- 1Department of Smart Computing and Cyber Resilience, School of Engineering & Technology, Sunway University, Sunway, Malaysia
- 2Department of Information and Communications Engineering, College of Information Engineering, Al-Nahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq
- 3Department of Electrical, Electronic & Systems Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), Bangi, Malaysia
The increasing amount of data sensors generate, and the dynamic nature of climate and environment pose challenges for conventional smart environmental monitoring systems. These systems encounter difficulties in long-distance data communication, accurate data processing, and generalized prediction modeling, particularly in large-scale, remote, and hard-to-reach areas. Moreover, they are costly, complex, and inefficient, especially in regions with limited telecommunications infrastructure. Consequently, there is a pressing need for more efficient and effective monitoring techniques to safeguard natural resources and ecosystems. To address these challenges, we propose the concept of a novel environmental monitoring system that integrates aerial access networks (AAN), federated learning (FL), and hybrid LoRa Point-to-Point (P2P)/LoRaWAN technologies. This integration offers a reliable and efficient solution for monitoring remote regions. We provide an overview of the AAN, FL, and aerial FL paradigms and discuss the benefits and challenges of their integration. Preliminary simulation results demonstrated the proposed system’s feasibility and effectiveness. Lastly, we outline open challenges and potential research directions to advance this field.
1 Introduction
Machine learning (ML) offers effective solutions to complex problems. However, the success of ML relies on accurate, large, and unbiased datasets, which are often extremely challenging, costly, or impossible to obtain.
Aerial access networks (AANs) are wireless networks that use flying platforms like unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to provide connectivity and communication services. AANs overcome terrestrial access network (TAN) limitations, offering extended coverage, improved communication quality, and enhanced mobility. They are particularly valuable in remote and inaccessible areas, where TANs are unavailable or have limited coverage.
Integrating low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies like LoRaWAN® or LoRa P2P into UAV-assisted AANs offers a comprehensive solution for environmental monitoring in remote regions. These technologies enhance communication range and enable direct device-to-device communication, addressing conventional wireless sensor networks (WSNs) constraints. However, challenges remain in ensuring reliable communication links, especially in harsh environments where environmental factors significantly impact channel conditions and hinder the transmission of large volumes of raw data from terrestrial to aerial nodes.
In recent years, the surge in data generation has driven the adoption of ML for data analysis. However, traditional centralized ML techniques have limitations concerning data privacy, raw data transmission, and resource-intensive processing. To address these challenges, Google introduced federated learning (FL) in 2016 as a promising approach (Konečný, 2016). FL mitigates privacy risks and communication costs by training ML models locally on devices rather than centralizing data. This approach addresses privacy concerns and reduces the need for high-bandwidth and low-latency communication links, which can be expensive in large Internet of Things (IoT) networks.
The original FL architecture faces technical challenges, such as ensuring reliable connectivity between end devices (EDs) and aggregation servers (AS). This issue becomes more pronounced in scenarios with poor or non-existent connectivity between EDs and AS. To address this issue, aerial federated learning (AFL)—a variant of FL leveraging AANs—has emerged as a promising approach (Pham et al., 2022). AAN platforms can serve as relays to transmit local models from EDs to the AS or aggregate models directly. Recent studies, such as (Pham et al., 2022), have proposed AFL and emphasized the significance of AANs and mobile edge computing (MEC) for next-generation networks.
MEC brings computing and storage resources closer to the network edge, enabling low-latency real-time applications and reducing reliance on cloud-based data transmission. It is a key technology for next-generation networks, facilitating IoT, 5G, and edge AI use cases.
Integration of MEC, FL, and AANs offers the potential for developing advanced intelligent environmental monitoring systems in remote areas. However, research on their integration and associated challenges for environmental monitoring is lacking. This work introduces the UAV-assisted Federated Learning system for Environmental Monitoring (UFEM), which integrates AANs, FL, MEC, and a hybrid LoRa P2P/LoRaWAN topology. The system addresses the limitations of conventional environmental monitoring approaches and provides an efficient framework for deploying intelligent IoT solutions in remote and harsh environments.
In summary, the contributions of this article are:
• A technical review of FL and AFL, discussing their benefits and limitations. This review contextualizes the challenges of deploying federated learning in aerial environments, emphasizing the need for hybrid solutions like the proposed system.
• The design and proposal of the UFEM system architecture, which integrates FL, AANs, LPWAN technologies. This includes the integration of AFL workflows and hybrid LoRaWAN®/LoRa P2P topology to enable dual-hop communication tailored for environmental monitoring in remote areas.
• Identifying key challenges and research directions for AFL and UFEM development.
2 Related works, concepts, and limitations
In this section, we provide an overview of recent wireless sensing technologies and then delve into the concepts of AAN and FL, including their various paradigms. We then examine the specific application of AFL and its associated benefits and limitations.
