- National Center for Disaster Preparedness, Columbia Climate School, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States
Introduction
Hurricane Sandy hit the New York City region on October 29th, 2012. Various coastal communities recorded extensive damage, including Oakwood Beach, a small community on the southern coast of Staten Island (McNeil et al., 2015). Under a New York State-led buyout program, funded by a Community Development Block Grant (CDBG) provided by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) (2023), the majority of the residents of this community agreed to and advocated for a community relocation (Salles, 2022; Shailer, 2022). The Oakwood Beach Buyout Program is significant, as it is considered to be one of the first in the country to take advantage of a state-led managed retreat buyout program. The ways in which this program was implemented are now considered a critical case study for buyouts across the United States (Spidalieri et al., 2017). Parties that laud the project's success largely attribute it to the high level of community involvement and engagement in the form of a community-led Oakwood Beach Buyout Committee. In total, 180 out of 184 homeowners were approved for this buyout program, and the majority of the community was relocated (Spidalieri et al., 2017).
As a condition of the Oakwood buyouts, parts of the land were intended to be ecologically restored to provide a natural buffer against storm surges and flooding caused by superstorms and hurricanes (Spidalieri et al., 2017; Governor's Office of Storm Recovery, 2023; Kensinger, 2022). However, key terms such as “natural” and “restoration” are often left too open for policymakers and practitioners to interpret. Significantly, the legislation introduced shortly after the buyouts, such as New York State Assembly Bill A05499A (2015), includes wording that categorizes recreational areas under the broad umbrella of natural ecosystems. Consequently, a clear example of the misuse of this phrasing and interpretation is that it currently permits soccer fields, laid with concrete foundations, to be constructed in areas that were originally reserved for natural floodplain functions by the Staten Island Youth Soccer League (Shailer, 2022; Kensinger, 2022). Furthermore, according to documents from a City Planning Commission Review (2017), land originally purchased by the state from residents was eventually sold to New York City, and later sold to unidentified, private entities in 2023 (CountyOffice.org, 2024).
Due to this outcome, views about the program's long-term success have diverged sharply. While both experts and community members view the short-term program as a success, in recent years, Oakwood Beach community members who participated in the Buyout Committee have expressed disappointment at a mixed-use outcome that deprioritizes the true efforts at ecosystem restoration (Spidalieri et al., 2017; Shailer, 2022). Comments from community members include, “I thought they were going to let everything grow. I envisioned swamp,” “People could have seen all the nature here; it would have been beautiful,” and “I don't see where the success is…” (Shailer, 2022).
The progression of missteps in long-term program implementation in this case study that contributed to many discrepancies in program outcomes raises important questions about how to 1. Define, communicate, and implement the concept of nature-based solutions (NbS) among experts, and 2. Advocate for the prolonged administration, involvement, and accountability of managed retreat programs by experts.
Although the nature of this article primarily reflects the viewpoints of its authors, a literature and document review were required to piece together the program timeline and experience of Oakwood Beach residents. Sources for this article were found on Google Scholar (scholar.google.com) and google.com. Search terms used on Google Scholar included “nature-based solutions”, “NbS”, “managed retreat”, “Oakwood Beach”, “Oakwood Beach buyout program”. Search terms used on Google.com included “managed retreat”, “Oakwood Beach”, “Oakwood beach buyout program”, “Oakwood Beach nature-based solutions”. Public records were accessed through the Automated City Register Information System (ACRIS) at https://www.nyc.gov/site/finance/property/acris.page and County Office Property Records https://www.countyoffice.org/ny-property-records/.
Nature-based solutions
Currently, Nature-based Solutions (NbS) are defined by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) as: “…sustainable planning, design, environmental management and engineering practices that weave natural features or processes into the built environment to promote adaptation and resilience” (United States, 2023). This definition is also utilized by HUD when implementing Community Development Block Grants such as the Oakwood Beach Buyout Program (U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, 2023).
