- 1Department of Radiology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 2Department of Radiology, Zhuzhou Central Hospital, Zhuzhou, Hunan, China
- 3Department of Ultrasound, The Air Force Hospital of Southern Theater Command, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 4Department of Nuclear Medicine, Weifang People’s Hospital, Shandong Second Medical University, Weifang, Shandong, China
Eliciting anti-tumor immune responses and improving the tumor microenvironment crucial for boosting the effectiveness of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), the primary types of immune cells infiltrating tumors, play a critical role in the formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment. In this study, we constructed a novel Evans Blue (EB)-based in vivo self-assembled nanocarrier system, mUNO-EB-ICG-Fc@Alb nanoparticles (designated as MA NPs), for targeted imaging and clearance of M2-TAMs to elicit antitumor immunotherapy of PD-1 inhibitor. In vitro experiments demonstrated the specific fluorescence imaging and killing effect of MA NPs on M2-TAMs. In vivo experiments shown that MA NPs-induced chemodynamic therapy (CDT) successfully reversed the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment (ITM), promoted intratumoral infiltration of T lymphocytes, and ultimately enhancing the anti-tumor immunotherapy effect of PD-1 inhibitors. This study might provide good inspiration for improving the therapeutic efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.
1 Introduction
Immunotherapy has emerged as a viable and attractive treatment option for many cancer patients (Hargadon et al., 2018). Unlike previous surgical, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and targeted therapy, tumor immunotherapy is a therapeutic strategy that utilizes multiple means to stimulate and enhance the immune function of the body, and ultimately achieves the goal of removing tumor cells (Sanmamed and Chen, 2018). With the in-depth understanding of tumor immune escape mechanism, immune checkpoint inhibitors represented by Programmed Death 1/Programmed cell Death-Ligand 1(PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors are becoming increasingly significant in cancer medication treatment (Li et al., 2021). Tumor tissues limit antitumor immunity by up-regulating immunosuppressive factors such as PD-1 ligand (PD-L1) that binds to PD-1 on tumor-specific CD8 T cells (Chen and Mellman, 2013). Drugs targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint axis can block immunosuppressive signals and enable T cell–mediated elimination of cancer cells (Topalian et al., 2012). Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the PD-1 have demonstrated impressive benefits for the treatment of some cancers (Zhan et al., 2016). However, PD-1 mAbs is not always effective, and we lack a complete understanding of the mechanisms that contribute to efficacy and resistance (Garon et al., 2015).
A key factor responsible for the poor response is the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) mediated by tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) (Mathew et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2023). TAMs represent one of the main tumor-infiltrating immune cell types, play a crucial part in tumor invasion and metastasis (Quail and Joyce, 2013; Vitale et al., 2019). According to different activation signals, they are mainly classified as classical activated M1 macrophages and alternatively activated M2 macrophages (Hinshaw and Shevde, 2019). Usually, TAMs are dominated by M2 macrophages that promotes tumor progression in the tumor microenvironment (Yahaya et al., 2019; Fang et al., 2021). Mounting evidence indicates that TAMs are closely associated with non-response to anti-PD-1 therapy (Mantovani et al., 2017; Osipov et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2023). The study by Gyo et al. found that PD-1 mAbs effectively bind PD-1 tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cells at early time points after administration. However, this engagement is transient, and PD-1 mAbs are captured and inactivated within minutes from the T cell surface by M2 macrophages (Arlauckas et al., 2017). These findings support M2 macrophages as a potential biomarker for treatment response or target to improve anti-PD-1 therapy in cancer. Although there are many studies dedicated to the repolarization of M2 macrophages to M1 macrophages, M1/M2 polarization is a dynamic equilibrium, and successfully polarized M1 macrophages may return to M2 macrophages under the influence of TME (Xu et al., 2022). Therefore, complete removal of M2-TAMs may be a more effective means (Zhu et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023).
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an effective therapeutic modality that kills cells by utilizing photosensitizers to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) under laser irradiation, with great spatiotemporal selectivity and minimal invasiveness (Dolmans et al., 2003; Xu et al., 2017). Indocyanine green (ICG) is the only near-infrared (NIR) dye approved for clinical application by the FDA (Hu et al., 2022). ICG has good optical properties and reactive oxygen generation ability, which can be used for near infrared second window (NIR-II) imaging and photodynamic therapy (Fang et al., 2019). However, the therapeutic benefits of PDT for deep tumors are greatly attenuated, due to the hypoxic tumor microenvironment and the attenuation of infrared light (Zhou et al., 2016; Dang et al., 2017). A promising strategy to amplify PDT effect is Fenton reaction-based chemodynamic therapy (CDT) (Liu et al., 2018). Catalyzed by Fe2+/Fe3+ ions, the cascade reaction can not only convert endogenous H2O2 into •OH, one of the most toxic ROS, but also produce O2 to improve the efficacy of PDT (Dai et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2022). On the other hand, stable H2O2 is also produced during the PDT process, which promotes the virtuous circle of Fenton reaction (Li et al., 2020). Ferrocene (Fc) is an organometallic compound with reversible redox properties, which can achieve swift Fenton reaction in a physiological environment and provide ferrous ions to improve CDT efficacy (van Staveren and Metzler-Nolte, 2004; Wang et al., 2018). Therefore, constructing a nanoplatform to co-deliver Fc and ICG to tumor is a promising strategy for effective CDT (Chen et al., 2023; Ning et al., 2023).