2.1 Wireless sensing technologies for environmental monitoring
Several studies have examined using WSNs to monitor different phenomena in remote and hard-to-reach environments, driven by recent IoT breakthroughs in low-cost sensing devices, machine-to-machine (M2M) connectivity, and wireless IoT technologies. However, the difficult backhaul deployment, harsh wireless channel conditions, and lack of public network coverage make collecting data from these remote areas difficult.
In this context (Zhang and Li, 2020), suggested a drone-assisted IoT relay system in which drones were implemented as mobile relays for remote data gathering from monitoring equipment positioned in challenging areas with no public network coverage. The system aims to provide a high-speed and cheap method of monitoring the environment using two different types of wireless communication. The first uses 5 GHz Wi-Fi to transmit low-latency data between the drone and ground-based monitoring devices. Meanwhile, LoRa technology was implemented as a Wi-Fi module wake-up approach to save power.
Low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) such as LoRaWAN®, SigFox, and NarrowBand-IoT (NB-IoT) have long-range capabilities and high energy efficiency. However, each has limitations; for example, direct communication between LoRa nodes is not permitted by LoRaWAN®, making it unsuitable for private LoRa networks where one gateway (GW) is placed for wide monitoring areas, and nodes cannot be in the communication range of the GW. One possible solution is wireless mesh networking that allows multi-hop communication and data forwarding between nodes until it reaches the GW. This approach was considered in (Lee and Ke, 2018), which proposed a LoRa mesh networking system for large-area monitoring. The results showed that the suggested LoRa mesh networking system outperformed LoRa star-network architecture regarding packet delivery ratio (PDR) by 30%.
Similarly (Cecílio, 2021), investigated the use of LoRa in private network deployments for IoT applications. The study then presented an improved LoRa reliable protocol (AQUAMesh) with mesh networking capabilities for remote monitoring applications that can replace LoRaWAN®. It uses the LoRa physical layer, which provides long-range communications and enables point-to-point communications to be dealt with using custom time-division multiple access (TDMA). The results showed that the proposed protocol overcomes the shortcomings of the existing LoRaWAN® and can be effectively deployed in private networks for various applications.
2.2 Aerial access networks
AANs, with their unique characteristics, including flexibility, dynamic deployment, and increased coverage capabilities, play a crucial role in developing 5G and 6G networks. They enhance performance by supplementing terrestrial, underground, and marine communication networks (Geraci et al., 2022), (Hu et al., 2024).
AANs can be classified into high-altitude platforms (HAPs) and low-altitude platforms (LAPs). HAPs, such as satellites, are hindered by limitations, including weather conditions, limited mobility, high latency, the need for large and power-intensive equipment, and high operational costs. These factors make HAPs less suitable for environmental monitoring in remote and hard-to-reach areas.
In contrast to HAPs, LAPs, such as UAVs, offer several advantages as aerial base stations (ABSs) or aerial users. These advantages include mobility, low latency for real-time applications, suitability for harsh environments, lower operational costs, and the high probability of line-of-sight (LoS) communication due to the dynamic nature of UAVs. Despite that, effective implementation of AANs faces challenges, such as power constraints, spectrum utilization, and interference management.
2.3 Federated learning
FL enables data collection and local model training on edge devices (EDs). The trained local models are transmitted to the AS for model aggregation, employing techniques such as FedAvg or other FL algorithms (Fu et al., 2024). Then, the global model is sent back to the EDs. This process is repeated until the desired performance is met. Therefore, EDs do not need to send their raw data to the AS, which requires less bandwidth and lower energy for data transmission. On the other hand, as the raw data are kept at the EDs, data privacy can be further protected. This decentralized approach improves efficiency and privacy.
Based on the data distribution, FL can be categorized into three groups: horizontal FL (HFL), vertical FL (VFL), and transfer FL (TFL) (Du et al., 2020). HFL uses datasets with similar features from EDs of the same type to train a common model. In contrast, VFL collects data from EDs of different types to train personalized models, while TFL focuses on knowledge transfer between domains or tasks by pretraining on one dataset and fine-tuning on another.
FL can also be categorized based on network topology: centralized and distributed. Centralized FL uses a central server (AS) for model aggregation, while distributed FL allows EDs to share local models with each other based on trust and network protocols, performing model aggregation in a distributed, decentralized manner (Shayan et al., 2020), (Fu et al., 2024).
2.4 Aerial federated learning
In AFL, the location of AS can be fixed or dynamic. In scenarios where EDs have limited access to the AS, an AAN platform serves as a relay or directly aggregates models, either centrally or in a distributed manner, as described earlier in the introduction. Previous research, such as (Ng et al., 2020), has proposed and discussed the concept of aerial aggregation, where a UAV is deployed to collect local models from EDs and execute model aggregation. However, the number of deployed UAVs depends on the coverage area size.
