- Dairy Microbiology Division, ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal, Haryana, India
Yogurt is one of the most popular fermented milk products consumed worldwide. Fortification of yogurt with different food components, including fruit pulp, is a common practice to make it more palatable and healthier. In India, mango fruit is easily available. It is rich in nutrients and bioactive components. However, in-depth studies on mango fruit yogurt are scarce. Therefore, in this study, we prepared synbiotic mango fruit yogurt using response surface methodology (RSM) with three different independent factors (sugar 4%–6%; prebiotic inulin 1%–3%, and mango pulp 5%–15%) to determine the response antioxidant activity. The optimal conditions were as follows: sugar 6%, mango fruit pulp 6.562%, and prebiotic inulin 1%. There were no significant differences between the results of the experimental and predicted values of antioxidant activity by this model. The optimized product was analyzed for physicochemical, biofunctional, and technofunctional properties, including total polyphenol content, total flavonoid content, proteolytic activity, antioxidant activity, and ACE-inhibitory activity. The bioactive peptides derived from synbiotic mango fruit yogurt were also extracted (3 kDa, 5 kDa and 10 kDa) and determined for their biofunctional attributes. The antioxidant activity was recorded as 1,047.95 ± 2.20 mmol/L, 1,208.07 ± 2.92 mmol/L, and 1,293.09 ± 1.10 mmol/L Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity, while ACE-inhibitory activity was 45.68% ± 1.23%, 64.20% ± 1.24% and 82.72% ± 1.24% inhibition in 3 kDa, 5 kDa, and 10 kDa, respectively. The 10 kDa bioactive peptide exhibited superior results than the 3 kDa and 5 kDa peptides. The synbiotic mango fruit yogurt and its bioactive peptides showed significant biofunctional activities.
1 Introduction
Fermented milk product yogurt is a healthy and nutrient-rich dairy product made by yogurt culture Lactobacillus bulgaricus subsp. delbrueckii and Streptococcus thermophilus. Yogurt can be prepared as plain or fortified types, based on the consumer’s demand. Recently, consumers have become aware of healthy dairy products, including nutritional and biofunctional rich yogurt. The preparation of nutritional and biofunctional rich yogurt requires either incorporation of well-proven probiotic bacteria, prebiotic inulin, or other compatible food components such as fruit pulp, purees, or fruits. The FAO/WHO defines probiotics as “live microorganisms, which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host” (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization, 2006). Probiotic bacteria have many health benefits such as improvement in lactose digestion (EFSA Panel on Dietetic ProductsNutrition and Allergies, 2010), support digestive health system (Sanders et al., 2018), reduction of risk of high blood pressure (Beltrán-Barrientos et al., 2018), improvement on immune system via maintaining gut barrier function (George Kerry et al., 2018) and colonization (O’Flaherty et al., 2010), immunomodulation (Sanders et al., 2013; Bodke and Jogdand, 2022), improvements in antioxidant activity and fasting blood glucose (Ejtahed et al., 2012), improvement in insulin sensitivity (Tonucci et al., 2017), reduction of serum cholesterol (Munir et al., 2022), and many more. The application of probiotic yogurt bacteria along with other probiotic lactic acid bacteria also increases the functionality of the developed product (Minj et al., 2021). Therefore, yogurt prepared with probiotic bacteria is beneficial for overall human health.
The addition of probiotic bacteria along with prebiotic components such as inulin further improves the biofunctional properties of developed yogurt. A prebiotic is defined as “a substrate that is selectively utilized by host microorganisms conferring a health benefit” (Gibson et al., 2017). A daily dose of prebiotics must be at least 2.5 gm (Costa et al., 2019) for its benefits. Prebiotic inulin not only promotes the growth of probiotic bacteria but also plays an important role in the technological properties of yogurt. The addition of 1% inulin enhances the sensory, textural, and microtextural properties of yogurt and improves the viability of yogurt bacteria (El-Kholy et al., 2020). Low-fat yogurt containing 0.5% (w/v) inulin improves the sensory properties and probiotic counts to 7.8 log cfu/g (Ghaderi-Ghahfarokhi et al., 2021). Many characteristics of prebiotic inulin make it highly compatible with yogurt fortification, such as solubility, degree of polymerization, fat replacer, stability at processing conditions (pH, temperature), and easily accessible to the probiotic yogurt bacteria (Kheto et al., 2023).
In India, mango fruits are easily available and could be used for the development of functional fruit yogurt. Mango fruit is rich in functional ingredients such as polyphenols, flavonoids, carotenoid pigment, vitamin C, and dietary fibers, which synergize with probiotic and prebiotic inulin to enhance products’ technofunctional properties and promote health benefits. Polyphenols and dietary fibers could have a significant prebiotic effect via promoting the growth of probiotic bacteria and other beneficial gut bacteria (Minj et al., 2024; Alves-Santos et al., 2020). These components can be metabolized by the probiotic and gut bacteria and provide them with a readily available energy source to exert various physiological functions such as inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria, production of bioactive compounds, and immune modulatory components such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFA). These properties make probiotic bacteria flourish in the gut environment. Research studies have shown that the addition of mango juice in a fermented dairy-based beverage improves the viability of probiotic bacteria and improves the sensory properties (Ryan et al., 2020). In another study, supplementation with 1% Moringa oleifera leaf powder improves the overall technological properties, sensory attributes, and acceptability of mango-flavored yogurt (Saeed et al., 2021). Apart from technological properties, the potential health benefits of combining yogurt and fruits based on their prebiotic and probiotic properties are described by Fernandez and Marette (2017). Therefore, fortifying with mango fruit juice or pulp could have multiple benefits in the development of an innovative synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. A high-quality probiotic yogurt should have live probiotic bacteria, a smooth and firm texture, and good sensorial properties. Fortification with mango fruit juice or pulp will provide all the requirements in terms of product technological properties, prebiotic effects, health benefits, and overall acceptability.
Fortification with probiotic yogurt bacteria (Minj et al., 2020), prebiotic inulin (Minj and Vij, 2017), and mango fruit pulp in the development of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt will not only enhance its biofunctional and technological properties, but it will also be a great source of biologically active peptides. These bioactive peptides are generated by the proteolytic activity of yogurt bacteria during the fermentation process. These peptides are very specific protein fragments with a positive impact on human health. Many studies suggest that yogurt and derived bioactive peptides have various physiological roles, such as antioxidant and antimicrobial activities (Taha et al., 2017), ACE-inhibitory activity (Kim et al., 2021), antimutagenic activity (Heydari et al., 2023), antidiabetic and cytotoxic activity (Kayacan Çakmakoğlu et al., 2024), and immunomodulatory activity (Rivero-Pino et al., 2024). During yogurt production, the processing method and fermentation process are responsible for the release of small biologically active peptides from their native protein sequences. The size of biologically active peptides in milk and milk products can vary from 2 to 20 amino acids (Mohanty et al., 2016). The structural feature of a bioactive peptide is directly linked to its physiological function. For example, the peptide sequences VPYPQ, KVLPVPE (Rival et al., 2001), IPIQY, and GVRGPFPII (Hernández-Ledesma et al., 2005) from a yogurt sample have been reported for their radical scavenging activity whereas APFPEVFGK and FLPYPY (Chen et al., 2024) from peanut yogurt and HLPLP, IAK, and VYPFTGPIPN from milk-casein-derived peptide (Miguel et al., 2010) have been reported for ACE-inhibitory activity. The isolation and separation of these small molecular peptide sequences are possible with the application of ultrafiltration with molecular cutoff sizes of 3 kDa, 5 kDa, and 10 kDa. These sizes of bioactive peptide fractions have various biological activities, including antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities. Similarly sized peptide sequences from yogurt samples have been reported for their biological activities (Kayacan Çakmakoğlu et al., 2024; Karimi et al., 2021; Sabeena Farvin et al., 2010).
Fermented dairy product yogurt is made by yogurt bacteria, namely, L. bulgaricus subsp. delbrueckii and S. thermophilus. These lactic acid bacteria could produce proteolytic enzymes inside the cell (endopeptidases) as well as in the external medium (exopeptidases). These proteolytic enzymes break down the milk protein casein into smaller-size peptide sequences, which are responsible for specific biological activities such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anticancer, immune-modulatory, and ACE-inhibitory activities. Additionally, the use of well-proven probiotic yogurt bacteria, along with prebiotic inulin and mango fruit pulp, in the preparation of yogurt further increases its biofunctional properties. Mango fruit containing dietary fibers, polyphenols, and prebiotic inulin acts as a nutrient source for the probiotic yogurt bacteria and helps to maintain its viability and survivability in the gut for the long term. The addition of mango fruit pulp also increases its sensory properties. There is limited research available on the preparation of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt, along with its detailed biofunctional activities. A comprehensive study on the optimization of synbiotic mango yogurt preparation, chemical and technological analysis, isolation of bioactive peptides, and analysis of these bioactive peptides for biofunctional attributes could be an innovative idea for commercial synbiotic mango fruit yogurt production. Therefore, this study aims to optimize synbiotic mango fruit yogurt through response surface methodology, isolate the bioactive peptides, and analyze its biofunctional attributes, focusing on its antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Fresh, chilled, raw cow milk (∼3% fat) and skim milk (0.5% fat) were collected from the Experimental Dairy, ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal, India. Spray-dried skim milk powder was collected from the Modern Dairy, Karnal, India. Sugar (Grade A) was obtained from the Experimental Dairy, ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal, India. The frozen commercial mango fruit pulp (1 Kg pack) was procured in frozen and sterilized form from Delta Nutritive Mumbai. Mango pulp was thawed, mixed thoroughly, and aliquoted into individual packs of 90 g in sterile plastic bottles (Tarson) and stored at −20°C till use. Inulin as a prebiotic (Minj and Vij, 2017) was procured from Beneo Orafti, Mumbai, India. Polypropylene (PP) cups were procured from the Experimental Dairy, ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal, India. Previously studied probiotic yogurt culture NCDC 144 (Minj et al., 2020) was used for the yogurt preparation.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Preparation of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
2.2.1.1 Standardization
The fat percentage of cow milk was determined by the Gerber method (Kleyn et al., 2001). Standardization was done by adjusting the fat percentage of cow and skim milk using the Pearson square method (Tamime and Robinson, 1999). The solid-not-fat (SNF %) percentage of milk was calculated using the following formula and adjusted by adding skim milk.
CLR: calibrated lactometer reading using an ISI lactometer at 29°C; F: fat (%)
2.2.1.2 Synbiotic mango fruit yogurt preparation
Synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was prepared as described in Figure 1.
