- 1School of Computer Science, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
- 2Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, Transilvania University of Brasov, Brasov, Romania
- 3School of Nursing and Midwifery, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
Introduction: The world’s population is aging at a rapid rate. Nursing homes are needed to care for an increasing number of older adults. Palliative care can improve the quality of life of nursing home residents. Artificial Intelligence can be used to improve palliative care services. The aim of this scoping review is to synthesize research surrounding AI-based palliative care interventions in nursing homes.
Methods: A PRISMA-ScR scoping review was carried out using modified guidelines specifically designed for computer science research. A wide range of keywords are considered in searching six databases, including IEEE, ACM, and SpringerLink.
Results: We screened 3255 articles for inclusion after duplicate removal. 3175 articles were excluded during title and abstract screening. A further 61 articles were excluded during the full-text screening stage. We included 19 articles in our analysis. Studies either focus on intelligent physical systems or decision support systems. There is a clear divide between the two types of technologies. There are key issues to address in future research surrounding palliative definitions, data accessibility, and stakeholder involvement.
Discussion: This paper presents the first review to consolidate research on palliative care interventions in nursing homes. The findings of this review indicate that integrated intelligent physical systems and decision support systems have yet to be explored. A broad range of machine learning solutions remain unused within the context of nursing home palliative care. These findings are of relevance to both nurses and computer scientists, who may use this review to reflect on their own practices when developing such technology.
1 Background
As the world’s population continues to age rapidly, the number of older adults in need of care is increasing; the UN has indicated that by 2030 over 60 countries will have 2 million or more people aged 65 or older (1). Adequate nursing home care is needed to facilitate the personal and medical requirements of these people in a timely and efficient manner (2). In nursing homes where palliative care (PC) is implemented, improvements can be seen in the levels of clinical care received, reductions in hospitalizations, and enhanced family perceptions (3). There is a growing realization that new forms of care, such as PC, are needed to effectively care for our changing society (4).
While PC is becoming increasingly more popular, the field is complex, full of ethical issues and uncertainty surrounding the best time to provide such care (4). Education on the subject also needs improvement, with many burgeoning health professionals lacking adequate knowledge about such care (5, 6). Additionally, there are many interpretations of what comprises the discipline across cultures, countries, and clinical norms (7). This situation leads to confusion about what exactly constitutes PC (8). In this review, we describe PC as an approach to care which emphasizes relief from suffering and improved well-being, especially in the terminal stage of illness or the final period of life (6–8).
Technology can be utilized to provide health professionals with care tools, while also creating a higher quality of life for older adults. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has already proven itself to be useful within the context of PC (9). AI is a broad field encompassing all systems which exhibit human-like intelligence (10). Often used synonymously with AI, machine learning (ML) is a subset of the overarching discipline (10). ML involves “learning” on data while using computational algorithms (10). While applications of AI have been explored and consolidated within the context of general nursing care (11), AI interventions in nursing homes have yet to be reviewed in depth.
As PC is a highly sensitive area, including those who will use proposed AI systems in their development would have quite an influence over system designs. Feedback from healthcare professionals on the utility of using such technology and the ethics of AI analysis may ensure that AI interventions are in-keeping with palliative principles. PC is a subtle area, full of sensitivities; the involvement of system end-users in the creation of these tools is paramount to their success.
AI and ML technologies could prove to be quite useful in nursing home settings. There has already been work on the impact of such tools in geriatric clinical care (12), revealing that AI can be used for early detection and prevention of severe illnesses. Algorithm choice can increase the accuracy of results, reduce computational load, and make such tools more lightweight and easy-to-use. Deep Learning (DL), a subsection of machine learning, has also shown extensive capabilities in the field of geriatric clinical care (12).
We chose to undertake a scoping review due to the breadth and depth of our topic. In this paper, we will consolidate past work, examine emerging areas of exploration, and identify knowledge gaps. Due to the wide range of possible interventions and studies on the subject, a scoping review was deemed appropriate. The objectives of this review are to explore what AI technologies are used in palliative nursing home research, to discern what types of ML algorithms and AI methods are used in palliative nursing home studies, and to assess the role of end-users in palliative technological developments and assessments.
To the best of the authors’ knowledge, our review is the first of its kind to focus exclusively on this topic. As a result, a broad range of PC interventions and technologies are considered. There does not seem to be much analysis of data accumulated in nursing homes as of yet, whether in the form of data science techniques or AI interventions (13). In this paper, we will investigate how, even if limited, nursing homes have adopted AI specifically for PC.
This review’s research questions were chosen to encompass the breadth of material which could be considered AI-related within palliative nursing home contexts.
1. What palliative systems or strategies incorporating AI have been designed for, used in, or studied in nursing home settings?
2. What AI techniques are used within palliative technologies in nursing home settings?
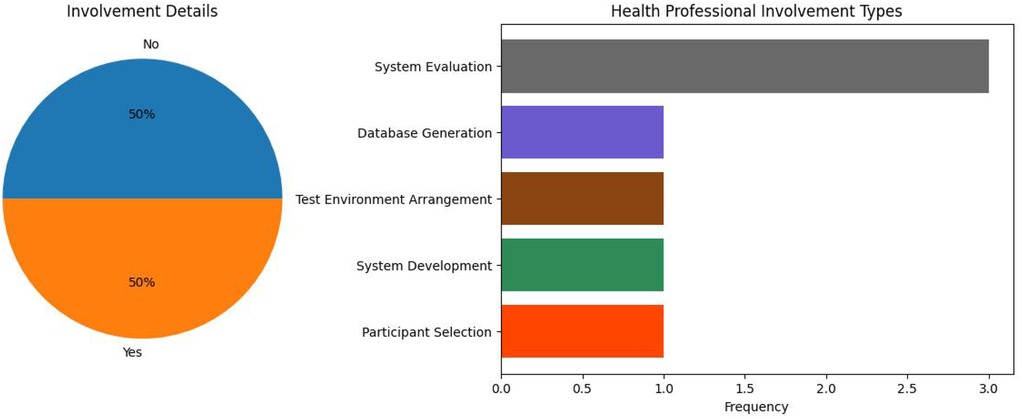
3. How do relevant projects include health professionals and/or nursing home residents and/or their families in project design, deployment, or testing processes?
Question 1 aims to capture the broad range of palliative approaches that can be considered when using AI. Question 2 concentrates on the different AI techniques used to approach PC. Algorithms, data inputs, and data outputs will also be examined. Question 3 addresses key stakeholder involvement. User-centered testing procedures associated with AI-based interventions will also be explored.
This review’s main contribution to the literature is an up-to-date collation of artificially intelligent nursing home PC studies. This review could be of use to AI researchers and developers, along with decision-makers in nursing homes. The rest of this paper is divided into the following sections: methods, results, discussion, and conclusions.
2 Methods
This review was carried out during the months of April and May 2024. The Parsifal review and Zotero reference manager softwares were used for content organization (14, 15). Specifically, Parsifal was used to record screening decisions and extracted data points. Zotero was used to store and read all relevant materials. All searching and screening was predominantly carried out by the first author, with guidance from other authors. Three of these authors also contributed to the study selection process.
2.1 Operational definitions
Our research questions are framed around the use of “palliative systems or strategies” in nursing homes. These terms need clarification in order to be used effectively in this review. When we refer to a “palliative system” we are referring to a technological system designed specifically for PC or built with a palliative module included. We do not refer to general systems which do not involve technology. When we refer to “palliative strategy,” we are also referring to some form of technological process. As this is a broad review, we were not to be too prescriptive when choosing these terms. However, we insisted that there must be a technological element involved in any system or strategy we selected for inclusion in this review.
2.2 Protocol and registration
We drafted our protocol using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR). We also incorporated elements of a pre-existing systematic review guide for computer science research by Carrera-Rivera et al. into our work (16). This guide outlines an algorithmic approach to the review process, which we found useful for structuring our own research. We did not register our protocol.
2.3 PICOC criteria
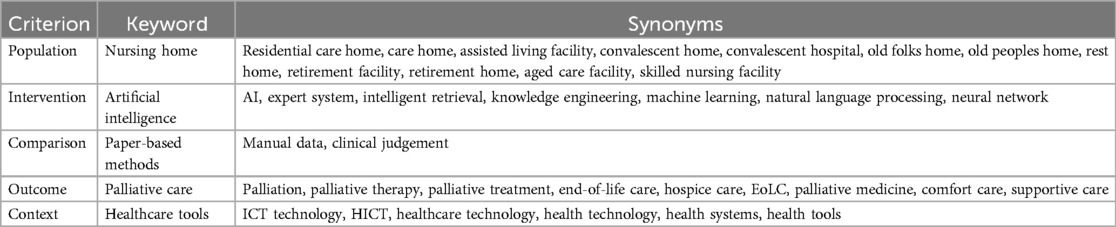
The Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, and Context (PICOC) criteria were used to define the specificity and focus areas of the review. These criteria were carefully chosen to encompass nursing homes, PC, and AI research. Table 1 outlines the different criteria chosen along with their associated keywords and synonyms.
