- Department of Pediatrics, Maternity and Child Health Hospital of Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, China
In the face of bacterial hazards to human health and resistance to multiple antibiotics, there is an urgent need to develop new antibiotics to meet the challenge. In this paper, the triazolyl heterocyclic (3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, D) was synthesised efficiently using thiourea as starting material. Finally, the end product E was obtained by aldehyde-amine condensation reaction and the structures of all compounds were determined by spectral analysis. In vitro antimicrobial activity showed that E10 had a MIC of 32 μg/mL against the tested Escherichia coli and 16 μg/mL against the tested Staphylococcus aureus strain. Meanwhile, E10 has a good anti-biofilm effect. Antibacterial mechanism studies have shown that E10 has a good membrane targeting ability, thus disrupting cell membranes, leading to leakage of intracellular proteins and DNA and accelerating bacterial death. In terms of anti-inflammation, E10 dose-dependently inhibits the levels of inflammatory factors NO and IL-6, which deserves further exploration in the treatment of asthma. The study of metal ion removal capacity showed that the synthesised triazole derivatives have high capacity to remove heavy metals Pb2+, Cd2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+,Cr3+ and Al3+ in the range of 42%–60%.
1 Introduction
The ESKAPE (E. coli/Escherichia coli, S. aureus/Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumonia/K. pneumoniae, Acinetobacter Baumannii/A. baumannii, Pseudomonas aeroginosa/P. aeroginosa and Enterobacter species) pathogens pose an enormous health and economic threat to humans and the farming industry. These pathogens are resistant to drugs through a variety of mechanisms, rendering them invulnerable to human intervention (Ma et al., 2020; Jadimurthy et al., 2022; Patil et al., 2021). It has even been reported that bioepidermal infections account for about 2/3 of these infections (Wang et al., 2022). The emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR) and pan-drug-resistant (PDR) bacteria triggered by conventional antibiotics has exacerbated the problem, and therefore there is an urgent need to develop new therapeutic approaches for the treatment of bacterial drug resistance and biofilm infections (Mulani et al., 2019; Rakesh et al., 2018).
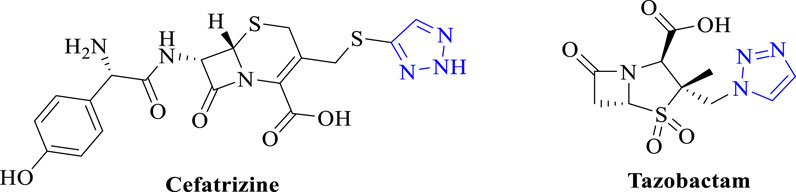
Triazoles are common pharmacophores in many drugs and have important advantages in overcoming drug resistance, reducing toxicity and improving pharmacokinetics due to their unique molecular structure and mechanism of action (Zafar et al., 2021). Triazole derivatives have various pharmacological properties such as anti-tuberculosis (Zhang et al., 2017), anti-fungal (Dheer et al., 2017), and antibacterial (Fan et al., 2018). Triazoles can also act as stable linkage units, mimicking the electronic properties of amide bonds, carboxylic acids, etc., to link different pharmacophores (Li and Zhang, 2022). Schiff bases are an important class of organic compounds because they readily form stable complexes with most transition metals and play an important role in the development of coordination chemistry (Dalia et al., 2018). This complex has become a new type of antibacterial drug due to its better antibacterial activity and reduction of antibiotic resistance (Teran et al., 2019). Therefore, the combination of triazoles with Schiff bases is a sensible strategy in order to develop new effective drug candidates against bacterial threats (Matin et al., 2022). Therefore, the compounds designed in this paper are the couplings of triazole and Schiff bases to study their antimicrobial and anti-biofilm capabilities. As shown in Figure 1, several antimicrobial derivatives containing triazole structures have been used in clinical applications for the treatment of infections caused by a wide range of microorganisms.
Water quality is vital to human survival, as water is an essential element for life (Scorza et al., 2024). However, a major reason for the serious water pollution nowadays is the excessive heavy metal ions (Botle et al., 2023). Therefore, how to purify heavy metal ions in water is a difficult problem we face, and Schiff bases tend to have better metal chelating properties. More studies have reported that the antibacterial activity of Schiff base may be related to its complexing metals (Manhas et al., 2021). Schiff bases can chelate ions essential for microbial development or interact with DNA to cause irreversible damage to pathogens (Arag´on-Muriel et al., 2021). For these reasons, the ability of synthetic triazole derivatives coupled with Schiff bases to remove heavy metal ions from water was measured in this paper. We also know that infections are often accompanied by inflammation when they occur, and we also tested the anti-inflammatory effects of compounds.
In summary, in this paper, 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (D) was synthesised using thiourea as a starting material, and finally the antimicrobial agent E, a coupling of triazoles and Schiff bases, was obtained by aldehyde-amine condensation reaction. The synthesised triazole derivatives have high removal rate of heavy metal ions and good antibacterial and anti-biofilm effect.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Chemical synthesis
We used thiourea as a starting material in a three-step reaction to obtain the intermediate triazole derivative 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (D) (Manning et al., 2002; Stojković et al., 2023). The reaction yields of the first three steps were above 85%, and finally the end product E, a coupling of triazoles and Schiff bases, was obtained by aldehyde-amine condensation reaction, and the synthetic route is showed in Scheme 1. All products were characterised by NMR and mass spectra.
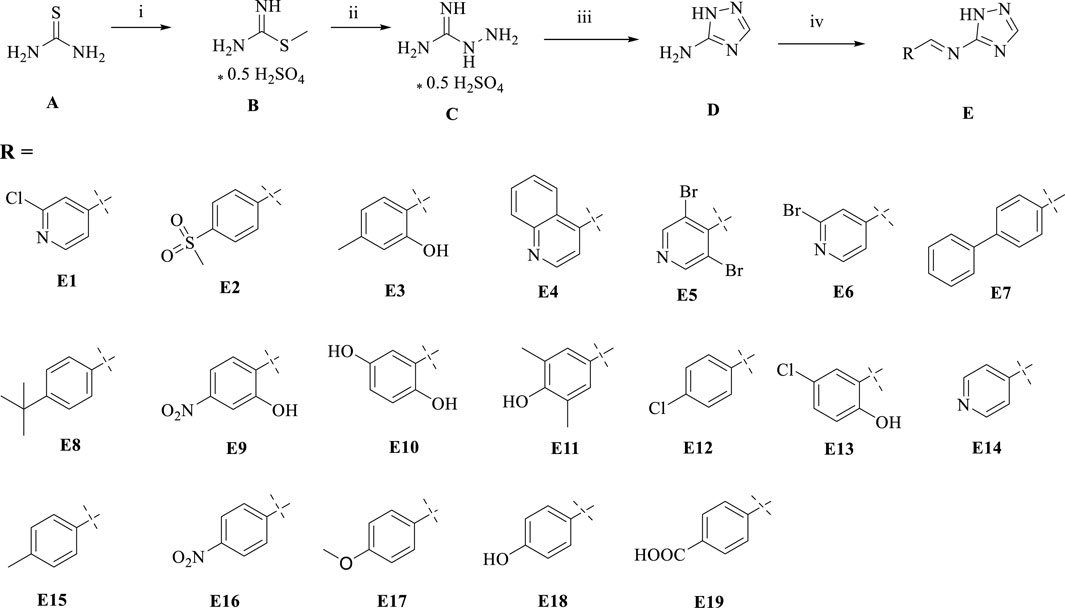
Scheme 1. Synthesis of triazole derivatives. Conditions and reagents: (i) Methanol and CH3I, reflux, 12h, yield 93%; (ii) Ethanol, NH2NH2, reflux, yield 88%; (iii) Ethanol, HCOOH, reflux, yield 85%; (iV) Ethanol, different aldehyde groups, reflux, yield 50%–91%.
