- Faculty of Design and Architecture, University of Putra Malaysia, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
Introduction: Safety signs are essential visual communication tools that convey critical information regarding hazards, regulations, and emergency procedures across various environments. Their significance has garnered considerable attention due to their role in enhancing public safety. However, existing studies have predominantly focused on design factors, with limited research addressing the interaction of non-design factors among specific age groups and safety communication in public spaces, particularly concerning young children’s cognitive abilities and perceptions.
Methods: This systematic review aims to comprehensively analyze the characteristics and effectiveness of safety signs within the school environment. A systematic review of the literature on safety signs—specifically their design within school premises—was conducted using the Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) approach to identify research gaps. Query strings were utilized to extract papers, identifying 48 peer-reviewed articles from 2000 to 2024 for review.
Results: The review found that visual elements, such as dynamic safety signs and the use of highly saturated colors, significantly enhance the effectiveness of warnings. Several factors were identified that influence the efficacy of safety signs, including age-related cognitive abilities and the contextual understanding of young children. Additionally, the study highlights the effectiveness of technological tools, such as eye tracking and virtual reality (VR), for assessing human perception and improving testing methodologies. The role of enjoyment and experiential learning in enhancing safety communication are beneficial.
Discussion: This systematic review underscores the importance of considering both design and non-design factors in safety sign development, particularly in school environments. The findings suggest that dynamic, visually appealing signs, along with the use of advanced technological tools, can improve the effectiveness of safety messages. The integration of experiential learning also contributes to a better understanding of safety information. This review is a valuable resource for safety science researchers, visual designers, and policymakers by providing insights into the current state of research, identifying research gaps, and offering perspectives on the future of school safety signage pertinent to school-age children.
Introduction
The importance of students’ safety in schools
School safety is a multifaceted concept that encompasses the physical, emotional, and psychological well-being of students, staff, and visitors within educational environments (Thapa et al., 2013; Lester et al., 2017). According to research, it involves creating and maintaining an environment free from violence, bullying, harassment, and other threats, promoting a secure and supportive atmosphere conducive to learning and personal development (Espelage and Swearer, 2009; Collie et al., 2011). Additionally, school safety includes implementing policies and practices that prevent and respond to emergencies, ensuring preparedness and resilience in the face of potential crises (Robers et al., 2014).
School-related accidents and injuries are a significant public health concern, impacting students’ safety and educational outcomes. According to scholars (Dorney et al., 2020), in the 21st century, injuries continue to be a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among children, adolescents, and young adults aged 1–20 years in industrialized countries. In this demographic, injuries account for more deaths than all other causes combined in the United States. Some researchers analyzed global data and found that elementary school students have a higher incidence of injuries compared to their older counterparts, especially in unintentional injuries, such as sports-related injuries (Sun, 2004; Caine et al., 2006; Al-Hajj et al., 2020; Macpherson et al., 2010). For example, the studies highlighted that playground-related injuries constitute most of these incidents (Olsen and Kennedy, 2020; Filchner, 2022). Richmond et al. (2018) stated that playground equipment was responsible for the most reported injuries in elementary schools. The authors discuss factors contributing to these injuries and recommend enhanced safety protocols and equipment standards.
The school environment, often referred to as “the third teacher” by renowned experts, constitutes various elements such as laboratories, corridors, building materials, wall colors, lighting, furniture, and all educational resources. It is a unique environment where students can live, learn, experience, and interact with others (Nikolić et al., 2013). Due to the various settings in school spaces, each presents unique hazards that can lead to student accidents and injuries. School incidents involving slips, trips, and falls rank among educational institutions’ leading causes of injuries. Such occurrences frequently occur in areas like hallways, classrooms, and playgrounds, often attributed to wet floors, disorganization, and uneven ground (Peden, 2008). Additionally, Shendell et al. (2004) argued that school laboratory accidents involving chemicals, burns, and cuts are prevalent. Proper safety protocols and supervision are crucial to minimize these risks. Moreover, inefficiently designed furnishings and unsuitable ergonomics may result in musculoskeletal pain and chronic health issues for students (Rajan and Koti, 2013). Issues such as improper desk height and inadequate chair support are common in many educational settings, and these problems are often seen in academic institutions (Hammond et al., 2017). Notably, many of these injuries are preventable. Understanding these common hazards is essential for implementing effective safety measures. After all, one significant factor influencing a child’s personality is their environment, and the school environment represents one of the primary settings in which children spend considerable time. Researchers assert that personality development results from the interaction between the individual and their environment. According to Washburn, children’s engagement with their physical and social surroundings is crucial for effective learning, which can only be fostered through deep and meaningful relationships within that environment (DeGregori, 2007). Therefore, school safety issues deserve investigation.
Types of safety signs used at school- emergency evacuation signs
Various prohibition, warning, and instructional signs are prevalent in the school environment. For instance, such signs are commonly found in chemical laboratories and on the labels of certain chemical experiments, while warning signs typically appear at the entrances and exits of educational buildings, as well as on stairways. These signs are vital in schools, especially those indicating emergency evacuation routes and exits. Given the large number of school personnel, most underage students, emergency evacuation signs play a crucial role in facilitating orderly and rapid evacuations during incidents such as fires or earthquakes. They help students escape the building efficiently, minimizing the risk of secondary injuries from falls, stampedes, or other accidents. Research in safety science has increasingly focused on the effectiveness of emergency evacuation safety signs, captivating the interest of numerous scholars. For example, Kim et al. (2016) investigated how a running figure’s forward direction and horizontal position influence exit direction selection. By integrating these factors, they devised a modified spatial Stroop task as a non-forced choice experiment. Their findings underscored the importance of understanding the meanings of emergency exit signs for effective evacuation during disasters. The results revealed facilitation and inhibition effects, conflict adaptation, and post-error deceleration, demonstrating that the orientation of the Running Man exit sign is significantly directional. Consequently, the authors recommend considering this characteristic when designing and implementing standardized emergency exit signs. Hu et al. (2022) investigate the effectiveness of following evacuation signs or surrounding people during building evacuation. The research emphasizes the importance of evacuation signage in ensuring a safe evacuation process. Some scholars have employed innovative research methods and scientific technologies to study emergency signage under varying visibility conditions. For instance, Occhialini et al. (2016) electroencephalography to assess the reflectivity, photoluminescence, and positioning of fire evacuation signs in a virtual environment. They aimed to quantify individuals’ perceived attention and decision-making processes during emergency wayfinding. The findings indicated that low-positioned signs exhibited the poorest performance, while the performance disparity for blackout scenarios involving photoluminescent signs was less pronounced. Furthermore, it is recommended that the variety of evacuation signs be expanded beyond mere reflective and photoluminescent types.
The application of EEG and other innovative technologies, such as eye tracking, could also be extended to encompass additional types of evacuation signs and guidance systems, as well as to investigate premotor and motor behaviors. Subsequently, other scholars conducted similar investigations, setting the research environment under smoke conditions. They evaluated signage systems equipped with backlights and introduced the concept of the “effective cognitive area (ECA),” which refers to the region where the observer visually and cognitively recognizes signage. Experimental results demonstrated that the visual distance diminished as the viewing angle decreased and smoke concentration increased. In smoky conditions, the observation distance at a 75° viewing angle was greater than at a 90° viewing angle due to the effects of light scattering and sign brightness (Kim et al., 2022). Recently, Akizuki (2024) also examined the design of evacuation routes based on visibility, asserting that reduced visibility in evacuation spaces complicates evacuees’ ability to locate appropriate evacuation routes, potentially leading to fatalities. Enhancing the visual environment of evacuation routes—by ensuring their visibility, clearly indicating the endpoints, and providing guidance for these endpoints—can significantly reduce evacuation delays. A model is proposed to predict the walking speed of evacuees based on their visual acuity under disaster lighting conditions, which is instrumental in evaluating visual performance during emergencies.
