- 1School of Energy and Power Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 2Engineering Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, China
Studies on cerium oxo clusters (CeOCs) are not only significant for understanding the redox and hydrolysis behaviors of Ce(III/IV) ions but also crucial for the rational synthesis of novel clusters and nanoceria with specific Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratios. Here, two sets of reactions were conducted using cerium nitrate and H2O2-oxidized cerium nitrate, resulting in the formation of two distinct mixed-valent CeOCs [CeIII4CeIV10O14(OH)2(PhCO2)22(DMF)6] (Ce14) and [CeIII2CeIV22O28(OH)8(PhCO2)30(DMF)4] (Ce24C). These two clusters exhibit different structures and Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratios, demonstrating the critical role of cerium oxidation states and the occurrence of redox reactions in cluster formation. Ce14 is the first tetradecanuclear CeOC with a novel structure, whereas Ce24C differed in its Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratio, protonation levels of O atoms, and ligands from previously reported 24-nuclear CeOCs. Furthermore, various techniques were employed to investigate the formation process of these two clusters. X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) revealed that the white precipitates formed during the preparation of Ce14 contain Ce(III) ions, while the reddish-brown precipitates formed during the preparation of Ce24C contain a mixture of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) ions. These two precipitations were individually dissolved in N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF). The evolution of solution color and ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectra over time revealed the gradual oxidation of partial Ce(III) ions by oxygen in the solution of the white precipitation. As Ce(IV) ions increased in this solution, time-resolved small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) data demonstrated the self-assembly of the Ce14 clusters after 4 days. In contrast, SAXS data and UV-Vis spectra revealed the rapid assembly of Ce24C clusters within 2 h due to the initial coexistence of Ce(IV) and Ce(III) ions in the DMF solution of the reddish-brown precipitation. The continued reduction of partial Ce(IV) ions in this solution does not affect Ce24C clusters’ formation and stability. Our studies expand the family of CeOCs and enhance our understanding of the effects of cerium’s oxidation states on cluster formation.
1 Introduction
Metal oxo clusters (MOCs) are polynuclear species that consist of several to hundreds of metal ions, bridged together by O2-, OH−, and/or H2O ligands (Nyman, 2016). MOCs have been extensively investigated owing to their diverse structures, intriguing properties, as well as broad applications in many fields (Qiu and Burns, 2013; Zheng et al., 2019; Long et al., 2010). One representative family of MOCs is lanthanide oxo clusters, which are typically formed due to the hydrolysis reaction of lanthanide ions (Zheng et al., 2019).
Cerium (Ce) is the most abundant lanthanide element (Chauvel, 2018). Unlike other lanthanide elements, cerium exhibits two stable oxidation states (+3 and +4), giving rise to its reversible redox behaviors observed in various compounds (Piro et al., 2014). This distinctive feature makes cerium materials have significant applications in diverse fields such as catalysis (Ahmad et al., 2020), energy (Fan et al., 2013), and biomedicine (Chen et al., 2024). Cerium ions readily undergo hydrolysis reactions to form cerium oxo clusters (CeOCs) (Hennig et al., 2013). CeOCs typically consist of cores Cex (O/OH)y (where x is the count of cerium ions, and y is the count of O2- and/or OH− groups in the core), passivated by various organic/inorganic ligands including carboxylate (Hennig et al., 2013), phosphonate (Russell-Webster et al., 2021a), and sulfate (Colliard et al., 2021). These cores mostly exhibit a fluorite-like structure akin to cerium oxide, classifying CeOCs as a class of nanoceria with well-defined structures (Mitchell et al., 2017). Therefore, exploring CeOCs could not only advance our understanding of the hydrolysis behaviors of metal ions but also facilitate the rational design and synthesis of novel MOCs and nanoceria with controlled properties.
So far, CeOCs containing up to 100 cerium ions have been reported (Russell-Webster et al., 2021b). Compared to MOCs of transition metals and other lanthanides (Long and Cronin, 2021; Zheng et al., 2019), CeOCs have not been fully explored. It is worth mentioning that earlier research on CeOCs mainly focused on their syntheses and structures (Malaestean et al., 2012). Some recent studies have investigated the catalytic performance of specific CeOCs (Wasson et al., 2022). Nevertheless, studies investigating the assembly process of CeOCs remain limited. For example, Nyman’s group explored the roles of countercations in the self-assembly process of Ce70 and (Ce62)2 clusters (Colliard et al., 2021; Colliard et al., 2023) and the stacking mode of Ce70 clusters (Colliard and Nyman, 2021) using SAXS. Knope’s group investigated the transformation of a Ce10 cluster to a Ce12 cluster using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and SAXS (Blanes-Díaz et al., 2024).
CeOCs are synthesized using various Ce(III) (Blanes-Díaz et al., 2024; Mathey et al., 2015) or Ce(IV) compounds (Mitchell et al., 2021; Mitchell et al., 2017) as reactants. Interestingly, these clusters consist of either solely Ce(IV) ions or a blend of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) ions in their structures, indicating the occurrence of in-situ redox reactions during the formation of certain clusters. However, in-situ redox reactions of cerium ions, especially the effects of these processes on the formation of CeOCs, remain largely unexplored, although such studies are significant for the understanding of the catalytic reactivity of CeOCs and the rational construction of novel nanoceria with tailored Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratios. In addition, the variations in compositions of cerium compounds used as in previous studies might affect the formation and types of cerium clusters, thus posing a challenge in understanding the influence of cerium oxidation states on cluster formation.
In this study, we conducted two sets of reactions to investigate the effect of cerium oxidation states on cluster formation. To eliminate the effects of compositional differences from various cerium sources used in previous studies, we exclusively used cerium (III) nitrate. One set used it directly. In the other set, H2O2 was first employed to oxidize Ce(III) ions to Ce(IV) ions, as it does not introduce additional impurities (Djuričić and Pickering, 1999). The subsequent synthesis processes were identical. Ultimately, two distinct mixed-valent cerium oxo clusters, Ce14 and Ce24C, were formed from the two sets of reactions. Here, we report on their syntheses, structures, and formation processes.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Cerium nitrate hexahydrate (Ce(NO3)3·6H2O, AR), anhydrous methanol (AR), ferric perchlorate (Fe(ClO4)3, AR), nitric acid (HNO3, 65–68 wt%, AR), hydrogen peroxide solution (H2O2, 30 wt%, AR), sodium benzoate (PhCOONa, AR), and dimethylformamide (DMF, AR) were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. and used as received. All solutions were prepared by using 18.25 MΩ deionized water.