2.2 The antibacterial activity of the compounds
2.2.1 Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration
Some triazole derivatives have been reported to have good in vitro antibacterial activity (Tian et al., 2023). In this experiment, the in vitro inhibitory activity (MIC) of the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus ATCC 29213, S. aureus ATCC 43300, S. aureus ATCC 33731, S. aureus MRSA2 and the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli ATCC 25922, E. coli DE 17 were determined using the micro broth dilution method. The antimicrobial results of the compounds are shown in Table 1. Among the tested compounds, E10 showed good inhibitory activity against E. coli at a concentration of 32 μg/mL. In addition, compound E10 showed inhibitory activity against all S. aureus strains at a concentration of 64 μg/mL. We found that the addition of hydroxyl group to the ligand benzaldehyde increased the antimicrobial activity by analysing the structure-activity relationship between compounds E3, E9, E10 and E13.
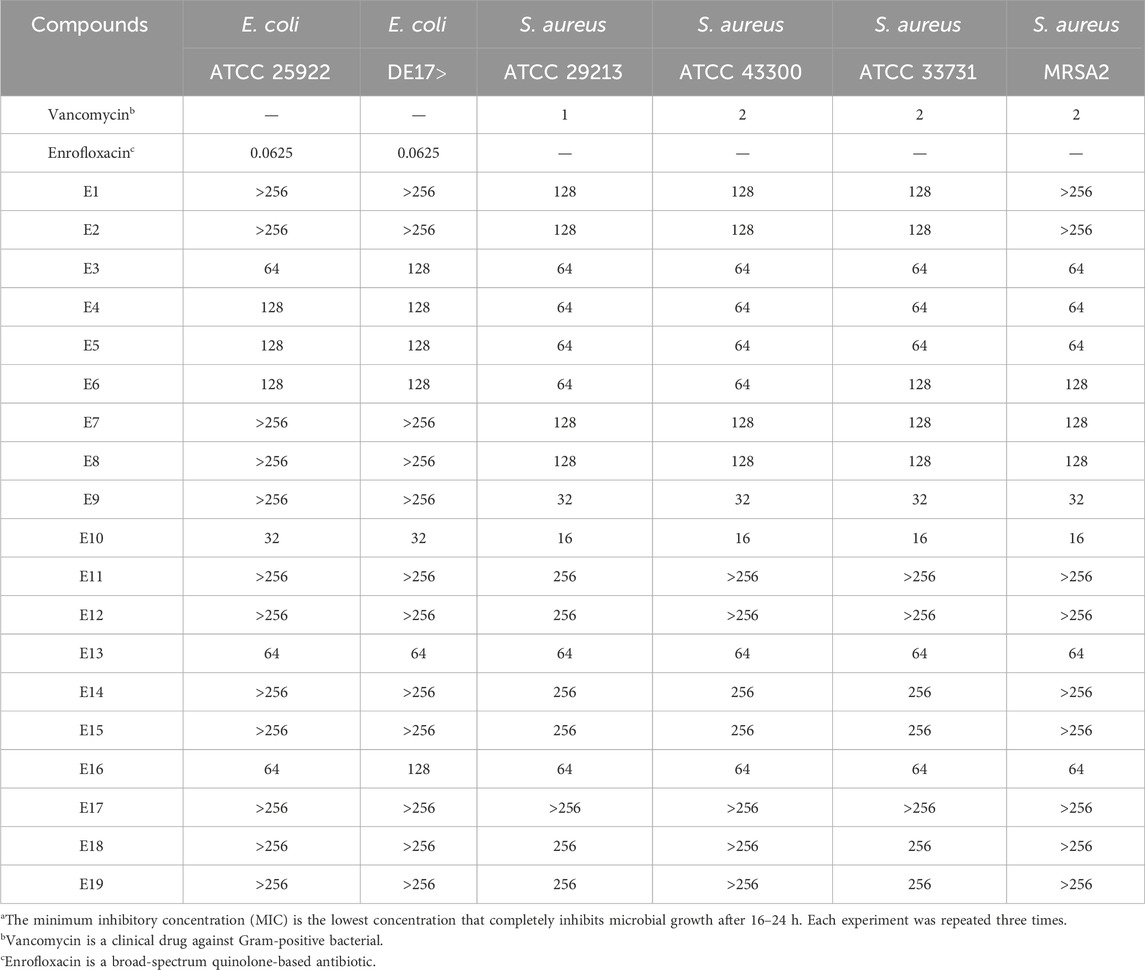
Table 1. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)a [µg/mL] of triazole derivatives on reference bacterial strains.
2.2.2 Time-killing curve determinations
In order to evaluate the bactericidal ability of E10 against S. aureus ATCC 29213 and E. coli ATCC 25922, we determined the time-kill curves of the compounds by counting the bacterial colonies at different time points using DMSO as a negative control. The results are shown in Figure 2, and the growth of S. aureus ATCC 29213 and E. coli ATCC 25922 can be completely inhibited at 4-fold MIC.
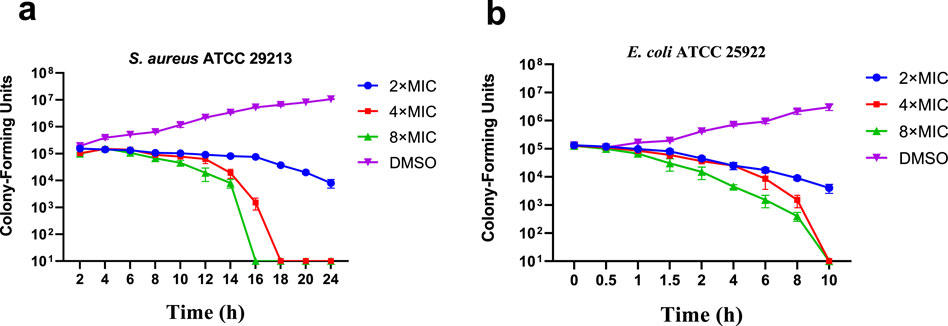
Figure 2. Time-kill kinetics of E10 against (A) Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 and (B) Escherichia coli ATCC 25922. Data are presented as means ± SEM (Standard Error of Mean) from three independent experiments.
