
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Detect. Sci. Technol. , 05 March 2025
Sec. Detectors Apparatus and Methods
Volume 3 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fdest.2025.1551757
This article is part of the Research Topic Advancements in Radiation Detection Technology: Safeguarding the Future View all articles
 G. Agostini1
G. Agostini1 F. Ambrosino2
F. Ambrosino2 M. Antonelli3
M. Antonelli3 G. Aquilanti1
G. Aquilanti1 P. Bellutti4,5
P. Bellutti4,5
 G. Bertuccio
6,7
G. Bertuccio
6,7 G. Borghi5
G. Borghi5 L. Bosisio3,8
L. Bosisio3,8 R. Campana9,10
R. Campana9,10 G. Cautero1
G. Cautero1 F. Ceraudo2
F. Ceraudo2 D. Cirrincione3,11
D. Cirrincione3,11 E. Del Monte2
E. Del Monte2 G. Della Casa2
G. Della Casa2 G. Dilillo2
G. Dilillo2 I. Dedolli6
I. Dedolli6 E. Demenev5
E. Demenev5 Y. Evangelista2
Y. Evangelista2 M. Feroci2
M. Feroci2 F. Ficorella5,12
F. Ficorella5,12 M. Fiorini9
M. Fiorini9 F. Fuschino9,10
F. Fuschino9,10
 F. Fiore
13
F. Fiore
13 M. Gandola6
M. Gandola6
 A. Gianoncelli
1
A. Gianoncelli
1 D. Giuressi1
D. Giuressi1
 M. Grassi
14
M. Grassi
14 G. Kourousias1
G. Kourousias1 C. Labanti9,10
C. Labanti9,10
 P. Malcovati
14
P. Malcovati
14
 F. Mele
6,7
F. Mele
6,7
 R. H. Menk
1,3,4,15
R. H. Menk
1,3,4,15
 L. Olivi
1
L. Olivi
1 G. Orzan3
G. Orzan3
 G. Pepponi
5,12
G. Pepponi
5,12
 A. Picciotto
5,12
A. Picciotto
5,12 A. Rachevski3
A. Rachevski3 I. Rashevskaya12
I. Rashevskaya12 M. Sammartini6,7
M. Sammartini6,7 S. Schillani1
S. Schillani1 L. Stebel1
L. Stebel1
 G. Zampa
3
G. Zampa
3 N. Zampa3,11
N. Zampa3,11
 N. Zorzi
5,12
N. Zorzi
5,12
 Andrea Vacchi
3,11*
Andrea Vacchi
3,11*The efficient detection of low-energy X-rays at the keV level with the best possible energy resolution requires the application of silicon drift detectors (SDDs) and advanced application specific integrated circuits (ASICs). Their widespread use in material sciences, alongside dedicated basic science projects, has long been restricted to single, selected SDD elements working at low temperatures. This is because of the limits incurring in the quite elaborated planar technology production process and the need to reach very low leakage current levels, together with the need for highly specialized readout electronics. We describe, in this review work, the concrete outcomes of the efforts of the ReDSoX collaboration to develop high energy resolution detection systems working at near room temperature based on multi-pixel monolithic silicon drift detectors and custom-designed advanced readout electronics capable of dealing with high photon fluxes, developed for specific projects but suitable for a variety of applications.
The detection of the total energy released within a detector, as needed for low-energy X-ray spectroscopy and spectral X-ray imaging, or the detection of the differential energy released within the detector by passing particles, which is primarily used for particle identification, tracking, and calorimetry, roughly define the fields of application of silicon detectors. The optimal features of the detectors are directly impacted by the differences in the requirements of those two application directions. This includes thickness, total area, electrode layout, segmentation, total active volume, and charge carrier collection mechanism. Because of its versatility, since its invention almost 40 years ago by E. Gatti and P. Rehak (Gatti and Rehak, 1984; Rehak et al., 1986), the SDD, which uses particular sideward depletion properties in the silicon bulk, allowing to realize precisely defined potentials and control the signal charge drift toward very low capacitance collection anodes, has found a variety of applications in both particle and X-ray detection (Guazzoni, 2010). Building on the progressive development of the planar production technology for silicon detectors, which was initially invented by J. Kemmer (Kemmer et al., 1982), and subsequently P. Burger (Rashevsky et al., 2002), in recent years, it has been possible to achieve the quality levels needed for ideal spectroscopic performance at near room temperature (Bertuccio et al., 2016; FBK). The recent SDD detector development took two distinct directions; the unique capability to unambiguously resolve the two coordinates of the particle impact point in the presence of high track multiplicity was successfully applied (Gatti et al., 1988; Vacchi et al., 1993). This gave rise to the development of large-area silicon drift detector (LASDD), often exploiting the whole usable area of the high-resistivity silicon wafer, allowing for large-scale applications of SDD at accelerators as, for instance, is described in Piemonte et al. (2006), Rashevsky et al. (2001), Bonvicini et al. (2000), Alessandro et al. (2010), and Gatti and Rehak (2005). As a consequence of the achieved energy resolution for low-energy X-rays, which is due to the highly refined detector design and the quality of the production technology (Zampa et al., 2007; Zampa et al., 2011), the LASDD was subsequently also proposed to be applied in ongoing space missions (Feroci et al., 2012), and those are at present in their realization phase (Zhang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2019; Wilson-Hodge et al., 2017). This progression is illustrated in some detail in Vacchi (2023). Given the possibility to use silicon bulk thicknesses ranging from approximately a hundred microns to a millimeter, SDDs can have a significant X-ray detection efficiency. To maintain noise from leakage current at a level compatible with the best possible energy resolution, it is essential to employ selected specialized SDD with an area smaller than a few tens of square millimeters. SDD-based detectors can maintain high efficiency in the presence of high flux while achieving optimum energy resolution for X-ray photons in the 1–30 keV range. In this scenario, highly sophisticated, low-noise, charge-sensitive preamplifiers have been developed to make full use of the low leakage current allowed by the production technology and SDD’s low collecting anode capacitance (O’Connor et al., 1997; Bertuccio and Caccia, 2007; Bombelli et al., 2011; Bertuccio et al., 2014; Bertuccio et al., 2024; Bertuccio et al., 2016). To overcome the initial bottleneck for such detectors, namely, the small area, various attempts have been made to investigate the possible uses of monolithic multi-pixel silicon drift detectors (Fiorini et al., 2006; Fiorini and Longoni, 2003; Rehak et al., 2010; Rachevski et al., 2013; Alberti et al., 2007), with integrated FET (Niculae et al., 2006; Gauthier et al., 1996), and more recently (Gugiatti et al., 2022; Quaglia et al., 2016). The widespread practical use of these detection systems out of a basic research context appeared initially prohibitive, mainly because of the expected low production yield and the consequent costs. A concurrent evolution of sophisticated integrated CMOS front-end systems (Ahangarianabhari et al., 2014; Bertuccio et al., 2016), tailored to each application and of the planar process (FBK, 2015), has allowed to launch a collaborative effort merging the research and application requirements born in apparently distant fields driven by the objective of reaching frontier performances of SDD systems. We will describe some applications of monolithic array of silicon drift detectors (MASDDs) in the following sections. Section 2 introduces a few basic tools on the working principle and design aspects for SDD dedicated to high-energy resolution X-ray detection. Section 3 covers the solutions proposed to some of the most demanding issues posed by the users of two synchrotron radiation source beamlines. Here, along with the high-energy resolution and sensitivity down to approximately 100 eV, the solid angle coverage of the sample surroundings and the acquisition speed are the factors that contribute to the operational efficiency. Section 4 presents two astrophysics-dedicated developments where MASDD detectors open ways to new observational capabilities. Section 5 is a synthetic summary of the ASIC CMOS electronics that have been designed for the different MASDD-based instruments described in this work.
Recalling some aspects of the silicon detectors’ working principles is helpful for reading the following text, even though a thorough explanation of the aspects underlying a reversely biased p-n junction is outside the scope of this work given the abundance of specialized literature available [see, for instance (Lutz, 2007)]. The architecture of the electrodes, hence of the biased junctions, on the SDD detector surface must allow efficient depletion of the entire silicon bulk volume from the majority carriers and establish at the same time the electric-field shape needed to impose on the incoming radiation’s generated charge the drift toward the charge-collecting electrodes. Depletion voltage VB is the minimum voltage, brought through the biasing junctions, at which the bulk of the silicon sensor is fully depleted from the free charge carriers. Bias voltage VB needed to obtain the complete expansion of the space charge region W and to reach full depletion depends on the characteristics and on the resistivity ρ of the semiconductor material,
where μ is the mobility of the majority charge carriers, electrons in case of an n type bulk, approximately 1,450 cm2/Vs @ 300K.
ρ is the resistivity of the n type material, which is a function of the doping concentration.
ε is the semiconductor dielectric constant, for Si 11,9 ε0.
Vbi is the built in potential (approximately 0.7 V in case of high resistivity bulk material).
VB is the externally applied reverse bias voltage.
In a typical silicon detector p-n junction, the effective doping concentration is Nd = 1012 cm−3 in the n- bulk and Na = 1018 cm−3 in the p+ region; hence, for a typical Si p-n junction, Na >> Nd. The higher the silicon bulk resistivity, the lower the doping concentration and the needed bias voltage to reach full depletion
while the detector capacitance is
where d is the detector thickness and A is its surface. Most used detectors are built on n-type silicon bulk. The absorbed radiation in the depleted silicon volume generates electron–hole pairs, and, in the presence of the electric field, the charges separate and drift toward the surface electrodes. The drift time that depends on the carrier’s mobility and the field is of the order of a few tens of nanoseconds depending on the path length. This drifting charge generates the signal current at the collecting electrodes. A crucial parameter is the reverse current (leakage current). This current, determined by the production technology, the quality of the silicon wafers, and the detector design, is dominated by thermally generated e-h+ pairs. Designing a detector turns out to be finding the optimal shape of the potential distribution in the depleted semiconductor volume, depicted as a homogeneous distribution of positive charges, to obtain a complete fast and efficient charge collection, while minimizing the electric field at the edges of the various biasing structures. The potential distribution within the silicon bulk, determined by its resistivity, can be evaluated through Poisson’s equation
The charge collection mechanism through anodes of minimal surface grants the best possible energy resolution and makes the SDD the detector of choice for spectroscopy applications. In the detector, the clouds of electrons and of holes generated by ionization drift in opposite directions following the electric field lines. The holes are collected on the surface cathodes while the electrons are focused and drift toward the anode. Because of the charge cloud diffusion mechanism, the size of the electron cloud increases with time or, equivalently, with the total drift distance as
where D is the diffusion coefficient, kB is the Boltzmann’s constant, μ is the electron mobility, T is the absolute temperature, t is the drift time and x is the drift length, and σ0 is the width of the initial distribution. The diffusion in the depleted silicon bulk causes the electron cloud to expand by a factor depending on the square root of the drift time. The charge distribution collected at the anodes then depends on the potential distribution and on the X-ray absorption point in the detector.
A variety of SDD pixel detectors structured in very different geometries have been designed; it is an extremely ductile detection method that can be tailored to the needs of every specific application. The simulation drafting in Figure 1 provides the details of generic SDD pixels; the detector’s volume has p+ cathode structures on both faces of the detector, while the collecting n+ anodes are on one face (n-side). This allows, once reaching the full depletion of the bulk, for the focusing potential to direct the electrons toward the collecting anode.
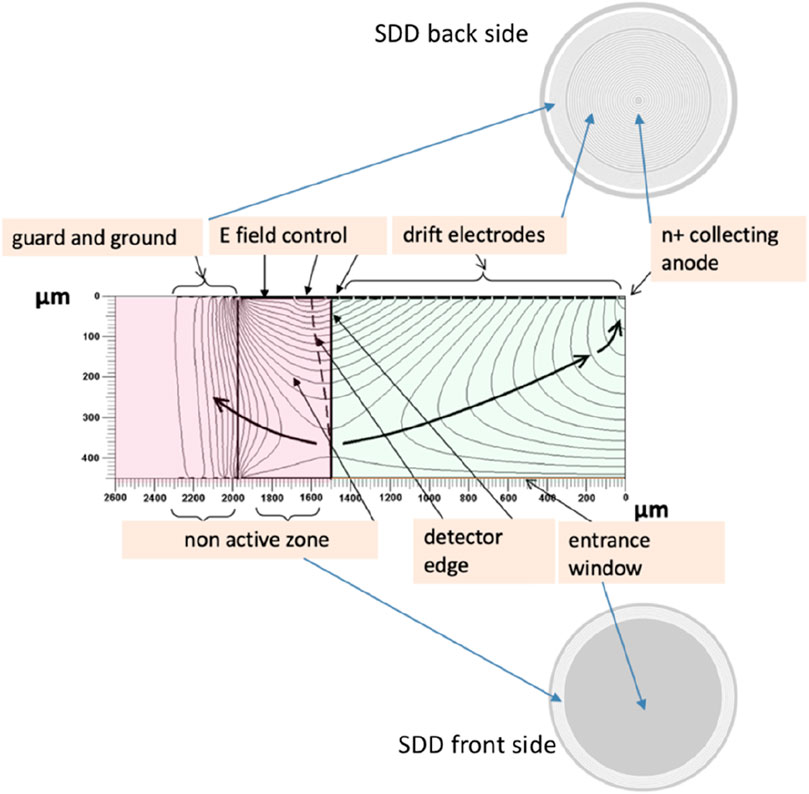
Figure 1. Field lines and potential direction in an SDD pixel cross-section, the bulk is n type, the thickness is 450 μm, and the total diameter 4,000 μm. Represented in the simulation reported in this figure is one-half of the detector from the edge to the central axis where the collecting n+ anode is positioned (Espacenet, 2025). The black arrow indicates the direction of the field leading the electrons toward the collection anode. The drift region active area (greenish) and the edge structure (reddish) are highlighted in this image. The description of the various elements is in the text.
The main building blocks of the SDD pixel detector in Figure 1 are as follows:
- Drift region: by means of a series of p+ cathodes implanted on the back structured face of the detector, biased through an implanted divider that provides a potential degrading toward the anodes, and a continuous p+ cathode on the other side serving as the entrance window, a drift field is established within the silicon bulk, which channels the majority carriers (electrons) toward the small area readout n+ anode of the SDD. The drift cathodes’ pitch and the SiO2 gap between adjacent junctions are determined through simulations according to the specific characteristics of the detector. The biasing system of cathodes is an integrated voltage divider and is based on a lightly doped p-implant in silicon.
