- Department of Health Informatics, Institute of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Introduction: The appropriate implementation of telemedicine in the healthcare system has the potential to overcome global problems such as accessibility and quality healthcare services. Thus assessing the knowledge of health professionals before the actual adoption of telemedicine is considered a prominent solution to the problems.
Objective: This study aimed to assess healthcare professionals' knowledge of telemedicine and its associated factors at private hospitals in low-resource settings.
Method: An institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 423 health professionals at private hospitals in low-income settings in Ethiopia, from March to April 2021. Data collection was performed by pretested and self-administered questionnaires. This study employed statistical packages for social sciences software. This study employed multivariable logistic regression to determine dependent and independent variables associated with adjusted odd ratio and 95% CI.
Result: in this study about 65.8% of health professionals have good knowledge on Telemedicine .Computer literacy (AOR = 2.9; 95% CI: 1.8, 4.6), computer training (AOR = 2.0; 95% CI: 1.2, 3.3), Internet availability at workplace (AOR = 2.1; 95%CI: 1.3, 3.4), had private laptop (AOR = 1.7; 95% CI: 1.1, 2.9) were significantly associated with knowledge.
Conclusion and recommendation: In general health professionals had good knowledge of Telemedicine. Inclusive packages of capacity by training among health providers are fundamental for the successful implementation of telemedicine.
Introductions
Even though the field of digital technology rapidly moving forward in our worldwide, its utilization in the practice of medicine and patient care has remained suboptimal (1).
Compared to other sectors healthcare sectors are ineffective in the utilization of digital technologies. Telemedicine is the use of information technology to endorse and enable long-distance patient care, the upkeep of patient health records, and the offers patient and professional health (2). According to the World health organization (WHO), Telemedicine is an affordable use of information technology to support health and health-related fields such as healthcare service, medical education, and public health surveillance (3). Today Telemedicine is the fastest growing sector of health care, and much of this growth can be attributed to the benefits of telemedicine, such as shorter wait times, reduced travel, and fewer missed appointments (4). it has been recognized as a means to improve remote access, quality, and efficiency of care (5). Telemedicine employs a variety of technologies, including smartphones, computer tablets, mobile applications, and video conferencing, to enable health care providers to virtually evaluate, diagnose, monitor, treat, and educate patients (6). Although uses of various technologies to assist patients and have historically been used to provide care to patients is low in resource-constrained settings (7, 8). Thus, World Health Organization agreed on the contribution of telemedicine and approved that appropriate usage of this technology can support the healthcare sector in many countries, and considerably expand the quality of well-being care facilities, especially for low-income, and medically underserved communities (9).
Many possible explanations for why this technology adoption remains difficult include the knowledge and understanding of the principles, learning, perception, and workplace conditions of the concerned professionals (10).
A study conducted in Saudi Arabia on health professionals' knowledge of telemedicine stated that 46.1%of health professionals had good knowledge (11).
A study carried out in Ethiopia's public facilities on health professionals’ knowledge of telemedicine found that 37.6%of respondents had enough knowledge (12).
Therefore the users' knowledge of the technology is an important issue that should be considered before beginning a telemedicine program (13).
There are multiple explanations for how telemedicine system advancement and incorporation remain complicated in this area of the globe. Any innovative technology's effectiveness and future growth are largely influenced by factors such as user knowledge and understanding of the current principle, abilities needed for implementation, and a workplace atmosphere enabling technology acceptance (8, 14–16). Thus, for telemedicine to be properly implemented in the Ethiopian healthcare industry, research to demonstrate telemedicine understanding among health providers is needed.
As a result, recognizing health workers' telemedicine insight as well as attributes has been essential for emphasizing action to enhance telemedicine system adoption. Given this context, promoting the rewards of telemedicine platforms, policies, and approaches is necessary to boost affordable healthcare for disadvantaged communities, as well as the standard of healthcare and the ability to share legitimate healthcare information for scientific proof-of-concept among healthcare workers. Nevertheless, the incorporation of a telemedicine system is essential; according to the researcher's knowledge, few studies on the Knowledge of telemedicine systems are among Ethiopian health workers working in non-governmental hospitals.
Therefore this study aimed to assess health professionals' knowledge of telemedicine and its associated factors at private hospitals in northwest Ethiopia.
Method
Study period and design
From March 3 to April 7, 2021, and institutional cross-sectional study with a quantitative approach was conducted at private hospitals in resource-limited settings in northwest Ethiopia.