2.2.3 Drug resistance study
The results of the resistance study showed that E10 had a low frequency of spontaneous resistance to E. coli ATCC 25922, S. aureus ATCC 29213 and MRSA2. As shown in Figure 3, E. coli ATCC 25922, S. aureus ATCC 29213, and MRSA2 did not increase their MIC values more than 8-fold after 28 generations. These results indicate that E10 can effectively kill bacteria and avoid the development of drug resistance.
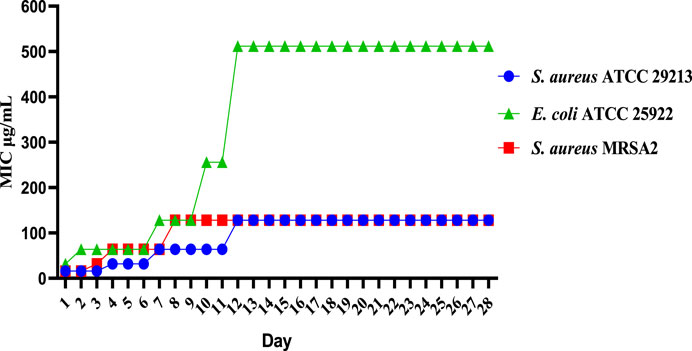
Figure 3. Resistance development of E10. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.3 The toxicity of the compounds
2.3.1 Hemolysis assay
To ensure the safety of our compounds, we first performed a haemolysis test on all compounds. We used 1% Triton X-100 as a positive control and sterile PBS as a negative control compounds in 4% rabbit erythrocytes after incubation at 37°C for 24 h. The results for E10 are shown in Figure 4. Test compound E10 at concentrations of 2–256 μg/mL showed no haemolytic properties. This indicates that E10 does not cause haemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes even at its antibacterial concentration.
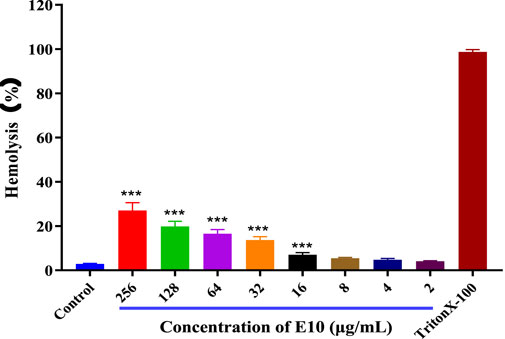
Figure 4. Percentage of hemolysis of rabbit blood cells at various E10 concentrations. Difference is considered significant at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.3.2 Cell cytotoxicity assay
We then evaluated the cytotoxicity of the active compound E10 against the African green monkey kidney cell line (VERO cells) using the CCK8 assay (Huang et al., 2022). As shown in Figure 5, the maximum inhibitory concentration of E10 tolerated on VERO cells was 128 μg/mL, indicating that E10 was not cytotoxic to VERO cells at concentrations up to 64 μg/mL.
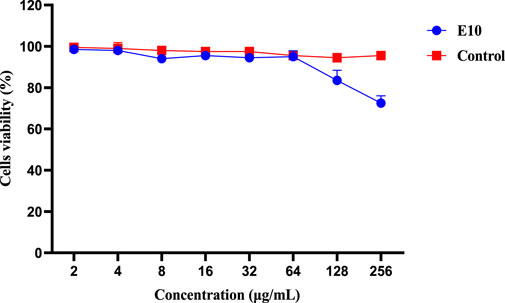
Figure 5. Cytotoxicity of compound E10 against Vero cells after 24 h. Difference is considered significant at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.4 Inhibitory effects towards S. Aureus biofilm formation
More than 80% of chronic bacterial infections in humans are associated with biofilms, which are surface-associated bacterial communities encased in a secreted exopolysaccharide matrix that resists to environmental and chemical damage (Vishwakarma et al., 2021). Biofilm formation increases bacterial resistance to conventional antibiotic treatments and host immune responses by nearly 1,000-fold (Yang et al., 2024). Failure of antibiotics to eliminate biofilms leads to persistent chronic infections and may promote the development of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop drugs that are effective in preventing biofilm formation and eradicating formed biofilms.
Therefore, we investigated whether compound E10 inhibits biofilm formation in S. aureus ATCC 29213. Biofilms were quantified using the crystal violet method and the inhibition of S. aureus ATCC 29213 biofilm by compound E10 at concentrations ranging from 2–256 μg/mL is shown in Figure 6A. Black is the group without biofilm formation and Contol is the group that formed biofilm without drug. Compound E10 showed significant biofilm inhibitory activity against S. aureus ATCC 29213 with 63.0% inhibition of biofilm at 32 μg/mL.
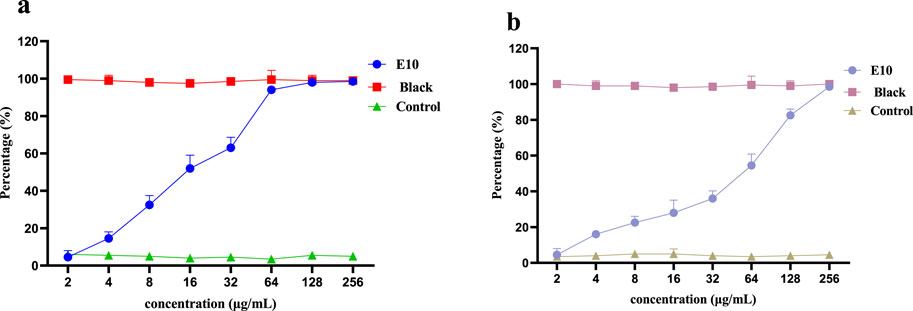
Figure 6. A dose-dependent response was observed in the biofilm inhibition (A) and eradication (B) activity of compound E10 against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
We next investigated whether compound E10 could eradicate biofilms formed by S. aureus ATCC 29213. E10 showed significant biofilm eradication activity against S. aureus ATCC 29213 by adding E10 treatment for 24 h after complete growth of biofilm as shown in Figure 6B. Compound E10 showed 54.5% eradication from biofilm at a concentration of 64 μg/mL.