These criteria were subsequently used to focus our digital library searches.
2.4 Eligibility criteria
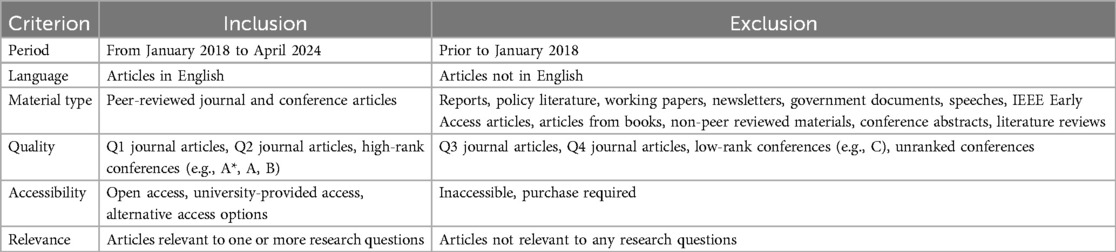
Eligibility criteria were defined in order to screen articles from initial searches. Articles were screened based on their titles and abstracts. Table 2 outlines the chosen criteria.
Material within the last seven years (i.e., January 2018 to April 2024) was chosen based on the constantly fluctuating technological landscape. This time period broadens the scope of the review, while not including papers that are potentially out-of-date. Articles were limited to those in English due to resource constraints; obtaining adequate translations for other languages was unfeasible. Only peer-reviewed academic articles from journals and conferences were included to ensure high-quality materials are discussed in our findings; this criterion strengthens the validity of this review’s results. Other types of material were not considered due to difficulties in proving the quality of the same. Additionally, other literature reviews were excluded as they are secondary sources of information.
Journal articles within the first or second impact factor quartiles were considered within this review to ensure that high quality studies are discussed in our findings. All quartile-related information on journals was found in the Journal Citation Reports website (17). All reputable conference articles were included; the ICORE Conference Portal was used for computer science conferences (18). Relevant healthcare conferences were assessed by one of the nursing-related authors involved in the review to determine quality and subsequent inclusion or exclusion. Inaccessible or costly articles were not included in this review. Articles had to be relevant to at least one of the research questions to be considered for inclusion.
2.5 Information sources
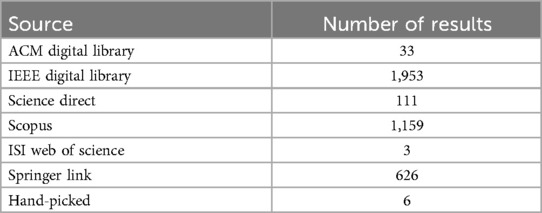
Digital libraries were selected for searching based on their relevance to the problem area. Some of these repositories were also chosen based on their appearance in other systematic literature reviews on similar subjects (11). Namely, the ACM Digital Library, IEEE Digital Library, ISI Web of Science, Science Direct, Scopus, and Springer Link were used.
Additionally, all authors contributed to the search for materials by hand-picking a selection of studies they deemed potentially relevant to the review; these studies were included in subsequent filtering processes to ensure their relevance and quality. As these hand-picked studies were chosen by authors with research backgrounds in either computer science or nursing, we incorporate both health and computing perspectives into the search process.
2.6 Search
Each library has its own search engine features, facilitating advanced search strings and keyword usage. The keywords used were derived from the PICOC criteria. Search queries all followed a similar structure involving primary keywords such as “nursing home,” “palliative care,” and “artificial intelligence.” Search strings were adjusted from a base string to facilitate an accurate search of each database. Figure 1 shows the base search string as displayed in Parsifal (14).
Results of searches were filtered by year, content type, and accessibility. Subsequently, the results were exported as BibTeX files and imported into the Parsifal software for screening.
2.7 Selection of sources of evidence
Each article was read and assessed using a four-question quality instrument; these questions were inspired from example questions provided by Carrera-Rivera et al. (16). Each question was answered using a 3-point answer scale; all answers were then summed to create an overall score for each article. A cut-off threshold was then outlined to ensure only high-quality articles were included in the findings of this review. Articles that scored higher than 2 were included and articles that scored lower than or equal to 2 were excluded. The aforementioned quality instrument is outlined in Table 3.
The concept of relevance, as used in our quality instrument, involved a couple of key considerations. These considerations are outlined below:
• Material must have a nursing-home focus or at least a dedicated discussion of nursing home settings.
• Material must explicitly mention PC or have a section discussing the same.
• Material must explicitly mention AI or at least have a section discussing AI or AI-based applications.
• Material does not focus on one disease specifically (e.g., residents with dementia only), but can target a specific illness if the entire nursing home population is included in the intervention (e.g., MCI or frailty).
2.8 Data charting process and data items
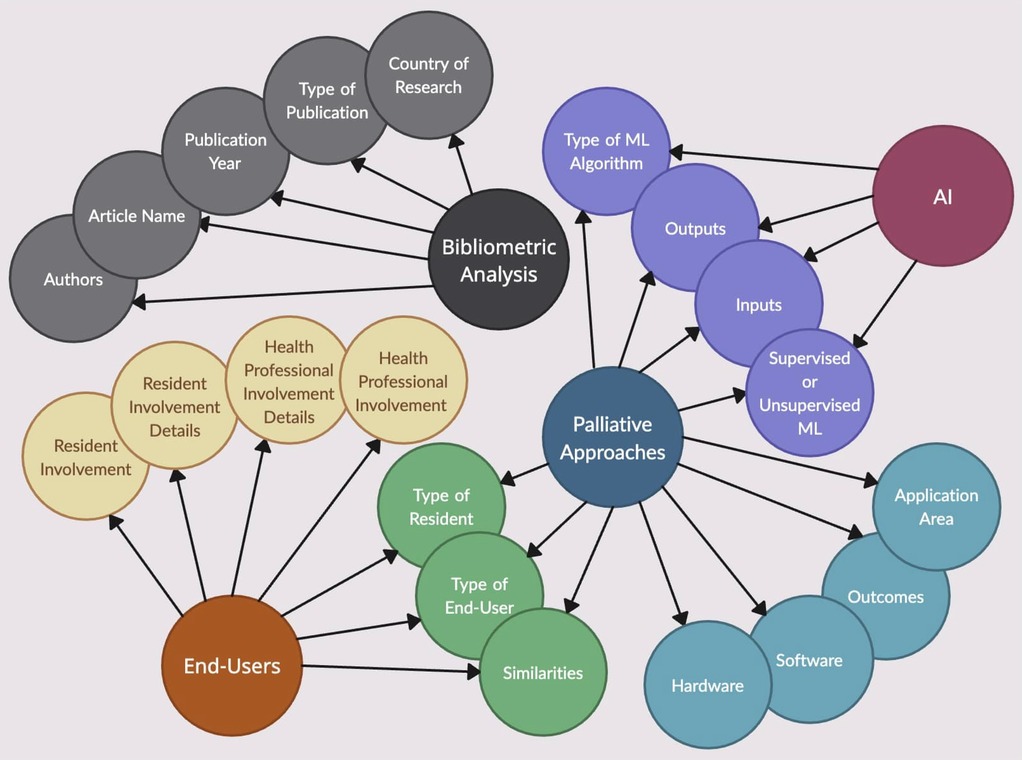
A data extraction form was created using Parsifal in order to collect the key features of each article (14). These key features were used during subsequent analysis. Features collected included nurse involvement, data inputs and outputs, and palliative outcomes. A test sample of 5 papers was used to assess the quality of the form; standardized terms were then chosen and used in subsequent data recording. For example, if a study mentioned the use of an Android smartphone or an iPhone, we simply recorded “phone” in the form. All form elements are outlined in Figure 2.
2.9 Synthesis of results
Data was processed using Python and Jupyter Notebooks to allow for easy visualization of results. Additionally, by using a code-based synthesis process, we ensure our analysis can be repeated. Various data points from the data charting process were collated and visualized in graphs.