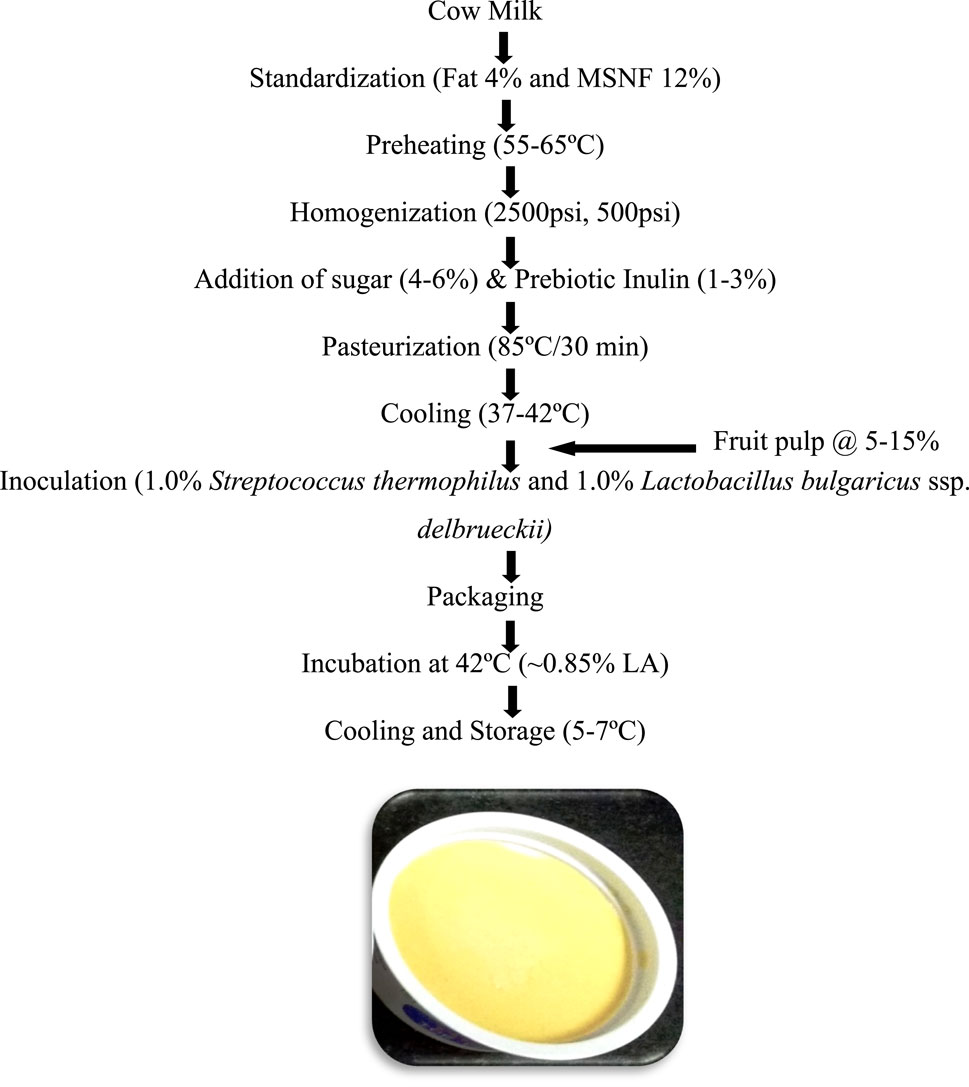
Figure 1. Flowchart for the preparation of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. Probiotic yogurt cultures Streptococcus thermophilus 144 and Lactobacillus bulgaricus ssp. delbrueckii 144 (1:1) were used for the preparation of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. MSNF, milk solids not fat; Fruit pulp, mango.
2.2.2 Optimization of independent factors for response antioxidant activity
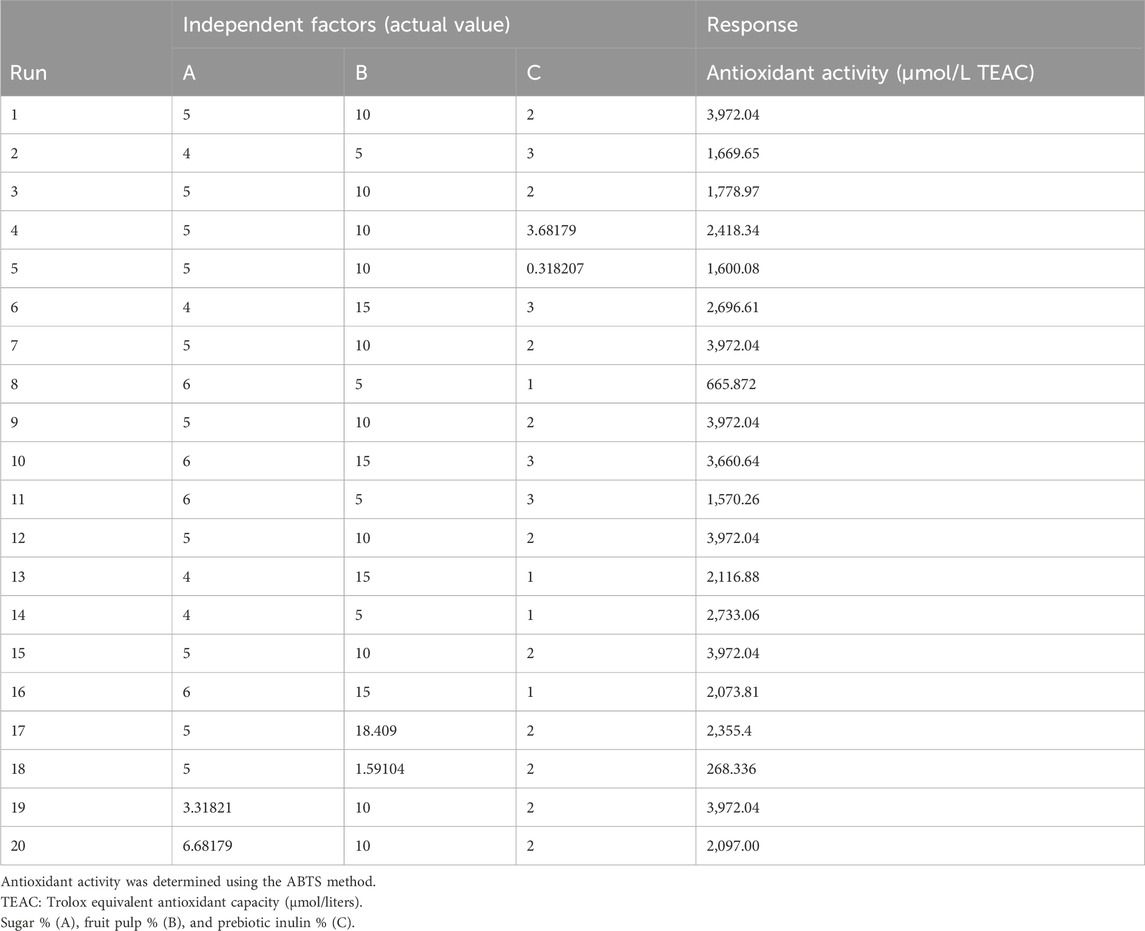
Response surface methodology (RSM) was used for the optimization of three independent factors (sugar 4%–6%, prebiotic inulin 1%–3%, and mango fruit pulp 5%–15%) for the response antioxidant activity in the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt preparation. These independent factors were chosen based on our preliminary tests, where we found that very low and very high sugar and mango fruit pulp concentrations were not accepted by the consumers. In the case of prebiotic inulin, our previous research (Minj and Vij, 2017) demonstrated that 1%–3% supplementation of prebiotic inulin promotes the growth of probiotic bacteria. The values of independent factors at actual levels for 20 different runs were generated by the Design-Expert software for the dependent response antioxidant activity (Table 1).
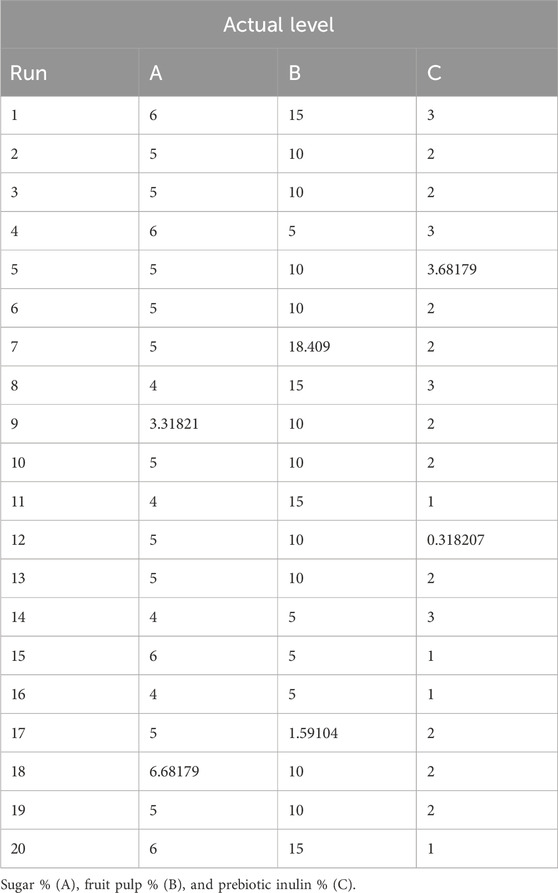
Table 1. Experimental values of sugar, mango fruit pulp, and prebiotic inulin given by central composite rotatable design (CCRD).
Synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was prepared as per the actual levels (Table 1) to determine the response antioxidant activity.
2.2.2.1 Determination of antioxidant activity by the ABTS method
This method assesses the total radical scavenging capacity based on the ability of a compound to scavenge the stable 2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical in 10 min (Re et al., 1999). The ABTS working solution was prepared and diluted with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) to adjust the absorbance at 734 nm to 0.7 ± 0.02. An aliquot of 10 µL of product supernatant, collected after centrifugation at 14,000×g for 30 min, was coated in a 96-well microplate, and to this, 100 µL ABTS in PBS solution was added and mixed for 10 s. The decrease in absorbance at 734 nm was recorded over a period of 10 min at 10 s intervals using a multi-plate reader. The results were expressed as Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) values. A standard curve was prepared using Trolox concentrations of 0–1,000 µM.
2.2.3 Preparation of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt extract and its bioactive peptides
Optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt extract was prepared by taking 10 g of sample in a 50 mL centrifuge tube and centrifuging it at 5,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C. The supernatant was collected in another clean Falcon tube for analysis of the biofunctional properties.
2.2.3.1 Extraction of bioactive peptides
The smaller size amino acid sequences of ∼2–20 amino acids are known for their biological activity.
Therefore, it is important to isolate these small molecular peptide sequences. Most of the small-size peptides were easily isolated and separated by ultrafiltration with molecular cutoff sizes of 3 kDa, 5 kDa, and 10 kDa. Therefore, the bioactive peptide fractions (10 kDa, 5 kDa, and 3 kDa) were extracted using a membrane cutoff Millipore filter. The filtrate was collected and analyzed for antioxidant activity by the ABTS method (described in Section 2.2.2.1) and angiotensin I (ACE)-inhibitory activity (described in Section 2.2.5.2). These methods have been previously adopted for the determination of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activity in isolated bioactive peptide samples (Singh et al., 2015).
2.2.4 Physicochemical analysis of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
The optimized product has been analyzed for pH, acidity (Buono et al., 1990), total solids (TS) (AOAC, 2002), fat content by the Mojonnier extraction method (Richardson, 2001), and total protein content (Lowry et al., 1951).
2.2.5 Biofunctional analysis of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
2.2.5.1 Determination of antioxidant activity
Previously, the antioxidant activity of yogurt samples has been successfully determined and reported by the ABTS method (Pereira et al., 2024; Yoon et al., 2019), the 2, 2 diphenyl-1-picryl hydrazyl (DPPH) method (Atik et al., 2024; Yoon et al., 2019; Senadeera et al., 2018; Gjorgievski et al., 2014) and the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) method (Yoon et al., 2019; Senadeera et al., 2018). Therefore, we have adopted similar methods to determine the antioxidant activity in synbiotic mango fruit yogurt samples.
2.2.5.1.1 Determination of antioxidant activity by the DPPH method
The antioxidant activity was determined by the DPPH method by following the method described by Brand-Williams et al. (1995) and Yoon et al. (2019) with some modifications. In brief, a stock solution was prepared by taking 27.7 mg of DPPH (Sigma–Aldrich, molecular weight-394.32) in a 50 mL amber reagent bottle and dissolving it in 25 mL methanol by stirring over a magnetic stirrer overnight at 4°C. The final volume was adjusted with methanol to 25 mL using a volumetric flask, and it was stored at −20°C. The working solution was prepared by dissolving 142 μL of stock in 9.858 mL of methanol. The working solution was prepared freshly prior to analysis and kept in an amber glass bottle. Next, 100 μL of the appropriate dilution of the product supernatant was loaded into a 96-well microplate and was mixed with 100 μL of freshly prepared DPPH working solution. The contents were mixed for 10 s and incubated in the dark for 120 min at 37°C after covering the microplate with aluminum foil. The absorbance of the solution was measured spectrophotometrically at 517 nm against methanol. For blank determination, 100 μL methanol was taken instead of the sample, and absorbance was measured immediately against methanol. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
The results were calculated and expressed as
2.2.5.1.2 Determination of antioxidant activity by the FRAP method
The ferric-reducing antioxidant potential assay was conducted following the method described by Benzie and Strain (1996) with some modifications. In brief, a stock solution of acetate buffer (300 mM,
2.2.5.2 Angiotensin I (ACE) inhibitory activity
ACE inhibitory activity was determined following the method described by Cushman and Cheung (1971). In brief, approximately 25°g of the product was centrifuged at 4,000°g for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant was collected, and the
where
A = the absorbance in the presence of ACE and the ACE-inhibitory component (sample),
B = the absorbance without the ACE-inhibitory component (control) and
C = the absorbance without ACE (blank).
