- 1Faculty of Pharmacy, Pharmacological and Diagnostic Research Centre, Al-Ahliyya Amman University, Amman, Jordan
- 2Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Applied Science Private University, Amman, Jordan
- 3Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry and Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Applied Science Private University, Amman, Jordan
- 4Faculty of Pharmacy, Applied Science Private University, Amman, Jordan
- 5Faculty of Medicine, The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Jordan
- 6School of Pharmacy, Medical Biology Centre, Queen's University Belfast, Belfast, United Kingdom
Background: Empathy is an essential skill for healthcare professionals, including pharmacists, because it improves person-centered care and treatment outcomes. Measuring the level of empathy among pharmacy students gives an understanding and insight into their readiness for incorporating a person-centered practice in their future work. This study aimed to assess empathy levels among Jordanian pharmacy students and explore the factors influencing these levels.
Methods: A cross-sectional study using a web-based survey was conducted among currently enrolled pharmacy students from various academic years at both public and private Jordanian universities. The survey consisted of three sections; demographics, the Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI) to identify pharmacy students’ empathy level, and items specifically related to the pharmacist-patient relationship. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS software. Multiple linear regression was used to reveal the factors affecting students’ empathy.
Results: A total of 396 pharmacy students participated in the current study, with a mean age of 21.65 years (SD = 2.865), and about three-quarters were female (73.5%). The mean IRI score for the students was 70.89 (SD = 12.82), with subscale means as follows: perspective-taking (18.52), fantasy (17.05), empathic concern (20.16), and personal distress (15.16). Students’ age, gender, awareness of the term empathy, and studying empathy at universities were among the factors that significantly affected the students’ empathy scores.
Conclusion: The present study reveals moderate empathy levels among Jordanian pharmacy students and sheds light on an understudied aspect within the pharmacy practice in Jordan. Significant demographic and educational factors affected the pharmacy students’ empathy levels. Incorporating empathy education in pharmacy curricula can better prepare pharmacy students for person-centered care.
Introduction
Humans rely on both verbal and nonverbal communication to develop and build interpersonal relationships, which has been demonstrated to have positive physical and mental health benefits (Fjortoft et al., 2011). Pharmacy is a profession that focuses on the proper dispensing of medications, to enhance the health and wellbeing of patients. Like other compassionate professions, empathy is crucial for pharmacists and is considered a fundamental skill that should be cultivated during their education (Tamayo et al., 2016). In healthcare, empathy involves emotionally connecting with patients, striving to understand their perspectives, feelings, and emotions without criticism, to ensure they receive appropriate treatment and feel supported (Pratiwi et al., 2023).
Empathy is a multifaceted construct with four key dimensions; emotive, moral, cognitive, and behavioral empathy. Emotive empathy involves imagining and sharing a patient’s psychological state or feelings. Moral empathy represents the healthcare provider’s internal motivation to express empathy. Cognitive empathy involves the intellectual capacity to recognize and comprehend a patient’s viewpoints and emotions. Behavioral empathy involves a deep understanding of the patient’s perspectives and emotions (Kelm et al., 2014). Addressing the intersection of empathy, communication, and healthcare education is a critical component of effective healthcare communication (Nembhard et al., 2023).
Several studies demonstrated a decline in empathy levels among students in various healthcare fields, including medical, dental, nursery, and pharmacy schools (Hojat et al., 2009; Nunes et al., 2011; Díaz-Narváez et al., 2017; Walker et al., 2022). This decline in empathy levels can be attributed to several factors, including insufficient formal empathy training in the curriculum, inadequate mentoring, inappropriate learning settings, and other external factors such as students’ academic stress, heavy workloads, and emotional exhaustion (Neumann et al., 2011; Raab, 2014; Wilkinson et al., 2017). As a result, students may struggle to empathize and understand patients’ viewpoints, sometimes resorting to depersonalization as a protective mechanism (Zenasni et al., 2012; Thomas et al., 2007; Brazeau et al., 2010). Conversely, studies have indicated that healthcare providers who maintain the ability to empathize and compassion toward patients experience higher levels of professional satisfaction, which subsequently reduces depersonalization (Krasner, 2009; Silva and Figueiredo-Braga, 2019). Specifically, in the pharmacy field, some studies focused on empathy; for example, a study was conducted to assess empathy longitudinally in a cohort of pharmacy students, examining how empathy scores changed over time. The findings highlighted empathy as a crucial skill for pharmacy students to develop, with a noted decrease in empathy during the early years of their training (Walker et al., 2022). Another study assessed the impact of patient empathy modeling assignments on pharmacy students’ empathy. The study showed improved empathy scores and highlighted students’ deeper understanding of certain challenges. This approach demonstrated the value of integrating empathy exercises into clinical training to enhance patient care (Chen et al., 2008).
Equivalent evolution has occurred in Jordan, as is true in various nations across the world, concerning the healthcare system. Despite impressive progress in the level of infrastructure and access to resources (Obeidat and Alourd, 2024), there are still some barriers to overcome such as population growth, the increasing need for healthcare services, as well as new health threats (Madaeen and Adeinat, 2018; Government of Jordan, 2024). Therefore, pharmacists are in a vital position to offer the best possible treatment for patients. Consequently, in order to develop a person-centered healthcare workforce in Jordan, it is essential to understand the underlying factors that would affect pharmacy students’ empathy.
The current study’s importance lies in its potential to guide educational organizations and enhance person-centered care among future pharmacists. Effective communication in person-centered care is crucial for establishing strong and appropriate interpersonal relationships with patients, making the consultation process more effective, and reinforcing the pharmacist’s professionalism in community pharmacy settings (Ilardo and Speciale, 2020). Empathy is crucial for healthcare providers as it enhances patient communication, adherence to treatment, and overall health outcomes. In Jordan, there is a gap between pharmacy practice and educational curricula (Fino et al., 2022; Abu Blan et al., 2018); thus, the current study’s findings could drive future curriculum development to ensure pharmacy students are adequately prepared to address the evolving needs of patient care in Jordan.
To date, no studies have specifically assessed empathy levels among pharmacy students in Jordan, making this research the first of its kind. This gap in the literature highlights the significance of the present study, as it offers a foundational understanding of empathy within the context of pharmacy education in Jordan. By evaluating the empathy levels among pharmacy students, this research provides valuable insights into their preparedness for patient-centered care and investigates the factors that influence these levels, which were not reported before in the literature.
Methods
Study design, and participants
A cross-sectional study using a web-based survey, to assess empathy levels among Jordanian pharmacy students, was conducted. The students were invited to complete the study’s survey by sending the survey link. The study included currently enrolled pharmacy students from any academic year at Jordanian universities, including both public and private universities. Seven pharmacy schools were approached, to ensure different perspectives on empathy in pharmacist-patient relations. The nature and the objective of the study were explained to the potential students at the beginning of the survey. The study was conducted voluntarily, ensuring no risk to participants.
Approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board Committee at the Faculty of Pharmacy, Applied Science Private University before the commencement of the study.
Study’s survey
The initial draft of the study survey was developed after an extensive review of the literature (Fjortoft et al., 2011; Tamayo et al., 2016; Keaton, 2017; De Corte et al., 2007; Hasan et al., 2023; Cuff et al., 2015; Van Hooser et al., 2022). Several sources were used to create a pool of questions that were relevant to the study’s aim. Subsequently, these questions were reviewed by the research team to combine concepts and eliminate duplicates.
To ensure the face and content validity of the survey, experienced independent researchers with backgrounds in pharmacy practice and related fields evaluated the developed draft of the survey. They assessed the relevance and comprehensibility of the survey items, and informed the research team whether the items were clear and easily understood. Subsequently, the survey was piloted with 25 pharmacy students, whose responses were excluded from the final analysis. The pilot study aimed to evaluate the internal consistency through measuring Cronbach’s alpha, in addition, to assessing the survey’s comprehension, clarity, and readability. The result of the pilot study resulted in a coefficient of 0.71.