3 Results
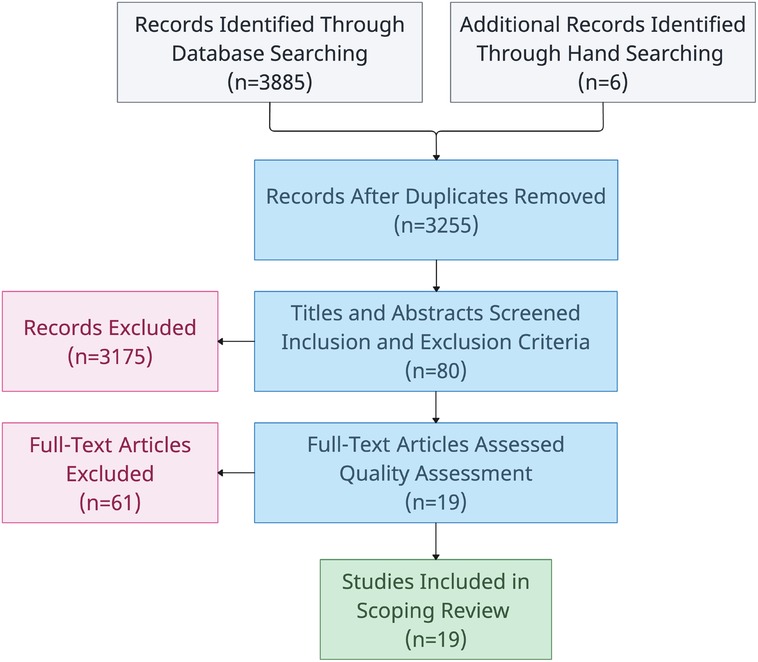
The search process along with its associated results are outlined in a PRISMA-style flowchart in Figure 3 (19). Additionally, a summary of material sources is outlined in Table 4. A total of 636 duplicates were removed after the initial search process.
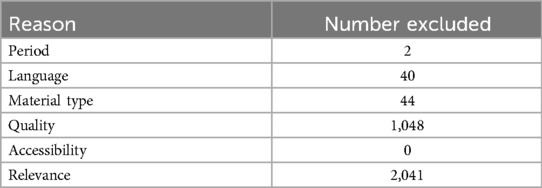
The number of excluded materials from the title and abstract screening stage are outlined in Table 5. Most journal articles were excluded due to their quartile ranking or relevance at this stage in the review process. By the end of the title and abstract screening process, 80 articles were deemed suitable for full-text screening and quality assessment. 61 of these articles were excluded during quality assessment, leaving 19 articles eligible for data extraction and subsequent inclusion in this review.
3.1 Bibliometric analysis
3.1.1 Authors
All papers were authored by different academics with no repeated names appearing between papers. Therefore, no researchers stand out as being particularly prolific within the field of palliative nursing home AI interventions. This circumstance may reflect the fragmented nature of the field.
3.1.2 Research topics
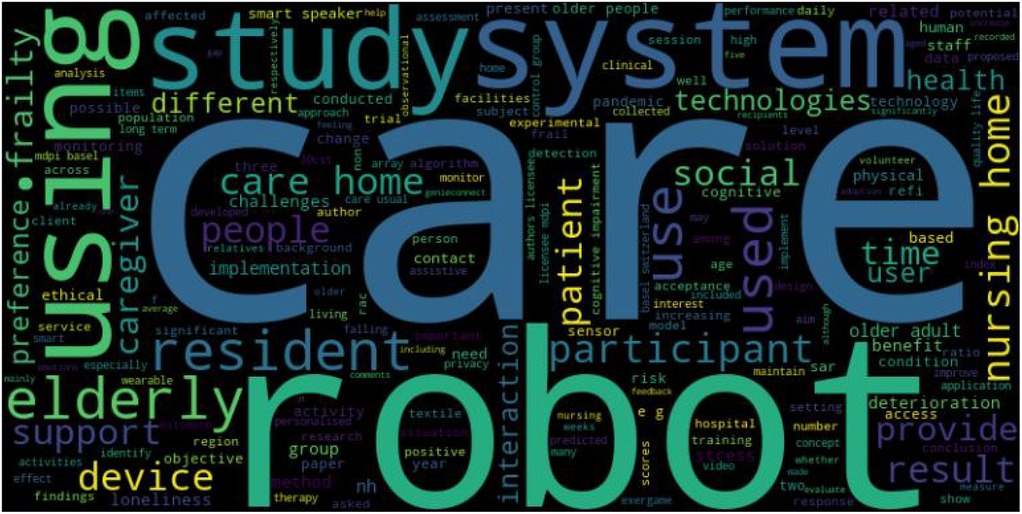
As shown in Figure 4, abstract analysis reveals that the ten most common words found across studies were “care,” “robot,” “system,” “using,” “study,” “elderly,” “resident,” “use,” “used,” and “participant.” Words such as “care,” “robot” and “elderly” reveal potential focus on robot usage in older adult care settings. Additionally, words such as “study,” “system,” “participant,” “using,” “use,” and “used” suggest that the literature may focus on practical applications of systems and user responses to the same.
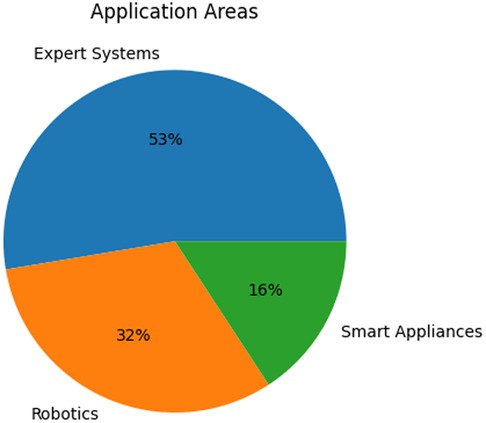
Analysis of application areas obtained during the data extraction process confirm the suppositions outlined above. Figure 5 shows that the majority of the studies focus on the use of expert systems or decision support (DS) systems in nursing homes, while other research involves the smart devices and robotics which comprise intelligent physical (IP) systems.
3.1.3 Publication year
Figure 6a conveys the temporal publishing landscape surrounding our research questions. Overall trends show that there was a significant spike in publications in 2021. As shown in Figure 6b there was a sudden surge in interest in IP technology in 2021. This spike in interest could be attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic, wherein non-contact forms of care were prioritized to preserve patient safety. In recent years, there seems to be interest in both DS systems and IP systems.
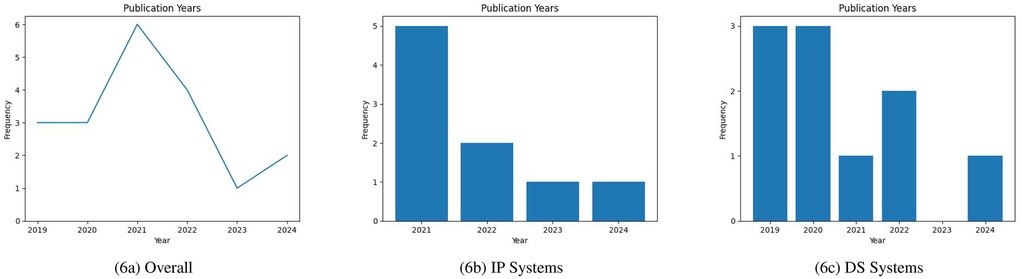
Figure 6. (a) Overall publication years; (b) IP systems publication years; (c) DS systems publication years (incomplete data for 2024).
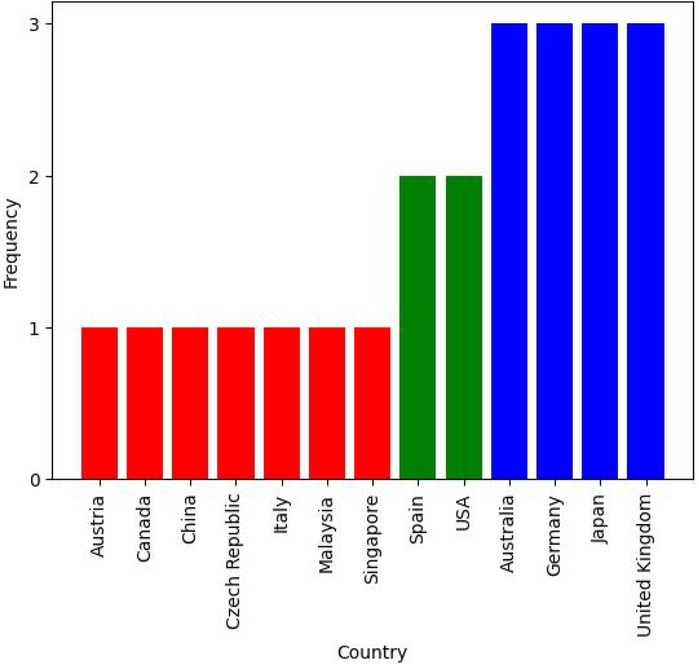
3.1.4 Location
As outlined in Figure 7, the majority of studies in this review are from Europe. Asia, Oceania, and North America also feature in the literature. The proportion of research outputs per continent is fairly equal for both IP and DS systems, indicating that both subcategories are represented well geographically. There is also a pronounced absence of studies from Africa and South America; from this absence, one can posit that either the PC needs of people from these locations are not adequately addressed or there is not comparable research activity in these regions. This absence reflects findings from other palliative reviews focusing on these continents (20, 21).
