- 1Child Well-Being Research Institute, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand
- 2Faculty of Health, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand
Introduction: Early and middle childhood are times of rapid development, and critical periods for laying the foundations of life-long trajectories of socioemotional well-being. High levels of screen media use are of growing concern to parents, health professionals, and researchers, given the increasing body of research demonstrating detrimental impacts of excessive screen use in young children. One particular consequence is the risk that children encounter online content or experiences that are upsetting or distressing, including exposure to inappropriate or adult content, cyberbullying, and interactions with strangers that they don't know.
Methods: This research examined experiences of online harm reported in a sample of 8-year-old children, with a focus on identifying risk factors and psychosocial correlates of online harm. Data for this study were collected from children and their mothers as part of the prospective longitudinal Growing Up in New Zealand (GUiNZ) study (n = 4,920 children with data at age 8). Children were assessed at 4.5-years-old and 8-years-old.
Results: The findings of this research indicate that approximately a quarter of New Zealand children have experienced online harm (that is, have encountered online content that worried, upset, or bothered them) by the age of 8. Our analysis indicates that children with behavioral difficulties are at greater risk of online harm, as are children with more personal devices. Experiences of online harm were found to be negatively associated with child self-worth and positively associated with depressive symptoms.
Discussion: Findings highlighting the critical importance of considering online harm as a contributing factor to child and youth well-being and mental health in our media-saturated world. Our results also point to practical solutions for parents, such as limiting the number of personal media devices that children have in early and middle childhood.
Introduction
The internet has become increasingly integrated into our daily life, with approximately 95% of New Zealanders using it at home daily (InternetNZ, 2022; Pacheco and Melhuish, 2020a). While offering various affordances such as access to information, educational resources, entertainment, and social connections, it is also a conducive environment for online risks. These risks include exposure to inappropriate and/or explicit content, cyberbullying, engaging with developmentally inappropriate materials or games, and inappropriate marketing and advertising. However, research examining these online risks have disproportionately focused on school-age children and adolescents, whereas exposure to online risks likely occurs much earlier in life with young children being particularly vulnerable. Recently concerns about children's access and exposure to inappropriate content have surged (see InternetNZ, 2022; Stoilova et al., 2021), yet there remains a paucity of research examining the frequency and impact of young children's exposure to online risks globally and in New Zealand. This paper aims to address this gap by exploring online risk and online harm when children are 8 years old.
Online risk and online harm
Online risks are described as the hazards or dangers individuals encounter while online. In contrast, online harm is the consequence or negative impact that results from exposure to these online risks (Livingstone, 2013). The spectrum of online risks is broad, with individuals either actively seeking out such risks or inadvertently stumbling upon them through algorithmic and socio-technical designs inherent in online platforms. Online risks have been categorized in terms of content (e.g., viewing inappropriate or illegal material), contact (e.g., unwanted, harassing, or harmful communication), and conduct (e.g., revealing or misusing personal information or illegally downloading content). New Zealand children aged 9–17 specifically reported being contacted by a stranger, having either seen or received media that made them feel uncomfortable, having felt under pressure to send photos or other information about themselves, and having accidentally spent money online that they did not mean to spend (Pacheco and Melhuish, 2020a).
Online contexts, including chat rooms, video games, and social media, provide an environment conducive to perpetrating and experiencing harm given the anonymity and lack of regulation often inherent to these applications. Most online platforms are not child-centered by default, rather they are based on industry incentives that prioritize engagement and advertising revenue at the expense of children's safety and privacy (Radesky and Hiniker, 2022). For example, Papadamou et al. (2020) found an alarming number of disturbing and inappropriate videos that were recommended when browsing preschooler-oriented content on YouTube. The monetization opportunities on YouTube and other platforms as well as the advent of algorithmic content creation are likely contributors to this issue (Papadamou et al., 2020). Given there may be less parental monitoring of children's online activities compared to offline activities (e.g., Ellonen et al., 2021; GerŽičáková et al., 2023), understanding the risks and harms associated with children's online activities is paramount.
Once exposed to online risks, the factors influencing an individual's vulnerability to harmful consequences remain unclear. Researchers have argued that children who are vulnerable to offline risks are also more likely to be vulnerable to exposure to online risks (Livingstone, 2013). Similarly, factors that contribute to vulnerability and protection offline may also be relevant online. Given that internet use begins at an early age, and that young children's internet use predominately occurs in the family home (Pacheco and Melhuish, 2020a), this study investigated the role of child characteristics, parenting styles and behaviors, and digital media use factors related to young children's susceptible to exposure to online risks and, consequently, online harms—particularly over time.
While previous research has tended to focus on exposure to online risks and the psychosocial outcomes associated with this exposure, in this study we move to examining online harm and the psychosocial consequences of this harm. It is important to note that exposure to online risks is a precursor to online harm, not a determining factor. Not every exposure to online risk will lead to harm. As described above, further research is required to identify the moderating factors determining whether risk eventuates to harm in an online context.
Child characteristics
Research led by the European Kids Online network of over 25,000 children aged 9–16 and their parent found that 41% of children had been exposed to an online risk with exposure increasing considerably with age (Livingstone et al., 2011). However, with increasing numbers of younger children watching videos and playing games online (Pacheco and Melhuish, 2020a), they are not immune from online risks. Exposure to online risk has also been shown to differ for boys and girls. In a cross-national study of young people aged 15–30 in the United States and Finland, Keipi et al. (2015) found that boys were more likely to report viewing online content related to self-injury and suicide, whereas girls were more likely to report viewing online content related to pro-eating disorders. Similar gender differences in exposure to online risks have been identified in younger people (aged 11–16) across 25 European countries (Almenara et al., 2016). With the exception of privacy risks, Livingstone and Helsper (2008) found that boys aged 12–17 were significantly more likely to encounter all types of online risks compared to same age girls. How the associations between child age, gender and exposure to online risk manifest during early childhood when young children are first exploring their online worlds, is unknown.
Child temperament, including emotional and behavioral traits have been shown to be related to children's use of media (Coyne et al., 2017; Radesky et al., 2016; Thompson et al., 2013; Zimmerman and Christakis, 2007). Increased socio-emotional difficulties in children such as frequent crying, irritability, and behavioral difficulties have led some parents to use media to calm their child down (Radesky et al., 2016) or cope with and control their child (Elias and Sulkin, 2019; Tang et al., 2018). During this process of regulation, children may not be supervised, with the parent opting to give the child (and themselves) space to regulate from a heightened and intense emotional experience. Inadvertently, this unsupervised time online may contribute to vulnerability to online risks, to the extent that children use this unsupervised time to engage in risky online behavior. Further, increased autonomy and boundary-testing related to children's temperament during early childhood may also influence the types of online experiences and activities children partake in. Indeed, some children have stronger risk-taking propensity which may be seen in both online and offline environments (Livingstone, 2013). However, we are yet to understand how emotional and behavioral traits of young children relate to their exposure to online risks, and consequently, online harm. Further investigation of these associations will improve our understanding of some of the early individual factors contributing to young children's vulnerability to online risks.
Parenting styles and behaviors
As the majority of young children's media use occurs in the home, parents are the gatekeepers of children's media use. With greater attention and concern being shown for children's access and exposure to inappropriate content (InternetNZ, 2022; Stoilova et al., 2021), parents may seek out ways to regulate their child's online activities. Media-specific parenting, such as parental mediation of media represent various strategies that parents use to maximize the positive benefits and reduce vulnerability to online risk and harm (Livingstone et al., 2017). Mediation strategies for the internet specifically include active co-use (e.g., talking and providing guidance to children about online activities, in real time in front of the computer or in the same room), technical restrictions (e.g., filtering, monitoring, or blocking risky online activities or material), interaction restrictions (e.g., setting rules restricting or banning certain peer-peer activities), and parental monitoring (e.g., covert or overt checking of children's online activity) (Livingstone and Helsper, 2008). Theoretically, parental mediation should reduce young people's exposure to online risks, however, research examining these associations in middle childhood and adolescence has been mixed. Some researchers report that providing a rationale for screen time and content restrictions reduced 10–14-year-olds exposure to online media violence (e.g., Fikkers et al., 2017), whereas others have found no association between commonly practiced mediation strategies such active co-use and 12–17 year olds' exposure to online risks (e.g., Livingstone and Helsper, 2008). These mixed findings may be explained by parents' involvement in their child's activities. More specifically, parents typically use more parental mediation strategies for younger children (Livingstone and Helsper, 2008), suggesting greater involvement in their online activities, thereby reducing exposure to online risks. Conversely, low parental involvement may heighten a child's vulnerability to online risks. To our knowledge, no studies have investigated parental involvement in children's activities alongside media-specific and general parenting behaviors as potential predictors of children's exposure to online harm.