Regarding implementing AFL, UAVs can be deployed in three ways: as relays, EDs, or as part of a UAV swarm.
2.4.1 UAVs as Relays
UAVs extend network coverage by relaying local models from EDs outside the AS’s range to the AS and transmitting the global model back to the EDs. Previous research, such as (Du et al., 2020), has investigated the implementation of UAVs as aerial relays for FL in the context of the Internet of Vehicles (IoV).
2.4.2 UAVs as EDs
UAVs can also be deployed as EDs to provide FL services. In this case, UAVs cooperate to perform a complex learning task. Literature such as (Zhang and Hanzo, 2020) has explored using UAVs as EDs for object detection and classification applications. The coordination of UAVs can be accomplished through self-coordination or a ground control station (GCS). When a reliable link exists between the UAVs and GCS, a terrestrial server can coordinate the UAVs. However, when reliable links are unavailable or computation power at the GCS is sufficient, one of the UAVs may assume the coordinator role.
2.4.3 UAVs Swarm
A swarm of UAVs can connect in an ad hoc manner and perform the FL task. In such a network, UAVs can establish a fully aerial network or connect to terrestrial infrastructure. In the latter scenario, only a limited number of UAVs need to be directly connected to the infrastructure, while the remainder of the UAVs can establish an indirect connection through intermediate UAVs. The authors of (Lee, 2022)- (Liu et al., 2020) have examined the potential of UAV swarms in FL, with (Lee, 2022) focusing on federated reinforcement learning in aerial remote sensing, (Hoang et al., 2023), proposing a clustered and scalable FL framework, and (Ding et al., 2024) addressing distributed machine learning with a focus on computing, sensing, and semantics. However, implementation challenges, including routing, communication protocols, and dynamic topology, require further examination.
3 Motivation
The main limitations of conventional environmental monitoring systems include the need for long-range, reliable, and high-bandwidth communication links, which become more challenging in remote and hard-to-reach environments that lack telecommunications infrastructure. Additionally, monitoring large-scale areas results in large amounts of raw data that need to be transmitted, which increases power consumption. Conventional FL faces fixed deployment and coverage constraints, making adaptation to dynamic ED behavior and deployment in remote areas difficult and costly.
To address these limitations, we propose a novel approach that incorporates the advantages of AANs, AFL, and a hybrid LoRa P2P/LoRaWAN communication system to improve the efficiency of environmental monitoring in remote areas by bringing intelligence to wireless sensor networks and enabling the efficient extraction and transfer of meaningful data to points of interest.
4 UAV-assistant FL system for environmental monitoring
4.1 General concept
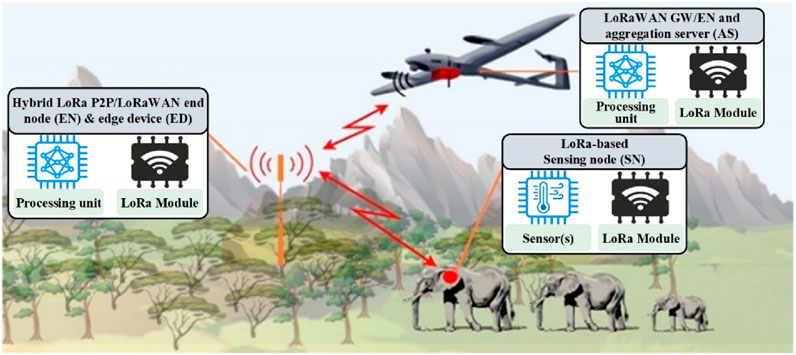
Figure 1 depicts the general concept of the proposed UFEM system. As an example of a large-scale, remote, and hard-to-reach environment, the simulation and results analysis utilize Malaysia’s National Park tropical forest, which covers an area of 4,343 km2 and is believed to be 130+ million years old, making it one of the oldest deciduous rainforests identified to date.
To increase the efficacy of data collection, mobile sensing nodes (SNs) equipped with LoRa transceivers for WSN capabilities are implemented. This can be achieved by attaching the SNs to selected wildlife, e.g., in the form of collar tags. This approach leverages the animals’ access to hard-to-reach environments and their tendency to move within a specific territory, which aids in developing a local network for retrieving data from the SNs and transmitting it to the EDs.
The proposed UFEM system comprises three main components: SNs, EDs, and AS. The system employs many SNs distributed throughout the environment to collect data. The EDs use the collected local data to train local models, while the AS aggregates these local models - centrally or distributedly - to update the global model.
Subsequent sections detail the network topology, components, and FL workflow for environmental monitoring.
