
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Commun., 04 October 2024
Sec. Organizational Communication
Volume 9 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomm.2024.1402820
This article is part of the Research TopicEmerging Technologies and Organizational Communication: Envisioning the Future of WorkView all 5 articles
 Wolfram Lipp*
Wolfram Lipp* Alwine Mohnen
Alwine MohnenResearchers and practitioners alike are interested in understanding the specifics of electronic negotiations as more and more negotiations are conducted electronically. Intuitively, we would expect differences across negotiation media, but research provides diverging results as to the impact of the medium. This research contributes to this discourse and aims to uncover differences across media and investigates the impact of individual factors on e-negotiation behavior and outcomes. While we know from previous research that individual factors influence job performance and preference for negotiation media, the impact on behaviors and outcomes in different computer-mediated negotiation media is yet to be explored. This paper proposes the individual x medium fit hypothesis, which asserts that individual factors play a distinct role in different electronic negotiation media. We tested this hypothesis using an online, mixed-motive negotiation simulation in which participants (n = 187) negotiated either in a chat or in a video conference system. The impacts of individual factors on the outcome and mediator variables were estimated with a structural equation model. We confirmed the hypothesis that individual factors have different impacts in a video and a chat negotiation: In the video negotiation, gender significantly predicted negotiation outcomes. Women used fewer words compared to men, which leads both to a lower individual profit and a better subjective value. In the chat negotiation, openness, conscientiousness, and extraversion predicted negotiation outcomes. In addition, individual factors affected attitudes toward the negotiation and behaviors. The results indicate that some individuals have an advantage in certain media. Overall, the impact of individual factors in e-negotiations seems to be limited even though such an impact is intuitively assumed by many negotiators.
The ubiquity of digital communication media is perhaps one of the greatest disruptors in negotiations over the last few decades. The COVID-19 pandemic has acted as an additional catalyst, forcing more negotiations into digital media. However, in a review of the field of e-negotiations, Geiger (2020) concluded that “this research field within group decision and negotiation is still far from consensus as to the effects of different media on most negotiation processes and outcomes.” This is exemplified by individual profits in negotiations. While some authors found that face-to-face (F2F) settings resulted in higher individual economic gains than electronic settings (Lim, 2000; Arunachalam and Dilla, 1995), others did not find any significant differences (Geiger, 2014; Giordano et al., 2007; Galin et al., 2007). Purdy et al. (2000) compared four different media with varying richness (F2F, videoconference, telephone, and computer-mediated communication); besides no difference in objective outcomes, the authors reported a medium difference in time higher in less rich media, bargaining approach (more collaborative in rich media), outcome satisfaction (higher in rich media), and desire for future negotiation (higher in rich media).
One element that could contribute to reconcile the mixed results is the impact of individual factors on negotiation behavior and outcomes. Several authors (Barry and Friedman, 1998; Elfenbein et al., 2008; Sharma et al., 2013) investigated the role of individual factors in F2F negotiations, including personality, gender, and attitudes (a settled way of thinking or feeling about something) toward the negotiation. However, to our knowledge, no studies that investigate the interaction between individual factors and different electronic negotiation media have been published to date.
In this paper, we focus on the individual factors of personality and gender and draw on the findings on individual x situation fit (Judge and Zapata, 2015). The authors showed that a situation could activate an individual’s traits, which could in turn affect job performance. We argue that this fit is transferrable to e-negotiations; thus, we expected to observe differences across negotiation media because the “fit” of the negotiator to the medium activates the right behaviors. The main proposition of the individual x situation fit theory is that “the better the fit, the better the outcome” (Diener et al., 1984). Therefore, we posited that individuals May have a significantly better fit with one negotiation situation or medium than another. As a result, they May behave differently and achieve superior outcomes. We refer to this hypothesis as the “individual x medium fit hypothesis.”
We investigated the individual x medium fit hypothesis in an experimental study in which participants negotiated an integrative negotiation issue in either a video conference or chat system. We have chosen those two media as they have a high difference in richness. Further, face-to-face negotiations were not possible due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the associated restrictions. Besides individual factors [five-factor model of personality and gender (McCrae and Costa, 1987)] and outcome variables (economic and subjective value), we measured attitudes (positive and negative affect and aspiration) and behaviors (words spoken), which we hypothesized as mediators.
We found significant differences between the two negotiation media: Although participants’ individual profits were not significantly different between media, those assigned to the chat condition were less satisfied with the negotiation. Regarding individual factors, we observed significant differences between the two negotiation media. In the video negotiations, gender significantly predicted negotiation outcomes. Female participants used fewer words than male participants, which led to both lower economic outcomes and higher subjective value. In the chat negotiations, openness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion significantly predicted negotiation outcomes. Furthermore, we found that positive affect increased subjective value in the video negotiations and that negative affect and aspirations decreased subjective value in the chat negotiations.
Our contributions to the discourse are multifaceted. Overall, our results confirmed the individual x medium fit hypothesis. Personality seemed to drive the results of chat negotiations more than video negotiations. In addition, we uncovered the mechanism of word count, which was positively associated with economic outcomes in video negotiations. Finally, gender predicted the number of spoken words in video negotiations only. These findings contribute to the understanding of performance differences between women and men. Furthermore, this gender effect was not significant in the chat negotiations; a less rich medium appeared to counteract some of the negative effects of gender.
However, many of our predictions could not be verified and individual factors thus seem to play a lower role than negotiators might intuitively assume.
Sondern and Hertel (2023) categorized electronic or computer-mediated negotiation research into two traditions: organizational behavior/management (focusing on technology as a tool that enables communication) and group decision support systems (focusing on negotiation support systems). The present manuscript is situated in the behavioral stream of literature as it investigates how the communication medium affects the negotiation process.
Geiger (2020) provided a comprehensive review of 97 publications in the field of electronic negotiations and categorized the findings into the categories of negotiation process, economic negotiation outcomes, and socio-economic negotiation outcomes. In the following, we use Geiger’s categories to provide an overview of the current research and also the most recent findings.
Regarding the negotiation process, electronic negotiations seem to require more time (e.g., Purdy et al., 2000; Geiger, 2014; Wang and Doong, 2014) compared to face-to-face negotiations. However, there are also conflicting findings that report no significant time differences (e.g., Barkhi et al., 1999; Sondern and Hertel, 2023).
There also seems to be an impact on trust and credibility. While Lu et al. (2017) report lower trust in electronic media, Sondern and Hertel (2023) did not find any significant difference in trust between media. Regarding credibility, Yashiro et al. (2024) showed that visual cues increased credibility for both female and male salespersons and that video communication leads to the highest credibility. Even though this experiment was not a negotiation task, it shows how the representation in the medium can alter the process.
In addition, electronic negotiation seem to be more hostile compared to face-to-face negotiations (e.g., Stuhlmacher and Citera, 2005; Galin et al., 2007). The findings regarding hostility are related to a more recent finding of Kleshinski et al. (2023). The authors showed that relationship conflict and outcome inequality were minimized when negotiators’ interpersonal and informational justice perceptions were congruent in the face-to-face condition. This was not the case in the virtual negotiation. Kleshinski et al. (2023) used an adapted version of the “New Recruit” (Neale, 1997) negotiation case for their experiment. The “New Recruit” case was also the basis of the case used in this research.
There are also some findings on how the differences of the negotiation media could be overcome. Kornfield et al. (2021) showed that embodiment (the representation of a geographically distant negotiator by a robot) eliminated the distance disadvantage of the electronic negotiation. The authors also used an adapted version of the “New Recruit” negotiation case.
As outlined in the introduction the existing research unveiled differing results regarding the economic negotiation results across media. On top of the references mentioned in the introduction, additional studies highlight the differing results: While a meta-study of Stuhlmacher and Citera (2005) showed higher profits for the face-to-face medium compared to electronic media, several studies find no significant effects (e.g., Geiger, 2014; Sondern and Hertel, 2023; Short, 1974).
But also, for socio-economic outcomes, there is no clear picture. Some authors show highest satisfaction in face-to-face negotiation (Barkhi et al., 1999; Wachter, 1999), but others show text-based negotiations at an advantage (Geiger, 2014).
Overall, we can conclude that there is no consensus regarding the mechanics and influencing factors of electronic negotiations. This is especially true for the individual factors of negotiators. We did not obtain any studies that investigate the interaction of individual factors with the negotiation medium and we address this gap with the present study. The following sections introduce the underlying theories and then derive our predicted effects.
Before exploring the literature on individual factors, we outline overarching theories that influenced our research and provided the foundations of our theory building in the following sections. Both strategic communication theories and the individual x situation fit theory were relevant for the study.
As part of the media richness theory, Daft and Lengel (1983) classified different communication media according to their information richness or ability to transmit information. While F2F communication exhibits the highest richness, media such as letters have lower richness and thus can transmit lower amounts of information. For complex decision problems such as negotiations, the authors recommended richer media.
McGrath and Hollingshead (1993) extended the information richness theory to the task media fit hypothesis. The author asserted that different tasks require a certain medium to achieve the best outcomes. If the task is complex and requires considerable communication, a richer medium is predicted to lead to better outcomes. The task media fit hypothesis has also been tested in negotiation settings and found to predict outcomes (Mennecke et al., 2000). Mennecke et al. (2000) found no differences in outcomes between F2F and video communication, but negotiation dyads that used audio or computer-mediated negotiation resulted in inferior outcomes. However, Geiger (2020) noted that there is mixed evidence on the theory’s propositions, which might be related to the theory’s multiple applications beyond negotiations.
Another effect is the “barrier effect” (Carnevale and Isen, 1986), which proposes that physically separating the negotiators reduces the use of contentious tactics, increases integrative capacity, and encourages the formulation of integrative solutions. E-negotiations introduce different kinds of barriers; for example, visual and audio channels are not available in chat negotiations.
Also the Social Information Processing Theory (Walther, 1994; Walther et al., 1994) has been applied to understand communication media in negotiations. The theory posits that people have a need to affiliate when communicating. This is expected to work better in richer media than in electronic media as more channels exist.