2.5 The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds
Inflammation often accompanies the onset of infection, and since triazole derivatives have been reported to inhibit inflammation, we further examined the effect of compound E10 on the levels of the inflammatory factor NO (Jiaranaikulwanitch et al., 2021). The results are shown in Figure 7, where LPS alone significantly induced NO production in RAW 264.7 cells compared to NO produced by the control, and treatment with the studied compound E10 affected NO levels. Model is the inflammation forming group and Control is the normal without inflammation group. Compound E10 showed significant inhibition of NO production at concentrations 16 μg/mL.
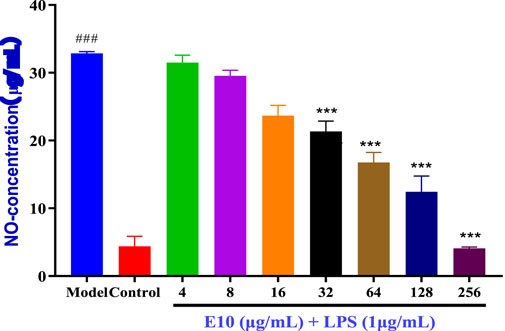
Figure 7. Anti-inflammatory activity of the E10 compounds in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells was evaluated in the LPS-enhanced leukocyte migration assay. Compared with the LPS model group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ###p < 0.001 vs. control group. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
To further expand the drug application scenario, we performed other inflammatory factor assays. We know that allergic asthma is the airway disease caused by some abnormal inflammatory factors. Th2 cells play an important role in triggering and pushing airway inflammation by producing, e.g., interleukin (IL)-4, (IL)-6 and TNF-α, cytokines that exacerbate the disease with immunoglobulin E (IgE) and mucus production (Li et al., 2022). We preliminarily evaluated the cytotoxicity of E10 using the CCK8 assay, and as shown in Figure 8A, E10 showed no significant cytotoxic effects on BEAS-2B cells at concentrations below 30 μg/mL. Next, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of E10 on IL-4/TNF-α- stimulated BEAS-2B cells. As shown in Figure 8B, E10 inhibited the IL-4/TNF-α-induced production of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6. This suggests that E10 deserves further exploration in the treatment of asthma.
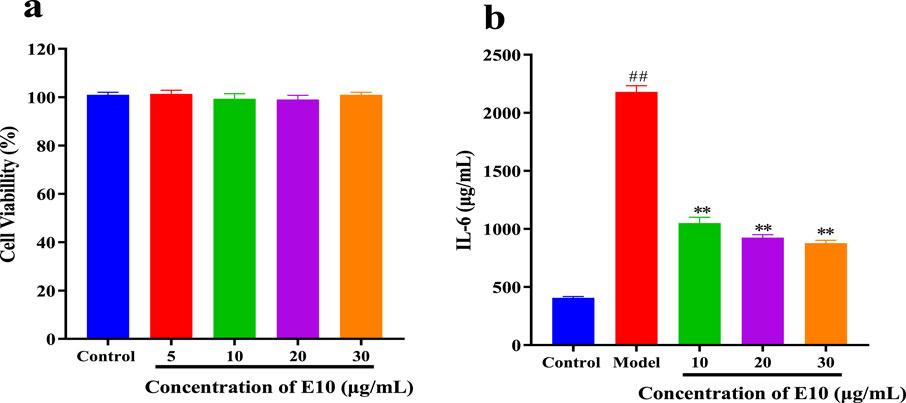
Figure 8. (A) Cytotoxic activity of E10 against BEAS-2B cells. (B) Level of IL-6 treated with E10 in IL-4/TNF-α-stimulated BEAS-2B cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ###p < 0.001 vs. control group. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.6 Antimicrobial mechanism investigation
2.6.1 Membrane depolarization and permeabilization assay
It has been reported that the antibacterial activity of Schiff bases is related to their hydrophobicity, which favours membrane interactions with pathogenic bacteria (Pervaiz et al., 2022). Based on the action of compound E10 on bacterial cell membranes, it may cause changes in bacterial cell membrane depolarisation and permeability. We therefore investigated the effect of E10 on the depolarisation and permeability of bacterial membranes using the fluorescent probes 3,3-dipropylthiodicyanoiodide (DISC35) and SYTOX Green (Yang et al., 2022; Kong et al., 2023).
After 10 min, compound E10 was added to a solution of S. aureus ATCC 29213 containing the fluorescent probes DiSC35 or SYTOX Green, and the fluorescence intensity of the mixed bacterial solution continued to increase (Figures 9A, B). When the E10 concentration was 4×MIC or 32×MIC, the fluorescence intensity of the mixed bacterial solution at 35 min was significantly increased compared to the initial fluorescence intensity, while the fluorescence intensity of the blank control without E10 remained unchanged. This suggests that E10 perturbs the positive and negative polarisation states of the interior and exterior of the bacterial cell membrane, thereby enhancing permeability. Similarly, the fluorescence intensity of melittin, a membrane-targeted natural antimicrobial peptide, was significantly enhanced in the positive control group. These results suggest that E10 can affect the bacterial cell membrane, leading to bacterial death.
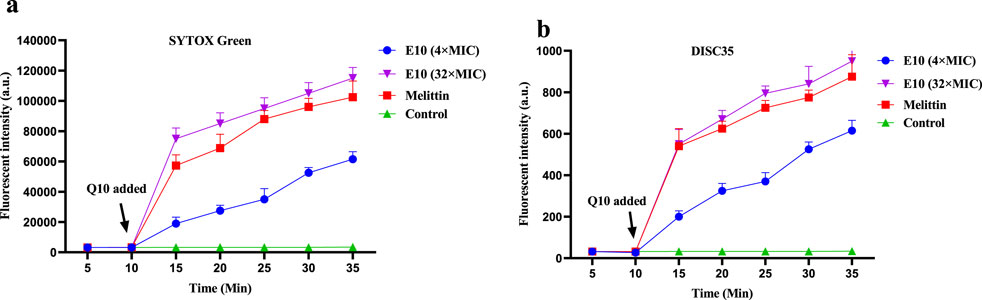
Figure 9. Antibacterial mechanism of E10 against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. (A) Cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization ability of E10 using a SYTOX Green assay. (B) Cytoplasmic membrane depolarization of E10 using the DiSC35 probe. The blank control was bacteria without compound treatment, and melittin was used as a reference drug. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.6.2 Leakage of proteins and DNA
We further determined the changes in intracellular protein and DNA concentrations after the addition of different concentrations of E10 to S. aureus ATCC 29213 medium (Raman et al., 2014). Compared with the blank control group, E10 treatment of S. aureus ATCC 29213 resulted in a significant and dose-dependent increase in the concentration of leaked proteins and DNA (Figures 10A, B). This suggests that E10 can cause membrane damage in S. aureus ATCC 29213 cells, leading to leakage of intracellular proteins and DNA.
