- 1Department of Epidemiology and Population Health, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon
- 2Research Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- 3Department of Neurology, University of Michigan School of Nursing, Ann Arbor, MI, United States
- 4Division of Neurosurgery, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, American University of Beirut Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon
Objective: To provide the first estimates of dementia incidence rates among elderly in Lebanon.
Methods: The cohort established in 2013 consisted of 470 elderly from Beirut and Mount Lebanon, who consented to be followed-up. In 2017, we reached 341 participants/informants, achieving a response rate of 72.6%. The validated Arabic version of the 10/66 Dementia Research Group diagnostic tool was administered through face-to-face interviews. Direct age standardization was applied to the data using the Western European population distribution. Age-, sex- and location-specific incidence rates were estimated.
Results: After 3.5 years of follow up, 19 new cases of dementia were identified among 229 surviving participants. The crude incidence rate was 16.8 per 1,000 p-y, and the age standardized rate was 20.5 per 1,000 p-y. The incidence rate increased with age, going from 6.5 for those aged 65–74 years to 54.0 for those aged 85–89 years. Incidence rate was higher among females than males (20.7 vs.12.0), and higher in Mount Lebanon, as compared to the capital city Beirut (19.5 vs.14.9).
Conclusion: Dementia incidence rate was close to European and North American countries' estimates. The use of validated tools increased the internal validity of our results. A large cohort study is warranted to confirm these results.
1 Introduction
Dementia represents a significant public health challenge, exerting both emotional and financial tolls on society at large, and on individuals in particular. According to the most recent data from the Global Burden of Disease study, dementia contributes to almost 5% of total disability-adjusted life years (DALYS) for individuals aged 70 years and above globally (IHME, 2021). Worldwide, 55 million live with dementia, and this number is expected to increase to 139 million by 2050 (WHO, 2021). Notably, the prevalence is higher among women as compared to men (8.1% and 5.4%, respectively) (WHO, 2021). High-income countries are experiencing a decreasing trend in age-specific dementia incidence (Matthews et al., 2016; Qiu et al., 2013; Schrijvers et al., 2012); however, the global burden continues to escalate due to aging populations (Satizabal et al., 2016).
The increase in the aging population in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region is consistent with the global trend (Yaghmour et al., 2019). However, in 10 countries (48%) within the MENA region, there is notable lack of information regarding dementia burden or risk, indicating knowledge and awareness deficit about dementia in this region (Bhalla et al., 2018; El-Metwally et al., 2019). The only study reporting on dementia incidence in the MENA region is a systematic review. The evidence indicates a scarcity of available data on incidence rates, with a significant proportion of countries in the region needing more information on dementia (Bhalla et al., 2018).
Lebanon presents a unique case study for dementia research. The country's diverse population genetic makeup, its distinct socio-economic and cultural context, and the high proportion of older adults (10.8%, the highest in the region) provide crucial insights into the dementia risk (Saxena, 2008). A 2013 cross-sectional study in Lebanon found a 9.0% age-standardized prevalence of dementia in individuals aged 65 years and above (Phung et al., 2017). This prevalence exceeds worldwide estimates, suggesting a potentially crippling burden of dementia in Lebanon (Qassem et al., 2023).
This study aims to estimate the overall dementia incidence rate in Lebanon, as well as age- and gender-specific rates, to address the gap in knowledge of dementia incidence in the MENA region.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design
The Cohort of Lebanese Elderly: a Dementia Study, or COLDS for short, is a prospective population-based cohort study among elderly aged 65 years and above. Data were collected at two timepoints: baseline data was collected in 2013 with follow-up assessments conducted in 2017. Interviews were administered in the participants' homes.