Finally, the Communication Orientation Model of Swaab et al. (2012) can be considered the current state of the art with regard to the psychology of communication media (Geiger, 2020). Swaab et al. (2012) found that the outcomes of negotiations differed depending on the orientation of the negotiators. If the orientation was neutral, the presence of communication mediums increased achievement. In case of a cooperative orientation, communication mediums did not affect outcomes. Finally, in case of a noncooperative orientation, outcomes were decreased.
In summary, there is some evidence to suggest that computer-mediated communication (CMC) media would significantly influence negotiation outcomes. One question of interest is if individual factors interact with the medium when it comes to predicting negotiation outcomes.
Judge and Zapata (2015) integrated the “Big Five” traits (McCrae and Costa, 1987) into the individual-situation perspective and found that personality traits predicted job performance in different situations. Their main argument was that performance improves when there is a good fit between the person and the task. As the negotiation situation arguably differs between video or F2F negotiations and chat negotiations, individual factors are expected to drive a difference in negotiation behavior and outcomes as they trigger different behaviors of the negotiators as per the situation x fit hypothesis (see above).
There is already some evidence on these differences. Dunaetz et al. (2015) found that individual factors predict media richness preferences (i.e.; the participants preferred a specific medium). The authors reported that people with higher levels of extraversion and agreeableness had a greater preference for media richness. Moreover, Stritzke et al. (2004) showed that online settings equalized differences in shyness between individuals thanks to the absence of visual and auditory cues. In addition, Hertel et al. (2008) showed the impact of personality on media choice. Extraverts and people with low neuroticism both preferred media with high richness. In the context of negotiation, media preferences also predicted the choice of a negotiation medium (Geiger and Laubert, 2018).
According to the individual-situation fit perspective, the individual x medium fit should also lead to different behaviors and outcomes. Dimotakis et al. (2012) argued that the fit between the negotiator and the situation resonates well with the wider literature on individual x situation fit. A meta-study by Kristof-Brown et al. (2005) showed that an individual’s fit with a situation is largely relevant in work settings. This is also supported by the trait activation model (Tett and Burnett, 2003; Tett and Guterman, 2000), which posits that different tasks activate relevant personality traits and in turn influence behaviors. The idea of fit has already been confirmed in negotiations by Geiger and Parlamis (2014) who showed that email affinity led to better results in email negotiations. This is also expected to hold true for different negotiation media. For example, a neurotic negotiator May be more anxious before a video negotiation than a chat negotiation due to the higher media richness and more intense interactions associated with the latter medium.
In negotiations, commonly investigated individual factors are expectations and beliefs, motivational styles, abilities, enduring dispositions, and gender (Elfenbein et al., 2008). In this paper, we focus on the negotiator’s personality and gender as the most relevant individual factors. We expected the individual x medium fit to affect negotiation outcomes both directly and indirectly via mediators such as affective states, attitudes, and behaviors. In terms of outcomes, we considered both quantitative (i.e., negotiators’ individual profit) and qualitative results (i.e., subjective value) of the negotiations. The overarching research question was formulated as follows:
How do personality characteristics and gender affect the outcomes of different types of e-negotiations?
Figure 1 depicts our research model. We compared a rich and synchronous communication medium (i.e., video chats) and a low richness/synchronous communication medium (i.e., text chats). While video chats are close to F2F negotiations (Mennecke et al., 2000), text chat drastically reduces available information and can thus be considered a different setting. A negotiator who is a good fit for video chats could be a poor fit for text chats, and vice versa.
The most widely accepted measure of personality is the five-factor model (Big 5) of personality (Judge and Ilies, 2002). The five factors are extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and openness (McCrae and Costa, 1987). Personality traits have been shown to affect job performance in that conscientiousness and neuroticism significantly predict job performance (Hurtz and Donovan, 2000). In negotiation research, evidence on the influence of individual factors on negotiation has been mixed (Pruitt and Carnevale, 1993). Although studies have shown the impact of the Big Five personality traits on preferences for negotiation styles (Antonioni, 1998), individual factors have long been assumed not to have a significant impact on negotiation outcomes, leading to an “irrelevance consensus” (Sharma et al., 2013). Sharma et al. (2013) refuted the irrelevance consensus and uncovered the impact of five personality constructs (cognitive ability, emotional intelligence, creativity, personality traits, and attitudes) on economic and subjective negotiation outcomes in a meta-study. In addition, these five personality traits have been found to have a significant impact on cooperative behavior and subjective value but not economic negotiation outcomes (Sharma et al., 2013). This finding partly contradicts the results of other studies; for example, Sass and Liao-Troth (2015) found a positive correlation between personality and negotiation outcomes in distributive negotiations but no effect in integrative and compatible negotiations. In addition, Le and Jang (2023) found that individual factors (gender and personality) do influence the negotiation planning phase. The authors found that agreeableness predicted persistence in search when the search space was large and that women spend more time on the task, and looked more for relationship and value creating information. These results indicate that personality influences negotiation outcomes, but the conditions under which personality traits play a role are not yet fully understood. In the following sections, we review previous findings on each element of the five-factor model of personality and explain our research hypotheses, which concern the impact of each factor on negotiation outcomes and mediators.
To limit complexity, we concentrated on aspects for which we expected to observe differences between the two negotiation media chosen for this study.
Extraverts are described as sociable, self-confident, active, talkative, assertive, energetic and optimistic (Borkenau and Ostendorf, 2008). Extraverts like to be part of groups or other social encounters. By contrast, introverts prefer to be alone but are not necessarily afraid of social interactions. One of the earlier studies that confirmed the effect of personality in negotiations was conducted by Barry and Friedman (1998). The authors found that extraversion was a liability in distributive bargaining, but it had no impact on integrative settings. This finding aligns with the strategies needed to solve different tasks: sharing information might harm distributive negotiations, but it is essentially required in integrative negotiations. In addition, Antonioni (1998) reported an association between extraversion and an integrating style. A later study on individual differences (Elfenbein et al., 2008) did not report a relationship between extraversion and negotiation outcome even though the study used the New Recruit case (Neale, 1997). The New Recruit case is a commonly used case in negotiation research (e.g., Kray and Haselhuhn, 2007; Overbeck et al., 2010; Curhan et al., 2010; Swaab et al., 2011) and can be considered a mixed-motive negotiation task in which communication is key to a good performance. In addition, the authors reported a significant and positive relationship between extraversion and the subjective value of the negotiation. The above effects were replicated in a meta-study by Sharma et al. (2013), who showed that extraversion was associated with cooperative tendencies and a higher subjective value for the negotiator. In other words, extraversion positively predicted subjective value in integrative settings and negatively predicted individual profit in distributive settings. In addition, the authors found support for the idea that extraversion predicts higher negotiation performance in field studies with supervisor ratings.
Regarding different media, previous research has shown that extraversion is a significant predictor of a preference for richer negotiation media (Hertel et al., 2008; Dunaetz et al., 2015). This preference could be considered a first indicator of fit in that if a negotiator prefers a medium this translates to better performance. Moreover, Blau and Barak (2012) showed that extraversion drives anticipated and actual participation in online group discussions. Furthermore, actual participation was lower than in audio and F2F negotiations. If these findings are transferrable to a negotiation setting, we would expect extraverts to engage in greater information exchange and in turn achieve better negotiation outcomes than introvert negotiators, as this strategy is required in integrative negotiations. However, this effect was expected to be more pronounced in video settings, as per Blau and Barak (2012); thus, extraverts were expected to be a better fit for video settings than for chat settings, which is formulated in our first hypothesis:
H1a: Extraversion is positively associated with economic negotiation outcomes in video and chat negotiations, with a greater effect in video negotiations.
In addition, we also expect extraversion to drive positive affect. Extraversion has been shown to be positively correlated with positive affect (McNiel and Fleeson, 2006). Thus, we expected extraverted participants to have a generally higher positive affect than introverted participants. In addition, in line extraverts’ preference for higher richness media (Hertel et al., 2008, Dunaetz et al., 2015), the correlation between extraversion and positive affect was expected to be stronger in video negotiations.
H1b: Extraversion is positively associated with positive affect in video and chat negotiations, with a greater effect in the video negotiations.
Furthermore, extraversion is associated with higher goal-setting motivation (Judge and Ilies, 2002). In addition, a meta-study showed that extraversion was associated with both achievement goals and goal orientation (McCabe et al., 2013). Therefore, we predicted that extraverts set higher goals in general but that this effect would be more pronounced in the video condition due to their preference for this medium.
H1c: Extraversion is positively associated with aspirations in video and chat negotiations, with a greater effect in the video negotiations.
The above preference was also expected to be valid for the number of spoken words in negotiations. Thus, we expected extraverts to speak more than introverts in negotiations. This assertion has empirical support; Mehl et al. (2006) investigated the impact of personality characteristics on the use of language. Extraversion was found to predict a higher number of spoken words. Smolensky et al. (1990) showed a similar effect for a problem-solving task and the variable of uninhibited speech. These results, in combination with Blau and Barak (2012) findings about higher participation, led us to expect that the association between extraversion and number of spoken words would be less pronounced in a chat setting.
H1d: Extraversion is positively associated with the number of spoken words in video and chat negotiations, with a greater effect in the video negotiations.
The openness scale measures interest in and time spent on new experiences and impressions (Borkenau and Ostendorf, 2008). Open individuals are intellectual, open to experimentation, and interested in art. This leads to experimentation with new experiences and independent reflection on those experiences. A low openness score indicates a preference for known and proven behaviors. Openness has been found to predict subjective value for the negotiator and cooperative tendencies (Elfenbein et al., 2008). However, Elfenbein et al. (2008) did not uncover any impact on objective outcomes. In online settings, openness has been associated with a cooperative strategy in integrative negotiations (Falcão et al., 2018). A preference for experimentation was also documented by Nov and Ye (2008), who reported that personal innovativeness in IT (information technology) is driven by openness. Thus, we might expect open negotiators to approach unusual negotiation medium more openly and thus perform better. LePine et al. (2000) contributed the adaptability perspective and showed that openness drives adaptability and, in turn, performance in tasks that require adaptability. We argue that chat negotiations require a great deal of adaptability, as they require negotiators to change their approach and first probe how this new medium works. We argue that this openness is not needed for a video negotiation as this mode is very close to a face-to-face negotiation as both visual and audio channels are available. A chat negotiation significantly alters the way to negotiate. In summary, we predicted that negotiators with a high level of openness have a good fit with chat negotiations and will thus have higher economic outcomes than negotiators low on the openness trait. In line with previous results on openness, we did not expect this factor to have any other effects, leading to our hypothesis 2.