Inhibition was expressed as the concentration of component that inhibits 50% of ACE activity (IC50), and 1 unit of ACE-inhibitory activity was expressed as the potency showing 50% ACE inhibition under these conditions.
2.2.5.3 Determination of proteolytic activity
The proteolytic activity of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was determined by measuring liberated amino acids and peptides using the o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) method described by Church et al. (1983) with some modifications. In brief, 2.5 mL of sample supernatant was added to 5 mL of 0.75% trichloroacetic acid and allowed to stand for 10 min, and the mixture was filtered using Whatman filter paper 42 (Quantitative Filter Paper, Ashless, Whatman 1,442-055, United States). Then 150 µL of permeate was added to 3 mL of OPA reagent, which was kept on ice. After 2 min of incubation at room temperature (20oC), the absorbance of the solution was measured spectrophotometrically at 340 nm. The standard curve was prepared using serine with a concentration range of 25–250 μg/mL. The proteolytic activity was expressed as serine equivalents.
2.2.5.4 Total polyphenol content
The total phenolic content of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was analyzed using the Folin–Ciocalteu method (Kähkönen et al., 1999). In brief, 400 μL of appropriately diluted sample/gallic acid standard was taken in a test tube. Next, 2000 μL of diluted Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was added and mixed on a vortex mixer (Mohammed et al., 2019). After 3 min, 1,600 μL of sodium carbonate solution was added and incubated under dark at room temperature for 30 min. For the blank preparation, 400 μL of distilled water was taken instead of the sample. The absorbance of the sample was measured against a blank at 765 nm by a double-beam spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan). The standard curve was prepared with 400 μL of a 10–100 μg/mL concentration of the gallic acid solution.
2.2.5.5 Total flavonoid content
Total flavonoid contents were determined by following the method described by Zhishen et al. (1999). In brief, a 0.5 mL volume of 2% AlCl3 ethanol solution was added to 0.5 mL of sample solution. After 1 h at room temperature, the absorbance was measured at 420 nm using a double-beam spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan). A yellow color indicated the presence of flavonoids. Distilled water was used as a blank and a control. Extracted samples were evaluated at a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. The results were reported as quercetin equivalents per mL of extract. The standard curve was prepared with 0.5 mL of a 1–6 mg/100 mL concentration of quercetin.
2.2.6 Technological analysis of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
2.2.6.1 Texture profile analysis
The texture profile of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was determined following the method described by Narender Raju and Pal (2009) using a texture analyzer TAXT21 (Stable Micro Systems, Godalming, Surrey, United Kingdom) fitted with a 5 kg load cell. For texture analysis, samples were prepared in 100 mL sterilized sample containers, and the set samples were kept in an immersion chamber maintained at 25°C before the analysis. The samples were subjected to mono-axial compression of 20 mm distance on the texture analyzer by the crosshead speed of 2 mm/s.
The test conditions maintained were as follows:
Measured force in compression
Probe
Load cell = 25 kg
Pre-test speed = 2 mm/s
Test speed = 1 mm/s
Post-test speed = 2 mm/s
Compression = 50% of distance
Single TPA (texture profile analysis) = single-time penetration
After completion of the analysis, a graph was obtained with the force experienced by the probe on the Y-axis and time on the X-axis. The firmness of the yogurt sample was estimated as the height of the positive peak force up to the rupture point.
2.2.6.2 Flow behavior
The flow behavior property of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was analyzed following the method described by Meena et al. (2016). In brief, a rheometer (Modular compact rheometer, MCR 52) attached with a cone and plate geometry (CP 75) with 0.149 mm gap setting at 20°C constant temperature using a variable shear rate (0–100 s-1) was used to measure the flow behavior.
2.2.6.3 Water holding capacity (WHC)
The water-holding capacity was determined by following the method described by Remeuf et al. (2003). In brief, 20 g of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was taken in 50 mL centrifuge tubes and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 min. The weight of separated clear whey was measured, and whey syneresis was expressed as grams of whey per 20 g of sample. The water holding capacity (WHC) % was expressed as
where NY = Weight of native synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
WE = Weight of expelled whey
2.2.7 Microbiological quality analysis
Microbiological quality analysis for total count and coliform count was performed according to the method described by Arnott et al. (1974) for the milk quality as well as for the optimized product quality.
2.2.8 Statistical analysis
The response surface methodology (RSM) was adopted for the experimental design and analysis. Multiple regression analysis was done to fit the model. Statistical analyses of the data and 2D-contour and 3D plot designs were computed using Design-Expert software (V 23.1.4; Stat-Ease Corporation, Minneapolis, MN, United States). Other experimental data were analyzed in GraphPad Prism version 10.4.0 (527) software.
3 Results and discussion
Previously studied prebiotic inulin (Minj and Vij, 2017) and probiotic yogurt culture NCDC 144 (Minj et al., 2020) were used for the preparation of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. Raw materials such as cow milk and mango fruit pulp were analyzed before the preparation of the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. Cow milk was analyzed for fat and SNF content and microbiological quality. As per the requirements, the fat content was adjusted to 3.0% either by cream separation or by adding extra cream. Adjustment of fat content is important because it has a significant impact on the quality of yogurt, such as viscosity, taste, appearance, texture, flavor, and aroma. Milk fat breakdown is the main source for the accumulation of free fatty acids, which could be a precursor of aroma compounds in the yogurt. Milk fat also helps to reduce whey separation by enhancing the water-holding capacity and increasing the adhesiveness and hardness (Su et al., 2022). Similarly, SNF content is important in yogurt because it affects the viscosity, firmness, cohesiveness, consistency, fermentation, and coagulation time. SNF content increases the cohesiveness and firmness of yogurt (Walstra et al., 2006); positively affects viscoelasticity, texture, and viscosity of the yogurt (Yu et al., 2016); and increases the duration of fermentation time (Kristo et al., 2003). In this study, the SNF content was adjusted to 11%–12% by the addition of skimmed milk powder (SMP). The whole standardization procedure was followed by the Pearson square method. Results of standardized fat and SNF contents and microbiological quality of cow milk are presented in Table 2.
Similarly, mango fruit pulp was also analyzed for the pH, acidity, and microbiological quality. The pH and acidity of mango fruit pulp were fruit pulp were 4.35 ± 0.01 and 1.25% ± 0.01%, respectively (Table 3). The pH value of fresh mango pulp was reported slightly lower was reported slightly lower, at 4.21 ± 0.0, by Laophongphit et al. (2024) and 4.02 ± 0.15 by Kaushik et al. (2014), whereas the acidity of mango pulp was reported as 0.48% ± 0.05% TA (lactic acid) and 0.49 ± 0.09 g citric acid/100 g pulp, respectively, which was quite lower than our results.
3.1 Optimization of process conditions for the preparation of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
There is an increasing trend of dairy product formulation, mainly yogurt, to enhance its functional, nutritional, textural, and technological properties. Fortification with any form of fruit (raw fruit, pulp, dried form) not only enhances its palatability and appearance but also improves the overall quality of the product. Because fruits are rich in minerals, polyphenols, flavonoids, fibers, and carotenoids, they significantly affect the overall quality of fortified products. Many health benefits of mango fruit and fruit pulp intake have been reported, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties (Lauricella et al., 2017). Prebiotic inulin, on the other hand, also improves the physicochemical properties of yogurt and promotes the growth of probiotic bacteria (Minj and Vij, 2017; Minj et al., 2020). A high-quality yogurt should have a high consumer acceptance score in terms of flavor and taste. Therefore, the addition of sugar is also important to increase the overall acceptability of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. Overall, the present study was conducted to optimize the fruit pulp, prebiotic inulin, and sugar content to develop a high-quality biofunctional rich yogurt by focusing on its antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities.
The 20 different runs of the combined effect of sugar (A), fruit pulp (B), and prebiotic inulin (C) on the antioxidant activity of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt are shown in Table 4. The results showed that the lowest antioxidant activity was 268.336 μmol/L TEAC, and the second lowest antioxidant activity was 665.872 μmol/L TEAC. These results indicated that the low concentration of mango fruit pulp fortification significantly affected the antioxidant activity of the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. According to the reports, the fortification of mango increases the antioxidant activity of probiotic yogurt compared to the control yogurt (Mohamed et al., 2023). Overall, the antioxidant activity of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt ranged from 268.336 µmolL/ TEACH to 3,972.04 μmol/L TEAC.
3.1.1 Diagnostic check of the fitted model
The experimental data of the central composite rotatable design (CCRD) were fitted and calculated with a second-order quadratic function and multiple linear regressions. The model adequacy was checked using the coefficient of correlation, lack of fit test, and F-ratio (Table 5). The correlation coefficient was 0.89. The lack of fit test was found to be insignificant, which indicates that the model is adequately accurate to predict the antioxidant activity for any combination of independent factors in the ranges studied. This suggested that the obtained model can be used to determine the relative effect of the independent factors, determine the optimum parameter combinations for the highest and desirable response antioxidant activity, and predict the result.
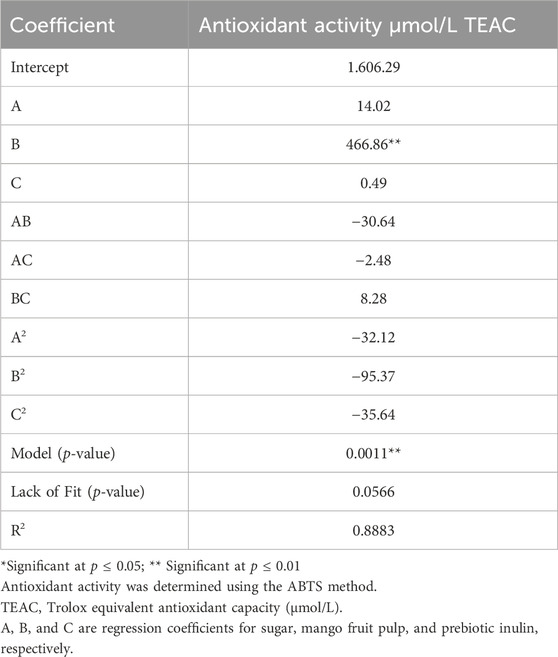
Table 5. Regression coefficients of independent coded factors and ANOVA data for the response (antioxidant activity in µmol/L TEAC) in synbiotic mango fruit yogurt.
3.1.2 RSM model for antioxidant activity
The quadratic model fitted to antioxidant activity was significant (p ≤ 0.05). Lack of fit was insignificant relative to pure error.
where Y represents the response antioxidant activity, and test variables are A (sugar), B (mango fruit pulp), and C (prebiotic inulin).
All three variables individually affected the antioxidant activity. The antioxidant activity was minimal at a low concentration of mango pulp and increased with increased concentration except for the very high concentration. Interestingly, sugar concentration and prebiotic inulin concentration have less impact on the antioxidant activity of the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt.
3.1.3 Optimization of the level of independent factors
In order to optimize the level of independent factors, the response antioxidant activity was assigned equal importance on the basis of their effect on biofunctional properties as well as the overall acceptability of the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. The criterion used and predicted and actual responses are given in Table 6. With the model, the optimized value for sugar concentration was 6%, the value for mango fruit pulp was 6.562%, and the value for prebiotic inulin was 1%. The synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was developed according to the optimized process conditions. The actual experiment value for antioxidant activity was found to be very close to the predicted value (Table 6). The t-test analysis revealed that there were no significant (
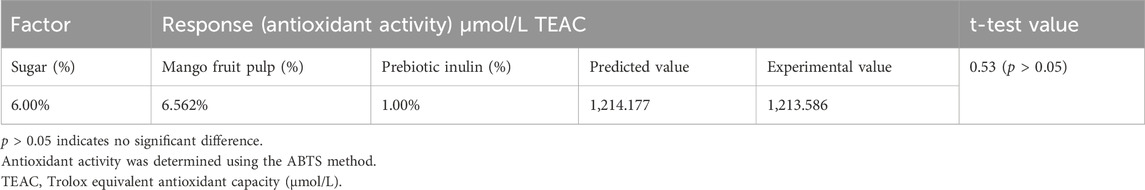
Table 6. Predicted and experimental response values at the optimum formulation condition and t-test value.