General parenting styles, characterized by dimensions of parental responsiveness, warmth, demandingness, and control (Baumrind, 1991) have been studied in the context of children's and parent's media-related behaviors. Several studies have shown that primary school age children from permissive families (high warmth, low demand) were >5 times more likely to watch >4 h of television per day (Jago et al., 2011) and have the highest internet usage (Valcke et al., 2010), whereas older (10–11 year olds), primary school age, and younger (5 year olds) children from authoritarian (low warmth, high demand) and authoritative (high warmth, high demand) families had lower levels of screen exposure (Jago et al., 2011; Veldhuis et al., 2014) and internet use (Valcke et al., 2010). However, these associations between general parenting styles and children's vulnerability to online risks are only assumed through increases or decreases in time spent online. It is well recognized in the literature that focusing on screen time, without including variables related to the quality of screen content, seriously constrains our understanding of the types of activities that are more or less likely to contribute to short- and long-term online harm (see Stoilova et al., 2021 for a review). Notably, parent-child interactions characterized by warmth and open communication about internet use and content may help parents to scaffold and teach their child about e-safety, reducing potential exposure to online risks (Cho and Cheon, 2005).
Family context
Beyond parenting styles and behaviors, other aspects of children's home environment may influence their exposure to online harm. In this research, we examined socioeconomic status (SES) and the presence of older siblings as predictors of harm. While there is a relation between SES and adverse life events generally, research is mixed on whether SES influences the likelihood of online harm. Skogen et al. (2022) found that low SES was associated with greater frequency of negative experiences on social media, including negative acts, exclusion, and unwanted attention from others, within high school students. However, other studies have found no association between SES and cybervictimization (Rodríguez-Enríquez et al., 2019).
Research on the influence of siblings on exposure to online risks and harm is also still in its infancy. Despite a body of research examining peer influences on online risk (e.g., Festl, 2021; Mascheroni et al., 2015), research has yet to determine the influence of siblings. Ólafsson et al. (2018) found that while the presence of older siblings increases the range and number of online activities pursues by younger siblings, there was no increase in risk for harm. However, from a social learning perspective, younger siblings may observe and model the online behaviors of their older siblings, potentially imitating risky online behaviors. This modeling could make younger siblings more vulnerable to online harm. Given the lack of research on the presence of older siblings in relation to experiences of online harm, this was investigated as a potential predictor of online harm in the present research.
Digital media use factors
With greater accessibility and affordability of mobile technologies, personal ownership of devices is occurring earlier in childhood. Recent evidence from New Zealand's Netsafe suggests that cellphone ownership increases with children's age; however, less is known about ownership of other mobile devices such as tablets. Rideout and Robb (2020) reported that 48% of 0–8-year-olds in the United States own their own mobile device (either a tablet, smartphone, iPod touch or similar). The type of device owned by a child may contribute to exposure to online risks. For instance, gaming devices are typically an activity that children do independently of their parents. These devices may be set up in the child's room, or in a separate area of the living space, where regular monitoring is difficult or infrequent. Conversely, cellphones and tablets used by the family (or owned by the parent) may be restricted to communal areas of the house. Research has shown that children aged 8 to 12 were more likely to engage with screen for longer periods of time if they had a device set up in their bedroom (Lee et al., 2018), potentially putting them at higher risk for being exposed to risks online.
Guidelines published by child health authorities, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, advocate restricting screen use to video chatting for children until 18 to 24 months of age; limiting children aged 2–5 years to an hour or less of screen time per day; and emphasizing parental regulation and monitoring of young children's media use (Hill et al., 2016). However, a recent meta-analysis of 95 studies and screen time data for 89,163 children revealed that adherence to these recommendations is low, with only 1 in 4 children under 2 years and 1 in 3 children between 2 and 5 years following suggested guidelines (McArthur et al., 2022). Increased time spent online affords young children the opportunity to develop digital skills and reap the benefits of the internet. However, concurrently, excessive time spent online increases the potential for encountering online risks and harm. While various factors related to digital media use have been documented, there remains limited understanding of which specific factors contribute to young children's susceptibility to online risks and harm.
Consequences of experiencing online risk
With young children's media use continually increasing, the propensity for exposure to online risk is also ever increasing. Recent research (Pacheco and Melhuish, 2020a; Stoilova et al., 2021) has called for more research to examine online risks in young children. As noted earlier, with online risks comes the potential for online harm. A recent rapid review of the literature on online risks and wellbeing demonstrates that considerable attention has been given to harmful effects of cyberbullying, online harassment, and sexual online activities on the psychosocial outcomes of school-age children and adolescents (see Stoilova et al., 2021 for a review). The findings typically demonstrate that online risks are differentially associated with psychosocial outcomes. More generally, young people aged 15–30 years across three European countries and the United States described feeling lower levels of happiness after exposure to negative content online (Oksanen et al., 2016). Further, research conducted with adolescents aged 10–17 years indicated that 25% described feeling upset or extremely upset after exposure to harmful content online while 19% felt stressed in the days following exposure to online risks. While our understanding of the associations between online risk and psychosocial outcomes is expanding, it is still limited to a focus on school-age and adolescent populations; very little is known about the potential long-term psychosocial outcomes associated with experiencing online harm for younger children.
The current research
In this research we go beyond measuring online risks, such as exposure to adult content, to measure online harm, the distress caused by exposure to online risks (Livingstone, 2013). The vast majority of previous research on online risks and online harm has focused on teenagers and adolescents (from age 9 onwards; e.g., Machimbarrena et al., 2018; Smahel et al., 2020). Given the rapidly growing prevalence of screen media use in younger children, including internet use, we aimed to understand how many children experience online harm by the age of 8. Using a large, prospective sample of children, we examined vulnerability and protective factors for experiencing online harm by age 8, spanning aspects of child characteristics, parenting styles and behaviors, and digital media use factors. We also examined the psychosocial correlates of experiencing online harm, including depressive symptoms, emotional symptoms, and self-worth. Our specific research aims were as follows:
1. To understand the frequency with which children have had experiences on the internet that worried or upset them (online harm) by age 8.
2. To determine vulnerability and protective factors for children experiencing online harm.
3. To determine concurrent associations at age 8 of online harm with depressive symptoms, emotional adjustment, and self-worth.
Materials and methods
Participants
The data used in this analysis came from the Growing Up in New Zealand (GUiNZ) study, a prospective longitudinal study following more than 6,000 New Zealand children since before birth. A total of 6,822 pregnant women with an estimated delivery date between April 2009 and March 2010 were recruited from the Auckland, Counties Manukau, and Waikato District Health Board regions of New Zealand. See Morton et al. (2010, 2013, 2015) for a detailed description of the study's design, conceptual framework and recruitment procedures. In these analyses, we use data collected at two assessment points, when children were aged 4.5-years-old and 8-years-old. Data was collected using face-to-face interviews with mothers at the 4.5-year assessment point, and through face-to-face interviews with mothers and children at the 8-year assessment point. At both time points Computer Assisted Personal Interviews (CAPI) were conducted by trained interviewers, usually in the child's home.
Measures
Child-reported measures
Online harm (age 8)
At age 8, children were asked to self-report on harmful internet experiences. They were asked “What have you come across on the internet that has worried, bothered, or upset you, or that you don't like seeing?” Response options were:
• Nothing,
• Site, games, or images that are meant for grownups,
• Bullying (of you or others),
• Advertising on websites,
• Someone I don't know/or shouldn't talk to,
• Peer pressure to watch particular content, play certain games, follow particular sites or YouTubers,
• Buying something by mistake,
• Don't know.
Children could select as many types of online harm as was applicable.
Child depressive symptoms (age 8)
Child depressive symptoms at age 8 were measured with the child-administered Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CESD-10; Fendrich et al., 1990; Andresen et al., 1994). This scale includes 10 items that ask children to report on how much they “felt this way during the past week”. Example items are “I felt down and unhappy”, “It was hard to get started doing things”, and “I felt happy” (reverse-coded). All items were rated on a 4-point scale from Not at all (0) to A lot (3). A total score out of 30 was calculated by summing across the 10 items (after reverse coding 2 items). Cronbach's alpha across the 10 items in the present sample was 0.69.
Child self-worth (age 8)
Child self-worth at age 8 was assessed using the child-reported global self-worth subscale of the Self-Perception Profile for Children (SPPC; Harter, 2012). This subscale has 6 items that are each scored a value between 1 and 4. All scale items are phrased as follows: “Some kids like the kind of person they are BUT other kids often wish they were someone else.” Children select which option is most like them, and then indicate whether the statement is “Really true for me” or “Sort of true for me”. A self-worth score was calculated by summing the 6 items. Reliability and validity of the scale have been demonstrated by Harter (1999), with an internal reliability of 0.8.
Personal media devices (age 8)
At the 8-year assessment, children were asked to report whether or not they had their own personal device (yes or no). Those who answered yes were then asked to indicate whether or not they owned each of the following types of devices: a tablet (e.g., iPad), a desktop computer or laptop, a TV, a smartphone (e.g., an iPhone or a Samsung Galaxy), a gaming console (e.g., an Xbox, PSP, or Playstation), an iPod, iPod touch, or MP3 player, a kindle or other eReader, a Smart watch, a virtual reality headset, a camera (also includes digital and GoPro), and other. A total score was created to indicate the total number of personal devices a child owned by summing across devices, with scores of 0 for children who indicated they did not own a personal device.
Parent-reported measures
Child emotional symptoms (age 4.5)
Child emotional symptoms at age 4.5 were measured using the Emotional Symptoms subscale of the parent-report version of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ; Goodman, 1997). This subscale includes the five items of: “Often complains of headaches”, “Has many worries”, “Often unhappy, downhearted”, “Nervous or clingy in new situations”, and “Many fears, easily scared”. All items are rated by parents as Not true (0), Somewhat true (1), or Certainly true (2). A total score was calculated as the sum of these 5 items. These 5 items had a Cronbach's alpha of 0.65 in the present sample.
