- 1Department of Chinese Materia Medica and Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, The Air Force Medical University, Xi’an, China
- 2School of Pharmacy, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang, China
- 3School of Public Health, Health Science Center, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
Since ancient times, plants have provided humans with important bioactive compounds for the treatment of various diseases. Nine compounds were isolated from the roots and rhizomes of Caulophyllum robustum (a plant in the family Panaxaceae), including two new saponins C. Spanion A and C. Spanion B (1-2) and seven known saponins (3-9). The cytotoxicity of these compounds on human cancer cell lines was analyzed using MTT method. Compounds 6 and 9 exhibit cytotoxicity towards these three types of human cancer cells (<10 μM). By utilizing the SEA platform for target prediction, a common tumor related target CD81 was identified. The molecular docking of saponins 1, 2, 6, and 9 with CD81 protein showed strong binding affinities ranging from -4.5 to -7.1 kcal/mol. Research has shown that these compounds can become potential anti-tumor drugs. Further research is still recommended to understand its exact molecular mechanism and toxicological effects.
1 Introduction
Cancer is a widespread and highly destructive disease, and it is one of the leading causes of death in today’s society. The causes of cancer are diverse, and early symptoms are often difficult to detect, making the treatment process challenging (Siegel et al., 2021; Siegel et al., 2023). According to GLOBOCAN 2020 statistics, there are 19.29 million new cancer cases and 9.95 million deaths worldwide each year (Ferlay et al., 2021). Common chemotherapy drugs may lead to drug resistance in cancer cells due to long-term use and other reasons (Lopez and Banerji, 2017). Therefore, the search for new anti-cancer lead compounds has become particularly urgent.
From 1981 to 2019, approximately 23.5% of approved new drugs were derived from secondary metabolites of natural products (Newman and Cragg, 2020). Plants produce a wide variety of chemical substances, known as secondary metabolites. Among these secondary metabolites, saponins are a very important class of active compounds (Tian et al., 2021; Qu et al., 2023; He et al., 2023; Tian et al., 2023; Yin et al., 2023; Tian et al., 2024). Although a large number of saponin compounds have been isolated from plants, there are still some saponin components in plants that have not been isolated and studied. Therefore, further research is needed on saponins in plants to discover more compounds with anticancer activity.
Within the Berberidaceae family, Caulophyllum constitutes a small genus of perennial herbaceous plants. This genus comprises merely three species. Caulophyllum robustum is indigenous to Northeast Asia, encompassing countries such as China, Korea, and Japan. Caulophyllum robustum Maxim is predominantly found in regions of China like Heilongjiang, Shaanxi, and Hubei. The roots and rhizomes are known in Chinese as Hong Mao Qi. Extracts from it are widely employed as folk medicine in China for treating stomach aches, inflammations, irregular menstrual periods, and tumors. Modern research has shown that it has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti myocardial ischemia, anti-tumor, and anti acetylcholinesterase effects (Madgula et al., 2009; Lee et al., 2012; Hideji et al., 1991; Si et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2011). Previous phytochemical studies have uncovered a series of triterpene saponins, alkaloids, and sterols in C. robustum Maxim. Some of these compounds possess cytotoxic properties. This indicates that there might be differences in chemical compositions of C. robustum Maxim grown in different areas. Hence, C. robustum Maxim from Mount Taibai in Shaanxi was chosen for the separation of chemical components.
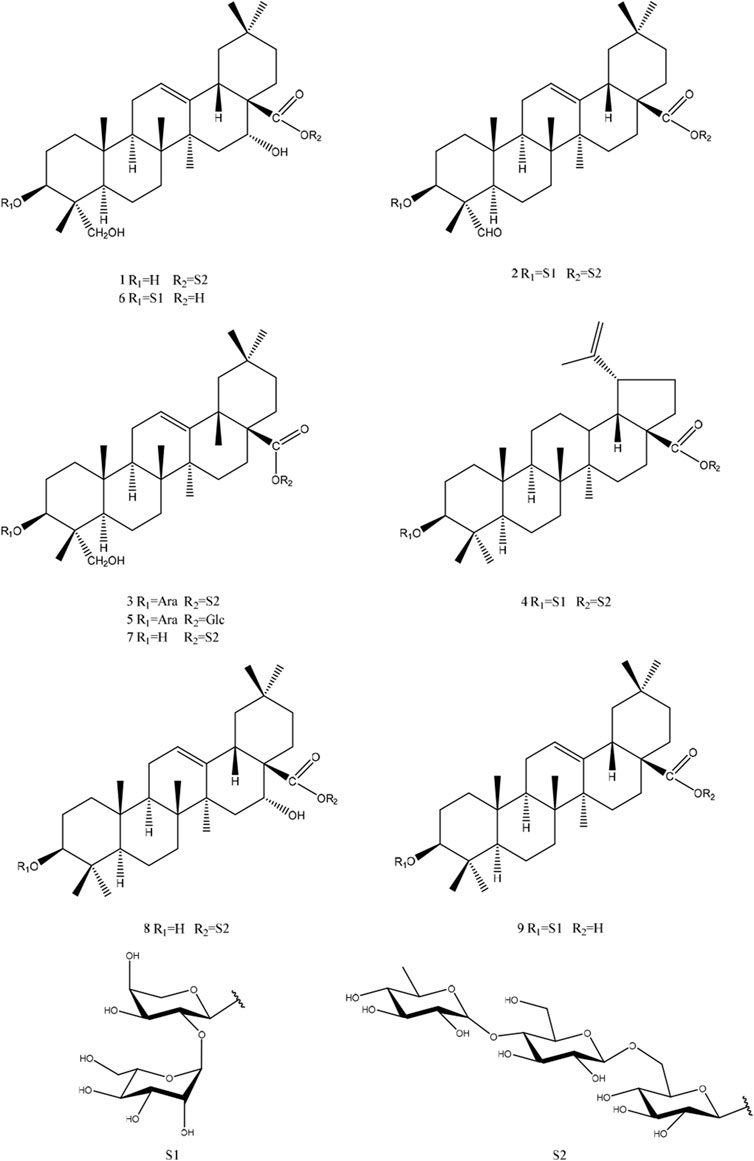
In this study, nine triterpene saponins were obtained (Figure 1), two of which had not been previously reported in the literature (1 and 2). Additionally, the isolated triterpene saponins were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities, and the interactions of saponins 1, 2, 6, and 9 with CD81 were described in detail. This research not only enriches our understanding of the chemical constituents of C. robustum Maxim but also provides potential leads for the development of new drugs targeting specific biological activities.