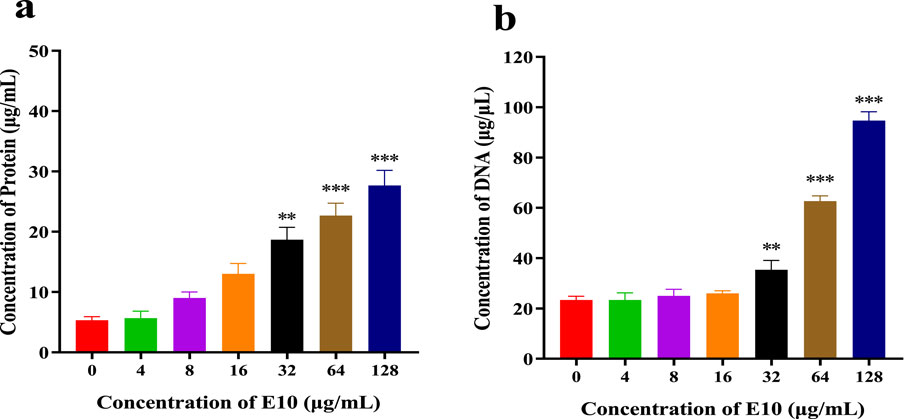
Figure 10. (A) DNA leakage resulting from the treatment of E10 on Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. (B) Protein leakage caused by the treatment of E10 on Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.7 Screening of heavy metals and metal ion removal from aqueous solution
We previously speculated that E10 should have good metal chelating ability to remove heavy metal ions from water, or be modified to act as a molecular probe to detect water quality. pH is a key parameter for the adsorption of heavy metals and metal ions. Since metal ions may interact with hydroxyl ions in water when the pH value is greater than 7, affecting the accuracy of our determination, the adsorption experiments in this study were carried out at a pH value of 6.0. After testing, we found that, as shown in Figure 11A, the removal amount of E10 for divalent metal ions is 55%–60%, and the removal rate of E10 for trivalent metal ions is 42%–45%. We infer that the removal rate of metal ions is related to the coordination form of the compound to the metal ion. One possible mechanism is shown in Figure 11B, where E10 chelates 1:1 with divalent metal ions and 3:1 with trivalent metal ions, which also directly reduces its removal of trivalent metals.
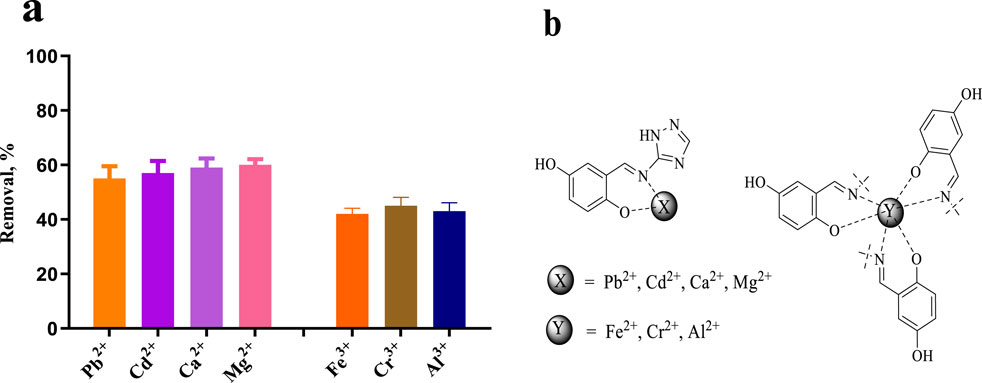
Figure 11. (A) Removal efficiencies of Pb2+, Cd2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ and Al3+ using compound E10, (B) Possible mechanism of metal and heavy metal ion removal. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
3 Conclusion
In this paper, 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (D) was synthesised using thiourea as a starting material, and finally the coupling end product E of triazole and Schiff base was obtained by aldolamine condensation reaction, and the structures of all the compounds were determined by spectroscopic analysis. In vitro antimicrobial activity showed that E10 had a MIC of 32 μg/mL against the tested E. coli and 16 μg/mL against the tested S. aureus strains. Meanwhile, E10 has a good anti-biofilm effect. Antibacterial mechanism studies have shown that E10 has a good membrane targeting ability, thus disrupting cell membranes, leading to leakage of intracellular proteins and DNA and accelerating bacterial death. In terms of anti-inflammation, E10 dose-dependently inhibits the levels of inflammatory factors NO and IL-6, which deserves further exploration in the treatment of asthma. The study of metal ion removal capacity showed that the synthesised triazole derivatives have high capacity to remove heavy metals Pb2+, Cd2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ and Al3+ in the range of 42%–60%. Next step, we will use E10 as a lead compound to further optimise its antimicrobial capacity and investigate its antimicrobial targets in depth.
4 Experimental section
4.1 Chemically synthetical experiments
4.1.1 Methyl-isothiourea (B)
We added iodomethane solution (1.7 g, 12 mmol) dropwise to an ethanol (10 mL) solution of thiourea (0.76 g, 10 mmol) at room temperature. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h and the solvent was spun off at the end of the reaction. Final recrystallisation from methanol gave white solid B (2.2 g, yield: 93%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, dmso) δ 7.76 (s, 1H), 7.21 (s, 1H), 2.69 (s, 3H). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C2H7N2S+, 91.0330, found: 91.0337.
4.1.2 Hydrazinecarboximidamide (C)
B (1 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol, appropriate amount of sodium hydroxide was added to adjust the pH to neutral and stirred for 10 min, then hydrazine hydrate (2 mmol) was added and the reaction was heated to 50°C for 6 h. The solvent was spun off, and the target product C (66 mg, yield: 88%) was finally recrystallised from ethanol. 1H NMR (400 MHz, dmso) δ 8.82 (s, 1H), 4.67 (s, 2H). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for CH7N4+, 75.0670, found: 75.0675.
4.1.3 1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine (D)
We added sodium hydroxide 7.5 mmol, 5 mL of water to aminoguanidine C (7.5 mmol) and stirred the reaction for 10 min. Then formic acid (7.40 mmol) was added, and the reaction mixture was heated to 80°C to dissolve all of it, and then was dissolved at 120°C for 6 h. The reaction was stopped by the addition of ice water. After the reaction was stopped, the reaction was stopped by adding ice water and recrystallised from ethanol to give a white solid D (541 mg, yield: 85%) (Manning et al., 2002; Stojković et al., 2023). 1H NMR (400 MHz, dmso) δ 7.43 (s, 1H), 5.75 (s, 2H). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C2H5N4+, 85.0514, found: 85.0519.
