
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Chem. , 19 February 2025
Sec. Catalytic Reactions and Chemistry
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2025.1552002
This article is part of the Research Topic Catalysis for Environmental Applications: Addressing Global Challenges View all articles
In this study, CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts were successfully synthesized via ultrasonic impregnation, and their performance in degrading nitrobenzene within a Fenton-like system was investigated. The catalyst materials were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscope(TEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts featured well-distributed CuO-CoOx nanoparticles within the mesoporous SBA-15 support. Compared to CuO/SBA-15 and Co3O4/SBA-15 catalysts with similar microstructures, the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts exhibited Cu-Co dual active centers and a higher abundance of redox-active sites. During catalytic degradation, H2O2 was continuously activated on the catalyst surface through efficient Cu+/Cu2+ and Co2+/Co3+ redox cycles. The experimental conditions (initial pH, catalyst dosage, and H2O2 dosage) were optimized, resulting in 99% nitrobenzene removal over a wide pH range (3.0–9.0). The primary mechanisms for the oxidation and subsequent removal of nitrobenzene in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system were identified as reactions with hydroxyl radicals (·OH).
• CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst synthesized using ultrasonic impregnation method.
• Contaminants effectively degraded across a wide pH range (3.0–9.0).
• Cu-Co dual active centers drive the continuous activation of H2O2.
• Nitrobenzene degradation driven by ·OH in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system.
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have gained significant attention in wastewater treatment due to their exceptional effectiveness in rapidly and efficiently removing pollutants. These processes rely on highly reactive free radicals, such as hydroxyl radicals (Silveira et al., 2015; Zhu et al., 2019). Among the various AOPs, the Fenton reaction—where Fe2+ activates H2O2—remains the most widely studied. However, this homogeneous reaction typically operates within a low pH range (2.0–4.0) and produces a substantial amount of iron sludge (Blanco et al., 2016). As a result, heterogeneous catalysts have been explored as an alternative, leading to the development of heterogeneous Fenton-like systems that offer several advantages over traditional homogeneous Fenton reaction (Lei et al., 2015; Nidheesh, 2015).
Heterogeneous Fenton-like pollutant degradation systems primarily utilize transition metal-based catalysts (Bokare and Choi, 2014; Anipsitakis and Dionysiou, 2004) due to their excellent catalytic activity, low cost, widespread availability, and abundant reserves. In recent decades, the development of ultra-efficient heterogeneous Co- and Cu-based catalysts has garnered significant attention, driven by the broad pH tolerance and remarkable catalytic activity of these metals (Zhao Y. B. et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020). When employed as catalysts in Fenton-like reactions, nano Cu-Co bimetallic oxides have demonstrated high efficiency in degrading pollutants such as nitrobenzene and humic acid in water (Tan et al., 2024; Li et al., 2021). These metals can catalyze the generation of ⋅OH from H2O2 through the conversion between their different valence states, behaving similarly to Fe in Fenton-like reactions. At the same time, many studies suggest that the synergistic effect between different metals can accelerate electron transfer and the redox cycle of metal ions (Hammouda et al., 2017). More importantly, the uniform electronic distribution induced by oxygen vacancies in catalysts prepared with two different metals further promotes the adsorption and activation of reactant species on Cu-Co bimetallic oxides (Yu et al., 2019; Zhao Z. et al., 2023). However, despite the high performance of some bimetallic catalysts, bimetallic oxide nanoparticles often exhibit low crystallinity and significant particle size variations. Additionally, van der Waals forces and electrostatic interactions can lead to the agglomeration of these nanoparticles into larger particles, which negatively impacts their catalytic or adsorptive performance. Due to their small size, further challenges, such as difficulties in separation and issues with diffusion, hinder the widespread practical use of nanoparticle catalysts in wastewater treatment. Therefore, developing methods to prepare nanoparticles on an appropriate support matrix to achieve good particle dispersion and facilitate easy separation from treated wastewater, while maintaining excellent Fenton-like catalytic activity, would be highly desirable.
To address the aforementioned issues, some researchers have immobilized bimetallic oxides onto various supports, such as metal oxide (Sehati and Entezari, 2017), clay, zeolites, and carbon-based materials (Liu et al., 2019; Du et al., 2019; Prathap et al., 2012). The use of these supports helps prevent metal ion leaching and provides a larger specific surface area (Galarneau et al., 2007), thereby enhancing catalyst stability and promoting reactant adsorption. The performance of heterogeneous catalytic materials is closely linked to their active centers, which are directly influenced by their nanomorphology. A well-designed heterogeneous catalyst features numerous highly dispersed active centers on a porous support. As a result, materials with high mesoporosity have garnered significant interest. However, the nanochannels in these mesoporous supports can become blocked, leading to reduced support utilization and diminished performance.
In this study, an innovative ultrasonic impregnation method was employed to synthesize heterogeneous catalyst materials with novel nanoarchitectures within the confined spaces of ordered mesoporous hosts. First, an alcohol precursor solution was prepared, and the mesoporous host was added to this solution. Thorough impregnation of the host’s pore channels with the precursors was ensured through continuous stirring and ultrasonication. Subsequently, a heating step was applied to decompose the precursors within the confined pore spaces. This strategy was used to produce well-dispersed and uniform metal oxide nanoparticles within the nanochannels of the host material.
Ultrasonic impregnation was then used to prepare a series of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts. Mesoporous SBA-15 (Santa Barbara Amorphous-15), with its large surface area, excellent structural stability in water (Galarneau et al., 2007), highly ordered pores and channels, and narrow pore size distribution, is an ideal support material for catalysts. The suitable pore sizes range (5–8 nm or more) provided by SBA-15 creates a confined microenvironment that facilitates the growth of nanoparticles. Nitrobenzene, a common organic intermediate and emerging environmental contaminant, was chosen as the target pollutant to assess the catalytic degradation efficiency of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 as a Fenton-like catalyst. A series of characterization techniques were employed to study the chemical composition and physical structure of the prepared catalysts. The synergistic effect of the copper and cobalt oxides on catalytic nitrobenzene degradation was evaluated, and the experimental degradation parameters (pH, catalyst dosage, and H2O2 dosage) were optimized to enhance nitrobenzene removal. Finally, a potential H2O2 activation mechanism over CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 was proposed. Overall, this study provides a straightforward preparation strategy for obtaining highly active Fenton-like catalysts.