Method
Literature search strategy
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) standard procedures. The Scopus literature search engine was selected due to its status as the repository with the most significant number of articles that fulfil the quality requirements of scientific peer review (Harzing and Alakangas, 2016; Zhang and Eichmann-Kalwara, 2019). The key terms included in the search query were derived from the fields identified in published reviews and studies (Huang et al., 2023; Pokrivcakova, 2019). Consequently, the query strings and phrases for advanced literature searches in the Scopus database were formulated as follows: ALL (“(“safety sign” OR “school safety signage”) AND (“identifiably” OR “legibility” OR “attention”) AND (“colour “OR “signal word” OR “shape” OR “font”) AND (“individual behaviours” OR “behavioural response” OR “individual factors”)). The publications selected for this study span a period of 25 years, from 2000 to 2024.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
A set of inclusion and exclusion criteria was established for selecting the articles. Academic journals primarily publish in English, so the language criterion was restricted to English. To ensure the quality of the selected articles, the document types were limited to those published in peer-reviewed academic journals, excluding conference papers and book chapters. Since related research gained prominence in the early 2000s, only articles published from 2000 to the present were considered. Furthermore, articles that focus solely on conceptual discussions or literature reviews without a specific investigation into the application of safety signs on campus or that do not address the effectiveness of safety signs—such as the impact of their design characteristics on effectiveness—were also excluded.
Consequently, the articles selected for this systematic review must meet the following criteria: (i) be written in English, (ii) be published in a peer-reviewed journal, including article and review papers, (iii) be published between the year 2000 to 2024, (iv) and explore the design of safety signs in school settings or testing the effectiveness of safety signs.
Screening process
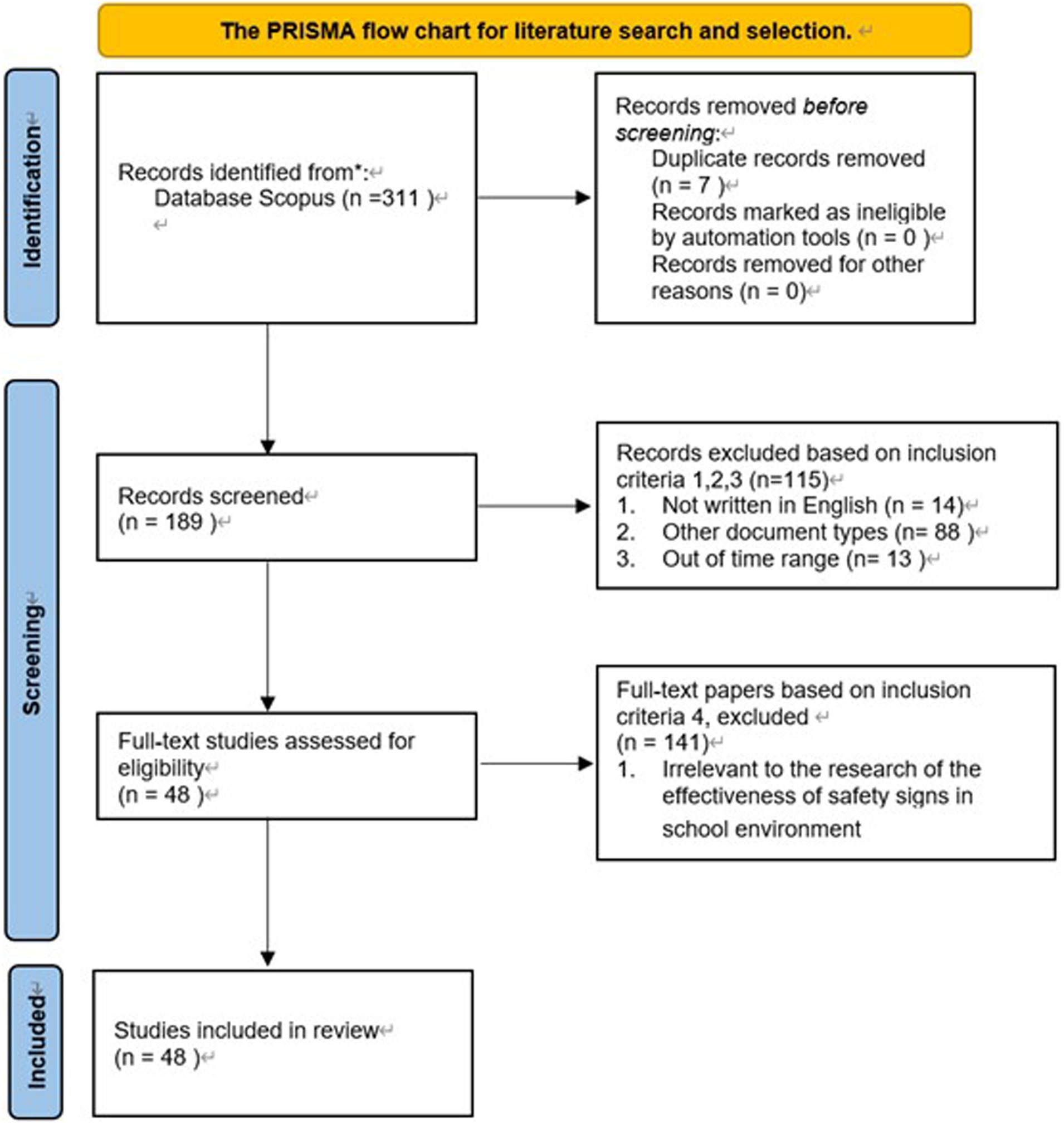
The article screening and selection process adhered to the PRISMA framework (Moher et al., 2010), as illustrated in Figure 1. Initially, articles that satisfied the first three criteria were selected, resulting in 193 articles. Subsequently, these articles underwent a full-text review to assess their compliance with the fourth criterion. Articles were deemed irrelevant if their titles or abstracts did not reference the design elements of safety signs or the effectiveness of safety signs. The inclusion criteria stipulated that titles or abstracts must contain terms related to ‘safety sign design elements’, such as ‘color’, ‘shape’, or ‘signal words’, as well as synonyms for ‘effectiveness’, such as ‘recognizability’, ‘conspicuousness’, ‘readability’, or ‘individual behavioral factors.’ Articles meeting these criteria were considered likely relevant to this study and were included in the review. Ultimately, 141 articles were excluded, resulting in the inclusion of 48 articles for further analysis.