Child behavioral difficulties (age 4.5)
Child behavioral adjustment at age 4.5 was measured using total scores on the SDQ (described above), reflecting overall behavioral difficulties across the domains of peer problems, conduct problems, hyperactivity-inattentiveness, emotional symptoms and (low) prosocial behavior. Thus, note that this measure includes the emotional symptoms subscale described above. All items are rated by parents as Not true (0), Somewhat true (1), or Certainly true (2). A total score is typically calculated as the sum of the 25 items (5 items per subscale). In the present sample, an item from the conduct problems subscale was mistakenly omitted from the questionnaire. To correct for this error, the 4 conduct problems items have been re-scaled to reflect a score out of 10, by multiplying the mean of individual item scores by 5. This results in a total behavioral difficulties score out of 50 (maximum of 2 points per item) despite only including 24 items in the measurement. For more information see the GUiNZ Data User Guide (Growing Up in New Zealand, 2023). Previous research has demonstrated the and predictive validity of the SDQ (Stone et al., 2010, 2015). Cronbach's alpha for the 24 items used in the present sample was 0.68.
Electronic media use (ages 4.5 and 8)
Parents reported on the amount of time children spent per day using screen media outside of school time. We focused on electronic media use (and did not include watching television or movies), given this is when children would be accessing the internet. At age 4.5, mothers were asked to report how much time their child spent on a typical weekday “Using electronic media eg computer or laptop, including children's computer systems such as Leapfrog, iPad, tablets, smart phones and any electronic gaming devices” Parents reported an amount of time in hours and minutes per day.
At age 8, mothers were asked to report on a normal weekday how much time their child “Spent time doing activities and tasks, e.g., homework, playing games, or sending messages, on any screen-based device including computers, laptops, tablets, smartphones, or gaming devices”. Parents reported an amount of time in hours and minutes per day.
Given that time duration at both ages 4.5 and 8 were positively skewed (age 4.5: skewness = 2.64, kurtosis = 9.41; age 8: skewness = 2.48, kurtosis = 6.83), both variables were divided into quartiles for analysis. At age 4.5, children were assigned to quartiles using the following values (equating to duration of daily electronic media use in hours): Q1 = 0.08, Q2 = 0.50, and Q3 = 1.00. At age 8, children were assigned to quartiles using the following values: Q1 = 0.33, Q2 = 1.00, and Q3 = 2.00. Thus, final scores on both electronic media use variables ranged from 1 to 4.
Parenting style (age 4.5)
Parenting style was assessed when children were 4.5-years-old using a shortened version of the Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire (PSDQ; Robinson et al., 1995, 2001). A total of 21 items assessed the three subscales of Authoritative parenting (8 items), Authoritarian parenting (8 items), and Permissive parenting (5 items). Authoritarian items reflect a style of parenting guided by reasoning and responsiveness to the child's thoughts and needs. Authoritarian items reflect a style of parenting guided by punitive punishment, and permissive items reflect a lack of discipline.
Each of the 21 items was rated from 1 (Never) to 5 (Always). The three subscale scores were computed by taking the mean of the items making up each of authoritarian, authoritative, and permissive parenting. The PSDQ is used worldwide for measuring parenting style and the reliability and validity of the scale, including the shortened version, have been demonstrated (Robinson et al., 2001; Oliveira et al., 2018). Cronbach's alpha for the three subscales was as follows: Authoritative α = 0.82, Authoritarian α = 0.78, and Permissive α = 0.60.
Parental involvement (age 8)
At the 8-year assessment, parental involvement was assessed using 11 items that asked mothers to report how often they engaged in certain activities with their child. Items included reading books to/with their child, getting the child ready for school, baking or cooking together, and talking about their child's feelings or issues, or comforting them. These items were rated on a 5-point scale of: Never/almost never (1), Once a week (2), Several times a week (3), Once a day (4), or Several times a day (5). The 11 items had a Cronbach's alpha of 0.72. A total score of parental involvement was calculated as the mean of the 11 items.
Digital parenting (age 8)
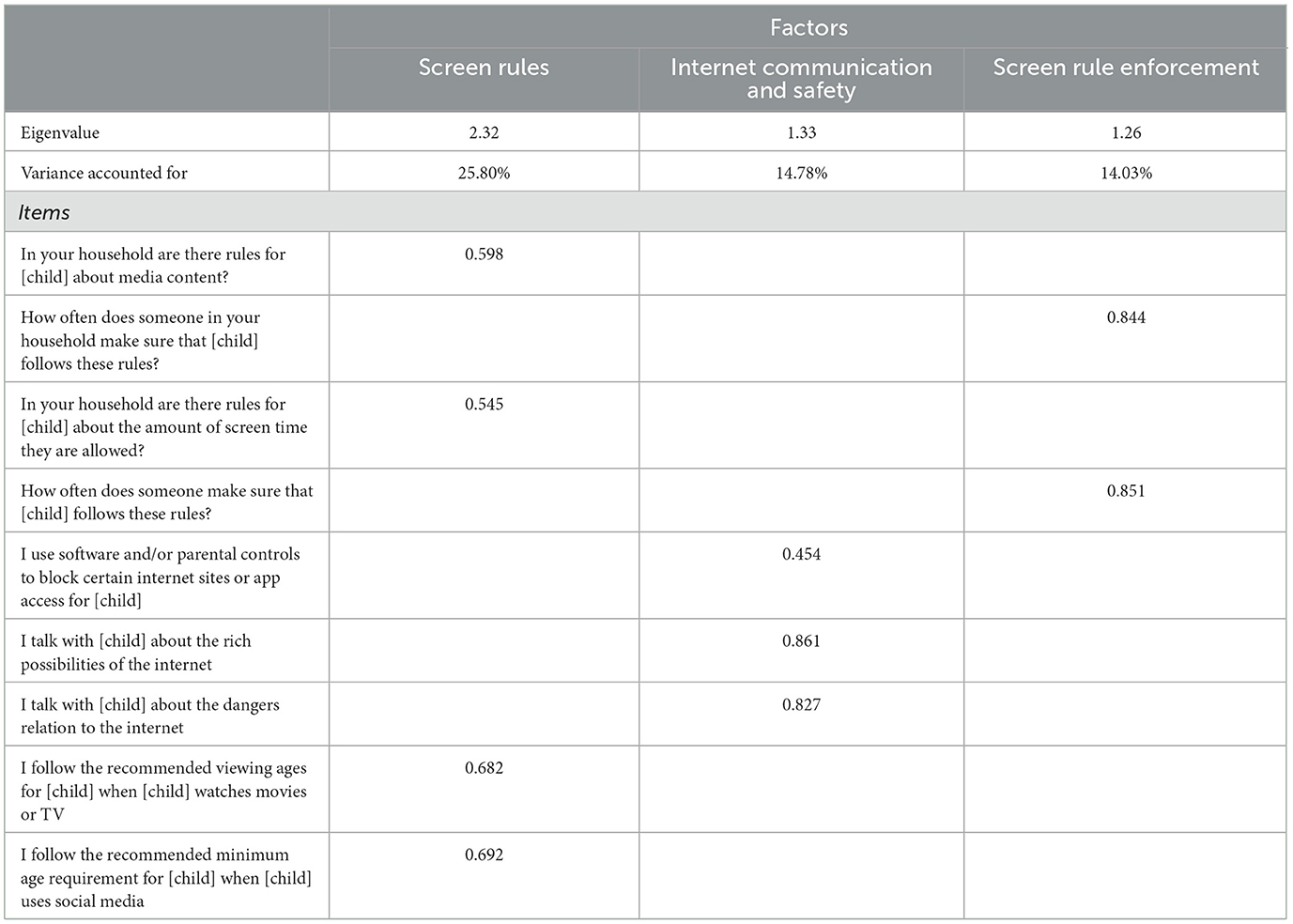
Mothers reported on the extent to which rules around media use were used in the household at the 8-year assessment. Nine items were used to assess the existence of rules about media content and screen time, the extent to which these rules were enforced, use of parental control settings, adherence to recommended age requirements for media content, and the frequency with which parents talked to their child about the dangers and the possibilities associated with internet usage. Five of these items were taken from the Internet Parenting Style Instrument (IPSI; Valcke et al., 2010; Álvarez et al., 2014). These items were rated on a 5-point scale either from “Never/almost never” to “Always/almost always” or from “Never” to “All of the time” depending on the specific item. A principal components analysis was used identify the factor structure of the nine items. Examination of the rotated factor loadings produced using Quartimax rotation indicated three factors with eigenvalues >1, accounting for a combined 54.6% of variance in the items. Table 1 provides the items loading on each of the three factors identified (Screen Rules, Screen Rule Enforcement, and Communication about Internet) along with factor loadings. For ease of interpretation, only the highest factor loading is presented, identifying the factor each item loads to. Factor scores on each of the three factors (each with mean of 0, SD of 1) were used for analysis.
Demographic characteristics
Finally, three demographic characteristics were obtained from the GUiNZ data:
• child gender, as reported by parents when the child was 9-months old,
• the presence of older siblings in the household, as identified at the 8-year assessment point, and
• household income, reported by mothers at the 4.5-year assessment point and classified into seven categories ranging from < $20,000 to >$150,000.