The FEMA definition would therefore include the aforementioned recreational areas, suggesting that such recreational areas act as effective mitigation against flooding as more biodiverse and efficiently-selected ecosystem restoration measures (United States, 2023). Both recreational areas and ecological areas are encompassed by Community Development Block Grants. The widespread assumption that recreational areas and ecological areas are equivalent in addressing community needs is also reflected in the definition established in the New York State Assembly Bill A05499A in 2015. However, the loose practical definition of NbS raises questions about whether high-maintenance recreational monocultures, such as soccer field turf, should be considered as effective a hazard mitigation strategy as floodplain restoration based on the location provided (Ferreira et al., 2022; Li and Guo, 2024; Lo et al., 2021). NbS must show effective hazard mitigation, but due to a lack of data it is difficult to ascertain whether recreational areas are effective flood mitigation in this case (Lo et al., 2021). Given the diverse array of definitions from academic and governmental sectors, practitioners and communities are likely to come to the conclusion that recreational areas with concrete foundations are considered successful hazard mitigation strategies (Frantzeskaki et al., 2019). The specific location requirements, as a result, may not be considered or analyzed adequately with potential consequences for NbS functionality (Ferreira et al., 2022).
Community-led buyout program
This case study also raises questions about how subject matter experts and policymakers may better communicate nature-based solutions with vulnerable communities and manage the long-term protection of coastlines from more extreme storms. Oakwood Beach residents initially understood and agreed that a more traditional restoration approach would be implemented in their community. However, due to the wording in the established policy, this was not the case.
In September 2017, vacant lots in Oakwood Beach were rezoned to minimize future developments (Spidalieri et al., 2017). Some lots that were not passed to the Staten Island Youth Soccer League were later passed from the state to the city government in 2021 and then sold to unknown entities in 2023 (CountyOffice.org, 2024). A long-term environmental plan for the lots purchased by New York State after Hurricane Sandy has not been located by the authors of this paper.
Case synthesis
There is a major divide between how experts and residents view the outcomes of the Oakwood Beach buyout program in terms of balancing and contrasting program theory and residents' lived experiences. While experts originally lauded this case as a successfully managed retreat, residents currently see it as returning to an unprepared pre-disaster status quo. Due to climate change, future storms are expected to hit New York City more frequently and intensely. The solutions that experts employ and endorse must be led by a community and include nature-based restoration to reduce damage.
The solutions required to protect communities warrant long-term project plans that protect such communities before, during, and after a disaster. Solutions to these types of existing and emerging climatic challenges are difficult; often, the creation and sustainment of NbS does not exist in a vacuum, and projects must fit into the built environment while also enhancing a community landscape using an ecosystem's maximum capabilities. These high expectations for NbS as a panacea, combined with a lack of communication and management, can lead to negative outcomes that can cause further harm to a community and distort understanding of NbS and its use cases (Frantzeskaki et al., 2019; Seddon et al., 2021; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), 2020).
Key questions for alignment on nbs within communities
Our analysis determined three key objectives that, when addressed, may prevent barriers to NbS implementation similar to those faced by the Oakwood Beach community. These objectives may support a variety of subject matter experts for future project collaboration, management, and implementation of vital NbS practices. From these objectives, a table of guiding questions (Figure 1) was developed. These guiding questions aim to support academics, subject matter experts, practitioners, and policymakers as they help communities navigate a post-disaster landscape. In addition, recommendations are given that may assist various academic, subject matter, policy, and practitioner experts in their long-term goals of protecting communities from future hazards.