4.1.4 (E)-1-(2-chloropyridin-4-yl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E1)
We dissolved the product D (1 mmol) in anhydrous ethanol, added aldehyde derivatives with different substituents, such as 2-chloroisonicotinaldehyde, and reacted at reflux for 8 h. After the reaction was stopped, the reaction solution was concentrated and finally the end product E1 (104 mg, yield: 50%) was obtained by recrystallisation from ethanol. The rest of the E-series products were obtained in the same way as E1 and will not be repeated thereafter. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.23 (s, 1H), 8.59 (s, 2H), 7.97 (d, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 160.16, 156.93, 148.96, 147.02, 125.31, 121.88. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C8H7ClN5+, 208.0390, found: 208.0395.
4.1.5 (E)-1-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl) methanimine (E2)
Compound E2 (205 mg, Yield: 82%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.31 (s, 1H), 8.24 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 8.13 (s, 1H), 8.06 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 3.27 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.33, 193.12, 145.80, 139.78, 130.69, 130.22, 128.22, 128.01, 43.78. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C10H11N4O2S+, 251.0602, found: 251.0609.
4.1.6 (E)-2-(((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)-5-methylphenol (E3)
Compound E3 (162 mg, Yield: 80%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.34 (s, 1H), 8.55 (s, 1H), 7.55 (s, 1H), 7.24 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 2.25 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 158.68, 144.74, 137.69, 132.59, 129.32, 128.54, 122.35, 117.62, 117.03, 20.37. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C10H11N4O+, 203.0933, found: 203.0940.
4.1.7 (E)-1-(quinolin-4-yl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E4)
Compound E4 (188 mg, Yield: 85%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.81 (s, 1H), 9.06 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.63 (s, 0H), 8.11 (dd, J = 18.4, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 7.80 (dt, J = 37.7, 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.33 (s, 1H), 3.42 (q, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 1.03 (td, J = 7.0, 1.1 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 151.14, 149.01, 144.82, 129.60, 128.58, 126.29, 125.05, 124.71, 123.80, 123.21. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C12H10N5+, 224.0936, found: 224.0946.
4.1.8 (E)-1-(3,5-dibromopyridin-4-yl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E5)
Compound E5 (183 mg, Yield: 55%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.09 (s, 0H), 9.22 (s, 1H), 8.98–8.78 (m, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 161.07, 152.25, 151.64, 144.95, 120.95, 119.95. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C8H6BrN5+, 331.8969, found: 331.8975.
4.1.9 (E)-1-(2-bromopyridin-4-yl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E6)
Compound E6 (192 mg, Yield: 58%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.23 (s, 1H), 8.59 (d, J = 16.6 Hz, 2H), 8.16 (s, 1H), 7.99 (s, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 160.53, 159.10, 153.65, 147.52, 146.81, 132.95, 128.57, 125.34. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C8H7BrN5+, 251.9885, found: 251.9889.
4.1.10 (E)-1-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E7)
Compound E7 (226 mg, Yield: 91%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.26 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.53 (s, 1H), 8.08 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.96–7.65 (m, 4H), 7.61–7.29 (m, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO) δ 166.69, 165.53, 163.18, 144.42, 143.97, 139.65, 135.05, 130.64, 130.13, 129.56, 128.65, 127.76, 127.63, 127.36. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C15H13N4+, 249.1140, found: 249.1146.
4.1.11 (E)-1-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E8)
Compound E8 (201 mg, Yield: 88%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.19 (s, 1H), 7.93 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.57 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 1.32 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 164.20, 155.96, 133.16, 129.91, 129.57, 126.32, 35.34, 31.35. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C13H17N4+, 229.3068, found: 229.3075.
4.1.12 (E)-2-(((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)-5-nitrophenol (E9)
Compound E9 (138 mg, Yield: 62%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.49 (s, 1H), 8.76 (s, 1H), 8.23 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 165.71, 162.05, 140.29, 131.07, 129.23, 126.84, 124.82, 120.25, 118.24. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C9H8N5O3+, 224.0627, found: 224.0634.
4.1.13 (E)-2-(((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)benzene-1,4-diol (E10)
Compound E10 (139 mg, Yield: 68%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.63 (s, 1H), 9.32 (d, J = 20.1 Hz, 1H), 9.09 (s, 1H), 8.54 (s, 1H), 7.13 (s, 1H), 6.99–6.73 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 164.69, 153.69, 150.31, 144.68, 124.99, 122.38, 119.75, 117.83, 116.77. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C9H9N4O2+, 205.0725, found: 205.0725.
4.1.14 (E)-4-(((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)-2,6-dimethylphenol (E11)
Compound E11 (168 mg, Yield: 78%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.01 (s, 1H), 7.58 (s, 2H), 2.23 (s, 6H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 158.26, 151.29, 148.40, 145.02, 130.34, 130.30, 125.15, 17.04. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C11H13N4O+, 217.1089, found: 217.1095.
4.1.15 (E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E12)
Compound E12 (165 mg, Yield: 80%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.21 (s, 1H), 8.01 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.59 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 160.74, 158.57, 149.77, 136.42, 133.98, 130.60, 128.96. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C9H8ClN4+, 207.0617, found: 207.0625.
4.1.16 (E)-2-(((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol (E13)
Compound E13 (138 mg, Yield: 62%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.20 (s, 0H), 9.39 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.43 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 7.00 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 190.18, 163.28, 159.97, 159.31, 136.18, 127.83, 123.94, 119.99, 119.20. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C9H8ClN4O+, 223.0386, found: 223.0394.
4.1.17 (E)-1-(pyridin-4-yl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E14)
Compound E14 (121 mg, Yield: 70%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.24 (s, 1H), 8.87 (s, 1H), 8.76 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 2H), 7.96–7.86 (m, 3H), 7.79 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 160.68, 158.26, 149.78, 146.71, 143.30, 124.53. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C8H8N5+, 174.0779, found: 174.0785.
4.1.18 (E)-1-p-tolyl-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E15)
Compound E15 (166 mg, Yield: 89%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.95 (s, 1H), 7.80 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 2H), 7.42 (d, J = 10.4 Hz, 2H), 2.40 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 160.68, 157.46, 147.23, 142.67, 130.55, 129.45, 126.36, 23.24. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C10H11N4+, 187.0983, found: 187.0988.
4.1.19 (E)-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E16)
Compound E16 (195 mg, Yield: 90%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.33 (s, 1H), 8.45–8.15 (m, 4H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 160.53, 158.93, 149.77, 146.86, 141.38, 128.96, 124.51. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C9H8N5O2+, 218.0678, found: 218.0685.
4.1.20 (E)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-N-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methanimine (E17)
Compound E17 (141 mg, Yield: 70%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.12 (s, 1H), 8.48 (s, 1H), 7.93 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 7.06 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 3.82 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 164.68, 162.92, 151.32, 144.20, 132.26, 131.35, 130.11, 114.95, 56.12. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C10H11N4O+, 203.0933, found: 203.0937.