2.2 Study population and sample
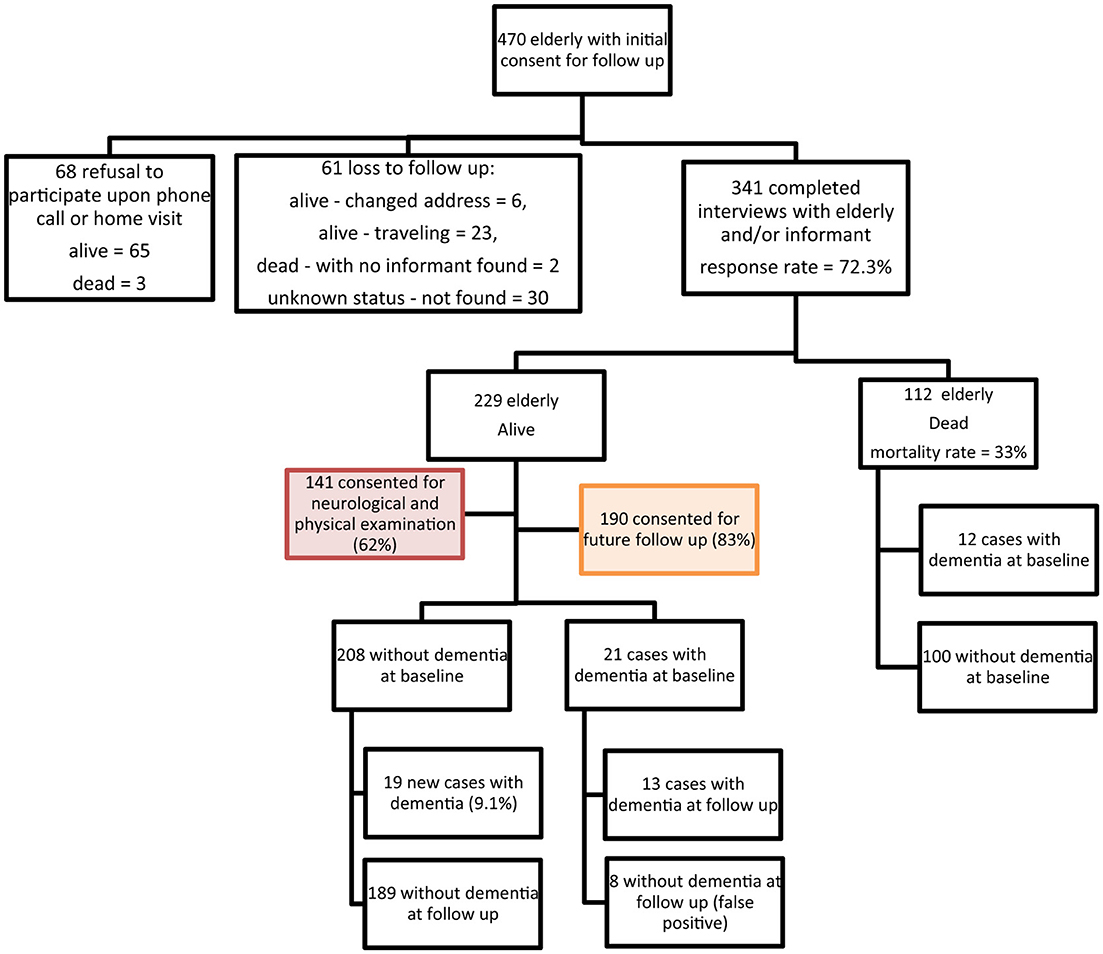
The study was conducted in two of the eight governorates of Lebanon: (i) Beirut, the capital, characterized by its dense urban setting and crowded neighborhoods and (ii) Mount Lebanon (Shouf and Aley districts; two out of six districts in Mount Lebanon), a peri-urban district. Study participants were recruited using a multi-stage random sampling approach based on the Lebanese population distribution data from the latest census. Initially, we divided Lebanon into major administrative regions, selecting Beirut and Mount Lebanon (Shouf and Aley districts) to represent urban and peri-urban areas, respectively. Using a sampling frame from another survey, Beirut governorate was divided into 594 clusters, each containing 50 residential buildings, with complete detailed household listing for 60 randomly selected clusters. Since there was no existing sampling frame in Chouf and Aley districts, villages and towns were randomly chosen and weighed based on their respective sizes. All households within the randomly selected clusters were approached and within each household, eligible individuals (aged 65 and above) were identified, and one participant per household was randomly selected for inclusion. This method ensured coverage of diverse household types. At baseline 502 elderly were interviewed and assessed for dementia. Of those, 470 gave their initial consent for a follow-up visit, and 341 were included in the follow-up interviews (Figure 1). Of these, 19 were diagnosed with dementia. During the 2017 follow-up, eight cases initially classified as dementia were identified as false positives upon re-evaluation. This misclassification may have been influenced by testing limitations, including hearing impairments in two participants and the 10/66 Dementia Research Group diagnostic tool while having high specificity (92%), has a false positive rate of up to 8%, especially among those with no formal education. The result is 328 elderly at risk of dementia.
2.3 Diagnosis of dementia
Arabic validated one-stage 10/66 Dementia Research Group (DRG) diagnostic assessment tools were used (The 10/66 Dementia Research Group, 2015). These tools include (i) the community screening instrument for Dementia (CSI-D), (ii) the modified Consortium to Establish a Registry of Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD) animal naming tests and modified 10-word list recall, (iii) the CSI-D informant interview, (iv) the physical assessment, (v) the Geriatric Mental State (GMS) examination test, and (vi) brief neurological examination (NEUROEX). The algorithm, initially developed by Prince et al. (2003), yields a binary outcome for each older adult to assess dementia status (Phung et al., 2014).