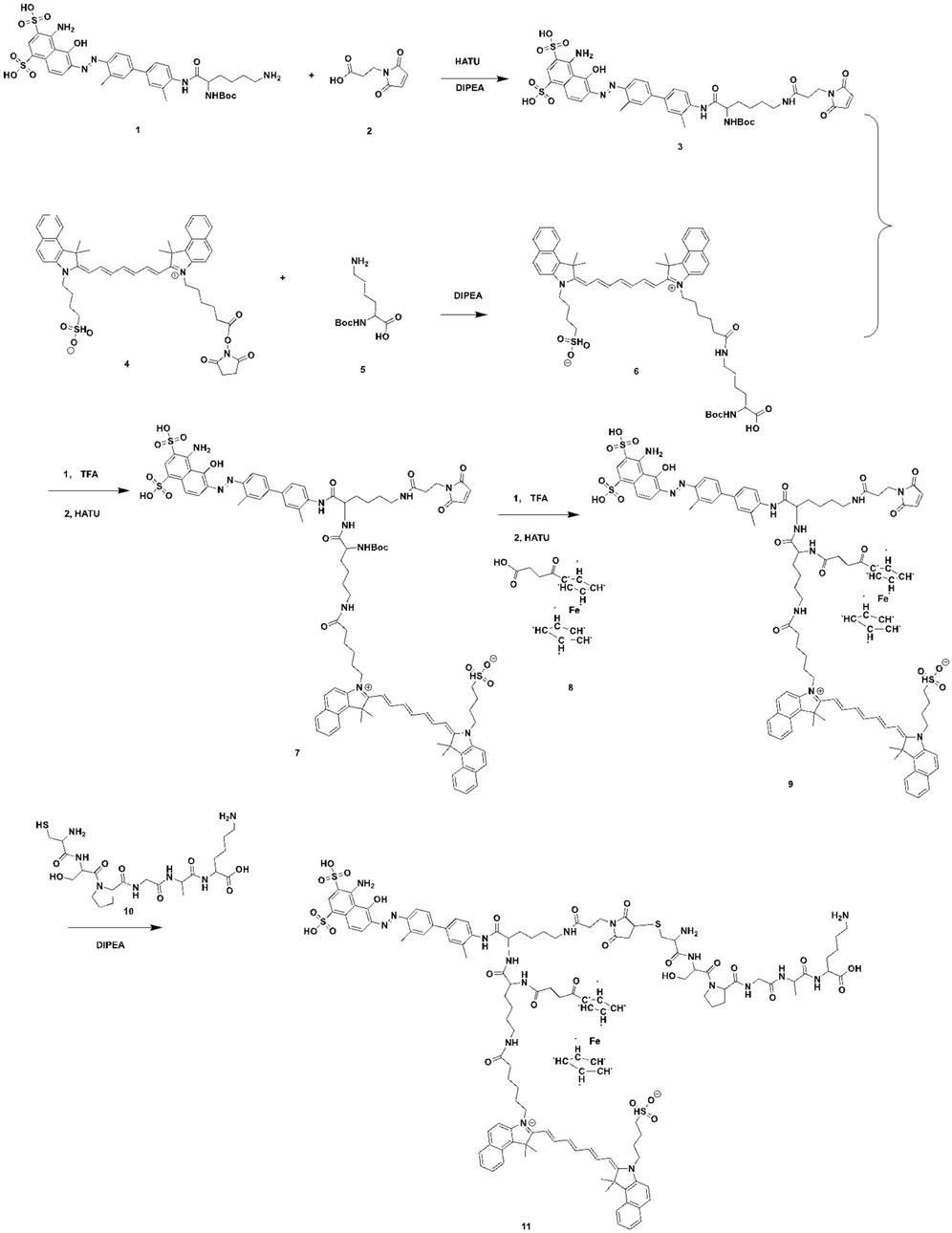
Traditional nanocarriers can deliver drugs to the site of action, improve efficacy and reduce side effects, but themselves may cause toxic side effects and immunogenicity (Jacobson et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2020). In this study, we constructed a novel Evans Blue (EB)-based drug self-delivery system (DSDS), mUNO-EB-ICG-Fc@Alb nanoparticles (designated as MA NPs), for targeted imaging and clearance of M2-TAMs to elicit antitumor immunotherapy of PD-1 inhibitor. The synthesis route is shown in Scheme 1. As a high-affinity albumin binding agent, EB can be assembled into nanoparticles with serum albumin in vivo and self-delivered to tumor areas (Ehlerding et al., 2018; Jaynes et al., 2020). The molecular docking model is shown in Scheme 2 mUNO is a short homing peptide that targets the marker of M2-macrophages, CD206 (Movahedi et al., 2010). After mUNO-mediated cell uptake, MA NPs generate fluorescence and ROS under laser excitation, achieving real-time quantitative NIR-II imaging and photodynamic effects on M2-TAMs. Moreover, the cascade Fenton reaction catalyzed by Fc generated •OH and O2 to relieve hypoxia and amplify PDT efficiency, achieving chemodynamic effects on M2-TAMs. In turn, ROS generated by PDT promoted shape-transformation and continuous occurrence of Fenton reaction, achieving complete clearance of M2-TAMs, thereby reversing the immunosuppressive microenvironment of tumors and eliciting the anti-tumor immunity of PD-1 mAbs. In vitro experiments have demonstrated the specific fluorescence imaging and killing effect of MA NPs on M2-TAMs. In vivo experiments shown that MA NPs-induced chemodynamic therapy (CDT) significantly improved the tumor immune microenvironment, promoted intratumoral infiltration of T lymphocytes, and ultimately enhancing the anti-tumor immunotherapy effect of PD-1 inhibitors. This study provides insights into potential therapeutic targets to improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade and key clues to developing novel tumor immunotherapies.