Results
Experiences of online harm
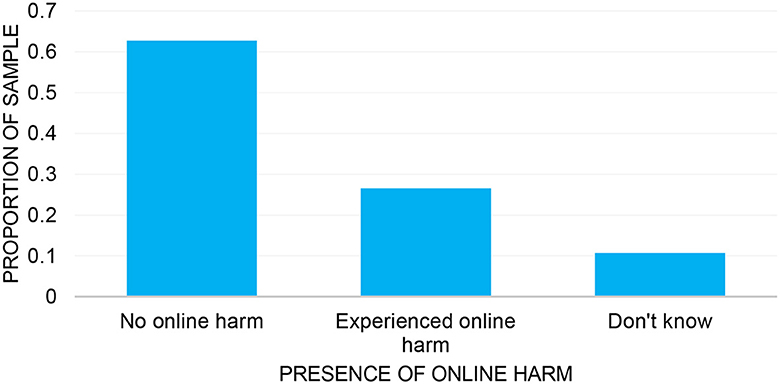
Data was available for 4,920 children who had completed the questions on online harm at age 8. Within this sample, 26.6% of children (n = 1,307) indicated they had experienced at least one type of online harm, while 62.7% (n = 3,086) indicated no online harm. The remaining 10.7% of children (n = 527) had responded with “Don't Know” when asked whether they had encountered anything on the internet that worried, bothered or upset them (see Figure 1).
Figure 2 provides the frequencies of each type of online harm enquired about, as a proportion of the total sample. The most common type of experience that worried or upset children was encountering sites, games or images meant for grownups (reported by 12.6% of children). Roughly 5% of the sample reported being worried or upset by each of: buying something by mistake, advertising on websites, and bullying. Peer pressure was the least common form of online harm that was enquired about.
There were 314 children (6.4% of the sample) who reported being worried or upset by more than one type of online harm.
Vulnerability and protective factors for online harm
There are a number of child and family factors that may increase or decrease risk of experiencing online harm. Based on existing literature and theory, we examined the following set of child and family predictors: child gender, presence of older sibling(s), household income, parenting style (age 4.5), daily time spent using electronic media (ages 4.5 and 8), child behavioral difficulties (age 4.5), parental involvement (age 8), the child's number of personal devices (age 8), and three variables relating to digital parenting—screen rules, screen rule enforcement, and internet communication and safety (all assessed at age 8).
For these analyses, we examined online harm collapsed across all forms. We compared those who have and have not been worried/upset by negative internet experiences, and we have excluded “Don't Know” responses from analysis. This resulted in a sample of 4,393 children who have (29.8%) and who have not (70.2%) been worried or upset by at least type of online harm.
Table 2 provides means (SDs) or percentages and statistical tests for each of the vulnerability and protective factors based on presence or absence of online harm experiences at age 8. Chi-square tests were used for categorical predictors and independent samples t-tests were used for continuous predictors. Hedges' g effect size was used to examine the strength of association for continuous variables and the Phi statistic (ϕ) was used for categorical outcomes. For Hedges' g, which is similar to Cohen's d but adjusted for unequal group sizes, effect sizes of 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8 are considered to be small, medium, and large, respectively (Cohen, 1988, 1992). For the ϕ effect size, values of 0.1, 0.3, and 0.5 are considered small, medium, and large effects, respectively (Cohen, 1988).
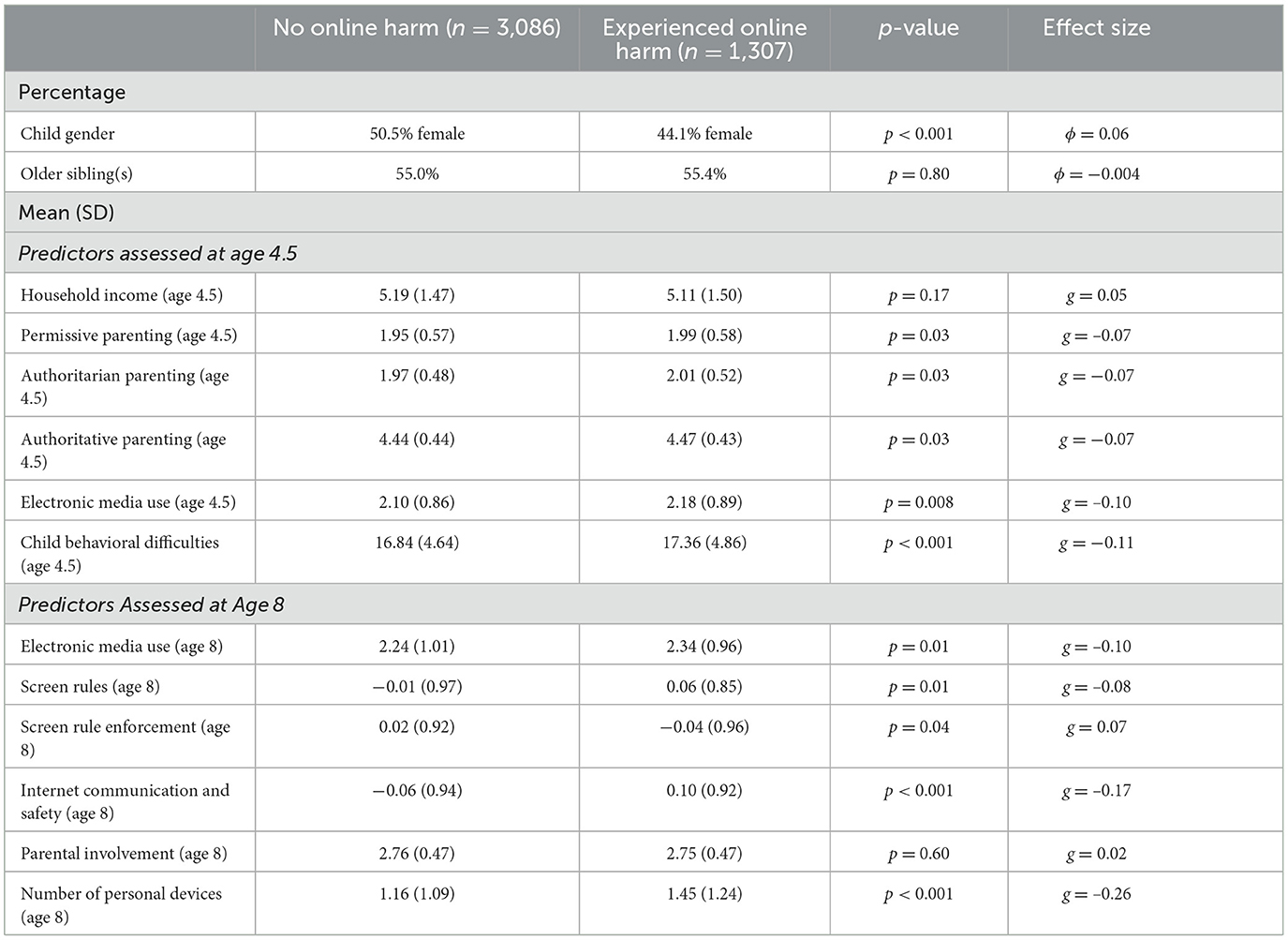
Table 2. Comparison of child and family predictors between children with and without experiences of online harm.
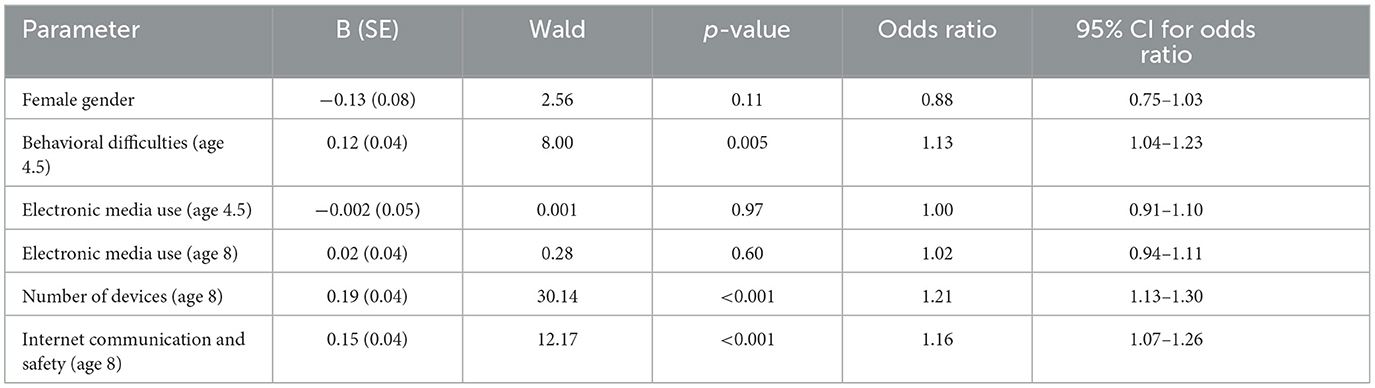
We next used a logistic regression to predict the experience of online harm by age 8 from the predictors simultaneously. For this analysis, we included any predictors in Table 2 with effect sizes of ϕ > 0.05 or g > 0.10, as our threshold for a meaningful effect size. Thus, our logistic regression included the predictors of child gender, behavioral difficulties at age 4.5, electronic media use at ages 4.5 and 8, internet communication and safety at age 8, and the number of personal devices at age 8. For ease of interpretation, SDQ behavioral difficulties were standardized to a mean of 0 (SD = 1) prior to inclusion in the logistic model. The overall logistic model was significant [ = 71.38, p < 0.001; Nagelkerke R2 = 0.03]. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test was not significant [ = 8.21, p = 0.41], indicating an acceptable model fit. Table 3 presents the results for each parameter in the model.
