
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Clim., 09 April 2025
Sec. Climate, Ecology and People
Volume 7 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fclim.2025.1563176
Climate change and variability are changes in the state of climate and weather conditions due to anthropogenic and physical factors. The main aim of this review paper is to examine the impacts of climate change and variability on rural livelihood and adaptation strategies employed in southern Ethiopia. In this review paper, the selection of literature was mainly based on search engines and raised areas from Google Scholar, Web of Science, Research Gate, Science Direct, and many other scientific journal publishing websites. This review focuses on climate change and variability in southern Ethiopia, highlighting its impact on rural livelihoods and adaptation strategies. Climate change and its variability affect sub-Saharan countries such as Ethiopia, crop production, livestock rearing, land productivity, water availability, biotic growth, rangeland quality, and soil productivity. This was due to rain-fed agricultural activity, low adaptation capacity, less attention given to policy development/implementation, lack of awareness, lack of modern agricultural input, and lack of effective, and efficient technology, etc. Ethiopian rural livelihoods need a comprehensive approach to mitigate climate change impacts. Mitigation should focus on sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and non-farm activities, while adaptation involves livelihood diversification, early warning systems, community-based initiatives, policy frameworks, and capacity-building programs. Despite adaptation measures such as cropping practices, modern input, crop diversification, and land management, climate change variability remains severe in Ethiopia, particularly in pastoral and semi-pastoral regions. The reviewer suggested that the government, NGOs, community, and private organizations should work together to address climate change and variability, focusing on enhancing adaptive capacity and sustainable environments.
Climate change and variability are among the most pressing global challenges of the 21st century, with profound implications for ecosystems, economies, and livelihoods, particularly in developing countries (IPCC, 2021). In the 21st century, climate change has been identified as a global environmental problem (Mekonen and Berlie, 2021; Ekpenyong et al., 2011). The composition of the global and/or regional atmosphere is altered by climate change, and natural climate variability is observed over similar periods. Animals and people alike are not immune to the effects of climate change (Cherinet, 2019; Panel et al., 2007). The most difficult and complicated issue affecting agricultural development globally is climate change (Gitima and Indonesia, 2021). Globally, climate change has reduces agricultural productivity, pushing some regions of the world to unsafe levels (Collier et al., 2008; Tadesse and Paper, 2010). Because the majority of Africans rely on natural resources for their livelihoods agriculture, pastoralism, and fishing the continent is also vulnerable to climate threats (Araro et al., 2020; Serdeczny et al., 2016; Chapman et al., 2020).
Sub-Saharan African rural farmers face increased vulnerability to climate change and variability owing to poverty, low infrastructure, and reliance on rain-fed agriculture (Collier et al., 2008; Serdeczny et al., 2016; Tadesse and Paper, 2010). Over 95% of the agricultural production in sub-Saharan Africa depends on rain (Haile and Tang, 2020). Ethiopia, a country heavily reliant on rain-fed agriculture, is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including increased temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and frequent droughts (Deressa et al., 2009). This vulnerability to climate change due to high poverty, rapid population growth, reliance on rain-fed agriculture, environmental degradation, food insecurity, and frequent natural drought cycles (Cherinet, 2019, Li Ching, 2018). Not only these, Erratic rainfall and prolonged droughts have led to crop failures, livestock losses, and reduced agricultural productivity, exacerbating poverty and food insecurity in rural areas (Mekonnen et al., 2018).
Climate change adaptation involves minimizing vulnerability and adjusting livelihood strategies to future impacts (African and Bank, 2012; Etana et al., 2021). Farmers in Ethiopia use various strategies, including cropping adjustments, resource management, and diversification to non-farm activities, to adapt to climate change variability (Etana et al., 2021; Cherinet, 2019; Serdeczny et al., 2016). As the impacts of climate change and variability on people vary from one to another, the adaptation strategies implemented by people are also not the same.
A sustainable livelihood can mitigate risks, recover from climate change, maintain or enhance capabilities, and provide net livelihood benefits in the short and long term (Etana et al., 2021; Nelson et al., 2014; Tadesse and Paper, 2010). This review research at the regional, zonal, and woreda levels is crucial for understanding climate change patterns and their impact on pastoralist livelihoods, aiming for multidimensional economic, social, and environmental objectives.
The main aim of this review is to examine the impacts of climate change and variability on rural livelihood and adaptation strategies employed in southern Ethiopia. In this review, the authors adopted an integrated iterative approach by searching various related literature and analyzing related articles. The selection of literature was mainly based on search engines and raised areas from Google Scholar, Web of Science, Research Gate, Science Direct, and many other scientific journal publishing websites. In addition, citations in key documents were used to identify additional relevant publications. This review did not cover all causes of climate change and variability in rural livelihood and its impact on all communities in Ethiopia, but focused on causes of climate change and variability in rural livelihood and adaptation strategies in southern Ethiopia. Source materials, peer-reviewed papers, institutional publications, and very few unpublished sources (MSc theses) were included.
The study searched for English-language electronic papers on climate change, livelihood, and environmental degradation using keywords such as Borena. Over 75 papers were recovered, with 62 used for review and analysis, and 47 combining original research articles and organizational reports.
The natural climate change and variability fluctuations of the climate system have been part of Earth’s history however, there have been changes in concentrations of GHGs in the atmosphere growing at an unprecedented rate and magnitudes in recent years (Onoja et al., 2011; Abouelfadl, 2012; EFD, 2012; World Bank, 2014). The causes of climate change and variability are broadly categorized into natural and anthropogenic factors (IPCC, 2014; Kaddo, 2016; Ochieng et al., 2016; World Bank, 2014). The Earth’s climate is grossly influenced and changed through natural causes such as ocean currents, volcanic eruptions, the Earth’s orbital changes, solar variations, and man-made greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels for electricity, cars, trains, aircraft, homes, land use, and deforestation (Onoja et al., 2011; Society, 2021; Taylor et al., 2017).
In light of these since climate change and variability are already occurring, it is possible to predict potential future changes by looking at previous and current changes. Ethiopia’s temperature has risen by roughly 0.2°C every decade during the past few decades (Keller, 2009; Abouelfadl, 2012). Owing to climate change and unpredictability, Ethiopia is among the nations most vulnerable to drought and flooding. By 2030, the average annual temperature across the nation is expected to increase by 0.9°C to 1.1°C. The occurrence and severity of droughts are projected to pose a growing threat to rural farming communities owing to climate fluctuations.