The feedback provided by the independent researchers and the pilot study was carefully reviewed, incorporated where appropriate, and followed by minor revisions (e.g., questions order, and editing the response options). Subsequently, the research team held discussions to ensure that the survey items were appropriate for addressing the study objectives. Consensus was reached among the team members, and the final version of the survey was approved for use without requiring further changes.
The study’s survey consisted of three sections, each addressing a different point of interest. The first section focused on the demographics including gender, age, marital status, residence place, chronic conditions, and medications. In this section, information regarding students was also collected such as university type, academic year, whether they study the term empathy at university, and lastly, whether they have any idea about the meaning of empathy. The last question was included in the survey to gauge pharmacy students’ initial recognition of empathy, before providing any formal definition, this approach assessed baseline students’ knowledge and helped determine whether they already had an understanding of the term before explaining its detailed definition.
The second section of the survey focused on measuring students’ empathy through the well-established Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI). It is a reliable validated assessment tool developed by Mark H. Davis in 1980 to measure empathy. While other tools exist, the IRI was specifically chosen for its detailed subscales, which allow for a more comprehensive evaluation of empathy dimensions relevant to our sample.
The IRI consists of 28 items divided into four subscales (perspective taking, fantasy, empathic concern, and personal distress), each intended to capture a unique component of empathy. Each IRI item can be answered using a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “Does not describe me well” to “Describes me very well” (Keaton, 2017). Although the originally published IRI did not report the reliability; subsequent studies among different populations have assessed its’ Cronbach alpha. For example, research conducted among the Dutch population examined the psychometric properties of a Dutch version of the IRI, with Cronbach’s alpha coefficients of 0.73, 0.83, 0.73, and 0.77 for each subscale (De Corte et al., 2007). The IRI does not have universally established thresholds for classifying empathy levels. Instead, empathy is typically treated as a continuous variable, with higher scores indicating greater levels of empathy. In the current study, a standard practice was followed by reporting pharmacy students’ subscale scores. For further analysis, the correlation between the mean empathy scores and the independent factors (demographics) was assessed using the regression analysis to explore potential influences on empathy levels.
The third and last section, developed by the research team, aimed to assess the students’ empathy through specific items related to the pharmacist-patient relationship (n = 7). These items focused on understanding patients’ anxieties, adopting the patient’s perspective, recognizing the importance of emotional wellbeing and body language, and gauging students’ perceptions of whether certain situations would contribute to better healthcare, enhance person-centered care, and improve treatment outcomes. To ensure the reliability of the survey instrument, the internal consistency of the entire survey was measured, including the third section, using Cronbach’s alpha.
Survey implementation
The pharmacy students were recruited through social media platforms such as Facebook and WhatsApp, or by sending email. Firstly, potential students were provided with a webpage link with ethics committee-approved information about the study. Then, students were invited to complete the self-administered online survey created using Google Forms. No follow-up requests were made after the initial invitation, in order to minimize participant burden. The survey was distributed from November 2023 until the end of June 2024. The estimated survey completion time (5 min) was provided to the participants to give them a realistic expectation of the time commitment required.
Sample size
The sample size was calculated based on a 5% margin of error, a confidence level of 95%, and the assumption of 50% response distribution, resulting in a minimum of 384 participants.
Statistical analysis
Following response collection, they were coded and entered into a customized database utilizing the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), Version 24.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, New York, USA). Continuous variables were reported as means and standard deviations, while percentages were used for categorical variables.
In order to identify factors affecting the score of each IRI subscale, as well as the total IRI score, multiple linear regression was conducted. Initially, simple linear regression for each independent variable was carried out, the research team considered any variable that had a p-value below 0.25 eligible to be entered in the multiple linear regression. A p-value threshold of 0.25 was used for variable eligibility in simple linear regression to allow for broader inclusion of potential predictors, in addition, it is often used in preliminary studies to capture variables that may have meaningful correlations, even if they do not reach the conventional threshold of 0.05. This threshold has been used in other published studies, confirming its validity for identifying potential factors in regression (Abu Farha et al., 2021; Saleh et al., 2021).
Afterward, a multiple linear regression was carried out, and a variable that had a p-value of 0.05 or lower was identified as a statistically significant variable. It was ensured that no multicollinearity (tolerance > 0.2, VIF < 5) exists between the independent variables.
Results
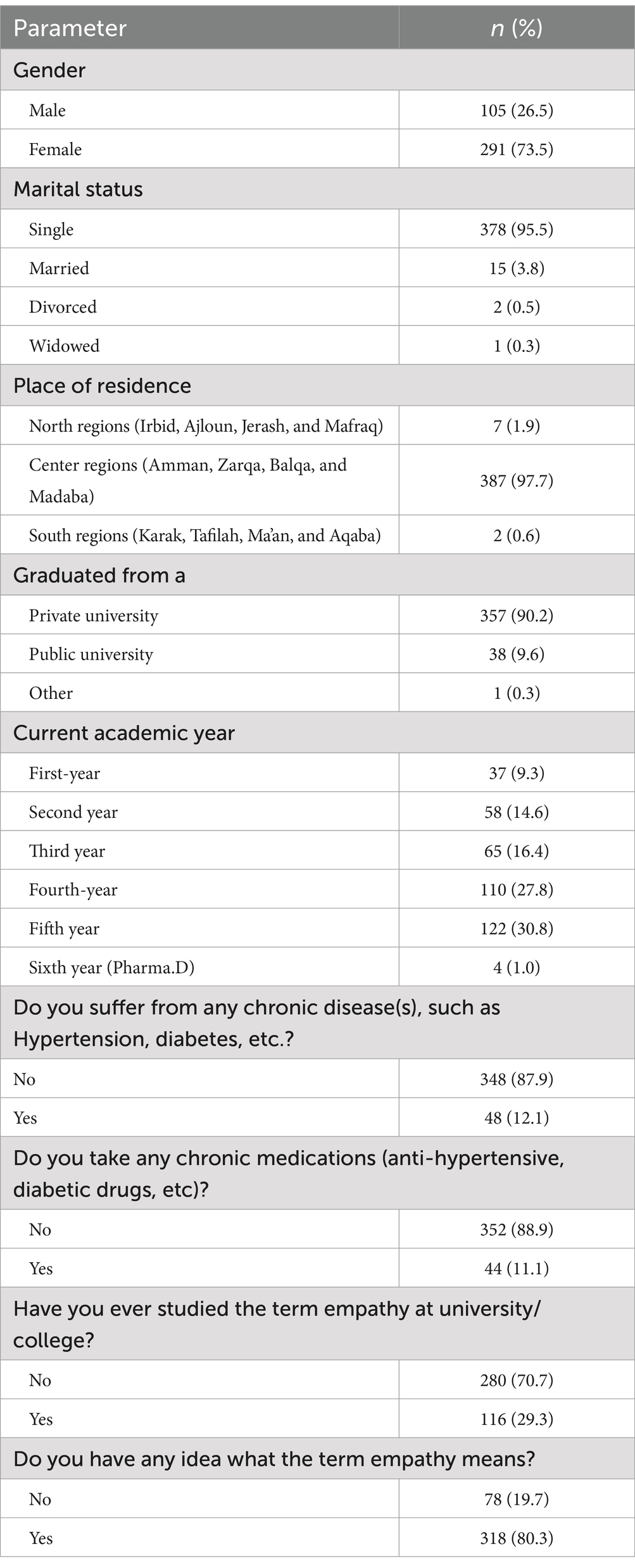
A total of 396 students participated in the current study. They had a mean age of 21.65 years (SD = 2.865), with approximately three-quarters being female (73.5%, n = 291). More than 95.0% of the students were single (n = 378). Similarly, a high percentage (97.7%) resided in the center regions of Jordan (n = 387). In terms of education, most students graduated from private universities (90.2%). Regarding students’ academic year, the highest number were in their fifth-year students (30.8%), followed by the fourth-year students (27.8%). Regarding students’ health, 87.9% reported no chronic conditions such as hypertension or diabetes, and 88.9% were not taking any chronic medications (Table 1).
