- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Yixing Hospital Affiliated to Jiangsu University, Yixing, China
- 3School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
Introduction: Rapid detection of amino acids plays an important role in the field of medical diagnosis. By combining Rhodamine B with triphenylamine, a novel double-response fluorescence probe (E)-4-((4-(((3′,6′-bis(diethylamino)-3-oxospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenyl)(phenyl)amino)benzaldehyde (RBTPA) was prepared for rapid identification of different amino acids.
Methods: Under daylight and 365 nm irradiation, it was found that the color change was most bright at pH = 3, and changed to dim at pH = 4. When pH = 3 and pH = 4, the photophysical properties of the two strong acids are very different. The maximum redshift of UV absorption light is 110 nm, and the maximum fluorescence emission intensity is 4 times different.
Results and Discussion: In order to further observe their binding structure analysis with different amino acids, qualitative analysis of each response structure was determined by mass spectrometry according to different molecular weights. The fluorescence probe RBTPA has two different isomers for recognition response in aldehyde group and imine group, respectively.
Introduction
Amino acids are the “raw materials” that the human body uses to construct different proteins. These proteins are used to build or repair cell tissues, make hormones, enzymes, antibody proteins, and other substances, as well as to control metabolism and immunity (Bi et al., 2024; Ye et al., 2024). The foundation of human health is an adequate and balanced amount of amino acids (Guo et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024). People will be in a sub-health state and more susceptible to illness if there is no supply of amino acids, since this will impair their immune systems and other regular processes (Jin et al., 2020a; Jin et al., 2020b).
Currently, an imbalance in amino acids is responsible for about 300 different types of illnesses, including immune system disorders, cancers, viral diseases, nervous system disorders, and geriatric diseases (Yin et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024). The body’s imbalance of amino acids can give information about a wide range of linked disorders as well as a thorough and dynamic evaluation of the levels of neurotransmitter metabolism, urea cycle, and amino acid functional metabolism. Additionally, early risk assessment may be carried out for malignant and chronic illnesses (Xiao et al., 2020; Deng et al., 2024; Fan et al., 2024). At present, major medical institutions mainly detect small molecule substances such as amino acids through full spectrum amino acid detection LC-MS/MS technology and small molecule fluorescent probe used in laboratories (Deng et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2024; Shao et al., 2022; Schumann et al., 2023). Such as formaldehyde titration method: this method is simple to operate and has high accuracy, but it is prone to interference by other acidic substances. High performance liquid chromatography: This method has good separation effect, high sensitivity, and can detect a variety of amino acids at the same time. However, the operation is complicated, the cost is high, and the use of organic solvents is required. Although they have high sensitivity and fast detection speed, their equipment requirements are high, the fluorescence effect is poor, and the rapid and immediate detection of different amino acids cannot be visually monitored (Ye et al., 2024; Hu et al., 2022; Hao et al., 2024). Therefore, how to develop an efficient, qualitative and rapid visualization fluorescent probe to solve this difficulty has important value and significance (Rong et al., 2024).
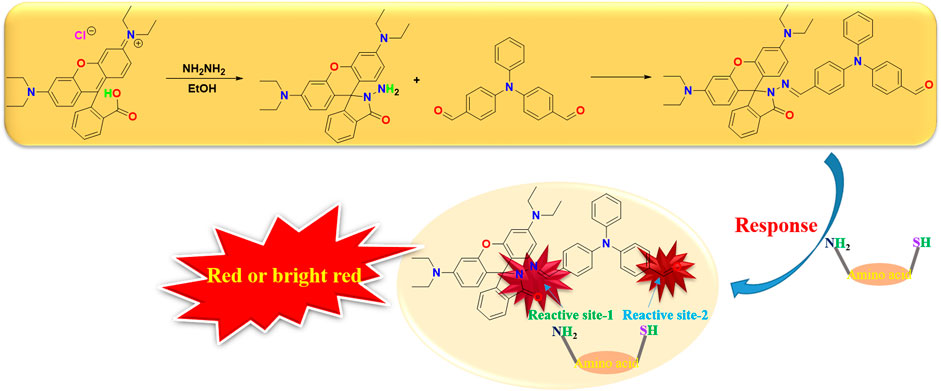
In this paper, we designed a new type of double response binding site, using rhodamine B’s amide and triphenylamino aldehyde groups to combine with different amino acids or sulfhydryl groups to emit strong fluorescence chromophore, to achieve simple, qualitative and visual fluorescence effect.