4.2 Proposed network topology
Among the latest LPWAN technologies, LoRaWAN® has received significant attention from the scientific and industrial communities due to its unique features and flexibility for long-range communication requirements. It utilizes the LoRa physical layer with an added Medium Access Control (MAC) mechanism to enable nodes in the network to communicate with multiple GWs in range. However, its reliance on multiple GWs limits deployments in remote areas lacking infrastructure or feasibility for private LoRaWAN® networks.
In such scenarios, the P2P communication feature of the private LoRa network is much needed. As suggested by multiple studies, one solution would be utilizing the LoRa mesh network to support multi-hop communications between nodes. The latter, however, increases the network’s routing complexity with a major drop in power consumption efficiency, making it unsuitable for the harsh deployment scenarios targeted in this work.
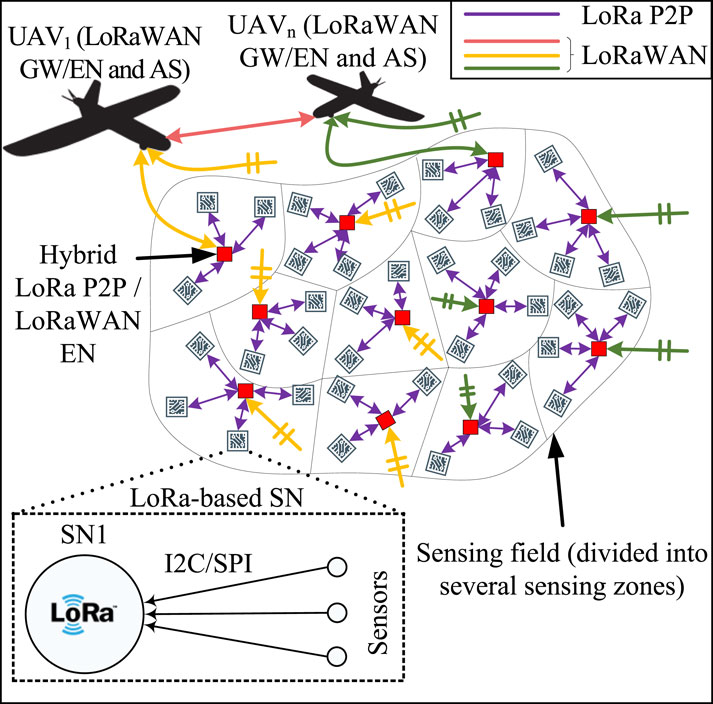
This work addresses these challenges by proposing a hybrid network topology combining LoRaWAN® and LoRa P2P communication to enable dual-hop communication, as shown in Figure 2. The proposed network consists of three main components: (i) a LoRaWAN®-based GW, (ii) a hybrid LoRa P2P/LoRaWAN® end node (EN), and (iii) a LoRa-based SN. SN transmits collected data sequentially to an EN once or twice daily with limited retransmissions to address communication failure while maintaining full compliance with the spectrum and LoRaWAN® regulations.
On the other hand, EN functions as a hybrid LoRa P2P/LoRaWAN® node to relay data between SNs and the GW and is mounted at relatively high altitudes. Hybrid networking can be achieved by modifying the LoRaWAN® MAC layer of the ENs to switch between two different networks. Accordingly, ENs may only switch to LoRaWAN® mode when receiving a downlink message from the GW that triggers the start or end of the LoRaWAN® communication session.
Finally, GW is a typical private LoRaWAN® based GW that may collect and forward local/global model parameters from/to ENs in the sensing field. Similarly, when one or multiple UAVs are deployed for large-scale monitoring, the LoRaWAN® modem is configurable to switch between GW or EN functionality. Thus, UAVs communicate by modifying the LoRaWAN® MAC layer to switch between modes.
4.3 Aerial federated learning workflow
The proposed UFEM system’s FL training process is composed of the following steps:
1) Initialization: The AS sets the hyperparameters of the training model (e.g., number of hidden layers and neurons, learning rate, optimizer) and updates the EDs with the model hyperparameters.
2) Data collection: SNs collect and store data from the field.
3) Data transmission to the EDs: SNs transmit data to the EN based on a defined schedule, and the EN conveys the data to the ED.
4) Local model training: Each ED trains a local model.
5) Local model update: After training for a predefined batch number, each ED transfers its local model to the AS (on the UAV).
6) Model aggregation: This process depends on the type of FL (number of UAVs):
• Centralized FL: A single UAV retrieves and aggregates all local models across the field.
• Distributed FL: Multiple UAVs, each retrieving and aggregating local models within its defined sectors to compute a semi-global model. Based on a predefined path, these UAVs gather in a particular zone and share semi-global models. Finally, one of the UAVs aggregates the semi-global models and shares the computed global model with other UAVs.