Climate change and variability directly and indirectly impact humans through health, food security, and economic activity. They induce changes in agriculture, leading to changes in the crop mix, input use, production, food demand, consumption, and trade (Taylor et al., 2017). All these are what Ethiopia has experienced this time with climate change variability and its effect on climate.
According to the USAID, 2015, the technical report on climate change and variability in the Ethiopian region, related to temperature and rainfall trends between 1981 to 2014 summarized in three paragraphs.
Between 1981 and 2014, the temperature trend in the Amhara region showed higher maximum temperatures during the summer/kiremt (June–September; +0.4–0.6°C/decade) and higher belg season (March–May) temperatures, together with trends in the amount of rainfall in the same year. There is minimal evidence of significant changes in the features of rainfall, although increasing rainfall with more dry days in a row suggests increased intensity, and probably more frequent heavy rainfall. There is also the possibility of an increased core seasonal rainfall.
Between 1981 and 2014, the temperature trend in Oromia, North East, and Afar, Ethiopia, was hotter, with more rapid increases in the later part of the belg (March–May; 0.6°C/decade), but significant increases in kiremt (June–September; +0.4–0.6°C/decade). During the same year, the rainfall trend intensified, with drier conditions for the first rainfall season (March–May), intensified wet events during the kiremt (June–September), and tentative evidence of increased and extended (later cessation) long-season rainfall (kiremt) (Funk et al., 2019; World Bank, 2021). In Ethiopia’s Oromia South region, the period from 1981 to 2014 saw hotter temperature changes, with later springtime rises (March to May) of 0.6°C/decade, but notable summertime increases (June to September) of +0.4–0.6°C/decade. That year’s rainfall trend was variable but suggested a possible drying trend (east).
In Tigray’s, northern Ethiopia temperature rends (1981–2014) showed decreasing maximum temperatures during the dry period (June–September), hotter temperatures during October–December, and rainfall trends in the same year were tentative messages of increased rainfall during the main rainy season and a possible extension of the season (later cessation) with very tentative evidence of increased rainfall intensity and frequency of heavy rainfall events.
Variations in climate variability, particularly in temperature and rainfall, were revealed in the USAID technical study. Regional temperature patterns indicate increases, although the pace and timing of these increases differ. Seasonal variations also affect the temperature patterns, with some areas seeing sharp drops in temperature and others seeing sharp rises. For example, the temperature in Tigray decreased from June to September and again from October to December. In Afar, the temperature rises quickly from March to May, by more than 0.6°C.
Based on the trends of change in climate and variability of Ethiopia from the report we can easily understand its adverse impacts are much diversified and damage the economy, biotic life, ecosystem, and social interaction of human life in rural livelihood. It is not only rural livelihood, but also the lives of people who live wherever in the world but also severe to pastoralist and semi-pastoralist parts of the world.
According to Ethiopia’s Climate Resilient and Green Economy Strategy (CRGES), the country’s mean annual temperature increased by 1.3°C between 1960 and 2006; there were also more hot days and nights and fewer cold days and nights; and the mean annual rainfall varied greatly from year to year and decade to decade, showing no discernible trend that led to extreme weather events such as frequent, severe flooding, and droughts. 2020 was predicted to see an increase in mean annual temperature of +1.2°C (range: 0.7–2.3°C) and in the mean annual rainfall of +0.496. Extreme weather events in these years included heavier rainfall events, unpredictable El Nino behavior in the future, an increase in flood and drought events, heat waves, and higher evaporation that occurred or may occur. The average annual temperature was predicted to rise to +2.2°C (1.4–2.9°C) in 2050, while the average annual rainfall was predicted to rise by +1.196. Furthermore, yearly temperature is predicted to rise by +3.3°C (range: 1.5°C–5.1°C), and the mean yearly rainfall is predicted to reach wetter conditions in the 2090s.
Predictions indicate that Ethiopia’s climate pattern will continue to shift until 2090. The strategy for a climate resilient and green economy indicates rising mean annual temperature and rainfall, with notable differences between a 1.3°C increase in 1960–2006 and over 1.2°C increase in 2006–2020, as well as more than 0.4 percent increase in mean annual rainfall.
By 2050, Ethiopia predicted that it is mean annual temperature will increase by more than 2.2°C and 3.3°C by 2050 and 2090, respectively. The prediction also shows that the mean annual rainfall in Ethiopia may increase by more than 1.1% and wetter conditions may occur in 2090. According to Ethiopia’s climate resilient and green economy strategy, there will be notable increases in temperature and precipitation, leading to extreme weather events such as severe flooding, drought, heavy rainfall, El Nino, heat waves, and increased evaporation. As the majority of Ethiopians depend on rain-fed agriculture, these changes have a substantial impact on rural livelihoods, particularly livestock and crop production.
In general temperature and rainfall variability seriously affect sectoral production, especially the agriculture sector such as crop production and livestock rearing (Solomon et al., 2021; World Bank, 2014). This is what we are observing today in most parts of Ethiopia especially pastoralist and semi-pastoralist regions such as Borena, Somalia, and some parts of Guji Land in which not only livestock died but also people of an area faced severe starvation. Thus, the Borena zone needs great aid from Ethiopian society and the world (Abrham et al., 2020; Okpanachi et al., 2013).
Most Ethiopian households expressed dissatisfaction with crop failure due to pests, heavy and unseasonal rain, early and late rainy seasons, and frequent droughts. In Somalia, shocks and pressures connected to climate change have resulted in lower crops for the majority of agro-pastoral households (93.7%; Abrham et al., 2020; Ochieng et al., 2016). Farmlands have become drier and more challenging to plow because of droughts and delayed rainy seasons. Additionally, stunted crop development and delayed seed germination have resulted in early crop wilting and a decrease in agricultural output, sometimes leading to crop loss. Melaku et al. (2018) and Osumanu et al. (2015) both found similar results, indicating that drought occurrences also showed that occurrences of droughts had led to crop failure in the Afar Region.