The following reagents were obtained from Aladdin (Shanghai, China): nitrobenzene (C6H5NO2, NB, 99.0%), tetraethylorthosilicate (Si(OC2H5)4, TEOS, 98%), ethanol (C2H5OH, 99.8%), and polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide-polyethylene (P123, MW = 5800). Cu(NO3)2·4H2O and Co(NO3)3·6H2O were purchased from Tianjin Guangfu Fine Chemical Co. (China). H2O2 (30%) was obtained from Beijing Chemical (China). HPLC-grade methanol was purchased from Fisher Scientific (United States). H2SO4 (0.1 M) and NaOH (0.1 M) were used to adjust the pH of the reaction solution.
SBA-15 was synthesized hydrothermally (Liu et al., 2019). In detail, 4.0 g of P123 was added to 120 mL of an aqueous HCl solution (100 mL water +20 mL HCl). This solution was then heated to 40°C and stirred until it became clear. Next, 8.6 mL of TEOS was slowly added to the solution, which was stirred for 24 h to obtain a sol. The sol was hydrothermally reacted in a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined autoclave reactor for 48 h at 100°C. The resulting solid product was cooled, washed with deionized water until a neutral pH was achieved, and then dried. Finally, the product was calcined for 6 h at 500°C to obtain pure SBA-15.
An ultrasonic impregnation method was used to prepare CuO-CoOx/SBA-15. Specifically, 0.5 g Cu(NO3)2·3H2O and 0.122 g Co(NO3)3·6H2O were dissolved in 5 mL ethanol. This ethanol solution was gradually added to 0.6 g SBA-15, and the mixture was stirred for 3 h to form a paste. Ultrasonic impregnation was then performed for 30 min with an ultrasonic power of 0.5 W/cm3, followed by calcination for 5 h at 300°C in a muffle furnace to obtain CuO-CoOx/SBA-15. A series of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts were prepared by varying the total metal content, Cu/Co molar ratio, and calcination temperature. Samples labeled M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 were prepared with total metal oxide contents of 1.08 wt%, 2.3 wt%, 3.4 wt%, 4.9 wt%, and 5.1 wt%, as determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The Cu/Co molar ratio of in all samples was 1:2, unless otherwise specified.
N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms were acquired with a TRISTAR II 3020 (Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, United States), and the Barrett-Joyner-Hallender (BJH) pore size distributions were determined from the desorption branch. Specific surface areas were calculated using the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) theory. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was conducted with a Bruker AXS D8 system, using Cu Ka radiation (λ = 1.540598 Å) in the 2θ range of 10°–80° to assess the crystal structures. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed with an ESCALAB 250Xi (Thermo Electron Corporation, United States) using Al Kα radiation (1,486.6 eV). The C 1s peak at 284.6 eV was used as a reference for peak calibration. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (STEM-EDS) (JEM-3200FS) were employed to examine the morphology, particle size, phases, and surface elemental distributions of the samples. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, NexION 2000, PerkinElmer) was used to quantify the metal content in each sample.
The catalytic degradation of nitrobenzene (NB) was performed at room temperature. An NB solution with a concentration of 50 mmol/L was first prepared and adjusted to the desired pH. About 0.2 g of catalyst was then added to 100 mL of this solution. Before adding H2O2, the mixture was magnetically stirred for 30 min in the dark to ensure adsorption equilibrium. Afterward, a specified amount of 30.0 wt% H2O2 was added under continuous stirring to initiate the Fenton-like degradation reaction. At regular intervals of 15 min, small samples of the reaction mixture were withdrawn with a syringe and filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane filter. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was employed to analyze each filtered sample, and the NB concentration was determined using a Waters e2695 system with a C18 column. The chromatography analysis was performed with a mobile phase of 70% methanol and 30% formic acid solution (0.1 vol%), a flow rate of 1 mL/min, an injection volume of 50 μL, and a detection wavelength of 265 nm.
The NB removal efficiencies of H2O2 (100 mmol/L), CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 (2.0 g/L), and CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 (2.0 g/L catalyst, 100 mmol/L H2O2) systems are shown in Supplementary Figure S1. Less than 20% NB removal was achieved by H2O2 or CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 alone, demonstrating that neither of these reagents alone could effectively degrade NB. However, the combination of both H2O2 and CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 resulted in an NB degradation efficiency of approximately 80.0% within 60 min. This demonstrates that CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 can effectively catalyze H2O2 for the removal of NB, which is consistent with our previous report (Li et al., 2021).
Different CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts were prepared by calcining at temperatures of 300°C, 400°C, and 500°C.Both Pure SBA-15 and the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts exhibited typical N2 adsorption-desorption type-IV isotherms, each featuring H1-type hysteresis loops in the range of p/p0 = 0.6–0.8 (Supplementary Figure S2). This behavior is attributed to the well-defined hexagonal pore structure of pure SBA-15. The CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts calcined at different temperatures had similar pore volumes (approximately 0.80 cm3/g) and pore sizes (about 5.5 nm). The specific surface areas of the calcined CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts (Table 1) were slightly lower than that of pure SBA-15 but significantly higher than those of CuO-CoOx and other CuO-containing catalyst materials, such as CuO/rGO (56.1 m2/g) (Du et al., 2019) and CuO/Ti6O13 (6.93 m2/g) (Sehati and Entezari, 2017). Higher specific surface areas facilitate faster electron transfer (Prathap et al., 2012), thereby enhancing catalytic activity. These results suggest that the ultrasonic impregnation method enables a uniform distribution of CuO-CoOx on the SBA-15 surface, which likely altered the surface structure of the catalyst and facilitated the catalytic reaction. The observed decrease in pore diameters and volumes of the catalysts after ultrasonic impregnation further confirms the successful loading of CuO-CoOx onto SBA-15 support material.