Regarding empathy awareness, only 29.3% of the pharmacy students had formally studied the empathy term. Yet, 80.3% indicated familiarity with the definition (Table 1).
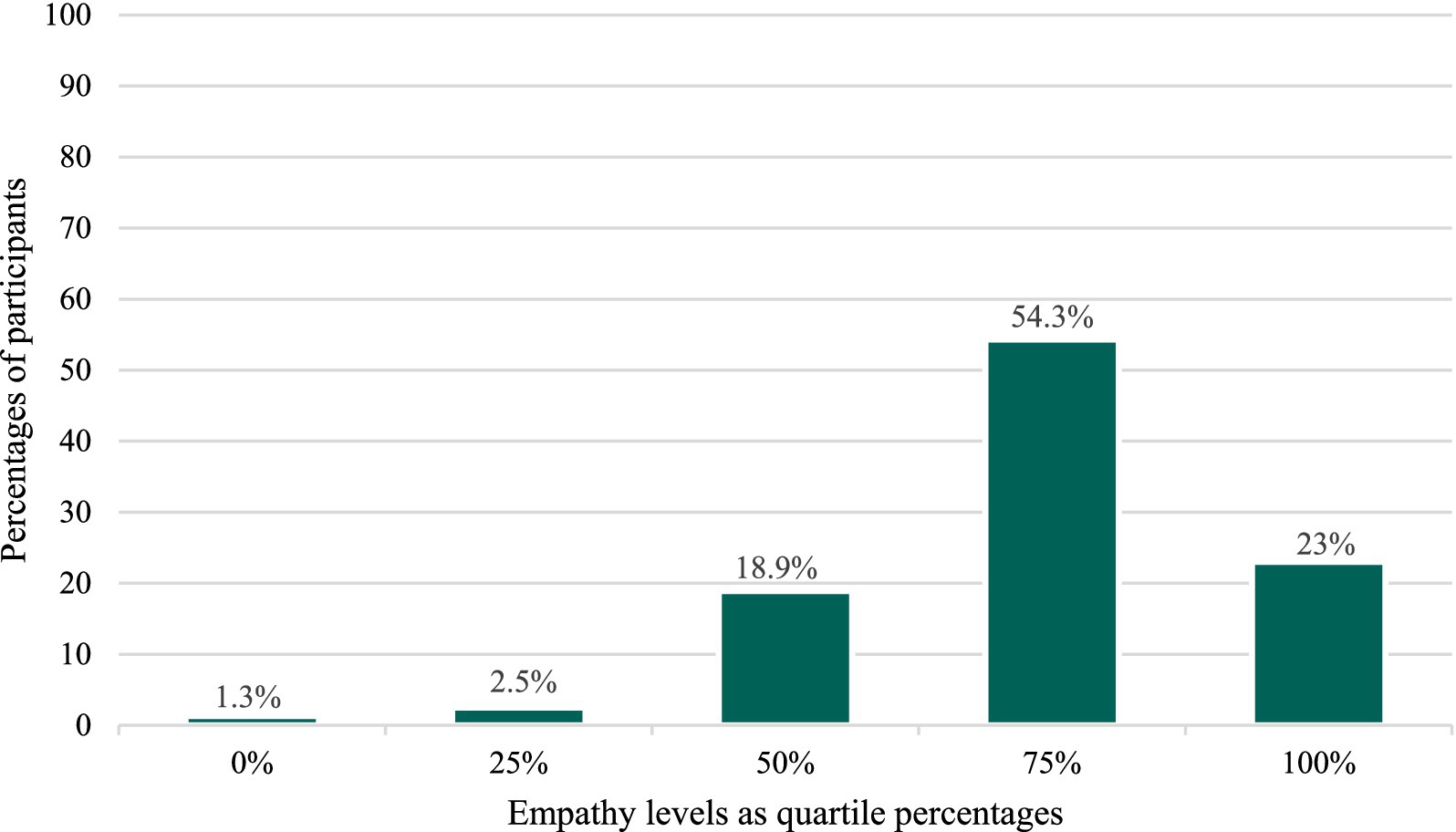
Students were asked to self-assess their level of empathy (Figure 1), after providing them with the definition of empathy as “The ability to understand and share the feelings of another.” While more than half of the students selected a level of 75%, almost one-quarter selected a 100% level (23.0%). The remaining students reported lower levels, with 18.9% at 50%, 2.5% at 25%, and only 1.3% at 0%.
The students’ Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI) scores ranged from 26 to 99, on a scale of 0 (lowest possible score) to 112 (highest possible score). The mean IRI score was 70.89 (SD = 12.82).
Examining the four subscales of the IRI more closely, the perspective-taking (PT) scores ranged from 5 to 28 with a mean of 18.52 (SD = 4.49). The fantasy subscale (FS) had the widest range (1–28) and a mean of 17.05 (SD = 5.16). The empathic concern (EC) scores fell between 7 and 28, with a mean of 20.16 (SD = 4.68). The personal distress (PD) scores ranged from 3 to 27, with a mean of 15.16 (SD = 4.52). The mean scores for each of the IRI’s four subscales are illustrated in Figure 2.
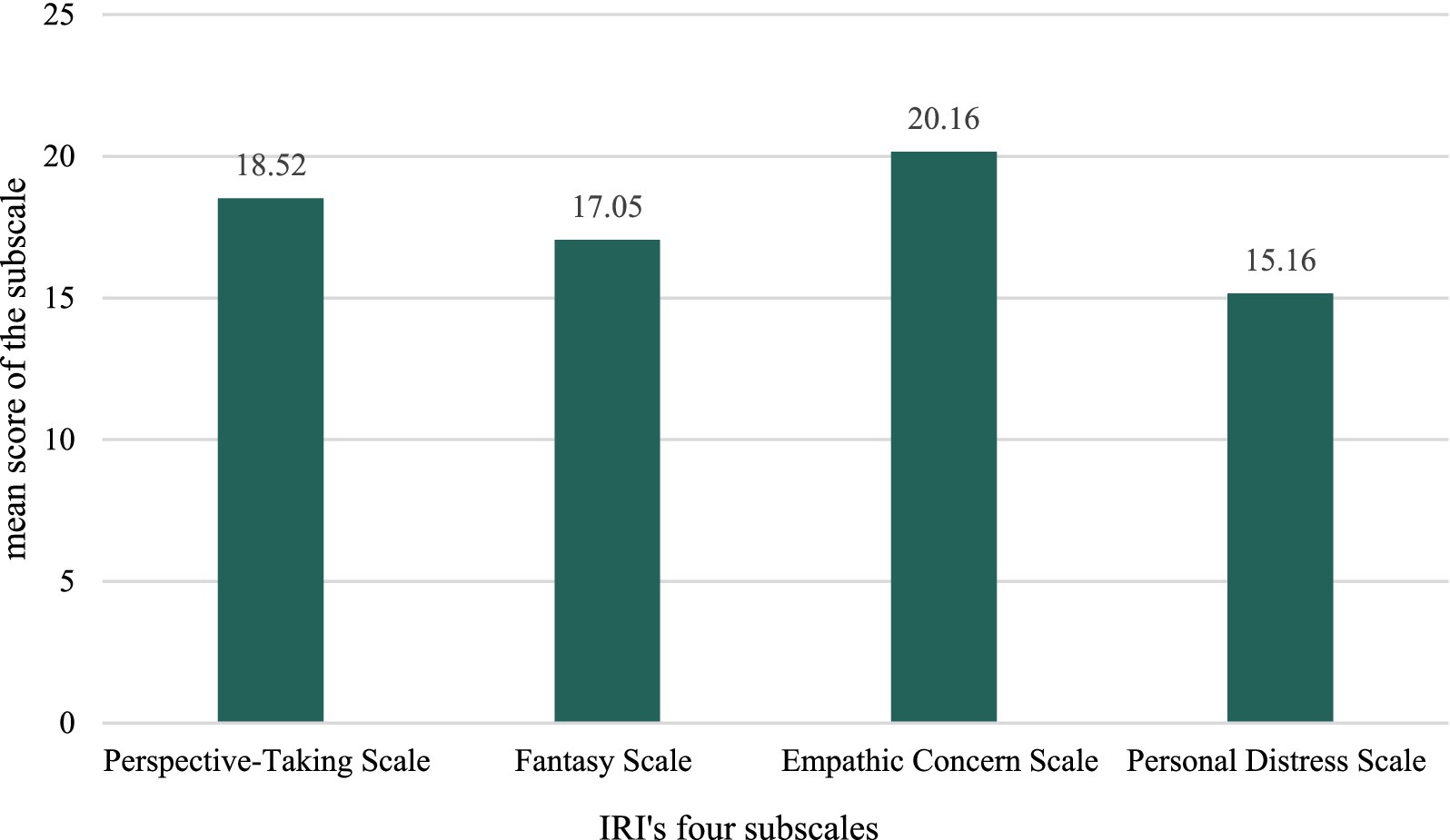
Figure 2. Mean scores for each of the interpersonal reactivity index (IRI) four subscales among students (n = 396).