- Collection zone: the field lines point toward the collecting anode whose area is the smallest compatible with the need to establish a contact toward the readout electronics; this depends on the bonding technology used. An optimized minimal anode area, and hence low readout capacitance (few tens of Femto Farad), means the best possible coupling to the front-end electronics.
- Entrance window is a homogeneous shallow p+ implant used to minimize volume near the surface where the detection efficiency might be reduced. The high efficiency of the detector depends on the characteristics of this implant.
- Field control and guard region non-active volume: the drift cathode arrays are flanked by p+ implants (guard rings) having the function to degrade the potential from the highest negative voltages to the ground voltages. Through an accurate design of the guard and drift cathodes, the active volume and the detection efficiency can be optimized (Espacenet, 2025). The effective sensitive area is normally screened by a dedicated collimator used to define the active area and minimize the number of events in which the generated charge is shared between the non-active region and the active region.
The 3D potential distribution of a generic SDD pixel is drafted in Figure 2. As we have seen, in SDD devices, reversely biased implants are on both the detectors’ faces, allowing in this way to realize a potential distribution that, by depleting the entire volume, also provides for the focusing of the charge carriers at the single, small-area n+ implant, the collection anode (Figure 2A). The resulting potential distribution, seen in three dimensions, is funnel-shaped (Figure 2B), which forces the electrons generated by the ionizing radiation toward the extremely low capacitance anode (less than 0.1 pF), (Figure 2C). The path to the best possible detector for low-energy X-ray spectroscopy is indicated by the pixel SDD’s unbeatable low capacitance of less than 0.1 pF and the advancement of the planar production technology of the detector. The very small capacitance of the SDD’s anode reduces the contribution of the system series noise and allows reduction of the optimum shaping time so that the contribution of the parallel white noise, arising from the detector current, is reduced as well. Because of the shorter shaping time, low-noise operation at high photon flux can be obtained. This leads to training the production process toward leakage current levels down to a fraction of nA/cm2 at room temperature. SDD pixels have been obtained from low leakage current processes, with areas from tens of mm2 to cm2, and when coupled to custom-designed front-end electronics (FEE), an energy resolution better than 130 eV FWHM @ 5.9 keV at room temperature can be reached (Bertuccio et al., 2016). Figure 3 shows the results from a detector realized on 150-mm diameter n-type, floating zone silicon wafer (100) crystal orientation and 450 μm thickness. Developed at FBK (FBK, 2015), this hexagonal SDD with an active area of 13 mm2 is realized with a technological process aimed to minimize the dark current. This technology sets a new state of the art lowering the current density at room temperature. Custom-designed CMOS front-end systems for high-resolution X-ray spectroscopy can be optimized to every spectroscopic application requiring pixelized SDD systems (Mele et al., 2021a; Mele et al., 2021b). Renouncing to integrate parts of the front end on the detector itself, becoming completely dependent on the external ASIC, differently from what has been performed in other solutions, is a weighted choice that requires an explanation. It means having to face the problem of the inadequate coupling between the anode and the first stage of the preamplifier. The positive aspect is that the two separate technologies, of the detectors and of the VLSI electronics designs, can be managed without having to mediate between quite elaborate technologies, resulting in rather practical and less costly final solutions. In addition to this, the performance of the transistors in the ASIC is much better than what can be achieved with detector technology. This (over) compensates for the higher capacitance at the preamplifier input.
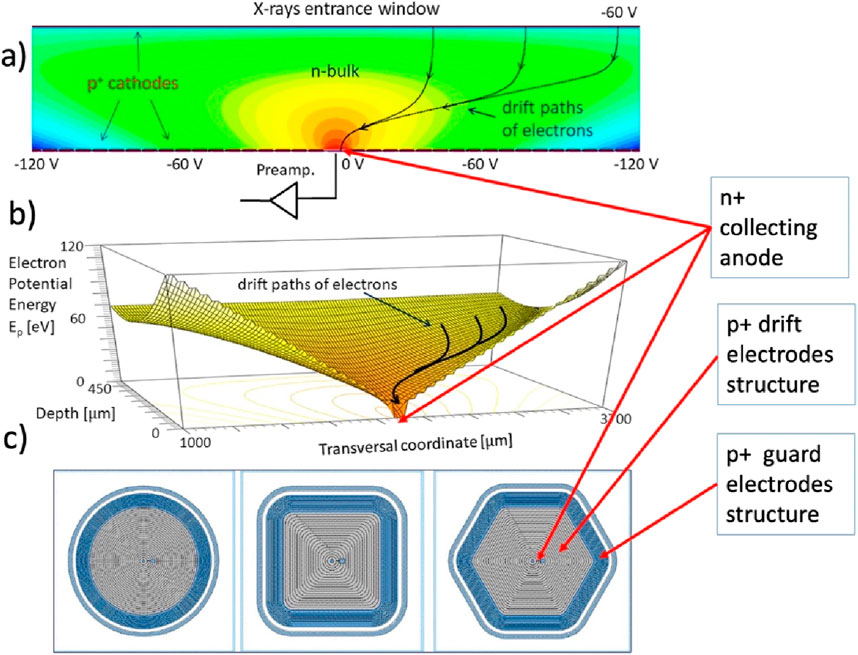
Figure 2. Relevant characteristics of a single-pixel SDD: (A) cross-section showing the distribution of the drift field in an SDD pixel 2D simulation; the upper edge is the thin radiation entrance window, and the lower edge shows the back window with the drift cathodes bias structure that surrounds the n+ collecting anode. The device is powered with a potential that reduces, in absolute value, from the outside toward the center. The outermost cathode is the one powered with the highest potential (in absolute value). At the edge, the field is defined by the guard structure. (B) Three-dimensional simulation cross-section of the potential distribution indicating the funnel field shape that, by depleting the entire volume, also provides for the focusing of the charge carriers at the n+ implant of the collecting anode. (C) Backside (anode or n side) structures of three different SDD pixel shapes among the possible solutions: visible are the anode, the drift cathode structure, and the guard region structure.
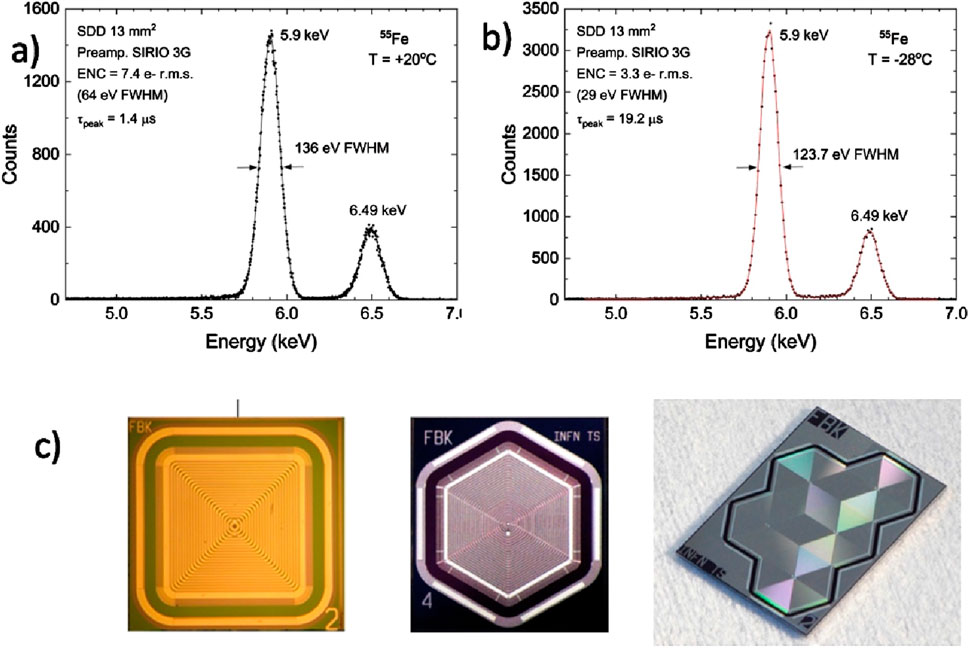
Figure 3. Characterization using a 55 Fe source of an X-ray spectroscopic system constituted by an SDD pixel manufactured by FBK (active area of 13 mm2) and a custom-designed CMOS integrated preamplifier, demonstrating the very high-energy resolution obtained by operating at room temperature. (A) Spectrum acquired at 20°C and at optimum peaking time (1.4 μs). The pulser line width is 64 eV FWHM, corresponding to 7.4 electrons RMS (root mean square). (B) Spectrum acquired at −28°C and at the optimum peaking time (19.2 μs). (C) Examples of silicon drift chambers with single-cell or matrix structures, developed by the REDSOX collaboration; the detector in the center is the one from which the results in the top panel were obtained.
The attainment of these outcomes was enabled by parallel research efforts linked to enhanced detector simulation (Espacenet, 2025), advanced design of CMOS charge-sensitive preamplifiers (Bertuccio and Caccia, 2007; Bertuccio et al., 2014; Bertuccio et al., 2016), and manufacturing technology (FBK, 2015). The latter aspect has enabled the reduction of the reverse current density of p-n junctions at very low levels (anode current density down to 25 pA/cm2 at room temperature). The energy resolution measured at 20°C of 136 eV FWHM at 5.9 keV, shown in Figure 3 is the best result ever obtained at room temperature by a detector of a similar active area. This opens new avenues for the technological implementation and applications of monolithic multi-pixel SDD-based X-ray spectrometers able to overcome the fundamental limitation of the available spectroscopic single-pixel SDDs, the small sensitive area. Figure 4 shows a variety of different MASDDs designs and test structures present in a multi-project wafer; some of those designs that have reached a final successful application are described as follows. When considering monolithic multi-pixel architectures, the ratio active/non-active volume of single elements is important to eventually allow for tiling on larger sensitive surfaces; this topic has been the focus of investigations; see, for example, (Castoldi et al., 2016; Cirrincione et al., 2019).
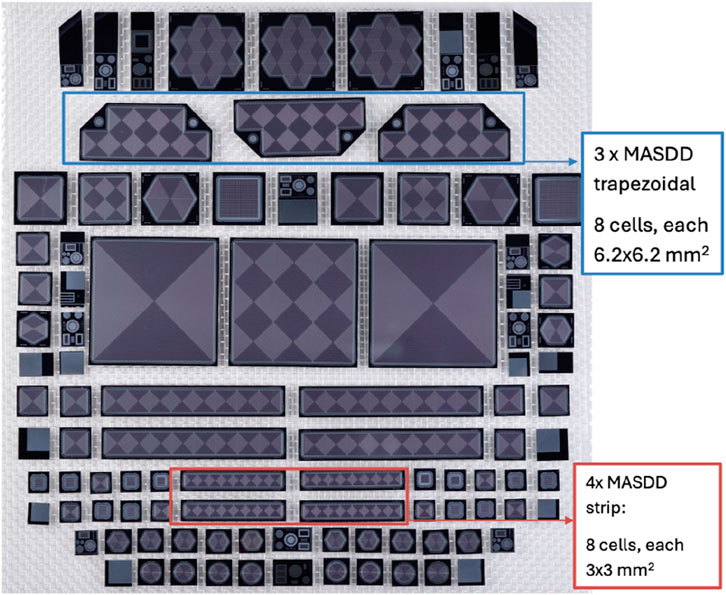
Figure 4. Detectors resulting from a multi-project wafer dedicated to designing monolithic multi-pixel SDD. Visible are MASDD linear structures with eight SDD pixels with different areas and trapezoidal structures with eight cells. The big central detector is an array of 3 × 3 SDD, each 1 cm2 in size. Those will be subject to a more detailed description in what follows.
The discussion about the quantum efficiency in the frame of low-energy X-ray spectroscopy is very much bound to the applicative context since the aspects to be considered are purely related to the detector in terms of the thickness of the bulk, to the quality of the entrance window, and to the capability to extract the signal from the noise. This points directly to the quality of the planar technology employed, the detector design, and crucially to the quality of the electronics. Through the photoelectric effect, X-rays are transformed into electron–hole pairs in the silicon material that makes up the sensor. The externally applied bias voltage causes the produced charge carriers to drift in the direction of the anodes, generating the electrical signal that the readout electronics processes. Some of the signal is lost because of the recombination of the charge carriers, particularly in the passive layers, whose thickness must be minimized. The likelihood of detecting an incident photon is the definition of a sensor’s quantum efficiency for X-ray detection Figure 5; this is a function of the photon energy.
The quantum efficiency at very low energy is related to the materials of the layers that the radiation must cross before reaching the sensitive bulk of the detector. A thin protective passivation layer and approximately 1 μm of mostly undepleted p-n junction thickness, which has a very poor charge collection efficiency, normally forms the entrance window where photons hit the detector. For X-ray energies below 2 keV, the detection efficiency declines as more photons are absorbed in the ineffective entrance window. For a deeper insight, see, for instance (Carulla et al., 2024). For the high end of the energy range, the thickness of the silicon bulk turns out to be a problem; silicon sensors 1 mm thick are almost transparent at photon energy greater than 20 keV. To expand the energy range of sensitivity, the X gamma spectrometer is used, which is introduced in paragraph 3.5.
The radiation damage aspects would require a detailed analysis for each specific application planned for the MASDD. There are two types of radiation damage mechanisms in silicon detectors: bulk displacement damage due to non-ionizing energy loss and surface damage due to the energy deposited because of ionization damaging the silicon surfaces and Si–SiO2 interfaces. The displacement damage caused by charged and neutral particles in the silicon bulk may increase the leakage current. According to the kind and energy of the impacting particles, the displacement damage is linearly proportional to the incident fluence and to the hardness factor. This is evaluated in Lindström (2003). For systems used in astrophysics applications, where detectors must deal with protons trapped in the Earth’s magnetic field at a flux that can be estimated based on the different orbits, this aspect can be particularly sensitive. SDDs have been characterized for this in various developments (Del Monte et al., 2014a; Monte et al., 2014b), even for the extreme situation of collider experiments (Kushpil et al., 2006). As pointed out previously, the crucial factor that may cause performance degradation is the SDDs’ leakage current. This effect, which impacts on the device use across various applications, should be addressed at the very beginning of planning, taking into consideration factors that can lessen this effect of radiation, like the operating temperature.