2.2 Syntheses
2.2.1 Synthesis of Ce14
Cerium nitrate hexahydrate (0.434 g, 1 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous methanol (1 mL), resulting in a colorless solution. This solution was then mixed with a solution prepared by dissolving sodium benzoate (0.576 g, 4 mmol) in anhydrous methanol (20 mL). The resulting solution was stirred for 15 min, leading to the formation of a white precipitate (around 0.6 g), labeled as Precipitate-1. Precipitate-1 was filtered and added to DMF (10 mL), followed by stirring until fully dissolved. The resulting solution (pH ≈ 9.3) was left to evaporate under ambient conditions. After approximately 10 days, light yellow plate crystals (Supplementary Figure S1) containing Ce14 clusters were obtained.
The yield of crystals prepared using the above method was low. Numerous reactions were conducted to optimize the synthesis method. It was found that the addition of a ferric salt to the solution of cerium nitrate can increase the crystal yield. For example, ferric perchlorate (0.5 M, 150 μL) and nitric acid (0.5 M, 450 μL) were added to the solution that was prepared by dissolving cerium nitrate hexahydrate (0.434 g, 1 mmol) in anhydrous methanol (1 mL). The next steps were the same as above. After approximately 10 days, light yellow plate crystals containing Ce14 formed with a yield of 17.4% based on the cerium used.
2.2.2 Synthesis of Ce24C
Cerium nitrate (0.434 g, 1 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous methanol (1 mL). Subsequently, H2O2 (50 μL, 30 wt%) was added. The resulting reddish-brown solution was then mixed with a solution prepared by dissolving sodium benzoate (0.576 g, 4 mmol) in anhydrous methanol (20 mL). The resulting solution was stirred for 15 min, leading to the formation of a reddish-brown precipitate (around 0.58 g), labeled as Precipitate-2. Precipitate-2 was filtered and added to DMF (10 mL), followed by stirring until fully dissolved. The resulting solution (pH ≈ 8.6) was left to evaporate under ambient conditions. After approximately 8 days, light orange block crystals (Supplementary Figure S1) containing Ce24C clusters formed with a yield of 18.1% based on the cerium used.
2.3 Instruments and characterization
2.3.1 Single crystal X-ray diffraction measurements
Single crystal X-ray diffraction data for the crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C were collected using a Bruker D8 Quest diffractometer with Mo Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å). The structures were solved via the intrinsic phasing method with SHELXT (Sheldrick, 2015b) and refined using the SHELXL program (Sheldrick, 2015a). All non-hydrogen atoms could be located in the different Fourier maps and refined anisotropically. Types of O atoms, namely, O2- and OH− were assigned based on the bond valence sum (BVS) analysis. Most H atoms were positioned in idealized positions and refined as riding on their parent atoms and H atoms from μ3-OH in both Ce14 and Ce24C were located using Fourier maps. H atoms from μ4-OH groups in Ce24C could not be located using Fourier maps and were not included in the refinement of its structure. The disordered solvent molecules were removed by the SQUEEZE command. A total of 41 and 300 electrons were removed for the crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C, respectively. Elemental analysis suggested that these electrons are attributed to the presence of 5 and 7 DMF molecules. The crystallographic data were deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre with deposition codes CCDC 2328826 and 2328827 for Ce14 and Ce24C, respectively.
2.3.2 Composition and property measurements of crystals and precipitations
The powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) data for the crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C, as well as the precipitations formed during their preparation process, were collected using a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54056 Å), at a scan rate of 0.05°/s. Additionally, XPS data of these crystals and precipitations were measured using a Thermo Fisher ESCALAB Xi + spectrometer equipped with a monochromatic Aluminum 400 W X-ray source.
The contents of Ce in the crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C were measured using a PerkinElmer NexION 350D inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). The contents of C, H, and N in these crystals were measured using a EUROVECTOR EA3000 elemental analyzer. Anal. calcd (found) for crystals of Ce14 (C199H217Ce14N15O75): Ce, 32.79% (33.20%); C, 39.97% (39.66%); H, 3.66% (3.45%); N, 3.51% (3.96%). Anal. Calcd (found) for crystals of Ce24C (C282H326Ce24N24O120): Ce, 36.03% (36.09%); C, 36.29% (36.36%); H, 3.52% (3.95%); N, 3.60% (3.91%).
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of the crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C were recorded using a Bruker VERTEX 70 spectrometer. Their Raman spectra were acquired using a Renishaw inVia Qontor spectrometer with an excitation wavelength of 532 nm. Their thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) data were collected by heating crystals (Ce14: 2.33 mg, Ce24C: 2.89 mg) from 35°C to 1,200°C at a rate of 10 °C/min under flowing N2 in a Mettler Toledo TGA/DSC3+ instrument.
2.3.3 Measurements of reaction solutions
Time-resolved UV-Vis spectra of the DMF solutions of Precipitate-1 and Precipitate-2 with reaction times from 0 h (immediately after the completion of the reaction) to 8 days were recorded using a GENESYS 150 spectrophotometer. Time-resolved SAXS data of these solutions were collected using an Anton Paar SAXSpoint 2.0 instrument with Cu Kα radiation. The solutions were individually placed into glass capillaries and then put on the sample stage. The distance between the sample stage and the detector was 250 mm. The exposure time was 30 min. SAXS data of pure DMF solution was also collected under the same condition for the background subtraction.
3 Result and discussion
3.1 Syntheses of Ce14 and Ce24C
To eliminate the effects of compositional differences from different cerium sources, all synthesis reactions were conducted exclusively using cerium nitrate. To change the oxidation states of cerium ions, the H2O2 solution was employed for oxidizing cerium nitrate. We found that the Ce14 crystals are formed from reactions using cerium nitrate. In contrast, the Ce24C crystals are formed from reactions using cerium nitrate that was oxidized by the H2O2 solution. These observations suggest that the oxidation states of cerium ions in reactants play an important role in the formation and types of CeOCs.