2 Experiment
2.1 Instruments and reagents
The separation process was performed using column chromatography (CC), including silica gel (300–400 mesh) purchased from Qingdao Marine Chemical Co., Ltd., reverse phase silica gel (RP-18, 40–63 μm) purchased from Merck&Co., Ltd. in New York, United States, and Sephadex LH-20 (GEHealthcare) purchased from Uppsala, Sweden. HPLC was performed on a Gilson PLC 2050 liquid chromatograph equipped with a Gilson PLC 2050 UV detector at a wavelength of 206 nm, using a Hedera ODS-2 column (250 × 20 mm, 10 μm, 10 nm) for semi preparation. The separated chemical reagents were purchased from Tianjin Fuyu Chemical Co., Ltd. in China. The standard samples of D-glucose (D-Glc), L-rhamnose (L-Rha), and L-arabinofuranose (L-Ara) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Chemical Co. in St. Louis, Missouri, United States.Perform GC-MS analysis on the simadzu GC-MS QP 2010 instrument to obtain information on sugar chains, which select RXI-5 SIL MS column (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm). ESI-MS and HRESI-MS were acquired utilizing an Agilent Q-TOF mass spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, United States). Optical rotation was performed on the INESA SGC-568 polarimeter (Yidian Physical Optics Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Conducted on a Bruker Ascend 800 spectrometer (Karlsruhe Bruker GmbH, Germany), TMS was used as an international standard for NMR. Additionally, the use of these advanced instruments and high-quality reagents ensures accurate and reliable results in the analysis and separation of complex chemical compounds. The combination of different chromatographic techniques and spectroscopic methods provides a comprehensive understanding of the chemical structures and properties of the substances under investigation.
2.2 Plant medicinal materials
In June 2016, the roots and rhizomes were harvested from Taibai Mountain in Shaanxi Province, China, and were authenticated as C. robustum Maxim by Dr. Hai-Feng Tang. A voucher specimen, designated as JB20160605, has been archived in the Herbarium of the Department of Chinese Medicinal Materials and Natural Drugs at the School of Pharmacy, Air Force Medical University in Xi’an, China.
2.3 Extraction and isolation
The roots and rhizomes of plants (5 kg) were chopped into pieces and extracted with 15 L of 70% ethanol at a reflux temperature of 85°C for 2 h, repeated three times. The extracts were combined and concentrated using a rotary evaporator to obtain a residue (413.2 g) Equal volumes of water were added to the residue to disperse it, followed by partitioning with petroleum ether and then with n-butanol successively. The n-butanol fraction (202.6 g) was subjected to column chromatography on silica gel, using a solvent system of CHCl3-MeOH-H2O with a volume ratio that varied from 100:1:0 to 6:3:0.5, resulting in the collection of seven fractions labeled as Fr.1 through Fr.7. Fr.4–2-1 (470 mg) underwent further purification through semi-preparative HPLC, utilizing a mobile phase of MeOH-H2O (60:40) at a flow rate of 8.0 mL/min, resulting in the isolation of compound 1 (5 mg, tR = 26.5 min). Fr.6 (14.77 g) was processed with a Sephadex LH-20 column using CHCl3-MeOH(1:1) as the eluent, yielding two subfractions, Fr.6–1 and Fr.6–2. From Fr.6–1 (12.66 g), three subfractions (Fr.6–1-1 to Fr.6–1-3) were separated using an ODS column. Fr.6–1-3 (699.7 mg) was then subjected to semi-preparative HPLC with a MeOH-H2O (70:30) mobile phase at a flow rate of 8.0 mL/min, leading to the purification of compound 2 (23.3 mg, tR = 23.5 min), 3 (28.3 mg, tR = 40.1 min), and 4 (11.9 mg, tR = 20.8 min). Fr.1 (5.11 g) was chromatographed on a Sephadex LH-20 column with MeOH as the eluent to obtain four subfractions (Fr.1–1 to Fr.1–4). Two subfractions (Fr.1–3-1 and Fr.1–3-2) were derived from Fr.1–3 (3.05 g) after passage through an ODS column. Fr.1–3-1 (50 mg) was further purified by semi-preparative HPLC with a MeOH-H2O (70:30) mobile phase at a flow rate of 8.0 mL/min, affording compound 5 (19.8 mg, tR = 24.1 min). Compound 6 (20 mg, tR = 17.8 min) was extracted from Fr.1-3-1-2 (40.02 mg) using HPLC with a MeOH-H2O (70:30) eluent at a flow rate of 8.0 mL/min. Fr.3 (2.73 g) was