Experimental section
Reagents and instrumentation
All reagents were purchased commercially and further purified when used. All the reactions involved were monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and analyzed with ultraviolet lamps at 254 and 365 nm. Products were separated and purified by column chromatography (200–300 mesh silica gel). NMR were recorded by Bruker avance II instrument in deuterium chloroform (400 MHz for 1H and 100 MHz for 13C). Chemical shifts are reported in ppm, versus internal tetramethylsilane (TMS) as a standard. The mass spectrum was obtained on a Thermo LXQ by liquid chromatgraphy-ion trap mass spectrometry. Absorption spectra were recorded with a UV-2550 spectrophotometer. The fluorescence emission spectra were measured by Shimazu RF-5301PCS fluorescence spectrophotometer with excitation wavelength of 500 nm. The molecular weight by MS-ESI (Jeol LTD JMS-HX 110/110A) was performed.
Synthesis
(E)-4-((4-(((3′,6′-bis(diethylamino)-3-oxospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-2-yl)imino)methyl) phenyl)(phenyl)amino)benzaldehyde
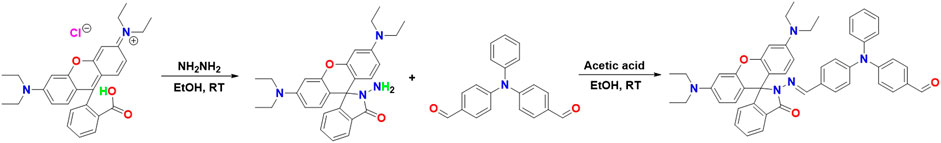
2-amino-3′,6′-bis(diethylamino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one (0.58 g, 1.3 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (3 mL), 4,4'-(phenylazanediyl)dibenzaldehyde (0.38 g, 1.3 mmol) and acetic acid (0.1 mL) were added. The reaction was stopped after magnetic stirring at room temperature for 3 h. Yellowish compound (0.52 g, 56%) was isolated by column chromatography (petroleum ether: EtOAc = 4:1). 1H-NMR: (400 MHz, CDCl3, ppm): 8.65 (s, 1H), 7.98–7.97 (dd, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.48–7.39 (m, 1H), 7.23–7.19 (m, 1H), 7.12–7.10 (m, 1H), 7.03–6.98 (m, 1H), 6.91–6.89 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 6.53–6.51 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 6.42 (s, 2H), 6.26–6.23 (dd, J = 3.0 Hz, 2H), 4.15–4.10 (m, 1H), 3.34–3.29 (m, 9H), 2.05 (s, 2H), 1.28–1.24 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 1.17–1.13 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 12H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm)164.73, 153.21, 151.70, 148.89, 148.55, 129.43, 128.53, 128.44, 125.49, 123.83, 123.08, 107.29, 97.44, 66.06, 60.40, 44.33, 21.07, 14.23, 12.67. ITMS (ESI) calcd for C29H33BF2N6O2S [M + H]+ m/z 740.92; found 739.85.
Spectroscopic properties
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectra were recorded using a 1 cm quartz tube on a UV-2550 spectrophotometer, and fluorescence spectra were performed at room temperature on a Shimadzu RF-5301PCS fluorescence spectrophotometer. The making phosphate buffers with pH values of 3.0, and 4.0 each buffer was mixed with different equivalents of amino acids. Appropriate amount of RBTPA to be measured was weighed and dissolved in EtOH to prepare a solution with a concentration of 20 μg/mL for use. Different concentrations of amino acids in solvents were detected by ultraviolet and fluorescence methods. The wavelength range of UV-Vis is 450–700 nm. The fluorescence of the compound was obtained at the optical path of 10 mm and the excitation wavelength of 560 nm, and the emission wavelength was recorded in the range of 400–700 nm.
Fluorescence stability data
The fluorescence stability data was determined using a Japanese Shimadzu RF-5301PC fluorescence spectrophotometer, DMSO was used as the solvent, and the sample concentration was continuously diluted with DMSO until the fluorescence intensity of the RBTPA remained stable. Fluorescence intensity stability over 5 min and 10 min was measured, respectively.
Mass spectrometry
The mass spectrums were obtained at the Thermo LXQ by liquid chromatgraphy-ion trap mass spectrometry. To verify this mechanism, a random selection of RBTPA solutions containing 1.0 mg/mL of different amino acid solutions was performed by mass spectrometry to confirm our proposed mechanism.