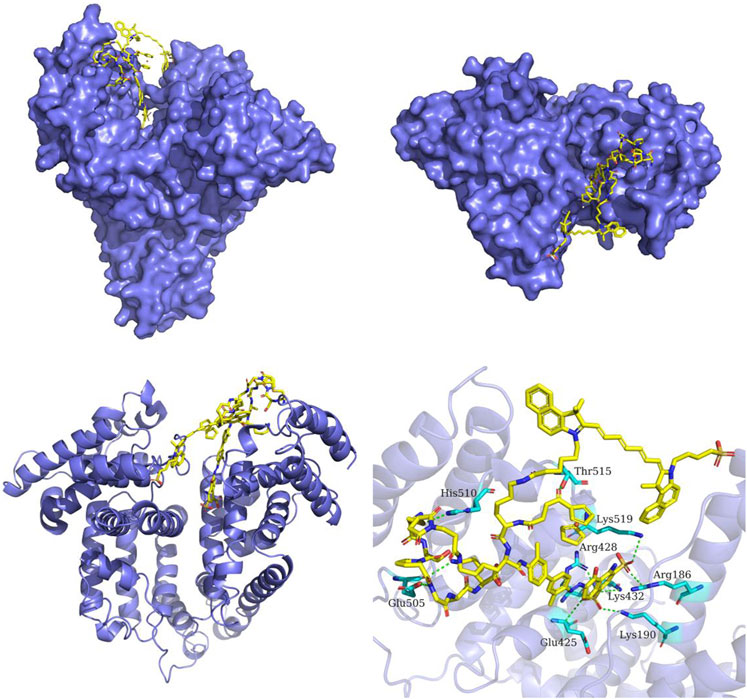
Scheme 2. The predicted binding mode of MA NPs and serum albumin. The structure of serum albumin is colored in slate-blue. MA NPs is shown as yellow sticks. The interacting residues in serum albumin are shown as cyan sticks. The hydrogen bonds between MA NPs and serum albumin are depicted as green dashed lines.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 •OH generation performance of MA NPs
The efficient generation of highly toxic •OH is a crucial step in Fenton reaction-based CDT. Therefore, the catalytic ability of MA NPs for Fenton reaction was evaluated by terephthalic acid (TA), a fluorescence probe for detecting •OH. After TA was oxidized to 2-hydroxyp-benzoic acid by •OH, a characteristic fluorescence peak at 435 nm can be observed. As shown in Figure 1A, the fluorescence intensity of MA NPs group was much higher than that of the other control groups, revealing their promising ability in producing •OH. The concentration-dependent •OH generation behavior was also researched. The fluorescence intensity dramatically elevated with the increase of MA NPs concentration. 2′,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate was used to further detect the •OH production ability of MA NPs at the cellular level to verify the feasibility of MA NPs as a CDT agent. As shown in Figure 1B, no obvious fluorescence was observed in MA NPs without laser irradiation group, indicating Fc hardly increased •OH level, due to ineffective Fenton reactions with insufficient endogenous H2O2 in M2 macrophages. In contrast, significant fluorescence intensity was observed in MA NPs with laser irradiation group, indicating the PDT effect of MA NPs could provide sufficient H2O2 for Fenton reactions to produce •OH. Overall, MA NPs can generate sufficient ROS within cells to achieve efficient CDT.
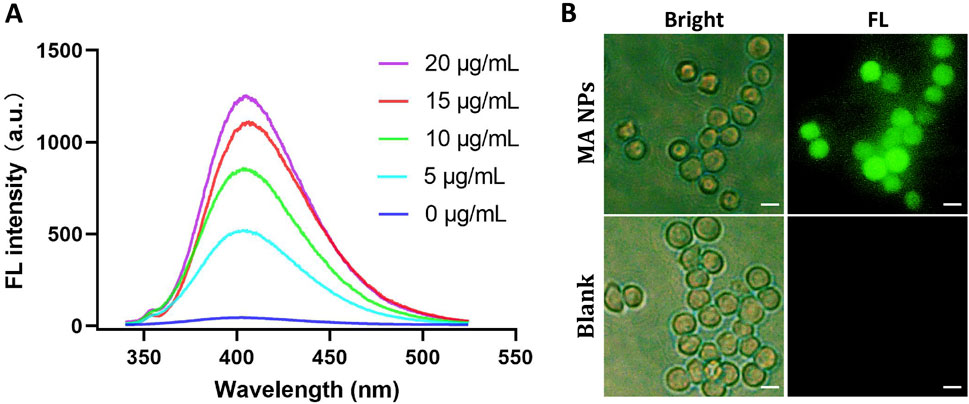
Figure 1. (A). FL emission spectra of the mixture of TA, H2O2, and MA NPs at different concentrations. (B). FL images of ROS in M2 macrophages treated with MA NPs with/without laser. Scale bar: 50 µm.