2.4 Statistical methods
We calculated the age-specific incidence rate by 5-year age intervals. We divided the number of cases by the number of person-years (p-y) which was calculated by summing up every participant's contribution of follow-up duration per age interval. The follow-up period ended at the date of the follow-up interview, which was considered as the age of dementia onset for positive cases. Incidence per 1,000 p-y was estimated as the number of new cases of dementia divided by the at-risk p-y multiplied by 1,000. The incidence rates presented in this study reflect a follow-up period of 3.5 years, spanning from 2013 to 2017. This time frame defines the observation window and scope of measured dementia incidence in the cohort. We calculated incidence rates per 1,000 person-years to account for person-time at risk, ensuring a clear representation of dementia risk over time in our cohort. Confidence intervals were calculated assuming a Poisson distribution for the number of cases within each reporting category. The standardized incidence rate of dementia was reported using direct age standardization based on the Western European population distribution. We applied standardization using the Western European population distribution to enable comparability with global dementia incidence studies.
2.5 Ethical considerations
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the American University of Beirut approved the study (protocol # FHS.MC.34). A decision-making capacity test was conducted before every interview to ensure the participants' comprehension of the study. Written consent was secured from both participant and his/her informant and in the presence of a witness in case the participant is unable to give written consent. All participants were offered brochures that highlight the common symptoms of dementia individuals and essential information for the caregiver on how to care for the persons living with dementia. In addition, a list of health care centers that provide affordable primary care services was also provided.
3 Results
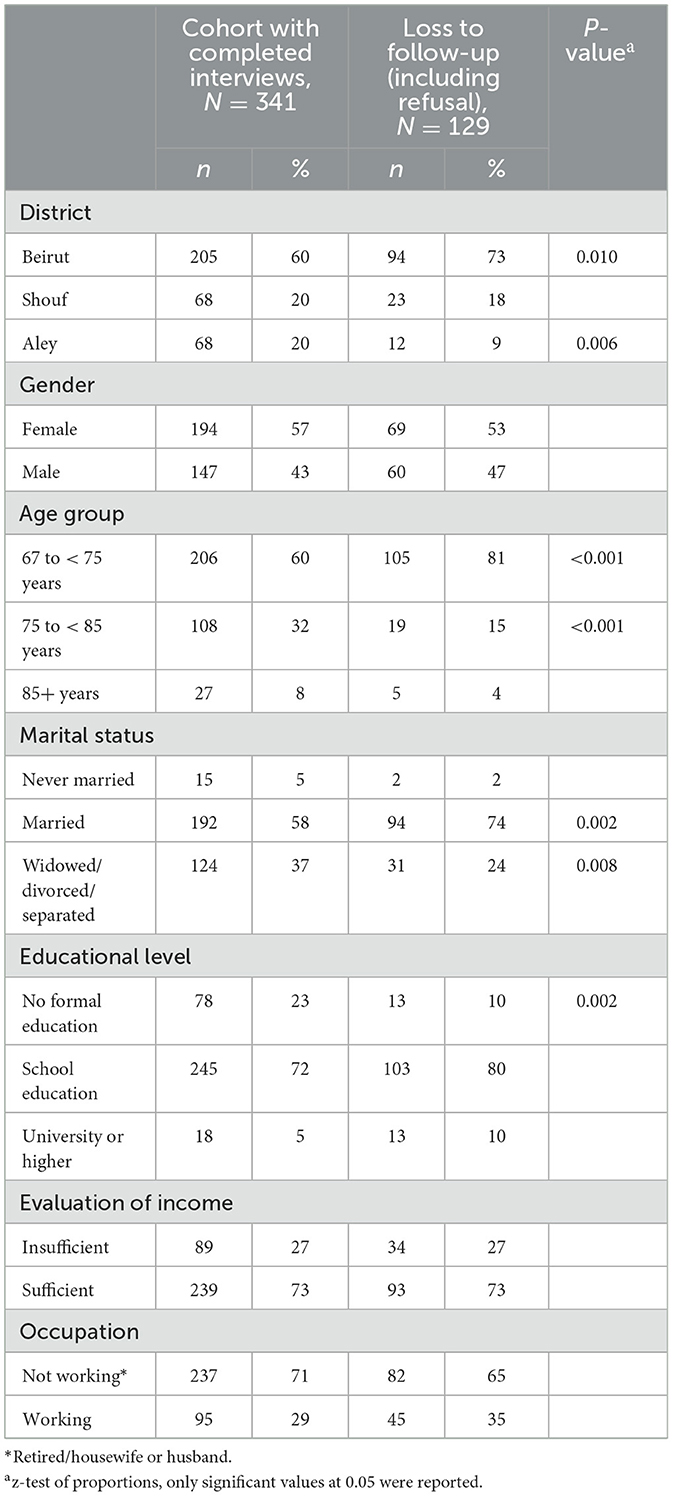
Table 1 displays a comparison of the socio-demographic profile between the 341 participants included in the follow-up cohort and the 129 participants who lost to follow-up. The majority of the follow-up sample was recruited from Beirut (60%), were females (57%), were under 75 years of age (60%), were married (72%) and have completed some school education (72%). As compared to the follow-up sample, a significantly higher proportion of those who were lost to follow-up were residents of Beirut district, younger than 75 years old, married, and had some school education.