The interaction between sugar, mango fruit pulp, and prebiotic inulin is depicted in Figure 2. As the concentration of mango fruit pulp increased, the antioxidant activity also increased (Figure 2A; 3D-plot and 2D-contour). The interaction between prebiotic inulin and sugar concentration slightly increased the antioxidant activity of the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt (Figure 2B; 3D-plot and 2D-contour). The third interactive graph 3D-plot and 2D-contour) between the prebiotic inulin and mango fruit pulp showed that the antioxidant activity was not affected by the combination of these two factors (Figure 2C).
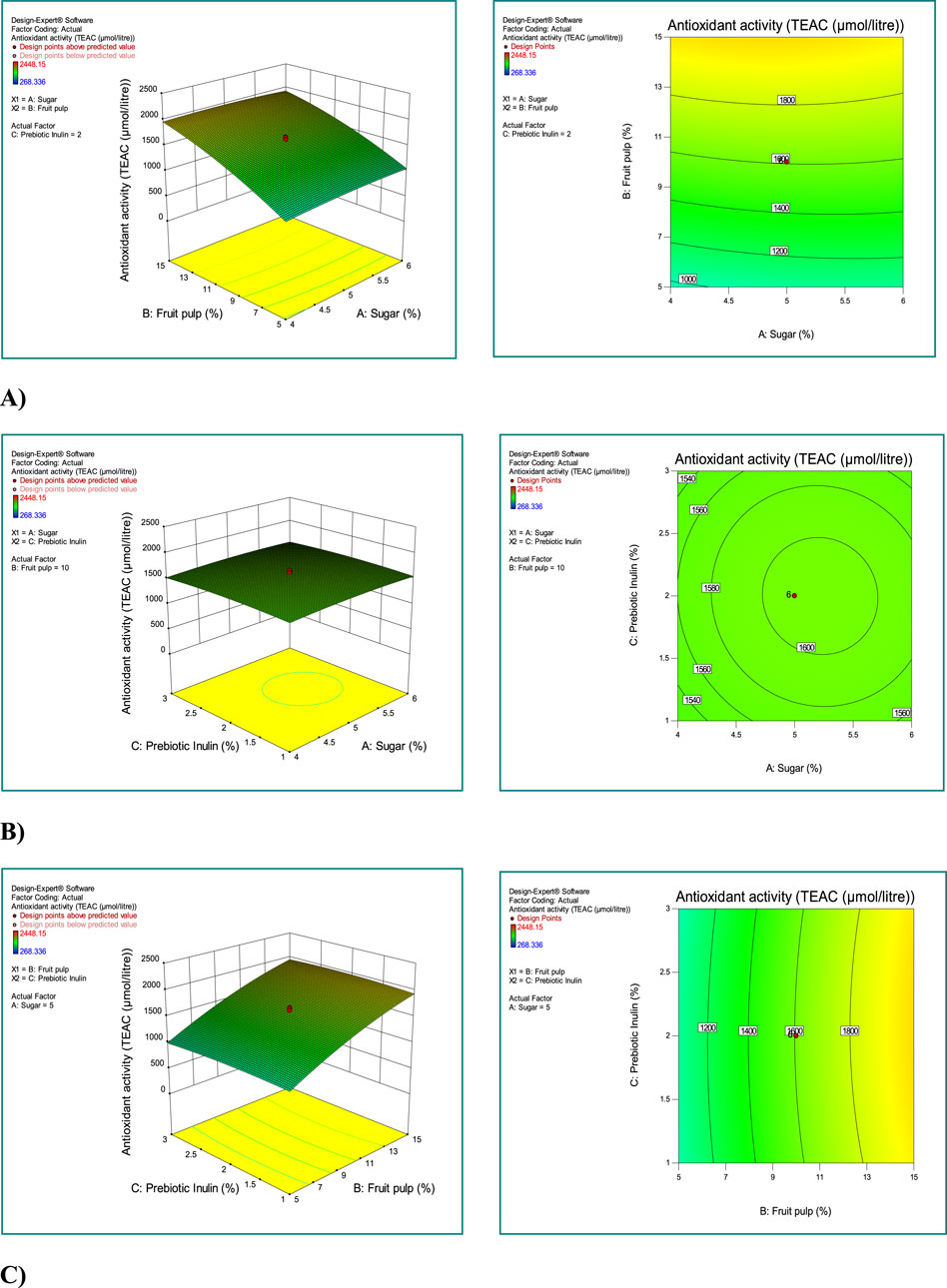
Figure 2. Investigating the simultaneous effect of independent variables (sugar, fruit pulp, and prebiotic inulin) on the response antioxidant activity. (A) Combined effect of fruit pulp and sugar concentration on antioxidant activity; (B) combined effect of prebiotic inulin and sugar concentration on antioxidant activity; (C) combined effect of prebiotic inulin and mango fruit pulp concentration on antioxidant activity. Response surface plots for antioxidant activity; 3D plots (left side) and 2D contour plots (right side).
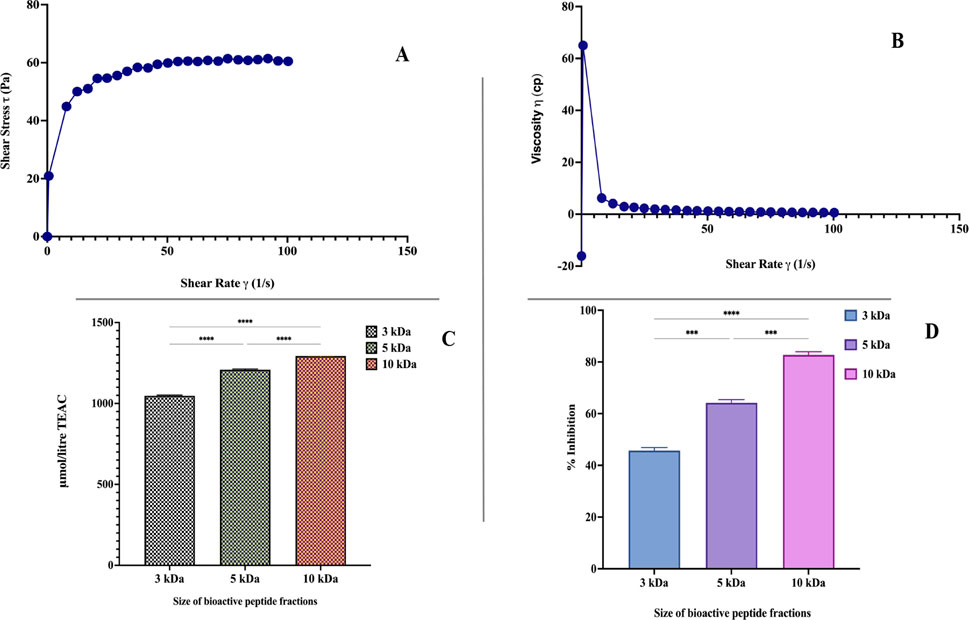
Figure 3. (A) Shear stress as a function of the flow behavior of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. (B) Relationship between apparent viscosity and shear rate of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. (C) Antioxidant activity of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt derived-bioactive peptide fractions (3 kDa, 5 kDa, and 10 kDa). (D) ACE-inhibitory activity of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt-derived bioactive peptide fractions (3 kDa, 5 kDa, and 10 kDa). * indicates results differ significantly (
3.2 Physicochemical and biofunctional analysis of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
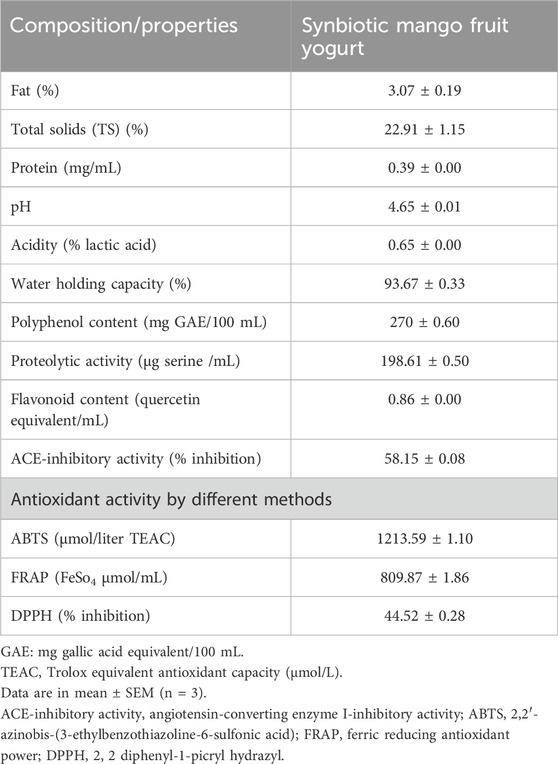
Synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was prepared under optimized conditions as per the values given in Table 6, and the physicochemical and biofunctional properties were analyzed. The physicochemical parameters such as fat, TS, protein content, pH, acidity, WHC, polyphenol content, proteolytic activity, and flavonoid content were determined and are shown in Table 7. The fat content of 3.07% ± 0.19%, TS content of 22.91% ± 1.15%, and protein content of 0.39 ± 0.00 mg/mL were found in the optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. The
The biofunctional properties of plain yogurt could be enhanced by fortification with fruits, prebiotics, probiotics, and proteolytic bacteria. Fortification with fruit pulp not only enhances the sensory properties but also enhances potential antioxidant compounds such as total phenolic compounds, flavonoid content, and prebiotic components, which further increases the viability of probiotic bacteria. In this study, the polyphenol and flavonoid contents in synbiotic mango fruit yogurt were noted as 270 ± 0.60 mg GAE/100 mL and 0.86 ± 0.00 quercetin equivalent/mL, respectively. Fortification with different fruit pulps has different impacts on the functionality of yogurt. Pereira et al. (2024) used a similar Folin–Ciocalteau method to evaluate the total phenols of different types of exotic fruit pulp-fortified yogurt and reported that yogurt containing araçá, blueberry, and grumixama had a significant increase of total phenolics after the fermentation process, but it decreased at the end of the storage at 28 days. Pădureţ et al. (2024) reported that yogurts supplemented with black chokeberry fruit, juice, and pomace have different levels of total phenolic content with the highest content in yogurt with chokeberry pomace at 3% (392.14 ± 2.06 µg GAE/g) followed by the lowest in yogurt sample with 1% chokeberry juice (104.45 ± 2.63 µg GAE/g). In another study, Zahid et al. (2023) reported that mango peel powder improves the prebiotic functions and health-promoting effect of fortified yogurt. The presence of phenolic compounds improved the production of SCFA and the microbial population associated with yogurt fortified with mango peel powder and lactic acid bacteria. Therefore, fortification with different fruit components could be a promising method of developing biofunctional fruit yogurt to increase its commercial value and effect on gut health.
The incorporation of probiotic bacteria and prebiotics, such as inulin, improves the proteolytic activity of yogurt. Pinto et al. (2020) reported that the degree of hydrolysis of yogurt B (yogurt starter + probiotic L. acidophilus + Bifidobacteria spp.) was almost double that of yogurt A (conventional yogurt added only yogurt starter). The degree of hydrolysis of yogurt C (yogurt starter + probiotic L. acidophilus + Bifidobacteria spp. + 1% inulin (w/w)) appeared to be more pronounced than yogurt B. The higher concentration of prebiotic inulin in yogurt D (yogurt starter + probiotic L. acidophilus + Bifidobacteria spp. + 3% inulin (w/w)) greatly modified the proteolytic activity. Therefore, fortifying yogurt with probiotics, prebiotics, and mango fruits containing dietary fibers could increase its proteolytic activity. In this study, the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt showed 198.61 ± 0.50 μg serine/mL proteolytic activity.
