
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT article
Front. Conserv. Sci., 24 January 2025
Sec. Animal Conservation
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcosc.2025.1431348
The conservation of freshwater turtle species depends on precise and effective monitoring techniques. Environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis is a potential method for identifying cryptic and elusive turtle species in aquatic ecosystems. eDNA analysis can help to identify key regions for conservation efforts and monitor changes in population levels over time. This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of a rapid eDNA detection method for the yellow mud turtle (Kinosternon flavescens, an indicator species that is endangered in some states in the USA), which inhabits local oxbow lakes (e.g., resacas) in Cameron County, South Texas. A species-specific nested PCR assay was designed to enhance the detection of yellow mud turtle species. Water samples were collected from five locations within Cameron County for the detection of yellow mud turtle eDNA. Our results revealed the presence of yellow mud turtles in two out of the five surveyed locations. Our study shows great potential for eDNA monitoring for yellow mud turtle species. This study also provides insights on using eDNA monitoring to protect yellow mud turtle species and recommendations for future research and conservation initiatives.
Turtles are one of the most endangered groups of tetrapod vertebrates on the planet (Cox et al., 2022). However, the global disappearance of turtles is a worrying phenomenon that has grabbed the attention of environmentalists and scholars due to its significant effects on ecological diversity and the health of ecosystems (Petrov et al., 2023). About 52% of turtle species face extinction, with 20% critically endangered, and 61% designated as threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) (Howell et al., 2019; Rhodin et al., 2018; Stanford et al., 2020; IUCN, 2023). The yellow mud turtle (Kinosternon flavescens) is an important species native to North America (Christiansen et al., 1985). Yellow mud turtles help balance ecosystems by eating insects, snails, and crayfish, cleaning water as scavengers, and serving as prey for many animals (Missouri Department of Conservation, 2024). K. flavescens is a small yellow-olive-colored turtle (Figure 1A) distributed in the south-central region of the United States, spanning from Nebraska to Texas. Moreover, there are more populations of this species in northern Mexico, specifically in the territories of Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Nuevo Leon (Christiansen et al., 2020). Globally, K. flavescens is not a species of concern (i.e., Red List: Least Concern) by the IUCN (2023). However, it is designated as a state-endangered species in the states of Iowa, Illinois, and Missouri in the United States (Bickham et al., 1984; Christiansen et al., 1985). Notably, K. flavescens has had significant population reductions across its distribution in the Midwest region in the United States (Berger, 2010; Bernstein and Christiansen, 2011; Christiansen et al., 2012; Missouri Department of Conservation, 2024). Moreover, the decreasing numbers of yellow mud turtles can be attributed to significant environmental disturbances, as well as the presence of permanently water-adapted aquatic turtles (e.g., Chrysemys picta), which act as competitors for resources and predators of juveniles (Bernstein and Christiansen, 2011). Predation of eggs and adults by raccoons and other mammalian predators poses an ongoing threat to this species (Missouri Department of Conservation, 2024). Additionally, lowered levels of water further exacerbate the challenges faced by this species (Christiansen et al., 2012). Traditional turtle monitoring techniques such as trapping and visual census pose laborious obstacles (Davy et al., 2015; Kirtane et al., 2019). Moreover, depending solely on human surveys can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process, which can also limit the extent of the evaluation of turtle populations, hindering the ability to obtain a comprehensive and correct understanding of their populations (Bogolin et al., 2021; Nordstrom et al., 2022).
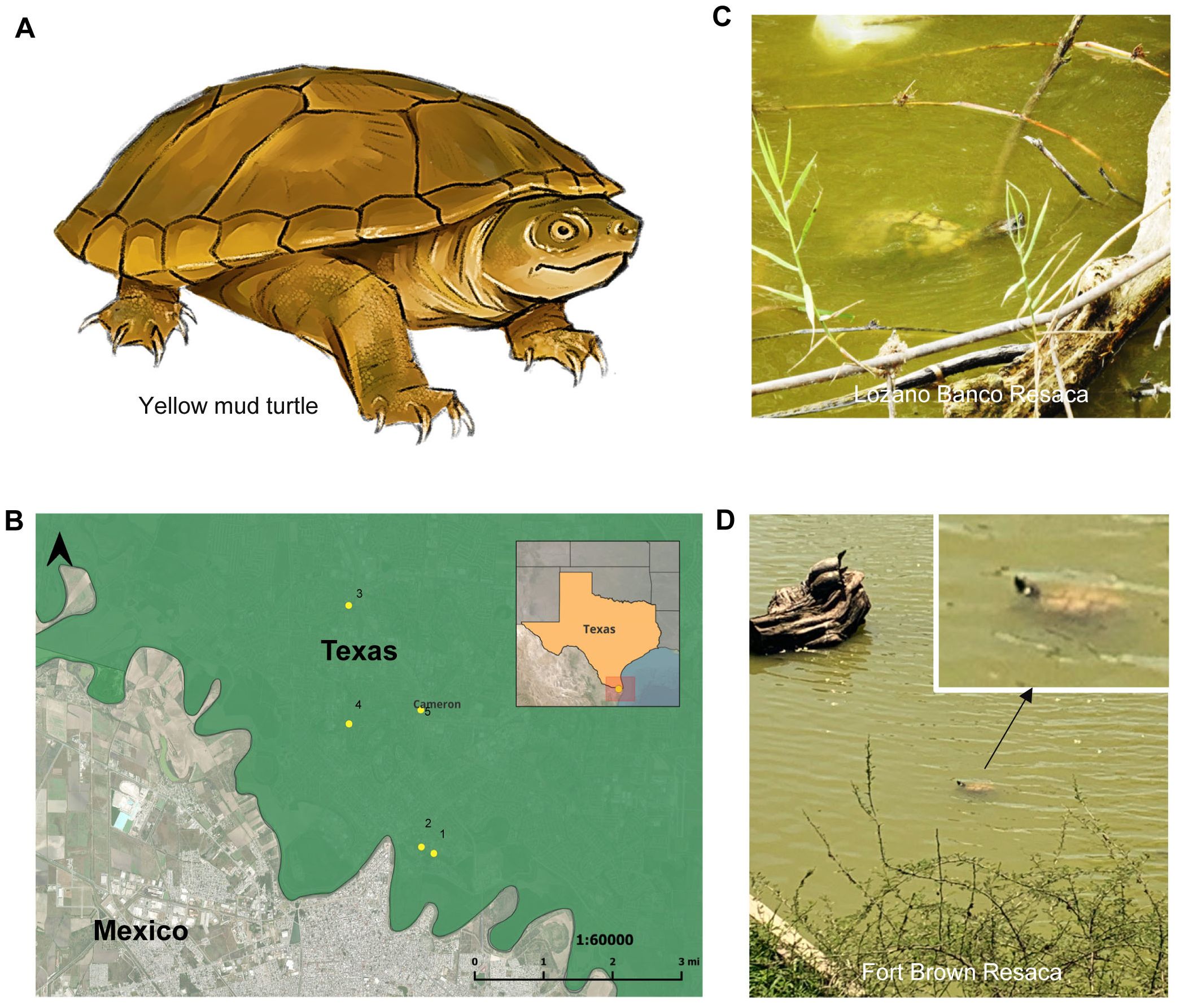
Figure 1. Sampling locations to collect water samples for detection of yellow mud turtle eDNA. (A) Schematic diagrams of yellow mud turtle (Kinosteron flavescens). (B) Map illustrating the locations of five sampling sites in Cameron County where water samples were collected to detect yellow mud turtle eDNA. The site numbers align with those indicated in Table 1. (C, D) Photographs show turtles in the Lozano Banco Resaca (C) and Fort Brown Resaca (D) where water samples were collected to detect yellow mud turtle eDNA.
