
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Chem., 29 January 2025
Sec. Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2025.1545908
Introduction: The multi-targeted ligands (MTDL) strategy has been recognized as a promising Approach for the development of effective treatments against Alzheimer’s disease (AD), due to the presence of multiple pathological mechanisms in AD. In this study, a series of bis(7)-harmine derivatives were designed and synthesized as multifunctional drugs for the treatment of AD.
Methods: The derivatives were synthesized by chemical methods and their structure was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The Ellman’s assay was utilized to assess the inhibitory potential of derivatives against hAChE and hBuChE. The inhibitory activity of these derivatives on both hMAO-A and hMAO-B was assessed using a fluorescence-based method. The thioflavin T (Th-T) fluorescence assay was used to assess the inhibition of Aβ1−42 self-aggregation. The cytotoxicity was evaluated using the MTT assay. The Surflex-Dock program in Sybyl-X2.0 Software was employed for molecular docking.
Results: In vitro studies revealed that numerous synthesized compounds exhibited potent inhibitory activity against hAChE, and hMAO-B (IC50 < 1 μM), as well as Aβ1−42 aggregation (IC50 < 20 μM). Importantly, the multitarget compounds 6d, 8c, and 8d exhibited remarkable efficacy in simultaneously mitigating Aβ-induced toxicity in SH−SY5Y cells while demonstrating minimal cytotoxicity. Furthermore, predicted ADMET results suggested that 6d, 8c, and 8d possessed favorable pharmacokinetic properties and demonstrated low toxicity levels. Additionally, molecular docking studies of 6d within the activesites of hAChE, hMAO-B, and Aβ1−42 elucidated the inhibition mechanism.
Discussion and conclusion: Based on these findings, it is evident that 6d, 8c, and 8d hold potential as promising multi-functional drugs for AD treatment.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive and irreversible neurodegenerative disorder that leads to a significant number of fatalities. Clinically, the primary cognitive symptoms of AD include progressive short-term memory loss, disorientation, and neuropsychological disturbances (Mendiola-Precoma et al., 2016). According to the World Health Organization (WHO) report, the global prevalence of AD is alarming, currently affecting nearly 45 million individuals, with projections indicating that this figure could surpass 150 million by 2050 (Prince et al., 2016). To date, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only four small molecule drugs (rivastigmine, galantamine, donepezil, and memantine) and two immunotherapy drugs (aducanumab and lecanemab) for the treatment of AD. However, these four drugs offer only symptomatic relief, while the two immunotherapy drugs are limited to treating mild-to-moderate AD and are associated with significant adverse effects, raising concerns about their safety and efficacy (Tan et al., 2014; Terao and Kodama, 2024). The current state of AD treatment is indeed a cause for serious concern, highlighting the urgent need for intensified efforts in the research and development of more effective therapies. In addition to the three main hypotheses—the cholinergic, amyloid-β (Aβ), and tau protein hypotheses—considered the primary pathological pathways of AD, several other targets have emerged, such as neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, many of which are interconnected (Hsu et al., 2023; Nasb et al., 2024). Given the complex and multifactorial nature of AD pathogenesis, current drug discovery research is shifting towards multitarget strategies aimed at simultaneously affecting multiple nodes of the intricate neurodegenerative network.
In the amyloid cascade hypothesis, the accumulation of Aβ peptides is regarded as a crucial factor in the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. The neurotoxic effects of Aβ are diverse and multifaceted. For example, Aβ oligomers can bind to neuronal surface receptors, disrupting synaptic function and plasticity, which are essential for learning and memory processes (Jeremic et al., 2021). Moreover, Aβ can induce oxidative stress and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to further neuronal damage. Over time, these toxic effects accumulate, resulting in substantial impairments in cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and executive function (Kepp et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023). Due to the pivotal role of Aβ in the pathogenesis of AD, significant research efforts have been devoted to developing effective strategies to either reduce Aβ production or enhance its clearance from the brain (Yadollahikhales and Rojas, 2023).
Acetylcholine (ACh), a major neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS), plays a crucial role in the neurological regulation of various functions. In AD, ACh depletion is associated with cognitive deficits, arousing the cholinergic hypothesis in the physiopathology of AD and thus the search for inhibitors of its degrading enzymes, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE). Both AChE and BuChE are present in the brain with different specificities and expression activities. A selective inhibition of AChE is more crucial in the early stage, while BuChE inhibition may be critical in the mid to later stages of the pathogenesis (Abeysinghe et al., 2020). Selective inhibition of AChE is particularly important in the early stages of AD, whereas inhibition of BuChE becomes more critical in the mid to late stages of the disease (Marucci et al., 2021). Beyond its catalytic function, AChE also influences non-cholinergic processes through its peripheral anionic site (PAS) and contributes to the aggregation and progression of amyloid proteins (Ahmed et al., 2021; Marucci et al., 2021; Tonelli et al., 2023). Consequently, AChE remains a primary therapeutic target.
Monoamine oxidases (MAOs) constitute a family of mitochondrial enzymes that selectively catalyze the oxidative deamination of various biogenic and xenobiotic amines, including neurotransmitters such as 5-HT, dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine (Cai, 2014; Riederer and Youdim, 1986). The significance of MAOs in neurobiology and pharmacology is highlighted by their role in modulating the levels of these neurotransmitters, thus affecting mood, behavior, and other physiological functions (Behl et al., 2021). Two distinct isoforms of monoamine oxidase exist: MAO-A and MAO-B. These isoforms exhibit differences in substrate specificity and inhibitor sensitivity. Selective MAO-A inhibitors have been widely acknowledged for their effectiveness in treating mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety. In contrast, MAO-B inhibitors are predominantly used in the management of neurological conditions to mitigate the production of neurotoxic substances, thereby safeguarding neuronal integrity and promoting neuronal survival (Banerjee et al., 2024). Importantly, activated MAO-B exacerbates neurodegenerative processes by elevating H2O2 levels, leading to oxidative stress, and by modulating Aβ production through γ-secretase activity in neurons (Schedin-Weiss et al., 2017). Consequently, a compound with dual inhibitory actions on AChE, MAO-B, and Aβ aggregation holds promise as a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Harmine (Figure 1), a naturally occurring β-carboline alkaloid, exhibits a broad spectrum of biological activities, including antimicrobial, antitumor, antiviral, and antiparasitic properties (Patel et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2020). Its core structure consists of a tricyclic pyrido [3,4-b]indole ring, which resembles human tryptamine-based neurotransmitters such as serotonin and melatonin. This structural similarity, combined with the increased rigidity provided by the additional ring, has been leveraged in the design of bioactive compounds to modulate various CNS targets (Warren et al., 2024). In particular, harmine and its derivatives have been reported as inhibitors of several biomolecular targets implicated in AD, such as Aβ aggregation, AChE, MAOs, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) (Beato et al., 2021; Li et al., 2023). Therefore, with the emergence of multitarget strategies against AD, the harmine scaffold is naturally well positioned to become a dedicated platform able to concurrently reach a variety of neurological biomolecules and processes. Several studies have demonstrated that dimeric compounds exhibit significantly enhanced activity compared to monomeric compounds in multi-target anti-AD therapies. For instance, bis-tacrine (2) shows IC50 values of 0.81 nM, 5.66 nM, and 7.5 μM for inhibiting AChE, BuChE and BACE1, respectively (Bolognesi et al., 2010). Similarly, bis-(arylvinyl)pyrazines (3) exhibit IC50 values of 17 nM and 13 nM for inhibiting Aβ aggregation and tau protein phosphorylation, respectively (Boländer et al., 2012). Moreover, while some bis-(2)-β-carbolines and bis-(9)-β-carbolines have been synthesized for the treatment of AD, such as 4 and 5 in Figure 1 (Rook et al., 2010; Zhao et al., 2018). This is noteworthy given that evidence suggests 7-substituted derivatives, such as 6 and 7, can enhance activity against ACh, MAO, and Aβ aggregation to a certain extent (Du et al., 2023; Haider et al., 2018). Additionally, studies have shown that introducing various functional groups, such as allyl, propyl, and ethyl, at position 9 consistently enhances the anti-MAO activity (Beato et al., 2021).
Therefore, in this work, we propose the design of 9-substituted bis-(7)-harmine derivatives as multitarget-directed ligands (MTDLs) for management of AD. The potent inhibitory effects of these derivatives for hAChE, hBuChE, hMAO-B, hMAO-B, and Aβ aggregation were evaluated. Then the most promising derivatives were further evaluated for in vitro cytotoxic effects and their protective effects against amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity, their mechanism of action through molecular docking studies, and their basic metabolic properties via ADMET computer predictions.