The ACE-inhibitory activity of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was estimated as 58.15% ± 0.08% inhibition. Wang et al. (2024) reported that fortification of yogurt with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and casein significantly affects the ACE-inhibitory activity of yogurt. Yogurt group 883 + M11-CS fortified with starter culture YO-MIX 883 (0.5 × 107), Lb. plantarum M11 (1 × 107), and sodium caseinate (2%) had a significantly higher ACE inhibition rate of 83.15% ± 0.52% than yogurt group 883-CS, which was fortified with YO-MIX 883 (1.5 × 107) and sodium caseinate (2%), which had a 78.39% ± 0.56% ACE inhibition rate. Yogurt group 883 + M11, which was fortified with YO-MIX 883 (0.5 × 107) and Lb. plantarum M11 (1 × 107), showed a 77.65% ± 0.51% ACE inhibition rate. Yogurt group 883 fortified with YO-MIX 883 (1.5 × 107) exhibited the lowest ACE inhibition rate, at 74.73% ± 0.89%. The ACE-inhibitory activity of the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was comparatively less than this report because different components affect the ACE inhibition rate of yogurt. Supplementation of probiotic culture along with yogurt culture also improves the ACE-inhibitory activity of yogurt. Kim et al. (2021) reported that yogurt supplemented with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NK181 had the highest ACE-inhibitory activity (51.3% ± 10.3%) of other supplemented yogurt samples. The ACE-inhibitory activity was comparatively higher in this study in synbiotic mango fruit yogurt. Yi et al. (2024) reported that fermented buffalo milk yogurt with commercial starter and probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum B exhibited 84.51% ACE-inhibitory activity that showed an antihypertensive effect in the pregnancy-induced hypertensive rat. An in vivo study on the antihypertensive effect of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt is needed in the future.
The antioxidant activities of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt were 1,213.59 ± 1.10 μmol/L TEAC, 809.87 ± 1.86 FeSo4 μmol/mL, and 44.52% ± 0.28% inhibition by the ABTS, FRAP, and DPPH methods, respectively. Pădureţ et al. (2024) reported that yogurts supplemented with different concentrations of black chokeberry fruit, juice, and pomace had different DPPH radical scavenging activities. Yogurt supplemented with 3% chokeberry fruit had higher inhibition of DPPH radical formation, followed by 2% chokeberry fruit supplementation (73.57% ± 0.11%) and 1% chokeberry fruit supplementation (57.84% ± 0.05%); yogurt with 3% chokeberry fruit pomace had up to 64.8% ± 0.11% inhibition. According to this study, adding fruit and fruit components increased the antioxidant activity of yogurt, which supports our results.
According to Erkaya-Kotan (2020), the percent DPPH scavenging is a criterion for in vitro antioxidant activity. The antioxidant activity of probiotic yogurt incorporated with orange fiber increased during 14 days of storage, while it decreased until the 21st day of storage. Yogurt incorporated with orange fiber had significantly higher antioxidant activity (23.56%–32.94%) than the control sample (20.36%–24.51%) during all days of storage. In another study, the antioxidant activity of a water-soluble peptide extract (WSPE) of fresh and cold stored yogurt samples was determined by ABTS and DPPH assays. The WSPE of fresh and cold stored yogurt samples made with yogurt culture alone had the highest (13.7%) antioxidant activity by ABTS assay compared to the WSPE of Lb. acidophilus 20,552 ATCC + yogurt culture (13.2%) and the WSPE of yogurt culture along with Lb. helveticus CH5 (10.5%). Similarly, the DPPH scavenging activity of the same samples was 56.88%–71.71%, 70.14%–80.62%, and 79.45%–81.62%, respectively (Taha et al., 2017). Although the antioxidant activity of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt extract by DPPH (44.52% ± 0.28%) was less than this research study, it was higher than the antioxidant activity of fermented milk (39.43%) made by the symbiotic cultures and Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus and S. thermophilus (Gjorgievski et al., 2014). Yogurt culture L. delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus could ferment milk protein into amino acid sequences that affect radical scavenging activity (Kudoh et al., 2001). Kim et al. (2021) also reported that yogurt supplemented with L. delbrueckii KU200171 had the highest antioxidant activities by ABTS (39.3% ± 1.0%) and DPPH assays (86.5% ± 0.3%) compared to other probiotic culture-supplemented yogurt samples. Fruit supplementation improves the antioxidant activity of yogurt, and supplementation with prebiotic and lactic acid bacteria also improves oxidative stress in adults with metabolic syndrome (Zolghadrpour et al., 2024).
Many fermented dairy products have been studied for their potential antioxidant activity due to the presence of antioxidant peptide sequences. Recently, the antioxidant activity of probiotic fermented milk cheese ultrafiltered fractions and water-soluble extracts have been reported for their potential antioxidant activity. Peptides AMKPWIQPK and EMPFPK exhibited antioxidant properties due to their amino acid sequences, such as methionine and proline residues (Yang, 2024). The presence of lactic acid bacteria in fermented milk is important in the production of antioxidant peptides. The lactic acid bacteria isolated from Iranian dairy products have the potential for antioxidant activity. The isolated L. delbrueckii PTCC 1900 had the highest (59.43%) DPPH free radical scavenging activity, and L. paracasei ssp. paracasei PTCC 1945 had the highest (85.93%) ABTS free radical scavenging activity at 48 h (Shirkhan et al., 2023).
3.3 Technological analysis of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt
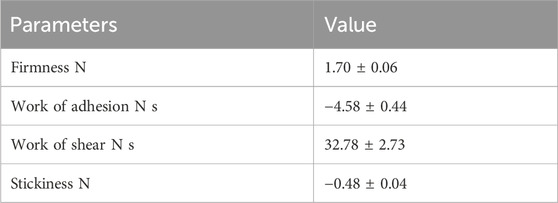
Texture profile analysis of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was done on the basis of a back extrusion test, which was suited for the gels because it is not affected by the free whey on the surface of the samples (Pereira et al., 2003). For this, different parameters, such as firmness, work of shear, work of adhesion, and stickiness, were taken into consideration. The firmness value is the peak force obtained during penetration of the probe in the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt (Table 8). The values for firmness, work of adhesion, work of shear, and stickiness were 1.70 ± 0.06 N, −4.58 ± 0.44 N s, 32.78 ± 2.73 N s, and −0.48 ± 0.04 N, respectively (Table 8). The flow behavior and viscosity of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt are presented in Figures 3A, B, respectively.
The improvements in textural profile and viscosity could be due to the addition of prebiotic inulin and mango fruit pulp containing dietary fibers. Brennan and Tudorica (2008) reported that levels above 2% w/w of inulin are needed to exert significant improvements in apparent viscosity. In this study, the optimized condition for prebiotic inulin was 1%. This concentration of inulin was sufficient to maintain the viscosity and textural properties of the product because mango fruit pulp also contains some amounts of dietary fiber. According to Buriti et al. (2008), inulin is responsible for the apparent viscosity and firmness in the symbiotic cheese. The addition of passion fruit peel powder and vegetal oil emulsion did not influence the fermentation time, but the firmness of the yogurt was significantly affected (Perina et al., 2015).
The value of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt increases with its beneficial health aspects, technological properties, and consumer acceptance. Janoušek Honesová et al. (2024) reported that yogurt made with the addition of skimmed milk powder and fruit jams improved the acceptance of fruit yogurt compared to natural yogurt. Supplementations with different fruits have different acceptance rates. Pădureţ et al. (2024) reported that yogurt incorporated with 3% and 2% black chokeberry had the highest acceptance score, while a yogurt sample with 3% black chokeberry pomace had the lowest acceptance score. Saeed et al. (2021) studied the physicochemical properties of mango-flavored yogurt supplemented with moringa oleifera leaf powder and reported that supplementation with 1% moringa oleifera leaf powder had the highest sensory attribute scores and overall acceptability. Recently, Cao et al. (2024) reported that yogurt incorporated with red beetroot powder (3%) showed the highest viable counts, followed by the second highest viable counts in mango fruit powder (3%)-fortified yogurt after 15 days of storage at refrigerated storage. Yogurt fortified with mango fruit powder had the highest consumer acceptability scores for texture, flavor, and overall acceptability, while other yogurts had lower acceptability scores. The initial study on the development of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt also scored the highest sensory attributes and overall acceptance.
3.4 Determination of the biofunctional attributes of optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt-derived bioactive peptides
Bioactive peptides were extracted by ultrafiltration membranes (Vivaspin) of 10 kDa, 5 kDa, and 3 kDa molecular weight cut off using high-speed centrifugation and were tested for antioxidant (by ABTS method) and ACE-inhibitory activity. The degree of proteolysis is highly correlated with these biofunctional activities. In our previous study, yogurt cultures S. thermophilus ST 144 and L. bulgaricus ssp. delbrueckii LB 144 were evaluated for proteolytic activity with 113.47 ± 0.91 μg serine mL−1 and 201.11 ± 0.74 μg serine mL−1, respectively (Minj et al., 2020). The proteolytic nature of yogurt bacteria could be a useful indicator for the production of small bioactive peptides in the developed synbiotic mango fruit yogurt.
3.4.1 Antioxidant activity of bioactive peptide fractions
The antioxidant activity of the bioactive peptide fraction was evaluated using the ABTS method. Results showed that the antioxidant activity was significantly (
Generally, milk protein sources have reported contradictory results on antioxidant activity. Some researchers reported that the 3 kDa peptide fraction had higher antioxidant activity than the 10 kDa or >10 kDa fractions (Shirkhan et al., 2023; Qian et al., 2011). The low molecular weight peptide fractions have significantly higher ABTS and DPPH free radical scavenging activity (Shirkhan et al., 2023). The milk protein hydrolyzed peptide fraction of <1 kDa demonstrated the highest ABTS radical scavenging activity (Abdel-Hamid et al., 2017; De Gobba et al., 2014). The suggested mechanism of action of low molecular weight peptide could quickly react with fat radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation (Ren et al., 2008).
The ABTS radical scavenging activity and antioxidant activity mainly depend on the peptide sequence, size, molecular mass, amino acid composition, concentration, conformation, and nature of peptides (Karami and Akbari-adergani, 2019; Zou et al., 2016). The antioxidant activity of yogurt peptides can also be affected by the denaturation process and secondary structures (Yuan et al., 2018). The presence of aromatic and hydrophobic amino acid residues in the peptides is a determining factor in the radical scavenging activity. It has also been reported that certain amino acids, such as His (imidazole group), Phe (aromatic amino acid), Pro (hydroxyl radical scavenger), Trp (indolic group), and Tyr (phenolic group), are correlated with the antioxidant activity (Ajibola et al., 2011). These amino acids could be involved in the reduction of oxidative stress by increasing the level of antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Furthermore, they can also play an important role in minimizing the inflammatory cytokines in adipocytes and eliminating reactive oxygen species.
In another study, antioxidant peptides from goat milk protein fractions exhibited ABTS radical scavenging activity where tyrosine seemed to be a fundamental peptide; however, phenylalanine seemed to play a key role in inhibiting the formation of secondary lipid oxidation products (De Gobba et al., 2014). The presence of hydrophobic amino acids like leucine and valine increases the existence of antioxidant peptides at the interface between the lipid and water phases and increases access to free radicals in the lipid phase (Sarmadi and Ismail, 2010). Overall, it can be stated that different size peptide fractions have different abilities to scavenge free radicals. Therefore, further analysis of the antioxidant peptide profile from the 10 kDa fractions is needed.
3.4.2 ACE-inhibitory activity of bioactive peptide fractions
The bioactive peptide fractions of 3 kDa, 5 kDa, and 10 kDa were evaluated for the ACE-inhibitory activity. Figure 3D illustrates the ACE-inhibitory activity of 10 kDa, 5 kDa, and 3 kDa fractions. The 10 kDa bioactive peptide fraction exhibited significantly higher (82.72% ± 1.24%) ACE-inhibitory activity than the 5 kDa (64.20% ± 1.24%) and 3 kDa (45.68 ± 1.23) fractions. The ACE-inhibitory activity is mainly affected by the presence of specific peptide sequences and probiotic yogurt bacteria, which could be responsible for the production of these bioactive peptide sequences. Korhonen (2009) reviewed the many ACE-inhibitory peptides and their sequences from the milk and milk products. Some of the best-known peptide sequences, Val-Pro-Pro (VPP) and IIe-Pro-Pro (IPP), have been reported for their ACE-inhibitory activity (Nakamura et al., 1995; Sipola et al., 2002). Similar peptide sequences might be present in the 10 kDa peptide fraction and be responsible for the significantly higher ACE-inhibitory activity.