Environmental DNA (eDNA) is a highly effective technology utilized in ecological study and conservation for determining the existence of species in their native environments (Deiner et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Sahu et al., 2023; Rishan et al., 2024a). Various techniques are used to obtain eDNA from water bodies, offering a non-intrusive and effective approach to conserving aquatic ecosystems (Ruppert et al., 2019; Rishan et al., 2023). The eDNA technique has been highly advantageous in detecting turtles, especially due to its exceptional sensitivity and reliability (Akre et al., 2019; Davy et al., 2015; Lam et al., 2022). eDNA analysis enables investigators to identify the existence of turtles by examining the genetic information they release in water bodies (Harper et al., 2020). The utilization of eDNA for turtle detection has several benefits, such as enhanced efficacy, economic feasibility, and minimized disruption to the native ecosystem (Petruniak et al., 2021). It can identify the existence of turtles even if they aren’t visually present, providing a more thorough picture of their location and abundance (Davy et al., 2015; Petruniak et al., 2021; Lam et al., 2022). Moreover, turtles are challenging to detect due to their aquatic habitat, overwintering behavior, cryptic coloration, and low population densities, making eDNA a particularly effective method for monitoring their presence (Miller and Dinkelacker, 2007; Christiansen et al., 2020).
The objective of this study was to develop a rapid and cost-effective eDNA detection assay to facilitate frequent and efficient monitoring of yellow mud turtles for conservation purposes. This included developing methods for water collection and filtration, as well as processes for DNA extraction, PCR, and sequencing. The study aimed to confirm the presence or absence of turtle eDNA in samples collected from the field. This study also provides a foundation for future eDNA research to enhance the detection and monitoring of critically endangered yellow mud turtle species.
Based on known turtles’ occurrence in various reservoirs in the Brownsville area in Cameron County, Texas (Mali et al., 2014), five different resacas and lakes were chosen for collecting water samples to detect yellow turtles using eDNA (Figures 1B–D; Table 1). The sampling sites in the Brownsville area in the south Texas region were chosen due to documented occurrences and suitable habitats for yellow mud turtles (Mali et al., 2014). Notably, these sampling sites also represent habitats within the turtle species’ known range, making them ideal for evaluating the effectiveness of eDNA detection protocol and providing a relevant context for potential application in similar habitats. The water bodies were shallow 1-2 m depth and lentic, and the only water movements were typically wind driven. The water temperature ranged from 25 to 28°C and the pH ranged from 8.0 to 8.8.
The collection of water samples for eDNA was conducted according to the method described previously by Ruppert et al. (2022) and Collins (2022). Briefly, 1 L of water filtration was executed through a filter cup (XX1104700, MilliporeSigma, Darmstadt, Germany), which is attached to a manually driven vehicle fluid evacuator (MV7400, Mityvac, St. Louis, MO, USA) (Figures 2A–C). Before water collection, equipment was thoroughly cleaned using 50% chlorine bleach solution for 20 sec to prevent contamination. The equipment was then washed with 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate solution to neutralize bleach. Finally, all types of equipment were rinsed with distilled water.