Once including the predictors simultaneously, the predictors remaining significant were child behavioral difficulties, internet communication and safety, and the child's number of personal devices. As indicated by the odds ratios in Table 3, an increase of one standard deviation in behavioral difficulties corresponded with a 13% increase in the odds of experiencing online harm. Notably, every additional personal device a child had resulted in a 21% increase in the odds of experiencing online harm. Once accounting for all other variables, there was no longer a significant predictive effect of gender or the amount of electronic media use (neither longitudinally nor concurrently). Counterintuitively, our results indicate that higher levels of internet communication and safety in the home (as reported by parents) are associated with increased odds of online harm, which may reflect an effect in the opposite direction, as discussed further in the Discussion section.
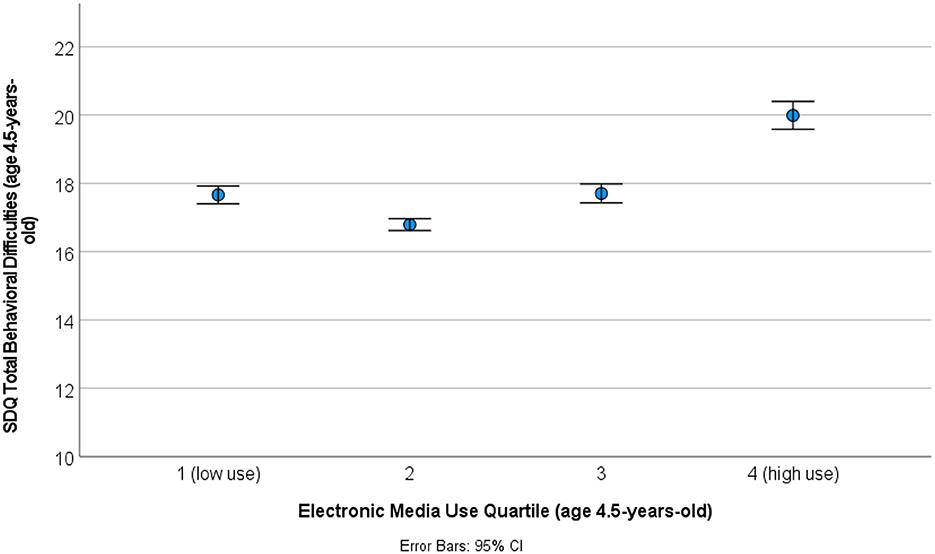
The fact that gender and extent of electronic media use were not significant in the final model is due to the shared variance amongst predictors. For example, children in the highest quartile of electronic media use at age 4.5-years-old scored higher in behavioral difficulties at the same age than the rest of the sample (see Figure 3).
Personal devices
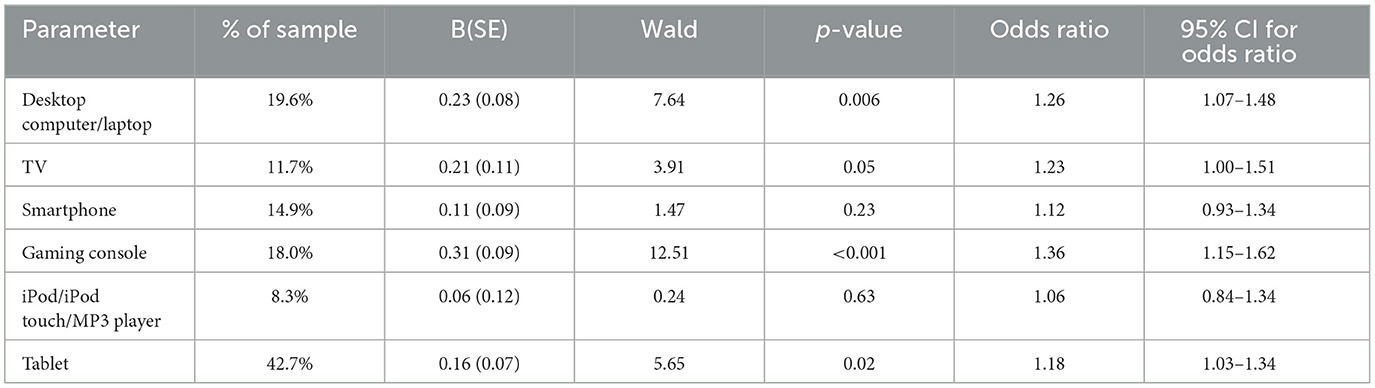
Given the results of the above analysis, demonstrating a strong association between the number of personal devices and online harm, a post-hoc analysis was undertaken examining individual types of personal devices. We ran a logistic regression predicting experience of online harm from indicator variables for all types of personal devices occurring with frequencies >5% of the sample. These were: a desktop computer or laptop, a TV, a smartphone, a gaming console (e.g., Xbox, Playstation), an iPod/iPod touch/MP3 player, and a tablet (e.g., an iPad).
The overall logistic model was significant [ = 48.18, p < 0.001; Nagelkerke R2 = 0.02]. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test was not significant [ = 4.16, p =0.43], indicating an acceptable model fit. Table 4 presents the results for each parameter in the model.
The results of this analysis indicate that the odds of online harm are significantly increased when children have the personal devices of desktop computers or laptops, TVs, gaming consoles, and tablets. The largest increase in risk was observed for gaming consoles. In contrast, there was no significant impact on online harm risk from the personal devices of smartphones and music players.
Associations between online harm and psychosocial adjustment
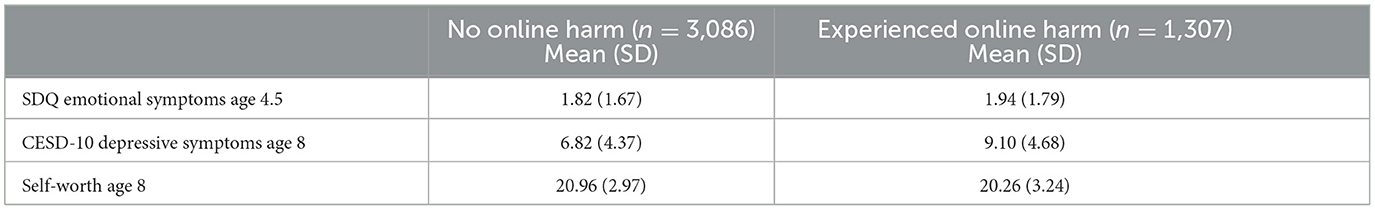
Our final set of analyses compared psychosocial adjustment between children who had experienced online harm and those who had not. Our dependent variables were child depressive symptoms assessed with the CESD-10 and child-reported self-worth. Table 5 provides the means and standard deviations for child-reported depressive symptoms and self-worth at age 8 and parent-reported emotional symptoms at age 4.5 (our control variable) based on the experience of online harm.
We used a multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA) to predict both outcome variables at age 8 from the presence vs. absence of online harm, while controlling for earlier emotional adjustment at age 4.5 and gender.1 Earlier emotional adjustment at age 4.5 was assessed with the SDQ emotional symptoms subscale. We also examined the interaction between online harm and gender in predicting emotional outcomes.
The overall multivariate tests indicated a significant effect of both earlier emotional adjustment at age 4.5 [F(2, 4324) = 8.29, p < 0.001; =0.004] and online harm [F(2, 4324) = 116.62, p < 0.001; = 0.05]. There was not a significant effect of either gender or the interaction of gender with online harm (p's > 0.07, both = 0.001).
When examining the effects for each dependent variable, it was seen that earlier emotional adjustment was a significant predictor of both outcomes (F's > 7.92, p's < 0.006). Further, experiencing online harm was a significant predictor of child-reported depressive symptoms, with a medium sized effect (F(1, 4325) = 232.92, p < 0.001; = 0.05), and child-reported self-worth, with a small effect size (F(1, 4325) = 43.36, p < 0.001; = 0.01). Figure 4 provides the adjusted mean depressive symptoms (after controlling for earlier emotional adjustment) based on the presence or absence of online harm. Children who had experienced online harm scored higher on self-reported depressive symptoms (M = 9.02, SD = 4.60) than children who had not experienced online harm (M = 6.73, SD = 4.34).