4.1.21 (E)-4-(((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)phenol (E18)
Compound E18 (160 mg, Yield: 85%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.31 (s, 1H), 9.76 (s, 0H), 9.06 (s, 1H), 7.82 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 163.79, 161.81, 137.04, 135.11, 132.57, 129.15, 116.31. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C9H9N4O+, 189.0776, found: 189.0779.
4.1.22 (E)-4-(((1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)benzoic acid (E19)
Compound E19 (173 mg, Yield: 80%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.31 (s, 1H), 9.76 (s, 0H), 9.06 (s, 1H), 7.82 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 170.05, 160.08, 158.65, 149.17, 141.01, 130.30, 128.74, 124.04. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H+], calcd. for C10H9N4O2+, 217.0725, found: 217.0733.
4.2 The antibacterial activity of the compounds
4.2.1 Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration
Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) were determined for all compounds according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines (Mei et al., 2023). Detailed procedures can be found in the Supplementary Information.
4.2.2 Time-killing kinetics
We determined time-kill kinetics by plate colony counting. Details of the operation can be found in the previously reported literature (Song et al., 2021).
4.2.3 Drug resistance study
The drug resistance study is similar to the MIC assay, but the process needs to be repeated for 28 days, and some details can be found in the literature (Yang et al., 2024).
4.3 The toxicity of the compounds
4.3.1 Hemolysis assay
The detailed procedure for the hemolysis experiment is included in the Supplementary Information (Xu et al., 2024).
4.3.2 Cytotoxicity assay
The cytotoxicity test was conducted according to previous literature reports (Xu et al., 2024). Cell viability was assessed using the cell counting kit 8 (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) method. Cytotoxicity assay was done as described before with minor modifications. The results were calculated as follows: Cell viability (%) = (OD450 sample value − OD450 blank hole value)/(OD450 value of untreated control − OD450 blank hole value) × 100%.
4.4 Biofilm formation assay
Detailed procedures for biofilms are provided in the Supplementary Information (Etayash et al., 2021).
4.5 The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds
LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells were studied using methods reported in the literature (Jiaranaikulwanitch et al., 2021).
4.5.1 BEAS-2B Cell culture and viability. Human bronchial epithelial
Detailed procedures are provided in the Supplementary Information (Li et al., 2022).
4.5.2 Anti-inflammatory assay in BEAS-2B Cells
Detailed procedures are provided in the Supplementary Information (Li et al., 2022).
4.6 Membrane depolarization study
Detailed procedures for biofilms are provided in the Supplementary Information (Yang et al., 2024).
4.7 DNA and protein leakage
We refer to the literature for our experiments (Lu et al., 2023). Detailed procedures for biofilms are provided in the Supplementary Information.
4.8 Adsorption studies
Determination of metal ion removal was carried out with reference to previously reported methods (Xu et al., 2024; Hozien et al., 2020). We only determined a few more trivalent metal ions using the previous method. The removal percentage (Removal, %), was calculated as presented in Equation: Removal, % = [(C0-Ce)/C0] × 100.
4.9 Statistical analysis
The above experimental data is the average ±SEM independent experiment of three data points. One-way analysis of variance was used to process the statistical differences between the two groups.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
SH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HL: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. DT: Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YC: Investigation, Software, Writing–review and editing. QL: Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. FG: Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2025.1545259/full#supplementary-material
References
Arag´on-Muriel, A., Liscano, Y., Upegui, Y., Robledo, S. M., Ramírez-Apan, M. T., Morales-Morales, D., et al. (2021). In vitro evaluation of the potential pharmacological activity and molecular targets of new benzimidazole-based schiff base metal complexes. Antibiotics 10, 720–728. doi:10.3390/antibiotics10060728
Botle, A., Salgaonkar, S., Tiwari, R., Ambadekar, S., and Barabde, G. R. (2023). Brief status of contamination in surface water of rivers of India by heavy metals: a review with pollution indices and health risk assessment. Enviro. Geochem. Hlth 45, 2779–2801. doi:10.1007/s10653-022-01463-x
Dalia, S. A., Afsan, F., Hossain, S., Mannan, M., Haque, M., and Kudrat-E-Zahan, M. (2018). Spectral and thermal characterization of Mn(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes containing schiff base ligands towards potential biological application, Asian J. Chem. Sci. 4, 1–11. doi:10.9734/AJOCS/2018/42355
Dheer, D., Singh, V., and Shankar, R. (2017). Medicinal attributes of 1,2,3-triazoles: current developments. Bioorg. Chem. 71, 30–54. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2017.01.010
Etayash, H., Alford, M., Akhoundsadegh, N., Drayton, M., Straus, S. K., and Hancock, R. E. W. (2021). Multifunctional antibiotic-host defense peptide conjugate kills bacteria, eradicates biofilms, and modulates the innate immune response. J. Med. Chem. 25, 16854–16863. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01712
Fan, Y. L., Ke, X.Li. M., and Liu, M. (2018). Coumarin-triazole hybrids and their biological activities. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55, 791–802. doi:10.1002/jhet.3112
Hozien, Z. A., El-Mahdy, A. F. M., Abo Markeb, A., Ali, L. S. A., and El-Sherief, H. A. H. (2020). Synthesis of Schiff and Mannich bases of news-triazole derivatives and their potential applications for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution and as antimicrobial agents. RSC Adv. 10, 20184–20194. doi:10.1039/d0ra02872j
Huang, T., Jiang, H., Zhao, Y., He, J., Cheng, H., and Martyniuk, C. J. (2022). A comprehensive review of 1,2,4-triazole fungicide toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio): a mitochondrial and metabolic perspective. Sci. Total. Environ. 25, 151177–77. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151177
Jadimurthy, R., Mayegowda, S. B., Nayak, S. C., Mohan, C. D., and Rangappa, K. S. (2022). Escaping mechanisms of ESKAPE pathogens from antibiotics and their targeting by natural compounds. Biotech. Rep. 34, e00728–28. doi:10.1016/j.btre.2022.e00728
Jiaranaikulwanitch, J., Pandith, H., Tadtong, S., Thammarat, P., Jiranusornkul, S., Chauthong, N., et al. (2021). Novel multifunctional ascorbic triazole derivatives for amyloidogenic pathway inhibition, anti-inflammation, and neuroprotection. Molecules 12, 1562–1584. doi:10.3390/molecules26061562
Kong, H., Qin, S., Yan, D., Shen, B., Zhang, T., Wang, M., et al. (2023). Development of aromatic-linked diamino acid antimicrobial peptide mimics with low hemolytic toxicity and excellent activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J. Med. Chem. 66, 7756–7771. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01583