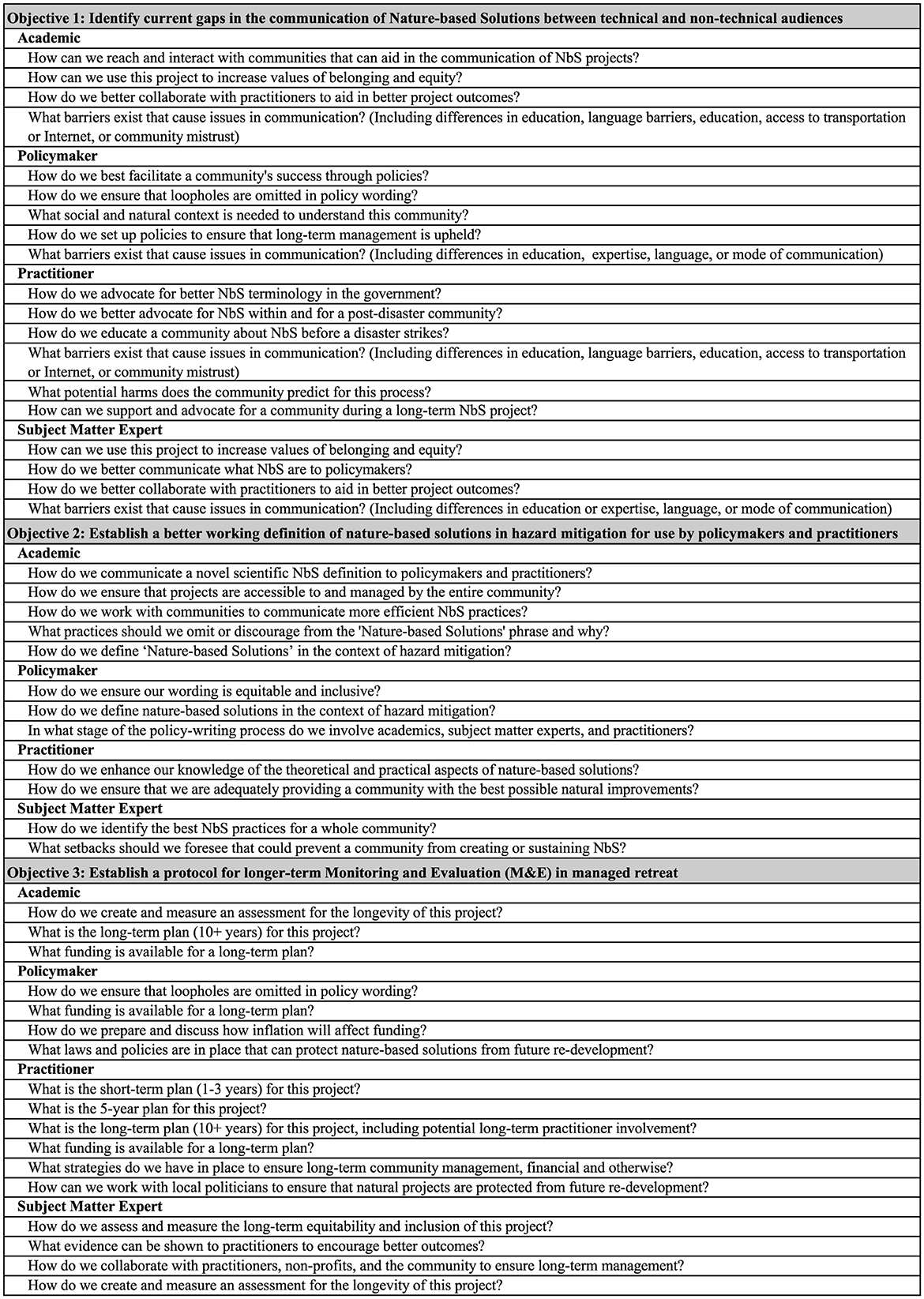
Figure 1. Nature-based solutions community alignment checklist. A list of key questions that various parties involved should consider in order to assure better outcomes for a managed retreat program within a community affected by a disaster. An academic is noted as any scientist affiliated with a university; a subject matter expert is noted as any other academic expert not affiliated with a university; a policymaker is noted as any governmental or legislative employee that may write or aid in the creation of policies; a practitioner is noted as any community worker or community-facing official that serves or advocates for the community.
The guiding questions for academics, subject matter experts, practitioners, and policymakers in Figure 1 will address the three following objectives:
1. How to identify current gaps in the communication of Nature-based Solutions between technical and non-technical audiences,
2. How to establish a better working definition of Nature-based Solutions in hazard mitigation for use by policymakers and practitioners; specifically, how to define and operationalize “ecosystem function” as a hazard mitigation practice, and
3. How to establish a protocol for longer-term Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) involvement by practitioners, academics, and subject matter experts in the ecosystem restoration aspects of managed retreat practices, in order to ensure that communication with the community remains at the forefront of the project during its entire lifecycle.
The majority of these questions follow a similar track, focusing on the equitable aspects of involving a community in its long-term restoration. When restoring a community in a post-disaster environment, experts in the field act out of good conscience; however, bad actors or mistakes may severely affect the outcome of a project or potentially harm a community. These questions intend to reduce harm by increasing communication and consideration between experts.