Perspective-taking scale (PT)
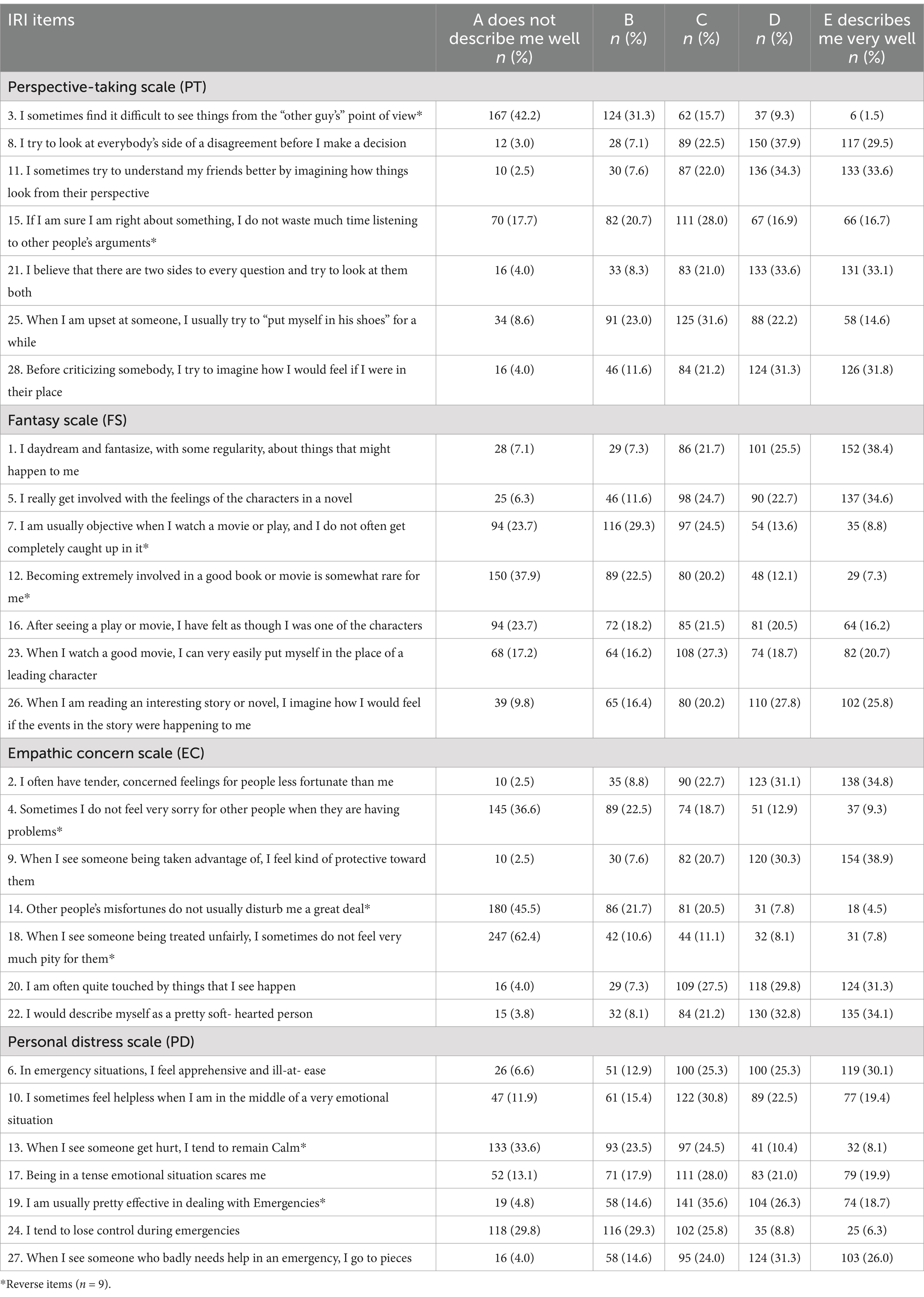
Table 2 displays students’ responses to the Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI). Students showed different perspective-taking abilities. For “I sometimes find it difficult to see things from the “other guy’s” point of view,” 42.2% disagreed, indicating a strong perspective-taking, however, a small percentage of the students agreed (1.5%). Furthermore, students’ responses about consideration of multiple sides of a disagreement (item 8), 29.5% agreed, representing well-adjusted judgment before making a decision, while 3.0% disagreed.
One-third of the students (33.6%) indicated their understanding of friends by visualizing their perspective (item 11), and only 2.5% disagreed. Regarding not listening to others’ arguments, 16.7% agreed, while 17.7% did not (item 15). Considering both sides of a question was reported by one-third of the students (33.1%), while only 4.0% disagreed (item 21). While 14.6% of the students reported trying to put themselves in others’ shoes when upset (item 25), 8.6% disagreed. Imagining others’ feelings before criticism (item 28) was reported by 31.8%, while 4.0% did not (Table 2).
Fantasy scale (FS)
The tendency to be involved and engage with scenarios and fictional characters in books, movies, and plays varied among the students (Table 2). Regular daydreaming was reported by more than one-third of the students (38.4%), while 7.1% disagreed (item 1). Similarly, getting emotionally involved with novel characters was reported by 34.6%, while 6.3% indicated a lack of involvement (item 5). Maintaining objectivity when watching a movie was not common for 23.7%, while 8.8% reported being objective (item 7). Becoming involved in books or movies was rare for 37.9%, but 7.3% were highly involved (item 12). Feeling like a character after watching a play or movie was not common for 23.7%, while 16.2% strongly agreed (item 16). Putting oneself in the place of a leading character after watching a good movie was reported by 20.7%, while 17.2% disagreed (item 23). Imagining oneself in a story was common for over a quarter of the students (25.8%), while 9.8% did not engage in this (item 26).
Empathic concern scale (EC)
The tendency to experience feelings of concern for others among the students varied as shown in Table 2. Tender and concerned feelings for those less fortunate were reported by 34.8%, with 2.5% disagreeing (item 2). Not feeling sorry for others’ problems was disagreed by 36.6%, while 9.3% agreed (item 4). Feeling protective toward someone taken advantage of was high among the students (38.9%), with 2.5% disagreeing (item 9). Being distributed by others’ misfortunes was reported by 45.5%, while 4.5% did not feel this way (item 14). Lacking of pity for unfair treatment was disagreed by 62.4%, while 7.8% agreed (item 18). Feeling touched by events was reported by 31.3%, while 4.0% disagreed (item 20). Describing oneself as soft-hearted was reported by 34.1%, while 3.8% disagreed (item 22).
