
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Chem. , 01 October 2024
Sec. Photocatalysis and Photochemistry
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2024.1448700
This article is part of the Research Topic Novel Materials for Photocatalytic Energy and Environmental Applications View all articles
Titanium carbide (Ti3C2) MXenes due to their structural and optical characteristics rapidly emerged as the preferred material, particularly in catalysis and energy applications. On the other hand, because of its enormous surface/volume ratio and porosity, Metal-organic Frameworks (MOFs) show promise in several areas, including catalysis, delivery, and storage. The potential to increase the applicability of these magic compounds might be achieved by taking advantage of the inherent flexibility in design and synthesis, and optical characteristics of MXenes. Thus, coupling MOF with Ti3C2 MXenes to construct hybrid composites is considered promising in a variety of applications, including energy conversion and storage. This paper presents a systematic discussion of current developments in Ti3C2 MXenes/MOF composites for photocatalytic reduction of CO2, and production of hydrogen through water splitting. Initially, the overview and characteristics of MXenes and MOFs are independently discussed and then a detailed investigation of efficiency enhancement is examined. Different strategies such as engineering aspects, construction of binary and ternary composites and their efficiency enhancement mechanism are deliberated. Finally, different strategies to explore further in various other applications are suggested. Although Ti3C2 MXenes/MOF composites have not yet been thoroughly investigated, they are potential photocatalysts for the production of solar fuel and ought to be looked into further for a range of applications.
The risks associated with climate change and global warming are becoming worse due to the rising emissions of greenhouse gases, such as CO2. Sustainable climate action and renewable energy should complement or replace fossil fuels to reduce this impact (Tahir, 2024). Among the different approaches, the reutilization of greenhouse gas CO2 and its conversion to valuable clean products, such as the production of hydrogen as a clean energy source, is a promising pathway to contribute in minimizing the effect of global warming (Jiang et al., 2023; Jiang et al., 2024). Among the available technologies, photocatalysis is one developing technology that can realize this ambition; it has gained popularity as a green technology since it can potentially use renewable sun energy. To achieve this goal, various semiconductor materials are under exploration, however, they have lower efficiency and are unable to fully utilize solar energy (Zhang et al., 2021; Suman, 2018). Addressing substantial overpotential and sluggish kinetics is imperative to enhance the speed of photocatalytic CO2 reduction and hydrogen production by applying efficient catalysts. While precious metals exhibit high catalytic activity, their prohibitive cost and limited availability hinder their utilization in large-scale photocatalysis technology. Consequently, photocatalysis requires advancing affordable, non-precious metal-based materials with high catalytic activity and product selectivity (Xie et al., 2018; Liu M. et al., 2020; Zong et al., 2021).
Recently, researchers have given more of their attention to the use of two dimensional (2D) materials which composited of transition metal and carbide materials in areas of catalysis, energy storage and conversion. Several reports unveiled the potential advantages of 2D MXenes layered structure to couple with other semiconductors as co-catalysts and found promising to enhance photocatalytic hydrogen generation and CO2 conversion. These materials are considered as a viable alternative to noble-metal catalysts (Qin et al., 2021; Sharma S. K. et al., 2022). Because of their varied chemical composition, MXenes showcase a wide range of intriguing mechanical, electrical, magnetic, and electrochemical characteristics (Han et al., 2019). MXenes due to their 2D layered structure can be combined with several other materials to develop layered configurations which can be beneficial for several applications. Among the MXenes, titanium carbide (Ti3C2) is a promising material due to its numerous benefits such as increasing catalytic activity and stability, ease of preparation and the inclusion of useful functional groups over the surface. However, MXenes alone have lower efficiency due to strong conductive characteristics, therefore, they can be widely explored as cocatalysts with other semiconductor materials. Thus, MXenes-based composites, sparked considerable interest for their substantial potential in numerous applications, particularly in the realm of photocatalytic CO2 reduction and hydrogen generation (Han et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2015).
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have been the subject of an increased investigation for photocatalytic uses in the recent years. Their noteworthy properties, such as their large specific surface area, varied crystalline structures, changeable bandgap, and flexible chemistry and usefulness, are what have sparked this interest (Liu et al., 2022; Lin et al., 2014). However, MOFs’ intrinsic crystalline structure creates structural imperfections such as limited electrical conductivity and electron-hole recombination centres. Ultimately, these limitations limit their efficiency in the process of photocatalysis (Liu S. et al., 2020; Reddy et al., 2020). To overcome the issues, a number of initiatives have been started, including the incorporation of additional semiconductors, naturally occurring nanoparticles, and precious metal nanoparticles into MOFs (Reddy et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2020). When used in conjunction with MOFs, Ti3C2 MXenes are permitted materials. Charge transport efficiency substantially impacts the efficiency in the production of H2 through hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and CO2 reduction to various useful chemicals and products. Thus, to resolve the lower MOF conductivity for the transport of charges, it is necessary to use a highly conductive nature with an ability to trap and transport photoinduced charge carriers. Ti3C2 MXenes exhibit robust electrical conductivity and exceptional stability. Significantly, Ti3C2 MXene’s higher conductivity can enhance charge carrier transport efficiency, enabling precise adjustments to catalytic performance in multicomponent catalyst systems such as MXenes/MOF (Wu et al., 2019; Sharma et al., 2022b). Few studies have explored using MXenes-based metal-organic framework (MOF) composites in photocatalytic CO2 reduction and primarily focusing on photocatalytic water splitting.
Herein, recent advances in titanium carbide (Ti3C2) MXenes and MOF-based composites for photocatalytic CO2 reduction and water splitting to produce hydrogen has been disclosed. Initially, an overview and characteristics of utilizing both materials have been discussed. The latest advancements in utilizing MXenes and MOFs composites such as binary and ternary heterojunction formations for applications such as photocatalytic hydrogen (H2) production, and carbon dioxide (CO2) reduction are demonstrated. The discussion predominantly delves into the characteristics and performance of previously documented nanocomposites and nanohybrids featuring Ti3C2 MXene-based MOFs. Finally, this review outlines existing challenges and potential avenues for future research in Ti3C2 MXene-based MOF composites. Although not much research has been done on Ti3C2-MOF composites, it is obvious that they are potential photocatalysts for the production of solar fuel and that more research should be done on them for a range of uses.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are porous materials characterized by a high specific surface area and a three-dimensional structure. The fundamental units of MOFs are created by joining metal clusters with organic ligands to create a three-dimensional organized network (Karthik et al., 2017). In comparison to other semiconductors, these materials, significantly, have a greater specific surface area due to their increased porosity, which is a result of their geometrically well-defined framework structure (Ren et al., 2024). Although these materials had been acknowledged earlier, significant attention was drawn to MOFs in the late 1990s due to the work reported by Omar Yaghi and his colleagues. They were able to synthesize extraordinarily rigidly synchronized networks with organic linkers and metal ions known as MOF-5 (Li et al., 1999; Li D. et al., 2019). Due to the distinctive and exceptional qualities inherent in MOFs, there has been a notable surge among researchers focused on developing new materials and exploring their applications. MOFs exhibit significant potential across diverse fields, including gas sorption and separation, luminescence, catalysis, proton conductivity, and sensor development. Their extremely configurable features, higher crystallinity, long-lasting porosity, incredibly huge surface area, compelling and extensive permutations, and highly changeable framework topology are all responsible for this (Li D. et al., 2019; Zhou and Kitagawa, 2014; Li et al., 2009; Corma et al., 2010; Cui et al., 2012).
In addition to MOF as a pure material, they can be converted to several metal oxides and porous materials with a larger surface area and abundance of surface-active sites. In the last 10 years, MOF research has drawn a lot of interest from the chemistry and materials science communities. Heterogeneous catalysis was one of the many uses of MOFs that was first investigated in 1994 (Fujita et al., 1994). It continues to capture the attention of researchers owing to its chemical adaptability, custom-designed pore structures, and expansive, easily accessible internal surface areas. There are four primary categories of MOF materials based on their synthesis: 1) Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs), 2) Matériaux de l′Institut Lavoisier (MILs), 3) Universitet I Oslo (UIO), and 4) Isoreticular Metal-Organic Frameworks (IRMOFs) (Zhao et al., 2022). MOFs have metal clusters in the parent MOFs, primarily transitional ones like Ti, Zr, Fe, and Zn. Figures 1A–C shows the recent developments in various MOFs and their structures and uses in various applications (Tahir et al., 2023a).
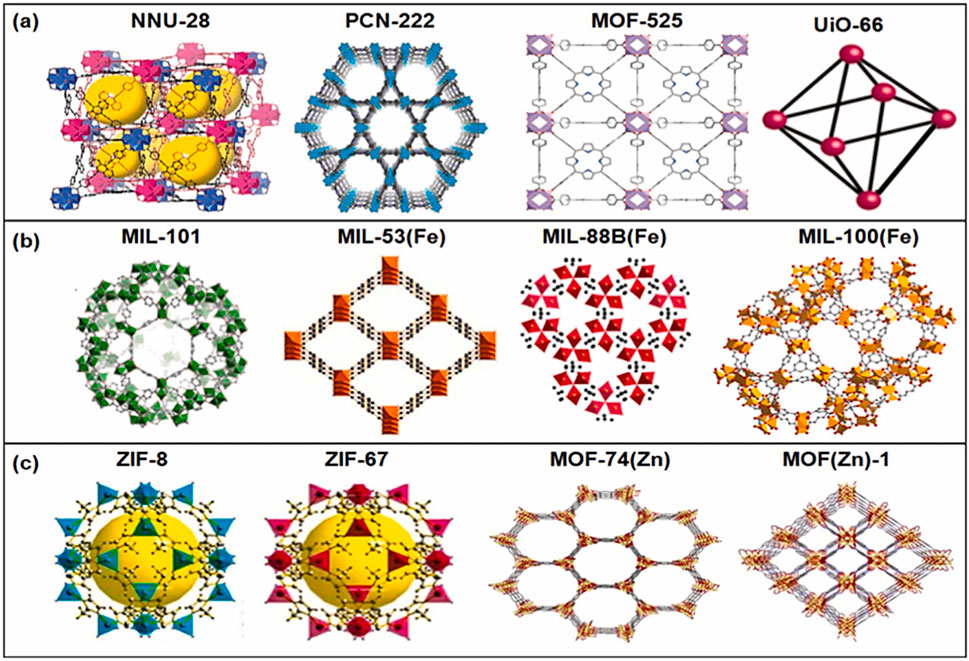
Figure 1. (A–C) Developments of MOFs and their various structures. Reproduced with permission from (Tahir et al., 2023a). Copyright 2023 Elsevier.
MOFs are distinguished from all other solids by their exceptional qualities of high specific surface area and porosity, which are a result of their structural and tunability traits. Because of their strong physical adsorption capabilities, MOFs, a porous material with a large surface area, are thought to be the best adsorbents for gas storage and separation, primarily of CO2 and H2. However, by using analogies with other related MOF structures and the relative dimensions of the ligands, it is possible to anticipate, change, and control the pore shape/size, and dimensions (Li et al., 2011).
MOF structure consists of organic linkers that connect the secondary building blocks to form regularly spaced porous structures, which can be either clusters or metal ions (Jiao et al., 2019). The vast diversity of MOFs arises from the numerous possible combinations of these structural elements. The multifunctionality of MOFs is rooted in their diverse crystalline forms. Secondary building units (SBUs) in MOFs which can either be metals or metal clusters are coupled with organic linkers, primarily carboxylic acids or nitrogen-containing ligands, to form MOFs.
Unlike other porous materials like carbons and zeolites, MOFs possess a unique tunability that sets them apart. The configuration of MOFs is defined by the size, shape, and arrangement of organic linkers relative to the SBUs (Tahir et al., 2021a). Through careful selection of SBUs and connectors, MOFs can be finely adjusted, enabling customization of structure, pore size, shape and functionality to meet required application requirements. Theoretically, MOF morphology/structures can be predicted by considering the organic linker-building components and metals involved. It is worth noting that a database containing over 20,000 recorded MOF forms has recently become available, and further are under exploration (Jiao et al., 2019; Furukawa et al., 2013). MOFs having specific shapes and structures facilitate higher light penetration and reactant attachment. In MOF having active sites can help organic bonds with functional groups such as amine and pyridyl to make it possible to identify particular tiny molecules.
It is possible to add functional groups to SBUs or organic linkers after synthesis that are not suitable for MOF synthesis. The structure and type of MOF and their characteristics such as active sites, surface area and functional groups all depend on the type of metal ions/clusters and organic linkers. MOFs have distinct magnetic, electrical, and optical properties that can be precisely altered to achieve specific objectives. Moreover, MOFs’ pore space can hold a variety of functional hosts with multitasking capabilities. MOFs are resistant to a wide range of species, including organic dyes, nanoparticles, polyoxometalates, single metal atoms, metal complexes, tiny enzymes and polymers (Jiao et al., 2019; Perry Iv et al., 2009; Tranchemontagne et al., 2009; Lu et al., 2014; Deng et al., 2012). The spectrum of possible uses within a single MOF is greatly expanded upon the introduction of a guest species (Jiao et al., 2019). In the past 20 years, numerous novel compounds have been discovered, however, it has been observed that MOFs have poor stability with acid/base, lower thermal stability, and unacceptable mechanical properties. Therefore, ensuring the resilience of MOFs is crucial for many real-world applications. Over the last few years, several initiatives have been launched, resulting in significant progress in addressing this challenge (Burtch et al., 2014; Howarth et al., 2016; Bosch et al., 2014). Numerous MOFs with water stability have been extensively investigated such as the MIL-101 series based on chromium being explored to date (Férey et al., 2005), MAFs (metal isolate frameworks) (Huang et al., 2006), ZIFs (zeolitic imidazolate frameworks) (Park et al., 2006), pyrazole-based MOFs (Colombo et al., 2011), the aluminium-based carboxylates (Loiseau et al., 2004) and the zirconium-based carboxylates (Furukawa et al., 2014; Cavka et al., 2008; Feng et al., 2012). To enhance MOFs’ resistance to water and moisture, recent efforts have concentrated on imparting hydrophobic surfaces or interfaces to them. For example, Nguyen and Cohen employed a medium with extended alkyl groups as an effective approach to safeguard moisture-sensitive MOFs (Nguyen and Cohen, 2010). Due to their super-hydrophobic nature, fluorinated MOFs (FMOFs) were reported to have good water stability (Yang et al., 2011). On the other hand, for gas phase reaction that can occur at high temperatures such as dry reforming of methane, thermal stability is also very important for their practical applications. Controlling thermal stability frequently means to select a suitable and more linkers with each metal node with their stronger connections. The metal ions with higher valence state such as Ti4+, Zr4+, Ln3+, and Al3+ are frequently utilized to produce MOFs with their higher thermal stability. While most MOFs are stable between 350 and 400°C, a few, such as MIL-53 (Loiseau et al., 2004) and UiO-66 (Cavka et al., 2008), are stable over 500°C. Because thermal stability offers a consistent indicator of resistance to other stressors, it is frequently the only type of stability tested for novel MOFs (Jiao et al., 2019).
Most MOFs under explorations are microporous which exhibits an excellent gas adsorption property, particularly for gases like hydrogen and carbon dioxide, with pore diameters typically around 2 nm. Large surface areas and substantial micropore volumes are desirable for many applications, yet such tiny holes cannot support enormous particles or molecular processes. Their limited ability to facilitate rapid mass diffusion and transfer makes them less useful for medication administration, storage, separation, and catalysis (Jiao et al., 2019). For some more contemporary applications, such as drug delivery and catalysis, mesoporous MOFs with their size in the range of 2 to 50 nm are most favoured (Furukawa et al., 2013; Xuan et al., 2012).
Large pore-size MOFs can be created and modified using a variety of efficient techniques. Lengthening ligands is an obvious and practical method to do this (Eddaoudi et al., 2002). The record for the largest pores in MOFs is now held by IR-MOF-74-XI, which has an amazing pore diameter (Feng et al., 2012). The functionalities of MOFs depend on both the pore diameter and the Langmuir and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface areas (Senkovska and Kaskel, 2014). The surface area of NU-110 is the highest of any known material, at 7,140 m2 g−1 (Farha et al., 2012). Based on calculations, the maximum possible surface area of MOFs can be reached to 14,600 m2 g−1 (Farha et al., 2012), however, determining this number experimentally remains challenging (Jiao et al., 2019).