H2: Openness is positively associated with negotiation outcomes in chat negotiations.
Agreeableness mainly concerns interpersonal behavior (Borkenau and Ostendorf, 2008). Altruism lies at its core; agreeable individuals interact with others with understanding, goodwill, and compassion. They tend to cooperate and to give in and favor harmony in their relations. Barry and Friedman (1998) argued that agreeable negotiators are at a disadvantage in distributive negotiation settings, which they empirically confirmed. However, Elfenbein et al. (2008) did not find any effect of agreeableness on outcomes in an integrative simulation. This is in line with Barry and Friedman (1998) reasoning that the disadvantage only applies in distributive situations. An online simulation also confirmed that agreeable negotiators exhibited lower performance in distributive settings (Falcão et al., 2018). Furthermore, Elfenbein et al. (2008) found that agreeableness positively affects the negotiator’s subjective value. This was confirmed in a meta-study, which found that agreeableness drove cooperative tendencies and subjective value (Sharma et al., 2013). In field studies with supervisor ratings, the authors found support for the impact of agreeableness on negotiation performance. Dimotakis et al. (2012) strengthened this argument by showing that a good fit (e.g., agreeable negotiators in integrative settings) predicts the physiological, psychological, and behavioral activation of negotiators, which in turn leads to better economic outcomes. Based on the above findings, we expected to find no differences in negotiation outcomes by medium. However, agreeableness does predict medium preference for high richness media (Dunaetz et al., 2015). If agreeableness does not lead to a performance difference, it well could affect attitudes and behaviors. As agreeableness is based on interpersonal behavior, the reduced interpersonal component caused by a chat negotiation could indeed reduce the need to be agreeable compared to video negotiations. In general, agreeableness is associated with higher negative affect (Côté and Moskowitz, 1998). In our study, negative affect was only relevant to the video condition due to a higher social interaction component. Thus, we only expect agreeableness to influence affect in the video negotiations.
H3a: Agreeableness predicts negative affect in video negotiations only.
In addition, we expected agreeableness to influence negotiators’ aspirations in different ways in the chat and video conditions. Negotiators were expected to reduce their aspirations to “price in” concessions (increase aspirations to have negotiation leeway) that they had to make in favor of the relationship in video negotiations. This was not expected to be the case in the chat negotiations, as no relationship had to be maintained.
H3b: Agreeableness is negatively associated with aspirations in video negotiations only.
The neuroticism scale captures individual differences in emotional stability and emotional lability (Borkenau and Ostendorf, 2008). Individuals with a high level of neuroticism tend to be concerned, insecure, ashamed, or anxious. They have a lower ability to control their needs compared to individuals with low neuroticism. By contrast, individuals with low neuroticism are relaxed, balanced, and stable even in stressful situations. A low level of neuroticism has been found to predict job performance (Hurtz and Donovan, 2000) but has a lower impact on job performance than conscientiousness. Elfenbein et al. (2008) showed that neuroticism negatively impacts subjective value for the negotiator. Sharma et al. (2013) found that lower neuroticism is associated with negotiation performance in field studies with supervisor ratings. In an online setting, Falcão et al. (2018) also found that negotiators with higher levels in neuroticism achieved lower negotiation outcomes in distributive settings. These results, in addition to Elfenbein et al. (2008) finding that there is no correlation between neuroticism and economic outcomes in integrative negotiations, hint toward that neuroticism May have a contextual effect on negotiation outcomes. Therefore, the negotiation medium May play a role. Since neuroticism has a high social component, chat negotiations May better fit for neurotic negotiators, as they are often perceived as less threatening. This reasoning is in line with Hertel et al. (2008) finding that neuroticism predicts anxiety, which in turn predicts a preference for less rich media. The authors also showed that these effects are moderated by how threatening the situation was perceived; thus, this finding is particularly relevant for social conflicts. A preference for less rich media was also supported by Amichai-Hamburger et al. (2002), who found that neurotic persons more frequently positioned their “real me” (measuring where participants are more themselves: chat vs. F2F) in chat communication. This positioning of the “real me” indicates that there is a preference and potential fit with neuroticism and chat negotiations. Based on these relationships, we expected that neuroticism would drive negative affect to a higher extent in video negotiations than in chat negotiations.
H4a: Neuroticism is positively associated with negative affect in video and chat negotiations, with a greater effect in the video negotiations.
In the same manner, chat negotiations were expected to reduce the negative impact of neuroticism on subjective value. This expectation was consistent with the findings of Elfenbein et al. (2008).
H4b: Neuroticism is negatively associated with subjective value in video and chat negotiations but to a lower extent in chat negotiations.
Conscientiousness is related to self-control in terms of planning, organizing, and completing tasks (Borkenau and Ostendorf, 2008). Individuals with a high conscientiousness score are goal-oriented, ambitious, enduring, hard-working, systematic, orderly, and punctual. A low conscientiousness score indicates carelessness, half-heartedness, and inconsistency. Conscientiousness was confirmed to have the highest impact on job performance in a meta-study (Hurtz and Donovan, 2000). However, in the context of negotiation, Sharma et al. (2013) meta-study did not reveal any influence of conscientiousness on outcome variables. The authors referred to a “performance paradox”: conscientiousness has high predictive validity for job performance, but negotiations are not impacted. Similarly, Barry and Friedman (1998) did not find that conscientiousness had any impact on bargaining success. Although Elfenbein et al. (2008) confirmed that conscientiousness did not have an effect on negotiation success, they found that it had predictive validity for the negotiator’s subjective value. With regard to negotiation media, Dunaetz et al. (2015) found that conscientiousness did not predict media preference. Thus, we did not hypothesize that conscientiousness would influence the two negotiation media examined in this study.
Gender has been found to significantly influence negotiation performance. For example, in a meta-study, Stuhlmacher and Walters (1999) found that women achieved significantly lower negotiation outcomes than men. In a later publication, they summarized the mechanisms of this effect: women adopted a different negotiation approach due to the influence of their negotiation counterpart’s expectations (Stuhlmacher et al., 2007). The authors called this a “social role effect” and theorized that the negotiator’s expected role influenced women’s behavior. Stuhlmacher and Walters (1999) also theorized that online media mitigated this effect and found that female negotiators were more hostile in virtual negotiations compared to F2F. In addition, they found that women performed better in virtual negotiations than in FTF negotiations. If greater distance and lower media richness equalized negotiation outcomes across genders, we expected that women would have an advantage in chat negotiations.
H5a: Gender is associated with negotiation outcomes, with women achieving inferior results than men in video negotiations but not in chat negotiations.
In addition, the social role effect was expected to influence affect. In a negotiation, a poor fit between the negotiator and their social role was expected to be associated with a lower positive affect and a higher negative affect. However, this effect was expected to be less pronounced if social cues are filtered out in chat negotiations.
H5b: Female negotiator gender is positively associated with negative affect but to a lesser extent in chat negotiations than in video negotiations.
H5c: Female gender is negatively associated with positive affect but to a lesser extent in chat negotiations than in video negotiations.
Finally, men have been found to be generally more talkative than women (Leaper and Ayres, 2007). This could also be related to the social role theory (Stuhlmacher et al., 2007), as women May talk less to conform to social expectations (i.e., being more passive in negotiations). Again, if richness is reduced, the requirement to act according to act congruent to expectations is decreased.
H5d: Female negotiator gender is negatively associated with number of spoken words but to a lesser extent in chat negotiations than in video negotiations.
In the previous paragraphs, we focused on the relationships for which we expect the medium to make a difference between predictors and outcomes as well as mediators. For the effect of mediators on outcomes, we can adopt a more general perspective as no differential effects of the mediators per medium were expected.
Although the two dimensions of affect appear to be correlated, positive and negative affect are distinctive dimensions of emotion (Watson et al., 1988). Positive affect is characterized by high energy, full concentration, and pleasurable engagement, whereas negative affect is a general dimension of subjective distress and unpleasurable engagement (Watson et al., 1988).
Multiple studies have shown that affect influences negotiation outcomes. Forgas (1998) reported that a positive affect leads to more cooperative behavior and thus better outcomes, while negative affect leads to a more competitive strategy. Carnevale and Isen (1986) showed that positive affect leads to lower use of contentious tactics and more joint benefits of the negotiation dyad. In addition, Kramer et al. (1993) confirmed that positive affect leads to greater confidence and a more positive evaluation of outcomes. The authors also reported that positive affected led to better economic outcomes. The impact of positive and negative affect was replicated in a meta-analysis by Sharma et al. (2013), who reported a positive correlation between positive affect and individual economic outcomes, a positive correlation between positive affect and subjective value, and a negative correlation between negative affect and subjective value. We expected to replicate these effects in our experiment. Specifically, positive affect was expected to support the integrative negotiation process and the subjective value for negotiators, while negative affect was expected to have the opposite effect.
H6a: Positive affect is positively associated with economic outcomes in both media.
H6b: Positive affect is positively associated with subjective value in both media.
H6c: Negative affect is negatively associated with economic outcomes in both media.
H6d: Negative affect is negatively associated with subjective value in both media.
Previous studies have demonstrated that aspirations influence economic outcomes in negotiations. In a meta-analysis, Zetik and Stuhlmacher (2002) reported a correlation between aspirations and economic outcomes. In addition, this effect was stronger non-F2F negotiations. Thompson (1995) also demonstrated the effect of aspirations and discovered that higher aspirations led to more demands from negotiators. Accordingly, we also expected to replicate this aspiration effect in the current study.
H7a: Aspirations are positively associated with economic outcomes to a greater extent in chat negotiations than in video negotiations.