The characteristics of the study sample are summarized in Figure 1. Initially, 470 participants consented to a follow-up visit, and among them, 341 (73%) were included in the cohort study, out of which 112 (33%) died during the follow-up period. Dementia diagnosis was performed for 229 subjects, out of which 190 consented for a third follow-up visit. After a mean follow-up period of 42 months ± 2.7 (3.5 years ± 0.22) and 1130 person-years follow-up, 19 new dementia cases were identified.
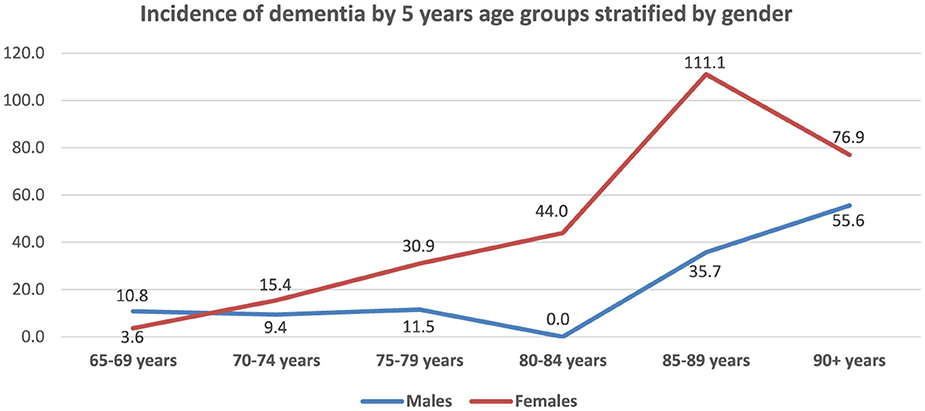
Figure 2 presents age, gender, and location-specific incidence rates of dementia. The overall incidence rate was 16.8 per 1,000 p-y [95% CI: (10.1; 26.2)], and the standardized incidence rate was 20.5 per 1,000 [95% CI: (13.5; 27.5)]. The incidence rate of dementia showed a sharp increase with age ranging from 6.5 per 1,000 p-y [95% CI: (1.3; 19.0)] at the ages of 65–69 years to 75.0 per 1,000 p-y [95% CI: (15.4; 219.2)] at age 90 and older. The age-specific incidence rates (Figure 3), increased steeply for women as compared to men after 80 years of age, but dropped back to closer rates (55.6 per 1,000 for men and 76.9 per 1,000 for women) at the age of 90.
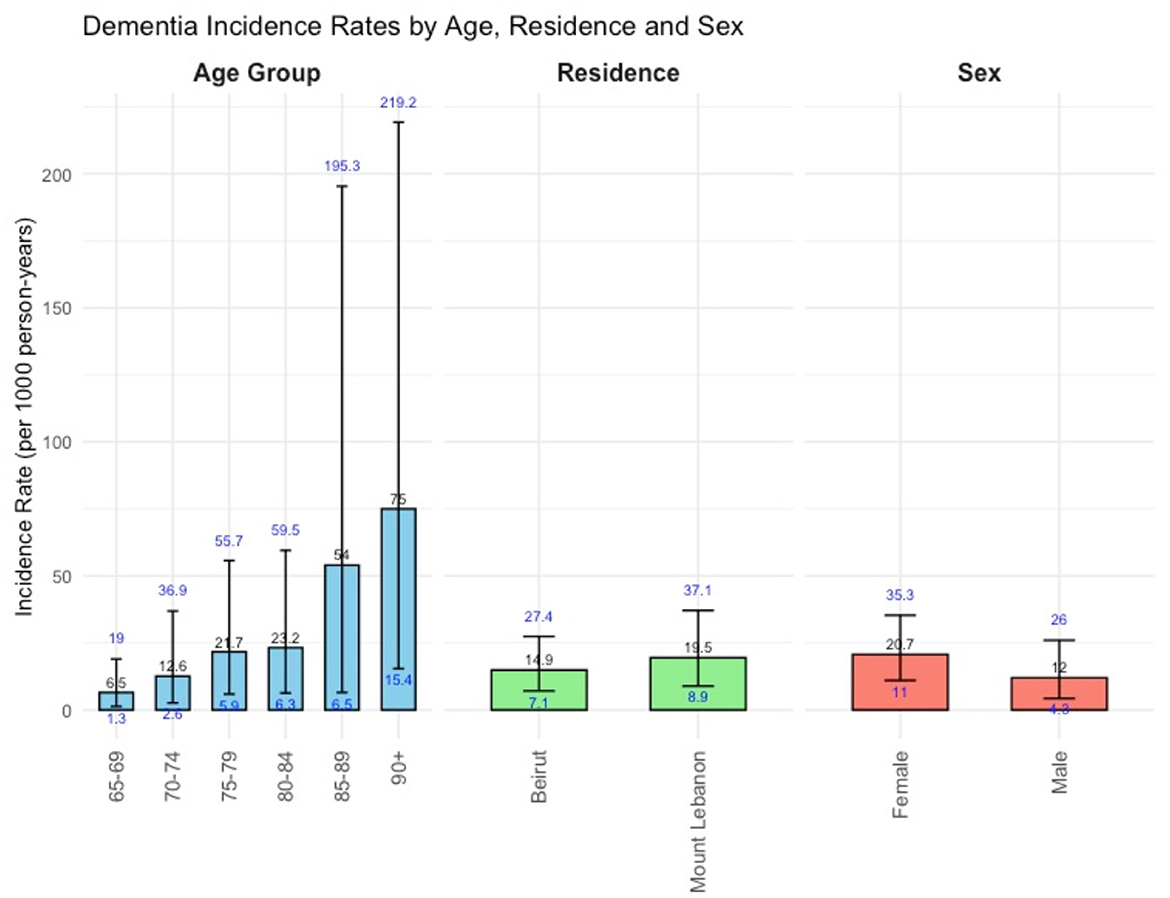
Figure 2. Bar plot illustrating dementia incidence rates (per 1,000 person-years) with 95% CI by age, gender, and location.
The incidence rate in Mount Lebanon was 19.5 per 1,000 p-y [95% CI: (8.9; 37.1)], higher than Beirut's 14.9 per 1,000 p-y [95% CI: (7.1; 27.4)], with overlapping confidence intervals.
4 Discussion
The estimated dementia incidence in our study is comparable to that reported in European and North American populations. However, further research with larger samples and extended follow-up periods is essential for confirming this pattern in the Lebanese context. The standardized incidence rate is 20.5 per 1,000 person-years, higher than the global age- and gender-standardized incidence of 17.30 per 1,000 person-years for those aged 60 and above reported in the World Alzheimer Report 2015 (Prince et al., 2015). It is also higher than rates observed in Low and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) and Latin America, which were 14.06 and 15.11 per 1000 person-years, respectively (Prince et al., 2015). The high incidence rate of dementia in Lebanon might be attributed