Despite having a relatively high specific surface area, the majority of MOFs that have been described have poorer electrical conductivity. MOF’s low conductivity is caused by its tight charge localization and low electron density, whereas charge carriers are trapped on the lattice sites. The conductivity of MOFs can be enhanced by developing new strategies for their synthesis with mandatory characteristics such as the band transport within their metallic crystal structure. In a recent review paper by Ren and co-authors, the conductive characteristics of various MOFs have been summarized. For example, Cu [Ni(pdt)2] MOF depicted conductivity of 1 × 10−4 S cm−1 and Co-HAB has an electrical conductivity of 1.57 S cm−1. Similarly, many other MOFs have an electrical conductivity of 1.3 × 10−7 S cm−1 for NU-1,000 and 1580 S cm−1 for Cu-BHT. The MOF conductivity can be increased through variety of ways with respect to their synthesis and surface modification (Ren et al., 2021). Additionally, MOFs containing organic linkers may be able to absorb light and become functionalized by adding other groups, such as amino groups. The conductive characteristics of MOFs can also be improved by their contact with highly conductive materials with matched Fermi levels. In this perspective, MOF combined with MXenes and in particular titanium carbide (Ti3C2) MXenes can be beneficial to enhance photocatalytic efficiency. The detailed properties and characteristics of MXenes are discussed in the following sections.
MXenes are a type of 2D transition metal carbide that can be likened to graphene. Mn+1XnTx (n = 1 to 3) is the general MXenes formula, however, M, X and T can be varied depending on the types of MXenes and metals involved. So far, several metals (M) MXenes are used to produce different type of MXenes such as Ti, Sc, V, Zr, Cr, Ta, Mo, Nb, Hf, and Mn. The T in the MXenes represent the surface termination element, which can be oxygen (-O), hydroxyl (-OH), or fluorine (-F) (Hong W. et al., 2020; Gogotsi and Anasori, 2019). The recent discovery of novel 2D transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbon nitrides—referred to as MXenes—has reignited interest in investigating cutting-edge ideas and their possible uses. Surface terminations arise as a result of exposure to the environment, affecting MXenes’ chemically active exterior layer. MXenes can be classified into mono-M, double-M, or solid-solution M elements based on their atomic lattices and composition (Jiang et al., 2020; De et al., 2022).
Figures 2A–D shows different combinations of elements to produce MXenes with their different structures. The crystal structure of MXenes is typically hexagonal closed-packed, but different MXenes exhibit distinct sequences of M atoms. For instance, the face centre cubic sequences of M3X2 and M4X3 are different from the ABABAB pattern of M2X’s hexagonal closed-packed structure (ABCABC). Different MAX ternary carbides and nitrides are utilized in the MXenes class to create a variety of MXenes, such as Ti2C, Ti3CN, Cr2TiC2, MO2C, V2C, Ti3C2, Zr3C2, Ti4N3, and Mo2ScC2 (De et al., 2022; Anasori et al., 2017). Among several MXenes, Ti3C2, which is etched from the hexagonal compressed MAX parent material (Ti3AlC2) by weak Ti–Al bond breaking, is recognized as a hotspot for MXenes-based photocatalysts.
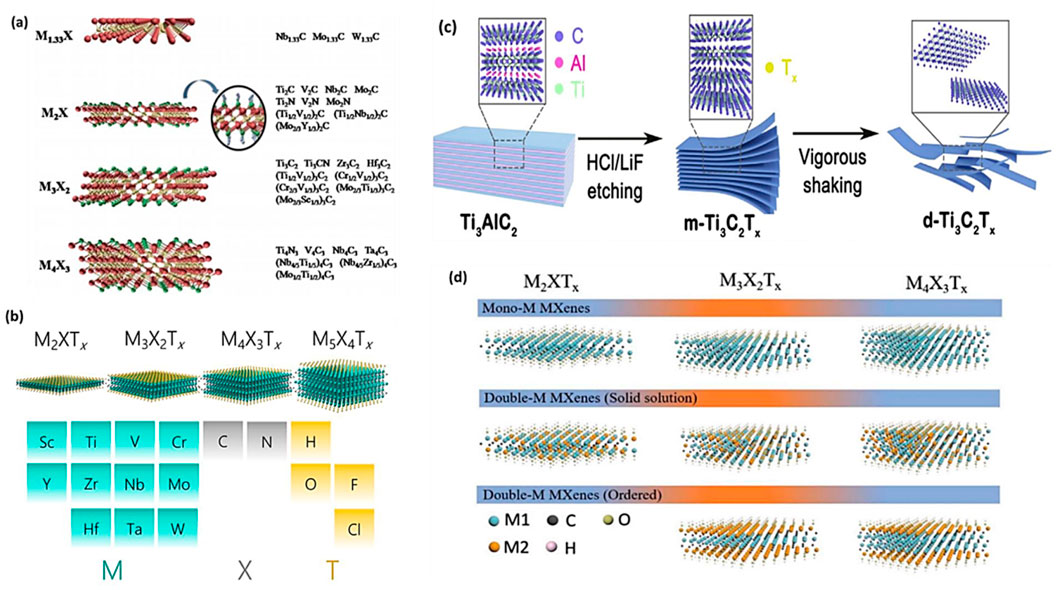
Figure 2. (A,B) Illustration of structural categories of 2D MXenes, (C,D) Structural classification of MXenes. Reproduced with permission from (Tahir et al., 2023b). Copyright 2023 Elsevier.
MXenes are composed of earth-abundant and non-toxic elements, forming 2D substances. Furthermore, when compared to other 2D materials like graphene, MXenes are thought to be superior due to their hydrophilic nature and metal-like electric conductivity. These features are as follows: i) effective metallic hydroxide sites; ii) complex surface chemistry; iii) enhanced electronic conductivity; iv) remarkable chemical durability; v) resistance to corrosion and vi) modifiable optoelectronic properties that can be achieved by varying the particle size, layer spacing, and layer quantity (Sharma et al., 2022b; Liu and Dong, 2021; Lim et al., 2020). In the Mn+1XnTx formula, representing termination count, the robust metallic connections between M and A are disengaged, giving way to less formidable links such as (-O, -F, or -OH, for instance. Three distinct MXenes kinds—M2X, M3X2, and M4X3—appear after etching as presented in Figure 2. They are all composed of the same hexagonal closed-pack crystal structure, where the MX octahedrons are surrounded by X atoms. Transition metal honeycomb lattices arranged in a hexagonal pattern are present on the upper layer of the M2X phase. Regarding the M3X2 and M4X3 phases, they have out-of-plane structures where other atoms occupy the middle region while transition metals are located on the outer layer (Sharma et al., 2022b; Khazaei et al., 2017). The M2X phase consists of three-layer sheets with X (either C or N) positioned between 2 M layers. Within the early transition metal strata is where X is located. In the M2X phase, there are two hollow spaces between the transition metal interlayers, each containing one “X” atom or none at all (Sharma et al., 2022b; Li and Wu, 2019). The M3C2 and M4C3 phases have a face-centred cubic stacking structure. The attributes of MXenes include a strong electrical and thermal conductivity, a programmable band gap, and a high Young modulus. Graphene and most other 2D materials are not like MXenes due to their hydrophilic surfaces and strong metallic conductivities (Alhabeb et al., 2017; Persson et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2018). Ultimately, their properties and performances can be altered by alterations in i) composition, ii) surface functionalization and iii) structure/morphology (Anasori et al., 2017; Halim et al., 2018; Kong et al., 2018; Kayali et al., 2018; Papadopoulou et al., 2020; Ronchi et al., 2019). The different properties of Ti3C2 MXenes are summarized in Figure 3A.
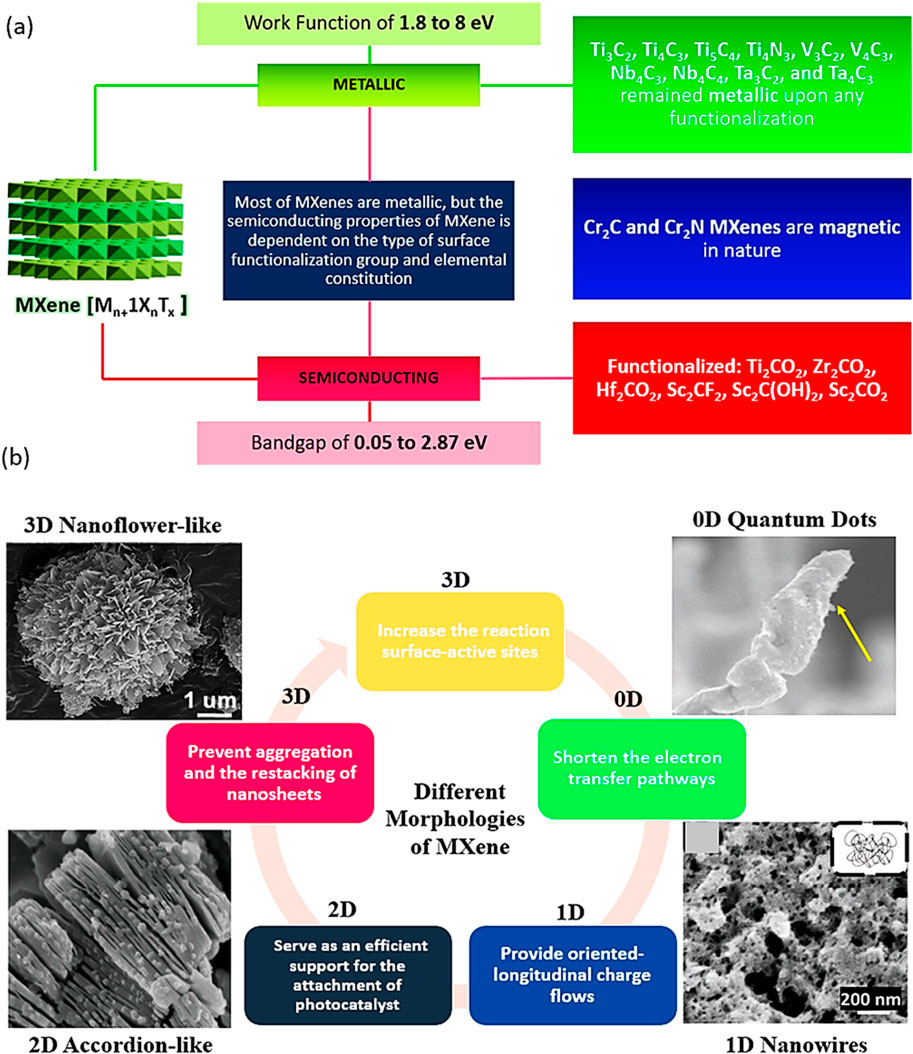
Figure 3. (A) Characteristics of different types of materials, (B) Morphological classification of MXenes.
Jiang et al. (2020) in their work indicated that MXenes, which are not terminated, typically exhibit metallic properties characterized by a substantial density of states (DOS) in the vicinity of the Fermi region. This is explained by an exterior layer made up of metallic transition elements. The p-electrons of the X atoms contribute to energy bands that are situated between −3 and −5 eV below the Fermi surface and d-electrons of the transition metals that surround the Fermi surface mostly affect the DOS (Enyashin and Ivanovskii, 2013; Khazaei et al., 2012). The electrical characteristics of MXenes are said to be more influenced by the outside transition metal layers than by the interior transition metal layers (Ivanovskii and Enyashin, 2013; Anasori et al., 2015; Dong et al., 2017). Hence, surface terminations linked to transition metal atoms in the outer layer possess the capability to notably modify electrical properties, including band structures. One or two electrons from the outer transition metal layers are absorbed by the electronegative termination, reducing the density of states (DOS) below the Fermi surface and creating a new energy band. Both -OH and -F groups exert similar effects on the electrical arrangement of MXenes since they can only accept one electron each. However, an O-group can accept two electrons, resulting in a more significant impact. In MXenes, surface functional groups also influence thermal and electronic transport. For F-terminated MXenes, electronic transmission is excellent, whereas surface functionalization with O atoms significantly diminishes electronic communication (Berdiyorov, 2015).
Until yet, the electrical properties of terminated MXenes have been identified by tests or anticipated theoretically; these properties range from extremely conductive metallic states (Ying et al., 2017; Dillon et al., 2016; Urbankowski et al., 2017) and from semiconducting to highly insulating topological states (Si et al., 2016). Stoichiometry tailoring can modify the energy structure of MXenes, except for surface terminations (Wong et al., 2018), doping (Balcı et al., 2017), an external electric field (Balcı et al., 2018), crystal lattice symmetry (Hong et al., 2016), and stresses (Lee et al., 2014). Over the past few years, MXenes have demonstrated several fascinating optical characteristics. These demonstrate effective photothermal conversion, plasmonic behaviour, and optical transparency (Papadopoulou et al., 2020). The diverse ways in which MXenes interact with light have greatly influenced study. Again, a material’s optical characteristics are largely determined by its surface terminations (Papadopoulou et al., 2020; Chaudhuri et al., 2019). The optical characteristics of MXenes can be adjusted by modifying the intrinsic properties of transition metals (Halim et al., 2019). Ti3C2Tx’s optical non-linearity was claimed to be achieved by using excitation sources at several wavelengths, including 800, 1,064, 1,550, and 1800 nm (Jiang et al., 2018). These compounds are highly suitable for photocatalytic applications because of their functional groups (such as -OH and -O groups) and wide surface area (Jiang et al., 2020; Jeon et al., 2020; Shi et al., 2021).
Since their discovery in 2011, a novel and expanding class of transition-metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides known as MXenes has emerged. MXenes represent a next-generation nanomaterial for investigating sustainable energy resources, particularly in catalysis for energy and environmental technologies, owing to their intriguing electrical and structural properties. Figure 3B illustrates various MXenes topologies, including 0D, 2D, and 3D structures, which have been explored for a range of applications over time.
Zero-dimensional (0D) Ti3C2 quantum dots offer several advantages over their two-dimensional (2D) counterparts. The quantum confinement effect results in a wider band gap, a higher negative Fermi level, an increased number of active edge sites, and enhanced dispersibility for Ti3C2 quantum dots compared to Ti3C2 sheets. Similar to 2D Ti3C2 sheets, Ti3C2 quantum dots can serve as electron acceptors to facilitate carrier migration (Xu et al., 2023).
MXenes are known for having higher electrical conductivities than multi-layered graphene, surpassing other multi-layered materials such as carbon nanotubes and reduced graphene oxide (Bansal et al., 2024). The conductivity of MXenes is dependent on the presence of surface functional groups such as -OH, -F, and -Cl. To enhance electrical conductivity, surface -OH groups can be substituted with -F or -Cl groups. Additionally, conductivity can be boosted by doping MXenes with elements like carbon or nitrogen or by introducing surface imperfections such as vacancies or dislocations. Intercalation serves as another method to increase conductivity. MXenes fabricated with shorter etching intervals and lower HF concentration levels tend to exhibit larger lateral dimensions and fewer defects, resulting in higher electronic conductivities—up to five times higher in larger flake sizes compared to smaller ones. Thermal and/or alkaline treatments effectively enhance the electrical properties of MXenes, leading to conductivity increases by two orders of magnitude. This improvement is dependent on the functional groups, particularly -F and also it changes with the addition or removal of intercalated molecules (Alli et al., 2024).
While MXenes show promise for a variety of applications, their stability presents a significant challenge for long-term use in real-world settings. Atomic-scale flaws and storage conditions lead to rapid oxidation, which alters their microstructure and degrades their electrochemical properties. Additionally, MXenes tend to react with trace amounts of oxygen, even in controlled environments. This instability, which can occur at room temperature or below, means that the preparation and storage methods of MXenes critically influence their final characteristics.