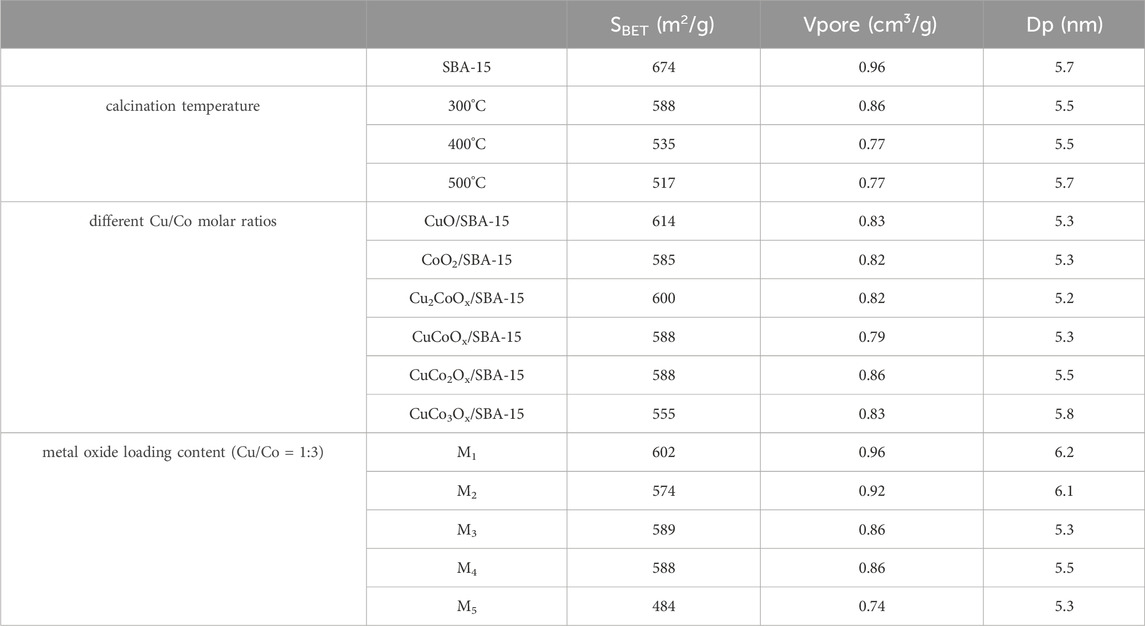
Table 1. BET specific surface area, pore volume, and pore size of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts prepared at different calcination temperatures, Cu/Co molar ratios, and metal oxide loadings.
The phases of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 and pure SBA-15 were evaluated by XRD, as shown in Supplementary Figure S3. All samples exhibited a broad peak in the 2θ range of 20°–23° (Supplementary Figure S3a), confirming the formation of SBA-15. According to Thahir et al. (Thahir et al., 2019), this peak is attributed to the [100] planar orientation of SBA-15. The samples calcined at 300°C and 400°C did not display any other diffraction peaks, indicating that metal oxide crystals did not form at these calcination temperatures. However, when the calcination temperature was increased to 500°C, overlapping peaks ascribed to Cu2O and Co3O4 were observed at 38°, indicating that higher calcination temperatures promote the formation of metal oxide particles. The absence of other diffraction peaks indicated that no other phases were generated or that they were present in negligible amounts.
The morphologies of SBA-15 and CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 were analyzed by SEM and TEM, as shown in Figure 1and Supplementary Figure S5. The SEM image of SBA-15 (Figure 1A) revealed long cylindrical rod-shaped particles, consistent with previous studies on SBA-15 (Kumaravel et al., 2020). In contrast, SEM analysis of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 (Figure 1B) demonstrated that CuO-CoOx was uniformly distributed throughout the SBA-15 structure. TEM analysis of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15(Supplementary Figure S5) shown that the CuO-CoOx particles were smaller than 80 nm, which is expected to enhance the degradation performance. This observation confirms that SBA-15 effectively control the shape and size of CuO-CoOx nanoparticles. EDS analysis (Figures 1D–F) and elemental mapping (Figure 1C) further validated the uniform dispersion of Co, Cu, and Si within the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst. The even distribution of elements and the uniform particle size of CuO-CoOx can be attributed to the cavitation effect induced by ultrasonication, which created a highly intense environment during catalyst preparation.
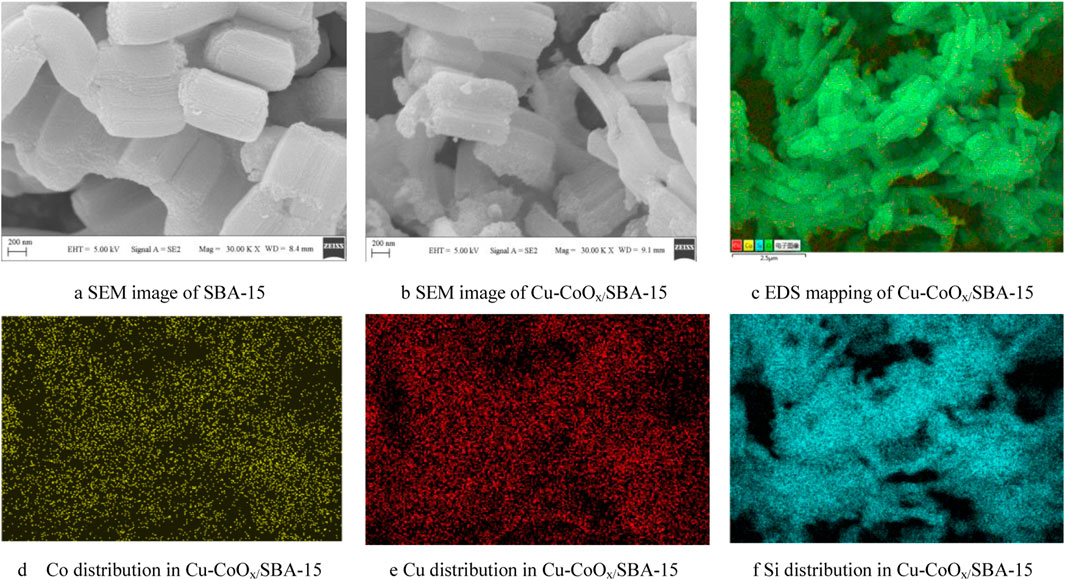
Figure 1. SEM images of SBA-15 (A) and CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 (B); EDS analysis showing the distributions of Co, Cu, and Si in CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 (C–F).
The CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts, calcined at different temperatures, were evaluated for NB degradation in the presence of H2O2 under the following conditions: 25°C reaction temperature, 2.0 g/L catalyst dosage, 100 mmol/L H2O2 dosage, 50 mmol/L NB concentration, initial pH of 7.5, and a reaction time of 90 min, as shown in Figure 2A. After calcination at 300°C, 400°C, and 500°C, the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts achieved degradation efficiencies of 67.24%, 50.21%, and 51.49%, respectively. The characterization results of the specific surface area (as shown in Table 1) indicate that as the calcination temperature increases from 300°C to 500°C, the specific surface area of the obtained catalysts gradually decreases from 588 m2/g to 517 m2/g, and the catalytic activity of the corresponding sample also gradually decreases. The lower degradation efficiencies observed at higher calcination temperatures are consistent with the poor crystal shape, rough surface, low dispersibility, and lack of regularity observed at lower temperatures. Based on these findings, 300 °C was determined to be the optimal calcination temperature.

Figure 2. Degradation efficiencies of NB by CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts prepared using different calcination temperatures (A), Cu/Co molar ratios (B), and metal oxide content (C).
Heterogeneous bimetallic oxide catalysts (e.g., Cu-Mn) can be effectively employed for the removal of target contaminants in Fenton-like degradation systems. Zhang et al. (2020), Qin et al. (2020) reported that the combined advantages of each catalytic component in bimetallic oxide catalysts can be effectively leveraged, resulting in synergistically enhanced reaction performance compared to pure transition metal oxide catalysts. However, the underlying synergistic mechanisms and the individual contributions of the two metals in bimetallic oxide catalysts remain poorly understood.
In this study, to evaluate the effect of the Cu/Co metal oxide ratio on NB degradation, a series of monometallic and bimetallic oxide catalysts supported on SBA-15 were prepared. As shown in Figure 2B, the monometallic oxide catalysts exhibited low NB removal efficiencies, highlighting the synergistic effect of combining Cu and Co oxides in the Fenton-like reaction. With a fixed CuO-CoOx content of 3.4 wt%, the NB removal efficiency was significantly enhanced as the cobalt content increased. The CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst prepared with a Cu/Co molar ratio of 1:2 demonstrated the highest NB removal efficiency.
The CuO/SBA-15 catalyst exhibited a specific surface area of 614 m2/g (Table 1), suggesting that ultrasonic impregnation effectively facilitated the uniform distribution of CuO on the SBA-15 surface. However, as the CoOx content increased, the specific surface area decreased to 588 m2/g and 555 m2/g, respectively. The CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts prepared with varying CuO/CoOx ratios showed similar pore volumes (0.79–0.86 cm3/g), although the pore size increased to 5.8 nm when the CuO/CoOx ratio was 1:3. So, the effect of copper/cobalt ratio on the specific surface area of the catalyst is not significantly positively correlated with their respective degradation efficiencies.
The XRD patterns of the monometallic and bimetallic CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts with various Cu/Co ratios are shown in Supplementary Figure S3B. As the CoOx content increased, the diffraction peak corresponding to Co3O4 became more prominent, while the diffraction peaks for CuO remained relatively unchanged. This suggests that the presence of CoOx helps to disperse CuO and inhibits its aggregation, suggesting a synergistic effect between the two metal oxides.
The Cu 2p and Co 2p XPS spectra of the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts prepared with different metal ratios are shown in Figure 3. The Cu 2p3/2 peak was deconvoluted into two distinct peaks corresponding to Cu(II) and Cu(I) at 934.56 eV and 933.10 eV, respectively (Liu et al., 2019; Lyu et al., 2015). A satellite peak for CuO was observed at 942.27 eV, approximately 9 eV higher than the main peak. The Cu(I)/Cu(II) atomic ratio, calculated from the areas of Cu(I) and Cu(II) peaks, increased with the cobalt content, with the lowest ratio (0.27:1) observed for CuO/SBA-15. This indicates a strong interaction between copper and cobalt, enhancing the redox cycle of the copper species. The Co 2p XPS spectra of the CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst (prepared without Cu) showed two main 2p3/2 peaks at 783.10 eV and 781.07 eV, corresponding to Co(II) and Co(III), respectively. Additionally, a CoOx satellite peak was observed at 787.6 eV (Wang et al., 2020). Notably, the XPS spectra of the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts exhibited a slight shift in binding energy. For the catalyst synthesized with a Cu/Co ratio of 1:3, the Co3+ peaks were located at 781.01 and 795.82 eV, the Co2+ peaks at 783.04 and 798.52 eV, and the satellite peaks at 787.3 and 804.3 eV. This shift in peak positions suggest a sttrong synergistic interaction between Co and Cu (Liu et al., 2019), which facilitates the Co and Cu redox processes and enhances ·OH production. The Co2+/Co3+ ratio in these catalysts varied with increasing CuOx content, reaching its highest value at a Cu/Co ratio of 1:2. According to the report of Meng et al. (2024), the lower valance state of Co is closely related to the vast oxygen vacancy (Ov) in CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts. From Supplementary Figure S5, it can be seen that O 1s spectra are fitted into two peaks, with the peak at 530.96 eV in accordance with the lattice oxygen (Olatt) and the peak at 531.78 eV belong to surface oxygen (Osurf) (Meng et al., 2024; Sui et al., 2024). As is well recognized, Osurf is incubated by trapping of gaseous O2 in the oxygen vacancy (Ov) structure, which was a reactive oxygen specie to attack organics.This kind of conversion demonstrated that Olatt species participated in the degradation process of NB, which was consistent with the study by Sedmak et al. (2003).
The CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts with higher metal oxide loading exhibited smaller specific surface areas, as shown in Table 1. This was likely due to the aggregation of CuO-CoOx into larger crystalline particles. Additionally, increasing the CuO-CoOx content resulted in a reduction in pore volume, which was attributed to excessive metal oxide loading blocking the pores. The XRD patterns of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts prepared with varying CuO-CoOx content are shown in Supplementary Figure S3C. For catalysts with CuO-CoOx content of 3.4% or less, no distinct diffraction peaks for Cu2O and Co(OH)2 were observed. However, when the CuO-CoOx content increased to 5.1%, clear and sharp diffraction peaks for Cu2O and Co3O4 appeared at 38.8° and 44.4°, indicating the formation of more crystalline Cu2O and Co3O4 with larger grain sizes. This phenomenon was consistent with the nitrogen adsorption-desorption analysis.
The NB degradation efficiencies of the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts with varying metal oxide content are presented in Figure 2C. The catalysts with CuO-CoOx contents of 1.08 wt%, 2.3 wt%, 3.4 wt%, 4.9 wt%, and 5.1 wt% achieved NB degradation efficiencies of 43.1%, 59.1%, 67.3%, 80.25%, and 16.7%, respectively. The NB degradation efficiency initially increased and then decreased with increasing CuO-CoOx content, with the highest performance observed at 4.9 wt%. This enhanced efficiency can be attributed to the increased amount of active catalytic components at this loading, which facilitated the degradation reaction.