Study population and sample size determination
The subjects of the study were health professionals from private hospitals in low-resource settings. The sample size was determined using a single population proportion equation, assuming a 50% response rate and a 10% non-response rate because no previous research had been conducted. Subsequently, a required sample size of 423 was acquired. The health professionals with less than six months of clinical practice and experience were excluded from the study. Respondents were chosen from private hospitals by simple random sampling technique.
Data collection tool and quality assurance
Data were collected by using A structured self-administered questionnaire designed for the study. For linguistic uniformity, the questionnaire was first written in English and then translated into Amharic. Four health informatics professionals' supervisors were recruited and eight health information technicians were data collectors. The one-day training was given to supervisors and data collectors on the objective of the study, data collection process, how to approach respondents and quality of the data, and safeguarding of information. The 10% of respondents were assessed before the actual data collection.
Statistical analysis
The data entry and analysis were done by using Epi info 7.2 version and SPSS version 20 respectively. Descriptive statistics from sociodemographic characteristics, organization factors, and technical factors were computed .this presented in the form of a table, graph, and text. We used binary logistic regression to analyze the association of independent variables with the outcome variables. Variables having statistically significant association with the outcome variable (p < 0.2), in the bi-variable analysis, were included in multivariable logistic regression analysis for controlling the effect of the confounder. Variables' significant association was determined based on adjusted odd ration (AOR), with 95% Cl and variables with (p < 0.05) were considered as determinant factors for health professional knowledge on Telemedicine.
Measurement
Knowledge
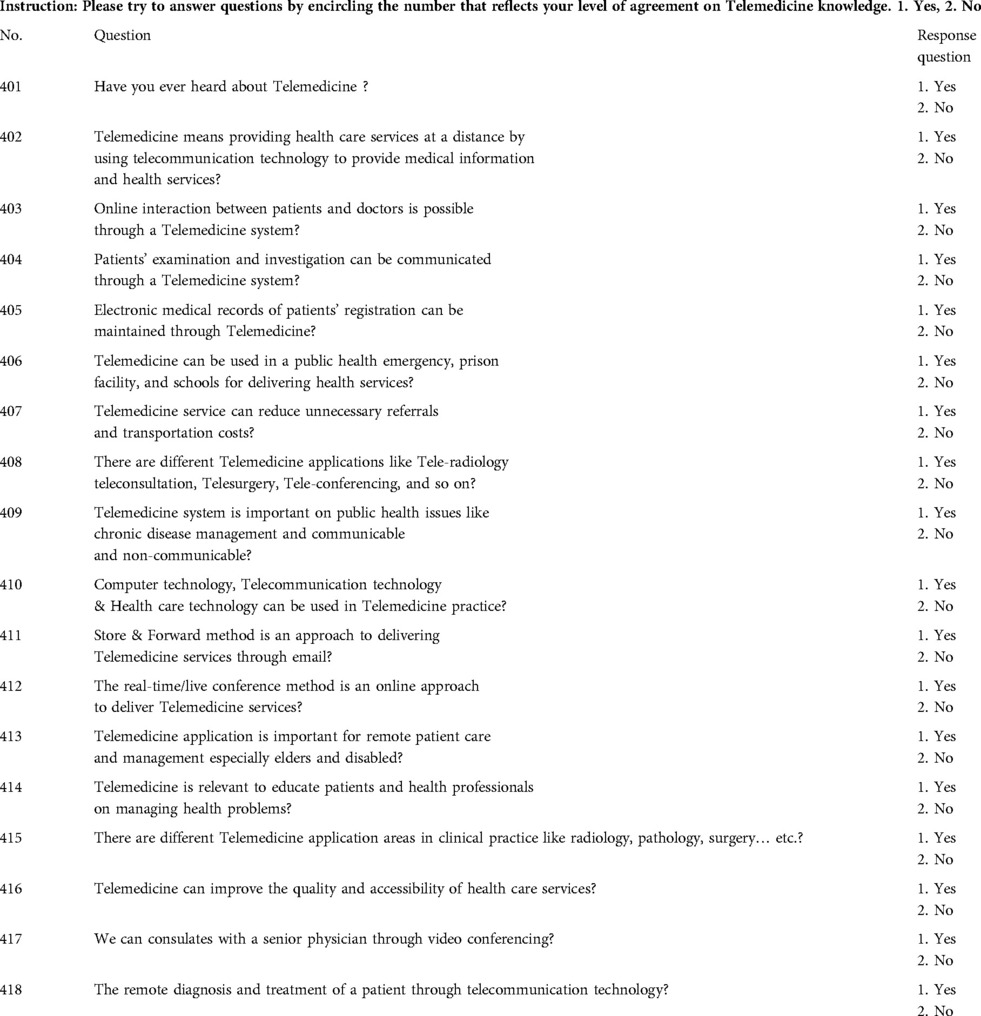
The level of knowledge of respondents about telemedicine was assessed using 18 questions. This research used the average score of 9 (50%) from the 18 questions as a cutoff point to determine the level of telemedicine knowledge. The mean knowledge score of less than nine was labeled as poor knowledge of telemedicine, and the more than average score of nine was labeled as good knowledge of telemedicine (12).