An increasing number of synchrotron light sources are being realized for use, among others, in the fields of soft X-ray spectroscopy, absorption spectroscopy, and X-ray fluorescence microscopy. These facilities deliver on dedicated beamlines a photon flux of the order of 1011 photons s−1. Commercial SDDs (area of approximately 100 mm2) are the detectors of choice for those applications. The sample’s element identification, quantification, and mapping require the best possible energy resolution together with a good position resolution and a speed compatible with the beamline’s photon rates. Although there have been many developments in detector technologies for X-ray fluorescence (XRF) applications, there is still a need for custom-tailored efficient, reliable, and yet affordable detector systems, and that are highly effective for soft X-ray spectroscopy. We describe a multielement detector system based on low leakage current silicon drift detectors coupled to ultra-low noise custom CMOS preamplifiers, developed for synchrotron-based XRF. This system helps shorten the data collection time at an energy resolution comparable to that of single-element SDD. The sensitive area and the quantity of sensitive elements are the two criteria that affect the performance. At low flux, the count increases proportionally to the sensitive area, while when the counting rate tends to saturate, the ability to work at higher flows is proportional to the number of sensitive elements. Additionally, a correction for the pileup and dead time should be used to attain the best performance. From the perspective of the beamline specialists themselves, it is evident that a customized, state-of-the-art multi-pixel SDD that meets the demands of solid angle coverage, speed, and energy resolution is required. This will enable quick and precise measurements as well as quick user turnover. This perspective lies on the progressive potentials of the production technology, making it possible to have high production yield and contained costs to produce high-quality, larger-area devices. The goal is to build detection systems with optimal energy resolution, large area coverage, intrinsic position sensitivity, and the ability to sustain high photon fluxes for X-ray spectroscopic imaging in the 0.1–20 keV energy range. It was natural to look for the possibility of constructing SDD monolithic arrays, MASDD, to answer some of the most demanding questions posed by the users of synchrotron radiation source beamlines.
The project whose outcomes we will discuss here has been centered on creating a modular detection system incorporating monolithic multi-pixel SDD elements, Figures 6A, B. This original MASDD detection system’s concept has been specifically conceived and developed to fully meet the expectations of experiments in the XAFS beamlines (Fabiani et al., 2016; Cirrincione, 2019; Rachevski et al., 2019). The state-of-the-art device that presently equips the XRF/XAFS beamlines of the SESAME synchrotron (Jordan) and of ELETTRA Sincrotrone Trieste (Italy) was progressively developed by effecting a collaboration between INFN-Trieste, FBK Foundation Trento, the Polytechnic di Milano, and ELETTRA Sincrotrone Trieste (Figure 6). This instrument has reached unique characteristics that have been addressed by the requirements proposed by beamline scientists, Figures 6C, D). It is optimized for and largely integrated with the beamline for which it has been designed. This system consists of eight monolithic multipixel arrays, each comprising eight SDD cells with dimensions of 3 × 3 mm2.
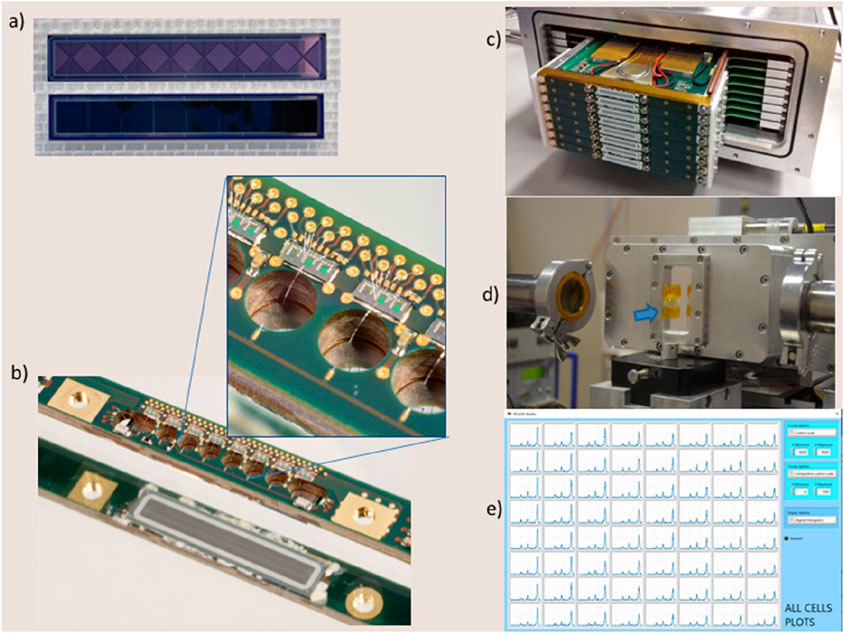
Figure 6. (A) One appreciates the front and back sides of the eight cells MASDD; the total active area of the strip is 72 mm2. (B) The picture shows the multilayer circuit designed to support and bias the detector and the SIRIO preamplifier ASIC. Visible is also the sensitive area of the detector. In the zoomed-in square, the wire bonding from the detector’s anode to the preamplifier and the bias and service lines of the preamplifiers are evidenced. (C) Visible are the eight MASDD strips already assembled to complete the 64-channel detecting system; this reaches a 576 mm2 uncollimated sensitive area. Also visible are parts of the temperature-stabilizing cooling system. (D) Here we see the complete assembled instrument positioned on the beamline facing the sample exposed to the beam; the blue arrow indicates the 25 µm of the polyamide entrance window coated with 50 nm of Al. (E) Screenshot from the FICUS acquisition and control software: simultaneous live acquisition of the 64 channels with the calibration sample (K, Ti, Mn, Zn, Br, and Zr). As one can see, all channels are uniform in characteristics and performance.
This 64-channel modular detection system features a large total collection area of 500 mm2. It can operate with low dead time and a high count rate. At near room temperature, it presents an energy resolution integrated on all 64 channels at the Mn 5.9 keV Kα line below 170 eV FWHM, (Figure 6E).
Each sensor element is a strip made on n-type, 450-µm-thick silicon with a resistivity of 9 kΩcm containing eight SDD elements. The entrance window is a shallow implant p+ common to all eight cells; this enables optimal sensitivity down to a few hundreds of eV. The back side carries the decreasingly negatively biased p+ electrodes (drift cathodes); the common bias voltage is applied to the outermost drift cathode that separates the cells. The innermost cathode near the center of each SDD cell is kept at the lowest negative potential, and the read-out anode is placed at the center. The entrance window is biased to optimize the full depletion of the bulk and to ensure an effective charge collection. The whole sensitive area is surrounded, both on the back and the front sides, by several floating p+ rings (guard cathodes) needed to scale the bias voltage to the ground potential. Each readout anode features an average leakage current below 100 pA/cm2 at 20°C and a capacitance of approximately 40 fF. To eliminate the effects of charge splitting at the edges, a 127-µm-thick tungsten collimator defines the entrance window; the resulting collimated sensitive area is 500 mm2 (Cirrincione et al., 2023). A custom-built ultra-low-noise charge-sensitive amplifier (CSA), the SIRIO-6 targets a high resolution at sub-microsecond peaking times, fostering a reduction in the system dead-time and thus increasing the overall output count rate. The SIRIO version designed for this detection system is characterized by a dynamic range of approximately 250 keV and a conversion gain of ≃ 1.6 mV/keV and, under optimal test conditions, can reach an intrinsic equivalent noise charge of 3.2 electrons rms at room temperature (Mele et al., 2021a). The preamplifier operates in the pulsed reset mode, with reset signals and test signals for the CSAs being distributed to all eight channels of the strip. The preamplifiers are diced in triplets, allowing a quick and easy backup replacement in case of malfunctions due to accidental damage during the mounting process, representing a compact footprint of 1.8 × 0.7 mm2. The CSAs are connected to a board that provides both signal conditioning and configurable analog pre-shaping, as well as service signals and power supplies. This board is then connected to the back-end printed circuit board (PCB), which hosts an 8-channel, 12-bit ADC and an FPGA for the data processing and control. Each of these multi-pixel MASDD elements, once integrated, can be assembled in turn to compose larger matrixes. The arrays are highly integrated for all practical aspects such as temperature management and stability, digital filtering, and back-end electronics. After the digital processing, the data are transmitted by an Ethernet adapter to a computer-running custom-developed software for control and acquisition. The detector was subjected to laboratory and beamline tests using standard samples. Figure 6E shows the uniformity of behavior between the detector cells, whose sum signal is used for the final output spectra (Vacchi et al., 2022; Carlomagno et al., 2021). Figure 7 (top panel left) shows the energy resolution (FWHM) for the Mn Kα emission line at 5.9 keV as a function of peaking time. There is little difference between the room temperature operation (red line) and the lightly cooled detector (blue line), indicating the effectiveness of the temperature stabilization throughout the system and the remarkably low noise level related to the SDD leakage current.
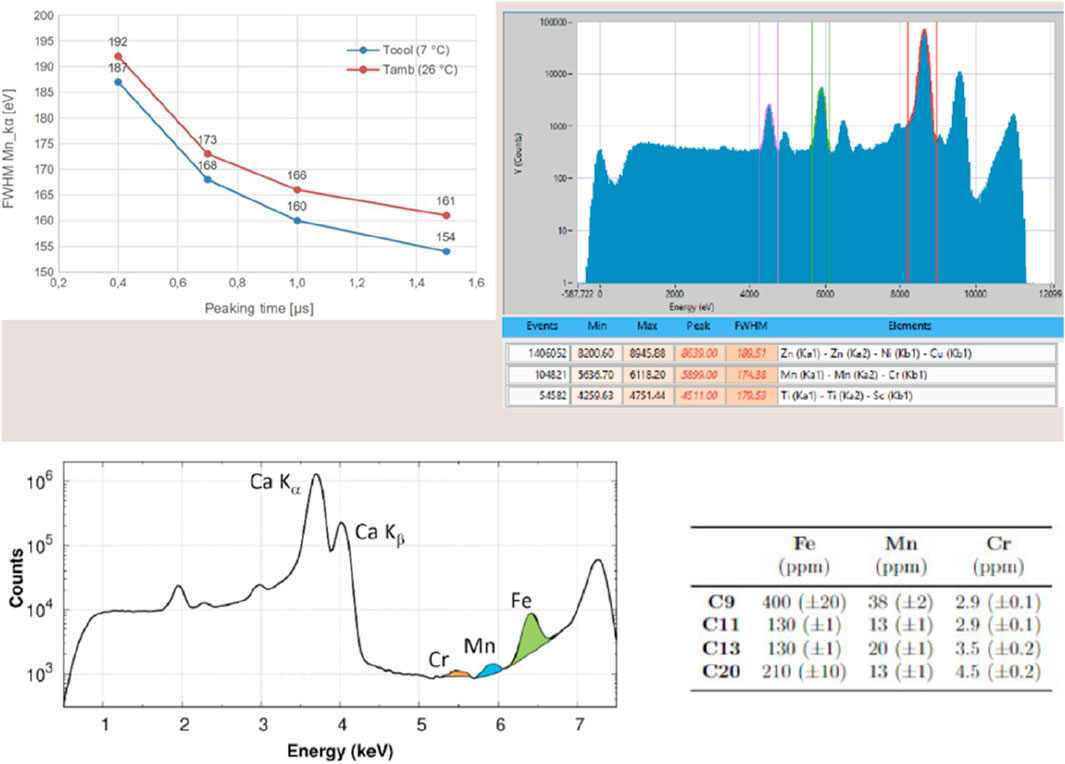
Figure 7. Top panel left, energy resolution versus peaking time at room temperature (red line) and for the cooled detector (blue line) with an average temperature of the sensors of 26°C and of 6°C, respectively; top panel right, acquisition screenshot of data collected from the 64 channels aligned at room temperature (27°C) with a peaking time of 1.45 μs; bottom panel on the left, XRF spectrum (sum signal of the 64 aligned channels) of the C20 sample: the fluorescence intensities are shown in log-scale, the Fe, Mn, and Cr Kα fluorescence signals are emphasized in color. On the right is shown the Table with the concentrations (in ppm) of Fe, Mn, and Cr in the investigated samples. Uncertainties are reported in parentheses.
The particular in Figure 7 top panel right shows a screenshot of the calibration sample (signal sum of 64 channels aligned) acquired at room temperature and with a peaking time of 1.45 μs, while the performance of the system is evidenced in the analysis of a scientific sample of known composition by type and quantity of elements (bottom panel). The XRF spectrum shows the evidence of spectral lines due to traces of elements present down to approximately 3 ppm. The specialized LabView-based acquisition software is fully incorporated into the beamline’s control system for data collection, and it facilitates the control, calibration, and monitoring of instrumental performances.
To confirm the reconstruction of the incident flux, or ICR incident counting rate, on the single 9-mm2 SDD cell, several measurements were made, starting from the live time counts of the detector, which are here referred to as the output count rate (OCR). A graph derived from the analysis of the data collected on the XAFS beam line at the Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste using the most recent detector version is shown in Figure 8. The fluorescence of a copper sample exposed to a 9-keV photon beam at various intensities was measured. A fast filter (rise time of 700 ns and flat top of 100 ns) is used to collect the data. Although the results from one of the detector’s central cells are shown in the figure, all other SDD cells produce results that are comparable. A linear function of the beam intensity, as determined through the ionization chamber, RB, of the XAFS line (the black line in the plot indicated as 2.5 RB), serves as a guide in the visual estimation of the ICR reconstruction quality. To make reading easier, lines are drawn connecting the points that represent the different measurements (the statistical error bars are too small to be shown). Because of the way in which it has been defined here, the OCR (yellow curve) contains also the piled-up events. The spectrum count rate (SCR) green curve in Figure 8 shows the count rate after the pileup rejection operated by the detector acquisition system. The spectrum so obtained is still contaminated by the pileup due to the dead time of the trigger system. Since the residual pileup is due to closely spaced events, in these measurements, it is easy to select only the clean counts represented by the red curve in Figure 8. The cyan shaded area corresponds to the pileup events that cannot be detected by the detector trigger system. In the table, we summarize the maximum counts obtainable from a single SDD cell in the different conditions.