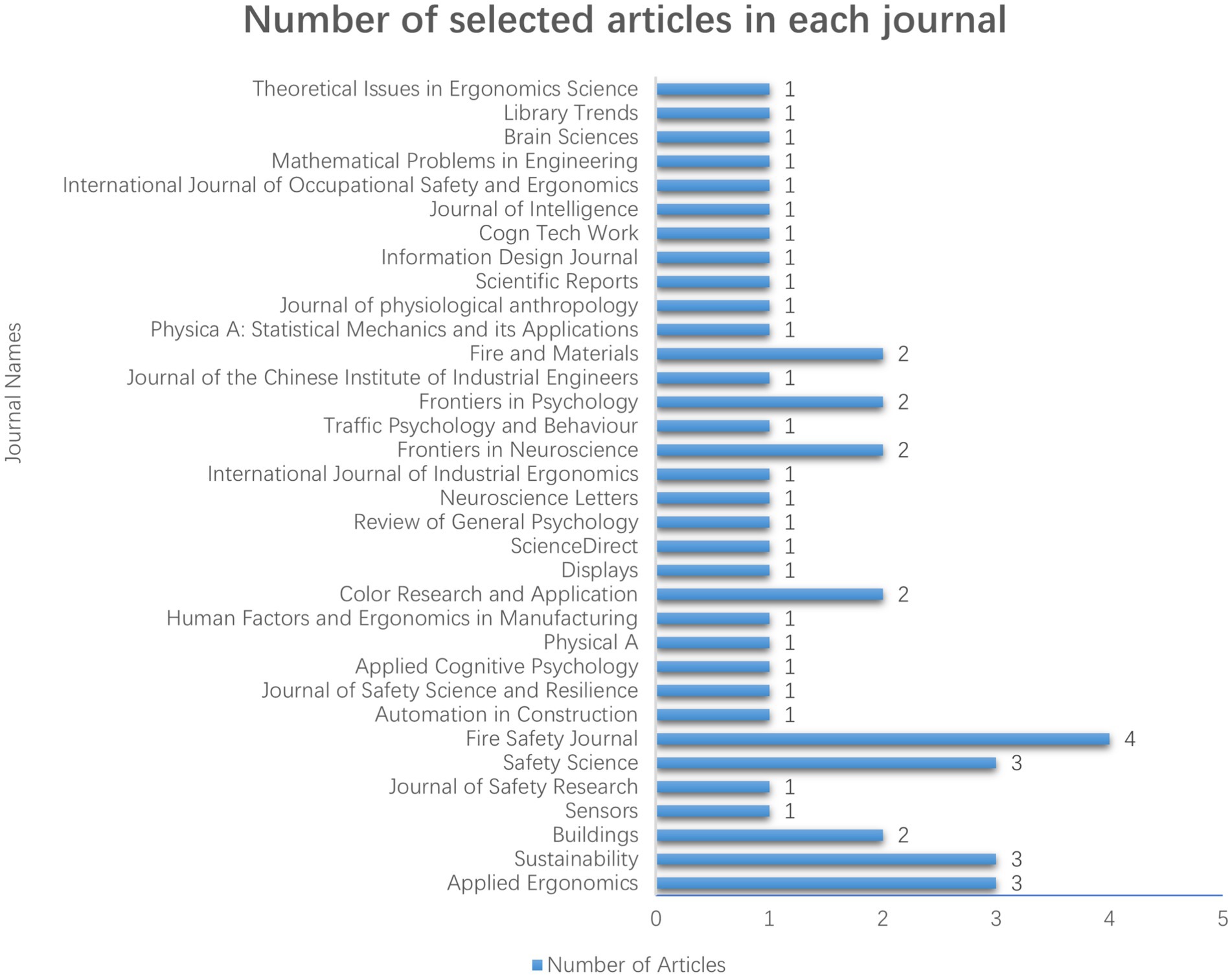
Figure 2 depicts the journal list, and the number of articles selected from each peer-reviewed journal for this systematic literature review. In this systematic literature review, In the journals listed, the following distribution of articles was noted: “Applied Ergonomics” (n = 3), “Sustainability” (n = 3), “Buildings” (n = 2), “Sensors” (n = 1), “Journal of Safety Research” (n = 1), “Safety Science” (n = 3), “Fire Safety Journal” (n = 4), “Automation in Construction” (n = 1), “Journal of Safety Science and Resilience” (n = 1), “Applied Cognitive Psychology” (n = 1), “Physical A” (n = 1), “Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing” (n = 1), “Color Research and Application” (n = 2), “Displays” (n = 1), “ScienceDirect” (n = 1), “Review of General Psychology” (n = 1), “Neuroscience Letters” (n = 1), “International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics” (n = 1), “Frontiers in Neuroscience” (n = 2), “Traffic Psychology and Behavior” (n = 1), “Frontiers in Psychology” (n = 2), “Journal of the Chinese Institute of Industrial Engineers” (n = 1), “Fire and Materials” (n = 2), “Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications” (n = 1), “Journal of Physiological Anthropology” (n = 1), “Scientific Reports” (n = 1), “Information Design Journal” (n = 1), “Cogn Tech Work” (n = 1), “Journal of Intelligence” (n = 1), “International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics” (n = 1), “Mathematical Problems in Engineering” (n = 1), “Brain Sciences” (n = 1), “Library Trends” (n = 1), and “Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science” (n = 1). A total of 48 studies were included in this systematic review, comprising a large number of research articles alongside a few review papers.
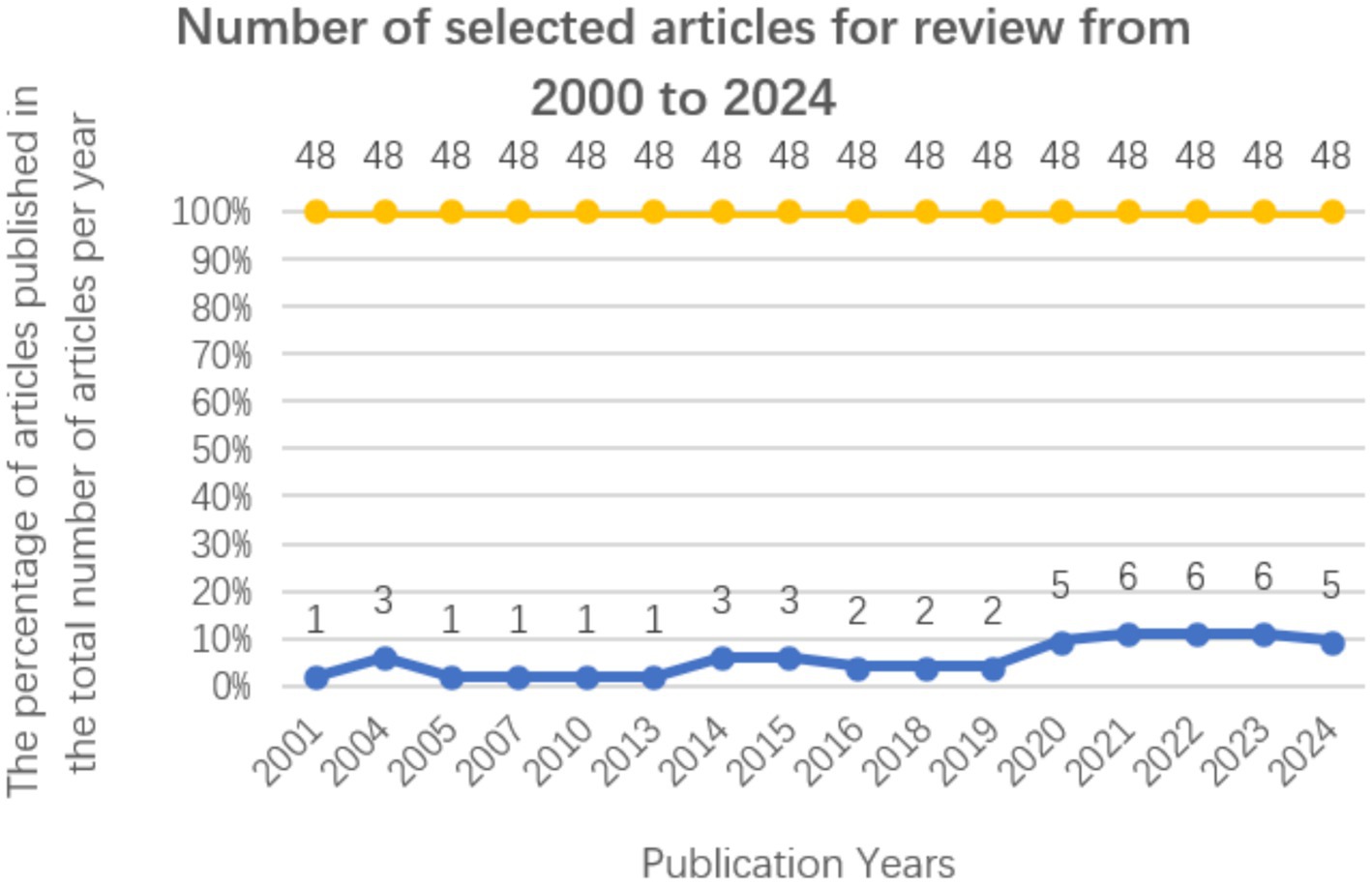
Figure 3 illustrates the evolution of research on safety signs over time. From 2000 to 2024, there has been an overall upward trend in this area of study, particularly notable during the periods from 2001 to 2004, 2013 to 2014, and 2019 to 2021. Prior to 2010, the volume of research was relatively low; however, it began to increase steadily until a decline was observed after 2015, followed by a significant turning point in 2019. The number of studies increased significantly and rapidly in the subsequent year, reaching a peak over three consecutive years in 2021, 2022, and 2023. This pattern underscores the growing interest in safety sign research over the last 5 years.