to several factors. One possibility is the use of a higher age cut-off when estimating the incidence rate which was 5 years higher compared to other low-to-middle income countries. Additionally, the high prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension and other cardiovascular risk factors in the older age group may contribute (Gauthier Serge et al., 2022). Specifically, 35% of elderly in Lebanon experience uncontrolled hypertension (Fakhri et al., 2020). Moreover, the widespread lifestyle factors, such as smoking and dietary habits (Alzheimer's Disease International, 2023; Jeong et al., 2023), may also play a role; 70.9% of Lebanese adults are smokers (Nakkash et al., 2022), and a notable proportion follow unfavorable dietary patterns (Hoteit et al., 2024). Furthermore, the high consanguinity rate, which was reported as 35.5% in Lebanon in 2009, may also influence disease occurrence (Barbour and Salameh, 2009). Additionally, differences in methodologies and case identification may also contribute to differences in incidence rate from other published estimates.
It is difficult to compare our study's incidence rate to the few estimates available from the Arab region (Bhalla et al., 2018). The source population for the dementia cases used in the numerators of the previously cited incidence rate estimates was unclear, making it difficult to interpret accurately. Moreover, these estimates did not consider individuals' time contributions to the risk of dementia, which is an important factor. Our study followed dementia-free participants for 3 years, contributing updated incidence rate data from the Arab region. However, divergent methodologies used across studies limit conclusions about trends.
According to various studies conducted globally, the incidence rate trend of dementia varies with age, and our study aligns with those trends. For instance, the World Alzheimer Report of 2015 showed that the incidence rate of dementia doubled every 6.3 years, ranging from 3.9 to 104 per 1,000 person-years for ages 60–64 to 90+ years (Prince et al., 2015). Similarly, our study found that the age-specific incidence rate of dementia in LMICs and Latin America was comparable to other studies using the 10/66 DRG tools, which reported 18.2 to 30.4 dementia cases per 1,000 person-years (Prince et al., 2015, 2012).