2.2 Cellular uptake study
The efficacy of MA NPs delivery to M2 macrophages was assessed via applying confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). We successfully extracted bone marrow cells and induced them to differentiate into M2 macrophages. Flow cytometry and immunofluorescence staining were used to confirm the markers of M2 macrophages. As shown in Figure 2A, a significant increase from 20.3% to 98.2% in the CD206+ M2 macrophages was induced after IL-4/IL-13 stimulation. Immunofluorescence co-staining of F4/80 and CD206 antibodies further determined the functional phenotype of M2 macrophages (Figure 2B). Subsequently, the cellular uptake of MA NPs on M2 macrophages was investigated by CLSM. As shown in Figure 2C, after incubation with MA NPs, the CLSM images displayed strong red fluorescence signals in the cytoplasm of M2 macrophages, which perfectly integrated with the green fluorescence signals of CD206 and blue fluorescence signals of DAPI. These results demonstrate that MA NPs could effectively target M2 macrophages for FL imaging and chemodynamic therapy.
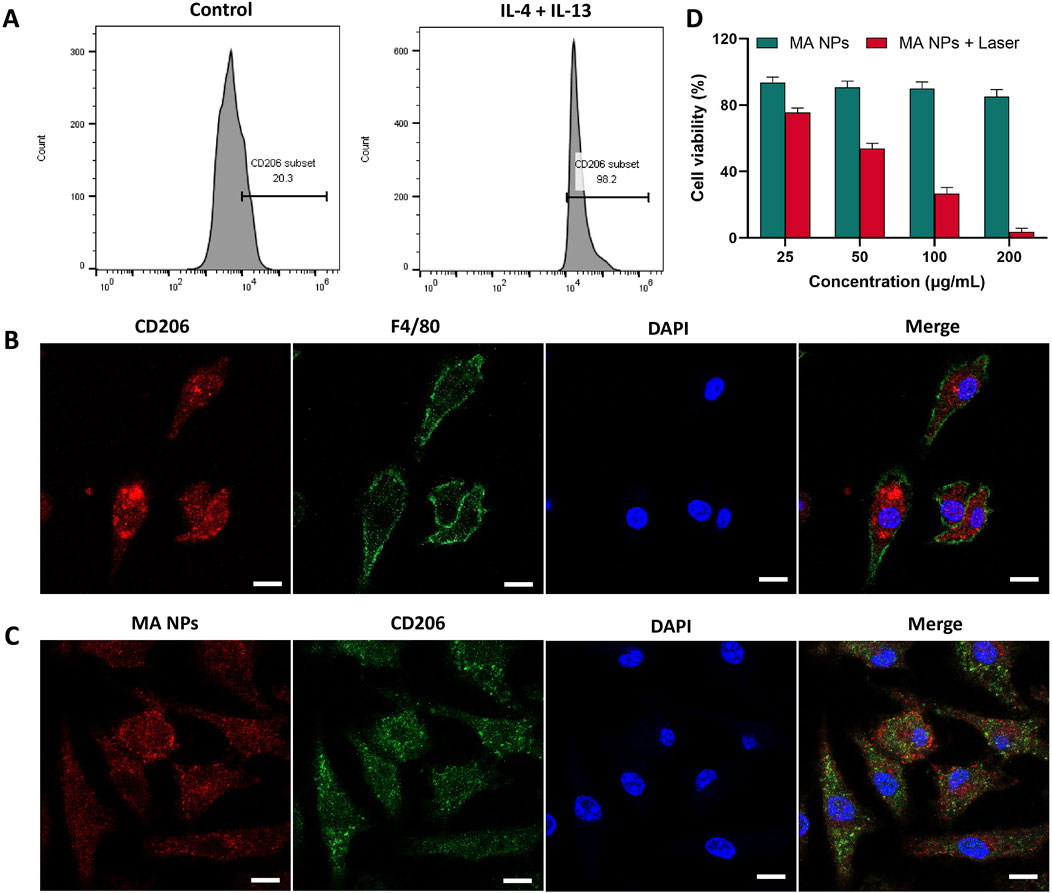
Figure 2. (A) Flow cytometry analysis and (B) immunocytochemical images showing BMDMs polarization to M2 functional phenotype using IL-4 and IL-13. (C) CLSM images of M2 macrophages treated with MA NPs. (D) Cell viability of M2 macrophages treated with MA NPs at various concentrations with and without laser irradiation. Scale bar: 20 µm.
2.3 In vitro CDT effects
The in vitro CDT Performance of Fc and MA NPs against M2 macrophages were evaluated by CCK-8 cell proliferation kit. In the MA NPs without laser irradiation group, negligible cytotoxicity was detected in M2 macrophages, even when the maximum concentration reached up to 200 μg/mL (Figure 4A). These results indicated that the conventional CDT efficacy with iron source supply only was severely compromised by insufficient endogenous H2O2 in M2 macrophages. Due to the fact that the PDT process has been proven to produce stable H2O2 for Fenton reaction to achieve efficient CDT effect, a significant killing effect of MA NPs on M2 macrophages can be observed under laser irradiation (Figure 2D). Meanwhile, the Fenton reaction can also generate O2 to enhance the PDT efficacy, which promotes the virtuous circle of CDT. Thus, only weak cell viability was observed at concentrations of MA up to 200 μg/mL. These results indicate that MA NPs could be utilized as an efficient nanoagents and achieve amplified CDT efficacy through self-supplying O2 and H2O2.