Result
Socio-demographic characteristics of study subjects
As shown in Table 1, about 423 health professionals were approached for this study, with 410 responding at a 96.9 percent response rate. More than half 226 (55.1%). of respondents were males. The majority of study participants (44.6%) were between the ages of 25 and 29 (Table 1).
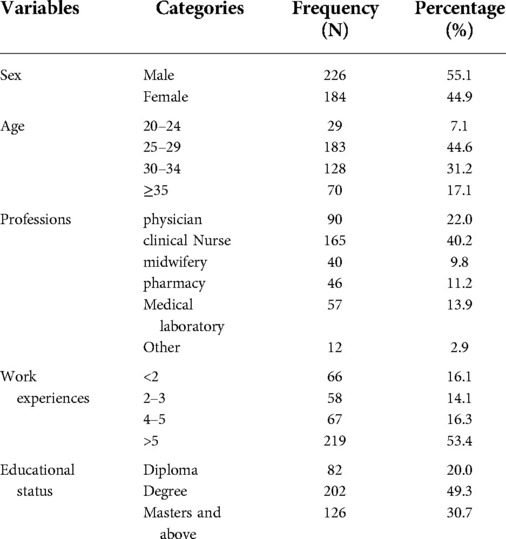
Table 1. Socio-demographic characteristics of respondents working at private hospitals limited resource settings Ethiopia 2021.
Institutional factors
Roughly 245 (59.8%) of study subjects had access to a computer at the workplace. Regarding internet connectivity workplace, nearly two-thirds of 251 (61.2%) of the study subjects have available to it (Table 2).
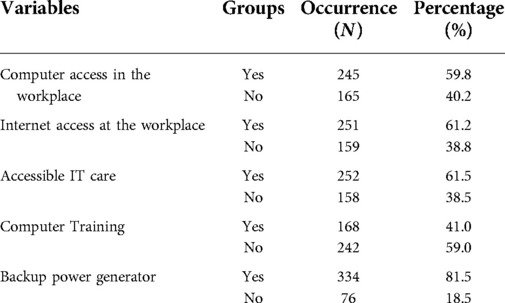
Table 2. Institutional factors respondents’ knowledge of telemedicine at private hospitals limited resource settings Ethiopia 2021.
Knowledge of study subjects on telemedicine
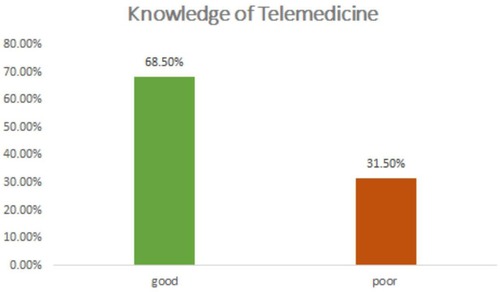
As shown in Figure 1 more than two-thirds of 281 (68.5%) of the respondents had good knowledge.
Factors affecting health professionals’ telemedicine knowledge
In Multiple logistic regression variables these as own personal laptop, internet connectivity at the workplace, computer literacy, and computer training has been associated with knowledge of Telemedicine, as shown (Table 3). Study subjects who had laptops were about 1.7 times more likely (AOR = 1.7; 95%CI: [1.1, 2.9]) to have good knowledge of Telemedicine than study participants who did not own a laptop.