Result and discussion
Design
The design concept of the amino acid fluorescence probe in this paper is to consider the double response effect. Triphenylamino aldehyde, the most widely used luminescent electron donor in the semiconductor field, is selected as the terminal binding point, and the fluorophore rhodamine B is introduced. This design not only greatly reduces the fluorescence quenching problem of the probe, but also has the rapid response function in the acid environment in the overall structure, the best of both worlds (Scheme 1).
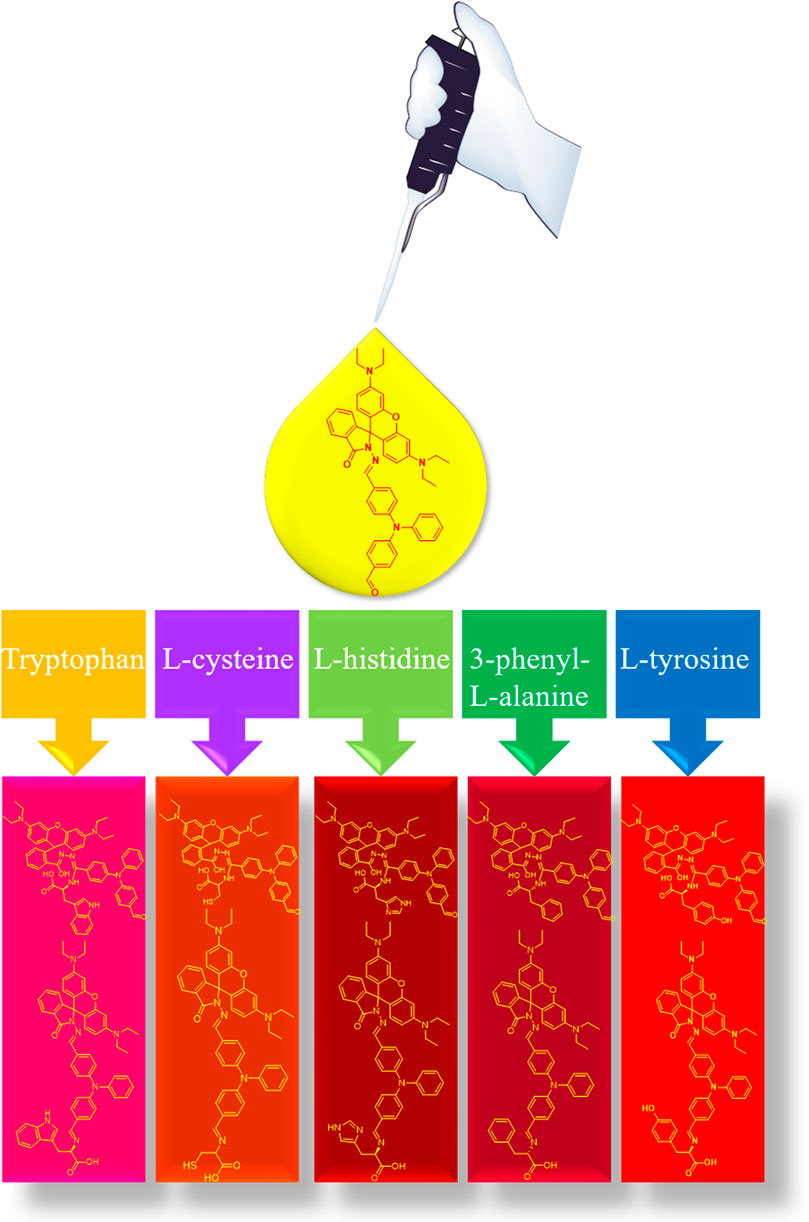
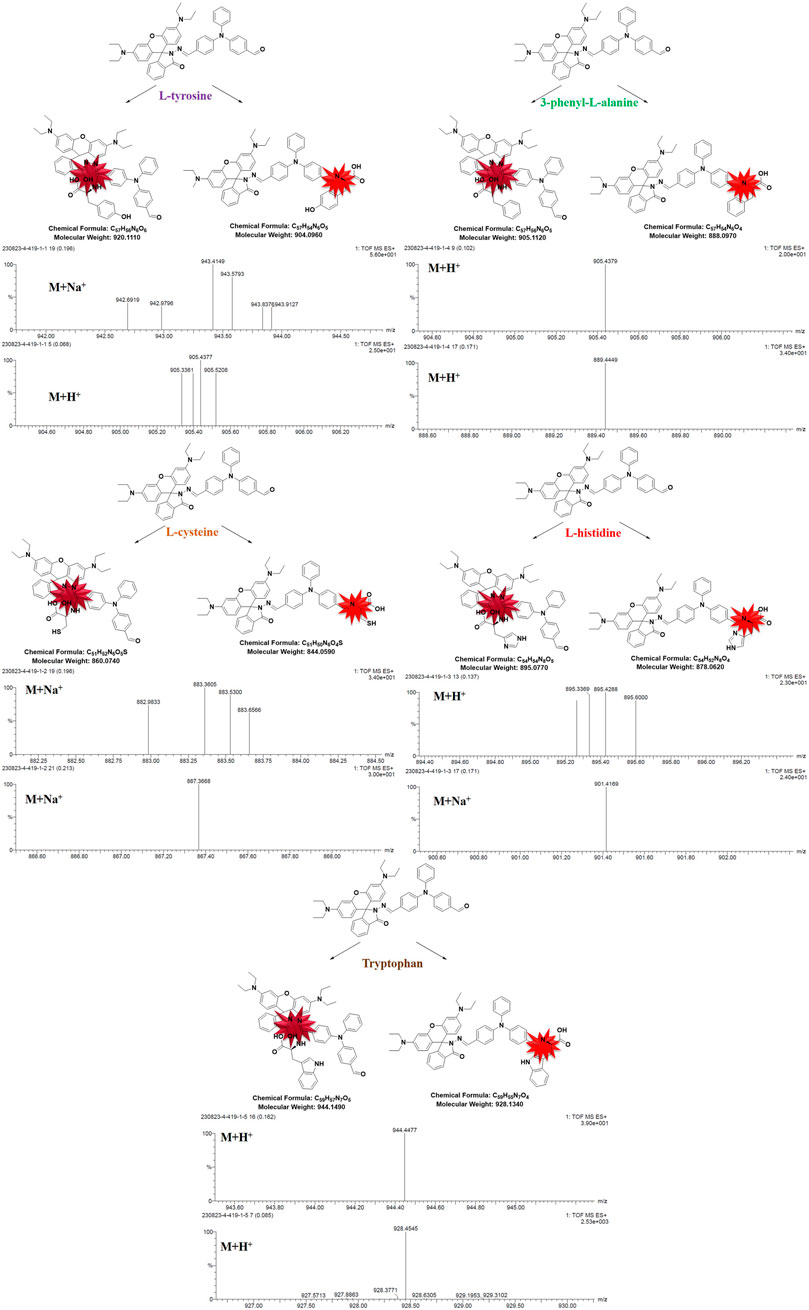
The rhodamine B structure’s iminopentane nitrogen heterocyclic ring is easily opened, and the pentane nitrogen heterocyclic ring is extremely unstable, forming an open ring rhodamine B structure and releasing strong fluorescence when the external electron is combined with imine through the Michael addition reaction. Furthermore, the conjugation of the big link is enhanced and given a high fluorescence effect and stability when triphenylamino aldehyde is combined with amino acids. Due to the change of the overall structure, different amino acid compounds produce different color changes under the irradiation of 365 nm wavelength, and the qualitative analysis of their mass spectrometry was determined by LC-MS, so as to detect the identification of different amino acids (Figure 1).
Continuous testing from 0 to 40 equivalents were conducted in order to examine the variations of RBTPA with different equivalents and different amino acids at pH = 3 and 4 in ethanol solvents. As can be seen in Figure 2, RBTPA’s blank absorption wavelength is 562 nm at pH = 3. The absorption strength of RBTPA is marginally decreased when mixed with other amino acids, yet it exhibits a clear wavelength redshift of 665 nm, with a gap of approximately 100 nm between the blank and control groups. The blank group and the control group showed no change in absorption wavelength at pH = 4, but there was a considerable drop in absorption intensity to around 0.8, with the total difference remaining at the same level. The outcomes demonstrated that the fluorescence impact and amino acid double response binding capacity improved with increasing acidity of RBTPA. Conversely, at high pH values, the reaction is less and fluorescence quenching occurs (Figures 2, 3) (Table 1).