2.4 In vivo NIR-II imaging
The in vivo targeted fluorescence imaging of MA NPs in TAMs was investigated in the 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma model, which is a typical immunosuppressive tumor model with abundant infiltrating macrophages (Movahedi et al., 2010; Gu et al., 2021). After tail vein injection of MA NPs, representative NIR-II fluorescence images at different time points were simultaneously recorded by NIR-II in vivo imaging system. As shown in Figure 3A, within 6 h after injection, MA NPs continues to accumulate in the tumor and reaches its peak, which was attributed to the EPR effect of tumors. Afterward, the fluorescence signal in the tumor gradually decreased, but the fluorescence signal in certain areas remained for 96 h. We speculate that the drugs in the tumor matrix are gradually cleared, while the drugs taken up by M2-TAMs remain in the tumor. Supplementary Figure S2 illustrates ex vivo fluorescence images of major organs and tumors harvested from mice at 96 h. There is almost no fluorescence in major organs, only the tumor has moderate fluorescence retention. Subsequently, the tumor tissue was stained for CD206, which is a marker of M2-TAMs. As shown in Figure 3B, the nearly coincident fluorescence of MA NPs and CD206 antibodies can be observed on confocal images, which demonstrates the targeting imaging ability of MA NPs for M2-TAMs in tumors.
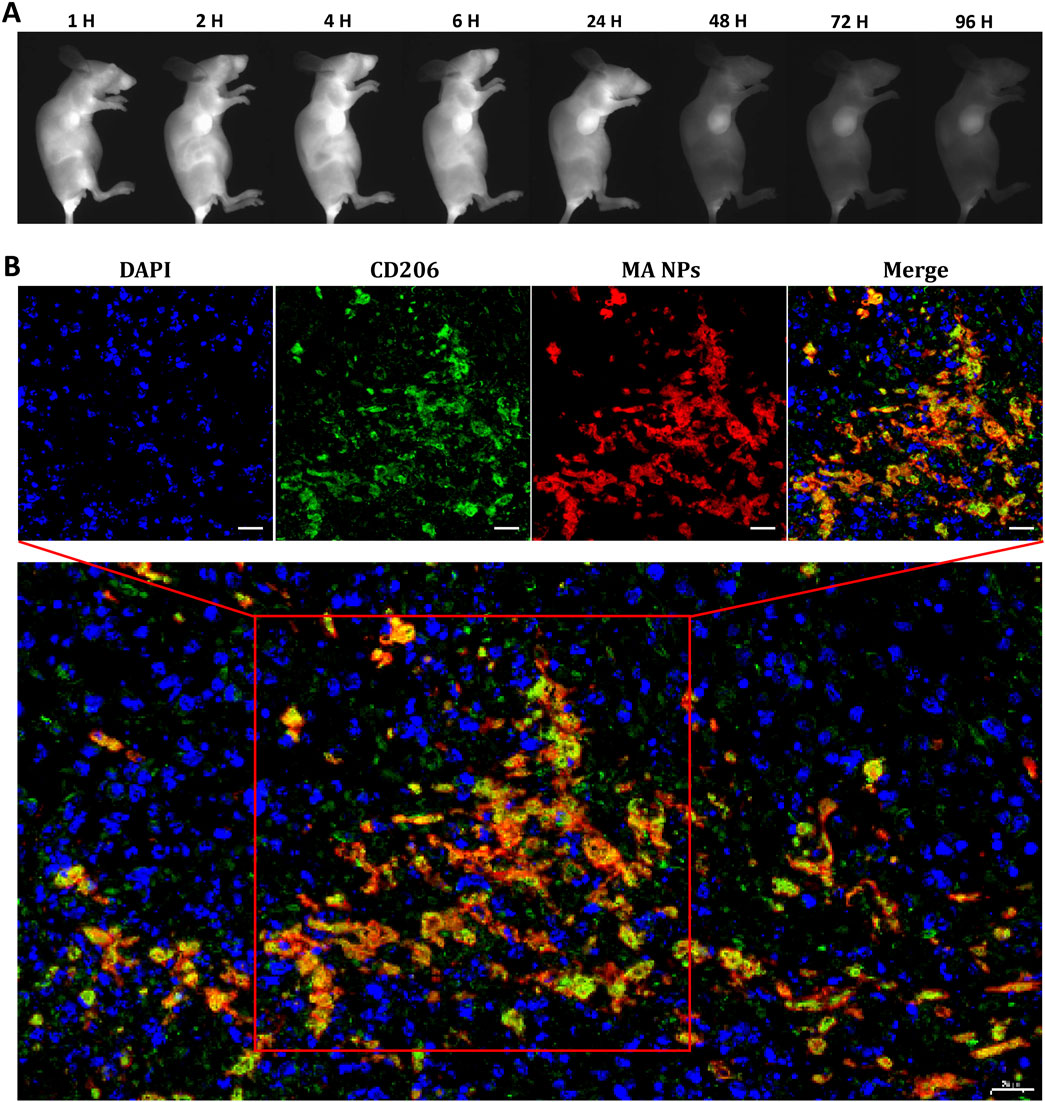
Figure 3. (A) In vivo NIR-II FL imaging of mice 4T1-bearing tumors. (B) MA NPs targets M2-TAMs in 4T1 tumor. Scale bar: 20 µm.