In photocatalytic CO2 reduction applications, the performance of a semiconductor is dependent on the band gap energy, specific surface area, electrical conductivity, light harvesting efficiency and charge transfer ability (Bao et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), because of their excellent CO2 adsorption properties, large surface areas, flexible structures and tunable optical properties, have recently gained attention as promising photocatalysts for CO2 reduction. Since photocatalysis uses solely naturally occurring solar energy as the reaction system energy input, it is a relatively new and sustainable method of inducing catalysis. MOFs can provide a high surface area with a porous structure to maximize the attachment of reactants and also to enable the use of UV and visible light irradiations.
Figure 4 illustrates the four essential phases that make up the photocatalysis pathway. These are the occurrence of a redox reaction, light harvesting, charge excitation, and charge carrier recombination (Sherryna et al., 2021). The photo-responsive materials are initially subjected to light radiation. There are two kinds of charge transfer in MOFs: band-like transport and metal-ligand bond transport. In the case of metal-ligand transport, the interaction between ligand π and metal d-orbital builds a donor-bridge-acceptor path, which in compounds with mixed valence can encourage electron transport. The conductivity can be enhanced by this kind of electron transfer up to a magnitude of 10–102 S cm−1. An electrical conductivity of 1580 S cm-1 at room temperature can be attained by the use of band-like transport (Ren et al., 2021).
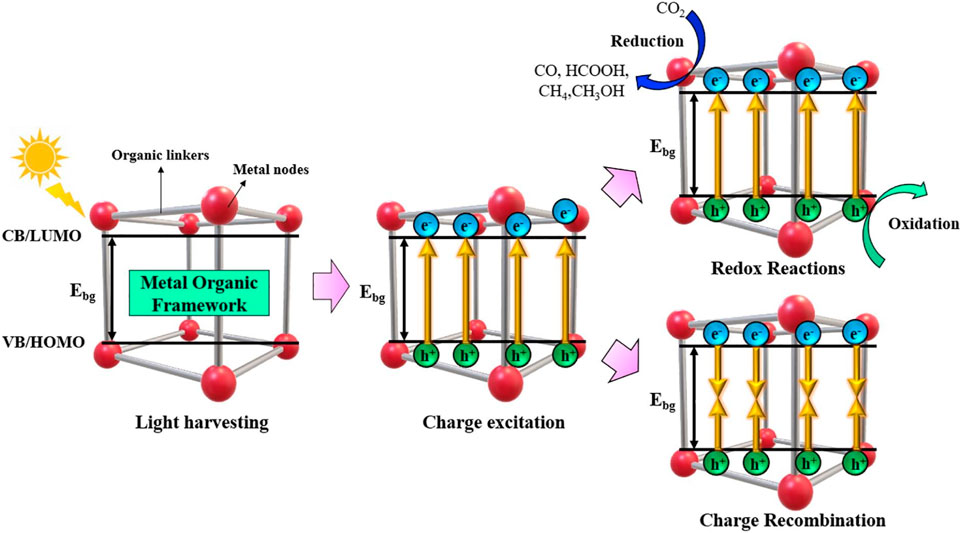
Figure 4. Schematic showing the general process for producing and reducing CO2 through photocatalysis. Reproduced with Permission from (Fan and Tahir, 2022). Copyright 2022 Elsevier.
The mechanism of CO2 reduction to various products is further shown by Equation 1–5 (Bao et al., 2024). The reduction of CO2 to CO2− radical is illustrated in Equation 1, however, this reaction has a high redox potential, thus it is considered unrealistic (Costentin et al., 2013). Furthermore, a photocatalyst cannot provide enough potential to move even one electron to a CO2 molecule (Habisreutinger et al., 2013). Reactions with low redox potentials can occur in a variety of materials (Barton Cole et al., 2010), due to their characteristics as proton-assisted multi-electron reactions. Equation 2–5 illustrate that using photocatalysis, CO2 can be converted to a variety of chemicals and useful products including CO, HCOOH, CH4, CH3OH and others. The quantity of electrons provided to the CO2 molecule determines the product selectivity. For example, it often favours the formation of CO and HCOOH because the process requires just two electrons to start the reaction. However, for the formation of CH3OH and CH4 an additional 6 and 8 protons and electrons, respectively, are needed (Sherryna and Tahir, 2022a; Huang et al., 2019).
In photocatalysis, after light harvesting is successful, electrons are stimulated to a high enough energy to cross the Ebg and move from the highest occupied molecular orbital (VB) (HOMO) to the valence band (VB), also known as the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). Alternatively, the holes created by the photons are subsequently retained in the VB or HOMO (Fan and Tahir, 2022). After the electron/hole pairs are created during the charge excitation step, two things can happen: either the charge carriers recombine unfavourably, resulting in energy loss, or the electron/hole pairs are employed favourably for redox reactions. The CO2 reduction occurs over CB or LUMO with the involvement of photogenerated electrons and protons to convert it into various products (Tahir et al.). Recombination can take place in two different ways: either on the surface of the material, where an electron/hole has the potential to recombine or they can even recombine in the bulk (Khan and Tahir, 2019).
MOFs have a higher surface area which enables to provide more active sites for the attachment of reactants. In photocatalytic applications, higher visible light absorbance and superior separation of photoinduced charge carriers are essential to maximize photocatalytic efficiency. The light absorbance of MOFs from the UV to visible can be obtained by changing the colour. These materials, however, have poor electrical conductivity, and become a major obstacle in photocatalytic applications (Ren et al., 2021). Hence, it is crucial to prevent recombination by employing various techniques such as sensitizing using cocatalysts and heterojunction formation. These methods can trap electrons and induce spatial separation, thereby prolonging the lifespan of photo-generated electron/hole pairs.
In the photocatalytic CO2 reduction process over the MOF and other semiconductor materials, one of the biggest challenges is the lower efficiency and product selectivity. Pure MOFs exhibit photocatalytic activity for the generation of solar fuel but with lower efficiency (Li N. et al., 2019; Liao et al., 2018) and the rapid recombination of charge carriers is the reason for lower productivity. Ti3C2 MXenes are thus employed to regulate the photoactivity of MOF. Ti3C2 MXenes can function as co-catalysts to establish Schottky junctions with other photo-active materials to efficiently capture photogenerated electrons because of their metallic characteristics. It has been suggested to combine MOF with more conductive materials and create binary composites in order to overcome the barrier causing low photocatalytic activity and efficiency.
Numerous investigations on 2D layered Ti3C2 MXenes and their composites such as Ti2C3/MOF and their application in photocatalytic solar fuels production have been carried out in the past few years (Li et al., 2022). MOF composites based on Ti3C2 MXene offer some beneficial synergies. First off, MXenes can be hosted by MOFs, which have a high porosity and surface area and can stop MXenes layers from aggregating and restacking. Because of the synergistic effects between the functions of MOFs and the surface terminal groups of MXenes, the composite is also able to demonstrate increased stability (Najam et al., 2022). Furthermore, the MXenes and MOF create an intrinsic electric field which is associated to Schottky junction, which facilitates the effective separation, quick mobility, and transfer of charge carriers (Yu et al., 2021). Ti3C2 MXenes-based MOF heterojunctions can serve as appealing photocatalysts for water-splitting-based H2 production and CO2 reduction. Nevertheless, the composite for the manufacture of solar fuel has been the subject of very few studies.
The use of binary Ti3C2 composite with Co-Co LDH nanosheets produced from MOF for CO2 reduction with the involvement of [Ru (bpy)3]Cl2 sensitizer under visible light is shown in Figure 5A. Ultrasonic exfoliation was used to produce Ti3C2Tx nanosheets after the bulk Ti3AlC2 MAX was etched to remove the Al layers (TNS). Next, ZIF-67 was grown in situ on the Ti3C2Tx nanosheets. After ZIF-67 was successfully loaded, the nanocomposite underwent solvothermal treatment to produce Co-Co LDH/TNS nanosheets. No CO2 reduction activity was observed by photocatalytic in pristine Ti3C2Tx nanosheets. However, as Figures 5B–D illustrates, there was a noticeable increase in the rate of CO generation over MOF-derived Co-Co LDH during the CO2 reduction process. As shown in Figure 5E, the nanocomposite also demonstrated outstanding stability, retaining strong photocatalytic activity for up to five cycles. Figure 5F shows the Co-Co LDH/TNS heterojunction to maximize the charge separation efficiency and light absorbance ability of the composite using a photosensitizer. The photosensitizer is activated by visible light irradiation, however, TEOA works as a hole scavenger and electron donors are used to generate the reduced state [Ru (bpy)3]Cl2. After that, the electrons are transferred to the nanocomposite, where they quickly move to the co-active sites to reduce CO2 to CO (Chen et al., 2020).
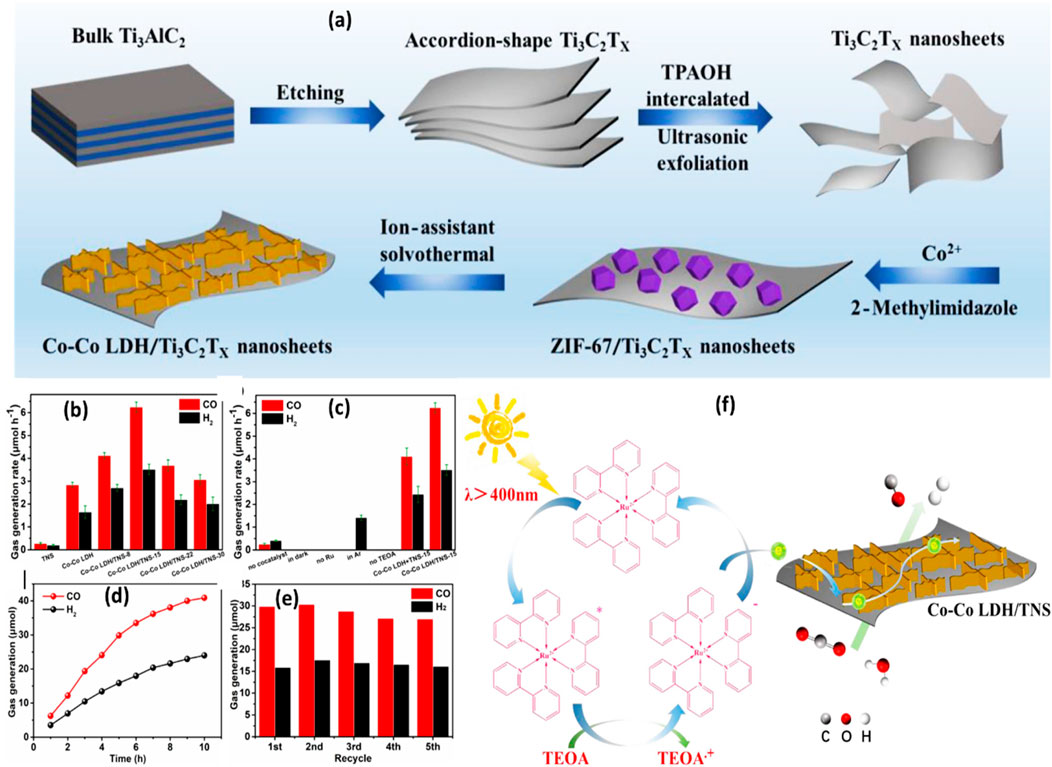
Figure 5. (A) A schematic diagram illustrating the process of creating Co-Co LDH/Ti3C2Tx nanosheets using MOF; (B–E) photocatalytic activity and stability for the CO2 reduction process over Co-Co LDH/Ti3C2T; (F) The mechanism of CO2 reduction over the nanocomposite using TEOA as a sacrificial agent and [Ru (bpy)3]Cl2 photosensitizer. Reproduced with permission from (Chen et al., 2020). Copyright 2020 Elsevier.
The Ti3C3 MXenes were further investigated with other Fe-based MOFs. Because of their outstanding CO2 adsorption capabilities, wide surface areas, high porosities, tuneable optical properties, and flexible architectures, Fe-MOF has recently shown great promise as a photocatalyst for CO2 reduction. However, due to their rapid carrier recombination and limited charge transport efficiency, pure Fe-MOF exhibits comparatively low photocatalytic activity. In recent work, Ti3C2 QDs coupled with NH2-MIL (101) were examined for photocatalytic CO2 reduction applications (Xu et al., 2023). As seen in Figure 6A, a straightforward electrostatic adsorption method was used to create the T3C2 QDs on the surface of 3D octahedral NH2-MIL-101(Fe). By hydrothermally reacting Ti3C2 in an N2 environment and ultrasonic stripping, Ti3C2 quantum dots of size of 4–5 nm were produced. Because of the -NH2 groups, NH2-MIL-101(Fe) has a wide light absorption range from UV to visible light. The hybrid NH2-MIL-101(Fe)/Ti3C2 QD samples exhibit higher light absorption than the NH2-MIL101(Fe), and the absorption intensity increases as the Ti3C2 content increases. For NH2-MIL-101(Fe), NMTQ0.5, NMTQ0.75, and NMTQ1.0, the corresponding band gap energy values are 2.45, 2.41, 2.29, and 2.15 eV, were reported. The decrease in charge recombination rate was also observed with QDs loading to Fe-MOF.
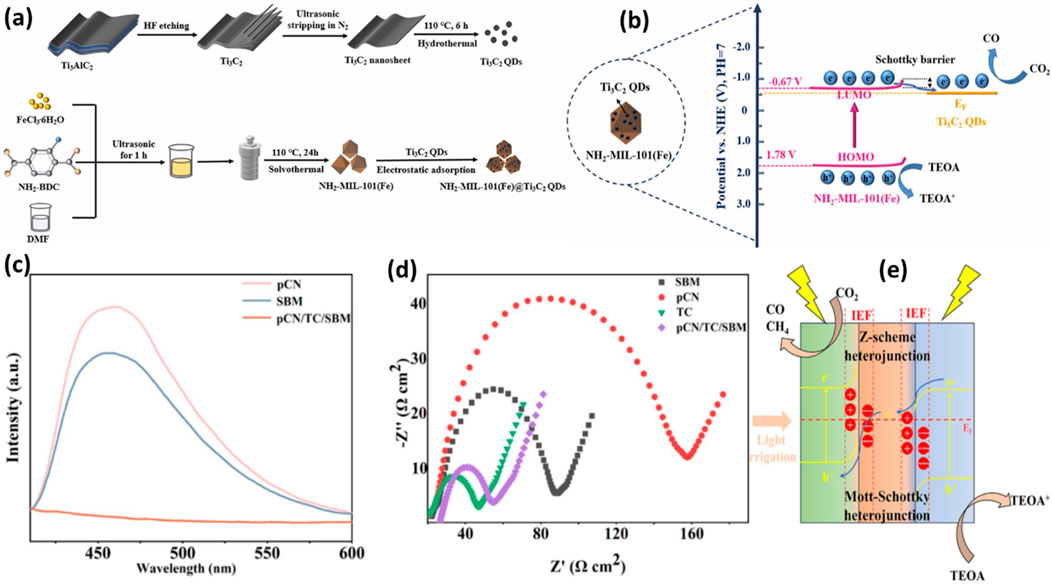
Figure 6. (A) Schematic for the synthesis of Ti3C2 QDs assisted NH2-MIL-101 composite, (B) Schematic illustration of charge separation over Ti3C2 QDs/NH2-MIL-101 composite. Reproduced with Permission from (Xu et al., 2023). Copyright 2023 Elsevier; (C,D) PL and EIS spectra of pCN, SBM, pCN/TC/SBM samples, (E) The photocatalytic mechanism of the pCN/TC/SBM. Reproduced with Permission from (Song et al., 2024). Copyright 2024 Elsevier.
As discussed previously, Ti3C2 QDs have the potential to increase visible light and charge separation efficiency, which was beneficial to increasing CO2 reduction efficiency to maximize CO formation during the photocatalysis process. Due to good interface interaction, this binary composite was stable enough to produce CO for consecutive five cycles. Effective charge separation and band modification were responsible for the remarkable CO2 photoreduction activity of NH2-MIL-101(Fe)/Ti3C2 QDs, as shown in Figure 6B. Under visible light, NH2-MIL-101 (Fe) produces electrons and holes and due to good interface contact photoexcited electrons migrated to Ti3C2 QDs because of the low Fermi energy level and excellent charge transfer efficiency. The formation of the Schottky barrier prevents electrons from backflowing and recombining with holes, resulting in significantly increased CO2 photoreduction efficiency.