In the present investigation, we aimed to synthesize a series of bis(7)-harmine derivatives 4a–8d by connecting two 9-substituted harmine units through an ether linkage (Scheme 1). The synthesis commenced with harmine 1, which was subjected to treatment with bromo-hydrocarbon and NaH in anhydrous DMF under conditions of 40°C to yield the 9-substituted harmine derivatives 2a–2d. Subsequently, 2a–2d were refluxed in AcOH and HBr for demethylation, resulting in the formation of 3a–3d. Finally, the symmetrical dimers 4a–8d were prepared by reacting different dibromo-alkanes with 3a–3d in acetone using a catalytic amount of KCO3 (Du et al., 2023).
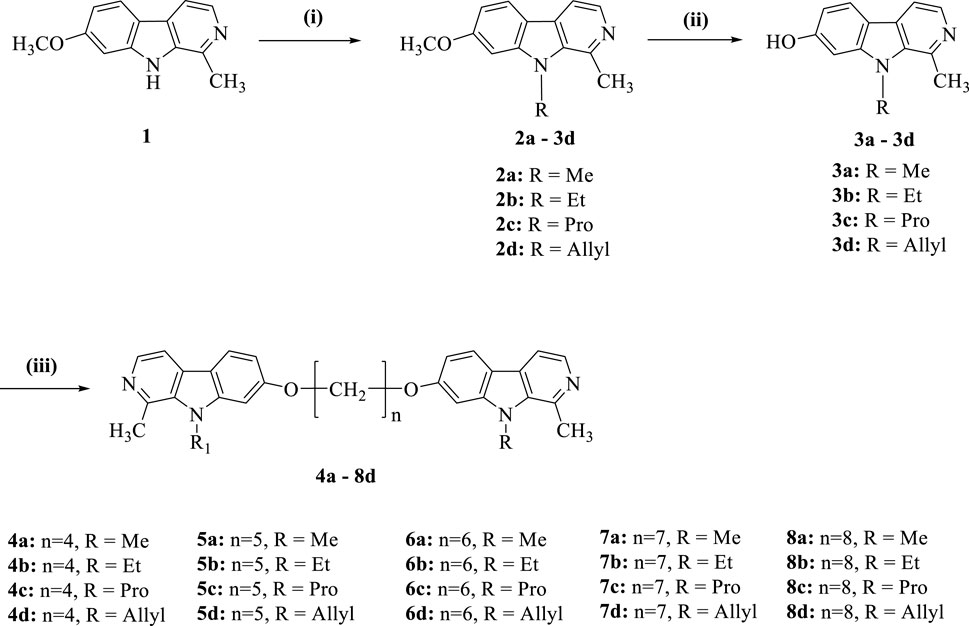
Scheme 1. Synthesis of compounds 4a−8d. Reagents and conditions: (i) NaH, RBr, DMF, rt.; (ii) AcOH, HBr, reflux; (iii) Cs2CO3, (CH2)nBr2, DMF.
With a series of derivatives synthesized, we next conducted screenings against hAChE (1 μM), hBuChE (1 μM), hMAO-A (1 μM), hMAO-B (1 μM), and Aβ1−42 aggregation (20 μM) for all compounds, followed by determination of IC50 values for those demonstrating more than 50% inhibitory activity in the primary screening (Table 1).
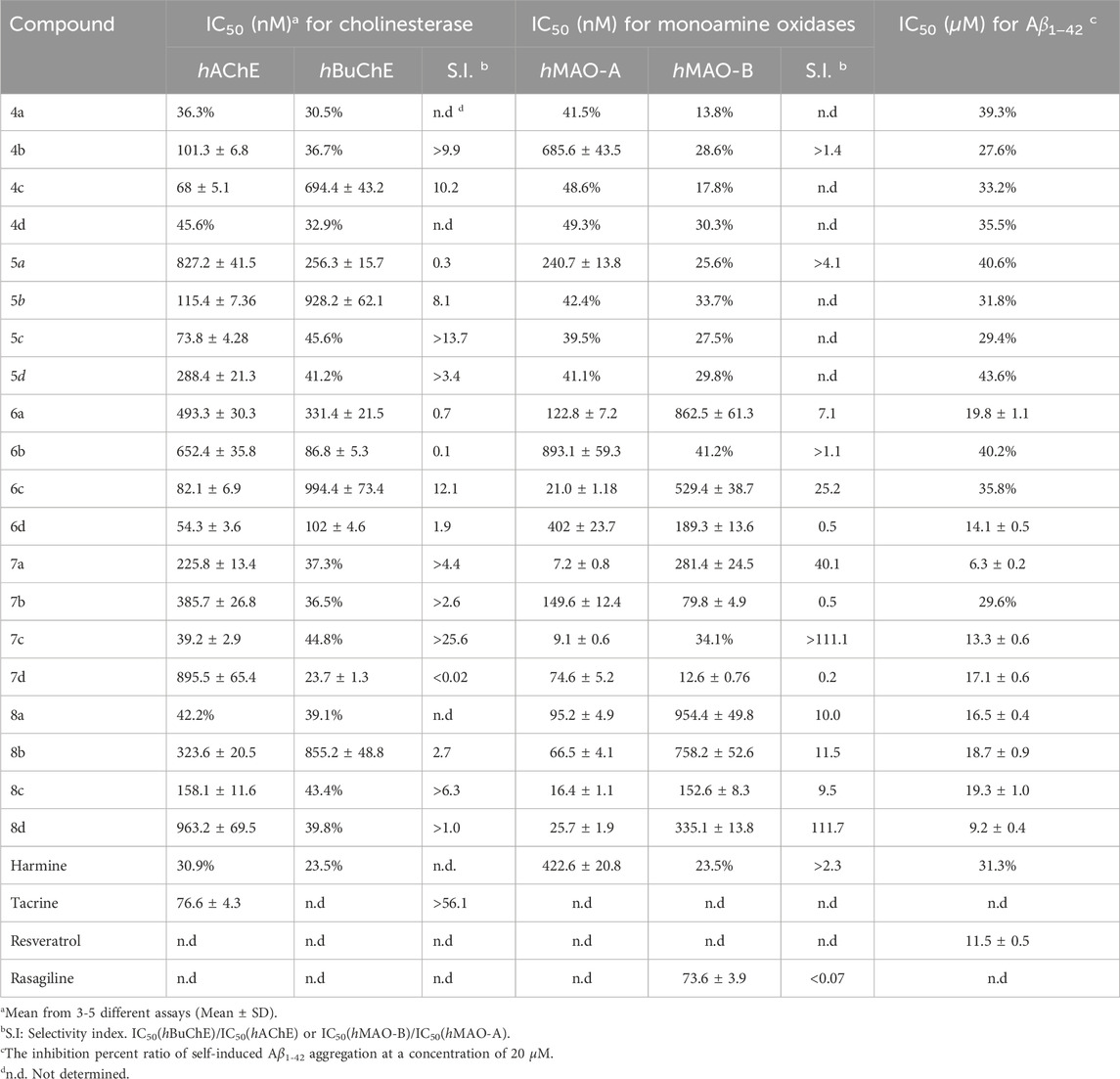
Table 1. Inhibition of cholinesterase, monoamine oxidases and Aβ1−42 aggregation by the synthesized compounds.
The Ellman’s assay was employed in this study to investigate the inhibitory potential of novel bis(7)-harmine derivatives on hAChE and hBuChE, along with tacrine as a reference compound (Ellman et al., 1961). As shown in Table 1, the majority of the tested target compounds exhibited superior inhibitory activity against hAChE compared to parent compound (harmine), with IC50 values at the nanomolar level. Furthermore, these compounds demonstrated remarkable selectivity towards hAChE over hBuChE. The initial analysis of the structure-activity relationship (SAR) suggested that both the nature of the 9-position substituents and the lengths of the carbon spacer significantly influenced their inhibitory activity against hAChE. Compounds featuring propyl substitution exhibited pronounced hAChE inhibition (IC50 in the range of 39.2–158.1 nM), suggesting a consistent superior inhibitory effect with propyl substituents at 9-position. However, as the carbon chain length increased, compounds containing propyl group showed diminished inhibition of hAChE. Moreover, when the substituent group at 9-position was methyl or allyl, hAChE inhibition initially increased and subsequently decreased with increasing spacer length. Conversely, compounds bearing an ethyl group demonstrated an initial decrease followed by an increase in inhibitory activity with elongation of the spacer. Notably, 4c, 5c, 6d, and 7c exhibited superior inhibitory activity against hAChE (IC50 = 68.0, 73.8, 54.3 and 39.2 nm, respectively), surpassing that of tacrine (positive control, IC50 = 76.6 nM). Additionally, 6a−6d displayed dual inhibitory activities against both hAChE and hBuChE at nanomolar levels (IC50 values), indicating their potential as promising candidates for simultaneous targeting of the two enzymes in AD management. Compared with bis-(2)-β-carbolines and bis-(9)-β-carbolines, bis-(7)-β-carbolines exhibit comparable inhibitory activity against AChE. Notably, their inhibitory activity at the nanomolar level was significantly higher compared to monomer compounds at the micromolar level (Rook et al., 2010; Zhao et al., 2018). Therefore, bis-β-carbolines may be considered more promising candidates for anti-AD drug development compared to monovalent compounds.