According to Donkor et al. (2007), yogurt made with yogurt culture alone or in combination with probiotic bacteria has significant ACE-inhibitory activity, with higher activity in the probiotic yogurt. The origin of ACE-inhibitory peptides, VPP and IPP, was from αs2-casein, mainly κ- and β-casein. The proportion of αs2-casein varies between ruminants and is considered to comprise up to 10% of casein in bovine milk. The αs2-casein appears to be readily susceptible to proteolysis and breakdown into small biologically active peptides.
Many bioactive peptides with potential ACE-inhibitory activity have been isolated from yogurt and milk proteins (Gobbetti et al., 2000; Fitzgerald and Murray, 2006). Most of the documented ACE-inhibitory peptides in fermented dairy products are associated with a potential antihypertensive effect. The ACE-inhibitory peptides have a proline residue at the carboxyl-terminal end, are known to be resistant to degradation by digestive enzymes, directly reach the small intestine, and enter the blood circulation in the form of small sequence peptides (Pan et al., 2005). ACE is an important part of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and is known for its peripheral blood pressure regulation. This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of angiotensin I into angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor leading to elevated blood pressure. Due to this important role of ACE, the inhibition of this enzyme has been used to treat hypertension (Coppey et al., 2006). Therefore, ACE-inhibitory peptides could play an important role in the reduction of blood pressure through ACE-inhibitory activity.
Fermented milk products, including yogurt, are considered to have a positive effect on high blood pressure. Many studies have shown that fermented milk products made by probiotic bacteria have ACE-inhibitory activity (Chen et al., 2024; Dhakal et al., 2024; Guzmán-Rodríguez et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2021; Ayyash et al., 2018; Ong and Shah, 2008; Donkor et al., 2007). Most of the ACE-inhibitory bioactive peptides are produced by L. delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus during milk fermentation from αs1-and β-casein (Yu et al., 2021). Fermentation with L. delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus produces ACE-inhibitory peptides (Kim et al., 2021; Sultan et al., 2018; Kliche et al., 2017; Qian et al., 2011). The addition of probiotic culture L. plantarum K25 along with yogurt culture increases the ACE-inhibitory activity throughout the 21 days of storage from 22.3% to 49.3% (Min et al., 2020). However, the concentration of ACE-inhibitory peptides could vary depending on the different strains of L. delbrueckii used in the yogurt preparation. Based on these studies, probiotic yogurt bacteria NCDC 144 could be considered a potent ACE-inhibitory peptide producer.
Yogurt fortified with prebiotics also affects the production of ACE-inhibitory peptides. Kariyawasam et al. (2021) reported that ACE-inhibitory activity was higher in the synbiotic yogurt than in non-synbiotic yogurt. Similarly, Habibi Najafi et al. (2019) also reported that the presence of prebiotics increased the ACE-inhibitory activity. Yogurt containing prebiotic inulin (Shakerian et al., 2015; Ramchandran and Shah, 2009) and polysaccharides had higher ACE-inhibitory activity (Ramchandran and Shah, 2010). Our finding agrees with published results that found that supplementation with prebiotics increased ACE-inhibitory activity.
The size of the bioactive peptide fraction also has an impact on the ACE-inhibitory activity. According to Schlothauer et al. (2002), the 10 kDa and 50 kDa peptide concentrates had high ACE inhibition, which supports this study. Other studies showed that 3 kDa or <3 kDa fraction had a higher percentage of inhibition (Wu et al., 2019; Rubak et al., 2020); Rubak et al. (2022) reported that ACE inhibition in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis BD17 fermented skimmed goat milk exhibited 57.31%, 24.57%, and 60.33% in <3 kDa, >3 kDa, and supernatant samples, respectively. According to Parmar et al. (2018), goat milk fermented with different lactic acid bacteria has different %ACE inhibition in the peptide fraction. L. casei (NK9) fermented goat milk 10 kDa permeates exhibited the presence of AFPEHK ACE-inhibitory peptides. Shukla et al. (2023) reported that fermented camel milk showed higher ACE-inhibitory peptides in 3 kDa permeate fraction. Recently, Devecioglu et al. (2024) reported that the ACE-inhibitory activity of peptide fractions is significantly affected by ultrafiltration. Unfractionated samples had lower ACE-inhibitory activity than fractionated samples. Therefore, ultrafiltration or additional purification increases the ACE-inhibitory activity. The limitation of this study is the identification of ACE-inhibitory peptide sequence in the 10 kDa sample through reverse-phase liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (RPLC-MS) as well as in vivo testing of 10 kDa bioactive peptides to confirm health benefits at the molecular level. This future research direction will provide strength to this study.
4 Conclusion
In the present study, the combined effects of three different independent factors (sugar, prebiotic inulin, and mango pulp) were evaluated for their effect on response antioxidant activity. Optimization was successfully conducted by utilizing RSM, and sugar 6%, mango fruit pulp 6.562%, and prebiotic inulin 1% were found to be optimum for the synbiotic mango fruit yogurt preparation. The optimized synbiotic mango fruit yogurt was found to be rich in biofunctional and technofunctional properties, mainly total polyphenol content, total flavonoid content, proteolytic activity, antioxidant, and ACE-inhibitory activity, and best from a microbiological quality point of view. The peptides released from yogurt during the fermentation process exhibited specific bioactivity, with the 10 kDa peptide fraction showing significantly higher antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activity than the 3 kDa and 5 kDa fractions.
Recently, with increasing interest in health-promoting food, consumers and functional food industries are looking for products that could help prevent lifestyle-related diseases like hypertension, cancer, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. This research study offers potential for technological and biofunctional advances in synbiotic mango fruit yogurt production. The product could be an excellent candidate to meet the needs of the innovative yogurt development market. However, further research is needed to identify the specific peptide sequences with a metabolomic approach. It is expected that this study will be useful in the application of commercial production of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt with enhanced biofunctional properties. In addition, specific bioactive peptide sequences will be useful in the pharmaceutical industry after a thorough investigation of the bioavailability of these peptides in clinical trials.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JM: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, software, visualization, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. SV: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship (F1-17.1/2012-13/RGNF-2012-13-ST-CHH-22748/(SA-III/Website), University Grants Commission.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel-Hamid, M., Otte, J., De Gobba, C., Osman, A., and Hamad, E. (2017). Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity and antioxidant capacity of bioactive peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysis of buffalo milk proteins. Int. Dairy J. 66, 91–98. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2016.11.006
Ajibola, C. F., Fashakin, J. B., Fagbemi, T. N., and Aluko, R. E. (2011). Effect of peptide size on antioxidant properties of african yam bean seed (sphenostylis stenocarpa) protein hydrolysate fractions. IJMS 12, 6685–6702. doi:10.3390/ijms12106685
Alves-Santos, A. M., Sugizaki, C. S. A., Lima, G. C., and Naves, M. M. V. (2020). Prebiotic effect of dietary polyphenols: a systematic review. J. Funct. Foods 74, 104169. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2020.104169
AOAC (2002). Official methods of analysis of the AOAC. 15th ed. Arlington, VA, USA: Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
Arnott, D. R., Duitschaever, C. L., and Bullock, D. H. (1974). Microbiological evaluation of yogurt produced commercially in Ontario. J. Milk Food Technol. 37, 11–13. doi:10.4315/0022-2747-37.1.11
Atik, A., Atik, İ., Akarca, G., and Denizkara, A. J. (2024). Incorporating Ganoderma lucidum extract and powder with probiotic cultures (Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis) enhanced the functional, textural, and sensory qualities of yogurt. J. Food Sci. Technol. doi:10.1007/s13197-024-06068-z
Ayyash, M., Al-Nuaimi, A. K., Al-Mahadin, S., and Liu, S.-Q. (2018). In vitro investigation of anticancer and ACE-inhibiting activity, α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition, and antioxidant activity of camel milk fermented with camel milk probiotic: a comparative study with fermented bovine milk. Food Chem. 239, 588–597. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.06.149
Beltrán-Barrientos, L. M., González-Córdova, A. F., Hernández-Mendoza, A., Torres-Inguanzo, E. H., Astiazarán-García, H., Esparza-Romero, J., et al. (2018). Randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial of the blood pressure–lowering effect of fermented milk with Lactococcus lactis: a pilot study. J. Dairy Sci. 101, 2819–2825. doi:10.3168/jds.2017-13189
Benzie, I. F. F., and Strain, J. J. (1996). The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 239, 70–76. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0292
Bodke, H., and Jogdand, S. (2022). Role of probiotics in human health. Cureus 14, e31313. doi:10.7759/cureus.31313
Brand-Williams, W., Cuvelier, M. E., and Berset, C. (1995). Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 28, 25–30. doi:10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5
Brennan, C. S., and Tudorica, C. M. (2008). Carbohydrate-based fat replacers in the modification of the rheological, textural and sensory quality of yoghurt: comparative study of the utilisation of barley beta-glucan, guar gum and inulin. Int J Food Sci Tech 43, 824–833. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2007.01522.x
Buono, M. A., Setser, C., Erickson, L. E., and Fung, D. Y. C. (1990). Soymilk yogurt: sensory evaluation and chemical measurement. J. Food Sci. 55, 528–531. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1990.tb06802.x
Buriti, F. C. A., Cardarelli, H. R., and Saad, S. M. I. (2008). Textura instrumental e avaliação sensorial de queijo fresco cremoso simbiótico: implicações da adição de Lactobacillus paracasei e inulina. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Farm. 44, 75–84. doi:10.1590/S1516-93322008000100009
Cao, Y., Fang, Y., and Hekmat, S. (2024). Impact of fruit powders incorporation on probiotic viability and sensory properties of yogurt. NFS. doi:10.1108/NFS-06-2024-0195
Chen, B., Wang, X., Zhang, J., and Wang, L. (2024). Peptidomics-based study of antihypertensive activity: discovery of novel ACE inhibiting peptides from peanut yogurt. Food Funct. 15, 6705–6716. doi:10.1039/D4FO00299G
Church, F. C., Swaisgood, H. E., Porter, D. H., and Catignani, G. L. (1983). Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 66, 1219–1227. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(83)81926-2
Coppey, L. J., Davidson, E. P., Rinehart, T. W., Gellett, J. S., Oltman, C. L., Lund, D. D., et al. (2006). ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist attenuates diabetic neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 55, 341–348. doi:10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-0885
Costa, M. F., Pimentel, T. C., Guimaraes, J. T., Balthazar, C. F., Rocha, R. S., Cavalcanti, R. N., et al. (2019). Impact of prebiotics on the rheological characteristics and volatile compounds of Greek yogurt. LWT 105, 371–376. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2019.02.007
Cushman, D. W., and Cheung, H. S. (1971). Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 20, 1637–1648. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9
De Gobba, C., Espejo-Carpio, F. J., Skibsted, L. H., and Otte, J. (2014). Antioxidant peptides from goat milk protein fractions hydrolysed by two commercial proteases. Int. Dairy J. 39, 28–40. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2014.03.015
Devecioglu, D., Sarıakcalı, B., Orhan, B., Daskaya-Dikmen, C., Ozcelik, B., and Karbancioglu-Guler, F. (2024). Releasing angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory (ACE-I) peptides by Yamadazyma spp. in non-fat milk. Int J Food Sci Tech 59, 5598–5605. doi:10.1111/ijfs.17282
Dhakal, D., Younas, T., Bhusal, R. P., Devkota, L., Li, L., Zhang, B., et al. (2024). The effect of probiotic strains on the proteolytic activity and peptide profiles of lupin oat-based yoghurt. Food Hydrocoll. 149, 109570. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109570
Donkor, O. N., Henriksson, A., Singh, T. K., Vasiljevic, T., and Shah, N. P. (2007). ACE-inhibitory activity of probiotic yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 17, 1321–1331. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2007.02.009
EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) (2010). Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to live yoghurt cultures and improved lactose digestion (ID 1143, 2976) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. 8, EFS2 8. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1763
Ejtahed, H. S., Mohtadi-Nia, J., Homayouni-Rad, A., Niafar, M., Asghari-Jafarabadi, M., and Mofid, V. (2012). Probiotic yogurt improves antioxidant status in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutrition 28, 539–543. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2011.08.013
El-Kholy, W. M., Aamer, R. A., and Ali, A. N. A. (2020). Utilization of inulin extracted from chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) roots to improve the properties of low-fat synbiotic yoghurt. Ann. Agric. Sci. 65, 59–67. doi:10.1016/j.aoas.2020.02.002
Erkaya-Kotan, T. (2020). In vitro angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory and antioxidant activity of probiotic yogurt incorporated with orange fibre during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 57, 2343–2353. doi:10.1007/s13197-020-04272-1
Fernandez, M. A., and Marette, A. (2017). Potential health benefits of combining yogurt and fruits based on their probiotic and prebiotic properties. Adv. Nutr. 8 (1), 155S–164S. doi:10.3945/an.115.011114
Fitzgerald, R. J., and Murray, B. A. (2006). Bioactive peptides and lactic fermentations. Int J Dairy Tech 59, 118–125. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0307.2006.00250.x
Food and Agriculture Organization of th e United Nations and World Health Organization (2006). in Probiotics in food: health and nutritional properties and guidelines for evaluation. Food and agriculture organization of the united Nations (Rome: World Health Organization).