purified over a Sephadex LH-20 column with MeOH as the eluent, resulting in two subfractions (Fr.3–1 and Fr.3–2). Two subfractions (Fr.3–1-1 and Fr.3–1-2) were obtained from Fr.3–1 (0.72 g) following passage through an ODS column. Fr.3–1-2 (100 mg) was further purified by semi-preparative HPLC using a MeOH-H2O (70:30) mobile phase at a flow rate of 8.0 mL/min, yielding compounds 7 (55.9 mg, tR = 30.5 min) and 8 (6.8 mg, tR = 43.3 min). Fr.4 (5.89 g) was processed on a Sephadex LH-20 column with MeOH as the eluent to yield two subfractions (Fr.4–1 and Fr.4–2). Five subfractions (Fr.4–2-1 to Fr.4–2-5) were separated from Fr.4–2 (4.47 g) using an ODS column. Fr.4–2-5 (60 mg) was then purified by semi-preparative HPLC with a MeOH-H2O (60:40) mobile phase at a flow rate of 8.0 mL/min, resulting in the isolation of compound 9 (169.8 mg, tR = 20.7 min).
2.3.1 Compound 1
Amorphous solid; [α] −10.6 (c 0.54, MeOH); 1H (800 MHz, pyridine-d5) and 13C (200 MHz, pyridine-d5) NMR data see Table 1; HR-ESI-MS m/z 957.5076 [M - H]- (calcd. For C48H78O19, 957.5059).
2.3.2 Compound 2
Amorphous solid; [α] +9.6 (c 0.24, MeOH); 1H (800 MHz, pyridine-d5) and 13C (200 MHz, pyridine-d5) NMR data see Table 2; HR-ESI-MS m/z 1233.5892 [M - H]- (calcd. For C59H94O27, 1233.5904).
2.4 Sugar analysis of new compounds
The gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) technique was employed to analyze the monosaccharide content of compounds 1 and 2, adhering to a procedure akin to those reported in existing scientific literature. Each compound, weighing 5 mg, was subjected to hydrolysis by being treated with 1 mL of 2 M trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) at a temperature of 110°C for a duration of 90 min. Following hydrolysis, acetylation was performed using acetic anhydride. The reaction mixture was then diluted with 2 mL of distilled water and reduced using 100 mg of sodium borohydride (NaBH4). After reduction, the mixture was re-acetylated with acetic anhydride at 100°C for 60 min. Standard monosaccharide controls—D-glucose (D-Glc), L-rhamnose (L-Rha), and L-arabinose (L-Ara), each at a concentration of 5 mg—were processed using the identical method and analyzed via GC–MS.
The GC-MS analysis was conducted under the specified conditions: the column temperature was ramped from 130°C to 180°C at a rate of 3°C per minute and held at 180°C for 5 min. Subsequently, the temperature was programmed to increase to 310°C at a rate of 10°C per minute, where it was maintained for 15 min. The temperatures of both the injector and the flame ionization detector (FID) were set to 285°C. Nitrogen gas (N2) with a purity of at least 99.999% was used as the carrier gas, flowing at a rate of 20.0 mL per minute. The retention times for the standard monosaccharides were recorded as follows: D-Glc at 12.89 min, L-Rha at 5.65 min, and L-Ara at 5.15 min.
2.5 Cytotoxicity assay
The cytotoxicity of compounds 1–9 against human cancer cells was detected using the MTT method in 96-well microplates. The DMEM or RPMI-1640 culture medium (Hyclone, United States) was supplemented with 10% FBS (GIBCO, United States), 1% penicillin, and streptomycin (Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China), in which the cell lines were cultured at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cells in the logarithmic phase (5000 cells/well) were seeded in 96-well plates (100 μL/well) incubated for 24 h, then treated with various concentrations of saponins 1–9 (<0.1% DMSO) for 24 h, separately. Then, 20 μL MTT reagent (Sigma Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was added to each well incubated for 2 h at 37°C with 5% CO2. The optical density of each well was measured using a microplate reader (BioTek, United States) at a wavelength of 450 nm. The IC50 values of saponins 1–9 were evaluated according to their optical densities. The experiment was conducted three independent replicates, with doxorubicin and nimustine hydrochloride (Sigma, purity ≥99%) used as positive controls.
2.6 Target prediction and molecular docking
By means of the SEA platform (https://sea16.docking.org/), the target prediction of compounds with favorable activity was carried out, and common targets were selected for molecular docking simulation.