The inhibitory potency against both hMAO-A and hMAO-B was investigated using recombinant human enzymes, with rasagiline serving as a positive control drug (Giovannuzzi et al., 2024). Generally, compounds containing a four- or five-carbon spacer exhibited limited inhibitory activity against both hMAO-A and hMAO-B (with IC50 values above 1 μM), except for 4b and 5a which demonstrated inhibition of hMAO-A. In contrast, the twelve compounds featuring a six-, seven-, or eight-carbon spacer all exhibited significant inhibitory activity against hMAO-A, with the IC50 values ranging from 7.2 to 893.1 nM, while ten of these compounds also demonstrated notable inhibition towards hMAO-B (IC50 in the range of 12.6–954.4 nM). The findings suggested that the inhibition of hMAO by compounds was enhanced when employing a linker with a carbon spacer ranging from 6 to 8 atoms in length. Interestingly, 6d, 7b, and 7d exhibited significant and selective inhibition of hMAO-B activity with IC50 values of 189.3 nM, 79.8 nM, and 12.6 nM, respectively. These values were comparable to or greater than that of rasagiline (IC50 = 73.6 nm).
The Thioflavin-T (ThT) fluorescence assay is a widely employed method for assessing the inhibitory efficacy of compounds on Aβ1−42 self-aggregation (Bian et al., 2024). In this study, bis(7)-harmine derivatives were examined for their inhibitory activity against Aβ1−42 self-aggregation, with resveratrol serving as a reference compound. As presented in Table 1, 4a−5d featuring a four- or five-carbon spacer, exhibited relatively modest inhibitory activity against Aβ1−42 self-aggregation with IC50 values exceeding 20 μM, indicating limited effectiveness in preventing amyloid plaque formation. Conversely, among the remaining twelve compounds with six-, seven-, or eight-carbon spacer, it was observed that nine of them demonstrated significant inhibition of Aβ1−42 aggregation. Interestingly, his trend exhibited a similar inhibitory pattern to that observed for MAO inhibitors. Moreover, 6d, 7a, 7c, and 8d demonstrated significant inhibition of Aβ1−42 aggregation (IC50 = 14.1, 6.3, 13.3, and 9.2 μM, respectively), which were comparable to or greater than achieved by resveratrol (IC50 = 12.3 μM). These results indicate that these compounds have the potential to effectively prevent or slow down the formation of a Aβ1−42 plaques in AD.
The toxicological properties of 6d, 7a, 8b, 8c, and 8d were evaluated in the SHSY5Y human neuroblastoma cell model using an MTT reduction assay (Ellman et al., 1961). These compounds were selected based on their simultaneous inhibition of hAChE, hMAO-B, and Aβ1−42 self-aggregation. As depicted in Figure 2, 6d exhibited no significant impact on cell viability within the concentration range of 0.1–100 μM after a 48 h incubation period, thereby indicating its favorable safety profile. 8c and 8d demonstrated negligible cytotoxicity at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 μM; however, an evident decrease in SHSY5Y cell viability was observed when the concentration was increased to 10 μM. These findings suggest that these compounds are considered safe at concentrations below or equal to 10 μM. Unfortunately, 7a and 8b exerted a pronounced detrimental effect on SHSY5Y cell viability at a concentration of only 1 μM. Consequently, due to their low toxicity profiles, 6d, 8c, and 8d were consequently chosen for subsequent investigation.
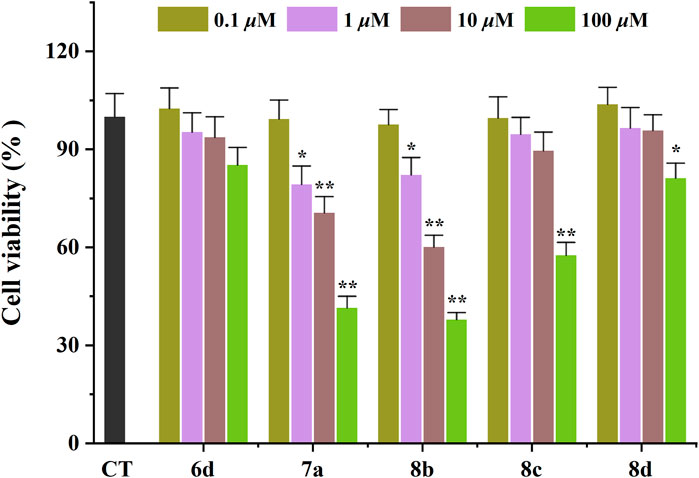
Figure 2. Neurotoxicity of compounds in SH-SY5Y cells. *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01 vs. control group (untreated cells).
The protective effect of the test compounds against Aβ1-42-induced damage was assessed by monitoring MTT reduction in cells co-exposed to the compound and Aβ1-42 for 48 h (Figure 3) (Ellman et al., 1961). The 6d, 8c, and 8d were tested at concentrations of 1, 5, and 10 μM. The viability of SHSY5Y neuroblastoma cells was significantly reduced by 48.7% after treatment with Aβ1−42. Surprisingly, the three compounds exhibited a notable neuroprotective efficacy within the concentration range of 5–10 μM. Specifically, 6d and 8d exhibited remarkable efficacy, demonstrating significant cellular recovery even at a minimal concentration of only 1 μM. Moreover, the two compounds exhibited nearly complete protection against neuronal damage when their concentration reached 10 μM. The results demonstrate that the tested compounds exhibit the potential to alleviate Aβ-related toxicity, thereby presenting promising therapeutic prospects for AD. Therefore, it is imperative to elucidate the underlying mechanisms responsible for these protective effects.
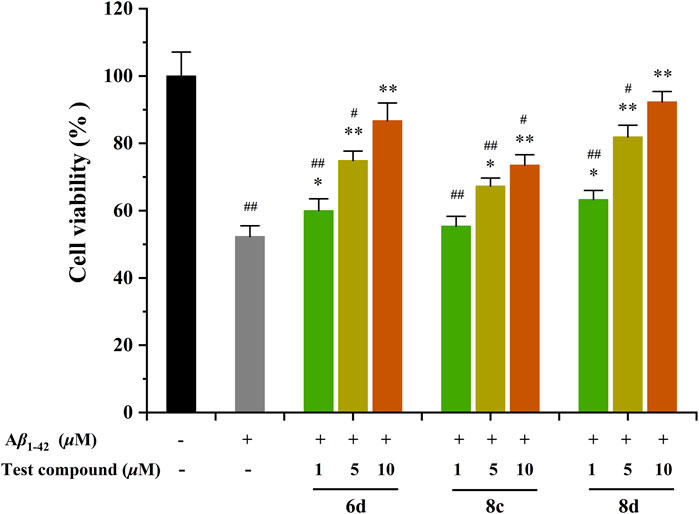
Figure 3. Neuroprotective effects of compounds 6d, 8c, and 8d against Aβ1-42-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 vs. control group (untreated cells); *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001 vs. Aβ1-42-treated cells.
To elucidate the binding mechanism of bis(7)-harmine derivatives towards their target enzymes, we investigated the binding interactions of one of the most potent compound, 6d, with hAChE (PDB code: 4EY7), hMAO-B (PDB code: 2V60) and Aβ1-42 (PDB code: 1IYT), respectively (Binda et al., 2007; Cheung et al., 2012; Crescenzi et al., 2002). The Sybyl−X 2.0 software was used to predict the most energetically stable configurations of the ligand-target complexes (Figures 4A–F).