To further optimize NB degradation in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 Fenton-like system, the catalyst dosage, H2O2 dosage, and initial pH were adjusted.
The NB removal performance of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 at different catalyst dosages is shown in Figure 4A. As the catalyst dosage increased from 0.5 to 3.0 g/L, the NB removal efficiency improved from 50.0% to 89.0%. This increase was attributed to a higher catalyst dosage providing more surface active sites. However, when the catalyst dosage was further increased to 4.0 g/L, no significant improvement in performance was observed. This plateau effect is likely due to the sufficient availability of active sites at the 3.0 g/L dosage. Therefore, a CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 dosage of 3.0 g/L was determined to be optimal for the best degradation performance.
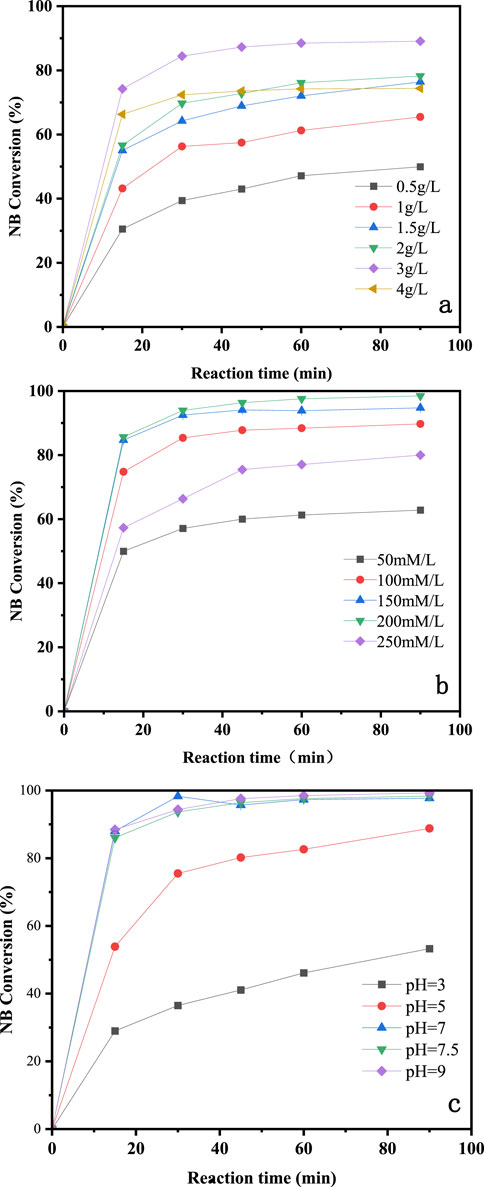
Figure 4. Influence of catalyst dosage (A), concentration of H2O2 (B), and initial pH (C) on degradation of NB by CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 in water.
The presence of H2O2 in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system resulted in the generation of ·OH, making the H2O2 dosage a key factor influencing the NB oxidation process. In this study, NB degradation was evaluated with H2O2 dosages rangin from 50 to 250 mmol/L, as shown in Figure 4B. As the H2O2 dosage increased to 200 mmol/L, the NB removal efficiency correspondingly improved, reaching 99.0%. However, further increasing the H2O2 dosage to 250 mmol/L led to a decrease in NB removal efficiency. This decline was attributed to excess H2O2 reacting with ·OH (thereby negatively affecting NB removal) or decomposing into H2O and O2, which did not contribute to NB degradation (Ghasemi et al., 2020; He et al., 2020). Based on these findings, and considering the treatment cost, the optimal H2O2 dosage was determined to be 200 mmol/L.
The degradation of organic compounds by AOPs is notably affected by pH. Conventional Fenton reactions typically operate optimally in the pH range of 2–4 (Bokare and Choi, 2014), while heterogeneous Fenton-like systems usually show broader pH tolerance (Zhang et al., 2020; He et al., 2020; Xing et al., 2008). For example, Xing et al. (2011) developed an Fe3O4/FeMnOx Fenton-like catalyst that achieved excellent methylene blue (MB) removal performance in the pH range of 3.5–9.0. In this study, NB degradation was evaluated at initial pH values of 3.0, 5.0, 7.5, and 9.0, as shown in Figure 4C (reaction conditions: 25°C reaction temperature, 3.0 g/L catalyst dosage, 200 mmol/L H2O2 dosage, 50 mmol/L NB concentration, and a reaction time of 90 min). The highest NB removal efficiency of 99.0% was achieved at an initial pH of 9.0, with similar performance observed at pH 7.0 and 7.5. A pH of 5.0 resulted in slightly reduced performance, and the NB removal efficiency significantly decreased at pH 3.0. These results demonstrate that NB degradation was notably influenced by the initial pH, and the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system was highly effective in decomposing NB under neutral or alkaline conditions.
The reactive radicals in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system were identified using p-benzoquinone (BQ) and t-butanol (TBA) as quenching agents for ·O2− and ·OH, respectively, as shown in Figure 5. In a blank experiment without any quencher, the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system achieved 99% NB degradation after 90 min. However, the addition of TBA significantly inhibited the degradation process. Specifically, the addition of 100 mmol/L TBA reduced the NB degradation efficiency from 99% to 48.1%, and the reaction was completely inhibited with a TBA concentration of 200 mmol/L. Similar results were obtained when 200 mmol/L TBA and 10 mmol/L BQ were introduced simultaneously. Interestingly, the addition of 1 mmol/L or 10 mmol/L BQ did not hinder NB removal, suggesting that ·O2− was not involved in the degradation process.
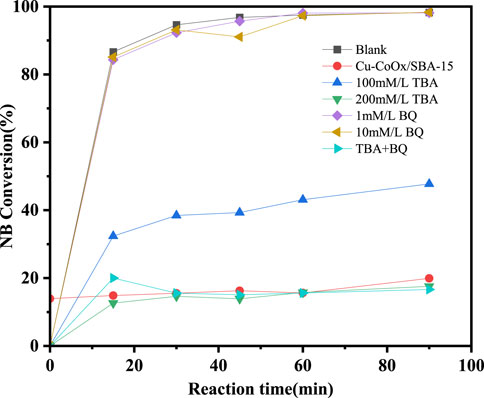
Figure 5. Inhibitory effects of TBA and BQ on degradation of nitrobenzene in CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system.