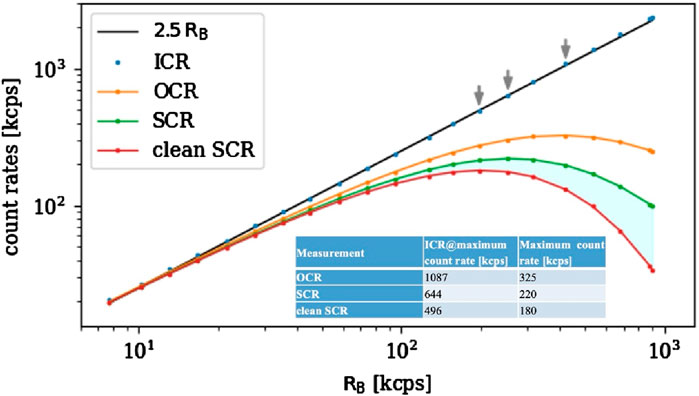
Figure 8. Count rates as defined in the text are reported in this graph, the black reference curve 2.5RB is obtained with an ionization chamber which estimates the incoming rate ICR. The orange points represent the rate of events in the live time of the detector. The other two curves are obtained with a progressive elimination of the pile-up events, and the cyan shaded area corresponds to the fraction of pileup counts that are not rejected due to the dead time of the trigger system. Gray arrows highlight the maximum ICR count rate for the different OCR curves.
According to those results, this detector can easily face high photon rates and reduce the required measurement time by at least an order of magnitude when compared to commercial detectors. It does this by integrating eight MASDD arrays, each of which has eight SDD pixel elements equipped with specially developed electronics; the whole is engineered in a fully integrated system. The dead time and pileup corrections implemented in the detector read-out system allow compensating for the loss of events they cause in such a way that the data acquired by the 64 SDD cells can be combined easily. In this way, the detector behaves equivalently to a large single-sensor device.
A crucial technique for materials whose composition is dominated by light components is low-energy X-ray fluorescence, or LEXRF. The goal is to detect fluorescence photons of light elements like carbon (277 eV), hence operating at energies lower than 2 keV. This needs detectors with thin entrance windows, in-vacuum operations to prevent in-air photon absorption, and a photon incidence angle close to 90° to reduce the absorption by passive layers and coatings.
It is important to cover a significant portion of the solid angle around the sample because of the low fluorescence yield of light elements. Additionally, to differentiate in the energy spectra elements with near emission lines, the detection system’s energy resolution needs to be near the Fano limit (Fano, 1947). Silicon drift devices in a multi-element structure are the best option for applications that call for large solid-angle coverage and a high energy resolution. An MASDD-based solution offers several advantages: a lower anode leakage current is guaranteed by smaller-volume individual elements, and a multi-element structure reduces event loss due to pile-ups by enabling better efficiency at higher photon flux. Furthermore, using a mosaic of customized components to span a significant percentage of the solid angle makes it simple to establish suitable geometries for a specific experimental setting. A system made up of four monolithic multi-element silicon MASDD drift detectors has been built to provide all these characteristics (see Figures 9A, B).
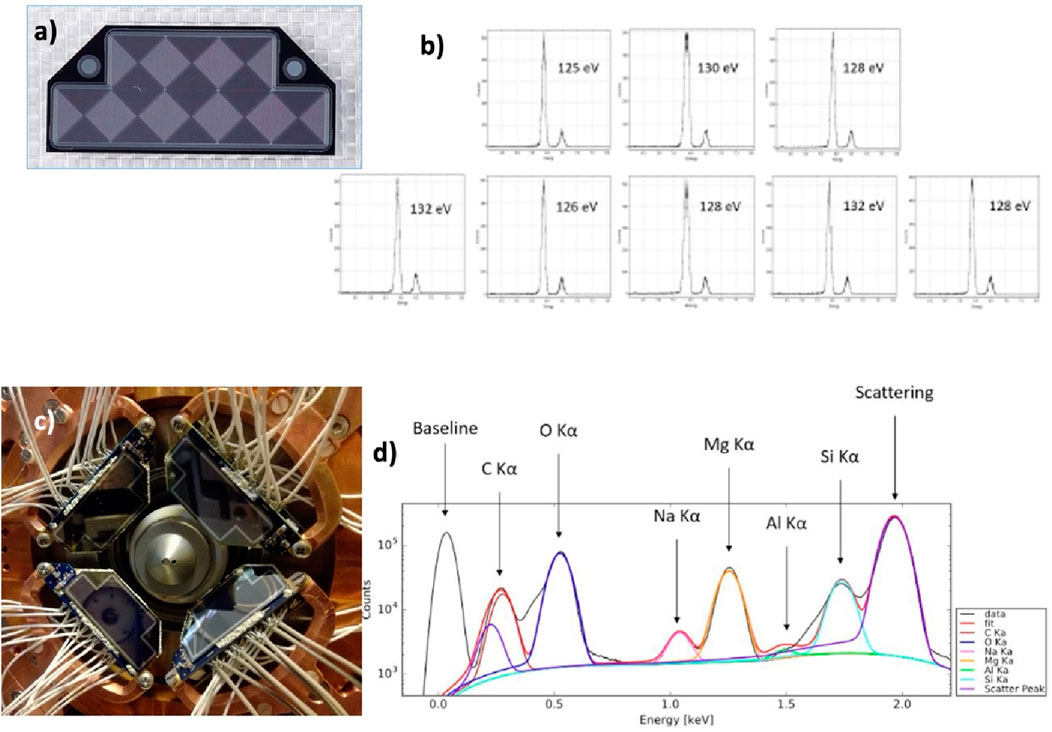
Figure 9. (A) displays the 8-cell MASDD’s specially designed shape. (B) Multi-channel spectra acquired with one monolithic SDD array composed of eight squared pixels with the 55Fe calibration source. In panel (C), the detectors deployed at the TwinMic facility at Elettra Synchrotron in Trieste. Visible is the entrance window of the four detectors, covering a large fraction of the solid angle. The detectors are inclined to minimize the material crossed by the lowest-energy X-rays. (D) shows the reconstructed spectrum and composition of a soybean root sample obtained from a single trapezoidal detector channel at 6.5°C.
This detection system is especially designed for TwinMic beamline at ELETTRA Sincrotrone Trieste that provides a photon beam with an energy below 2.2 keV (Gianoncelli et al., 2016a; Gianoncelli et al., 2016b). Four monolithic SDD arrays covering a total non-collimated active area of 1,232 mm2 and a total collimated active area of 1,113 mm2 are used in this new system. Each trapezoidal-shaped sensor is composed of eight square SDD cells of 6.2 × 6.2 mm2. The focused synchrotron beam exits from the center of the detector system and hits the specimen placed just in front of the detectors, as illustrated in Figure 9C. The only option to provide broad solid-angle coverage and an optimal incidence angle while maintaining an adequate quantum efficiency is by using MASDDs. The large area coverage and the incidence angle on each sensor element have been tuned to the optimal ones by using four different detector units. On top of this, the multi-element SDD solution reduces the leakage current on each single anode; this, when used with ultra-low noise preamplifiers, facilitates the achievement of an energy resolution near the Fano limit (Fano, 1947). This total efficiency, enabling the best use of the beamtime, could not be achieved with the use of individual SDD pixel sensors. This, because beamlines with XRF capabilities can be so flexible and multipurpose, effectively means that a detector should be developed specifically for each experimental station. The versatility of MASDD seems to indicate the way to go. The energy range covered by Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste’s TwinMic beamline is 400–2,200 eV. The TwinMic microscope integrates scanning X-ray microscopy and full-field imaging into one device, enabling X-ray imaging for dynamic studies, morphological characterization, and Spectro microscopic analysis with sample mapping and chemical element identification.
The mapping of light elements such as C, N, O, Mg, and Na is made possible by use of vacuum-operated low-energy XRF (LEXRF) instruments, which provide significant information for the investigation of biological processes. One can see the system’s low energy capabilities in Figure 9D, which shows the spectra obtained by a single channel of the trapezoidal MASDD. The final detecting system for TwinMic beamline is still being finalized and optimized. The TwinMic Elettra beamline proved the novel detection system’s potential and suitability for common LEXRF applications. A set of measurements made with the new detector system was analyzed to exploit the angular dependence of XRF detection to carry out the topographical study of the specimen, reaching quite interesting results (Kourousias et al., 2019).
The development outlined previously naturally leads to building even more compact SDD multipixel structures and to look for applications elsewhere in science, for example, in the field of high-energy astronomy. X-ray charge coupled devices (CCDs) have shown excellent spatial and spectral performances, thanks to their very small pixels that share the same readout circuitry, resulting in extremely low output capacitance and a high signal-to-noise ratio. However, CCDs are not suited for high-throughput timing studies nor for observations of high-flux sources since they may suffer from issues of dead time and pile-up (Ballet, 1999; Ballet, 2003) caused by them being image-integrating devices and by their long readout times. Moreover, low operating temperatures (<-70°C) (Strüder et al., 2001; Turner et al., 2001; Meidinger et al., 2014) are required to mitigate the accumulation of leakage current in the pixels, which can be further reduced by employing smaller pixels, with the consequence of even longer readout times and worse timing performances (Herrmann et al., 2022). All the limitations additionally imply a high power consumption, which is not ideal for scenarios with limited resources, such as for satellite operations, from where X-ray astronomy is performed. Finally, CCDs are usually operational only in the 0.1–10 keV range. New-generation detectors such as depleted p-channel field effect transistors (DEPFETs) only solve a few of the issues of CCDs, especially relatively to timing performances, by reaching excellent energy resolutions and > 10 kHz frame rates at the expense of an even higher power consumption (Kemmer et al., 1990; Lutz et al., 2001; Meidinger et al., 2014; Porro et al., 2012).
Silicon drift detectors are used to meet the demands of X-ray astronomy, with the goal of creating pixelated devices with fast response, asynchronous readout, and single-photon sensitivity. Such a technology can be tailored to different operating energy ranges (from < 1 keV to > 1 MeV), also with the coupling with other detector technologies (e.g., scintillators). This allows SDDs to be adapted to varied applications, from the focal plane of X-ray optics to large field-of-view hard X-ray and γ-ray monitors.
A pixelized SDD-based structure cannot compete with the spatial resolution of a CCD but, at the same time, can be designed to be efficient for unreachable energy ranges of CCDs. However, a 300-μm pitch can already provide the necessary oversampling of the typical point spread function of X-ray concentrators (Okajima et al., 2016) and lobster-eye optics (Mercier et al., 2018), which then qualify as natural applicable scenarios for this technology. The Pixelated Silicon Drift Detector (PixDD) project aims to develop a low-energy (0.5–15 keV) position-sensitive high-throughput X-ray detection system featuring single-photon sensitivity and nearly Fano-limited spectral performances already at room temperature or with mild cooling (150 eV resolution at 6 keV at 0°C) (Sammartini et al., 2020; Evangelista et al., 2018).
The PixDD sensor design is based on the optimization of the single pixel. Every pixel element is a miniature drift detector with two p+ cathodes surrounding a central circular n+ anode. The internal resistive divider is not required because the two cathodes share contacts at the matrix edge. These two cathodes supply the transversal field to provide uniform charge collection for all pixels, even for those on the detector’s edges. An external n+ guard ring is present to collect charge carriers generated outside the matrix. On the opposite side of the chip, a continuous shallow p+ implant constitutes the entrance window for X-rays, thus maximizing the low energy efficiency (Bufon et al., 2019). Figure 10 outlines the structure of the sensor.

Figure 10. In (A) spectrum of 55Fe and pulser acquired at 0 C at the peaking time of 5.6 μs. Acquired at +20 C and a peaking time of 2.4 μs, the resolution becomes 130 eV FWHM. (B) We see the design of the artist view of the mosaic structure of single drift elements with common biases. (C) Energy resolution for the 15 working readout channels at 4.51 keV and its related equivalent noise charge (ENC) as a function of peaking time. (D) Final layout of the 4 × 4, 500 × 500 μm2 SDD pixel detector and a photograph of the details of a corner of the same detector. The basic biasing structure of the single drift element based on two concentric cathodes controlling the drift toward the central anode is also depicted.
This design must consider various limitations and fundamental requirements, such as minimal power consumption and structural simplicity to reduce pixel size for optimal imaging performance. Small pixel size entails a reduction in the allowed transversal drift field. Additionally, the pixel isolation as well as the punch-through current threshold between the two drift cathodes are critical aspects. Significant design and simulation effort was devoted to all aspects of this device (Figure 11A). The efficiency for the peripheral cells is optimized with a proper design and bias of the guard region surrounding the array; the width of this region needs to be at least twice the detector thickness. The efficiency for low-energy X-rays (interacting close to the entrance window) can be tailored by adapting the bias configurations between the entrance window and the cathodes (Figure 11B). The layout of the cathodes on the anode side that induce the drift field in the bulk was arranged in a way to maximize the punch-through current threshold between them (Figure 11C). This allows using high transversal drift fields that reduce the charge collection time. Simulations and measurements on the produced samples showed that the punch-through threshold ranges between 8 V and 15 V depending on the pixel size. Moreover, experimental tests have confirmed that the drift field in each pixel efficiently collects all the charges at the anode, allowing even the peripheral cells to have a sensitive volume very close to the ideal one.