The result from Figure 1 shows that Ethiopia’s agricultural food production and amount of income generation are negatively impacted by climate change on a national level. There has been a significant drop in rural, urban, and non-farming areas, and this trend is expected to continue. From 2020 to 2030, then to 2040, and then to 2050, the rate of degradation in the poor society was greater than in the non-poor society. Comparable to this, in rural impoverished areas, the cause was more severe than that of rural non-farm causes as we advanced into the next 30 years.
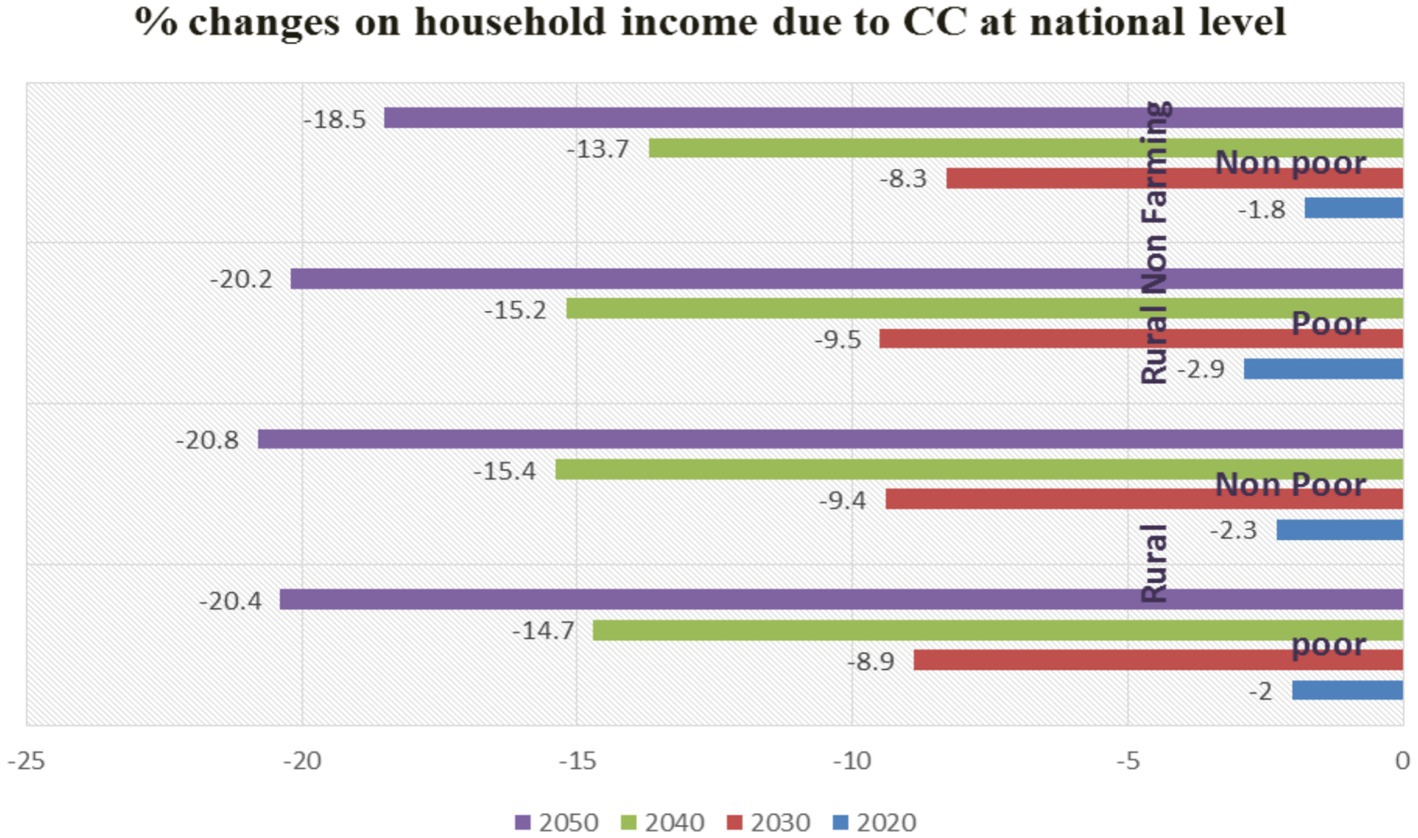
Figure 1. Percentage changes in household income due to climate change at the national level. Source: Solomon et al. (2021).
The impact of climate change and variability on the agro ecological zone is demonstrated in Figure 2, where household income has dropped and will continue to decline. The figure depicted above shows that the income of the community decreased by more than 10 to 15 percent in each of the agro ecological zones between 2020 and 2050. Every instance of an agro ecological zone hurts household income between 2020 and 2050. Cereals with enough moisture only displayed a positive 0.3 in 2050, but they reached a negative 15. For drought-prone households, moisture-sufficient Onset was −13.9 in 2020 and is projected −40.1 in 2050, which is a very large negative shift; nevertheless, for pastoralist households, it was 6.7 in 2020. Moisture sufficient Onset was −6.1 in 2020 but will reach −27.3 in 2050.