In addition to economic outcomes, Thompson (1995) showed that aspirations influence subjective evaluations of success. Low aspirations led to higher perceived success for negotiators. This is intuitive, as more ambitious goals are more difficult to achieve or exceed. Thus, we expected that aspirations influence both economic and subjective outcomes.
H7b: Aspirations are negatively associated with the subjective evaluation of negotiation.
In an earlier study, Thompson (1991) showed that information exchange is an important driver of negotiation success, even if only one party shares information. This effect was replicated in later studies. Kemp and Smith (1994) showed that exchange in integrative negotiations was associated with higher profits. In line with these findings, Butler (1999) found in an experiment that the quantity of information had a significant and positive effect on the negotiators’ climate of trust, logrolling, and expenses.
Since the negotiation task used in this study was mainly integrative in nature and required participants to share information, we expected that a higher number of words spoken would lead to better agreements.
H8a: A higher word count leads to higher individual profits in both media.
Regarding subjective evaluations of the negotiations, an intuitive assumption is that greater exchange would lead to higher satisfaction among negotiators. However, some studies have shown the opposite effect. For instance, Naquin (2003) demonstrated that a higher number of negotiable issues lead to lower satisfaction. The author also found that counterfactual thoughts about the performance (i.e., negotiators thought a better agreement was possible) led to lower observed satisfaction. In another study that compared counterfactual thoughts across communication media, Ow et al. (2014) showed that use of technology reduced counterfactual thoughts.
H8b: A higher word count leads to lower satisfaction in both media, with a lower effect in chat negotiations than in video negotiations.
Oliver et al. (1994) showed that the economic outcomes of negotiations predict satisfaction. However, Wang et al. (2010) were unable to replicate this effect in a negotiation support system (NSS) negotiation. In their study, individual outcomes were only correlated with satisfaction if paired with the negotiator’s objectives. Thus, there is some support for the hypothesis that outcomes become less important in low richness media.
H9: Economic outcomes are positively associated with subjective value in video negotiations only.
A summary of the hypotheses can be found in Table 1.
The study was conducted at the laboratory for experimental research of a German university. Participants were compensated EUR 15 each for their participation in the simulation. In addition, students from two negotiation seminars (n = 11) participated in the study at the beginning of their seminar. Since the simulation was conducted before the lectures, these students were comparable with the subject pool from the laboratory. A total of 187 individuals (nfemale = 102, nmale = 85) participated in the negotiation simulation and generated valid data. We had to remove one incomplete dataset as the participant did not complete the post-negotiation survey and this led to the uneven number. Their ages ranged from 17 to 60 years (M = 23.6, SD = 5.2). Random treatment assignment resulted in the following division: a total of 96 (nfemale = 57, nmale = 39) individuals were assigned to the video treatment, while 91 individuals (nfemale = 45, nmale = 46) were assigned to the chat condition.
For the simulation task, we chose the Sahara Sun case developed by Geiger and Hüffmeier (2020). This task resembles the New Recruit negotiation case (Neale, 1997), which is frequently used in negotiation research. The detailed case instructions can be found in the Appendix. We used the Sahara Sun case because it was tested in German and not as widely known as the New Recruit case. In the task, a plant construction firm called Solartechnik GmbH (seller) negotiates with a plant operator, Sahara Sun AG (buyer). The negotiation issue is a solar thermal power plant in the Sahara Desert. The case encompasses distributive items (one party gains, the other loses), integrative items (more value to either the buyer or the seller), and aligned items (same value for the buyer and the seller).
The participants were invited to join online experiment sessions via email and registered via the experiment organization software ORSEE (Greiner, 2015). The data protection declaration was referenced in the invitation, and participants were informed that they consented to video recording by registering for the experiment. Participants took part in the experiment online and not at the laboratory due to the COVID-19 restrictions that were in place at the time of the study. Before the experiment began, the participants were invited to a short briefing session to ensure that the equipment functioned correctly. Then, they received a link and were randomly assigned to groups of two and a negotiation media. The experiment itself was programmed in oTree (Chen et al., 2016). For the chat negotiation, we used the oTree chat functionality and the video negotiation was implemented using the Daily Video Client.1 The simulation began with survey pages and descriptions of the roles, which included a short summary of the roles and the payoff matrix (showing which negotiation outcomes lead to which individual profits). After both parties completed the instructions, the negotiation page was displayed. On it, participants saw either a text chat or a video chat interface alongside the negotiation issues and related payoffs. The payoffs were associated with the items to be negotiated and displayed as radio buttons to enable participants to negotiate and document the results on the same page. Negotiation time was limited to 30 min in the video condition and 40 min (33% more time) in the chat condition, as participants had to read and write messages. The practice of allowing more time for chat negotiations is in line with previous research (Damen et al., 2020). All participants had 5 min of setup time to familiarize themselves with the system and their counterpart. After the negotiations ended, participants were prompted to complete a post-negotiation questionnaire and a demographics questionnaire. The detailed experiment flow with screenshots can be found in the Appendix.
To measure personality traits, the German version of the NEO-FFI questionnaire (Borkenau and Ostendorf, 2008) was used at the beginning of experiment. The 60-item scale measures individual characteristics of personality on a five-point scale ranging from 0 (strong disagreement) to 4 (strong agreement) and yields a single value per characteristic.
Gender was captured in the demographics section of the survey.
To measure the mediating variable of affect, we used the German version of the positive and negative affect scale PANAS (Watson et al., 1988; Breyer and Bluemke, 2016). The 20-item questionnaire was displayed after the role descriptions, and participants were asked to evaluate how they felt about the impending negotiation. The negotiation medium was displayed both at the beginning of the survey and in the role instructions to ensure that participants knew which negotiation medium they would use. Items on the PANAS scale range from 1 (not at all) to 5 (extremely), and separates score were calculated for positive affect and negative affect.
The negotiators’ aspirations were collected after the participants read the role instructions. Participants reported their aspiration out of a maximum of 22,400 points that can be achieved in the Sahara Sun case.
The outcome variables were the negotiators’ individual profitsand the negotiators’ subjective value. The negotiation profit was derived from the negotiated items ranging from 0 to 22,400 points per role. If no agreement was reached, the data was excluded from the analysis (n = 13, odd number due to one participant’s incomplete response).
Subjective value was measured using the subjective value inventory (SVI; Curhan et al., 2006). The SVI features 16 items across four categories: feelings about the instrumental outcome, feelings about oneself, feelings about the process, and feelings about the relationship. Scale items range from 1 (not at all) to 7 (a great deal). For this research, we used the single global subjective value item, which was calculated based on outcomes from all four categories.
Before the model estimation, we calculated descriptive statistics. The results are presented in Table 2.
Group differences in the outcome variables (video negotiations versus chat negotiations) can be found Table 3. A Wilcoxon rank sum test was performed to investigate the significance of these group differences. The negotiators’ individual profits were not significantly different (w = 4,551, p = 0.698) across groups. The video group exhibited higher subjective value (M = 4.021, SD = 0.496) than the chat group (M = 3.723, SD = 0.618; w = 3,095, p = 0.000). Regarding positive affect, the chat group demonstrated higher positive affect (M = 3.199, SD = 0.638) than the video group (M = 2.985, SD = 0.689; w = 5,187, p = 0.027). Negative affect and aspirations were not significantly different in the two groups. As expected, the word count was significantly higher in the video group (M = 870, SD = 530) than in the chat group (M = 280, SD = 130; w = 814, p = 0.000). Standard deviations in word count were notably high (cvVideo = 60.9, cvChat = 46.3).
To test the hypotheses, we estimated a structural equation model (SEM) with the LAVAAN package from the statistical software suite R (Rosseel, 2012). In the next section, we first discuss the overall model validity, then proceed to hypothesis testing.
We modeled both direct and mediated paths to profits and subjective value, as per the hypotheses (see Appendix for full model details). The variables of profit, word count, and aspirations were mean centered to enable SEM estimation. We used the robust MLM estimator due to the non-normality of some mediator and outcome variables. The model test statistic was 40.985, with 46 degrees of freedom (p = 0.682); thus, it was significantly different from the baseline model, and we could proceed to evaluate fit statistics. To evaluate fit, we used the comparative fit index (CFI), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), and standardized root mean square residual (SRMR). For CFI and TLI, Hu and Bentler (1999) recommended a cutoff of 0.95 in combination with an SRMR cutoff of 0.09. For RMSEA, the authors recommended <0.05. This is in line with MacCallum et al. (1996) recommendations; they proposed that <0.01 is an excellent fit, < 0.05 is a good fit, and < 0.08 is a mediocre fit. Our model exhibited a good fit (χ2 = 40.985, CFI = 1.000, TLI = 1.071, RMSEA = 0.000, and SRMR = 0.05). In addition, we verified that the model was significantly different for the two groups by restricting the model path coefficients and intercepts to equality. Therefore, we ran the same model with equality constraints on regression coefficients and intercepts. The resulting model exhibited reduced fit (χ2 = 80.289 at p = 0.146, CFI = 0.869, TLI = 0.826, RMSEA = 0.045, and SRMR = 0.076). However, the main utility of this second model was that it enabled a comparison with the unconstrained model. The ANOVA test revealed a significant difference [Δ χ2 (22) = 44.213, p = 0.003]. Therefore, we concluded that the group difference in model fit was significant and that a group-wise analysis was meaningful. The detailed model outcomes for the two groups are shown in Figures 2, 3.