Molecular docking was employed to depict the interactions between proteins and ligands. The protein CD81, identified by its UniProt accession number P60033, was sourced from the UniProt database (https://www.uniprot.org/). Meanwhile, the ideal molecular configurations for compounds 1–9 were derived from Chem3D. In the molecular docking process, the structure of CD81 was modified using PyMOL 2.5.4 and AutoDock Tools 1.5.6 software. Additionally, the affinity between CD81 and its ligand was assessed using Auto Dock Vina 1.1.2 software. PyMOL 2.5.4 was utilized to visualize the molecular docking outcomes. This comprehensive approach of target prediction and molecular docking provides valuable insights into the potential mechanisms of action of these compounds. It helps in understanding how the compounds interact with specific proteins and may offer clues for further research and development of novel therapeutics.
3 Results
3.1 Isolated phytochemicals from Caulophyllum robustum Maxim
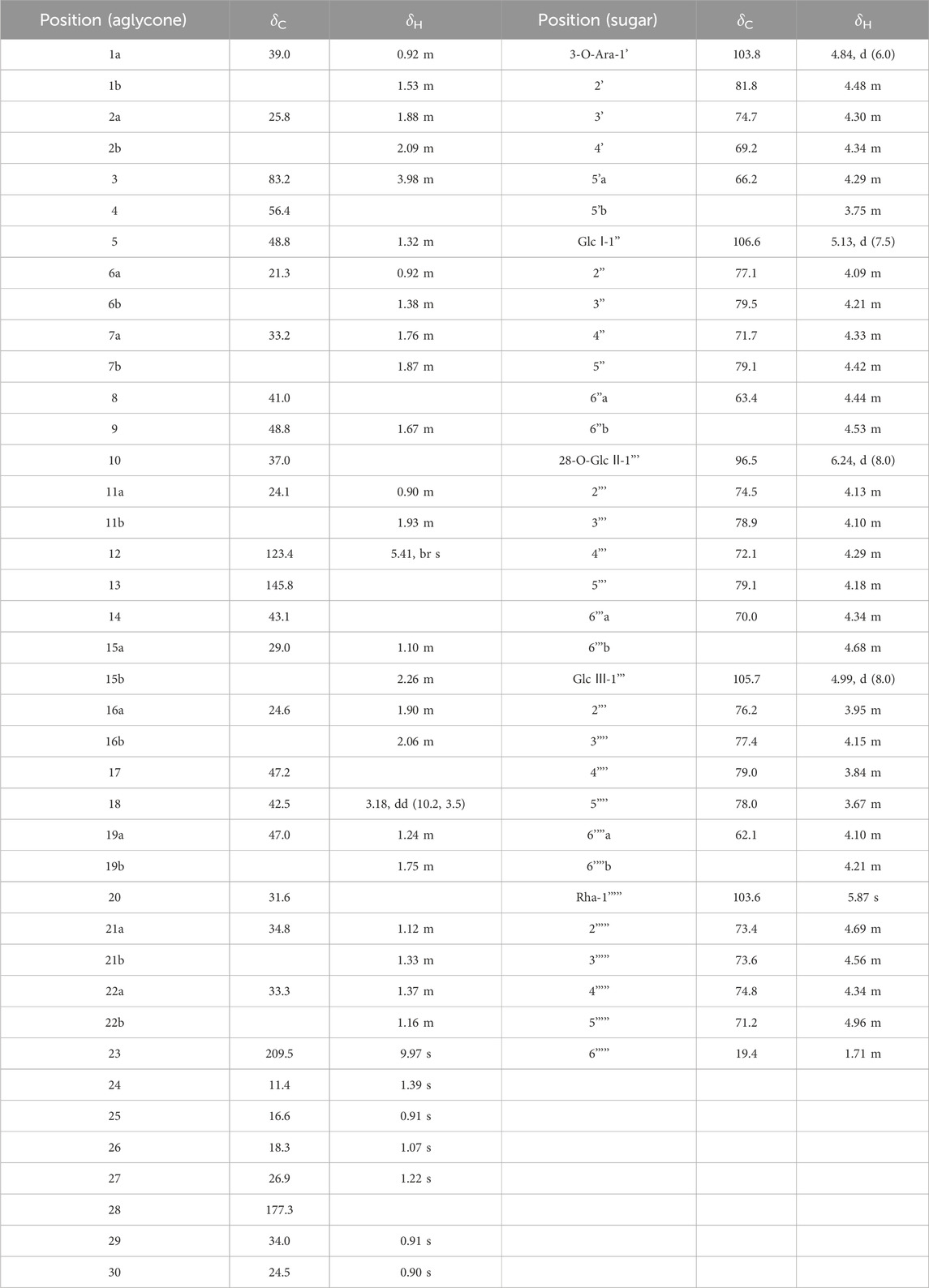
The Liebermann-Burchard and Molish tests indicated that compound 1 (1) was a saponin (Liu et al., 2023). The molecular formula was identified as C56H88O27 by HR-ESI-MS at m/z 957.5076 [M - H]- (calcd. For C48H78O19, 957.5059).The NMR spectrum (Table 1) showed six methyl signals at δH 0.98 (s, H-29), 1.05 (s, H-30), 1.09 (s, H-24), 1.09 (s, H-25),1.23 (s, H-26),1.80(s, H-27), an ene proton δH 5.64 (br s, H-12). Correspondingly, six methyl carbon signals at δC 13.2 (C-24),16.3 (C-25),17.8 (C-26),24.7 (C-30),27.3(C-27),33.2 (C-29). Meanwhile, one oxygenated methine δC 73.7 (C-3) and δC 74.4 (C-16), two olefinic carbons at δC 122.9 (C-12) and 144.5 (C-13), as well as one carboxyl at δC 176.1 (C-28) can be found in the 13C NMR spectrum (Table 1). The NOESY spectrum revealed correlations between H-3/H-23 and H-3/H-5, which pointed to the β-configuration of the oxygen atom at the C-3 position. In the 1H–1H COSY spectrum, the proton signal is correlated with the two proton signals of the methylene group at δH 2.57 (br d, 1H, J = 12.2 Hz, H-15b) and δH 1.77 (15a).Based on the broad single peak of the hydrogen proton on the methylene carbon in the 1H-NMR, HMBC and DEPT spectra, it is inferred that the hydroxyl group at position 16 should be in the alpha configuration (Shashi and Mahato, 1994). Taken together, the spectroscopic of the aglycone closely matched that of caulophyllogenin (Strigina et al., 1974).