Results and discussion
Evaluating the effectiveness of safety signs
Visual design cues safety signs
The visual design elements of safety signs are fundamental factors influencing their effectiveness, including recognizability, understandability, and eye-catching. This topic has been the focus of extensive research by scholars, particularly concerning the color, shape, and symbolism of safety signs. Additionally, the visual properties of the text and the interactions between textual elements are critical.
In the early 21st century, several studies examined the impact of symbol and text color, surrounding color, training, and environmental illumination on the visual recognition performance of users regarding three hazardous material labels (Wang et al., 2004; Chan and Ng, 2010; Yuan et al., 2021). These studies found that using black for both symbol and text colors, along with appropriate training, significantly enhanced performance. Furthermore, compared to white symbols and text colors, black symbols and text colors on hazardous materials labels markedly improved visual recognition performance. However, surrounding color and ambient illumination did not show a significant effect. Consequently, it is recommended to utilize black symbols and text colors, along with training, to enhance users’ visual recognition performance on hazardous material labels (Wang et al., 2004).
At the same time, Shieh and Huang (2004) conducted a study on the legibility of prohibited safety symbols. The results indicated that the interaction of graphic size influenced the legibility of these symbols, the diagonal thickness of the red circle, brightness contrast, and exposure time. Under degraded visibility conditions characterized by low brightness contrast and short exposure times, larger graphic sizes and thinner diagonal lines were found to enhance legibility. It is recommended that the graphic size be at least 75% of the inner diameter of the red circle’s diagonal line, with diagonal line thicknesses of either 25 or 35%, particularly in adverse viewing conditions. This study has significant implications, suggesting that environmental factors such as low brightness contrast and brief exposure times diminish the legibility of prohibitive symbols.
Future research could expand the experiment to include additional scenarios, such as driving conditions. Furthermore, some scholars have investigated the perceptions of danger associated with signal words and shapes in safety signs among individuals from different cultural backgrounds, specifically in China and the United States. The research revealed that participants’ characteristics, including cross-cultural backgrounds, age, occupation, and gender, exhibited significant differences in their perceived levels of moral danger. Although the participants were not evaluated in a real-world setting regarding signal words and shapes, the findings provide valuable evidence for international warning sign standards, highlighting similarities and differences in perceived danger levels between U.S. and Chinese participants (Yu et al., 2004). In the following year, Ochiai and Sato (2005) investigated the saliency of safety sign colors, specifically examining the influence of surrounding brightness on the visual search for safety colors, specifically examining the influence of surrounding brightness on the visual search for safety colors such as red, orange, and yellow. The findings indicate that the search efficiency for orange decreases as the number of distractors increases, whereas the search efficiency for red and yellow remains consistently high.
Moreover, as illumination decreases, searching for orange becomes increasingly challenging compared to red and yellow. The study also demonstrates that variations in target color significantly affect visual search more than the luminance contrast between the target and the background. A notable limitation of the research is that using phosphors may not accurately replicate the appearance of surface colors, necessitating further investigations to determine if the results align with real-world conditions.
It is important to acknowledge that color plays a crucial role in influencing individuals’ psychological functions and subjective perceptions. As reviewed by Elliot (2019), red, yellow, and orange are frequently associated with heightened arousal and excitement, whereas blue and green are linked to calmness and relaxation. Blue ranks as the most popular color overall, followed by red, while yellow tends to be the least favored color. Additionally, saturated colors generally enjoy greater popularity than their unsaturated counterparts. The relationship between color and time perception remains ambiguous; for instance, red tends to elicit longer time estimates than green or blue, although other studies have reported null or contradictory findings. Effectively utilizing the properties of color in the design of safety signs can enhance their visibility.
Nevertheless, significant limitations in color research methodologies have been identified, including small sample sizes in most surveys and a lack of precise specification of color attributes such as hue, brightness, and chroma, as well as inadequate control of background colors and lighting conditions (Wrolstad and Smith, 2017; Brown et al., 2011).
The various attributes of lightness, hue, and saturation of the color, along with their interactions in specific visual environments, can serve as significant variables for in-depth study. Over the past 20 years, numerous scholars have employed event-related potential methods to investigate the neural processes and responses of the human brain in relation to danger perception. This research ultimately provides a more scientific and objective basis for the measurement results and findings related to safety signs. Ma et al. (2010), noted that the processing of warning signal words occurs in two stages: an initial automatic stage focused on hazard perception and detection, followed by a later controlled stage dedicated to hazard assessment. It is essential to ensure that warning signal words, which convey equivalent levels of danger information, are recognized without leading to desensitization or habituation.
Subsequently, Ma et al. (2018) employed this method again to assess the danger perception of 19 participants, approximately 20 years of age, regarding the shapes surrounding warning signs. They found that the surrounding shapes of a UPRIGHT TRIANGLE attracted more attention and were associated with negative valence. Moreover, the arousal level was elevated, evoking more uncomfortable, unsettling, and unsafe information, which was more strongly suppressed at the cognitive level than round shapes. This indicates that the UPRIGHT TRIANGLE shape is more effective for conveying hazard information in warning signs than the CIRCLE shape.
Similarly, Zhu et al. (2020) utilized this research method to conduct electroencephalography studies to investigate the mechanisms underlying undergraduate students’ danger perception of the signal words and surrounding shapes of warning signs. The study revealed that high-danger level warning signs facilitate rapid matching of hazards to semantic knowledge, potentially due to the necessity of retrieving more emotional experiences from episodic memory while simultaneously reducing the amount of information encoded. The findings emphasize that changes in electrophysiological signals can be a reliable means of evaluating warning signal designs. Additionally, some researchers have employed event-related potential investigations to explore the electrophysiological correlations of warning signals with varying background colors.