In a recent development, a trimetallic Sn/Ti3C2-supported Bi-MOF was tested for the conversion of CO2, and the potential products are discussed in Figure 6 (Song et al., 2024). First, Ti3C2 MXene was prepared by passing LiF-HCl through Ti3AlC2 MAX and etching it for 48 h at 60°C. The g-C3N4-Sn-Bi-MOF exhibited a good interaction, achieved using a straightforward electrostatic self-assembly process.
The photochemical characteristics of the produced catalysts were investigated using UV-visible spectroscopy. The absorption band limits for pCN/SBM and pCN/TC/SBM are observed at wavelengths of 492 nm and 493 nm, respectively. Additionally, TC shows no discernible absorption edge, indicating its nature as a pure electrical conductor without light absorption. The composite photocatalysts, as shown in Figure 6C, exhibit reduced photoluminescence (PL) intensity, suggesting a low recombination rate of photogenerated electron-hole pairs in pCN/TC/SBM. Furthermore, in Figure 6D, TC displays the shortest semicircle in the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) plot due to its exceptional conductivity. The conductivity of pCN/TC/SBM is intermediate between that of pCN/SBM and TC. The CO yield significantly increases to 36.33 μmol⋅g−1⋅h−1, which is 4.36 times greater than that of pCN and 3.5 times higher than SBM, when the heterojunction is formed. The pCN/TC/SBM was very selective to produce CO and reached to 95.49 percent. In situ infrared spectroscopy can be employed to investigate the root cause.
Figure 6E illustrates the reaction mechanism, providing clarity on the reduction process. Photogenerated electrons over pCN under light irradiation migrate to TC until equilibrium is reached. As a result of the space charge generated on the pCN side, the band bends downward to form a Schottky junction. The photogenerated electrons from pCN are captured and prevented from recombining due to TC’s high conductivity, enhancing space charge separation and accelerating electron transport. The integration of the heterojunction with the Schottky junction enables efficient separation of space charges and much faster electron transit.
Table 1 summarises various types of Ti3C2 MXene/MOF composites used for various CO2 reduction and H2 production reactions. More research has been conducted for hydrogen production, however, only limited data was available for CO2 reduction applications. It can be seen that CO2 reduction to CO was significantly enhanced with Ti3C2 MXene coupling with MOF-derived materials. Similarly, for water splitting, the production of hydrogen was significantly enhanced in Ti3C2 MXenes-based MOF composites.
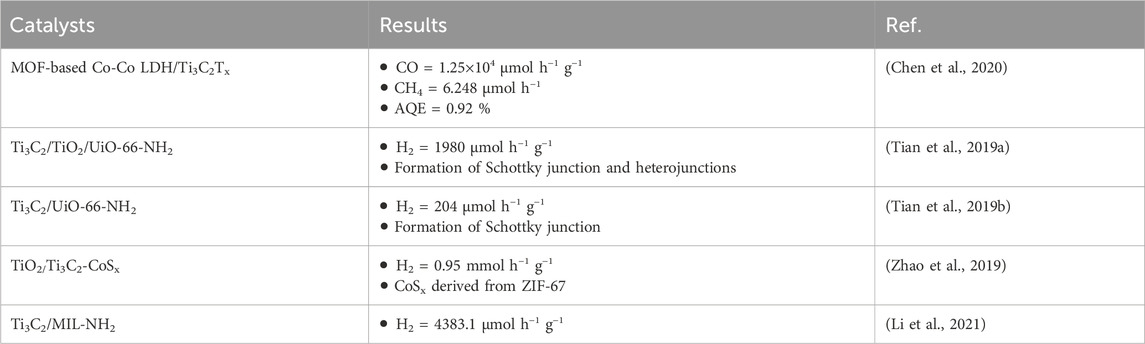
Table 1. An overview of Ti3C2 MXenes-based MOF photocatalyst for producing H2 and reducing CO2 is given.
A low-carbon economy and the accomplishment of sustainable development objectives depend heavily on hydrogen as a clean and sustainable energy source. While there are other sustainable methods for producing hydrogen, two of the more common ones are electrocatalytic and photocatalytic water splitting (Zhang et al., 2024). Despite being environmentally benign and emitting no CO2, photocatalytic hydrogen production has a lower photocatalytic efficiency because light and catalysts are required. In photocatalytic hydrogen production, the hydrogen yield depends on three factors: the band position of the semiconductor, the band gap energy, and the efficiency of charge separation. Ti3C2 MXenes-based photocatalysts have been widely utilized in photocatalytic H2 production due to their remarkable properties. Figure 7A presents a schematic of hydrogen production over Ti3C2 MXenes with a semiconductor.
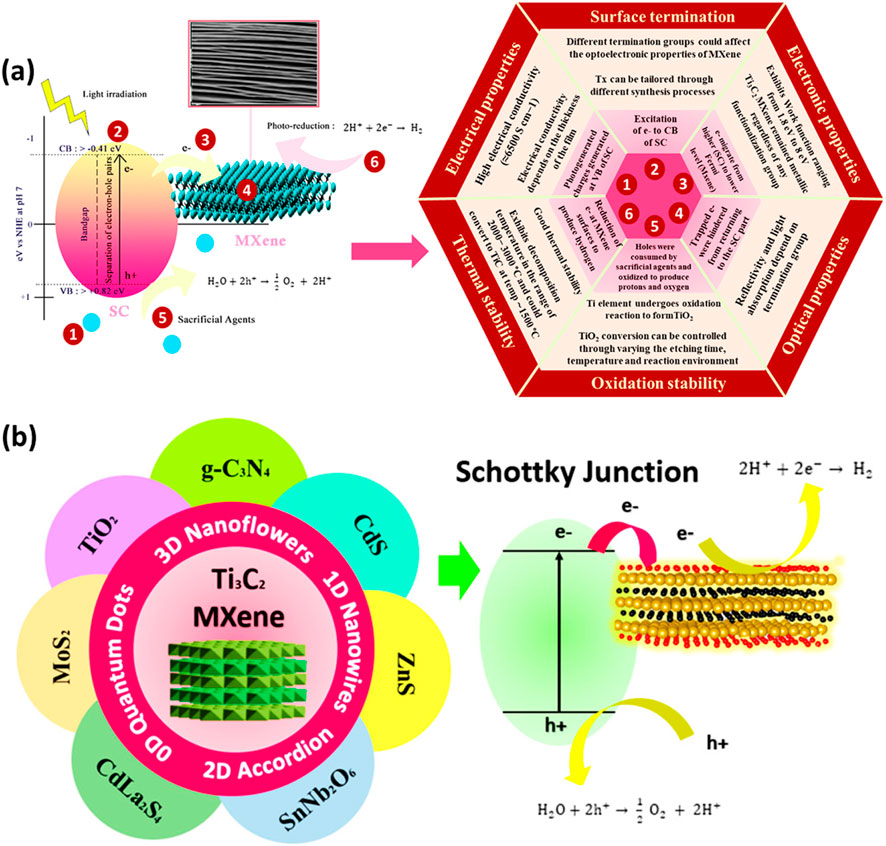
Figure 7. (A) Mechanism of H2 production over MXenes/semiconductor composites, (B) Ti3C2 MXenes coupled with different semiconductors and the process of charge separation. Reproduced with permission from (Sherryna and Tahir, 2021). Copyright 2021 Elsevier.
In photocatalysis, four steps are involved to complete the process which includes charge production under the light energy, charge separation within the bulk, oxidation and reduction reactions over the catalyst surface. In the first step, when the light energy which have enough power strikes the catalyst surface, it enables to generates electrons and holes. The number of charges depends on the band gap of the photocatalysts, light intensity and wavelength. During the excitations, charges (e−/h+) are produced at the valance band (VB) of the semiconductor and then electrons are moved to the conduction band (CB), which enables their separation. If the charges are successful to separate from the bulk surface to outer surface without recombination, then oxidation and reduction reactions occurs. In general, oxidation occur at VB position with the use of holes to produce protons and oxygen. However, production of hydrogen occurs at the CB position through the reduction of protons with electrons (Alfaifi et al., 2018; Shkrob and Sauer, 2004; Maeda, 2011; Jalil et al., 2021; Linsebigler et al., 1995).
The process of producing H2 through photocatalytic water-splitting involves two crucial stages. Equation 6 shows the oxidation process, whereas in the first stage oxidize water molecules to produce two protons and oxygen. Equation 7 describes the reduction process, in which protons and electrons are used to produce hydrogen.
The Ti3C2 MXenes have several attractive characteristics such as thermal stability, electrical conductivity, surface terminal groups, optical characteristics and others, which are beneficial to be coupled with any semiconductor to maximize photocatalytic efficiency. The charge transfer mechanism in the MXenes-based composite is accomplished by the semiconductors and metallic MXenes’ different work functions. Figure 7B illustrates the basic mechanism of water splitting through photocatalysis under light irradiation over various type of semiconductors. Typically, a Schottky junction forms when Ti3C2 is used as a cocatalyst with a semiconductor, aiding the separation of electron-hole pairs. When MXenes and the semiconductor are in close contact, a Schottky barrier is created, leading to strong interfacial charges at the metal-semiconductor interfaces. Upon light exposure, the semiconductor generates photogenerated charges. Excited electrons move to the semiconductor’s conduction band (CB), leaving photogenerated holes in the valence band (VB). MXenes, acting as electron acceptors, generally possess a larger work function and a lower Fermi level than the semiconductor. Electrons will transfer from the semiconductor with the higher Fermi level to the MXene until the Fermi levels align (Sherryna and Tahir, 2021).
To enhance photocatalytic efficiency, MXenes work as cocatalysts with other semiconductors to create binary composites and heterojunctions. The electrical mobility of Ti3C2 MXene has sparked considerable attention in photocatalysis, primarily owing to its ability to facilitate adequate carrier segregation. In this development, Ti3C2 MXenes are frequently employed as catalysts in photocatalytic water splitting, which yields H2 higher hydrogen compared to pure semiconductor materials (Jacobs et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2019). Numerous research findings indicate that Ti3C2 is a highly effective co-catalyst in photocatalysis, enhancing the activity of semiconductors (Jacobs et al., 2011; Ibragimova et al., 2021). Because of the functional groups–O, and–F, –OH over the surface of Ti3C2, electrostatic adsorption is frequently used to modify semiconductors. The organic ligand of the MOF can more easily coordinate with metals because of its structure Hence, there is a high probability that the organic ligand in MOFs will form a bond with titanium in Ti3C2, resulting in a distinct interaction mechanism. This could have an impact on MOFs’ photocatalytic efficiency when combined with Ti3C2 (Liu et al., 2019; Ibragimova et al., 2021; Im et al., 2021).
Previously, synthesis and characterization of NH2-MIL-88 and MXenes/MOF composites were conducted and observed increased photocatalytic properties (Long et al., 2021). Ti3C2 MXene was synthesized using HF as the etching agent, while NH2 -MIL-88 MOF was produced via a hydrothermal method. Compared to pure MOF, the binary composite of the two materials exhibited higher light absorbance. NH2-MIL-88B shows light absorbance over the full spectrum ranging from 200 to 700 nm, effectively capturing both visible and UV light. The significant absorption in the UV range is due to the π-π* transition in the organic linker. When MXene is added to the composite, the light absorption rate increases above 667 nm. When more MXene is added, light absorption first rises but eventually falls. This is probably because too much MXene causes NH2-MIL-88B to take on an unpredictable shape and size. When compared to the original material, 0.25-MXene/NH2-MIL-88B band gap was reduced which exhibits notable light absorbance ability. In addition to this, charge separation efficiency was also increased using composites. The creation of a heterojunction can enhance the photocatalyst’s activity by promoting the separation of photo-generated electron-hole pairs. The PL spectrum intensity of the composite material 0.25-MXene/NH2-MIL-88B lies between those of its constituent parts, indicating that the inclusion of MXenes may promote NH2-MIL-88B electrons and holes separation to maximize the photocatalytic efficiency.
Using Ti3C2-based MOF binary composites for photocatalytic hydrogen production is recently attained significant considerations. In recent work, Li and co-workers produced a Ti3C2-loaded MIL-NH2 composite and tested it for photocatalytic hydrogen production (Li et al., 2021). A schematic representation of the synthesis of Ti3C2 MXenes via HF etching of Ti3AlC2 and the subsequent production of the Ti3C2/MIL-NH2 composite is shown in Figure 8A. The Ti3C2 MXenes were produced using an HF etching agent, while the reaction was conducted for 72 h to get a 2D layered structure of Ti3C2 MXenes. The composite of Ti3C2/NH2-MIL was synthesized using the in-situ approach, by heating at 120°C for 84 h Ti3C2 exhibits an accordion-like layered MXenes configuration. Figure 8B shows the results of the composites in which both materials have good interface contact. The absorbance edge of the MIL-NH2 was 600 nm, which was increased to 800 nm when Ti3C2 was coupled with MIL-NH2. Furthermore, a band gap of 2.6 eV and a CB position of −0.76 eV were reported, which are beneficial to maximize the visible light absorbance and efficient hydrogen production. In addition to this, Ti3C2/NH2-MIL shows higher current density than using pure NH2-MIL under dark and solar light irradiation. These findings were further confirmed by EIS, in which a lower recombination process of photo-generated carriers was obtained with Ti3C2-MXene-loaded NH2-MIL.
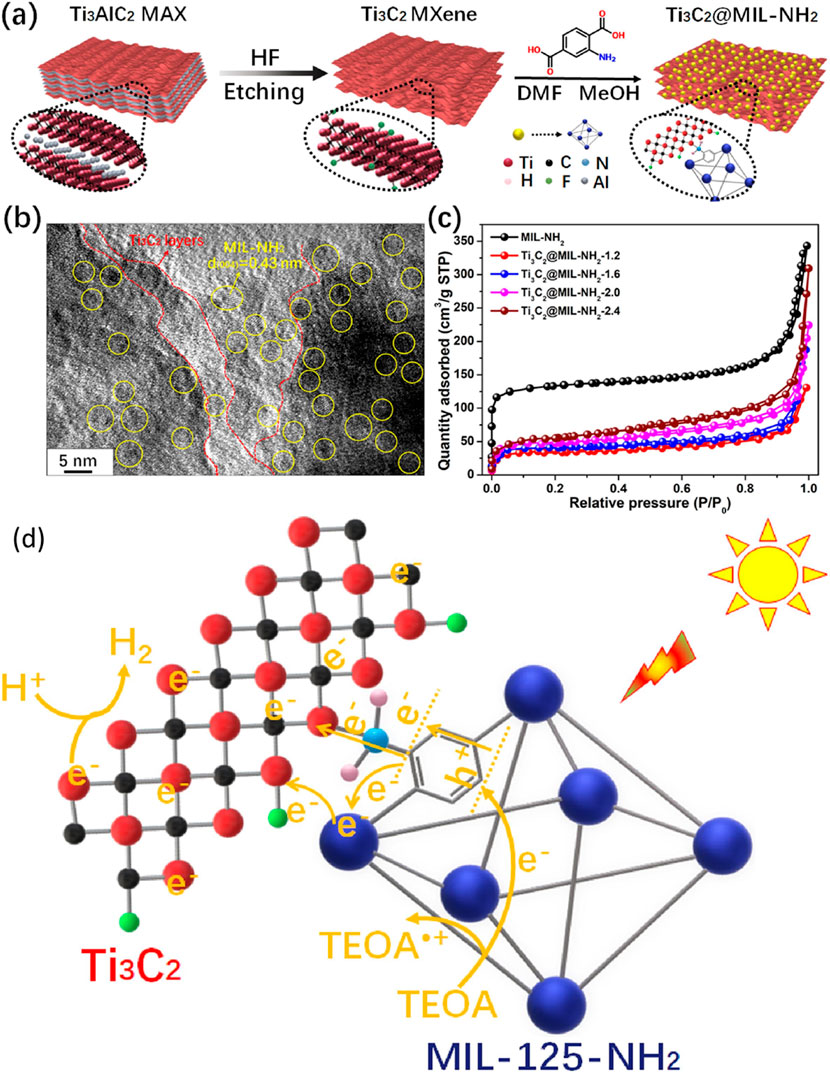
Figure 8. (A) Schematic illustration of Ti3C2/NH2-MIL-125 composite formation, (B) TEM images of the composites, (C) N2 adsorption-desorption analysis of Ti3C2/NH2-MIL-125 composite, (D) proposed mechanism of efficiency enhancement over Ti3C2/NH2-MIL-125 composite. Reproduced with permission from (Li et al., 2021). Copyright 2021 Elsevier.