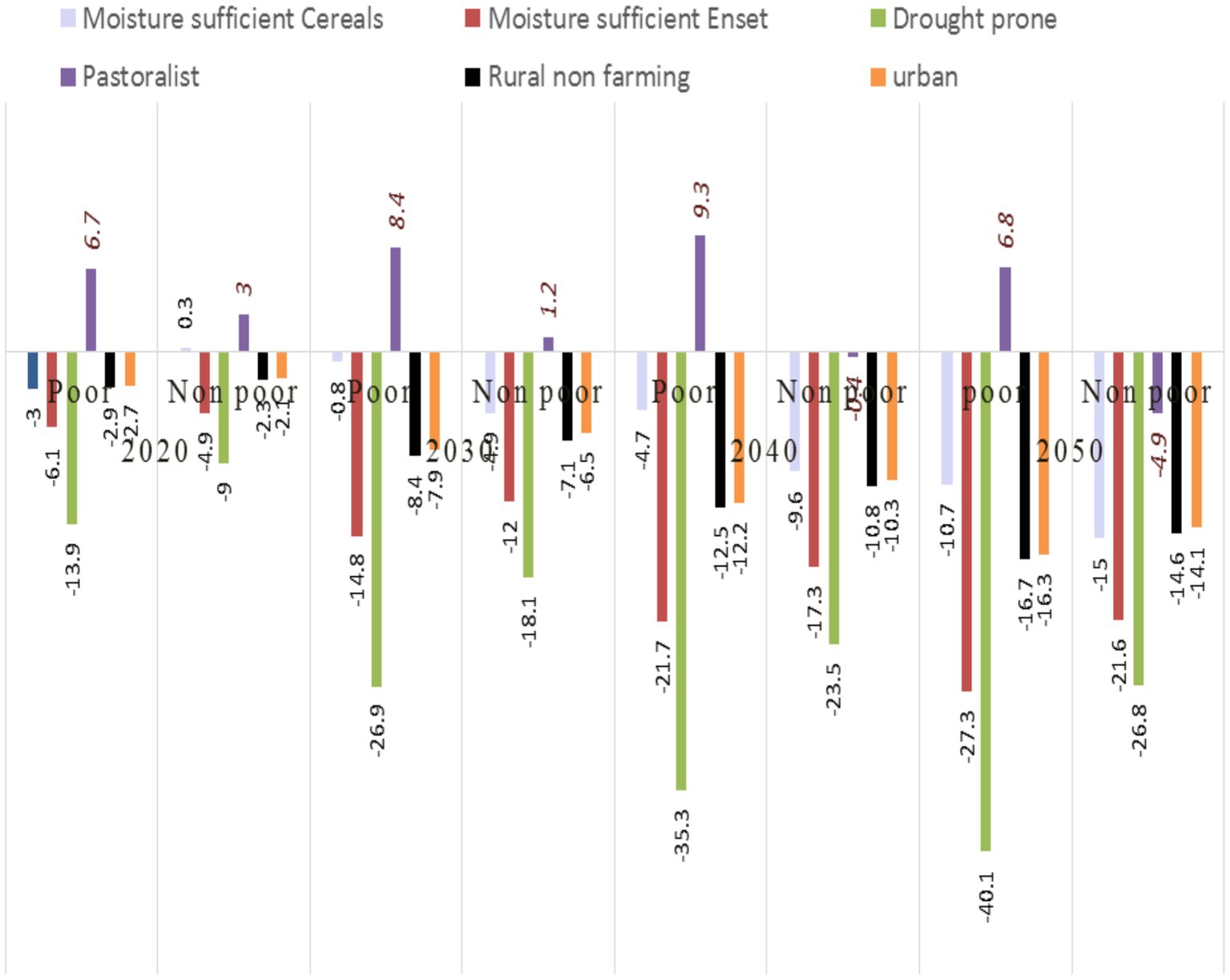
Figure 2. Percentage change in household income by decades and AEZ. Source: Pantuliano and Wekesa (2008).
The implications of climate change and variability exhibit periodic fluctuations, but their intensities vary among Ethiopian regions (Abrham et al., 2020). Based on agro ecological zones ranging from Kur to the desert, Ethiopia is experiencing a wide range of consequences from climate change and variability. The socioeconomic effects of drought are severe in various regions with arid and semi-arid characteristics, such as Somalia, Borena, Afar, and some parts of Guji and Bale, which have less than 500 mm of annual precipitation (Asrat and Simane, 2018). Drought is one of the most painful natural disasters occurring in arid tropical environments.
Figure 3 illustrates how significant declines in the main economic variables at the national level were caused by climate change and variability. In the past, present, and future, the effects of climate variability and change not only drive GDP at market price, but also adversely affect rural livelihoods and Ethiopia as a whole (Maalin et al., 2022; Ochieng et al., 2016).
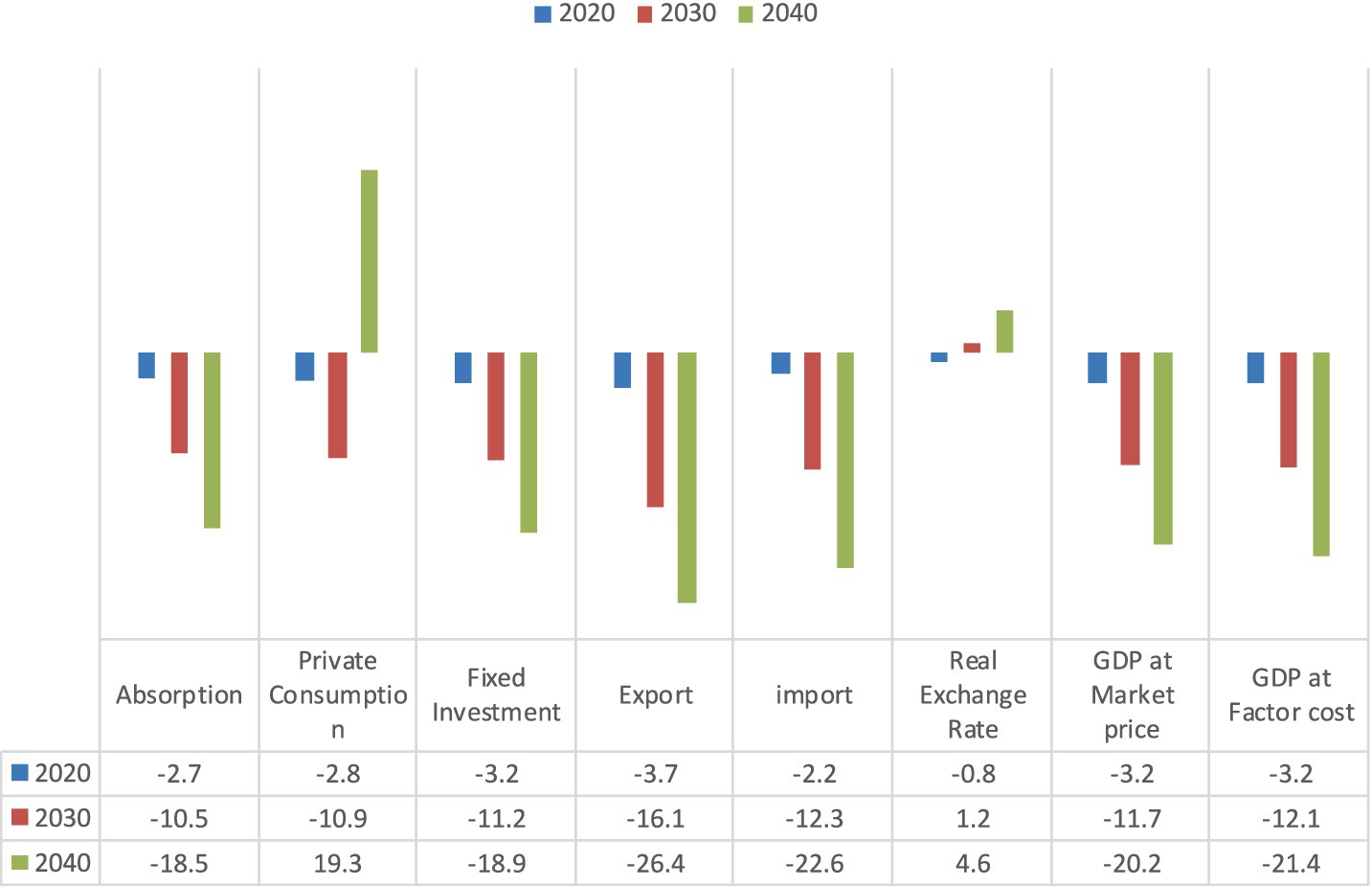
Figure 3. Percentage change in major economic variables at the national level by decades in Ethiopia. Source: Solomon et al. (2021).