7) Global model sharing: In the next mission, the UAV broadcasts the updated global model to the EDs.
The above procedure is repeated until the desired performance is achieved. This iterative process is adaptable to both centralized and distributed federated learning configurations. The centralized approach minimizes computational overhead on EDs, making it ideal for deployments with fewer UAVs and simpler network topologies. In contrast, the distributed approach enhances scalability by leveraging multiple UAVs for sector-based aggregation, enabling the system to handle large-scale deployments efficiently. These design choices balance scalability, resource constraints, and performance requirements, catering to diverse environmental monitoring scenarios.
As detailed in Section 4.1, the proposed workflow is directly applicable to large-scale environmental monitoring scenarios, such as Malaysia’s National Park, where sensing nodes on wildlife collect data for federated learning.
5 Performance evaluation
The feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed system architecture are evaluated through both LoRa coverage analysis and FL performance analysis. The LoRa results are discussed first, followed by the FL simulation results. The simulations were conducted using the Cloud-RF® RF planning tool for the LoRa coverage analysis and Tensorflow Federated for the FL simulations.
As illustrated in the previous section, ENs function as hybrid LoRa P2P/LoRaWAN® nodes to communicate with both SNs and the GW. This makes ENs the most important component in the proposed system, where achievable coverage directly depends on ENs placement and the physical layer configuration parameters for LoRa, including spreading factor (SF), transmission power, and bandwidth. It is assumed that 33 ENs are deployed throughout Malaysia’s National Park. Then, simulations were performed to predict the average coverage range per EN, considering both EN to SN and EN to GW communication scenarios.
The simulations considered the ENs mounting height 20 m above ground level (AGL). Meanwhile, SNs and GW were considered at 1 m and 60 m AGL, respectively. Other physical layer configuration parameters of LoRa were comparable to simulation parameters in (Alobaidy et al., 2022), (Alobaidy et al., 2024), including a transmission power of 20 dBm, AS923 frequency band with a 125 kHz bandwidth, receiver sensitivity of −137 dBm, and a 3 dBi omnidirectional antenna for all node types. The Longley-Rice Irregular Terrain Model (ITM) was used for its ability to account for irregular terrain impacts, with knife-edge diffraction enabled and the default tropical climate profile applied for accurate coverage modeling. It should be noted that the simulations were performed by utilizing the API calculation feature of Cloud-RF® then coverage results from each node were combined into one supper layer to plot the coverage heatmap of the achieved results, as shown in Figure 3.
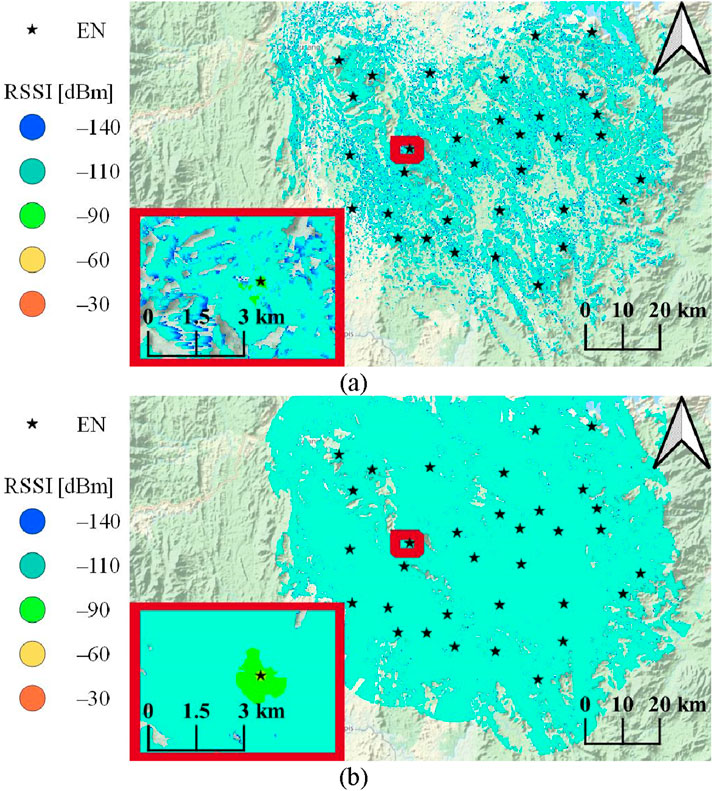
Figure 3. LoRa coverage heatmap, with an example showing captured results for one of the ENs (highlighted in a red frame); for (A) ENs to SNs communication scenario and (B) ENs to GW communication scenario.