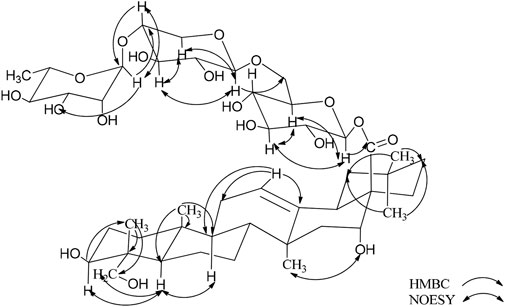
According to the results of GC-MS analysis, after acid hydrolysis treatment three monosaccharides were identified as D-Glc and L-Rha, and the ratio of them is 2:1. By analyzing 1H NMR, the hydrocarbon signals of three sugar groups were assigned (Table 1). The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 exhibited three sugar anomeric protons at δH 6.26 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, Glc’ H-1), δH 4.99 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, Glc’’ H-1) and 5.88 (s, Rha’ H-1), which showed HSQC correlations with the anomeric carbon signals at δC 95.9, 105.0 and 102.8, respectively. The trisaccharide chain was established to be Rha (1→4)-Glc ((1→6)-Glc- by the observation of HMBC correlations from Glc-H-1′ to C-28 of the aglycone, Glc-H-1′′ (δH 4.99) to Glc-C-6′ (δC 69.3) and Rha-H-1‴(δH 5.87) to Glc-C-4′′ (δC 78.3). This conclusion was confirmed by the NOESY correlations, as shown in Figure 2. Therefore, the chemical structure of 1 was elucidated as caulophyllogenin-28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, named C. Spanion A.
Compound 2 (2) is a white, amorphous substance. When we used compound 2 (2) for Lieberman-Burchard and Molish tests, the results of both experiment were showed positively, indicating that compound 2 may be a saponin (Liu et al., 2023). Its molecular formula was established as C59H94O27 by HR-ESI-MS at m/z 1233.5892 [M - H]- (calcd. For C48H78O19, 1233.5904). As compound 2 are similar to compond 1, indicating that they may gain similar structures (Table 2). The C-3 carbon was observed at δC 83.2, which suggested that the sugar linkage was formed at C-3. The main difference existed in the chemical shifts of H-16 and H-23 (δH-16 1.90, 2.06 and δH-23 9.97 for 2 and δH-16 4.29 and δH-23 4.15, 3.69 for 1). Furthermore, the aglycone’s spectroscopic details were found to be highly consistent with those of gypsogenin (Zhou et al., 1989).
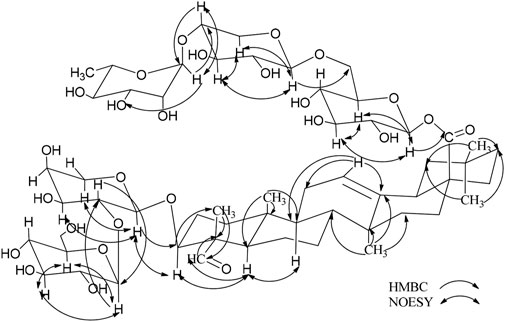
By using the same method as described above, the results of GC-MS indicating the existence of D-Glc, L-Rha and L-Ara, and the ratio of them is 3:1:1. Comparing the NMR spectra and extensive 2D NMR studies, we found that 2 and 1 have the same linked trisaccharide chain Aglycone C-28. Through the analysis of HMBC spectrum of 2, Ara was connected to C-3 of the aglycone as a cross-peak exists between C-3 of the aglycone and H-1 of Glc I. Key HMBC and NOESY shows in Figure 3. Therefore, the chemical structure of 2 was elucidated as 3-O-α-L-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-gypsogenin-28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, named C. Spanion B.
By correlating the NMR data with the information documented in the existing literature, the known saponins were characterized as 3-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-hederagenin-28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (3) (Wang et al., 2010), 3-O-α-L-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-betulinic acid 28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (4) (Liu et al., 2021), HN-saponin F (5) (Fumie et al., 1990), cauloside C (6) (Anisimov and Chaikina, 2015), Kalopanax saponin G (7) (Miyakoshi et al., 1999), echinocystic acid-28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (8) (Xia et al., 2014), oleanolic acid 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-arabinopyranoside (9) (Sobolev et al., 2000). See Supplementary Data Sheet 1 for relevant data.