3.2 Results of individual sources of evidence
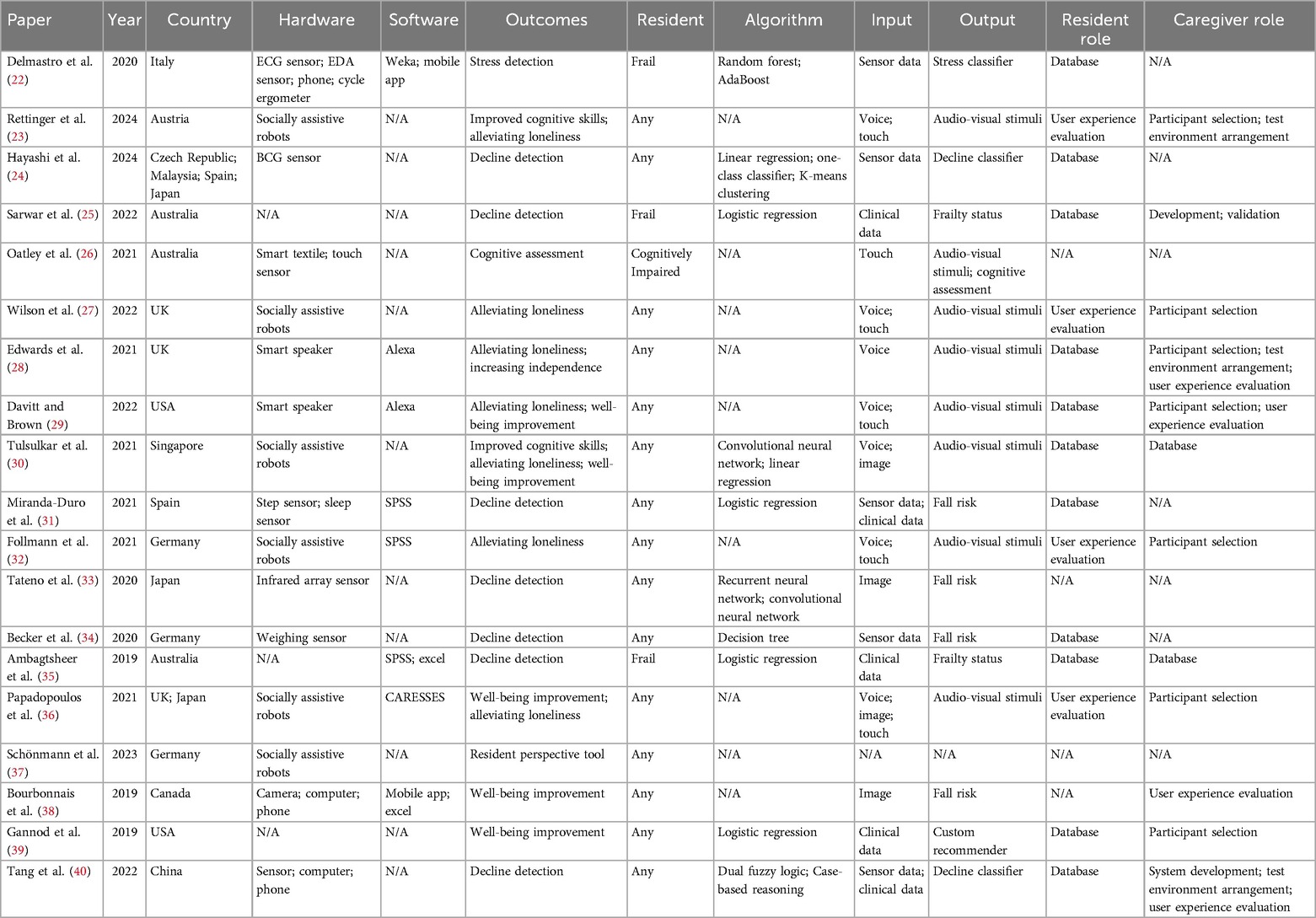
Table 6 outlines all relevant outcomes data for each source of evidence.
3.2.1 Nursing home data availability
Regarding IP systems, most of the studies were based on resident observations; thus data collected in these studies is reported within the material itself, and, in the majority of cases, is the basis of the publication. There was only one IP study which focused on the development of a system as opposed to resident observations (26). This study did not include actual nursing home residents, their caregivers, or their families in any part of their research process and thus data collected for this study does not come from nursing homes.
Within the context of data-heavy DS systems, one study had system-specific data freely available to download and use (24); this sensor data is not generally applicable to a wide variety of nursing home settings. One study did not explicitly mention any system-reliant data collected as part of their research. Instead, they focused on caregiver perspectives to hypothetical technologies; similarly to the majority of IP literature, this study’s data is reported within the material itself (38). Four DS system studies did not disclose the datasets used in their studies, their data could not be found, or their data did not come from nursing homes (31, 33, 39, 40). Four DS studies were asked about potential data access (22, 25, 34, 35). Two of these studies explicitly mention the availability of their data upon reasonable request (25, 34). Three kind responses were obtained, but data was not available in the two aforementioned cases (25, 34). One response indicated that data was available, provided research to be undertaken using the same was appropriate (22). Overall, data from these nursing home studies is not openly available and quite difficult to obtain.
3.3 Synthesis of results
3.3.1 Types of systems or strategies
The literature exhibits a strong focus on IP systems along with DS systems. IP systems are entities capable of interacting with the physical world using sensors, actuators, processors or a combination of the same; these systems can be cognizant of their environments, perform tasks, and make decisions based on user input (41). DS systems utilize ML to analyse data and provide informed recommendations for end-users; these systems use domain-specific information to create data-driven insights for decision-makers (42).
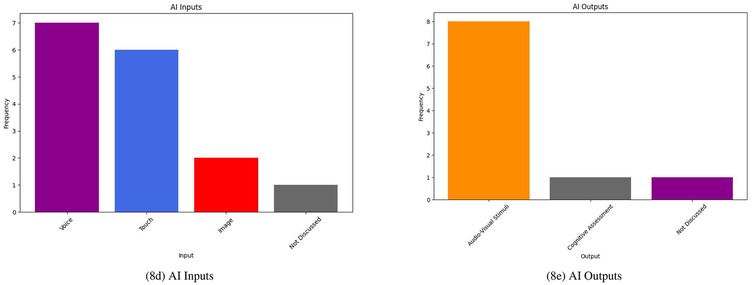
Many of the IP systems in this review use socially assistive robots (SARs) in their research (23, 27, 30, 32, 36, 37). Smart speakers are used in a few studies to provide means of communication for residents, caregivers, and family members (28, 29). One study describes a smart textile for the nursing home use case (26). As shown in Figure 8 the majority of these systems focused on providing audio-visual stimuli for their users and accepted both voice and touch as the primary forms of input.
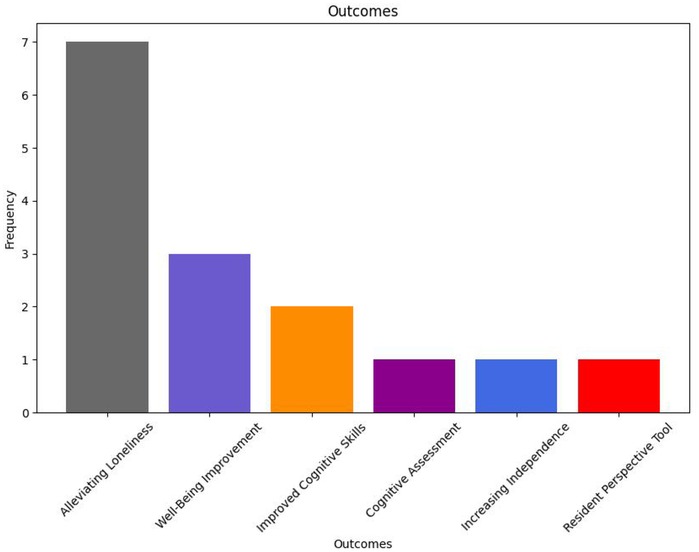
Figure 9 conveys the fractured landscape surrounding palliative outcomes of IP studies. As in the examples outlined above, many relevant studies discussed the potential social benefits of such systems. There seems to be a focus on research surrounding loneliness alleviation (23, 27–30, 32, 36). Well-being improvement and improved cognitive skills are also discussed in a few studies (23, 29, 30, 36). However, no clear palliative definitions are discussed in any of the relevant studies, making fundamental comparison between them difficult.