Multiple studies have indicated that women are at a higher risk of developing dementia compared to men. For instance, a study of 16,926 Swedish twins, half of whom were women, revealed that women had higher rates of dementia incidence for all types of dementia (Beam et al., 2018). Likewise, a 27-year study of dementia incidence trends across Europe and the United States discovered that while men experienced a 24% decrease in incidence, women only experienced an 8% decrease (Wolters et al., 2020). This smaller decrease in incidence among women exacerbates the already substantial burden of dementia on them. In addition, women are more prone to psychological problems, like depression, than men (Eid et al., 2019), and female brains are influenced by sex hormones which create higher risk factors for developing Alzheimer's disease (Zhu et al., 2021). In addition, women tend to have a longer life expectancy than men (Tower, 2017), making them an aging population with increased risk of developing dementia.
Although the number of events in our study is relatively low, the consistency of the observed trend in LMICs on age, and gender-specific incidence estimates reinforce the reported findings.
A scant literature exists concerning regional variations in dementia incidence, with more emphasis historically placed on prevalence. However, some studies have examined rural-urban differences. A nationwide study in Taiwan reported higher dementia prevalence in rural (8.69%) vs. urban areas (4.46%) (Liu et al., 2022). Similarly, a study in the United States found higher Alzheimer's disease incidence in rural compared to metropolitan counties (Rahman et al., 2021). Additionally, a systematic review reported worse dementia care quality and outcomes in rural areas (Arsenault-lapierre et al., 2023). Those findings align with those observed in our study which also reports higher dementia incidence rates in less urbanized areas. This pattern suggests that geographical factors might influence the epidemiology of dementia. Our analysis revealed significant educational disparities between Beirut and Mount Lebanon, where 36.03% of participants from Mount Lebanon lacked formal education, compared to only 14.15% in Beirut. Furthermore, 81.46% of Beirut participants had school-level education, while this figure was markedly lower (57.35%) in Mount Lebanon. Such disparities in foundational education levels may contribute to the observed differences in dementia incidence, as lower education is associated with reduced cognitive reserve, a factor known to impact dementia onset (Darwish et al., 2018; Wilson et al., 2019). The cognitive reserve theory posits that education enhances the brain's resilience to cognitive decline, thereby delaying dementia onset. Therefore, the lower overall educational attainment in Mount Lebanon may partly explain the higher dementia incidence in this region. Future studies should explore educational influences on dementia in more depth, particularly in settings with similar urban-rural educational gaps.
4.1 Limitations
The study's limitations stem from a restricted participant and dementia case pool, focusing solely on two out of eight governorates in Lebanon, which makes the findings less applicable beyond the sample and reduces the generalizability of the results. The original cohort was established to assess the feasibility of following up with older adults in Lebanon and document any challenges. This led to the creation of a larger cohort, which is part of an ongoing, more extensive cohort study design called the “Lebanon Study on Aging and Health” (Lebanon Study on Aging Health, 2024). However, factors such as loss of follow-up and participant mortality might have led to an underestimation of dementia incidence rate. The study had a response rate of 72.3%, with 129 participants lost to follow-up due to changes in address, travel, or refusal to participate when contacted for the second interview. This could introduce selection bias, which might have affected the estimate of dementia incidence rate. To assess potential biases from attrition, we compared the sociodemographic characteristics of retained participants and those lost to follow-up. We documented the differences to ensure that the reported dementia incidence rate was not affected by non-responding participants' data. Selection bias is likely to have partially explained the high incidence rate of dementia in the cohort. Compared to the retained participants, we found that a significantly higher proportion of those lost to follow-up were from urban areas (Beirut), aged 67–75 years, and formally educated. Although we applied standardization using the Western European population distribution, we recognize that a future standardization based on the Lebanese population structure could offer additional insight specific to the local context.
4.2 Strengths
According to the World Alzheimer Report, there is a lack of data on dementia incidence from regions including Australasia, Asia Pacific, South Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, and the Middle East. In their meta-analysis, only 5% of person-years came from these regions (Prince et al., 2015). Our study is significant because it provides the first dementia incidence rate estimates in the Arab region using the validated tools from the 10/66 Dementia Research Group, which have been tested in diverse Lebanese populations. Despite the small sample size, the incidence rate found is similar to that of other low and middle-income countries, indicating accurate observed data.
5 Conclusion
There is a scarcity of longitudinal studies on dementia in developing countries, with none specifically focusing on the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. This study addresses this gap by presenting the inaugural estimates of dementia incidence rates in Lebanon using a cohort design, contributing crucial data for the MENA region. The study reveals that dementia incidence rates increase with age, which aligns with the global trends. Furthermore, women have slightly higher incidence rates than men, and the incidence rates vary by region. These baseline incidence rates and demographic patterns will serve as a valuable foundation for researchers to conduct future studies on dementia etiology and risk factors in Lebanon and the region. The next phase of the study will involve a larger cohort that covers more areas of Lebanon to gain a fuller understanding of dementia epidemiology in this population and allow for a more detailed analysis of gender and regional variations in the dementia incidence in Lebanon.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the American University of Beirut. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
MC: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SA: Writing – review & editing. HD: Writing – review & editing. MH: Writing – original draft. RK: Writing – review & editing. DS: Writing – review & editing. KE: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RH: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The baseline cohort study was funded by the Fogarty International Center, American National Institutes of Health and National Institute of Aging, grant No. 1R21AG039333-01, under the program “Brain Disorders in the Developing World: Research across the Lifespan (BRAIN).” The follow up was funded by a grant from the Medical Practice Plan (MPP), at the American University of Beirut Medical Center.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alzheimer's Disease International (2023). World Alzheimer Report 2023. Reducing Dementia Risk: Never too early, never too late. London: Alzheimer's Disease International.