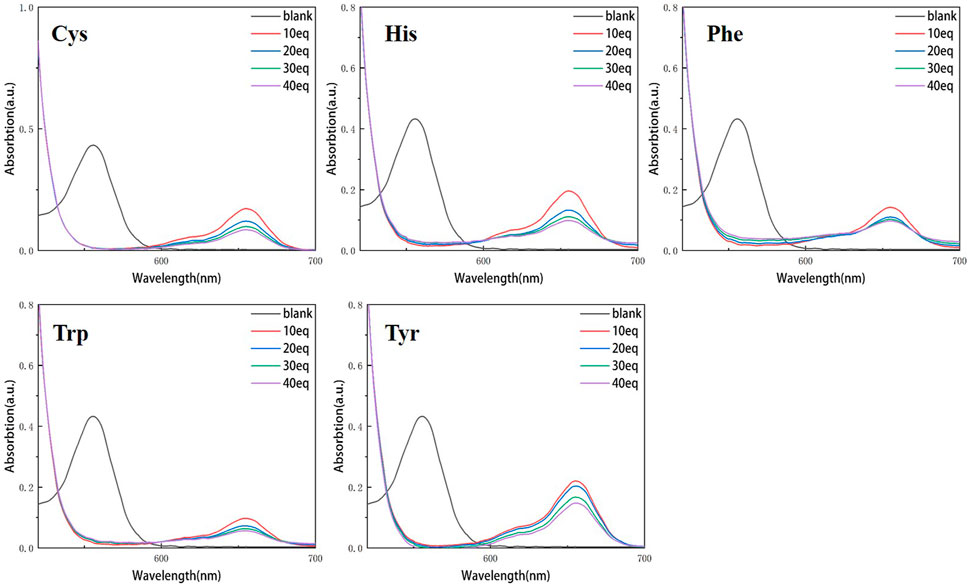
Figure 2. UV spectrum of RBTPA probe at different concentrations and different amino acids (pH = 3).
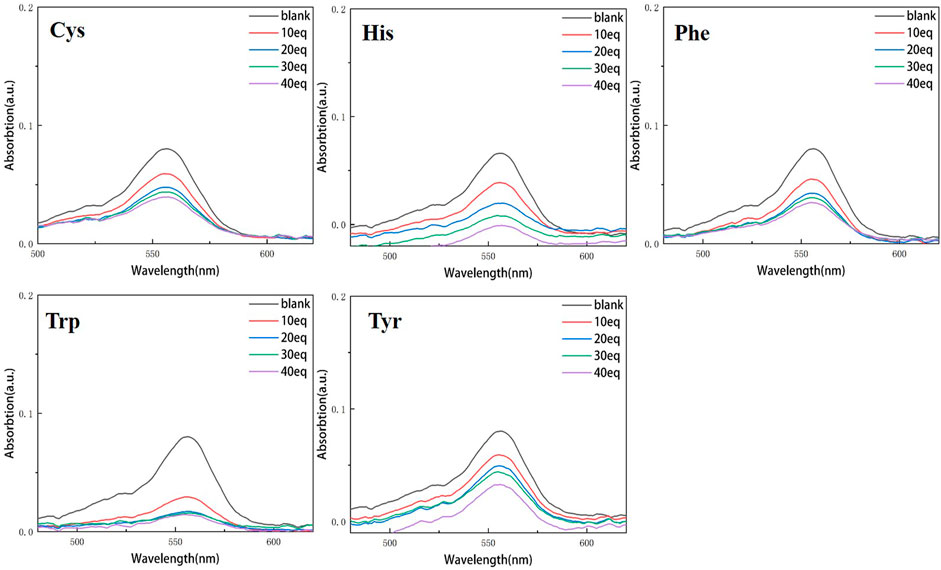
Figure 3. UV spectrum of RBTPA probe at different concentrations and different amino acids (pH = 4).
Figures 4, 5 show that the total fluorescence spectrum’s wavelength range remains largely constant and that the outcomes are comparable. The intensity of the fluorescence emission is clearly visible at pH = 3, and it is essentially between 1,150 and 1,750, with histamine having the lowest intensity. The intensity of the fluorescence emission is essentially between 400 and 500 at pH = 4. The best effect occurs at pH = 3, and the emission intensity is roughly three times different from the former, which is compatible with the aforementioned UV spectrum data (Figures 4, 5).