Personal distress scale (PD)
The students’ degrees of experiencing distress and anxiety varied (Table 2). Feeling apprehensive in emergencies was reported by 30.1%, while 6.6% disagreed (item 6). Helplessness in emotional situations was reported by nearly a fifth of the students (19.4%), while 11.9% did not experience this (item 10). Remaining calm when seeing someone getting hurt was reported by 8.1%, with 33.6% disagreeing (item 13). Fear in tense situations was reported by 19.9%, with 13.1% not feeling scared (item 17). Effectiveness in dealing with emergencies was reported by 18.7%, while 4.8% disagreed (item 19). Losing control during emergencies was reported by 6.3%, with 29.8% disagreeing (item 24). Falling apart when seeing someone who badly needs help in emergencies was reported by 26.0%, with 4.0% reporting not feeling this way (item 27).
Evaluating students’ empathy through the specific items related to the pharmacist-patient relationship (Table 3), revealed that most students (67.9%) strongly agreed that pharmacists should take the time to understand patients’ anxieties and concerns to improve their experience. Similarly, more than half of the students (57.1%) strongly agreed that pharmacists should make an effort to understand things from the patient’s perspective. Understanding the emotional wellbeing of both, patients and their families was also strongly agreed by 35.6% of the students.
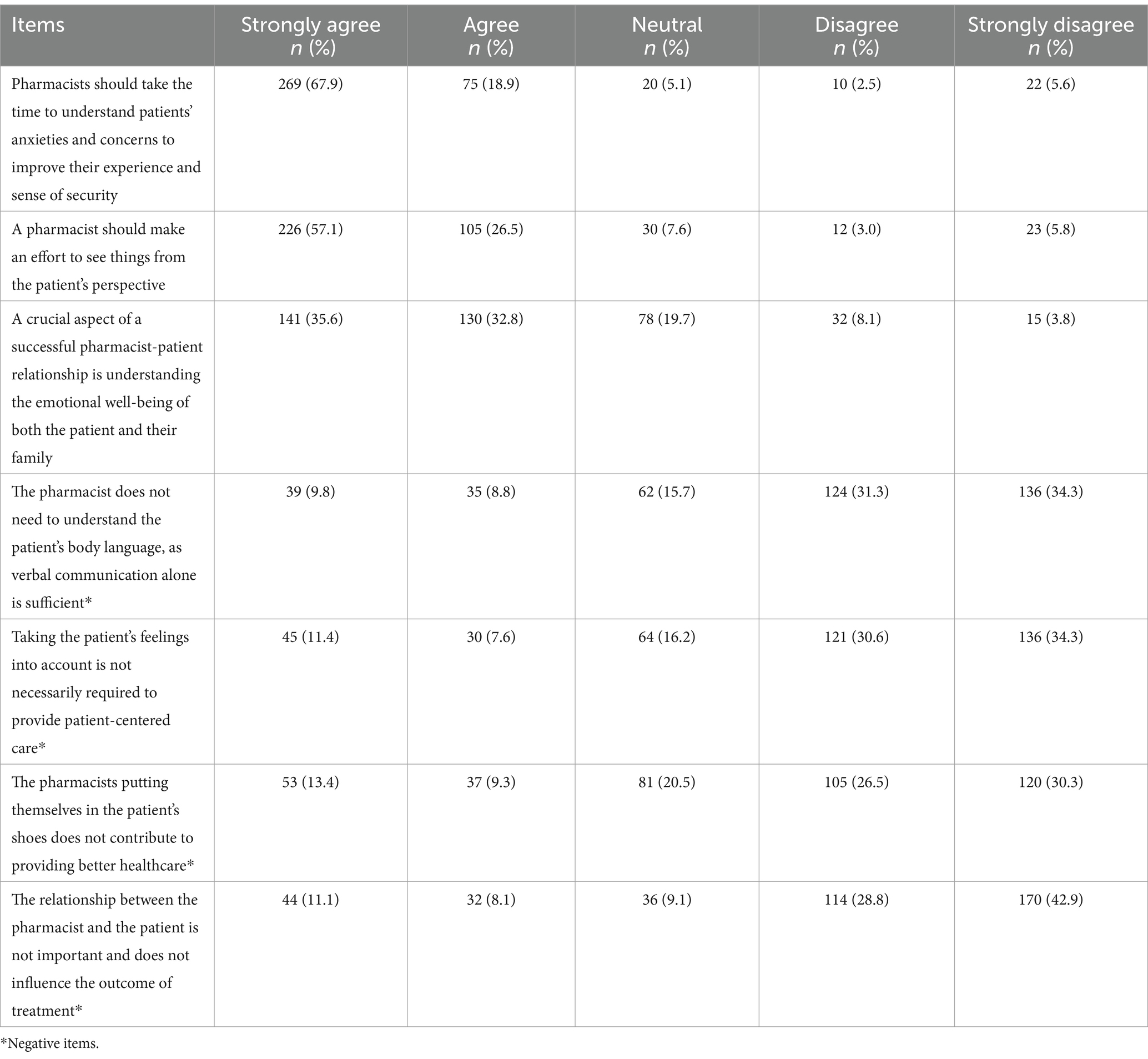
Table 3. Pharmacy students’ responses to the specific empathy items (n = 7) concerning the pharmacist-patient relationship.
Additionally, a significant portion of students disagreed with the negative statements: 34.3% strongly disagreed that verbal communication alone is sufficient and that there is no need to understand body language. Similarly, an equal percentage strongly disagreed that considering patients’ feelings is unnecessary for patient-centered care. Moreover, 30.3% strongly disagreed that pharmacists putting themselves in the patient’s shoes does not offer better healthcare, and 42.9% strongly disagreed that the pharmacist-patient relationship is unimportant and does not impact treatment outcomes (Table 3).