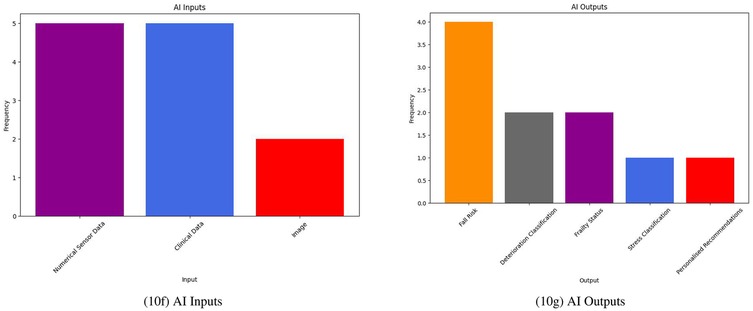
Many of the DS system studies included the use of some form of sensor-based dataset to create algorithmically-driven solutions; these sensors generated either some form of numerical data or image which could be used to train ML algorithms. As outlined in Figure 10, all studies discussed some form of ML inputs and outputs in their work. Inputs to the majority of these systems were either sensor data or clinical data; one study included a mixture of the two (31).
A wide variety of different sensors were used in the DS systems from the literature, such as weight, ballistocardiogram (BCG), electrocardiogram (ECG), electrodermal activity (EDA), step and sleep sensors (22, 24, 31, 34). Images extracted from infrared array sensors or cameras are also mentioned in a few DS studies (33, 38).
All DS studies used different forms of sensor and clinical data to infer patient outcomes. Clinical variables widely varied from country-specific assessments to collected data from patient-level tools (25, 31, 35, 39). Sarwar et al. includes the use of progress notes, a common, but somewhat underutilized, form of data collection in nursing homes (25, 43). Ambagtsheer et al. developed their findings using the Australian Aged Care Funding Instrument (ACFI) (35). However, this tool is not applicable to nursing homes outside of Australia.
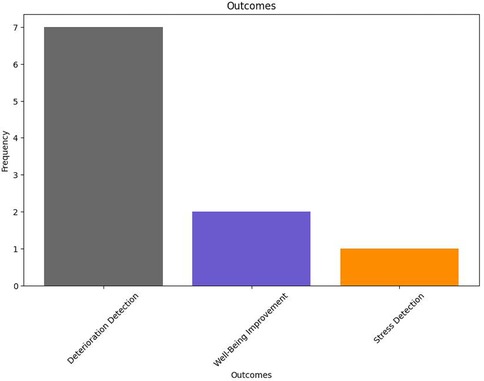
As shown in Figure 11, DS systems feature a much narrower range of palliative outcomes than IP systems. Most DS system interventions placed emphasis on deterioration detection as their primary palliative outcome (24, 25, 31, 33–35). Similarly to IP systems, a few DS system studies also considered general well-being improvement as their primary goal (38, 39). Furthermore, in line with findings from IP systems, no studies define exactly what PC means within the context of their research. All studies focus on a more broad view of the same.
3.3.2 AI techniques
Most IP system papers did not discuss the AI techniques used in their research. Only one reported the use of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and linear regression as part of their resident assessment (30). Most of these papers assessed pre-existing smart devices and robots, which may not necessarily have been designed for a nursing home setting, leaving little by way of new developments specifically targeting nursing homes. This circumstance reveals that many IP systems are focused on applying preexisting software and hardware to the nursing home setting.
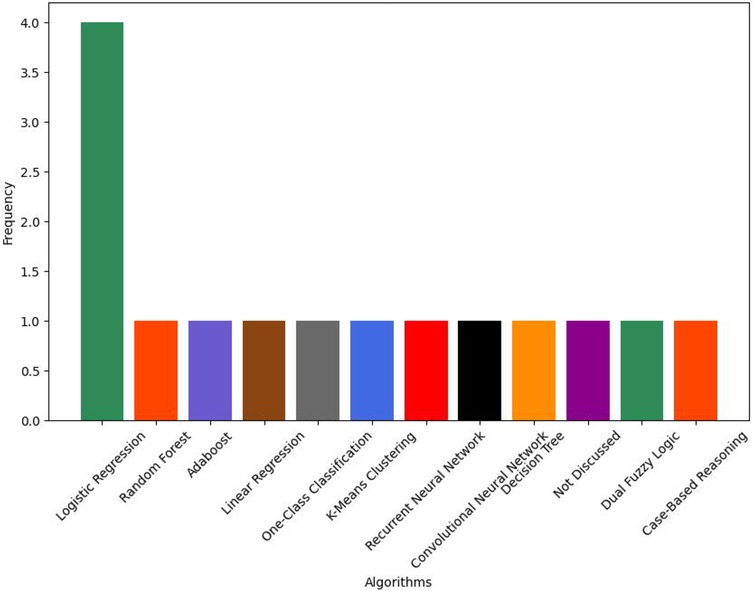
The majority of DS systems in this review included some form of ML. Only one relevant study did not discuss any specific details regarding types of AI used; instead it reported user-centered exploratory qualitative research (38). All of the studies that discussed details of their AI-based implementation used supervised ML algorithms. One study also incorporated unsupervised learning into their system design (24). As shown in Figure 12, there are a vast number of different ML algorithms discussed in the literature.
These algorithms generally seem to be chosen for simplicity, conventionality, or due to the types of data available (31). For instance, all studies which used clinical data also used logistic regression (25, 31, 35, 39). Due to the wide variety of sensors used across studies, a wide variety of different algorithms are used for contrasting sensors. For example, ECG and EDA sensor data were used with Random Forest and AdaBoost algorithms, whereas BCG sensor data was used alongside one-class classification, K-means clustering, and linear regression (22, 24). Overall, there seems to be an over-reliance on supervised algorithms; much of this may be due to the limited types of data available.
As shown in Table 7, many studies, especially within Europe, seem to implement solutions with extremely small datasets (22, 24, 31, 33, 34, 38). The few studies that used bigger clinical datasets exhibited better results with similar algorithms (25, 35, 39). Whether novel insights may be uncovered from unsupervised learning using small datasets has yet to be explored. Additionally, sensor-based methods seem to be heterogeneous and may benefit from standardization to optimize algorithm choice for context-based discovery, rather than relying on traditional approaches and familiar algorithmic options.
3.3.3 End-user involvement
The majority of IP system research focused on observational responses within nursing homes. As shown in Figure 13, residents are the end-users of all of these systems; a small amount of the relevant literature also included caregivers as potential users.
There were only four IP studies which included residents in system evaluation (23, 27, 32, 36). As the majority of such systems are created to improve the lives of those residing in nursing homes, the residents themselves should be considered in design and evaluation processes. Additionally, the vast majority of these studies do not report feedback from healthcare professionals; only two studies reported on caregiver system evaluation (28, 29). As healthcare professionals are major stakeholders in the adoption of such technologies, there is a clear need for an increase in feedback from the same.
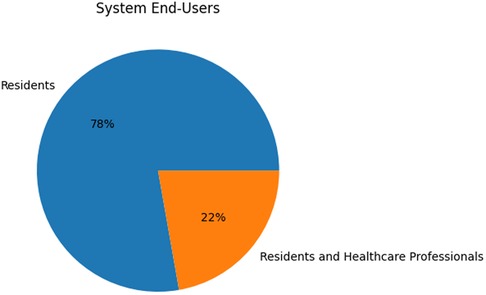
100% of the end-users in DS system research were healthcare professionals. However, the majority of studies did not include healthcare professionals in their research at all. As shown in Figure 14, only two of the systems included healthcare professionals in system evaluation processes (25, 38). In all other involvements, healthcare professionals were part of simple data collection and experimental setup procedures. Furthermore, as systems primarily revolve around data collected from residents in nursing homes, resident feedback should also be of importance to researchers in the field. However, no studies incorporated resident feedback into their work.
4 Discussion
There seems to be a general consensus that sensors and clinical data can generate useful palliative results. However there are no standardized or common types of clinical or sensor data collected across these studies. As a result, direct comparisons between studies are difficult to create; this situation is exacerbated by the lack of clear palliative definitions across studies. Additionally, without adequate feedback from system end-users, it is not possible to assess the feasibility and acceptability of proposed interventions in future nursing homes. Overall, there are some note-worthy gaps in the literature which provide ample scope for future research.