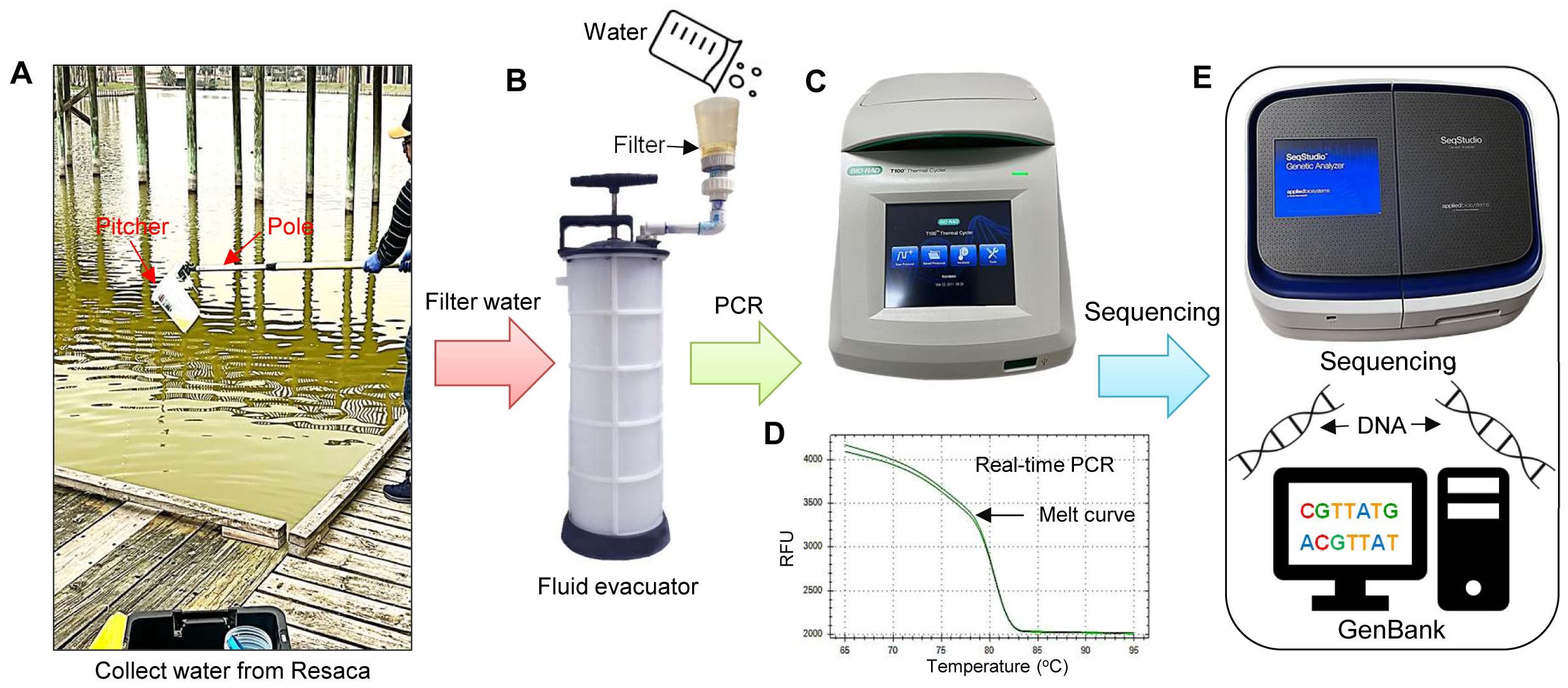
Figure 2. eDNA collection and PCR analysis to detect yellow mud turtles. (A) Collection of eDNA samples from water using a pitcher connected to a telescopic pole, (B) Filtration of eDNA using a hand-powered automotive fluid evacuator, (C) polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and gel electrophoresis, (D) real-time-PCR, and (E) DNA sequencing and analysis. RFU, Relative fluorescence unit.
To evaluate the potential contamination of field samples, the distilled water was filtered and analyzed as a blank (i.e., negative control). Additionally, fresh gloves were also worn for each site visit to minimize contamination. In the field study, water samples (1 L/sample, 3 samples/site) were collected through a pitcher connected to a telescopic pole (Figures 2A, B). The cellulose filters used for eDNA collection consisted of 47-mm diameter with a particle size of 25 μm (Figure 2C; Whatman Grade 4, Cytiva, Marlborough, MA, USA). The filter papers were placed individually in labeled 2 mL RNAse/DNase-free vials, containing 700 μL of DNAzol, a genomic DNA isolation reagent (DNAZOL® Molecular Research Center Inc, Cincinnati, OH, USA). The filter paper and DNAzol were vortexed for 20-30 sec every day and stored at room temperature until eDNA extraction.
To validate the field eDNA results, 50 mL of water was collected from an aquarium containing yellow mud turtle and mixed with 950 mL of fresh water collected from a pond where turtles were not present. Afterward, the water was filtered according to the filtration method described above.
eDNA was extracted from filter paper and DNAzol samples using a nucleic acid extraction kit (Epoch Life Science Inc., Sugar Land, TX, USA) according to the method described previously by Robinson et al. (2022) and Collins (2022). Briefly, filter paper and DNAzol were incubated on a heat block at 55°C for 30 min. Afterward, each tube vortexed for 30 sec, followed by centrifugation at 5,000 rpm for 1 min. The filters were subsequently squeezed into their respective centrifuge tubes using sterile forceps to extract any residual DNAzol from the filters before disposing of them. Fresh gloves were used for each sample extraction to avoid contamination and false positive results across different sampling locations. Subsequently, 600 μL of DNAzol was collected from the tube and transferred into a new tube, and then added 10 μL of RNAase and incubated at 37°C for 10 min. Following a 1-min incubation period at ambient temperature, 10 μL of proteinase-K was introduced into the solution. The solution was incubated at 60°C for 1 h and vortexed every 15 min throughout the incubation period. After incubation, 500 μL of extraction buffer was added to the solution and incubated at 70°C for 20 min. Then, 50 μL of elution buffer (EB) had been preheated at 70°C. After the 20-min incubation period, the solution was allowed to remain at room temperature for 5 min, and 500 μL of 100% ethanol was added into the solution. The solution was then added into a GenCatch column (Epoch Life Science Inc.) and centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 2 min. The column was then washed two times with 500 µL of wash buffer. After washing, the column was transferred to a fresh 1.5 mL tube, and 50 μL of pre-heated EB was added. The resulting solution was allowed to incubate at room temperature for 2 min and then centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 2 min. Afterward, 50 μL of nuclease-free water was carefully placed onto the column and centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 2 min. An inhibitor removal kit was used to eliminate the PCR inhibitor following the instructions provided by the manufacturer (OneStep PCR Inhibitor Removal, Zymo Research, Irvine, CA). A total of 100 μL of DNA was purified and the concentration of DNA was measured using a nanodrop (Nanodrop, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The purified eDNA was stored at -20°C until PCR analysis.