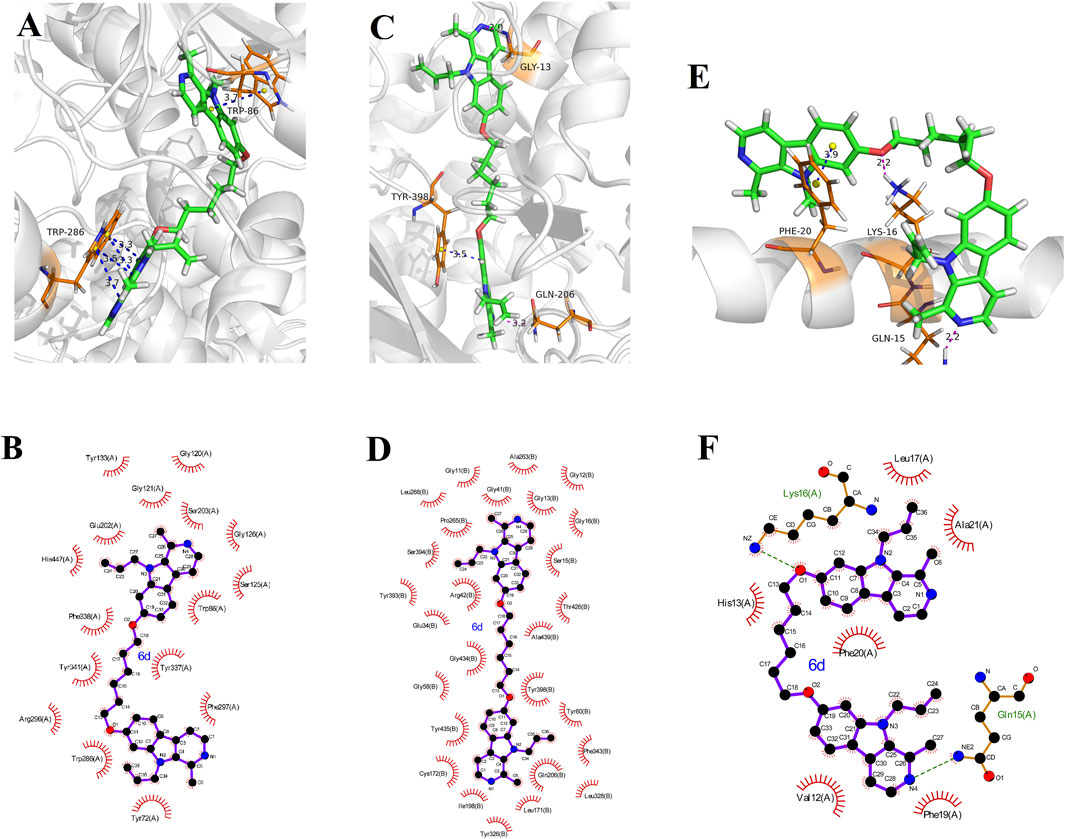
Figure 4. Molecule docking results: (A, B) were 3D and 2D docking models of compound 6d with AChE (4EY7); (C, D) were 3D and 2D docking models of compound 6d with hMAO-B (2V60); (E, F) were 3D and 2D docking models of compound 6d with Aβ1-42 (1IYT). The blue dashed lines stand for π-π stacking, and the magentas dashed lines represent hydrogen bond.
The 3D docking model (Figure 4A) illustrates a π−π stacking interaction between the pyrrole ring of harmine and residue Trp86 at a distance of 3.8 Å, facilitating binding to the CAS of AChE. Furthermore, another harmine group binds to the PAS of AChE through four π−π interactions with residue Trp286 at distances of 3.3 Å, 3.3 Å, 3.5 Å, and 3.7 Å, respectively. This observation indicates that these derivatives possess the ability to simultaneously interact with both the CAS and PAS domains as intended in our design objective. Additionally, hydrophobic contacts were observed between 6 and residues Tyr72, Trp86, Gly120, Gly121, Ser125, Gly126, Tyr133, Glu202, Ser203, Trp286, Arg296, Phe297, Tyr337, Phe338, Tyr341, and His447 in the 2D docking model (Figure 4B). These favorable interactions are likely to contribute to the enhanced inhibitory efficacy of ligands. Therefore, the enhancement of electron-donating groups on the harmine structure and/or increased hydrophobicity of the derivatives could potentially enhance hAChE inhibitory activity as supported by structure-activity relationship studies.
The Figure 4C reveals intriguing hydrogen bonds formed by N atoms of pyridines in two harmine fragments with Gly13 and Gln206 at distances of 2.0 and 3.2 Å, respectively. Additionally, one of the harmine fragments engages in a π−π stacking interaction with residue Try398 at a distance of 3.5 Å. Moreover, we have identified twenty-seven residues (including Gly12, Gly13, Ser15 etc., as shown in Figure 4D) that participate in hydrophobic interactions potentially enhancing the hMAO-B inhibition efficacy.
In Figure 4E, it is noteworthy that residue Phe20 of Aβ1-42 forms a π−π stacking interaction with the benzene ring in one of the harmine fragments at a distance of 3.9 Å. Additionally, the N atom of pyridine in other harmine moieties interacts with residue Gln15 through intermolecular hydrogen bonding at a distance of 2.2 Å. Furthermore, the O atom at 7-position of the harmine fragment engages in an intermolecular hydrogen bonding interaction with residue Lys16 at a distance of 2.2 Å. Moreover, hydrophobic interactions between 6d and residues (such as Val12, His13, Leu17, Phe19, Phe20, and Ala21) from Figure 4F are observed. These observed interactions provide potential mechanisms for the high inhibitory activity against Aβ1−42 aggregation exhibited by this ligand.
The absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity properties (ADMET) of the most potent derivatives 6d, 8c, and 8d were evaluated using in silico ADMET prediction methods (Xiong et al., 2021; Banerjee et al., 2018). Tacrine, resveratrol, and rasagiline were utilized as reference drugs for comparative analysis. As presented in Table 2, the in vitro permeability of CaCo-2 (Caucasian colon adenocarcinoma) cells fell within the intermediate range (31.6–34.7 nm/s), demonstrating a significantly higher value compared to resveratrol (5.2 nm/s) and closely resembling that of tacrine (25.9 nm/s). Moderate values of invitro MDCK (Madin–Darby canine kidney) cells were observed (51.7–65.5 nm/s), indicating an acceptable range of permeability for these derivatives. One crucial aspect assessed was high intestinal absorption (HIA). It was found that all target derivatives exhibited HIA values ranging from 98.3% to 98.4%, which are remarkably similar to those observed for reference drugs like tacrine (96.5%) and rasagiline (100%). This suggests that these derivatives have a high potential for efficient absorption through the intestines.
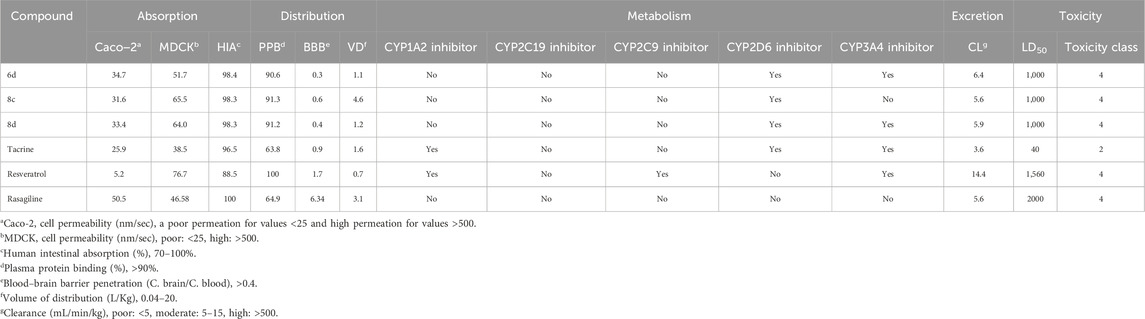
Table 2. ADMET properties predicted in silico for some active compounds, tacrine, resveratrol and rasagiline.
The predicted PPB (Plasma protein binding) values for the tested derivatives, ranging from 90.6% to 91.3%, were found to be comparable to that of resveratrol (100%). This suggests that these derivatives exhibit a high affinity for plasma proteins, potentially enhancing their stability and prolonging their therapeutic effects in the bloodstream. Furthermore, the calculated BBB (blood−brain barrier) permeabilities of 6d, 8c, and 8d were determined as 0.3, 0.6 and 0.4 respectively, which closely approximate the required value of 0.4. These results imply favorable characteristics of these compounds in terms of crossing the blood-brain barrier and reaching target sites within the CNS effectively. Additionally, all three derivatives exhibited predicted VD (volumes of distribution) falling within an optimal range between 0.04 and 20 L/kg, suggesting a well-balanced distribution throughout various tissues in the body after administration.