2.5 In vivo therapeutic performance
Inspired by the satisfactory CDT efficacy in vitro and enhanced tumor accumulation in vivo, we further investigated the in vivo synergistic anti-tumor efficacy of MA in vivo. The 4T1 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice were randomly divided into 4 groups: (a) MA NPs + PD-1 mAbs + laser (b) PD-1 mAbs (c) MA NPs + laser (d) PBS. As shown in Figures 4A, B, compared to the control group, the tumors in the MA NPs + laser group exhibited slight restriction in tumor growth rate, indicating that the removal of M2-TAMs alone do not significantly affect tumor growth. Treatment with PD-1 mAbs alone inhibited limited growth of tumors, which was attributed to the immunosuppressive microenvironment in the tumor. However, the combination of M2-TAMs clearance and PD-1 mAbs treatment resulted in a maximal control of tumor burden and the smallest tumor volume, achieving the highest tumor inhibition ratio.
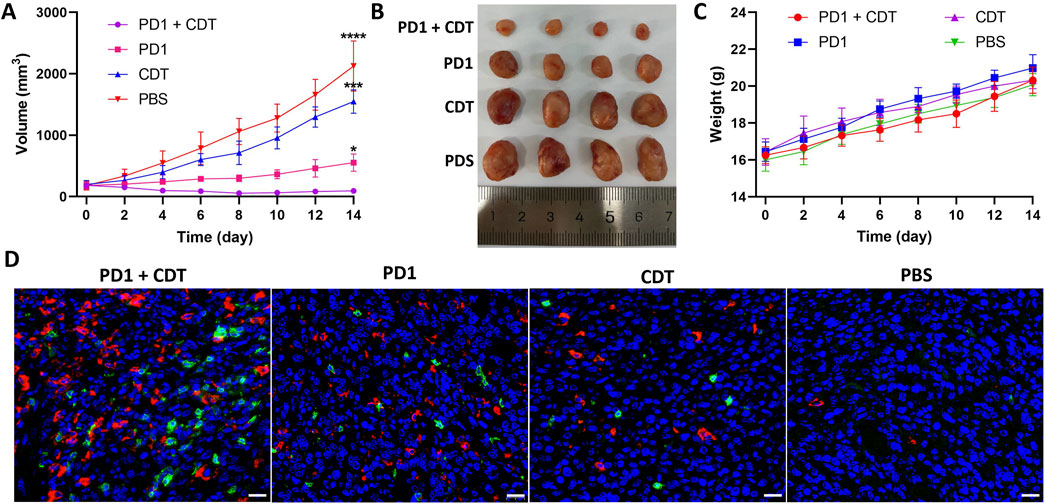
Figure 4. (A) Tumor volume evolvement curves of tumor-bearing mice. (B) Photographs of the dissected tumors by the end of treatment. (C) Body weight growth curve of tumor-bearing mice. (D) Immunofluorescence images for CD4 (red) and CD8 (green) of tumor sections. Scale bar: 20 µm.
The recruitment of immune cells into the TME is a critical parameter directly associated with anti-tumor immune responses. Therefore, we used immunofluorescence staining to detect the infiltration of T lymphocytes in the tumor tissues of each group. As shown in Figure 4D, MA NPs + PD-1 mAbs + laser treatment showed a mass of CD4 (green) and CD8 T cells (red) infiltration in tumors, compared to the PD-1 mAbs group with limited tumor-infiltrating T cells. These results indicate that MA NPs can effectively clear M2-TAMs and eliminate the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment, thereby significantly enhancing the anti-tumor immunotherapeutic effect of PD-1 mAbs. Moreover, no significant differences in body weight were observed in the corresponding groups, suggesting low systemic toxicity in all the treatments (Figure 4C).
3 Conclusion
In summary, we developed a in vivo self-assembled albumin nanoparticle MA NPs for eliciting antitumor immunity of PD-1 inhibitor. The precursor of nanoparticle was composed of mUNO for targeting M2-TAMs, ICG and ferrocene for NIR-II FL imaging guided CDT, and EB for albumin binding. When precursors enter the bloodstream, they quickly assemble into nanoparticles with serum albumin and self deliver to the tumor area. After mUNO-mediated cell uptake, MA NPs can effectively label and real-time fluorescence quantitative monitor M2-TAMs. The synergistic CDT of MA NPs significantly improved the immunosuppressive TME and elicited antitumor immunity of PD-1 inhibitor, which resulted in a large number of intratumoral infiltration of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and a significant tumor inhibition effect. This study might provide good inspiration for improving the therapeutic efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Animal Ethics Committee, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, China. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CY: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft. LH: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. QY: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. YR: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. MZ: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. LG: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. SL: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. JW: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. EX: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing–review and editing. ZC: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing–review and editing. QS: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing–review and editing. PX: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from Hunan Provincial Health High-level Talent Major Scientific Research Project (grant no. R2023022); Clinical Research Center for Medical Imaging in Hunan Province (grant no. 2020SK4001); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (grant no. 2022ZZTS0829); Joint Project between Provincial Natural Science Foundation and Science and Technology of Hunan (grant no. 2022JJ70142); Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation Science and Health Joint Project (grant no. 2022JJ70133).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2024.1469568/full#supplementary-material
References
Arlauckas, S. P., Garris, C. S., Kohler, R. H., Kitaoka, M., Cuccarese, M. F., Yang, K. S., et al. (2017). In vivo imaging reveals a tumor-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 9 (389), eaal3604. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3604
Chen, D. S., and Mellman, I. (2013). Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 39 (1), 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012
Chen, H., Luo, X., Huang, Q., Liu, Z., Lyu, M., Chen, D., et al. (2023). Platelet membrane fusion liposome loaded with type I AIE photosensitizer to induce chemoresistance cancer pyroptosis and immunogenic cell death for enhancing cancer immunotherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 476, 146276. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2023.146276