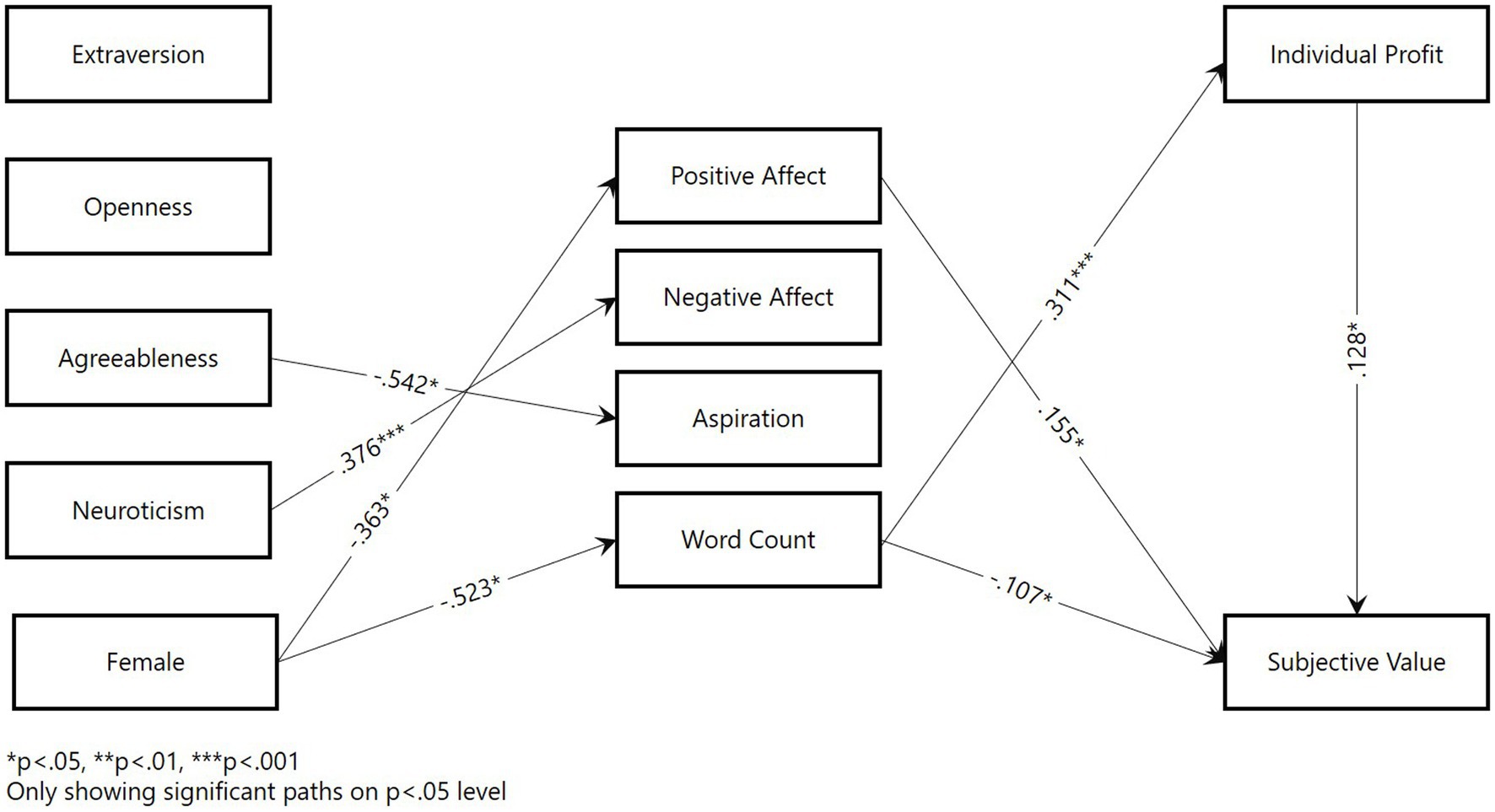
Figure 2. Structural equation model results for video condition. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Figure only shows significant paths below the p < 0.05 level.
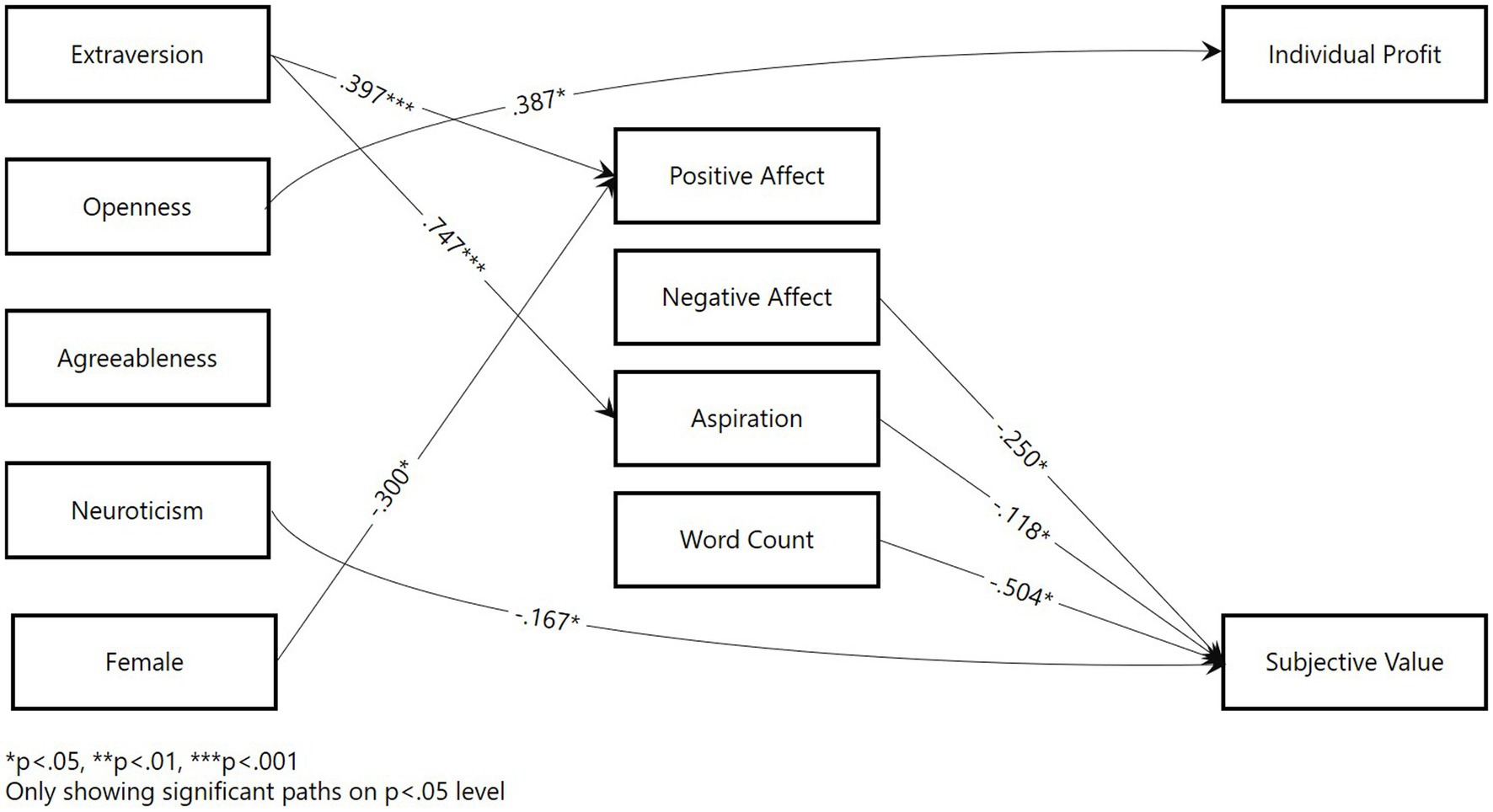
Figure 3. Structural equation model results for chat condition. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Figure only shows significant paths below the p < 0.05 level.
According to H1a, extraverted negotiators were expected to have a greater advantage in video settings compared to individuals low on extraversion. However, the analysis did not show any association between extraversion and the economic outcomes of the negotiations. In the video negotiations, this effect fell narrowly short of the required significance level of 5% (b = 0.552, SE = 0.295, p = 0.064). Thus, H1a was rejected.
According to H1b, we predicted an association between extraversion and positive affect. The analysis showed that extraversion had a positive effect in chat negotiations (b = 0.394, SE = 0.106, p = 0.000). However, no significant relationship was identified in the video condition. Thus, this hypothesis was only partly supported.
Regarding aspirations (H1c), we identified a similar pattern as positive affect. Extraversion predicted aspirations in chat negotiations (b = 0.747, SE = 0.176, p = 0.000), but no significant effect was found for video negotiations. Thus, only partial support was found for H1c.
Finally, no association between extraversion and word count (H1d) was identified.
Under H2, we predicted a positive association between openness and economic outcomes in chat negotiations. This hypothesis was confirmed, as a significant correlation was found (b = 0.287, SE = 0.172, p = 0.024).
Under H3a, we predicted that agreeableness would be related to negative affect in video negotiations only. This hypothesis was rejected, as no significant association was identified. However, in video negotiations, this effect was only slightly above the 5% significance level (b = −0.542, SE = 0.076, p = 0.066).
Furthermore, we expected agreeableness to be associated with lower aspirations in the video condition only (H3b). This hypothesis can be confirmed (effect size of b = −0.552, SE = 0.217, p = 0.012), with no significant effect found in the chat condition.
Neuroticism was expected to drive negative affect in both negotiation media, but it was predicted to have a lower impact in chat negotiations (H4a). We found that neuroticism had a significant effect on negative affect in video negotiations (b = 0.376, SE = 0.076, p = 0.000). However, no significant effect was found in chat negotiations. Thus, H4a was partially supported.
Hypothesis 4b was rejected, as the results were contrary to our prediction. Neuroticism decreased subjective value in chat negotiations (b = −0.167, SE = 0.079, p = 0.034).
Under H5a, we expected to replicate the effect of gender on economic outcomes in video negotiations only. However, this effect fell below the 5% significance level for both media. Thus, H5a was rejected.
In addition, contrary to H5b, the effect of gender on negative affect was not significant at the 5% level.
However, the predicted association between female gender and positive affect showed the predicted effects (H5c). In both video negotiations (b = −0.363, SE = 0.142, p = 0.011) and chat negotiations (b = −0.300, SE = 0.120, p = 0.013), being a woman was associated with lower positive affect. In addition, the coefficient was lower for the chat condition. These results support H5c.