When addressing current gaps in the communication of Nature-based Solutions between technical and non-technical audiences (Objective 1), it is imperative to identify barriers that exist in a community that may be exacerbated by an NbS project. For example, the creation of a park that protects a community against storm surges or wildfires may raise property values for homeowners, yet push lower-income residents out. Not only must communities be involved in decision-making processes and long-term plans, but they must also be given the capacity to continue management and maintenance long after the experts conclude the project (Li and Guo, 2024).
It is difficult to measure how well a functioning ecosystem can mitigate the effects of a hazard or disaster on a community (Buma et al., 2024; Li and Guo, 2024). To expand upon this concept, it is even more challenging to measure how well a functioning ecosystem works when in comparison to a more managed, less diverse ecosystem as no two projects are alike or exist in a vacuum (Li and Guo, 2024). Therefore, when identifying a better working definition of NbS in hazard mitigation for use by non-scientists, Objective 2, a variety of factors must be considered. The term, “Nature-based Solutions” is used in multiple different contexts and has many different meanings depending on the field. However, we suggest that a new definition of Nature-based Solutions across academic, governmental, and policy contexts contain the following parameters:
• Improves community physical health through scientifically sound practices (via hazard mitigation, pollution reduction, and sustainable food and water access) while minimizing harm.
• Can be managed by a community over a long term, and if the community is unable to manage it, then overseen by local, Tribal, or territorial government.
• Contains a portion (>50% of the patch) that is a self-sufficient, healthy, and biodiverse ecosystem with predominantly native species.
• A farm that uses permaculture practices (“biodiverse” farm) may fit these criteria
The continuity of a project through Monitoring and Evaluation (Objective 3) is seemingly the most difficult issue to address. When practitioners, academics, and subject matter experts are involved in the implementation of a multidisciplinary project such as an NbS, continuity is essential, but momentum is limited. Professionals may make mistakes, switch jobs, or retire; companies may be shut down, or governmental departments may be merged or dissolved. It should be at the forefront that teams, not single experts, work with the community on a project. Funding is limited, and projects may prove difficult to balance. Experts must keep in mind that they have the ability to leave a project. A community does not necessarily have this ability.
Discussion
As practical and effective Nature-based Solutions are more incorporated by communities, acknowledging realistic project implementation becomes more and more imperative. Academics, subject matter experts, policymakers, and practitioners must ensure that funding, capacity, and support can be secured for long-term projects. By identifying key communication gaps, standardizing crucial definitions, and establishing long-term protocols, project implementation can be more consistent and streamlined. Managing proper communication and expectations between experts and community members is perhaps one of the most important skills any expert may possess and must be incorporated into best practices. Experts tend to “shoehorn” themselves into one subject. However, with the climate crisis causing increased disaster risk, experts must fill interdisciplinary shoes.
As authors, we acknowledge that these solutions are idyllic but necessary. In a perfect world, the current residents of Oakwood Beach would be living beside effective Nature-based Solutions that provide storm surge protection for the next hurricane season. However, it must be acknowledged that hazard mitigation is a constant game of chasing perfection and balancing tradeoffs. There will never be a “perfect storm” or a “perfect solution”, but for the good of the communities that benefit from Nature-based Solutions and investments, it is essential to gain alignment and commit to communities' long-term hazard mitigation.
Author contributions
HD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SJ: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fclim.2024.1514000/full#supplementary-material
References
Buma, B., Poulos, H., Brown, T., Johnson, K., Smith, R., Harris, P., et al. (2024). Expert review of the science underlying nature-based Climate Solutions. Nat. Climate Chang. 14, 402–406. doi: 10.1038/s41558-024-01960-0
CountyOffice.org (2024). Fox Ln, Staten Island, NY Property Records. Available at: https://www.countyoffice.org/ny-property-records/ (accessed July 21, 2024).
Ferreira, C.S.S., Soneja, A., Liu, H., and Wright, N. (2022). Nature-based Solutions for Flood Mitigation: Environmental and Socio-economic Aspects. Cham: Springer.