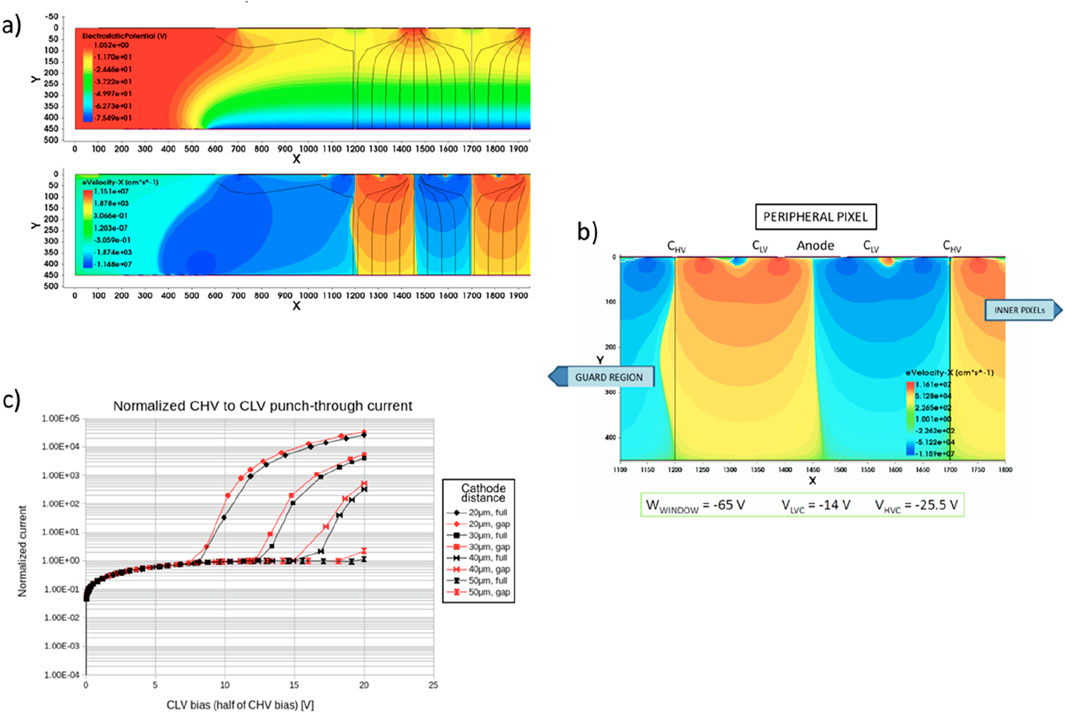
Figure 11. Simulations of the PixDD showing the electric field distribution and drift paths of electrons (A) top, while in (A) bottom, the transversal velocity of the electrons is reported, where blue represents leftward motion and orange is rightward motion. In the plots, the vertical gray lines mark the cell dimension. (B) Part of the simulated structure at a specific bias optimized for complete charge collection. (C) Punch-through current for different bias of various CHV to CLV cathode geometry (field plate covering the whole surface of the gap between implants, “full,” or just extending few μm from the implants, “gap”); increasing the distance between cathodes allows improving the punch-through threshold.
A 4 × 4 matrix prototype of 500 × 500 μm2 pixels was produced on a 9 kΩcm 450 μm thick silicon wafer to test the detector design described above (Figure 10). The noise characteristics of the PixDD, coupled to an extremely low-noise readout electronics, were thoroughly examined using an X-ray facility equipped with a commercial Ti-anode X-ray tube and a custom collimation device to create a ∼40 μm FWHM X-ray spot on the detector surface. In the 2–15 keV energy band, a flux of 7.0 × 104 counts cm2⋅s−1 was applied to every PixDD pixel. An equivalent noise charge between 7.0 and 8.7erms was measured at room temperature for all pixels, at an optimum peaking time of 1.8 μs (Evangelista et al., 2018). Further temperature tests yielded an energy resolution of 125.5 eV at 5.9 keV at 0 deg with a 5.6 μs peaking time (Sammartini et al., 2020).
Two versions of the complete PixDD system have been developed: 128 pixels (16 rows, 8 columns) and 256 pixels (16 rows, 16 columns) with a pixel size of 300 × 300 μm2. Both have undergone extensive testing for investigation of their performances (Ceraudo et al., 2022a; Dedolli et al., 2022). For the 256 pixel version, an energy resolution of FWHM (5.9 keV) ≈ 150 eV at 0°C for single pixels has been measured, with a median value of ≈ 160 eV across the whole matrix (Figure 12). In the future, detailed measurements of the low-energy response and the timing capabilities will be carried out.
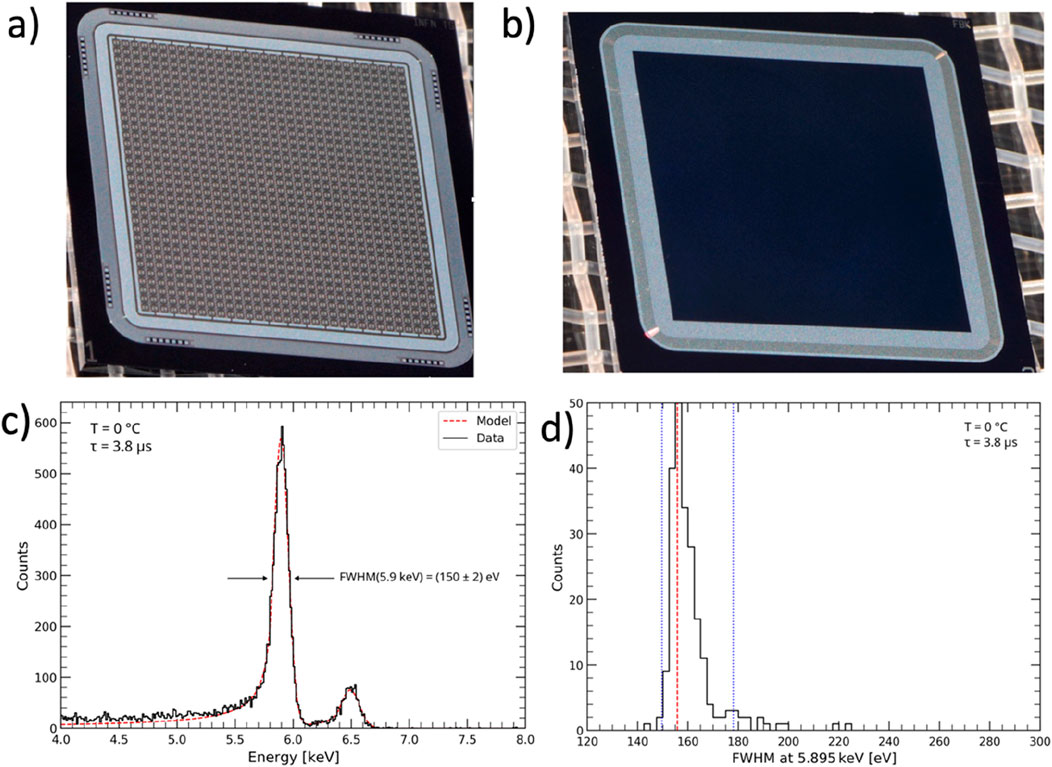
Figure 12. (A, B) Pictures of a 1,024 pixels PixDD sensor (32 rows, 32 columns), (A) structure side and (B) entrance window. (C) Spectral resolution at 5.9 keV and 0°C of the 256-pixel integrated PixDD system single pixel. (D) FWHM distribution across the matrix.
To ensure the matching between the sensor and its readout electronics, hence ensuring the best performances, an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) was developed. The RIGEL (Gandola et al., 2022; Ceraudo et al., 2022b) is a two-dimensional mixed-signal ASIC featuring a matrix of 300 μm × 300 μm front-end readout pixel cells (RPCs), each one consisting of a full analog readout chain with low-power continuous-reset charge-sensitive amplifier, CR-RC shaper, amplitude discriminator, and peak stretcher. Along with some auxiliary digital back-end circuitry, the matrix of RPCs is completed by a set 10-bit Wilkinson ADCs (one per row of RPCs) for immediate signal digitization. With a selectable < 5 μs shaping time constant and an asynchronous readout architecture for the front-end cells, the RIGEL aims to reach a time resolution < 10 μs, all the while maintaining an ENC ≈10 e- RMS and a power consumption of 640 μW/channel. Due to purely geometric consideration, if the ASIC and the sensor were to be connected via traditional wire bonding, it would result in large parasitic capacitance, with the consequent degradation of both the spectral and the time performance of the integrated system. To minimize the issue, a die-level gold-stud flip-chip bump-bonding technique is applied (Caselle et al., 2016).
Although sensors larger than 16 × 16 pixels have already been produced (see in Figures 12A, B the picture of the 32 × 32 channel structure together with the first results obtained from the prototype Figures 12C, D), the same does not apply to the ASIC. Due to their limited dimensions (300 μm × 300 μm), RIGEL RPCs cannot host the routing necessary to connect all the cells of a larger matrix to the surrounding back end in a fully two-dimensional architecture. For this reason, future prototypes will be based on fully separating the analog front-end cells from the digital back-end circuitry on two individual chips featuring through-silicon vias (TSVs) (Manazza et al., 2012). In this configuration, the connection between the chips and with the electronic board underneath will be ensured by a bump-bonding process analogous to the one linking the ASIC and the sensor in the currently available versions.
A final limitation of the current design that is to be overcome in future versions is the guard rings. As mentioned above, to ensure the correct charge-collecting properties of the outermost pixel of the detector matrix, the active area of the sensor is surrounded by an n+ guard ring extending at least twice the thickness of the bulk. Of course, this places a limitation on how close two sensors can be, which in turn decreases the overall fill factor of the integrated detector, an important parameter in relation to the optical systems featuring large focal planes, such as lobster-eye optics, one of the goal applications of PixDD. The technology to design and build slim-edge or edge-less sensors is under investigation and will rely on the employment of doped three-dimensional trenches in place of two-dimensional guard rings, in a technique called deep reactive ion etching, or DRIE (Kenney et al., 1999; Kenney et al., 2006).
A similar approach has led to a qualified high-performance detection system (Porro et al., 2021), demonstrating the wide path available for further practical innovative solutions.
The SDD is based on a sideward depletion process in the silicon bulk; this allows realizing the potentials apt to reach the full depletion and to control the signal charge drifting toward very low capacitance collection anodes. Once we have chosen the thickness based on the needed efficiency, the pixel pitch is determined by the required imaging resolution considering the following aspects:
- The anode diameter depends on the bonding technology used to connect the sensor to the front-end electronics. Various techniques are available, from wafer level bump bonding down to die-to-die gold stub bonding with the smallest ball or pillar realized experimentally down to diameters of 5 μm, with positioning precision of the order of a few μm (Caselle et al., 2016). Reasonable anode diameters range from 40 to 10 μm.
- At most two drift cathodes must be used, and their distance defines the maximum allowed bias potential difference, and thus the maximum transversal drift field. In principle, one could implement a single cathode design, but this would more appropriately be called a pixel sensor.
- Over-depleting the sensor bulk would improve the imaging performance by minimizing the effect of local electric fields generated by the doping concentration variations. Since the maximum voltage between the entrance window implant and the drift cathodes is limited by Vfd, to allow a larger bias, one must maximize the breakdown voltage between the anode and the cathode enclosing it. Presently, a breakdown threshold marginally larger than 30 V has been achieved with an anode diameter of 40 μm and an anode–cathode gap of 20 μm. The breakdown could occur sooner with a smaller anode because of the higher curvature of the implants; hence, the doping profiles must be designed properly.
- Finally, the minimum dimension of the pixel depends also on the front-end ASIC technology and architecture: the more functions are required at pixel level and the greater effort will be needed toward compacting the layout and fitting the shielding critical circuits and routing all signal toward the ASIC periphery. Using more scaled CMOS technologies alleviates in part these issues, but ultimately to compete with the minimum CCD pixel pitches a 3D electronics development with just the charge preamplifier and a simple shaper on the first layer will be necessary provided small through-silicon vias (diameters approximately few μm) are available.
One notable hybrid application of the pixelized SDD is the X and gamma imaging spectrometer (XGIS). The High-Energy Modular Ensemble of Satellites (HERMES) project (Fiore et al., 2022) and the Transient High-Energy Sky and Early Universe Surveyor (THESEUS) (Amati et al., 2021) are the two practical applications for which this detection concept has been gradually developed as sky monitoring instruments for X/gamma-ray transient detection. In order to build a position-sensitive detection plane with a large effective area over an energy band ranging from soft X-rays to soft gamma-rays with the timing resolution down to a few μs, the XGIS further develops an innovative technology coupling MASDD (Figures 13A, B) with crystal scintillator bars (Figure 13C) and very low-noise distributed front-end electronics ASICs (Gandola et al., 2019; Fuschino et al., 2019; Labanti et al., 2020) Figure 13D. The XGIS detector’s unconventional and challenging design operates in the 2 keV–10 MeV energy range Figure 14.
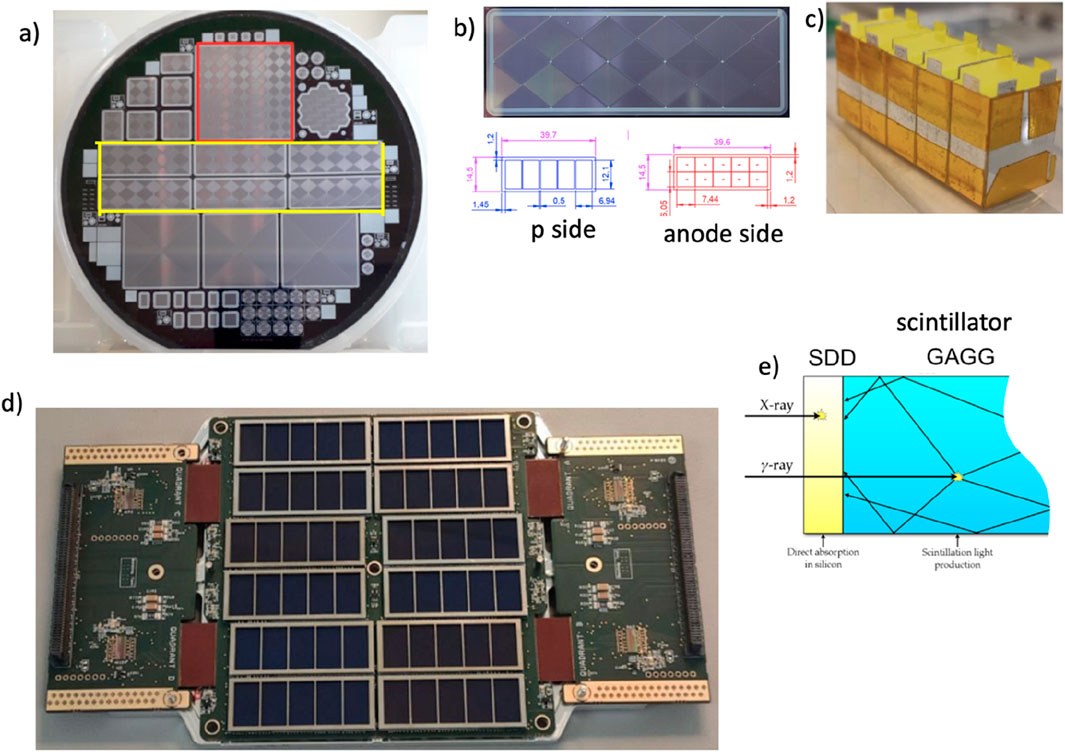
Figure 13. In (A) photo of a wafer from the ReDSoX 2019 batch, anode and drift electrodes n-side, which is the input side for X radiation in XGIS. Highlighted in red is the 64-channel MASDD matrix designed for the XGIS instruments for THESEUS, while evidenced in yellow are six HERMES detectors. In (B), we see a picture of the anode side of one MASDD HERMES element, where one can identify five couples of single SDD; the geometry of the MASDD is evidenced in the bottom panel dimensions are in mm. In (C), the packaged five crystals to be optically connected to the detector so that each SDD couple faces a single crystal. In (D), a photo presenting the HERMES 12 MASDD detection unit is shown. It is composed of 120 SDD coupled to the LYRA dedicated system of readout ASICs. In (E), the working principle of an XGIS detection system: the SDD, directly facing the source is coupled with a GAGG: Ce scintillator crystal. The low-energy radiation (below ∼20 keV) interacts in the SDD. Photons with higher energy cross the SDD and interact in the scintillator. The light output is collected by SDD.