The N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms were further used to understand the surface properties and the results are shown in Figure 8C. The BET surface area was decreased with Ti3C2-loaded NH2-MIL samples, which confirmed that it is not important in photocatalytic applications. Enhancing carrier segregation and transfer efficiency is well recognized to always be advantageous for photocatalytic process activation (Li et al., 2021). In simulated sunlight, the hybrid Ti3C2/MIL-NH2 significantly enhances H2 generation. On the other hand, the Ti3C2-loaded MIL-NH2 hybrids show significantly increased activity which was due to prevented charge carrier recombination and higher visible light absorbance. The highest hydrogen yield of 4383.1 μmol h−1g−1 was reported with the optimized Ti3C2/MIL-NH2-1.6 composite. This productivity was about five times higher than a physical combination of MIL-NH2 and Ti3C2 samples, and it was six times higher than that of MIL-NH2. More intriguing results included the discovery of an apparent quantum efficiency of 3.140 percent for Ti3C2-MIL-NH2-1.6 composite. Nonetheless, after consecutive four cycles, the H2 generation rate over Ti3C2-MIL-NH2-1.6 did not substantially drop, indicating good photostability of the Ti3C2-supported MOF composite. Figure 8D shows the efficiency enhancement approach over the Ti3C2/MIL-NH2 under visible light irradiation. The charges were produced over the NH2-MIL under visible light and were trapped by the Ti3C2 MXenes, which resulted in efficient charge carrier separation and improved hydrogen production. By using terephthalic acid and replacing MIL-125-NH2 with MIL-125, Ti and N’s cooperation can operate. When compared to Ti3C2/MIL-NH2, the resulting Ti3C2/MIL shows significantly reduced activity, according to the photocatalytic H2 generation rate.
These results can be further explained based on the various MXenes characteristics. Ti3C2 MXenes due to 2D structure can improve the interaction between water molecules and the photocatalyst and have a high hydrophilicity (Sharma et al., 2022c). For example, Tian et al. altered Ti3C2 nanosheets for an effective photocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction by adding a porous, water-stable Zr-based UiO-66-NH2 (HER). Compared to pure UiO-66-NH2 and the Ti3C2, the composite of UiO-66-NH2/TiC3C2 displayed a lower PL intensity, suggesting a decreased recombination rate. The results showed that just 25.6 μmol h−1 g−1 of H2 was evolved using pristine UiO-66-NH2 MOF. Furthermore, Ti3C2 nanosheets produced 204 µmol H2 h−1 g−1 of hydrogen, eight times the photocatalytic activity of the composite (TU10). The formation of a Schottky connection between Ti3C2 and UiO-66-NH2 was responsible for efficient charge carrier separation and increased lifetime of the electrons. Due to its extremely positive Fermi level and low Gibbs free energy, the O-terminated Ti3C2 can capture electrons from the MOF for the generation of H2. This is the major reason for the efficient migration and separation of charge carriers (Tian et al., 2019b).
In summary, binary Ti3C2-supported MOF composites are beneficial to maximize the charge carrier separation and higher visible light absorbance, which are beneficial to stimulate photocatalytic hydrogen production.
The performance of the binary composite can be further enhanced by adding third materials to construct a ternary composite, which can exhibit excellent photocatalytic performance due to their elevated Fermi levels, outstanding conductivity, and efficient carrier transport properties (Tian et al., 2019b; You et al., 2021). Heterostructures can be formed using MXenes and semiconductor combinations, establishing a Schottky junction at the material interface. The addition of third materials with the binary junction has the potential to enhance the migration of photo-generated electrons (Hong L.-f. et al., 2020). Enhancing the effective facilitation of charge-carrier transport often requires the strategic optimisation of interfacial architecture. This involves meticulous component selection and minimising imperfections at the interface. The combination of Ti3C2 MXenes, known for their outstanding conductivity, with porous MOFs featuring fully utilized photoactive sites is anticipated to accelerate the migration of photo-generated electrons. This augmentation is poised to enhance the efficiency of extended photocatalytic hydrogen generation (Tian et al., 2019b; You et al., 2021; Hong L.-f. et al., 2020).
There are only limited reports available on the use of ternary composite to maximize the photocatalytic hydrogen production efficiency. In recent work, Tian et al. (Tian et al., 2018) thoroughly analysed Ti3C2/TiO2/UiO-66-NH2 for its potential in photocatalytic hydrogen generation. As a typical Metal-Organic Framework (MOF), the photo-responsive photocatalyst UiO-66-NH2 was studied with Ti3C2Tx to promote interfacial charge transfer. In this process, TiO2 layers, or TCA, were initially created by annealing the Ti3C2Tx MXenes. The one-step hydrothermal method employed to electrostatically adsorb UiO-66-NH2 onto the annealed Ti3C2Tx surfaces is illustrated in Figure 9A. Compared to Ti3C2Tx and UiO-66-NH2, the Ti3C2-based TiO2/UiO-66-NH2 composite exhibited superior photocatalytic activity for H2 production. TCA served as a platform and stored charge carriers, prolonging the lifetime of co-catalysts and UiO-66-NH2. Interestingly, after HF etching, Ti3C2Tx exhibited accordion-like structures, indicating the successful removal of the Al layers in Ti3AlC2. Despite its low concentration, TCA displayed a layered structure similar to pure Ti3C2Tx without noticeable TiO2. Ti3C2Tx was tightly wrapped in UiO-66-NH2, resulting in significant agglomeration. In contrast, Ti3C2-assisted TiO2 and UiO-66-NH2 composite showed higher charge separation with enhanced accessibility to reactive sites.
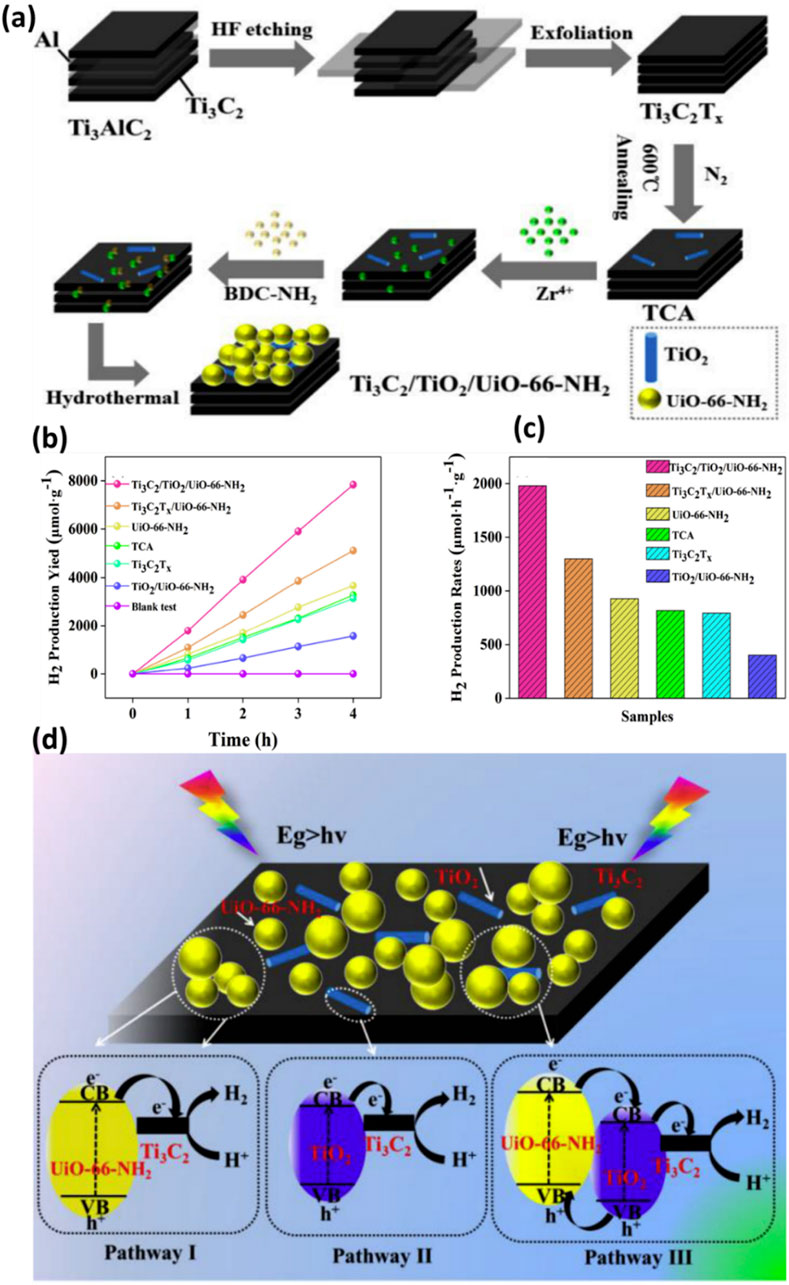
Figure 9. (A) A suggested chemical process is schematically depicted for the synthesis of Ti3C2-TiO2-UiO-66-NH2, (B,C) Performance analysis of pure and Ti3C2-TiO2-UiO-66-NH2 composite materials, (D) Proposed mechanism of photocatalytic charge separation and efficiency enhancement. Reproduced with permission from (Tian et al., 2018). Copyright 2018 Elsevier.
Photocatalytic H2 generation was conducted under artificial sunlight and the results are shown in Figures 9B,C. Ti3C2/TiO2/UiO-66-NH2 outperforms other combinations with the maximum hydrogen yield (7,840 μmol g−1). This is because of its synergistic effect and increased light-collecting ability. A H2 yield of 1980 μmol h−1 g−1 was obtained by adding TCA to the H2 evolution rates. This is 1.5 times higher than Ti3C2Tx-UiO-66-NH2 and 2.1 times higher than pure UiO-66-NH2, respectively. The stability test, which lasted 12 h and revealed a modest decrease in HER activity after three cycles, proved the Ti3C2-TiO2-UiO-66-NH2 structure’s longevity. Like this, TiO2 layers were originally produced by annealing Ti3C2 MXenes in the N2 environment. Ti3C2-TiO2-UiO-66-NH2 was the composite that was produced after UiO-66-NH2 was applied to the surface of Ti3C2Tx layers. Compared to its Ti3C2-UiO-66-NH2 cousin, the photocatalytic output was boosted 1.5 times by annealing Ti3C2 to create TiO2. This is because the Mott-Schottky plots showed a negative shift due to the production of TiO2, which clarified stronger reducibility and an increased electron/hole pair separation. The first and second paths, as shown in Figure 9D, traverse the Schottky junction between Ti3C2 nanosheets containing TiO2 and UiO-66-NH2, respectively. Type II heterojunction formation among TiO2 and UiO-66-NH2 is the third process involves, in which electron transfer from the CB of TiO2 to Ti3C2 MXenes (Tian et al., 2019a). Interestingly, Li et al. (Li et al., 2021) managed to successfully synthesized Ti/TiC MXenes with MIL-NH2 through in-situ growth, resulting in the formation of a Ti3C2/MIL-NH2 composite. When comparing the in-situ grown Ti3C2/MIL-NH2 to the usual physical mixing with MIL-NH2, the H2 generation rate was five times higher. This is a result of the Ti3C2 and MIL-NH2 coming into close contact. Furthermore, Ti3C2/MIL-NH2 showed exceptional stability; even after four cycles, there was hardly any decrease in the rate of H2 generation. The promising results were due to the presence of Ti/MXene with MOF. Consequently, the Ti3C2 becomes more electron-rich, efficiently adsorbing H+ and reducing it to H2. However, despite the paucity of research, 2D Ti3C2 sheets combined with MOF composites exhibit significant potential as a photocatalyst for effective chemicals and other products and need further investigation in the coming years. Table 2 shows the summary of TI3C2/MOF composites for photocatalytic hydrogen production.
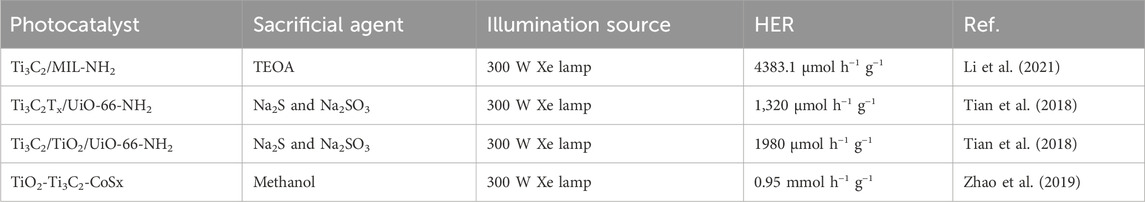
Table 2. Comparison of photocatalytic hydrogen evolution rate by the use of different TiC MXene-based MOF Composites.
Instead of using MOF, their derived materials can be coupled with other semiconductors and materials to enhance photocatalytic efficiency and stability under extreme reaction temperatures. The MOF-derived materials provide higher specific surface area and nanostructure properties, which make them superior compared to conventional methods of materials synthesis (Fan et al., 2024). For example, ZIF-67-templated CoSx coupled with TiO2/Ti3C2 was investigated by Zhao et al. (Zhao et al., 2019) for photocatalytic H2 production. The ZIF-67-templated CoSx’s porous morphology improved charge transfer segregation and utilization efficiency in addition to the shape of TiO2 nanoparticles. In addition to increasing heterostructure conductivity, the conductive Ti3C2 MXenes may also improve photo-generated carrier transfer. Consequently, the photocatalytic activity of the resulting TiO2-Ti3C2-CoSx heterostructure exhibited notable enhancements. The hydrogen production activity of pure TiO2 is measured at 0.14 mmol/h/g. However, incorporating just 1% of ZIF-67-templated CoSx led to a significant enhancement in photocatalytic activity. As the concentration of CoSx increased, so did the rates of hydrogen production by TiO2-CoSx. The optimal H2 generation occurred at 0.54 mmol/h/g, representing a 2.8-fold increase compared to pure TiO2, achieved after the molar ratio of CoSx reached 1%. Although the rate of hydrogen yield was decreased with higher CoSx loading, yet higher H2 was obtained than pure TiO2.
Pure TiO2 produces H2 of 0.14 mmol/h/g. On the other hand, a small addition of 1 per cent ZIF-67-templated CoSx increased photocatalytic activity significantly. The rates at which TCx generated hydrogen increased with the content of CoSx. At a molar ratio of 1 percent for CoSx, the best H2 generation was seen at 0.54 mmol/h/g, or 2.8 times that of pure TiO2. While the activity of hydrogen creation remained higher than that of pure TiO2, the rate of hydrogen synthesis reduced as the concentration of CoSx rose. In a similar vein, the interaction of TiO2-Ti3C2 with Ti3C2 demonstrated that the maximum photocatalytic activity was obtained at a concentration of 0.5% Ti3C2, likely due to the high conductivity of Ti3C2. As the quantity of black Ti3C2 was raised, the colour of the sample darkened, resulting in a drop in optical absorption in TiO2 and a reduction in photocatalytic efficiency. A detailed analysis contrasting pure TiO2 with the will provide a more complete picture of how ZIF-67-derived CoSx and Ti3C2 affect TiO2 photocatalytic activity. In the presence of conductive Ti3C2 and porous CoSx produced from ZIF-67, the photocatalytic HER rate increased from 0.14 to 0.54 and 0.33 mmol/h/g, respectively. Remarkably, this value was increased to 0.95 mmol/h/g by the synergistic effect of co-loading CoSx and Ti3C2. For the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution process, all three materials exhibited remarkable durability. There was no noticeable decrease in the rate of H2 evolution for any of the three materials during five cycles in 15 h under UV irradiation. Significant improvements were made to the cocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction and their photocatalytic H2-production activities by adding highly conductive Ti3C2 and a highly porous MOF-templated CoSx. This work provides guidelines for designing and manufacturing efficient photocatalysts with good charge carrier transport and utilization efficiency for a range of energy and environmental applications.