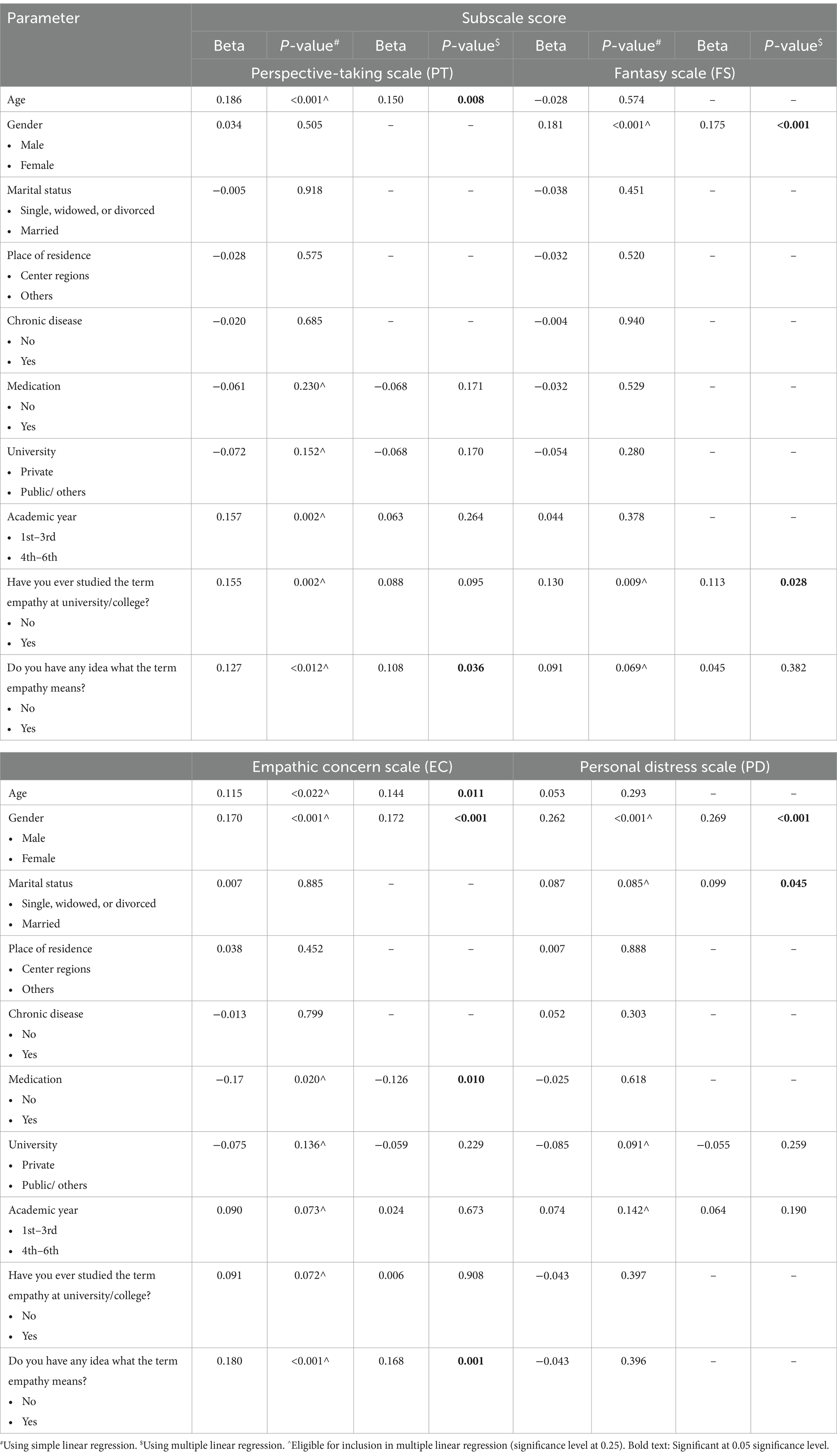
According to the multiple linear regression analysis (Table 4), the student’s age (p = 0.008), and their familiarity with the term empathy (p = 0.036) significantly affected the first IRI subscale (perspective-taking) score. The student’s gender (p ≤ 0.001), and whether they had formally studied the empathy term (p = 0.028) significantly affected the second IRI subscale (fantasy) score. The student’s age (p = 0.011), gender (p ≤ 0.001), whether they are taking medications (p = 0.010), and their familiarity with the term empathy (p = 0.001) significantly affected the third IRI subscale (empathic concern) score. Regarding the last subscale (personal distress), it was significantly affected by the student’s gender (p ≤ 0.001), and the marital status (p = 0.045).
Evaluating the scores from a different angle (Figure 3), the multiple linear regression revealed that the IRI total score was significantly influenced by the student’s age (p = 0.031), gender (p ≤ 0.001), whether they are taking medications (p = 0.050), and their familiarity with the term empathy (p = 0.014).
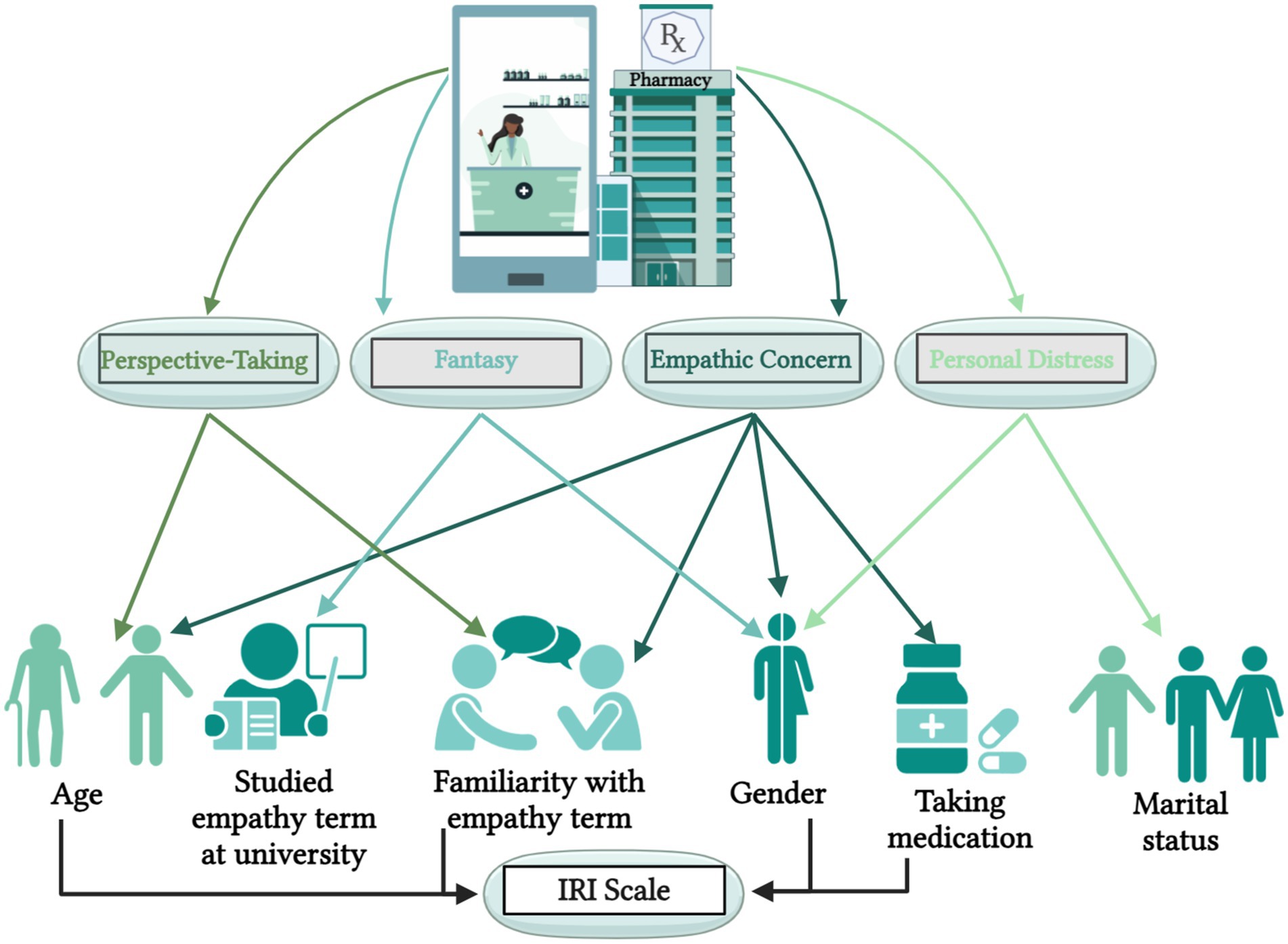
Figure 3. The significant impacts of students’ demographics on the IRI total score and the subscales scores.
Discussion
This study is the first to assess empathy levels among Jordanian pharmacy students and investigate the factors that impact their empathy levels, aiming to shed light on an understudied aspect within the pharmacy practice in Jordan.
The study’s results revealed a gap in education regarding empathy, as only 29.3% of students reported that they had studied the empathy term during their academic years, yet, 80.3% reported that they were familiar with its’ meaning. This inconsistency suggests that empathy awareness exists, however, it is not formally integrated into pharmacy curriculums. This could be an identified potential area of improvement in pharmacy education (Fino et al., 2022), as the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE) emphasizes the importance of incorporating the humanistic value in pharmacy education curriculum (Tamayo et al., 2016; Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education, 2015).