The initial yield of Ce14 crystals was low. Therefore, we conducted numerous reactions to optimize the synthesis method and found that the addition of appropriate ferric salts and nitric acid could be beneficial. Their addition increases the acidity of the reaction solution and may affect the oxidation process of Ce(III) ions. However, the exact function of the ferric salts and nitric acid remains uncertain, despite our efforts to understand it through various studies. It is noteworthy that Fe(NO3)3 has been previously used in syntheses of CeOCs (Mitchell et al., 2021).
3.2 Structures of Ce14 and Ce24C
The crystallographic analysis revealed that crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C containing two distinct types of CeOCs with different structures and Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratios (Figures 1A, 2A). Specifically, Ce14 cluster crystallizes in the triclinic space group P-1 (Supplementary Table S1). Its structure comprises 14 cerium ions, with four of them being Ce(III) ions and the remaining ten being Ce(IV) ions, as demonstrated by BVS calculations (Supplementary Table S2). To our knowledge, Ce14 is the first tetradecanuclear CeOC. All ten Ce(IV) ions are eight-coordinated, forming Ce-O bonds with distances ranging from 2.157 Å to 2.586 Å (Supplementary Table S4). In contrast, two Ce(III) ions are nine-coordinated and the other two are ten-coordinated, with much longer Ce-O bond distances spanning from 2.387 Å to 2.968 Å. As shown in Figure 1B, the ten Ce(IV) ions are connected through bridging O2- groups, forming a decamer. The four Ce(III) ions are divided into two groups and situated on opposite sides of the decamer through connections of μ4-O2- and μ3-OH- groups, resulting in the formation of Ce14 core (Figures 1B, C; Supplementary Table S3). Similar to cores of other CeOCs, this core also exhibits a fluorite structure (Supplementary Figure S2).
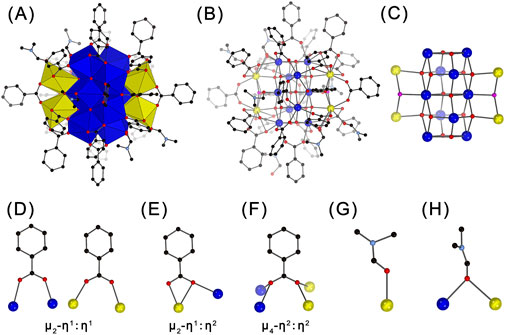
Figure 1. Polyhedral (A) and ball-and-stick (B–H) representations of the structure of Ce14 (A, B), its core (C), the coordination modes of benzoate groups (D–F), and the coordination modes of DMF molecules (G–H). Ce(IV) ions are shown in blue; Ce(III) ions in yellow, O2- ions in red; OH− ions in pink; C atoms in black; N atoms in light blue. H atoms are omitted for clarity.
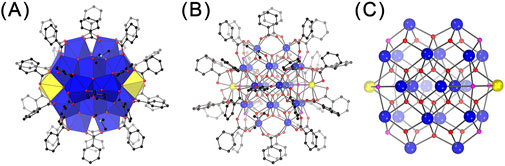
Figure 2. Polyhedral (A) and ball-and-stick (B, C) representations of the structure of Ce24C (A, B) and its core (C). Legends as that in Figure 1.
The core of Ce14 is coordinated by 22 PhCO2- and six DMF groups, forming the complete structure of the Ce14 cluster with a formula of [CeIII4CeIV10O14(OH)2(PhCO2)22(DMF)6]. The coordination modes of PhCO2- groups are quite diverse. Twelve of them adopt the common μ2-η1:η1-bridging mode (Figure 1D), eight exhibit the μ2-η1:η2 chelating and bridging mode (Figure 1E), and the remaining two adopt a rare μ4-η2:η2-bridging mode (Figure 1F) which was only observed in cluster Ce100 (Russell-Webster et al., 2021b). The six DMF groups exhibit two coordination environments. Four of them bond to one Ce ion through the O atom, while the remaining two bridge two adjacent Ce ions through the O atom (Figures 1G,H). The crystallographic analysis also revealed the presence of DMF molecules dispersed among the Ce14 clusters (Supplementary Figure S3). The elemental analysis indicated approximately 9 DMF molecules per cluster. Thus, the Ce14 crystal has a formula of [CeIII4CeIV10O14(OH)2(PhCO2)22(DMF)6]·9DMF.
The combination of the crystallographic and elemental analyses revealed that Ce24C is a 24-nuclear cluster containing two Ce(III) ions and 22 Ce(IV) ions, and it crystallizes with DMF molecule in the P-1 space group to form crystals with a formula of [CeIII2CeIV22O28(OH)8(PhCO2)30(DMF)4]·20DMF (Figure 2; Supplementary Figure S4; Supplementary Table S1; Supplementary Tables S5-S7). The structure of Ce24C is similar to those of previously reported Ce24A (Mitchell et al., 2017) and Ce24B (Mitchell et al., 2021) clusters. The primary differences among these three clusters lie in the ratio of Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ions, the number of OH− groups, and the type of ligands on their surface. The ratio of Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ions in the cores of Ce24A and Ce24C is 2:22, while that in Ce24B is 3:21. Both Ce24A and Ce24C contain eight OH− groups, while Ce24B contains nine OH− groups. The core of Ce24C is capped by 30 PhCO2- and four DMF groups, whereas Ce24A and Ce24B feature four pyridine groups instead of DMF groups. These structural variations demonstrate that the protonation levels of O atoms and the amount of Ce(III) ions in the cores of cerium oxo clusters are variable, and their surface ligands are replaceable. Similar results have been observed in other metal oxo clusters (Zhang et al., 2021).