This section highlights the challenges and comparisons of Ti3C2 MXenes with alternative materials, as illustrated in Figure 10. Ti3C2Tx MXenes offer enhanced electron trapping and a higher work function, which provide advantages for maximizing solar fuel generation. However, the control of termination functional groups in Ti3C2Tx MXenes presents a challenge for its use as a photoactivity enhancer. The electrical and optical properties are significantly influenced by tunable termination groups (Tx), with studies indicating that the terminal groups in MXenes materials can determine their metallic or semiconducting properties (Khazaei et al., 2017). Variations in the work function value can lead to differences in termination properties, which can affect Ti3C2Tx MXenes photocatalytic efficiency (Chertopalov and Mochalin, 2018). Theoretical investigations revealed a work function range of 5.75–6.25 eV for -O terminated Ti3C2Tx MXenes, while -OH terminated Ti3C2Tx MXenes were found to have a work function ranging from 1.6 to 2.8 eV (Sherryna and Tahir, 2022b). Photocatalysis studies suggest that maximizing the conversion of solar energy to hydrogen is best achieved by ensuring a substantial variation in the metalwork function between the main catalyst and the metal co-catalyst (Fajrina and Tahir, 2019). Ti3C2Tx MXenes stand out among metallic materials, including noble metals, due to their unique capability to adapt their work function to specific application requirements. The disparity between theoretical analysis and experimental evaluation arises from the difficulty in achieving a perfect single termination group. Additionally, controlling the distribution of termination groups in MXene materials poses a significant challenge (Naguib et al., 2011). Hence, synthesizing mixed terminating Ti3C2Tx MXene can yield diverse outcomes and catalytic efficiencies. Nevertheless, most research affirms that employing Ti3C2Tx MXene as a co-catalyst undeniably enhances the semiconductor’s capabilities, yielding positive outcomes (Tahir, 2021a; Tahir, 2021b; Khan and Tahir, 2021; Tahir and Tahir, 2020). The superior electrical conductivity and distinctive qualities make these materials stand out as potential replacements for costly and inefficient co-catalysts.
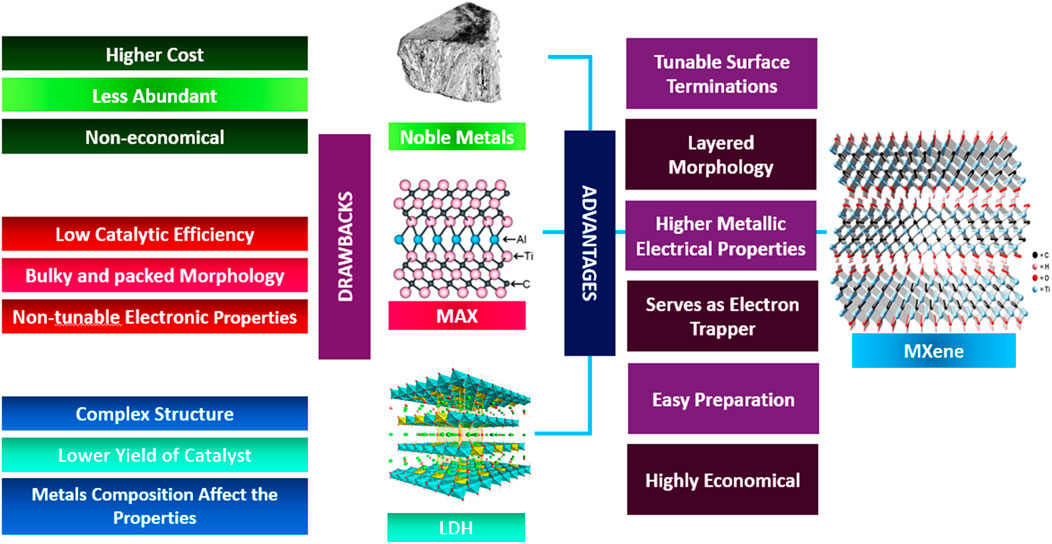
Figure 10. Comparative analysis of MXenes benefits and limitations of other co-catalysts (Fan et al., 2022).
Transition metals are important for improving the photocatalytic efficiency because of their distinct electronic structures and capacity to create variety of oxidation states. The higher photocatalytic efficiency of NH2-MIL-125-Ti MOF for hydrogen production was achieved by incorporating various transition metals such as Co, Cu and Ni. The multi-metal sites speed up the separation of charge carriers and greatly improve optical absorption by d-d transitions when M2+ ions are coordinated with MOF. This increases the activity of solar light-driven H2 generation (Karthik et al., 2020). Noble metals like Ag, Au, and Pt share characteristics with Ti3C2Tx MXene and are considered excellent metal co-catalysts in energy conversion due to their ability to form the Schottky barrier and exhibit surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effects. However, their high costs remain a significant drawback for their practical use in photocatalytic applications (Afroz et al., 2018). Ti3C2Tx MXene emerges as a cost-effective alternative to noble metals, offering comparable functionality at a lower material cost, making it commercially feasible for large-scale semiconductor fabrication. Its work function closely aligns with noble metals (3.9 to 6.25 eV), and both share functional qualities that enhance carrier dynamics and facilitate electron transfer, forming a potential energy barrier in metal-semiconductor interfaces.
Ti3C2Tx MXene features a structurally layered, two-dimensional design often likened to an accordion-like form. This unique structure offers a significantly larger surface area compared to the bulky, compact, and densely layered Ti3AlC2 MAX precursor (Tahir et al., 2021b). Unlike the densely packed layers of MAX material, Ti3C2Tx MXene loosely arranged layers with larger intervals provide effective sites for attaching other semiconductors. This loose structure enhances interfacial contact, speeding up redox reactions and facilitating quick charge transfer. Ti3C2Tx MXene also prevents agglomeration, offering a stable foundation for the uniform dispersion of particle semiconductors, and its well-defined layers with space intervals support redox reactions in both inner and outer layers (Tahir, 2021b). While several studies indicate that Ti3AlC2 MAX may help convert solar energy into fuel, Ti3C2Tx MXene’s catalytic efficiency still outperforms Ti3AlC2 MAX (Tasleem et al., 2020). As mentioned earlier, the surfaces of Ti with functional groups such as -OH, -F, and -O can be terminated through chemical etching, eliminating the Al layer. These surface terminations, known for increased hydrophilicity, exhibit superior interaction with water molecules. Notably, functional groups like -OH facilitate hydrogen generation through reduction from water capture, a capability not shared by Ti3AlC2 MAX. Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH), a frequently utilized co-catalyst in various material research, exhibits a flexible and diverse compositional matrix. Like MXene materials, LDH has several layers that can be easily adjusted to change its electrical properties by changing the kinds of metal cations and anions that are present in its matrix structures (Sherryna et al., 2021).
To increase photocatalytic efficiency, meal-free carbon compounds can be employed as cocatalysts with the metal-organic framework (MOF). As discussed previously, although, MOF have several promising characteristics such as a porous structure with high surface area and tuneable pore structure. However, in photocatalysis, the main challenge is the charge recombination within the semiconductor during the photocatalysis process. In addition to Ti3C2 MXenes, carbon materials such as graphene can be used as a cocatalyst to prevent charge recombination rate. Coupling MOFs with graphene can construct a good interface interaction and it can reduce charge recombination and makes charge carrier separation and transportation easier. For example, Karthik et al. (Karthik et al., 2018) investigated the role of graphene with MOF for photocatalytic hydrogen production. The strong π−π interaction between MOF and rGO was beneficial to construct good interface interaction and it was responsible for the efficient transfer and separation of photoinduced electron−hole pairs, resulting in a steady and increased production of hydrogen. In another development, charge transfer was regulated in bimetallic ZnCd-ZIF-8 with the use of graphene oxide. The π−π interactions between GO and ZnCd-ZIF-8 were responsible for the efficient separation of electron−hole charges, which resulted in significantly higher hydrogen production. It was also recommended that the stability of MOF be enhanced by using bimetallic MOF such as ZnCd-MOF (Gonuguntla et al., 2023). In contrast, Ti3C2Tx MXene emerges as the ideal option due to its easy fabrication, unique structural features, economic feasibility, and outstanding photocatalytic efficiency.
In summary, there is ongoing research on the use of metallic-organic framework (MOF) due to their unique advantages such as porous structure and higher specific surface area. MOFs have structural flexibility due to the use of a large variety of precursor building blocks. The lower electrical conductivity and photocatalytic efficiency of MOFs can be enhanced by using higher conductive materials as the cocatalysts. Since the discovery of Ti3C2 in 2011, the family of 2D transition metal carbides carbonitrides, and nitrides—collectively known as MXenes—has garnered significant attention in the academic community. MXenes are particularly promising due to their excellent electrical conductivity, broad and controllable layer spacing, tunable surface functional groups, and high real density. This review paper explores the effectiveness of documented TiC MXene-based MOF nanohybrids and nanocomposites for photocatalytic CO2 reduction and water-splitting applications.
The expanded surface area of TiC MXenes makes it widely used as a co-catalyst in photocatalysis. The compelling characteristics of TiC MXenes have led to their exploration in combination with Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Reported successes in these studies are attributed to the synergistic enhancements achieved through their combination. As a result, common challenges associated with inefficient photocatalysts, such as rapid recombination rates of electron-hole pairs and suboptimal charge-carrier separation, have been overcome, leading to heightened efficiency under illumination.
Scalability issues with TiC with MOFs, however, make it necessary to make efficient use of TiC MXenes’ co-catalytic properties in order to produce high-efficiency photocatalysts. The characteristics and paths of charge transfer in TiC MXene-based MOF composites are largely determined by the surface termination groups of the MXenes. There is little overlap between theory and experiment when studying MXenes in photocatalysis. Understanding the mechanisms underlying interfacial charge transfer will be crucial to the advancement of TiC MXene-based composites to increase both photoactivity and stability.
Significant promise for increasing photocatalytic activity has been demonstrated by the development of TiC MXene-based MOF photocatalysts. This improvement is credited to synergistic effects, including enhanced stability and the establishment of a Schottky junction, creating a built-in electric field. While promising results have been achieved in solar fuel production with TiC-based MOF composites, comprehensive studies are necessary. Therefore, more research on TiC with other MOFs is advised, especially focusing on photocatalytic CO2 reduction and water-splitting reactions.
The present challenges and suggestions for future research into Ti3C2 MXenes for various applications are summarized in Figure 11. TiC MXene-based MOF composites and hybrids need further thought and investigation. Even if the initial results seem promising, more investigation is needed to provide the scientific community with a deeper understanding of scalability and useful applications. Despite several benefits of MOFs, they have limitations of lower stability and lower charge transfer ability. The metals ions with higher valence state such as Ti4+, Zr4+, Ln3+, and Al3+ can be utilized to produce MOFs with their higher thermal stability. The structural tuning and with the selection of new synthesis methods, light absorbance and electrical properties can be improved. Although Ti3C2 MXenes have limited applications on their own, they are commonly used in conjunction with various semiconductors, including metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), for photocatalytic energy and environmental applications. Their superior conductivity and surface area lead to unprecedented improvements in efficiency and sustainability in hydrogen production and CO2 reduction. When used as cocatalysts, MXenes composites can enhance charge separation efficiency and improve solar energy utilization.
BT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. AA: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing–review and editing. MT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by United Arab Emirates University under research grant no. 12N135.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Afroz, K., Moniruddin, M., Bakranov, N., Kudaibergenov, S., and Nuraje, N. (2018). A heterojunction strategy to improve the visible light sensitive water splitting performance of photocatalytic materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 21696–21718. doi:10.1039/c8ta04165b
Alfaifi, B. Y., Ullah, H., Alfaifi, S., Tahir, A. A., and Mallick, T. K. (2018). Photoelectrochemical solar water splitting: from basic principles to advanced devices. Veruscript Funct. Nanomater. 2, BDJOC3. doi:10.22261/fnan.bdjoc3
Alhabeb, M., Maleski, K., Anasori, B., Lelyukh, P., Clark, L., Sin, S., et al. (2017). Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chem. Mater. 29, 7633–7644. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02847
Alli, Y. A., Bamisaye, A., Nancy, P., Zachariah, S. M., Oladoye, P. O., Bankole, O. M., et al. (2024). MXene composites: properties, synthesis and its emerging application in rechargeable batteries. J. Energy Storage 77, 109954. doi:10.1016/j.est.2023.109954
Anasori, B., Lukatskaya, M. R., and Gogotsi, Y. (2017). 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 16098. doi:10.1038/natrevmats.2016.98
Anasori, B., Xie, Y., Beidaghi, M., Lu, J., Hosler, B. C., Hultman, L., et al. (2015). Two-dimensional, ordered, double transition metals carbides (MXenes). ACS Nano 9, 9507–9516. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b03591
Balcı, E., Akkuş, Ü. Ö., and Berber, S. (2017). Band gap modification in doped MXene: Sc2CF2. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 5956–5961. doi:10.1039/c7tc01765k
Balcı, E., Akkuş, Ü. Ö., and Berber, S. (2018). Controlling topological electronic structure of multifunctional MXene layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 113, 083107. doi:10.1063/1.5042828
Bansal, S., Chaudhary, P., Sharma, B. B., Saini, S., and Joshi, A. (2024). Review of MXenes and their composites for energy storage applications. J. Energy Storage 87, 111420. doi:10.1016/j.est.2024.111420
Bao, L., Jia, Y., Ren, X., Liu, X., Dai, C., Ali, S., et al. (2024). Cr dopants and S vacancies in ZnS to trigger efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution and CO2 reduction. J. Mater. Sci. and Technol. 199, 75–85. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2024.01.094
Barton Cole, E., Lakkaraju, P. S., Rampulla, D. M., Morris, A. J., Abelev, E., and Bocarsly, A. B. (2010). Using a one-electron shuttle for the multielectron reduction of CO2 to methanol: kinetic, mechanistic, and structural insights. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 11539–11551. doi:10.1021/ja1023496
Berdiyorov, G. R. (2015). Effect of surface functionalization on the electronic transport properties of Ti3C2 MXene. EPL Europhys. Lett. 111, 67002. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/111/67002
Bosch, M., Zhang, M., and Zhou, H.-C. (2014). Increasing the stability of metal-organic frameworks. Adv. Chem. 2014, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2014/182327
Burtch, N. C., Jasuja, H., and Walton, K. S. (2014). Water stability and adsorption in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 114, 10575–10612. doi:10.1021/cr5002589
Cavka, J. H., Jakobsen, S., Olsbye, U., Guillou, N., Lamberti, C., Bordiga, S., et al. (2008). A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 13850–13851. doi:10.1021/ja8057953
Chaudhuri, K., Wang, Z., Alhabeb, M., Maleski, K., Gogotsi, Y., Shalaev, V., et al. (2019). Optical properties of MXenes, 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes). Springer International Publishing, 327–346.