The mean IRI students’ score was 70.89, suggesting moderate empathy levels. However, varying degrees across the four IRI subscales were observed; the highest score was observed in empathic concern (mean = 20.16), followed by perspective-taking, and fantasy (mean = 18.52, 17.05, respectively), while personal distress had the lowest mean score (mean = 15.16). These results indicate that while students can understand and share others’ feelings, they may struggle with personal anxiety and nervousness in tense interpersonal situations, potentially affecting their ability to maintain professional composure in clinical settings. This offers an opportunity to improve the educational framework for pharmacy studies. Several students have recommended integrating emotional intelligence content into pharmacy curricula (Butler et al., 2022; Buckley et al., 2020). Integrating courses on empathy, interpersonal skills, and emotional intelligence into continuing professional development (CPD) programs improves pharmacists’ clinical practice competencies and their ability to manage stress (Larose-Pierre et al., 2023).
The empathy score obtained from the study participants was relatively high compared to the results obtained from similar studies conducted for pharmacy students in Malaysia (Hasan et al., 2023), South Korea (Jeon and Cho, 2015), the United States (Fjortoft et al., 2011; Van Winkle et al., 2012; Williams et al., 2020), and the United Kingdom (Wilson et al., 2012).
The study revealed varying empathy levels among the students, with some demographics playing a significant role including age, which was a significant predictor for perspective-taking, indicating that older students exhibited higher empathy, specifically by understanding another person’s viewpoint.
Gender significantly affected the fantasy, empathic concern, and personal distress subscales, with females scoring higher. This was also observed in a study conducted in Jordan that assessed empathy among nursing students at public universities (Altwalbeh et al., 2018). Additionally, it aligns with the findings of similar studies conducted in Portugal (Silva and Figueiredo-Braga, 2019), South Korea (Jeon and Cho, 2015), the United States (Van Hooser et al., 2022; Tamayo et al., 2016), and the United Kingdom (Wilson et al., 2012). Furthermore, a study conducted in the UK tested the hypothesis that female medical students are more empathetic compared to males and found results supporting this hypothesis (Tavakol et al., 2011). On the other hand, a study conducted in Malaysia targeting pharmacy students in public and private universities found that male students are more empathic than females (Hasan et al., 2023).
Therefore, it is important to highlight that the impact of gender on empathy is not entirely conclusive. Other studies did not find significant differences in nonverbal communication or physiological responses related to empathy between genders (De, 1995). Further research is needed to understand the complex relationship between gender and empathy.
The specific items related to the pharmacist-patient relationship manifested the students’ recognition of the importance of empathy in clinical practice. The results showed that most of the students agreed that pharmacists should take time to understand patients’ anxieties and make efforts to see things from their perspective. This acknowledgment is crucial, as empathy in pharmacist-patient interactions can enhance patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment, and overall healthcare outcomes (Garza et al., 2023).
Some studies have implemented methods to enhance the level of empathy and understanding of its concept among students. For example, an educational intervention simulating the experience of being a hemodialysis patient was conducted, resulting in improved cognitive and affective empathy among pharmacy students toward these patients. Such interventions can better prepare students to become more compassionate healthcare professionals (Sjoquist et al., 2020).
The present study has some limitations that must be acknowledged. The cross-sectional design limits the ability to observe variations in empathy levels over time, as data were collected at only one point. Additionally, self-selection bias may affect the generalizability of the findings, as potential participants chose independently whether to participate. Furthermore, the sample was drawn from certain pharmacy institutions in Jordan, which may limit the applicability of the results to other regions or healthcare disciplines. Lastly, while seven pharmacy schools were approached to recruit students, the exact response rate from each school is unclear; therefore, future studies could address this by exploring response rates more closely at the school level.
The study’s findings hold several practical implications for pharmacy education and practice, especially, in the Jordan context. It shed light on the importance of incorporating empathy training into pharmacy education to improve person-centered care. This training can be derived in several methods, such as workshops and role plays, which could improve pharmacy students’ interpersonal skills and emotional intelligence. Additionally, the results would inspire educational institutions and policymakers to prioritize developing curricula, to contain more practical exercises to equip students with essential skills such as empathy. Strengthening empathy within pharmacy education would contribute to better person-centered care and also align with the broader goal of developing compassionate healthcare professionals who can successfully address patients’ needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the present study reveals moderate empathy levels among Jordanian pharmacy students, provides valuable insights into the levels of empathy among pharmacy students in Jordan, and identifies key factors that influence these levels. Significant demographic and educational factors affected the students’ empathy levels.
The findings emphasize the importance of integrating empathy training into pharmacy education to improve students’ ability to connect with patients and improve overall patient care. As the healthcare landscape continues to grow, fostering empathy will be vital in developing pharmacy professionals. Future research could track empathy trends among pharmacy students and assess the efficiency of empathy training on patient outcomes and medication adherence.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Review Board Committee at the Faculty of Pharmacy, Applied Science Private University (Approval number: 2023-PHA-49). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AlA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ST: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AnA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AhA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abu Blan, R. S., Nazer, L. H., Jaddoua, S. M., and Treish, I. M. (2018). A hospital-based pharmacy internship program in Jordan. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 83:6547. doi: 10.5688/ajpe6547
Abu Farha, R., Yousef, A., Gharaibeh, L., Alkhalaileh, W., Mukattash, T., and Alefishat, E. (2021). Medication discrepancies among hospitalized patients with hypertension: assessment of prevalence and risk factors. BMC Health Serv. Res. 21:1338. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07349-5
Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (2015). Accreditation standards and key elements for the professional program in pharmacy leading to the doctor of pharmacy degree. Chicago, IL: Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education.
Altwalbeh, D., Khamaiseh, A. M., and Algaralleh, A. (2018). Self-reported empathy among nursing students at a University in Jordan. Open Nurs J. 12, 255–263. doi: 10.2174/1874434601812010255
Brazeau, C. M. L. R., Schroeder, R., Rovi, S., and Boyd, L. (2010). Relationships between medical student burnout, empathy, and professionalism climate. Acad. Med. 85, S33–S36. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181ed4c47
Buckley, K., Bowman, B., Raney, E., Afolabi, T., Fettkether, R. M., Larson, S., et al. (2020). Enhancing the emotional intelligence of student leaders within an accelerated pharmacy program. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 84:8056. doi: 10.5688/ajpe8056
Butler, L., Park, S. K., Vyas, D., Cole, J. D., Haney, J. S., Marrs, J. C., et al. (2022). Evidence and strategies for including emotional intelligence in pharmacy education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 86:ajpe8674. doi: 10.5688/ajpe8674
Chen, J. T., LaLopa, J., and Dang, D. K. (2008). Impact of patient empathy modeling on pharmacy students caring for the underserved. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 72:40. doi: 10.5688/aj720240
Cuff, B. M., Brown, S. J., Taylor, L., and Howat, D. J. (2015). Empathy: a review of the concept. Emot. Rev. 8, 144–153. doi: 10.1177/1754073914558466%0A
De, L. J. (1995). Gender and communication in social work education. J. Soc. Work. Educ. 31, 75–81. doi: 10.1080/10437797.1995.10778841
De Corte, K., Buysse, A., Verhofstadt, L. L., Roeyers, H., Ponnet, K., and Davis, M. H. (2007). Measuring empathic tendencies: reliability and validity of the Dutch version of the interpersonal reactivity index. Psychol. Belg. 47:235. doi: 10.5334/pb-47-4-235
Díaz-Narváez, V. P., Coronado, A. M. E., Bilbao, J. L., González, F., Padilla, M., Calzadilla-Nuñez, A., et al. (2017). Reconsidering the ‘decline’ of dental student empathy within the course in Latin America. Acta Medica Port. 30, 775–782. doi: 10.20344/amp.8681
Fino, L., Alsayed, A., Basheti, I., Saini, B., Moles, R., and Chaar, B. (2022). Implementing and evaluating a course in professional ethics for an undergraduate pharmacy curriculum: a feasibility study. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 14, 88–105. doi: 10.1016/j.cptl.2021.11.031
Fjortoft, N., van Winkle, L. J., and Hojat, M. (2011). Measuring empathy in pharmacy students. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 75, 109–106. doi: 10.5688/ajpe756109
Garza, K. B., Grabowsky, A., Moseley, L. E., Wright, B. M., Davis, B. R., and Ford, C. R. (2023). Activities to promote empathy for patients among pharmacy learners: a scoping review. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 15, 911–922. doi: 10.1016/j.cptl.2023.08.003
Government of Jordan . (2024). Facts about Jordan. Available at: https://www.jordan.gov.jo/Default/Ar (Accessed April 22, 2024).