Based on the coverage heatmaps shown in Figure 3A, it can be noted that moderate coverage may be achieved with an average radius of 1–3 km while also achieving wider ranges, in some cases, depending on the terrain, foliage, and other signal-influencing factors that may impact the communication between EN and SNs. Meanwhile, it is clear from Figure 3B that a GW carried out by a UAV at 60 m may cover all 33 ENs with a signal strength that is, on average, equal to or greater than −110 dBm.
It can be concluded that the proposed system may be operated successfully in the considered environment by considering an SF9 for the EN to SN link and an SF7 for the EN to GW link. On the other hand, the bandwidth may be maintained at 125 kHz for the EN to SN communication scenario, while it may be increased to 250 kHz or even 500 kHz for the EN to GW communication scenario.
Meanwhile, to maintain the duty cycle and maximum allowed airtime between the nodes, especially for EN to SN or vice versa communication link due to limited bandwidth, the SNs may be configured to transfer or receive data to/from EN once or twice per day in a sequential manner. Further, nodes may also be configured to consider two to three retransmissions to cater to any packet losses due to communication failure.
To evaluate FL under different scenarios, simulations were conducted utilizing the MNIST dataset to represent non-i.i.d. data distribution. The dataset was partitioned and distributed among multiple EDs to train the model locally on each ED’s data.
Generally, the performance of FL is affected by factors such as the nature of the data, the optimization technique employed, the model architecture, the number of EDs, and the other hyperparameter settings. The study used a set of specific hyperparameters, model architecture, and optimization methods that align with the parameters and configurations outlined in (TensorFlow, 2024).
Figure 4A compares the performance of FL with 33 EDs to that of conventional ML (CML). CML uses a centralized approach where all data is sent to a central server for training, resulting in higher accuracy due to access to all data. In contrast, FL distributes data among multiple EDs and trains the model locally on each ED’s data, leading to lower accuracy as the model does not have access to all data. However, increasing the number of training rounds can reduce the gap in performance between CML and FL to a small margin (0.08) after 20 rounds. The performance gap depends on factors such as the data, optimization technique, model architecture, and hyperparameters, which can be further optimized to improve performance.
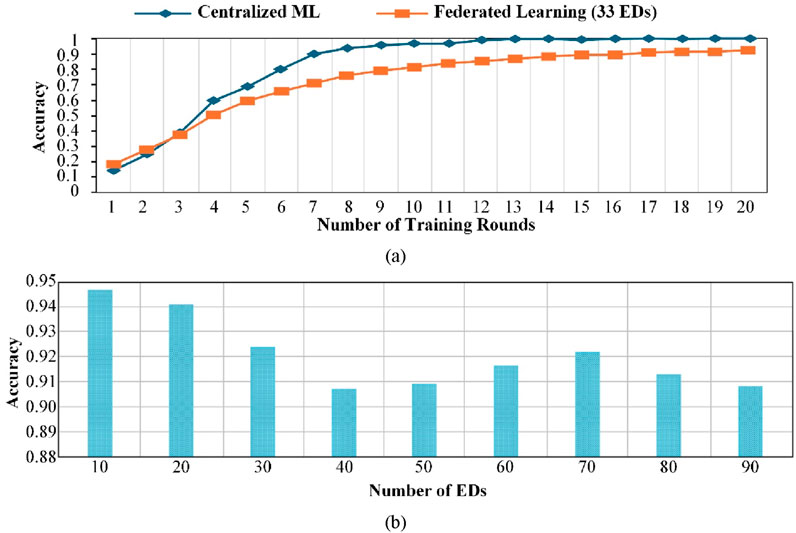
Figure 4. (A) Comparison of centralized/conventional ML with federated learning (FL). (B) Performance of FL under different numbers of edge devices (EDs).
Figure 4B presents the performance evaluation results of FL under varying numbers of EDs. The impact of EDs on FL performance depends on the dataset and model architecture utilized. It is important to note that in the proposed system, a large set of sensors are collecting environmental data, such as meteorology data, from a large-scale environment; therefore, the expected type of data likely would be non-i.i.d. From the results, it can be observed that an increase in the number of EDs initially slightly decreases FL performance; however, the accuracy fluctuates around 0.92%, which indicates that FL can effectively handle the learning task in a distributed manner.
In general, FL performance is expected to improve with increased EDs; however, when dealing with non-i.i.d data, this may not always be the case. More EDs do not necessarily provide more diverse and representative data to the model but may lead to a more robust model. Therefore, it is important to consider the trade-offs between the benefits of having more EDs and the increased complexity and communication costs.
6 Open research challenges and future directions
While there are numerous challenges in this domain, this section focuses on the most critical ones directly impacting the development and deployment of the proposed UFEM system. These challenges require further investigation and present significant open research opportunities.