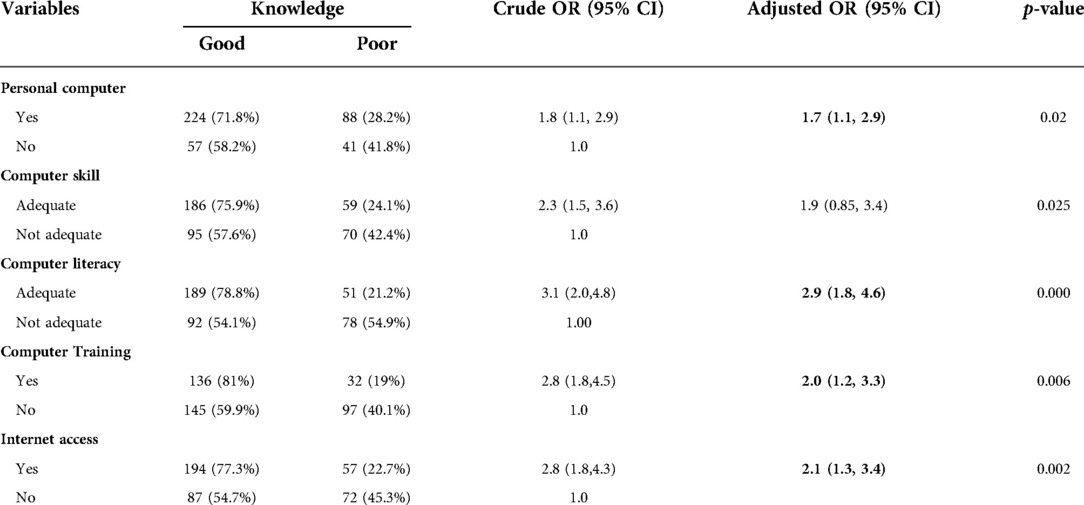
Table 3. Bivariable and multi-variable regression for determinants for telemedicine knowledge among study subjects at private hospitals north west Ethiopia 2021.
Computer literacy was found positively associated with knowledge .study subjects who had good compute literacy were 2.9 times more likely to be knowledgeable about Telemedicine than their equivalents (AOR = 2.9; % CI: [1.8, 4.6]).
Participants have received computer training were about 2.0 times more probable to be knowledgeable about Telemedicine than their equivalents (AOR = 2.0; % CI: [1.2, 3.3]).
Discussion
The primary participants in telemedicine adoption are health care providers, who are expected to be more knowledgeable than others. According to the findings of our research, respondents have a better understanding of telemedicine.
In this study, the majority of health professionals had good knowledge of telemedicine. This finding is significantly higher than that of another Ethiopian study (12).
This substantial difference might be due to sample size, study area and more than study subjects at private hospitals in this study have access to the internet and computer. In contrast, this finding is lower than studies done (17, 18). This significant difference may be due to differences in information communication infrastructure, and socio-economic differences.
We found that own personal computer was positively associated with knowledge of telemedicine. Participants who own personal computers were 1.7 times more likely to know about telemedicine compared to their counterparts. This finding is consistent with a study conducted (19).
Computer training was found significantly associated with knowledge of telemedicine. Those study subjects who took computer training were 2.0 times more likely to have knowledge of telemedicine compared with those who did not take it. The result is consistent with studies conducted on health professionals' knowledge and attitude towards telemedicine (20–22). A possible reason for this could be computer training is more likely to increase participant familiarity with using technologies. Additionally, the explanation might be training and education usually changes people's views, and upgrade knowledge levels, and perceptions. Knowing the updated technology passionate for upcoming in their institution.
Computer literacy was found positively associated with knowledge of telemedicine. In this study, those computer-literate health professionals were 2.9 times more likely knowledgeable than their counterparts. This is in line with studies done (21, 23).
The possible explanation might be knowing how to use computer technologies in day-to-day activities increase to use of advanced technologies.
Internet availability was found positively associated with knowledge of telemedicine. Health professionals having Internet availability in the workplace were 2.1more likely to have good knowledge than equivalents. This is consistent with studies done in (24–26). This might be because the internet influences access how new advanced technologies applications in the health system. Internet exposure can impact humankind's daily life.
Conclusion and recommendations
In general, nearly two-thirds of health professionals know telemedicine Variables including having a laptop, computer literacy, computer training, and internet availability at workplace were the significant factors for knowledge. These findings indicate that providing training for health professionals to lay the base for the fruitful adoption of Telemedicine systems in limited resource settings.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical clearance was obtained from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the University of Gondar College of medicine and health sciences, institute of public health. Informed consent was obtained from the study participant after describing the objective of the study, they were also informed about the benefits of the study. All methods performed in this research were done according to relevant guidelines and the Helsinki declaration.