Recurrent droughts and erratic precipitation have lowered livestock and agricultural productivity, leading to an increase in food poverty and revenue loss. 97.5% of the pastoralists and most agro-pastoral households faced food insecurity because of livestock losses and crop failure during droughts (Abrham et al., 2020; Ochieng et al., 2016).
According to the 2013 IPCC assessment, climate variability and change in East Africa will exacerbate food insecurity, lead to the collapse of food systems, cause rural livelihoods to disappear, result in revenue losses, and reduce crop and livestock productivity. Zenebe et al. (2011), found a decline in the average incomes of rural farmers as a result of climate-related shocks, and EFD (2012) also found a 30% loss of income in Ethiopian rural areas as a result of climate change and variability.
The agro-ecological zone climate change and variability in Ethiopia, as reported by the USAID in 2015 and CRGE in 2011, is largely similar in terms of its hazards, impacts, and consequences across regions. Most of the risks were drought (low rainfall, late-onset), high rainfall, early cessation of rainfall, hailstorms, heavy rain/floods, and modifications to the timing and length of seasonal rains.
The main effects were significant food shortage, decreased livestock production, farmers turning to selling livestock, extensive crop damage, decreased yield, loss of water points and pastures, loss of grazing, dwellings and properties, soil erosion, loss of soil fertility, and water-logging of fields. Food scarcity, the need to buy food, vulnerability to hunger, financial strain, inflation, labor migrations, social unrest, loss of assets and income, selling household possessions like oxen and other livestock, migration in search of non-farm labor opportunities, water and sanitation crises, significant loss of life and an increase in the number of homeless people, milk shortage, poor nutrition among children and nursing mothers, and complete reliance on outside food sources were the results (Weldemariam et al., 2023).
According to the technical reports of USAID (2015) and CRGE (2011), the impact of climate change is based on the similarity of the agro-ecological zones to a greater or less degree. Lowland and semi-lowland areas are more sensitive to climate change and variability than highland agro-ecological zones. In the lowland part, the adverse impact of climate change and variability is noticeable in two extreme weather events, drought, and flood, which increase the vulnerability of society and result in repeated severe food deficiency and poverty problems by citing (Asfaw et al., 2013).
Therefore,; climate change and variability hazards are events or occurrences that have the potential to cause injury to life, or damage to property or the environment on which the community depends on its social and economic existence (Cherinet, 2019; Ward, 2014).
We have seen severe hunger and starvation in Borena, Somalia, Guji, and West Guji in recent years. Common climate change hazards include drought, flood, landslide, and soil erosion. These have resulted in crop infestation and livestock diseases, as well as the death of biotic organisms such as life like cattle, sheep, and goats. According to the IPPC report (Abbass et al., 2022), rising temperatures, storms, floods, and droughts linked to climate change and variability would result in population displacement, fatalities, and negative effects on freshwater availability and quality According to USAID (2015), climate change effects have been felt strongly by all communities, particularly by rural livelihoods. These effects include extensive crop damage, decreased yield, loss of water points and pastures, livestock disease, loss of grazing land, soil erosion, loss of soil fertility, and field waterlogging of fields. Additionally, there is a significant scarcity of food, farmers resorting to selling their livestock, and migration in search of pastures and water. All of these issues mostly impact rural livelihoods.
This research clarifies how changes in temperature and precipitation affect the environment, biotic life, and socioeconomic standing of a region, particularly in less-developed nations such as Ethiopia. This is what Ethiopians are witnessing. Thus, the majority of Ethiopian societies experienced food insecurity and had to wait for food assistance. Animal holdings per household are affected by frequent droughts and rising heat stress. In Somalia, 81% of agro-pastoralists and 100% of pastoralists reported that climate change negatively affected cattle quantity and production (Food and Agriculture Organization, 2020; United Nations Development Programme, 2019).
The above-mentioned effects of climate change and variability in Ethiopia were also reported by Nkomwa et al. (2014), who found that in the same agroecology of southern Malawi, climate variability has led to increased crop failure, higher losses of livestock assets, migration, food shortages, loss of biodiversity, and negative effects on human development.
Ethiopian farmers use a variety of strategies, considering their particular agro-ecological characteristics, to adapt to climate change and variability. The highland, lowland, and mid-altitude regions of Ethiopia are shown in Figure 4; along with the adaptation mechanisms that Ethiopian society has evolved to deal with fluctuations in the climate. The figure indicates that the highland, lowland, and mid-altitude regions were the main users of improved seed, irrigation, and non-farm pursuits including trading, such as Borena (Belay et al., 2017). Farmers also employed non-farm, low-return, and less capital-intensive occupations, such as everyday labor work.