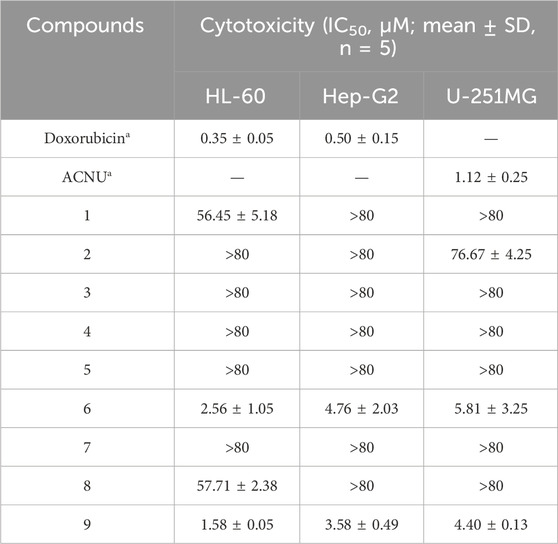
3.2 Cytotoxicity assay
The MTT assay was used to determine the cytotoxic properties of compounds 1–9, and the findings are outlined in Table 3. Notably, compounds 6 and 9 demonstrated potent cytotoxic effects (IC50 ≤ 10 μM) against a panel of three human cancer cell lines: U251MG, HepG2, and HL-60. Compound 1 exhibits weak activity against HL-60(IC50 = 56.45 ± 5.18 μM), while compound 2 shows weak activity against U-251MG (IC50 = 76.67 ± 4.25 μM).
3.3 Target prediction and molecular docking
3.3.1 Target prediction
Target prediction of compounds 1, 2, 6, and 9 through the SEA platform. Take the intersection of the targets of four compounds and select CD81 as the target.
3.3.2 Molecular docking
We then molecularly docked the proteins and compounds to study their binding patterns and interactions. The protein is first pretreated (including hydrogenation, water removal, energy minimization, etc.), followed by the formation of a lattice with coordinates X: 21.42, Y: 36.31, Z: 21.35 and a size of 20 Å. Finally, the treated compound is docked with the protein. By docking, we found that both compounds and proteins had acceptable binding energy (the Docking score, the smaller the value, the stronger the binding energy, generally less than −5 to prove a strong binding energy). To our excitement, compound 2 was the strongest with protein, reaching −7.042 kcal/mol, proving excellent affinity between the compound and protein. In addition, we studied the binding patterns and interactions between the compounds and proteins, as shown in the figure above. Each compound can bind to an active pocket of the protein. Specifically, for compound 6, the compound can form 1 hydrogen bond interaction with ALA-208 on the protein. For compound 9, the compound can form a hydrogen bond with GLU-105 on the protein.The visual representations of these interactions are depicted in Figure 4.
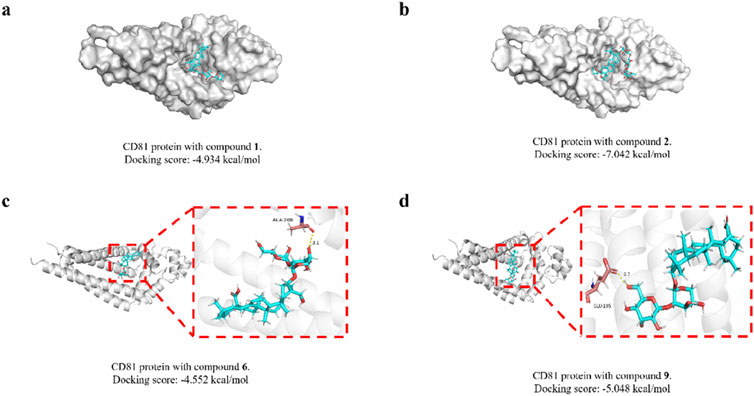
Figure 4. Molecular docking modeling of saponins 1, 2, 6 and 9 with CD81. Compound 1 (A); compound 2 (B); compound 6 (C); compound 9 (D).
4 Discussion
The study on in vitro anti-tumor activity found that compounds 6 and 9 have strong cytotoxicity against HL-60, Hep-G2, and U-251MG cells. Among them, compound 6 has significant activity against HL-60, Hep-G2, and U-251MG cells, with IC50 values of 2.56, 4.76, and 5.81 μM, respectively; compound 9 exhibits significant activity against HL-60, Hep-G2, and U-251MG cells, with IC50 values of 1.58, 3.58, and 4.40 μM. Regrettably, the remaining seven compounds, including two novel entities (1 and 2), that formed glycosides at the 28th position, exhibited diminished cytotoxicity against the aforementioned cancer cells. Nonetheless, compound 1 displayed moderate cytotoxicity towards HL-60 cells, and compound 2 showed a modest effect on U251MG cells. As illustrated in Table 3, the presence of carboxyl groups at the 28th position is associated with enhanced cytotoxicity in comparison to glycosides at the same position. Additionally, it is observed that the saponin activity of the oleanolic acid type is notably robust.