Author contributions
SMW contributes to the conception of the study. SMW and MDT contributes to the analysis and interpretation of the data. SMW prepare and revised the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work. SMW and MDT contributes to the full write-up of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the University Of Gondar Institute Of Public Health for granting ethical clearance. Private hospitals, data collectors, and research participants
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. IMPACT E. The conceptual framework of interoperable electronic health record and ePrescribing systems. Bonn, Germany: EHR IMPACT European Commission, DG INFSO / Media (2008).
2. Kiberu VM, Scott RE, Mars M. Assessing core, e-learning, clinical and technology readiness to integrate telemedicine at public health facilities in Uganda: a health facility–based survey. BMC Health Serv Res. (2019) 19(1):1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3827-x
3. Ryu S. Telemedicine: opportunities and developments in member states: report on the second global survey on eHealth 2009 (global observatory for eHealth series, volume 2). J Healthc Inform Res. (2012) 18(2):153–5. doi: 10.4258/hir.2012.18.2.153
4. Petimani MS, Bhat NP, Preethishree P, Adake P. Knowledge, attitude, and practices of telemedicine among the health-care practitioners during COVID pandemic: a cross-sectional study. J Curr Res Sci Med. (2022) 8(1):37. doi: 10.4103/jcrsm.jcrsm_59_21
5. Al-Samarraie H, Ghazal S, Alzahrani AI, Moody L. Telemedicine in middle eastern countries: progress, barriers, and policy recommendations. Int J Med Inf. (2020) 141:104232. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104232
6. Yaghobian S, Ohannessian R, Iampetro T, Riom I, Salles N, de Bustos EM, et al. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of telemedicine education and training of French medical students and residents. J Telemed Telecare. (2022) 28(4):248–57. doi: 10.1177/1357633X20926829
7. Leu DJ Jr, Kinzer CK. The convergence of literacy instruction with networked technologies for information and communication. Read Res Q. (2000) 35(1):108–27. doi: 10.1598/RRQ.35.1.8
8. Bali S. Barriers to development of telemedicine in developing countries. Bonn, Germany: Telehealth: IntechOpen. (2018) 1:2. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.81723
9. Whitten P, Holtz B, Nguyen L. Keys to a successful and sustainable telemedicine program. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. (2010) 26(2):211–6. doi: 10.1017/S026646231000005X
10. Meher SK, Tyagi RS, Chaudhry T. Awareness and attitudes to telemedicine among doctors and patients in India. J Telemed Telecare. (2009) 15(3):139–41. doi: 10.1258/jtt.2009.003011
11. Albarrak AI, Mohammed R, Almarshoud N, Almujalli L, Aljaeed R, Altuwaijiri S, et al. Assessment of physician’s knowledge, perception and willingness of telemedicine in Riyadh region, Saudi Arabia. J Infect Public Health. (2021) 14(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2019.04.006
12. Biruk K, Abetu E. Knowledge and attitude of health professionals toward telemedicine in resource-limited settings: a cross-sectional study in north west Ethiopia. J Healthc Eng. (2018) 2018:1–2. doi: 10.1155/2018/2389268
13. Ayatollahi H, Sarabi FZP, Langarizadeh M. Clinicians’ knowledge and perception of telemedicine technology. Perspect Health Inf Manag. (2015) 12(Fall):4–5. PMC4632872
14. Ashfaq A, Memon SF, Zehra A, Barry S, Jawed H, Akhtar M, et al. Knowledge and attitude regarding telemedicine among doctors in karachi. Cureus. (2020) 12(2):3–5. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6927
15. Olok GT, Yagos WO, Ovuga E. Knowledge and attitudes of doctors towards e-health use in healthcare delivery in government and private hospitals in northern Uganda: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2015) 15(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12911-015-0129-7
16. Kifle M, Payton FC, Mbarika V, Meso P. Transfer and adoption of advanced information technology solutions in resource-poor environments: the case of telemedicine systems adoption in Ethiopia. Telemed J e-Health. (2010) 16(3):327–43. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2009.0008