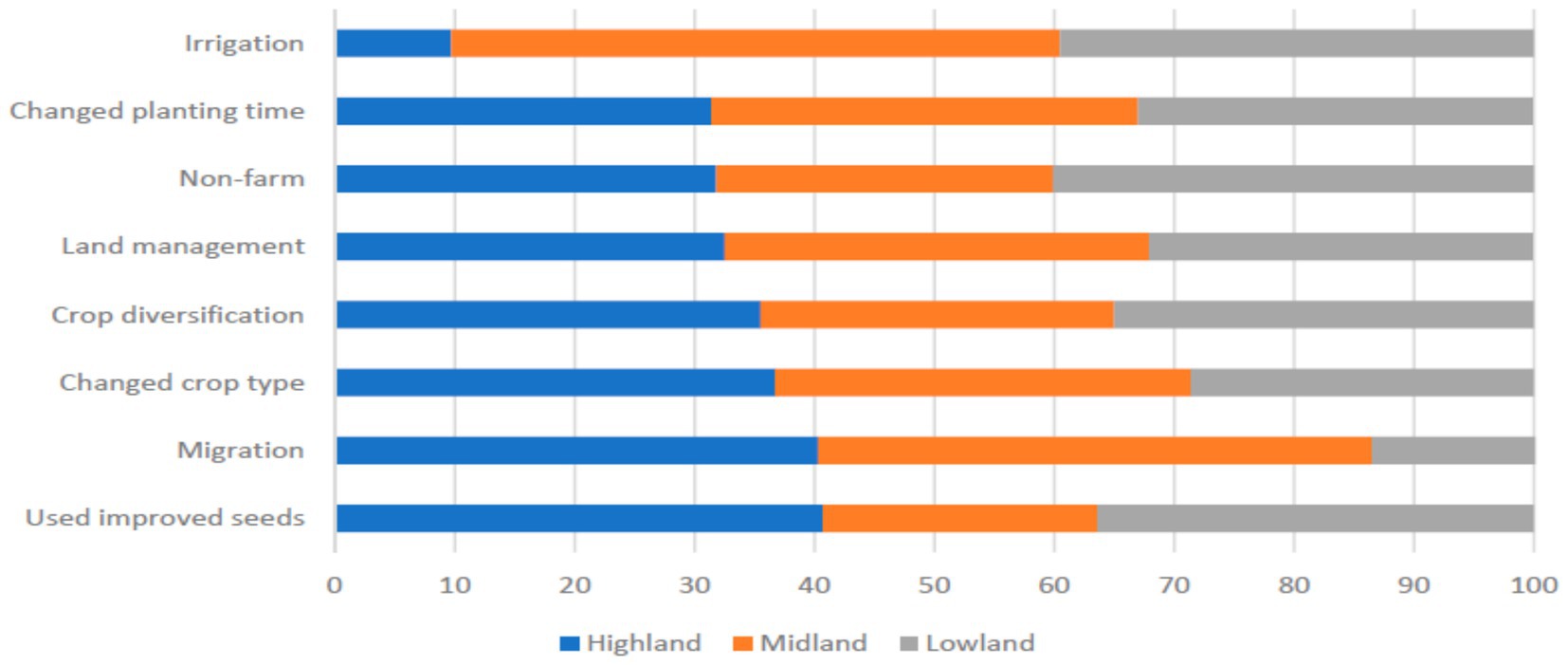
Figure 4. Relative distribution of the use of adaptation strategies by agro-ecological settings. Source: Etana et al. (2021).
Therefore, households use crop diversification, seasonal cropping, and land management practices, along with agricultural inputs such as pesticides and fertilizers, to increase productivity and adapt to farm-based techniques.
Crop failure risks are reduced for rural livelihoods by using selected agricultural strategies (Etana et al., 2021; Jervis, 2011). In Ethiopia, farmers face unpredictable production conditions, such as erratic rainfall and drought, either waiting for the long rainy season or sacrificing long-duration crops. Modern irrigation systems in lowland areas provide market-targeted crops and fruits. Nevertheless, shifting planting dates has less of an impact on lowland farmers. According to Etana et al. (2021), these area have shorter crop-growing seasons than highland and midland areas, suggesting that there are fewer possibilities for adjusting planting times in lowland areas.
Crop diversification is an effective technique to deal with climate change and variability, and it lowers production risks, because various crops respond differently to different climatic circumstances owing to genetic differences (Bangwayo-skeete et al., 2012). In addition, crop diversification benefits farmers with larger landholdings by increasing their livelihoods, boosting productivity, and improving yield stability. It is crucial for low-income households to address, food assistance, starvation, and hunger, and create a society free from poverty (Dessie et al., 2019). This was also reported by Mussema et al. (2015).
Terracing, building stone or soil bunds, planting trees, and other land management techniques are crucial for adapting and adjusting to the variability of climate change based on agro-ecological settings. These results may indicate that farmers’ livelihoods that employ land management techniques are more sustainable than those of farmers who do not (Regulations and Management, 2020; Liu et al., 2018). Water logging is a major issue for agricultural productivity in highland locations, whereas slope topography, flash floods, erosion, and other variables contribute to Ethiopian farmers’ susceptibility to climate change and variability. Thus, land management and land use planning contribute to the reduction of issues by increasing agricultural output and promoting ecosystem functioning, all of which enhance the sustainability of rural communities’ livelihoods (Robbins and Williams, 2005; Squires and Feng, 2018).
In Ethiopia, climate change and variability are fundamental. According to several authors, the analysts concluded that Ethiopia has experienced several unique problems as a result of climate change and variability, including recurrent dry seasons, especially in the country’s southern and southeast, a decline in horticultural productivity and efficiency due to Ethiopia’s rainy season, an increase in flooding events, including the arrival of Borena in 2023, a rise in temperature, a decrease in precipitation, and a deeply fractured socioeconomic system as a result of Ethiopians’ declining sources of income and production.
Ethiopia is experiencing negative effects of climate change and unpredictability on several fronts, including crop productivity, livestock productivity, and rearing, land productivity, water availability, biotic growth, and rangeland quality and, soil productivity. As a result, the government and community should place a proper prioritize forestation, reforestation, area enclosure, and soil and water conservation.