3.3 Characterizations of Ce14 and Ce24C crystals
Crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C were characterized using PXRD, FTIR, TGA, Raman spectroscopy, and XPS to confirm their chemical composition and oxidation states of cerium ions within their structures. Specifically, the experimental PXRD patterns match well with simulated patterns calculated using single crystal X-ray diffraction data for both Ce14 and Ce24C, indicating that crystals of both Ce14 and Ce24C are pure (Figures 3A,B). FTIR spectra for crystals of Ce14 and Ce24C are similar (Figure 3C). Assignments of main IR peaks were provided in Supplementary Table S8. These peaks demonstrated the presence of Ce-O bonds, benzoate groups, and DMF molecules within these crystals. Their Raman spectra also exhibit the same features (Figure 3D and the inset). The peak at 451 cm-1 is related to the F2g mode of the Ce-O-Ce bond, which is formed due to the hydrolysis and condensation reactions of cerium ions (Miller and Irish, 1967; Weber et al., 1993). The peaks at 618 and 718 cm-1 are related to the out-of-plane deformation of the C=O and C-H bonds in the benzoate group, respectively (Klausberger et al., 1977). The peak at 660 cm-1 is attributed to the bending vibration of the O=C-N group in the DMF molecule (Kislina et al., 1994). The peak at 680 cm-1 corresponds to the in-plane deformation of the aromatic ring in the benzoate group (Klausberger et al., 1977). The peaks located at 1,003 and 1,604 cm-1 are related to the vibration of the phenyl ring of the benzoate group, and those at 1,418 and 1,550 cm-1 are related to the symmetric and asymmetric vibration of CO2− groups of the benzoate group (Lewandowski and Baranska, 1986). Moreover, as observed in their XPS spectra (Figures 3E,F), the 3d5/2 and 3d3/2 peaks of cerium are located within the ranges of 877–890 eV and 897–910 eV, respectively. The spin-orbit splitting of these two peaks, along with the satellite peak located at 917 eV, confirms the coexistence of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) ions in the structures of Ce14 and Ce24C (Wacker et al., 2022). Specifically, in the spectrum of Ce14, the peaks at 881.2 (v0), 886.2 (v), 899.7 (u0), and 904.6 (u) eV are ascribed to Ce(III) ions, while the peaks at 883.6 (v1), 887.8 (v2), 898.9 (v3), 902.1 (u1), 906.6 (u2), and 917.2 (u3) eV are ascribed to Ce(IV) ions (Wacker et al., 2022). In the spectrum of Ce24C, the peaks at 880.8 (v0), 885.7 (v), 899.4 (u0), and 904.2 (u) eV are ascribed to Ce(III) ions, while the peaks at 883.1 (v1), 887.4 (v2), 898.6 (v3), 901.7 (u1), 906.3 (u2), and 917.0 (u3) eV are ascribed to Ce(IV) ions (Wacker et al., 2022).
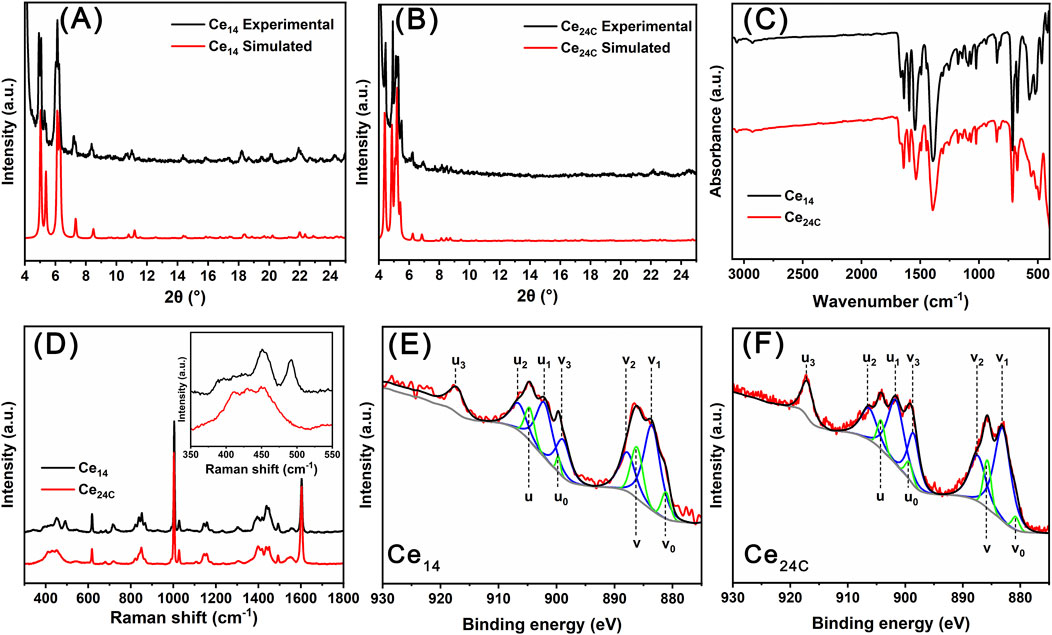
Figure 3. PXRD patterns (A, B), FTIR spectra (C), Raman spectra (D), and XPS data (E, F) for Ce14 and Ce24C crystals.
3.4 Self-assembly of Ce14 and Ce24C clusters
As mentioned above, both Ce14 and Ce24C clusters exhibit mixed valence, even though they were synthesized using Ce(NO3)3 and oxidized Ce(NO3)3, respectively. This suggests that cerium ions undergo redox reactions during the preparation process of these clusters. Therefore, we investigated the effects of redox reactions of cerium ions on the formation process of Ce14 and Ce24C using various techniques.
In the preparation process of Ce14, the combination of solutions of Ce(NO3)3 and sodium benzoate yielded a white precipitate, designated as Precipitate-1. In contrast, during the preparation of Ce24C, the combination of solutions of Ce(NO3)3, H2O2, and sodium benzoate yielded a reddish-brown precipitate, designated as Precipitate-2. In the XPS spectrum of Precipitate-1 (Figure 4A), all four peaks at 881.8 (v0), 885.5 (v), 900.0 (u0), and 904.2 (u) eV are ascribed to Ce(III) ions (Wacker et al., 2022). In contrast, in the XPS spectrum of Precipitate-2 (Figure 4B), the peaks at 881.8 (v0), 885.9 (v), 899.4 (u0), and 904.3 (u) eV are ascribed to Ce(III) ions, while the peaks at 883.4 (v1), 887.6 (v2), 898.8 (v3), 901.7 (u1), 906.4 (u2), and 917.1 (u3) eV are ascribed to Ce(IV) ions (Wacker et al., 2022). These XPS spectra (Figure 4A) demonstrate the presence of Ce(III) ions in Precipitate-1 and the coexistence of Ce(IV) ions along with a small amount of Ce(III) ions in Precipitate-2 (Figure 4B). One possible reason for this coexistence is the incomplete oxidation of Ce(III) ions by H2O2. Another reason could be that the Ce(IV) ions generated through the oxidation of Ce(III) ions by H2O2 are unstable and prone to partially transforming back to Ce(III) ions (Das et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2013). Both PXRD patterns and Raman spectra (Figures 4C,D) of Precipitate-1 and Precipitate-2 differ from those of Ce14 and Ce24C crystals. Additionally, the Raman spectra indicate the incorporation of benzoate groups into the precipitates (Lewandowski and Baranska, 1986). These findings suggest that Precipitate-1 and Precipitate-2 are intermediate cerium benzoate complexes formed during the synthesis of Ce14 and Ce24C, respectively.