Under the last gender-related hypothesis (H5d), we expected women to exhibit a lower word count in negotiations but that this effect would be weaker in chat negotiations. The analysis provided partial support for this hypothesis, as being a woman was significantly associated with word count in video negotiations (b = −0.523, SE = 0.239, p = 0.028) but not chat negotiations.
We expected positive affect to be positively associated with negotiation outcomes (H6a) and subjective value (H6b) across both media. However, positive affect was only significantly associated with subjective value in video negotiations (b = 0.155, SE = 0.063, p = 0.013). This led to the rejection of H6a and provided partial confirmation of H6b, as the effect was only found in one medium.
With regard to negative affect, we predicted a negative relationship between negative affect and economic outcomes (H6c) and subjective outcomes (H6d) in both media. However, the model only revealed a negative correlation between negative affect and subjective outcomes in the chat condition (b = −0.250, SE = 0.108, p = 0.020). The other relationships were not significant. Thus, we found only partial support for H6d and rejected H6c.
We expected aspirations to have a positive impact on economic outcomes (H7a) and a negative impact on subjective outcomes (H7b). However, we found limited support for these hypotheses, as aspirations only predicted lower subjective outcomes in chat negotiations (b = −0.118, SE = 0.056, p = 0.035). All other hypothesized associations were not significant. Thus, only partial support was found for H7b, and H7a was rejected.
Under H8a, we expected word count to predict higher economic outcomes. This effect was confirmed for video negotiations only (b = 0.311, SE = 0.074, p = 0.000), which partially confirmed H8a.
According to H8b, we expected a negative association between word count and subjective value based on counterfactual thoughts. We confirmed this effect for both video negotiations (b = −0.107, SE = 0.044, p = 0.016) and chat negotiations (b = −0.504, SE = 0.213, p = 0.018). However, only partial support was found for H8a, as the effect was higher in chat negotiations; this ran counter to our prediction.
Finally, we predicted that economic outcomes would drive subjective outcomes in video negotiations only (H9). This effect was found to be significant in video negotiations (b = 0.128, SE = 0.053, p = 0.014) but not in chat negotiations and thus, Hypothesis 9 is confirmed.
An overview of the findings related to the hypotheses is shown in Table 4.
In addition to testing the hypothesized relationships, we also estimated a model with all possible paths to uncover additional effects (see Appendix 2). In addition to the abovementioned effects, we found additional effects for conscientiousness. Conscientiousness was found to predict both subjective value (b = −0.385 at p = 0.015) and negative affect (b = −0.377 at p = 0.001) in chat negotiations.
The main goal of this study was to determine whether there is an individual x negotiation medium fit. The results confirmed that individual factors had differential impacts on behaviors and outcomes depending on the negotiation medium. In video negotiations, being a woman significantly predicted lower negotiation outcomes. In chat negotiations, openness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion predicted negotiation outcomes. However, most hypothesized effect could not be confirmed. We conclude that individual factors have a limited interaction with the investigated e-negotiation media. This integrates well with the existing literature on the impact of individual factors in negotiations.
Further, although we replicated several previous findings from the literature, our results are also partly contrary to previous findings and not in line with our hypotheses. Even though we uncovered that there is an individual x medium fit, it seems that additional boundary conditions are yet to be explored to disentangle the effects of individual factors. In the following sections, we discuss the findings according to each factor.
We predicted that personality-driven medium preferences would affect economic outcomes. Our rejection of H1a aligns with previous null-results on extraversion (Elfenbein et al., 2008) but conflicts with the results of Sharma et al. (2013) meta-study, which reported that extraversion had a significant effect on economic outcomes. Koole et al. (2001) findings May provide some insight, as the authors found that extraversion was negatively associated with cooperation, which is key to integrative negotiations. On this front, Sharma et al. (2018) provided conflicting results, as they found that extraversion is associated with cooperative tendencies. However, the 5% significance level for video negotiations was only marginally missed and further investigation seems to be warranted.
In addition, the results on positive affect and aspirations only partly aligned with our expectations. Because we hypothesized that extraverts would be a better fit for video negotiations compared to individuals low in this trait, we predicted a higher positive association between extraversion and aspirations in video negotiations. However, extraversion only predicted positive affect and aspirations in chat negotiations. The root cause of this observed effect is yet to be understood.
Finally, we rejected the hypothesis that extraverts use more words in negotiations compared to introverts. This counterintuitive finding May be related to the possibility that extraversion is relevant to the content of conversations (e.g., more open exchanges), not word count itself.
Thus, extraversion does not appear to play a significant role in differences between negotiation media.
As expected, openness was significantly associated with higher negotiation outcomes in chat negotiations. The fact that no association was found in video negotiations was in line with previous findings (Elfenbein et al., 2008). Thus, the positive association found in chat negotiations May indicate an isolated personality x medium fit in new negotiation media. However, this May also mean that this advantage will diminish over time as “uncommon” media become standard. Since this finding constitutes first evidence on the effects of openness, replication and further studies are required to substantiate these effects. However, this finding is notable, as openness was not yet found to play a role in predicting negotiation behavior and outcomes in previous literature; chat negotiations seem to make this trait relevant.
No association between agreeableness and negative affect (H3a) was observed in the data, and agreeableness generally did not appear to not drive affect. This partly contradicts the results of Dimotakis et al. (2012), which found that agreeableness predicted psychological arousal in integrative negotiations. Furthermore, we were unable to replicate the effects of agreeableness on economic and subjective outcomes in the full analysis (Appendix 2). However, H3b was confirmed, as agreeableness was only associated with lower aspirations in video negotiations. This could mean that negotiators adjust their aspirations according to expectations of different media, which would be another type of fit.
Neuroticism predicted negative affect in video negotiations. Notably, it was not correlated with chat negotiations; thus, this disadvantage seemed to be neutralized in a less rich media. This seems logical, as chat settings are less threatening due to their lower richness. Thus, neurotic negotiators seemed to have a better fit with chat negotiations. However, subjective value was found to be negatively affected by neuroticism in chat negotiations, which conflicts with the findings of Elfenbein et al. (2008) despite the use of a negotiation case with similar underlying logic. However, since Elfenbein et al.’s study was conducted in an F2F setting, the online setup in this study May explain the lack of significance in the correlation of neuroticism and subjective value.
At first, we were unable to directly replicate the effect of gender on economic negotiation outcomes (H5a). Contrary to the hypothesis, it fell slightly below the 5% significance level for chat negotiations, and the effect was not significant for video negotiations. However, gender had an indirect effect on economic outcomes via word (H5d). Via this indirect effect, being a woman was associated with lower individual profits in video negotiations, but this effect was absent in chat negotiations. This finding supports our hypothesis that women have an advantage in chat negotiations and extends the literature regarding gender in negotiations with the discovery of an important mechanism. Furthermore, we found that being a woman was associated with a lower positive affect, with a weaker effect in chat negotiations. The results also indicated that women had an advantage in chat negotiations.
We were unable to fully replicate previous findings regarding affect in negotiations. Affect was only found to have an impact on subjective value on the video condition. A possible explanation is that chat negotiations are so content-oriented that any difference in affect would be too weak to make a difference on subjective value. However, we would also expect affect to influence economic outcomes in video negotiations in such cases. Potentially, our case design was responsible for this deviation from the previous findings in the literature.
Against expectations, aspirations mostly did not affect economic and subjective outcomes. The only exception is that aspirations were associated with lower subjective value in chat negotiations. This could be a reason for lower satisfaction with the chat negotiations, but it is unclear why this happened. A potential mechanism is that aspirations have a higher importance in chat negotiations, as relationship goals have lower salience in a low richness medium. Furthermore, a lack of correlation between aspirations and economic outcomes could also be driven by the relatively inexperienced subject pool and the fact that we did not incentivize participants to perform.
A higher word count only predicted higher individual profits in the video condition. The lack of effect in chat negotiations is counterintuitive as more exchange should lead to more value generated in this integrative negotiation. In addition, there is support for the hypothesis that “talking too much” leads to lower subjective value. This effect is more pronounced in video negotiations and May indicate that it is caused by counterfactual thoughts (i.e., “I revealed too much”).
Finally, we observed that an economic outcome drove higher subjective value. However, this effect was only observed in video negotiations. Along with the fact that outcomes were not significantly different between the negotiation media, this missing correlation in the chat negotiation May be attributable to the fact that chat negotiations are already perceived as “so bad” that better outcomes do not balance out this negative evaluation. This finding is highly relevant: if obtaining favorable results in chat negotiations does not result in satisfaction, this could affect future negotiations or even the evaluator’s propensity to engage in future negotiations.
This study had some limitations. First, the research design was complex, as it investigated many factors. Thus, future studies could lower complexity by investigating a limited set of individual factors rather than all five factors of personality and uncover the mechanisms that drive the relationships identified in this study.
Furthermore, the pairing of the dyad could be a relevant factor that influences the results. As this study is an initial investigation of the role of personality, we did not include this additional complexity. A methodology for investigating dyadic pairing would be the actor-partner interdependence model (APIM) (Cook and Kenny, 2005).
In addition, the sample size was at the lower end of what is acceptable for SEM research. Future studies could aim to replicate the findings in a setup that requires lower sample size or simplify the design so that it requires lower sample size.
A further limitation can be seen in the measure of “word count.” Even though the total amount of information exchanged is relevant, further development of the variable might add value. Daly-Jones et al. (1998) studied audio vs. video negotiation and operationalized the spoken words into number of turns, turn length (in words), and number of overlaps. However, these variables are highly related to the word count. However, research in this area seems to be interesting.
Finally, incentivizing participants to achieve better negotiation results May have uncovered effects that would not otherwise be visible (e.g., the nature of the association between aspirations and economic results).
To our knowledge, this study is the first to compare the impact of individual factors on different negotiation media. Therefore, additional research is needed to substantiate the effects presented in this study. In particular, the findings on the role of openness in chat negotiations should be further explored to validate the hypothesized mechanisms. It is necessary to identify additional mediators to explain the mechanisms that underlie the abovementioned effects. In addition, we found first evidence that the number of used words makes a difference in predicting outcomes. Since research on word count is sparse, additional studies are needed to substantiate these promising findings. In addition, further factors could be considered in comparisons of different negotiation media, such as participants’ culture, generation, and occupation. These factors could affect how negotiation media are used, which May in turn influence outcomes.