Arsenault-lapierre, G., Bui, T. X., Le berre, M., Bergman, H., and Vedel, I. (2023). Rural and urban differences in quality of dementia care of persons with dementia and caregivers across all domains: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 23:102. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09100-8
Barbour, B., and Salameh, P. (2009). Consanguinity in Lebanon: prevalence, distribution and determinants. J. Biosoc. Sci. 41, 505–517. doi: 10.1017/S0021932009003290
Beam, C. R., Kaneshiro, C., Jang, J. Y., Reynolds, C. A., Pedersen, N. L., Gatz, M., et al. (2018). Differences between women and men in incidence rates of dementia and Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 64:1077. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180141
Bhalla, D., Lotfalinezhad, E., Amini, F., Salmannejad, M., Reza Borhani Nezhad, V., Rezai Kooshalshah, S. F., et al. (2018). Incidence and risk profile of dementia in the regions of middle east and North Africa. Neuroepidemiology 50, 144–152. doi: 10.1159/000487761
Darwish, H., Farran, N., Assaad, S., and Chaaya, M. (2018). Cognitive reserve factors in a developing country: education and occupational attainment lower the risk of dementia in a sample of Lebanese older adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 10:277. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00277
Eid, R. S., Gobinath, A. R., and Galea, L. A. M. (2019). Sex differences in depression: Insights from clinical and preclinical studies. Pro. Neurobiol. 176:86. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2019.01.006
El-Metwally, A., Toivola, P., Al-Rashidi, M., Nooruddin, S., Jawed, M., Alkanhal, R., Albawardi, N., et al. (2019). Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease and dementia in arab countries: a systematic review. Behav. Neurol. 2019:3935943-14. doi: 10.1155/2019/3935943
Fakhri, G., Assaad, S., and Chaaya, M. (2020). Hypertension prevalence and control among community-dwelling lebanese older adults. J. Clin. Hypertens. 22, 1727–1731. doi: 10.1111/jch.13995
Gauthier Serge, W. C., Stijn, S., José, M., and Pedro, R.-N. (2022). World Alzheimer Report 2022. Life after diagnosis: Navigating treatment, care and support. London.
Hoteit, M., Khattar, M., Malli, D., Antar, E., Al Hassani, Z., Abdallah, M., et al. (2024). Dietary intake among lebanese adults: findings from the updated LEBANese natiONal Food Consumption Survey (LEBANON-FCS). Nutrients 16:1784. doi: 10.3390/nu16111784
IHME (2021). GBD Compare. Available at: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/ (accessed June 1, 2024).
Jeong, S. M., Park, J., Han, K., Yoo, J., Yoo, J. E., Lee, C. M., et al. (2023). Association of changes in smoking intensity with risk of dementia in Korea. JAMA Netw. Open 6:e2251506. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.51506
Lebanon Study on Aging and Health (2024). Lebanon Study on Aging and Health. Available at: https://www.aub.edu.lb/fhs/lsaha/Pages/default.aspx (accessed June 4, 2024).
Liu, C.-C., Liu, C.-H., Sun, Y., Lee, H.-J., Tang, L.-Y., and Chiu, M.-J. (2022). Rural-urban disparities in the prevalence of mild cognitive impairment and dementia in Taiwan: a door-to-door nationwide study. J. Epidemiol. 32, 502–509. doi: 10.2188/jea.JE20200602
Matthews, F. E., Stephan, B. C. M., Robinson, L., Jagger, C., Barnes, L. E., Arthur, A., et al. (2016). A two decade dementia incidence comparison from the cognitive function and ageing studies I and II. Nat. Commun. 7:11398. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11398
Nakkash, R., Khader, Y., Chalak, A., Abla, R., Abu-Rmeileh, N. M. E., Mostafa, A., et al. (2022). Prevalence of cigarette and waterpipe tobacco smoking among adults in three Eastern Mediterranean countries: a cross-sectional household survey. BMJ Open 12:e055201. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055201
Phung, K. T., Chaaya, M., Waldemar, G., Atweh, S., Asmar, K., Ghusn, H., et al. (2014). Validation of the 10/66 dementia research group diagnostic assessment for dementia in Arabic: a study in Lebanon. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 27, 282–290. doi: 10.1177/0891988714532019
Phung, K. T. T., Chaaya, M., Prince, M., Atweh, S., El Asmar, K., Karami, G., et al. (2017). Dementia prevalence, care arrangement, and access to care in Lebanon: a pilot study. Alzheimers Dement. 13, 1317–1326. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.04.007
Prince, M., Acosta, D., Chiu, H., Scazufca, M., and Varghese, M. (2003). Dementia diagnosis in developing countries: a cross-cultural validation study. Lancet 361, 909–917. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12772-9
Prince, M., Acosta, D., Ferri, C. P., Guerra, M., Huang, Y., Rodriguez, J. J. L., et al. (2012). Dementia incidence and mortality in middle-income countries, and associations with indicators of cognitive reserve: a 10/66 Dementia Research Group population-based cohort study. Lancet 380, 50–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60399-7
Prince, M. J., Wimo, A., Guerchet, M. M., Ali, G. C., Wu, Y.-T., Prina, M., et al. (2015). World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of Dementia. An analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. London.