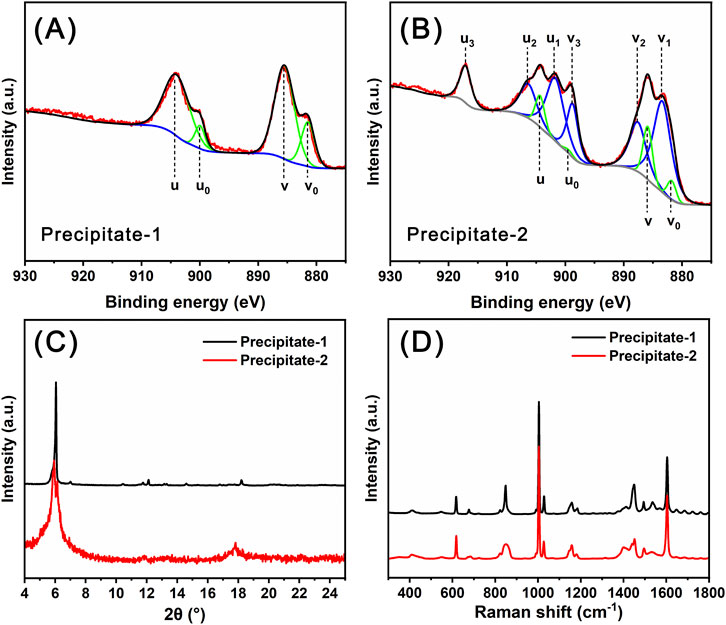
Figure 4. XPS data (A, B), PXRD patterns (C), and Raman spectra (D) for Precipitate-1 and Precipitate-2.
Precipitate-1 and Precipitate-2 were individually dissolved in DMF, yielding a colorless and reddish-brown solution, respectively. These two solutions were subsequently allowed to evaporate under ambient conditions. As shown in Figure 5A, the solution color of Precipitate-1 gradually changed from colorless to brownish-yellow over time and essentially no longer changed after the solution was stood for about 4 days. The corresponding time-resolved UV-Vis spectra (Figure 5B) exhibit a pronounced red shift in the spectra over time, particularly during the initial 4 days. These observations indicate the gradual oxidation of Ce(III) ions to Ce(IV) ions in the DMF solution of Precipitate-1 (Das et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2013). Considering the absence of strong oxidizing agents in this solution, the oxidation of Ce3+ ions likely occurs due to exposure to atmospheric oxygen. To eliminate the presence of oxygen, the solution was placed in a nitrogen-filled glove box. After 15 days, the solution remained colorless, and no crystals were observed. This outcome strongly suggests that the presence of molecular oxygen is crucial for the oxidation of Ce(III) ions.
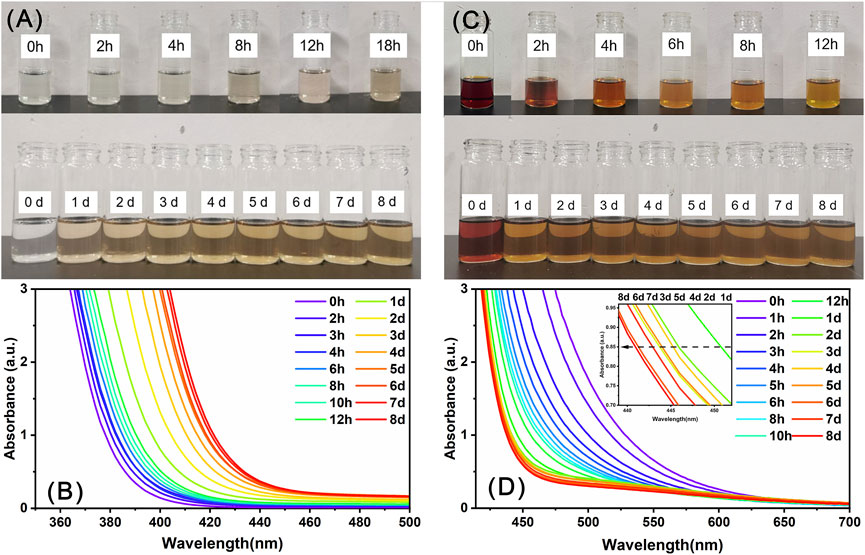
Figure 5. The evolution of the color (A, C) and UV-Vis spectra (B, D) of the DMF solutions of Precipitate-1 (A, B) and Precipitate-2 (C, D) over time.
In contrast, the solution color of Precipitate-2 lightened at a faster rate and nearly stabilized after about 1 day (Figure 5C). The corresponding time-resolved UV-Vis spectra (Figure 5D) exhibited a noticeable blue shift within 1 day, suggesting that partial Ce(IV) ions in the solution are rapidly reduced to Ce(III) ions (Das et al., 2007; Perez et al., 2008). After a day, a noticeable oscillation appears in the absorption spectrum around 445 nm (The insert in Figure 5D), indicating that the reduction of Ce(IV) ions and oxidation of Ce(III) ions occurred simultaneously in the solution and the Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratio eventually reached dynamic equilibrium (Perez et al., 2008). Notably, the final stable color of the DMF solution of Precipitate-1 was lighter than that of Precipitate-2, indicating a higher Ce(III/IV) ratio in the former (Perez et al., 2008). This is probably why the Ce(III/IV) ratio in Ce14 is higher than that in Ce24C. Furthermore, the faster stabilization of the color and UV-Vis spectra for the DMF solution of Precipitate-2 suggests that the reduction reaction of Ce(IV) ions in this solution occurred at a faster rate.