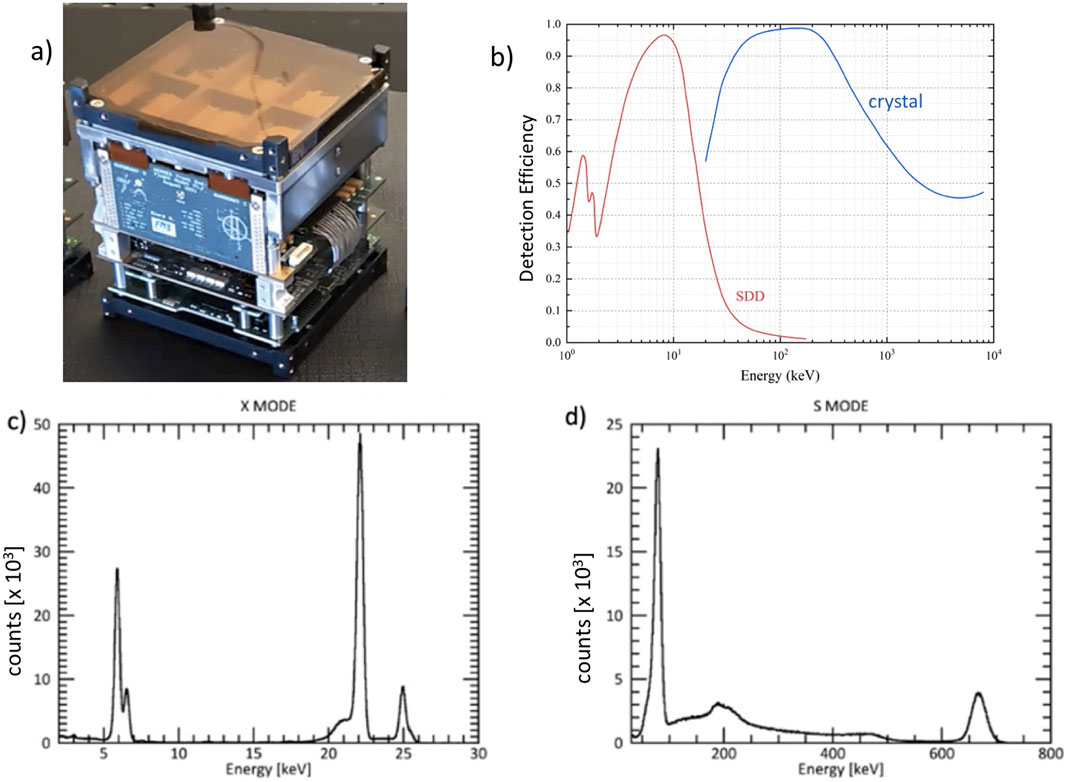
Figure 14. In (A), the completely assembled HERMES detection unit, which is made up of 60 cesium-doped Gadolinium-Aluminum Gallium Garnet (GAGG: Ce) scintillators connected to 120 Silicon Drift Detectors (SDDs). In HERMES, the SDD is on one face of the GaGG scintillating crystal, while in the THESEUS applications, the SDDs are foreseen on both crystal’s faces. In (B), simulated efficiency vs. photon energy in the case of THESEUS for the direct detection in the SDD (red curve) and through light conversion in the scintillating crystal CsI (Tl) (blue curve). SDD and crystal thicknesses were assumed, 0.45 and 30 mm, respectively. In (C), X-ray spectra obtained by illuminating the detector with 55Fe and 109Cd radioactive sources, while in (D), spectra acquired with 109Cd and 137Cs radioactive sources.
More specifically, the HERMES space-borne project is designed to investigate the temporal emission of brilliant high-energy transients like gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) using a constellation of nanosatellites in low-Earth orbit equipped with a hybrid XGIS detection system. This hybrid detector, made of GAGG: Ce scintillator crystals (Figure 13C) optically connected to silicon drift detectors (SDDs) (Figures 13B, E), can measure both soft X-rays and γ-rays (Figure 14). The SDDs directly detect soft X-rays up to approximately 20 keV, while, at higher energies, they collect light emitted by the γ-rays in the scintillator crystals (Figure 14B). The SDDs function as a photodiode in this case, generating a charge signal proportional to the quantity of the scintillator light gathered.
The discrimination between the two signals in the SDD (soft X-rays or optical photons) is achieved by exploiting a segmented detector design (Figures 13B, C). Each scintillator crystal is read-out by two SDD cells. This means that events detected in one SDD are linked to soft X-rays converted in that single SDD cell, whereas events detected in two SDDs at the same time are caused by the light that an incoming hard X-ray or γ-ray produces in the scintillator. The MASDD detector design and production process have been focused on low power consumption of sensors, low dark current, high detection efficiency (both for ionizing radiation and optical photons), enhanced efficiency on the sensor edges, and optimized charge collection efficiency. The HERMES SDD design is shown in Figure 13B, the thickness is 450 μm, and each MASDD is organized in a 2 × 5 array. Guard rings surround the SDD matrix, allowing for a correct electric field termination. The guard ring area is passive; thus, the overall geometric area of the SDD device is 39.6 × 14.5 mm2, while the sensitive area of each SDD cell is 6.05 × 7.44 mm2. A single GAGG crystal (∼12.1 × 6.94 mm2 and 15.0 mm thick) is coupled on the p-side of two SDD channels. On this side, to avoid optical crosstalk coming from different crystals, a metal implant strip 0.5 mm wide is present between the adjoining couple of cells Figure 13D). With this configuration, a signal from a single isolated SDD channel will be interpreted as originated by the direct absorption of an X-ray in silicon, while a signal (with comparable amplitude) from the two SDD channels coupled to the same crystal will be considered a γ-ray event. Figure 14A displays the completely assembled HERMES detection unit, which is made up of 60 cesium-doped Gadolinium–Aluminum Gallium Garnet (GAGG: Ce) scintillators connected to 120 SDDs. The LYRA dedicated readout ASIC (Dedolli et al., 2024) is organized in a multi-chip architecture: 120 front-end chips placed close to the anode of the SDDs send their preprocessed signals to four 32-channel back-end chips. LYRA ASIC has a maximum input charge of 5.2 fC (2.2 MeV in GAGG) with a linearity error within ±1.5%, and the specified intrinsic equivalent noise charge is 14 electrons RMS at 1.6 μs peaking time with a nominal power consumption of 600 μW/channel.
In HERMES, the MASDD is on one face of the scintillating crystal, while the XGIS detector proposed to ESA for the THESEUS mission is a further evolution of the concept developed in HERMES. Here, the scintillator bar, CsI(Tl) is 4.5 × 4.5 × 30 mm in size, with the SDDs positioned at the top and bottom of the bar. Figure 15 represents the module: two sets of SDDs (top and bottom), organized in the 8 × 8 array that can be seen in Figure 15A, are optically connected through a transparent silicone pad to the scintillator crystals. The SDDs are mounted on a PCB where also the first stages of the electronic chain, the FE preamplifiers (Mele et al., 2021b), one for each SDD, are mounted.
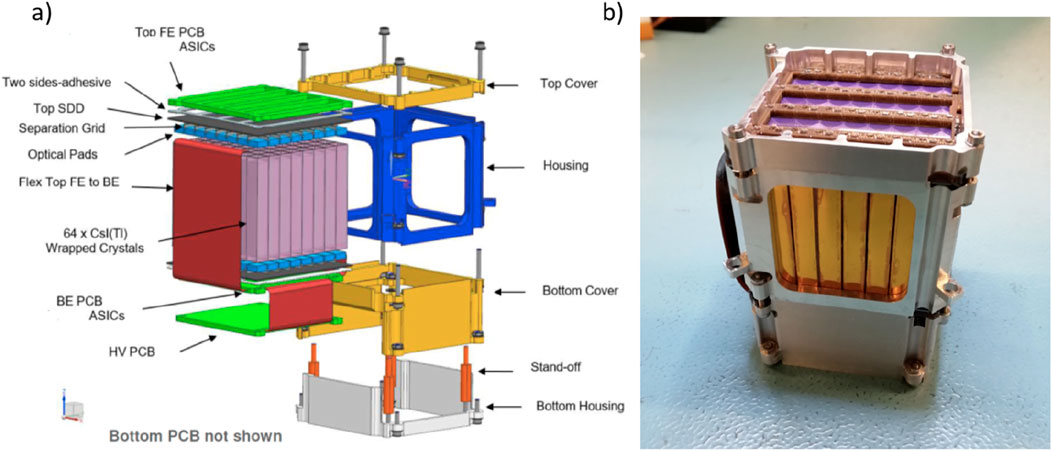
Figure 15. In (A), magnified view of a detection module and in (B) XGIS module prototype realized during THESEUS studies.
The front face of the “top PCB” is exposed to the incoming radiation. The MASDD are glued on the back face of the “top PCB” that presents large openings to avoid the low-energy radiation being absorbed. The SDD acts as both a low-energy X-ray detector (2 ÷ ∼ 20 keV) and as a photodiode for the scintillator light. The top-FE ASICs collecting the SDD charge deliver a pre-amplified signal to the bottom part of the module via a rigid-flex cable. In the “bottom PCB” SDD, with ASIC, operate as a photodiode. The crystal wrapping optically insulates one crystal from the other; therefore, the scintillation light of each crystal can reach only its two coupled SDDs. The other board contains the electronics that deal with the signals of the preamplifiers, the power distribution, and interfaces with the rest of the system. In each XGIS camera are foreseen 6,400 detection elements; the ASICs for readout are twice as many. Amplification, ADC conversion, and time marking of the signal imply an overall power consumption of approximately 50 W.
The module mechanical rigid housing (Figure 15B), packing and pushing together all the elements, has been tested to withstand vibration and thermo-elastic stress due to the combination of components with different thermal expansion coefficients. The housing allows modules to be assembled with a “dead area” between them having the same size of the single element to be compatible with code mask techniques. Like the Hermes case, the scintillator readout allows the discrimination between low-energy X events, detected just in the top SDD, and gamma events interacting in the scintillator and producing top and bottom coincident SDD signals. By weighting top and bottom signals, the position of the gamma interaction along the bar can be evaluated, obtaining a position resolution of the order of 3–5 mm; summing top and bottom signals, the energy of the event is measured, showing a lower energy threshold overlapping the X-range of the top SDD stand alone.
Finally, it is helpful to emphasize that in MASSD-based X-γ ray spectroscopic systems, the front-end (FE) and back-end (BE) electronics are essential for two reasons: 1) the final performance of the spectrometer in terms of energy resolution, minimum detectable photon energy and maximum photon rate, is strictly determined by a careful design which must take into consideration the characteristics and the interplay of all the components of the system (detector, interconnection, and readout electronics) (Bertuccio and Mele, 2023) and 2) the simultaneous operation of several spectroscopic-grade channels requires particular care in the system architecture design to maintain low noise and minimum interference in a mixed-signal environment. At this aim, several application specific integrated circuits in CMOS technology have been designed for the different MASSD-based instruments here. For synchrotron applications, an ultralow-noise charge-sensitive preamplifier (SIRIO) has been developed, able to reach intrinsic noise level as low as 0.9 electron RMS, thanks to an accurate design that minimizes all the noise components originating in the front-end electronics itself (Bertuccio and Caccia, 2007; Bertuccio, 2012; Bertuccio and Mele, 2023). For MASSD devoted to astrophysics, several mixed-signal ASICs have been developed in the last decade, as reported in Table 1. For each MASDD coupled to the corresponding ASICs, the ultimate obtainable energy resolution (last column) is determined by all the system parameters such as the SDD volume, anode area, front-end power consumption, operating temperature, and processing time. Excluding SIRIO, all these ASICs include a full signal processing chain, from the charge preamplifier to the shaper, peak stretcher, amplitude discriminator, pile-up rejector, configuration logic, and signal multiplexing. A common feature of all these ASICs is the relatively low power consumption, approximately 0.5 mW per channel, except for ORION whose 1.6 mW/ch is justified by its three processing chains for each detecting pixel because a XGIS pixel delivers the signal from two SDDs and a scintillator to cover a very wide energy dynamic range from X- or γ-rays. We remind that all multi-channel ASICs embed memory registers for common parts and every single channel re-configuration and that they are designed, both for standard operation and complete testability. Two multiplexers (one analog and one digital) are always provided to address the selected channel energy value and event trigger toward two common outputs, to make instrument PCB design feasible. Again, ORION also provides A/D conversion of the energy value and on-chip elaboration of read-out data including event type estimation (X or γ), timestamp assignment, and rise-time protection to wait for multiple channels to settle before their sampling. In LYRA and ORION ASIC, the signal processing is divided between two chips, FE and BE: the FE contains the charge amplifier and first stage of the pulse shaper for a single pixel, and it is placed very close to the SDD anode; the BE contains all the other signal processing stages for several FE chips and other analog/digital sections. The FE analog output signal is transmitted to the BE in the current mode, to avoid any inter-channel crosstalk which could generate false triggering and limits the minimum detectable photon energy.