To further reveal the reaction mechanism, the radical species generated in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system were detected by performing EPR analysis with DMPO as a spin-trapping agent, as displayed in Supplementary Figure S4. The presence of ·OH was demonstrated by the DMPO-·OH adduct quartet peaks (1:2:2:1 intensity ratio, ɑN = ɑH = 14.9 G). Peaks ascribed to DMPO-·O2− adducts were also observed. Therefore, both O2− and ·OH existed in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system, and as indicated by the BQ and TBA quenching experiments, the ·OH radicals were responsible for NB degradation. It should be noted that not all of the OH generated in this system took part in NB oxidation. Instead, some of these ·OH radicals would be converted to O2− or other species. The relative contribution of each of these reactive species will be further studied in subsequent research.
The CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst surface was evaluated by XPS before and after the NB degradation reaction to further reveal the mechanism explaining its enhanced performance, as exhibited in Figure 6. The survey spectra confirmed the existence of both Co and Cu in the fresh and used catalysts as well as the absence of impurities. The Cu 2p spectrum of the fresh CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst contained Cu 2p3/2 and Cu 2p1/2 peaks at 934.9 and 954.4 eV (Liu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020), respectively. The splitting energy of 19.50 eV was close to the standard value of 19.75 eV for Cu 2p orbits, indicating that the Cu in this catalyst existed in a mixed valence state. The Cu 2p3/2 peak was deconvoluted into two peaks ascribed to Cu(I) and Cu(II) that were located at 933.12 and 935.06 eV, respectively. The Cu2+/Cu+ ratios of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 before and after the reaction were 1.48 and 1.64, respectively. These results indicate the oxidation of Cu(I) to Cu(II), which was responsible for generating ·OH as shown in Equation 1. The Co 2p spectrum of the fresh CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst showed two notable peaks at 782.5 eV (Co 2p3/2) and 796.8 eV (Co 2p1/2) as well as satellite peaks at 786.6 eV and 802.5 eV (Xing et al., 2011; Ren et al., 2015; Rekha et al., 2015; Cheng et al., 2013; Yao et al., 2015). The Co 2p3/2 peak was deconvoluted into Co2+ and Co3+ peaks, which were respectively located at 780.68 eV and 782.92 eV. The Co2+/Co3+ ratios of the catalyst before and after the reaction were 1.26 and 1.58, respectively. This indicated that Co(II)/Co(III) oxidation played a minor role in generating ·O2−, as described by Equation 8, (Tan et al., 2024). This analysis confirms that the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst was oxidized during the NB degradation reaction, which led to greater Co3+ and Cu2+ surface content. These chemical state changes are associated with the presence of H2O2. As described in Equations 1, 7, (Yao et al., 2015), the active sites on the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 surface undergo oxidation from MsurfCo2+ and MsurfCu+ to MsurfCo3+ and MsurfCu2+. This generates oxidizing radicals (i.e., OH−and ·OH) that contribute to NB degradation. To complete the catalytic cycle, the MsurfCu2+ and MsurfCo3+ can be reduced via a mechanism involving H2O2, as described in Equations 2–5, 8–10 (Tan et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2020). Therefore, in the presence of the Co-Cu binary oxides of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15, H2O2 is continuously activated and oxidizing radicals are continuously generated, promoting NB oxidation.
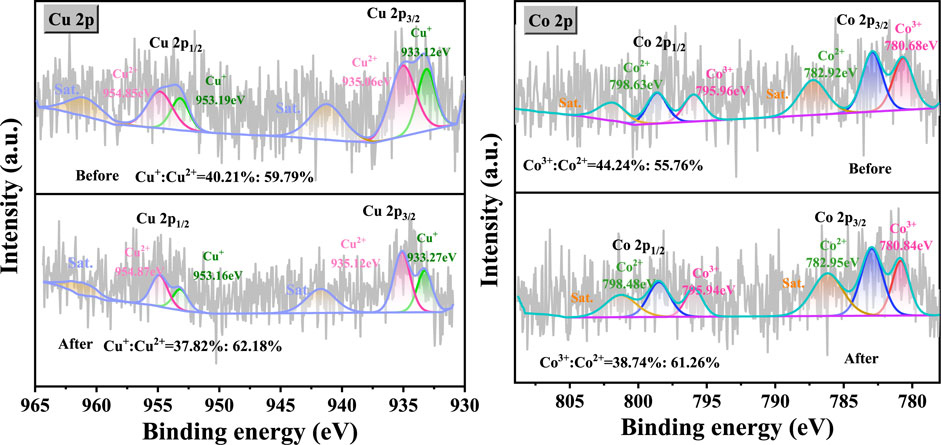
Figure 6. Cu 2p and Co 2p XPS spectra of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst before and after NB degradation reaction.
According to the XPS analysis, the catalytic NB degradation process involved both Co and Cu active sites. Due to its unique structure and intrinsic properties, the Co-Cu binary oxide catalyst effectively provides Co2+, Co3+, Cu+, and Cu2+ surface sites. Furthermore, the Co and Cu cations can undergo reversible oxidation and reduction without disrupting the catalyst’s structure. While Co2+ sites activate H2O2 more efficiently than Cu2+ sites, the Co-Cu binary oxide catalysts exhibited superior NB removal performance compared to the Co3O4 catalyst, as shown in Figure 2, this phenomenon is effectively explained by Equation 6, which describes the interaction between Cu2+ and Co3+. Overall, based on the XPS analysis and quenching experiments, the H2O2 activation mechanism in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 system for NB degradation is depicted in Figure 7.
The successful real-world application of heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation catalysts relies on their good reusability. In this study, the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst was recovered from the precipitate at the bottom of the reaction solution after NB degradation and reused. As shown in Figure 8, CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 exhibited stable NB degradation performance over four consecutive reaction cycles under the same conditions. To assess the catalyst’s stability, ICP-MS was used to monitor the potential dissolution of metal ions in the recycled reaction solution after the 60-min reaction. After four cycles leached Cu and Co concentrations were found to be 0.075 mg/L and 0.407 mg/L, respectively, which comply with the World Health Organization (WHO) drinking water quality standards and the Chinese standard GB 25467-2010. These results confirm the excellent stability of the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst, suggesting its protential for long-term use and highlighting the effectiveness of ultrasonic impregnation in encapsulating active metal components within the SBA-15 channels.