Generally, the Ce(III) state is favored under acidic conditions with poor donor ligands, while the Ce(IV) state is favored under basic conditions with strong donor ligands, particularly anionic oxygen donor ligands (Piro et al., 2014). Ce(NO3)3 is an acidic chemical, whereas sodium benzoate is weakly basic (Rived et al., 1998). Mixing methanol solutions of these two compounds causes Ce(III) ions to react with benzoate groups, forming Precipitate-1 in a relatively basic environment compared to the acidity of Ce(NO3)3 solid. DMF is considered a basic solvent due to its strong hydrogen-bond-accepting property (Kütt et al., 2018). Eventually, the dissolution of Precipitate-1 in DMF results in a weakly basic solution with a pH of 9.3. This indicates that Ce(III) ions in the DMF solution of Precipitate-1 are in a more basic condition compared to their initial state in Ce(NO3)3 solid. Furthermore, the benzoate group is a strong anionic oxygen donor ligand for cerium ions, as evidenced by our Raman spectra. Therefore, the oxidation of Ce(III) ions in the DMF solution of Precipitate-1 is likely driven by the basic solution environment and their complexation with benzoate groups. Notably, previously reported synthesis reactions of mixed-valent CeOCs using cerium (III) salts also employed neutral or alkaline solvents like methanol, acetonitrile, and pyridine, along with anionic oxygen donor ligands such as benzoate (Mitchell et al., 2021), acetylacetone (Blanes-Díaz et al., 2024), pivalate (Mathey et al., 2015), and isobutyrate (Malaestean et al., 2012; Canaj et al., 2017) groups. The exact reduction mechanism of Ce(IV) ions during CeOCs synthesis remains unclear. Blanes-Díaz et al. proposed that the reduction of Ce(SO4)2 during the formation of Ce10 may occur through the oxidation of acetylacetone (Blanes-Díaz et al., 2024). However, they did not provide conclusive evidence. Here, we propose the reduction of partial Ce4+ ions by DMF in this solution. DMF has been shown to act as a reducing agent in reduction reactions of certain transition metal ions, for example, transforming Ag+ ions to Ag0 and Cu2+ to Cu+ ions (Muzart, 2009).
Time-resolved SAXS data (Figures 6A,C) were collected to investigate the self-assembly process of Ce14 and Ce24C clusters in the DMF solutions. Based on these experimental data, Rg values were calculated using Guinier analysis (Feigin et al., 1987). As shown in Figure 6B, the Rg value for the 2 h solution of Precipitate-1 is 2.97 Å, which is smaller than that (4.94 Å) of the Ce14 core, as calculated using single crystal diffraction data and the CRYSOL method (Svergun et al., 1995). This observation indicates that Ce14 has not formed at 2 h. According to the solution color and UV-Vis spectra introduced above, the insufficient oxidation of Ce3+ ions and low concentration of Ce(IV) ions in the solution at this time may hinder the formation the Ce14. By day 4, the Rg value increases to ∼4.47 Å which is closer to that of the Ce14 core, indicating that Ce14 clusters had begun to form. As indicated by the above-mentioned solution color and UV-Vis spectra, the ratio of Ce(III)/Ce(IV) nearly reaches dynamic equilibrium at day 4, which may facilitate the formation of Ce14 clusters. This conclusion is further supported by the Rg value (∼4.58 Å) for the day 8 solution. In contrast, Rg values for different time-aged (from 2 h to 8 days) solutions of Precipitate-2 are almost the same and around 5.61 Å (Figure 6D), which is comparable with that (5.35 Å) of the Ce24C core calculated using the CRYSOL method. This finding suggests that the Ce24C cluster rapidly assembles within 2 h and keeps stable in the solution after its formation. As demonstrated by the XPS data, Ce(IV) ions coexist with a small amount of Ce(III) ions in Precipitate-2. This coexistence may facilitate the rapid formation of Ce24C. Although some Ce(IV) ions are continuously reduced over several days, this reduction process does not hinder the formation and stability of Ce24C.
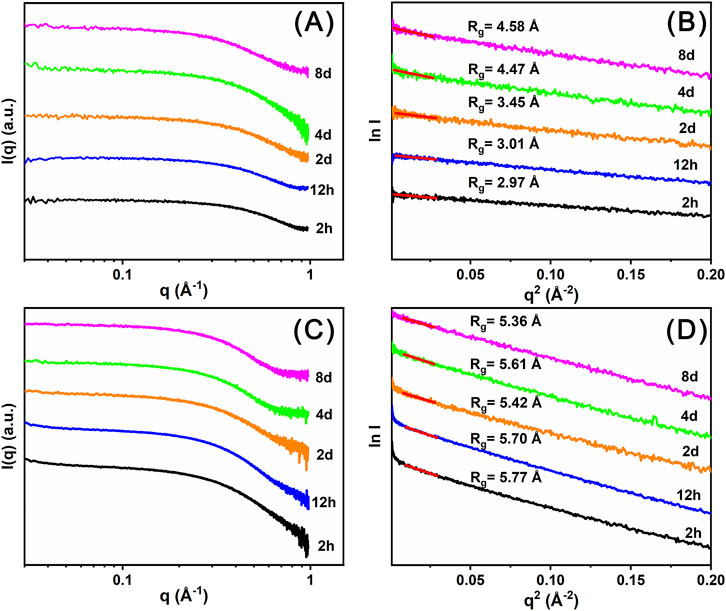
Figure 6. Time resolved SAXS plots (A, C) and corresponding Guinier analysis plots (B, D) of the DMF solutions of Precipitate-1 (A, B) and Precipitate-2 (C, D).
The formation of CeOC requires the hydrolysis of cerium ions to form a Cex (O/OH)y core (Hennig et al., 2013). CeOCs in this study and previously reported studies are composed either entirely of Ce(IV) ions or of a mixture of Ce(IV) ions and a small number of Ce(III) ions, indicating that the formation of CeOCs mainly relies on the hydrolysis reactions of Ce(IV) ions due to their stronger hydrolysis ability compared to Ce(III) ions. After the dissolution of Precipitate-1 in DMF, the solution only contains Ce(III) ions and the transformation of Ce(III) ions to Ce(IV) ions takes time. Thus the formation of Ce14 requires several days. In contrast, after the dissolution of Precipitate-2 in DMF, the solution contains a high concentration of Ce(IV) ions and a small amount of Ce(III) ions, which is why Ce24C can self-assemble rapidly. Additionally, this study may indicate multiple roles of DMF in the formation of the two cerium clusters, including acting as surface ligands to stabilize the clusters, providing a basic environment to facilitate the oxidation of Ce(III) ions, and reducing some Ce(IV) ions to maintain a dynamic equilibrium in the Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratio.