Yuan et al. (2021) asserted that, based on self-report data, warning signs with yellow and white backgrounds were perceived as more hazardous and readable than those with blue backgrounds. Both perceptual and cognitive ERP components were influenced by variations in the background color of the warning signs, indicating automatic processing of the danger information conveyed by color. This suggests that individuals can recognize differences in warning sign colors and the associated danger information, even when their attention is not explicitly directed toward the sign. In the past 2 years, many scholars have employed ERP methods to investigate the neural processing mechanisms underlying participants’ hazard perception of the color attributes of safety signs.
This research provides both theoretical and empirical foundations for safety science and sign design (Bai et al., 2024; Horinouchi et al., 2023). Studies examining reaction times and brain oscillations within the Go/No-go task reveal that during the simple reaction and Go/No-go tasks, the presentation of a blue signal results in greater frontal surface beta event-related desynchronization (ERD) and theta event-related synchronization (ERS). Notably, the onset of theta ERS is delayed in Red Go trials compared to Blue Go trials. Furthermore, theta ERS and beta ERD are more pronounced in blue No-go trials than in red No-go trials, indicating that blue signals facilitate motor responses even during No-go trials (Horinouchi et al., 2023).
Bai et al. (2024) utilized neuroscientific methods to investigate the neural processing mechanisms associated with surrounding shapes in safety sign design. Their findings indicate that surrounding shapes convey emotional information during the early stages of perception, with triangles eliciting more negative emotions than circles, thereby providing stronger support for the efficacy of surrounding shapes. Furthermore, incorporating graphic symbols into these shapes enhances the early cognitive processing of combined signs.
However, there are notable research gaps regarding the human brain’s neural mechanisms and sensations as measured by ERP methods. Future research could be expanded to explore the interactions of various colors and their distinct attributes and examine the interplay of signal words with surrounding shapes across different age groups and larger sample sizes. Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches could be employed to engage multiple senses, such as vision and hearing, in perceiving danger. For instance, Wang et al. (2004) studied the effects of signal tones and background music on alertness, revealing that different tones of background music and visual signals, particularly yellow and red, significantly influence alertness levels. Their research suggests that red signals and low background music can enhance overall alertness performance; however, the heightened alertness induced by red signals may be challenging to sustain over extended periods.
Compliance and behavioral responses
Research indicates that the effectiveness of safety signs is also influenced by a range of personal factors, including demographic variables such as age, gender, cultural background, and other individual differences (Wogalter et al., 2002). Williams and Noyes (2007) conducted a comprehensive review of the factors influencing risk perception and its impact on decision-making, focusing on the design of risk information and warnings. Their research indicates that risk perception is a critical element in decision-making, and the presentation of risk information significantly influences this perception. The authors provide several recommendations for warning design: Firstly, it is essential to consider various factors related to the design of risk messages, including content, source, and target audience, to communicate risks and encourage appropriate decision-making and safe behaviors effectively. Secondly, offering more detailed information, particularly regarding the likelihood of a risk occurring, can enhance the effectiveness of warnings. Gaming tasks can serve as a means to study the impact of warning messages on information behavior. Haddad et al. (2020) investigated how various components of online warning messages influence self-reporting and behavioral compliance in an online environment susceptible to potential malware exposure.
Their findings indicated that message clarity was the only component with a significant preventive effect; clear warning messages were more effective in enhancing behavioral compliance and were perceived as more credible, serious, and severe than less clear messages. This clarity may increase the intention to comply. Conversely, the inclusion of eye images in warning messages did not enhance behavioral compliance and resulted in lower ratings of credibility and intention to comply. Although the participants in this study were adult males, future research could explore this topic further among school students, which may be particularly relevant for younger students due to the engaging nature of the gaming task. It is also important to note that visual elements of the safety sign itself, such as color and shape, can influence individuals’ cognitive abilities. Jin et al. (2022) employed the perceptual load paradigm to investigate cognitive performance in a sample of 34 young individuals aged 20–26, comprising an equal number of men and women.
The findings revealed that under conditions of high cognitive load, color played a crucial role in enhancing cognitive ability. In contrast, the combined effect of color and shape did not yield significant improvements. However, under moderate and low cognitive load, the interaction of color and shape significantly enhanced cognitive performance. Notably, as cognitive load decreased, the importance of semantic information in the combined symbol became increasingly vital for improving cognitive performance.
Concurrently, other researchers utilized flanker tasks and electroencephalography to assess the influence of safety signs with varying levels of danger on the neural correlations of monitoring conflicts and errors, which are essential processes in cognitive control. They discovered that monitoring for conflicts and errors was heightened following exposure to high-danger safety signs; however, this did not translate into improved behavioral performance on the flanker task, and no significant effect of the danger level of the safety signs on behavioral performance was observed (Hu et al., 2022).
Conversely, the various display states of safety signs, namely static and dynamic, can significantly influence individuals’ behavioral compliance, particularly regarding emergency evacuation signs positioned at safety exits within school premises. Duarte et al. (2013) investigated the effects of dynamic and static safety signs on behavioral compliance in immersive virtual environments. Their primary findings indicate that compliance with dynamic signs is markedly higher than that associated with static and minimal or absent signs. Furthermore, no significant differences were observed in compliance among the different types of signs that prompted safety awareness.
In sum, compliance during emergency evacuations was significantly greater for dynamic and static exit signs than scenarios with no or minimal exit signs. In recent years, research methods concerning cognitive ability and its impact on safety behavior have increasingly integrated more accurate and interdisciplinary testing approaches, leveraging scientific and technological advancements. Among these, neurosafety science has emerged as a discipline capable of elucidating the neural mechanisms underlying safety issues.
This field investigate investigates individuals’ psychological and behavioral safety through neuroscientific methods and techniques (Zhang et al., 2023). In summary, when examining compliance with safety behaviors and responses, integrating novel methods and interdisciplinary research can broaden the experimental population to include school-age children. Given the unique cognitive development characteristics of this age group and their individual physical and psychological vulnerabilities, findings from studies assessing students’ perceptions of school safety signs may carry significant implications for both personal and public safety, warranting greater attention.
Improving the effectiveness of warnings
Laughery and Wogalter (2014) reviewed and summarized research on product warnings and environmental safety labels, highlighting key factors that influence their effectiveness. They proposed a three-stage warning processing model consisting of Attention, Knowledge, and Compliance. Each stage is influenced by design factors (such as size, color, and wording) and non-design factors (such as target audience characteristics and situational context).
This underscores the importance of creating safety signs that are eye-catching, easy to understand, and motivate users to comply with the warning messages. The findings guide designers in developing warnings that effectively communicate safety messages and reduce risks. Over the past 25 years, many scholars have investigated the design of visual factors affecting the effectiveness of safety signs. McDougald and Wogalter (2014) asserted that pictures can aid in conveying warning messages; however, they found that viewers may only sometimes interpret them correctly.
The researchers conducted two experiments to determine whether highlighting relevant areas of an image enhances viewers’ understanding of its intended message compared to not highlighting or highlighting irrelevant areas. The results consistently indicated that highlighting relevant areas significantly improves comprehension, while highlighting irrelevant areas results in decreased comprehension. This further emphasizes the importance of the conspicuousness of safety signs, as understanding warning messages can be enhanced by attracting the audience’s attention and focusing it on prominent key information.