6.1 Aerial access networks
The use of AANs in environmental monitoring offers several distinct advantages; however, several technical challenges must be addressed to leverage their potential fully. One of the main challenges is optimizing the path planning of the UAVs for maximum performance. This includes optimizing parameters such as travel distance, communication link reliability, energy consumption (particularly during aggregation and relaying tasks), and time-on-air. In addition, the impact of factors such as altitude, speed, and mobility of the UAVs on the performance of the AANs and the overall system needs to be investigated.
There are also challenges in channel modeling for harsh communication environments that need further study. To improve the performance of FL service, UAVs’ autonomy level and decision-making capability need to be improved. Additionally, the security and privacy of transmitted data must be considered, and new networking protocols may be needed to improve communication and coordination between UAVs or other networks/devices.
6.2 Edge devices
Several technical challenges and potential research directions must be addressed to fully leverage the potential of EDs in environmental monitoring systems. These challenges include ensuring the security and privacy of data, developing efficient data pre-processing and feature selection methods, and investigating the impact of factors like the number and distribution of EDs on system performance. Additionally, developing methods for handling the dynamic behavior of EDs, such as the ability to join or leave the FL network and the ability to adjust the resources allocated to the EDs based on their capabilities and requirements, is also important.
The scalability of the proposed system to support large-scale deployment of EDs and handle the increase in data volume and complexity is an important area of research. Additionally, investigating the energy efficiency of EDs, and developing methods for power management and energy-aware resource allocation are important future research directions. The robustness and fault tolerance of the proposed system to handle potential failures or malfunctions of EDs must also be investigated.
The non-i.i.d. nature of the data used in the FL system is also a challenge that should be addressed by investigating methods for addressing the non-i.i.d. nature of the data, such as data pre-processing techniques or modifying the FL algorithms themselves to better handle non-i.i.d data. In addition, real-time model adaptation remains critical, requiring FL algorithms that can dynamically adjust to changes in environmental conditions while balancing computational efficiency and performance.
6.3 Sensing nodes
One of the key challenges that need to be addressed in the proposed system is designing and implementing energy-efficient SNs that can operate for prolonged periods in remote and harsh environments. Ensuring the robustness and reliability of data collection from these SNs is also crucial, which includes addressing issues such as sensor failure and missing/incomplete data. The impact of different sensor configurations, such as the number of sensors, the types of sensors, and the placement of sensors, on the system’s overall performance needs to be investigated.
Additionally, methods for pre-processing and selecting features at the sensor level can improve the performance of the FL model by reducing the amount of data transmitted. The use of machine learning techniques for data processing and analysis at the sensor level is an active area of research that can further improve the system’s efficiency, e.g., refer to (Warden, 2022).
7 Conclusion
In conclusion, this paper proposes a novel environmental monitoring system that integrates advanced technologies, including aerial access networks (AAN), federated learning (FL), and hybrid LoRa P2P/LoRaWAN communication. It examines FL and aerial FL, highlighting their strengths and limitations. The initial simulation results validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed system, showcasing improved coverage and performance in large-scale and extreme environments. Furthermore, the research highlights the challenges and identifies potential research directions in AANs, aerial FL, and sensing nodes. The proposed system offers a promising approach to address the limitations of conventional monitoring systems and contributes to the advancement of environmental monitoring technologies.
Future work involves deploying the proposed UFEM system in real-world environments, such as Malaysia’s National Park, which served as a case study for this research. These deployments aim to validate the system’s performance under dynamic environmental conditions, including varying terrain and weather, while also offering critical insights into optimizing its scalability and reliability for large-scale monitoring in challenging environments.
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Author contributions
MB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. RN: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Validation. NA: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by Sunway University under Grant GRTIN-RAG(02)-DEN-03-2024, and in part by the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia under the Royal Academy of Engineering UK Grant Ref: ESMN 2123\2\63 (UKM Ref: KK-2021-020).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alobaidy, H. A., Nordin, R., Singh, M. J., Abdullah, N. F., Haniz, A., Ishizu, K., et al. (2022). Low-Altitude-Platform-Based airborne IoT network (LAP-AIN) for water quality monitoring in harsh tropical environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 9 (20), 20034–20054. doi:10.1109/jiot.2022.3171294
Alobaidy, H. A. H., Nor, F. A., Nordin, R., Behjati, M., Abu-Samah, A., Maizan, H., et al. (2024). Empowering extreme communication: propagation characterization of a LoRa-based internet of things network using hybrid machine learning. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 5, 3997–4023. doi:10.1109/OJCOMS.2024.3420229
Cecílio, J. (2021). “AQUAMesh: a low-power wide-area mesh network protocol for remote monitoring applications in water environments,” in IECON 2021–47th annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society (IEEE).