4 Conclusion
In summary, two sets of reactions were conducted using cerium nitrate and H2O2-oxidized cerium nitrate, resulting in the formation of two distinct mixed-valent cerium oxo clusters, Ce14 and Ce24C. Ce14 represents the first tetradecanuclear cerium oxo cluster with a unique structure. Ce24C is structurally similar to the two previously reported 24-nuclear cerium clusters. The structural difference among these three 24-nuclear clusters demonstrates that the protonation levels of O atoms and the Ce(III)/Ce(IV) ratio in the cores of cerium clusters are variable, and their surface ligands are replaceable. Furthermore, the formation process of Ce14 and Ce24C clusters was investigated using various techniques. The PXRD and Raman data indicated that the white and reddish-brown precipitations formed during their preparation process are intermediate cerium benzoate complexes. The XPS data proved that these two precipitations contain Ce(III) ions and a mixture of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) ions, respectively. Time-resolved UV-Vis spectra demonstrated the gradual oxidation of partial Ce(III) ions by oxygen in the DMF solution of the white precipitation. With the continued increase of Ce(IV) ions, Time-resolved SAXS data indicated that the Ce14 clusters begin to form in the solution at day 4. In contrast, the initial coexistence of Ce(IV) ions and a small amount of Ce(III) ions in the DMF solution of the reddish-brown precipitation facilitate the rapid formation of Ce24C clusters within 2 h.
Similar to nanoceria, both Ce14 and Ce24C exhibit a fluorite-type structure containing Ce4+ and Ce3+ ions, suggesting their potential catalytic activity. Ongoing investigations are underway to explore their catalytic capabilities.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The name of the repository and accession number(s) can be found in the article and Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
YG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing–review and editing. ZH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. CW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing–review and editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. JQ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Investigation, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22076152, 22276147, 22476158, 21806127).
Acknowledgments
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data were collected using a Bruker D8 Quest diffractometer in the State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow in Power Engineering.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2024.1507834/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmad, T., Iqbal, J., Bustam, M. A., Zulfiqar, M., Muhammad, N., Al Hajeri, B. M., et al. (2020). Phytosynthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles and investigation of their photocatalytic potential for degradation of phenol under visible light. J. Mol. Struct. 1217, 128292. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128292
Blanes-Díaz, A., Shohel, M., Rice, N. T., Piedmonte, I., McDonald, M. A., Jorabchi, K., et al. (2024). Synthesis and characterization of cerium-oxo clusters capped by acetylacetonate. Inorg. Chem. 63, 9406–9417. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c02141
Canaj, A. B., Siczek, M., Lis, T., Murrie, M., Brechin, E. K., and Milios, C. J. (2017). A [Ce21] keplerate. Dalton Trans. 46, 7677–7680. doi:10.1039/c7dt01883e
Chauvel, C. (2018). “Cerium,” in Encyclopedia of geochemistry: a comprehensive reference source on the chemistry of the earth. Editor W. M. White (Cham: Springer International Publishing).
Chen, Z., Zhou, X., Mo, M., Hu, X., Liu, J., and Chen, L. (2024). Systematic review of the osteogenic effect of rare earth nanomaterials and the underlying mechanisms. J. Nanobiotechnol. 22, 185. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02442-3
Colliard, I., Brown, J. C., Fast, D. B., Sockwell, A. K., Hixon, A. E., and Nyman, M. (2021). Snapshots of Ce70 toroid assembly from solids and solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 9612–9621. doi:10.1021/jacs.1c04095
Colliard, I., Brown, J. C., and Nyman, M. (2023). Metal–oxo cluster formation using ammonium and sulfate to differentiate MIV (Th, U, Ce) chemistries. Inorg. Chem. 62, 1891–1900. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c01309
Colliard, I., and Nyman, M. (2021). CeIV70 oxosulfate rings, frameworks, supramolecular assembly, and redox activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 7308–7315. doi:10.1002/anie.202016522
Das, M., Patil, S., Bhargava, N., Kang, J. F., Riedel, L. M., Seal, S., et al. (2007). Auto-catalytic ceria nanoparticles offer neuroprotection to adult rat spinal cord neurons. Biomaterials 28, 1918–1925. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.11.036
Djuričić, B., and Pickering, S. (1999). Nanostructured cerium oxide: preparation and properties of weakly-agglomerated powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 1925–1934. doi:10.1016/s0955-2219(99)00006-0
Fan, L., Wang, C., Chen, M., and Zhu, B. (2013). Recent development of ceria-based (nano)composite materials for low temperature ceramic fuel cells and electrolyte-free fuel cells. J. Power Sources 234, 154–174. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.01.138
Feigin, L. A., Svergun, D. I., and Taylor, G. W. (1987). “Determination of the integral parameters of particles,” in Structure analysis by small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering. Editors L. A. Feigin, D. I. Svergun, and G. W. Taylor (Boston, MA: Springer US).
Hennig, C., Ikeda-Ohno, A., Kraus, W., Weiss, S., Pattison, P., Emerich, H., et al. (2013). Crystal structure and solution species of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) formates: from mononuclear to hexanuclear complexes. Inorg. Chem. 52, 11734–11743. doi:10.1021/ic400999j
Kislina, I. S., Librovich, N. B., and Maiorov, V. D. (1994). Raman spectra of complexes of HCl with DMF with a strong quasisymmetric H-bond in solutions. Russ. Chem. Bull. 43, 1505–1507. doi:10.1007/bf00697136
Klausberger, G., Furić, K., and Colombo, L. (1977). Vibrational spectra and normal mode calculations of benzoic acid single crystals. J. Raman Spectrosc. 6, 277–281. doi:10.1002/jrs.1250060604
Kütt, A., Selberg, S., Kaljurand, I., Tshepelevitsh, S., Heering, A., Darnell, A., et al. (2018). pKa values in organic chemistry – making maximum use of the available data. Tetrahedron Lett. 59, 3738–3748. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2018.08.054
Lee, S. S., Song, W., Cho, M., Puppala, H. L., Phuc, N., Zhu, H., et al. (2013). Antioxidant properties of cerium oxide nanocrystals as a function of nanocrystal diameter and surface coating. ACS Nano 7, 9693–9703. doi:10.1021/nn4026806
Lewandowski, W., and Baranska, H. (1986). Vibrational and electronic spectroscopic study of lanthanides and effect of sodium on the aromatic system of benzoic-acid. J. Raman Spectrosc. 17, 17–22. doi:10.1002/jrs.1250170105
Long, D.-L., and Cronin, L. (2021). “Chapter Seven - advances in gigantic polyoxomolybdate chemistry,” in Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Editors C. D. Hubbard, and R. Van Eldik (Academic Press).