The mitochondrial cytochrome b (CYT b) gene contains species-specific information and is commonly used in DNA research because of its higher specificity in detecting eDNA (Shu et al., 2020). Gene-specific primers (i.e., forward, reversed, and nested primers; Eurofins MWG Genomics, Louisville, KY, USA) were designed to detect yellow mud turtles from a published sequence in GenBank (accession number: KF301376; Iverson et al., 2013) eDNA using NCBI Primer-BLAST tool (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/) and Primer3 software (Untergasser et al., 2012). During primer design, four potential co-occurring species of aquatic turtle were considered (Apalone spinifera, Pseudemys gorzugi, Trachemys scripta elegans, and Trachemys venusta) and sequence regions with high similarity were avoided. The resulting DNA sequences from first and nested PCR had sufficient nucleotide differences to be distinguished from yellow mud turtle from the four other species. Table 2 shows primer sequences with their respective denaturing, annealing, and extension steps, and the amplified sequence of yellow mud turtle species. The primer sets were tested using ethanol preserved leg muscle tissue from a voucher specimen collected in Karnes county, Texas (Texas Natural History Museum # 114597) and field samples collected from Cameron county and Presidio county, Texas. The PCR was performed using a T100 thermocycler (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). PCR analysis was performed in a 25 μL reaction containing 12.5 μL of PCR master mix (GoTaq® G2 Hot Start Green Master Mix, Promega, Madison, WI, USA), 9.5 μL nuclease-free water, 1 μL of 5 μM forward primer, 1 μL of 5 μM reverse primer, and 1 μL of DNA sample (Figure 2C). The initial and nested PCR amplification for both species comprised 40 cycles, involving denaturation at 95°C for 15 sec, variable annealing temperature for 30 sec, and elongation at 72°C for 15 sec. The initial and nested primers’ annealing temperatures were 59°C and 60°C, respectively. For nested PCR, the PCR reactions contained 2 μL of purified PCR product obtained from the initial PCR. To screen for potential contamination of laboratory reagents, a negative template control (NTC) was employed. The NTC was performed by adding 1 μL of molecular-grade water in substitution of template DNA and running alongside each PCR cycle. To assess the specificity of primers, real-time PCR was conducted and analyzed the melting curve (Figure 2D) according to the methods described by Rodríguez et al. (2015). Gel electrophoresis was performed to verify the PCR result. A 2% agarose gel containing 40 mL of 1xTBE buffer (Tris-Borate-EDTA, 10X Solution, Fisher Scientific, Hampton, NH, USA) and 800 mg of agarose (TopVision Agarose, Thermo Scientific, Vilnius, Lithuania), was used for electrophoresis.
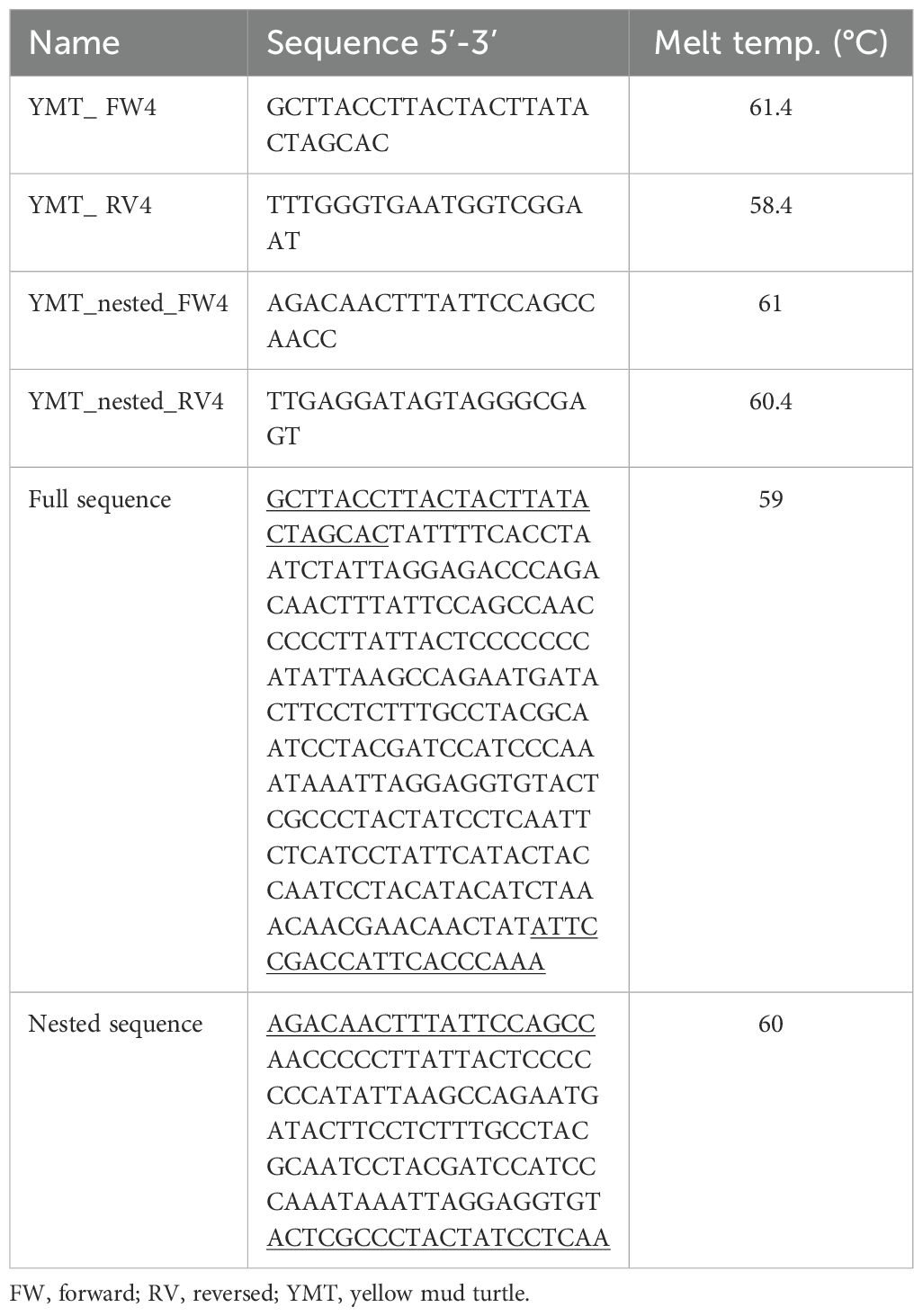
Table 2. Sequences and melting temperatures for yellow mud turtles primers and amplified sequences corresponding to each primer set.
For sequencing, the PCR products were purified using a DNA purification kit following the guidelines provided by the manufacturer (Monarch Nucleic Acid Purification, New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) and quantified DNA using a nanodrop (Thermo Fisher). Samples containing detectable amounts of DNA (2-5 ng/μL) were selected for Sanger sequencing (Figure 2E). The sequencing procedure was performed by Eurofins Genomics’ Simpleseq premixed approach (i.e., 5 μL of forward primer and 5 μL of purified PCR product, or 5 μL of reverse primer and 5 μL of purified PCR product). The resultant sequence was subjected to a comparative analysis with sequences accessible on the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database using a MultAlin sequence alignment with a hierarchical clustering tool (Corpet, 1988; http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/).