The metabolism of drugs in the body is a complex process that greatly influences their concentration in the bloodstream. To better understand how certain drugs interact with enzymes involved in drug metabolism, such as cytochrome P450 isoforms, researchers often rely on in silico studies. In this study, the focus was on predicted inhibitors targeting specific cytochrome P450 isoforms, such as CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4. These isoforms are known to play crucial roles in drug metabolism and can significantly affect the efficacy and safety of medications. Among the three tested derivatives (6d, 8c, and 8d), they exhibited a similar profile to tacrine by lacking inhibitory effects on the CYP2C19 and CYP2C9 isoforms while demonstrating inhibitory activity towards the CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 isoforms. Notably, similar to rasagiline, none of these derivatives displayed any inhibitory potential against the CYP1A2 isoform.
Excretion plays a pivotal role in pharmacokinetics as it governs the efficient elimination of drug derivatives from the body. To comprehend this process, predictions were made based on their CL (clearance rate). It is noteworthy that all three derivatives exhibited moderate clearance rates ranging from 5.6 to 6.4 mL/min/kg.
The toxicity properties predicted for 6d, 8c, and 8d have provided valuable insights into their safety profiles. These compounds exhibited LD50 values (1,000 mg/kg) that were 25-times as high as tacrine (40 mg/kg), but significantly lower than those of resveratrol (1,560 mg/kg) and rasagiline (2000 mg/kg). All tested compounds were classified at level 4 for toxicity, similar to the control drugs (resveratrol and rasagiline). Based on these predictions, it can be inferred that the derivatives possess low toxicity levels and exhibit favorable safety profiles.
The majority of predicted ADMET property parameters in 6d, 8c, and 8d fall within the optimal range for favorable pharmacokinetic characteristics. Consequently, these compounds demonstrate promising potential as lead candidates for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. However, further investigation is warranted to assess their in vivo activity.
In this study, a series of bis(7)-harmine derivatives were designed and synthesized with the aim of developing effective multi-target ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The researchers evaluated the biological profile of these derivatives against various AD-related targets, including cholinesterases, monoamine oxidase, and Aβ aggregation. Out of the 20 compounds investigated, seventeen showed significant inhibitory activity against hAChE at nanomolar levels. This suggests that these compounds have the potential to effectively inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme involved in the breakdown of acetylcholine in the brain. Furthermore, ten compounds demonstrated nanomolar inhibitory activity against hMAO-B. MAO-B is another target implicated in AD pathology. Inhibiting MAO-B can help prevent the breakdown of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which are important for maintaining proper brain function. Additionally, nine derivatives displayed noteworthy inhibition of Aβ1−42 aggregation. Aβ aggregation is a hallmark feature observed in AD patients' brains. By preventing or reducing Aβ aggregation, these compounds may potentially slow down disease progression. Further investigation revealed that three specific compounds 6d, 8c, and 8d exhibited significant neuroprotective activity against Aβ1−42-induced damage in SH-SY5Y cells while showing low toxicity towards neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). This indicates their potential as therapeutic agents for protecting neurons from harmful effects associated with amyloid-beta accumulation. Molecular modeling studies provided valuable insights into the mechanism of action of 6. It was found that the binding processes were primarily driven by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and π-π stacking interactions with important residues of hAChE, hMAO-B and Aβ. Furthermore, ADMET prediction results indicated favorable characteristics for 6d, 8c, and 8d as potential drugs for AD management. These compounds showed promising pharmacokinetic properties such as good absorption, distribution within the brain tissue, metabolism without generating toxic metabolites or exhibiting significant drug-drug interactions. Overall, these findings provided strong evidence supporting the further development of bis(7)-harmine derivatives as lead compounds in research towards potential anti-AD drug candidates.
The solvents, chemicals, and reagents were procured from commercial suppliers without undergoing additional purification steps. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) was utilized to monitor the progress of the reactions. Silica gel (200–300 mesh) obtained from Qingdao Marine Chemical Company was employed for flash chromatography purification. The Bruker Avance III instrument operating at 500 MHz for 1H and 125 MHz for 13C was used to acquire the 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra. Chemical shifts were reported in parts per million (ppm, δ), with CDCl3 serving as the solvent and tetramethylsilane (TMS) acting as an internal standard. Singlet (s), doublet (d), triplet (t), doublet of doublet (dd), or multiplet (m) designations were assigned based on multiplicities observed. Agilent 6520 Q−TOF LC/MS was employed to obtain high resolution mass spectra (HRMS).
The synthesis of compounds was carried out using a previously reported method (Du et al., 2023). To a solution of harmine 1 (5 mmol) and bromo-hydrocarbon (7.5 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (100 mL), the mixture was stirred at 0°C for 5 min. Subsequently, NaH (10 mmol) was added to the suspension with stirring at 40°C for 8 h under TLC monitoring. Upon completion of the reaction, the solvent was gradually added to a 50 mL ice-water solution and left at 5°C for 12 h. After filtration, the solid underwent recrystallization with acetone, resulting in the formation of 9-substituted harmine derivatives 2a–2d. Subsequently, 2a–2d (3 mmol) were refluxed in a mixture of AcOH (30 mL) and HBr (v: v = 1: 1) for 24 h. After completion of the reaction, the solvents were evaporated under reduced pressure followed by addition of distilled water to precipitate the resulting solid. The obtained solid (3a–3d) was used in subsequent steps without further purification. Different dibromo-alkanes (1 mmol) were added to a solution of 3a–3d (2 mmol) in acetone (20 mL). Then KCO3 (8 mmol) and a small amount of KI were added to the mixture which was heated to reflux for 12 h. Afterward, the mixture was concentrated in vacuo and washed with water three times. Finally, the product was purified by column chromatography to yield 4a–8d.
White solid; yield 91%; 1H NMR (500 MHz Chloroform-d) 8.24 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.92 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (dd, J = 6.5, 1.7 Hz, 2 H), 6.78 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 4.00 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H), 3.02 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.9, 143.6, 141.0, 138.2, 136.0, 129.0, 122.3, 114.9, 112.2, 108.9, 92.9, 55.7, 32.2, and 23.5.
White solid; yield 84%; 1H NMR (500 MHz Chloroform-d) 8.27 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1 H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.72 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (dd, J = 1.8, 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 4.54 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 3.95 (s, 3H), 3.02 (s, 3H), 1.44 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.9, 142.7, 140.5, 138.2, 135.1, 129.4, 122.4, 115.3, 112.3, 108.8, 93.1, 55.7, 39.5, 23.2, 15.5.
White solid; yield 75%; 1H NMR (500 MHz Chloroform-d) 8.27 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1 H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (dd, J = 1.8, 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.83 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 3.93 (s, 3H), 2.99 (s, 3H), 1.88–1.78 (m, 2 H), 1.00 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.8, 143.1, 140.6, 138.3, 135.4, 129.3, 122.3, 115.2, 112.2, 108.6, 93.5, 55.7, 46.3, 23.9, 23.4, and 11.3.
Light yellow; yield 87%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.30–6.22 (m, 1H), 5.30 (dt, J = 3.9, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 5.29 (dd, J = 10.5, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 4.80 (dd, J = 17.3, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.94 (s, 3H), 3.00 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.8, 143.1, 140.6, 138.3, 135.3, 133.2, 129.3, 122.3, 115.2, 114.1, 112.2, 108.5, 93.5, 47.5, 44.7, and 23.5.
White solid; yield 55%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.26 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 6.91 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 6.85 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.20 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 4.01 (s, 6H), 3.01 (s, 6H), 1.98–1.92 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.4, 143.7, 140.4, 136.9, 135.7, 129.4, 122.1, 114.3, 112.2, 109.6, 93.5, 68.0, 32.3, 28.7, and 22.4; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C30H30N4O2 [M + H]+ 479.2402, found 479.2463.
White solid; yield 59%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.24 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.70 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 6.86 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.1 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.40 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 4H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 1.97–2.02 (m, 4H), 1.43 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.6, 143.2, 141.2, 138.5, 135.8, 129.7, 122.8, 115.6, 112.7, 109.5, 94.4, 68.4, 44.8, 28.6, 22.5, and 14.9; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C32H34N4O2 [M + H]+ 507.2715, found 507.2733.
White solid; yield 54%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 6.83–6.87 (m, 4H), 4.38 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 4H), 4.16 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 4H), 3.00 (s, 6H), 1.98–2.02 (m, 4H), 1.88–1.91 (m, 4H), 0.99 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.2, 143.3, 140.1, 137.9, 135.0, 129.2, 122.1, 115.3, 112.2, 109.5, 93.5, 68.3, 56.2, 28.5, 24.2, 22.4, and 11.5; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C34H38N4O2 [M + H]+ 535.3028, found 535.3040.