Long, D.-L., Tsunashima, R., and Cronin, L. (2010). Polyoxometalates: building blocks for functional nanoscale systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 1736–1758. doi:10.1002/anie.200902483
Malaestean, I. L., Ellern, A., Baca, S., and Kögerler, P. (2012). Cerium oxide nanoclusters: commensurate with concepts of polyoxometalate chemistry? Chem. Commun. 48, 1499–1501. doi:10.1039/c1cc14725k
Mathey, L., Paul, M., Copéret, C., Tsurugi, H., and Mashima, K. (2015). Cerium(IV) hexanuclear clusters from cerium(III) precursors: molecular models for oxidative growth of ceria nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 21, 13454–13461. doi:10.1002/chem.201501731
Miller, J. T., and Irish, D. E. (1967). Infrared and Raman spectra of the cerium(IV) ion – nitrate ion – water system. Can. J. Chem. 45, 147–155. doi:10.1139/v67-030
Mitchell, K. J., Abboud, K. A., and Christou, G. (2017). Atomically-precise colloidal nanoparticles of cerium dioxide. Nat. Commun. 8, 1445. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-01672-4
Mitchell, K. J., Goodsell, J. L., Russell-Webster, B., Twahir, U. T., Angerhofer, A., Abboud, K. A., et al. (2021). Expansion of the family of molecular nanoparticles of cerium dioxide and their catalytic scavenging of hydroxyl radicals. Inorg. Chem. 60, 1641–1653. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03133
Muzart, J. (2009). N,N-Dimethylformamide: much more than a solvent. Tetrahedron 65, 8313–8323. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2009.06.091
Nyman, M. (2016). “Polyoxometalates and other metal-oxo clusters in nature,” in Encyclopedia of geochemistry: a comprehensive reference source on the chemistry of the earth. Editor W. M. White (Cham: Springer International Publishing).
Perez, J. M., Asati, A., Nath, S., and Kaittanis, C. (2008). Synthesis of biocompatible dextran-coated nanoceria with pH-dependent antioxidant properties. Small 4, 552–556. doi:10.1002/smll.200700824
Piro, N. A., Robinson, J. R., Walsh, P. J., and Schelter, E. J. (2014). The electrochemical behavior of cerium(III/IV) complexes: thermodynamics, kinetics and applications in synthesis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 260, 21–36. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2013.08.034
Qiu, J., and Burns, P. C. (2013). Clusters of actinides with oxide, peroxide, or hydroxide bridges. Chem. Rev. 113, 1097–1120. doi:10.1021/cr300159x
Rived, F., Rosés, M., and Bosch, E. (1998). Dissociation constants of neutral and charged acids in methyl alcohol. The acid strength resolution. Anal. Chim. Acta 374, 309–324. doi:10.1016/s0003-2670(98)00418-8
Russell-Webster, B., Lopez-Nieto, J., Abboud, K. A., and Christou, G. (2021a). Phosphorus-based ligand effects on the structure and radical scavenging ability of molecular nanoparticles of CeO2. Dalton Trans. 50, 15524–15532. doi:10.1039/d1dt02667d
Russell-Webster, B., Lopez-Nieto, J., Abboud, K. A., and Christou, G. (2021b). Truly monodisperse molecular nanoparticles of cerium dioxide of 2.4 nm dimensions: a {Ce100O167} cluster. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 12591–12596. doi:10.1002/anie.202103110
Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C-Struct. Chem. 71, 3–8. doi:10.1107/s2053229614024218
Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). SHELXT - integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 71, 3–8. doi:10.1107/s2053273314026370
Svergun, D., Barberato, C., and Koch, M. H. J. (1995). CRYSOL– a program to evaluate X-ray solution scattering of biological macromolecules from atomic coordinates. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 28, 768–773. doi:10.1107/s0021889895007047
Wacker, J. N., Ditter, A. S., Cary, S. K., Murray, A. V., Bertke, J. A., Seidler, G. T., et al. (2022). Reactivity of a chloride decorated, mixed valent CeIII/IV38–oxo cluster. Inorg. Chem. 61, 193–205. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c02705
Wasson, M. C., Wang, X., Melix, P., Alayoglu, S., Wolek, A. T. Y., Colliard, I., et al. (2022). Interfacial unit-dependent catalytic activity for CO oxidation over cerium oxysulfate cluster assemblies. ACS Appl. Mat. Interfaces 14, 33515–33524. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c05937
Weber, W. H., Hass, K. C., and McBride, J. R. (1993). Raman study of CeO2: second-order scattering, lattice dynamics, and particle-size effects. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 48, 178–185. doi:10.1103/physrevb.48.178
Zhang, Y., de Azambuja, F., and Parac-Vogt, T. N. (2021). The forgotten chemistry of group(IV) metals: a survey on the synthesis, structure, and properties of discrete Zr(IV), Hf(IV), and Ti(IV) oxo clusters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 438, 213886. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213886
Keywords: cerium oxo cluster, mixed-valent, redox reaction, self-assembly, hydrolysis behaviors
Citation: Gao Y, Zhang Y, Han Z, Wang C, Zhang L and Qiu J (2024) Two mixed-valent cerium oxo clusters: synthesis, structure, and self-assembly. Front. Chem. 12:1507834. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1507834
Received: 08 October 2024; Accepted: 18 November 2024;
Published: 02 December 2024.
Edited by:
Truc Kim Nguyen, The Ohio State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Biswarup Chakraborty, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, IndiaThomas Auvray, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, Canada
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Zhang, Han, Wang, Zhang and Qiu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Qiu, cWl1amllMTIyOEB4anR1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Yuan Gao
Yuan Gao Yang Zhang
Yang Zhang Zhe Han
Zhe Han Chunhui Wang
Chunhui Wang Lei Zhang
Lei Zhang Jie Qiu
Jie Qiu