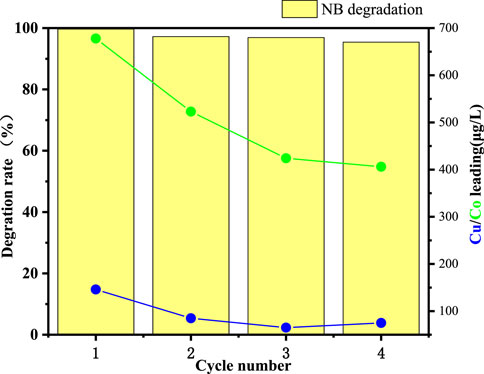
Figure 8. NB degradation performance of CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 and corresponding leached concentrations of Cu and Co across four reaction cycles.
Mesoporous SBA-15 was synthesized using sol-gel and hydrothermal methods, and CuO-CoOx nanoparticles were introduced into the mesopores of SBA-15 through ultrasonic impregnation. The resulting CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalysts exhibited highly porosity, large specific surface areas, and uniform dispersion of the active components.
HRTEM analysis revealed the uniformity of the Cu/Co bimetallic oxide particles and their excellent dispersion within the nanochannels of SBA-15. XPS analysis confirmed that H2O2 was activated by the Cu+ and Co2+ active sites on the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst surface, with these active sites being oxidized to Cu2+ and Co3+. An efficient redox cycle between Cu+/Cu2+ and Co2+/Co3+ facilitated the continuous activation of H2O2.
The optimum CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst was prepared with a CuO-CoOx content of 4.9 wt% and a Co/Cu molar ratio of 1:2. This catalyst demonstrated excellent NB removal performance over four reaction cycles, indicating good recyclability and stability. The optimal operating conditions for NB degradation in the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15-H2O2 system were an initial pH of 7–9, a CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst dosage of 2.0 g/L, and a H2O2 dosage of 200 mg/L. Under these conditions, 99.0% NB removal was achieved. The degradation of NB primarily proceeded via reaction with ·OH. Overall, the outstanding performance and stability of the CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst highlight its significant potential for practical treatment of refractory organic pollutants.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
JL: Funding acquisition, Writing–original draft. YW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. QL: Resources, Writing–review and editing. HG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. CJ: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing–review and editing. XS: Data curation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52170007 and No.51778374) and the Shenzhen Polytechnic University Research Fund (6023310040K).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2025.1552002/full#supplementary-material
Anipsitakis, G. P., and Dionysiou, D. D. (2004). Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 38, 3705–3712. doi:10.1021/es035121o
Blanco, L., Hermosilla, D., Merayo, N., and Blanco, A. (2016). Assessing the use of zero-valent iron microspheres to catalyze Fenton treatment processes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 69, 54–60. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2016.08.014
Bokare, A. D., and Choi, W. (2014). Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 275, 121–135. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054
Cheng, K., Yang, F., Wang, G., Yin, J., and Cao, D. (2013). Facile synthesis of porous (Co, Mn)3O4 nanowires free-standing on a Ni foam and their catalytic performance for H2O2 electroreduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 1669–1676. doi:10.1039/c2ta00219a
Du, X. D., Zhang, Y. Q., Si, F., Yao, C. H., Du, M. M., Hussain, I., et al. (2019). Persulfate non-radical activation by nano-CuO for efficient removal of chlorinated organic compounds: reduced graphene oxide-assisted and CuO (001) facet-dependent. Chem. Eng. J. 356, 178–189. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.216
Galarneau, A., Nader, M., Guenneau, F., Di Renzo, F., and Gedeon, A. (2007). Understanding the stability in water of mesoporous SBA-15 and MCM-41. J. Phys. Chem. C 111 (23), 8268–8277. doi:10.1021/jp068526e
Ghasemi, M., Khataee, A., Gholami, P., Soltani, R. D. C., Hassani, A., and Orooji, Y. (2020). In-situ electro-generation and activation of hydrogen peroxide using a CuFeNLDH-CNTs modified graphite cathode for degradation of cefazolin. J. Environ. Manag. 267, 110629. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110629
Guo, W., Bi, J., Zhu, Q., Ma, J., Yang, G., Wu, H., et al. (2020). Highly selective CO2 electroreduction to Co on Cu-Co bimetallic catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. and Eng. 8, 12561–12567. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c03797
Hammouda, B., Zhao, F., Safaei, Z., Babu, I., Ramasamy, D. L., and Sillanpaa, M. (2017). Reactivity of novel Ceria-Perovskite composites CeO2-LaMO3(MCu, Fe) in the catalytic wet peroxidative oxidation of the new emergent pollutant ’Bisphenol F′: characterization, kinetic and mechanism studies. Appl. Catal. B-Environment Energy 218, 119–136. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.06.047
He, X., Sun, B., He, M., Chi, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, W., et al. (2020). Highly efficient simultaneous catalytic degradation and defluorination of perfluorooctanoic acid by the H2O2-carbon/MnO2 system generating O2- and OH synchronously. Appl. Catal. B-Environment Energy 277, 119219. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119219
Kumaravel, S., Thiripuranthagan, S., Durai, M., Erusappan, E., and Vembuli, T. (2020). Catalytic transfer hydrogenation of biomass-derived levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone over Sn/Al-SBA-15 catalysts. New J. Chem. 44, 8209–8222. doi:10.1039/d0nj01288b
Lei, Y., Chen, C. S., Tu, Y. J., Huang, Y. H., and Zhang, H. (2015). Heterogeneous degradation of organic pollutants by persulfate activated by CuO-Fe3O4: mechanism, stability, and effects of pH and bicarbonate ions. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 49, 6838–6845. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b00623
Li, J., Shen, J., Liu, Q., and Jiang, C. (2021). The highly efficient degradation on nitrobenzene by using nano-copper-cobalt bimetallic oxide as heterogeneous fenton catalysts: efficiency, dynamic and mechanism. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 687, 012131. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/687/1/012131
Liu, P. T., Hu, Y. T., Liu, X. K., Wang, T. T., Xi, P. X., Xi, S. B., et al. (2019). Cu and Co nanoparticle-Co-decorated N-doped graphene nanosheets: a high efficiency bifunctional electrocatalyst for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 12851–12858. doi:10.1039/c9ta02894c
Lyu, L., Zhang, L. L., and Hu, C. (2015). Enhanced Fenton-like degradation of pharmaceuticals over framework copper species in copper-doped mesoporous silica microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 274, 298–306. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.137