CD81 is involved in several crucial cellular activities, including the arrangement of the cell membrane, the movement of proteins, the merging of cells, and interactions between cells. Within the immune system, CD81 plays a role in managing the immune synapse, the gathering of receptors, and the transmission of signals. It also influences the suppression of both adaptive and innate immune responses. It is found in a broad spectrum of cancers, such as those affecting the breast, lungs, prostate, skin (melanoma), brain, and lymph nodes. The level of CD81 expression—whether it is increased or decreased—has been linked to different outcomes in cancer prognosis, with implications for both favorable and unfavorable outcomes (Vences-Catalán et al., 2017). All of these binding energies are below the threshold of −4.5 kcal/mol, suggesting a strong interaction. The findings suggest a possible link between the cytotoxic effects of these saponins on tumor cells and their interaction with CD81. This relationship warrants further investigation in subsequent research to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
5 Conclusion
A total of nine compounds were isolated and identified, comprising two new compounds and seven known ones. The anticancer activities of these compounds were assessed using the MTT method, and it was found that compounds 1, 2, 6 and 9 have potential anticancer properties. The target prediction and molecular docking results for these compounds suggest that saponin compounds may have some correlation with the CD family of proteins. This discovery implies that saponin compounds might not only kill tumor cells through cytotoxicity but could also possess a novel mechanism for combating tumor cells. This suggests that these compounds may serve as potential anti-cancer precursor compounds for further investigation. Regrettably, we have not yet been able to validate this phenomenon, and there is a lack of experimental evidence to confirm whether saponins indeed bind to CD family proteins and how they exert their cytotoxic effects on tumor cells.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
C-YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. Y-MW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. P-CQ: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. J-YF: Data curation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. B-WW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. YC: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. Y-SW: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. Y-TZ: Project administration, Validation, Writing–original draft. H-FT: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. Y-YL: Validation, Writing–review and editing, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision. QZ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing–review and editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by the Social R&D program of Shaanxi (2023-YBSF-514) (Hai-Feng Tang) and Project of Shaanxi Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (SZY-KJCYC-2023-001) (Qian Zhang).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2024.1507891/full#supplementary-material
References
Anisimov, M. M., and Chaikina, E. L. (2015). The effect of the hederagenin glycosides from Caulophyllum robustum max. On the growth of roots of cucumis sativus L. Seedlings. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 41 (7), 767–770. doi:10.1134/S106816201507002X
Ferlay, J., Colombet, M., Soerjomataram, I., Parkin, D. M., Piñeros, M., Znaor, A., et al. (2021). Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int. J. Cancer 149 (4), 778–789. doi:10.1002/ijc.33588
Fumie, MIZUI, Ryoji, KASAI, OhTANI, K., and Tanaka, O. (1990). Saponins from bran of quinoa, Chenopodium quinoa willd. II. Chem. Pharm.Bull. 38 (2), 375–377. doi:10.1248/cpb.38.375
He, Z., Hu, Y., Niu, Z., Zhong, K., Liu, T., Yang, M., et al. (2023). A review of pharmacokinetic and pharmacological properties of asiaticoside, a major active constituent of Centella asiatica (L.) urb. J. Ethnopharmacol. 302, 115865. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115865
Hideji, ITOKAWA, Yoshitatsu, ICHIHARA, Miwako, MOCHIZUKI, Enomori, T., Morita, H., Shirota, O., et al. (1991). A Cytotoxic Substance from Sangre de Grado. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 39 (4), 1041–1042. doi:10.1248/cpb.39.1041
Lee, Y., Jung, J.-C., Ali, Z., Khan, I. A., and Oh, S. (2012). Anti-inflammatory effect of triterpene saponins isolated from blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2012/798192
Liu, Y., Hai-feng, T., Yu-mei, W., Yun-yang, L., Qian, Z., Yang, L., et al. (2021). A new lupane-type triterpenoid saponin from Caulophyllum robustum. Cent. South Pharm. 19 (11), 2263–2268. doi:10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2021.11.004
Liu, Y., Liu, M.-Y., Bi, L.-L., Tian, Y.-Y., Qiu, P.-C., Qian, X.-Y., et al. (2023). Cytotoxic steroidal glycosides from the rhizomes of Paris polyphylla var. Yunnanensis. Phytochemistry 207, 113577. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113577
Lopez, J. S., and Banerji, U. (2017). Combine and conquer: challenges for targeted therapy combinations in early phase trials. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 14 (1), 57–66. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.96
Madgula, V., Ali, Z., Smillie, T., Khan, I., Walker, L., and Khan, S. (2009). Alkaloids and saponins as cytochrome P450 inhibitors from blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides) in an in vitro assay. Planta Med. 75 (04), 329–332. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1112207