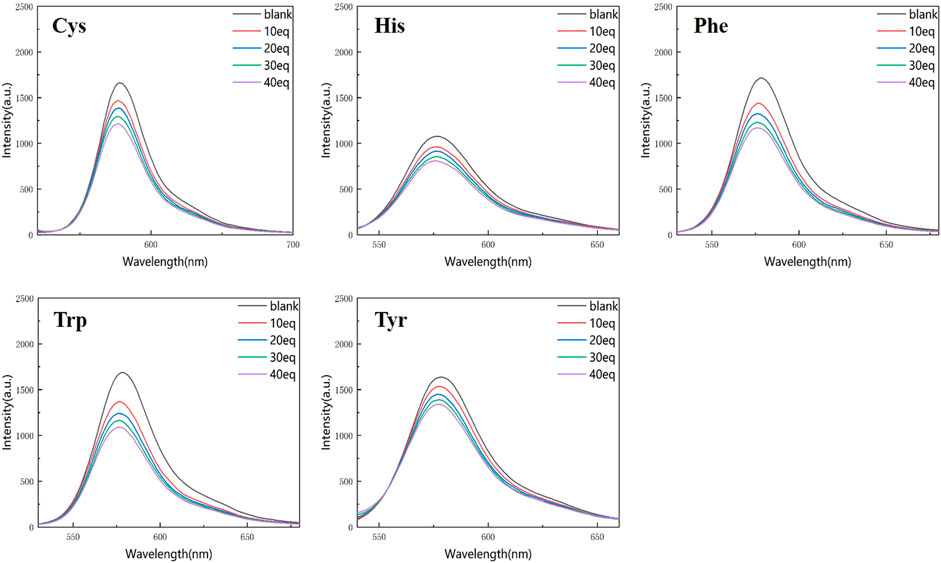
Figure 4. Fluorescence spectrum of RBTPA probe at different concentrations and different amino acids (pH = 3).
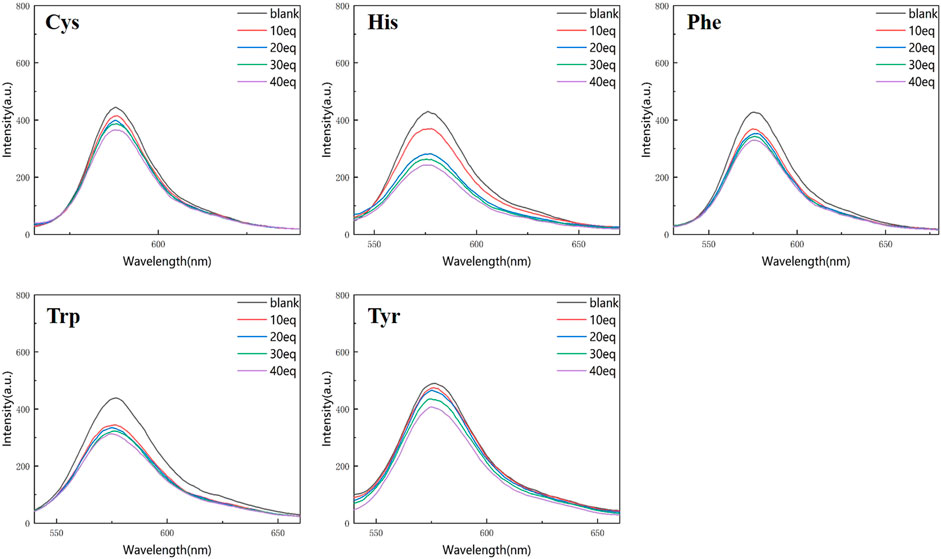
Figure 5. Fluorescence spectrum of RBTPA probe at different concentrations and different amino acids (pH = 4).
Compared with the above four figures, there are obvious curve changes in Figures 2, 3. Each of the corresponding amino acids showed strong reactivity with RBTPA, indicating a response effect between them. Although the fluctuation decline rate of the overall curve is somewhat obvious, there are differences in the absorption intensity. In particular, it shows strong responsiveness at pH = 3 (Table 2).
By comparing the color response recognition of five different amino acids and RBTPA, it can be observed that at pH = 3, the color of RBTPA is opaque except for tryptophan at daylight and 365 nm, and the others are transparent pink or dark red. The color of the blank sample is bright yellow. The results showed that the double response with imino and aldehyde group of RBTPA resulted in color change under the strong acid environment of pH = 3. On the other hand, at pH = 4, the color response recognition of five different amino acids and RBTPA is somewhat dim compared to the former, and there is almost no bright luster at daylight and 365 nm. The results show that one part of RBTPA reacts with imino and aldehyde group in double response, while the other part directly generates acid salt, which affects the fluorescence intensity. These phenomena are in complete agreement with the ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence emission intensity data explained above (Figure 6).