Dai, Y., Yang, Z., Cheng, S., Wang, Z., Zhang, R., Zhu, G., et al. (2018). Toxic reactive oxygen species enhanced synergistic combination therapy by self-assembled metal-phenolic network nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 30 (8). doi:10.1002/adma.201704877
Dang, J., He, H., Chen, D., and Yin, L. (2017). Manipulating tumor hypoxia toward enhanced photodynamic therapy (PDT). Biomaterials Sci. 5 (8), 1500–1511. doi:10.1039/c7bm00392g
Dolmans, D., Fukumura, D., and Jain, R. K. (2003). Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3 (5), 380–387. doi:10.1038/nrc1071
Ehlerding, E. B., Lan, X., and Cai, W. (2018). Albumin hitchhiking with an Evans blue analog for cancer theranostics. Theranostics 8 (3), 812–814. doi:10.7150/thno.24183
Fang, C., Yan, P., Ren, Z., Wang, Y., Cai, X., Li, X., et al. (2019). Multifunctional MoO2-ICG nanoplatform for 808nm-mediated synergetic photodynamic/photothermal therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 15, 472–481. doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2019.03.008
Fang, W., Zhou, T., Shi, H., Yao, M., Zhang, D., Qian, H., et al. (2021). Progranulin induces immune escape in breast cancer via up-regulating PD-L1 expression on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and promoting CD8+ T cell exclusion. J. Exp. and Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 4. doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01786-6
Garon, E. B., Rizvi, N. A., Hui, R., Leighl, N., Balmanoukian, A. S., Eder, J. P., et al. (2015). Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 372 (21), 2018–2028. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1501824
Gu, Z., Liu, T., Liu, C., Yang, Y., Tang, J., Song, H., et al. (2021). Ferroptosis-strengthened metabolic and inflammatory regulation of tumor-associated macrophages provokes potent tumoricidal activities. Nano Lett. 21 (15), 6471–6479. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01401
Hargadon, K. M., Johnson, C. E., and Williams, C. J. (2018). Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for cancer: an overview of FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 62, 29–39. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2018.06.001
Hinshaw, D. C., and Shevde, L. A. (2019). The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res. 79 (18), 4557–4566. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-3962
Hu, X., Li, J., Chen, Y., Long, Q., Bai, Y., Li, R., et al. (2022). A self-assembly ICG nanoparticle potentiating targeted photothermal and photodynamic therapy in NSCLC. Acs Biomaterials Sci. and Eng. 8, 4535–4546. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00620
Jacobson, O., Kiesewetter, D. O., and Chen, X. (2016). Albumin-binding Evans blue derivatives for diagnostic imaging and production of long-acting therapeutics. Bioconjugate Chem. 27 (10), 2239–2247. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00487
Jaynes, J. M., Sable, R., Ronzetti, M., Bautista, W., Knotts, Z., Abisoye-Ogunniyan, A., et al. (2020). Mannose receptor (CD206) activation in tumor-associated macrophages enhances adaptive and innate antitumor immune responses. Sci. Transl. Med. 12 (530), eaax6337. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aax6337
Li, L., Yang, Z., Fan, W., He, L., Cui, C., Zou, J., et al. (2020). In situ polymerized hollow mesoporous organosilica biocatalysis nanoreactor for enhancing ROS-mediated anticancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30 (4), 1907716. doi:10.1002/adfm.201907716
Li, Z., Sun, G., Sun, G., Cheng, Y., Wu, L., Wang, Q., et al. (2021). Various uses of PD1/PD-L1 inhibitor in oncology: opportunities and challenges. Front. Oncol. 11, 771335. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.771335
Liu, C., Wang, D., Zhang, S., Cheng, Y., Yang, F., Xing, Y., et al. (2019). Biodegradable biomimic copper/manganese silicate nanospheres for chemodynamic/photodynamic synergistic therapy with simultaneous glutathione depletion and hypoxia relief. Acs Nano 13 (4), 4267–4277. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b09387
Liu, Y., Zhen, W., Jin, L., Zhang, S., Sun, G., Zhang, T., et al. (2018). All-in-One theranostic nanoagent with enhanced reactive oxygen species generation and modulating tumor microenvironment ability for effective tumor eradication. Acs Nano 12 (5), 4886–4893. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b01893
Mantovani, A., Marchesi, F., Malesci, A., Laghi, L., and Allavena, P. (2017). Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 14 (7), 399–416. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.217
Mathew, A. A., Zakkariya, Z. T., Ashokan, A., Manohar, M., Keechilat, P., V. Nair, S., et al. (2023). 5-FU mediated depletion of myeloid suppressor cells enhances T-cell infiltration and anti-tumor response in immunotherapy-resistant lung tumor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 120, 110129. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110129
Movahedi, K., Laoui, D., Gysemans, C., Baeten, M., Stange, G., Van den Bossche, J., et al. (2010). Different tumor microenvironments contain functionally distinct subsets of macrophages derived from Ly6C(high) monocytes. Cancer Res. 70 (14), 5728–5739. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-09-4672