PCR results obtained from water samples and turtle tissue were subjected to electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel (Figure 3). A single PCR cycle failed to generate enough target DNA for Sanger sequencing or produce a clear identification signal. This challenge was overcome through the implementation of the nested PCR approach which enhanced the accuracy of detection by reducing non-specific binding and increasing target DNA visibility. This challenge was overcome through the implementation of a nested PCR approach. Nested PCR-amplified DNA sequences from both the tissue and field samples (Figures 3A–C), were able to effectively identify turtles through a search using the NCBI BLAST database. The primers for eDNA designed specifically for yellow mud turtles effectively amplified 134 bp DNA fragments (Figures 3A–C) which had high sequence identity (98-100%) with the yellow mud turtles’ tissue DNA (tDNA) sequence (Figure 3D). The eDNA sample obtained from an aquarium known to be inhabited by yellow mud turtles also generated an identifiable band of the estimated size (Figure 3C). Real-time PCR results showed a single, distinct melting peak of 80.5 °C that corresponded to the predicted melting temperature for the amplified sequence for yellow mud turtle (Figure 3E). This melting peak confirmed the specificity of the primers and helped to rule out potential false positives.
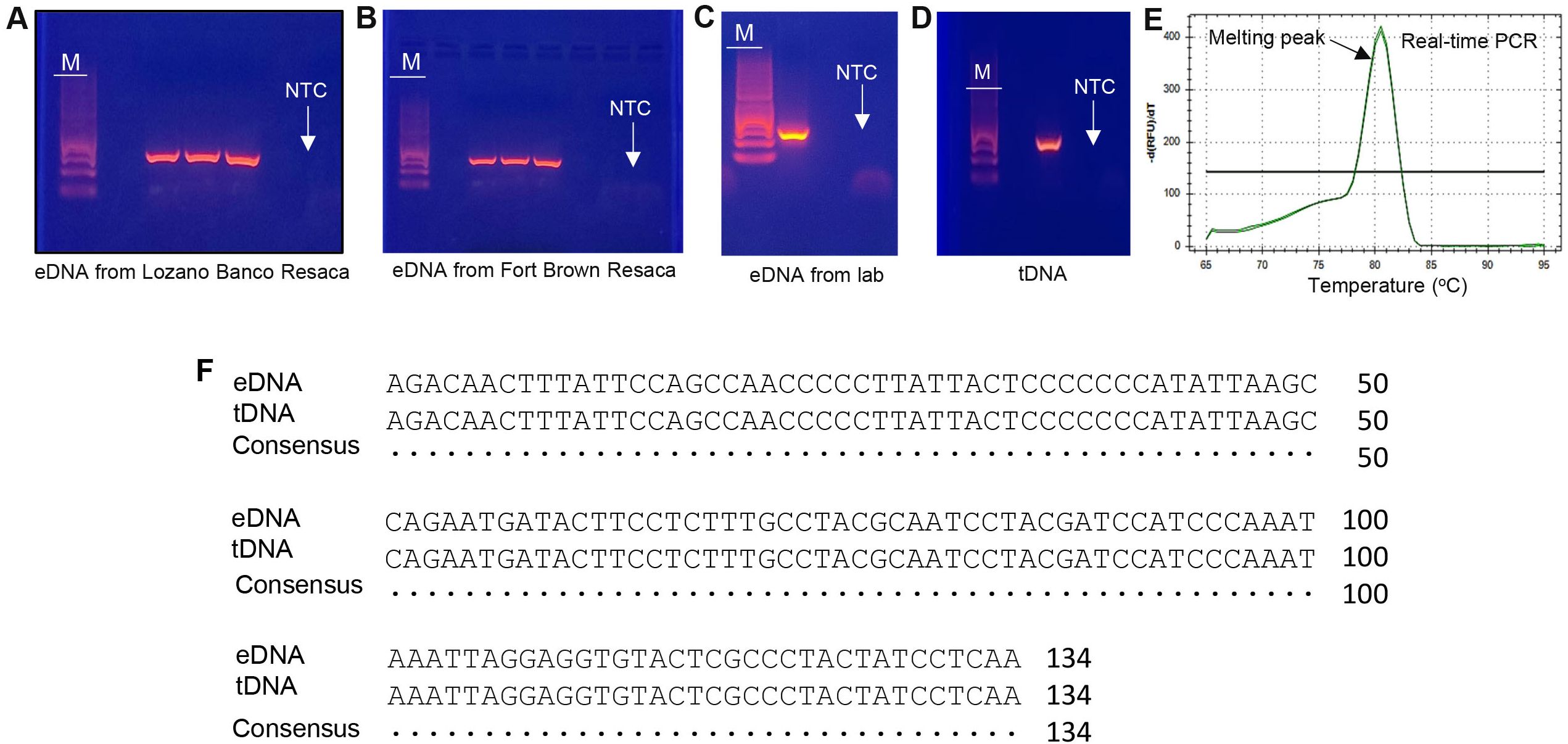
Figure 3. Determination of eDNA by PCR and Sanger sequencing. (A–E) PCR products (134 bp detected in gel electrophoresis) and real-time PCR amplification of yellow mud turtle eDNA were amplified with the species-specific primer set. (F) Alignment of the amplified eDNA and tissue DNA (tDNA) sequences of yellow mud turtles. NTC, negative control; M, DNA marker; Lozano Banco Resaca.
PCR amplification effectively identified the presence of yellow mud turtles’ eDNA in field samples collected from different locations in Texas. eDNA from yellow mud turtles was identified in all three replicate samples collected from two specific locations in Cameron County. All other samples were negative.
In this study, we successfully detected yellow mud turtles in Cameron County, Texas, using rapid eDNA methods. The primer sets and PCR technique are suitable for amplifying eDNA from yellow mud turtles. Importantly, the PCR method presented, including initial and nested primers, effectively amplified, and produced matched sequences to the GenBank library for yellow mud turtles from many areas in Texas. Utilizing these sequences facilitated the precise identification and categorization of mud turtles in conservation research. Establishing a PCR assay that possesses exceptional specificity and sensitivity for identifying yellow mud turtles in environmental samples exhibits potential as a valuable instrument for tracking the recovery of these species which are currently declining. Mud turtles do not typically bask, but stay in the water, making them challenging to locate using standard methods (Tuma, 2006; Platt et al., 2016). In recent years, the use of eDNA presents a more promising opportunity to detect turtles than traditional surveys such as trapping (Davy et al., 2015; Lam et al., 2022; Nordstrom et al., 2023). Although this study focused on Texas, the findings presented here can be applied to other geographical regions for extensive monitoring of mud turtle species using rapid eDNA detection method.