George Kerry, R., Patra, J. K., Gouda, S., Park, Y., Shin, H.-S., and Das, G. (2018). Benefaction of probiotics for human health: a review. J. Food Drug Analysis 26, 927–939. doi:10.1016/j.jfda.2018.01.002
Ghaderi-Ghahfarokhi, M., Yousefvand, A., Ahmadi Gavlighi, H., and Zarei, M. (2021). The effect of hydrolysed tragacanth gum and inulin on the probiotic viability and quality characteristics of low-fat yoghurt. Int J Dairy Tech 74, 161–169. doi:10.1111/1471-0307.12742
Gibson, G. R., Hutkins, R., Sanders, M. E., Prescott, S. L., Reimer, R. A., Salminen, S. J., et al. (2017). Expert consensus document: the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14, 491–502. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75
Gjorgievski, N., Tomovska, J., Dimitrovska, G., Makarijoski, B., and Shariati, M. A. (2014). Determination of the antioxidant activity in yogurt. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 8, 88–92.
Gobbetti, M., Ferranti, P., Smacchi, E., Goffredi, F., and Addeo, F. (2000). Production of angiotensin-I-Converting-Enzyme-Inhibitory peptides in fermented milks started by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus SS1 and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris FT4. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 3898–3904. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.9.3898-3904.2000
Guzmán-Rodríguez, F., Gómez-Ruiz, L., and Cruz-Guerrero, A. (2024). Antithrombotic and ACE -inhibitory activity of milk fermented by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG and Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus. Int J Food Sci Tech, ijfs 59, 9417–9424. doi:10.1111/ijfs.17589
Habibi Najafi, M. B., Fatemizadeh, S. S., and Tavakoli, M. (2019). Release of proteolysis products with ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant activities in probiotic yogurt containing different levels of fat and prebiotics. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 25, 367–377. doi:10.1007/s10989-018-9679-8
Hernández-Ledesma, B., Miralles, B., Amigo, L., Ramos, M., and Recio, I. (2005). Identification of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides in fermented milk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 85, 1041–1048. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2063
Heydari, S., Hosseini, S. E., Mortazavian, A. M., and Taheri, S. (2023). Extraction of bioactive peptides produced in probiotic yoghurt and determination of their biological activities. Int. Dairy J. 139, 105544. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2022.105544
Janoušek Honesová, S., Samková, E., Dadáková, E., Hasoňová, L., Jarošová, M., Reindl, K., et al. (2024). Effect of skimmed milk powder and fruit jams addition on the physicochemical characteristics of yogurt. Fermentation 10, 462. doi:10.3390/fermentation10090462
Kähkönen, M. P., Hopia, A. I., Vuorela, H. J., Rauha, J.-P., Pihlaja, K., Kujala, T. S., et al. (1999). Antioxidant activity of plant extracts containing phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 47, 3954–3962. doi:10.1021/jf990146l
Karami, Z., and Akbari-adergani, B. (2019). Bioactive food derived peptides: a review on correlation between structure of bioactive peptides and their functional properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 56, 535–547. doi:10.1007/s13197-018-3549-4
Karimi, N., Pourahmad, R., Taheri, S., and Eyvazzadeh, O. (2021). Isolation and purification of bioactive peptides from yogurt whey: application as a natural preservative in a model food system. J. Food Process. Preserv. 45. doi:10.1111/jfpp.16086
Kariyawasam, K. M. G. M. M., Lee, N.-K., and Paik, H.-D. (2021). Synbiotic yoghurt supplemented with novel probiotic Lactobacillus brevis KU200019 and fructooligosaccharides. Food Biosci. 39, 100835. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100835
Kaushik, N., Kaur, B. P., Rao, P. S., and Mishra, H. N. (2014). Effect of high pressure processing on color, biochemical and microbiological characteristics of mango pulp (Mangifera indica cv. Amrapali). Innovative Food Sci. and Emerg. Technol. 22, 40–50. doi:10.1016/j.ifset.2013.12.011
Kayacan Çakmakoğlu, S., Dere, S., Beki̇roglu, H., Bozkurt, F., Karasu, S., Dertli̇, E., et al. (2024). Production of bioactive peptides during yogurt fermentation, their extraction and functional characterization. Food Biosci. 61, 104805. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104805
Kheto, A., Bist, Y., Awana, A., Kaur, S., Kumar, Y., and Sehrawat, R. (2023). Utilization of inulin as a functional ingredient in food: processing, physicochemical characteristics, food applications, and future research directions. Food Chem. Adv. 3, 100443. doi:10.1016/j.focha.2023.100443
Kim, E.-D., Lee, H.-S., Kim, K.-T., and Paik, H.-D. (2021). Antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of yogurt supplemented with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NK181 and Lactobacillus delbrueckii KU200171 and sensory evaluation. Foods 10, 2324. doi:10.3390/foods10102324
Kleyn, D. H., Lynch, J. M., Barbano, D. M., Bloom, M. J., Mitchell, M. W., Cooper, L. S., et al. (2001). Determination of fat in raw and processed milks by the gerber method: collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 84, 1499–1508. doi:10.1093/jaoac/84.5.1499
Kliche, T., Li, B., Bockelmann, W., Habermann, D., Klempt, M., De Vrese, M., et al. (2017). Screening for proteolytically active lactic acid bacteria and bioactivity of peptide hydrolysates obtained with selected strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 101, 7621–7633. doi:10.1007/s00253-017-8369-3
Korhonen, H. (2009). Milk-derived bioactive peptides: from science to applications. J. Funct. Foods 1, 177–187. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2009.01.007
Kristo, E., Biliaderis, C. G., and Tzanetakis, N. (2003). Modelling of the acidification process and rheological properties of milk fermented with a yogurt starter culture using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 83, 437–446. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00126-2
Kudoh, Y., Matsuda, S., Igoshi, K., and Oki, T. (2001). Antioxidative peptide from milk fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus IFO13953. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 48, 44–50. doi:10.3136/nskkk.48.44
Laophongphit, A., Wichiansri, S., Siripornadulsil, S., and Siripornadulsil, W. (2024). Enhancing the nutritional value and functional properties of mango pulp via lactic acid bacteria fermentation. LWT 197, 115878. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2024.115878
Lauricella, M., Emanuele, S., Calvaruso, G., Giuliano, M., and D’Anneo, A. (2017). Multifaceted health benefits of mangifera indica L. (Mango): the inestimable value of orchards recently planted in Sicilian rural areas. Nutrients 9, 525. doi:10.3390/nu9050525
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(19)52451-6
Meena, G. S., Singh, A. K., Borad, S., and Panjagari, N. R. (2016). Effect of concentration, homogenization and stabilizing salts on heat stability and rheological properties of cow skim milk ultrafiltered retentate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 53, 3960–3968. doi:10.1007/s13197-016-2388-4
Miguel, M., Gómez-Ruiz, J. Á., Recio, I., and Aleixandre, A. (2010). Changes in arterial blood pressure after single oral administration of milk-casein-derived peptides in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 54, 1422–1427. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200900448
Min, Z., Yunyun, J., Miao, C., and Zhennail, Y. (2020). Characterization and ACE inhibitory activity of fermented milk with probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum K25 as analyzed by GC-MS-based metabolomics approach. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30, 903–911. doi:10.4014/jmb.1911.11007
Minj, J., Chandra, P., Paul, C., and Sharma, R. K. (2021). Bio-functional properties of probiotic Lactobacillus: current applications and research perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 61, 2207–2224. doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1774496
Minj, J., Riordan, J., Teets, C., Fernholz-Hartman, H., Tanggono, A., Lee, Y., et al. (2024). Diet-induced rodent obesity is prevented and the fecal microbiome is improved with elderberry (Sambucus nigra ssp. canadensis) juice powder. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 12555–12565. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01211
Minj, J., Singh, B. P., and Vij, S. (2020). Screening of yoghurt cultures for their potential proteolytic, antioxidant and probiotic properties. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 9, 1811–1831. doi:10.20546/ijcmas.2020.908.208
Minj, J., and Vij, S. (2017). Effect of prebiotic inulin on the fermentation and growth kinetics pattern of probiotic yoghurt bacteria. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 6, 1755–1768. doi:10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.199
Mohamed, I. K. R., Magied, S. S. A., El-Kader, Y. A., and Bakry, N. I. (2023). 'A Comparative study the effect of mango (Mangifera India L.) and pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juices on probiotic yogurt. Egypt. J. Nutr. 38 (1), 63–101. doi:10.21608/enj.2023.301794
Mohammed, A. R., Omar, M. M., El-Abbassy, M. M., and Khalifa, S. A. (2019). Manufacture of yoghurt drink supplemented with carrot and guava pulps. Zagazig. J. Agri. Res. 46, 1975–1984. doi:10.21608/ZJAR.2019.51912
Mohanty, D. P., Mohapatra, S., Misra, S., and Sahu, P. S. (2016). Milk derived bioactive peptides and their impact on human health – a review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 23, 577–583. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.06.005
Moslehishad, M., Ehsani, M. R., Salami, M., Mirdamadi, S., Ezzatpanah, H., Naslaji, A. N., et al. (2013). The comparative assessment of ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant activities of peptide fractions obtained from fermented camel and bovine milk by Lactobacillus rhamnosus PTCC 1637. Int. Dairy J. 29, 82–87. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2012.10.015
Munir, A., Javed, G. A., Javed, S., and Arshad, N. (2022). Levilactobacillus brevis from carnivores can ameliorate hypercholesterolemia: in vitro and in vivo mechanistic evidence. J. Appl. Microbiol. 133, 1725–1742. doi:10.1111/jam.15678
Nakamura, Y., Yamamoto, N., Sakai, K., and Takano, T. (1995). Antihypertensive effect of sour milk and peptides isolated from it that are inhibitors to angiotensin I-converting enzyme. J. Dairy Sci. 78, 1253–1257. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(95)76745-5
Narender Raju, P., and Pal, D. (2009). The physico-chemical, sensory, and textural properties of misti dahi prepared from reduced fat Buffalo milk. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2, 101–108. doi:10.1007/s11947-008-0137-z
O’Flaherty, S., Saulnier, D., Pot, B., and Versalovic, J. (2010). How can probiotics and prebiotics impact mucosal immunity? Gut Microbes 1, 293–300. doi:10.4161/gmic.1.5.12924
Ong, L., and Shah, N. P. (2008). Influence of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. helveticus on proteolysis, organic acid profiles, and ACE-inhibitory activity of cheddar cheeses ripened at 4, 8, and 12 °C. J. Food Sci. 73, M111–M120. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00689.x
Pădureţ, S., Ghinea, C., Prisacaru, A. E., and Leahu, A. (2024). Physicochemical, textural, and antioxidant attributes of yogurts supplemented with black chokeberry: fruit, juice, and pomace. Foods 13, 3231. doi:10.3390/foods13203231
Pan, D., Luo, Y., and Tanokura, M. (2005). Antihypertensive peptides from skimmed milk hydrolysate digested by cell-free extract of Lactobacillus helveticus JCM1004. Food Chem. 91, 123–129. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.05.055
Parmar, H., Hati, S., and Sakure, A. (2018). In vitro and in silico analysis of novel ACE-inhibitory bioactive peptides derived from fermented goat milk. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 24, 441–453. doi:10.1007/s10989-017-9630-4
Pereira, E. P., Ferreira, B. M., Freire, L., Neri-Numa, I. A., Guimarães, J. T., Rocha, R. S., et al. (2024). Enhancing the functionality of yogurt: impact of exotic fruit pulps addition on probiotic viability and metabolites during processing and storage. Food Res. Int. 196, 115057. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2024.115057