White solid; yield 46%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.30 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 8.00 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.76 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (dd, J = 2.0, 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.87 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 2H), 6.30–6.22 (m, 2H), 5.34–5.26 (m, 6H), 4.84–4.78 (m, 2H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 2.90 (s, 6H), 1.98–2.01 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.6 143.2, 140.5, 138.4, 135.4, 132.8, 129.3, 122.4, 112.1, 115.4, 114.0, 112.1, 109.4, 94.3, 67.9, 46.2, 23.5, and 15.3; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C34H34N4O2 [M + H]+ 531.2715, found 531.2747.
White solid; yield 43%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 6.91 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.85 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 2H), 4.18 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 4H), 4.02 (s, 6H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 2.08–1.94 (m, 4H), 1.90–1.81 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.4, 143.8, 140.4, 136.9, 135.7, 129.3, 122.1, 114.3, 112.2, 109.5, 93.4, 68.0, 31.9, 29.8, 22.5, and 22.0; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C31H32N4O2 [M + H]+ 493.2559, found 493.2598.
White solid; yield 52%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.95–6.87 (m, 2H), 6.86 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 2H), 4.50 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 3.01 (s, 6H), 2.03–1.96 (m, 4H), 1.84–1.76 (m, 2H), 1.42 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.4, 142.7, 140.5, 138.1, 135.1, 129. 5, 122.4, 115.3, 112.3, 109.1, 93.8, 68.3, 39.5, 29.2, 23.2, 22.9, and 15.5; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C33H36N4O2 [M + H]+ 521.2872, found 521.2903.
Light yellow solid; yield 47%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.24 (2H, d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.92 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.74 (2H, d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.86 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.1 Hz, 2H, 2H), 6.82 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 2H), 4.40 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 2.98 (s, 6H), 1.94–1.98 (m, 4H), 1.76–1.83 (m, 4H), 1.63–1.68 (m, 2H), 0.98 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 6H); 13C–NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.7, 143.1, 140.4, 138.2, 135.3, 129.1, 122.2, 115.0, 112.1, 109.0, 93.8, 67.9, 56.6, 29.2, 25.4, 23.1, 21.2, and 11.6; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C35H40N4O2 [M + H]+ 549.3185, found 549.3218.
Light yellow solid; yield 61%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.28 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.99 (d, J = 8 .6 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.96 (dd, J = 2.0, 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 6.29–6.22 (m, 2H), 5.28 (dt, J = 4.0, 2.1 Hz, 4H), 5.26 (dd, J = 10.2, 2.1 Hz, 2H), 4.80 (dd, J = 16.8, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 2.98 (s, 6H), 2.14–2.06 (m, 4H), 1.80–1.74 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.5, 143.0, 142.3, 139.1, 135.5, 129.4, 127.3, 126.2, 122.4, 115.3, 112.5, 109.6, 95.8, 67.9, 48.3, 27.2, 21.5, and 15.4; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C35H36N4O2 [M + H]+ 545.2872, found 545.2803.
Yellow solid; yield 59%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.26 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.76 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.89–6.91 (m, 4H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 4.05 (s, 6H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 2.02–1.98 (m, 4H), 1.72–1.64 (m, 4H); 13C–NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform -d) δ 160.4, 142.6, 139.8, 137.0, 134.9, 129.6, 122.1, 114.8, 112.3, 109.3, 93.8, 65.8, 39.1, 29.3, 24.9, and 22.4; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C32H34N4O2 [M + H]+ 507.2715, found 507.2769.
White solid; yield 41%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.26 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.76 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 6.99–6.80 (m, 4H), 4.54 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 4H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 1.95 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 4H), 1.76–1.69 (m, 4H), 1.44 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.5, 142.8, 140.0, 137.1, 134.9, 129.7, 122.3, 114.8, 112.3, 109.4, 93.6, 68.2, 39.9, 29.1, 25.8, 22.1, and 15.3; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C34H38N4O2 [M + H]+ 535.3073, found 535.3098.
White solid; yield 53%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.26 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.92–6.83 (m, 4H), 4.38 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 4H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 1.96–2.00 (m, 4H), 1.78–1.83 (m, 4H), 1.58–1.62 (m, 4H), 0.99 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.4, 143.3, 140.1, 138.2, 135.0, 129.5, 122.6, 115.3, 112.1, 109.4, 94.5, 68.2, 59.3, 29.8, 25.7, 24.2, 23.1, and 11.5; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C36H42N4O2 [M + H]+ 563.3341, found 563.3386.
Light yellow solid; yield 68%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.87 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.28–6.20 (m, 2H), 5.33 (dt, J = 4.0, 2.1 Hz, 4H), 5.28 (dd, J = 10.5, 1.7 Hz, 2H), 4.82–4.76 (m, 2H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 4H), 3.00 (s, 6H), 1.85–1.74 (m, 4H), 1.50–1.38 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.5, 142.8, 140.0, 137.1, 134.9, 133.2, 129.7, 122.3, 114.8, 113.0, 112.3, 109.4, 93.6, 68.2, 29.1, 25.8, and 22.1; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C36H38N4O2 [M + H]+ 559.3028, found 559.3043.
White solid; yield 60%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.87 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.83 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 2H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 4H), 3.92 (s, 6H), 3.00 (s, 6H), 1.82–1.76 (m, 4H), 1.42–1.35 (m, 4H), 1.33 (d, J = 3.3 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.2, 143.0, 140.6, 138.2, 135.3, 129.3, 122.3, 115.2, 112.2, 108.8, 94.1, 68.7, 32.7, 29.2, 23.4, 22.9, and 20.2; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C33H36N4O2 [M + H]+ 521.2872, found 521.2904.
White solid; yield 49%; mp 187°C–188°C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.25 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.74 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.92–6.86 (m, 4H), 4.51 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 4H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 4H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 1.84–1.78 (m, 4H), 1.43 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H), 1.32–1.26 (m, 4H), 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.4, 143.1, 140.7, 138.4, 135.5, 129.7, 122.4, 115.4, 112.3, 109.2, 93.8, 68.8, 40.3, 29.6, 23.2, 22.6, and 15.3; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C35H40N4O2 [M + H]+ 549.3185, found 549.3208.
White solid; yield 58%; mp 193°C–195°C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.23 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.92 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.69 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 6.90–6.81 (m, 4H), 4.45 (4H, q, J = 7.2 Hz, 4H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 2.98 (s, 6H), 1.86–1.80 (m, 4H), 1.72–1.64 (m, 4H), 1.43–1.35 (m, 4H), 1.30–1.24 (m, 2H), 0.96 (6H, t, J = 7.2 Hz); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.5, 142.9, 140.1, 138.2, 134.9, 128.7, 122.4, 116.9, 112.4, 109.4, 93.6, 68.9, 58.6, 30.2, 25.2, 24.1, 23.5, 23.0, and 12.0; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C37H44N4O2 [M + H]+ 577.3498, found 577.3533.
Light yellow solid; yield 54%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.26 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.87 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.33–6.25 (m, 2H), 5.34–5.26 (m, 6H), 4.78 (dd, J = 17.2, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.18 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 3.01 (s, 6H), 2.01–1.95 (m, 4H), 1.70–1.64 (m, 4H), 1.46–1.1.38 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.6, 142.8, 140.2, 138.3, 135.2, 133.4, 129.1, 122.4, 115.2, 114.1, 112.1, 108.9, 93.4, 66.9, 47.1, 32.0, 28.9, 23.2, and 20.2; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C37H40N4O2 [M + H]+ 573.3185, found 573.3214.
White solid; yield 55%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.26 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.98 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.88 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 2H), 4.14 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 4H), 4.00 (s, 6H), 3.01 (s, 6H), 1.92–1.84 (m, 4H), 1.60–1.56 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 4H), 1.52–1.49 (s, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.2, 143.1, 140.2, 137.8, 134.8, 129.5, 122.5, 114.9, 112.2, 109.3, 93.4, 68.0, 39.5, 29.4, 29.1, 25.2, and 21.3; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C34H38N4O2 [M + H]+ 535.3028, found 535.3059.
White solid; yield 61%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.28 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.73 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.88 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.1 Hz, 2H), 6.86 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.43 (q, J = 7.4 Hz, 4H), 4.16 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 4H), 3.01 (s, 6H), 2.02–1.95 (m, 4H), 1.89–1.69 (m, 6H), 1.45 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 4H), 1.34–1.26 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.2, 143.0, 140.6, 138.2, 135.3, 129.3, 122.3, 115.2, 112.2, 108.8, 94.1, 68.2, 44.6, 32.7, 29.2, 23.4, 20.2, and 13.90. ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C36H42N4O2 [M + H]+ 563.3341, found 563.3348.