Subsequently, Siswandari and Xiong (2015) investigated individuals’ understanding of safety signs by examining their eye movements and brain activity. The study revealed that the clarity of the signs significantly influenced eye movements and brain wave patterns. Signs that were more challenging to interpret resulted in slower blink frequency, larger pupil size, and longer initial gaze duration. Furthermore, distinct differences in brainwave activity were observed in the frontal lobes and visual areas of the brain when participants viewed easily comprehensible signs compared to those that were difficult to understand.
This indicates that employing technology that integrates eye movement and brain wave measurements with existing methodologies can yield a more comprehensive assessment of the comprehensibility of symbolic safety signs. Similarly, Liu et al. (2015) provided compelling evidence supporting the conclusion that pictures can effectively convey hazard information. They developed a ‘5-factor accident sequence’ model and created a sequence diagram to investigate the use of visual aids in teaching young children about burn accidents. This visualization tool breaks down an incident into its key components: pre-existing factors, human error, unsafe actions, occurrence, and consequences.
The researchers tested the diagrams by presenting two groups of 6 and 7 years old with a story about a little boy who was burned by hot water. One group received the story accompanied by a sequence diagram, while the other received the story without visual aid. The study found that the group exposed to the sequence diagram demonstrated a better understanding of the story’s details, particularly in recalling dangerous objects, unsafe behaviors, and emotional responses to the accident. This suggests that incorporating pictures alongside oral storytelling can be valuable for teaching young children about accident prevention. It is recommended that future studies further refine the effectiveness of this approach for various types of accidents and evaluate its impact on children’s actual behaviors.
Kim and Wogalter (2015) investigated the effectiveness of using emphatic terms in signal words or warning statements on safety signs. The authors hypothesized that incorporating words or phrases such as ‘important’ or ‘mandatory’ into basic warning signal words would influence compliance intentions and enhance comprehensibility. They conducted three experiments to systematically assess various types of emphasis words, their impact on individuals’ likelihood to follow instructions, and the ease of understanding warnings. The results indicate that the strategic selection of emphatic terms can enhance the effectiveness of warnings, supporting Laughery and Wogalter's (2014) findings that such terms contribute to the effectiveness of safety signs by motivating compliance with warning instructions. In recent years, the emergence of new technological means, particularly virtual reality technology, has prompted numerous studies aimed at assessing the effectiveness of safety signs.
This approach enhances interest in safety precautions and safety experience education and fosters greater cross-sector cooperation across various subject areas. Furthermore, it facilitates the application of effective safety communication tools and enables more scientific and comprehensive testing of human perception regarding the efficacy of safety signs. For instance, Cavalcanti et al. (2021) conducted a qualitative study to analyze users’ behavior and perception of three types of warning signals (static, dynamic, and intelligent) through the immersive game “Safety Game.”
Utilizing the bipolar ladder assessment technique, the study reveals users’ thoughts and opinions on the gaming environment and the different warning signals. The findings indicate that dynamic warning signals, particularly those featuring intermittent LED lights, are more visible and effective in capturing attention. In contrast, smart signals receive lower user ratings due to increased cognitive demands. The goal of this research is to enhance understanding of user behavior in high-risk situations and to explore the potential of VR gamification as a tool for improving safety training and communication in real-life environments.
Numerous factors influence the effectiveness of safety signs. From a design perspective, visual elements can convey meaning rapidly, particularly when accompanied by text (Laughery and Wogalter, 2014; Liu et al., 2015). Safety signs’ effectiveness is assessed by testing individuals’ perceptions of danger. When combined with rigorous scientific and technological methods, such as eye movement tracking and brain wave analysis, it becomes possible to evaluate the effectiveness of safety signs more comprehensively and scientifically. This evaluation encompasses the smooth transmission of safety information and individuals’ perception and reception. Additionally, we can engage in interdisciplinary collaboration and exploration, utilizing scientific and technological approaches to enhance the safety experience, especially for school-age children. Such enhancements may significantly improve their understanding of safety information and willingness to comply with safety interventions.
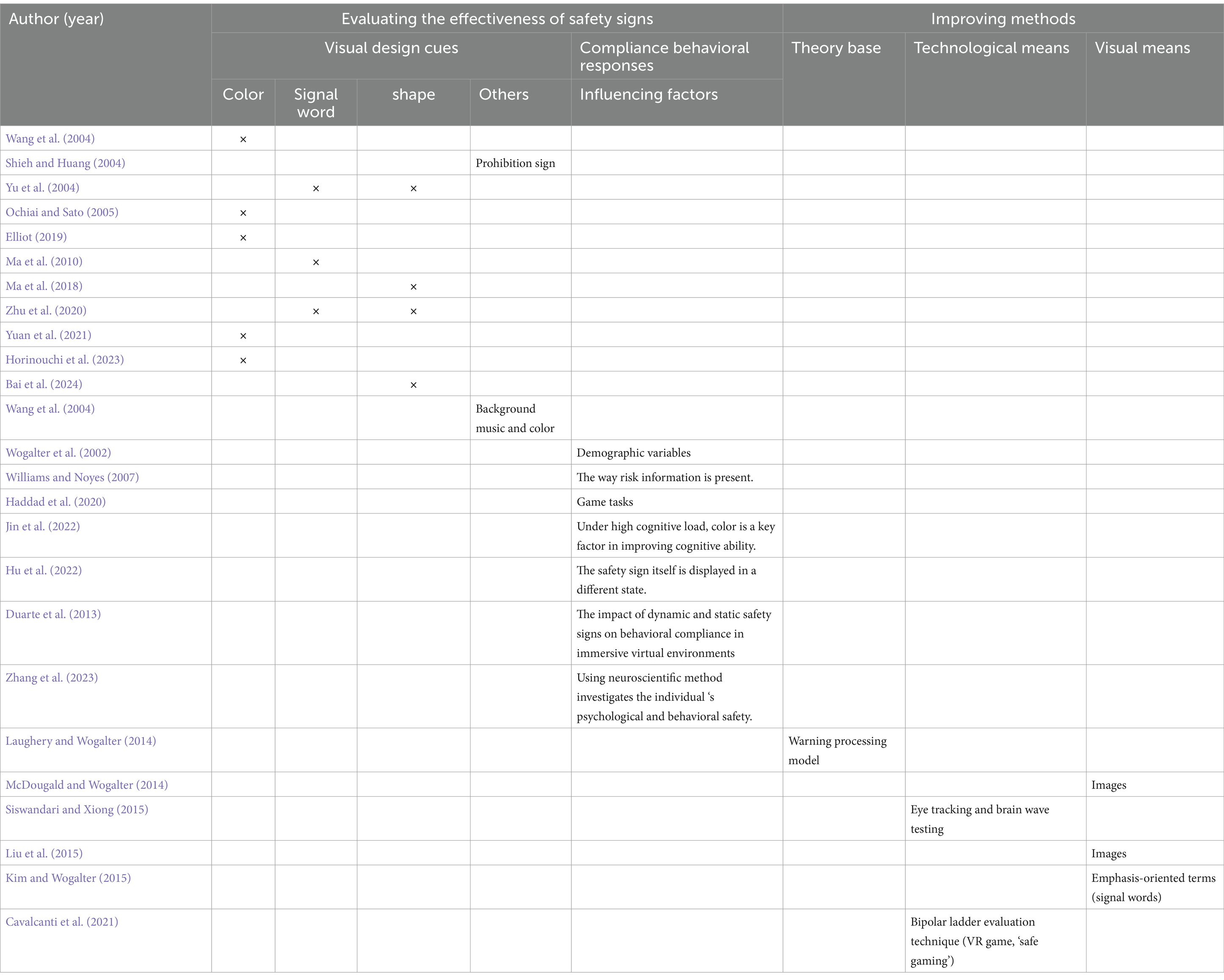
The review not only underscores the importance of campus safety but also reveals that the factors influencing the effectiveness of safety signs are multifaceted, primarily discussed through two perspectives: design factors and non-design factors. These influencing factors interact throughout the safety communication process, ultimately impacting the effectiveness of warning. The results of studies on safety signs in school settings summarized in Table 1.