The aim of this work is to show how systems based on monolithic multielement SDDs, developed for high-rate X-ray spectroscopy, have become an indispensable detection method for a wide range of scientific applications and have the potential to expand into the wider field of material analysis, thanks to the evolution of the two essential components of a dedicated low leakage current production process and specially designed FE electronics.
We hope to contribute to the general understanding of MASDD by offering a detailed explanative progression based on successful applications and providing the pertinent bibliography.
GAg: writing–review and editing, data curation, and investigation. FA: writing–review and editing, data curation, investigation, and methodology. MA: writing–review and editing, investigation, methodology, and supervision. GAq: writing–review and editing, investigation, and methodology. PB: conceptualization, methodology, resources, validation, and writing–review and editing. GBe: conceptualization, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. GBo: writing–review and editing, data curation, investigation, and methodology. LB: writing–review and editing, supervision, and validation. RC: writing–review and editing, data curation, investigation, and validation. GC: conceptualization, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. FC: writing–review and editing, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, and methodology. DC: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, visualization, and writing–review and editing. EDM: writing–review and editing, data curation, investigation, methodology, validation, and visualization. GDe: writing–review and editing, data curation, investigation, and methodology. GDi: writing–review and editing, data curation, investigation, methodology, and supervision. ID: writing–review and editing, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, and methodology. ED: writing–review and editing, investigation, methodology, and validation. YE: data curation, investigation, methodology, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. MFe: conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, and writing–review and editing. FFc: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, and writing–review and editing. MFi: data curation, investigation, validation, and writing–review and editing. FFu: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing–review and editing. FFo: conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, investigation, and writing–review and editing. MGa: investigation, methodology, validation, and writing–review and editing. AG: conceptualization, methodology, validation, and writing–review and editing. DG: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, and writing–review and editing. MGr: conceptualization, methodology, validation, and writing–review and editing. GK: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing–review and editing. CL: conceptualization, methodology, validation, and writing–review and editing. PM: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. FM: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing–review and editing. RM: investigation, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. LO: conceptualization, data curation, methodology, supervision, and writing–review and editing. GO: methodology, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. GP: conceptualization, data curation, methodology, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. AP: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. AR: investigation, methodology, supervision, validation, visualization, and writing–review and editing. IR: data curation, investigation, supervision, validation, visualization, and writing–review and editing. MS: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, supervision, visualization, and writing–review and editing. SS: data curation, methodology, software, validation, and writing–review and editing. LS: data curation, investigation, software, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. GZ: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. NZa: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. NZo: investigation, methodology, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. AV: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing, validation, and visualization.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work has been made within the ReDSoX-2 INFN research project, supported with the contribution of the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research within the EUROFEL Project and FBK-INFN agreement 2015-03-06. The ReDSoX (Research Drift for Soft X-Rays) R&D project is a broad collaboration between universities and research institutes that share a strong experience in the design, manufacturing, and characterization of high-resolution soft X-ray detectors based on SDDs with custom FEE. The collaboration, born from the financial support of the Italian National Institute of Nuclear Physics (INFN) board 5, is committed to the realization of advanced detection systems for astrophysics instrumentation and for synchrotron light sources through the development of state-of-the-art large area SDDs and ultra-low noise ASICs. Among the research institutes taking part in the collaboration, we find the following: Italian National Institute of Nuclear Physics (INFN), Fondazione Bruno Kessler (FBK), Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste, Italian Space Agency (ASI), Italian National Institute of Astrophysics (INAF), Trento Institute for Fundamental Physics and Applications (TIFPA), and Karlsruhe Institut für Technologie (KIT). Among the university research laboratories: Polytechnic of Milan (PoliMi), University of Pavia (UniPv), University of Trieste (UniTs), University of Udine (UniUd), and University of Bologna (UniBo).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ahangarianabhari, M., Bertuccio, G., Macera, D., Malcovati, P., Grassi, M., Rashevsky, A., et al. (2014). A low-power CMOS ASIC for X-ray Silicon Drift Detectors low-noise pulse processing. J. Instrum. 9 (03), C03036. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/9/03/c03036
Ahangarianabhari, M., Macera, D., Bertuccio, G., Malcovati, P., and Grassi, M. (2015). VEGA: a low-power front-end ASIC for large area multi-linear X-ray silicon drift detectors: design and experimental characterization. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 770, 155–163. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2014.10.009
Alberti, R., Fiorini, C., Guazzoni, C., Klatka, T., and Longoni, A. (2007). Elemental mapping by means of an ultra-fast XRF spectrometer based on a novel high-performance monolithic array of Silicon Drift Detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 580 (2), 1004–1007. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2007.06.056
Alessandro, B., Antinori, S., Bala, R., Batigne, G., Beolè, S., Biolcati, E., et al. (2010). Operation and calibration of the Silicon Drift Detectors of the ALICE experiment during the 2008 cosmic ray data taking period. J. Instrum. 5 (04), P04004. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/5/04/P04004
Amati, L., O’Brien, P. T., Götz, D., Bozzo, E., and Santangelo, A. (2021). “The THESEUS space mission: updated design, profile and expected performances,” arXiv. doi:10.48550/ARXIV.2102.08702
Ballet, J. (1999). Pile-up on X-ray CCD instruments. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 135 (2), 371–381. doi:10.1051/aas:1999179
Ballet, J. (2003). Pile-up on X-ray CCD instruments. Adv. Space Res. 32 (10), 2077–2082. doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(03)90647-8
Bertuccio, G. (2012). The silence of the amps: integrated circuits for very-low-noise processing of random signals from radiation detectors. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 4 (3), 36–45. doi:10.1109/MSSC.2012.2203171
Bertuccio, G., Ahangarianabhari, M., Graziani, C., Macera, D., Shi, Y., Gandola, M., et al. (2016). X-ray silicon drift detector–CMOS front-end system with high energy resolution at room temperature. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 63 (1), 400–406. doi:10.1109/tns.2015.2513602
Bertuccio, G., and Caccia, S. (2007). Progress in ultra-low-noise ASICs for radiation detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 579 (1), 243–246. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2007.04.042
Bertuccio, G., Macera, D., Graziani, C., and Ahangarianabhari, M. (2014). “A CMOS Charge Sensitive Amplifier with sub-electron equivalent noise charge,” in 2014 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC), Seattle, WA, 08-15 November 2014 (IEEE), 1–3. doi:10.1109/NSSMIC.2014.7431123
Bertuccio, G., and Mele, F. (2023). Electronic noise in semiconductor-based radiation detection systems: a comprehensive analysis with a unified approach. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 70 (10), 2310–2321. doi:10.1109/TNS.2023.3310357
Bertuccio, G., Mele, F., Quercia, J., and Shi, Y. (2024). Anode capacitance measurement of silicon drift detectors in operating conditions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1062, 169212. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2024.169212
Bombelli, L., Fiorini, C., Frizzi, T., Alberti, R., and Longoni, A. (2011). “CUBE, A low-noise CMOS preamplifier as alternative to JFET front-end for high-count rate spectroscopy,” in 2011 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, Valencia, Spain, 23-29 October, 2011 (IEEE), 1972–1975. doi:10.1109/NSSMIC.2011.6154396
Bonvicini, V., Cerello, P., Crescio, E., Giubellino, P., Hernandez-Montoya, R., Kolojvari, A., et al. (2000). Silicon drift detectors in the ALICE experiment. AIP Conf. Proc. 531, 360–364. doi:10.1063/1.1315065
Bufon, J., Altissimo, M., Aquilanti, G., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., Billè, F., et al. (2019). “Large solid angle and high detection efficiency multi-element silicon drift detectors (SDD) for synchrotron based x-ray spectroscopy,” in Presented at the proceedings of the 13th international conference on synchrotron radiation instrumentation – sri2018 (Taipei, Taiwan). doi:10.1063/1.5084692060061
Carlomagno, I., Antonelli, M., Aquilanti, G., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., Borghi, G., et al. (2021). Trace-element XAFS sensitivity: a stress test for a new XRF multi-detector. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 28 (6), 1811–1819. doi:10.1107/S1600577521008857
Carulla, M., Barten, R., Baruffaldi, F., Bergamaschi, A., Borghi, G., Boscardin, M., et al. (2024). Quantum efficiency measurement and modeling of silicon sensors optimized for soft X-ray detection. Sensors 24 (3), 942. doi:10.3390/s24030942
Caselle, M., Blank, T., Colombo, F., Dierlamm, A., Husemann, U., Kudella, S., et al. (2016). Low-cost bump-bonding processes for high energy physics pixel detectors. J. Instrum. 11 (01), C01050. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/11/01/C01050
Castoldi, A., Guazzoni, C., Montemuro, G. V., Liu, C., Zorzi, N., Fashevskaya, I., et al. (2016). “2-D mapping of the response of SDD cells of different shape in monolithic arrays for XRF spectroscopy,” in presented at the Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room-Temperature Semiconductor Detector Workshop (NSS/MIC/RTSD), Strasbourg, France, 29 October 2016 (IEEE), 1–3.
Ceraudo, F., Dedolli, I., Cirrincione, D., Del Monte, E., Mele, F., Ambrosino, F., et al. (2022b). Radiation-induced effects on the RIGEL ASIC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1037, 166903. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2022.166903
Ceraudo, F., Ambrosino, F., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., Borghi, G., Campana, R., et al. (2022a). “PixDD: a multi-pixel silicon drift detector for high-throughput spectral-timing studies,” in X-ray, optical, and infrared detectors for astronomy X. Editors A. D. Holland, and J. Beletic (Canada: SPIE: Montréal), 41. doi:10.1117/12.2630450
Cirrincione, D. (2019). First characterization of the detector system for the XAFS beam-line of the synchrotron light source SESAME. Il Nuovo Cimento C 42 (5), 1–8. doi:10.1393/ncc/i2019-19235-2
Cirrincione, D., Ahangarianabhari, M., Ambrosino, F., Bajnati, I., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., et al. (2019). High precision mapping of single-pixel Silicon Drift Detector for applications in astrophysics and advanced light source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 936, 239–241. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2018.10.114
Cirrincione, D., Antonelli, M., Aquilanti, G., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., Borghi, G., et al. (2023). A new collimated multichannel modular detection system based on Silicon Drift Detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1049, 168118. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2023.168118
Dedolli, I., Mele, F., Ceraudo, F., Gandola, M., Grassi, M., Bellutti, P., et al. (2022). “Experimental characterization of the RIGEL sparse readout ASIC for soft X-ray PixDD detector,” in 2022 IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference (NSS/MIC) (Italy: IEEE), 1–3. doi:10.1109/NSS/MIC44845.2022.10399142
Dedolli, I., Mele, F., and Bertuccio, G. (2024). “Updates on the multi-channelchannel LYRA ASIC for X/$$\gamma $$- ray spectrometer onboard HERMES space mission,” in Proceedings of SIE 2023. Lecture notes in electrical engineering. Editors C. Ciofi, and E. Limiti (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 1113, 150–157. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-48711-8_17
Espacenet (2025).WO2020075051A1 Semiconductor drift detector with an optimized effective area. Available at: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/064902245/publication/WO2020075051A1?q=pn%3DWO2020075051A1 (Accessed April 9, 2020).
Evangelista, Y., Ambrosino, F., Feroci, M., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., Borghi, G., et al. (2018). Characterization of a novel pixelated silicon drift detector (PixDD) for high-throughput X-ray astrophysics. J. Instrum. 13 (09), P09011. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/13/09/P09011
Fabiani, S., Ahangarianabhari, M., Baldazzi, G., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., Bruschi, M., et al. (2016). Development and tests of a new prototype detector for the XAFS beamline at Elettra Synchrotron in Trieste. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 689 (1), 012017. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/689/1/012017
Fano, U. (1947). Ionization yield of radiations. II. The fluctuations of the number of ions. Phys. Rev. 72 (1), 26–29. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.72.26
FBK, “FBK **Fondazione Bruno kessler** center for sensors & devices via sommarive 18 povo (TN) - Italy.