Finally, developing theory and integrating the above findings into theories like the Communication Orientation Model is required to delineate the currently inconclusive results. Especially the hypothesis that personality could influence the communication orientation is an intriguing possible line of research.
The most relevant advice for practice lies in the few statistically significant results of this article. Negotiators should challenge the intuitive assumption of the role of individual factors in electronic negotiations and put more emphasis on the “classic” ways to improve negotiation results (e.g., information exchange, making first offers etc.) and use them as well in electronic media.
Based on our results, it May be too early to recommend specific negotiation medium according to different individual factors. More research is needed to substantiate the effects presented in the current study. However, it May be beneficial for negotiators to reflect on their personality type and the medium they select for negotiations. In addition, having knowledge on the potential mechanisms of improving outcomes could reinforce helpful behaviors, such as talking more in negotiations.
This study investigated the individual x medium fit hypothesis in negotiations. We confirmed the hypothesis that different individual factors, specifically gender and personality, have differential impacts on video and chat negotiations. The results suggest that the choice of negotiation medium can amplify and reduce the impacts of personal factors. While gender significantly predicted negotiation outcomes in video negotiations, the personality traits of openness, extraversion, conscientiousness, and neuroticism predicted negotiation outcomes in chat negotiations. However, the impact of individual factors is lower than theorized. This research contributes to the field of electronic negotiations by strengthening explanations of how individual factors shape e-negotiations.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
WL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcomm.2024.1402820/full#supplementary-material
1. ^ www.daily.co
Amichai-Hamburger, Y., Wainapel, G., and Fox, S. (2002). “On the internet no one knows I'm an introvert”: extroversion, neuroticism, and internet interaction. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 5, 125–128. doi: 10.1089/109493102753770507
Antonioni, D. (1998). Relationship between the big five personality factors and conflict management styles. Int. J. Confl. Manag. 9, 336–355. doi: 10.1108/eb022814
Arunachalam, V., and Dilla, W. N. (1995). Judgment accuracy and outcomes in negotiation: a causal modeling analysis of decision-aiding effects. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 61, 289–304. doi: 10.1006/obhd.1995.1023
Barkhi, R., Jacob, V. S. F., and Pirkul, H. (1999). An experimental analysis of face to face versus computer mediated communication mediums. Group Decis. Negot. 8, 325–347. doi: 10.1023/A:1008621423120
Barry, B., and Friedman, R. A. (1998). Bargainer characteristics in distributive and integrative negotiation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 74, 345–359. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.74.2.345
Blau, I., and Barak, A. (2012). How do personality, synchronous media, and discussion topic affect participation? J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 15, 12–24.
Borkenau, P., and Ostendorf, F. (2008). Neo-Ffi: Neo-Fünf-Faktoren-inventar nach costa und mccrae, manual.
Breyer, B., and Bluemke, M. (2016). Deutsche version der positive and negative affect schedule Panas. Gesis Panel.
Butler, J. K. (1999). Trust expectations, information sharing, climate of trust, and negotiation effectiveness and efficiency. Group Org. Manag. 24, 217–238. doi: 10.1177/1059601199242005
Carnevale, P. J., and Isen, A. M. (1986). The influence of positive affect and visual access on the discovery of integrative solutions in bilateral negotiation. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 37, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(86)90041-5
Chen, D. L., Schonger, M., and Wickens, C. (2016). oTree—an open-source platform for laboratory, online, and field experiments. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 9, 88–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jbef.2015.12.001
Cook, W. L., and Kenny, D. A. (2005). The actor–partner interdependence model: a model of bidirectional effects in developmental studies. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 29, 101–109. doi: 10.1080/01650250444000405
Côté, S., and Moskowitz, D. S. (1998). On the dynamic covariation between interpersonal behavior and affect: prediction from neuroticism, extraversion, and agreeableness. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 75, 1032–1046. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.75.4.1032
Curhan, J. R., Elfenbein, H. A., and Eisenkraft, N. (2010). The objective value of subjective value: a multi-round negotiation study. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 40, 690–709. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2010.00593.x
Curhan, J. R., Elfenbein, H. A., and Xu, H. (2006). What do people value when they negotiate? Mapping the domain of subjective value in negotiation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 91, 493–512. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.91.3.493
Daft, R. L., and Lengel, R. H. (1983). Information richness. A new approach to managerial behavior and organization design. Texas A and M Univ College Station Coll of Business Administration.
Daly-Jones, O., Monk, A., and Watts, L. (1998). Some advantages of video conferencing over high-quality audio conferencing: fluency and awareness of attentional focus. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 49, 21–58. doi: 10.1006/ijhc.1998.0195
Damen, D., Van Der Wijst, P., Van Amelsvoort, M., and Krahmer, E. (2020). The effect of perspective-taking on trust and understanding in online and face-to-face mediations. Group Decis. Negot. 29, 1121–1156. doi: 10.1007/s10726-020-09698-8
Diener, E., Larsen, R. J., and Emmons, R. A. (1984). Person× situation interactions: choice of situations and congruence response models. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 47, 580–592. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.47.3.580
Dimotakis, N., Conlon, D. E., and Ilies, R. (2012). The mind and heart (literally) of the negotiator: personality and contextual determinants of experiential reactions and economic outcomes in negotiation. J. Appl. Psychol. 97, 183–193. doi: 10.1037/a0025706
Dunaetz, D. R., Lisk, T. C., and Shin, M. M. (2015). Personality, gender, and age as predictors of media richness preference. Adv. Multimed. 2015, 1–9. doi: 10.1155/2015/243980
Elfenbein, H. A., Curhan, J. R., Eisenkraft, N., Shirako, A., and Baccaro, L. (2008). Are some negotiators better than others? Individual differences in bargaining outcomes. J. Res. Pers. 42, 1463–1475. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2008.06.010
Falcão, P. F., Saraiva, M., Santos, E., and Cunha, E. M. P. (2018). Big five personality traits in simulated negotiation settings. EuroMed J. Bus. 13, 201–213. doi: 10.1108/EMJB-11-2017-0043
Forgas, J. P. (1998). On feeling good and getting your way: mood effects on negotiator cognition and bargaining strategies. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 74, 565–577. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.74.3.565
Galin, A., Gross, M., and Gosalker, G. (2007). E-negotiation versus face-to-face negotiation what has changed – if anything? Comput. Hum. Behav. 23, 787–797. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2004.11.009
Geiger, I. (2014). Media effects on the formation of negotiator satisfaction: the example of face-to-face and text based electronically mediated negotiations. Group Decis. Negot. 23, 735–763. doi: 10.1007/s10726-012-9317-3
Geiger, I. (2020). From letter to twitter: a systematic review of communication Media in Negotiation. Group Decis. Negot. 29, 207–250. doi: 10.1007/s10726-020-09662-6
Geiger, I., and Hüffmeier, J. (2020). “The more, the merrier” or “less is more”? How the number of issues addressed in B2B sales negotiations affects dyadic and seller economic outcomes. Ind. Mark. Manag. 87, 90–105. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.02.013
Geiger, I., and Laubert, C. (2018). Situational strategic versus personal influences on negotiation medium choice. Int. J. Confl. Manag. 29, 398–423. doi: 10.1108/IJCMA-06-2017-0054
Geiger, I., and Parlamis, J. (2014). Is there more to email negotiation than email? The role of email affinity. Comput. Hum. Behav. 32, 67–78. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.11.016
Giordano, G. A., Stoner, J. S., Brouer, R. L., and George, J. F. (2007). The influences of deception and computer-mediation on dyadic negotiations. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 12, 362–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1083-6101.2007.00329.x
Greiner, B. (2015). Subject pool recruitment procedures: organizing experiments with Orsee. J. Econ. Sci. Assoc. 1, 114–125. doi: 10.1007/s40881-015-0004-4
Hertel, G., Schroer, J., Batinic, B., and Naumann, S. (2008). Do shy people prefer to send e-mail?: personality effects on communication media preferences in threatening and nonthreatening situations. Soc. Psychol. 39, 231–243. doi: 10.1027/1864-9335.39.4.231
Hu, L. T., and Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 6, 1–55. doi: 10.1080/10705519909540118
Hurtz, G. M., and Donovan, J. J. (2000). Personality and job performance: the big five revisited. J. Appl. Psychol. 85, 869–879. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.85.6.869
Judge, T. A., and Ilies, R. (2002). Relationship of personality to performance motivation: a meta-analytic review. J. Appl. Psychol. 87, 797–807
Judge, T. A., and Zapata, C. P. (2015). The person–situation debate revisited: effect of situation strength and trait activation on the validity of the big five personality traits in predicting job performance. Acad. Manag. J. 58, 1149–1179. doi: 10.5465/amj.2010.0837
Kemp, K. E., and Smith, W. P. (1994). Information exchange, toughness, and integrative bargaining: the roles of explicit cues and perspective-taking. Int. J. Confl. Manag. 5, 5–21. doi: 10.1108/eb022734
Kleshinski, C. E., Wilson, K. S., Derue, D. S., and Conlon, D. E. (2023). Does justice need to be in the eyes of both beholders? Examining face-to-face and virtual Negotiators' interactional justice congruence. Negotiation & Conflict Management Research, p. 16.