In the present investigation, conventional PCR was used to detect the eDNA of mud turtles. The utilization of nested PCR has demonstrated its efficacy in enhancing the identification of eDNA by Sanger sequencing, potentially by removing inhibitors during the second stage of PCR (Jackson et al., 2017; Ruppert et al., 2022). Furthermore, conducting two rounds of PCR can enhance the precision of amplification by employing two distinct sets of primers (Jackson et al., 2017; Stoeckle et al., 2018). This technological improvement enhances the reliability and precision of evaluating mud turtles’ eDNA. It has been hypothesized that quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) can provide quantitative evaluations of population abundance (Lodge et al., 2012). However, these methods may encounter several challenges when it comes to their implementation and effectiveness, specifically regarding factors such as the mass of the creature, the water quality, and the degree to which the target organisms release DNA-containing materials (Barnes et al., 2014; Brozio et al., 2017). Using qPCR methods to detect eDNA has several benefits, including enhanced sensitivity, but the limited quantities of water and the feasibility of employing this technique in laboratories having advanced qPCR machines render conventional PCR more advantageous in this scenario (Lodge et al., 2012; Brozio et al., 2017). We have also successfully developed a qPCR assay, which will enable future investigations to a quantitative eDNA-based approach to monitor mud turtle species. Although it is currently not feasible to quantify the precise abundance of species present using eDNA alone, it may be possible to estimate their relative abundances through repeated and/or similar sampling (Ruppert et al., 2019; Sard et al., 2019).
Our study detected the presence of yellow mud turtles from two locations in Cameron County using eDNA techniques. Our findings align with previous studies investigating the application of eDNA methods for turtle detection. Mali et al. (2014) captured yellow mud turtles from Lower Rio Grande Valley in Brownsville by trapping methods. Recently, Lam et al. (2022) assessed the effectiveness of eDNA methods in identifying populations of the big-headed turtle (Platysternon megacephalum, an endangered species in Hong Kong). They demonstrated that the eDNA approaches continue to show promise for turtle detection, as the percentage of positive detections was positively associated with the size of the overall population in water bodies where the turtle populations are already known. Moreover, Feng et al. (2020) evaluate the effectiveness of eDNA assessments to identify the overwintering habitats of northern map turtles (Graptemys geographica) in a Canadian temperate lake. The researchers detected eDNA signals that matched the patterns observed in documented overwintering locations and regions that were previously thought to serve as overwintering sites.
In the present study, however, the inability to identify yellow mud turtles in some areas generates some questions about the variables that affect eDNA detection and the constraints of our methodology. The water bodies where we sampled for yellow mud turtles in this study were shallow, lentic, and the only water movements were typically wind driven. The pH was basic with pH 8.0 or higher, and the temperatures were typically warm to hot. These conditions including high algal growth make sampling eDNA for turtles challenging. Notably, environmental factors such as water movement, temperature, pH, UV, and seasonal fluctuations can influence the spread and longevity of eDNA in aquatic environments, which may have an impact on the accuracy of detection of turtle species (Strickler et al., 2015; Qian et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2022). Strickler et al. (2015) reported that aquatic environments with lower temperatures, greater UV light protection, and higher alkalinity can retain detectable eDNA levels of American bullfrog tadpoles (Lithobates catesbeianus) for a more extended period compared to more humid, sunny environments with neutral or acidic conditions. There might be a possibility that eDNA is affected by temperature fluctuations, UV, and pH in the water and generates false negative results (Strickler et al., 2015; Qian et al., 2022). Moreover, according to the Missouri Department of Conservation (https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/yellow-mud-turtle), yellow mud turtles exhibit some unique behavioral characteristics, such as overland movement during active months and winter hibernation. The distinct attributes can impact the concentration of eDNA in a water body and hence affect the ability to detect yellow mud turtles in certain regions. In addition, the possibility of DNA degradation over time could have played a role in producing false negative outcomes in our findings (Strickler et al., 2015; Joseph et al., 2022). Although there are certain challenges and limitations, our study highlights how eDNA approaches can be a significant tool for ecological and conservation biology research and for protecting the declining turtle species. Routine eDNA monitoring can provide critical insights into the environmental and anthropogenic factors driving population fluctuations, such as habitat fragmentation, water pollution, and the presence of non-native species. By identifying these underlying causes, eDNA-based methods can inform targeted conservation strategies and support long-term management efforts. Additionally, advancements such as drone-based water sampling could further enhance the efficiency and applicability of eDNA monitoring, especially in hard-to-reach areas, ensuring more comprehensive and effective conservation outcomes for vulnerable turtle populations.
Our results highlight the efficacy of rapid eDNA technique for non-invasive monitoring of freshwater turtle species in their natural habitats in Texas. This demonstrates the effectiveness of our eDNA method for detecting mud turtle species. Several important directions for further investigation should be considered in the future. Enhancing the precision and sensitivity of species identification through optimized eDNA methodologies and sampling techniques would significantly improve detection accuracy. Furthermore, expanding the application of eDNA investigations to include more locations and species within the Kinosternidae family could provide valuable insights into the distribution and abundance of mud turtles. Furthermore, it would be essential to examine the variables that affect the detection of eDNA, including habitat features, atmospheric conditions, and human-caused disturbances in the ecosystems. Long-term monitoring programs that incorporate eDNA and environmental RNA (eRNA; Rishan et al., 2024b) methods could be implemented to follow population trends and evaluate the efficacy of conservation initiatives over an extended period. By exploring these prospective areas of eDNA and eRNA research, we can enhance our comprehension of mud turtle ecology and contribute to the conservation of these ecologically vulnerable endangered species.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
The field studies were conducted following the ethical guidelines of the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley (UTRGV) Institutional Animal Care and USE Committee (IACUC protocol no.: AUP-22-12). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
SR: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Texas Parks & Wildlife Department for eDNA research funding (grant no. F16AF00993 to RK and SR.