4.1 PC definitions
None of the studies within this review define exactly what PC means in their research. This circumstance reflects the same ambiguity found in the broader palliative research field (7). Additionally, to the best of our knowledge, there is no non-disease-specific core outcome measure for palliative and end of life care in nursing homes. While concepts of well-being and quality of life may be loosely discussed in many publications, the lack of a distinct understanding of PC brings uncertainty to research. Studies are not directly comparable as they do not discuss the same palliative values. This inconsistency also allows such research to spread to indefinite and extreme solutions, from social applications to obscure care personalization methods. Additionally, many of the hazy and underdeveloped interpretations of PC do not seem to be informed by clinical practice, standards, or protocols. As common PC approaches are not considered in these solutions, caregivers are less likely to become familiar with new forms of palliative technology. Lack of familiarity makes such systems less likely to be accepted in future practice; caregivers want to understand the technology that is created to help them (44).
While definitions of PC are not provided and palliative outcomes for both IP and DS systems are fractured, PC is most commonly linked with improved quality of life in the literature. Most outcomes are aimed towards improving emotional and social elements of the lives of those in nursing homes. There is also an element of finality about the approaches to care discussed. These interventions are mostly about comfort and control in the last stages of life. However, providing a more concrete sense of PC across studies is difficult given the lack of discussion in the papers themselves.
Future researchers ought to include clear definitions of PC in publications in order to begin standardizing on the same. Palliative experts should be consulted to clarify what nursing home PC should be described as in technological research. Concept analysis of PC reveals the field to be quite broad; this allows many interpretations and misconceptions to co-exist in education and application (45). Core outcome measures for palliative and end of life care in nursing homes also need to be created; these measures need to factor in technological research. In order to further ideas from past projects, concrete conceptual foundations need to be built, preventing ill-conceived technologies and strengthening further work.
4.2 Data availability
Of those studies which used ML, there seems to be a paucity of internationally standardized data available. Only one open-source dataset could be obtained from the research publications included in this review. This constrained information landscape seems to be partially fueled by data privacy policies, such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe (46). Additionally, issues surrounding health data interoperability further complicate matters in European countries (47). European DS system studies in this review feature small, unstandardized datasets with limited results; not only are findings potentially restricted to their countries of creation, they may also not be applicable outside of the nursing home in which the relevant data was collected. These types of disparate data, especially sensor data, may not be feasible for many nursing homes to collect, making such solutions impractical in common practice (48). ML usage in research with clinical data all seems to revolve around the use of conventional and familiar algorithms. This signifies that AI usage itself is stagnating within nursing home studies; the focus seems to be on applying the same methods to new data, not optimizing algorithms for standard data. Without homogeneity between clinical datasets, researchers limit themselves to the same algorithms as their counterparts; this situation hinders the use of novel approaches to valuable health information.
Comparison between European and Australian-American ML studies reveals that more data fuels more successful research. DS research from Australia and America exhibits the use of standardized datasets from multiple nursing homes; these large datasets prove themselves useful in generating more accurate algorithmic results. However, even with standardization, these findings may not be applicable outside of the countries in which they are created. Nursing documentation, which is collected across clinical settings and countries, is not adequately exploited in research (49, 50). While not standardized in themselves, nurse notes from care home documentation, could be utilized to create internationally-applicable ML models.
In general, healthcare data is not easy to access (51). Without moves to make data more accessible, future ML-based nursing home solutions may not be relevant in countries where data is not available. Anonymized datasets made openly accessible to researchers from multinational nursing homes could accelerate future research. However, in efforts to make ML-based palliative solutions, researchers must not disrespect resident values surrounding privacy and data usage. Resident data for research cannot be collected without consent due to ethical concerns. These data availability and standardization issues may take decades to fully resolve; therefore, new approaches to data generation may provide temporary solutions for present researchers.
In a manner similar to the pre-clinical investigation of drugs, future AI solutions may undergo trial processes with standard sets of generated data (52). AI itself can be used to make these synthetic datasets, such as artificial clinical note creation (53). These datasets ought to be validated by experts to guarantee pseudo-authenticity. Noise and hallucinations in the data should also be controlled. If future ML solutions were trained using this freely available information, it would make comparison between algorithmic approaches a lot more viable. Furthermore, should these datasets be created to contain information which is known to be collected internationally, such as nurse notes, future research may be pertinent to a wider range of nursing homes. These “pre-clinical” investigations may also encourage nursing homes and their residents to more openly share their data in “human” trials; subsequently, widespread adoption of standardized ML solutions may be possible.
4.3 Stakeholder involvement
Across studies, there is a lack of research involving both patient and health professional perspectives. Additionally, many DS systems do not include caregivers in any evaluation processes. The use of ML in monitors, analysis tools, care planners and recommender systems along with smart devices for entertainment and socialisation needs a diverse range of perspectives from both caregivers and nursing home residents. As end-users are of primary importance to system success, the lack of inclusion of caregivers and residents in design and development procedures calls the feasibility of proposed solutions into question (54).
In past research on older adult care technology and caregiver perspectives, it was found that nurses want to be involved in the development of solutions; there is an emphasis placed on including stakeholders such that future systems are designed based on need, not on the availability of certain technologies (44). Furthermore, residents’ opinions should also be included in system analysis due to their inherent involvement in the use of such technologies (55). None of the studies included in this review report on the inclusion of residents’ family members in research processes; family members often act as proxies for residents in nursing homes and can be crucial in PC discussions (56).
It is important to involve these stakeholders in the design of such technology to understand what tools are most needed in PC settings. Additionally, it is important to consider what impact these systems have on those interacting with them. If a PC system is not perceived positively by those it aims to help, then it is in need of improvement. It cannot be improved effectively without help from those who are face-to-face with PC scenarios on a daily basis. While ethical issues can make the inclusion of all parties difficult, future work should aim to consider as many stakeholders as possible in the design and implementation of AI-based systems.
4.4 Alternative technologies
Caregivers want to have more time to spend with their residents (44). Documentation is time-consuming; logging information in nursing homes can outweigh the time caregivers have to spend with residents (44). Text-centered solutions have been cited as promising areas of exploration within PC research (57). AI has the potential to alleviate the nurse’s workload while increasing the amount of person-centered care a resident receives (58). Additionally, caregivers do not want AI substitutes, they want collaborators; all aspects of care should not be replaced with machines (58). While many studies in this review focus on the use of AI for human-centered processes, such as socialization and qualitative interaction, there is a lack of research into the use of AI for task automation, such as documentation creation.
Similar to findings reported by Cunha et al., we believe that an integrated approach to care, involving multiple technologies, is possible in the future (59). There is a clear divide between research into IP systems and DS systems in the literature. Niche systems with narrow scope ought to be integrated into a wider care landscape in order to be practical. IP components beyond the scope of robots and speakers, such as glasses, can be explored in conjunction with decision support (DS) intelligent physical (IP) methods (55). These devices could be utilised as new tools to aid nurses in everyday activities, such as documentation and clinical data generation.
Privacy is a clear issue in nursing homes; surveillance-based technologies have been discouraged in multiple studies due to the potential to violate resident wishes (38, 58). While many studies in this review focus on the use of AI in sensitive everyday care scenarios, no study considers the application of smart devices or ML in less-private nursing home settings, such as family meetings. Family meetings are a crucial aspect of PC in nursing homes; they help define resident wishes and needs, ensuring all relevant parties are in communication with each other. These meetings enable improved quality of life for residents (60). Subsequent documentation of the same is also extremely important when updating advanced care plans for patients (61). Advanced care planning (ACP) is the process of recording patient preferences concerning goals of care (62). However, accurate and appropriate documentation of the same takes a lot of caregivers’ time (60, 63). Smart technologies such as speakers, glasses, and other audio-visual technologies could be utilised to transcribe, annotate, and document such meetings in an efficient and privacy-centred manner.
4.5 Limitations
No literature review can exist without its own set of limitations. For this review, we focused on six databases pertinent to the field of computer science. In limiting ourselves to these sources, we potentially exclude publications from alternative locations, such as those from health-focused databases. Additionally, although all authors have been involved in a comprehensive assessment of this review, the primary author conducted the majority of the study selection procedure; this circumstance was due to resource constraints. While the use of a pre-existing protocol limits some potential for selection bias, there may still be bias present.
We chose to use stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria. While these criteria ensure only articles of the highest quality, relevance, and validity are included in our analysis, there may be useful information in excluded articles. Articles not in English and articles prior to 2017 may provide a different overview of the field. By relaxing the impact criterion, a broader view of the research landscape may be obtained. Furthermore, only conference and journal articles are considered, limiting the breadth of review results; prospective reviews could consider book chapters and other forms of academic literature in their analysis.