Koole, S. L., Jager, W., Van Den Berg, A. E., Vlek, C. A., and Hofstee, W. K. (2001). On the social nature of personality: effects of extraversion, agreeableness, and feedback about collective resource use on cooperation in a resource dilemma. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 27, 289–301. doi: 10.1177/0146167201273003
Kornfield, R., Rae, I., and Mutlu, B. (2021). So close and yet so far: how embodiment shapes the effects of distance in remote collaboration. Commun. Stud. 72, 967–993. doi: 10.1080/10510974.2021.2011362
Kramer, R. M., Newton, E., and Pommerenke, P. L. (1993). Self-enhancement biases and negotiator judgment: effects of self-esteem and mood. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 56, 110–133. doi: 10.1006/obhd.1993.1047
Kray, L. J., and Haselhuhn, M. P. (2007). Implicit negotiation beliefs and performance: experimental and longitudinal evidence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 93, 49–64. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.93.1.49
Kristof-Brown, A. L., Zimmerman, R. D., and Johnson, E. C. (2005). Consequences of Individuals' fit at work: a meta-analysis of person–job, person–organization, person–group, and person–supervisor fit. Pers. Psychol. 58, 281–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.2005.00672.x
Le, D. Q., and Jang, D. (2023). Individual differences and situational constraint predict information search in negotiation planning. Group Decis. Negot. 32, 667–699. doi: 10.1007/s10726-023-09824-2
Leaper, C., and Ayres, M. M. (2007). A meta-analytic review of gender variations in adults' language use: talkativeness, affiliative speech, and assertive speech. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 11, 328–363. doi: 10.1177/1088868307302221
Lepine, J. A., Colquitt, J. A., and Erez, A. (2000). Adaptability to changing task contexts: effects of general cognitive ability, conscientiousness, and openness to experience. Pers. Psychol. 53, 563–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.2000.tb00214.x
Lim, J. (2000). An experimental investigation of the impact of Nss and proximity on negotiation outcomes. Behav. Inform. Technol. 19, 329–338. doi: 10.1080/014492900750000036
Lu, S. C., Kong, D. T., Ferrin, D. L., and Dirks, K. T. (2017). What are the determinants of interpersonal trust in dyadic negotiations? Meta-analytic evidence and implications for future research. J. Trust Res. 7, 22–50. doi: 10.1080/21515581.2017.1285241
Maccallum, R. C., Browne, M. W., and Sugawara, H. M. (1996). Power analysis and determination of sample size for covariance structure modeling. Psychol. Methods 1, 130–149. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.1.2.130
Mccabe, K. O., Van Yperen, N. W., Elliot, A. J., and Verbraak, M. (2013). Big five personality profiles of context-specific achievement goals. J. Res. Pers. 47, 698–707. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2013.06.003
Mccrae, R. R., and Costa, P. T. (1987). Validation of the five-factor model of personality across instruments and observers. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 52, 81–90. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.52.1.81
Mcgrath, J. E., and Hollingshead, A. (1993). Putting the “Group” Back in group support Systens: Some Thepretical issues about dynamic processes in groups with technological enhancements. Group support systems: New perpectives. New York: Macmillan.
Mcniel, J. M., and Fleeson, W. (2006). The causal effects of extraversion on positive affect and neuroticism on negative affect: manipulating state extraversion and state neuroticism in an experimental approach. J. Res. Pers. 40, 529–550. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2005.05.003
Mehl, M. R., Gosling, S. D., and Pennebaker, J. W. (2006). Personality in its natural habitat: manifestations and implicit folk theories of personality in daily life. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 90, 862–877. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.90.5.862
Mennecke, B. E., Valacich, J. S., and Wheeler, B. C. (2000). The effects of media and task on user performance: a test of the task-media fit hypothesis. Group Decis. Negot. 9, 507–529. doi: 10.1023/A:1008770106779
Naquin, C. E. (2003). The agony of opportunity in negotiation: number of negotiable issues, counterfactual thinking, and feelings of satisfaction. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 91, 97–107. doi: 10.1016/S0749-5978(02)00532-0
Neale, M. (1997). New recruit negotiation case. Evanston, IL: Dispute Resolution Research Center, Northwestern University.
Nov, O., and Ye, C. (2008). Personality and technology acceptance: Personal innovativeness in it, openness and resistance to change. Proceedings of the 41st annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences (Hicss 2008), 2008 2008. IEEE, pp. 448–448.
Oliver, R. L., Balakrishnan, P. S., and Barry, B. (1994). Outcome satisfaction in negotiation: a test of expectancy disconfirmation. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 60, 252–275. doi: 10.1006/obhd.1994.1083
Overbeck, J. R., Neale, M. A., and Govan, C. L. (2010). I feel, therefore you act: intrapersonal and interpersonal effects of emotion on negotiation as a function of social power. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 112, 126–139. doi: 10.1016/j.obhdp.2010.02.004
Ow, T. T., O’Neill, B. S., and Naquin, C. E. (2014). Computer-aided tools in negotiation: negotiable issues, counterfactual thinking, and satisfaction. J. Organ. Comput. Electron. Commer. 24, 297–311. doi: 10.1080/10919392.2014.956597
Pruitt, D. G., and Carnevale, P. J. (1993). Negotiation in social conflict. Buckingham: Open University Press.
Purdy, J. M., Nye, P., and Balakrishnan, P. V. (2000). The impact of communication media on negotiation outcomes. Int. J. Confl. Manag. 11, 162–187. doi: 10.1108/eb022839
Rosseel, Y. (2012). Lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling and more. Version 0.5–12 (Beta). J. Stat. Softw. 48, 1–36.
Sass, M., and Liao-Troth, M. (2015). Personality and negotiation performance: The people matter. SSRN Electron. J. 2015:2549992. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2549992
Sharma, S., Bottom, W. P., and Elfenbein, H. A. (2013). On the role of personality, cognitive ability, and emotional intelligence in predicting negotiation outcomes. Organ. Psychol. Rev. 3, 293–336. doi: 10.1177/2041386613505857
Sharma, S., Bottom, W. P., and Elfenbein, H. A. (2018). Predicting negotiation performance from personality traits: A field study across multiple occupations. Hum. Perform. 31:1481407. doi: 10.1080/08959285.2018.1481407
Short, J. A. (1974). Effects of medium of communication on experimental negotiation. Hum. Relat. 27, 225–234. doi: 10.1177/001872677402700303
Smolensky, M. W., Carmody, M. A., and Halcomb, C. G. (1990). The influence of task type, group structure and extraversion on uninhibited speech in computer-mediated communication. Comput. Hum. Behav. 6, 261–272. doi: 10.1016/0747-5632(90)90022-9
Sondern, D., and Hertel, G. (2023). Building negotiator trust through social presence-effects of communication media and information Reprocessability on Trust in Negotiations. Negotiat. Conflict Manag. Res. 16, 290–319.
Stritzke, W. G., Nguyen, A., and Durkin, K. (2004). Shyness and computer-mediated communication: a self-presentational theory perspective. Media Psychol. 6, 1–22. doi: 10.1207/s1532785xmep0601_1
Stuhlmacher, A. F., and Citera, M. (2005). Hostile behavior and profit in virtual negotiation: a meta-analysis. J. Bus. Psychol. 20, 69–93. doi: 10.1007/s10869-005-6984-y
Stuhlmacher, A. F., Citera, M., and Willis, T. (2007). Gender differences in virtual negotiation: theory and research. Sex Roles 57, 329–339. doi: 10.1007/s11199-007-9252-y
Stuhlmacher, A. F., and Walters, A. E. (1999). Gender differences in negotiation outcome: a meta-analysis. Pers. Psychol. 52, 653–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.1999.tb00175.x
Swaab, R. I., Galinsky, A. D., Medvec, V., and Diermeier, D. A. (2012). The communication orientation model: explaining the diverse effects of sight, sound, and synchronicity on negotiation and group decision-making outcomes. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 16, 25–53. doi: 10.1177/1088868311417186
Swaab, R. I., Maddux, W. W., and Sinaceur, M. (2011). Early words that work: when and how virtual linguistic mimicry facilitates negotiation outcomes. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 47, 616–621. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2011.01.005
Tett, R. P., and Burnett, D. D. (2003). A personality trait-based interactionist model of job performance. J. Appl. Psychol. 88, 500–517. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.3.500
Tett, R. P., and Guterman, H. A. (2000). Situation trait relevance, trait expression, and cross-situational consistency: testing a principle of trait activation. J. Res. Pers. 34, 397–423. doi: 10.1006/jrpe.2000.2292
Thompson, L. L. (1991). Information exchange in negotiation. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 27, 161–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-1031(91)90020-7
Thompson, L. (1995). The impact of minimum goals and aspirations on judgments of success in negotiations. Group Decis. Negot. 4, 513–524. doi: 10.1007/BF01409713
Wachter, R. M. (1999). The effect of gender and communication mode on conflict resolution. Comput. Hum. Behav. 15, 763–782. doi: 10.1016/s0747-5632(99)00046-1
Walther, J. B. (1994). Anticipated ongoing interaction versus channel effects on relational communication in computer-mediated interaction. Hum. Commun. Res. 20, 473–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2958.1994.tb00332.x
Walther, J. B., Anderson, J. F., and Park, D. W. (1994). Interpersonal effects in computer-mediated interaction: a meta-analysis of social and antisocial communication. Commun. Res. 21, 460–487. doi: 10.1177/009365094021004002
Wang, H.-C., and Doong, H.-S. (2014). Revisiting the task-media fit circumflex: a further examination of negotiation tasks. Inf. Manag. 51, 738–746. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2014.07.001
Wang, Z., Lim, J., and Guo, X. (2010). Negotiator satisfaction in Nss-facilitated negotiation. Group Decis. Negot. 19, 279–300. doi: 10.1007/s10726-009-9181-y
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., and Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the Panas scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 54, 1063–1070. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063
Yashiro, K., Haruyama, S., and Shirasaka, S. (2024). Gender differences in the effects of online visual and audio combinations on credibility. Int. J. Serv. Knowl. Manag. 8:1. doi: 10.52731/ijskm.v8.i1.800
Keywords: negotiation, communication medium, individual fit, personality, gender, experiment
Citation: Lipp W and Mohnen A (2024) Communication media in electronic negotiations: how the individual x medium fit influences negotiation behaviors and outcomes. Front. Commun. 9:1402820. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2024.1402820
Received: 18 March 2024; Accepted: 11 September 2024;
Published: 04 October 2024.
Edited by:
Ashwani Kumar Upadhyay, Symbiosis International University, IndiaReviewed by:
Raiyan Abdul Baten, University of South Florida, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Lipp and Mohnen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wolfram Lipp, d29sZnJhbS5saXBwQHR1bS5kZQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.