Qassem, T., Itani, L., Nasr, W., Al-Ayyat, D., and Javaid, S. F. H. (2023). Prevalence and economic burden of dementia in the Arab world. BJPsych Open 9:e126. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2023.517
Qiu, C., Von Strauss, E., Bäckman, L., Winblad, B., and Fratiglioni, L. (2013). Twenty-year changes in dementia occurrence suggest decreasing incidence in central Stockholm, Sweden. Neurology 80, 1888–1894. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318292a2f9
Rahman, M., White, E. M., Mills, C., Thomas, K. S., and Jutkowitz, E. (2021). Rural-urban differences in diagnostic incidence and prevalence of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Alzheimers Dement. 17, 1213–1230. doi: 10.1002/alz.12285
Satizabal, C. L., Beiser, A. S., Chouraki, V., Chêne, G., Dufouil, C., Seshadri, S., et al. (2016). Incidence of dementia over three decades in the Framingham Heart Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 374, 523–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504327
Saxena, P. (2008). Ageing and age-structural transition in the Arab countries: Regional variations, socioeconomic consequences, and social security. Genus 64, 37–74. doi: 10.2307/41430835
Schrijvers, E. M., Verhaaren, B. F., Koudstaal, P. J., Hofman, A., Ikram, M. A., Breteler, M. M., et al. (2012). Is dementia incidence declining?: trends in dementia incidence since 1990 in the Rotterdam Study. Neurology 78, 1456–1463. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182553be6
The 10/66 Dementia Research Group (2015). The 10/66 Dementia Research Group. Available at: https://1066.alzint.org/ (accessed June 3, 2024).
Tower, J. (2017). Sex-Specific gene expression and life span regulation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 28, 735–747. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.07.002
WHO (2021). Global status report on the public health response to dementia. Geneva: WHO. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00215-2
Wilson, R. S., Yu, L., Lamar, M., Schneider, J. A., Boyle, P. A., Bennett, D. A., et al. (2019). Education and cognitive reserve in old age. Neurology 92:10. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007036
Wolters, F. J., Chibnik, L. B., Waziry, R., Anderson, R., Berr, C., Beiser, A., et al. (2020). Twenty-seven-year time trends in dementia incidence in Europe and the United States: The Alzheimer Cohorts Consortium. Neurology 95, e519–e531. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010022
Yaghmour, S. M., Bartlett, R., and Brannelly, T. (2019). Dementia in Eastern Mediterranean countries: a systematic review. Dementia 18, 2635–2661. doi: 10.1177/1471301217753776
Keywords: dementia incidence, Alzheimer's disease, MENA region, incidence rates, gender differences, regional differences, lebanese older adults
Citation: Chaaya M, Assaad S, Darwish H, Haber M, Khoury R, Saab D, El Asmar K and Hajjar R (2025) Dementia incidence among a cohort of lebanese older adults: first incidence estimates from the Middle East and North Africa region. Front. Dement. 3:1494719. doi: 10.3389/frdem.2024.1494719
Received: 11 September 2024; Accepted: 25 November 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Dong Woo Kang, The Catholic University of Korea, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Gihwan Byeon, Kangwon National University Hospital, Republic of KoreaMatěj Kučera, National Institute of Mental Health, Czechia
Copyright © 2025 Chaaya, Assaad, Darwish, Haber, Khoury, Saab, El Asmar and Hajjar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Khalil El Asmar, a2UwNUBhdWIuZWR1Lmxi
 Monique Chaaya
Monique Chaaya Sarah Assaad2
Sarah Assaad2 Hala Darwish
Hala Darwish Marc Haber
Marc Haber Rosemary Khoury
Rosemary Khoury Khalil El Asmar
Khalil El Asmar