5 Conclusions
This PRISMA-ScR scoping review was undertaken to investigate the current state of research on AI usage for PC in nursing homes (16). Our findings are based on 19 research articles; our discussion centered on palliative definitions, data accessibility measures, stakeholder involvement, and future technological directions.
Bibliometric analysis revealed that European studies were most prevalent; North American, Australian and Asian studies also feature. There is a notable paucity of research from South American and African studies, indicating that people from these locations have unmet PC needs or that there is not comparable research activity in these regions. No authors were found to be particularly prevalent within this field. While indicating that a diverse range of views are incorporated into our review, this finding also reveals the fragmented research landscape.
Key nursing home stakeholders are not consistently involved in system design and evaluation processes. Healthcare professionals, residents, and relevant family members should be involved in research to ensure any outputs from studies are feasible in practice. Additionally, palliative outcomes from relevant materials are varied and definitions of PC are not mentioned; this situation reflects the confusion found in the general palliative research area (8). In order to compare future studies without ambiguity, definitions of PC need to be included in publications. PC experts should be consulted, or at least referenced, in order to avoid disparate solutions.
Our findings indicate that novel ML approaches to clinical data for DS systems need to be investigated; researchers ought to move beyond the use of simple regression models. Palliative research involving ML may be stagnating due to the lack of data available. Data sharing procedures could be established to accelerate and instigate further research in the field. Data issues may take years to resolve; artificial data may be used to convey the advantages of AI usage in nursing homes, thus encouraging future facilities and their residents to share their data for further research. There is also scope to investigate internationally-collected types of data, such as nurse notes and free-text documentation. Additionally, sensor-based DS research seems to be heterogeneous, unstandardized, and invasive; this finding indicates that such technologies are inapplicable in many facilities and unsuitable for present nursing home environments.
Our study also finds that there is a clear divide between research focusing on IP and DS systems. Integrated DS and IP systems need to be developed. IP systems are mainly focused on socially assistive robots; other devices, such as smart glasses, have not been adequately explored. Task automation tools involving elements of both IP and DS systems have yet to be investigated.
The main contribution of this study is a review of AI systems for PC in nursing homes. Our findings indicate that there is ample room for research into data availability solutions, integrated IP and DS systems, and stakeholder involvement. Combining multiple forms of data collection and technology together may be possible in future systems. Clearer definitions of PC in subsequent research are also needed in order to be able to accurately compare studies. Additionally, future research should include healthcare professionals, residents’ families, and the residents themselves in the system design and assessment processes. Alternative technologies focused on everyday tasks may be developed in consultation with these stakeholders in order to increase the amount of person-centered care provided by caregivers. By addressing these challenges, it will be possible to create a stronger palliative landscape for our aging population using AI.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://github.com/isabel-ronan/reviewNursingHomeAI.
Author contributions
IR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ST: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DM: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. NC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. MMS: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. PC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This publication has emanated from research conducted with the financial support of Science Foundation Ireland under Grant number 18/CRT/6222. This research is also supported by a PhD scholarship from the Catherine McAuley School of Nursing and Midwifery at University College Cork.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fdgth.2025.1484304/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
ACFI, Australian aged care funding instrument; ACP, advanced care planning; AI, artificial intelligence; BCG, ballistocardiogram; CNN, convolutional neural network; DL, deep learning; DS systems, decision support systems; ECG, electrocardiogram; EDA, electrodermal activity; GDPR, general data protection regulation; IP systems, intelligent physical systems; ML, machine learning; PC, palliative care; PICOC, population, intervention, comparison, outcome, and context; PRISMA-ScR, preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses extension for scoping reviews; SAR, socially assistive robot.
References
2. Schweighart R, O’Sullivan JL, Klemmt M, Teti A, Neuderth S. Wishes and needs of nursing home residents: a scoping review. Healthcare. (2022) 10:854. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10050854
3. Cimino NM, McPherson ML. Evaluating the impact of palliative or hospice care provided in nursing homes. J Gerontol Nurs. (2014) 40:10–4. doi: 10.3928/00989134-20140909-01
4. Alanazi MA, Shaban MM, Ramadan OME, Zaky ME, Mohammed HH, Amer FGM, et al. Navigating end-of-life decision-making in nursing: a systematic review of ethical challenges and palliative care practices. BMC Nurs. (2024) 23:467. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02087-5
5. Younis N, Ahmed M. Knowledge and attitude of nursing students’ towards palliative care. J Curr Med Res Opin. (2024) 7:2345–53. doi: 10.52845/CMRO/2024/7-4-21
7. Van Mechelen W, Aertgeerts B, De Ceulaer K, Thoonsen B, Vermandere M, Warmenhoven F, et al. Defining the palliative care patient: a systematic review. Palliat Med. (2013) 27:197–208. doi: 10.1177/0269216311435268
8. Wallerstedt B, Benzein E, Schildmeijer K, Sandgren A. What is palliative care? perceptions of healthcare professionals. Scand J Caring Sci. (2019) 33:77–84. doi: 10.1111/scs.12603
9. Reddy V, Nafees A, Raman S. Recent advances in artificial intelligence applications for supportive and palliative care in cancer patients. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. (2023) 17:125–34. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000645
10. Helm JM, Swiergosz AM, Haeberle HS, Karnuta JM, Schaffer JL, Krebs VE, et al. Machine learning and artificial intelligence: definitions, applications, and future directions. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. (2020) 13:69–76. doi: 10.1007/s12178-020-09600-8
11. Seibert K, Domhoff D, Bruch D, Schulte-Althoff M, Fürstenau D, Biessmann F, et al. Application scenarios for artificial intelligence in nursing care: rapid review. J Med Internet Res. (2021) 23:e26522. doi: 10.2196/26522
12. Moghadam MP, Moghadam ZA, Qazani MRC, Pławiak P, Alizadehsani R. Impact of artificial intelligence in nursing for geriatric clinical care for chronic diseases: a systematic literature review. IEEE Access. (2024) 12:122557–87. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3450970
13. Hendriks A, Hacking C, Verbeek H, Aarts S. Data science techniques to gain novel insights into quality of care: a scoping review of long-term care for older adults. Explor Digit Health Technol. (2024) 2:67–85. doi: 10.37349/edht.2024.00012
16. Carrera-Rivera A, Ochoa W, Larrinaga F, Lasa G. How-to conduct a systematic literature review: a quick guide for computer science research. MethodsX. (2022) 9:101895. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2022.101895
17. Krampl A. Journal citation reports. J Med Libr Assoc. (2019) 107:280–3. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2019.646
19. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
20. Aliaga Chávez RA, Bustamante Coronado RI, Chumbes Sipan ML, Grados Sánchez OA, Paredes Pascual RR, Salinas Paz JL, et al. Current state and future perspectives for palliative care in latin america with a special focus on Peru. Future Oncol. (2023) 19:855–62. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-1033
21. Agom DA, Onyeka TC, Iheanacho PN, Ominyi J. Barriers to the provision and utilization of palliative care in Africa: a rapid scoping review. Indian J Palliat Care. (2021) 27:3–17. doi: 10.4103/IJPC.IJPC_355_20
22. Delmastro F, Martino FD, Dolciotti C. Cognitive training and stress detection in MCI frail older people through wearable sensors and machine learning. IEEE Access. (2020) 8:65573–90. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985301
23. Rettinger L, Fürst A, Kupka-Klepsch E, Mühlhauser K, Haslinger-Baumann E, Werner F. Observing the interaction between a socially-assistive robot and residents in a nursing home. Int J Soc Robot. (2024) 16:403–13. doi: 10.1007/s12369-023-01088-9
24. Hayashi T, Cimr D, Studnička F, Fujita H, Bušovský D, Cimler R. Patient deterioration detection using one-class classification via cluster period estimation subtask. Inf Sci. (2024) 657:119975. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.119975
25. Sarwar T, Jimeno Yepes A, Zhang X, Chan J, Hudson I, Evans S, et al. Development and validation of retrospective electronic frailty index using operational data of aged care homes. BMC Geriatr. (2022) 22:922. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03616-0
26. Oatley G, Choudhury T, Buckman P. Smart textiles for improved quality of life and cognitive assessment. Sensors. (2021) 21:8008. doi: 10.3390/s21238008
27. Wilson R, Keane I, Jones R. Affective responses of older adults to the anthropomorphic GenieConnect companion robot during lockdown of the COVID19 pandemic. In: ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (2022). Vol. 2022-March, p. 1095–9.