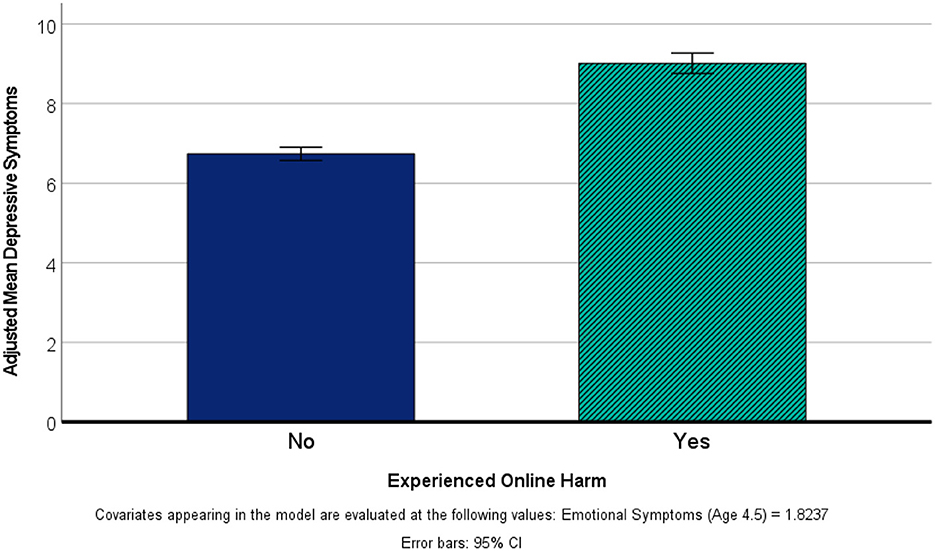
Figure 4. Depressive symptoms based on experience of online harm, with adjustment for earlier emotional symptoms.
Discussion
Given the rapidly growing presence of digital media in the lives of children and youth, it is critically important to understand the potential risks of this media use and to identify vulnerability and protective factors for those risks. In this research, we examined reports of online harm at age 8 and aimed to determine predictive factors for experiencing online harm, as well as the psychosocial correlates of online harm.
Our results show that approximately a quarter of 8-year-old children have experienced online harm. Most research on online harm has examined older populations, focusing on teenagers and adolescents (e.g., Machimbarrena et al., 2018; Smahel et al., 2020); however, our analysis shows that these experiences start early for some children, with a substantial number experiencing harmful experiences in middle childhood or earlier. The most commonly experienced form of online harm was exposure to adult content (content intended for grown-ups, as determined by the child). It is important to note that online harm was assessed through children's own reports of internet experiences that caused them distress, which will differ among individual children and may differ from what adults perceive to be harmful experiences. In light of prior research indicating a discrepancy between parents' and children's accounts of online harm (Pacheco and Melhuish, 2020b), it was important to investigate the child's subjective experience and recollection of the event as distressing.
As data for this study was collected as part of a large, longitudinal study with an extensive battery of measures collected, the data available on online harms was less detailed than would be the case if a study specific to online harms was conducted. Future research is required to provide a more nuanced understanding of the types of online situations and experiences that young children find to be distressing.
Predictors of online harm
We found evidence of both longitudinal and concurrent predictors of children experiencing online harm by age 8, and these included child characteristics, parenting behaviors, and child digital use factors. Males were more likely to report experiences of online harm than females, and children who spent more time using electronic media, as assessed earlier at age 4.5-years-old and concurrently at 8-years-old, were more likely to experience online harm. However, in our final predictive model, these two factors (gender and extent of electronic media use) were not significantly predictive of online harm once accounting for the other factors in the model.
The factors remaining predictive of online harm in the final model were child behavioral difficulties, parent communication and behavior related to internet safety, and the number of personal devices owned by the child. Children with higher levels of behavioral problems, as reported by their parents when the child was 4.5-years-old, were more likely to experience online harm by age 8. These children may be more prone to risky and defiant behavior, both offline and online, consistent with previous literature identifying overlapping vulnerability for harm online and offline due to risk factors common to both, including proclivity for risk-taking (Livingstone, 2013). Further, children with more behavioral difficulties may end up spending more time using electronic media, if parents use this as a means to cope with and control child behavior (e.g., Elias and Sulkin, 2019; Tang et al., 2018). In the present sample, children in the highest quartile of electronic media use at 4.5-years-old were reported by their parents as having significantly higher levels of behavioral difficulties than the rest of the sample.
As noted above, previous research such as that by Livingstone (2013), has found that children vulnerable to offline risks are also more likely to be at risk online. Interestingly, however, in the present sample we found no impact of socioeconomic status, with children's risk of online harm not differing based on household income. This finding is surprising given differences often found in the way that screen media is used by children of differing socioeconomic backgrounds (e.g., Mollborn et al., 2022; Nagata et al., 2022); however, these differences in patterns of screen use may not translate to differential risk for online harm in young children.
We found that the strongest predictor of online harm was the number of personal devices owned by the child at age 8. Gaming devices had the greatest impact on increasing the odds of online harm, followed by computers/laptops, and TVs. Note that this question asked about personal devices, not those shared within the household, perhaps reflecting situations where children have TVs and computers set up in their bedrooms and they engage with media content outside of any adult supervision. Indeed, previous research has identified bedroom media (either a TV or a gaming device in the bedroom) as a risk factor for exposure to media violence and video game addiction (Gentile et al., 2017). Continuing to explore the specific harms associated with different types of devices presents an interesting area for future research.
Finally, we found that online harm was associated with internet communication and safety, a factor reflecting the parenting behaviors of talking with children about the benefits and the risks of using the internet and using software and/or parental controls to restrict child internet access. In this case, our results showed the opposite pattern to what we expected–parents scoring higher on the use of internet communication and safety were more likely to have children who had experienced online harm. One explanation for this counterintuitive finding may be that the discussions about internet safety and use of parental controls were prompted by online harm experiences; in response to a child's distressing internet experience, parents may be more likely to talk with their child about internet dangers and implement control measures, resulting in the significant association between these variables. Similarly, children who are using screen media in more inappropriate ways (whether or not they have yet experienced online harm) might be more likely to (1) have parental restrictions placed on them, and (2) experience online harm. However, there is some evidence that control-oriented managing of children's media use can actually exacerbate problematic media use (Lee and Ogbolu, 2018), so further work in this area is required. In general, parenting strategies for preventing online harm that are more collaborative (such as co-viewing) are more effective than those that are control-based (like restricting internet use; Elsaesser et al., 2017).
Overall, the model only accounted for a small amount of the variance in predicting the likelihood of online harm, suggesting that there are other important factors not considered in this analysis. However, our results point to a few key risk factors for early experiences of online harm.
Psychosocial adjustment
Our analysis of the psychosocial functioning of children at age 8 indicates that those who reported experiencing online harm also reported higher levels of depressive symptoms and lower self-worth, even after controlling for earlier emotional symptoms (assessed at age 4.5). While these reports were gathered concurrently (and all self-reported by the child), the results could indicate adverse psychological consequences for young children who experience distressing situations online, including viewing adult content, bullying, and talking to strangers. Previous research has demonstrated in teenagers that more time spent using the internet and on social media predicts higher depressive symptoms and lower self-esteem (Twenge and Farley, 2021) and that specific types of online harm, such as cyberbullying, are associated with poorer mental health and psychosocial outcomes (Kwan et al., 2020). The present research extends upon this literature to show disadvantageous associations with psychosocial functioning as early as age 8. The results suggest that adverse or distressing experiences online may impact psychological functioning and mental health in the same way that experiencing offline adverse events in childhood can lead to mental health problems such as anxiety and depression (e.g., Chapman et al., 2007).
Given the rapid changes in digital technology use by young children, our findings highlight the importance of ensuring age-appropriate online activities for minimizing risks for online harm in our youngest children. Importantly, research has shown that there is substantial overlap in online and offline harm (for example, youth who experience cyberbullying often experience offline bullying as well; Finkelhor et al., 2021). It will be important in future research to disentangle the unique association of online harm with psychosocial functioning, after controlling for offline experiences of harm.
Given the previous literature in this field, we have interpreted our results as indicative of online harm influencing young children's depressive symptoms and self-worth. However, it may also be the case that children with poor psychosocial adjustment (lower self-worth and higher depressive symptoms) either (1) are more likely to use the internet in risky or problematic ways and in turn more likely to experience online harm, or (2) are more likely to report experiencing distressing situations online than other children (for example, because they differ in how they perceive these situations in the first place or in how they recall these situations later on).
While the effect size for group differences in self-worth was relatively small, the mean difference in depressive symptoms was substantial (half a standard deviation). It is important to note, however, that although significant differences were observed based on experiences of online harm, the actual level of depressive symptoms in the online harm group (9.10 out of a possible score of 30) is still low in an absolute sense.
It is also important to note that when children experience online harm, there may also be the opportunity to build resilience, and these adverse experiences may lead to coping, adaptation and the development of resilience (e.g., Ólafsson et al., 2018). While we did not find evidence of this in the present study, investigation of longer-term outcomes for these children (which will be possible as the Growing Up in New Zealand study continues) has the potential to demonstrate that these children end up developing stronger digital safety skills and digital resilience. For example, Mensonides et al. (2023) theorize that “digital risky play” may help to build resilience in the same way that offline risky play is important for building resilience in childhood. This remains to be demonstrated empirically.
Finally, it is worth noting that all measures of psychosocial functioning included in this analysis are measures of broad/everyday functioning and are not media-specific. Understanding specific emotional and depressive symptoms and self-worth related to media and when exposed to online risks is an important avenue for future research. Some research with older children has found that exposure to different online risks leads to differential consequences (González-Cabrera et al., 2018; Montiel et al., 2016; Temple et al., 2014). In the present sample, given the relatively low frequency of each individual type of online harm we grouped all types of harm together; however, it will be important for future research to examine the differential impacts of different types of online harm in young children as well. Additionally, it is crucial to acknowledge the evolution of the internet since the collection of this data in 2009–2010. While online applications have been designed specifically with the safety of young children in mind (e.g., YouTube Kids), parents are still required to be vigilant and monitor their child's online engagement due to the detection of inappropriate and risky content on these “child-friendly” platforms (Tahir et al., 2019).