Frantzeskaki, N., Kabisch, N., McPhearson, T., and Hansen, R. (2019). Nature-Based Solutions for Urban Climate Change Adaptation: Linking Science, Policy, and Practice Communities for Evidence-Based Decision-Making. Oxford: Oxford University Press Academic. Available at: https://academic.oup.com/bioscience/article/69/6/455/5492440 (accessed July 21, 2024). doi: 10.1093/biosci/biz042
Governor's Office of Storm Recovery (2023). 5th Anniversary Report 2012–2017: Five Years Later – a Retrospective. Available at: https://hcr.ny.gov/system/files/documents/2023/06/fifth-anniversary-report.pdf (accessed November 20, 2024).
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) (2020). Nature-Based Solutions for Climate Resilience, 1st edn. Available at: https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2020-021-En.pdf (accessed November 21, 2024).
Kensinger, N. (2022). Sea Level Rise and Brooklyn's Jamaica Bay Communities: Storm surge Barriers and Managed Retreat. New York: City University of New York (CUNY). Available at: https://academicworks.cuny.edu/ny_pubs/905 (accessed July 21, 2024).
Li, J., and Guo, Z. (2024). “Leveraging greenspace to manage urban flooding: An investigation of nature-based solutions implementation in U.S. public parks,” in MDPI. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/13/9/1531 (accessed August 12, 2024).
Lo, W., Huang, C.-T., Wu, M.-H., Doong, D.-J., Tseng, L.-H., Chen, C.-H., and Chen, Y.-J. (2021). Evaluation of flood mitigation effectiveness of nature-based solutions: potential cases with an assessment model for flood mitigation. Water 13:3451. doi: 10.3390/w13233451
McNeil, S., Cohen, P., Davis, T., Smith, L., and White, J. (2015). Household Residential Decision-Making in the Wake of Disaster: Report of Results Prepared for Sea Bright Residents. Available at: https://udspace.udel.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/3f464b74-9242-4717-9da9-aa1cdc5a9ad2/content (accessed July 20, 2024).
Salles, J. (2022). “What life is like for the last residents of Staten Island's Oakwood Beach,” in Grist. Available at: https://grist.org/equity/oakwood-beach-staten-island-buyouts-superstorm-sandy/ (accessed April 20, 2024).
Seddon, N., Chausson, A., Berry, P., Girardin, C.A.J., Smith, A., and Turner, B. (2021). ‘Getting the message right on nature-based solutions to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 27, 1518–1546. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15513
Shailer, L. (2022). “They lied to all of us: ten years after Hurricane Sandy,” in New York Focus. Available at: https://nysfocus.com/2022/10/29/hurricane-sandy-oakwood-beach-buyout/ (accessed April 19, 2024).
Spidalieri, K., Smith, I., and Grannis, J. (2017). Managing the Retreat from Rising Seas. Washington, DC: Georgetown Climate Center. Available at: https://www.georgetownclimate.org/files/MRT/GCC_20_FULL-3web.pdf (accessed April 19, 2024).
U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (2023). Climate Resilience Implementation Guide: Nature-Based Solutions. Available at: https://files.hudexchange.info/resources/documents/Climate-Resilience-Implementation-Guide-Nature-Based-Solutions.pdf (accessed November 20, 2024).
United States, Federal Emergency Management Agency. (2023). Building Community Resilience with Nature-Based Solutions. Available at: https://www.fema.gov/sites/default/files/documents/fema_riskmap-nature-based-solutions-guide_2021.pdf (accessed November 20, 2024).
Keywords: managed retreat, nature-based solutions, New York (City), community-led buyout program, hurricane sandy
Citation: Dancy HM, Jah SK and DeVincenzo JL (2025) What are you doing in my swamp? A case study of a community-led buyout and ecosystem restoration program in Staten Island, NY, from 2012 to 2024. Front. Clim. 6:1514000. doi: 10.3389/fclim.2024.1514000
Received: 19 October 2024; Accepted: 09 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Charles Krishna Huyck, ImageCat, United StatesReviewed by:
John Malcolm Gowdy, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, United StatesJiayang Li, University of Florida, United States
Copyright © 2025 Dancy, Jah and DeVincenzo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hannah M. Dancy, aG1kMjE0NEBjb2x1bWJpYS5lZHU=
 Hannah M. Dancy
Hannah M. Dancy Syeda Kainaat Jah
Syeda Kainaat Jah Joshua L. DeVincenzo
Joshua L. DeVincenzo