Damage to agricultural productivity and efficiency directly and indirectly affects employment in rural areas. When we reviewed various studies related to climate change and variability in Ethiopia’s adjustment capacity and commonsense exercises to diminish climate change and variability, we found that a variety of measures have been employed to moderate the antagonistic impact of climate change and variability. These measures include selecting trimming hones, using advanced input, editing expansion, arriving at administration exercises, and more. The research highlights the importance of mitigation strategies in addressing climate change’s root causes and reducing its adverse effects on rural livelihoods in Ethiopia. Key strategies include sustainable agriculture, renewable energy access, reforestation, and efficient water resource management. This holistic approach ensures long-term sustainability and improved quality of life for rural communities. The recommendations for addressing climate change impacts on Ethiopian rural livelihoods include enhancing localized research, promoting integrated mitigation and adaptation strategies, strengthening policy support, and fostering collaboration and funding through international partnerships and climate finance.
BD: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. TR: Writing – review & editing. SM: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer GSO declared a shared affiliation with the author SM to the handling editor at the time of review.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbass, K., Qasim, M. Z., Song, H., Murshed, M., Mahmood, H., and Younis, I. (2022). A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 42539–42559.
Abouelfadl, S. (2012). Global warming – causes, effects, and Solution’s trials. JES. J. Eng. Sci. 40, 1233–1254. doi: 10.21608/jesaun.2012.114490
Abrham, T., Mekuyie, M., and Management, R. (2020). Effects of climate change on pastoral households in the Harshin District of the Somali region, Ethiopia, 1–10. doi: 10.4102/jamba.v14i1.1202
African, T., and Bank, D. (2012). Solutions for a changing climate. Platz der Vereinten Nationen, Bonn, Germany: UN Campus. Available at: www.unccd.int
Araro, K., Addisu, S., Derege, L., and Meshesha, T. (2020). Climate Change and variability impacts on rural livelihoods and adaptation strategies in southern Ethiopia Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia intergovernmental Panel on climate Change United Nations environmental programs. Earth Syst. Environ. 4, 15–26. doi: 10.1007/s41748-019-00134-9
Asfaw, A., Almekinders, C. J. M., Struik, P. C., and Blair, M. W. (2013). Scientific research and essays farmers’ common bean variety and seed management in the face of drought and climate instability in southern Ethiopia. Sci. Res. Essays 8, 1022–1037. doi: 10.5897/SRE12.732
Asrat, P., and Simane, B. (2018). Farmers’ perception of climate change and adaptation strategies in the Dabus watershed, north-West Ethiopia. Ecol. Process. 7, 6–8. doi: 10.1186/s13717-018-0118-8
Bangwayo-skeete, P. F., Bezabih, M., and Zikhali, P. (2012). Crop biodiversity, productivity, and production risk: Panel data micro-evidence from Ethiopia crop biodiversity, productivity and production risk: Panel data micro-evidence from Ethiopia. Nat. Res. Forum 36, 263–273. doi: 10.1111/1477-8947.12000
Belay, A., Recha, J. W., Woldeamanuel, T., and Morton, J. F. (2017). Smallholder farmers’ adaptation to climate change and determinants of their adaptation decisions in the central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Agricul. Food Security 6, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s40066-017-0100-1
Chapman, S., Birch C, E., Pope, E., Sallu, S., Bradshaw, C., Davie, J., et al. (2020). Impact of climate change on crop suitability in sub-Saharan Africa in parameterized and convection-permitting regional climate models. Environ. Res. Lett. 15, 11–12. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab9daf
Cherinet, A. (2019). Climate Change/variability impacts on Farmer's liLivelihoodsnd adaptation strategies: in the case of Ensaro District, Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Natural Resources 18, 1–7. doi: 10.19080/IJESNR.2019.18.555976
Deressa, T. T., Hassan, R. M., and Ringler, C. (2009). Assessing the economic impact of climate change on agriculture in Ethiopia: a Ricardian approach. World Bank Policy Res. 4342, 9–12.
Dessie, A. B., Abate, T. M., Mekie, T. M., and Liyew, Y. M. (2019). Crop diversification analysis on red pepper dominated smallholder farming system: evidence from Northwest Ethiopia. Ecol. Process. 8, 7–9. doi: 10.1186/s13717-019-0203-7
EFD (2012). Climate Change and the Ethiopian economy, Gothenburg, Sweden: Department of Economics, University of Gothenburg. 1–3.
Ekpenyong, A. B., William, F., and Duru, E. (2011). Climate Change, food security and agricultural productivity in Africa: issues and policy directions. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 1, 205–223.
Etana, D., Snelder, D. J. R. M., and Wesenbeeck, C. F. A. (2021). The impact of adaptation to climate Change and variability on the livelihood of smallholder farmers in Central Ethiopia. Sustain. For. 13, 11–16. doi: 10.3390/su13126790
Food and Agriculture Organization. (2020). Climate-related vulnerability and adaptive capacity in Somalia’s pastoral and agro-pastoral systems. Available at: https://www.fao.org/3/cb1205en/cb1205en.pdf
Funk, C., Harrison, L., Shukla, S., Korecha, D., Magadzire, T., and Husak, G. (2019). Examining the potential for predictive skill in the eastern Horn of Africa short rains. J. Clim. 32, 4923–4943. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0726.1
Gitima, G., and Indonesia, G. (2021). Geosfera Indonesia assessing the impacts of climate variability on rural households. Geosfera Indonesia 6, 96–126.
Haile, G. G., and Tang, Q. (2020). Projected impacts of climate Change on drought patterns over East Africa earth s future. Earth's Future, 1–23. doi: 10.1029/2020EF001502
IPCC (2014). Effects of global climate change on agriculture: an interpretative review. Clim. Res. 11, 19–30.
IPCC. (2021). “Climate Change 2021: the physical science basis.” Contribution of working group I to the sixth assessment Report of the intergovernmental Panel on climate Change. Cambridge University Press. Available at: www.sprep.org
Jervis, Rowe. (2011). Crop selection and Management. Available online at: http://www.cardi.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/Crop-Selection-and-Management
Kaddo, J. R. (2016). Climate Change: causes, effects, and solutions. J. Petrol. 56, 823–844. Available at: http://spark.parkland.edu/ah/164
Keller, M. (2009). Climate risks and development projects assessment Report for a community-level project in (2009) : Bread for All, Swiss Protestant Churches’ development agency 1–35.
Liu, S., Oeding, J., Tan, Z., and Schmidt, G. L., (2018). Major land-Management activities and natural disturbances considered in this assessment baseline and projected future carbon storage and greenhouse-gas fluxes in ecosystems of the Western United States. Available online at: http://pubs.usgs/gov/pp/1797.