Conclusions
The findings of this research indicate that approximately a quarter of New Zealand children have experienced online harm (that is, have encountered online content that worried, upset, or bothered them) by the age of 8. While our growing digital landscape offers new opportunities and advantages, understanding the risks that come with early online experiences and how to protect young children is critically important. Our analysis indicates that children with behavioral difficulties are at greater risk of online harm, as are children with more personal devices. Limiting children's personal devices, particularly those that are accessed without adult supervision, and using collaborative rather than controlling strategies for managing child media use are two key steps parents can take to prevent online harm. Preventing early experiences of online harm is particularly important given our finding that children who report experiencing online harm also report more depressive symptoms and lower self-worth at age 8 than children who have not experienced online harm.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: access to the data used in this study can be obtained through application to the Growing Up in New Zealand team. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to https://www.growingup.co.nz/.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ministry of Health Northern Y Regional Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
MG: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Canterbury Medical Research Foundation.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the children and the families who are part of the Growing Up in New Zealand study and contribute their valuable time and knowledge. We also acknowledge all members of the Growing Up in New Zealand team and the support provided by Auckland UniServices and The University of Auckland. Funding for the Growing Up in New Zealand study has been provided by the Ministry of Social Development and the Health Research Council (HRC). Other agencies have also contributed funding, including: Ministries of Health; Education; Justice; Research; Science and Technology; Women's Affairs and Pacific Island Affairs; the Families Commission; Departments of Corrections and Labor; Housing New Zealand; Te Puni Kokiri; Office of Ethnic Affairs; Children's Commission; Statistics New Zealand; the New Zealand Police; and Sport and Recreation New Zealand and the Treasury.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1. ^Note that the same pattern of results was found when using SDQ total behavioral difficulties as the covariate instead of the emotional symptoms subscale.
References
Almenara, C. A., Machackova, H., and Smahel, D. (2016). Individual differences associated with exposure to “Ana-Mia” websites: an examination of adolescents from 25 European countries. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 19, 475–480. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2016.0098
Álvarez, M., Torres, A., Rodríguez, E., Padilla, S., and Rodrigo, M. (2014). Attitudes and parenting dimensions in parents' regulation of Internet use by primary and secondary school children. Comput. Educ. 67, 69–78. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2013.03.005
Andresen, E. M., Malmgren, J. A., Carter, W. B., and Patrick, D. L. (1994). Screening for depression in well older adults: evaluation of a short form of the CES-D. Am. J. Prev. Med. 10, 77–84. doi: 10.1016/S0749-3797(18)30622-6
Baumrind, D. (1991). The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. J. Early Adolesc. 11, 56–95. doi: 10.1177/0272431691111004
Chapman, D. P., Dube, S. R., and Anda, R. F. (2007). Adverse childhood events as risk factors for negative mental health outcomes. Psychiatr. Ann. 37:5. doi: 10.3928/00485713-20070501-07
Cho, C.-H., and Cheon, H. J. (2005). Children's exposure to negative internet content: effects of family context. J. Broadcast. Electron. Media 49, 488–509. doi: 10.1207/s15506878jobem4904_8
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Cohen, J. (1992). Methods in psychology. A power primer. Psychol. Bullet. 112, 155–159. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155
Coyne, S. M., Radesky, J., Collier, K. M., Gentile, D. A., Linder, J. R., Nathanson, A. I., et al. (2017). Parenting and digital media. Pediatrics 140, S112–S116. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-1758N
Elias, N., and Sulkin, I. (2019). Screen-assisted parenting: the relationship between toddlers' screen time and parents' use of media as a parenting tool. J. Family Stud. 4, 2801–2822. doi: 10.1177/0192513X19864983
Ellonen, N., Minkkinen, J., Kaakinen, M., Suonpää, K., Lee Miller, B., and Oksanen, A. (2021). Does parental control moderate the effect of low self-control on adolescent offline and online delinquency? Just. Quart. 38, 827–848. doi: 10.1080/07418825.2020.1738526
Elsaesser, C., Russell, B., Ohannessian, C. M., and Patton, D. (2017). Parenting in a digital age: a review of parents' role in preventing adolescent cyberbullying. Aggress. Violent Behav. 35, 62–72. doi: 10.1016/j.avb.2017.06.004
Fendrich, M., Weissman, M. M., and Warner, V. (1990). Screening for depressive disorder in children and adolescents: validating the center for epidemiologic studies depression scale for children. Am. J. Epidemiol. 131, 538–551 doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115529
Festl, R. (2021). Social media literacy & adolescent social online behavior in Germany. J. Child. Media 15, 249–271. doi: 10.1080/17482798.2020.1770110
Fikkers, K. M., Piotrowski, J. T., and Valkenburg, P. M. (2017). A matter of style? Exploring the effects of parental mediation styles on early adolescents' media violence exposure and aggression. Comput. Human Behav. 70, 407–415. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.029
Finkelhor, D., Walsh, K., Jones, L., Mitchell, K., and Collier, A. (2021). Youth internet safety education: aligning programs with the evidence base. Trauma, Viol. Abuse 22, 1233–1247. doi: 10.1177/1524838020916257
Gentile, D. A., Berch, O. N., Choo, H., Khoo, A., and Walsh, D. A. (2017). Bedroom media: One risk factor for development. Dev. Psychol. 53:2340. doi: 10.1037/dev0000399
GerŽičáková, M., Dedkova, L., and Mýlek, V. (2023). What do parents know about children's risky online experiences? The role of parental mediation strategies. Comput. Human Behav. 141:107626. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2022.107626
González-Cabrera, J., León-Mejía, A., Beranuy, M., Gutiérrez-Ortega, M., Alvarez-Bardón, A., and Machimbarrena, J. M. (2018). Relationship between cyberbullying and health-related quality of life in a sample of children and adolescents. Qual. Life Res. 27, 2609–2618. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1901-9
Goodman, R. (1997). The strengths and difficulties questionnaire: a research note. J. Child Psychol. Psychiat. 38, 581–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01545.x
Growing Up in New Zealand (2023). DCW12: Data Release 2023. Data User Guide. Available at: https://www.growingup.co.nz/ (accessed February 1, 2024).
Harter, S. (2012). “Emerging selfprocesses during childhood and adolescence,” in Handbook of Self and Identity, eds. M. Leary, and J. Tangney (New York: The Guilford Press), 680–715.
Hill, D., Ameenuddin, N., Reid Chassiakos, Y. L., Cross, C., Hutchinson, J., Levine, A., et al. (2016). Media and young minds. Pediatrics 138:2591 doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-2591
InternetNZ (2022). New Zealand's Internet Insights 2022: A Kantar Public Research Report. Available at: https://internetnz.nz/assets/Uploads/Internet-insights-2022.pdf (accessed February 1, 2024).
Jago, R., Davison, K. K., Thompson, J. L., Page, A. S., Brockman, R., and Fox, K. R. (2011). Parental sedentary restriction, maternal parenting style, and television viewing among 10-to 11-year-olds. Pediatrics 128, e572–e578. doi: 10.1542/peds.2010-3664
Keipi, T., Oksanen, A., Hawdon, J., Näsi, M., and Räsänen, P. (2015). Harm-advocating online content and subjective well-being: a cross-national study of new risks faced by youth. J. Risk Res. 20, 634–649. doi: 10.1080/13669877.2015.1100660
Kwan, I., Dickson, K., Richardson, M., MacDowall, W., Burchett, H., Stansfield, C., et al. (2020). Cyberbullying and children and young people's mental health: a systematic map of systematic reviews. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 23, 72–82. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2019.0370
Lee, E. J., and Ogbolu, Y. (2018). Does parental control work with smartphone addiction?: A cross-sectional study of children in South Korea. J. Addict. Nurs. 29, 128–138. doi: 10.1097/JAN.0000000000000222
Lee, J., Kubik, M. Y., and Fulkerson, J. A. (2018). Media devices in parents' and children's bedrooms and children's media use. Am. J. Health Behav. 42, 135–143. doi: 10.5993/AJHB.42.1.13
Livingstone, S. (2013). Online risk, harm and vulnerability: reflections on the evidence base for child Internet safety policy. ZER: J. Commun. Stud. 18, 13–28.
Livingstone, S., Haddon, L., Görzig, A., and Ólafsson, K. (2011). “Risks and safety on the internet: the perspective of European children: full findings and policy implications from the EU Kids Online survey of 9-16 year olds and their parents in 25 countries,” in EU Kids Online, Deliverable D4 (London: EU Kids Online Network).