28. Edwards KJ, Jones RB, Shenton D, Page T, Maramba I, Warren A, et al. The use of smart speakers in care home residents: implementation study. J Med Internet Res. (2021) 23:e26767. doi: 10.2196/26767
29. Davitt J, Brown J. Using voice and touchscreen controlled smart speakers to protect vulnerable clients in long-term care facilities. Innov Aging. (2022) 6:759. doi: 10.1093/geroni/igac024
30. Tulsulkar G, Mishra N, Thalmann N, Lim H, Lee M, Cheng S. Can a humanoid social robot stimulate the interactivity of cognitively impaired elderly? a thorough study based on computer vision methods. Vis Comput. (2021) 37:3019–38. doi: 10.1007/s00371-021-02242-y
31. Miranda-duro M, Nieto-riveiro L, Concheiro-moscoso P, Groba B, Pousada T, Canosa N, et al. Analysis of older adults in spanish care facilities, risk of falling and daily activity using xiaomi mi band 2. Sensors. (2021) 21:3341. doi: 10.3390/s21103341
32. Follmann A, Schollemann F, Arnolds A, Weismann P, Laurentius T, Rossaint R, et al. Reducing loneliness in stationary geriatric care with robots and virtual encounters—a contribution to the covid-19 pandemic. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:4846. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094846
33. Tateno S, Meng F, Qian R, Hachiya Y. Privacy-preserved fall detection method with three-dimensional convolutional neural network using low-resolution infrared array sensor. Sensors. (2020) 20:1–22. doi: 10.3390/s20205957
34. Becker H, Garcia-Agundez A, Müller P, Tregel T, Miede A, Göbel S. Predicting functional performance via classification of lower extremity strength in older adults with exergame-collected data. J Neuroeng Rehabil. (2020) 17:164. doi: 10.1186/s12984-020-00778-z
35. Ambagtsheer RC, Beilby J, Seiboth C, Dent E. Prevalence and associations of frailty in residents of australian aged care facilities: findings from a retrospective cohort study. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2020) 32:1849–56. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01379-0
36. Papadopoulos C, Castro N, Nigath A, Davidson R, Faulkes N, Menicatti R, et al. The CARESSES randomised controlled trial: exploring the health-related impact of culturally competent artificial intelligence embedded into socially assistive robots and tested in older adult care homes. Int J Soc Rob. (2022) 14:245–56. doi: 10.1007/s12369-021-00781-x
37. Schönmann M, Bodenschatz A, Uhl M, Walkowitz G. The care-dependent are less averse to care robots: an empirical comparison of attitudes. Int J Soc Rob. (2023) 15:1007–24. doi: 10.1007/s12369-023-01003-2
38. Bourbonnais A, Rousseau J, Lalonde MH, Meunier J, Lapierre N, Gagnon MP. Conditions and ethical challenges that could influence the implementation of technologies in nursing homes: a qualitative study. Int J Older People Nurs. (2019) 14:e12266. doi: 10.1111/opn.12266
39. Gannod GC, Abbott KM, Van Haitsma K, Martindale N, Heppner A. A machine learning recommender system to tailor preference assessments to enhance person-centered care among nursing home residents. Gerontologist. (2019) 59:167–76. doi: 10.1093/geront/gny056
40. Tang V, Lam HY, Wu CH, Ho GTS. A two-echelon responsive health analytic model for triggering care plan revision in geriatric care management. JOEUC. (2022) 34:1–29. doi: 10.4018/JOEUC.289224
42. Kononenko I. Machine learning for medical diagnosis: history, state of the art and perspective. Artif Intell Med. (2001) 23:89–109. doi: 10.1016/S0933-3657(01)00077-X
43. Wei Q, Courtney KL. Nursing information flow in long-term care facilities. Appl Clin Inf. (2018) 9:275–84. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1642609
44. Hermann J, Mäder AD, Kubullek AK, Hey CC, Dogangün A. (Intelligent) technical systems in elderly care: the caregivers perspective. In: Proceedings of the 34th Australian Conference on Human-Computer Interaction. Association for Computing Machinery (2023). OzCHI ’22, p. 81–7.
45. Wantonoro W, Suryaningsih EK, Anita DC, Nguyen TV. Palliative care: a concept analysis review. SAGE Open Nurs. (2022) 8:23779608221117379. doi: 10.1177/23779608221117379
46. Voigt P, von dem Bussche A. Data from: The EU general data protection regulation (GDPR): a practical guide. SpringerLink. (2024).
47. Stellmach C, Muzoora MR, Thun S. Digitalization of health data: interoperability of the proposed european health data space. Stud Health Technol Inf. (2022) 298:132–6. doi: 10.3233/SHTI220922
48. Courtney KL, Demiris G, Hensel BK. Obtrusiveness of information-based assistive technologies as perceived by older adults in residential care facilities: a secondary analysis. Med Inf Internet Med. (2007) 32:241–9. doi: 10.1080/14639230701447735
49. Hansebo G, Kihlgren M, Ljunggren G. Review of nursing documentation in nursing home wards – changes after intervention for individualized care. J Adv Nurs. (1999) 29:1462–73. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.1999.01034.x
50. Voutilainen P, Isola A, Muurinen S. Nursing documentation in nursing homes – state-of-the-art and implications for quality improvement. Scand J Caring Sci. (2004) 18:72–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2004.00265.x
51. Garg R, Karim HMR. Healthcare research data sharing and academic journal: a challenging but fruitful initiative. Indian J Anaesth. (2023) 67:763–6. doi: 10.4103/ija.ija_797_23
53. Kweon S, Kim J, Kim J, Im S, Cho E, Bae S, et al. Data from: Publicly shareable clinical large language model built on synthetic clinical notes (2023).
54. Shiells K, Diaz Baquero A, Štěpánková O, Holmerová I. Staff perspectives on the usability of electronic patient records for planning and delivering dementia care in nursing homes: a multiple case study. BMC Med Inf Decis Mak. (2020) 20:159. doi: 10.1186/s12911-020-01160-8
55. Klinker K, Wiesche M. Smart glasses in health care: a patient trust perspective. In: Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Hawaii: ScholarSpace (2020).
56. Shippee TP, Henning-Smith C, Gaugler JE, Held R, Kane RL. Family satisfaction with nursing home care: the role of facility characteristics and resident quality-of-life scores. Res Aging. (2017) 39:418–42. doi: 10.1177/0164027515615182
57. Vu E, Steinmann N, Schröder C, Förster R, Aebersold DM, Eychmüller S, et al. Applications of machine learning in palliative care: a systematic review. Cancers. (2023) 15:1596. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051596
58. Rony MKK, Kayesh I, Bala SD, Akter F, Parvin MR. Artificial intelligence in future nursing care: exploring perspectives of nursing professionals - a descriptive qualitative study. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e25718. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25718
59. Cunha CR, Moreira A, Pires L, Fernandes PO. Using mixed reality and machine learning to assist caregivers in nursing home and promote well-being. Procedia Comput Sci. (2023) 219:1081–8. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2023.01.387
60. Cornally N, McGlade C, Weathers E, Daly E, Fitzgerald C, O’Caoimh R, et al. Evaluating the systematic implementation of the “let me decide” advance care planning programme in long term care through focus groups: staff perspectives. BMC Palliat Care. (2015) 14:55. doi: 10.1186/s12904-015-0051-x
61. Cahill PJ, Lobb EA, Sanderson CR, Phillips JL. Patients receiving palliative care and their families’ experiences of participating in a “patient-centered family meeting”: a qualitative substudy of the valuing opinions, individual communication, and experience feasibility trial. Palliat Med Rep. (2021) 2:305–15. doi: 10.1089/pmr.2020.0109
62. Brinkman-Stoppelenburg A, Rietjens JA, van der Heide A. The effects of advance care planning on end-of-life care: a systematic review. Palliat Med. (2014) 28:1000–25. doi: 10.1177/0269216314526272
Keywords: nursing, artificial intelligence, scoping review, palliative care, nursing home
Citation: Ronan I, Tabirca S, Murphy D, Cornally N, Saab MM and Crowley P (2025) Artificially intelligent nursing homes: a scoping review of palliative care interventions. Front. Digit. Health 7:1484304. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1484304
Received: 21 August 2024; Accepted: 27 January 2025;
Published: 11 February 2025.
Edited by:
Karin Wolf-Ostermann, University of Bremen, GermanyReviewed by:
Cathy H. Y. Lam, Hang Seng University of Hong Kong, ChinaKathrin Seibert, University of Bremen, Germany
Copyright: © 2025 Ronan, Tabirca, Murphy, Cornally, Saab and Crowley. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Isabel Ronan, i.ronan@cs.ucc.ie
 Isabel Ronan
Isabel Ronan