Miyakoshi, M., Shirasuna, K., Hirai, Y., Shingu, K., Isoda, S., Shoji, J., et al. (1999). Triterpenoid saponins of acanthopanax nipponicus leaves. J. Nat. Prod. 62 (3), 445–448. doi:10.1021/np9804334
Newman, D. J., and Cragg, G. M. (2020). Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 83 (3), 770–803. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285
Qu, L., Liu, Y., Deng, J., Ma, X., and Fan, D. (2023). Ginsenoside Rk3 is a novel PI3K/AKT-Targeting therapeutics agent that regulates autophagy and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pharm. Anal. 13 (5), 463–482. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2023.03.006
Shashi, B., and Mahato, A. K. (1994). 13CNMR spectra of pentacyclic triterpenoids-a compilation and some salient features. Phytochemistry 37 (6), 1517–1575. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)89569-2
Si, K., Liu, J., He, L., Li, X., Gou, W., Liu, C., et al. (2010). Effects of caulophine on caffeine-induced cellular injury and calcium homeostasis in rat cardiomyocytes. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 107 (6), 976–981. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00618.x
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E., and Jemal, A. (2021). Cancer statistics, 2021. Ca. Cancer J. Clin. 71 (1), 7–33. doi:10.3322/caac.21654
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Wagle, N. S., and Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics, 2023. Ca. Cancer J. Clin. 73 (1), 17–48. doi:10.3322/caac.21763
Sobolev, E. A., Grishkovets, V. I., Shashkov, A. S., Tolkacheva, N. V., and Chirva, V.Ya. (2000). Triterpenoid glycosides of fatsia japonica. III. Isolation and structure of glycosides from fruit pericarp. Chem. Nat. Compd. 36 (5), 538–539. doi:10.1023/a:1002868330015
Strigina, L. I., Chetyrina, N. S., Isakov, V. V., Dzizenko, A. K., and Caulophyllogenin, G. B.ELYAKOV. (1974). Caulophyllogenin: a novel triterpenoid from roots of Caulophyllum robustum. Phytochemistry 13, 479–480. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)91237-8
Tian, L., Zhao, J.-L., Kang, J.-Q., Guo, S., Zhang, N., Shang, L., et al. (2021). Astragaloside IV alleviates the experimental DSS-induced colitis by remodeling macrophage polarization through STAT signaling. Front. Immunol. 12, 740565. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.740565
Tian, Y.-Y., Bi, L.-L., Chen, W.-W., Zheng, S.-X., Cao, Y., Xie, Y.-H., et al. (2024). Two previously undescribed cholestanol saponins from the rhizomes of Paris fargesii var. Petiolata. Fitoterapia 175, 105881. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.105881
Tian, Y.-Y., Liu, Y., Qiu, P.-C., Li, Y., Hu, J.-M., Li, T.-Y., et al. (2023). Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Paris fargesii var. Petiolata. Bioorg. Chem. 131, 106305. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106305
Vences-Catalán, F., Duault, C., Kuo, C.-C., Rajapaksa, R., Levy, R., and Levy, S. (2017). CD81 as a tumor target. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 45 (2), 531–535. doi:10.1042/BST20160478
Wang, D., Tian, J., Zhou, G.-P., Yang, Y.-S., Su, Y.-L., and Ji, T.-F. (2010). Triterpenoid glycosides from stauntonia chinensis. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 12 (2), 150–156. doi:10.1080/10286020903479709
Wang, X.-L., Liu, B.-R., Chen, C.-K., Wang, J.-R., and Lee, S.-S. (2011). Four new fluorenone alkaloids and one new dihydroazafluoranthene alkaloid from Caulophyllum robustum Maxim. Fitoterapia 82 (6), 793–797. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2011.04.010
Xia, Y.-G., Li, G.-Y., Liang, J., Ortori, C. A., Yang, B.-Y., Kuang, H.-X., et al. (2014). A strategy for characterization of triterpene saponins in Caulophyllum robustum hairy roots by liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 100, 109–122. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.024
Yin, M., Dong, J., Sun, C., Liu, X., Liu, Z., Liu, L., et al. (2023). Raddeanin A enhances mitochondrial DNA-cGAS/STING Axis-mediated antitumor immunity by targeting transactive responsive DNA-binding protein 43. Adv. Sci. 10 (13), 2206737. doi:10.1002/advs.202206737
Keywords: Caulophyllum robustum Maxim, Triterpenoid saponin, structure identification, antitumor activity, molecular docking
Citation: Zhang C-Y, Wang Y-M, Qiu P-C, Feng J-Y, Wang B-W, Cao Y, Wei Y-S, Zhou Y-T, Tang H-F, Lu Y-Y and Zhang Q (2025) Two previously undescribed triterpenoid saponins from the roots and rhizomes of Caulophyllum robustum Maxim. Front. Chem. 12:1507891. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1507891
Received: 08 October 2024; Accepted: 11 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaoxiao Huang, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Pradeep Kumar Jaiswal, Texas A&M University College Station, United StatesSafaet Alam, Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (BCSIR), Bangladesh
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Qiu, Feng, Wang, Cao, Wei, Zhou, Tang, Lu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hai-Feng Tang, dGFuZ2hhaWZlbmc3MUAxNjMuY29t; Yun-Yang Lu, bHV5dW55YW5nZ3FAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Qian Zhang, cWlhbnFpYW5nb29kb2tAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Cong-Yu Zhang
Cong-Yu Zhang Yu-Mei Wang2†
Yu-Mei Wang2† Peng-Cheng Qiu
Peng-Cheng Qiu Jia-Yu Feng
Jia-Yu Feng Hai-Feng Tang
Hai-Feng Tang