White solid; yield 52%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.27 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 6.90–6.84 (m, 4H), 4.46 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 4.15 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 4H), 3.00 (s, 6H), 1.99–1.93 (m, 4H), 1.86–1.82 (m, 4H), 1.68–1.60 (m, 4H), 1.36–1.28 (m, 4H), 0.99 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.5, 142.9, 140.5, 138.1, 135.0, 129.1, 122.3, 115.4, 112.0, 109.0, 93.6, 67.9, 54.6, 32.4, 26.8, 24.4, 22.2, 23.4, and 12.0; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C38H46N4O2 [M + H]+ 591.3654, found 591.3678.
Light yellow solid; yield 54%; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.26 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H), 6.87 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 2H), 6.30–6.22 (m, 2H), 5.32 (dt, J = 4.0, 2.1 Hz, 4H), 5.30 (dd, J = 10.8, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.80 (dd, J = 17.1, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.16 (4H, t, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 2.02–1.97 (m, 4H), 1.79–1.74 (m, 4H), 1.59–1.51 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 160.8, 143.0, 140.5, 138.5, 135.5, 133.6, 129.3, 122.5, 115.4, 114.3, 112.2, 109.1, 93.7, 67.5, 47.3, 32.2, 29.3, 23.4, and 20.3; ESI–MS m/z Calcd for C38H42N4O2 [M + H]+ 587.3341, found 587.3374.
The Ellman’s assay was utilized to assess the inhibitory potential of novel bis(7)-harmine derivatives against hAChE and hBuChE. 50 μL of hAChE (0.02 unit/mL) or hBChE (0.02 unit/mL) were incubated with 10 μL of the compound in 96-well plates at 37°C for 6 min. Subsequently, 30 μL of a substrate solution containing acetylthiocholine iodide (ATCI) or butyrylthiocholine iodide (BTCI) at a concentration of 0.01 M was added, and the mixture was further incubated at 37°C for an additional duration of 12 min. Finally, the activity was measured by adding 150 μL of a solution containing 5,5′−dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) at a concentration of 0.01 M, followed by measuring absorbance at a wavelength of 415 nm using an Evolution 300 PC UV-Vis Spectrophotometer.
The inhibitory activity of these derivatives on both recombinant hMAO-A and hMAO-B (Sigma-Aldrich) was assessed using a fluorescence-based method as previously described (Giovannuzzi et al., 2024). Briefly, the compounds under investigation and the reference inhibitor were preincubated with kynuramine at 37°C for 10 min in 96-well microplates. Then, the reaction was started with the addition of hMAO-A or hMAO-B. Initial velocities were determined spectrophotometrically in a microplate reader at 37°C by measuring the formation of 4-hydroxyquinoline at 316 nm, over a period of at least 30 min. The enzymatic reactions were terminated by adding 400 μL of 2 N NaOH and 1,000 μL of water, followed by centrifugation at 16,000 g for 10 min. Subsequently, the concentrations of MAOs that produced 4-hydroxyquinoline were determined by measuring the fluorescence of the supernatant using a Varioskan Flash Multimode Reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation and emission wavelengths set at 310 nm and 400 nm, respectively. The IC50 values were calculated from dose-response curves and expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. These values were determined based on at least three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.
The thioflavin T (Th-T) fluorescence assay was used to assess the inhibition of Aβ1−42 self-aggregation. Aβ1-42 (20 μM final concentration) was incubated with test compounds (20 μM final concentration) in a 50 mM phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) at 37°C for 24 h. Subsequently, the reaction was terminated to a final volume of 200 μL using Th-T (10 μM) solution. The detailed procedure followed our previous work (Du et al., 2023).
The inhibition of AChE-induced aggregation of the Aβ1-42 peptide was achieved by co-incubating synthesized compounds (at concentrations of 0.1 μM and 1 μM) with AChE (at a concentration of 10 μM). Control experiments were conducted in the absence of test compounds. The aggregation process of the Aβ1-42 peptide was monitored at 37°C for a duration of 24 h using Th-T, with an excitation wavelength set at 446 nm and emission ranging from 490 nm.
The cytotoxicity of the compounds was evaluated using an MTT assay, following a previously described protocol (Ellman et al., 1961). Briefly, SHSY5Y cells were cultured in 96-well plates at a density of 1.0 × 104 cells per well for 24 h. Subsequently, the cells were treated with various concentrations of each compound (0.1, 1, 10, and 100 μM) for a duration of 48 h. After incubation, the culture medium was removed and replaced with 100 μL of MTT solution which was then incubated at 37°C for 1 hour. Following this incubation period, the MTT solution was substituted with 100 mL of DMSO and further incubated at room temperature for 10 minutes to dissolve formazan crystals formed by viable cells. Sorensen Buffer (5 mL) was added subsequently followed by measuring absorbance at a wavelength of 570 nm to determine cell viability based on calculated values obtained from control samples without compound treatment. This experimental procedure was repeated independently three times.
The SHSY5Y cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 104 cells per well and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Each compound was dissolved in DMSO, followed by direct dilution in the cell culture medium to achieve final concentrations of 1 μM, 5 μM, and 10 μM. Aβ1−42 was added to each well at a concentration of 5 μM. The cells were then further incubated at 37°C for an additional period of 48 h. Cell viability was subsequently assessed using the MTT assay protocol (Ellman et al., 1961).
The ADMETlab 2.0 (https://admetmesh.scbdd.com), preADMET (https://preadmet.qsarhub.com/) and ProTox−II (http://tox.charite.de/protox_II) were employed to predict ADME properties and toxicity, utilizing a dedicated webserver for this purpose (Xiong et al., 2021; Banerjee et al., 2018).
The Surflex-Dock program in Sybyl-X 2.0 Software was employed for molecular docking, with the ligand structures being sketched using the Sybyl package. Atom types were validated, hydrogen atoms were added, and Gasteiger-Marsili charges were assigned using Sybyl-X 2.0 Software. The protein structures of hAChE (PDB code: 4EY7), hMAO-B (PDB code: 2V60) and Aβ1-42 (PDB code: 1IYT) were obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank website (https://www.rcsb.org/). To facilitate molecular docking studies, the ligand was extracted from the crystal structure, water molecules were eliminated, and side-chain amides were verified before generating a protomold for further analysis. Visualization of docking results was aided by PyMOL and LigPus software tools.
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: doi: 10.6084/m9.figshare.28254113.
HD: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. FM: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. YC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. MB: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. XG: Investigation, Resources, Writing–original draft. ZY: Investigation, Resources, Writing–original draft. YX: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. YY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Program for Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (No. 21602178), Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project (No. 222102310438), Qin ChuanYuan Cited the High-level Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talent Program of Shaanxi under Grant (Nos QCYRCXM-2022–172 and QCYRCXM-2022–196), Doctoral Research Initiation Project of Yan’an University under Grant (No. 205040406, 205040422), and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Chinese Jujube (No. sxhzdsys-zj23-04).