Ding, Y., Yang, Z., Pham, Q.-V., Hu, Ye, Zhang, Z., and Shikh-Bahaei, M. (2024). Distributed machine learning for UAV swarms: computing, sensing, and semantics. IEEE Internet Things J. 11 (5), 7447–7473. doi:10.1109/JIOT.2023.3341307
Du, Z., Wu, C., Yoshinaga, T., Yau, K. L. A., Ji, Y., and Li, J. (2020). Federated learning for vehicular internet of things: recent advances and open issues. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 1, 45–61. doi:10.1109/ojcs.2020.2992630
Fu, M., Shi, Y., and Zhou, Y. (2024). Federated learning via unmanned aerial vehicle. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 23 (4), 2884–2900. doi:10.1109/TWC.2023.3303492
Geraci, G., Garcia-Rodriguez, A., Azari, M. M., Lozano, A., Mezzavilla, M., Chatzinotas, S., et al. (2022). What will the future of UAV cellular communications be? A flight from 5G to 6G. IEEE Commun. Surv. and tutorials 24 (3), 1304–1335. doi:10.1109/comst.2022.3171135
Hoang, D., Vu, T. T., Hung, D.Le, and Long, B.Le (2023). Clustered and scalable federated learning framework for UAV swarms. TechRxi. doi:10.36227/techrxiv.22730012.v1
Hu, G., Zhu, D., Shen, J., Hu, J., Han, J., and Li, T. (2024). FedBeam: reliable incentive mechanisms for federated learning in UAV-enabled internet of vehicles. Drones 8 (10), 567. doi:10.3390/drones8100567
Konečný, J. (2016). Federated learning: strategies for improving communication efficiency. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1610.05492. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1610.05492
Lee, H.-C., and Ke, K.-H. (2018). Monitoring of large-area IoT sensors using a LoRa wireless mesh network system: design and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 67 (9), 2177–2187. doi:10.1109/tim.2018.2814082
Lee, W. (2022). “Federated reinforcement learning-based UAV swarm system for aerial remote sensing,” in Wireless Communications and mobile computing 2022, 1–15. doi:10.1155/2022/4327380
Liu, Y., Nie, J., Li, X., Ahmed, S. H., Lim, W. Y. B., and Miao, C. (2020). Federated learning in the sky: aerial-ground air quality sensing framework with UAV swarms. IEEE Internet Things J. 8 (12), 9827–9837. doi:10.1109/jiot.2020.3021006
Ng, J. S., Lim, W. Y. B., Dai, H. N., Xiong, Z., Huang, J., Niyato, D., et al. (2020). Joint auction-coalition formation framework for communication-efficient federated learning in UAV-enabled internet of vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transp. Syst. 22 (4), 2326–2344. doi:10.1109/tits.2020.3041345
Pham, Q.-V., Zeng, M., Huynh-The, T., Han, Z., and Hwang, W. J. (2022). Aerial access networks for federated learning: applications and challenges. IEEE Netw. 36 (3), 159–166. doi:10.1109/mnet.013.2100311
Shayan, M., Fung, C., Yoon, C. J., and Beschastnikh, I. (2020). Biscotti: a blockchain system for private and secure federated learning. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distributed Syst. 32 (7), 1513–1525. doi:10.1109/tpds.2020.3044223
TensorFlow (2024). TensorFlow federated. Available at: https://github.com/google-parfait/tensorflow-federated/blob/v0.46.0/docs/tutorials/federated_learning_for_image_classification.ipynb. Accessed on 16 January 2025.
Zhang, H., and Hanzo, L. (2020). Federated learning assisted multi-UAV networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69 (11), 14104–14109. doi:10.1109/tvt.2020.3028011
Keywords: federated learning, aerial access network, UAV, LORA, wireless sensor networks, environmental conservation
Citation: Behjati M, Alobaidy HAH, Nordin R and Abdullah NF (2025) UAV-assisted federated learning with hybrid LoRa P2P/LoRaWAN for sustainable biosphere. Front. Commun. Netw. 6:1529453. doi: 10.3389/frcmn.2025.1529453
Received: 16 November 2024; Accepted: 07 January 2025;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Tawfik Al-Hadhrami, Nottingham Trent University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Mariem Thaalbi, Tunis Business School, TunisiaAhmad Bazzi, New York University Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Copyright © 2025 Behjati, Alobaidy, Nordin and Abdullah. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mehran Behjati, bWVocmFuYkBzdW53YXkuZWR1Lm15; Haider A. H. Alobaidy, aGFpZGVyYWxvYmFpZHlAbmFocmFpbnVuaXYuZWR1Lmlx
 Mehran Behjati
Mehran Behjati Haider A. H. Alobaidy
Haider A. H. Alobaidy Rosdiadee Nordin
Rosdiadee Nordin Nor Fadzilah Abdullah
Nor Fadzilah Abdullah