Figure 6. The color response of RBTPA to different amino acids under sunlight and 365 nm irradiation changes.
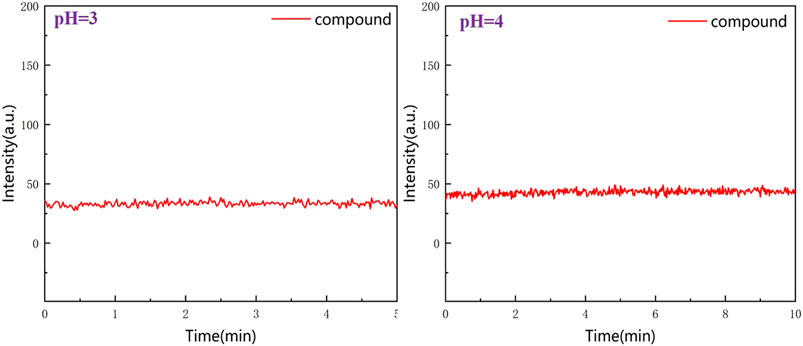
To observe the stability of RBTPA, a test was performed for 5–10 min at pH = 3 and 4 strong acids. It can be seen from Figure 7 that the two lines maintain a relatively flat state, indicating that the compound RBTPA does not change under the condition of strong acid, and is a stable fluorescent probe (Figure 7).
In order to further determine the binding of RBTPA to different amino acids in acidic environments for qualitative analysis, each response reaction solution was tested in detail by mass spectrometry. It can be seen from Figure 8 that the mass spectra of tyrosine and phenylalanine are 943.41, 905.43, 905.43, and 889.44, respectively. It can be analyzed as (M + Na+), (M + H+), (M + H+), and (M + H+) respectively. By analogy method, cysteine and can be resolved as respectively histidine (M + Na+), (M + Na+), (M + H+) and (M + Na+); tryptophan can be resolved as (M + H+) and (M + H+).
Conclusion
A novel RBTPA fluorescent probe for rapid and efficient identification of different amino acids is described in this paper. It has the characteristics of simple preparation, strong practicability and short reaction time. Among them, the high efficiency fluorescence spectrometry-mass spectrometry is the highlight of this project. The response of different amino acids can be preliminarily determined by the change of fluorescence chromophores, and then qualitative analysis of their molecular weight can be determined by mass spectrometry. The probe is suitable for research or diagnosis in the field of disease easily and quickly. It will provide important reference for developing more fluorescent probes in the same field in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
XD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. TJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. BM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. SS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research reported in this publication was supported by the scientific research foundation of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine (Grant No. 22JLC221).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bi, Y., Ni, J., Xue, X., Peng, W., Fang, X., Orsat, V., et al. (2024). Effect of different drying methods on the amino acids, α-dicarbonyls and volatile compounds of rape bee pollen. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 13, 1–21. doi:10.26599/fshw.2022.9250045
Deng, P., Xiao, F. Y., Wang, Z., and Jin, G. F. (2021). A novel BODIPY quaternary ammonium salt-based fluorescent probe: synthesis, physical properties, and live-cell imaging. Front. Chem. 9, 650006. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.650006
Deng, Z., Gao, W., Kohram, F., Li, E., Kalin, T.-V., Shi, D., et al. (2024). Fluorinated amphiphilic Poly(β-Amino ester) nanoparticle for highly efficient and specific delivery of nucleic acids to the Lung capillary endothelium. Bioact. Mater. 31, 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.07.022
Fan, Y., Zhao, Q., Wei, Y., Qing, J., Ga, Y., Zhang, Y.-N., et al. (2024). Qingjie decoction attenuated E.coli-induced diarrhea by regulating energy metabolism and alleviating inflammation based on network analysis and metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 318, 116806. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116806
Guo, S., Sun, Y. W., Ting, K., Zhang, H., Sun, Z., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Co-fermented milk beverage has better stability and contains more health-promoting amino acid metabolites than single-strain-fermented milk beverage over one-month storage. Food Chem. 430, 136840. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136840
Hao, Y., Li, J., Zhao, Z., Xu, W., Wang, L., Lin, X., et al. (2024). Flavor characteristics of Shanlan rice wines fermented for different time based on HS-SPME-GC-MS-O, HS-GC-IMS, and electronic sensory analyses. Food Chem. 432, 137150. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137150
Hu, J. P., Wang, Y. L., Jin, G. F., Lian, G., Hu, K., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Simple and practical, highly sensitive and responsive recognition of cysteine: design, synthesis and mechanism study of a novel curcumin fluorescent probe. Arabian J. Chem. 15, 104087. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104087