Chen, W., Han, B., Xie, Y., Liang, S., Deng, H., and Lin, Z. (2020). Ultrathin Co-Co LDHs nanosheets assembled vertically on MXene: 3D nanoarrays for boosted visible-light-driven CO2 reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123519. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.123519
Chertopalov, S., and Mochalin, V. N. (2018). Environment-sensitive photoresponse of spontaneously partially oxidized Ti3C2 MXene thin films. ACS Nano 12, 6109–6116. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b02379
Colombo, V., Galli, S., Choi, H. J., Han, G. D., Maspero, A., Palmisano, G., et al. (2011). High thermal and chemical stability in pyrazolate-bridged metal–organic frameworks with exposed metal sites. Chem. Sci. 2, 1311–1319. doi:10.1039/c1sc00136a
Corma, A., García, H., and Llabrés i Xamena, F. X. (2010). Engineering metal organic frameworks for heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 110, 4606–4655. doi:10.1021/cr9003924
Costentin, C., Robert, M., and Savéant, J.-M. (2013). Catalysis of the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 2423–2436. doi:10.1039/c2cs35360a
Cui, Y., Yue, Y., Qian, G., and Chen, B. (2012). Luminescent functional metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 112, 1126–1162. doi:10.1021/cr200101d
De, S., Acharya, S., Sahoo, S., Shim, J.-J., and Nayak, G. C. (2022). From 0D to 3D MXenes: their diverse syntheses, morphologies and applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 6, 818–842. doi:10.1039/d2qm00002d
Deng, H., Grunder, S., Cordova Kyle, E., Valente, C., Furukawa, H., Hmadeh, M., et al. (2012). Large-pore apertures in a series of metal-organic frameworks. Science 336, 1018–1023. doi:10.1126/science.1220131
Dillon, A. D., Ghidiu, M. J., Krick, A. L., Griggs, J., May, S. J., Gogotsi, Y., et al. (2016). Highly conductive optical quality solution-processed films of 2D titanium carbide. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 4162–4168. doi:10.1002/adfm.201600357
Dong, L., Kumar, H., Anasori, B., Gogotsi, Y., and Shenoy, V. B. (2017). Rational design of two-dimensional metallic and semiconducting spintronic materials based on ordered double-transition-metal MXenes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 422–428. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b02751
Eddaoudi, M., Kim, J., Rosi, N., Vodak, D., Wachter, J., O'Keeffe, M., et al. (2002). Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 295, 469–472. doi:10.1126/science.1067208
Enyashin, A. N., and Ivanovskii, A. L. (2013). Two-dimensional titanium carbonitrides and their hydroxylated derivatives: structural, electronic properties and stability of MXenes Ti3C2−xNx(OH)2 from DFTB calculations. J. Solid State Chem. 207, 42–48. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2013.09.010
Fajrina, N., and Tahir, M. (2019). A critical review in strategies to improve photocatalytic water splitting towards hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 540–577. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.10.200
Fan, W. K., Sherryna, A., and Tahir, M. (2022). Advances in titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx) MXenes and their metal-organic framework (MOF)-Based nanotextures for solar energy applications: a review. ACS Omega 7, 38158–38192. doi:10.1021/acsomega.2c05030
Fan, W. K., and Tahir, M. (2022). Recent advances on cobalt metal organic frameworks (MOFs) for photocatalytic CO2 reduction to renewable energy and fuels: a review on current progress and future directions. Energy Convers. Manag. 253, 115180. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2021.115180
Fan, W. K., Tahir, M., Alias, H., and Mohamed, A. R. (2024). Well-Designed morphology regulated ZIF-67 derived 0D/1D Co3O4@TiO2 NWs integrated with in-situ grown Ni/Co-Active metals for Low-Temperature driven CO2 methanation. Fuel 357, 130024. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130024
Farha, O. K., Eryazici, I., Jeong, N. C., Hauser, B. G., Wilmer, C. E., Sarjeant, A. A., et al. (2012). Metal–organic framework materials with ultrahigh surface areas: is the sky the limit? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 15016–15021. doi:10.1021/ja3055639
Feng, D., Gu, Z.-Y., Li, J.-R., Jiang, H.-L., Wei, Z., and Zhou, H.-C. (2012). Zirconium-metalloporphyrin PCN-222: mesoporous metal–organic frameworks with ultrahigh stability as biomimetic catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 10307–10310. doi:10.1002/anie.201204475
Férey, G., Mellot-Draznieks, C., Serre, C., Millange, F., Dutour, J., Surblé, S., et al. (2005). A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science 309, 2040–2042. doi:10.1126/science.1116275
Fujita, M., Kwon, Y. J., Washizu, S., and Ogura, K. (1994). Preparation, clathration ability, and catalysis of a two-dimensional square network material composed of cadmium(II) and 4,4'-bipyridine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116, 1151–1152. doi:10.1021/ja00082a055
Furukawa, H., Cordova, K. E., O’Keeffe, M., and Yaghi, O. M. (2013). The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 341, 1230444. doi:10.1126/science.1230444
Furukawa, H., Gándara, F., Zhang, Y.-B., Jiang, J., Queen, W. L., Hudson, M. R., et al. (2014). Water adsorption in porous metal–organic frameworks and related materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4369–4381. doi:10.1021/ja500330a
Gao, Y., Wang, L., Zhou, A., Li, Z., Chen, J., Bala, H., et al. (2015). Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2/Ti3C2 nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 150, 62–64. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2015.02.135
Gonuguntla, S., Vennapoosa, C. S., Abraham, B. M., Sainath, A. V. S., and Pal, U. (2023). Charge transfer-regulated bimetallic ZnCd-ZIF-8/Graphene oxide hybrid nanostructures for solar hydrogen generation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 7, 18146–18156. doi:10.1021/acsanm.3c02870
Habisreutinger, S. N., Schmidt-Mende, L., and Stolarczyk, J. K. (2013). Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on TiO2 and other semiconductors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 7372–7408. doi:10.1002/anie.201207199
Halim, J., Palisaitis, J., Lu, J., Thörnberg, J., Moon, E. J., Precner, M., et al. (2018). Synthesis of two-dimensional Nb1.33C (MXene) with randomly distributed vacancies by etching of the quaternary solid solution (Nb2/3Sc1/3)2AlC MAX phase. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1, 2455–2460. doi:10.1021/acsanm.8b00332
Halim, J., Persson, I., Moon, E. J., Kühne, P., Darakchieva, V., Persson, P. O. Å., et al. (2019). Electronic and optical characterization of 2D Ti2C and Nb2C (MXene) thin films. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 31, 165301. doi:10.1088/1361-648x/ab00a2
Han, F., Luo, S., Xie, L., Zhu, J., Wei, W., Chen, X., et al. (2019). Boosting the yield of MXene 2D sheets via a facile hydrothermal-assisted intercalation. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 11, 8443–8452. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b22339
Han, X., An, L., Hu, Y., Li, Y., Hou, C., Wang, H., et al. (2020). Ti3C2 MXene-derived carbon-doped TiO2 coupled with g-C3N4 as the visible-light photocatalysts for photocatalytic H2 generation. Appl. Catal. B 265, 118539. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118539
Hong, L., Klie, R. F., and Öğüt, S. (2016). First-principles study of size- and edge-dependent properties of MXene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 93, 115412. doi:10.1103/physrevb.93.115412
Hong, L.-f., Guo, R.-t., Yuan, Y., Ji, X.-y., Li, Z.-s., Lin, Z.-d., et al. (2020b). Recent progress of two-dimensional MXenes in photocatalytic applications: a review. Mater. Today Energy 18, 100521. doi:10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100521
Hong, W., Wyatt, B. C., Nemani, S. K., and Anasori, B. (2020a). Double transition-metal MXenes: atomistic design of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides. MRS Bull. 45, 850–861. doi:10.1557/mrs.2020.251
Howarth, A. J., Liu, Y., Li, P., Li, Z., Wang, T. C., Hupp, J. T., et al. (2016). Chemical, thermal and mechanical stabilities of metal–organic frameworks. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 15018. doi:10.1038/natrevmats.2015.18
Huang, K., Li, Z., Lin, J., Han, G., and Huang, P. (2018). Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 5109–5124. doi:10.1039/c7cs00838d
Huang, S., Long, Y., Ruan, S., and Zeng, Y. J. (2019). Enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction in defect-engineered Z-scheme WO3-x/g-C3N4 heterostructures. ACS Omega 4, 15593–15599. doi:10.1021/acsomega.9b01969
Huang, X.-C., Lin, Y.-Y., Zhang, J.-P., and Chen, X.-M. (2006). Ligand-directed strategy for zeolite-type metal–organic frameworks: zinc(II) imidazolates with unusual zeolitic topologies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 1557–1559. doi:10.1002/anie.200503778
Ibragimova, R., Erhart, P., Rinke, P., and Komsa, H.-P. (2021). Surface functionalization of 2D MXenes: trends in distribution, composition, and electronic properties. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12, 2377–2384. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03710
Im, J. K., Sohn, E. J., Kim, S., Jang, M., Son, A., Zoh, K.-D., et al. (2021). Review of MXene-based nanocomposites for photocatalysis. Chemosphere 270, 129478. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129478
Ivanovskii, A. L., and Enyashin, A. N. (2013). Graphene-like transition-metal nanocarbides and nanonitrides. Russ. Chem. Rev. 82, 735–746. doi:10.1070/rc2013v082n08abeh004398
Jacobs, C. B., Vickrey, T. L., and Venton, B. J. (2011). Functional groups modulate the sensitivity and electron transfer kinetics of neurochemicals at carbon nanotube modified microelectrodes. Analyst 136, 3557–3565. doi:10.1039/c0an00854k
Jalil, A., Zafar Ilyas, S., Agathopoulos, S., Qureshi, A., Ahmed, I., and Zhao, T. (2021). 2D CoGeSe3 monolayer as a visible-light photocatalyst with high carrier mobility: theoretical prediction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 565, 150588. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150588
Jeon, J., Yang, Y., Choi, H., Park, J.-H., Lee, B. H., and Lee, S. (2020). MXenes for future nanophotonic device applications. Nanophotonics 9, 1831–1853. doi:10.1515/nanoph-2020-0060
Jiang, X., Kuklin, A. V., Baev, A., Ge, Y., Ågren, H., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). Two-dimensional MXenes: from morphological to optical, electric, and magnetic properties and applications. Phys. Rep. 848, 1–58. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2019.12.006
Jiang, X., Liu, S., Liang, W., Luo, S., He, Z., Ge, Y., et al. (2018). Broadband nonlinear photonics in few-layer MXene Ti3C2Tx (T = F, O, or OH). Laser and Photonics Rev. 12, 1700229. doi:10.1002/lpor.201700229
Jiang, X., Ren, X., Chen, R., Ma, F., He, W., Zhang, T., et al. (2023). Cobalt(II)-complex modified Ag electrode for efficient and selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO. J. Electroanal. Chem. 949, 117860. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2023.117860
Jiang, X., Sun, S., Ren, X., Ma, F., Wen, Y., He, W., et al. (2024). Au modified TiO2 nanowires prepared by photodeposition for selective and efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 59, 168–175. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.02.007
Jiao, L., Seow, J. Y. R., Skinner, W. S., Wang, Z. U., and Jiang, H.-L. (2019). Metal–organic frameworks: structures and functional applications. Mater. Today 27, 43–68. doi:10.1016/j.mattod.2018.10.038
Karthik, P., Pandikumar, A., Preeyanghaa, M., Kowsalya, M., and Neppolian, B. (2017). Amino-functionalized MIL-101(Fe) metal-organic framework as a viable fluorescent probe for nitroaromatic compounds. Microchim. Acta 184, 2265–2273. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2215-2
Karthik, P., Shaheer, A. R. M., Vinu, A., and Neppolian, B. (2020). Amine functionalized metal-organic framework coordinated with transition metal ions: d-d transition enhanced optical absorption and role of transition metal sites on solar light driven H(2) production. Small 16, e1902990. doi:10.1002/smll.201902990
Karthik, P., Vinoth, R., Zhang, P., Choi, W., Balaraman, E., and Neppolian, B. (2018). π–π interaction between metal–organic framework and reduced graphene oxide for visible-light photocatalytic H2 production. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 1913–1923. doi:10.1021/acsaem.7b00245
Kayali, E., VahidMohammadi, A., Orangi, J., and Beidaghi, M. (2018). Controlling the dimensions of 2D MXenes for ultrahigh-rate pseudocapacitive energy storage. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 10, 25949–25954. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b07397
Khan, A. A., and Tahir, M. (2019). Recent advancements in engineering approach towards design of photo-reactors for selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction to renewable fuels. J. CO2 Util. 29, 205–239. doi:10.1016/j.jcou.2018.12.008
Khan, A. A., and Tahir, M. (2021). Well-designed 2D/2D Ti3C2TA/R MXene coupled g-C3N4 heterojunction with in-situ growth of anatase/rutile TiO2 nucleates to boost photocatalytic dry-reforming of methane (DRM) for syngas production under visible light. Appl. Catal. B 285, 119777. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119777
Khazaei, M., Arai, M., Sasaki, T., Chung, C.-Y., Venkataramanan, N. S., Estili, M., et al. (2012). Novel electronic and magnetic properties of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 2185–2192. doi:10.1002/adfm.201202502
Khazaei, M., Ranjbar, A., Arai, M., Sasaki, T., and Yunoki, S. (2017). Electronic properties and applications of MXenes: a theoretical review. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 2488–2503. doi:10.1039/c7tc00140a
Kong, F., He, X., Liu, Q., Qi, X., Zheng, Y., Wang, R., et al. (2018). Improving the electrochemical properties of MXene Ti3C2 multilayer for Li-ion batteries by vacuum calcination. Electrochimica Acta 265, 140–150. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2018.01.196
Lee, Y., Cho, S. B., and Chung, Y.-C. (2014). Tunable indirect to direct band gap transition of monolayer Sc2CO2 by the strain effect. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 6, 14724–14728. doi:10.1021/am504233d
Li, D., Xu, H.-Q., Jiao, L., and Jiang, H.-L. (2019a). Metal-organic frameworks for catalysis: state of the art, challenges, and opportunities. EnergyChem 1, 100005. doi:10.1016/j.enchem.2019.100005
Li, H., Eddaoudi, M., O'Keeffe, M., and Yaghi, O. M. (1999). Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 402, 276–279. doi:10.1038/46248
Li, J.-R., Kuppler, R. J., and Zhou, H.-C. (2009). Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1477–1504. doi:10.1039/b802426j
Li, J.-R., Ma, Y., McCarthy, M. C., Sculley, J., Yu, J., Jeong, H.-K., et al. (2011). Carbon dioxide capture-related gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 255, 1791–1823. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.02.012
Li, N., Liu, J., Liu, J. J., Dong, L. Z., Xin, Z. F., Teng, Y. L., et al. (2019b). Adenine components in biomimetic metal-organic frameworks for efficient CO2 photoconversion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 58, 5226–5231. doi:10.1002/anie.201814729
Li, S., Wu, F., Lin, R., Wang, J., Li, C., Li, Z., et al. (2022). Enabling photocatalytic hydrogen production over Fe-based MOFs by refining band structure with dye sensitization. Chem. Eng. J. 429, 132217. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.132217
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, P., Zheng, Z., Cheng, H., et al. (2021). In-situ growth of Ti3C2@MIL-NH2 composite for highly enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 411, 128446. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.128446
Li, Z., and Wu, Y. (2019). 2D early transition metal carbides (MXenes) for catalysis. Small 15, 1804736. doi:10.1002/smll.201804736
Liao, W. M., Zhang, J. H., Wang, Z., Lu, Y. L., Yin, S. Y., Wang, H. P., et al. (2018). Semiconductive amine-functionalized Co(II)-MOF for visible-light-driven hydrogen evolution and CO2 reduction. Inorg. Chem. 57, 11436–11442. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01265
Lim, K. R. G., Handoko, A. D., Nemani, S. K., Wyatt, B., Jiang, H.-Y., Tang, J., et al. (2020). Rational design of two-dimensional transition metal carbide/nitride (MXene) hybrids and nanocomposites for catalytic energy storage and conversion. ACS Nano 14, 10834–10864. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c05482
Lin, S., Song, Z., Che, G., Ren, A., Li, P., Liu, C., et al. (2014). Adsorption behavior of metal–organic frameworks for methylene blue from aqueous solution. Microporous mesoporous Mater. 193, 27–34. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.03.004
Linsebigler, A. L., Lu, G., and Yates, J. T. (1995). Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 95, 735–758. doi:10.1021/cr00035a013
Liu, H.-J., and Dong, B. (2021). Recent advances and prospects of MXene-based materials for electrocatalysis and energy storage. Mater. Today Phys. 20, 100469. doi:10.1016/j.mtphys.2021.100469
Liu, M., Zhou, L., Luo, X., Wan, C., and Xu, L. (2020a). Recent advances in noble metal catalysts for hydrogen production from ammonia borane. Catalysts 10, 788. doi:10.3390/catal10070788