We also thank to Esmirna Cantu, School of Earth, Environmental, and Marine Sciences, UTRGV, for the original drawing of mud turtle in the graphical abstract. We would like to thank the Texas Natural History Collections (TNHC) Museum for providing the yellow mud turtle tissue samples for research (TNHC# 114597).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
CYT b, cytochrome b; eDNA, environmental eDNA; IUCN, International Union for Conservation of Nature; NCBI, National Center for Biotechnology Information; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
Akre T. S., Parker L. D., Ruther E., Maldonado J. E., Lemmon L., McInerney N. R. (2019). Concurrent visual encounter sampling validates eDNA selectivity and sensitivity for the endangered wood turtle (Glyptemys insculpta). PloS One 14, e0215586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215586
Barnes M. A., Turner C. R., Jerde C. L., Renshaw M. A., Chadderton W. L., Lodge D. M. (2014). Environmental conditions influence eDNA persistence in aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 1819–1827. doi: 10.1021/es404734p
Berger A. J. (2010). Conservation and recovery of the yellow mud turtle (Kinosternon flavescens) in Mason and Tazewell counties, Illinois, M.Sc. Thesis. University of Illinois, Urbana.
Bernstein N. P., Christiansen J. L. (2011). Response of a yellow mud turtle (Kinosternon flavescens Agassiz) community to habitat change: Management implications for a nature preserve. Natural Areas J. 31, 414–419. doi: 10.3375/043.031.0412
Bickham J. W., Springer M. D., Gallaway B. J. (1984). Distributional survey of the yellow mud turtle (Kinosternon flavescens) in Iowa, Illinois, and Missouri: A proposed endangered species. Southwestern Nat. 29, 123–132. doi: 10.2307/3670777
Bogolin A. P., Davis D. R., Kline R. J., Rahman A. F. (2021). A drone-based survey for large, basking freshwater turtle species. PloS One 16, e0257720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257720
Brozio S., Manson C., Gourevitch E., Burns T. J., Greener M. S., Downie J. R., et al. (2017). Development and application of an eDNA method to detect the critically endangered Trinidad golden tree frog (Phytotriades auratus) in bromeliad phytotelmata. PloS One 12, e0170619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170619
Christiansen J. L., Bernstein N. P., Phillips C. A., Briggler J. T., Kangas D. (2012). Declining populations of yellow mud turtles (Kinosternon flavescens) in Iowa, Illinois, and Missouri. Southwestern Nat. 57, 304–313. doi: 10.1894/0038-4909-57.3.304
Christiansen J. L., Cooper J. A., Bickham J. W., Gallaway B. J., Springer M. D. (1985). Aspects of the natural history of the yellow mud turtle Kinosternon flavescens (Kinosternidae) in Iowa: a proposed endangered species. Southwestern Nat. 30, 413–425. doi: 10.2307/3671274
Christiansen J. L., Davis D. R., Jacobson E. R., LaDuc T. J. (2020). Carapacial shell disease process revealed by a long-term field study of the yellow mud turtle, Kinosternon flavescens, in Texas. J. Herpetology 54, 1–8. doi: 10.1670/19-032
Collins S. M. (2022). Examination of amphibian community and environmental relationships in south texas using environmental DNA (eDNA). M.Sc. Thesis. University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Brownsville, Texas.
Corpet F. (1988). Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 10881–10890. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10881
Cox N., Young B. E., Bowles P., Fernandez M., Marin J., Rapacciuolo G., et al. (2022). A global reptile assessment highlights shared conservation needs of tetrapods. Nature 605, 285–290. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04664-7
Davy C. M., Kidd A. G., Wilson C. C. (2015). Development and validation of environmental DNA (eDNA) markers for detection of freshwater turtles. PloS One 10, e0130965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130965
Deiner K., Yamanaka H., Bernatchez L. (2021). The future of biodiversity monitoring and conservation utilizing environmental DNA. Environ. DNA 3, 3–7. doi: 10.1002/edn3.v3.1
Feng W., Bulté G., Lougheed S. C. (2020). Environmental DNA surveys help to identify winter hibernacula of a temperate freshwater turtle. Environ. DNA 2, 200–209. doi: 10.1002/edn3.v2.2
Harper K. J., Goodwin K. D., Harper L. R., LaCasella E. L., Frey A., Dutton P. H. (2020). Finding crush: environmental DNA analysis as a tool for tracking the green sea turtle Chelonia mydas in a marine estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 6, 810. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00810
Howell H. J., Legere R. H. Jr., Holland D. S., Seigel R. A. (2019). Long-term turtle declines: protected is a verb, not an outcome. Copeia 107, 493–501. doi: 10.1643/CH-19-177
IUCN (2023). The IUCN red list of threatened species. Available online at: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (Accessed November 06, 2024).
Iverson J. B., Le M., Ingram C. (2013). Molecular phylogenetics of the mud and musk turtle family Kinosternidae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 69, 929–939. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2013.06.011
Jackson M., Myrholm C., Shaw C., Ramsfield T. (2017). Using nested PCR to improve detection of earthworm eDNA in Canada. Soil Biol. Biochem. 113, 215–218. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.06.009
Joseph C., Faiq M. E., Li Z., Chen G. (2022). Persistence and degradation dynamics of eDNA affected by environmental factors in aquatic ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 849, 4119–4133. doi: 10.1007/s10750-022-04959-w
Kirtane A. A., Wilder M. L., Green H. C. (2019). Development and validation of rapid environmental DNA (eDNA) detection methods for bog turtle (Glyptemys muhlenbergii). PloS One 14, e0222883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222883
Lam I. P., Sung Y. H., Fong J. J. (2022). Using eDNA techniques to find the endangered big-headed turtle (Platysternon megacephalum). PloS One 17, e0262015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262015
Lodge D. M., Turner C. R., Jerde C. L., Barnes M. A., Chadderton L., Egan S. P., et al. (2012). Conservation in a cup of water: estimating biodiversity and population abundance from environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 21, 2555–2558. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05600.x
Mali I., Brown D. J., Ferrato J. R., Forstner M. R. (2014). Sampling freshwater turtle populations using hoop nets: testing potential biases. Wildlife Soc. Bull. 38, 580–585. doi: 10.1002/wsb.v38.3
Miller J. D., Dinkelacker S. A. (2007). “Reproductive structures and strategies of turtles,” in Biology of turtles (Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press), 239–292.
