaya JA, Fraser HSF, Holt B. E-health technologies show promise in developing countries. Health Aff (Millwood). (2010) 29(2):244–51. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2009.0894
9. Lindquist A, Johansson P, Petersson G, Saveman BI, Nilsson G. The use of the personal digital assistant (PDA) among personnel and students in health care: a review. J Med Internet Res. (2008) 10(4):e1038. doi: 10.2196/jmir.1038
10. Global Digital Overview. DataReportal – Global Digital Insights. Available at: https://datareportal.com/global-digital-overview (Accessed May 20, 2024).
11. Kaplan AM, Haenlein M. Users of the world, unite! the challenges and opportunities of social media. Bus Horiz. (2010) 53(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/j.bushor.2009.09.003
12. Fitness App Revenue and Usage Statistics. Business of Apps. (2024). Available at: https://www.businessofapps.com/data/fitness-app-market/ (Accessed May 20, 2024).
13. Riley W, Augustson EM. Mobile phone-based smoking cessation interventions increase long-term quit rates compared with control programmes, but effects of the interventions are heterogeneous. Evid Based Nurs. (2013) 16(4):108–9. doi: 10.1136/eb-2012-101204
14. Wieland LS, Falzon L, Sciamanna CN, Trudeau KJ, Folse SB, Schwartz JE, et al. Interactive computer-based interventions for weight loss or weight maintenance in overweight or obese people. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2012) 8. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007675.pub2/full
15. Free C, Phillips G, Watson L, Galli L, Felix L, Edwards P, et al. The effectiveness of Mobile-health technologies to improve health care service delivery processes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. (2013) 10(1):e1001363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001363
16. Jane M, Hagger M, Foster J, Ho S, Kane R, Pal S. Effects of a weight management program delivered by social media on weight and metabolic syndrome risk factors in overweight and obese adults: a randomised controlled trial. PLoS One. (2017) 12(6):e0178326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178326
17. Kjær IGH, Anderssen SA, Torstveit MK. A tailored telephone and email based exercise intervention induced reductions in various measures of body composition in physically inactive adults: a randomized controlled trial. Prev Med Rep. (2018) 11:160–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2018.06.011
18. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Available at: http://www.bmj.com/content/343/bmj.d5928/suppl/DC1
19. Johnson KE, Alencar MK, Coakley KE, Swift DL, Cole NH, Mermier CM, et al. Telemedicine-based health coaching is effective for inducing weight loss and improving metabolic markers. Telemed J E Health. (2019) 25(2):85–92. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2018.0002
20. Thiessen Philbrook H, Barrowman N, Garg AX. Imputing variance estimates do not alter the conclusions of a meta-analysis with continuous outcomes: a case study of changes in renal function after living kidney donation. J Clin Epidemiol. (2007) 60(3):228–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.06.018
21. Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21(11):1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
22. Bowen PG, Affuso O, Opoku-Agyeman W, Mixon VR, Clay OJ. Texting older sisters to step to manage obesity in older black women: a feasibility study. Am J Prev Med. (2022) 63(1 Suppl 1):S56–66. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2022.03.014
23. Zhang N, Zhou M, Li M, Ma G. Effects of smartphone-based remote interventions on dietary intake, physical activity, weight control, and related health benefits among the older population with overweight and obesity in China: randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e41926. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37115608/37115608
24. Martin CK, Miller AC, Thomas DM, Champagne CM, Han H, Church T. Efficacy of SmartLoss, a smartphone-based weight loss intervention: results from a randomized controlled trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). (2015) 23(5):935–42. doi: 10.1002/oby.21063
25. Flores Mateo G, Granado-Font E, Ferré-Grau C, Montaña-Carreras X. Mobile phone apps to promote weight loss and increase physical activity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. (2015) 17(11):e253. doi: 10.2196/jmir.4836
26. Stevens J, Truesdale KP, McClain JE, Cai J. The definition of weight maintenance. Int J Obes (Lond). (2006) 30(3):391–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803175
27. Liu F, Kong X, Cao J, Chen S, Li C, Huang J, et al. Mobile phone intervention and weight loss among overweight and obese adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Epidemiol. (2015) 181(5):337–48. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwu260
28. Bacigalupo R, Cudd P, Littlewood C, Bissell P, Hawley MS, Buckley Woods H. Interventions employing mobile technology for overweight and obesity: an early systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. (2013) 14(4):279–91. doi: 10.1111/obr.12006
29. Azar KMJ, Lesser LI, Laing BY, Stephens J, Aurora MS, Burke LE, et al. Mobile applications for weight management: theory-based content analysis. Am J Prev Med. (2013) 45(5):583–9. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2013.07.005
30. DiFilippo KN, Huang WH, Andrade JE, Chapman-Novakofski KM. The use of mobile apps to improve nutrition outcomes: a systematic literature review. J Telemed Telecare. (2015) 21(5):243–53. doi: 10.1177/1357633X15572203
31. Gemesi K, Winkler S, Schmidt-Tesch S, Schederecker F, Hauner H, Holzapfel C. Efficacy of an app-based multimodal lifestyle intervention on body weight in persons with obesity: results from a randomized controlled trial. Int J Obes (Lond). (2024) 48(1):118–26. doi: 10.1038/s41366-023-01415-0
32. Dombrowski SU, McDonald M, Van Der Pol M, Grindle M, Avenell A, Carroll P, et al. Game of stones: feasibility randomised controlled trial of how to engage men with obesity in text message and incentive interventions for weight loss. BMJ Open. (2020) 10(2):e032653. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032653
33. Silina V, Tessma MK, Senkane S, Krievina G, Bahs G. Text messaging (SMS) as a tool to facilitate weight loss and prevent metabolic deterioration in clinically healthy overweight and obese subjects: a randomised controlled trial. Scand J Prim Health Care. (2017) 35(3):262–70. doi: 10.1080/02813432.2017.1358435
34. Balk-Møller NC, Poulsen SK, Larsen TM. Effect of a nine-month web- and app-based workplace intervention to promote healthy lifestyle and weight loss for employees in the social welfare and health care sector: a randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. (2017) 19(4):e108. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28396303/
Keywords: smartphone, Web 2.0, weight management, BMI, waist circumference, intervention
Citation: Khan MK, Liaqat A, Altokhais ZA, Alotaibi BA, Sadiq M, Rehman M, Allana ZA and Tahir HN (2025) Smartphones and Web 2.0. interventions for weight management. Front. Digit. Health 7:1497680. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1497680
Received: 17 September 2024; Accepted: 19 March 2025;
Published: 10 April 2025.
Edited by:
Charoula Konstantia Nikolaou, University of Greenwich, United KingdomReviewed by:
Efthalia Massou, University of Cambridge, United KingdomCopyright: © 2025 Khan, Liaqat, Altokhais, Alotaibi, Sadiq, Rehman, Allana and Tahir. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maryam Sadiq, bWFyeWFtLnNhZGlxMjIwQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.