Livingstone, S., and Helsper, E. J. (2008). Parental mediation of children's internet use. J. Broadcast. Electron. Media 52, 581–599. doi: 10.1080/08838150802437396
Livingstone, S., Ólafsson, K., Helsper, E. J., Lupiáñez-Villanueva, F., Veltri, G. A., and Folkvord, F. (2017). Maximizing opportunities, and minimizing risks for children online: The role of digital skills in emerging strategies of parental mediation. J. Commun. 67, 82–105. doi: 10.1111/jcom.12277
Machimbarrena, J. M., Calvete, E., Fernández-González, L., Álvarez-Bardón, A., Álvarez-Fernández, L., and González-Cabrera, J. (2018). Internet risks: an overview of victimization in cyberbullying, cyber dating abuse, sexting, online grooming and problematic internet use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:2471. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15112471
Mascheroni, G., Vincent, J., and Jimenez, E. (2015). ‘Girls are addicted to likes so they post semi-naked selfies': peer mediation, normativity and the construction of identity online. Cyberpsychology 9:5. doi: 10.5817/CP2015-1-5
McArthur, B. A., Volkova, V., Tomopoulos, S., and Madigan, S. (2022). Global prevalence of meeting screen time guidelines among children 5 years and younger: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 176, 373–383. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.6386
Mensonides, D., Van Cauwenberge, A., and Broersma, M. (2023). Playfully building resilience: Dutch children's risk-managing tactics in digital risky play. J. Child. Media 18, 80–98. doi: 10.1080/17482798.2023.2271100
Mollborn, S., Limburg, A., Pace, J., and Fomby, P. (2022). Family socioeconomic status and children's screen time. J. Marriage Family 84, 1129–1151. doi: 10.1111/jomf.12834
Montiel, I., Carbonell, E., and Pereda, N. (2016). Multiple online victimization of Spanish adolescents: results from a community sample. Child Abuse Negl. 52, 123–134. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2015.12.005
Morton, S. M., Atatoa Carr, P. E., Grant, C. C., Robinson, E. M., Bandara, D. K., Bird, A., et al. (2013). Cohort profile: growing up in New Zealand. Int. J. Epidemiol. 42, 65–75. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyr206
Morton, S. M. B., Atatoa Carr, P. E., Bandara, D. K., Grant, C. C., Ivory, V. C., et al. (2010). “Growing Up in New Zealand: a longitudinal study of New Zealand children and their families,” in Report 1: Before We are Born (Auckland: University of Auckland).
Morton, S. M. B., Ramke, J., Kinloch, J., Grant, C. C., Atatoa Carr, P., Leeson, H., et al. (2015). Growing Up in New Zealand cohort alignment with all New Zealand births. Aust. New Zealand J. Public Health 39, 82–87. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12220
Nagata, J. M., Ganson, K. T., Iyer, P., Chu, J., Baker, F. C., Gabriel, K. P., et al. (2022). Sociodemographic correlates of contemporary screen time use among 9-and 10-year-old children. J. Pediatr. 240, 213–220. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.08.077
Oksanen, A., Näsi, M., Minkkinen, J., Keipi, T., Kaakinen, M., and Räsänen, P. (2016). Young people who access harm-advocating online content: a four-country survey. Cyberpsychology 10:6. doi: 10.5817/CP2016-2-6
Ólafsson, K., Green, L., and Staksrud, E. (2018). Is big brother more at risk than little sister? The sibling factor in online risk and opportunity. New Media Soc. 20, 1360–1379. doi: 10.1177/1461444817691531
Oliveira, T. D., Costa, D. D. S., Albuquerque, M. R., Malloy-Diniz, L. F., Miranda, D. M., and de Paula, J. J. (2018). Cross-cultural adaptation, validity, and reliability of the Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire–Short Version (PSDQ) for use in Brazil. Braz. J Psychiatry 40, 410–419. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2017-2314
Pacheco, E., and Melhuish, N. (2020a). “New Zealand children's experiences of online risks and perceptions of harm,” in Evidence from Ngā taiohi matihiko o Aotearoa - New Zealand Kids Online (Wellington: Netsafe).
Pacheco, E., and Melhuish, N. (2020b). Factsheet: Parental Awareness of Children's Experiences of Online Risks and Harm Evidence From Ngā Taiohi Matihiko O Aotearoa – New Zealand Kids Online. Wellington: Netsafe.
Papadamou, K., Papasavva, A., Zannettou, S., Blackburn, J., Kourtellis, N., Leontiadis, I., et al. (2020). “Disturbed YouTube for kids: characterizing and detecting inappropriate videos targeting young children,” in Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media (Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence), 522–533.
Radesky, J., and Hiniker, A. (2022). From moral panic to systemic change: making child-centered design the default. Int. J. Child-Comp. Interact. 31:100351. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcci.2021.100351
Radesky, J. S., Peacock-Chambers, E., Zuckerman, B., and Silverstein, M. (2016). Use of mobile technology to calm upset children: associations with social-emotional development. JAMA Pediatr. 170, 397–399. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.4260
Rideout, V., and Robb, M. B. (2020). The Common Sense census: Media Use by Kids Age Zero to Eight, 2020. San Francisco, CA: Common Sense Media.
Robinson, C., Mandleco, B., Olsen, S. F., and Hart, C. H. (1995). Authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive parenting practices: development of a new measure. Psychol. Rep. 77, 819–830. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1995.77.3.819
Robinson, C. C., Mandleco, B., Olsen, S. F., and Hart, C. H. (2001). “The Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire (PSDQ),” in Handbook of Family Measurement Techniques: Vol. 3. Instruments & Index, eds.B. F. Perlmutter, J. Touliatos, and G. W. Holden (Thousand Oaks: Sage), 319–321.
Rodríguez-Enríquez, M., Bennasar-Veny, M., Leiva, A., Garaigordobil, M., and Yañez, A. M. (2019). Cybervictimization among secondary students: social networking time, personality traits and parental education. BMC Public Health 19, 1–7. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7876-9
Skogen, J. C., Bøe, T., Finserås, T. R., Sivertsen, B., Hella, R. T., and Hjetland, G. J. (2022). Lower subjective socioeconomic status is associated with increased risk of reporting negative experiences on social media. Findings from the “LifeOnSoMe”-study. Front. Public Health 10:873463. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.873463
Smahel, D., Machackova, H., Mascheroni, G., Dedkova, L., Staksrud, E., Ólafsson, K., et al. (2020). EU Kids Online 2020: Survey Results from 19 Countries. Hamburg: EU Kids Online.
Stoilova, M., Livingstone, S., and Khazbak, R. (2021). “Investigating Risks and Opportunities for Children in a Digital World: A rapid review of the evidence on children's internet use and outcomes,” in Innocenti Discussion Paper 2020-03. Florence: UNICEF Office of Research – Innocenti.
Stone, L. L., Janssens, J. M. A. M., Vermulst, A. A., Van Der Maten, M., Engels, R. C., and Otten, R. (2015). The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: psychometric properties of the parent and teacher version in children aged 4–7. BMC Psychol. 3:4. doi: 10.1186/s40359-015-0061-8
Stone, L. L., Otten, R., Engels, R. C., Vermulst, A. A., and Janssens, J. M. (2010). Psychometric properties of the parent and teacher versions of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire for 4-to 12-year-olds: a review. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 13, 254–274. doi: 10.1007/s10567-010-0071-2
Tahir, R., Ahmed, F., Saeed, H., Ali, S., Zaffar, F., and Wilson, C. (2019). “Bringing the kid back into youtube kids: Detecting inappropriate content on video streaming platforms,” in Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery), 464–469.
Tang, L., Darlington, G., Ma, D., and Haines, J. (2018). Mothers' and fathers' media parenting practices associated with young children's screen time: a cross-sectional study. BMC Obesity 5:37. doi: 10.1186/s40608-018-0214-4
Temple, J. R., Le, V. D., van den Berg, P., Ling, Y., Paul, J. A., and Temple, B. W. (2014). Brief report: teen sexting and psychosocial health. J. Adolesc. 37, 33–36. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2013.10.008
Thompson, A. L., Adair, L. S., and Bentley, M. E. (2013). Maternal characteristics and perception of temperament associated with infant TV exposure. Pediatrics 131, e390–e397. doi: 10.1542/peds.2012-1224
Twenge, J. M., and Farley, E. (2021). Not all screen time is created equal: associations with mental health vary by activity and gender. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 56, 207–217. doi: 10.1007/s00127-020-01906-9
Valcke, M., Bonte, S., De Wever, B., and Rots, I. J. C. (2010). Internet parenting styles and the impact on Internet use of primary school children. Children 55, 454–464. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2010.02.009
Veldhuis, L., van Grieken, A., Renders, C. M., Hirasing, R. A., and Raat, H. (2014). Parenting style, the home environment, and screen time of 5-year-old children; the 'be active, eat right' study. PLoS ONE 9:e88486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088486
Keywords: online harm, online risk, Growing Up in New Zealand, mental health, self-worth, digital media
Citation: Gath M and Swit C (2024) Digital media in early childhood: risk factors for online harm and psychosocial correlates. Front. Dev. Psychol. 2:1390276. doi: 10.3389/fdpys.2024.1390276
Received: 23 February 2024; Accepted: 29 October 2024;
Published: 15 November 2024.
Edited by:
Tiffany Munzer, University of Michigan, United StatesReviewed by:
Jennifer A. Emond, Dartmouth College, United StatesHelen Abadzi, University of Texas at Arlington, United States
Copyright © 2024 Gath and Swit. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Megan Gath, bWVnYW4uZ2F0aEBjYW50ZXJidXJ5LmFjLm56
†ORCID: Megan Gath orcid.org/0000-0002-8647-1262
Cara Swit orcid.org/0000-0002-7198-5869
 Megan Gath
Megan Gath Cara Swit2†
Cara Swit2†