Ning, S., Zhang, T., Lyu, M., Lam, J. W. Y., Zhu, D., Huang, Q., et al. (2023). A type I AIE photosensitiser-loaded biomimetic nanosystem allowing precise depletion of cancer stem cells and prevention of cancer recurrence after radiotherapy. Biomaterials 295, 122034. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122034
Osipov, A., Saung, M. T., Zheng, L., and Murphy, A. G. (2019). Small molecule immunomodulation: the tumor microenvironment and overcoming immune escape. J. Immunother. Cancer 7 (1), 224. doi:10.1186/s40425-019-0667-0
Quail, D. F., and Joyce, J. A. (2013). Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 19 (11), 1423–1437. doi:10.1038/nm.3394
Sanmamed, M. F., and Chen, L. (2018). A paradigm shift in cancer immunotherapy: from enhancement to normalization. Cell 175 (2), 313–326. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.035
Topalian, S. L., Hodi, F. S., Brahmer, J. R., Gettinger, S. N., Smith, D. C., McDermott, D. F., et al. (2012). Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 366 (26), 2443–2454. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1200690
van Staveren, D. R., and Metzler-Nolte, N. (2004). Bioorganometallic chemistry of ferrocene. Chem. Rev. 104 (12), 5931–5986. doi:10.1021/cr0101510
Vitale, I., Manic, G., Coussens, L. M., Kroemer, G., and Galluzzi, L. (2019). Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. 30 (1), 36–50. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.001
Wang, C., Chen, Q., Chen, M., Guo, S., Hou, P., Zou, Y., et al. (2023). Interaction of glioma-associated microglia/macrophages and anti-PD1 immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 72 (6), 1685–1698. doi:10.1007/s00262-022-03358-3
Wang, Y., Yin, W., Ke, W., Chen, W., He, C., and Ge, Z. (2018). Multifunctional polymeric micelles with amplified Fenton reaction for tumor ablation. Biomacromolecules 19 (6), 1990–1998. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.7b01777
Xu, J., Che, Y., Liu, X., Liu, C., Meng, D., Pang, X., et al. (2022). The regulating effect of CII-3 and its active components from Periplaneta americana on M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Molecules 27 (14), 4416. doi:10.3390/molecules27144416
Xu, J., Xu, L., Wang, C., Yang, R., Zhuang, Q., Han, X., et al. (2017). Near-infrared-triggered photodynamic therapy with multitasking upconversion nanoparticles in combination with checkpoint blockade for immunotherapy of colorectal cancer. Acs Nano 11 (5), 4463–4474. doi:10.1021/acsnano.7b00715
Yahaya, M. A. F., Lila, M. A. M., Ismail, S., Zainol, M., and Afizan, N. A. R. N. M. (2019). Tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) in colon cancer and how to reeducate them. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2019/2368249
Yu, L., Peng, Y., Jiang, L., and Qiu, L. (2023). Sequential diagnosis and treatment for colon cancer via derived iridium and indocyanine green hybrid nanomicelles. Acs Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 15 (29), 34617–34630. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c07742
Zhan, M.-M., Hu, X.-Q., Liu, X.-X., Ruan, B.-F., Xu, J., and Liao, C. (2016). From monoclonal antibodies to small molecules: the development of inhibitors targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. Drug Discov. Today 21 (6), 1027–1036. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.04.011
Zhao, J., Chen, A. X., Gartrell, R. D., Silverman, A. M., Aparicio, L., Chu, T., et al. (2019). Immune and genomic correlates of response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in glioblastoma. Nat. Med. 25(3), 462-469. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0349-y
Zhao, L.-P., Zheng, R.-R., Chen, H.-Q., Liu, L.-S., Zhao, X.-Y., Liu, H.-H., et al. (2020). Self-delivery nanomedicine for O2-economized photodynamic tumor therapy. Nano Lett. 20 (3), 2062–2071. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c00047
Zhou, Z., Song, J., Nie, L., and Chen, X. (2016). Reactive oxygen species generating systems meeting challenges of photodynamic cancer therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45 (23), 6597–6626. doi:10.1039/c6cs00271d
Zhu, D., Ling, R., Chen, H., Lyu, M., Qian, H., Wu, K., et al. (2022). Biomimetic copper single-atom nanozyme system for self-enhanced nanocatalytic tumor therapy. Nano Res. 15 (8), 7320–7328. doi:10.1007/s12274-022-4359-6
Keywords: albumin nanoparticle, tumor-associated macrophage, NIR-II imaging, CDT, immunotherapy
Citation: Yu C, Hu L, Yu Q, Ren Y, Zhang M, Gao L, Lyu S, Wang J, Xiao E, Chen Z, Shang Q and Xu P (2024) In vivo self-assembled albumin nanoparticle elicit antitumor immunity of PD-1 inhibitor by imaging and clearing tumor-associated macrophages. Front. Chem. 12:1469568. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1469568
Received: 24 July 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 03 October 2024.
Edited by:
Lorenzo Gontrani, University of Rome Tor Vergata, ItalyReviewed by:
ZIXIN WANG, Los Alamos National Laboratory (DOE), United StatesDaoming Zhu, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, China
Copyright © 2024 Yu, Hu, Yu, Ren, Zhang, Gao, Lyu, Wang, Xiao, Chen, Shang and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Enhua Xiao, eGlhb2VuaHVhNjRAY3N1LmVkdS5jbg==; Zhu Chen, Y2hlbnpodTQxNUBjc3UuZWR1LmNu; Quanliang Shang, c3FsanNkaEBjc3UuZWR1LmNu; Pengfei Xu, cGVuZ2ZlaXh1Y3N1QG91dGxvb2suY29t
 Cheng Yu
Cheng Yu Linan Hu2
Linan Hu2 Shiyi Lyu
Shiyi Lyu Enhua Xiao
Enhua Xiao Zhu Chen
Zhu Chen Quanliang Shang
Quanliang Shang