Hasan, S., Babar, M., Chan, K., Ahmed, S., and Mitha, S. (2023). An assessment of pharmacy students’ empathy levels in Malaysia. J. Adv. Pharm. Educ. Res. 3, 431–440.
Hojat, M., Vergare, M. J., Maxwell, K., Brainard, G., Herrine, S. K., Isenberg, G. A., et al. (2009). The devil is in the third year: a longitudinal study of Erosion of empathy in medical school. Acad. Med. 84, 1182–1191. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181b17e55
Ilardo, M. L., and Speciale, A. (2020). The community pharmacist: perceived barriers and patient-centered care communication. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:536. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17020536
Jeon, S., and Cho, E. (2015). Assessment of Korean pharmacy students’ empathy using the Jefferson scale of empathy. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 79:67. doi: 10.5688/ajpe79567
Keaton, S. A. (2017). “Interpersonal reactivity index (IRI)” in The sourcebook of listening research. eds. D. L. Worthington and G. D. Bodie (Amsterdam: Wiley), 340–347.
Kelm, Z., Womer, J., Walter, J. K., and Feudtner, C. (2014). Interventions to cultivate physician empathy: a systematic review. BMC Med. Educ. 14:219. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-14-219
Krasner, M. S. (2009). Association of an Educational Program in mindful communication with burnout, empathy, and attitudes among primary care physicians. JAMA 302, 1284–1293. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1384
Larose-Pierre, M., Cleven, A. J., Renaud, A., Hughes, J. A., McQuade, B., Griffin, B. L., et al. (2023). Reevaluating Core elements of emotional intelligence in professional identity formation for inclusion in pharmacy education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 87:100082. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpe.2023.100082
Madaeen, S., and Adeinat, M. (2018). The health sector in Jordan: effectiveness and efficiency. Mod. Appl. Sci. 12:234. doi: 10.5539/mas.v12n12p234
Nembhard, I. M., David, G., Ezzeddine, I., Betts, D., and Radin, J. (2023). A systematic review of research on empathy in health care. Health Serv. Res. 58, 250–263. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.14016
Neumann, M., Edelhäuser, F., Tauschel, D., Fischer, M. R., Wirtz, M., Woopen, C., et al. (2011). Empathy decline and its reasons: a systematic review of studies with medical students and residents. Acad. Med. 86, 996–1009. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e318221e615
Nunes, P., Williams, S., Sa, B., and Stevenson, K. (2011). A study of empathy decline in students from five health disciplines during their first year of training. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2, 12–17. doi: 10.5116/ijme.4d47.ddb0
Obeidat, B., and Alourd, S. (2024). Healthcare equity in focus: bridging gaps through a spatial analysis of healthcare facilities in Irbid, Jordan. Int. J. Equity Health 23:52. doi: 10.1186/s12939-024-02120-8
Pratiwi, H., Ari Kristina, S., Wahyuni Widayanti, A., and Suryo, P. Y. (2023). Pharmacy students’ empathy and its determinants: a systematic review. F1000Res 12:18. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.127017.1
Raab, K. (2014). Mindfulness, self-compassion, and empathy among health care professionals: a review of the literature. J. Health Care Chaplain. 20, 95–108. doi: 10.1080/08854726.2014.913876
Saleh, D., Abu Farha, R., and Darwish, E.-H. F. (2021). Antimicrobial stewardship in community pharmacies in Jordan: assessing current status. J. Pharm. Health Serv. Res. 12, 181–187. doi: 10.1093/jphsr/rmaa028
Silva, R. G., and Figueiredo-Braga, M. (2019). The roles of empathy, attachment style, and burnout in pharmacy students’ academic satisfaction. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 83:6706. doi: 10.5688/ajpe6706
Sjoquist, L. K., Cailor, S., Conkey, L., Wilcox, R., Ng, B., and Laswell, E. M. (2020). A simulated patient experience to improve pharmacy student empathy for patients on hemodialysis. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 12, 827–833. doi: 10.1016/j.cptl.2020.02.018
Tamayo, C. A., Rizkalla, M. N., and Henderson, K. K. (2016). Cognitive, behavioral and emotional empathy in pharmacy students: targeting programs for curriculum modification. Front. Pharmacol. 7:96. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00096
Tavakol, S., Dennick, R., and Tavakol, M. (2011). Empathy in UK medical students: differences by gender, medical year and specialty interest. Educ. Prim. Care 22, 297–303. doi: 10.1080/14739879.2011.11494022
Thomas, M. R., Dyrbye, L. N., Huntington, J. L., Lawson, K. L., Novotny, P. J., Sloan, J. A., et al. (2007). How do distress and well-being relate to medical student empathy? A multicenter study. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 22, 177–183. doi: 10.1007/s11606-006-0039-6
Van Hooser, J., Swanson, S., Conway, J. M., and Brown, J. T. (2022). Assessing pharmacy students’ baseline tolerance for ambiguity, burnout, empathy, quality of life, and stress. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 14, 966–971. doi: 10.1016/j.cptl.2022.07.008
Van Winkle, L. J., Fjortoft, N., and Hojat, M. (2012). Impact of a workshop about aging on the empathy scores of pharmacy and medical students. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 76:7619. doi: 10.5688/ajpe7619
Walker, P. C., Marshall, V. D., Sweet, B. V., and Vordenberg, S. E. (2022). Longitudinal measurement of empathy in student pharmacists. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 86:8752. doi: 10.5688/ajpe8752
Wilkinson, H., Whittington, R., Perry, L., and Eames, C. (2017). Examining the relationship between burnout and empathy in healthcare professionals: a systematic review. Burn. Res. 6, 18–29. doi: 10.1016/j.burn.2017.06.003
Williams, C. R., Rodgers, P. T., McLaughlin, J. E., Angelo, T. A., and Shepherd, G. (2020). Comparing empathy levels in doctor of pharmacy students and exemplary pharmacist preceptors. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 84:7497. doi: 10.5688/ajpe7497
Wilson, S. E., Prescott, J., and Becket, G. (2012). Empathy levels in first-and third-year students in health and non-health disciplines. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 76:24. doi: 10.5688/ajpe76224
Keywords: empathy, IRI, pharmacy students, communication, training, emotional intelligence, Jordan
Citation: Ahmad A, Nassar RI, Thiab S, Alostath M, Aldarawish R, Ramahi SM, Abed A and Assiri AA (2024) Measuring the empathy levels among pharmacy students: a journey toward enhancing effective communication and understanding in the pharmacist-patient relationship. Front. Commun. 9:1473771. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2024.1473771
Edited by:
Sabrina Anne Jacob, University of Doha for Science and Technology, QatarReviewed by:
Iuliana Raluca Gheorghe, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaPernille Sorensen, University of Strathclyde, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2024 Ahmad, Nassar, Thiab, Alostath, Aldarawish, Ramahi, Abed and Assiri. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Razan I. Nassar, Ul9uYXNzYXJAYXN1LmVkdS5qbw==
†ORCID: Razan I. Nassar, orcid.org/0000-0001-8952-0376
Samar Thiab, orcid.org/0000-0002-9625-4915
 Alhareth Ahmad1
Alhareth Ahmad1
 Razan I. Nassar
Razan I. Nassar Samar Thiab
Samar Thiab Mohammad Alostath
Mohammad Alostath Rania Aldarawish
Rania Aldarawish Sofiyan Mohd Ramahi
Sofiyan Mohd Ramahi