Conclusion
This article presents a systematic review of 48 published studies focused on methods to evaluate and enhance the effectiveness of safety signs in school environments. Numerous studies have confirmed that the use of images, highly saturated colors, and colors such as red, orange, and yellow, along with signal words, emphasis terms, and dynamic safety signs, can more effectively convey danger information and enhance compliance behavior (Elliot, 2019; Kim and Wogalter, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Duarte et al., 2013).
While this systematic review focuses on the effectiveness of safety signs, several limitations and knowledge gaps persist. First, this review exclusively collected relevant articles from the Scopus database only. Although the Scopus database is recognized as a repository that encompasses the largest number of articles meeting scientific peer review quality standards (Harzing and Alakangas, 2016; Zhang and Eichmann-Kalwara, 2019), it is possible that some pertinent studies were not included in this database and, consequently, are absent from this review. Secondly, the relatively small number of articles that met the selection criteria for this review may have constrained the findings, as the analysis primarily focused on qualitative assessments of the selected studies. Finally, it was observed that research on the types of safety signs in specific locations, such as schools and other public venues, predominantly concentrated on safe evacuation signs. However, there is a notable absence of detailed classifications for other safety signs relevant to schools, such as sports safety signs and those intended for students. The study also highlights the need to compare and classify differences based on various characteristics, including age, gender, cognition, and understanding ability. Notably, the age group of students primarily examined consists of adults over the age of 18, leaving a significant gap in research concerning young children. Additionally, school environments vary across different countries and regions. Therefore, it is recommended that a more comprehensive assessment be conducted regarding the specific school environment and the perceptions and preferences of students of various ages. This assessment should evaluate the effectiveness of safety signs in schools and incorporate innovative scientific and technological methods to test the understanding of school-age children. Ultimately, the goal is to propose safety sign design strategies that are better suited to specific age groups, particularly younger children.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
TW: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization. SA: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. MK: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. TZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Akizuki, Y. (2024). Evacuation route design based on visibility for reducing evacuation delays. Fire Saf. J. 144:104099. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2024.104099
Al-Hajj, S., Nehme, R., Hatoum, F., Zheng, A., and Pike, I. (2020). Child school injury in Lebanon: a study to assess injury incidence, severity and risk factors. PLoS One 15:e0233465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233465
Bai, X. X., Hu, L., and Ma, Q. G. (2024). Can’t ignore surrounding shapes: neural processing mechanisms of safety sign designs. Saf. Sci. 177:106594. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2024.106594
Brown, A. M., Lindsey, D. T., and Guckes, K. M. (2011). Color names, color categories, and color-cued visual search: sometimes, color perception is not categorical. J. Vis. 11:2. doi: 10.1167/11.12.2
Caine, D., Caine, C., and Maffulli, N. (2006). Incidence and distribution of pediatric sport-related injuries. Clin. J. Sport Med. 16, 500–513. doi: 10.1097/01.jsm.0000251181.36582.a0
Cavalcanti, J., Valls, V., Contero, M., and Fonseca, D. (2021). Gamification and hazard communication in virtual reality: a qualitative study. Sensors 21:4663. doi: 10.3390/s21144663
Chan, A. H., and Ng, A. W. (2010). Effects of sign characteristics and training methods on safety sign training effectiveness. Ergonomics 53, 1325–1346. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2010.524251
Collie, R. J., Shapka, J. D., and Perry, N. E. (2011). Predicting teacher commitment: the impact of school climate and social–emotional learning. Psychol. Sch. 48, 1034–1048. doi: 10.1002/pits.20611
DeGregori, A. (2007). Learning environments: redefining the discourse on school architecture [Master's thesis, New Jersey institute of technology]. NJIT Library. Available at: https://digitalcommons.njit.edu/theses/389/ (Accessed November 16, 2024).
Dorney, K., Dodington, J. M., and Rees, C. A. (2020). Preventing injuries must be a priority to prevent disease in the twenty-first century. Pediatr. Res. 87, 282–292. doi: 10.1038/s41390-019-0549-7
Duarte, E., Rebelo, F., Teles, J., and Wogalter, M. (2013). Behavioral compliance for dynamic versus static signs in an immersive virtual environment. Appl. Ergon. 45, 1367–1375. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2013.10.004
Elliot, A. J. (2019). A historically based review of empirical work on color and psychological functioning: content, methods, and recommendations for future research. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 23, 177–200. doi: 10.1037/gpr0000170
Espelage, D. L., and Swearer, S. M. (2009). “A social-ecological model for bullying prevention and intervention: understanding the impact of adults in the social ecology of youngsters” in Handbook of bullying in schools (London: Routledge), 61–71.
Filchner, D. (2022). Analysis of the epidemiology of playground-related injuries in relation to existing playground safety standards: How Should We Address Safe Play? [Bachelor]. Available at: https://digitalcommons.bucknell.edu/honors_theses/608/
Haddad, A., Sauer, J. D., Prichard, J., Spiranovic, C., and Gelb, K. (2020). Gaming tasks as a method for studying the impact of warning messages on information behavior. Libr. Trends 68, 576–598. doi: 10.1353/lib.2020.0012
Hammond, D. A., Killingsworth, C. A., Painter, J. T., Pennick, R. E., Chatterjee, K., Boye, B., et al. (2017). Impact of targeted educational interventions on appropriateness of stress ulcer prophylaxis in critically ill adults. Pharmacy Practice (Granada) 15:948. doi: 10.18549/PharmPract.2017.03.948
Harzing, A. W., and Alakangas, S. (2016). Google scholar, Scopus and the web of science: a longitudinal and cross-disciplinary comparison. Scientometrics 106, 787–804. doi: 10.1007/s11192-015-1798-9
Horinouchi, T., Watanabe, T., Kuwabara, T., Matsumoto, T., Yunoki, K., Ito, K., et al. (2023). Reaction time and brain oscillations in go/no-go tasks with different meanings of stimulus color. Cortex 169, 203–219. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2023.07.011
Hu, L. F., Feng, D., Li, Y., Xu, J., and Zheng, J. (2022). The effect of safety signs on the monitoring of conflict and erroneous response. Front. Psychol. 13:830929. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.830929
Huang, X., Zou, D., Cheng, G., Chen, X., and Xie, H. (2023). Trends, research issues and applications of artificial intelligence in language education. Educ. Technol. Soc. 26, 112–131. doi: 10.30191/ETS.202301_26(1).0009
Jin, T., Zhou, S., Lang, X., He, J., and Wang, W. (2022). Combined effect of color and shape on cognitive performance. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2022/3284313
Kim, Y., Baek, S., Bae, Y., Oh, R., and Choi, J. (2022). Evaluation of the effective cognition area (ECA) of signage systems with backlighting under smoke conditions. Sustain. For. 14:4057. doi: 10.3390/su14074057
Kim, C., Hur, M., Oh, Y., Choi, J. H., and Jeong, J. J. (2016). The effect of the running-man emergency exit sign and its installed location on human directional choice. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 30, 1014–1019. doi: 10.1002/acp.3293
Kim, S., and Wogalter, M. S. (2015). Effects of emphasis terminology in warning instructions on compliance intent and understandability. Journal of safety research. 55, 41–51.