Meng, W. H., Song, X. D., Bao, L. R., Chen, B. B., Ma, Z., Zhou, J., et al. (2024). Synergistic doping and de-doping of Co3O4 catalyst for effortless formaldehyde oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 494, 153028. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.153028
Nidheesh, P. V. (2015). Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the abatement of organic pollutants from aqueous solution: a review. RSC Adv. 5, 40552–40577. doi:10.1039/c5ra02023a
Prathap, M. U. A., Kaur, B., and Srivastava, R. (2012). Hydrothermal synthesis of CuO micro-/nanostructures and their applications in the oxidative degradation of methylene blue and non-enzymatic sensing of glucose/H2O2. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 370, 144–154. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.12.074
Qin, F. Z., Peng, Y. J., Song, G., Fang, Q. X., Wang, R. Z., Zhang, C., et al. (2020). Degradation of sulfamethazine by biochar-supported bimetallic oxide/persulfate system in natural water: performance and reaction mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 398, 122816. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122816
Rekha, V., Sumana, C., Douglas, S. P., and Lingaiah, N. (2015). Understanding the role of Co in Co–ZnO mixed oxide catalysts for the selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol. Appl. Catal. A General 491, 155–162. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2014.10.042
Ren, Y., Lin, L., Ma, J., Yang, J., Feng, J., and Fan, Z. (2015). Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M=Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Appl. Catal. B-Environment Energy 165, 572–578. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.051
Sedmak, G., Hocevar, S., and Levec, J. (2003). Kinetics of selective CO oxidation in excess of H2 over the nanostructured Cu0.1Ce0.9O2-y catalyst. J. Catal. 213, 135–150. doi:10.1016/S0021-9517(02)00019-2
Sehati, S., and Entezari, M. H. (2017). Sono-incorporation of CuO nanoparticles on the surface and into the mesoporous hexatitanate layers: enhanced Fenton-like activity in degradation of orange-G at its neutral pH. Appl. Surf. Sci. 399, 732–741. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.079
Silveira, J. E., Zazo, J. A., Pliego, G., Bidóia, E. D., and Moraes, P. B. (2015). Electrochemical oxidation of landfill leachate in a flow reactor: optimization using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 5831–5841. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3738-2
Sui, D., Luo, R. S., Xie, S., Zhang, H., Ma, T. T., Sun, H., et al. (2024). Atomic ruthenium doping in collaboration with oxygen vacancy engineering boosts the hydrogen evolution reaction by optimizing H absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 480, 148007. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2023.148007
Tan, S. W., Long, K., Chen, W., Liu, H., Liang, S. Y., and Zhang, Q. (2024). Synergistic oxidation of humic acid treated by H2O2/O3 activated by CuCo/C with high efficiency and wide pH range. J. Environ. Manag. 358, 120896. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120896
Thahir, R., Wahab, A. W., La Nafie, N., and Raya, I. (2019). Synthesis of high surface area mesoporous silica SBA-15 by adjusting hydrothermal treatment time and the amount of polyvinyl alcohol. Open Chem. 17, 963–971. doi:10.1515/chem-2019-0106
Wang, J., Liu, C., Feng, J. Y., Cheng, D., Zhang, C. Q., Yao, Y. N., et al. (2020). MOFs derived Co/Cu bimetallic nanoparticles embedded in graphitized carbon nanocubes as efficient Fenton catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 394, 122567. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122567
Xing, S. T., Hu, C., Qu, J. H., He, H., and Yang, M. (2008). Characterization and reactivity of MnOx supported on mesoporous zirconia for herbicide 2,4-D mineralization with ozone. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 42, 3363–3368. doi:10.1021/es0718671
Xing, S. T., Zhou, Z. C., Ma, Z. C., and Wu, Y. S. (2011). Characterization and reactivity of Fe3O4/FeMnOx core/shell nanoparticles for methylene blue discoloration with H2O2. Appl. Catal. B-Environ 107, 386–392. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.08.002
Yao, Y., Cai, Y., Wu, G., Wei, F., Li, X., Chen, H., et al. (2015). Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by cobalt manganese oxides (CoxMn3−xO4) for Fenton-Like reaction in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 296, 128–137. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.014
Yu, K., Lou, L. L., Liu, S., and Zhou, W. (2019). Asymmetric oxygen vacancies: the intrinsic redox active sites in metal oxide catalysts. Adv. Sci. 7, 1901970. doi:10.1002/advs.201901970
Zhang, N. Q., Yi, Y. Q., Lian, J. T., and Fang, Z. Q. (2020). Effects of Ce doping on the Fenton-like reactivity of Cu-based catalyst to the fluconazole. Chem. Eng. J. 395, 124897. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.124897
Zhao, Y. B., Deng, X. H., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y. Q., Wang, H., and Xin, B. F. (2023a). Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate-based Fenton-like system using CuCo2O4/g-C3N4 prepared by Cu+-Co2+ self-doped: g-C3N4 driven reduction-oxidation cycling mechanism of Cu and Co metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 110220. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2023.110220
Zhao, Z., Wang, P., Song, C., Zhang, T., Zhan, S., and Li, Y. (2023b). Enhanced interfacial electron transfer by asymmetric Cu-Ov-In sites on In2O3 for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202216403. doi:10.1002/anie.202216403
Keywords: CuO-CoOx/SBA-15, Fenton-like system, bimetallic oxides, synergistic effect, organic pollutant degradation
Citation: Li J, Wei Y, Liu Q, Guan H, Jiang C and Sun X (2025) Heterogeneous Fenton-like CuO-CoOx/SBA-15 catalyst for organic pollutant degradation: synthesis, performance, and mechanism. Front. Chem. 13:1552002. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1552002
Received: 27 December 2024; Accepted: 31 January 2025;
Published: 19 February 2025.
Edited by:
Hailong Zhang, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xingyun Li, Qingdao University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Wei, Liu, Guan, Jiang and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chengchun Jiang, amlhbmdjY19zenB0QDEyNi5jb20=; Xiaohui Sun, c3VueGlhb2h1aUBzenUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.