Liu, Q., Tan, X., Wang, S., Ma, F., Znad, H., Shen, Z., et al. (2019). MXene as a non-metal charge mediator in 2D layered CdS@ Ti3C2@TiO2 composites with superior Z-scheme visible light-driven photocatalytic activity. Environ. Sci. Nano 6, 3158–3169. doi:10.1039/c9en00567f
Liu, S., Zhang, C., Sun, Y., Chen, Q., He, L., Zhang, K., et al. (2020b). Design of metal-organic framework-based photocatalysts for hydrogen generation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 413, 213266. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213266
Liu, X., Shan, Y., Zhang, S., Kong, Q., and Pang, H. (2022). Application of metal organic framework in wastewater treatment. Green Energy and Environ. 8, 698–721. doi:10.1016/j.gee.2022.03.005
Loiseau, T., Serre, C., Huguenard, C., Fink, G., Taulelle, F., Henry, M., et al. (2004). A rationale for the large breathing of the porous aluminum terephthalate (MIL-53) upon hydration. Chem. - A Eur. J. 10, 1373–1382. doi:10.1002/chem.200305413
Long, R., Yu, Z., Tan, Q., Feng, X., Zhu, X., Li, X., et al. (2021). Ti3C2 MXene/NH2-MIL-88B(Fe): research on the adsorption kinetics and photocatalytic performance of an efficient integrated photocatalytic adsorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 570, 151244. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151244
Lu, W., Wei, Z., Gu, Z.-Y., Liu, T.-F., Park, J., Park, J., et al. (2014). Tuning the structure and function of metal–organic frameworks via linker design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 5561–5593. doi:10.1039/c4cs00003j
Maeda, K. (2011). Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductor particles: history and recent developments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 12, 237–268. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2011.07.001
Naguib, M., Kurtoglu, M., Presser, V., Lu, J., Niu, J., Heon, M., et al. (2011). Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 23, 4248–4253. doi:10.1002/adma.201102306
Najam, T., Shah, S. S. A., Peng, L., Javed, M. S., Imran, M., Zhao, M.-Q., et al. (2022). Synthesis and nano-engineering of MXenes for energy conversion and storage applications: recent advances and perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 454, 214339. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214339
Nguyen, J. G., and Cohen, S. M. (2010). Moisture-resistant and superhydrophobic Metal−Organic frameworks obtained via postsynthetic modification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 4560–4561. doi:10.1021/ja100900c
Papadopoulou, K., Chroneos, A., Parfitt, D., and Christopoulos, S.-R. G. (2020). A perspective on MXenes: their synthesis, properties, and recent applications. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 170902. doi:10.1063/5.0021485
Park, K. S., Ni, Z., Côté, A. P., Choi, J. Y., Huang, R., Uribe-Romo, F. J., et al. (2006). Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103, 10186–10191. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602439103
Perry Iv, J. J., Perman, J. A., and Zaworotko, M. J. (2009). Design and synthesis of metal–organic frameworks using metal–organic polyhedra as supermolecular building blocks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1400. doi:10.1039/b807086p
Persson, I., el Ghazaly, A., Tao, Q., Halim, J., Kota, S., Darakchieva, V., et al. (2018). Tailoring structure, composition, and energy storage properties of MXenes from selective etching of in-plane, chemically ordered MAX phases. Small 14, 1703676. doi:10.1002/smll.201703676
Qin, T., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Besenbacher, F., Otyepka, M., and Dong, M. (2021). Recent progress in emerging two-dimensional transition metal carbides. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 183. doi:10.1007/s40820-021-00710-7
Reddy, C. V., Reddy, K. R., Harish, V. V. N., Shim, J., Shankar, M. V., Shetti, N. P., et al. (2020). Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)-based efficient heterogeneous photocatalysts: synthesis, properties and its applications in photocatalytic hydrogen generation, CO2 reduction and photodegradation of organic dyes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45, 7656–7679. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.144
Reddy, D. A., Kim, Y., Gopannagari, M., Kumar, D. P., and Kim, T. K. (2021). Recent advances in metal–organic framework-based photocatalysts for hydrogen production. Sustain. Energy and Fuels 5, 1597–1618. doi:10.1039/c9se00749k
Ren, X., Liao, G., Li, Z., Qiao, H., Zhang, Y., Yu, X., et al. (2021). Two-dimensional MOF and COF nanosheets for next-generation optoelectronic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 435, 213781. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213781
Ren, X., Liu, Z., Zhang, T., Jiang, X., Fang, Q., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Review on two-dimensional metal–organic frameworks for biological sensing: current challenges and new frontiers. J. Mater. Sci. 59, 10724–10743. doi:10.1007/s10853-024-09818-8
Ronchi, R. M., Arantes, J. T., and Santos, S. F. (2019). Synthesis, structure, properties and applications of MXenes: current status and perspectives. Ceram. Int. 45, 18167–18188. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.114
Senkovska, I., and Kaskel, S. (2014). Ultrahigh porosity in mesoporous MOFs: promises and limitations. Chem. Commun. 50, 7089–7098. doi:10.1039/c4cc00524d
Sharma, K., Hasija, V., Patial, S., Singh, P., Nadda, A., Thakur, S., et al. (2022b). Recent progress on MXenes and MOFs hybrids: structure, synthetic strategies and catalytic water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 48, 6560–6574. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.01.004
Sharma, K., Hasija, V., Patial, S., Singh, P., Nguyen, V.-H., Nadda, A. K., et al. (2022c). Recent progress on MXenes and MOFs hybrids: structure, synthetic strategies and catalytic water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 48, 6560–6574. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.01.004
Sharma, S. K., Kumar, A., Sharma, G., Vo, D.-V. N., García-Peñas, A., Moradi, O., et al. (2022a). MXenes based nano-heterojunctions and composites for advanced photocatalytic environmental detoxification and energy conversion: a review. Chemosphere 291, 132923. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132923
Sherryna, A., and Tahir, M. (2021). Role of Ti3C2 MXene as prominent Schottky barriers in driving hydrogen production through photoinduced water splitting: a comprehensive review. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 4, 11982–12006. doi:10.1021/acsaem.1c02241
Sherryna, A., and Tahir, M. (2022a). Role of surface morphology and terminating groups in titanium carbide MXenes (Ti3C2Tx) cocatalysts with engineering aspects for modulating solar hydrogen production: a critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134573. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.134573
Sherryna, A., and Tahir, M. (2022b). Role of surface morphology and terminating groups in titanium carbide MXenes (Ti3C2Tx) cocatalysts with engineering aspects for modulating solar hydrogen production: a critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 134573. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.134573
Sherryna, A., Tahir, M., and Nabgan, W. (2021). Recent advancements of layered double hydroxide heterojunction composites with engineering approach towards photocatalytic hydrogen production: a review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 47, 862–901. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.10.099
Shi, Z., Khaledialidusti, R., Malaki, M., and Zhang, H. (2021). MXene-based materials for solar cell applications. Nanomaterials 11, 3170. doi:10.3390/nano11123170
Shkrob, I. A., and Sauer, M. C. (2004). Hole scavenging and photo-stimulated recombination of electron− hole pairs in aqueous TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 12497–12511. doi:10.1021/jp047736t
Si, C., Jin, K.-H., Zhou, J., Sun, Z., and Liu, F. (2016). Large-gap quantum spin Hall state in MXenes: d-band topological order in a triangular lattice. Nano Lett. 16, 6584–6591. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03118
Song, Z., Song, S., Zhang, W., Han, H., Wei, K., Liu, D., et al. (2024). The unique Z-scheme g-C3N4/Ti3C2/Sn-Bi-MOF photocatalyst for enhancing CO2 reduction activity. Fuel 366, 131154. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2024.131154
Suman, S. (2018). Hybrid nuclear-renewable energy systems: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 181, 166–177. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.262
Tahir, M. (2021a). Binary Ni2P/Ti3C2 multilayer cocatalyst anchored TiO2 nanocomposite with etchant/oxidation grown TiO2 NPs for enhancing photocatalytic H2 production. Energy and Fuels 35, 14197–14211. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c01340
Tahir, M. (2021b). Investigating the influential effect of etchant time in constructing 2D/2D HCN/MXene heterojunction with controlled growth of TiO2 NPs for stimulating photocatalytic H2 production. Energy and Fuels 35, 6807–6822. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c00204
Tahir, M. (2024). Synergistic effect of the V2CTx MXene@V2O5/TiO2 NP composite for stimulating photocatalytic CO2 reduction through bireforming of methanol to produce CO and CH4. Energy and Fuels 38, 10183–10202. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c05215
Tahir, M., Ajiwokewu, B., Bankole, A. A., Ismail, O., Al-Amodi, H., and Kumar, N. (2023a). MOF based composites with engineering aspects and morphological developments for photocatalytic CO2 reduction and hydrogen production: a comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 109408. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2023.109408
Tahir, M., Khan, A. A., Tasleem, S., Mansoor, R., Sherryna, A., and Tahir, B. (2023b). Recent advances in titanium carbide MXene-based nanotextures with influential effect of synthesis parameters for solar CO2 reduction and H2 production: a critical review. J. Energy Chem. 76, 295–331. doi:10.1016/j.jechem.2022.09.046
Tahir, M., Fan, W. K., and Tahir, B. (2021a). MOF-based catalysts for production of value-added fine chemicals from carbon dioxide, Metal−Organic frameworks for carbon capture and energy. ACS Publications, 155–171.
Tahir, M., Sherryna, A., and Zakaria, Z. Y. (2021b). Facile synthesis of MAX modified graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposite for stimulating hydrogen production through photocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Eng. Trans. 89, 571–576.
Tahir, M., and Tahir, B. (2020). 2D/2D/2D O-C3N4/Bt/Ti3C2Tx heterojunction with novel MXene/clay multi-electron mediator for stimulating photo-induced CO2 reforming to CO and CH4. Chem. Eng. J. 400, 125868. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.125868
Tasleem, S., Tahir, M., and Zakaria, Z. Y. (2020). Fabricating structured 2D Ti3AlC2 MAX dispersed TiO2 heterostructure with Ni2P as a cocatalyst for efficient photocatalytic H2 production. J. Alloys Compd. 842, 155752. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155752
Tian, P., He, X., Zhao, L., Li, W., Fang, W., Chen, H., et al. (2018). Enhanced charge transfer for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution over UiO-66-NH2 with annealed Ti3C2Tx MXenes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 788–800. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.11.016
Tian, P., He, X., Zhao, L., Li, W., Fang, W., Chen, H., et al. (2019a). Enhanced charge transfer for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution over UiO-66-NH2 with annealed Ti3C2Tx MXenes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 788–800. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.11.016
Tian, P., He, X., Zhao, L., Li, W., Fang, W., Chen, H., et al. (2019b). Ti3C2 nanosheets modified Zr-MOFs with Schottky junction for boosting photocatalytic HER performance. Sol. Energy 188, 750–759. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2019.06.060
Tranchemontagne, D. J., Mendoza-Cortés, J. L., O’Keeffe, M., and Yaghi, O. M. (2009). Secondary building units, nets and bonding in the chemistry of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1257–1283. doi:10.1039/b817735j
Urbankowski, P., Anasori, B., Hantanasirisakul, K., Yang, L., Zhang, L., Haines, B., et al. (2017). 2D molybdenum and vanadium nitrides synthesized by ammoniation of 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Nanoscale 9, 17722–17730. doi:10.1039/c7nr06721f
Wang, Q., Gao, Q., Al-Enizi, A. M., Nafady, A., and Ma, S. (2020). Recent advances in MOF-based photocatalysis: environmental remediation under visible light. Inorg. Chem. Front. 7, 300–339. doi:10.1039/c9qi01120j
Wong, Z. M., Tan, T. L., Yang, S.-W., and Xu, G. Q. (2018). Enhancing the photocatalytic performance of MXenes via stoichiometry engineering of their electronic and optical properties. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 10, 39879–39889. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b14325
Wu, H., Almalki, M., Xu, X., Lei, Y., Ming, F., Mallick, A., et al. (2019). MXene derived metal–organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 20037–20042. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b11446
Xie, J., Yang, C., Duan, M., Tang, J., Wang, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2018). Amorphous NiP as cocatalyst for photocatalytic water splitting. Ceram. Int. 44, 5459–5465. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.179
Xu, Q., Sun, Y., Lv, T., and Liu, H. (2023). Selective CO2 photoreduction into CO over Ti3C2 quantum dots decorated NH2-MIL-101(Fe) heterostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 954, 170088. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170088
Xuan, W., Zhu, C., Liu, Y., and Cui, Y. (2012). Mesoporous metal–organic framework materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 1677–1695. doi:10.1039/c1cs15196g
Yang, C., Kaipa, U., Mather, Q. Z., Wang, X., Nesterov, V., Venero, A. F., et al. (2011). Fluorous metal–organic frameworks with superior adsorption and hydrophobic properties toward oil spill cleanup and hydrocarbon storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 18094–18097. doi:10.1021/ja208408n
Ying, G., Dillon, A. D., Fafarman, A. T., and Barsoum, M. W. (2017). Transparent, conductive solution processed spincast 2D Ti2CTx (MXene) films. Mater. Res. Lett. 5, 391–398. doi:10.1080/21663831.2017.1296043
You, Z., Liao, Y., Li, X., Fan, J., and Xiang, Q. (2021). State-of-the-art recent progress in MXene-based photocatalysts: a comprehensive review. Nanoscale 13, 9463–9504. doi:10.1039/d1nr02224e
Yu, L., Liu, B., Wang, Y., Yu, F., and Ma, J. (2021). Recent progress on MXene-Derived material and its’ application in energy and environment. J. Power Sources 490, 229250. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229250
Zhang, B., Zhang, S.-X., Yao, R., Wu, Y.-H., and Qiu, J.-S. (2021). Progress and prospects of hydrogen production: opportunities and challenges. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 19, 100080. doi:10.1016/j.jnlest.2021.100080
Zhang, T., Ren, X., Mo, S., Cao, W., Zhou, C., Ma, F., et al. (2024). Modulating Fe/P ratios in Fe-P alloy through smelting reduction for long-term electrocatalytic overall water splitting. J. Mater. Sci. and Technol. 199, 66–74. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2024.02.037
Zhao, J.-H., Liu, L.-W., Li, K., Li, T., and Liu, F.-T. (2019). Conductive Ti3C2 and MOF-derived CoSx boosting the photocatalytic hydrogen production activity of TiO2. CrystEngComm 21, 2416–2421. doi:10.1039/c8ce02050g
Zhao, X., Lu, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhou, M., Xu, S., and Li, Z. (2022). A review of recent progress in modified metal–organic frameworks as photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 4737–4754. doi:10.1007/s10854-022-07717-9
Zhou, H.-C. J., and Kitagawa, S. (2014). Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 5415–5418. doi:10.1039/c4cs90059f
Zhou, Y., Ren, X., Wang, X., Mao, J., Zhang, H., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Promoting CuO/Cu(OH)2 for electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to HCOOH: the study on pyridine-modified surface active sites. Mol. Catal. 556, 113929. doi:10.1016/j.mcat.2024.113929
Keywords: titanium carbide (Ti3C2) MXenes, metal-organic frameworks (MOF), photocatalysis, CO2 reduction, hydrogen production, nanosheets
Citation: Tahir B, Alraeesi A and Tahir M (2024) Metal-organic framework (MOF) integrated Ti3C2 MXene composites for CO2 reduction and hydrogen production applications: a review on recent advances and future perspectives. Front. Chem. 12:1448700. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1448700
Received: 13 June 2024; Accepted: 05 September 2024;
Published: 01 October 2024.
Edited by:
Kezhen Qi, Dali University, ChinaReviewed by:
Karthik Peramaiah, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, Saudi ArabiaCopyright © 2024 Tahir, Alraeesi and Tahir. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abdulrahman Alraeesi, YS5hbHJhZWVzaUB1YWV1LmFjLmFl
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.