Feroci, M., Stella, L., van der Klis, M., Courvoisier, T. J. L., Hernanz, M., Hudec, R., et al. (2012). The large observatory for X-ray timing (LOFT). Exp. Astron. 34 (2), 415–444. doi:10.1007/s10686-011-9237-2
Fiore, F., Guzman, A., Campana, R., and Evangelista, Y. (2022). HERMES-Pathfinder. Handb. X-ray Gamma-ray Astrophysics, 1–19. doi:10.1007/978-981-16-4544-0_35-1
Fiorini, C., Gola, A., Longoni, A., Zanchi, M., Restelli, A., Perotti, F., et al. (2006). A large-area monolithic array of silicon drift detectors for medical imaging. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 568 (1), 96–100. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2006.07.025
Fiorini, C., and Longoni, A. (2003). Gamma-ray imaging detectors based on silicon drift detectors arrays coupled to a single scintillator. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 497 (1), 221–225. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(02)01915-0
Fuschino, F., Campana, R., Labanti, C., Evangelista, Y., Feroci, M., Burderi, L., et al. (2019). HERMES: an ultra-wide band X and gamma-ray transient monitor on board a nano-satellite constellation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 936, 199–203. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2018.11.072
Gandola, M., Grassi, M., Mele, F., Dedolli, I., Malcovati, P., and Bertuccio, G. (2022). The sparse readout RIGEL application specific integrated circuit for pixel silicon drift detectors in soft X-ray imaging space applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1040, 167249. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2022.167249
Gandola, M., Grassi, M., Mele, F., Malcovati, P., and Bertuccio, G. (2019). “LYRA: a multi-chip ASIC designed for HERMES X and gamma ray detector,” in 2019 IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference (NSS/MIC) (Manchester, United Kingdom: IEEE), 1–3. doi:10.1109/NSS/MIC42101.2019.9059616
Gatti, E., Longoni, A., Sampietro, M., Giacomelli, P., Vacchi, A., Rehak, P., et al. (1988). Silicon drift chamber prototype for the upgrade of the UA6 experiment at the CERN p collider. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 273 (2), 865–868. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(88)90109-X
Gatti, E., and Rehak, P. (1984). Semiconductor drift chamber — an application of a novel charge transport scheme. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 225 (3), 608–614. doi:10.1016/0167-5087(84)90113-3
Gatti, E., and Rehak, P. (2005). Review of semiconductor drift detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 541 (1–2), 47–60. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2005.01.037
Gauthier, C., Goulon, J., Moguiline, E., Rogalev, A., Lechner, P., Strüder, L., et al. (1996). A high resolution, 6 channels, silicon drift detector array with integrated JFET’s designed for XAFS spectroscopy: first X-ray fluorescence excitation spectra recorded at the ESRF. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 382 (3), 524–532. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(96)00814-5
Gianoncelli, A., Bufon, J., Ahangarianabhari, M., Altissimo, M., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., et al. (2016a). A new detector system for low energy X-ray fluorescence coupled with soft X-ray microscopy: first tests and characterization. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 816 (Suppl. C), 113–118. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2016.01.076
Gianoncelli, A., Kourousias, G., Merolle, L., Altissimo, M., and Bianco, A. (2016b). Current status of the TwinMic beamline at Elettra: a soft X-ray transmission and emission microscopy station. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 23 (6), 1526–1537. doi:10.1107/S1600577516014405
Guazzoni, C. (2010). The first 25 years of silicon drift detectors: a personal view. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 624 (2), 247–254. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.06.005
Gugiatti, M., King, P., Fink, D., Houdy, T., Siegmann, D., Urban, K., et al. (2022). Towards the TRISTAN detector: characterization of a 47-pixel monolithic SDD array. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1025, 166102. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2021.166102
Herrmann, S., Orel, P., Chattopadh, T., Morris, R. G., Chattopadhyay, T., Prigozhin, G., et al. (2022). “X-ray speed reading: enabling fast, low noise readout for next-generation CCDs,” in X-ray, optical, and infrared detectors for astronomy X. Editors A. D. Holland, and J. Beletic (Canada: SPIE: Montréal), 42. doi:10.1117/12.2630195
Kemmer, J., Burger, P., Henck, R., and Heijne, E. (1982). Performance and applications of passivated ion-implanted silicon detectors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 29 (1), 733–737. doi:10.1109/TNS.1982.4335947
Kemmer, J., Lutz, G., Prechtel, U., Schuster, K., Sterzik, M., Strüder, L., et al. (1990). Experimental confirmation of a new semiconductor detector principle. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 288 (1), 92–98. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(90)90470-Q
Kenney, C., Parker, S., Segal, J., and Storment, C. (1999). Silicon detectors with 3-D electrode arrays: fabrication and initial test results. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 46 (4), 1224–1236. doi:10.1109/23.785737
Kenney, C. J., Segal, J., Westbrook, E., Parker, S., Hasi, J., Da Via, C., et al. (2006). Active-edge planar radiation sensors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 565 (1), 272–277. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2006.05.012
Kourousias, G., Billè, F., Cautero, G., Bufon, J., Rachevski, A., Schillani, S., et al. (2019). XRF topography information: simulations and data from a novel silicon drift detector system. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 936, 80–81. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2018.10.142
Kushpil, S., Crescio, E., Giubellino, P., Idzik, M., Kolozhvari, A., Kushpil, V., et al. (2006). Beam test results of the irradiated silicon drift detector for ALICE. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 566 (1), 94–99. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2006.05.057
Labanti, C., Amati, L., Frontera, F., Merghetti, S., Gasent-Blesa, J. L., Tenzer, C., et al. (2020). “The X/Gamma-ray Imaging Spectrometer (XGIS) on-board THESEUS: design, main characteristics, and concept of operation,” in Space telescopes and instrumentation 2020: ultraviolet to gamma ray. Editors J.-W. A. Den Herder, K. Nakazawa, and S. Nikzad (United States: SPIE), 303. doi:10.1117/12.2561012
Lindström, G. (2003). Radiation damage in silicon detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 512 (1–2), 30–43. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(03)01874-6
Lutz, G. (2007). Semiconductor radiation detectors. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-71679-2
Lutz, G., Richter, R. H., and Strüder, L. (2001). Novel pixel detectors for X-ray astronomy and other applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 461 (1–3), 393–404. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(00)01258-4
Manazza, A., Gaioni, L., Manghisoni, M., Ratti, L., Re, V., Traversi, G., et al. (2012). “CMOS MAPS in a homogeneous 3D process for charged particle tracking,” in 2012 IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference record (NSS/MIC) (Anaheim, CA, USA: IEEE), 2041–2047. doi:10.1109/NSSMIC.2012.6551472
Meidinger, N., Andritschke, R., Bornemann, W., Coutinho, D., Emberger, V., Halker, O., et al. (2014). “Report on the eROSITA camera system,” in Presented at the SPIE astronomical telescopes + instrumentation. Editors T. Takahashi, J.-W. A. Den Herder, and M. Bautz (Quebec, Canada: Montréal), 91441W. doi:10.1117/12.2055703
Mele, F., Dedolli, I., Gandola, M., Grassi, M., Malcovati, P., Amati, L., et al. (2021b). ORION, a multichip readout electronics for satellite wide energy range X-/γ-Ray imaging spectroscopy: design and characterization of the analog section. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 68 (12), 2801–2809. doi:10.1109/TNS.2021.3130184
Mele, F., Gandola, M., and Bertuccio, G. (2021a). SIRIO: a high-speed CMOS charge-sensitive amplifier for high-energy-resolution X- γ ray spectroscopy with semiconductor detectors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 68 (3), 379–383. doi:10.1109/TNS.2021.3055934
Mercier, K., Gonzalez, F., Gotz, D., Boutelier, M., Boufracha, N., Burwitz, V., et al. (2018). “MXT instrument on-board the French-Chinese SVOM mission,” in Space telescopes and instrumentation 2018: ultraviolet to gamma ray. Editors J.-W. A. Den Herder, K. Nakazawa, and S. Nikzad (Austin, United States: SPIE), 72. doi:10.1117/12.2313561
Del Monte, E., Azzarello, P., Bozzo, E., Bugiel, S., Diebold, S., Evangelista, Y., et al. (2014a). “Radiation tests of the silicon drift detectors for LOFT,” in Presented at the space telescopes and instrumentation 2014: ultraviolet to gamma ray (Montréal, Quebec, Canada: SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation). 914464. doi:10.1117/12.2055747
Monte, E. D., Rachevski, A., Zampa, G., Zampa, N., Azzarello, P., Bozzo, E., et al. (2014b). Measurement of the effect of non ionising energy losses on the leakage current of silicon drift detector prototypes for the LOFT satellite. J. Instrum. 9 (07), P07016. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/9/07/P07016
Niculae, A., Lechner, P., Soltau, H., Lutz, G., Strüder, L., Fiorini, C., et al. (2006). Optimized readout methods of silicon drift detectors for high-resolution X-ray spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 568 (1), 336–342. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2006.06.025
O’Connor, P., Gramegna, G., Rehak, P., Corsi, F., and Marzocca, C. (1997). CMOS preamplifier with high linearity and ultra low noise for X-ray spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 44 (3), 318–325. doi:10.1109/23.603663
Okajima, T., Soong, Y., Balsamo, E. R., Enoto, T., Olsen, L., Koenecke, R., et al. (2016). “Performance of NICER flight x-ray concentrator,” in Presented at the SPIE astronomical telescopes + instrumentation. Editors J.-W. A. Den Herder, T. Takahashi, and M. Bautz (Edinburgh, United Kingdom), 99054X. doi:10.1117/12.2234436
Piemonte, C., Rashevsky, A., and Vacchi, A. (2006). Device simulation of the ALICE silicon drift detector. Microelectron. J. 37 (12), 1629–1638. doi:10.1016/j.mejo.2006.04.022
Porro, M., Andricek, L., Aschauer, S., Bayer, M., Becker, J., Bombelli, L., et al. (2012). Development of the DEPFET sensor with signal compression: a large format X-ray imager with mega-frame readout capability for the European XFEL. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 59 (6), 3339–3351. doi:10.1109/TNS.2012.2217755
Porro, M., Andricek, L., Aschauer, S., Castoldi, A., Donato, M., Engelke, J., et al. (2021). The MiniSDD-based 1-mpixel camera of the DSSC project for the European XFEL. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 68 (6), 1334–1350. doi:10.1109/TNS.2021.3076602
Quaglia, R., Schembari, F., Bellotti, G., Butt, A., Fiorini, C., Bombelli, L., et al. (2016). Development of arrays of silicon drift detectors and readout ASIC for the SIDDHARTA experiment. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 824, 449–451. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2015.08.079
Rachevski, A., Ahangarianabhari, M., Aquilanti, G., Bellutti, P., Bertuccio, G., Borghi, G., et al. (2019). The XAFS fluorescence detector system based on 64 silicon drift detectors for the SESAME synchrotron light source. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 936, 719–721. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2018.09.130
Rachevski, A., Zampa, G., Zampa, N., Rashevskaya, I., Vacchi, A., Giacomini, G., et al. (2013). X-ray spectroscopic performance of a matrix of silicon drift diodes. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 718, 353–355. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2012.10.017
Rashevsky, A., Bonvicini, V., Burger, P., Cerello, P., Crescio, E., Giubellino, P., et al. (2001). Characteristics of the ALICE silicon drift detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 461 (1), 133–138. doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(00)01189-X
Rashevsky, A., Bonvicini, V., Burger, P., Piano, S., Piemonte, C., and Vacchi, A. (2002). Large area silicon drift detector for the ALICE experiment. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 485 (1), 54–60. doi:10.1016/s0168-9002(02)00531-4
Rehak, P., Carini, G., Chen, W., De Geronimo, G., Fried, J., Li, Z., et al. (2010). Arrays of silicon drift detectors for an extraterrestrial X-ray spectrometer. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 624 (2), 260–264. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.05.058
Rehak, P., Walton, J., Gatti, E., Longoni, A., Sanpietro, M., Kemmer, J., et al. (1986). Progress in semiconductor drift detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 248 (2–3), 367–378. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(86)91021-1
Sammartini, M., Gandola, M., Mele, F., Bertuccio, G., Ambrosino, F., Bellutti, P., et al. (2020). Pixel Drift Detector (PixDD) – SIRIO: an X-ray spectroscopic system with high energy resolution at room temperature. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 953, 163114. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2019.163114
Strüder, L., Briel, U., Dennerl, K., Hartmann, R., Kendziorra, E., Meidinger, N., et al. (2001). The European photon imaging camera on XMM-Newton: the pn-CCD camera. Astronomy Astrophysics 365 (1), L18–L26. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000066
Turner, M. J. L., Abbey, A., Arnaud, M., Balasini, M., Barbera, M., Belsole, E., et al. (2001). The European photon imaging camera on XMM-Newton: the MOS cameras. Astronomy Astrophysics 365 (1), L27–L35. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000087
Vacchi, A. (2023). “Silicon drift detectors,” in Handbook of X-ray and gamma-ray astrophysics. Editors C. Bambi, and A. Santangelo (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore), 1–53. doi:10.1007/978-981-16-4544-0_18-1
Vacchi, A., Cirrincione, D., Altissimo, M., Antonelli, M., Aquilanti, G., Bellutti, P., et al. (2022). Recent progress in high resolution X-ray customised detection systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2380 (1), 012095. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/2380/1/012095
Vacchi, A., Cox, P., Giacomelli, P., Castoldi, A., Chinnici, S., Gatti, E., et al. (1993). Beam test of a large area silicon drift detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 326 (1), 267–272. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(93)90362-L
Wilson-Hodge, C. A., Ray, P. S., Gendreau, K., Chakrabarty, D., Feroci, M., Arzoumanian, Z., et al. (2017). STROBE-X: X-ray timing and spectroscopy on dynamical timescales from microseconds to years. Results Phys. 7, 3704–3705. doi:10.1016/j.rinp.2017.09.013
Zampa, G., Campana, R., Feroci, M., Vacchi, A., Bonvicini, V., Del Monte, E., et al. (2011). Room-temperature spectroscopic performance of a very-large area silicon drift detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 633 (1), 15–21. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.12.129
Zampa, G., Rashevsky, A., and Vacchi, A. (2007). Spectroscopic performances of a very large area silicon drift detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 572 (1), 328–329. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2006.10.200
Zhang, S., Santangelo, A., Feroci, M., Xu, Y., Lu, F., Chen, Y., et al. (2019). The enhanced X-ray Timing and Polarimetry mission—eXTP. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 62 (2), 29502. doi:10.1007/s11433-018-9309-2
Keywords: silicon drift detectors, high energy resolution X-ray detectors, monolithic multi-pixel silicon drift detectors, precision X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray imaging, X and gamma spectroscopy
Citation: Agostini G, Ambrosino F, Antonelli M, Aquilanti G, Bellutti P, Bertuccio G, Borghi G, Bosisio L, Campana R, Cautero G, Ceraudo F, Cirrincione D, Del Monte E, Della Casa G, Dilillo G, Dedolli I, Demenev E, Evangelista Y, Feroci M, Ficorella F, Fiorini M, Fuschino F, Fiore F, Gandola M, Gianoncelli A, Giuressi D, Grassi M, Kourousias G, Labanti C, Malcovati P, Mele F, Menk RH, Olivi L, Orzan G, Pepponi G, Picciotto A, Rachevski A, Rashevskaya I, Sammartini M, Schillani S, Stebel L, Zampa G, Zampa N, Zorzi N and Vacchi A (2025) Silicon drift detector monolithic arrays for X-ray spectroscopy. Front. Detect. Sci. Technol 3:1551757. doi: 10.3389/fdest.2025.1551757
Received: 26 December 2024; Accepted: 27 January 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Marco Cortesi, Michigan State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Alessandro Scordo, National Laboratory of Frascati (INFN), ItalyCopyright © 2025 Agostini, Ambrosino, Antonelli, Aquilanti, Bellutti, Bertuccio, Borghi, Bosisio, Campana, Cautero, Ceraudo, Cirrincione, Del Monte, Della Casa, Dilillo, Dedolli, Demenev, Evangelista, Feroci, Ficorella, Fiorini, Fuschino, Fiore, Gandola, Gianoncelli, Giuressi, Grassi, Kourousias, Labanti, Malcovati, Mele, Menk, Olivi, Orzan, Pepponi, Picciotto, Rachevski, Rashevskaya, Sammartini, Schillani, Stebel, Zampa, Zampa, Zorzi and Vacchi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Andrea Vacchi, dmFjY2hpQHRzLmluZm4uaXQ=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.