Jin, G. F., Xiao, F. Y., Sun, X. Y., and Qi, X. (2020b). Optimization of activity localization of quinoline derivatives: design, synthesis, and dual evaluation of biological activity for potential antitumor and antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Chem. 99, 103837. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103837
Jin, G. F., Xiao, F. Y., Sun, X. Y., Qi, X., and Zhao, L. (2020a). Design, synthesis, and dual evaluation of quinoline and quinolinium iodide salt derivatives as potential anticancer and antibacterial agents. ChemMedChem 15, 600–609. doi:10.1002/cmdc.202000002
Li, X., Ma, W., Yang, T., Wang, C., Li, H., Zhao, T., et al. (2024). Higher intakes of lysine, threonine and valine are inversely associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk: a community-based case-control study in the Chinese elderly. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 13, 191–197. doi:10.26599/fshw.2022.9250016
Lu, M., Zhu, C., Smetana, S., Zhao, M., Zhang, H., Zhang, F., et al. (2024). Minerals in edible insects: a review of content and potential for sustainable sourcing. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 13, 65–74. doi:10.26599/fshw.2022.9250005
Rong, P.-X., He, X.-Q., Gan, R.-Y., Liu, Y., Wu, D. T., Geng, F., et al. (2024). Untargeted metabolomics analysis of non-volatile metabolites and dynamic changes of antioxidant capacity in Douchi with edible mushroom by-products. Food Chem. 431, 137066. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137066
Schumann, A., Brutsche, M., Havermans, M., Gruenert, S. C., Koelker, S., Gross, O., et al. (2023). The impact of metabolic stressors on mitochondrial homeostasis in a renal epithelial cell model of methylmalonic aciduria. Sci. Rep. 13, 7677. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-34373-8
Shao, T. Y., Jin, G. F., Hu, K., and Lian, G. (2022). Nitrogen-boron eight-ring rigid cis/trans BODIPY-pyrimidine isomers for in vivo and in vitro fluorescence target recognition and evaluation of inhibitory activity. Dyes-and-Pigments 201, 110204. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2022.110204
Wang, Y. L., Xiao, F. Y., Jin, G. F., Hu, K., Lian, G., Feng, J., et al. (2021). A multiple acetal chalcone-BODIPY-based fluorescence: synthesis, physical property, and biological studies. Analytical-and-bioanalytical-chemistry. 413, 2529–2541. doi:10.1007/s00216-021-03208-8
Xiao, F. Y., Wang, Y. L., and Jin, G. F. (2020). Acetonitrilated Unsymmetric BODIPYs having glycine fluorescence responsive quenching: design, synthesis and spectroscopic properties. Spectrochimica Acta Part A-Molecular Biomol. Spectrosc. 233, 118211. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2020.118211
Ye, L., Zhang, B., Zhou, J., Li, X., Zhang, X., Tan, W., et al. (2024). LC-MS/MS-based targeted amino acid metabolic profile of auricularia cornea grown on pinecone substrate. Food Chem. 432, 137247. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137247
Yin, S., Li, Q., Tao, Y., Zhou, E., Wang, K., Chen, W., et al. (2024). Allergen degradation of bee pollen by lactic acid bacteria fermentation and its alleviatory effects on allergic reactions in BALB/c mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 13, 349–359. doi:10.26599/fshw.2022.9250029
Keywords: rhodamine B, rapid identification, different amino acid, fluorescence spectrum, mass spectrometry
Citation: Duan X, Jin T, Mao B, Shao S and Zhao L (2024) A novel rhodamine B fluorescence probe for rapid identification of different amino acids by high efficiency fluorescence spectrum-mass spectrometry. Front. Chem. 12:1409420. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1409420
Received: 30 March 2024; Accepted: 20 September 2024;
Published: 30 September 2024.
Edited by:
Nicolas Desbenoit, Univ. Bordeaux, FranceReviewed by:
Preeti Gupta, Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden (IFW Dresden), GermanyGongyu Li, Nankai University, China
Copyright © 2024 Duan, Jin, Mao, Shao and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Boneng Mao, bWFvYm9uZW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Shihe Shao, c2hhb3NoaWhlQDE2My5jb20=; Lei Zhao, emhhb2xlaTA0MzNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiujie Duan1†
Xiujie Duan1† Lei Zhao
Lei Zhao