Maalin, A., Abdimahad, K., Hassen, G., Mahamed, A., and Hassen, M. (2022). Management practices and production constraints of indigenous Somali cattle breed in Shabelle zone, Somali regional state. Ethiopia. Open J. Animal Sci. 12, 103–117. doi: 10.4236/ojas.2022.121008
Mekonen, A. A., and Berlie, A. B. (2021). Rural households’ livelihood vulnerability to climate variability and extremes: a livelihood zone-based approach in the northeastern highlands of Ethiopia. Ecol. Process. 10, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/s13717-021-00313-5
Mekonnen, Z., Kassa, H., Woldeamanuel, T., and Asfaw, Z. (2018). Analysis of observed and perceived climate change and variability in Arsi Negele District, Ethiopia. Environ. Develop. 25, 23–33.
Melaku, Y., Dirar, A., Feyissa, G. T., and Tamiru, D. (2018). Optimal dietary practices and nutritional knowledge of school adolescent girls in Jimma town, south West Ethiopia. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 23, 299–307. doi: 10.1080/02673843.2017.1369889
Mussema, R., Kassa, B., Alemu, D., and Shahidur, R. (2015). Determinants of crop diversification in Ethiopia: evidence from Oromia region. Ethiop. J. Agric. Sci 25, 65–76.
Nelson, G. C., Mensbrugghe, D., Blanc, E., and Calvin, K. (2014). Agriculture and climate change in global scenarios: why don’t the models agree. Agric. Econ. 45, 85–101. doi: 10.1111/agec.12091
Nkomwa, E. C., Joshua, M. K., Ngongondo, C., Monjerezi, M., and Chipungu, F. (2014). Assessing indigenous knowledge systems and climate change adaptation strategies in agriculture: a case study of Chagaka Village, Chikhwawa, southern Malawi. Phys. Chem. Earth 67-69, 164–172. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2013.10.002
Ochieng, J., Kirimi, L., and Mathenge, M. (2016). Effects of climate variability and change on agricultural production: the case of small scale farmers in Kenya. NJAS - Wageningen J. Life Sci. 77, 71–78. doi: 10.1016/j.njas.2016.03.005
Okpanachi, U., Musa, A. A., and Idachaba, K. E. (2013). International journal of agriculture and biosciences opportunities in Ethiopia. Int. J. Agricul. Biosci. 8, 89–98.
Onoja, U. S., Dibua, U. M. E., and Enete, A. A. (2011). Climate Change: causes, effects and mitigation measures-a review. Global J. Pure Appl. Sci. 17, 469–479. Available at: www.globaljournalseries.com
Osumanu, I. K., Ahmed, A., Salia, R. A., Abdulai, A.-R., and Dongzagla, A. (2015). Slums in semi-arid regions: an analysis of the vulnerability and coping strategies of selected Neighbourhoods in the Wa municipality. Ghana. Current Urban Stud. 3, 331–347. doi: 10.4236/cus.2015.34027
Panel, T. I., Change, C., Nations, U., and Programme, E., (2007). Climate Change 2007: Impacts, adaptation and Vulnerability.
Pantuliano, S., and Wekesa, M. (2008). Improving drought response in pastoral areas of Ethiopia. Overseas Develop. Institute. 1–42.
Regulations, C. L., and Management, F. (2020). Weston conservation commission conservation land use policy & Regulations, vol. 2020, 1–5.
Robbins, M., and Williams, T. (2005). Scientific and technical advisory Panel (STAP) to the global environment facility: land management and its benefits – the challenge, and the rationale for sustainable management of drylands. Global Environ. Facility. 5.
Serdeczny, O., Adams, S., Coumou, D., Hare, W., and Perrette, M. (2016). Repercussions. Reg. Environ. Chang. 17, 1585–1600. doi: 10.1007/s10113-015-0910-2
Society, T. R. (2021). Climate change and global warming: impacts on crop production. Genetically Modified Plants. 26, 283–296. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-818564-3.09991-
Solomon, R., Simane, B., and Zaitchik, B. F. (2021). The impact of climate Change on agriculture production in Ethiopia: application of a dynamic computable general equilibrium model. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 9, 32–50. doi: 10.4236/ajcc.2021.101003
Squires, V. R., and Feng, H. (2018). Sustainable land management. Sustain. Land Manag. Greater Central Asia, 75–98. doi: 10.9774/gleaf.9781315679396_5
Taylor, P. C., Fahey, D., and Doherty, S. (2017). DigitalCommon. Lincoln physical drivers of climate change I, 73–113. doi: 10.7930/J0513WCR.U.S.
United Nations Development Programme. (2019). Climate change adaptation in Somalia: Impacts on pastoral livelihoods. Available at: https://www.undp.org/somalia/publications
USAID. (2015). Climate variability and Change in Ethiopia, December 2015, United States agency for international development climate change adaptation thought leadership and assessments (ATLAS), 122.
Ward, J. (2014). “Climate Change 2014. Impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability.” Top-level findings from the working group II AR5 summary for policymakers. Ipcc.
Weldemariam, Lemlem Fitwi, Patrick, S., and Ayanlade, Ayansina. (2023). Household food-security strategies and migration in Tigray, northern Ethiopia. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2023.e01801
World Bank. (2021). Somalia climate risk profile: Changing rainfall patterns and extreme weather events (Report No. 145-SO). Available at: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/145891627632440315/somalia-climate-risk-profile
Keywords: adaptation, agriculture, Borena, climate change impact, livelihood
Citation: Daba B, Regasa T and Mammo S (2025) Impacts of climate change and variability on rural livelihoods and adaptation strategies in Ethiopia: a review paper. Front. Clim. 7:1563176. doi: 10.3389/fclim.2025.1563176
Received: 19 January 2025; Accepted: 20 March 2025;
Published: 09 April 2025.
Edited by:
Jose Antonio Rodriguez Martin, Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Tecnología Agroalimentaria (INIA), SpainReviewed by:
Addisu Damtew, Wolaita Sodo University, EthiopiaCopyright © 2025 Daba, Regasa and Mammo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Siraj Mammo, c2lyYWptYW1tb0BnbWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.