Pereira, R. B., Singh, H., Munro, P. A., and Luckman, M. S. (2003). Sensory and instrumental textural characteristics of acid milk gels. Int. Dairy J. 13, 655–667. doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(03)00071-2
Perina, N. P., Granato, D., Hirota, C., Cruz, A. G., Bogsan, C. S. B., and Oliveira, M. N. (2015). Effect of vegetal-oil emulsion and passion fruit peel-powder on sensory acceptance of functional yogurt. Food Res. Int. 70, 134–141. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2015.01.014
Pinto, G., Picariello, G., Addeo, F., Chianese, L., Scaloni, A., and Caira, S. (2020). Proteolysis and process-induced modifications in synbiotic yogurt investigated by peptidomics and phosphopeptidomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 8744–8754. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02603
Qian, B., Xing, M., Cui, L., Deng, Y., Xu, Y., Huang, M., et al. (2011). Antioxidant, antihypertensive, and immunomodulatory activities of peptide fractions from fermented skim milk with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus LB340. J. Dairy Res. 78, 72–79. doi:10.1017/S0022029910000889
Ramchandran, L., and Shah, N. P. (2009). Effect of exopolysaccharides and inulin on the proteolytic, angiotensin-I-converting enzyme- and α -glucosidase-inhibitory activities as well as on textural and rheological properties of low-fat yogurt during refrigerated storage. Dairy Sci. Technol. 89, 583–600. doi:10.1051/dst/2009039
Ramchandran, L., and Shah, N. P. (2010). Characterization of functional, biochemical and textural properties of synbiotic low-fat yogurts during refrigerated storage. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 43, 819–827. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2010.01.012
Re, R., Pellegrini, N., Proteggente, A., Pannala, A., Yang, M., and Rice-Evans, C. (1999). Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26, 1231–1237. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Remeuf, F., Mohammed, S., Sodini, I., and Tissier, J. P. (2003). Preliminary observations on the effects of milk fortification and heating on microstructure and physical properties of stirred yogurt. Int. Dairy J. 13, 773–782. doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(03)00092-X
Ren, J., Zhao, M., Shi, J., Wang, J., Jiang, Y., Cui, C., et al. (2008). Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from grass carp muscle hydrolysates by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 108, 727–736. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.11.010
Richardson, R. K. (2001). Determination of fat in dairy products using pressurized solvent extraction. J. AOAC Int. 84, 1522–1533. doi:10.1093/jaoac/84.5.1522
Rival, S. G., Boeriu, C. G., and Wichers, H. J. (2001). Caseins and casein hydrolysates. 2. Antioxidative properties and relevance to lipoxygenase inhibition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 49, 295–302. doi:10.1021/jf0003911
Rivero-Pino, F., Casquete, M., Castro, M. J., Redondo Del Rio, P., Gutierrez, E., Mayo-Iscar, A., et al. (2024). Prospective, randomized, double-blind parallel group nutritional study to evaluate the effects of routine intake of fresh vs. Pasteurized yogurt on the immune system in healthy adults. Nutrients 16, 1969. doi:10.3390/nu16121969
Rubak, Y. T., Nuraida, L., Iswantini, D., and Prangdimurti, E. (2020). Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in milk fermented by indigenous lactic acid bacteria. Vet. World 13, 345–353. doi:10.14202/vetworld.2020.345-353
Rubak, Y. T., Nuraida, L., Iswantini, D., and Prangdimurti, E. (2022). Angiotensin-I-Converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in goat milk fermented by lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented food and breast milk. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 42, 46–60. doi:10.5851/kosfa.2021.e55
Ryan, J., Hutchings, S. C., Fang, Z., Bandara, N., Gamlath, S., Ajlouni, S., et al. (2020). Microbial, physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of mango juice-enriched probiotic dairy drinks. Int J Dairy Tech 73, 182–190. doi:10.1111/1471-0307.12630
Sabeena Farvin, K. H., Baron, C. P., Nielsen, N. S., Otte, J., and Jacobsen, C. (2010). Antioxidant activity of yoghurt peptides: Part 2 – characterisation of peptide fractions. Food Chem. 123, 1090–1097. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.05.029
Saeed, M., Ali, S. W., and Ramzan, S. (2021). Physicochemical analysis of mango flavored yogurt supplemented with moringa oleifera leaf powder. J. Food Sci. Technol. 58, 4805–4814. doi:10.1007/s13197-021-05146-w
Sanders, M. E., Guarner, F., Guerrant, R., Holt, P. R., Quigley, E. M., Sartor, R. B., et al. (2013). An update on the use and investigation of probiotics in health and disease. Gut 62, 787–796. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302504
Sanders, M. E., Merenstein, D., Merrifield, C. A., and Hutkins, R. (2018). Probiotics for human use. Nutr. Bull. 43, 212–225. doi:10.1111/nbu.12334
Sarmadi, B. H., and Ismail, A. (2010). Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: a review. Peptides 31, 1949–1956. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2010.06.020
Schlothauer, R. C., Schollum, L. M., Reid, J. R., Harvey, S. A., Carr, A. J., and Fanshawe, R. L. (2002). No. 002421714A.
Senadeera, S. S., Prasanna, P. H. P., Jayawardana, N. W. I. A., Gunasekara, D. C. S., Senadeera, P., and Chandrasekara, A. (2018). Antioxidant, physicochemical, microbiological, and sensory properties of probiotic yoghurt incorporated with various Annona species pulp. Heliyon 4, e00955. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00955
Shakerian, M., Razavi, S. H., Ziai, S. A., Khodaiyan, F., Yarmand, M. S., and Moayedi, A. (2015). Proteolytic and ACE-inhibitory activities of probiotic yogurt containing non-viable bacteria as affected by different levels of fat, inulin and starter culture. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52, 2428–2433. doi:10.1007/s13197-013-1202-9
Shirkhan, F., Mirdamadi, S., Mirzaei, M., Akbari-adergani, B., and Nasoohi, N. (2023). The role of lactic acid bacteria in production of bioactive peptides in fermented milk with antioxidant and antidiabetic properties. Food Meas. 17, 4727–4738. doi:10.1007/s11694-023-01968-8
Shukla, P., Sakure, A., Maurya, R., Bishnoi, M., Kondepudi, K. K., Das, S., et al. (2023). Antidiabetic, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities of fermented camel milk and characterisation of novel bioactive peptides from lactic-fermented camel milk with molecular interaction study. Int J Dairy Tech 76, 149–167. doi:10.1111/1471-0307.12910
Singh, B. P., Vij, S., Hati, S., Singh, D., Kumari, P., and Minj, J. (2015). Antimicrobial activity of bioactive peptides derived from fermentation of soy milk by Lactobacillus plantarum C2 against common foodborne pathogens. Internat. Jour. Fermen. Foods 4, 91. doi:10.5958/2321-712X.2015.00008.3
Sipola, M., Finckenberg, P., Vapaatalo, H., Pihlanto-Leppälä, A., Korhonen, H., Korpela, R., et al. (2002). α-lactorphin and β-lactorphin improve arterial function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 71, 1245–1253. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(02)01793-9
Su, Y., Wang, H., Wu, Z., Zhao, L., Huang, W., Shi, B., et al. (2022). Sensory description and consumer hedonic perception of ultra-high temperature (UHT) milk. Foods 11, 1350. doi:10.3390/foods11091350
Sultan, S., Huma, N., Butt, M. S., Aleem, M., and Abbas, M. (2018). Therapeutic potential of dairy bioactive peptides: a contemporary perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 58, 105–115. doi:10.1080/10408398.2015.1136590
Taha, S., El Abd, M., De Gobba, C., Abdel-Hamid, M., Khalil, E., and Hassan, D. (2017). Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of bioactive peptides in buffalo’s yoghurt fermented with different starter cultures. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 26, 1325–1332. doi:10.1007/s10068-017-0160-9
Tamime, A. Y., and Robinson, R. K. (1999). Yoghurt: science and technology, 2. England: Woodhead Publishing.
Tonucci, L. B., Olbrich Dos Santos, K. M., Licursi De Oliveira, L., Rocha Ribeiro, S. M., and Duarte Martino, H. S. (2017). Clinical application of probiotics in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 36, 85–92. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2015.11.011
Walstra, P., Wouters, J. T. M., and Geurts, T. J. (2006). Dairy science and technology. Boca Raton, FL, USA: Taylor and Francis Group, LLC, 551–573. Chapter 22 Fermented milks.
Wang, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Li, J., Zhao, C., Ma, C., et al. (2024). Impact of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and casein fortification on angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in yogurt: identification and in silico analysis. Food Funct. 15, 3824–3837. doi:10.1039/D3FO04534J
Wu, N., Xu, W., Liu, K., and Xia, Y.Shuangquan (2019). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Lactobacillus delbrueckii QS306 fermented milk. J. Dairy Sci. 102, 5913–5921. doi:10.3168/jds.2018-15901
Yang, W. (2024). Evaluation of the antioxidant activity and identification of potential antioxidant peptides in commercially available probiotic Cheddar cheese. LWT 205, 116486. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116486
Yi, L., Min, J. T., Jun, C. L., Long, H. X., Khoo, H. E., Ying, Z. J., et al. (2024). Buffalo yogurt fermented with commercial starter and Lactobacillus plantarum originating from breast milk lowered blood pressure in pregnant hypertensive rats. J. Dairy Sci. 107, 62–73. doi:10.3168/jds.2023-23566
Yoon, J.-W., Ahn, S.-I., Jhoo, J.-W., and Kim, G.-Y. (2019). Antioxidant activity of yogurt fermented at low temperature and its anti-inflammatory effect on DSS-induced colitis in mice. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 39, 162–176. doi:10.5851/kosfa.2019.e13
Yu, H.-Y., Wang, L., and McCarthy, K. L. (2016). Characterization of yogurts made with milk solids nonfat by rheological behavior and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Food Drug Analysis 24, 804–812. doi:10.1016/j.jfda.2016.04.002
Yu, Y., Yu, W., and Jin, Y. (2021). Peptidomic analysis of milk fermented by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. Food Hydrocoll. Health 1, 100033. doi:10.1016/j.fhfh.2021.100033
Yuan, H., Lv, J., Gong, J., Xiao, G., Zhu, R., Li, L., et al. (2018). Secondary structures and their effects on antioxidant capacity of antioxidant peptides in yogurt. Int. J. Food Prop. 21, 2167–2180. doi:10.1080/10942912.2018.1501700
Zahid, H. F., Ali, A., Legione, A. R., Ranadheera, C. S., Fang, Z., Dunshea, F. R., et al. (2023). Probiotic yoghurt enriched with mango peel powder: biotransformation of phenolics and modulation of metabolomic outputs after in vitro digestion and colonic fermentation. IJMS 24, 8560. doi:10.3390/ijms24108560
Zhishen, J., Mengcheng, T., and Jianming, W. (1999). The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 64, 555–559. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00102-2
Zolghadrpour, M.-A., Jowshan, M.-R., Seyedmahalleh, M. H., Imani, H., Karimpour, F., and Asghari, S. (2024). Consumption of a new developed synbiotic yogurt improves oxidative stress status in adults with metabolic syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 14, 20333. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-71264-y
Keywords: yogurt, synbiotic, antioxidant activity, bioactive peptides, mango fruit yogurt, biofunctional yogurt
Citation: Minj J and Vij S (2025) Determination of synbiotic mango fruit yogurt and its bioactive peptides for biofunctional properties. Front. Chem. 12:1470704. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1470704
Received: 26 July 2024; Accepted: 03 December 2024;
Published: 20 January 2025.
Edited by:
Brij Pal Singh, Chandigarh University, IndiaReviewed by:
Sirasit Srinuanpan, Chiang Mai University, ThailandDiana Nur Afifah, Diponegoro University, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Minj and Vij. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shilpa Vij, c2hpbHBhdmlqbkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†Present address: Jagrani Minj, Department of Nutrition and Exercise Physiology, Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Washington State University, Spokane, WA, United States
 Jagrani Minj
Jagrani Minj Shilpa Vij
Shilpa Vij