Missouri Department of Conservation (2024). Yellow mud turtle. Available online at: https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/yellow-mud-turtle (Accessed November 06, 2024).
Nordstrom B., Budd A., Mitchell N., Cornish C., Byrne M., Kuchling G., et al. (2023). Environmental DNA reflects spatial distribution of a rare turtle in a lentic wetland assisted colonization site. Environ. DNA 6, e507. doi: 10.1002/edn3.507
Nordstrom B., Mitchell N., Byrne M., Jarman S. (2022). A review of applications of environmental DNA for reptile conservation and management. Ecol. Evol. 12, e8995. doi: 10.1002/ece3.v12.6
Petrov K., Sutcliffe S., Truscott H., Kutay C., Eisemberg C. C., Spencer R. J., et al. (2023). Turtles in trouble. Conservation ecology and priorities for Australian freshwater turtles. Austral Ecol. 48, 1603–1656. doi: 10.1111/aec.13418
Petruniak J., Bradley D., Kelly J. M., Hanner R. H. (2021). Commentary: integrating environmental DNA into applied ecological practice. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 11, 6–11. doi: 10.1007/s13412-020-00638-1
Platt S. G., Berezin A. R., Miller D. J., Rainwater T. R. (2016). A dietary study of the rough-footed mud turtle (Kinosternon hirtipes) in Texas, USA. Herpetological Conserv. Biol. 11, 142–149.
Qian T., Shan X., Wang W., Jin X. (2022). Effects of Temperature on the Timeliness of eDNA/eRNA: A Case Study of Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Water 14, 1155. doi: 10.3390/w14071155
Rhodin A. G., Stanford C. B., Van Dijk P. P., Eisemberg C., Luiselli L., Mittermeier R. A., et al. (2018). Global conservation status of turtles and tortoises (order Testudines). Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 17, 135–161. doi: 10.2744/CCB-1348.1
Rishan S. T., Kline R. J., Rahman M. S. (2023). Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) to detect subterranean and aquatic invasive species: A critical review on the challenges and limitations of eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. Adv. 12, 100370. doi: 10.1016/j.envadv.2023.100370
Rishan S. T., Kline R. J., Rahman M. S. (2024a). Exploitation of environmental DNA (eDNA) for ecotoxicological research: A critical review on eDNA metabarcoding in assessing marine pollution. Chemosphere 351, 141238. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141238
Rishan S. T., Kline R. J., Rahman M. S. (2024b). New prospects of environmental RNA metabarcoding research in biological diversity, ecotoxicological monitoring, and detection of COVID-19: a critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 11406–11427. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-31776-y
Robinson P. S., Davis D. R., Collins S. M., Kline R. J. (2022). Defining the current distribution of the imperiled black-spotted Newt across south Texas, USA. Global Ecol. Conserv. 36, e02131. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2022.e02131
Rodríguez A., Rodríguez M., Córdoba J. J., Andrade M. J. (2015). “Design of primers and probes for quantitative real-time PCR methods,” in PCR primer design. Methods in molecular biology. Ed. Basu C. (Humana Press, New York, NY, USA) 1275, 31–56.
Ruppert K. M., Davis D. R., Rahman M. S., Kline R. J. (2022). Development and assessment of an environmental DNA (eDNA) assay for a cryptic Siren (Amphibia: Sirenidae). Environ. Adv. 7, 100163. doi: 10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100163
Ruppert K. M., Kline R. J., Rahman M. S. (2019). Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Global Ecol. Conserv. 17, e00547. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00547
Sahu A., Kumar N., Singh C. P., Singh M. (2023). Environmental DNA (eDNA): Powerful technique for biodiversity conservation. J. Nat. Conserv. 71, 126325. doi: 10.1016/j.jnc.2022.126325
Sard N. M., Herbst S. J., Nathan L., Uhrig G., Kanefsky J., Robinson J. D., et al. (2019). Comparison of fish detections, community diversity, and relative abundance using environmental DNA metabarcoding and traditional gears. Environ. DNA 1, 368–384. doi: 10.1002/edn3.v1.4
Shu L., Ludwig A., Peng Z. (2020). Standards for methods utilizing environmental DNA for detection of fish species. Genes 11, 296. doi: 10.3390/genes11030296
Stanford C. B., Iverson J. B., Rhodin A. G., van Dijk P. P., Mittermeier R. A., Kuchling G., et al. (2020). Turtles and tortoises are in trouble. Curr. Biol. 30, R721–R735. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.04.088
Stoeckle M. Y., Das Mishu M., Charlop-Powers Z. (2018). GoFish: A versatile nested PCR strategy for environmental DNA assays for marine vertebrates. PloS One 13, e0198717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198717
Strickler K. M., Fremier A. K., Goldberg C. S. (2015). Quantifying effects of UV-B, temperature, and pH on eDNA degradation in aquatic microcosms. Biol. Conserv. 183, 85–92. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2014.11.038
Tuma M. W. (2006). Range, habitat use, and seasonal activity of the yellow mud turtle (Kinosternon flavescens) in northwestern Illinois: implications for site-specific conservation and management. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 5, 108–120. doi: 10.2744/1071-8443(2006)5[108:RHUASA]2.0.CO;2
Untergasser A., Cutcutache I., Koressaar T., Ye J., Faircloth B. C., Remm M., et al. (2012). Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, e115–e115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks596
Yang J., Zhang X., Jin X., Seymour M., Richter C., Logares R., et al. (2021). Recent advances in environmental DNA-based biodiversity assessment and conservation. Diversity Distributions 27, 1876–1879. doi: 10.1111/ddi.v27.10
Keywords: environmental DNA, biodiversity monitoring, nature conservation, global ecology, mud turtles
Citation: Rishan ST, Kline RJ and Rahman MS (2025) Development and validation of rapid eDNA detection method for yellow mud turtle, Kinosternon flavescens: a field study in South Texas, USA. Front. Conserv. Sci. 6:1431348. doi: 10.3389/fcosc.2025.1431348
Received: 11 May 2024; Accepted: 06 January 2025;
Published: 24 January 2025.
Edited by:
Eric Stolen, University of Central Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Luara Simões, University of Minho, PortugalCopyright © 2025 Rishan, Kline and Rahman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Md Saydur Rahman, bWQucmFobWFuQHV0cmd2LmVkdQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.