Authors HD and FM were employed by Shaanxi Qi Yuan Kang Bo Biotechnology Co. Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2025.1545908/full#supplementary-material
Abeysinghe, A. A. D. T., Deshapriya, R. D. U. S., and Udawatte, C. (2020). Alzheimer's disease; a review of the pathophysiological basis and therapeutic interventions. Life Sci. 256, 117996. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117996
Ahmed, S., Khan, S. T., Zargaham, M. K., Khan, A. U., Khan, S., Hussain, A., et al. (2021). Potential therapeutic natural products against Alzheimer's disease with reference of acetylcholinesterase. Biomed. Pharmacother. 139, 111609. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111609
Banerjee, C., Tripathy, D., Kumar, D., and Chakraborty, J. (2024). Monoamine oxidase and neurodegeneration: mechanisms, inhibitors and natural compounds for therapeutic intervention. Neurochem. Int. 179, 105831. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105831
Banerjee, P., Eckert, A. O., Schrey, A. K., and Preissner, R. (2018). ProTox-II: a webserver for the prediction of toxicity of chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (W1), W257–W263. doi:10.1093/nar/gky318
Beato, A., Gori, A., Boucherle, B., Peuchmaur, M., and Haudecoeur, R. (2021). β-Carboline as a privileged scaffold for multitarget strategies in Alzheimer’s disease therapy. J. Med. Chem. 64 (3), 1392–1422. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01887
Behl, T., Kaur, D., Sehgal, A., Singh, S., Sharma, N., Zengin, G., et al. (2021). Role of monoamine oxidase activity in Alzheimer's disease: an insight into the therapeutic potential of inhibitors. Molecules 26 (12), 3724. doi:10.3390/molecules26123724
Bian, Z. Y., Li, P. X., Feng, X. Y., Zhou, Y. R., Cheng, F. Y., Dong, W. X., et al. (2024). Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of imidazolylacetophenone oxime derivatives as novel brain-penetrant agents for Alzheimer's disease treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 278, 116794. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116794
Binda, C., Wang, J., Pisani, L., Caccia, C., Carotti, A., Salvati, P., et al. (2007). Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 50 (23), 5848–5852. doi:10.1021/jm070677y
Boländer, A., Kieser, D., Voss, C., Bauer, S., Schön, C., Burgold, S., et al. (2012). Bis(arylvinyl)pyrazines, -pyrimidines, and -pyridazines as imaging agents for tau fibrils and β-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease models. J. Med. Chem. 55 (21), 9170–9180. doi:10.1021/jm300653b
Bolognesi, M. L., Bartolini, M., Mancini, F., Chiriano, G., Ceccarini, L., Rosini, M., et al. (2010). Bis(7)-tacrine derivatives as multitarget-directed ligands: focus on anticholinesterase and antiamyloid activities. ChemMedChem 5 (8), 1215–1220. doi:10.1002/cmdc.201000086
Cai, Z. (2014). Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: promising therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease (Review). Mo.l Med. Rep. 9 (5), 1533–1541. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2040
Cheung, J., Rudolph, M. J., Burshteyn, F., Cassidy, M. S., Gary, E. N., Love, J., et al. (2012). Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 55 (22), 10282–10286. doi:10.1021/jm300871x
Crescenzi, O., Tomaselli, S., Guerrini, R., Salvadori, S., D'Ursi, A. M., Temussi, P. A., et al. (2002). Solution structure of the Alzheimer amyloid β-peptide (1–42) in an apolar microenvironment: similarity with a virus fusion domain. Eur. J. Biochem. 269 (22), 5642–5648. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03271.x
Du, H., Song, J., Ma, F., Gao, H., Zhao, X., Mao, R., et al. (2023). Novel harmine derivatives as potent acetylcholinesterase and amyloid beta aggregation dual inhibitors for management of Alzheimer's disease. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 38 (1), 2281893. doi:10.1080/14756366.2023.2281893
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. D., Andres, V., and Featherstone, R. M. (1961). A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 7, 88–95. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Giovannuzzi, S., Chavarria, D., Provensi, G., Leri, M., Bucciantini, M., Carradori, S., et al. (2024). Dual inhibitors of brain carbonic anhydrases and monoamine oxidase-B efficiently protect against amyloid-β-induced neuronal toxicity, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Med. Chem. 67 (5), 4170–4193. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00045
Haider, S., Alhusban, M., Chaurasiya, N. D., Tekwani, B. L., Chittiboyina, A. G., and Khan, I. A. (2018). Isoform selectivity of harmine-conjugated 1,2,3-triazoles against human monoamine oxidase. Future Med. Chem. 10 (12), 1435–1448. doi:10.4155/fmc-2018-0006
Hsu, Y. C., Huang, Y. Y., Tsai, S. Y., Kuo, Y. W., Lin, J. H., Ho, H. H., et al. (2023). Efficacy of probiotic supplements on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, inflammatory biomarkers, oxidative stress and cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's dementia: a 12-week randomized, double-blind active-controlled study. Nutrients 16 (1), 16. doi:10.3390/nu16010016
Jeremic, D., Jiménez-Díaz, L., and Navarro-López, J. D. (2021). Past, present and future of therapeutic strategies against amyloid-β peptides in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 72, 101496. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2021.101496
Kepp, K. P., Robakis, N. K., Høilund-Carlsen, P. F., Sensi, S. L., and Vissel, B. (2023). The amyloid cascade hypothesis: an updated critical review. Brain 146 (10), 3969–3990. doi:10.1093/brain/awad159
Li, D., Huang, Z., Xu, X., and Li, Y. (2023). Promising derivatives of rutaecarpine with diverse pharmacological activities. Front. Chem. 11, 1199799. doi:10.3389/fchem.2023.1199799
Marucci, G., Buccioni, M., Ben, D. D., Lambertucci, C., Volpini, R., and Amenta, F. (2021). Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 190, 108352. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108352
Mendiola-Precoma, J., Berumen, L. C., Padilla, K., and Garcia-Alcocer, G. (2016). Therapies for prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 1–17. doi:10.1155/2016/2589276
Nasb, M., Tao, W., and Chen, N. (2024). Alzheimer's disease puzzle: delving into pathogenesis hypotheses. Aging Dis. 15 (1), 43–73. doi:10.14336/AD.2023.0608
Patel, K., Gadewar, M., Tripathi, R., Prasad, S. K., and Patel, D. K. (2012). A review on medicinal importance, pharmacological activity and bioanalytical aspects of beta-carboline alkaloid ''Harmine. Asian pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2 (8), 660–664. doi:10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60116-6
Prince, M., Comas-Herrera, A., Knapp, M., Guerchet, M., and Karagiannidou, M. (2016). Alzheimer’s disease international. World Alzheimer Rep., 2016. Available at: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2016.pdf.
Riederer, P., and Youdim, M. B. (1986). Monoamine oxidase activity and monoamine metabolism in brains of parkinsonian patients treated with l-deprenyl. J. Neurochem. 46 (5), 1359–1365. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb01747.x
Rook, Y., Schmidtke, K. U., Gaube, F., Schepmann, D., Wünsch, B., Heilmann, J., et al. (2010). Bivalent β-carbolines as potential multitarget anti-alzheimer agents. J. Med. Chem. 53 (9), 3611–3617. doi:10.1021/jm1000024
Schedin-Weiss, S., Inoue, M., Hromadkova, L., Teranishi, Y., Yamamoto, N. G., Wiehager, B., et al. (2017). Monoamine oxidase B is elevated in Alzheimer disease neurons, is associated with γ-secretase and regulates neuronal amyloid β-peptide levels. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 9 (1), 57. doi:10.1186/s13195-017-0279-1
Tan, C. C., Yu, J. T., Wang, H. F., Tan, M. S., Meng, X. F., Wang, C., et al. (2014). Efficacy and safety of donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine, and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J.Alzheimer's Dis. Jad. 41 (2), 615–631. doi:10.3233/JAD-132690
Terao, I., and Kodama, W. (2024). Comparative efficacy, tolerability and acceptability of donanemab, lecanemab, aducanumab and lithium on cognitive function in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 94, 102203. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2024.102203
Tonelli, M., Catto, M., Sabaté, R., Francesconi, V., Laurini, E., Pricl, S., et al. (2023). Thioxanthenone-based derivatives as multitarget therapeutic leads for Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 250, 115169. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115169
Warren, H. T., Saeger, H. N., Tombari, R. J., Chytil, M., Rasmussen, K., and Olson, D. E. (2024). Psychoplastogenic DYRK1A inhibitors with therapeutic effects relevant to Alzheimer's disease. J. Med. Chem. 67 (9), 6922–6937. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01696
Xiong, G., Wu, Z., Yi, J., Fu, L., Yang, Z., Hsieh, C., et al. (2021). ADMETlab 2.0: an integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (W1), W5–W14. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab255
Yadollahikhales, G., and Rojas, J. C. (2023). Anti-amyloid immunotherapies for Alzheimer's disease: a 2023 clinical update. Neurotherapeutics 20 (4), 914–931. doi:10.1007/s13311-023-01405-0
Zhang, L., Li, D., and Yu, S. (2020). Pharmacological effects of harmine and its derivatives: a review. Arch. Pharm. Res. 43 (12), 1259–1275. doi:10.1007/s12272-020-01283-6
Zhang, Y., Chen, H., Li, R., Sterling, K., and Song, W. (2023). Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8 (1), 248. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01484-7
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, harmine, acetylcholinesterase, monoamine oxidase, amyloid peptide (Aβ)
Citation: Du H, Ma F, Cao Y, Bai M, Gao X, Yang Z, Xu Y and Yan Y (2025) Bis(7)-harmine derivatives as potential multi-target anti-Alzheimer agents. Front. Chem. 13:1545908. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1545908
Received: 16 December 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Hong Chen, Luoyang Normal University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Du, Ma, Cao, Bai, Gao, Yang, Xu and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongtao Du, ZHVob25ndGFvODQxMEAxNjMuY29t, ZGh0QHlhdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.