17. Lanre A, Makanjuola A. Knowledge and perception of e-health and telemedicine among health professionals in LAUTECH teaching hospital; osogbo; Nigeria. Int J Health Res. (2009) 2:51–8. doi: 10.4314/ijhr.v2i1.55388
18. Alajwari HA, Alfayez A, Alsalman D, Alanezi F, Alhodaib H, Al-Rayes S, et al. Knowledge and attitude of Saudi Arabian citizens towards telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int Health. (2021) 4:7–9. doi: 10.1093/inthealth/ihab082
19. Zailani S, Gilani MS, Nikbin D, Iranmanesh M. Determinants of telemedicine acceptance in selected public hospitals in Malaysia: clinical perspective. J Med Syst. (2014) 38(9):1–12. doi: 10.1007/s10916-014-0111-4
20. Al-Khalifa KS, AlSheikh R. Teledentistry awareness among dental professionals in Saudi Arabia. PLoS One. (2020) 15(10):e0240825. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240825
21. Parvin R, Shahjahan M. Knowledge, attitude and practice on ehealth among doctors working at selected private hospitals in Dhaka, Bangladesh. J Int Soc Telemed e-Health. (2016) 4:e15(1–11). https://journals.ukzn.ac.za/index.php/JISfTeH/article/view/80
22. Yaghobian S, Ohannessian R, Iampetro T, Riom I, Salles N, de Bustos EM, et al. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of telemedicine education and training of French medical students and residents. J Telemed Telecare. (2020) 28:1357633X20926829. doi: 10.1177/1357633X20926829
23. Datta R, Singh A, Mishra P. A survey of awareness, knowledge, attitude, and skills of telemedicine among healthcare professionals in India. Med J Armed Forces India. (2021) 77:10–12. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2021.08.017
24. Alvarez-Risco A, Del-Aguila-Arcentales S, Yáñez J. Telemedicine in Peru as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic: perspective from a country with limited internet access. Am J Trop Med Hyg. (2021) 105(1):6. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.21-0255
25. Al-Moosawi K, Nayyef M. Survey study: reality check of internet and telemedicine use in Iraqi hospitals. J Int Soc Telemed e-Health. (2017) 5:e7 (1–6). https://ojstest.ukzn.ac.za/index.php/JISfTeH/article/view/190
26. Frimpong KO, Asare S, Nomah DK, Antwi-Asante DOJIJHS. Knowledge and perception of telemedicine among health professionals at the koforidua regional hospital, Ghana. Int J Healthcare Sci. (2017) 4(2):96–103. ISSN: 2348-5728
27. Yusif S, Hafeez-Baig A, Soar J. An exploratory study of the readiness of public healthcare facilities in developing countries to adopt health information technology (HIT)/e-Health: the case of Ghana. J Healthc Inform Res. (2020) 4(2):189–214. doi: 10.1007/s41666-020-00070-8
28. Afolaranmi TO, Hassan ZI, Dawar BL, Wilson BD, Zakari AI, Bello KK, et al. Knowledge of electronic medical records system among frontline health care workers in Jos University teaching hospital, Plateau State Nigeria. Int J Res Med Sci. (2020) 8(11):3837–43. doi: 10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20204867
29. Awol SM, Birhanu AY, Mekonnen ZA, Gashu KD, Shiferaw AM, Endehabtu BF, et al. Health professionals' readiness and its associated factors to implement electronic medical record system in four selected primary hospitals in Ethiopia. Adv Med Educ Pract. (2020) 11:147–54. doi: 10.2147/amep.s233368
Keywords: knowledge, telemedicine, health professionals, factors, Ethiopia
Citation: Wubante SM and Tegegne MD (2022) Health professionals knowledge of telemedicine and its associated factors working at private hospitals in resource-limited settings. Front. Digit. Health 4:976566. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2022.976566
Received: 23 June 2022; Accepted: 22 August 2022;
Published: 16 September 2022.
Edited by:
Daihai He, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Jorge Calvillo-Arbizu, Sevilla University, SpainIvan Miguel Pires, Universidade da Beira Interior, Portugal
© 2022 Wubante and Tegegne. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sisay Maru Wubante c2lzYXk0MTlAZ21haWwuY29t
Specialty Section: This article was submitted to Health Informatics, a section of the journal Frontiers in Digital Health
Abbreviations TM, telemedicine; IT, information technology; WHO, world health organization; SPSS, statistical package for social sciences
 Sisay Maru Wubante*
Sisay Maru Wubante* Masresha Derese Tegegne
Masresha Derese Tegegne