Laughery, K. R., and Wogalter, M. S. (2014). A three-stage model summarizes product warning and environmental sign research. Saf. Sci. 61, 3–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2011.02.012
Lester, S., Lawrence, C., and Ward, C. L. (2017). What do we know about preventing school violence? A systematic review of systematic reviews. Psychol. Health Med. 22, 187–223. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2017.1282616
Liu, H. F., Lin, F. S., and Chang, C. J. (2015). The effectiveness of using pictures in teaching young children about burn injury accidents. Appl. Ergon. 51, 60–68. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2015.04.013
Ma, G. Q., Bai, X., Pei, G., and Xu, Z. (2018). The Hazard perception for the surrounding shape of warning signs: evidence from an event-related potentials study. Front. Neurosci. 12:824. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00824
Ma, G. Q., Jin, J., and Wang, L. (2010). The neural process of hazard perception and evaluation for warning signal words: evidence from event-related potentials. Neurosci. Lett. 483, 206–210. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.009
Macpherson, A. K., Jones, J., Rothman, L., Macarthur, C., and Howard, A. W. (2010). Safety standards and socioeconomic disparities in school playground injuries: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 10, 1–5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-542
McDougald, B. R., and Wogalter, M. S. (2014). Facilitating pictorial comprehension with color highlighting. Appl. Ergon. 45, 1285–1290. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2013.05.008
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G.PRISMA Group (2010). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 8, 336–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
Nikolić, V., Keković, A., Stanković, D., and Tanić, M. (2013). Remodeling of the interior of preschool institutions in the context of improvement of ambient value and quality of space. Facta Unive 11, 211–220. doi: 10.2298/FUACE1303211N
Occhialini, M., Bernardini, G., Ferracuti, F., Iarlori, S., D’Orazio, M., and Longhi, S. (2016). Fire exit signs: the use of neurological activity analysis for quantitative evaluations on their perceptiveness in a virtual environment. Fire Saf. J. 82, 63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2016.03.003
Ochiai, N., and Sato, M. (2005). Effects of surrounding brightness on visual search for safety colors. Color. Res. Appl. 30, 400–409. doi: 10.1002/col.20152
Olsen, H., and Kennedy, E. (2020). Safety of school playgrounds: field analysis from a randomized sample. J. Sch. Nurs. 36, 369–375. doi: 10.1177/1059840519827364
Peden, M. M. (2008). World report on child injury prevention. Inj. Prev. 14, 175–176. doi: 10.1136/ip.2008.019844
Pokrivcakova, S. (2019). Preparing teachers for the application of AI-powered technologies in foreign language education. J. Lang. Cult. Educ. 7, 135–153. doi: 10.2478/jolace-2019-0025
Rajan, P., and Koti, A. (2013). Ergonomic assessment and musculoskeletal health of the underprivileged school children in Pune, India. Health Promot. Perspect. 3, 36–44. doi: 10.5681/hpp.2013.005
Richmond, S. A., Clemens, T., Pike, I., and Macpherson, A. (2018). A systematic review of the risk factors and interventions for the prevention of playground injuries. Can. J. Public Health 109, 134–149. doi: 10.17269/s41997-018-0035-8
Robers, S., Kemp, J., Rathbun, A., and Morgan, R. E. (2014). Indicators of school crime and safety: 2013. NCES 2014-042/NCJ 243299. National Center for Education Statistics (ED); US Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Statistics.
Shendell, D. G., Barnett, C., and Boese, S. (2004). Science-based recommendations to prevent or reduce potential exposure to biological, chemical, and physical agents in schools. J. Sch. Health 74, 390–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.2004.tb06603.x
Shieh, K., and Huang, S. (2004). Effects of pictorial size and circle-slash thickness on glance legibility for prohibitive symbols. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 33, 73–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2003.09.001
Siswandari, Y., and Xiong, S. (2015). Eye movements and brain oscillations to symbolic safety signs with different comprehensibility. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 34, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s40101-015-0081-3
Sun, Y. (2004). Unintentional injuries among primary and middle school students and a randomized controlled intervention study on prevention in a midsize city of eastern China. Hong Kong: The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Thapa, A., Cohen, J., Guffey, S., and Higgins-D’Alessandro, A. (2013). A review of school climate research. Rev. Educ. Res. 83, 357–385. doi: 10.3102/0034654313483907
Wang, A., Chi, C., and Hu, Y. (2004). Effects of symbol- and wording-color of three hazardous material labels, surround color, and training on users' visual identification performance under different ambient illuminance. J. Chin. Institute Industrial Engin. 21, 597–605. doi: 10.1080/10170660409509439
Williams, D. J., and Noyes, J. (2007). How does our perception of risk influence decision-making? Implications for the design of risk information. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 8, 1–35. doi: 10.1080/14639220500484419
Wogalter, M. S., Conzola, V. C., and Smith-Jackson, T. L. (2002). Research-based guidelines for warning design and evaluation. Appl. Ergon. 33, 219–230. doi: 10.1016/S0003-6870(02)00009-1
Wrolstad, R. E., and Smith, D. E. (2017). Color analysis. Food Analysis, (Springer). 545–555. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-45776-5_31
Yu, R., Chan, A. H., and Salvendy, G. (2004). Chinese perceptions of implied hazard for signal words and surround shapes. Human Fact. Ergonom. Manufactur. Service Industries 14, 69–80. doi: 10.1002/hfm.10048
Yuan, J. P., Song, Z., Hu, Y., Fu, H., Liu, X., and Bian, J. (2021). Electrophysiological correlates of processing warning signs with different background colors: an event-related potentials investigation. Front. Psychol. 12:648871. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.648871
Zhang, L., and Eichmann-Kalwara, N. (2019). Mapping the scholarly literature found in Scopus on “research data management”: a bibliometric and data visualization approach. Journal of librarianship and scholarly. Communication 7:eP2266. doi: 10.7710/2162-3309.2266
Zhang, S., Ye, S., Huang, Y., and Shi, X. (2023). Neuro-safety science: an emerging discipline to reveal the neural mechanisms of safety problems. Front. Neurosci. 17: 1190995. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1190995
Keywords: safety sign, warning effectiveness, school environment, risk communication, visual elements, behavioral feedback
Citation: Wang T, Abdul Shukor SF, Kozlowski M, Wan Mohamed WS and Zhang T (2025) A systematic review on evaluating school safety signs and ways to improve its effectiveness. Front. Commun. 10:1550402. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2025.1550402
Edited by:
Mirian Tavares, University of Algarve, PortugalReviewed by:
Nigel Power, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, ThailandMauricio da Silva Oliveira Jr, Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Abdul Shukor, Kozlowski, Wan Mohamed and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shureen Faris Abdul Shukor, c2h1cmVlbkB1cG0uZWR1Lm15
 Tongxu Wang
Tongxu Wang Shureen Faris Abdul Shukor
Shureen Faris Abdul Shukor