Li, B., Xiao, Q., Liu, J., Mu, X., Zhang, J., Qi, Y., et al. (2022). Chemical characterization and potential mechanism of the anti-asthmatic activity of a subfraction from schisandra chinensis fruit extract. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 5015–5025. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c01034
Li, J., and Zhang, J. (2022). The antibacterial activity of 1,2,3-triazole- and 1,2,4-Triazole-containingHybrids against Staphylococcus aureus: an updated review (2020-present). Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 22, 41–63. doi:10.2174/1568026621666211111160332
Lu, Y., Guan, T., Wang, S., Zhou, C., Wang, M., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Novel xanthone antibacterials: semi-synthesis, biological evaluation, and the action mechanisms. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 83, 117232–117248. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2023.117232
Ma, Y. X., Wang, C. Y., Li, Y. Y., Li, J., Wan, Q., Chen, J., et al. (2020). Considerations and caveats in combating ESKAPE pathogens against nosocomial infections. Adv. Sci. 7, 172–182. doi:10.1002/advs.202000779
Manhas, N., Singh, P., Mocktar, C., Singh, M., and Koorbanally, N. (2021). Cytotoxicity and antibacterial evaluation of O-Alkylated/Acylated quinazolin-4-one schiff bases. Chem. Biodivers. 18, e2100096–e2100100. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202100096
Manning, C. O., Wadsworth, A. H., and Fellows, I. (2002). Synthesis of stable isotopically labelled versions of lamotrigine and its methylated metabolite. J. Label. Compd. Rad. 2002, 611–618. doi:10.1002/jlcr.590
Matin, M. M., Matin, P., Rahman, M. R., Ben Hadda, T., Almalki, F. A., Mahmud, S., et al. (2022). Triazoles and their derivatives: chemistry, synthesis, and therapeutic applications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9, 864286–86. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2022.864286
Mei, R., Heng, X., Liu, X., and Chen, G. (2023). Glycopolymers for antibacterial and antiviral applications. Molecules 18, 985–85. doi:10.3390/molecules28030985
Mulani, M. S., Kamble, E. E., Kumkar, S. N., Tawre, M. S., and Pardesi, K. R. (2019). Emerging strategies to combat ESKAPE pathogens in the era of antimicrobial resistance: a review. Front. Microbiol. 10, 539–39. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.00539
Patil, A., Banerji, R., Kanojiya, P., Koratkar, S., and Saroj, S. (2021). Bacteriophages for ESKAPE: role in pathogenicity and measures of control. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 19, 845–865. doi:10.1080/14787210.2021.1858800
Pervaiz, M., Ahmad, I., Saeed, Z., Sagir, M., Younas, U., Tahir, M. B., et al. (2022). Amalgamation and scrutinizing of leucine derivatives schiff bases complexes as antimicrobial agent. Comb. Chem. High. Throughput. Screen. 25, 1167–1180. doi:10.2174/1386207325666210927092623
Rakesh, K. P., Marichannegowda, M. H., Srivastava, S., Chen, X., Long, S., Karthik, C. S., et al. (2018). Combating a master manipulator: Staphylococcus aureus immunomodulatory molecules as targets for combinatorial drug discovery. Acs. Comb. Sci. 20, 681–693. doi:10.1021/acscombsci.8b00088
Raman, N., akthivel, A., and Pravin, S. N. (2014). Exploring DNA binding and nucleolytic activity of few 4-aminoantipyrine based amino acid Schiff base complexes: a comparative approach. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 125, 404–413. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2014.01.108
Scorza, F. A., Chaddad, F., and Beltramim, L. (2024). Water pollution and the brain. Clinics. 79, 14–24. doi:10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100424
Song, M., Liu, Y., Li, T., Liu, X., Hao, Z., Ding, S., et al. (2021). Plant natural flavonoids against multidrug resistant pathogens. Adv. Sci. 8, 2100749–2100760. doi:10.1002/advs.202100749
Stojković, P., Kostić, A., Lupšić, E., Jovanović, N. T., Novaković, M., Nedialkov, P., et al. (2023). Novel hybrids of sclareol and 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine show collateral sensitivity in multidrug-resistant glioblastoma cells. Bioorg Chem. 138, 106605–106613. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106605
Teran, R., Guevara, R., Mora, J., Dobronski, L., Barreiro-Costa, O., Beske, T., et al. (2019). Characterization of antimicrobial, antioxidant, and leishmanicidal activities of schiff base derivatives of 4-aminoantipyrine. Molecules 24, 2696–96. doi:10.3390/molecules24152696
Tian, G. M., Song, Q., Liu, Z., Guo, J., Cao, S., and Long, S. (2023). Recent advances in 1,2,3-and 1,2,4-triazole hybrids as antimicrobials and their SAR: a critical review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 259, 115603–115628. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115603
Vishwakarma, A., Dang, F., Ferrel, l A., and Barton, H. A. (2021). Peptidomimetic polyurethanes inhibit bacterial biofilm formation and disrupt surface established biofilms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 16, 13–24. Epub ahead of print. doi:10.1021/jacs.1c02324
Wang, J., Jiang, Z., Wei, Y., Wang, W., Wang, F., Yang, Y., et al. (2022). Multiplexed identification of bacterial biofilm infections based on machine-learning-aided lanthanide encoding. Acs. Nano. 16, 3300–3310. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c11333
Xu, C., Yang, N., Yu, H., and Wang, X. (2024). Synthesis of new triazole derivatives and their potential applications for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution and antibacterial activities. Front. Chem. 23, 1473097–1473109. doi:10.3389/fchem.2024.1473097
Yang, R., Hou, E., Cheng, W., Yan, X., Zhang, T., Li, S., et al. (2022). Membrane-targeting neolignan-antimicrobial peptide mimic conjugates to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections. J. Med. Chem. 65, 16879–16892. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01674
Yang, R., Xue, Z., Li, X., Xu, T., Zhong, Y., Hu, S., et al. (2024). Novel natural osthole-inspired amphiphiles as membrane targeting antibacterials against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 5, 116449–116462. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116449
Zafar, W., Sumrra, S. H., and Chohan, Z. H. (2021). A review: pharmacological aspects of metal based 1,2,4-triazole derived Schiff bases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 12, 113602–113644. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113602
Keywords: 1,2,4-triazole derivatives, anti biofilm, anti inflammatory, antiasthmatic, metal ion detection
Citation: Hong S, Lu H, Tian D, Chang Y, Lu Q and Gao F (2025) Discovery of triazole derivatives for biofilm disruption, anti-inflammation and metal ion chelation. Front. Chem. 13:1545259. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1545259
Received: 14 December 2024; Accepted: 05 February 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Stefania Villa, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Francesca Quartieri, Nerviano Medical Sciences, ItalyŽeljko Jaćimović, University of Montenegro, Montenegro
Copyright © 2025 Hong, Lu, Tian, Chang, Lu and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongzhi Lu, bHVob25nemhpMTdAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Shuang Hong
Shuang Hong Hongzhi Lu*
Hongzhi Lu*